Created by the Great Schools Partnership , the GLOSSARY OF EDUCATION REFORM is a comprehensive online resource that describes widely used school-improvement terms, concepts, and strategies for journalists, parents, and community members. | Learn more »


21st Century Skills
The term 21 st century skills refers to a broad set of knowledge, skills, work habits, and character traits that are believed—by educators, school reformers, college professors, employers, and others—to be critically important to success in today’s world, particularly in collegiate programs and contemporary careers and workplaces. Generally speaking, 21 st century skills can be applied in all academic subject areas, and in all educational, career, and civic settings throughout a student’s life.
It should be noted that the “21 st century skills” concept encompasses a wide-ranging and amorphous body of knowledge and skills that is not easy to define and that has not been officially codified or categorized. While the term is widely used in education, it is not always defined consistently, which can lead to confusion and divergent interpretations. In addition, a number of related terms—including applied skills , cross-curricular skills , cross-disciplinary skills , interdisciplinary skills , transferable skills , transversal skills , noncognitive skills , and soft skills , among others—are also widely used in reference to the general forms of knowledge and skill commonly associated with 21 st century skills. While these different terms may not be strictly synonymous, and they may have divergent or specialized meanings in certain technical contexts, these diverse sets of skills are being addressed in this one entry for the purposes of practicality and usefulness.
While the specific skills deemed to be “21 st century skills” may be defined, categorized, and determined differently from person to person, place to place, or school to school, the term does reflect a general—if somewhat loose and shifting—consensus. The following list provides a brief illustrative overview of the knowledge, skills, work habits, and character traits commonly associated with 21 st century skills:
- Critical thinking, problem solving, reasoning, analysis, interpretation, synthesizing information
- Research skills and practices, interrogative questioning
- Creativity, artistry, curiosity, imagination, innovation, personal expression
- Perseverance, self-direction, planning, self-discipline, adaptability, initiative
- Oral and written communication, public speaking and presenting, listening
- Leadership, teamwork, collaboration, cooperation, facility in using virtual workspaces
- Information and communication technology (ICT) literacy, media and internet literacy, data interpretation and analysis, computer programming
- Civic, ethical, and social-justice literacy
- Economic and financial literacy, entrepreneurialism
- Global awareness, multicultural literacy, humanitarianism
- Scientific literacy and reasoning, the scientific method
- Environmental and conservation literacy, ecosystems understanding
- Health and wellness literacy, including nutrition, diet, exercise, and public health and safety
While many individuals and organizations have proposed definitions of 21 st century skills, and most states have adopted learning standards that include or address cross-disciplinary skills, the following are three popular models that can serve to illustrate the concept and its applications in education:
- Framework for 21 st Century Learning (The Partnership for 21 st Century Skills)
- Four Keys to College and Career Readiness (David T. Conley and the Educational Policy Improvement Center)
- Seven Survival Skills (Tony Wagner and the Change Leadership Group at the Harvard Graduate School of Education)
For related discussions, see content knowledge and learning standards .
Generally speaking, the 21 st century skills concept is motivated by the belief that teaching students the most relevant, useful, in-demand, and universally applicable skills should be prioritized in today’s schools, and by the related belief that many schools may not sufficiently prioritize such skills or effectively teach them to students. The basic idea is that students, who will come of age in the 21 st century, need to be taught different skills than those learned by students in the 20 th century, and that the skills they learn should reflect the specific demands that will placed upon them in a complex, competitive, knowledge-based, information-age, technology-driven economy and society.
While 21 st century skills are relevant to all areas of schooling and academic study, and the skills may be taught in a wide variety of in-school and outside-of-school settings, there are a few primary ways in which 21 st century skills intersect with efforts to improve schools:
- Teachers may be more intentional about teaching cross-disciplinary skills in subject-area courses. For example, in a science course students might be required to learn research methods that can also be applied in other disciplines; articulate technical scientific concepts in verbal, written, and graphic forms; present lab results to a panel of working scientists; or use sophisticated technologies, software programs, and multimedia applications as an extension of an assigned project.
- States, accrediting organizations, and schools may require 21 st century skills to be taught and assessed in courses. For example, states can adopt learning standards that explicitly describe cross-disciplinary skills, and assessments may be designed or modified to evaluate whether students have acquired and mastered certain skills.
- Schools and teachers may use educational approaches that inherently encourage or facilitate the acquisition of cross-disciplinary skills. For example, educational strategies such as authentic learning , demonstrations of learning , or project-based learning tend to be cross-disciplinary in nature, and students—in the process of completing a research project, for example—may have to use a variety of applied skills, multiple technologies, and new ways of analyzing and processing information, while also taking initiative, thinking creatively, planning out the process, and working collaboratively in teams with other students.
- Schools may allow students to pursue alternative learning pathways in which students earn academic credit and satisfy graduation requirements by completing an internship, apprenticeship, or volunteer experience, for example. In this case, students might acquire a variety of practical, job-related skills and work habits, while also completing academic coursework and meeting the same learning standards required of students in more traditional academic courses.
While there is broad agreement that today’s students need different skills than were perhaps taught to previous generations, and that cross-disciplinary skills such as writing, critical thinking, self-initiative, group collaboration, and technological literacy are essential to success in higher education, modern workplaces, and adult life, there is still a great deal of debate about 21 st century skills—from what skills are most important to how such skills should be taught to their appropriate role in public education. Given that there is no clear consensus on what skills specifically constitute “21 st century skills,” the concept tends to be interpreted and applied in different ways from state to state or school to school, which can lead to ambiguity, confusion, and inconsistency.
Calls for placing a greater emphasis on cross-disciplinary skills in public education are, generally speaking, a response to the perception that most public schools pay insufficient attention to the postsecondary preparation and success of students. In other words, the concept has become a touchstone in a larger debate about what public schools should be teaching and what the purpose of public education should be. For example: Is the purpose of public education to get students to pass a test and earn a high school diploma? Or is the purpose to prepare students for success in higher education and modern careers? The push to prioritize 21 st century skills is typically motivated by the belief that all students should be equipped with the knowledge, skills, work habits, and character traits they will need to pursue continued education and challenging careers after graduation, and that a failure to adequately prepare students effectively denies them opportunities, with potentially significant consequences for our economy, democracy, and society.
A related debate centers on the distinction between “knowledge” and “skills,” and how schools and teachers may interpret—or misinterpret—the concepts. Some educators argue that it’s not possible to teach cross-disciplinary skills separately from knowledge and conceptual understanding—for example, students can’t learn to write well if they don’t have ideas, facts, principles, and philosophies to write about. The basic idea is that “21 st century skills” is an artificial concept that can’t be separated out from subject-area knowledge and instruction. Other educators may argue that cross-disciplinary skills have historically been ignored or under-prioritized in schools, and the push to give more emphasis and attention to these skills is simply a commonsense response to a changing world.
The following list provides a few additional examples of representative arguments that may be made in support of teaching 21 st century skills:
- In today’s world, information and knowledge are increasing at such an astronomical rate that no one can learn everything about every subject, what may appear true today could be proven to be false tomorrow, and the jobs that students will get after they graduate may not yet exist. For this reason, students need to be taught how to process, parse, and use information, and they need adaptable skills they can apply in all areas of life—just teaching them ideas and facts, without teaching them how to use them in real-life settings, is no longer enough.
- Schools need to adapt and develop new ways of teaching and learning that reflect a changing world. The purpose of school should be to prepare students for success after graduation, and therefore schools need to prioritize the knowledge and skills that will be in the greatest demand, such as those skills deemed to be most important by college professors and employers. Only teaching students to perform well in school or on a test is no longer sufficient.
- Given the widespread availability of information today, students no longer need teachers to lecture to them on the causes of the Civil War, for example, because that information is readily available—and often in more engaging formats that a typical classroom lecture. For this reason, educators should use in-school time to teach students how to find, interpret, and use information, rather than using most or all of the time to present information.
The following list provides a few examples of representative arguments that may be made against the concept of 21 st century skills:
- Public schools and teachers have always taught, and will continue to teach, cross-disciplinary skills—they just never gave it a label. The debate over “content vs. skills” is not new—educators have been talking about and wrestling with these issues for a century—which makes the term “21 st century skills” somewhat misleading and inaccurate.
- Focusing too much on cross-disciplinary skills could water-down academic courses, and students may not get “the basics.” The more time teachers spend on skill-related instruction, the less time they will have for content-based instruction. And if schools privilege cross-disciplinary skills over content knowledge , students may be denied opportunities because they are insufficiently knowledgeable. Students need a broad knowledge base, which they won’t receive if teachers focus too much on skill-related instruction or “learning how to learn.”
- Cross-disciplinary skills are extremely difficult to assess reliably and consistently. There are no formal tests for 21 st century skills, so the public won’t know how well schools are doing in teaching these skills.

