Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?

A conversation with a Wheelock researcher, a BU student, and a fourth-grade teacher

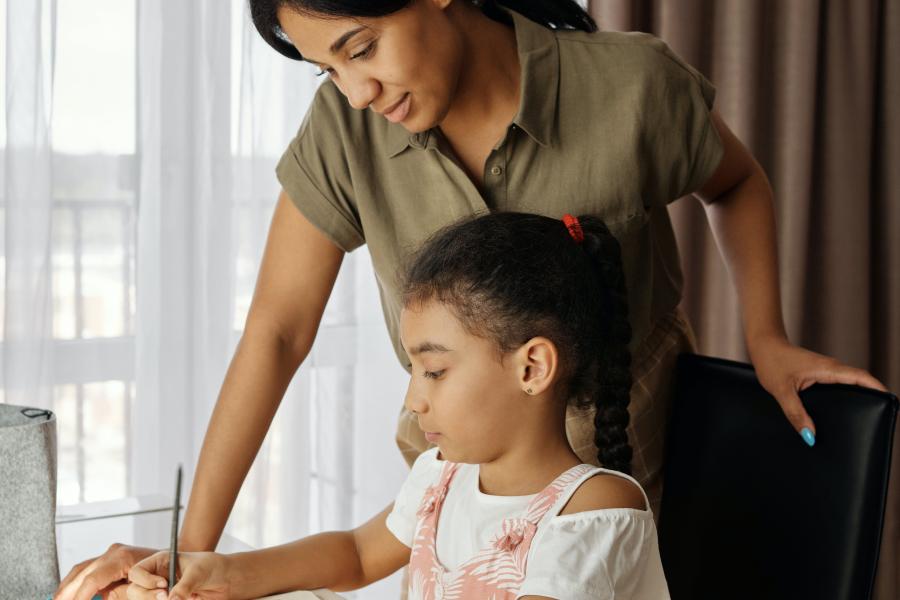
“Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives,” says Wheelock’s Janine Bempechat. “It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.” Photo by iStock/Glenn Cook Photography
Do your homework.
If only it were that simple.
Educators have debated the merits of homework since the late 19th century. In recent years, amid concerns of some parents and teachers that children are being stressed out by too much homework, things have only gotten more fraught.
“Homework is complicated,” says developmental psychologist Janine Bempechat, a Wheelock College of Education & Human Development clinical professor. The author of the essay “ The Case for (Quality) Homework—Why It Improves Learning and How Parents Can Help ” in the winter 2019 issue of Education Next , Bempechat has studied how the debate about homework is influencing teacher preparation, parent and student beliefs about learning, and school policies.
She worries especially about socioeconomically disadvantaged students from low-performing schools who, according to research by Bempechat and others, get little or no homework.
BU Today sat down with Bempechat and Erin Bruce (Wheelock’17,’18), a new fourth-grade teacher at a suburban Boston school, and future teacher freshman Emma Ardizzone (Wheelock) to talk about what quality homework looks like, how it can help children learn, and how schools can equip teachers to design it, evaluate it, and facilitate parents’ role in it.
BU Today: Parents and educators who are against homework in elementary school say there is no research definitively linking it to academic performance for kids in the early grades. You’ve said that they’re missing the point.
Bempechat : I think teachers assign homework in elementary school as a way to help kids develop skills they’ll need when they’re older—to begin to instill a sense of responsibility and to learn planning and organizational skills. That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success. If we greatly reduce or eliminate homework in elementary school, we deprive kids and parents of opportunities to instill these important learning habits and skills.
We do know that beginning in late middle school, and continuing through high school, there is a strong and positive correlation between homework completion and academic success.
That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success.
You talk about the importance of quality homework. What is that?
Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives. It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.

What are your concerns about homework and low-income children?
The argument that some people make—that homework “punishes the poor” because lower-income parents may not be as well-equipped as affluent parents to help their children with homework—is very troubling to me. There are no parents who don’t care about their children’s learning. Parents don’t actually have to help with homework completion in order for kids to do well. They can help in other ways—by helping children organize a study space, providing snacks, being there as a support, helping children work in groups with siblings or friends.
Isn’t the discussion about getting rid of homework happening mostly in affluent communities?
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That’s problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Teachers may not have as high expectations for lower-income children. Schools should bear responsibility for providing supports for kids to be able to get their homework done—after-school clubs, community support, peer group support. It does kids a disservice when our expectations are lower for them.
The conversation around homework is to some extent a social class and social justice issue. If we eliminate homework for all children because affluent children have too much, we’re really doing a disservice to low-income children. They need the challenge, and every student can rise to the challenge with enough supports in place.
What did you learn by studying how education schools are preparing future teachers to handle homework?
My colleague, Margarita Jimenez-Silva, at the University of California, Davis, School of Education, and I interviewed faculty members at education schools, as well as supervising teachers, to find out how students are being prepared. And it seemed that they weren’t. There didn’t seem to be any readings on the research, or conversations on what high-quality homework is and how to design it.
Erin, what kind of training did you get in handling homework?
Bruce : I had phenomenal professors at Wheelock, but homework just didn’t come up. I did lots of student teaching. I’ve been in classrooms where the teachers didn’t assign any homework, and I’ve been in rooms where they assigned hours of homework a night. But I never even considered homework as something that was my decision. I just thought it was something I’d pull out of a book and it’d be done.
I started giving homework on the first night of school this year. My first assignment was to go home and draw a picture of the room where you do your homework. I want to know if it’s at a table and if there are chairs around it and if mom’s cooking dinner while you’re doing homework.
The second night I asked them to talk to a grown-up about how are you going to be able to get your homework done during the week. The kids really enjoyed it. There’s a running joke that I’m teaching life skills.
Friday nights, I read all my kids’ responses to me on their homework from the week and it’s wonderful. They pour their hearts out. It’s like we’re having a conversation on my couch Friday night.
It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Bempechat : I can’t imagine that most new teachers would have the intuition Erin had in designing homework the way she did.
Ardizzone : Conversations with kids about homework, feeling you’re being listened to—that’s such a big part of wanting to do homework….I grew up in Westchester County. It was a pretty demanding school district. My junior year English teacher—I loved her—she would give us feedback, have meetings with all of us. She’d say, “If you have any questions, if you have anything you want to talk about, you can talk to me, here are my office hours.” It felt like she actually cared.
Bempechat : It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Ardizzone : But can’t it lead to parents being overbearing and too involved in their children’s lives as students?
Bempechat : There’s good help and there’s bad help. The bad help is what you’re describing—when parents hover inappropriately, when they micromanage, when they see their children confused and struggling and tell them what to do.
Good help is when parents recognize there’s a struggle going on and instead ask informative questions: “Where do you think you went wrong?” They give hints, or pointers, rather than saying, “You missed this,” or “You didn’t read that.”
Bruce : I hope something comes of this. I hope BU or Wheelock can think of some way to make this a more pressing issue. As a first-year teacher, it was not something I even thought about on the first day of school—until a kid raised his hand and said, “Do we have homework?” It would have been wonderful if I’d had a plan from day one.
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
Senior Contributing Editor

Sara Rimer A journalist for more than three decades, Sara Rimer worked at the Miami Herald , Washington Post and, for 26 years, the New York Times , where she was the New England bureau chief, and a national reporter covering education, aging, immigration, and other social justice issues. Her stories on the death penalty’s inequities were nominated for a Pulitzer Prize and cited in the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision outlawing the execution of people with intellectual disabilities. Her journalism honors include Columbia University’s Meyer Berger award for in-depth human interest reporting. She holds a BA degree in American Studies from the University of Michigan. Profile
She can be reached at [email protected] .
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
There are 81 comments on Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
Insightful! The values about homework in elementary schools are well aligned with my intuition as a parent.
when i finish my work i do my homework and i sometimes forget what to do because i did not get enough sleep
same omg it does not help me it is stressful and if I have it in more than one class I hate it.
Same I think my parent wants to help me but, she doesn’t care if I get bad grades so I just try my best and my grades are great.
I think that last question about Good help from parents is not know to all parents, we do as our parents did or how we best think it can be done, so maybe coaching parents or giving them resources on how to help with homework would be very beneficial for the parent on how to help and for the teacher to have consistency and improve homework results, and of course for the child. I do see how homework helps reaffirm the knowledge obtained in the classroom, I also have the ability to see progress and it is a time I share with my kids
The answer to the headline question is a no-brainer – a more pressing problem is why there is a difference in how students from different cultures succeed. Perfect example is the student population at BU – why is there a majority population of Asian students and only about 3% black students at BU? In fact at some universities there are law suits by Asians to stop discrimination and quotas against admitting Asian students because the real truth is that as a group they are demonstrating better qualifications for admittance, while at the same time there are quotas and reduced requirements for black students to boost their portion of the student population because as a group they do more poorly in meeting admissions standards – and it is not about the Benjamins. The real problem is that in our PC society no one has the gazuntas to explore this issue as it may reveal that all people are not created equal after all. Or is it just environmental cultural differences??????
I get you have a concern about the issue but that is not even what the point of this article is about. If you have an issue please take this to the site we have and only post your opinion about the actual topic
This is not at all what the article is talking about.
This literally has nothing to do with the article brought up. You should really take your opinions somewhere else before you speak about something that doesn’t make sense.
we have the same name
so they have the same name what of it?
lol you tell her
totally agree
What does that have to do with homework, that is not what the article talks about AT ALL.
Yes, I think homework plays an important role in the development of student life. Through homework, students have to face challenges on a daily basis and they try to solve them quickly.I am an intense online tutor at 24x7homeworkhelp and I give homework to my students at that level in which they handle it easily.
More than two-thirds of students said they used alcohol and drugs, primarily marijuana, to cope with stress.
You know what’s funny? I got this assignment to write an argument for homework about homework and this article was really helpful and understandable, and I also agree with this article’s point of view.
I also got the same task as you! I was looking for some good resources and I found this! I really found this article useful and easy to understand, just like you! ^^
i think that homework is the best thing that a child can have on the school because it help them with their thinking and memory.
I am a child myself and i think homework is a terrific pass time because i can’t play video games during the week. It also helps me set goals.
Homework is not harmful ,but it will if there is too much
I feel like, from a minors point of view that we shouldn’t get homework. Not only is the homework stressful, but it takes us away from relaxing and being social. For example, me and my friends was supposed to hang at the mall last week but we had to postpone it since we all had some sort of work to do. Our minds shouldn’t be focused on finishing an assignment that in realty, doesn’t matter. I completely understand that we should have homework. I have to write a paper on the unimportance of homework so thanks.
homework isn’t that bad
Are you a student? if not then i don’t really think you know how much and how severe todays homework really is
i am a student and i do not enjoy homework because i practice my sport 4 out of the five days we have school for 4 hours and that’s not even counting the commute time or the fact i still have to shower and eat dinner when i get home. its draining!
i totally agree with you. these people are such boomers
why just why
they do make a really good point, i think that there should be a limit though. hours and hours of homework can be really stressful, and the extra work isn’t making a difference to our learning, but i do believe homework should be optional and extra credit. that would make it for students to not have the leaning stress of a assignment and if you have a low grade you you can catch up.
Studies show that homework improves student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicates that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” On both standardized tests and grades, students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school.
So how are your measuring student achievement? That’s the real question. The argument that doing homework is simply a tool for teaching responsibility isn’t enough for me. We can teach responsibility in a number of ways. Also the poor argument that parents don’t need to help with homework, and that students can do it on their own, is wishful thinking at best. It completely ignores neurodiverse students. Students in poverty aren’t magically going to find a space to do homework, a friend’s or siblings to help them do it, and snacks to eat. I feel like the author of this piece has never set foot in a classroom of students.
THIS. This article is pathetic coming from a university. So intellectually dishonest, refusing to address the havoc of capitalism and poverty plays on academic success in life. How can they in one sentence use poor kids in an argument and never once address that poor children have access to damn near 0 of the resources affluent kids have? Draw me a picture and let’s talk about feelings lmao what a joke is that gonna put food in their belly so they can have the calories to burn in order to use their brain to study? What about quiet their 7 other siblings that they share a single bedroom with for hours? Is it gonna force the single mom to magically be at home and at work at the same time to cook food while you study and be there to throw an encouraging word?
Also the “parents don’t need to be a parent and be able to guide their kid at all academically they just need to exist in the next room” is wild. Its one thing if a parent straight up is not equipped but to say kids can just figured it out is…. wow coming from an educator What’s next the teacher doesn’t need to teach cause the kid can just follow the packet and figure it out?
Well then get a tutor right? Oh wait you are poor only affluent kids can afford a tutor for their hours of homework a day were they on average have none of the worries a poor child does. Does this address that poor children are more likely to also suffer abuse and mental illness? Like mentioned what about kids that can’t learn or comprehend the forced standardized way? Just let em fail? These children regularly are not in “special education”(some of those are a joke in their own and full of neglect and abuse) programs cause most aren’t even acknowledged as having disabilities or disorders.
But yes all and all those pesky poor kids just aren’t being worked hard enough lol pretty sure poor children’s existence just in childhood is more work, stress, and responsibility alone than an affluent child’s entire life cycle. Love they never once talked about the quality of education in the classroom being so bad between the poor and affluent it can qualify as segregation, just basically blamed poor people for being lazy, good job capitalism for failing us once again!
why the hell?
you should feel bad for saying this, this article can be helpful for people who has to write a essay about it
This is more of a political rant than it is about homework
I know a teacher who has told his students their homework is to find something they are interested in, pursue it and then come share what they learn. The student responses are quite compelling. One girl taught herself German so she could talk to her grandfather. One boy did a research project on Nelson Mandela because the teacher had mentioned him in class. Another boy, a both on the autism spectrum, fixed his family’s computer. The list goes on. This is fourth grade. I think students are highly motivated to learn, when we step aside and encourage them.
The whole point of homework is to give the students a chance to use the material that they have been presented with in class. If they never have the opportunity to use that information, and discover that it is actually useful, it will be in one ear and out the other. As a science teacher, it is critical that the students are challenged to use the material they have been presented with, which gives them the opportunity to actually think about it rather than regurgitate “facts”. Well designed homework forces the student to think conceptually, as opposed to regurgitation, which is never a pretty sight
Wonderful discussion. and yes, homework helps in learning and building skills in students.
not true it just causes kids to stress
Homework can be both beneficial and unuseful, if you will. There are students who are gifted in all subjects in school and ones with disabilities. Why should the students who are gifted get the lucky break, whereas the people who have disabilities suffer? The people who were born with this “gift” go through school with ease whereas people with disabilities struggle with the work given to them. I speak from experience because I am one of those students: the ones with disabilities. Homework doesn’t benefit “us”, it only tears us down and put us in an abyss of confusion and stress and hopelessness because we can’t learn as fast as others. Or we can’t handle the amount of work given whereas the gifted students go through it with ease. It just brings us down and makes us feel lost; because no mater what, it feels like we are destined to fail. It feels like we weren’t “cut out” for success.
homework does help
here is the thing though, if a child is shoved in the face with a whole ton of homework that isn’t really even considered homework it is assignments, it’s not helpful. the teacher should make homework more of a fun learning experience rather than something that is dreaded
This article was wonderful, I am going to ask my teachers about extra, or at all giving homework.
I agree. Especially when you have homework before an exam. Which is distasteful as you’ll need that time to study. It doesn’t make any sense, nor does us doing homework really matters as It’s just facts thrown at us.
Homework is too severe and is just too much for students, schools need to decrease the amount of homework. When teachers assign homework they forget that the students have other classes that give them the same amount of homework each day. Students need to work on social skills and life skills.
I disagree.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what’s going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Homework is helpful because homework helps us by teaching us how to learn a specific topic.
As a student myself, I can say that I have almost never gotten the full 9 hours of recommended sleep time, because of homework. (Now I’m writing an essay on it in the middle of the night D=)
I am a 10 year old kid doing a report about “Is homework good or bad” for homework before i was going to do homework is bad but the sources from this site changed my mind!
Homeowkr is god for stusenrs
I agree with hunter because homework can be so stressful especially with this whole covid thing no one has time for homework and every one just wants to get back to there normal lives it is especially stressful when you go on a 2 week vaca 3 weeks into the new school year and and then less then a week after you come back from the vaca you are out for over a month because of covid and you have no way to get the assignment done and turned in
As great as homework is said to be in the is article, I feel like the viewpoint of the students was left out. Every where I go on the internet researching about this topic it almost always has interviews from teachers, professors, and the like. However isn’t that a little biased? Of course teachers are going to be for homework, they’re not the ones that have to stay up past midnight completing the homework from not just one class, but all of them. I just feel like this site is one-sided and you should include what the students of today think of spending four hours every night completing 6-8 classes worth of work.
Are we talking about homework or practice? Those are two very different things and can result in different outcomes.
Homework is a graded assignment. I do not know of research showing the benefits of graded assignments going home.
Practice; however, can be extremely beneficial, especially if there is some sort of feedback (not a grade but feedback). That feedback can come from the teacher, another student or even an automated grading program.
As a former band director, I assigned daily practice. I never once thought it would be appropriate for me to require the students to turn in a recording of their practice for me to grade. Instead, I had in-class assignments/assessments that were graded and directly related to the practice assigned.
I would really like to read articles on “homework” that truly distinguish between the two.
oof i feel bad good luck!
thank you guys for the artical because I have to finish an assingment. yes i did cite it but just thanks
thx for the article guys.
Homework is good
I think homework is helpful AND harmful. Sometimes u can’t get sleep bc of homework but it helps u practice for school too so idk.
I agree with this Article. And does anyone know when this was published. I would like to know.
It was published FEb 19, 2019.
Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college.
i think homework can help kids but at the same time not help kids
This article is so out of touch with majority of homes it would be laughable if it wasn’t so incredibly sad.
There is no value to homework all it does is add stress to already stressed homes. Parents or adults magically having the time or energy to shepherd kids through homework is dome sort of 1950’s fantasy.
What lala land do these teachers live in?
Homework gives noting to the kid
Homework is Bad
homework is bad.
why do kids even have homework?
Comments are closed.
Latest from Bostonia
Six bu alums to remember this memorial day, american academy of arts & sciences welcomes five bu members, com’s newest journalism grad took her time, could boston be the next city to impose congestion pricing, alum has traveled the world to witness total solar eclipses, opening doors: rhonda harrison (eng’98,’04, grs’04), campus reacts and responds to israel-hamas war, reading list: what the pandemic revealed, remembering com’s david anable, cas’ john stone, “intellectual brilliance and brilliant kindness”, one good deed: christine kannler (cas’96, sph’00, camed’00), william fairfield warren society inducts new members, spreading art appreciation, restoring the “black angels” to medical history, in the kitchen with jacques pépin, feedback: readers weigh in on bu’s new president, com’s new expert on misinformation, and what’s really dividing the nation, the gifts of great teaching, sth’s walter fluker honored by roosevelt institute, alum’s debut book is a ramadan story for children, my big idea: covering construction sites with art.
- Our Mission

