Daring Leadership Institute: a groundbreaking partnership that amplifies Brené Brown's empirically based, courage-building curriculum with BetterUp’s human transformation platform.

What is Coaching?
Types of Coaching
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.
Find your coach
-1.png)
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals


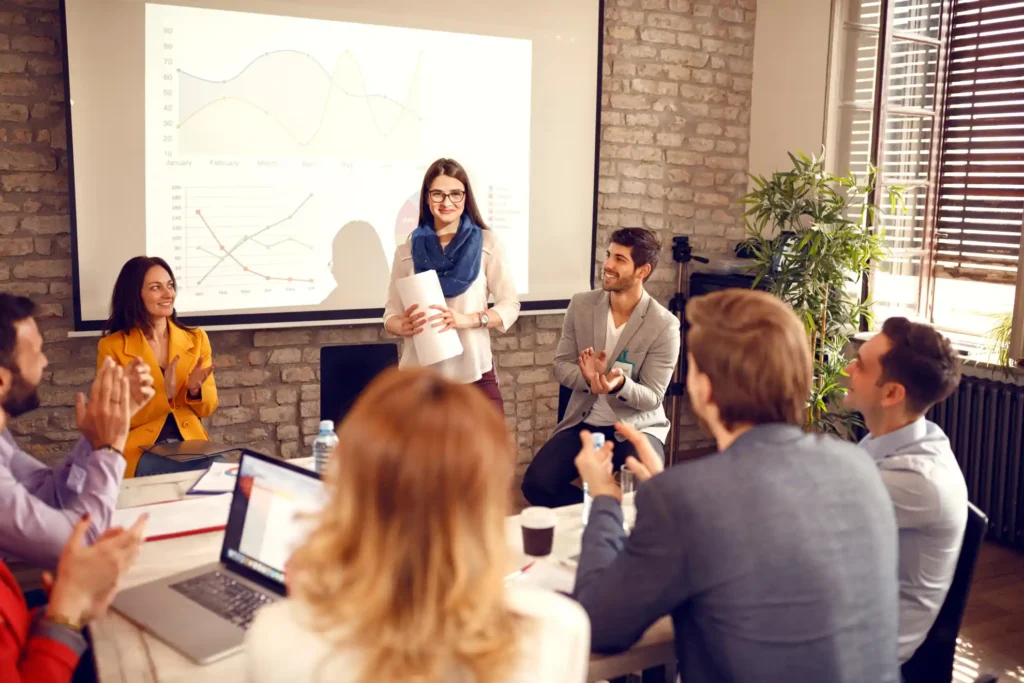
6 presentation skills and how to improve them

Jump to section
What are presentation skills?
The importance of presentation skills, 6 presentation skills examples, how to improve presentation skills.
Tips for dealing with presentation anxiety
Learn how to captivate an audience with ease
Capturing an audience’s attention takes practice.
Over time, great presenters learn how to organize their speeches and captivate an audience from start to finish. They spark curiosity, know how to read a room , and understand what their audience needs to walk away feeling like they learned something valuable.
Regardless of your profession, you most likely use presentation skills on a monthly or even weekly basis. Maybe you lead brainstorming sessions or host client calls.
Developing effective presentation skills makes it easier to contribute ideas with confidence and show others you’re someone to trust. Although speaking in front of a crowd sometimes brings nerves and anxiety , it also sparks new opportunities.
Presentation skills are the qualities and abilities you need to communicate ideas effectively and deliver a compelling speech. They influence how you structure a presentation and how an audience receives it. Understanding body language , creating impactful visual aids, and projecting your voice all fall under this umbrella.
A great presentation depends on more than what you say. It’s about how you say it. Storytelling , stage presence, and voice projection all shape how well you express your ideas and connect with the audience. These skills do take practice, but they’re worth developing — especially if public speaking makes you nervous.
Engaging a crowd isn’t easy. You may feel anxious to step in front of an audience and have all eyes and ears on you.
But feeling that anxiety doesn’t mean your ideas aren’t worth sharing. Whether you’re giving an inspiring speech or delivering a monthly recap at work, your audience is there to listen to you. Harness that nervous energy and turn it into progress.
Strong presentation skills make it easier to convey your thoughts to audiences of all sizes. They can help you tell a compelling story, convince people of a pitch , or teach a group something entirely new to them. And when it comes to the workplace, the strength of your presentation skills could play a part in getting a promotion or contributing to a new initiative.
To fully understand the impact these skills have on creating a successful presentation, it’s helpful to look at each one individually. Here are six valuable skills you can develop:
1. Active listening
Active listening is an excellent communication skill for any professional to hone. When you have strong active listening skills, you can listen to others effectively and observe their nonverbal cues . This helps you assess whether or not your audience members are engaged in and understand what you’re sharing.
Great public speakers use active listening to assess the audience’s reactions and adjust their speech if they find it lacks impact. Signs like slouching, negative facial expressions, and roaming eye contact are all signs to watch out for when giving a presentation.
2. Body language
If you’re researching presentation skills, chances are you’ve already watched a few notable speeches like TED Talks or industry seminars. And one thing you probably noticed is that speakers can capture attention with their body language.
A mixture of eye contact, hand gestures , and purposeful pacing makes a presentation more interesting and engaging. If you stand in one spot and don’t move your body, the audience might zone out.

3. Stage presence
A great stage presence looks different for everyone. A comedian might aim for more movement and excitement, and a conference speaker might focus their energy on the content of their speech. Although neither is better than the other, both understand their strengths and their audience’s needs.
Developing a stage presence involves finding your own unique communication style . Lean into your strengths, whether that’s adding an injection of humor or asking questions to make it interactive . To give a great presentation, you might even incorporate relevant props or presentation slides.
4. Storytelling
According to Forbes, audiences typically pay attention for about 10 minutes before tuning out . But you can lengthen their attention span by offering a presentation that interests them for longer. Include a narrative they’ll want to listen to, and tell a story as you go along.
Shaping your content to follow a clear narrative can spark your audience’s curiosity and entice them to pay careful attention. You can use anecdotes from your personal or professional life that take your audience along through relevant moments. If you’re pitching a product, you can start with a problem and lead your audience through the stages of how your product provides a solution.
5. Voice projection
Although this skill may be obvious, you need your audience to hear what you’re saying. This can be challenging if you’re naturally soft-spoken and struggle to project your voice.
Remember to straighten your posture and take deep breaths before speaking, which will help you speak louder and fill the room. If you’re talking into a microphone or participating in a virtual meeting, you can use your regular conversational voice, but you still want to sound confident and self-assured with a strong tone.
If you’re unsure whether everyone can hear you, you can always ask the audience at the beginning of your speech and wait for confirmation. That way, they won’t have to potentially interrupt you later.
Ensuring everyone can hear you also includes your speed and annunciation. It’s easy to speak quickly when nervous, but try to slow down and pronounce every word. Mumbling can make your presentation difficult to understand and pay attention to.

6. Verbal communication
Although verbal communication involves your projection and tone, it also covers the language and pacing you use to get your point across. This includes where you choose to place pauses in your speech or the tone you use to emphasize important ideas.
If you’re giving a presentation on collaboration in the workplace , you might start your speech by saying, “There’s something every workplace needs to succeed: teamwork.” By placing emphasis on the word “ teamwork ,” you give your audience a hint on what ideas will follow.
To further connect with your audience through diction, pay careful attention to who you’re speaking to. The way you talk to your colleagues might be different from how you speak to a group of superiors, even if you’re discussing the same subject. You might use more humor and a conversational tone for the former and more serious, formal diction for the latter.
Everyone has strengths and weaknesses when it comes to presenting. Maybe you’re confident in your use of body language, but your voice projection needs work. Maybe you’re a great storyteller in small group settings, but need to work on your stage presence in front of larger crowds.
The first step to improving presentation skills is pinpointing your gaps and determining which qualities to build upon first. Here are four tips for enhancing your presentation skills:
1. Build self-confidence
Confident people know how to speak with authority and share their ideas. Although feeling good about your presentation skills is easier said than done, building confidence is key to helping your audience believe in what you’re saying. Try practicing positive self-talk and continuously researching your topic's ins and outs.
If you don’t feel confident on the inside, fake it until you make it. Stand up straight, project your voice, and try your best to appear engaged and excited. Chances are, the audience doesn’t know you’re unsure of your skills — and they don’t need to.
Another tip is to lean into your slideshow, if you’re using one. Create something colorful and interesting so the audience’s eyes fall there instead of on you. And when you feel proud of your slideshow, you’ll be more eager to share it with others, bringing more energy to your presentation.
2. Watch other presentations
Developing the soft skills necessary for a good presentation can be challenging without seeing them in action. Watch as many as possible to become more familiar with public speaking skills and what makes a great presentation. You could attend events with keynote speakers or view past speeches on similar topics online.
Take a close look at how those presenters use verbal communication and body language to engage their audiences. Grab a notebook and jot down what you enjoyed and your main takeaways. Try to recall the techniques they used to emphasize their main points, whether they used pauses effectively, had interesting visual aids, or told a fascinating story.

3. Get in front of a crowd
You don’t need a large auditorium to practice public speaking. There are dozens of other ways to feel confident and develop good presentation skills.
If you’re a natural comedian, consider joining a small stand-up comedy club. If you’re an avid writer, participate in a public poetry reading. Even music and acting can help you feel more comfortable in front of a crowd.
If you’d rather keep it professional, you can still work on your presentation skills in the office. Challenge yourself to participate at least once in every team meeting, or plan and present a project to become more comfortable vocalizing your ideas. You could also speak to your manager about opportunities that flex your public speaking abilities.
4. Overcome fear
Many people experience feelings of fear before presenting in front of an audience, whether those feelings appear as a few butterflies or more severe anxiety. Try grounding yourself to shift your focus to the present moment. If you’re stuck dwelling on previous experiences that didn’t go well, use those mistakes as learning experiences and focus on what you can improve to do better in the future.
Tips for dealing with presentation anxiety
It’s normal to feel nervous when sharing your ideas. In fact, according to a report from the Journal of Graduate Medical Education, public speaking anxiety is prevalent in 15–30% of the general population .
Even though having a fear of public speaking is common, it doesn’t make it easier. You might feel overwhelmed, become stiff, and forget what you were going to say. But although the moment might scare you, there are ways to overcome the fear and put mind over matter.
Use these tactics to reduce your stress when you have to make a presentation:
1. Practice breathing techniques
If you experience anxiety often, you’re probably familiar with breathing techniques for stress relief . Incorporating these exercises into your daily routine can help you stop worrying and regulate anxious feelings.
Before a big presentation, take a moment alone to practice breathing techniques, ground yourself, and reduce tension. It’s also a good idea to take breaths throughout the presentation to speak slower and calm yourself down .
2. Get organized
The more organized you are, the more prepared you’ll feel. Carefully outline all of the critical information you want to use in your presentation, including your main talking points and visual aids, so you don’t forget anything. Use bullet points and visuals on each slide to remind you of what you want to talk about, and create handheld notes to help you stay on track.
3. Embrace moments of silence
It’s okay to lose your train of thought. It happens to even the most experienced public speakers once in a while. If your mind goes blank, don’t panic. Take a moment to breathe, gather your thoughts, and refer to your notes to see where you left off. You can drink some water or make a quick joke to ease the silence or regain your footing. And it’s okay to say, “Give me a moment while I find my notes.” Chances are, people understand the position you’re in.