Alphabetical Search
How do we teach 21st century skills in classrooms?
Subscribe to the center for universal education bulletin, esther care , esther care former nonresident senior fellow - global economy and development , center for universal education @care_esther helyn kim , and helyn kim former brookings expert @helyn_kim alvin vista alvin vista former brookings expert @alvin_vista.
October 17, 2017
This is the first in a six-part blog series on teaching 21st century skills, including problem solving , metacognition , critical thinking , collaboration , and communication in classrooms.
Over the past several decades, there has been increased demand for formal education to include the development of generic skills as well as traditional academic subjects, i.e., to include competencies for ways of thinking, ways of working, tools for working, and skills for living . These skills for today’s rapidly changing society, such as communication, problem solving, collaboration, and critical thinking, are being acknowledged increasingly all over the world. The big challenge, however, is knowing how to support and teach these skills in schools and classrooms.
In the absence of well-established, evidence-based approaches that demonstrate how to teach the skills and show how students have benefited from the process, countries are selecting a variety of paths to explore optimal models. For example, the “ Singapore Swiss Roll ” approach, which is starting to be implemented across the core curriculum, adopts a value-centric framework that incorporates 21st century competencies, including civic literacy, global awareness, and cross-cultural skills; critical and inventive thinking; communication, collaboration and information skills; as well as social and emotional competencies. Syllabi provided by the Ministry of Education offer guiding principles for the variety of teaching approaches that teachers can implement to enhance learning. Australia’s national curriculum of 2010 identified seven general capabilities , which teachers are expected to integrate throughout their teaching. They are guided by online resources provided by the Australian Curriculum Assessment and Reporting Authority.
In Costa Rica, with the understanding that the education system needs to progress to respond to the changing demands for skills, the National Development Plan for 2015-2018 and a new curriculum being rolled out in 2018, aims to emphasize the development and application of key 21st century skills and attitudes, such as socioemotional, communication, critical thinking, citizenships, and problem solving. Similarly, Kenya is currently developing their new competency-based curriculum , which is designed to integrate seven competencies within and across all subject areas, to ensure a comprehensive approach to skills development.
A major recommendation from an Asia-based review of the challenges facing countries as they adopt or integrate “21st century skills”, was to undertake in-depth research into the nature and development of the skills themselves. If we don’t understand what skills actually “look like” as children and adolescents at different levels of competence demonstrate them, then expecting our subject-based and trained teachers to teach them is an unfair impost at best and destined for failure at worst. We have historically taught children based on curricula—roadmaps to learning. These curricula have outlined the substance of what is to be taught, sequences to follow to ensure movement from the simple to complex, and expectations about the quality of anticipated student performance or knowledge.
Where are the curricula for skills? Surely, in order for teachers and students to know what simple forms of communication through to sophisticated look like, they need a roadmap . This roadmap then provides the guidelines for how educators can integrate development of student skills within existing and reform subject-based curricula. Creation of these roadmaps requires us to think developmentally, to identify how we develop the competencies. An important component is to identify what demonstration of these competencies might look like and how to elicit or stimulate performance so that we know what the individual is ready to learn.
In this new blog series, we will highlight classroom practices that provide concrete examples of how just a few different 21st century skills could be seamlessly integrated throughout the school day—not as a subject area, but by making it part of the classroom culture. We start with our next blog on problem solving, while the following one will be focused on a more “social” skill. Each blog will provide concrete examples of how professionals in teaching and research can pool their resources and expertise to demonstrate activities that can be undertaken with children in classrooms here and now.
Related Content
Kate Mills, Helyn Kim
October 31, 2017
David Owen, Alvin Vista
November 15, 2017
Education Technology Global Education K-12 Education
Global Economy and Development
Center for Universal Education
Annelies Goger, Katherine Caves, Hollis Salway
May 16, 2024
Sofoklis Goulas, Isabelle Pula
Melissa Kay Diliberti, Elizabeth D. Steiner, Ashley Woo
- Utility Menu
21st Century Education
At GEII we look at education for the 21 st century in the following ways:
See 21st Century Education in Action
Competencies in the Intrapersonal Domain

1) Intellectual Openness, including:
Flexibility, adaptability, artistic and cultural appreciation, personal and social responsibility, cultural awareness and competence, appreciation for diversity, adaptability, continuous learning, intellectual interest and curiosity
2) Work Ethic & Conscientiousness, including:
a. Initiative, self-direction, responsibility, perseverance, grit; productivity, type 1 self-regulation (metacognitive skills, including forethought, performance, and self-reflection), professionalism/ ethics; integrity; citizenship, career orientation
b. Positive Core Self-Evaluation, including: i. Type 2 self-regulation (self-monitoring, self-evaluation, self-reinforcement), physical and psychological health
For more about this domain, please see National Research Council. Education for Life and Work: Developing Transferable Knowledge and Skills in the 21st Century . Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2012. doi:10.17226/13398 .
Competencies in the Interpersonal Domain

1) Teamwork & Collaboration, including:
Communication, collaboration, teamwork, cooperation, coordination, interpersonal skills, empathy/perspective taking, trust, service orientation, conflict resolution, negotiation
2) Leadership, including:
Leadership, responsibility, assertive communication, self-presentation, social influence with others
Competencies in the Cognitive Domain
1) Cognitive Processes & Strategies, including:
Critical thinking, problem solving, analysis, reasoning and argumentation, interpretation, decision making, adaptive learning, and executive function
2) Knowledge, including:
Information literacy, including research using evidence and recognizing bias in sources; information and communication technology literacy, oral and written communication, active listening
3) Creativity, including:
Creativity and innovation
Values and Attitudes

The values and attitudes cultivated in participants by each program will vary by country, region, philosophies, and other social and cultural factors. However, as values and attitudes are central to developing a person’s character and shaping the beliefs, attitudes, decisions and actions of a person, we felt it was important to ask each organization included on our website to explicitly name the particular values and attitudes they seek to nurture in their program participants.
There are many sources about what kind of values, and we note that they vary according to different contexts. One document might be a helpful resource among many is the following by Margaret Sinclair titled, “ Learning to Live Together: Building Skills, Values, and Attitudes for the 21st Century ” published in 2005 by the International Bureau of Education:
Active, Engaging, and Empowering Pedagogy

21st Century pedagogy includes a focus on active, engaging, and empowering learning. Personalization, participation, and learning through authentic real-world contexts, solving problems creatively, developing projects from the beginning to the end, working collaboratively with peers and mentors, with a focus on developing metacognitive abilities, adapting and applying new knowledge while integrating it into existing conceptual frameworks are all examples of powerful pedagogy.
For more on this topic, please see this working paper from UNESCO (December, 2015) by Cynthia Luna Scott, titled, “ What Kind of Pedagogies for the 21st Century? ” among many others:
- Who is doing it?
- How are they selected?
How to Thrive in the 21st Century
- Posted November 22, 2016
- By Heather Beasley Doyle

When Fernando Reimers , a professor of international education at the Harvard Graduate School of Education (HGSE), talks and writes about what he wants children around the world to learn, the conversation runs deep and reaches far. Individual success, he says, increasingly depends upon students’ interpersonal dexterity, creativity, and ability to innovate. And our collective success — our ability to navigate complexities and to build and sustain a peaceful world — also hinges on these kinds of skills. Together, these skills form the basis of an emerging set of core competencies that will influence education policy and practice around the world.
In Teaching and Learning for the Twenty-First Century , Reimers and his co-editor, HGSE lecturer Connie K. Chung , explore how school systems in six countries are defining and supporting these global competencies. Their aim is to develop a shared framework for promoting the skills students will need in order to thrive as global citizens in a sustainable world in the decades ahead.
“Young people are in a context where they’re saturated and inundated with issues from around the world,” says Chung. Between new technologies, multiplying media, and layers of intercontinental connection, “global citizenship education is a ‘must have’ and not a ‘nice to have’ — for everyone,” says Chung.
Reimers and Chung used the National Research Council’s 2012 report, Education for Life and Work: Developing Transferable Knowledge and Skills in the 21st Century , as a jumping off point for their investigation of policies and curricula that are best positioned to nurture global citizens. That report (read the research brief here) identifies three broad domains of competence: cognitive, intrapersonal, and interpersonal. “This is not just talking about knowledge,” says Chung. Rather, it includes such strengths as intercultural literacy, self-discipline, and flexibility in social and work domains.
The Cognitive Competencies
As Chung suggests, the 21st-century global citizen’s cognitive skill set includes traditional, testable basics such as math and literacy, but extends beyond that to encompass a particularly strong emphasis on the world in which we live. “Current events highlight some of the fears around otherness,” she says. The key to informed citizenship is getting to know other cultures — and valuing them.
In addition to rounding out kids’ knowledge base to include a nuanced understanding of world geography and cultures , schools must teach them the skills to use this knowledge as active and engaged citizens.
That means being able to:
- Communicate effectively and listen actively
- Use evidence and assess information
- Speak at least one language beyond one’s native tongue
- Think critically and analyze local and global issues, challenges, and opportunities
- Reason logically and interpret clearly
- Become and remain digitally literate, including the ability to “weigh and judge the validity of the content that’s in front of you,” Chung says.
In some ways, digital literacy is a linchpin of the other competencies. “Technology gives us humans the possibility to collaborate in ways that are unprecedented, to think and produce things no one could produce individually,” Reimers says.
The Interpersonal Competencies
Empathy is a cornerstone 21st-century global competency. We’re all familiar with empathy between individuals: someone’s hurt, and another person deeply understands the pain. But Reimers and Chung envision the concept on a global scale. Empathy resides in the ability to consider the complexity of issues , Chung says — in an interconnected worldview that recognizes that “what we do impacts someone else.”
Anchored in tolerance and respect for other people, interpersonal intelligence breaks down into several overlapping skills, including:
- Collaboration
- Teamwork and cooperation
- Leadership and responsibility
- Assertive communication
- Social influence
As Reimers says, “We need to make sure that we can get along, and that we can see our differences as an opportunity, as a source of strength.” Both regionally and nationally, students need the skills to transcend the limits of fragmentation, “where people can only relate to those who they perceive to be like them.”
The Intrapersonal Competencies
A particular blend of honed personal characteristics underpins the cognitive and intrapersonal competencies. Reimers points to an ethical orientation and strong work and mind habits, including self-regulation and intellectual openness , as traits that 21st-century educators must nurture in their students.
The world is less predictable than it used to be: “People know that half of the jobs that are going to be around 10 years from now have not been invented,” Reimers says. That means teaching young people in such a way that makes them flexible and adaptable . It means enabling them to think of themselves as creators and inventors who feel comfortable taking the initiative and persevering — the skills necessary for starting one’s own business, for example.
Instilling in students the value of thinking beyond the short term will give them the best chance to tackle some of the world’s most daunting challenges, including climate change. For example, educators in Singapore were challenged to imagine their country not five, 10, or 15 years down the road, but 30 years in the future, Chung says. Encouraging students to think on that kind of a time scale helps them to grasp the reverberations of their actions and decisions.
Values, Attitudes, and Moving to Pedagogy
In Teaching and Learning for the Twenty-First Century (which has been published in Chinese, Portuguese, and Spanish editions as well), Reimers, Chung, and global colleagues interviewed education researchers and stakeholders in Chile (in a chapter by Cristián Bellei and Liliana Morawietz), China (by Yan Wang), India (by Aditya Natraj, Monal Jayaram, Jahnavi Contractor, and Payal Agrawal), Mexico (by Sergio Cárdenas), Singapore (by Oon-Seng Tan and Ee-Ling Low), and the United States (by Chung and Reimers). They explored curriculum frameworks, seeking to understand how values and attitudes unique to each country and region were informing policy goals and ultimately shaping students’ learning opportunities.
Drawing on that survey of 21st-century competencies and the frameworks for their support, Reimers, Chung, and their digitally connected global network of educators are now teasing out a pedagogy for educators everywhere. Reimers and Chung co-authored (with Vidur Chopra, Julia Higdon, and E.B. O’Donnell) another new book, Empowering Global Citizens, which lays out a K–12 curriculum for global citizenship education called The World Course. Its aim is to position students and communities to thrive amid globalization — to lead, to steward, and to safeguard this complex world in the current century and beyond.
Additional Resources
- The Think Tank on Global Education , a professional education program with Fernando Reimers that invites teachers to experiment with a new curriulum on empowering global citizens
- The Global Education Innovation Initiative , a multi-country exploration of education for the 21st century, led by Reimers
- The introduction [PDF] of Teaching and Learning in the 21st Century , which describes the rationale for the book’s comparative study
- Fifteen Letters on Education in Singapore , in which U.S. educators visit Singapore to learn how that country’s education innovations have fueled a prosperous knowledge economy — and what lessons may apply. (Available as a f ree Kindle book .)
- Reflections on turning students into global citizens
- Creating a Course for the World (a Harvard EdCast exploring the new global curriculum)
Get Usable Knowledge — Delivered Our free monthly newsletter sends you tips, tools, and ideas from research and practice leaders at the Harvard Graduate School of Education. Sign up now.