What’s the Right Amount of Homework?
Decades of research show that homework has some benefits, especially for students in middle and high school—but there are risks to assigning too much.
Many teachers and parents believe that homework helps students build study skills and review concepts learned in class. Others see homework as disruptive and unnecessary, leading to burnout and turning kids off to school. Decades of research show that the issue is more nuanced and complex than most people think: Homework is beneficial, but only to a degree. Students in high school gain the most, while younger kids benefit much less.
The National PTA and the National Education Association support the “ 10-minute homework guideline ”—a nightly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. But many teachers and parents are quick to point out that what matters is the quality of the homework assigned and how well it meets students’ needs, not the amount of time spent on it.
The guideline doesn’t account for students who may need to spend more—or less—time on assignments. In class, teachers can make adjustments to support struggling students, but at home, an assignment that takes one student 30 minutes to complete may take another twice as much time—often for reasons beyond their control. And homework can widen the achievement gap, putting students from low-income households and students with learning disabilities at a disadvantage.
However, the 10-minute guideline is useful in setting a limit: When kids spend too much time on homework, there are real consequences to consider.
Small Benefits for Elementary Students
As young children begin school, the focus should be on cultivating a love of learning, and assigning too much homework can undermine that goal. And young students often don’t have the study skills to benefit fully from homework, so it may be a poor use of time (Cooper, 1989 ; Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). A more effective activity may be nightly reading, especially if parents are involved. The benefits of reading are clear: If students aren’t proficient readers by the end of third grade, they’re less likely to succeed academically and graduate from high school (Fiester, 2013 ).
For second-grade teacher Jacqueline Fiorentino, the minor benefits of homework did not outweigh the potential drawback of turning young children against school at an early age, so she experimented with dropping mandatory homework. “Something surprising happened: They started doing more work at home,” Fiorentino writes . “This inspiring group of 8-year-olds used their newfound free time to explore subjects and topics of interest to them.” She encouraged her students to read at home and offered optional homework to extend classroom lessons and help them review material.
Moderate Benefits for Middle School Students
As students mature and develop the study skills necessary to delve deeply into a topic—and to retain what they learn—they also benefit more from homework. Nightly assignments can help prepare them for scholarly work, and research shows that homework can have moderate benefits for middle school students (Cooper et al., 2006 ). Recent research also shows that online math homework, which can be designed to adapt to students’ levels of understanding, can significantly boost test scores (Roschelle et al., 2016 ).
There are risks to assigning too much, however: A 2015 study found that when middle school students were assigned more than 90 to 100 minutes of daily homework, their math and science test scores began to decline (Fernández-Alonso, Suárez-Álvarez, & Muñiz, 2015 ). Crossing that upper limit can drain student motivation and focus. The researchers recommend that “homework should present a certain level of challenge or difficulty, without being so challenging that it discourages effort.” Teachers should avoid low-effort, repetitive assignments, and assign homework “with the aim of instilling work habits and promoting autonomous, self-directed learning.”
In other words, it’s the quality of homework that matters, not the quantity. Brian Sztabnik, a veteran middle and high school English teacher, suggests that teachers take a step back and ask themselves these five questions :
- How long will it take to complete?
- Have all learners been considered?
- Will an assignment encourage future success?
- Will an assignment place material in a context the classroom cannot?
- Does an assignment offer support when a teacher is not there?
More Benefits for High School Students, but Risks as Well
By the time they reach high school, students should be well on their way to becoming independent learners, so homework does provide a boost to learning at this age, as long as it isn’t overwhelming (Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). When students spend too much time on homework—more than two hours each night—it takes up valuable time to rest and spend time with family and friends. A 2013 study found that high school students can experience serious mental and physical health problems, from higher stress levels to sleep deprivation, when assigned too much homework (Galloway, Conner, & Pope, 2013 ).
Homework in high school should always relate to the lesson and be doable without any assistance, and feedback should be clear and explicit.
Teachers should also keep in mind that not all students have equal opportunities to finish their homework at home, so incomplete homework may not be a true reflection of their learning—it may be more a result of issues they face outside of school. They may be hindered by issues such as lack of a quiet space at home, resources such as a computer or broadband connectivity, or parental support (OECD, 2014 ). In such cases, giving low homework scores may be unfair.
Since the quantities of time discussed here are totals, teachers in middle and high school should be aware of how much homework other teachers are assigning. It may seem reasonable to assign 30 minutes of daily homework, but across six subjects, that’s three hours—far above a reasonable amount even for a high school senior. Psychologist Maurice Elias sees this as a common mistake: Individual teachers create homework policies that in aggregate can overwhelm students. He suggests that teachers work together to develop a school-wide homework policy and make it a key topic of back-to-school night and the first parent-teacher conferences of the school year.
Parents Play a Key Role
Homework can be a powerful tool to help parents become more involved in their child’s learning (Walker et al., 2004 ). It can provide insights into a child’s strengths and interests, and can also encourage conversations about a child’s life at school. If a parent has positive attitudes toward homework, their children are more likely to share those same values, promoting academic success.
But it’s also possible for parents to be overbearing, putting too much emphasis on test scores or grades, which can be disruptive for children (Madjar, Shklar, & Moshe, 2015 ). Parents should avoid being overly intrusive or controlling—students report feeling less motivated to learn when they don’t have enough space and autonomy to do their homework (Orkin, May, & Wolf, 2017 ; Patall, Cooper, & Robinson, 2008 ; Silinskas & Kikas, 2017 ). So while homework can encourage parents to be more involved with their kids, it’s important to not make it a source of conflict.

School Life Balance , Tips for Online Students
The Pros and Cons of Homework
Updated: December 7, 2023
Published: January 23, 2020

Homework is a word that most students dread hearing. After hours upon hours of sitting in class , the last thing we want is more schoolwork over our precious weekends. While it’s known to be a staple of traditional schooling, homework has also become a rather divise topic. Some feel as though homework is a necessary part of school, while others believe that the time could be better invested. Should students have homework? Have a closer look into the arguments on both sides to decide for yourself.

Photo by energepic.com from Pexels
Why should students have homework, 1. homework encourages practice.
Many people believe that one of the positive effects of homework is that it encourages the discipline of practice. While it may be time consuming and boring compared to other activities, repetition is needed to get better at skills. Homework helps make concepts more clear, and gives students more opportunities when starting their career .
2. Homework Gets Parents Involved
Homework can be something that gets parents involved in their children’s lives if the environment is a healthy one. A parent helping their child with homework makes them take part in their academic success, and allows for the parent to keep up with what the child is doing in school. It can also be a chance to connect together.
3. Homework Teaches Time Management
Homework is much more than just completing the assigned tasks. Homework can develop time management skills , forcing students to plan their time and make sure that all of their homework assignments are done on time. By learning to manage their time, students also practice their problem-solving skills and independent thinking. One of the positive effects of homework is that it forces decision making and compromises to be made.
4. Homework Opens A Bridge Of Communication
Homework creates a connection between the student, the teacher, the school, and the parents. It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student.
5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can’t see it in the moment.
6. Homework Reduces Screen Time
Many students in North America spend far too many hours watching TV. If they weren’t in school, these numbers would likely increase even more. Although homework is usually undesired, it encourages better study habits and discourages spending time in front of the TV. Homework can be seen as another extracurricular activity, and many families already invest a lot of time and money in different clubs and lessons to fill up their children’s extra time. Just like extracurricular activities, homework can be fit into one’s schedule.

The Other Side: Why Homework Is Bad
1. homework encourages a sedentary lifestyle.
Should students have homework? Well, that depends on where you stand. There are arguments both for the advantages and the disadvantages of homework.
While classroom time is important, playground time is just as important. If children are given too much homework, they won’t have enough playtime, which can impact their social development and learning. Studies have found that those who get more play get better grades in school , as it can help them pay closer attention in the classroom.
Children are already sitting long hours in the classroom, and homework assignments only add to these hours. Sedentary lifestyles can be dangerous and can cause health problems such as obesity. Homework takes away from time that could be spent investing in physical activity.
2. Homework Isn’t Healthy In Every Home
While many people that think homes are a beneficial environment for children to learn, not all homes provide a healthy environment, and there may be very little investment from parents. Some parents do not provide any kind of support or homework help, and even if they would like to, due to personal barriers, they sometimes cannot. Homework can create friction between children and their parents, which is one of the reasons why homework is bad .
3. Homework Adds To An Already Full-Time Job
School is already a full-time job for students, as they generally spend over 6 hours each day in class. Students also often have extracurricular activities such as sports, music, or art that are just as important as their traditional courses. Adding on extra hours to all of these demands is a lot for children to manage, and prevents students from having extra time to themselves for a variety of creative endeavors. Homework prevents self discovery and having the time to learn new skills outside of the school system. This is one of the main disadvantages of homework.
4. Homework Has Not Been Proven To Provide Results
Endless surveys have found that homework creates a negative attitude towards school, and homework has not been found to be linked to a higher level of academic success.
The positive effects of homework have not been backed up enough. While homework may help some students improve in specific subjects, if they have outside help there is no real proof that homework makes for improvements.
It can be a challenge to really enforce the completion of homework, and students can still get decent grades without doing their homework. Extra school time does not necessarily mean better grades — quality must always come before quantity.
Accurate practice when it comes to homework simply isn’t reliable. Homework could even cause opposite effects if misunderstood, especially since the reliance is placed on the student and their parents — one of the major reasons as to why homework is bad. Many students would rather cheat in class to avoid doing their homework at home, and children often just copy off of each other or from what they read on the internet.
5. Homework Assignments Are Overdone
The general agreement is that students should not be given more than 10 minutes a day per grade level. What this means is that a first grader should be given a maximum of 10 minutes of homework, while a second grader receives 20 minutes, etc. Many students are given a lot more homework than the recommended amount, however.
On average, college students spend as much as 3 hours per night on homework . By giving too much homework, it can increase stress levels and lead to burn out. This in turn provides an opposite effect when it comes to academic success.
The pros and cons of homework are both valid, and it seems as though the question of ‘‘should students have homework?’ is not a simple, straightforward one. Parents and teachers often are found to be clashing heads, while the student is left in the middle without much say.
It’s important to understand all the advantages and disadvantages of homework, taking both perspectives into conversation to find a common ground. At the end of the day, everyone’s goal is the success of the student.
Related Articles
Does homework really work?
by: Leslie Crawford | Updated: December 12, 2023
Print article

You know the drill. It’s 10:15 p.m., and the cardboard-and-toothpick Golden Gate Bridge is collapsing. The pages of polynomials have been abandoned. The paper on the Battle of Waterloo seems to have frozen in time with Napoleon lingering eternally over his breakfast at Le Caillou. Then come the tears and tantrums — while we parents wonder, Does the gain merit all this pain? Is this just too much homework?
However the drama unfolds night after night, year after year, most parents hold on to the hope that homework (after soccer games, dinner, flute practice, and, oh yes, that childhood pastime of yore known as playing) advances their children academically.
But what does homework really do for kids? Is the forest’s worth of book reports and math and spelling sheets the average American student completes in their 12 years of primary schooling making a difference? Or is it just busywork?
Homework haterz
Whether or not homework helps, or even hurts, depends on who you ask. If you ask my 12-year-old son, Sam, he’ll say, “Homework doesn’t help anything. It makes kids stressed-out and tired and makes them hate school more.”
Nothing more than common kid bellyaching?
Maybe, but in the fractious field of homework studies, it’s worth noting that Sam’s sentiments nicely synopsize one side of the ivory tower debate. Books like The End of Homework , The Homework Myth , and The Case Against Homework the film Race to Nowhere , and the anguished parent essay “ My Daughter’s Homework is Killing Me ” make the case that homework, by taking away precious family time and putting kids under unneeded pressure, is an ineffective way to help children become better learners and thinkers.
One Canadian couple took their homework apostasy all the way to the Supreme Court of Canada. After arguing that there was no evidence that it improved academic performance, they won a ruling that exempted their two children from all homework.
So what’s the real relationship between homework and academic achievement?
How much is too much?
To answer this question, researchers have been doing their homework on homework, conducting and examining hundreds of studies. Chris Drew Ph.D., founder and editor at The Helpful Professor recently compiled multiple statistics revealing the folly of today’s after-school busy work. Does any of the data he listed below ring true for you?
• 45 percent of parents think homework is too easy for their child, primarily because it is geared to the lowest standard under the Common Core State Standards .
• 74 percent of students say homework is a source of stress , defined as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss, and stomach problems.
• Students in high-performing high schools spend an average of 3.1 hours a night on homework , even though 1 to 2 hours is the optimal duration, according to a peer-reviewed study .
Not included in the list above is the fact many kids have to abandon activities they love — like sports and clubs — because homework deprives them of the needed time to enjoy themselves with other pursuits.
Conversely, The Helpful Professor does list a few pros of homework, noting it teaches discipline and time management, and helps parents know what’s being taught in the class.
The oft-bandied rule on homework quantity — 10 minutes a night per grade (starting from between 10 to 20 minutes in first grade) — is listed on the National Education Association’s website and the National Parent Teacher Association’s website , but few schools follow this rule.
Do you think your child is doing excessive homework? Harris Cooper Ph.D., author of a meta-study on homework , recommends talking with the teacher. “Often there is a miscommunication about the goals of homework assignments,” he says. “What appears to be problematic for kids, why they are doing an assignment, can be cleared up with a conversation.” Also, Cooper suggests taking a careful look at how your child is doing the assignments. It may seem like they’re taking two hours, but maybe your child is wandering off frequently to get a snack or getting distracted.
Less is often more
If your child is dutifully doing their work but still burning the midnight oil, it’s worth intervening to make sure your child gets enough sleep. A 2012 study of 535 high school students found that proper sleep may be far more essential to brain and body development.
For elementary school-age children, Cooper’s research at Duke University shows there is no measurable academic advantage to homework. For middle-schoolers, Cooper found there is a direct correlation between homework and achievement if assignments last between one to two hours per night. After two hours, however, achievement doesn’t improve. For high schoolers, Cooper’s research suggests that two hours per night is optimal. If teens have more than two hours of homework a night, their academic success flatlines. But less is not better. The average high school student doing homework outperformed 69 percent of the students in a class with no homework.
Many schools are starting to act on this research. A Florida superintendent abolished homework in her 42,000 student district, replacing it with 20 minutes of nightly reading. She attributed her decision to “ solid research about what works best in improving academic achievement in students .”
More family time
A 2020 survey by Crayola Experience reports 82 percent of children complain they don’t have enough quality time with their parents. Homework deserves much of the blame. “Kids should have a chance to just be kids and do things they enjoy, particularly after spending six hours a day in school,” says Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth . “It’s absurd to insist that children must be engaged in constructive activities right up until their heads hit the pillow.”
By far, the best replacement for homework — for both parents and children — is bonding, relaxing time together.
Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

How families of color can fight for fair discipline in school

Dealing with teacher bias

The most important school data families of color need to consider
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
Is Homework Good for Kids? Here’s What the Research Says
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.
The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in Texas went viral last week , earning praise from parents across the country who lament the heavy workload often assigned to young students. Brandy Young told parents she would not formally assign any homework this year, asking students instead to eat dinner with their families, play outside and go to bed early.
But the question of how much work children should be doing outside of school remains controversial, and plenty of parents take issue with no-homework policies, worried their kids are losing a potential academic advantage. Here’s what you need to know:
For decades, the homework standard has been a “10-minute rule,” which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 minutes of homework each night. High school seniors should complete about two hours of homework each night. The National PTA and the National Education Association both support that guideline.
But some schools have begun to give their youngest students a break. A Massachusetts elementary school has announced a no-homework pilot program for the coming school year, lengthening the school day by two hours to provide more in-class instruction. “We really want kids to go home at 4 o’clock, tired. We want their brain to be tired,” Kelly Elementary School Principal Jackie Glasheen said in an interview with a local TV station . “We want them to enjoy their families. We want them to go to soccer practice or football practice, and we want them to go to bed. And that’s it.”
A New York City public elementary school implemented a similar policy last year, eliminating traditional homework assignments in favor of family time. The change was quickly met with outrage from some parents, though it earned support from other education leaders.
New solutions and approaches to homework differ by community, and these local debates are complicated by the fact that even education experts disagree about what’s best for kids.
The research
The most comprehensive research on homework to date comes from a 2006 meta-analysis by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper, who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was stronger for older students—in seventh through 12th grade—than for those in younger grades, for whom there was a weak relationship between homework and performance.
Cooper’s analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school, self-discipline, inquisitiveness and independent problem solving skills. On the other hand, some studies he examined showed that homework can cause physical and emotional fatigue, fuel negative attitudes about learning and limit leisure time for children. At the end of his analysis, Cooper recommended further study of such potential effects of homework.
Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing two hours of homework each night, he said, but they also shouldn’t be doing no homework.
Not all education experts agree entirely with Cooper’s assessment.
Cathy Vatterott, an education professor at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, supports the “10-minute rule” as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary school.
“Correlation is not causation,” she said. “Does homework cause achievement, or do high achievers do more homework?”
Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs , thinks there should be more emphasis on improving the quality of homework tasks, and she supports efforts to eliminate homework for younger kids.
“I have no concerns about students not starting homework until fourth grade or fifth grade,” she said, noting that while the debate over homework will undoubtedly continue, she has noticed a trend toward limiting, if not eliminating, homework in elementary school.
The issue has been debated for decades. A TIME cover in 1999 read: “Too much homework! How it’s hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.” The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push for better math and science education in the U.S. The ensuing pressure to be competitive on a global scale, plus the increasingly demanding college admissions process, fueled the practice of assigning homework.
“The complaints are cyclical, and we’re in the part of the cycle now where the concern is for too much,” Cooper said. “You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness.”
Cooper acknowledged that some students really are bringing home too much homework, and their parents are right to be concerned.
“A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements,” he said. “If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- How Selena Gomez Is Revolutionizing the Celebrity Beauty Business
- TIME100 Most Influential Companies 2024
- Javier Milei’s Radical Plan to Transform Argentina
- How Private Donors Shape Birth-Control Choices
- The Deadly Digital Frontiers at the Border
- What's the Best Measure of Fitness?
- The 31 Most Anticipated Movies of Summer 2024
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Katie Reilly at [email protected]
- About the Hub
- Announcements
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Subscribe to the newsletter
Explore by Topic
- Arts+Culture
- Politics+Society
- Science+Technology
- Student Life
- University News
- Voices+Opinion
- About Hub at Work
- Gazette Archive
- Benefits+Perks
- Health+Well-Being
- Current Issue
- About the Magazine
- Past Issues
- Support Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Subscribe to the Magazine
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Credit: August de Richelieu
Does homework still have value? A Johns Hopkins education expert weighs in
Joyce epstein, co-director of the center on school, family, and community partnerships, discusses why homework is essential, how to maximize its benefit to learners, and what the 'no-homework' approach gets wrong.
By Vicky Hallett
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein , co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work," Epstein says.
But after decades of researching how to improve schools, the professor in the Johns Hopkins School of Education remains certain that homework is essential—as long as the teachers have done their homework, too. The National Network of Partnership Schools , which she founded in 1995 to advise schools and districts on ways to improve comprehensive programs of family engagement, has developed hundreds of improved homework ideas through its Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program. For an English class, a student might interview a parent on popular hairstyles from their youth and write about the differences between then and now. Or for science class, a family could identify forms of matter over the dinner table, labeling foods as liquids or solids. These innovative and interactive assignments not only reinforce concepts from the classroom but also foster creativity, spark discussions, and boost student motivation.
"We're not trying to eliminate homework procedures, but expand and enrich them," says Epstein, who is packing this research into a forthcoming book on the purposes and designs of homework. In the meantime, the Hub couldn't wait to ask her some questions:
What kind of homework training do teachers typically get?
Future teachers and administrators really have little formal training on how to design homework before they assign it. This means that most just repeat what their teachers did, or they follow textbook suggestions at the end of units. For example, future teachers are well prepared to teach reading and literacy skills at each grade level, and they continue to learn to improve their teaching of reading in ongoing in-service education. By contrast, most receive little or no training on the purposes and designs of homework in reading or other subjects. It is really important for future teachers to receive systematic training to understand that they have the power, opportunity, and obligation to design homework with a purpose.
Why do students need more interactive homework?
If homework assignments are always the same—10 math problems, six sentences with spelling words—homework can get boring and some kids just stop doing their assignments, especially in the middle and high school years. When we've asked teachers what's the best homework you've ever had or designed, invariably we hear examples of talking with a parent or grandparent or peer to share ideas. To be clear, parents should never be asked to "teach" seventh grade science or any other subject. Rather, teachers set up the homework assignments so that the student is in charge. It's always the student's homework. But a good activity can engage parents in a fun, collaborative way. Our data show that with "good" assignments, more kids finish their work, more kids interact with a family partner, and more parents say, "I learned what's happening in the curriculum." It all works around what the youngsters are learning.
Is family engagement really that important?
At Hopkins, I am part of the Center for Social Organization of Schools , a research center that studies how to improve many aspects of education to help all students do their best in school. One thing my colleagues and I realized was that we needed to look deeply into family and community engagement. There were so few references to this topic when we started that we had to build the field of study. When children go to school, their families "attend" with them whether a teacher can "see" the parents or not. So, family engagement is ever-present in the life of a school.
My daughter's elementary school doesn't assign homework until third grade. What's your take on "no homework" policies?
There are some parents, writers, and commentators who have argued against homework, especially for very young children. They suggest that children should have time to play after school. This, of course is true, but many kindergarten kids are excited to have homework like their older siblings. If they give homework, most teachers of young children make assignments very short—often following an informal rule of 10 minutes per grade level. "No homework" does not guarantee that all students will spend their free time in productive and imaginative play.
Some researchers and critics have consistently misinterpreted research findings. They have argued that homework should be assigned only at the high school level where data point to a strong connection of doing assignments with higher student achievement . However, as we discussed, some students stop doing homework. This leads, statistically, to results showing that doing homework or spending more minutes on homework is linked to higher student achievement. If slow or struggling students are not doing their assignments, they contribute to—or cause—this "result."
Teachers need to design homework that even struggling students want to do because it is interesting. Just about all students at any age level react positively to good assignments and will tell you so.
Did COVID change how schools and parents view homework?
Within 24 hours of the day school doors closed in March 2020, just about every school and district in the country figured out that teachers had to talk to and work with students' parents. This was not the same as homeschooling—teachers were still working hard to provide daily lessons. But if a child was learning at home in the living room, parents were more aware of what they were doing in school. One of the silver linings of COVID was that teachers reported that they gained a better understanding of their students' families. We collected wonderfully creative examples of activities from members of the National Network of Partnership Schools. I'm thinking of one art activity where every child talked with a parent about something that made their family unique. Then they drew their finding on a snowflake and returned it to share in class. In math, students talked with a parent about something the family liked so much that they could represent it 100 times. Conversations about schoolwork at home was the point.
How did you create so many homework activities via the Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program?
We had several projects with educators to help them design interactive assignments, not just "do the next three examples on page 38." Teachers worked in teams to create TIPS activities, and then we turned their work into a standard TIPS format in math, reading/language arts, and science for grades K-8. Any teacher can use or adapt our prototypes to match their curricula.
Overall, we know that if future teachers and practicing educators were prepared to design homework assignments to meet specific purposes—including but not limited to interactive activities—more students would benefit from the important experience of doing their homework. And more parents would, indeed, be partners in education.
Posted in Voices+Opinion
You might also like
News network.
- Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Get Email Updates
- Submit an Announcement
- Submit an Event
- Privacy Statement
- Accessibility
Discover JHU
- About the University
- Schools & Divisions
- Academic Programs
- Plan a Visit
- my.JohnsHopkins.edu
- © 2024 Johns Hopkins University . All rights reserved.
- University Communications
- 3910 Keswick Rd., Suite N2600, Baltimore, MD
- X Facebook LinkedIn YouTube Instagram
How Much Homework Is Enough? Depends Who You Ask