4. Practice makes progress
Before presenting, rehearse in front of friends and family members you trust. This gives you the chance to work out any weak spots in your speech and become comfortable communicating out loud. If you want to go the extra mile, ask your makeshift audience to ask a surprise question. This tests your on-the-spot thinking and will prove that you can keep cool when things come up.
Whether you’re new to public speaking or are a seasoned presenter, you’re bound to make a few slip-ups. It happens to everyone. The most important thing is that you try your best, brush things off, and work on improving your skills to do better in your next presentation.
Although your job may require a different level of public speaking than your favorite TED Talk , developing presentation skills is handy in any profession. You can use presentation skills in a wide range of tasks in the workplace, whether you’re sharing your ideas with colleagues, expressing concerns to higher-ups, or pitching strategies to potential clients.
Remember to use active listening to read the room and engage your audience with an interesting narrative. Don’t forget to step outside your comfort zone once in a while and put your skills to practice in front of a crowd. After facing your fears, you’ll feel confident enough to put presentation skills on your resume.
If you’re trying to build your skills and become a better employee overall, try a communications coach with BetterUp.
Understand Yourself Better:
Big 5 Personality Test
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
8 tips to improve your public speaking skills
The significance of written communication in the workplace, the 11 tips that will improve your public speaking skills, what is an entrepreneur understanding the different types and examples of entrepreneurship, get smart about your goals at work and start seeing results, 9 signs that you’re being pushed out of your job, goal-setting theory: why it’s important, and how to use it at work, the importance of good speech: 5 tips to be more articulate, empathic listening: what it is and how to use it, how to write a speech that your audience remembers, impression management: developing your self-presentation skills, 30 presentation feedback examples, your guide to what storytelling is and how to be a good storyteller, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, 8 clever hooks for presentations (with tips), how to make a presentation interactive and exciting, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case studies
- ROI of BetterUp
- What is coaching?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Personal Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Briefing
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Develop Effective Verbal Communication Skills
March 3, 2021 - Dom Barnard
Verbal communication skills are more important than ever. Countless meetings, presentations, code reviews, conferences and networking events mean that clear and assertive verbal communication are essential for current and future jobs .
Good communication skills can be the difference between getting a promotion or moving laterally, selling your product or struggling with slow growth, influencing colleagues with your idea or doing what you are told.
Article contents
Why is verbal communication important, characteristics of an effective communicator, the power of the mind, keep your audience in mind, actively listen, be empathetic, body language and posture, using the full range of your voice, watch videos from experts.
- 5 ways to practice communication skills
Communication skills are important to many aspects of your life and career, including:
- Managerial role – how do you command respect from your colleagues while building a strong culture and team spirit? How do you deal with an unexpected crisis and communicate your action plan to your team? Oral communication skills are essential for many areas of management.
- Workplace success – you’ll frequently be talking to clients, customers, talking in team meetings, requesting information, giving feedback and discussing problems. All require strong communication skills so that you are understood clearly without any misinterpretation.
- Secure a new job – in employer surveys, oral communication skills consistently rank amongst the top soft skills companies look for. They want new employees to be able to speak clearly, concisely and confidently.
- Advance your career – it’s important to be able to communicate your thoughts on how the processes, products or services can be improved. Business value these skills in management positions.
An effective communicator’s attributes include:
- Active listening
- Adaptability – adapting your communication styles to support the situation
- Confidence and assertiveness
- Constructive feedback – giving and receiving it
- Emotional intelligence – identifying and managing your emotions, as well as other people’s emotions
- Interpersonal skills – social skills which are especially useful in building strong rapports
- Interpretation of body language – this will help you understand how someone is feeling
- Open-mindedness
- Simplifying the complex
- Storytelling
Techniques for improving verbal communication
Communication is a skill which means that you can develop and improve it. Here are some techniques which can refine your skills.
Often we talk while we think but this can reduce our credibility because what we’re saying is usually meaningless and we come across as nervous. Much of presence is about stillness, listening and providing thoughtful response.
When answering questions and whilst engaging in conversation keep the following formula in mind and reply in a short, clear and concise way:
So don’t just say the first thing that comes to mind, instead be thoughtful and concentrate on the meaning of what you wish to communicate. When speaking, understand exactly what message you’re trying to get across. If you are unclear about your message then your audience won’t understand either.
Positive visualisation
This tactic is employed by athletes before a race , they visualise themselves winning and focus on this idea intensely. This gives them a mental boost which translates into a physical one.
You can use this technique before a big presentation – imagine standing on a podium in front of hundreds of people, imagine delivering your speech and the audience looking engaged, imagine finishing up your speech and the audience applause.
Repeating this several times and immersing yourself in the event and the emotions will build effective communication skills.
Exercise – Positive Visualisation
- Find a quiet place to sit down and relax
- Close your eyes
- Think back to an experience you have had that made you feel really good. It can be anything – a personal accomplishment, a youthful memory, a successful project at work
- Take yourself back there and replay the sequence of events
- Be as detailed as you can in reliving the moment for yourself
- Hear the sounds, see the sights and feel the emotions
- Replay this a few times until you are immersed in this event
- Now open your eyes
This is a great technique to do before a presentation as it will help you control your nerves and it will increase your confidence for the event.
You must understand your audience to communicate effectively. By having this understanding you can tailor your communication to suit them so your message has the most impact.
To develop this skill you must imagine yourself in the audience’s position – think of their demographic and shared characteristics. Ask: why are they attending? What do they want to find out? What level are they in terms of knowledge and experience?
Active listening is when you listen beyond the words being spoken – you understand the message being communicated. During conversations, a lot of the time the “listener” is thinking about how they’re going to respond rather than concentrating on what the speaker is saying.
- Course on Active Listening with Online Practice
By really listening you can provide a more thoughtful answer that takes the speaker’s thoughts and opinions into account. Like Richard Branson said, “Listen more than you talk.”

To develop active listening you should practice the following:
1. Pay attention
Give the speaker your complete attention:
- Look at them directly and maintain eye contact.
- Don’t think about your reply whilst they’re speaking.
- Interpret their body language.
- Try to avoid being distracted by what’s happening around you.
2. Show the speaker that you’re interested
- Use your body language to highlight your engagement, such as, nodding, smiling, maintaining an open posture etc.
- Use prompts, such as, “uh huh”, “yep” etc.
- Clarify your understanding…
3. Clarify your understanding
You need to ensure that you understand what the speaker is saying without your judgments and beliefs getting in the way:
- Reflect on what you have heard by summarising and paraphrasing, for example, “Sounds like you’re saying…”. Ensure you do this periodically in a conversation as it helps with your understanding and it’s also another way to show the speaker than you’re listening.
- Ask questions to ensure that you understand everything, such as, “What do you mean when you say…” Ensure that these questions are non-judgemental.
- Ask whether you’ve got it right and accept if you need to be corrected.
- Ask for specific examples.
- Admit if you’re unsure about what the speaker means.
- Ask the speaker to repeat something if you think it will help.
4. Don’t interrupt or redirect the conversation
Interrupting is not helpful as it’s irritating for the speaker and it reduces the time for you to understand the message:
- Before saying anything ensure that the speaker has finished a point.
5. Provide a suitable response
- Be honest when you respond but avoid attacking or making the speaker feel bad because this is unhelpful.
- Provide your opinions politely.
These are the most common obstacles to active listening:
- Losing concentration.
- Jumping to conclusions which subsequently leads to false assumptions.
- Hastily forming a response before the speaker is finished.
To be empathetic means that you are able to identify and understand others’ emotions i.e. imagining yourself in someone else’s position.
Understanding how people feel will help you communicate your thoughts and ideas in a way that makes sense to others and it helps you understand others when they communicate.
To develop empathy:
- Imagine yourself in someone else’s position. Even if you have not experienced a similar situation, remember a situation where you have felt the same emotion your colleague/employee is experiencing.
- Practice listening to your colleagues without interrupting them.
- Observe your colleagues and try to gauge how they’re feeling.
- Never ignore your colleagues’ emotions, for example, if someone looks upset don’t disregard this – address it.
- Try to understand first rather than form a judgement. For example, you may initially feel annoyed at a colleague who seems cold and disinterested. However, after discovering they suffer from social anxiety you may feel more sympathetic.
- To communicate your empathy, keep your body language open and regulate your voice to show your sincerity.
Your posture has the greatest impact on your communication. The impression you have on others is split approximately:
- Body (visuals) 55%
- Voice (sound) 38%
- Words (content) 7%
Folded arms, crossed legs, hunched shoulders, hands in pockets, looking down – these are just some of the protective measures that make us feel safer, and should be avoided when giving a presentation or speech. Appearing relaxed makes us exert dominance and authority.
If you watch politicians speak, notice how relaxed and confident they appear, talking slowly and making positive body movements. Use your arms to emphasis a point and illustrate the message.
Read our 8 Elements of Confident Body Language .
Exercise – Posture
- Place your feet the same width apart as your hips.
- Feel your weight at the heel of your foot on the floor
- Think of your shoulders expanding out from one another.
- Do not hunch forward or pull your shoulders back – allow them to rest centrally.
- Hold your head level.
- Let your arms hang relaxed by your side.
- Spend a moment getting used to this position.
- Do a mental check around your body and make any adjustments you need to get comfortable.
- Try moving to another spot, regaining this relaxed position.
When a person is centred, they are balanced and relaxed. Getting used to placing your attention in your centre of gravity will help you achieve an open, relaxed posture, and make room for deeper, freer breath.
Think about the place halfway between the front and back of your body, and just above your waist. Stand with your feet a shoulder length apart and let your arms hang loosely by your side. Try and put all your attention at this centre before an important meeting or presentation, it will increase your presence and bring you into the moment.
Visual rapport – things to consider
From top down: head, eyes, expressions, shoulders, posture, breathing, energy, arms, hands, gestures, movements, stance, legs and feet.

The human voice is capable of 24 notes on a musical scale. We use about three of these in everyday speech. Think about this next time you speak, as using a wider range will allow you to quickly develop effective communication skills. This will help enthuse, persuade and excite the person or people you are talking to.
Sound resonates in the mouth once your breath has delivered air to the vocal cords. Your tongue manipulates and shapes the sound, giving us speech, pitch and tone.
The more air in your lungs, the better the sounds resonate, giving us a wider range of audible voice. Most of us use less than a third of our vocal capacity and the reason is usually because we do not use our breath as well as we could.
To further understand how to use your voice, read the Toastmasters Speaking Voice Guide .
Breathe deeply to communicate effectively
Every time you think, you breathe. Every time you speak, you breathe. The fact that we breathe subconsciously, means we often don’t think about it when speaking. When we get nervous our breathing becomes shallow . Combine this with overlong sentences, which usually accompany speaking in public, and words begin to trail away at the end.
Maximising your breath and filling your lungs when speaking is very important for building effective communication skills. It makes you sound influential.
Remember to pause for emphasis, pause to take in a breath and pause to allow your message to sink in.
Exercise – Breathing
- Stand in the Neutral Position and put your hands on your stomach.
- Breathe deeply.
- Try to push your hands out as you breathe in by filling your ribs.
- Increase your awareness of this happening as you breathe – the movement and expansion of the ribs.
You can do this one in the comfort of your own home as there are lots of videos online from motivational speakers and communication experts. Watch how these people present themselves – where they look, their tone of voice, the speed at which they speak etc.
Make a list of things they do that you want to replicate in your own speaking and then imitate what the speakers do when you’re talking.
Start small and scale up to a larger audience as you become more comfortable and confident in your ability to deliver your message effectively.
This isn’t an overnight quick-fix (unfortunately, there isn’t one) and you’ll have to practice mastering speaking techniques and eliminate any bad linguistic habits you’ve picked up. If you persevere, you’ll improve your verbal communication skills quickly.
Here are two more videos to get you started:
- ‘ How great leaders inspire action ‘ – Simon Sinek presents a simple but powerful model for how leaders inspire action, starting with a golden circle and the question “Why?”
- ‘ Why We Do What We Do ‘ – Tony Robbins, motivational speaker. You can use this video to show you techniques such as pausing after important points, varying your pitch and using hand gestures to emphasise your message.
5 ways to practice verbal communication skills
Studies on the benefits of practice.
Many studies have taken place on the benefits of practice. We’ve summarised three key benefits for you.
Benefits of practicing oral communication skills:
- Practice greatly increases the likelihood that you’ll remember new information (Anderson, 2008).
- Practice increases your ability to apply knowledge automatically, without reflection. This is usually only achieved through extensive rehearsal and repetition , and frees up your cognitive resources to handle other tasks. (Brown & Bennett, 2002; Moors & De Houwer, 2006).
- Receive feedback on your communication skills so you know where and how to improve
You should think of practice not as rote repetition, but as deliberate, goal-directed rehearsal paired with reflection on communication skills.
- Practice for Knowledge Acquisition (Not Drill and Kill)
Learning vs. practicing
You may be accustomed to being good at what you do. Learning something new is hard, especially at the beginning when we’re likely to struggle and make mistakes. The reality is, the only way to learn something new is to practice.
In his book, Outliers , Malcolm Gladwell suggests that it takes 10,000 hours of practice to become expert at something. Perhaps more of a realist, Josh Kaufman, author of The Personal MBA , writes that to go from “knowing nothing to being pretty good” takes about 20 hours of practice. So whether you aspire to be “pretty good” or an “expert,” practice is essential.
Some people believe that intellectual understanding is enough for skill development. However, many studies have shown this is not that case – we need to practice, get feedback, refine our approach, practice again and generally apply the knowledge we learn. This is hard to do.
You can spend hours learning about communication skills, but without actually practicing what you learn, you’ll only have an intellectual understanding as opposed to skill development.
After learning how to communicate, you’ll need to practice what you’ve learnt in order to develop the skill. We’ve listed both traditional and new methods you can use to practice your communication skills.
1. Online simulator
More and more you may find yourself communicating over video conferencing platforms such as Zoom and Skype. These require a unique set of skills compared to in-person communication.
You can practice your oral communication skills in simulations which mimic video-conferencing software, as well as watch yourself back and receive automated feedback on your performance.
- How to Present over Video – Practice how to deliver successful video-based presentations on Zoom, Skype, Webex, Teams and more.
- Ace your Video Interview – Practice how to deliver successful video-based sales pitches on popular video conferencing platforms.
- Online Interview Training – Learn how to ace your video-based interview with best practices and a mock interview simulator.
Practice your communication skills with interactive online exercises .
2. Professional coaching
This can be in person or through a phone / Skype call. We’ve listed three examples of communication skills coaching.
- RADA Coaching – RADA can enable you to transform all aspects of your leadership, help you to master communication skills such as personal impact, presence and authenticity, or support you on a specific workplace challenge or presentation.
- Public Speaking and Presentation Coaching – get a tailored presentation skills coaching program to your skill level, over the phone or through Skype, so you achieve your goals as quickly as possible.
- Public Speaking and Communications Coaching – personalised sessions of communication skills, presentation skills or public speaking coaching to help you to develop your self-confidence, focus on specific issues or prepare for a particular event.
3. Virtual reality environments
Virtual reality (VR) lets you practice verbal communication techniques in realistic environments from the comfort of your own home. It’s a great middle ground between an online course and in-person coaching. For a more detailed list of VR apps, read our article on top public speaking apps .
- VirtualSpeech platform – practice communication skills, interview preparation, business networking, language learning, sales, and more with interactive exercises. Speech analysis technology provides instant feedback on your speech or conversation.
- Speech Trainer – this Steam based app provides a virtual auditorium where you can learn to overcome your fear of public speaking by addressing a virtual audience.