Usable Knowledge
Connecting education research to practice — with timely insights for educators, families, and communities
Related Articles

Growing Up Globally

What's Worth Learning in School?

After the Journey
- Skip to content
- Skip to search
- Staff portal (Inside the department)
- Student portal
- Key links for students
Other users
- Forgot password
Notifications
{{item.title}}, my essentials, ask for help, contact edconnect, directory a to z, how to guides, education for a changing world, key skills for the 21st century, about the report.
Stephen Lamb, Esther Doecke and Quentin Maire from Victoria University's Centre for International Research on Education Systems (CIRES) investigate the evidence for 21st-century skills and how they might be best taught and assessed.
The report investigates the evidence base for nine commonly identified 21st-century skills:
- Critical thinking
- Creative thinking
- Metacognition
- Problem-solving
- Collaboration
- Self-efficacy
- Conscientiousness
- Perseverance
Published: August 2017.
Download the report
Future Frontiers Analytical Report: Key Skills for the 21st Century [PDF 2MB]
Executive Summary [PDF 288KB]
Listen to the podcast
[School bell ringing, sounds of children playing in a playground; introductory sound bites]
Jennifer Macey:
From the New South Wales Department of Education – this is Charlie’s Future.
Stephen Lamb:
The concept for example of an inquiring mind, a lifelong learner, an ethical citizen, the concept of somebody who's entrepreneurial. You want people, in no matter what sphere of life, to become actively engaged as a citizen. These sorts of skills are important, and increasingly important in a world where the world of work itself is changing.
Welcome to Charlie’s Future, a podcast series that explores the role of education in preparing young people to thrive in an age of Artificial Intelligence. This podcast is part of the ‘Education for a Changing World initiative’ by the New South Wales Department of Education.
Join us as we meet some of the leading thinkers on this issue. We’ll explore the future of work, the future of education, and the future skills needed to navigate this brave new world.
At Sydney Olympic Park, high school students are competing in the annual regional first robotics challenge.
Female student:
So the robots start inside the field and then the robots have to try and get gears, and the robots drive over and catch the gears, which they put onto the steam ship.
Each school team have physically built and coded their own robot on wheels. They use remote controls to manoeuvre these machines across a field, make their robots climb a rope, and manipulate their robot to collect and drop plastic gears or discs into baskets.
The human player which is the pilot inside the tower will pick up the gear. Once they have a certain amount of gears, they can turn the gears and activate a rotor. There are four rotors and you get points for each rotor you get.
This high-stakes competition doesn’t just involve the ICT skills of coding, or engineering – these students are using all their 21st century skills, including collaboration, communication, computational thinking...
Male student:
One of the main things we have to talk about is where do we want to start and also discuss our end-game strategy:
... creativity, problem solving and even resilience when faced with a disappointing call from an umpire.
Critical thinking, problem solving, creativity, resilience – these are some of the 21st century skills that schools are now being encouraged to teach alongside traditional skills of numeracy and literacy. But what exactly are 21st century skills? How do you teach them? How do you assess them?
Remember Charlie and their friends? They’re starting school, which means they’ll be finishing school in about 2030 or 2040. So what skills that will best equip Charlie to navigate an AI future?
The New South Wales Department of Education commissioned some of the country’s leading thinkers on the future of education to consider these questions. The researchers at the Centre for International Research on Education Systems at Victoria University examine school systems around the world to find out where these 21st century skills are being taught and who’s doing it best.
Professor Stephen Lamb, Dr Quentin Maire and Esther Doeke collected evidence from around the world and produced a report titled ‘Key Skills for the 21st Century: an evidence-based review’ which is available on the Department’s website.
[While we were recording this interview – the Victorian police were testing their emergency alarms throughout the city.]
So to begin, what exactly are 21st century skills?
Quentin Maire:
Generally, we think about them as what students will need in the future to succeed in life, in work but also in life more broadly. As part of this report we identified nine skills that most states or countries focus on. They can be grouped in different ways but one way of looking at them would be to focus on the more cognitive heavy skills, so those where thinking is really at the centre, and these ones are critical thinking, creativity, metacognition, and problem solving. But also some more dispositional or attitudinal skills that matter as well and these can be skills like collaboration, working with others, motivation, self-efficacy (so: can I can I do it? can I succeed?), conscientiousness and grit or perseverance. So, these other nine skills that we've looked at.
And they're sometimes called soft skills aren't they?
Yes because they're not necessarily considered in the same way as literacy and numeracy and the things that we take as hard skills associated with the sort of traditional subject areas. So they’re more competencies or capacities that somebody has that they can apply across all areas of their life so to speak, in thinking about work and thinking about the way they live, the ways of thinking and so on.
It's important to note, right up front that this isn’t an exhaustive list and it’s not unassailable because a lot of this interest came around through thinking through the impact of digital literacy and sort of management of information and how it's important today to become very competent and being able to use computers for example and iPads and Facebook and all the sorts of things that are associated with it and apply across so many different domains and areas.
There are also these other sorts of skills that are associated with critical thinking and problem solving. So it’s more about the ways of thinking and the tools that we think with rather than just the knowledge that sits at the base of a lot of subject areas.
What about digital literacy? There seems to be a recent push in many schools to teach coding - but Esther Doeke says 21st century skills are more than just coding, and being able to critically analyse big data is one skill that will become increasingly important.
Esther Doeke:
I’ll start with digital literacy. That’s a really important skill, not only from the mechanics from being able to code or being able to set up the ICT infrastructure required, but also the ability to critically assess the information they get online. That’s obviously a big buzzword at the moment with fake news; but it’s true, it’s a real skill and students should be given opportunities to develop those skills within schools.
Critical thinking involves a judgment or an evaluation of claims of evidence of arguments to decide what is right or what should be done. So it's really that evaluation dimension of what is there and how solid is it that matters.
Then we have other and other skills that are important. Metacognition is really about is thinking about one's thinking, in a sense, so meta-thinking, if you wish, and really that's about monitoring how your thinking works in the achievement of a given goal. So if I want to solve something, I want to complete something, how's is my thinking helping or on track to get this done? So students can think about what they did right or wrong and still be, in a way, engaging with their own thinking.
I think it may also be worth mentioning that these skills do not replace some other skills like literacy and numeracy - these are not being discarded, they're coming in as a broader set of skills that students are expected to develop.
So why are these key 21st century skills so important?
There are various reasons why I think why countries or states are focusing on these skills. One of the reasons is because they are associated with positive outcomes in schools or in education. So, students who do well at examinations or in Year 12 for example, generally tend to do well in these areas as well: so they tend to be pretty good at considering that it can succeed, they are conscientious, they can focus on the tasks etc. So that's a first reason.
But there is another reason which is related to the changes that are happening in the workforce and the types of work or labour that these students will do in the future.
Yes - there is an economist called James Heckman who did all this work on, looking from very early on, what predicts future success. And he identified that these sorts of skills including some things that almost sound like traits which are, you know, your perseverance, your conscientiousness, your application, your motivation, these sorts of things and the levels of them, were associated with future success well beyond the impact of qualifications.
So how do you teach 21st century skills, such as critical thinking or meta-cognition in a classroom. Can they be taught as a subject like maths and English?
That’s a really good question because of a lot of systems and other countries spend a lot of time in defining these concepts - and there is no one real definition, there’s multiple definitions. So when it comes down to collecting evidence about teaching it, we actually can’t find a lot out there. We can point to some really positive practice that we can see, for instance, it comes to mind, applied learning, project based learning is a really great way to incorporate a range of these skills within various disciplines, and giving kids the chance to develop these skills in a meaningful way.
So for instance in VET or Vocational Education and Training, it’s about applied learning, students are say in a hospitality kitchen and within that there’s a unit on communication. So, students are learning how to communicate, how to work with the chef, and that’s very valuable, because it’s not communication being learnt in an esoteric way, they’re applying it.
Well one of the difficulties or one of the issues is that we have a long history of taking up our subject areas like mathematics and English and we've worked out over a period of time the sorts of texts and the way that this knowledge should be taught. With these sorts of skills these newly discussed sorts of skills that we're talking about, there isn't the long history we have about knowing how best to teach them. So in many of the schools and systems that have attempted to emphasise this in recent times, they have come to, even within their subject areas, focus on the sorts of tasks that may involve project based learning that Esther has just talked about as a means of promoting things like collaboration, communication skills, problem solving within the context of a project. Because this brings students and learners together and it allows them to operate together and emphasise the sorts of skills and outlooks that they need and that we're talking about in relation to these sorts of skills.
And what about things like grit or perseverance – aren’t these innate characteristics that can be developed in children before they even start school?
How do we teach young people to be resilient for example - there isn't necessarily easy tasks that we can go to or activities within a classroom that they can teach that in that sort of way. So this is where this new knowledge being having to be formed about the best sorts of ways in which resilience and grit and perseverance can happen, because we can see within subject areas like mathematics, as tasks become harder, to teach teacher can't afford really, doesn't want the children to give up. They've got to be able to display a capacity to keep on task and keep doing what's required. And that's true of every subject area - just because things become harder, we can't necessarily allow students to give up on their learning. So, it's how we teach that grit and perseverance so that they keep going even under some difficult circumstances. It's a very valuable skill and applies to so many different areas.