- Share article
Editor’s note: This is an adapted excerpt from You, Your Child, and School: Navigate Your Way to the Best Education ( Viking)—the latest book by author and speaker Sir Ken Robinson (co-authored with Lou Aronica), published in March. For years, Robinson has been known for his radical work on rekindling creativity and passion in schools, including three bestselling books (also with Aronica) on the topic. His TED Talk “Do Schools Kill Creativity?” holds the record for the most-viewed TED talk of all time, with more than 50 million views. While Robinson’s latest book is geared toward parents, it also offers educators a window into the kinds of education concerns parents have for their children, including on the quality and quantity of homework.
The amount of homework young people are given varies a lot from school to school and from grade to grade. In some schools and grades, children have no homework at all. In others, they may have 18 hours or more of homework every week. In the United States, the accepted guideline, which is supported by both the National Education Association and the National Parent Teacher Association, is the 10-minute rule: Children should have no more than 10 minutes of homework each day for each grade reached. In 1st grade, children should have 10 minutes of daily homework; in 2nd grade, 20 minutes; and so on to the 12th grade, when on average they should have 120 minutes of homework each day, which is about 10 hours a week. It doesn’t always work out that way.
In 2013, the University of Phoenix College of Education commissioned a survey of how much homework teachers typically give their students. From kindergarten to 5th grade, it was just under three hours per week; from 6th to 8th grade, it was 3.2 hours; and from 9th to 12th grade, it was 3.5 hours.
There are two points to note. First, these are the amounts given by individual teachers. To estimate the total time children are expected to spend on homework, you need to multiply these hours by the number of teachers they work with. High school students who work with five teachers in different curriculum areas may find themselves with 17.5 hours or more of homework a week, which is the equivalent of a part-time job. The other factor is that these are teachers’ estimates of the time that homework should take. The time that individual children spend on it will be more or less than that, according to their abilities and interests. One child may casually dash off a piece of homework in half the time that another will spend laboring through in a cold sweat.
Do students have more homework these days than previous generations? Given all the variables, it’s difficult to say. Some studies suggest they do. In 2007, a study from the National Center for Education Statistics found that, on average, high school students spent around seven hours a week on homework. A similar study in 1994 put the average at less than five hours a week. Mind you, I [Robinson] was in high school in England in the 1960s and spent a lot more time than that—though maybe that was to do with my own ability. One way of judging this is to look at how much homework your own children are given and compare it to what you had at the same age.
Many parents find it difficult to help their children with subjects they’ve not studied themselves for a long time, if at all.
There’s also much debate about the value of homework. Supporters argue that it benefits children, teachers, and parents in several ways:
- Children learn to deepen their understanding of specific content, to cover content at their own pace, to become more independent learners, to develop problem-solving and time-management skills, and to relate what they learn in school to outside activities.
- Teachers can see how well their students understand the lessons; evaluate students’ individual progress, strengths, and weaknesses; and cover more content in class.
- Parents can engage practically in their children’s education, see firsthand what their children are being taught in school, and understand more clearly how they’re getting on—what they find easy and what they struggle with in school.
Want to know more about Sir Ken Robinson? Check out our Q&A with him.
Q&A With Sir Ken Robinson
Ashley Norris is assistant dean at the University of Phoenix College of Education. Commenting on her university’s survey, she says, “Homework helps build confidence, responsibility, and problem-solving skills that can set students up for success in high school, college, and in the workplace.”
That may be so, but many parents find it difficult to help their children with subjects they’ve not studied themselves for a long time, if at all. Families have busy lives, and it can be hard for parents to find time to help with homework alongside everything else they have to cope with. Norris is convinced it’s worth the effort, especially, she says, because in many schools, the nature of homework is changing. One influence is the growing popularity of the so-called flipped classroom.
In the stereotypical classroom, the teacher spends time in class presenting material to the students. Their homework consists of assignments based on that material. In the flipped classroom, the teacher provides the students with presentational materials—videos, slides, lecture notes—which the students review at home and then bring questions and ideas to school where they work on them collaboratively with the teacher and other students. As Norris notes, in this approach, homework extends the boundaries of the classroom and reframes how time in school can be used more productively, allowing students to “collaborate on learning, learn from each other, maybe critique [each other’s work], and share those experiences.”
Even so, many parents and educators are increasingly concerned that homework, in whatever form it takes, is a bridge too far in the pressured lives of children and their families. It takes away from essential time for their children to relax and unwind after school, to play, to be young, and to be together as a family. On top of that, the benefits of homework are often asserted, but they’re not consistent, and they’re certainly not guaranteed.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

Should Kids Get Homework?
Homework gives elementary students a way to practice concepts, but too much can be harmful, experts say.

Getty Images
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful.
How much homework students should get has long been a source of debate among parents and educators. In recent years, some districts have even implemented no-homework policies, as students juggle sports, music and other activities after school.
Parents of elementary school students, in particular, have argued that after-school hours should be spent with family or playing outside rather than completing assignments. And there is little research to show that homework improves academic achievement for elementary students.
But some experts say there's value in homework, even for younger students. When done well, it can help students practice core concepts and develop study habits and time management skills. The key to effective homework, they say, is keeping assignments related to classroom learning, and tailoring the amount by age: Many experts suggest no homework for kindergartners, and little to none in first and second grade.
Value of Homework
Homework provides a chance to solidify what is being taught in the classroom that day, week or unit. Practice matters, says Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University 's Wheelock College of Education & Human Development.
"There really is no other domain of human ability where anybody would say you don't need to practice," she adds. "We have children practicing piano and we have children going to sports practice several days a week after school. You name the domain of ability and practice is in there."
Homework is also the place where schools and families most frequently intersect.
"The children are bringing things from the school into the home," says Paula S. Fass, professor emerita of history at the University of California—Berkeley and the author of "The End of American Childhood." "Before the pandemic, (homework) was the only real sense that parents had to what was going on in schools."
Harris Cooper, professor emeritus of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University and author of "The Battle Over Homework," examined more than 60 research studies on homework between 1987 and 2003 and found that — when designed properly — homework can lead to greater student success. Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary.
"Every child should be doing homework, but the amount and type that they're doing should be appropriate for their developmental level," he says. "For teachers, it's a balancing act. Doing away with homework completely is not in the best interest of children and families. But overburdening families with homework is also not in the child's or a family's best interest."
Negative Homework Assignments
Not all homework for elementary students involves completing a worksheet. Assignments can be fun, says Cooper, like having students visit educational locations, keep statistics on their favorite sports teams, read for pleasure or even help their parents grocery shop. The point is to show students that activities done outside of school can relate to subjects learned in the classroom.
But assignments that are just busy work, that force students to learn new concepts at home, or that are overly time-consuming can be counterproductive, experts say.
Homework that's just busy work.
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful, experts say. Assignments that look more like busy work – projects or worksheets that don't require teacher feedback and aren't related to topics learned in the classroom – can be frustrating for students and create burdens for families.
"The mental health piece has definitely played a role here over the last couple of years during the COVID-19 pandemic, and the last thing we want to do is frustrate students with busy work or homework that makes no sense," says Dave Steckler, principal of Red Trail Elementary School in Mandan, North Dakota.
Homework on material that kids haven't learned yet.
With the pressure to cover all topics on standardized tests and limited time during the school day, some teachers assign homework that has not yet been taught in the classroom.
Not only does this create stress, but it also causes equity challenges. Some parents speak languages other than English or work several jobs, and they aren't able to help teach their children new concepts.
" It just becomes agony for both parents and the kids to get through this worksheet, and the goal becomes getting to the bottom of (the) worksheet with answers filled in without any understanding of what any of it matters for," says professor Susan R. Goldman, co-director of the Learning Sciences Research Institute at the University of Illinois—Chicago .
Homework that's overly time-consuming.
The standard homework guideline recommended by the National Parent Teacher Association and the National Education Association is the "10-minute rule" – 10 minutes of nightly homework per grade level. A fourth grader, for instance, would receive a total of 40 minutes of homework per night.
But this does not always happen, especially since not every student learns the same. A 2015 study published in the American Journal of Family Therapy found that primary school children actually received three times the recommended amount of homework — and that family stress increased along with the homework load.
Young children can only remain attentive for short periods, so large amounts of homework, especially lengthy projects, can negatively affect students' views on school. Some individual long-term projects – like having to build a replica city, for example – typically become an assignment for parents rather than students, Fass says.
"It's one thing to assign a project like that in which several kids are working on it together," she adds. "In (that) case, the kids do normally work on it. It's another to send it home to the families, where it becomes a burden and doesn't really accomplish very much."
Private vs. Public Schools
Do private schools assign more homework than public schools? There's little research on the issue, but experts say private school parents may be more accepting of homework, seeing it as a sign of academic rigor.
Of course, not all private schools are the same – some focus on college preparation and traditional academics, while others stress alternative approaches to education.
"I think in the academically oriented private schools, there's more support for homework from parents," says Gerald K. LeTendre, chair of educational administration at Pennsylvania State University—University Park . "I don't know if there's any research to show there's more homework, but it's less of a contentious issue."
How to Address Homework Overload
First, assess if the workload takes as long as it appears. Sometimes children may start working on a homework assignment, wander away and come back later, Cooper says.
"Parents don't see it, but they know that their child has started doing their homework four hours ago and still not done it," he adds. "They don't see that there are those four hours where their child was doing lots of other things. So the homework assignment itself actually is not four hours long. It's the way the child is approaching it."
But if homework is becoming stressful or workload is excessive, experts suggest parents first approach the teacher, followed by a school administrator.
"Many times, we can solve a lot of issues by having conversations," Steckler says, including by "sitting down, talking about the amount of homework, and what's appropriate and not appropriate."
Study Tips for High School Students

Tags: K-12 education , students , elementary school , children
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
Should We Get Rid of Homework?
Some educators are pushing to get rid of homework. Would that be a good thing?

By Jeremy Engle and Michael Gonchar
Do you like doing homework? Do you think it has benefited you educationally?
Has homework ever helped you practice a difficult skill — in math, for example — until you mastered it? Has it helped you learn new concepts in history or science? Has it helped to teach you life skills, such as independence and responsibility? Or, have you had a more negative experience with homework? Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes?
Should we get rid of homework?
In “ The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, ” published in July, the Times Opinion writer Jay Caspian Kang argues that homework may be imperfect, but it still serves an important purpose in school. The essay begins:
Do students really need to do their homework? As a parent and a former teacher, I have been pondering this question for quite a long time. The teacher side of me can acknowledge that there were assignments I gave out to my students that probably had little to no academic value. But I also imagine that some of my students never would have done their basic reading if they hadn’t been trained to complete expected assignments, which would have made the task of teaching an English class nearly impossible. As a parent, I would rather my daughter not get stuck doing the sort of pointless homework I would occasionally assign, but I also think there’s a lot of value in saying, “Hey, a lot of work you’re going to end up doing in your life is pointless, so why not just get used to it?” I certainly am not the only person wondering about the value of homework. Recently, the sociologist Jessica McCrory Calarco and the mathematics education scholars Ilana Horn and Grace Chen published a paper, “ You Need to Be More Responsible: The Myth of Meritocracy and Teachers’ Accounts of Homework Inequalities .” They argued that while there’s some evidence that homework might help students learn, it also exacerbates inequalities and reinforces what they call the “meritocratic” narrative that says kids who do well in school do so because of “individual competence, effort and responsibility.” The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students. Calarco, Horn and Chen write, “Research has highlighted inequalities in students’ homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students’ home lives and in the support students’ families can provide.”
Mr. Kang argues:
But there’s a defense of homework that doesn’t really have much to do with class mobility, equality or any sense of reinforcing the notion of meritocracy. It’s one that became quite clear to me when I was a teacher: Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the weight of their socioeconomic status or ethnicity, I’m not sure what good it would do if the kids didn’t know how to do something relentlessly, over and over again, until they perfected it. Most teachers know that type of progress is very difficult to achieve inside the classroom, regardless of a student’s background, which is why, I imagine, Calarco, Horn and Chen found that most teachers weren’t thinking in a structural inequalities frame. Holistic ideas of education, in which learning is emphasized and students can explore concepts and ideas, are largely for the types of kids who don’t need to worry about class mobility. A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can’t think of one that matters more than the simple satisfaction of mastering something that you were once bad at. That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right.
Students, read the entire article, then tell us:
Should we get rid of homework? Why, or why not?
Is homework an outdated, ineffective or counterproductive tool for learning? Do you agree with the authors of the paper that homework is harmful and worsens inequalities that exist between students’ home circumstances?
Or do you agree with Mr. Kang that homework still has real educational value?
When you get home after school, how much homework will you do? Do you think the amount is appropriate, too much or too little? Is homework, including the projects and writing assignments you do at home, an important part of your learning experience? Or, in your opinion, is it not a good use of time? Explain.
In these letters to the editor , one reader makes a distinction between elementary school and high school:
Homework’s value is unclear for younger students. But by high school and college, homework is absolutely essential for any student who wishes to excel. There simply isn’t time to digest Dostoyevsky if you only ever read him in class.
What do you think? How much does grade level matter when discussing the value of homework?
Is there a way to make homework more effective?
If you were a teacher, would you assign homework? What kind of assignments would you give and why?
Want more writing prompts? You can find all of our questions in our Student Opinion column . Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate them into your classroom.
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Jeremy Engle joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2018 after spending more than 20 years as a classroom humanities and documentary-making teacher, professional developer and curriculum designer working with students and teachers across the country. More about Jeremy Engle
Are You Down With or Done With Homework?
- Posted January 17, 2012
- By Lory Hough

The debate over how much schoolwork students should be doing at home has flared again, with one side saying it's too much, the other side saying in our competitive world, it's just not enough.
It was a move that doesn't happen very often in American public schools: The principal got rid of homework.
This past September, Stephanie Brant, principal of Gaithersburg Elementary School in Gaithersburg, Md., decided that instead of teachers sending kids home with math worksheets and spelling flash cards, students would instead go home and read. Every day for 30 minutes, more if they had time or the inclination, with parents or on their own.
"I knew this would be a big shift for my community," she says. But she also strongly believed it was a necessary one. Twenty-first-century learners, especially those in elementary school, need to think critically and understand their own learning — not spend night after night doing rote homework drills.
Brant's move may not be common, but she isn't alone in her questioning. The value of doing schoolwork at home has gone in and out of fashion in the United States among educators, policymakers, the media, and, more recently, parents. As far back as the late 1800s, with the rise of the Progressive Era, doctors such as Joseph Mayer Rice began pushing for a limit on what he called "mechanical homework," saying it caused childhood nervous conditions and eyestrain. Around that time, the then-influential Ladies Home Journal began publishing a series of anti-homework articles, stating that five hours of brain work a day was "the most we should ask of our children," and that homework was an intrusion on family life. In response, states like California passed laws abolishing homework for students under a certain age.
But, as is often the case with education, the tide eventually turned. After the Russians launched the Sputnik satellite in 1957, a space race emerged, and, writes Brian Gill in the journal Theory Into Practice, "The homework problem was reconceived as part of a national crisis; the U.S. was losing the Cold War because Russian children were smarter." Many earlier laws limiting homework were abolished, and the longterm trend toward less homework came to an end.
The debate re-emerged a decade later when parents of the late '60s and '70s argued that children should be free to play and explore — similar anti-homework wellness arguments echoed nearly a century earlier. By the early-1980s, however, the pendulum swung again with the publication of A Nation at Risk , which blamed poor education for a "rising tide of mediocrity." Students needed to work harder, the report said, and one way to do this was more homework.
For the most part, this pro-homework sentiment is still going strong today, in part because of mandatory testing and continued economic concerns about the nation's competitiveness. Many believe that today's students are falling behind their peers in places like Korea and Finland and are paying more attention to Angry Birds than to ancient Babylonia.
But there are also a growing number of Stephanie Brants out there, educators and parents who believe that students are stressed and missing out on valuable family time. Students, they say, particularly younger students who have seen a rise in the amount of take-home work and already put in a six- to nine-hour "work" day, need less, not more homework.
Who is right? Are students not working hard enough or is homework not working for them? Here's where the story gets a little tricky: It depends on whom you ask and what research you're looking at. As Cathy Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework , points out, "Homework has generated enough research so that a study can be found to support almost any position, as long as conflicting studies are ignored." Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth and a strong believer in eliminating all homework, writes that, "The fact that there isn't anything close to unanimity among experts belies the widespread assumption that homework helps." At best, he says, homework shows only an association, not a causal relationship, with academic achievement. In other words, it's hard to tease out how homework is really affecting test scores and grades. Did one teacher give better homework than another? Was one teacher more effective in the classroom? Do certain students test better or just try harder?
"It is difficult to separate where the effect of classroom teaching ends," Vatterott writes, "and the effect of homework begins."
Putting research aside, however, much of the current debate over homework is focused less on how homework affects academic achievement and more on time. Parents in particular have been saying that the amount of time children spend in school, especially with afterschool programs, combined with the amount of homework given — as early as kindergarten — is leaving students with little time to run around, eat dinner with their families, or even get enough sleep.
Certainly, for some parents, homework is a way to stay connected to their children's learning. But for others, homework creates a tug-of-war between parents and children, says Liz Goodenough, M.A.T.'71, creator of a documentary called Where Do the Children Play?
"Ideally homework should be about taking something home, spending a few curious and interesting moments in which children might engage with parents, and then getting that project back to school — an organizational triumph," she says. "A nag-free activity could engage family time: Ask a parent about his or her own childhood. Interview siblings."