VR being used to practice a presentation.
4. Friends or colleagues
This is a great way to get detailed feedback on how you are performing. Set yourself a task and ask your colleague or friend to observe you and then give you feedback.
Giving and receiving feedback is a powerful process but needs to be handled sensitively and should follow these guidelines:
- Be specific on what needs to improve
- Provide evidence on where they can change
- Give feedback on any emotional impact you felt
- Be constructive, provide 3 positives and 2 areas to improve
- Listen and don’t interrupt
- Act on the feedback straight away if possible
5. Solo with a video camera or voice recorder
By using a video camera or voice recorder, you can work on your oral communication style. Work with short sections – for example if you need to make a presentation, start by working on your opening.
Perform and watch / listen back a number of times until you feel you have developed what you have done sufficiently to move on.
In this method of working, you alternate the role of subject and observer. When you are observing / listening to yourself, clarify any feedback by writing down what you are developing or changing. This will help you measure your progress as well as structuring your development.
- Free online voice recorder
Final thoughts
Communication is one of the most effective skills that you can cultivate for work so it’s worth the effort to develop it. It’s also helpful to keep in mind the following when working on your communication:
- What we hear last is remembered the easiest.
- We remember things that are presented with an impact, such as, using emotional appeals (pathos).
- We remember things that we have use for.
- We remember what we hear frequently so repetition is important.
How to make a great presentation
Stressed about an upcoming presentation? These talks are full of helpful tips on how to get up in front of an audience and make a lasting impression.

The secret structure of great talks

The beauty of data visualization

TED's secret to great public speaking

How to speak so that people want to listen

How great leaders inspire action
Types of Verbal Communication Skills: Tips, Importance and Styles
- By Judhajit Sen
- June 24, 2024
Verbal communication is essential for connecting with others and understanding them better. While nonverbal communication play a big part in our first impression of someone, the words we use in conversation confirm or change that impression.
Verbal communication involves using words to convey information. This can be through speaking or writing, although many think it is just spoken communication. The words you choose and how others interpret them are crucial.
Verbal communication is a key skill. It helps us express ourselves clearly, build relationships, influence others positively, and confidently handle challenges. Good communication skills can result in success in many walks of life, from advancing your career to personal growth.
This article will delve into the numerous types and styles of verbal communication, their importance in the workplace, and tips for improving them.
Key Takeaways
- Importance in Connection: Verbal communication is crucial for building connections and understanding others. It helps express ideas, convey information, and form relationships in both personal and professional settings.
- Types of Communication: There are various types of verbal communication, including intrapersonal (self-talk), interpersonal (between two people), group (small groups), public (large audiences), and mass communication (media and social platforms).
- Styles of Communication: Different communication styles include aggressive (forceful), passive (reserved), passive-aggressive (indirect hostility), and assertive (clear and respectful). Understanding these can improve how we interact with others.
- Improvement Tips: Key tips for enhancing verbal communication include listening actively, expanding vocabulary, reading non-verbal communication, and using simple language. These skills help ensure clear, effective, and respectful interactions.
Verbal Communication Explained
Verbal communication employs spoken or written words to express ideas, thoughts, and feelings to others. It’s a fundamental way we interact through conversations, presentations, or speeches. This form of communication allows us to convey information, practice storytelling , ask questions, and connect with others on a deeper level.
We start using verbal communication the moment we meet someone. It’s crucial in everyday interactions, helping us express ourselves clearly and understand others. By improving our verbal communication, we can become better communicators and convey our messages more confidently.
Verbal communication can be spoken and written. It includes face-to-face conversations, phone calls, video chats, and written communication like emails, letters, and texts. This form of communication is essential in fostering collaboration and building relationships, especially in professional settings, such as executive communication .
Effective verbal communication involves not just speaking clearly but also listening attentively. Clear messages and listening actively are key to avoiding misunderstandings and interpreting others’ words correctly. It’s also important to remember that non-verbal signals like facial expression, body language, eye contact and voice intonation play a vital role in how our words are received.
Verbal communication is a powerful tool for sharing information and expressing complex ideas. It helps us to connect, collaborate, and build meaningful relationships.
Importance of Workplace Verbal Communication

Communication is everywhere in our lives, from small gestures to big conversations. Whether spoken or unspoken, we always send and receive messages.
In the workplace, communication usually means using professional language and having polite but clear conversations. It’s essential to show your communication skills at work, whether you’re talking to your boss or a coworker.
Good communication at work has many benefits, as per the research paper “ Communication in the Workplace – Guidelines for Improving Effectiveness. ” Here are a few key points:
Employee satisfaction: When a company supports open communication among all employees, it helps everyone feel heard and valued.
Reduce conflicts: Conflicts at work are common, but open communication can help resolve misunderstandings. Clear and direct speech ensures that coworkers understand each other.
Build relationships: Open communication helps employees connect and establish credibility in a speech , essential for a healthy and productive workplace.
Increase productivity: Miscommunication can slow down work. Encouraging employees to communicate openly and ask for clarification reduces misunderstandings and boosts productivity.
Different Types of Verbal Communication

Verbal communication can take many forms. Intrapersonal communication is self-talk and reflection. Interpersonal communication happens between two people. Group communication involves talking in a small group. Public communication is speaking to a large audience. Mass communication reaches many people through TV or radio.
Following are the different types of verbal communication.
Intrapersonal Verbal Communication
Intrapersonal communication involves thinking, reflecting, and processing information internally. This type of communication helps us understand our thoughts, make decisions, and reflect on our experiences.
For example, talking to ourselves to prepare for a challenging situation can boost our confidence and improve our performance. We often engage in intrapersonal communication when processing confusing information, tackling strong emotions, or daydreaming.
This internal dialogue is a form of verbal communication, even though it happens silently within our brains. When you ask yourself questions like, “What should I wear today?” or mentally plan your day, you are using intrapersonal communication.
Intrapersonal communication is the internal speech that helps us navigate our thoughts and emotions daily.
Interpersonal Verbal Communication
Interpersonal communication happens between two or more people. It’s essential for building relationships, expressing emotions, and sharing information. This type of interactive communication , also known as dyadic communication, involves talking and listening. Chatting with a friend, speaking with a family member, or discussing a project with a coworker are all interpersonal verbal communication examples.
Key elements include listening actively, clear speaking, and effective responding. Words, tone of voice, and even nonverbal gestures like nodding or hand movements help convey messages accurately. Using these verbal and nonverbal signs ensures that information is exchanged clearly and connections are made meaningfully.
Group Verbal Communication
Group communication involves talking and interacting within a small to medium-sized group, typically three or more people. This can include team meetings, business plan discussions, study groups, or even friends planning a weekend getaway. Effective group communication requires everyone to participate actively, listen carefully, and treat each other respectfully.
In these settings, people share ideas, exchange information, and work together toward common goals. For example, everyone should feel encouraged to contribute equally in a team meeting or a collaborative discussion. Facilitating open dialogue and promoting equal participation are essential to successful group dynamics and effective collaboration.
Public Verbal Communication
Public communication involves speaking to a big group, like giving a speech or leading an event. It needs clear talking, exciting presentations , and good ways to connect with the listeners. Speaking well in public can inspire, persuade, and impact others, making it super important in many jobs and social situations.
In this type of communication, one person talks to a large crowd to share info. It happens in places where lots of people come together to hear one person speak, like election rallies or public speeches.
When someone talks to a bigger audience, it’s called public communication. It’s usually one person talking to many people, like a boss updating a big group, a politician making a persuasive speech , or a speaker at a conference.
Ever been to a TED Talk or a press conference? That’s public verbal communication, too, but you’re on the listening side. Public speaking differs from just chatting in a group because it has a speaker sharing info with a gathered audience.
Mass Verbal Communication
Mass verbal communication involves delivering messages to a large group through media like newspapers, TV, radio shows, and social media posts. Unlike other types of verbal communication, where there’s usually one speaker, mass verbal communication often features a small group of people sharing their ideas.
This type of communication uses these platforms to reach a large audience. It’s like when news is reported on TV or when a radio show discusses topics that interest many listeners. Social media also plays a significant role nowadays, spreading messages to people worldwide in seconds.
Different Styles of Verbal Communication

Following are the four different verbal communication styles published by Alvernia University.
The aggressive communication style is all about being forceful and confrontational with your words. People who use this style like to dominate conversations and don’t care much about what others think. They might even yell or attack verbally to get their point across. This way of talking can cause a lot of fighting and hard feelings, which makes it hard to have good conversations.
People who use aggressive communication styles often seem to don’t care about how others feel. They’re very direct and sometimes even mean. They like to be in charge and expect everyone to do what they say without question.
The passive communication style is when someone finds it hard to speak up about what they think or need. People who communicate this way often avoid arguments, but this can mean they don’t stand up for themselves or others. It might stop fights now, but it can make it challenging for them to get what they want in the long run.
People who use passive communication might seem shy, quiet, or distant. They usually try to keep everyone happy when there’s a disagreement. They often keep their thoughts to themselves and might be unclear when they finally share them. Passive speakers usually don’t mind following what others say or do. It doesn’t mean they’re weak; they just don’t like arguing and will do a lot to avoid it.
Passive-aggressive
The passive-aggressive style of communication blends passivity with hidden hostility. Instead of openly expressing displeasure, individuals using this style may resort to sarcasm, backhanded compliments, or subtle sabotage to convey their frustrations. This indirect approach often confuses and can harm relationships because true feelings are not openly communicated.
You’ve probably encountered passive-aggressive people before. They hide their true emotions and dissatisfaction, especially when faced with disagreement. While appearing passive on the surface, they quietly nurture their resentment underneath this facade. Their actions don’t always match their words. Rather than openly discussing their feelings, passive-aggressive individuals express their negative reactions indirectly.
Assertive communication means expressing your thoughts, feelings, and needs clearly and respectfully. It values everyone’s rights and opinions. People who use this style are not afraid to speak up and share their feelings and ideas in a positive manner. They listen actively to others and aim to find solutions for everyone involved. This approach builds healthy relationships, helps to understand each other better, and resolves disagreements constructively. It’s one of the best communication methods because it promotes cooperation and helps achieve common goals.
Tips to Improve Your Verbal Communication Skills