So we've been engaged with half a dozen schools that have taken on some sets of tasks in which we can look at how well students have acquired certain skills around critical thinking in particular. There was a task that actually involved trying to answer the question, think about the evidence that's available in and around whether we have landed on the moon. So there’s a set of tasks built up around that can which teachers take on and there's quite a range of evidence that’s there which people can pursue to look at about whether we have or haven't. There's evidence both ways and so it's getting somebody or some students to think through what that evidence looks like, where they would go to get it, and how that looks, and then to be able to make judgements and rational judgments themselves based on that evidence. What do they think coming to that point of view. There isn't necessarily a right or wrong answer here, but it's the process they go through, their reasoning that's what's important.
So the natural follow-up question would be: how should a school assess something like resilience or critical thinking skills?
Some of the skills can be assessed more directly through direct assessment like we'd have a NAPLAN test, but many of these skills that we're describing can't be got at in that sort of way. For example, the concept of resilience: it's not clear how you would get that through a direct assessment.
That could come about through teacher judgment and teachers standing back and judging how resilient a student is or their critical thinking or problem solving or other sorts of skills, or we can use self-reported tests, which is a longstanding way of doing this, which is to actually ask students a set of items give them a set of items to which they respond. And from that being able to assess their level of based on what they report their level of skill.
The research report found that in the US, the core districts of California have embraced the teaching of these 21st century skills and have already set up tools to test for and measure their students proficiency in these skills.
Look, the core districts are a good example. They cover about 1.2 million students across a series of districts in California that have grouped together. They have implemented it at a whole-of-district level, across all of their districts, and they apply it both in the learning and what students are expected to acquire whilst they’re at school, but they’ve also gone on to think about assessment and judgement.
I think the core districts really stood out for us because they’re not only interested in these concepts and putting them into the curriculum and defining them, they’re also measuring them within their students and using them as a way for school improvement. And they’re measuring these concepts, through a student self-reported measure: so, asking the students a series of questions that can then determine a rating of how well the students are going on concepts such as growth mindset, and self-efficacy and self-management.
The truth is that they’re one of the first school districts or school systems to do this type of stuff, to measure it in such a comprehensive way. Our systems here in Australia do run, say for instance in NSW, there’s the ‘Tell Them From Me’ survey, which is asking students every year in NSW, respond to a series of questions, defining how much they feel belonging, or how much they feel safe at school. But this is actually stepping back and measuring these key skills for 21st century in a different way and providing schools with the means from which to learn from each other and improve.
And they've done some work which compares whether teacher judgments, self-reporting and direct assessment, and found that the student assessment self-reporting is quite robust. And they've taken it as far now as including it within their school performance framework, so they actually judge schools by the levels of skills that students display and have acquired in school.
So this is going much further than most of the systems where we're still trying to identify what it is going to focus on and how we're going to do it. Here's a system that's actually taken that to a point of thinking about how well their schools are doing in delivering on these things.
The teaching and testing of 21st century skills are at different stages of development in school systems around the world. The researchers point out that one of the aspects holding some systems back is a lack of support for teachers to implement the concepts and assessments.
It’s really important that teachers are supported. We have to firstly value their teacher judgement of these concepts, know that they are already assessing students on many of these dimensions that we have identified as key skills. We should value what they’re already doing in schools. And something that we felt that came out to us when we were reading through all the materials is that, we’re seeing lots of development on the policy front in terms of schools, but we’re not seeing then teacher training programs taking it onboard, saying we’re going to start working this through our programs. If teachers aren’t prepared to work in this 'new frontier', so to speak, we can’t expect them to start delivering on it, it’s not fair.
I think you're right, I think the point that Esther made about teachers and their preparation, their readiness for teaching these skills is very important. And in fact, we have evidence from New Zealand actually showing that teachers and schools find it, or have found it difficult, to teach these skills and to make sure students learn these skills. But at the same time, we also have evidence from New Zealand, as well, of grass-root developments in schools of teachers and schools coming together to develop tools and instruments, pedagogical tools to help students learn these [skills]. So, I think we’re in the early stages of evidence based that we need to understand how we can teach and develop these skills.
Teacher training is very important, and so is professional development: I mean they’re the two main mechanisms. So at the present moment I don't think that these skills have necessarily filtered their way through to teacher training and have been taken up with the sort of systematic rigour that's required; but this is needed in the future.
Well I think that, the way it’s framed in the Australian Curriculum at the moment, which is that these [skills] should be across all disciplines, and ideally would like all teachers to come together and plan in a team-based approach which skill is coming into which subject and when – I think ideally, that would be great. But knowing how schools work, obviously not all teachers can make the time to do that. So, for instance, we see in the social and ethical understanding subjects in Victoria, we find a lot of PE (Physical Education) teachers being put into that type of planning because people think that’s the ideal fit. But really it would be great for all subjects to get onboard and see where it can fit in some way.
There has been an evaluation in New Zealand about these 21st century skills or key skills, and they looked at secondary schools and between 2012 and 2015. They found that little progress had occurred in student’s exposure to the skills or opportunities for developing these skills. And then they actually asked teachers and principals why that was the case, and they mentioned exactly what you said: that the schedule is too tight, there is too much, we have to focus on senior secondary examinations, there is a lot, and therefore this doesn't come high enough in our priority list, in a sense.
And there seems to be some agreement in this report with the previous report on ‘The Best and Worst of Times’ by the academics at Sydney University - that schools should not just be a preparing students for industry and university, but also to be critical and engaged citizens who can thrive in an increasingly complex future.
I think if we were to ask a group of employers, for example, they would point to these things as being critical. So yes, they want people with content knowledge, but they want people with more than just content knowledge, who can be adaptable and flexible, and think about things in new sorts of ways, so that they are creative and innovative in the way that they operate.
If we undertake this correctly. yeah, it could be very revolutionary. If we think it through deeply, and enact change over various fronts, and not just put this emphasis in the prep into year ten area of schooling - we mention in our report we don’t want our schools to be just ATAR factories or university preparatory systems - we want them also to factor this in for when students are in the crucial final stages of schooling. So, don’t create this just for the early years. And if we can transfer these learnings into the upper secondary years, perhaps that could be quite revolutionary, I think.
The concept for example of an inquiring mind, a lifelong learner, an ethical citizen, the concept of somebody who's entrepreneurial - these are goals that we're thinking about, and these tie over to professions and jobs that people have. You want people no matter what sphere of life to have those sorts of qualities. But they do cover all spheres of life, engaging for example in local politics, your local community, becoming actively engaged as a citizen. These sorts of skills are increasingly important in a world where the world of work itself is changing and we can't guarantee now the sorts of jobs that have been there in the past will be there in the future. But what we can ensure is that people who have and are equipped and skilled in certain ways, with these sorts of skills, will be more flexible will be more adaptable. The concept of an inquiry mind for example to learn for themselves and to be able to be more self-sufficient as learners and agents.
What final words of wisdom would our researchers have for little Charlie, who is starting school this year?
I would say remaining open minded to various approaches to learning, and learning about different things, and including these skills that can then broaden the perspective and the views or outlooks on life.
Well you could just focus in on the sorts of skills that Charlie may need in the future. An important message here is that systems have to be able to help Charlie along the way, and that's what this is really all about: trying to identify what schools can do, and school administrations, to be able to ensure that everything's in place so that Charlie can make the best out of their schooling and walk away with the sort of platform of skills that Charlie needs to be able to operate successfully in a future world.
I guess I would say to Charlie that the skills that we’re talking about also might change in 5 or 10 years, so hopefully, they will be able to be dynamic in the way they conceptualise skills in that we’re not being definitive, giving them that freedom for the future.
That was Professor Stephen Lamb, Dr Quentin Maire and Esther Doeke from the Centre for International Research on Education Systems at Victoria University in Melbourne, ending this episode of Charlie’s Future – a podcast series by the New South Wales Education Department.
Go online to read the full report - 'Key Skills for the 21st Century: an evidence-based review'. Just do a search for ‘Future Frontiers’ on the Department’s website. There you’ll also find links to all the reports commissioned for the Education for a Changing World initiative.
And do join this conversation. If you have comments get in touch with us through our Facebook group: Future Frontiers: Education for a Changing World. Our Twitter handle is: @education2040, Hashtag #futurefrontiers, or email us at [email protected].
Thanks so much for joining us. This is Charlie’s Future.
Additional resources
Watch the Charlie's Future animation that explores what the world will look like for children starting school today, and what skills they will need to flourish.
- Teaching and learning
Business Unit:
- Centre for Education Statistics and Evaluation
Level Up Your MTSS With Our Free Interventions and Progress Monitoring Toolkit.
- Multi-Tiered System of Supports Build effective, district-wide MTSS
- School Climate & Culture Create a safe, supportive learning environment
- Positive Behavior Interventions & Supports Promote positive behavior and climate
- Family Engagement Engage families as partners in education
- Platform Holistic data and student support tools
- Integrations Daily syncs with district data systems and assessments
- Professional Development Strategic advising, workshop facilitation, and ongoing support
- Surveys and Toolkits