Instead, as the authors of The Case Against Homework write, "Homework overload is turning many of us into the types of parents we never wanted to be: nags, bribers, and taskmasters."
Leslie Butchko saw it happen a few years ago when her son started sixth grade in the Santa Monica-Malibu (Calif.) United School District. She remembers him getting two to four hours of homework a night, plus weekend and vacation projects. He was overwhelmed and struggled to finish assignments, especially on nights when he also had an extracurricular activity.
"Ultimately, we felt compelled to have Bobby quit karate — he's a black belt — to allow more time for homework," she says. And then, with all of their attention focused on Bobby's homework, she and her husband started sending their youngest to his room so that Bobby could focus. "One day, my younger son gave us 15-minute coupons as a present for us to use to send him to play in the back room. … It was then that we realized there had to be something wrong with the amount of homework we were facing."
Butchko joined forces with another mother who was having similar struggles and ultimately helped get the homework policy in her district changed, limiting homework on weekends and holidays, setting time guidelines for daily homework, and broadening the definition of homework to include projects and studying for tests. As she told the school board at one meeting when the policy was first being discussed, "In closing, I just want to say that I had more free time at Harvard Law School than my son has in middle school, and that is not in the best interests of our children."
One barrier that Butchko had to overcome initially was convincing many teachers and parents that more homework doesn't necessarily equal rigor.
"Most of the parents that were against the homework policy felt that students need a large quantity of homework to prepare them for the rigorous AP classes in high school and to get them into Harvard," she says.
Stephanie Conklin, Ed.M.'06, sees this at Another Course to College, the Boston pilot school where she teaches math. "When a student is not completing [his or her] homework, parents usually are frustrated by this and agree with me that homework is an important part of their child's learning," she says.
As Timothy Jarman, Ed.M.'10, a ninth-grade English teacher at Eugene Ashley High School in Wilmington, N.C., says, "Parents think it is strange when their children are not assigned a substantial amount of homework."
That's because, writes Vatterott, in her chapter, "The Cult(ure) of Homework," the concept of homework "has become so engrained in U.S. culture that the word homework is part of the common vernacular."
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn.
"Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of time that children will have to do something every night (or several times a week). … This commitment to the idea of homework in the abstract is accepted by the overwhelming majority of schools — public and private, elementary and secondary."
Brant had to confront this when she cut homework at Gaithersburg Elementary.
"A lot of my parents have this idea that homework is part of life. This is what I had to do when I was young," she says, and so, too, will our kids. "So I had to shift their thinking." She did this slowly, first by asking her teachers last year to really think about what they were sending home. And this year, in addition to forming a parent advisory group around the issue, she also holds events to answer questions.
Still, not everyone is convinced that homework as a given is a bad thing. "Any pursuit of excellence, be it in sports, the arts, or academics, requires hard work. That our culture finds it okay for kids to spend hours a day in a sport but not equal time on academics is part of the problem," wrote one pro-homework parent on the blog for the documentary Race to Nowhere , which looks at the stress American students are under. "Homework has always been an issue for parents and children. It is now and it was 20 years ago. I think when people decide to have children that it is their responsibility to educate them," wrote another.
And part of educating them, some believe, is helping them develop skills they will eventually need in adulthood. "Homework can help students develop study skills that will be of value even after they leave school," reads a publication on the U.S. Department of Education website called Homework Tips for Parents. "It can teach them that learning takes place anywhere, not just in the classroom. … It can foster positive character traits such as independence and responsibility. Homework can teach children how to manage time."
Annie Brown, Ed.M.'01, feels this is particularly critical at less affluent schools like the ones she has worked at in Boston, Cambridge, Mass., and Los Angeles as a literacy coach.
"It feels important that my students do homework because they will ultimately be competing for college placement and jobs with students who have done homework and have developed a work ethic," she says. "Also it will get them ready for independently taking responsibility for their learning, which will need to happen for them to go to college."
The problem with this thinking, writes Vatterott, is that homework becomes a way to practice being a worker.
"Which begs the question," she writes. "Is our job as educators to produce learners or workers?"
Slate magazine editor Emily Bazelon, in a piece about homework, says this makes no sense for younger kids.
"Why should we think that practicing homework in first grade will make you better at doing it in middle school?" she writes. "Doesn't the opposite seem equally plausible: that it's counterproductive to ask children to sit down and work at night before they're developmentally ready because you'll just make them tired and cross?"
Kohn writes in the American School Board Journal that this "premature exposure" to practices like homework (and sit-and-listen lessons and tests) "are clearly a bad match for younger children and of questionable value at any age." He calls it BGUTI: Better Get Used to It. "The logic here is that we have to prepare you for the bad things that are going to be done to you later … by doing them to you now."
According to a recent University of Michigan study, daily homework for six- to eight-year-olds increased on average from about 8 minutes in 1981 to 22 minutes in 2003. A review of research by Duke University Professor Harris Cooper found that for elementary school students, "the average correlation between time spent on homework and achievement … hovered around zero."
So should homework be eliminated? Of course not, say many Ed School graduates who are teaching. Not only would students not have time for essays and long projects, but also teachers would not be able to get all students to grade level or to cover critical material, says Brett Pangburn, Ed.M.'06, a sixth-grade English teacher at Excel Academy Charter School in Boston. Still, he says, homework has to be relevant.
"Kids need to practice the skills being taught in class, especially where, like the kids I teach at Excel, they are behind and need to catch up," he says. "Our results at Excel have demonstrated that kids can catch up and view themselves as in control of their academic futures, but this requires hard work, and homework is a part of it."
Ed School Professor Howard Gardner basically agrees.
"America and Americans lurch between too little homework in many of our schools to an excess of homework in our most competitive environments — Li'l Abner vs. Tiger Mother," he says. "Neither approach makes sense. Homework should build on what happens in class, consolidating skills and helping students to answer new questions."
So how can schools come to a happy medium, a way that allows teachers to cover everything they need while not overwhelming students? Conklin says she often gives online math assignments that act as labs and students have two or three days to complete them, including some in-class time. Students at Pangburn's school have a 50-minute silent period during regular school hours where homework can be started, and where teachers pull individual or small groups of students aside for tutoring, often on that night's homework. Afterschool homework clubs can help.
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.) Other schools offer an extended day that allows teachers to cover more material in school, in turn requiring fewer take-home assignments. And for others, like Stephanie Brant's elementary school in Maryland, more reading with a few targeted project assignments has been the answer.
"The routine of reading is so much more important than the routine of homework," she says. "Let's have kids reflect. You can still have the routine and you can still have your workspace, but now it's for reading. I often say to parents, if we can put a man on the moon, we can put a man or woman on Mars and that person is now a second-grader. We don't know what skills that person will need. At the end of the day, we have to feel confident that we're giving them something they can use on Mars."
Read a January 2014 update.
Homework Policy Still Going Strong
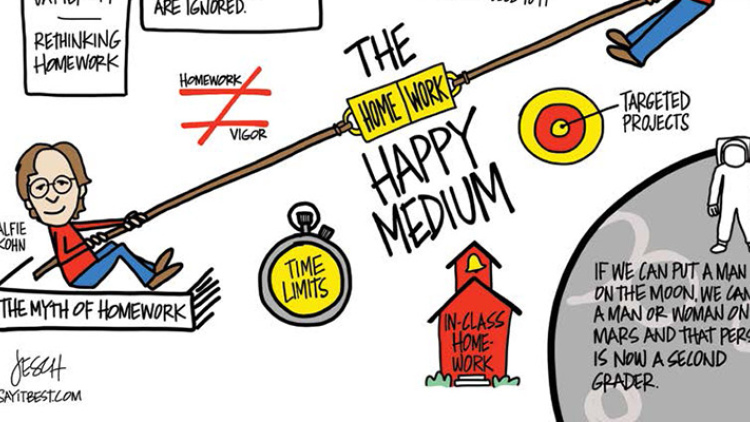
Ed. Magazine
The magazine of the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Commencement Marshal Sarah Fiarman: The Principal of the Matter

Making Math “Almost Fun”
Alum develops curriculum to entice reluctant math learners
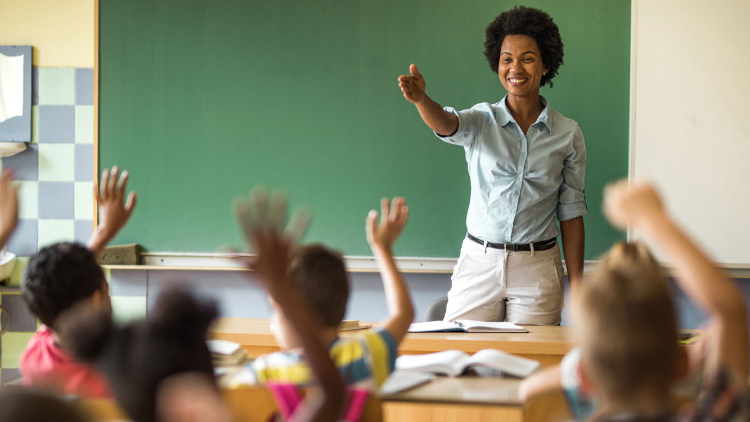

Reshaping Teacher Licensure: Lessons from the Pandemic
Olivia Chi, Ed.M.'17, Ph.D.'20, discusses the ongoing efforts to ensure the quality and stability of the teaching workforce

Studying 101: Study Smarter Not Harder
Do you ever feel like your study habits simply aren’t cutting it? Do you wonder what you could be doing to perform better in class and on exams? Many students realize that their high school study habits aren’t very effective in college. This is understandable, as college is quite different from high school. The professors are less personally involved, classes are bigger, exams are worth more, reading is more intense, and classes are much more rigorous. That doesn’t mean there’s anything wrong with you; it just means you need to learn some more effective study skills. Fortunately, there are many active, effective study strategies that are shown to be effective in college classes.
This handout offers several tips on effective studying. Implementing these tips into your regular study routine will help you to efficiently and effectively learn course material. Experiment with them and find some that work for you.
Reading is not studying
Simply reading and re-reading texts or notes is not actively engaging in the material. It is simply re-reading your notes. Only ‘doing’ the readings for class is not studying. It is simply doing the reading for class. Re-reading leads to quick forgetting.
Think of reading as an important part of pre-studying, but learning information requires actively engaging in the material (Edwards, 2014). Active engagement is the process of constructing meaning from text that involves making connections to lectures, forming examples, and regulating your own learning (Davis, 2007). Active studying does not mean highlighting or underlining text, re-reading, or rote memorization. Though these activities may help to keep you engaged in the task, they are not considered active studying techniques and are weakly related to improved learning (Mackenzie, 1994).
Ideas for active studying include:
- Create a study guide by topic. Formulate questions and problems and write complete answers. Create your own quiz.
- Become a teacher. Say the information aloud in your own words as if you are the instructor and teaching the concepts to a class.
- Derive examples that relate to your own experiences.
- Create concept maps or diagrams that explain the material.
- Develop symbols that represent concepts.
- For non-technical classes (e.g., English, History, Psychology), figure out the big ideas so you can explain, contrast, and re-evaluate them.
- For technical classes, work the problems and explain the steps and why they work.
- Study in terms of question, evidence, and conclusion: What is the question posed by the instructor/author? What is the evidence that they present? What is the conclusion?
Organization and planning will help you to actively study for your courses. When studying for a test, organize your materials first and then begin your active reviewing by topic (Newport, 2007). Often professors provide subtopics on the syllabi. Use them as a guide to help organize your materials. For example, gather all of the materials for one topic (e.g., PowerPoint notes, text book notes, articles, homework, etc.) and put them together in a pile. Label each pile with the topic and study by topics.
For more information on the principle behind active studying, check out our tipsheet on metacognition .
Understand the Study Cycle
The Study Cycle , developed by Frank Christ, breaks down the different parts of studying: previewing, attending class, reviewing, studying, and checking your understanding. Although each step may seem obvious at a glance, all too often students try to take shortcuts and miss opportunities for good learning. For example, you may skip a reading before class because the professor covers the same material in class; doing so misses a key opportunity to learn in different modes (reading and listening) and to benefit from the repetition and distributed practice (see #3 below) that you’ll get from both reading ahead and attending class. Understanding the importance of all stages of this cycle will help make sure you don’t miss opportunities to learn effectively.
Spacing out is good
One of the most impactful learning strategies is “distributed practice”—spacing out your studying over several short periods of time over several days and weeks (Newport, 2007). The most effective practice is to work a short time on each class every day. The total amount of time spent studying will be the same (or less) than one or two marathon library sessions, but you will learn the information more deeply and retain much more for the long term—which will help get you an A on the final. The important thing is how you use your study time, not how long you study. Long study sessions lead to a lack of concentration and thus a lack of learning and retention.
In order to spread out studying over short periods of time across several days and weeks, you need control over your schedule . Keeping a list of tasks to complete on a daily basis will help you to include regular active studying sessions for each class. Try to do something for each class each day. Be specific and realistic regarding how long you plan to spend on each task—you should not have more tasks on your list than you can reasonably complete during the day.
For example, you may do a few problems per day in math rather than all of them the hour before class. In history, you can spend 15-20 minutes each day actively studying your class notes. Thus, your studying time may still be the same length, but rather than only preparing for one class, you will be preparing for all of your classes in short stretches. This will help focus, stay on top of your work, and retain information.
In addition to learning the material more deeply, spacing out your work helps stave off procrastination. Rather than having to face the dreaded project for four hours on Monday, you can face the dreaded project for 30 minutes each day. The shorter, more consistent time to work on a dreaded project is likely to be more acceptable and less likely to be delayed to the last minute. Finally, if you have to memorize material for class (names, dates, formulas), it is best to make flashcards for this material and review periodically throughout the day rather than one long, memorization session (Wissman and Rawson, 2012). See our handout on memorization strategies to learn more.
It’s good to be intense
Not all studying is equal. You will accomplish more if you study intensively. Intensive study sessions are short and will allow you to get work done with minimal wasted effort. Shorter, intensive study times are more effective than drawn out studying.
In fact, one of the most impactful study strategies is distributing studying over multiple sessions (Newport, 2007). Intensive study sessions can last 30 or 45-minute sessions and include active studying strategies. For example, self-testing is an active study strategy that improves the intensity of studying and efficiency of learning. However, planning to spend hours on end self-testing is likely to cause you to become distracted and lose your attention.
On the other hand, if you plan to quiz yourself on the course material for 45 minutes and then take a break, you are much more likely to maintain your attention and retain the information. Furthermore, the shorter, more intense sessions will likely put the pressure on that is needed to prevent procrastination.
Silence isn’t golden
Know where you study best. The silence of a library may not be the best place for you. It’s important to consider what noise environment works best for you. You might find that you concentrate better with some background noise. Some people find that listening to classical music while studying helps them concentrate, while others find this highly distracting. The point is that the silence of the library may be just as distracting (or more) than the noise of a gymnasium. Thus, if silence is distracting, but you prefer to study in the library, try the first or second floors where there is more background ‘buzz.’
Keep in mind that active studying is rarely silent as it often requires saying the material aloud.
Problems are your friend
Working and re-working problems is important for technical courses (e.g., math, economics). Be able to explain the steps of the problems and why they work.
In technical courses, it is usually more important to work problems than read the text (Newport, 2007). In class, write down in detail the practice problems demonstrated by the professor. Annotate each step and ask questions if you are confused. At the very least, record the question and the answer (even if you miss the steps).
When preparing for tests, put together a large list of problems from the course materials and lectures. Work the problems and explain the steps and why they work (Carrier, 2003).
Reconsider multitasking
A significant amount of research indicates that multi-tasking does not improve efficiency and actually negatively affects results (Junco, 2012).
In order to study smarter, not harder, you will need to eliminate distractions during your study sessions. Social media, web browsing, game playing, texting, etc. will severely affect the intensity of your study sessions if you allow them! Research is clear that multi-tasking (e.g., responding to texts, while studying), increases the amount of time needed to learn material and decreases the quality of the learning (Junco, 2012).
Eliminating the distractions will allow you to fully engage during your study sessions. If you don’t need your computer for homework, then don’t use it. Use apps to help you set limits on the amount of time you can spend at certain sites during the day. Turn your phone off. Reward intensive studying with a social-media break (but make sure you time your break!) See our handout on managing technology for more tips and strategies.
Switch up your setting
Find several places to study in and around campus and change up your space if you find that it is no longer a working space for you.
Know when and where you study best. It may be that your focus at 10:00 PM. is not as sharp as at 10:00 AM. Perhaps you are more productive at a coffee shop with background noise, or in the study lounge in your residence hall. Perhaps when you study on your bed, you fall asleep.
Have a variety of places in and around campus that are good study environments for you. That way wherever you are, you can find your perfect study spot. After a while, you might find that your spot is too comfortable and no longer is a good place to study, so it’s time to hop to a new spot!
Become a teacher
Try to explain the material in your own words, as if you are the teacher. You can do this in a study group, with a study partner, or on your own. Saying the material aloud will point out where you are confused and need more information and will help you retain the information. As you are explaining the material, use examples and make connections between concepts (just as a teacher does). It is okay (even encouraged) to do this with your notes in your hands. At first you may need to rely on your notes to explain the material, but eventually you’ll be able to teach it without your notes.
Creating a quiz for yourself will help you to think like your professor. What does your professor want you to know? Quizzing yourself is a highly effective study technique. Make a study guide and carry it with you so you can review the questions and answers periodically throughout the day and across several days. Identify the questions that you don’t know and quiz yourself on only those questions. Say your answers aloud. This will help you to retain the information and make corrections where they are needed. For technical courses, do the sample problems and explain how you got from the question to the answer. Re-do the problems that give you trouble. Learning the material in this way actively engages your brain and will significantly improve your memory (Craik, 1975).
Take control of your calendar
Controlling your schedule and your distractions will help you to accomplish your goals.
If you are in control of your calendar, you will be able to complete your assignments and stay on top of your coursework. The following are steps to getting control of your calendar:
- On the same day each week, (perhaps Sunday nights or Saturday mornings) plan out your schedule for the week.
- Go through each class and write down what you’d like to get completed for each class that week.
- Look at your calendar and determine how many hours you have to complete your work.
- Determine whether your list can be completed in the amount of time that you have available. (You may want to put the amount of time expected to complete each assignment.) Make adjustments as needed. For example, if you find that it will take more hours to complete your work than you have available, you will likely need to triage your readings. Completing all of the readings is a luxury. You will need to make decisions about your readings based on what is covered in class. You should read and take notes on all of the assignments from the favored class source (the one that is used a lot in the class). This may be the textbook or a reading that directly addresses the topic for the day. You can likely skim supplemental readings.
- Pencil into your calendar when you plan to get assignments completed.
- Before going to bed each night, make your plan for the next day. Waking up with a plan will make you more productive.
See our handout on calendars and college for more tips on using calendars as time management.
Use downtime to your advantage
Beware of ‘easy’ weeks. This is the calm before the storm. Lighter work weeks are a great time to get ahead on work or to start long projects. Use the extra hours to get ahead on assignments or start big projects or papers. You should plan to work on every class every week even if you don’t have anything due. In fact, it is preferable to do some work for each of your classes every day. Spending 30 minutes per class each day will add up to three hours per week, but spreading this time out over six days is more effective than cramming it all in during one long three-hour session. If you have completed all of the work for a particular class, then use the 30 minutes to get ahead or start a longer project.
Use all your resources
Remember that you can make an appointment with an academic coach to work on implementing any of the strategies suggested in this handout.
Works consulted
Carrier, L. M. (2003). College students’ choices of study strategies. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 96 (1), 54-56.
Craik, F. I., & Tulving, E. (1975). Depth of processing and the retention of words in episodic memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 104 (3), 268.
Davis, S. G., & Gray, E. S. (2007). Going beyond test-taking strategies: Building self-regulated students and teachers. Journal of Curriculum and Instruction, 1 (1), 31-47.
Edwards, A. J., Weinstein, C. E., Goetz, E. T., & Alexander, P. A. (2014). Learning and study strategies: Issues in assessment, instruction, and evaluation. Elsevier.
Junco, R., & Cotten, S. R. (2012). No A 4 U: The relationship between multitasking and academic performance. Computers & Education, 59 (2), 505-514.
Mackenzie, A. M. (1994). Examination preparation, anxiety and examination performance in a group of adult students. International Journal of Lifelong Education, 13 (5), 373-388.
McGuire, S.Y. & McGuire, S. (2016). Teach Students How to Learn: Strategies You Can Incorporate in Any Course to Improve Student Metacognition, Study Skills, and Motivation. Stylus Publishing, LLC.
Newport, C. (2006). How to become a straight-a student: the unconventional strategies real college students use to score high while studying less. Three Rivers Press.
Paul, K. (1996). Study smarter, not harder. Self Counsel Press.
Robinson, A. (1993). What smart students know: maximum grades, optimum learning, minimum time. Crown trade paperbacks.
Wissman, K. T., Rawson, K. A., & Pyc, M. A. (2012). How and when do students use flashcards? Memory, 20, 568-579.