Practice Active Listening
Improving how we talk isn’t just about what we say but also about how we listen. One big mistake we all make is listening just to respond. Instead, we should listen to really understand. That means getting what the other person is saying so the message gets across right. Listening actively isn’t just hearing the words; it’s seeing things from their side and picking up on the small stuff that matters.
To listen actively, focus on the speaker, look them in the eye, and don’t interrupt. When we chat, we often worry too much about what to say next and how to say it, forgetting to listen. Active listening keeps us tuned in and shows the speaker we’ve got their full attention. It’s a way to say, “Hey, what you’re saying matters to me.”
Remember, listening actively isn’t just about our ears. It’s about our eyes, too—keeping them on the speaker without distractions. If it’s noisy, ask to move somewhere quieter. When we listen, it’s easier to respond well. So, next time, let’s focus on understanding before jumping in with our thoughts.
Build Your Vocabulary
Reading is essential for improving how you talk with others. When you read, you concentrate and keep an open mind to understand what the author is saying. This helps you get information better and learn how to say things more clearly.
To get better at talking, keep learning new words. Read books, articles, and talk with people to build your vocabulary. This way, you can express yourself more clearly and make your point easier to understand.
Learn to Read Nonverbal Cues
Nonverbal cues play a major role in how we communicate. Studies say they can make up to half of all communication. People often show their real feelings more with body language and gestures than words. That’s why noticing these subtle signs when talking to others is crucial so you can respond correctly.
To improve how you communicate:
Watch Your Posture: Sit or stand straight. This shows you’re attentive and confident.
Use Your Hands: Gesturing can emphasize what you’re saying and keep listeners interested.
Show Openness: Face the person you’re talking to. Lean in slightly to show you’re engaged and interested in what they’re saying.
By being aware of these nonverbal signals, you can improve communication skills and connect better with others.
Use Simple Language
The main aim of conversations is to share and understand ideas clearly. To achieve this, it’s best to use straightforward words instead of complicated ones. Simple language helps ensure that everyone can easily grasp what you’re saying. It’s also crucial to be clear and direct when talking to others.
When expressing your thoughts, be clear and concise. Avoid using fancy words or complex language that might confuse people. Stick to simple words everyone can understand, and your message will be more effective.
Mastering Verbal Communication: Key Insights and Practical Tips
Effective verbal communication is vital for connecting with others and achieving success in various aspects of life. We express our thoughts, convey information, and build relationships by using spoken or written words. Good verbal communication techniques help us navigate personal and professional interactions like business communication with confidence.
Clear and respectful communication fosters employee satisfaction, reduces conflicts, builds trust, and increases productivity. Different kinds of verbal communication, such as intrapersonal, interpersonal, group, public, and mass communication, serve distinct purposes in different contexts.
Understanding and improving verbal communication involves listening actively, expanding vocabulary, reading nonverbal cues, and using simple language. Listening actively ensures messages are understood correctly, while a rich vocabulary enhances clarity. Nonverbal cues, such as posture and gestures, significantly impact how our words are received. Using straightforward language ensures our messages are easily comprehended.
By honing these skills, we can become more effective communicators, fostering better understanding and stronger connections in our personal and professional lives. Verbal communication is a powerful tool; mastering it is essential for success and meaningful interactions.
1. What is verbal communication?
Verbal communication employs written or spoken words to convey information, ideas, and feelings. It includes face-to-face conversations, phone calls, video chats, emails, and texts.
2. What is the purpose of verbal communication in the workplace?
Good verbal communication at work boosts employee satisfaction, reduces conflicts, builds strong relationships, and increases productivity. Clear and respectful conversations help ensure everyone understands each other.
3. What are the different verbal communication types?
Verbal communication can be intrapersonal (self-talk), interpersonal (between two people), group (small groups), public (large audiences), and mass (through media like TV and radio).
4. How can I improve my verbal communication skills?
You can enhance your skills by listening actively, expanding your vocabulary, understanding nonverbal cues, and using simple language. These practices help you communicate more effectively and confidently.
Elevate Your Presentations and Communication with Prezentium
Unlock the power of effective verbal communication with Prezentium , your go-to AI-powered business presentation service provider. Our Overnight Presentations ensure that your requirements are met with excellence by the next business day, while our Presentation Specialists transform your ideas into stunning presentations that leave a lasting impact. Additionally, our Zenith Learning program offers interactive workshops that combine problem-solving and visual storytelling, designed to help you master the art of verbal communication.
Mastering verbal communication is crucial for building relationships, conveying ideas clearly, and achieving professional success. Whether it’s through clear speech, listening actively, or reading nonverbal cues, our services equip you with the skills needed to excel in any setting. Enhance your communication and presentation capabilities with Prezentium and experience the difference.
Visit prezentium.com to learn more about how we can help you elevate your presentations and become a more effective communicator. Let us help you turn your ideas into compelling stories and master the art of verbal communication today!
Why wait? Avail a complimentary 1-on-1 session with our presentation expert. See how other enterprise leaders are creating impactful presentations with us.
Shark Tank Presentation Tips: Winning Shark Tank Pitch Elements
Visual communication: benefits, importance, and examples, 7 public speaking tips for enhancing your public speaking abilities.
Ideas and insights from Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning

Powerful and Effective Presentation Skills: More in Demand Now Than Ever

When we talk with our L&D colleagues from around the globe, we often hear that presentation skills training is one of the top opportunities they’re looking to provide their learners. And this holds true whether their learners are individual contributors, people managers, or senior leaders. This is not surprising.
Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way.
For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget, or explain a new product to a client or prospect. Or you may want to build support for a new idea, bring a new employee into the fold, or even just present your achievements to your manager during your performance review.
And now, with so many employees working from home or in hybrid mode, and business travel in decline, there’s a growing need to find new ways to make effective presentations when the audience may be fully virtual or a combination of in person and remote attendees.
Whether you’re making a standup presentation to a large live audience, or a sit-down one-on-one, whether you’re delivering your presentation face to face or virtually, solid presentation skills matter.
Even the most seasoned and accomplished presenters may need to fine-tune or update their skills. Expectations have changed over the last decade or so. Yesterday’s PowerPoint which primarily relied on bulleted points, broken up by the occasional clip-art image, won’t cut it with today’s audience.
The digital revolution has revolutionized the way people want to receive information. People expect presentations that are more visually interesting. They expect to see data, metrics that support assertions. And now, with so many previously in-person meetings occurring virtually, there’s an entirely new level of technical preparedness required.
The leadership development tools and the individual learning opportunities you’re providing should include presentation skills training that covers both the evergreen fundamentals and the up-to-date capabilities that can make or break a presentation.
So, just what should be included in solid presentation skills training? Here’s what I think.
The fundamentals will always apply When it comes to making a powerful and effective presentation, the fundamentals will always apply. You need to understand your objective. Is it strictly to convey information, so that your audience’s knowledge is increased? Is it to persuade your audience to take some action? Is it to convince people to support your idea? Once you understand what your objective is, you need to define your central message. There may be a lot of things you want to share with your audience during your presentation, but find – and stick with – the core, the most important point you want them to walk away with. And make sure that your message is clear and compelling.
You also need to tailor your presentation to your audience. Who are they and what might they be expecting? Say you’re giving a product pitch to a client. A technical team may be interested in a lot of nitty-gritty product detail. The business side will no doubt be more interested in what returns they can expect on their investment.
Another consideration is the setting: is this a formal presentation to a large audience with questions reserved for the end, or a presentation in a smaller setting where there’s the possibility for conversation throughout? Is your presentation virtual or in-person? To be delivered individually or as a group? What time of the day will you be speaking? Will there be others speaking before you and might that impact how your message will be received?
Once these fundamentals are established, you’re in building mode. What are the specific points you want to share that will help you best meet your objective and get across your core message? Now figure out how to convey those points in the clearest, most straightforward, and succinct way. This doesn’t mean that your presentation has to be a series of clipped bullet points. No one wants to sit through a presentation in which the presenter reads through what’s on the slide. You can get your points across using stories, fact, diagrams, videos, props, and other types of media.
Visual design matters While you don’t want to clutter up your presentation with too many visual elements that don’t serve your objective and can be distracting, using a variety of visual formats to convey your core message will make your presentation more memorable than slides filled with text. A couple of tips: avoid images that are cliched and overdone. Be careful not to mix up too many different types of images. If you’re using photos, stick with photos. If you’re using drawn images, keep the style consistent. When data are presented, stay consistent with colors and fonts from one type of chart to the next. Keep things clear and simple, using data to support key points without overwhelming your audience with too much information. And don’t assume that your audience is composed of statisticians (unless, of course, it is).
When presenting qualitative data, brief videos provide a way to engage your audience and create emotional connection and impact. Word clouds are another way to get qualitative data across.
Practice makes perfect You’ve pulled together a perfect presentation. But it likely won’t be perfect unless it’s well delivered. So don’t forget to practice your presentation ahead of time. Pro tip: record yourself as you practice out loud. This will force you to think through what you’re going to say for each element of your presentation. And watching your recording will help you identify your mistakes—such as fidgeting, using too many fillers (such as “umm,” or “like”), or speaking too fast.
A key element of your preparation should involve anticipating any technical difficulties. If you’ve embedded videos, make sure they work. If you’re presenting virtually, make sure that the lighting is good, and that your speaker and camera are working. Whether presenting in person or virtually, get there early enough to work out any technical glitches before your presentation is scheduled to begin. Few things are a bigger audience turn-off than sitting there watching the presenter struggle with the delivery mechanisms!
Finally, be kind to yourself. Despite thorough preparation and practice, sometimes, things go wrong, and you need to recover in the moment, adapt, and carry on. It’s unlikely that you’ll have caused any lasting damage and the important thing is to learn from your experience, so your next presentation is stronger.
How are you providing presentation skills training for your learners?
Manika Gandhi is Senior Learning Design Manager at Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning. Email her at [email protected] .
Let’s talk
Change isn’t easy, but we can help. Together we’ll create informed and inspired leaders ready to shape the future of your business.
© 2024 Harvard Business School Publishing. All rights reserved. Harvard Business Publishing is an affiliate of Harvard Business School.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Information
- Terms of Use
- About Harvard Business Publishing
- Higher Education
- Harvard Business Review
- Harvard Business School
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience. By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Cookie and Privacy Settings
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
Click on the different category headings to find out more. You can also change some of your preferences. Note that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our websites and the services we are able to offer.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refusing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
We also use different external services like Google Webfonts, Google Maps, and external Video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data like your IP address we allow you to block them here. Please be aware that this might heavily reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will take effect once you reload the page.
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Map Settings:
Google reCaptcha Settings:
Vimeo and Youtube video embeds:
You can read about our cookies and privacy settings in detail on our Privacy Policy Page.
10 Tips for Improving Your Public Speaking Skills
Few are immune to the fear of public speaking. Marjorie North offers 10 tips for speakers to calm the nerves and deliverable memorable orations.
Marjorie North
Snakes? Fine. Flying? No problem. Public speaking? Yikes! Just thinking about public speaking — routinely described as one of the greatest (and most common) fears — can make your palms sweat. But there are many ways to tackle this anxiety and learn to deliver a memorable speech.
In part one of this series, Mastering the Basics of Communication , I shared strategies to improve how you communicate. In part two, How to Communicate More Effectively in the Workplace , I examined how to apply these techniques as you interact with colleagues and supervisors in the workplace. For the third and final part of this series, I’m providing you with public speaking tips that will help reduce your anxiety, dispel myths, and improve your performance.
Here Are My 10 Tips for Public Speaking:
1. nervousness is normal. practice and prepare.
All people feel some physiological reactions like pounding hearts and trembling hands. Do not associate these feelings with the sense that you will perform poorly or make a fool of yourself. Some nerves are good. The adrenaline rush that makes you sweat also makes you more alert and ready to give your best performance.
The best way to overcome anxiety is to prepare, prepare, and prepare some more. Take the time to go over your notes several times. Once you have become comfortable with the material, practice — a lot. Videotape yourself, or get a friend to critique your performance.
Communication Strategies: Presenting with Impact
Search all Communication programs.
2. Know Your Audience. Your Speech Is About Them, Not You.
Before you begin to craft your message, consider who the message is intended for. Learn as much about your listeners as you can. This will help you determine your choice of words, level of information, organization pattern, and motivational statement.
3. Organize Your Material in the Most Effective Manner to Attain Your Purpose.
Create the framework for your speech. Write down the topic, general purpose, specific purpose, central idea, and main points. Make sure to grab the audience’s attention in the first 30 seconds.
4. Watch for Feedback and Adapt to It.
Keep the focus on the audience. Gauge their reactions, adjust your message, and stay flexible. Delivering a canned speech will guarantee that you lose the attention of or confuse even the most devoted listeners.
5. Let Your Personality Come Through.
Be yourself, don’t become a talking head — in any type of communication. You will establish better credibility if your personality shines through, and your audience will trust what you have to say if they can see you as a real person.
6. Use Humor, Tell Stories, and Use Effective Language.
Inject a funny anecdote in your presentation, and you will certainly grab your audience’s attention. Audiences generally like a personal touch in a speech. A story can provide that.