18 Research-Based MTSS Interventions
Download step-by-step guides for intervention strategies across literacy, math, behavior, and SEL.
- Connecticut
- Massachusetts
- Mississippi
- New Hampshire
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- West Virginia
- Testimonials
- Success Stories
- About Panorama
- Data Privacy
- Leadership Team
- In the Press
- Request a Demo

- Popular Posts
- Multi-Tiered System of Supports
- Family Engagement
- Social-Emotional Well-Being
College and Career Readiness
Show Categories
A Comprehensive Guide to 21st Century Skills

Jenna Buckle

The concept of "21st century skills" isn't new—skills like critical thinking, collaboration, and problem solving have been taught in classrooms for decades.
Yet, as the demands of our changing economy rise, many school districts are now including 21st century skills in strategic plans to better prepare students for college, career, and life.
What are 21st century skills, why do they matter, and how can your district implement 21st century learning strategies into curriculum, assessment, and instruction? This guide shares information, research, and examples to bring you up to speed.
Table of Contents
1. What Are 21st Century Skills?
2. The Importance of 21st Century Skills
3. Frameworks and Examples of 21st Century Skills
4. 21st Century Learning Strategies and Implementation
5. Additional Resources
Free Download: Panorama's Social-Emotional Learning Survey
What Are 21st Century Skills?
Districts, schools, and organizations prioritize different 21st century skills depending on what is most important to their respective communities. Generally, however, educators agree that schools must weave these skills into learning experiences and common core instruction. Here is a non-exhaustive list of the most commonly cited 21st century skills.
- Critical thinking
- Communication skills
- Problem solving
- Perseverance
- Collaboration
- Information literacy
- Technology skills and digital literacy
- Media literacy
- Global awareness
- Self-direction
- Social skills
- Literacy skills
- Civic literacy
- Social responsibility
- Innovation skills
- Thinking skills
The Importance of 21st Century Skills
While the bar used to be high school graduation, the bar for today's students is now college, career, and real-world success. Let’s take a look at why 21st century skills matter.
- Higher-education and business leaders cite soft skills as being the most important driver of success in higher-level courses and in the workplace.
- In today’s world, our schools are preparing students for jobs that might not yet exist. Career readiness means equipping students with a nuanced set of skills that can prepare them for the unknown.
- Social media has changed human interaction and created new challenges in navigating social situations.
- The age of the Internet has dramatically increased access to knowledge. Students need to learn how to process and analyze large amounts of information.
- Content knowledge from core subjects can only go so far; students need to be taught how to apply facts and ideas towards complex problems.
We've reviewed the definition of 21st century skills and why they're important in a changing world. Now, let's review a few frameworks and how school districts are putting 21st century learning into practice.
Frameworks for 21st Century Skills
The framework for 21st century learning.
This popular framework was designed by the Partnership for 21st Century Skills (P21) . Describing the skills, knowledge, and expertise students must master to succeed in work and life, the framework combines content knowledge, specific skills, expertise, and literacies. P21 believes that the "base" of 21st century learning is the acquisition of key academic subject knowledge, and that schools must build on that base with additional skills including Learning Skills, Life Skills, and Literacy Skills.
- Learning Skills: Also known as the "four Cs" of 21st century learning, these include critical thinking, communication, collaboration, and creativity.
- Life Skills: Flexibility, initiative, social skills, productivity, leadership
- Literacy Skills: Information literacy, media literacy, technology literacy
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies the fundamental life skills as decision-making and problem solving, creative thinking and critical thinking, communication and interpersonal skills, self-awareness and empathy, and coping with emotions and stress. The WHO focuses on broad psychosocial skills that can be improved over time with conscious effort.
Redefining Ready! Initiative
The American Association of School Administrators (AASA) Redefining Ready! initiative offers a framework that many districts use to define college, career, and life readiness. AASA provides readiness indicators to capture the educational landscape of the 21st century. Metrics include Advanced Placement courses, standardized testing, college credits, industry credentials, attendance, community service, and more. On the topic of life readiness, AASA argues:
School District Frameworks
21st century skills take hold in various ways for school districts. A " Portrait of a Graduate " is one common strategy for communicating what it means for students to be college, career, and future ready. To develop a profile of a graduate, districts often adapt existing 21st century skill frameworks to fit their needs. Input from stakeholders—such as the district board, teachers, parents, partner organizations, and students—ensures that the final "portrait" is authentic to their community. Here are some Portrait of a Graduate examples.

Everett Public Schools in Everett, Washington defines 21st century skills as citizenship, collaboration, communication, creativity, critical thinking, and growth mindset. The district believes that graduates are college, career, and life ready when they have the academic knowledge, attitudes, and skills to transition to college level coursework, workforce training, and/or employment.

Gresham-Barlow School District (GBSD) in Gresham, Oregon has a mission to develop culturally responsive graduates who will thrive in an ever-changing global community. The district’s Portrait of a Graduate represents the GBSD community's collective vision of what their graduates should look like. The portrait consists of six learner profiles: Independent Lifelong Learner, Adaptable Collaborator, Compassionate Communicator, Responsible Creator, Open-Minded Critical Thinker, and Globally Aware Community Member.
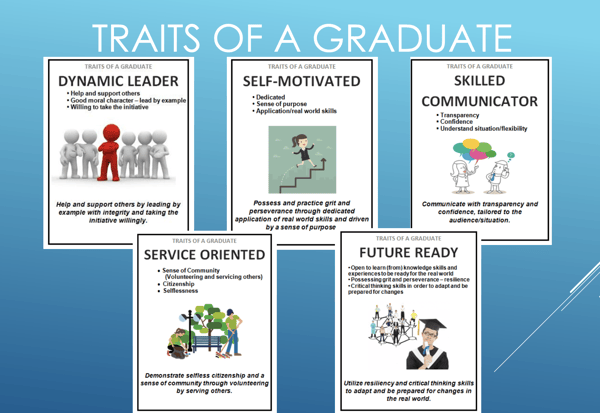
Schertz-Cibolo-Universal City Independent School District (SCUC ISD) in Schertz, Texas has a strategic goal around graduating college and/or career and/or military ready students. Within this vision, SCUC ISD has outlined five Traits of a Graduate: Dynamic Leader, Self-Motivated, Skilled Communicator, Service Oriented, and Future Ready.
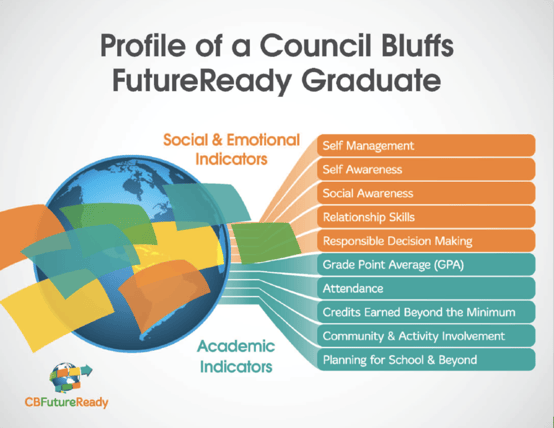
Council Bluffs Community School District in Council Bluffs, Iowa, developed a Profile of a FutureReady Graduate that encompasses both academic and social-emotional indicators of success. The district’s social-emotional indicators—aligned to the CASEL framework—include Self-Management, Self Awareness, Social Awareness, Relationship Skills, and Responsible Decision Making.
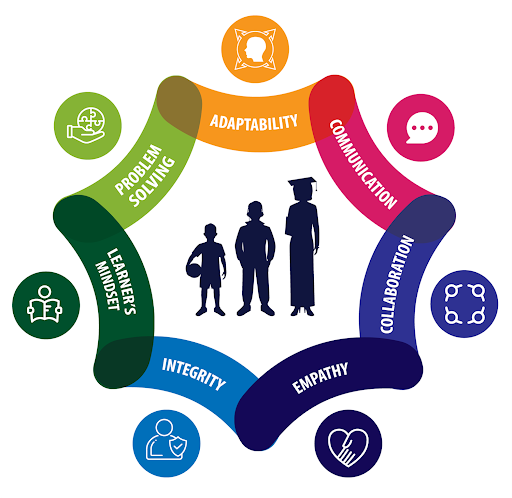
North Kansas City Schools just north of Kansas City, Missouri, identified seven competencies that span time, space, jobs, and occupations, ensuring that students' life skills are highly transferable. The district's competencies—developed with input from students, community and business leaders, teachers, and administrators—include Adaptability, Communication, Collaboration, Empathy, Integrity, Learner's Mindset, and Problem Solving.
Download our guide to developing your district's own vision for college, career, and life readiness
21st Century Learning Strategies & Implementation
Having a strong vision for 21st century learning is just the first step. Without an intentionally designed plan for implementation, it's unlikely that your students will acquire the skills outlined in your district's vision. Here are some best practices from Panorama's partner districts to set you up for success.
1. Build staff capacity to demonstrate 21st century skills in support of student learning.
It all starts with the adults in your building. Teachers and staff need to deeply understand and model the skills that you want your students to develop. Integrate 21st century skills into staff professional development as a precursor to growing these competencies in students. Download our Adult SEL Toolkit for ideas, worksheets, and activities to build adult SEL.
2. Develop strategies to support teachers with implementation of 21st century skills.
It can be helpful to create a playbook of recommended strategies and approaches that span across content areas. For instance, you might encourage teachers to add comments to report cards about students' 21st century skills.
3. Assess students’ 21st century learning skills.
What gets measured matters. Regularly collect data on how students are progressing in this area, whether the data is anecdotal, qualitative, or quantitative. For example, you might administer a biannual survey in which students reflect on their development of 21st century, social-emotional skills . Keep in mind that the data you gather should be formative rather than evaluative. Be transparent about the purpose.
4. Equip educators with data to proactively identify and support students who are off track.
Once you have data on students' 21st century skills, you'll want to ensure that the data is actionable for educators. Many districts opt to implement an early warning system with indicators across academics, attendance, behavior, and social-emotional learning/21st century skills. This helps educators make data-driven decisions about the best way to keep each student on track.
Additional Resources
Looking for more information on 21st century skills? Here are some other articles and resources to explore:
- "Why Social and Emotional Learning and Employability Skills Should Be Prioritized in Education" via CASEL and Committee for Children
- "Teaching 21st Century Skills For 21st Century Success Requires An Ecosystem Approach" via Forbes
- "Bringing 21st Century Skill Development to the Forefront of K-12 Education" via Hanover Research
- "How Do You Define 21st-Century Learning?" via Education Week
Honing in on 21st century skills is essential to ensuring that students are prepared for college, career, and civic life . While there is no one "right" way to approach this work, we hope that the information in this guide inspires you to explore what 21st century learning could look like in your district!
Develop students' 21st century skills with Panorama's Social-Emotional Learning Survey

Related Articles

A Comprehensive Guide to a Portrait of a Graduate
A Portrait of a Graduate represents a school district's vision for the 21st century skills, character traits, and/or social-emotional competencies that students need to succeed in college, career, and life.