If you enjoy using our handouts, we appreciate contributions of acknowledgement.
Make a Gift

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to do homework: 15 expert tips and tricks.
Coursework/GPA

Everyone struggles with homework sometimes, but if getting your homework done has become a chronic issue for you, then you may need a little extra help. That’s why we’ve written this article all about how to do homework. Once you’re finished reading it, you’ll know how to do homework (and have tons of new ways to motivate yourself to do homework)!
We’ve broken this article down into a few major sections. You’ll find:
- A diagnostic test to help you figure out why you’re struggling with homework
- A discussion of the four major homework problems students face, along with expert tips for addressing them
- A bonus section with tips for how to do homework fast
By the end of this article, you’ll be prepared to tackle whatever homework assignments your teachers throw at you .
So let’s get started!

How to Do Homework: Figure Out Your Struggles
Sometimes it feels like everything is standing between you and getting your homework done. But the truth is, most people only have one or two major roadblocks that are keeping them from getting their homework done well and on time.
The best way to figure out how to get motivated to do homework starts with pinpointing the issues that are affecting your ability to get your assignments done. That’s why we’ve developed a short quiz to help you identify the areas where you’re struggling.
Take the quiz below and record your answers on your phone or on a scrap piece of paper. Keep in mind there are no wrong answers!
1. You’ve just been assigned an essay in your English class that’s due at the end of the week. What’s the first thing you do?
A. Keep it in mind, even though you won’t start it until the day before it’s due B. Open up your planner. You’ve got to figure out when you’ll write your paper since you have band practice, a speech tournament, and your little sister’s dance recital this week, too. C. Groan out loud. Another essay? You could barely get yourself to write the last one! D. Start thinking about your essay topic, which makes you think about your art project that’s due the same day, which reminds you that your favorite artist might have just posted to Instagram...so you better check your feed right now.
2. Your mom asked you to pick up your room before she gets home from work. You’ve just gotten home from school. You decide you’ll tackle your chores:
A. Five minutes before your mom walks through the front door. As long as it gets done, who cares when you start? B. As soon as you get home from your shift at the local grocery store. C. After you give yourself a 15-minute pep talk about how you need to get to work. D. You won’t get it done. Between texts from your friends, trying to watch your favorite Netflix show, and playing with your dog, you just lost track of time!
3. You’ve signed up to wash dogs at the Humane Society to help earn money for your senior class trip. You:
A. Show up ten minutes late. You put off leaving your house until the last minute, then got stuck in unexpected traffic on the way to the shelter. B. Have to call and cancel at the last minute. You forgot you’d already agreed to babysit your cousin and bake cupcakes for tomorrow’s bake sale. C. Actually arrive fifteen minutes early with extra brushes and bandanas you picked up at the store. You’re passionate about animals, so you’re excited to help out! D. Show up on time, but only get three dogs washed. You couldn’t help it: you just kept getting distracted by how cute they were!
4. You have an hour of downtime, so you decide you’re going to watch an episode of The Great British Baking Show. You:
A. Scroll through your social media feeds for twenty minutes before hitting play, which means you’re not able to finish the whole episode. Ugh! You really wanted to see who was sent home! B. Watch fifteen minutes until you remember you’re supposed to pick up your sister from band practice before heading to your part-time job. No GBBO for you! C. You finish one episode, then decide to watch another even though you’ve got SAT studying to do. It’s just more fun to watch people make scones. D. Start the episode, but only catch bits and pieces of it because you’re reading Twitter, cleaning out your backpack, and eating a snack at the same time.
5. Your teacher asks you to stay after class because you’ve missed turning in two homework assignments in a row. When she asks you what’s wrong, you say:
A. You planned to do your assignments during lunch, but you ran out of time. You decided it would be better to turn in nothing at all than submit unfinished work. B. You really wanted to get the assignments done, but between your extracurriculars, family commitments, and your part-time job, your homework fell through the cracks. C. You have a hard time psyching yourself to tackle the assignments. You just can’t seem to find the motivation to work on them once you get home. D. You tried to do them, but you had a hard time focusing. By the time you realized you hadn’t gotten anything done, it was already time to turn them in.
Like we said earlier, there are no right or wrong answers to this quiz (though your results will be better if you answered as honestly as possible). Here’s how your answers break down:
- If your answers were mostly As, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is procrastination.
- If your answers were mostly Bs, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is time management.
- If your answers were mostly Cs, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is motivation.
- If your answers were mostly Ds, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is getting distracted.
Now that you’ve identified why you’re having a hard time getting your homework done, we can help you figure out how to fix it! Scroll down to find your core problem area to learn more about how you can start to address it.
And one more thing: you’re really struggling with homework, it’s a good idea to read through every section below. You may find some additional tips that will help make homework less intimidating.

How to Do Homework When You’re a Procrastinator
Merriam Webster defines “procrastinate” as “to put off intentionally and habitually.” In other words, procrastination is when you choose to do something at the last minute on a regular basis. If you’ve ever found yourself pulling an all-nighter, trying to finish an assignment between periods, or sprinting to turn in a paper minutes before a deadline, you’ve experienced the effects of procrastination.
If you’re a chronic procrastinator, you’re in good company. In fact, one study found that 70% to 95% of undergraduate students procrastinate when it comes to doing their homework. Unfortunately, procrastination can negatively impact your grades. Researchers have found that procrastination can lower your grade on an assignment by as much as five points ...which might not sound serious until you realize that can mean the difference between a B- and a C+.
Procrastination can also negatively affect your health by increasing your stress levels , which can lead to other health conditions like insomnia, a weakened immune system, and even heart conditions. Getting a handle on procrastination can not only improve your grades, it can make you feel better, too!
The big thing to understand about procrastination is that it’s not the result of laziness. Laziness is defined as being “disinclined to activity or exertion.” In other words, being lazy is all about doing nothing. But a s this Psychology Today article explains , procrastinators don’t put things off because they don’t want to work. Instead, procrastinators tend to postpone tasks they don’t want to do in favor of tasks that they perceive as either more important or more fun. Put another way, procrastinators want to do things...as long as it’s not their homework!
3 Tips f or Conquering Procrastination
Because putting off doing homework is a common problem, there are lots of good tactics for addressing procrastination. Keep reading for our three expert tips that will get your homework habits back on track in no time.
#1: Create a Reward System
Like we mentioned earlier, procrastination happens when you prioritize other activities over getting your homework done. Many times, this happens because homework...well, just isn’t enjoyable. But you can add some fun back into the process by rewarding yourself for getting your work done.
Here’s what we mean: let’s say you decide that every time you get your homework done before the day it’s due, you’ll give yourself a point. For every five points you earn, you’ll treat yourself to your favorite dessert: a chocolate cupcake! Now you have an extra (delicious!) incentive to motivate you to leave procrastination in the dust.
If you’re not into cupcakes, don’t worry. Your reward can be anything that motivates you . Maybe it’s hanging out with your best friend or an extra ten minutes of video game time. As long as you’re choosing something that makes homework worth doing, you’ll be successful.
#2: Have a Homework Accountability Partner
If you’re having trouble getting yourself to start your homework ahead of time, it may be a good idea to call in reinforcements . Find a friend or classmate you can trust and explain to them that you’re trying to change your homework habits. Ask them if they’d be willing to text you to make sure you’re doing your homework and check in with you once a week to see if you’re meeting your anti-procrastination goals.
Sharing your goals can make them feel more real, and an accountability partner can help hold you responsible for your decisions. For example, let’s say you’re tempted to put off your science lab write-up until the morning before it’s due. But you know that your accountability partner is going to text you about it tomorrow...and you don’t want to fess up that you haven’t started your assignment. A homework accountability partner can give you the extra support and incentive you need to keep your homework habits on track.
#3: Create Your Own Due Dates
If you’re a life-long procrastinator, you might find that changing the habit is harder than you expected. In that case, you might try using procrastination to your advantage! If you just can’t seem to stop doing your work at the last minute, try setting your own due dates for assignments that range from a day to a week before the assignment is actually due.
Here’s what we mean. Let’s say you have a math worksheet that’s been assigned on Tuesday and is due on Friday. In your planner, you can write down the due date as Thursday instead. You may still put off your homework assignment until the last minute...but in this case, the “last minute” is a day before the assignment’s real due date . This little hack can trick your procrastination-addicted brain into planning ahead!

If you feel like Kevin Hart in this meme, then our tips for doing homework when you're busy are for you.
How to Do Homework When You’re too Busy
If you’re aiming to go to a top-tier college , you’re going to have a full plate. Because college admissions is getting more competitive, it’s important that you’re maintaining your grades , studying hard for your standardized tests , and participating in extracurriculars so your application stands out. A packed schedule can get even more hectic once you add family obligations or a part-time job to the mix.
If you feel like you’re being pulled in a million directions at once, you’re not alone. Recent research has found that stress—and more severe stress-related conditions like anxiety and depression— are a major problem for high school students . In fact, one study from the American Psychological Association found that during the school year, students’ stress levels are higher than those of the adults around them.
For students, homework is a major contributor to their overall stress levels . Many high schoolers have multiple hours of homework every night , and figuring out how to fit it into an already-packed schedule can seem impossible.
3 Tips for Fitting Homework Into Your Busy Schedule
While it might feel like you have literally no time left in your schedule, there are still ways to make sure you’re able to get your homework done and meet your other commitments. Here are our expert homework tips for even the busiest of students.
#1: Make a Prioritized To-Do List
You probably already have a to-do list to keep yourself on track. The next step is to prioritize the items on your to-do list so you can see what items need your attention right away.
Here’s how it works: at the beginning of each day, sit down and make a list of all the items you need to get done before you go to bed. This includes your homework, but it should also take into account any practices, chores, events, or job shifts you may have. Once you get everything listed out, it’s time to prioritize them using the labels A, B, and C. Here’s what those labels mean:
- A Tasks : tasks that have to get done—like showing up at work or turning in an assignment—get an A.
- B Tasks : these are tasks that you would like to get done by the end of the day but aren’t as time sensitive. For example, studying for a test you have next week could be a B-level task. It’s still important, but it doesn’t have to be done right away.
- C Tasks: these are tasks that aren’t very important and/or have no real consequences if you don’t get them done immediately. For instance, if you’re hoping to clean out your closet but it’s not an assigned chore from your parents, you could label that to-do item with a C.
Prioritizing your to-do list helps you visualize which items need your immediate attention, and which items you can leave for later. A prioritized to-do list ensures that you’re spending your time efficiently and effectively, which helps you make room in your schedule for homework. So even though you might really want to start making decorations for Homecoming (a B task), you’ll know that finishing your reading log (an A task) is more important.
#2: Use a Planner With Time Labels
Your planner is probably packed with notes, events, and assignments already. (And if you’re not using a planner, it’s time to start!) But planners can do more for you than just remind you when an assignment is due. If you’re using a planner with time labels, it can help you visualize how you need to spend your day.
A planner with time labels breaks your day down into chunks, and you assign tasks to each chunk of time. For example, you can make a note of your class schedule with assignments, block out time to study, and make sure you know when you need to be at practice. Once you know which tasks take priority, you can add them to any empty spaces in your day.
Planning out how you spend your time not only helps you use it wisely, it can help you feel less overwhelmed, too . We’re big fans of planners that include a task list ( like this one ) or have room for notes ( like this one ).
#3: Set Reminders on Your Phone
If you need a little extra nudge to make sure you’re getting your homework done on time, it’s a good idea to set some reminders on your phone. You don’t need a fancy app, either. You can use your alarm app to have it go off at specific times throughout the day to remind you to do your homework. This works especially well if you have a set homework time scheduled. So if you’ve decided you’re doing homework at 6:00 pm, you can set an alarm to remind you to bust out your books and get to work.
If you use your phone as your planner, you may have the option to add alerts, emails, or notifications to scheduled events . Many calendar apps, including the one that comes with your phone, have built-in reminders that you can customize to meet your needs. So if you block off time to do your homework from 4:30 to 6:00 pm, you can set a reminder that will pop up on your phone when it’s time to get started.

This dog isn't judging your lack of motivation...but your teacher might. Keep reading for tips to help you motivate yourself to do your homework.
How to Do Homework When You’re Unmotivated
At first glance, it may seem like procrastination and being unmotivated are the same thing. After all, both of these issues usually result in you putting off your homework until the very last minute.
But there’s one key difference: many procrastinators are working, they’re just prioritizing work differently. They know they’re going to start their homework...they’re just going to do it later.
Conversely, people who are unmotivated to do homework just can’t find the willpower to tackle their assignments. Procrastinators know they’ll at least attempt the homework at the last minute, whereas people who are unmotivated struggle with convincing themselves to do it at a ll. For procrastinators, the stress comes from the inevitable time crunch. For unmotivated people, the stress comes from trying to convince themselves to do something they don’t want to do in the first place.
Here are some common reasons students are unmotivated in doing homework :
- Assignments are too easy, too hard, or seemingly pointless
- Students aren’t interested in (or passionate about) the subject matter
- Students are intimidated by the work and/or feels like they don’t understand the assignment
- Homework isn’t fun, and students would rather spend their time on things that they enjoy
To sum it up: people who lack motivation to do their homework are more likely to not do it at all, or to spend more time worrying about doing their homework than...well, actually doing it.
3 Tips for How to Get Motivated to Do Homework
The key to getting homework done when you’re unmotivated is to figure out what does motivate you, then apply those things to homework. It sounds tricky...but it’s pretty simple once you get the hang of it! Here are our three expert tips for motivating yourself to do your homework.
#1: Use Incremental Incentives
When you’re not motivated, it’s important to give yourself small rewards to stay focused on finishing the task at hand. The trick is to keep the incentives small and to reward yourself often. For example, maybe you’re reading a good book in your free time. For every ten minutes you spend on your homework, you get to read five pages of your book. Like we mentioned earlier, make sure you’re choosing a reward that works for you!
So why does this technique work? Using small rewards more often allows you to experience small wins for getting your work done. Every time you make it to one of your tiny reward points, you get to celebrate your success, which gives your brain a boost of dopamine . Dopamine helps you stay motivated and also creates a feeling of satisfaction when you complete your homework !
#2: Form a Homework Group
If you’re having trouble motivating yourself, it’s okay to turn to others for support. Creating a homework group can help with this. Bring together a group of your friends or classmates, and pick one time a week where you meet and work on homework together. You don’t have to be in the same class, or even taking the same subjects— the goal is to encourage one another to start (and finish!) your assignments.
Another added benefit of a homework group is that you can help one another if you’re struggling to understand the material covered in your classes. This is especially helpful if your lack of motivation comes from being intimidated by your assignments. Asking your friends for help may feel less scary than talking to your teacher...and once you get a handle on the material, your homework may become less frightening, too.
#3: Change Up Your Environment
If you find that you’re totally unmotivated, it may help if you find a new place to do your homework. For example, if you’ve been struggling to get your homework done at home, try spending an extra hour in the library after school instead. The change of scenery can limit your distractions and give you the energy you need to get your work done.
If you’re stuck doing homework at home, you can still use this tip. For instance, maybe you’ve always done your homework sitting on your bed. Try relocating somewhere else, like your kitchen table, for a few weeks. You may find that setting up a new “homework spot” in your house gives you a motivational lift and helps you get your work done.

Social media can be a huge problem when it comes to doing homework. We have advice for helping you unplug and regain focus.
How to Do Homework When You’re Easily Distracted
We live in an always-on world, and there are tons of things clamoring for our attention. From friends and family to pop culture and social media, it seems like there’s always something (or someone!) distracting us from the things we need to do.
The 24/7 world we live in has affected our ability to focus on tasks for prolonged periods of time. Research has shown that over the past decade, an average person’s attention span has gone from 12 seconds to eight seconds . And when we do lose focus, i t takes people a long time to get back on task . One study found that it can take as long as 23 minutes to get back to work once we’ve been distracte d. No wonder it can take hours to get your homework done!
3 Tips to Improve Your Focus
If you have a hard time focusing when you’re doing your homework, it’s a good idea to try and eliminate as many distractions as possible. Here are three expert tips for blocking out the noise so you can focus on getting your homework done.
#1: Create a Distraction-Free Environment
Pick a place where you’ll do your homework every day, and make it as distraction-free as possible. Try to find a location where there won’t be tons of noise, and limit your access to screens while you’re doing your homework. Put together a focus-oriented playlist (or choose one on your favorite streaming service), and put your headphones on while you work.
You may find that other people, like your friends and family, are your biggest distraction. If that’s the case, try setting up some homework boundaries. Let them know when you’ll be working on homework every day, and ask them if they’ll help you keep a quiet environment. They’ll be happy to lend a hand!
#2: Limit Your Access to Technology
We know, we know...this tip isn’t fun, but it does work. For homework that doesn’t require a computer, like handouts or worksheets, it’s best to put all your technology away . Turn off your television, put your phone and laptop in your backpack, and silence notifications on any wearable tech you may be sporting. If you listen to music while you work, that’s fine...but make sure you have a playlist set up so you’re not shuffling through songs once you get started on your homework.
If your homework requires your laptop or tablet, it can be harder to limit your access to distractions. But it’s not impossible! T here are apps you can download that will block certain websites while you’re working so that you’re not tempted to scroll through Twitter or check your Facebook feed. Silence notifications and text messages on your computer, and don’t open your email account unless you absolutely have to. And if you don’t need access to the internet to complete your assignments, turn off your WiFi. Cutting out the online chatter is a great way to make sure you’re getting your homework done.
#3: Set a Timer (the Pomodoro Technique)
Have you ever heard of the Pomodoro technique ? It’s a productivity hack that uses a timer to help you focus!
Here’s how it works: first, set a timer for 25 minutes. This is going to be your work time. During this 25 minutes, all you can do is work on whatever homework assignment you have in front of you. No email, no text messaging, no phone calls—just homework. When that timer goes off, you get to take a 5 minute break. Every time you go through one of these cycles, it’s called a “pomodoro.” For every four pomodoros you complete, you can take a longer break of 15 to 30 minutes.
The pomodoro technique works through a combination of boundary setting and rewards. First, it gives you a finite amount of time to focus, so you know that you only have to work really hard for 25 minutes. Once you’ve done that, you’re rewarded with a short break where you can do whatever you want. Additionally, tracking how many pomodoros you complete can help you see how long you’re really working on your homework. (Once you start using our focus tips, you may find it doesn’t take as long as you thought!)

Two Bonus Tips for How to Do Homework Fast
Even if you’re doing everything right, there will be times when you just need to get your homework done as fast as possible. (Why do teachers always have projects due in the same week? The world may never know.)
The problem with speeding through homework is that it’s easy to make mistakes. While turning in an assignment is always better than not submitting anything at all, you want to make sure that you’re not compromising quality for speed. Simply put, the goal is to get your homework done quickly and still make a good grade on the assignment!
Here are our two bonus tips for getting a decent grade on your homework assignments , even when you’re in a time crunch.
#1: Do the Easy Parts First
This is especially true if you’re working on a handout with multiple questions. Before you start working on the assignment, read through all the questions and problems. As you do, make a mark beside the questions you think are “easy” to answer .
Once you’ve finished going through the whole assignment, you can answer these questions first. Getting the easy questions out of the way as quickly as possible lets you spend more time on the trickier portions of your homework, which will maximize your assignment grade.
(Quick note: this is also a good strategy to use on timed assignments and tests, like the SAT and the ACT !)
#2: Pay Attention in Class
Homework gets a lot easier when you’re actively learning the material. Teachers aren’t giving you homework because they’re mean or trying to ruin your weekend... it’s because they want you to really understand the course material. Homework is designed to reinforce what you’re already learning in class so you’ll be ready to tackle harder concepts later.
When you pay attention in class, ask questions, and take good notes, you’re absorbing the information you’ll need to succeed on your homework assignments. (You’re stuck in class anyway, so you might as well make the most of it!) Not only will paying attention in class make your homework less confusing, it will also help it go much faster, too.