7. Don’t Read Unless You Have to. Work from an Outline.
Reading from a script or slide fractures the interpersonal connection. By maintaining eye contact with the audience, you keep the focus on yourself and your message. A brief outline can serve to jog your memory and keep you on task.
8. Use Your Voice and Hands Effectively. Omit Nervous Gestures.
Nonverbal communication carries most of the message. Good delivery does not call attention to itself, but instead conveys the speaker’s ideas clearly and without distraction.
9. Grab Attention at the Beginning, and Close with a Dynamic End.
Do you enjoy hearing a speech start with “Today I’m going to talk to you about X”? Most people don’t. Instead, use a startling statistic, an interesting anecdote, or concise quotation. Conclude your speech with a summary and a strong statement that your audience is sure to remember.
10. Use Audiovisual Aids Wisely.
Too many can break the direct connection to the audience, so use them sparingly. They should enhance or clarify your content, or capture and maintain your audience’s attention.
Practice Does Not Make Perfect
Good communication is never perfect, and nobody expects you to be perfect. However, putting in the requisite time to prepare will help you deliver a better speech. You may not be able to shake your nerves entirely, but you can learn to minimize them.
Find related Communication programs.
Browse all Professional & Executive Development programs.
About the Author
North is a consultant for political candidates, physicians, and lawyers, and runs a private practice specializing in public speaking, and executive communication skills. Previously, she was the clinical director in the department of speech and language pathology and audiology at Northeastern University.
Why Gender Equity in the Workplace is Good for Business
Research indicates a correlation between gender equity and organizational success, yet it also points to obstacles for women in leadership.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Give a Killer Presentation
- Chris Anderson

For more than 30 years, the TED conference series has presented enlightening talks that people enjoy watching. In this article, Anderson, TED’s curator, shares five keys to great presentations:
- Frame your story (figure out where to start and where to end).
- Plan your delivery (decide whether to memorize your speech word for word or develop bullet points and then rehearse it—over and over).
- Work on stage presence (but remember that your story matters more than how you stand or whether you’re visibly nervous).
- Plan the multimedia (whatever you do, don’t read from PowerPoint slides).
- Put it together (play to your strengths and be authentic).
According to Anderson, presentations rise or fall on the quality of the idea, the narrative, and the passion of the speaker. It’s about substance—not style. In fact, it’s fairly easy to “coach out” the problems in a talk, but there’s no way to “coach in” the basic story—the presenter has to have the raw material. So if your thinking is not there yet, he advises, decline that invitation to speak. Instead, keep working until you have an idea that’s worth sharing.
Lessons from TED
A little more than a year ago, on a trip to Nairobi, Kenya, some colleagues and I met a 12-year-old Masai boy named Richard Turere, who told us a fascinating story. His family raises livestock on the edge of a vast national park, and one of the biggest challenges is protecting the animals from lions—especially at night. Richard had noticed that placing lamps in a field didn’t deter lion attacks, but when he walked the field with a torch, the lions stayed away. From a young age, he’d been interested in electronics, teaching himself by, for example, taking apart his parents’ radio. He used that experience to devise a system of lights that would turn on and off in sequence—using solar panels, a car battery, and a motorcycle indicator box—and thereby create a sense of movement that he hoped would scare off the lions. He installed the lights, and the lions stopped attacking. Soon villages elsewhere in Kenya began installing Richard’s “lion lights.”
- CA Chris Anderson is the curator of TED.
Partner Center

17 Presentation Skills That Every Effective Presenter Must Develop
- Written by HIGH5 Content & Review Team
- August 8, 2024
- Professional skills
It’s no secret that effective presentations can help you get ahead in business. After all, what better way to show off your knowledge and expertise than by delivering a well-crafted presentation? The right presentation skills give you the ability to share your ideas with an audience convincingly and engagingly.
Unfortunately, not everyone is born a natural presenter. If you’re not used to standing up in front of an audience, the prospect of doing so can be daunting. Fortunately, understanding your unique strengths can help you overcome these challenges and improve your presentation skills. The HIGH5 strengths assessment is a powerful tool that can provide valuable insights into your natural abilities, allowing you to leverage your strengths and develop strategies to address areas for improvement.
With the right guidance, there are a few simple things you can do to enhance your presentation skills and become a more confident and effective communicator. In this article, we’ll share some tips on how to do just that, allowing you to deliver an effective presentation. Let’s get right into it.
What are presentation skills?
Presentation skills are the abilities you need to deliver a clear and effective presentation. After all, a good presenter is someone who can communicate their ideas in a way that engages and motivates their audience.
There are many different aspects to presentation skills, from knowing how to structure your talk to using visuals effectively, to dealing with nerves. Developing strong presentation skills will help you to communicate your ideas more effectively and make a positive impression on your audience.
Presentation skills are important because they can help you to communicate your ideas clearly and effectively. A good presentation can make a big impact on your audience and can help to persuade them of your point of view. Presentation skills are also important in other areas of life, such as job interviews, sales pitches, and networking events. Being able to present your ideas clearly and concisely can give you a big advantage over others who are not as confident in their presentation skills.
Importance and benefits of presentation skills
One of the most important reasons to recognize presentation skills is because they are a valuable asset for any profession. Good presentation skills can help you in your career by making it easier to sell your ideas, get promoted, and be successful in business. Identifying your unique strengths through the HIGH5 assessment can provide invaluable insights into your natural communication abilities, allowing you to leverage your strengths and develop targeted strategies to enhance your presentation skills. By understanding your strengths, you can tailor your approach to deliver more impactful and persuasive presentations, increasing your chances of success in any professional setting.
In addition, good presentation skills can also help you in your personal life by making it easier to give speeches, make presentations, and teach classes. In addition, recognizing presentation skills can also help you improve your presentations. If you are not aware of the importance of presentation skills, you may not be using them to their full potential. By taking the time to learn about presentation skills and how to use them effectively, you can make your presentations more effective and persuasive.
Here’s a list of benefits that come with good presentation skills:
- Increased confidence
- The ability to think on your feet
- Improved public speaking skills
- Enhanced written communication skills
- The ability to lead and motivate others
- Enhanced problem-solving abilities
- Improved negotiation skills
- Stronger time management skills
- Greater creativity
- The opportunity to make a positive impact on others
Pro Tip From HIGH5 Take the HIGH5 strengths assessment to gain a deeper understanding of your natural communication style and preferences. Use this knowledge to play to your strengths when preparing and delivering presentations, such as leveraging your creativity for engaging visuals or your analytical skills for structured content.
17 crucial presentation skills
Let’s now explore some practical examples of presentation skills that will help you ace your next big presentation.
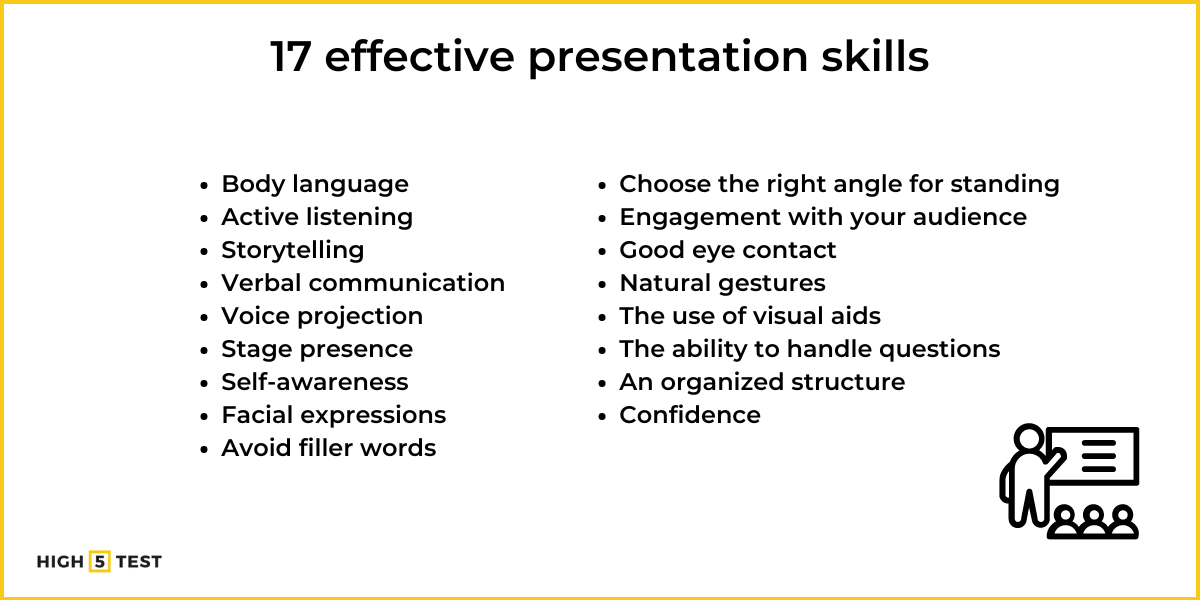
Body language
Effective body language, including posture and gestures, enhances your message and engages your audience.
Active listening
Active listening helps you respond appropriately and adjust your presentation based on audience feedback.
Storytelling
Storytelling is a great way to engage your audience and make your points more memorable. And while it might not seem like a traditional presentation skill, it can be extremely effective. If you possess strengths like creativity, communication, or persuasion, you may find it easier to weave captivating stories into your presentations.
The HIGH5 strengths assessment can help you identify these natural storytelling abilities and provide strategies for leveraging them to captivate your audience. So, if you can find ways to weave stories into your presentation, it’ll go a long way in captivating your audience and making your message more impactful.
- Verbal communication
Clear and concise verbal communication ensures your message is understood and retained by your audience.
Voice projection
Projecting your voice confidently ensures that your message is heard clearly by everyone in the room.
Stage presence
Good stage presence involves commanding attention through confident movement and engagement with the audience.
Self-awareness
Being self-aware helps you identify your strengths and weaknesses, allowing for continuous improvement in your presentation skills.
Facial expressions
Using appropriate facial expressions adds emotion and clarity to your spoken words, making your message more impactful.
Avoid filler words
Minimizing filler words like “um” and “uh” helps maintain your credibility and keeps your audience focused on your message.
Choose the right angle for standing
Standing at the right angle, typically facing the audience while occasionally turning to your visuals, keeps the audience engaged and ensures they follow along with your presentation.
Engagement with your audience
Another key presentation skill is the ability to engage with your audience. This means making eye contact, using gestures, and speaking in a way that is relatable and easy to understand.
If you’re just standing there reading off a slide, chances are your audience is going to get bored pretty quickly. But if you can find ways to keep them engaged, they’ll be more likely to listen to what you have to say.
Good eye contact
One of the best ways to engage with your audience is through eye contact. When you make eye contact with someone, it shows that you’re interested in what they have to say and that you’re engaged in the conversation. It also helps to build trust and rapport. So, if you can find ways to make eye contact with your audience members, it will go a long way in keeping them engaged.
Natural gestures
Another great way to engage with your audience is through natural gestures. Using your hands and arms to gesture can help emphasize points and keep your audience engaged. Just be sure not to go overboard – too much gesturing can be distracting.
The use of visual aids
Visual aids can be a great way to engage your audience and make your points more clear. Using slides, charts, and graphs can help illustrate your ideas and make them easier to understand. Similar to using gestures, just be sure not to overdo it – too many visuals can be overwhelming and confusing.
The ability to handle questions
At some point during your presentation, you’re likely going to get questions from your audience; how you handle those questions can make or break your presentation. If you’re able to answer them confidently and without getting flustered, it’ll show that you know your stuff.
But if you start to get tongue-tied or defensive, it’s going to reflect poorly on you. So, be prepared for questions and try to stay calm when answering them.
An organized structure
Another important presentation skill is having a well-organized structure. This means having an introduction, main body, and conclusion to your presentation. It also means using transitions between sections to help your audience follow along. If your presentation is all over the place, it’s going to be hard for your audience to stay engaged and they’ll quickly tune out.
Last but not least, confidence is one of the most important presentation skills you can have. If you’re not confident in what you’re saying, it’s going to show – and your audience is going to pick up on it. So, even if you’re not feeling 100% sure of yourself, try to project confidence. It’ll make a big difference in how your audience perceives you and your message.
Pro Tip From HIGH5 Use the HIGH5 assessment to understand your unique storytelling style and preferences. Incorporate personal anecdotes, analogies, or case studies that align with your strengths to make your presentations more engaging and memorable.
How to identify presentation skills?
To identify your presentation skills you will need the help of self-assessment tools and feedback from your colleagues or friends. One of the self-assessment tools that we recommend is the HIGH5 strengths test which will help you discover your strengths and talents. From there you can connect your strengths with presentation skills to see which strength boosts your skill.
The second way is also called peer feedback. Ask your colleagues, friends or close family members to give you feedback on your presentation skills. From there you can identify what presentation skills you have and what skills you need to improve.
How to improve presentation skills in the workplace?
The workplace is one of the most important places to hone your presentation skills. After all, in the business world, first impressions are key, and being able to deliver a polished and professional presentation can make all the difference in whether or not you’re successful. Here are a few tips to help you improve your presentation skills in the workplace:
Preparation is key
This may seem like a no-brainer, but it’s worth repeating. When you’re preparing for a presentation, take the time to do your research and gather all of the necessary information. This will help ensure that your presentation is well-organized and flows smoothly.
Be aware of your body language
Your body language speaks volumes, so it’s important to be aware of what you’re communicating with your nonverbal cues. Make sure you’re standing up straight, making eye contact, and using gestures appropriately. These small tweaks can make a big difference in how your audience perceives you.
Practice, practice and practice
One of the best ways to improve your presentation skills is simply to practice as much as you can. The more you present, the more comfortable you’ll become and the better you’ll be at thinking on your feet and handling questions from the audience.
Seek feedback
After each presentation, take some time to reflect on what went well and what could be improved. Seek feedback from your colleagues or boss, and consider taking the HIGH5 strengths assessment to gain insights into your natural abilities and areas for growth. This will help you learn from your mistakes, leverage your strengths, and continue to improve.
By understanding your unique strengths, you can develop targeted strategies to enhance your presentation skills and make a more significant impact in the workplace. By following these tips, you can start to improve your presentation skills and make a positive impression in the workplace.
Pro Tip From HIGH5 After receiving feedback on your presentation, use the HIGH5 strengths assessment to identify areas where you excelled and areas for improvement. Develop an action plan that leverages your strengths while addressing your weaknesses, such as practicing more storytelling techniques if you have strong communication abilities or focusing on visual aids if you have strong creativity.
How do you highlight presentation skills in a resume and job interview?
Another important skill that is often overlooked is the ability to highlight presentation skills in both a resume and a job interview. This can be the difference between getting the job and not. When you are applying for a job, your resume is often the first thing that potential employers will look at. It is important to make sure that your resume includes any relevant presentation skills that you may have.
You can do this by including any experience you have in public speaking, leading presentations, or teaching courses. If you do not have any experience in these areas, consider listing any other relevant skills that could transfer over into presenting, such as customer service or sales experience.
In addition to your resume, it is also important to be able to highlight your presentation skills during a job interview. This is often done through behavioral interviewing, where you will be asked to describe specific examples of times when you have presented in the past. It is important to be prepared for this type of question and to have a few examples ready to go.
When you are highlighting your presentation skills, it is important to focus on any successes that you have had. This could be anything from getting positive feedback from an audience to successfully teaching a new course. No matter what the specific example is, it is important to focus on how you were able to positively impact the situation. This will show potential employers that you can effectively present information and that you are someone they would want on their team.
How to improve presentation skills in school as a student?
School students often have to present in front of their classmates and teachers, which can be a daunting experience, especially if you don’t feel confident in your abilities. However, understanding your unique strengths can help you approach presentations with greater confidence and effectiveness. The HIGH5 strengths assessment is a valuable tool that can provide insights into your natural abilities, allowing you to leverage your strengths and develop strategies to address areas for improvement. With the right guidance, there are some things you can do to improve your presentation skills while you’re still in school.
Join a club or organization that requires presentations
This will force you to get up in front of people regularly and hone your skills. If no club or organization at your school requires presentations, start one! Give speeches in front of the mirror. Practicing in front of a mirror can help you identify any nervous habits you have (like fidgeting or pacing) and correct them before you have to give a real speech.
Use note cards instead of a script
Reading from a script can make you sound robotic and unauthentic. Note cards will help you stay on track without sounding like you’re reciting memorized lines.
Record yourself giving a presentation
Then, watch the recording back to see how you can improve. This exercise can be painful, but it’s one of the best ways to identify your weaknesses and work on them.
Find a mentor
Ask a teacher or another adult you trust to give you feedback on your presentations. They can offer helpful tips and criticism that will help you improve. By following these tips, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a great presenter in no time!
Pro Tip From HIGH5 As a student, take the HIGH5 strengths assessment to identify your natural communication and leadership abilities. Use this knowledge to play to your strengths when preparing and delivering presentations, such as leveraging your analytical skills for structured content or your creativity for engaging visuals.
Presentation skills FAQ
What are the 7 presentation skills.
The 7 presentation skills are:
- Eye contact
What are the 4 types of presentation skills?
The 4 types of presentation skills are:
- Visual aids
- Non-verbal communication
- Listening skills
What is the rule of presentation?
The rule of presentation is to always keep the audience in mind. This means knowing who your audience is, what they want to hear, and how to best deliver your message so that they will listen and be able to understand it.
What are the 5 presentation skills?
The five essential presentation skills are clear communication, audience engagement, confident delivery, effective use of visuals, and proper body language.
What are 10 qualities of a good presentation?
A good presentation is clear, concise, engaging, well-structured, visually appealing, confident, interactive, relevant, well-paced, and memorable.
Every great presenter must have the majority of presenting skills already learned. It is beneficial for each individual to have some level of presentation skills, to be able to showcase and demonstrate their project, ideas and plans to their friends, family members and colleagues.
| Not at all Likely Extremely Likely | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Related Posts