23 Survey Questions to Understand Students’ Employability Skills
Discover how employability skills equip students for the workforce. Learn teaching strategies and explore 23 survey questions for skill assessment.

College-Career Readiness Goals: 3 Lessons from District Leaders
Learn 3 ways that school districts are creating and making progress on college and career readiness goals to support student success in school and beyond.

Featured Resource
Panorama social-emotional learning survey.
Download Panorama's Social-Emotional Learning Survey to access our topics and questions for students and adults.
Join 90,000+ education leaders on our weekly newsletter.
Ten 21st-century skills every student needs

Don't get left on the shelf ... brush up on your collaboration, communication and problem-solving skills Image: REUTERS/Eric Gaillard
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Jenny Soffel

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Future of Work is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, future of work.
The gap between the skills people learn and the skills people need is becoming more obvious, as traditional learning falls short of equipping students with the knowledge they need to thrive, according to the World Economic Forum report New Vision for Education: Fostering Social and Emotional Learning Through Technology.
Today's job candidates must be able to collaborate, communicate and solve problems – skills developed mainly through social and emotional learning (SEL). Combined with traditional skills, this social and emotional proficiency will equip students to succeed in the evolving digital economy.
21st-century skills for students
An analysis of 213 studies showed that students who received SEL instruction had achievement scores that averaged 11 percentile points higher than those who did not. And SEL potentially leads to long-term benefits such as higher rates of employment and educational fulfillment.
Good leadership skills as well as curiosity are also important for students to learn for their future jobs.

Another Forum report, The Future of Jobs , launched during the Annual Meeting 2016 in Davos, looked at the employment, skills and workforce strategy for the future.
The report asked chief human resources and strategy officers from leading global employers what the current shifts mean, specifically for employment, skills and recruitment across industries and geographies.

Policy-makers, educators, parents, businesses, researchers, technology developers, investors and NGOs can together ensure that development of social and emotional skills becomes a shared goal and competency of education systems everywhere.
Have you read? What does the future hold for your job? 10 skills you need in the Fourth Industrial Revolution More on Employment, Skills and Human Capital
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
The Agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Jobs and the Future of Work .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

What can employers do to combat STEM talent shortages?
May 21, 2024

Progress for women in the workplace stagnating in four key areas, global study reveals

The care economy is one of humanity's most valuable assets. Here's how we secure its future

Why companies who pay a living wage create wider societal benefits
Sanda Ojiambo
May 14, 2024

Age diversity will define the workforce of the future. Here’s why
Susan Taylor Martin
May 8, 2024

From start-ups to digital jobs: Here’s what global leaders think will drive maximum job creation
Simon Torkington
May 1, 2024
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Don't Miss a Post! Subscribe
- Guest Posts

- Educational AI
- Edtech Tools
- Edtech Apps
- Teacher Resources
- Special Education
- Edtech for Kids
- Buying Guides for Teachers

Educators Technology
Innovative EdTech for teachers, educators, parents, and students
Characteristics of The 21st Century Classroom
By Med Kharbach, PhD | Last Update: May 9, 2024

When I embarked on my teaching journey back in 2003, the landscape of the classroom was quite different from what we see today. Reflecting on this evolution, I’m struck by the radical changes that have shaped the educational environment, particularly in this early part of the 21st century.
It’s a transformation that’s been largely driven by the unprecedented pace of technological advancement. As I ponder these changes, I find it both fascinating and essential to articulate the characteristics that now define a modern classroom. These reflections are not just an academic exercise but a practical one, aimed at understanding and adapting to the evolving dynamics of education.
The changes are not just incremental; they are foundational, reshaping the very nature of how we teach and learn. The onset of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in education is a testament to this rapid evolution. We are on the cusp of a new era where AI could redefine educational experiences in ways we are only beginning to understand.
To make sense of this shift, I’ve distilled my observations and experiences into six broad characteristics of the 21st-century classroom. Each of these categories encapsulates elements that are shaping modern educational practices.
This is not just a list, but a conversation starter, an invitation to dialogue about these changes. It’s a personal take, rooted in years of firsthand experience, aiming to spark discussions and reflections among educators, parents, and anyone interested in the future of education.
If you have missed other posts in this series on the topic of 21st century education, make sure to check characteristics of 21st century learners , characteristics of 21st century teachers , and characteristics of 21st century learning .
Here are the six main characteristics that, I believe, define the 21st century classrooms.
1. Technological Integration
The 21st-century classroom is unimaginable without the integration of technology, and soon AI (artificial intelligence). This facet of modern education transcends the traditional use of textbooks and blackboards, weaving digital tools seamlessly into the learning process (NETP, 2017)). Smartboards, for instance, have transformed the way lessons are presented, offering interactive and dynamic content that can cater to various learning styles.
Tablets, laptops, and Chromebooks have become as commonplace as notebooks, enabling students to access a vast reservoir of information and educational resources at their fingertips. Educational software, ranging from language learning apps like Duolingo to math problem-solving platforms like Khan Academy, provides personalized learning experiences. These technologies not only make learning more engaging but also prepare students for a digitally driven world.
The concept of a 21st-century classroom has evolved significantly. No longer limited to the traditional four walls of an institutional setting, the modern classroom exists wherever there’s an internet connection. This digital shift enables students to learn flexibly, from any location, facilitated by the widespread use of video conferencing tools. These advancements have given rise to the cloud-based classroom, a dynamic and accessible learning environment that epitomizes educational innovation.
Through my journey in the EdTech world, I have seen first hand the transformative power of educational technology and its vast impact on students learning. And guess what? These learning technologies that are now part of our classroom teaching are not only optimizing students learning but are also fostering a more inclusive learning environment where every student can find a way to engage that suits their learning style .
2. Student-Centered Learning
The 21st century classroom is a student-centered learning hub. In these classrooms, ” students regularly communicate, collaborate, self-reflect, problem solve,and peer-evaluate about their learning” (Hansen & Imse, 2016, p. 20)
As I stated in a previous post on 21st century learning , student-centered learning marks a paradigm shift from the traditional teacher-led approach (AKA the sage on the stage) to a more collaborative and experiential framework. This approach places students at the heart of the learning process, empowering them to take charge of their educational journey. In such settings, the teacher acts more as a facilitator or guide, providing resources and support while allowing students to explore topics that interest them.
This method often involves collaborative and project-based activities that encourage teamwork, communication, and problem-solving skills. For example, in project-based learning, students work on complex questions or problems over extended periods, giving them the chance to delve deeply into subjects and apply what they learn in real-world contexts.
During my teaching career, I’ve observed that when students are given the autonomy to explore subjects that they are passionate about, their engagement and retention rates soar. This approach also emphasizes the development of soft skills such as leadership, teamwork, and communication. Group projects and collaborative assignments foster a sense of community and interdependence among students.
Additionally, student-centered learning is often intertwined with personalized learning paths. This can involve differentiated instruction strategies where tasks are tailored to each student’s learning pace and style.
3. Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
In the 21st-century classroom, developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills is a cornerstone of the educational experience. Critical thinking, as Finn (2011) defines it, “is applied rationality…a set of skills that people can learn and apply in their everyday or professional lives.” (p. 69). Problem solving, as Martinez (1998) stated, is “the process of moving toward a goal when the path to that goal is uncertain.”
Both critical thinking skills (e,g., analyzing, synthesizing, evaluating, etc) and problem solving skills are essential for navigating the complexities of modern life and for fostering innovation. Educational strategies that emphasize these skills involve challenging students to think deeply about issues, analyze information critically, and come up with creative solutions to problems.
For instance, inquiry-based learning, where students formulate their own questions and seek answers through research and experimentation, can be particularly effective. This method not only engages students in the subject matter but also hones their analytical skills.
Problem-solving, particularly in group settings, not only strengthens analytical skills but also teaches students how to collaborate and communicate effectively. Incorporating real-world problems into the curriculum makes learning more relevant and engaging.
For example, tasks that involve designing solutions for environmental issues or community problems can be highly impactful. This approach not only equips students with the necessary critical thinking and problem-solving skills but also instills a sense of social responsibility.
4. Cultural Relevance and Global Awareness
Emphasizing cultural relevance and global awareness in the classroom is essential for preparing students to navigate and contribute to an increasingly interconnected world. This involves integrating diverse perspectives into the curriculum and teaching about global issues.
By incorporating literature, historical events, and current affairs from various cultures, educators can foster a more inclusive and empathetic classroom environment. This approach helps students understand and appreciate different viewpoints and cultural backgrounds, which is crucial in today’s diverse society.
Global awareness extends beyond cultural studies; it encompasses teaching about global challenges such as climate change, poverty, and social justice. Encouraging students to explore these issues, perhaps through project-based learning or classroom discussions, helps them develop a sense of responsibility and empowerment. It’s important for students to realize that they are part of a larger global community and that their actions can have an impact.
5. Personalized Learning
Personalized learning in the 21st-century classroom is about tailoring education to meet the unique needs, skills, and interests of each student. With the help of technology and innovative teaching methods, educators can create a learning environment that accommodates different learning styles and paces. For example, adaptive learning technology can adjust the difficulty of tasks based on individual student performance, providing a customized learning experience.
This approach ensures that all students, regardless of their starting point, can achieve mastery at their own pace. Personalized learning also involves offering various pathways for students to explore their interests and strengths. This could mean providing different project options, elective courses, or extracurricular activities.
6. Digital Literacy
Digital literacy is a fundamental skill in the modern world, encompassing more than just the ability to use technology. It involves understanding how to navigate the digital landscape responsibly and effectively. This includes critical skills like discerning reliable from unreliable sources online, understanding online privacy, and engaging in appropriate and ethical digital practices.
Teaching digital literacy is not just about providing students with technical skills; it’s about guiding them to become smart, ethical digital citizens. In the 21st-century classroom, educators have the responsibility to integrate digital literacy into their teaching. This could be through lessons on internet safety , exercises in evaluating online sources , or discussions about the impact of digital footprints.
Final thoughts
As we have seen, the landscape of education is continuously evolving, particularly with the onset of the AI revolution. The changes we’ve witnessed and adapted to in recent years are just the tip of the iceberg. Looking ahead, the integration of AI in education promises to further transform the classroom in ways we are only beginning to imagine.
The future classroom, I predict, will be an even more personalized and adaptive learning environment. AI could tailor educational content to each student’s learning pace, style, and interests, making education a truly individualized experience.
We might see AI-assisted teachers providing real-time feedback to students, thereby enhancing learning outcomes and freeing up more time for teachers to engage in meaningful, one-on-one interactions. Moreover, AI-driven analytics could provide educators with deeper insights into student learning patterns, enabling more effective interventions and support.
However, with these advancements, comes the responsibility to navigate challenges such as ensuring equitable access to technology and maintaining a human-centric approach in education. The role of the teacher will remain irreplaceable, evolving alongside technological advancements. Teachers will continue to be the guiding force, mentors, and facilitators of empathy, critical thinking, and creativity.
- Finn, P. (2011). Critical thinking: Knowledge and skills for evidence-based practice. Language, Speech & Hearing Services in Schools , 42(1), 69–72. https://doi.org/10.1044/0161-1461
- Hansen, D., & Imse, L. A. (2016). Student-centered classrooms: Past initiatives, future practices. Music Educators Journal , 103 (2), 20–26. http://www.jstor.org/stable/44678226
- Martinez, M. E. (1998). What Is Problem Solving? The Phi Delta Kappan , 79(8), 605–609.
- National Education Technology Plan Update. (2017). Reimagining the Role of Technology in Education. U.S. Department of Education . Retrieved from: https://tech.ed.gov/files/2017/01/NETP17.pdf
Further readings
- 21st Century Learning Framework, Battle for Kids, accessed January 3, 2023, https://www.battelleforkids.org/networks/p21/frameworks-resources
- Becker, J. M. (1982). Goals for Global Education. Theory Into Practice , 21 (3), 228–233. http://www.jstor.org/stable/1476772
- Berger et al. (2014). Leaders of their own learning: Transforming schools through student-engaged assessment . Jossey-Brass.
- Cohen, A. (2018). Bringing the 1960s to the 21st-Century Classroom. Pennsylvania Legacies , 18 (2), 32–33. https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.5215/pennlega.18.2.0032
- Danielson, C. (2007). Enhancing Professional Practice . Alexandria, VA: ASAE
- Davies, I., Evans, M., & Reid, A. (2005). Globalising citizenship education? A critique of “Global Education” and “Citizenship Education.” British Journal of Educational Studies , 53 (1), 66–89. http://www.jstor.org/stable/1556020
- Martell, C. (1974). Age of creative insecurity: Student-centered learning. Journal of Education for Librarianship , 15 (2), 112–120. https://doi.org/10.2307/40322827
- Tye, K. A. (2003). Global education as a worldwide movement. The Phi Delta Kappan , 85 (2), 165–168. http://www.jstor.org/stable/20440529