What’s Next?
If you’re looking to improve your productivity beyond homework, a good place to begin is with time management. After all, we only have so much time in a day...so it’s important to get the most out of it! To get you started, check out this list of the 12 best time management techniques that you can start using today.
You may have read this article because homework struggles have been affecting your GPA. Now that you’re on the path to homework success, it’s time to start being proactive about raising your grades. This article teaches you everything you need to know about raising your GPA so you can
Now you know how to get motivated to do homework...but what about your study habits? Studying is just as critical to getting good grades, and ultimately getting into a good college . We can teach you how to study bette r in high school. (We’ve also got tons of resources to help you study for your ACT and SAT exams , too!)
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
25 Scientifically Proven Tips for More Effective Studying

Staying on top of schoolwork can be tough.
Whether you’re in high school, or an adult going back to college, balancing coursework with other responsibilities can be challenging. If you’re teetering on the edge of burnout, here are some study tips that are scientifically proven to help you succeed!
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
2024 Ultimate Study Tips Guide
In this guide, we explore scientifically-proven study techniques from scientific journals and some of the world’s best resources like Harvard, Yale, MIT, and Cornell.
In a hurry? Skip ahead to the section that interests you most.
- How to Prepare for Success
- Create Your Perfect Study Space
- Pick a Study Method that Works for You
- Effective Study Skills
- How to Study More Efficiently
- How to Study for Tests
- Memory Improvement Techniques
- Top 10 Study Hacks Backed by Science
- Best Study Apps
- Study Skills Worksheets
- Key Takeaways
This comprehensive guide covers everything from studying for exams to the best study apps. So, let’s get started!
Part 1 – How to Prepare for Success

1. Set a Schedule
“Oh, I’ll get to it soon” isn’t a valid study strategy. Rather, you have to be intentional about planning set study sessions .
On your calendar, mark out chunks of time that you can devote to your studies. You should aim to schedule some study time each day, but other commitments may necessitate that some sessions are longer than others.
Harder classes require more study time. So, too, do classes that are worth several credits. For each credit hour that you’re taking, consider devoting one to three hours to studying each week.
2. Study at Your Own Pace
Do you digest content quickly, or do you need time to let the material sink in? Only you know what pace is best for you.
There’s no right (or wrong) study pace. So, don’t try matching someone else’s speed.
Instead, through trial and error, find what works for you. Just remember that slower studying will require that you devote more time to your schoolwork.
3. Get Some Rest
Exhaustion helps no one perform their best. Your body needs rest ; getting enough sleep is crucial for memory function.
This is one reason that scheduling study time is so important: It reduces the temptation to stay up all night cramming for a big test. Instead, you should aim for seven or more hours of sleep the night before an exam.

Limit pre-studying naps to 15 or 20 minutes at a time. Upon waking, do a few stretches or light exercises to prepare your body and brain for work.
4. Silence Your Cell Phone
Interruptions from your phone are notorious for breaking your concentration. If you pull away to check a notification, you’ll have to refocus your brain before diving back into your studies.
Consider turning off your phone’s sounds or putting your device into do not disturb mode before you start. You can also download apps to temporarily block your access to social media .
If you’re still tempted to check your device, simply power it off until you’re finished studying.
Research shows that stress makes it harder to learn and to retain information.
Stress-busting ideas include:
- Taking deep breaths
- Writing down a list of tasks you need to tackle
- Doing light exercise
Try to clear your head before you begin studying.
Part 2 – Create Your Perfect Study Space
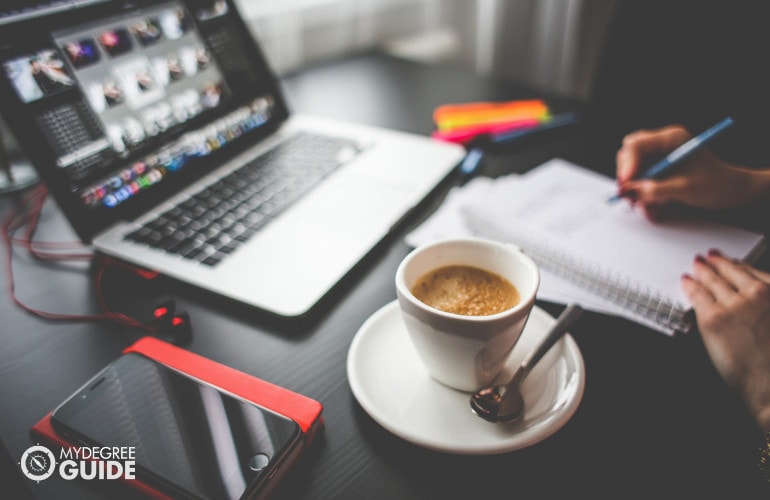

1. Pick a Good Place to Study
There’s a delicate balance when it comes to the best study spot : You need a place that’s comfortable without being so relaxing that you end up falling asleep. For some people, that means working at a desk. Others do better on the couch or at the kitchen table. Your bed, on the other hand, may be too comfy.
Surrounding yourself with peace and quiet helps you focus. If your kids are being loud or there’s construction going on outside your window, you might need to relocate to an upstairs bedroom, a quiet cafe or your local library.
2. Choose Your Music Wisely
Noise-canceling headphones can also help limit distractions.
It’s better to listen to quiet music than loud tunes. Some people do best with instrumental music playing in the background.

Songs with lyrics may pull your attention away from your textbooks. However, some folks can handle listening to songs with words, so you may want to experiment and see what works for you.
Just remember that there’s no pressure to listen to any music. If you do your best work in silence, then feel free to turn your music player off.
3. Turn Off Netflix
If song lyrics are distracting, just imagine what an attention sucker the television can be! Serious studying requires that you turn off the TV.
The same goes for listening to radio deejays. Hearing voices in the background takes your brainpower off of your studies.
4. Use Background Sounds
Turning off the television, talk radio and your favorite pop song doesn’t mean that you have to study in total silence. Soft background sounds are a great alternative.
Some people enjoy listening to nature sounds, such as ocean waves or cracks of thunder. Others prefer the whir of a fan.
5. Snack on Brain Food
A growling stomach can pull your mind from your studies, so feel free to snack as you work. Keep your snacks within arm’s reach, so you don’t have to leave your books to find food.
Fuel your next study session with some of the following items:
- Lean deli meat
- Grapes or apple slices
- Dark chocolate
Go for snacks that will power your brain and keep you alert. Steer clear of items that are high in sugar, fat and processed carbs.
Part 3 – Pick a Study Method That Works for You
Mindlessly reading through your notes or textbooks isn’t an effective method of studying; it doesn’t help you process the information. Instead, you should use a proven study strategy that will help you think through the material and retain the information.
Strategy #1 – SQ3R Method
With the SQ3R approach to reading , you’ll learn to think critically about a text.
There are five steps:
- Survey : Skim through the assigned material. Focus on headings, words in bold print and any diagrams.
- Question : Ask yourself questions related to the topic.
- Read : Read the text carefully. As you go, look for answers to your questions.
- Recite : Tell yourself the answers to your questions. Write notes about them, even.
- Review : Go over the material again by rereading the text and reading your notes aloud.
Strategy #2 – PQ4R Method
PQ4R is another study strategy that can help you digest the information you read.
This approach has six steps:
- Preview : Skim the material. Read the titles, headings and other highlighted text.
- Question : Think through questions that pertain to the material.
- Read : As you work through the material, try to find answers to your questions.
- Reflect : Consider whether you have any unanswered questions or new questions.
- Recite : Speak aloud about the things you just read.
- Review : Look over the material one more time.
Strategy #3 – THIEVES Method
The THIEVES approach can help you prepare to read for information.
There are seven pre-reading steps:
- Title : Read the title.
- Headings : Look through the headings.
- Introduction : Skim the intro.
- Every first sentence in a section : Take a look at how each section begins.
- Visuals and vocabulary : Look at the pictures and the words in bold print.
- End questions : Review the questions at the end of the chapter.
- Summary : Read the overview of the text.
Ask yourself thought-provoking questions as you work through these steps. After completing them, read the text.
Studying Online
Although these three study strategies can be useful in any setting, studying online has its own set of challenges.
Dr. Tony Bates has written a thoughtful and thorough guide to studying online, A Student Guide to Studying Online . Not only does he highlight the importance of paying attention to course design, but he also offers helpful tips on how to choose the best online program and manage your course load.
Part 4 – Effective Study Skills
1. Highlight Key Concepts
Looking for the most important information as you read helps you stay engaged with the material . This can help keep your mind from wandering as you read.
As you find important details, mark them with a highlighter, or underline them. It can also be effective to jot notes along the edges of the text. Write on removable sticky notes if the book doesn’t belong to you.
When you’re preparing for a test, begin your studies by reviewing your highlighted sections and the notes you wrote down.
2. Summarize Important Details
One good way to get information to stick in your brain is to tell it again in your own words. Writing out a summary can be especially effective. You can organize your summaries in paragraph form or in outline form.
Keep in mind that you shouldn’t include every bit of information in a summary. Stick to the key points.
Consider using different colors on your paper. Research shows that information presented in color is more memorable than things written in plain type. You could use colored pens or go over your words with highlighters.
After writing about what you read, reinforce the information yet again by reading aloud what you wrote on your paper.
3. Create Your Own Flashcards
For an easy way to quiz yourself , prepare notecards that feature a keyword on one side and important facts or definitions about that topic on the reverse.
Writing out the cards will help you learn the information. Quizzing yourself on the cards will continue that reinforcement.
The great thing about flashcards is that they’re easily portable. Slip them in your bag, so you can pull them out whenever you have a spare minute. This is a fantastic way to squeeze in extra practice time outside of your regularly scheduled study sessions.
As an alternative to paper flashcards, you can also use a computer program or a smartphone app to make digital flashcards that you can click through again and again.

4. Improve Recall with Association
Sometimes your brain could use an extra hand to help you hold onto the information that you’re studying. Creating imaginary pictures, crafting word puzzles or doing other mental exercises can help make your material easier to remember.
Try improving recall with the following ideas:
- Sing the information to a catchy tune.
- Think of a mnemonic phrase in which the words start with the same letters as the words that you need to remember.
- Draw a picture that helps you make a humorous connection between the new information and the things that you already know.
- Envision what it would be like to experience your topic in person. Imagine the sights, sounds, smells and more.
- Think up rhymes or tongue twisters that can help the information stick in your brain.
- Visualize the details with a web-style mind map that illustrates the relationships between concepts.
5. Absorb Information in Smaller Chunks
Think about how you memorize a phone number: You divide the 10-digit number into three smaller groups. It’s easier to get these three chunks to stick in your mind than it is to remember the whole thing as a single string of information.
You can use this strategy when studying by breaking a list down into smaller parts. Work on memorizing each part as its own group.
6. Make Your Own Study Sheet
Condensing your most important notes onto one page is an excellent way to keep priority information at your fingertips. The more you look over this sheet and read it aloud, the better that you’ll know the material.
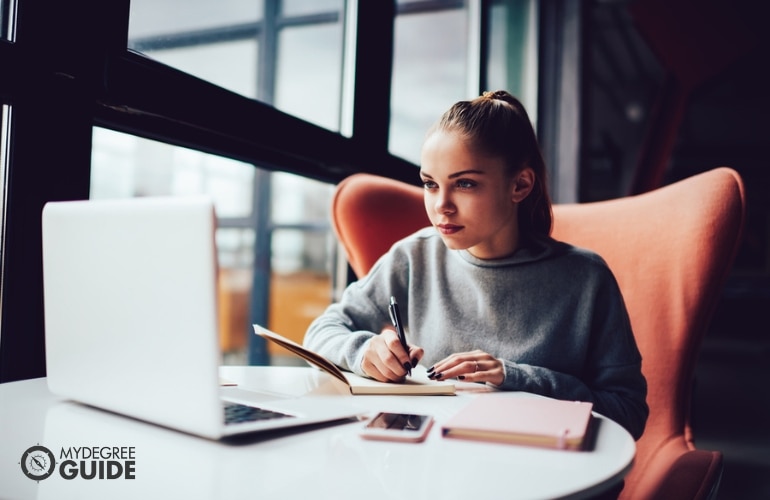

Furthermore, the act of typing or writing out the information will help you memorize the details. Using different colors or lettering styles can help you picture the information later.
Just like flashcards, a study sheet is portable. You can pull it out of your bag whenever you have a spare minute.
7. Be the Teacher
To teach information to others, you first have to understand it yourself. Therefore, when you’re trying to learn something new, challenge yourself to consider how you’d teach it to someone else. Wrestling with this concept will help you gain a better understanding of the topic.
In fact, you can even recruit a friend, a family member or a study group member to listen to your mini-lesson. Reciting your presentation aloud to someone else will help the details stick in your mind, and your audience may be able to point out gaps in your knowledge.
8. Know When to Call It a Day
Yes, you really can get too much of a good thing. Although your studies are important, they shouldn’t be the only thing in your life. It’s also important to have a social life, get plenty of exercise, and take care of your non-school responsibilities.
Studies show that too much time with your nose in the books can elevate your stress level , which can have a negative effect on your school performance and your personal relationships.
Too much studying may also keep you from getting enough exercise. This could lower your bone density or increase your percentage of body fat.
Part 5 – How to Study More Efficiently


1. Take Regular Breaks
Study sessions will be more productive if you allow yourself to take planned breaks. Consider a schedule of 50 minutes spent working followed by a 10-minute break.
Your downtime provides a good chance to stand up and stretch your legs. You can also use this as an opportunity to check your phone or respond to emails. When your 10 minutes are up, however, it’s time to get back to work.
At the end of a long study session, try to allow yourself a longer break — half an hour, perhaps — before you move on to other responsibilities.
2. Take Notes in Class
The things that your teacher talks about in class are most likely topics that he or she feels are quite important to your studies. So, it’s a good idea to become a thorough note-taker.
The following tips can help you become an efficient, effective note-taker:
- Stick to the main points.
- Use shorthand when possible.
- If you don’t have time to write all the details, jot down a keyword or a name. After class, you can use your textbook to elaborate on these items.
- For consistency, use the same organizational system each time you take notes.
- Consider writing your notes by hand, which can help you remember the information better. However, typing may help you be faster or more organized.
Recording important points is effective because it forces you to pay attention to what’s being said during a lecture.
3. Exercise First
Would you believe that exercise has the potential to grow your brain ? Scientists have shown this to be true!

In fact, exercise is most effective at generating new brain cells when it’s immediately followed by learning new information.
There are short-term benefits to exercising before studying as well. Physical activity helps wake you up so you feel alert and ready when you sit down with your books.
4. Review and Revise Your Notes at Home
If your notes are incomplete — for example, you wrote down dates with no additional information — take time after class to fill in the missing details. You may also want to swap notes with a classmate so you can catch things that you missed during the lecture.
- Rewrite your notes if you need to clean them up
- Rewriting will help you retain the information
- Add helpful diagrams or pictures
- Read through them again within one day
If you find that there are concepts in your notes that you don’t understand, ask your professor for help. You may be able to set up a meeting or communicate through email.
After rewriting your notes, put them to good use by reading through them again within the next 24 hours. You can use them as a reference when you create study sheets or flashcards.
5. Start with Your Toughest Assignments
Let’s face it: There are some subjects that you like more than others. If you want to do things the smart way, save your least challenging tasks for the end of your studies. Get the hardest things done first.
If you save the toughest tasks for last, you’ll have them hanging over your head for the whole study session. That can cost you unnecessary mental energy.

Furthermore, if you end with your favorite assignments, it will give you a more positive feeling about your academic pursuits. You’ll be more likely to approach your next study session with a good attitude.
6. Focus on Key Vocabulary
To really understand a subject, you have to know the words that relate to it. Vocabulary words are often written in textbooks in bold print. As you scan the text, write these words down in a list.
Look them up in a dictionary or in the glossary at the back of the book. To help you become familiar with the terms, you could make a study sheet with the definitions or make flashcards.
7. Join a Study Group
Studying doesn’t always have to be an individual activity.
Benefits of a study group include:
- Explaining the material to one another
- Being able to ask questions about things you don’t understand
- Quizzing each other or playing review games
- Learning the material more quickly than you might on your own
- Developing soft skills that will be useful in your career, such as teamwork and problem solving
- Having fun as you study
Gather a few classmates to form a study group.
Part 6 – How to Study for Tests
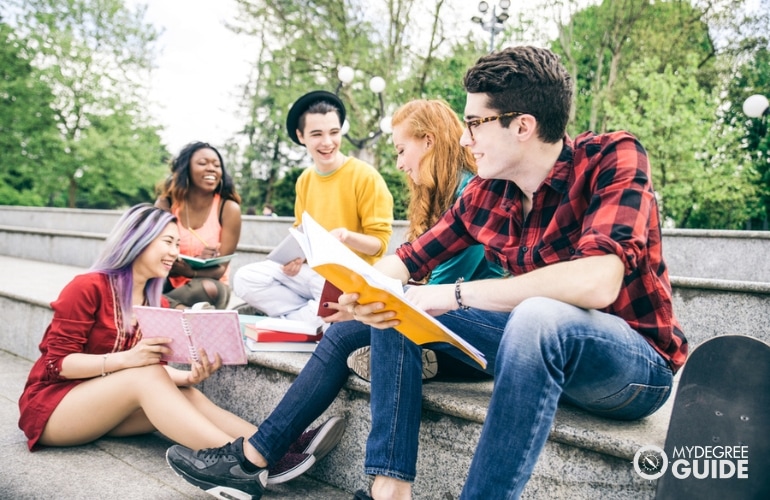

1. Study for Understanding, Not Just for the Test
Cramming the night before a big test usually involves trying to memorize information long enough to be able to regurgitate it the next morning. Although that might help you get a decent grade or your test, it won’t help you really learn the material .
Within a day or two, you’ll have forgotten most of what you studied. You’ll have missed the goal of your classes: mastery of the subject matter.
Instead, commit yourself to long-term learning by studying throughout the semester.
2. Begin Studying at Least One Week in Advance
Of course, you may need to put in extra time before a big test, but you shouldn’t put this off until the night before.
Instead, in the week leading up to the exam, block off a daily time segment for test preparation. Regular studying will help you really learn the material.
3. Spend at Least One Hour per Day Studying
One week out from a big test, study for an hour per night. If you have two big tests coming up, increase your daily study time, and divide it between the two subjects.

The day before the exam, spend as much time as possible studying — all day, even.
4. Re-write Class Notes
After each class, you should have fleshed out your notes and rewritten them in a neat, organized format. Now, it’s time to take your re-done notes and write them once again.
This time, however, your goal is to condense them down to only the most important material. Ideally, you want your rewritten notes to fit on just one or two sheets of paper.
These sheets should be your main study resource during test preparation.
5. Create a Study Outline
Early in the week, make a long outline that includes many of the details from your notes. Rewrite it a few days later, but cut the material in half.
Shortly before the test, write it one more time; include only the most important information. Quiz yourself on the missing details.
6. Make Your Own Flashcards
Another way to quiz yourself is to make flashcards that you can use for practice written tests.
First, read the term on the front side. Encourage yourself to write out the definition or details of that term. Compare your written answer with what’s on the back of the card.
This can be extra helpful when prepping for an entrance exam like the GRE, though there are a growing number of schools that don’t require GRE scores for admission.
7. Do Sample Problems and Essays from Your Textbook
There are additional things you can do to practice test-taking. For example, crack open your book, and solve problems like the ones you expect to see on the test.
Write out the answers to essay questions as well. There may be suggested essay topics in your textbook.
Part 7 – Memory Improvement Techniques

1. Study Right Before Bed
Although you shouldn’t pull all-nighters, studying right before bedtime can be a great idea.
Sleep helps cement information in your brain. Studies show that you’re more likely to recall information 24 hours later if you went to bed shortly after learning it.
Right before bed, read through your study sheet, quiz yourself on flashcards or recite lists of information.
2. Study Small Chunks at a Time
If you want to remember information over the long haul, don’t try to cram it all in during one sitting.
Instead, use an approach called spaced repetition :
- Break the information into parts
- Learn one new part at a time over the course of days or weeks
- Review your earlier acquisitions each time you study
The brain stores information that it thinks is important. So, when you regularly go over a topic at set intervals over time, it strengthens your memory of it.
3. Tell a Story
Sometimes, you just need to make information silly in order to help it stick in your brain.
To remember a list of items or the particular order of events, make up a humorous story that links those things or words together. It doesn’t necessarily need to make sense; it just needs to be memorable .