What are Interpersonal Skills? 20 Examples To Use for a Resume or CV
13 Essential Relationship Skills: Build Healthy Relationships

30 Technical Skills for a Resume or a Job Interview

23 Key Counseling Skills That Every Great Therapist Must Have

23 Facilitation Skills That Every Great Facilitator Must Have

21 Essential Decision-Making Skills and How To Improve Them
HIGH5 is a strengths test to unlock the full potential of individuals, teams and organizations by identifying and maximizing what motivates and energizes them.
Join over 4 000 000 happy test takers:
Free Strengths Test
Methodology
Affiliate Program
Feature Request
Help Center
CliftonStrengths
VIA Character Strengths
Comparisons
For individuals
For organizations
For coaches
For educators
Talent development
Leadership development
Team development
Diversity & Inclusion
Employee engagement
Change management
Full Strengths Report
Team Strengths Report
Strengths Planner
Strengths Discovery Guide
Strengths Reference Sheets
Strength Cards
Career Guides
Professional Skills
Job Interview Guides
Strengths in the Workplace
Copyright @ 2024 HIGH5TEST. All rights reserved. Terms & Conditions . Privacy Policy . Shipping Policy . Contact Info .

Verbal Communication Skills Examples in the Workplace
Why are verbal communication skills important in the workplace , how to include verbal communication skills in a job application, how to improve verbal communication skills, verbal communication: the bottom line, what are verbal communication skills.
- Share on Twitter Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn Share on LinkedIn

Forage puts students first. Our blog articles are written independently by our editorial team. They have not been paid for or sponsored by our partners. See our full editorial guidelines .
Table of Contents
If you’ve explained a difficult concept to a teammate or taught a friend about a project you’re working on, chances are you used verbal communication skills. These are the soft skills you use when talking to someone else. A person with good verbal communication skills communicates effectively, efficiently, and empathetically.
Verbal communication skills are crucial to succeeding in the workplace, both for sharing updates about your work and progress, but also understanding what others are working on. Showing you have stellar verbal communication skills can make you stand out in interviews — and help you thrive once you land the role.
So, what exactly do verbal communication skills look like and how can you build yours?
Verbal Communication Meaning
In the literal sense, verbal communication is oral communication with words that you or others speak out loud. On the other hand, nonverbal communication is about what’s not said out loud: gestures, facial expressions, and body language. Written communication is about words on the page (or in an email or Slack message).
You’re using your verbal communication skills every time you speak out loud to a coworker, whether in person or on Zoom.
Verbal Communication Types and Styles
There are a few different types of verbal communication depending on how many people you’re speaking with.
- Intrapersonal communication: communication you have with yourself, including how you process information and speak to yourself. These are your inner thoughts.
- Interpersonal communication: communication between two people. These are the conversations you have with one other person, whether you’re asking for feedback, sharing updates, or asking them what they had for lunch.
- Group verbal communication: communication between at least three people. Similar to interpersonal communication, these are the conversations you have about any topic — as long as it’s a smaller group.
- Public verbal communication: communication where there’s one speaker and an audience. For example, if you’ve attended a large workshop or class, you were a listener in public verbal communication.
- Mass verbal communication: communication where a small group of people passes down information to large groups of people. This may include communication types like television, social media, or radio.
There are also different verbal communication styles depending on how you communicate, regardless of who or how many people you’re communicating with.
- Aggressive verbal communication: communication focusing on getting your way at all costs, regardless of whether that requires hostility, intimidation, or manipulation.
- Passive communication: indirect communication that circles around your actual needs and wants, which can lead to confusion.
- Passive-aggressive communication: communication where you don’t always share your opinions directly, but feel negatively if others don’t understand your needs.
- Assertive communication: communication where you express your needs and opinions clearly, directly, and confidently.
Where do you apply verbal communication skills in the workplace? You use them any time you’re talking to someone else at work! Here are a few examples of when you’d use these skills.
Meetings are one way that teams get together live to communicate about projects, goals, progress, and general updates. You’ll use verbal communication skills not only if you share updates in a meeting, but also to ask clarifying questions and respond to others.
Presentations
Similar to meetings, presentations are a way to share information, progress, and updates live with other people. Presentations tend to take on more of a formal manner than meetings, meaning you’ll need to adjust your tone and presence when verbally communicating.
Working With Your Team
The everyday conversations you have with your team count as verbal communication, too! This is often less formal communication and may even include personal updates and questions, depending on how much you’d like to share. For example, everything from greeting your coworkers to asking them about their weekends counts as verbal communication!

Teaming@BCG
Practice effective communication skills to collaborate with your team and a client.
Avg. Time: 1-2 hours
Skills you’ll build: Communication, project management, prioritization, cross-functional collaboration
Working With a Client
Client-facing roles also require another type of verbal communication to work productively and serve the client’s needs. This communication is typically more formal and requires empathy and active listening skills to ensure you understand what the client is looking for.
Client Service
Learn how to navigate customer questions, issues, and requests to provide excellent client service.
Avg. Time: 3-4 hours
Skills you’ll build: Conflict resolution, triage, problem-solving, composure, customer retention
Giving and Asking for Feedback
Feedback is a crucial part of improving workplace processes, productivity, and company culture . Yet feedback needs to be given and asked for with the right tone and context. For example, you wouldn’t blurt out that your coworker needs to fix something with their presentation style when you first see them that day. Instead, you might ask if you could share a suggestion with them, then share your opinion and potential solutions. Verbal communication skills are key here for knowing what feedback you want to give, and how to deliver it.
>>MORE: How to Ask for Feedback at Work (With Example Questions)
Asking for Help
You won’t always know the right course of action at work, and that’s OK! Sometimes we need to ask for help, whether that’s with decision-making or figuring out who at the company may be able to get a specific task done. You’ll use verbal communication skills to figure out how to phrase your request and what context to make the request in.
Verbal communication skills are a core part of everyday workplace interactions. You’ll use these skills to tell your boss about what you’re working on, share results with stakeholders, and give your team updates. You’ll also use them when you respond to others, whether to ask a clarifying question or provide feedback. Employers want candidates with these skills because they’re more effective, collaborative team members.
It’s no surprise that the rise of remote work and hybrid schedules have decreased the amount of verbal communication we have with our teammates. We don’t have candid conversations when passing by someone’s desk or when we’re walking out to get coffee. Because we don’t talk to our coworkers as much in a remote workplace, when we do have the chance to communicate with them verbally, flexing this skill is crucial.
Verbal communication also doesn’t have to be synchronous. Using tools like Vimeo, Loom, or even voice messages, you can verbally communicate with team members asynchronously and they can hear your explanation, thoughts, and ideas, even if you’re not speaking to them in real time.
Whether working synchronously or asynchronously, remote or in-person, verbal communication skills are essential for communicating your ideas and understanding others’ work.
Because these skills are about what you’re saying rather than what you’ve written (like on a resume or cover letter ), the interview is where your verbal communication skills can shine.
You can show off these skills in the interview with:
- Tone : Have a positive, confident tone when speaking to the hiring manager .
- Responsiveness : Avoid simply responding to questions with structured, prepared answers. Instead, aim to make the interview more conversational rather than a rigid back-and-forth.
- Clarity : Be concise and straightforward, even if that means pausing to get your thoughts together before answering.
- Curiosity : Ask original questions during the interview that help you understand the company further and demonstrate your interest.
- Active listening: Listen carefully to what the interviewer is saying so you can respond appropriately. This includes not just the content of what they’re saying, but picking up on their tone and nonverbal cues.