Join our mailing list
Never miss an EdTech beat! Subscribe now for exclusive insights and resources .

Meet Med Kharbach, PhD
Dr. Med Kharbach is an influential voice in the global educational technology landscape, with an extensive background in educational studies and a decade-long experience as a K-12 teacher. Holding a Ph.D. from Mount Saint Vincent University in Halifax, Canada, he brings a unique perspective to the educational world by integrating his profound academic knowledge with his hands-on teaching experience. Dr. Kharbach's academic pursuits encompass curriculum studies, discourse analysis, language learning/teaching, language and identity, emerging literacies, educational technology, and research methodologies. His work has been presented at numerous national and international conferences and published in various esteemed academic journals.

Join our email list for exclusive EdTech content.

- Good to Great Schools Australia Pilot Program
- Online teaching and learning resources to support mathematics and numeracy
- Support for Arts and Languages
- Support for Humanities and Social Sciences
- Support for Literacy and Numeracy
- National STEM School Education Strategy 2016–2026
- STEM Education Resources Toolkit
- STEM program evaluations in the early years and schooling
- Research into Best Practice Models in mathematics teaching and learning
- Support for Social Cohesion
- Year 1 Phonics Check
Links to 21st century learning
On this page:, what is it.
21st century learning is the development of a highly valuable skill set for the future. 21st century skills are flagged as critical for the digital and evolving economy. Instead of specific subject knowledge, 21st century skills are ways of thinking, ways of working and ways of living.
The Australian Curriculum includes seven general capabilities:
- Information and communication technology (ICT) capability
- Critical and creative thinking
- Personal and social capability
- Ethical understanding
- Intercultural understanding
The list below from the Assessment & Teaching of 21st Century Skills website shows another approach to categorising these skills:
Ways of thinking
- Creativity and innovation
- Critical thinking, problem-solving, decision-making
- Learning to learn, metacognition
Ways of working
- Communication
- Collaboration
Tools for working
- Information literacy
- ICT literacy
Living in the world
- Citizenship — local and global
- Life and career
- Personal and social responsibility — including cultural awareness and competence
Best practice STEM education is complementary to 21st century learning. At the same time as developing important skills and knowledge in the STEM subjects, students engage in activities and projects that promote 21st century skills such as critical thinking, creativity, communication and collaboration.
How does it help?
Linking to 21st century learning prepares students for the future world of work, and arms them with critical life skills. It supports students to be critical and creative-thinkers, communicators and collaborators.
How do you do it?
21st century skills can be included in the classroom through:
- Project-based learning provided on the NSW Government Education website.
- Creating lessons that promote critical thinking, communication, collaboration and creativity.
Remove Product?
Are you sure, test takers.
- Registration How to Register ID Requirements Disability Accommodations Braille Proficiency American Sign Language Proficiency Fees & Waivers
- Preparation Prepare with Precision Study.com Free Praxis Core Prep Praxis Learning Paths Elementary Education Prep Video and Virtual Event Resources
- Test Day At Home Testing Test Center Testing Calculator Use
- Scores Getting Your Scores Understanding Your Scores Sending Your Scores
A Critical Resource: The Importance of Literacy Skills
Learn about the importance of literacy skills. This article explores how improved reading and writing abilities lead to student success and prepare learners for the challenges of the 21st-century job market.
Published on May 21, 2024
Literacy as a key to the future
As work in every job sector requires research, analysis, and effective communication, literacy skills have become indispensable tools for success.
The ability to read, write and comprehend information not only forms the foundation for academic achievement, but it also plays a significant role in shaping students’ future careers. According to Paul Deane, Principal Research Scientist at ETS, “To succeed in the twenty-first century economy, you have to have [literacy] skills that only a small percentage of the population may have needed in the 1920s.”
Many schools emphasize reading catch-up alongside basic writing skills: grammar, structure, and mechanics. While these skills are certainly important, educators must prepare for advanced writing matters , including intensive workshopping and revising , should students want to claim greater fluency over their literacy abilities. “Schools with better prepared kids,” notes Paul Deane, “can spend more time in writing and cover more ground in writing …When you do that, you get faster skill growth and more motivated kids.” Supporting this kind of well-structured and meaningful content, in turn, has a powerful impact on a student’s future , or, as Deane puts it, “If you can’t write a good admissions essay, you’re already behind the 8-ball.”
An urgent need for literacy skills
Reading scores have remained stagnant for the past two decades - in recent years, they have declined due to the pandemic .
Information like this, which was revealed by the Nation’s Report Card by the National Assessment of Educational Progress , makes the case that to perform in today's competitive job market, students must possess proficient literacy skills . Travis Park, Associate Professor of Agricultural Education at North Carolina State University in Raleigh, wonders, “ Are we creating students who can be lifelong learners, not just the oil changers and mechanics, but the managers, the owners of the business? ” His question emphasizes the urgent need for schools to address literacy skills before the job market demands them later : “If you’re in it for that game,” Park says, “then reading is vitally important for [students’] long-term success.”
To address the challenges of improving literacy skills, many schools are turning to tech-based solutions . The right technology can offer immediate auto-grading and diagnostic reviews. As such, educators can provide students with personalized learning experiences to improve their writing skills and guide the revision process. For example, tools like the Criterion® Online Writing Evaluation Service are designed to help students improve their core writing skills through unlimited opportunities to practice independent writing and invaluable automated feedback. Personalizing learning in this manner empowers students to engage with the material at their own pace .
Benefitting all student and teacher outcomes
We must recognize the interconnectedness of reading and writing when personalizing learning experiences.
In conjunction with this work, educators can empower students to face the challenges of the modern world with confidence and competence. Schools and districts can build better-developed students across all subjects with a renewed approach to critical writing concepts and systematic literacy approaches . Literacy skills unlock a world of opportunities: They are indispensable assets in every learner's journey towards a successful and fulfilling future.
Want to improve literacy skills in your classroom? Check out the Criterion Online Writing Evaluation Service.