4. Change Study Locations Often
Studying the same information in multiple places helps the details stick in your mind better.
Consider some of the following locations:
- Your desk at home
- A coffee shop
- The library
- Your backyard
It’s best to switch between several different study spots instead of always hitting the books in the same place.
5. Swap Topics Regularly
Keeping your brain trained on the same information for long periods of time isn’t beneficial. It’s smarter to jump from one subject to another a few times during a long study session.
Along those same lines, you should study the same material in multiple ways. Research shows that using varied study methods for the same topic helps you perform better on tests.
6. Quiz Yourself
Challenge yourself to see what you can remember. Quizzing yourself is like practicing for the test, and it’s one of the most effective methods of memory retention .
If it’s hard to remember the information at first, don’t worry; the struggle makes it more likely that you’ll remember it in the end.
7. Go Old-school: Use a Pen and Paper
The act of writing answers helps you remember the information. Here are some ways to use writing while studying:
- Recopy your notes
- Write the answers to flashcards
- Make a study sheet
- Practice writing essay answers
Writing by hand is best because it requires your attention and focus.
8. See It & Hear It
Say information out loud, and you’ll be more likely to remember it. You’re engaging your eyes as you read the words, your mouth as you say them, and your ears as you hear yourself.
Scientists call the benefit of speaking information aloud production effect .
Part 8 – Top 10 Study Hacks Backed by Science

1. Grab a Coffee
Drinking coffee (or your preferred high-octane beverage) while you study may help keep you alert so you don’t doze off mid-session. There’s even evidence that caffeine can improve your memory skills.
However, avoid sugary beverages. These could cause your energy level to crash in a few hours.
2. Reward Yourself
Studies show that giving yourself a reward for doing your work helps you enjoy the effort more.
Do it right away; don’t wait until the test is over to celebrate. For example, after finishing a three-hour study session, treat yourself to an ice cream cone or a relaxing bath.
3. Study with Others
Working with a study group holds you accountable so it’s harder to procrastinate on your work.
When you study together, you can fill in gaps in one another’s understanding, and you can quiz each other on the material.
Besides, studying with a group can be fun!
4. Meditate
It may be hard to imagine adding anything else to your packed schedule, but dedicating time to mindfulness practices can really pay off.
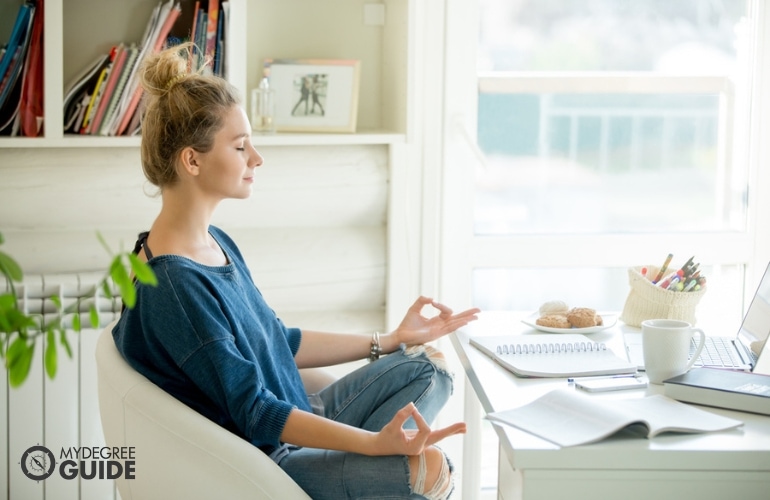

Studies show that people who meditate may perform better on tests , and they are generally more attentive.
Mindfulness apps can help you get started with this practice.
5. Hit the Gym
To boost the blood flow to your brain, do half an hour of cardio exercise before sitting down to study.
Aerobic exercise gives your brain a major dose of oxygen and other important nutrients, which may help you think clearly, remember facts and do your best work.
6. Play Some Music
Listening to tunes can help you focus. Studies show that the best study music is anything that features a rhythmic beat .
It’s smart to choose a style that you like. If you like classical, that’s fine, but you could also go for electronica or modern piano solos.
7. Grab Some Walnuts
A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids helps your brain do its best work.
Good sources include:
- Fish: cod liver oil, salmon and mackerel
- Vegetables: spinach and Brussels sprouts
To calm your pre-test jitters, eat a mix of omega-3 and omega-6 foods.
8. Take Regular Breaks
Your brain needs some downtime. Don’t try to push through for hours on end. Every hour, take a break for several minutes.

Breaks are good for your mental health . They also improve your attention span, your creativity and your productivity.
During a break, it’s best to move around and exercise a bit.
9. Get Some Sleep
Although studying is important, it can’t come at the expense of your rest. Sleep gives your brain a chance to process the information that you’ve learned that day.
If you don’t get enough sleep, you’ll have a hard time focusing and remembering information.
Even during busy test weeks, try to get seven to nine hours of sleep each night.
10. Eliminate Distractions
It’s hard to get much studying done when you’re busy scrolling Instagram. Put away your phone and computer while studying, or at least block your social media apps.
Turn off the television while you work, too.
If you’re studying in a noisy area, put on headphones that can help block the distracting sounds.
Part 9 – The Best Study Apps

1. iStudiez Pro Legend
Scheduling study time is a must, and iStudiez Pro Legend lets you put study sessions, classes and assignments on your calendar. Color coding the entries can help you stay organized.
For each class, you can enter meeting times and homework assignments, and you can keep track of your grades.
2. Dragon Anywhere
Instead of writing notes in the margins of your textbooks, you can use Dragon Anywhere’s voice dictation feature to record your thoughts and insights.
Just be sure to rewrite your dictated notes in your own handwriting later for maximum learning!
3. Evernote
When you’re in school, you have a lot of responsibilities to juggle, but Evernote can help you organize them.
You can add notes and documents to store them in one digital spot, and tagging them will help you quickly pull up all files for a class or a topic.
4. Quizlet Go
Make digital flashcards that you can practice on your mobile device with Quizlet Go .

This means that you can pull out your phone for a quick study session whenever you have a couple of minutes of downtime. You don’t even need internet access to practice these flashcards.
5. My Study Life
Enter your upcoming tests and assignments into My Study Life , and the app will send you reminder messages.
The app has a calendar so you can keep track of your class schedule. It can even notify you when it’s time to go to class.
6. Exam Countdown Lite
You should start studying for tests at least a week in advance. Input the dates for your exams and assignments into Exam Countdown Lite so you’ll have a visual reminder of when you should begin your test prep.
The app can send you notifications as well.
7. Flashcards+
With Chegg’s Flashcards+ , you can make your own digital flashcards or use ones designed by others.
Because you can add images to your cards, you can quiz yourself on the names of famous artworks, important historical artifacts or parts of a scientific diagram.
Organize information into categories by creating a visual mind map on XMind . This can help you classify facts and figures so you see how they relate to one another.

This visual representation can also help you recall the information later.
9. ScannerPro
Do you have piles of handwritten notes everywhere? Once you have written them out, consider scanning them into digital form. ScannerPro lets you use your phone as a scanner.
You can store your scanned files in this app or transfer them to Evernote or another organization system.
Part 10 – Study Skills Worksheets
Could you use more help to develop your study skills? Rutgers University has dozens of study skills worksheets online .
These documents are packed with tips that can help you become a better student. The checklists and charts can help you evaluate your current strengths and organize your work.
Part 11 – Key Takeaways
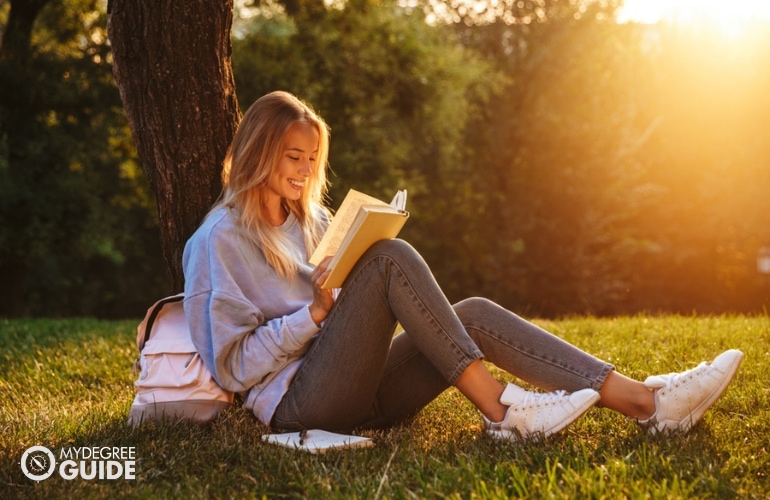

You’re a busy person, so you need to make the most of every study session.
By now, you should understand the basics of effective studies:
- Schedule study time
- Study regularly
- Minimize distractions
- Read for information
- Write the important stuff down
- Use creative memory tricks
- Quiz yourself
- Be good to your body and your brain
Put these study tips to good use, and you’ll soon learn that you’ve learned how to study smarter.

.png)
Why homework should be banned?

Banning homework could significantly reduce stress and pressure on students while promoting a more equitable and effective educational system. Homework exacerbates educational inequalities, lacks consistent effectiveness, encourages academic dishonesty, and hinders the promotion of lifelong learning.
There are many reasons why homework should be banned. Students claim they don’t have enough time for it. Nevertheless, professors give more and more assignments for self-education. As a result, the stress of deadlines adds up, diminishing students’ motivation to learn.
Many people argue that the modern curriculum leaves too much for self-study. Students don’t get enough explanation on the topic and end up with surface-level knowledge across many fields rather than an in-depth understanding of one.
Banning or at least reducing the amount of homework could be the answer to these concerns. Yet, many educational institutions are reluctant to change their curricula or don’t see the need for it.
8 Reasons why homework should be banned
When looking for arguments to support our stance, we stopped at eight. They are as follows:
Increased stress
- Less time for family
- Lack of equality among students
Poor sleep schedules
- No time for after-school development
Questionable academic benefit
- Worsened student-teacher relationships
- Risk of burnout
All these are real implications that homework has on students. In the later sections, we will expand on each in more detail.
When it comes to the reasons why should homework be banned, stress is the first one that comes to mind. With each year, academic demands only grow. It gets harder and harder to get into educational institutions, hence, it is also hard to stay. Students are expected to perform at an extraordinary level only to secure their spot.
At the same time, they hardly ever get any financial support, so some have to combine studying with work. With such a schedule, it’s very hard to find time for homework. Learners are forced to do it at night, in between classes or at work, running the risk of making their manager or professor mad. This is why students are under insurmountable pressure from their school, family, and themselves.
No time for family
The continuing debate on homework should be banned leads us to the next point. Students who are always busy with homework, hardly have time for themselves, not to mention their family. Reduced family visits or even conversation can lead to the feelings of loneliness and isolation.
Banning homework, or at least reducing its amount, could help students reconnect with their loved ones. For many students, especially freshers, loneliness is one of the biggest concerns. Many people struggle with making friends or even striking up a casual conversation with a stranger. Even a small encounter can make one feel less lonely, yet how do you find time for it if you’re always in your room doing homework?
Lack of equality
While the demands on students are approximately the same, some peoples’ resources are more limited than others’. Students from wealthier backgrounds have access to more modern technology, and, as a result, may even have more time on their hands.
At the same time, students with less resources are stuck with outdated library computers that take 20 minutes only to turn on. This inequality can lead to unfair judgment, resentment and even more inequality among students.
At the same time, in class, everyone has the same resources - the same amount of time, pen and paper. Doing assignments in class could ensure that everyone gets the same treatments based on their knowledge.
As we’ve already mentioned, some students have to work after school. And even if they don’t work, they may have multiple assignments due on the same day. Everybody needs some time to themselves, student or not. Relaxing is also vital for comprehension and memory. If you don’t sleep well, all that cramming just goes to waste, because it doesn’t make the trip from short-term memory to long-term storage.
Luckily, there is a solution. Using a do my homework service can provide students with more time for themselves or other important assignments. Getting help with homework will not only ensure that you are well-rested before class, it can also help you see a different perspective on a topic you may be struggling with. Because when a paper is completed by a professional writer, it can be an amazing learning resource.
No time for extracurriculars
Extracurricular classes, clubs and societies play a vital role in students’ holistic development. Participating in debates, math, or drama clubs can help you learn in practice, develop leadership skills, and gain real experience that can later help you excel in your profession.
Cutting all those things out for the sake of homework will leave you with theoretical knowledge only. Which is why homework should be banned.
College should give you a well-rounded education and prepare you for the real world. If you don’t engage in after-school development, don’t socialize with other students and don’t develop leadership skills, you’re going to have to learn those skills from scratch in the workplace. That makes you a less eligible candidate compared to those with practical skills.
With all the drawbacks presented above, it’s hard to argue for homework. When a student is stressed, lonely, isolated, and hasn’t had a good night’s sleep in months, writing another essay won’t do them much good.
Some research suggests that there is little to no correlation between homework and academic success, especially for younger students. That should push educators to reassess the current teaching methods and come up with better strategies for education.
When it comes to academic success, educators should focus on what can be achieved in class rather than at home. After classes, students should have time to rest, socialize and recharge.
But who invented homework and why ? Read our article to find out all about homework and its inventor!
Poor relationships between students and teachers
When teachers ask a lot from students, it can lead to resentment. Without properly explaining the task or the benefit behind it, teachers load students with an assignment every week. But when a student doesn’t understand why it’s important, they may end up doing the task haphazardly.
On the other hand, when a student who performs well in class comes back with an assignment done carelessly, the teacher may apply even more pressure on that student.
So, why should homework be abolished? Because it leads to a lot of miscommunication between teachers and students. Teachers tend to put a lot of expectations on students without considering that they have many other commitments and classes.
Academic burnout
Burnout has become increasingly more common among students. It can be characterized by the following symptoms:
- Chronic fatigue
- Irritability
- Distraction
- Loss of motivation
- Reduced performance.
It is usually caused by high expectations placed on a student by themselves, their teachers or parents. High workload can also lead a student to burn out. Perfectionism, lack of support and poor time management are among other contributors to burning out.
The easiest way to deal with burnout would, of course, be to ban homework. But, when it’s not possible, you could also try the following:
- Self-care . Take a day off or implement small habits into every day that would remind you that you are your own priority. It can be a nice meal, sports, or meditation.
- Setting goals . Determining your priorities and writing them down can be an efficient tool for those who lack motivation.
- Seeking support . Counseling services, therapy, or just talking to a friend can make a world of difference for people struggling with burnout.
Taking a break . Sometimes, it’s hard to think straight when you’re so close to the fire. Taking a vacation, a gap year or a week off can really help you evaluate your priorities and see what’s causing you stress.
Struggling with your Homework?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease.
Why homework should not be required?
Homework should not be required because it can cause significant stress for children. Research indicates that extra assignments, especially for younger students, can lead to unhealthy levels of stress. When students are bombarded with numerous lessons both at school and at home, they may experience stress and anxiety if they cannot complete the assignments on time.
Many studies have confirmed that homework negatively affects students’ performance, mood, motivation and even health. Those who have access to quality homework help can consider themselves lucky. But the rest may feel isolated, struggling on their own.
What educators must understand is that homework is already a full-time job. Those teachers do not come back from work and do more work, but students do, all the while paying insane amounts of money for that education. This inevitably poses the question of whether higher education is even worth it anymore.
It can lead to burnout, cause severe mental and physical health problems while draining your family of its life’s savings.
Banning homework for students with different learning styles
It’s no secret that people have different learning styles. However, homework is not adapted to that difference, which is another r eason why homework should be banned. The four commonly defined styles are:
- Read/Write,
- Kinaesthetic.
That means that for someone who derives most benefit from Kinaesthetic-styled learning, reading a book may not be efficient. In the same way, a visual learner will hardly benefit from writing an essay.
Yet, when it comes to homework, a teacher can’t give everyone a different task. They will normally assign the same project to everyone. That means that only ¼ of the group will benefit from that task.
Socialization should be prioritized
So, why homework should be banned? Because it takes away the time that could otherwise be spent socializing. Students that don’t have a social life do worse with their studies. When you don’t have anyone to talk to, you can feel isolated, lonely, and even depressed.
On the contrary, when you have a few friends or simply are in contact with your classmates, you have someone who can share your struggles with you. College can be a great time to bond, even if over a tyrant teacher.
Extracurriculars, study groups, and clubs can give you valuable experience that you can apply in class or even in the workplace.
Having a few extra minutes to call your family can help you reduce anxiety, feelings of separation and loneliness.
Stress doesn’t have to be an integral part of the college experience
Students are under a lot of pressure. Many of them report wanting to quit because the demands are so high. People who are the first generation from their family to attend college report even higher levels of pressure due to the feeling of responsibility before their family.
Yet, at the same time, the resources to help these students are quite scarce. Counselors’ offices are always booked weeks in advance, and therapy is not affordable to an average student with zero income.
Depression is very common among college students, while those are supposed to be the happiest years of one’s life. Could homework be the reason for that? We say yes. So, why homework should be abolished is not even a question anymore.
Final thoughts
Even though in this article, we argue against homework, we also have a few arguments on why is homework important :
It can help students dive deeper into the concepts explained in class. Lectures are limited in time, but a student may need longer to grasp a concept. While studying at home, they may use different resources and gain a deeper understanding of the topic in their own time.
Homework is also vital for teachers to be able to assess students’ understanding. There’s, unfortunately, no better way for teachers to know if you’ve understood a topic other than homework.
Overall, even though it has many drawbacks, homework doesn’t yet have an alternative. And while causing stress, it also has benefits, like deeper understanding and ease of assessment.
Did you like our Homework Post?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay writing services!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why should we ban homework.
Homework doesn’t make much sense in the modern world. Most students have to work to support themselves or their families. This leaves them with little to no time for self-education. While it used to be customary for young people to live with their parents throughout college, it’s no longer the case.
Most students have to fend for themselves - pay rent, buy groceries, and pay bills, starting at about 18 years old. Doing all that while also writing endless essays and projects for school is hardly impossible. Yet, people who combine all those things often end up stressed, burnt out and unmotivated. This may lead to frustration with the educational system and even dropping out.
On top of the stress of test scores, more homework can slow down school learning for elementary students and make them lose their motivation for further studying and academic performance. So, how can they find the motivation to go through it?
Where to find motivation for doing homework?
How to motivate yourself to do homework is a big and loaded question, but we’ll try to give you an easy answer. First of all, you should try to remember what you’re here for. Did you enter college to become a highly qualified professional? Do you want to make your parents proud? Are you internally curious and want to know everything about everything? Think of other reasons that made you go to college in the first place.
Planning out your assignments will also help. Break bigger tasks into smaller ones, plan breaks in between and come up with a course of action. This way, these assignments will seem more approachable.
You can view this from the perspective of educators who are preparing students and encouraging students for more difficult academic responsibilities later on. On the other side, it's perfectly normal for your motivation to waver when met with too much homework. Too much homework, long school hours, and a lot of time spent on even more homework can explain why banning homework can be an option.
How do I find time for leisure when homework exists?
So, why should homework be banned? Because students don’t have any time for their personal lives and end up stuck doing homework for hours on end.
If you feel it influences your mental health, it’s detrimental to take a break and find some time for yourself. It may be difficult when homework has no end.
Luckily, services like Studyfy can offer a helping hand in the time of need. Outsourcing your homework to a professional writer will not only give you a few hours to spare, but also a perfect paper sample you can use to educate yourself.
Alternatively, you can:
- Ask your professor for an extension
- Combine efforts with your friends to finish the task faster
- Get smaller tasks out of the way, your schedule will clear up, and you might find time for a walk in the park.
How to improve my performance in class?
All the way from elementary school to middle school and beyond, academic achievement and academic performance have been tied to test scores and assigning homework. You may have struggled with answering can homework improve academic achievement, especially with such repetitive homework tasks. The best thing you can do for your future education is to complete assignments on time, increase your academic performance, and use the education system for essential life skills.
It’s no secret that being active and communicating with the professor can get you some cookie points. If they notice you are trying hard, and you make a good impression, they may let some of your homework mistakes slide. This is why it’s important to address other aspects of your school performance since banning homework is not an option.
To get better in your teacher’s eyes is not that hard, really. You just have to be active. Try to sit closer to them, and maybe even further away from your friends so that you don;t get distracted. Take notes, write everything down and ask questions.
How and when to take study breaks for optimal learning
Study breaks are essential. Here's how and when to take them so that you power-up your studying and avoid getting distracted.