BCLP Interview Success
Wow the hiring manager in the interview by practicing five commonly asked interview questions.
Avg. Time: 4-5 hours
Skills you’ll build: Communication, presentation, public speaking, poise, attention to detail, analytical thinking, problem solving
Verbal communication skills are two-fold — you need to communicate your work clearly and understand and respond to others’ work. When improving these skills, focus on both aspects to become a well-rounded, more effective communicator.
Prepare for Any Audience
At work, you’ll need to communicate with many different people — people on your team, people in various departments, your manager, your manager’s manager, external clients, etc. Practice explaining your work in different situations by putting yourself in a variety of scenarios.
For example, let’s say you need to explain the process you used on your latest project. How can you explain what you did in two minutes? What about in 30 seconds? How can you explain this to a young student? How would you describe this to a grandparent? Challenging yourself to communicate the same process in different scenarios will prepare you for communicating with multiple team members and stakeholders.
Watch Your Tone
It’s not just what you say — it’s how you say it. How you speak to others at work reflects not only on your work but on you as a team member. Do you want to be positive and confident? Empathetic and clear? Your tone should reflect how you want others to perceive you in the workplace.
It can be hard to hear how we come off when we’re the ones talking. To practice this, record yourself explaining something or giving feedback to someone else, then watch the video back and make any adjustments.
Follow Your Coworkers’ Leads
While every person you work with might not have the best verbal communication skills, it can still be helpful to follow other people’s lead when you’re just starting out. It’s similar to how you might understand what the correct business attire is at your first workplace. While you should still keep your personal style, looking around to see what other people tend to wear can give you a good idea of whether the office is more casual or formal.
The same goes for verbal communication. Some workplaces use very formal and direct communication, while others might be more relaxed. While you should still communicate in a way that feels authentic to you, you can change the level of formality based on your office environment.
Give Feedback (That’s Actually Helpful)
It’s not enough to simply share your opinions on someone else’s work. The best feedback is constructive and actionable.
“Being able to give feedback in a meaningful and tactful way is a critical communication skill,” career coach Tazeen Raza says. “This is something that a lot of people struggle with at various levels.”
To give constructive and actionable feedback, start by asking yourself a few questions about the person’s work:
- What was this project’s biggest strength?
- What areas have room for improvement?
- What other resources can I or someone else offer to improve the project?
- What further context can I give this person?
The goal is to tell the person what was strong about their work and what needs improvement. Then, you’ll need to give them tangible ways to improve with clear paths to action.
Be an Active Listener
Communication is a two-way street, meaning your verbal communication skills will get you nowhere if you aren’t listening to what other people say. Active listening is a workplace skill that focuses on attentive and empathetic listening.
In practice, this means that you listen to what others have to say for the sake of listening. You don’t interrupt or have something ready to respond with. Instead, you focus entirely on what they have to say, then take time to process it before you reply.
Whether we’re aware of it or not, we use our verbal communication skills every time we speak out loud with a friend, family member, or coworker. Someone with good verbal communication skills stands out when they can clearly, effectively, and empathetically communicate their ideas — and truly listen to and give feedback on others’ ideas.
Looking to improve your communication and other professional skills? Check out Cisco’s Career Readiness Virtual Experience Program .
Image credit: Canva Studios / Pexels

Related Posts
6 negotiation skills to level up your work life, how to build conflict resolution skills: case studies and examples, what is github uses and getting started, upskill with forage.