Overcoming Praxis Test Challenges: Retaking and Succeeding
By Praxis Editorial Team
Published on May 7, 2024
.jpg)
Future Directions: How Praxis and Study.com Consider Educator Preparation and Support
Published on April 30, 2024
Unveiling Educational Impact: ETS Praxis Ventures into New Research Horizons
Published on April 23, 2024

Achieving Success: Our Innovative Test Prep for Praxis Core
Published on April 15, 2024
Unlocking Diversity: ETS and Study.com Research Explores Keys to the Classroom
Published on April 9, 2024

Enhancing Literacy Learning: Blending Technology and Education
Published on April 2, 2024

Get Your Dream Job: Top 10 Interview Questions
Published on March 25, 2024

Making the Grade: Finding Your Ideal First Teaching Job
Published on February 27, 2024

Assessment Strategies I Wish I Knew When I Started Teaching
Published on March 12, 2024

Empowering New Teachers with Professional Development
Published on March 5, 2024

Supercharging Education with Formative Learning
Published on March 19, 2024

Meet Praxis: Where Education Leads the Conversation
Published on February 20, 2024

Breaking Boundaries: Praxis and Study.com Partner to Empower Educators
Learn how study.com can lead you to praxis success..
- India Today
- Business Today
- Reader’s Digest
- Harper's Bazaar
- Brides Today
- Cosmopolitan
- Aaj Tak Campus
- India Today Hindi
Empowering educators with technology integration for 21st-century skills
Educational technology platforms, interactive multimedia content, and productivity tools can enhance teaching and learning experiences, making lessons more engaging and effective. however, it's essential to ensure that these resources align with curriculum objectives and support the development of 21st-century skills..
Listen to Story

We are facing unprecedented challenges – social, economic and environmental – driven by accelerating globalisation and a faster rate of technological development. The future is uncertain, and we cannot predict it, and we need to be open to it. The children entering education in 2018 will be young adults in 2030.
Schools can prepare them for jobs that have not yet been created, for technologies that have not yet been invented, to solve problems that have not yet been anticipated. It will be a shared responsibility to seize opportunities and find solutions. Neerja Birla, Founder and Chairperson, Aditya Birla Education Trust(ABET) will shed more light on this.
In this ever-changing landscape of education, to navigate through uncertainty, we need to develop skill sets like curiosity, imagination, resilience, and regulation. In these endeavours, integration of technology becomes imperative to equip our students with the necessary skill sets required for 21st century skills. The effective use of technology in class cannot just be restricted to the use of PowerPoint presentations, and YouTube videos.
The use of technology must be an aid that enhances student teaching – learning experiences.
With the advent of AI tools for teaching – learning, classroom preparation – a teacher can get innovative lesson plans with engaging ideas in just about a few minutes. It is key that teachers use these tools effectively and innovatively to make the most of it for better student learning experiences.
UPSKILLING AND TEACHER TRAINING
Here is where constant upskilling and teacher training plays a vital role. Pre-covid days, there were also the challenges of changing teachers' mindsets to the use of technology. Overnight, the pandemic saw a paradigm shift in teachers' mindsets on the use of technology. However, we seem to have gone back to the good old ways post the pandemic.
Now, technology throws challenges at teachers and that has become the new norm now. In order to leverage the challenges thrown by technology, educators must possess a mindset to enhance skillsets to empower themselves. Some ways to successfully embed technology into schools are to have continuous professional development of the teachers.
COLLABORATION AMONGST EDUCATORS
Furthermore, collaboration amongst educators is essential for sharing best practices and learning from each other. Forming professional learning communities (PLC’s) and online forums allow teachers to collaborate, exchange ideas and share best practices. By fostering a culture of collaboration, and sharing platforms helps better technology integration.
Support and encouragement from school leadership also plays an important role in empowering educators in integration of technology. Administrators should prioritise technology integration as a key component of the school's vision and provide the necessary resources and support to make it a reality. This includes investing in infrastructure, such as reliable internet connectivity and up-to-date devices, as well as allocating time and funding for professional development initiatives.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The report examines the challenges and opportunities of integrating 21st century skills into education systems, focusing on assessment and learning outcomes. It finds a gap between countries' policy intentions and implementation actions, and suggests ways to bridge it.
Learn what 21st century skills are, how they are defined and applied in education, and why they are important for success in today's world. Explore different models and perspectives on the concept, and the challenges and controversies it raises.
The education delivery system has a substantial impact on the way in which 21st-century skills develop in learners. Pedagogy, curriculum, school rules and climate, assessments, and benchmarking skill acquisition are all key factors in the way 21st-century skills develop and are monitored.
A report by an ad hoc committee that reviews and synthesizes research on the nature, importance, and development of skills such as problem solving, critical thinking, and collaboration. The report provides a common foundation for further research and policy work on these skills in K-16 education.
Learn how different countries and classrooms are integrating skills such as communication, problem solving, collaboration, and critical thinking into their curricula. The blog series provides examples of concrete activities and roadmaps for developing these skills across subjects and levels.
A report from a Harvard University Advanced Leadership Initiative Think Tank that explores how to equip students with 21st century skills and change the educational paradigm. The report synthesizes ideas from distinguished faculty, experts, and participants on the current situation, global perspective, and educational innovations.
Learn how GEII defines and promotes 21st century education, including competencies, values, and pedagogy. Explore examples of programs that foster intellectual openness, teamwork, leadership, creativity, and more.
The Future of Education and Skills 2030 aims to help education systems determine the knowledge, skills, attitudes and values students need to thrive in and shape their future. ... Towards a 21st Century Curriculum. Curriculum Overload: A Way Forward. BROCHURE: Curriculum (re)design | A series of thematic reports ...
21st century skills into education.The organization brings together the business community, education leaders and policymakers to define a powerful vision for 21st century education to ensure every child's success as citizens and workers in the 21st century.The Partnership encourages schools, districts and states to advocate for ...
Reimers and Chung used the National Research Council's 2012 report, Education for Life and Work: Developing Transferable Knowledge and Skills in the 21st Century, as a jumping off point for their investigation of policies and curricula that are best positioned to nurture global citizens.That report (read the research brief here) identifies three broad domains of competence: cognitive ...
Stephen Lamb, Esther Doecke and Quentin Maire from Victoria University's Centre for International Research on Education Systems (CIRES) investigate the evidence for 21st-century skills and how they might be best taught and assessed. The report investigates the evidence base for nine commonly identified 21st-century skills: Critical thinking
Learn what 21st century skills are, why they matter, and how to implement them in your school district. Explore different frameworks, examples, and strategies for teaching and assessing these essential skills for college, career, and life success.
21st century. The Partnership encourages schools, districts and states to advocate for the infusion of 21st century skills into education and provides tools and resources to help facilitate and drive change. 21st Century Skills, 1 Education & Competiveness Why We Need to Act Now 2 What We Need to Do Now 10 A Shared Vision of a 12 21st Century ...
Before going further, it is useful to establish what exactly the term "21st Century competencies" means. There is a diversity of terminologies employed interchangeably within this relatively crowded space: "21st Century skills/competencies", "soft skills", "interdisciplinary skills" and "transferable skills", to name just a few.
Learn what 21st Century skills are, how they help students succeed in the Information Age, and how to teach them in CTE courses. Explore the three categories of 21st Century skills: learning, literacy, and life skills, and see examples of each skill.
Learn how to use a presentation project to develop your learners' communication, creativity, critical thinking and collaboration skills. Download free worksheets and follow the 10-step process for a cross-curricular activity.
The main topics from the presentation included:Report: Education and skills for the 21st century 16 Key messages - Partnerships are essential to implementing SDG 4-E2030; - Institutional cooperation and coordination between all partners: duplication of efforts is unjustifiable, particularly given the limited amount of resources; it is critical ...
The 21st-century skills classroom focuses on asking questions to encourage critical thinking, inquiry, and reasoning. In all courses, students evaluate, synthesize, and translate ideas to solve problems and complete projects. Teachers also encourage students to hone their reasoning and inquiry skills. Well-developed thoughts and approaching ...
This paper discusses issues related to the teaching and assessment of 21st century skills and competencies in OECD countries drawing on the findings of a questionnaire study and other relevant background material such as white papers or curriculum documents.
The first couple of years for the 21st-century educator can be stressful, but also rewarding. Each year, you will get closer to becoming a master teacher. Always believe that each of your students can and will succeed. Best wishes in your teaching journey, for it truly is a calling. Being a 21st-century educator is a tall order.
Learn what 21st-century learning is and why it is essential for students to succeed in a global economy. Discover the skills students need for learning in the 21st century and how educators can support them.
21st-century skills for students. Image: World Economic Forum, New Vision for Education (2015) An analysis of 213 studies showed that students who received SEL instruction had achievement scores that averaged 11 percentile points higher than those who did not. And SEL potentially leads to long-term benefits such as higher rates of employment ...
Here are the six main characteristics that, I believe, define the 21st century classrooms. 1. Technological Integration. The 21st-century classroom is unimaginable without the integration of technology, and soon AI (artificial intelligence). This facet of modern education transcends the traditional use of textbooks and blackboards, weaving ...
Learn how 21st century skills are developed and promoted through the Australian Curriculum and STEM education. Find out what 21st century skills are, why they are important and how to apply them in the classroom.
A Critical Resource: The Importance of Literacy Skills. Learn about the importance of literacy skills. This article explores how improved reading and writing abilities lead to student success and prepare learners for the challenges of the 21st-century job market. Published on May 21, 2024.
Published On: May 22, 2024. Educational technology platforms, interactive multimedia content, and productivity tools can enhance teaching and learning experiences, making lessons more engaging and effective. However, it's essential to ensure that these resources align with curriculum objectives and support the development of 21st-century skills.