Build the skills you need to enter the workforce with confidence.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Career Planning
- Skills Development
Verbal Communication Skills List and Examples
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ADHeadshot-Cropped-b80e40469d5b4852a68f94ad69d6e8bd.jpg)
What Are Verbal Communication Skills?
- Verbal Communication at Work
- Examples of Verbal Communication
- Tips to Improve Your Skills
Verbal communication reflects the ability to effectively convey and interpret messages through spoken language and active listening.
Almost every job requires workers to use verbal communication skills. That’s why verbal skills are highly ranked on the candidate evaluation checklists used by many job interviewers.
The stronger your communication skills, the better your chances of getting hired regardless of the job for which you’re applying. You’ll do better during the interview, as well as on the job.
Effective verbal communication skills include more than just talking. Verbal communication encompasses both how you deliver messages and how you receive them. Communication is a soft skill that's important to every employer.
Workers who can convey information clearly and effectively are highly valued by employers.
Employees who can interpret messages and act appropriately on the information that they receive have a better chance of excelling on the job.
Verbal Communication Skills in the Workplace
What constitutes effective verbal communication on the job depends on the relationships between communication partners and the work context.
Verbal communication in a work setting takes place between many different individuals and groups such as co-workers, bosses and subordinates, employees, customers, clients, teachers and students, and speakers and their audiences.
It can occur in many different contexts including training sessions, presentations, group meetings, performance appraisals, one-on-one discussions, interviews, disciplinary sessions, sales pitches, and consulting engagements.
Examples of Verbal Communication Skills
Here are some examples of effective workplace verbal communication skills employed in different workplace contexts.
Verbal Communications for Supervisors
The best supervisors don’t merely tell their subordinates what to do and expect them to listen. Instead, they employ active listening skills to understand employee needs and perspectives, engage in verbal negotiation to defuse issues, and capitalize upon opportunities to praise individual and team achievement.
- Advising others regarding an appropriate course of action
- Assertiveness
- Conveying feedback in a constructive manner emphasizing specific, changeable behaviors
- Disciplining employees in a direct and respectful manner
- Giving credit to others
- Recognizing and countering objections
- Showing an interest in others, asking about and recognizing their feelings
- Speaking calmly even when you’re stressed
- Terminating staff
- Training others to carry out a task or role
- Using affirmative sounds and words like “uh-huh,” “got you,” “I understand,” “for sure,” “I see,” and “yes” to demonstrate understanding
- Using self-disclosure to encourage sharing
Verbal Communications for Team Members
Open and constant lines of communication are vital to team success, particularly when completing quality- and deadline-critical projects. One of the most important team-building skills, strong verbal communication helps to ensure issues will be spotted and resolved in formative stages, averting costly escalation.
- Conveying messages concisely
- Encouraging reluctant group members to share input
- Explaining a difficult situation without getting angry
- Explaining that you need assistance
- Paraphrasing to show understanding
- Posing probing questions to elicit more detail about specific issues
- Receiving criticism without defensiveness
- Refraining from speaking too often or interrupting others
- Requesting feedback
- Stating your needs, wants, or feelings without criticizing or blaming
Verbal Communications with Clients
If a large part of your work involves one-on-one communications with customers, it’s helpful to have a “gift of gab,” particularly if you are a sales professional. Keep in mind, though, that your conversations need to be focused on identifying and addressing your client’s needs; using your verbal talents to encourage consultative dialogues will ensure positive client relations.
- Anticipating the concerns of others
- Asking for clarification
- Asking open-ended questions to stimulate dialogue
- Calming an agitated customer by recognizing and responding to their complaints
- Emphasizing the benefits of a product, service, or proposal to persuade an individual or group
- Noticing non-verbal cues and responding verbally to verify confusion, defuse anger, etc.
Verbal Communications for Presenters
Public speaking is a talent that is honed both through practice and through formal training. Speaking articulately and persuasively to a live audience involves:
- Enunciating each word you speak clearly
- Introducing the focus of a topic at the beginning of a presentation or interaction
- Planning communications prior to delivery
- Projecting your voice to fill the room
- Providing concrete examples to illustrate points
- Restating important points towards the end of a talk
- Selecting language appropriate to the audience
- Speaking at a moderate pace, not too fast or too slowly
- Speaking confidently but with modesty
- Summarizing key points made by other speakers
- Supporting statements with facts and evidence
- Tailoring messages to different audiences
- Telling stories to capture an audience
- Using humor to engage an audience
Tips to Improve Your Verbal Communications
Even if you are a shy introvert who prefers to work independently, there are ways to improve your verbal communication skills so that you can more easily cultivate rapport with others.
Practice makes perfect, so take the time to actively practice these communication skills for workplace success: active listening, clarity and conciseness, confidence, empathy, friendliness, open-mindedness, giving and soliciting feedback, confidence, respectfulness, and non-verbal (body language, tone of voice, eye contact) communication.
Key Takeaways
- Verbal communication skills help effectively convey and interpret messages, so they're highly valued by employers across all job roles.
- Effective verbal communication in the workplace depends on the context and relationships involved; supervisors, for example, must be both assertive and empathetic to effectively lead their teams and address employee needs.
- Active listening skills include assertiveness, clarity, confidence, and active listening.
- Verbal communication skills can be developed through practice, formal training, and feedback.
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- How to prepare and...
How to prepare and deliver an effective oral presentation
- Related content
- Peer review
- Lucia Hartigan , registrar 1 ,
- Fionnuala Mone , fellow in maternal fetal medicine 1 ,
- Mary Higgins , consultant obstetrician 2
- 1 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin, Ireland
- 2 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin; Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Medicine and Medical Sciences, University College Dublin
- luciahartigan{at}hotmail.com
The success of an oral presentation lies in the speaker’s ability to transmit information to the audience. Lucia Hartigan and colleagues describe what they have learnt about delivering an effective scientific oral presentation from their own experiences, and their mistakes
The objective of an oral presentation is to portray large amounts of often complex information in a clear, bite sized fashion. Although some of the success lies in the content, the rest lies in the speaker’s skills in transmitting the information to the audience. 1
Preparation
It is important to be as well prepared as possible. Look at the venue in person, and find out the time allowed for your presentation and for questions, and the size of the audience and their backgrounds, which will allow the presentation to be pitched at the appropriate level.
See what the ambience and temperature are like and check that the format of your presentation is compatible with the available computer. This is particularly important when embedding videos. Before you begin, look at the video on stand-by and make sure the lights are dimmed and the speakers are functioning.
For visual aids, Microsoft PowerPoint or Apple Mac Keynote programmes are usual, although Prezi is increasing in popularity. Save the presentation on a USB stick, with email or cloud storage backup to avoid last minute disasters.
When preparing the presentation, start with an opening slide containing the title of the study, your name, and the date. Begin by addressing and thanking the audience and the organisation that has invited you to speak. Typically, the format includes background, study aims, methodology, results, strengths and weaknesses of the study, and conclusions.
If the study takes a lecturing format, consider including “any questions?” on a slide before you conclude, which will allow the audience to remember the take home messages. Ideally, the audience should remember three of the main points from the presentation. 2
Have a maximum of four short points per slide. If you can display something as a diagram, video, or a graph, use this instead of text and talk around it.
Animation is available in both Microsoft PowerPoint and the Apple Mac Keynote programme, and its use in presentations has been demonstrated to assist in the retention and recall of facts. 3 Do not overuse it, though, as it could make you appear unprofessional. If you show a video or diagram don’t just sit back—use a laser pointer to explain what is happening.
Rehearse your presentation in front of at least one person. Request feedback and amend accordingly. If possible, practise in the venue itself so things will not be unfamiliar on the day. If you appear comfortable, the audience will feel comfortable. Ask colleagues and seniors what questions they would ask and prepare responses to these questions.
It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don’t have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
Try to present slides at the rate of around one slide a minute. If you talk too much, you will lose your audience’s attention. The slides or videos should be an adjunct to your presentation, so do not hide behind them, and be proud of the work you are presenting. You should avoid reading the wording on the slides, but instead talk around the content on them.
Maintain eye contact with the audience and remember to smile and pause after each comment, giving your nerves time to settle. Speak slowly and concisely, highlighting key points.
Do not assume that the audience is completely familiar with the topic you are passionate about, but don’t patronise them either. Use every presentation as an opportunity to teach, even your seniors. The information you are presenting may be new to them, but it is always important to know your audience’s background. You can then ensure you do not patronise world experts.
To maintain the audience’s attention, vary the tone and inflection of your voice. If appropriate, use humour, though you should run any comments or jokes past others beforehand and make sure they are culturally appropriate. Check every now and again that the audience is following and offer them the opportunity to ask questions.
Finishing up is the most important part, as this is when you send your take home message with the audience. Slow down, even though time is important at this stage. Conclude with the three key points from the study and leave the slide up for a further few seconds. Do not ramble on. Give the audience a chance to digest the presentation. Conclude by acknowledging those who assisted you in the study, and thank the audience and organisation. If you are presenting in North America, it is usual practice to conclude with an image of the team. If you wish to show references, insert a text box on the appropriate slide with the primary author, year, and paper, although this is not always required.
Answering questions can often feel like the most daunting part, but don’t look upon this as negative. Assume that the audience has listened and is interested in your research. Listen carefully, and if you are unsure about what someone is saying, ask for the question to be rephrased. Thank the audience member for asking the question and keep responses brief and concise. If you are unsure of the answer you can say that the questioner has raised an interesting point that you will have to investigate further. Have someone in the audience who will write down the questions for you, and remember that this is effectively free peer review.
Be proud of your achievements and try to do justice to the work that you and the rest of your group have done. You deserve to be up on that stage, so show off what you have achieved.
Competing interests: We have read and understood the BMJ Group policy on declaration of interests and declare the following interests: None.
- ↵ Rovira A, Auger C, Naidich TP. How to prepare an oral presentation and a conference. Radiologica 2013 ; 55 (suppl 1): 2 -7S. OpenUrl
- ↵ Bourne PE. Ten simple rules for making good oral presentations. PLos Comput Biol 2007 ; 3 : e77 . OpenUrl PubMed
- ↵ Naqvi SH, Mobasher F, Afzal MA, Umair M, Kohli AN, Bukhari MH. Effectiveness of teaching methods in a medical institute: perceptions of medical students to teaching aids. J Pak Med Assoc 2013 ; 63 : 859 -64. OpenUrl
More From Forbes
Best practices for virtual presentations: 15 expert tips that work for everyone.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
In today’s COVID-19 world, virtual meetings and presentations have become the norm. While many presentation skills and best practices apply to both in-person and virtual presentations, expert virtual presenters understand the importance of adjusting their approach to match the medium. With in-person presentations, you more or less have a captive audience — you still need be engaging, but your audience is kind of stuck with you for the duration. But with virtual presentations, your audience has a greater opportunity to stray. You now have to compete for their eyes, ears, hearts, and minds against diminished attention spans, increased home and work life distractions, and conflicting priorities.
Here are 15 expert tips to set you up for success in your next virtual presentation:
1. Get the Lighting Right: As a presenter, it is essential that people can see you well. Make sure you have good front light—meaning the light shines brightly on your face. If your back is to a window, close the shades. While natural light is often the best choice, if your home office doesn’t have natural light and you do a lot of virtual presentations, consider purchasing supplemental lighting to enhance your image.
2. Choose the Right Background: Try to use a background that enhances your professional image and is aligned with your message. Avoid a cluttered background or anything that can be distracting. Learn whether your presentation platform enables you to use virtual backgrounds (like Zoom) or whether you can blur your background (like Microsoft Teams). Your background can either add to your professional presence or detract from it.
3. Know the Technology: Nothing kills a presentation faster than a presenter who fumbles with the technology. This is a performance, so make sure you know how to make it work. A dry run is essential so that you’re comfortable with the platform features. It’s best to have a co-host (or producer or moderator) assist you with the technology so that you can focus on your presentation. Make sure you practice with the same technical set up (computer and internet connection) that you will use when you deliver the presentation.
4. Play to the Camera: When you are the one speaking, look directly into your computer’s camera , not on the screen or at the other participants. This takes some practice, but it makes the viewer feel as if you are looking right at them. Some presenters turn off their self-view so that they aren’t distracted by their own image. Put the camera at eye level . Try not to have your camera too far above or below you. If it’s too low, then you run the risk of creating a double chin. A camera too high makes it difficult to maintain eye contact, as you may find your gaze dropping as you speak. If you are part of a panel or a team of presenters, make sure you are aware of when your camera is on. If you are not speaking but your camera is on, make sure you look like you are paying attention! Powerful presenters understand the importance of making eye contact with their audience, so this means you have to simulate the same effect virtually.
Best Travel Insurance Companies
Best covid-19 travel insurance plans.
5. Get Close (But Not Too Close). You want the camera to frame your face, neck, and shoulders. People are drawn to faces, so you don’t want to lose that connection by being too far away, but you also don’t want your face to take over the whole screen like a dismembered head because, well, that looks weird. Practice your positioning and distance.
6. Stand Up: If possible, use a standing desk or position your laptop so you can stand at eye level with your computer. Standing up provides a higher energy level and forces us to put our body in a more presentation-like mode. If you have to sit, lean forward as you would if you were presenting at a real meeting or as if you were a TV news anchor. Avoid slouching away from the camera, as that sends a signal that you are disconnected from the audience.
7. Be Animated: Just like in a live presentation, you want to present with a little energy and animation. Too slow or too monotone in your voice makes it easy for folks to disengage and tune out. Keeping people engaged virtually requires you to actually be engaging.
8. Pace Yourself: Without real-time visual audience feedback cues, getting the pacing right can be difficult. Even though you want to infuse some animation and energy into your presentation don’t pump up the speed too much. If you tend to be a fast talker in real life, practice slowing down just a bit. If you’re a slow talker, you may want to speed up just a bit.
9. Do A Sound Check: If your sound is garbled, people will tune out. While people may forgive less than perfect video, if they can’t clearly hear you, they will leave. Practice with someone on the other end of the presentation platform. Make sure your sound emits clearly. Sometimes headphones or external microphones work better than the computer audio, sometimes not. Every platform is different, so make sure your sound quality is excellent every time. And again, you should practice with the same technical configurations and location that you will use for your presentation.
10. Plug into Your Modem: If possible, plug your computer directly into your modem using an Ethernet cable. This will give you the strongest signal and most stable internet connection. The last thing you want to happen during your presentation is to have a weak or unstable internet signal.
11. Incorporate Redundant Systems. If using slides, make sure someone else (another webinar co-host or producer) also has a copy of the slides just in case your internet goes wonky and you have to present by calling in. If you are using slides, make them visually appealing. Use high-quality graphics and limit the amount of text on each slide. It’s your job as presenter to deliver the content. The slides are meant to enhance your spoken words, not replace them.
12. Engage Your Participants. Just as if you were doing an in-person presentation, craft your presentation to engage the audience. Incorporate chats, polls, raised hand features, etc. Try not to speak for more than ten minutes without some sort of audience engagement. Use the participant list to interact with your participants by name. Have people chat or raise a hand if they want to speak. Keep track of the order of people and then call on them to invite them to turn on their mics or cameras.
13. Let Someone Else Check the Chats. Don’t get sidetracked by the chats during your presentation. You’ll be shocked at how distracting it is to your train of thought if you attempt to read the chats while speaking. Instead, have your co-host or producer monitor the chats. If you ask people to chat you answers or comments to a question you’ve posed, then pause your talking and engage directly with the chats by acknowledging them, reading them out loud, and commenting on them.
14. Evaluate and Enhance: If possible, record the session and take the time to play back and look for areas that worked well and areas that you might want to improve upon. Great presenters, whether virtual or in person, understand the value of continually honing their craft. Be sure to acknowledge your strengths as well as your areas of improvement.
15. Be Yourself and Have Fun: Again, just like in face-to-face presentations, audiences connect to authenticity, so be yourself! Let your personality show through. Have fun. If you look like you’re enjoying the presentation so will others. Research shows that happy people retain information better than bored or disinterested people, so model the energy that you want to create. The audience takes its cue from you.
Remember, whether you are presenting in-person or virtually, all presentations are performances. And all performances are in service to your audience. Their time is valuable, so honor that time by delivering the best presentation you can. No matter what kind of presentation you are giving, you must find ways to create authentic audience connection, engagement, and value.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
To fully understand the impact these skills have on creating a successful presentation, it's helpful to look at each one individually. Here are six valuable skills you can develop: 1. Active listening. Active listening is an excellent communication skill for any professional to hone.
Here are some tips for improving your verbal communication skills, both spoken and written: 1. Consider your message. Decide what you want to convey during your next conversation, presentation or written communication. This might involve brainstorming or outlining a list of key points you'd like to make. By reviewing the information you want ...
You can use the following 10 steps to help improve your verbal communication at work: 1. Think before speaking. People often feel uncomfortable with silence, but pausing before answering a question can improve your response. Taking time to reflect allows you to organize your thoughts into a concise, clear statement.
Verbal communication skills are more important than ever. Countless meetings, presentations, code reviews, conferences and networking events mean that clear and assertive verbal communication are essential for current and future jobs.. Good communication skills can be the difference between getting a promotion or moving laterally, selling your product or struggling with slow growth ...
Stressed about an upcoming presentation? These talks are full of helpful tips on how to get up in front of an audience and make a lasting impression. Watch now. Add to list. 18:00. Nancy Duarte. The secret structure of great talks. 18 minutes . 18:00. David McCandless. The beauty of data visualization.
These skills help ensure clear, effective, and respectful interactions. Verbal Communication Explained. Verbal communication employs spoken or written words to express ideas, thoughts, and feelings to others. It's a fundamental way we interact through conversations, presentations, or speeches.
Verbal communication presentation skills include: Build your verbal communication skills by practicing interview skills in this free job simulation. Skills you'll build: Communication, presentation, public speaking, poise, attention to detail, analytical thinking, problem-solving.
This is not surprising. Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way. For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget ...
Inject a funny anecdote in your presentation, and you will certainly grab your audience's attention. Audiences generally like a personal touch in a speech. A story can provide that. 7. Don't Read Unless You Have to. Work from an Outline. Reading from a script or slide fractures the interpersonal connection.
Frame your story (figure out where to start and where to end). Plan your delivery (decide whether to memorize your speech word for word or develop bullet points and then rehearse it—over and ...
Here are a few tips to help you improve your presentation skills in the workplace: Preparation is key. This may seem like a no-brainer, but it's worth repeating. When you're preparing for a presentation, take the time to do your research and gather all of the necessary information. ... The 4 types of presentation skills are: Verbal ...
13. Be aware of your nonverbal cues. One way to show you are a confident public speaker is by being aware of your nonverbal cues. Throughout your presentation, make eye contact with your audience. While it's OK to glance at notes, use the majority of your presentation shifting eye contact from person to person.
Presentations. Similar to meetings, presentations are a way to share information, progress, and updates live with other people. ... How to Improve Verbal Communication Skills. Verbal communication skills are two-fold — you need to communicate your work clearly and understand and respond to others' work. When improving these skills, focus on ...
Verbal communication skills help effectively convey and interpret messages, so they're highly valued by employers across all job roles. Effective verbal communication in the workplace depends on the context and relationships involved; supervisors, for example, must be both assertive and empathetic to effectively lead their teams and address employee needs.
The objective of an oral presentation is to portray large amounts of often complex information in a clear, bite sized fashion. Although some of the success lies in the content, the rest lies in the speaker's skills in transmitting the information to the audience.1
Here are 15 expert tips to set you up for success in your next virtual presentation: 1. Get the Lighting Right: As a presenter, it is essential that people can see you well. Make sure you have ...
1. Use reinforcement. You can improve your verbal communication by consciously encouraging others during a conversation, also referred to as reinforcement. Reinforcement shows the other party that you are listening and helps to build rapport by letting the person know that you are hearing and understanding them.
Nonverbal Communication Skills That Affect Presentations Published: Jan 24, 2019 Modified: Apr 09, 2024 Updated On: May 8, 2023. Effective communication is a vital skill for any manager, and nonverbal communication is an essential component of that skill set.