Getting into the swing of studying is a bit like pushing an apple cart along a road. The hardest part is getting it going. You have to heave against its inertia, and then gradually you get some forward momentum. A bit more pushing, and finally, you’re rumbling happily along the road.
It’s right there in Newton’s laws: “every object in a state of uniform motion will remain in that state of motion unless an external force acts on it.”
It’s the same with studying. The hardest part is getting going. You gather some motivation to study , power through the first couple of minutes of resistance, and once you have momentum, things get easier.
After forty minutes, or an hour, you find your attention flagging. You want to take a break but this can be dangerous. At Brainscape, we know there are two types of study breaks. You can either:
- Take the right kind of break, and get back to studying with more energy and a sharper brain, or,
- Get sidetracked, realizing four hours later that it’s 11:30 pm, and you’ve wasted most of your study time Googling cat memes.
Here’s the important bit: there are good ways to take study breaks. And there are not-so-good ways (see option B above.) Check out Brainscape's complete guide on how to study efficiently to learn the good ways to study, and also the bad ways (so you can avoid them Or recommend them to your class rivals, though that’s morally questionable.)
How to take study breaks—the right way
Tip 1. set your boundaries.
Like tequila, all-you-can-eat buffets, and Vegas, the most important thing to understand about study breaks isn’t when to start, but when to stop . So before you start your break, decide how long it will be, and set a timer.
The length of your break should depend on how long you’ve been working, and therefore how long you need to recharge. If you’re using the Pomodoro method , take a 5-minute break every 25 minutes. However, if you’ve just spent the last two hours working through difficult math theorems, then a 20-30 minute break is fine.
Set an alarm on your phone or watch to go off when your time’s up. And as soon as you hear the alarm, don’t mess about: get back to studying . This is important. The willpower needed to get you back into the study groove is considerable, so keeping to a very exact time will prevent a 10-minute study break turning into an hour of procrastination.
It can also be helpful to decide how long you’re going to study before you take a break. This will help you stay focused while studying , and give your willpower that boost to save making an origami chimpanzee for your study break.
Tip 2. Exercise
Exercise is perhaps the most effective way to restore mind and body, with the added advantage of improving concentration . (Pink leg warmers and leotards optional.) Even a short exercise session of 5 to 10 minutes (a quick walk or set of push-ups) will get your blood flowing and oxygenate your brain. In addition to the physical benefits, exercise aids your memory .
Tip 3. Have something to eat
The best foods to eat during your study break are healthy , like fruit, nuts, lean proteins, and slow-release carbohydrates, which are shown to enhance brainpower . Unfortunately, sugary drinks, chips, and highly processed junk foods just aren’t on this list .
Sugar may spike your energy at first but it’s pretty soon followed by a crash in energy levels , thanks to increased production of insulin. This has the effect of making your head feel as heavy as a cannonball, compelling you to rest it on your books and nap the next hour away.
If fighting off sleep is something you often face, here are some other tips to stop being tired when you need to study .
The other danger of snacking on MSG-laced junk food is it’s hard to stop. Even if you get back to study, you may find yourself snacking on it for the rest of your study time. Mixing study with continual snacking isn’t a good option, as you’re diverting energy from your brain to your digestive system. And you’ll end up with MSG poisoning from eating far too many Cheetos.
Tip 4. Read something
This may not seem like a proper break at first if you’ve been reading as part of your study. But the key is to read something fun, and wholly unrelated to what you’ve been working on.
It could be an interesting magazine article, a graphic novel, or a fiction book. Non-fiction is all right, but fiction or humor will give your brain a chance to change gears from analytical to creative mode. Just remember that if your book’s a real page-turner, set your timer to “obnoxiously loud” to shatter your reverie and signal the end of your study break.
Tip 5. Have a nap
Napping can be a great way to recharge, provided you keep to certain guidelines. Famous nappers include Winston Churchill, John F. Kennedy, Napoleon, Albert Einstein, and Thomas Edison. They certainly got a few things done in between their naps.
As with some of the other options, successful napping comes down to knowing yourself . Some people are world-class nappers. They can close their eyes, fall asleep, and wake up five minutes later feeling thoroughly refreshed.
Other people try to have a nap and come out of it feeling groggy and awful. If that’s you, then this type of study break may not be your cup of tea.
When planning your nap, it’s important to set a timer so you don’t nap longer than twenty minutes . This should give you enough time to fall into the shallow stages of sleep, but not into the deeper stages, from which you can awaken feeling like you’ve been run over by an 18-wheeler truck. A short nap also shouldn’t interfere with your sleep at night, while a long nap can.
Tip 6. Make a quick phone call
This one can be a great way to catch up with friends and put your mind into a completely different state so it can recharge. Just don’t call that friend whose life is an endless series of dramas and likes to tell you about them in exhausting detail.
In other words, if you’re the kind of person who can’t interrupt and say ‘Thanks, that’s really interesting, but I have to go now,” then this tactic isn’t for you.
Otherwise, calling a friend is a nice way to break things up. And you can complain about having to study as well.
Tip 7. Check your text messages
This would be a great place to have a rant about how modern human beings need validation from mobile devices instead of you just loving your own true beautiful self ... but meh . If you really must make sure the world outside still exists, go ahead and check your text messages.
Texting falls into the "handle with caution, and we’d rather you didn’t" category. So there are a few caveats. Only check text messages if:
- You’re planning something time sensitive (like a surprise birthday party or bank robbery)
- You solemnly swear not to stray outside text-world into other apps. This is important.
Thus far, we’ve covered the good ways to take study breaks in order to recharge your brain, study efficiently, and ace your exams.
It’s now time to cross over to the dark side …
How to take study breaks—the wrong way
Below is a list of the "that’s-a-bad-idea" study break options. They’re in order of truly terrible to merely bad. Time to let the procrastination monkeys out of their cage ...
Tip 8. Avoid social media
Yes, the rumors are true: Mark Zuckerberg has engaged hordes of MIT engineers to ensure that Facebook will derail your study break . Well ... not quite. But it’s not far off either .
Social media of every description—Facebook, Youtube, Twitter, Pinterest, et al.—are incredibly distracting and attention-hungry platforms. The infinitely extendable scroll bar means you never get to the end of that colorful feed. It’s a bottomless ocean of attention-grabbing, socially-reinforced content designed to draw you in, waste your time, and prevent you from achieving your goals. And the worst thing is, we do it to ourselves.
That’s not to say all social media is bad . What’s not to like about Nicholas Cage memes? It’s just that if learning is a flame, social media is a bag of wet sand.
Tip 9. Avoid TV and streaming services
Netflix is not a good study buddy. Like social media, good movies and TV series are designed to grab and hold your attention. Midway through a murder mystery, with the killer stalking through the single mom’s house, are you really going to hit pause to get back to accounting 101?
Didn’t think so. (To be fair, we wouldn’t either.)
As Oscar Wilde said: “I can resist anything except temptation.” So, don’t tempt yourself.
Tip 10. Avoid long naps
As we mentioned before, a nap longer than 20-minutes is counter productive. If you’re constantly tired while studying, you’re better off taking a good look at your daily schedule and developing good sleep habits .
A healthy amount of restorative sleep is vital for your brain to work properly. While caffeine can get you going again after an all-nighter, it’s no substitute for a good night’s sleep.
Tip 11. Avoid junk food
We talked before about the sugar-high / energy-low phenomenon. Even though cookie dough may seem a good idea at the time, you’re far better off going with an apple. There’s even some science behind why a nice fresh apple can give you a boost similar to coffee .
If you want to make things easy for yourself (and we recommend you do) the best way to avoid junk food snacks is to control your environment. Make sure you don’t have this type of food handy when you sit down for a study session.
It’s highly unlikely your willpower will triumph if you’re three steps away from a pack of salted caramel cronuts—especially if you’re already tired from studying all afternoon. You can go out and get some as a reward once you’re finished.
The inverse strategy for taking study breaks
The last way to think about study breaks is to switch everything on its head. Sometimes, doing the opposite of what you’d normally do is the best way to get things done in half the time it usually takes you, and that’s where Brainscape comes in.
Brainscape is an online flashcard study tool that breaks complex, knowledge-intensive subjects down into bite-sized pieces of information. Students using it can halve the time it takes them to learn difficult information, due to Brainscape’s adaptive spaced repetition algorithm .
Here’s how it works. Instead of studying and taking study breaks, think of life as one big study session, and you’re taking ‘life breaks’ to go study. This means breaking your study into many small bite-sized portions you can scatter throughout your day.
When you use a study app like Brainscape, it’s easy to do this in short 5-10 minute rounds. With the mobile app, you can use those in-between times to learn what you need to in order to pass your tests.
You can study:
- On public transportation.
- While drinking your morning cup of joe.
- On the treadmill (yes, it is possible to study while exercising (NNL)).
- Waiting for your girlfriend/boyfriend to finish doing his/her makeup/piano lesson/kung fu session.
You get the picture. The most successful people are good at managing their work-life balance. When you have big goals, it doesn’t always have to be a tradeoff between Study Now vs. Live Later. Especially if you have the right tools to study productively, anywhere, at any time.
Taking good study breaks: the summary
If you’re studying for any decent length of time, you’ll need to take breaks to recharge and refocus. But like all things in life (including SNL skits and NYC taxis) not all study breaks are created equal.
Knowing how to take study breaks so that you summon study motivation and crank up concentration—and not get distracted—is critical. Some will return you on time to your study schedule, refreshed and ready to go. And others will lead you down a dark alley, knock you over the head, and steal your sneakers.
Now you know what these two kinds of study breaks look like, the choice, as always, is yours.
Altenburg, T. M., Chinapaw, M. J., & Singh, A. S. (2016). Effects of one versus two bouts of moderate intensity physical activity on selective attention during a school morning in Dutch primary schoolchildren: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport , 19 (10), 820-824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2015.12.003
Dhand, R. & Sohal, H. (2006). Good sleep, bad sleep! The role of daytime naps in healthy adults. Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine , 12 (6), 379-382. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mcp.0000245703.92311.d0
Mantantzis, K., Schlaghecken, F., Sünram-Lea, S. I., & Maylor, E. A. (2019). Sugar rush or sugar crash? A meta-analysis of carbohydrate effects on mood. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews , 101 , 45-67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.03.016
Flashcards for serious learners .
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Study Skills
- Homework Skills
How to Do Homework
Last Updated: May 6, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Ronitte Libedinsky, MS . Ronitte Libedinsky is an Academic Tutor and the Founder of Brighter Minds SF, a San Francisco, California based company that provides one-on-one and small group tutoring. Specializing in tutoring mathematics (pre-algebra, algebra I/II, geometry, pre-calculus, calculus) and science (chemistry, biology), Ronitte has over 10 years of experience tutoring to middle school, high school, and college students. She also tutors in SSAT, Terra Nova, HSPT, SAT, and ACT test prep. Ronitte holds a BS in Chemistry from the University of California, Berkeley, and an MS in Chemistry from Tel Aviv University. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 958,090 times.
Even though your parents probably complain about how hard it was in their day, students nowadays have more homework than ever before, even when just starting their first year at middle school. That homework doesn't need to be a struggle now. Learning to plan out an efficient schedule for completing your homework, working on it effectively, and knowing when to get help with difficult assignments can help take the stress out of studying. Don't put it off any longer. See Step 1 for more information.
Working on Homework

Once you go into your space and start working, try not to leave until you've got a break scheduled. If you want a quick snack or drink, get it now before you start. Hit the bathroom and make sure you'll be able to work for the amount of time before your next break, uninterrupted.

- It's common that students will try to multi-task, watching TV or listening to the radio or continuing to chat on Facebook or Instagram while also trying to do homework. It'll be so much more fun to do those things after you're already done with your homework, though, and your homework will take half as much time if you're focused on doing nothing but your homework.
- Check your phone or your social networking sites during your study break, but not before. Use these distractions as a carrot, not as a pacifier.

If one assignment proves challenging and time-consuming, it's okay to switch for a while to something else. Just make sure to save enough time to circle back and give it another shot.

- Try to figure out what works best for you. Some students might like to start their homework immediately after school to get it done as quickly as possible, while it may be better to give yourself an hour to relax before starting in on it and decompress from the long school day. Don't wait for the last minute.
- While it may seem like a better idea to work straight through and finish, it's possible that the quality of the work you're doing will start to suffer if you don't give your mind a rest. It's difficult to think hard for more than 45 minutes at a time on a particular subject. Give yourself a rest and come back refreshed.

- The first fifteen minutes after a break are your most effective minutes, because your mind will be cleared, and ready to work hard. Give yourself a pep talk and dive back in, refreshed and ready.

- If you have trouble staying focused, get a parent, sibling, or friend to help keep you honest. Give them your phone while you're working to avoid the temptation to check it, or give them the video game controller so you won't be able to plug in for a few minutes of alien-hunting when you're supposed to be doing your homework. Then, when you're finished, show them the finished product and earn back your fun. Make it impossible to cheat.

- You can make yourself take enough time by having your gate-keeper (the person with your phone or video game controller) check over your homework for quality when you're done. If you know you're not going to get it anyway unless it's done right, you won't have any reason to rush. Slow down and do it right.

Joseph Meyer
When doing practice problems, promptly check to see if your answers are correct. Use worksheets that provide answer keys for instant feedback. Discuss answers with a classmate or find explanations online. Immediate feedback will help you correct your mistakes, avoid bad habits, and advance your learning more quickly.
Planning Your Homework

- It's common to quickly write out the math problems you're supposed to do at the top of your notes, or scribble down the page number of the English reading on a textbook page, but try to recopy this information into a specific homework list so you will be sure to remember to do it.
- Write down as many details as you can about each assignment. It's good to include the due date, corresponding textbook pages, and additional instructions from your teacher. This will help you plan your night of homework more effectively. Also, it's a good idea to write about your homework in a planner.

- Homework doesn't have to wait until you get home. Look through an assignment as soon as it's been given, so you'll have the time to ask your teacher any questions you might have before you leave school for the day.

- At home , a desk in your bedroom might be the best place. You can shut the door and tune out any distractions. For some students, though, this is a good way to get distracted. You might have video games, computers, guitars, and all sorts of other distractions in your bedroom. It might be a better idea to sit at the kitchen table, or in the living room, where your parents can call you out for procrastinating. You'll get it done more quickly without the temptation of distraction.
- In public , the library is a great place to study and do homework. At all libraries, it's a rule that you have to be quiet, and you won't have any of the distractions of home. The school library will often stay open after school ends, making it a good option for finishing up homework before heading home, or your school may even have an after-school study spot specifically for the purpose. [11] X Research source
- Try to switch it up . Studying in the same place too often can make work more difficult. Some studies have shown that a change in environment can make your mind more active, since it's processing new information. You'll be able to vary your routine and remember what you learned more effectively.

- Try starting with the most difficult homework . Do you really hate the idea of getting into the algebra homework? Does reading for English take the longest? Start with the most challenging homework to give yourself the most time to complete it, then move on to the easier tasks you can complete more quickly.
- Try starting with the most pressing homework . If you've got 20 math problems to do for tomorrow, and 20 pages to read in a novel for Friday, it's probably better to start with the math homework to make sure you'll have enough time to complete it. Make homework due the next day the priority.
- Try starting with the most important homework . Your math homework might be difficult, but if it's only worth a few completion points, it might be less important to spend a lot of time on it than the big project for Social Studies that's due in two days. Devote the most time to the most valuable assignments.

- Set an alarm or a timer to keep yourself honest. The less time you spend procrastinating and checking your text messages, the more quickly you'll be done. If you think you can finish everything in a half hour, set a timer and work efficiently to finish in that amount of time. If you don't quite finish, give yourself a few extra minutes. Treat it like a drill.
- Keep track of how long you usually spend on particular assignments on average. If your math homework typically takes you 45 minutes to finish, save that much time each night. If you start plugging away for an hour, give yourself a break and work on something else to avoid tiring out.
- Schedule 10 minutes of break time for every 50 minutes of work time. It's important to take study breaks and give your mind a rest, or you'll work less effectively. You're not a robot!
Finding Extra Time

- Do you really need an hour of TV or computer after school to decompress? It might be easier to just dive into your homework and get it done while the skills are still fresh in your mind. Waiting a couple hours means you'll have to review your notes and try to get back to the same place you already were. Do it while it's fresh.
- If you've got three days to read an assignment, don't wait until the last evening to do it all. Space it out and give yourself more time to finish. Just because you've got a due date that's a long time away doesn't mean it wouldn't be easier to finish now. Stay ahead of the game. Try either waking up earlier or going to bed later. But don't get too tired!

- If you've got to read a bunch of stuff for homework, read on the bus. Pop in some headphones to white noise that'll drown out the shouting of other students and tune into your book.
- The bus can be distracting, or it can be a great resource. Since it's full of your classmates, try to get other students to work with you and get things done more quickly. Work together on the math problems and try to figure out things together. It's not cheating if everyone's doing the work and no one's just copying. Also, you might make some new friends while you're at it!

- Don't rely on this time to finish homework just before it's due. Rushing to finish your last few problems in the five minutes before you need to turn it in looks bad in front of the teacher, plus it doesn't give you any time to review your homework after you finish it. Rushing is a good way to make mistakes. And always check difficult problems you had trouble with.

- Work on your homework while you're waiting for a ride, while you're killing time at your brother's soccer game, or while you're waiting for your friend to come over. Take advantage of any extra time you have in the day.
Getting Homework Help

- Asking for help with your homework isn't a sign that you're bad at the subject or that you're "stupid." Every teacher on the planet will respect a student that takes their homework seriously enough to ask for help. Especially ask if you weren't there that day!
- Asking for help isn't the same thing as complaining about the difficulty of homework or making excuses. Spending ten minutes doing half your math problems and leaving most of them blank because they were hard and then telling your teacher you need help isn't going to win you any favors on the due date. If it's hard, see your teacher ahead of time and find the time to get help.

- If there's not an organized homework help group at your school, there are many private tutoring organizations that work both for-pay and non-profits. Sylvan Learning Center and other businesses have after-school hours that you can schedule appointments at to get help studying and completing your homework, while community centers like the YMCA, or even public libraries will often have homework help hours in your area.
- Getting help doesn't mean that you're bad at your homework. All variety of students visit tutoring centers for extra help, just to make sure they have enough time and motivation to get everything done. It's hard being a student! There's no shame in extra help. Imagine being afraid to ask for anything! You wouldn't be able to ask in restaurants, shops, anywhere!

- Make sure that your group study sessions don't cross the line into cheating. Dividing up an assigned so your friend does half and you copy each other's answers is considered cheating, but discussing a problem and coming up with a solution together isn't. As long as you each do the work separately, you shouldn't have any problems.

- Some parents don't necessarily know how to help with your homework and might end up doing too much. Try to keep yourself honest. Asking for help doesn't mean asking your parent to do your work for you.
- Likewise, some older relatives have outdated ways of completing specific tasks and might suggest forcefully that something you learned in class is wrong. Always use your teacher's approach as the correct approach, and discuss these alternative ways of completing an assignment with your teacher if necessary.
Supercharge Your Studying with this Expert Series

Expert Q&A

Reader Videos
- Make sure your little study space is well lit, quiet, and comfortable. This will make it much easier to do your homework properly. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- If you missed school that day, then you should call a friend to get the notes and/or homework from that day. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Take a piece of paper or wipe board and create a schedule for your homework. Be generous with the amount of time that you give for each task. If you end up finishing a task earlier than the schedule says, you will feel accomplished and will have extra time to complete the next task. It makes homework get done quicker than usual. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
Tips from our Readers
- Make sure you have what you need handy when you get stuck on homework. Don't be afraid to ask questions if you're confused — asking helps you understand things better. And get enough sleep since it's easier to get your work done when you're well-rested.
- Don't put off starting homework just to have more playtime. Jumping in early leaves more free time for later but ensures you don't miss out on sleep. Plus, the class material is still fresh right after school, so you'll understand your homework better.
- Do your homework as soon as you get home every day except Fridays. On Fridays, give yourself permission to relax for the evening. Also, take short breaks as you work to help you focus. Play a quick game, eat a healthy snack, or use the bathroom.
- Ask for help when you need it, but don't rely on others to give you all the answers. The point of homework is for you to practice what you've learned, so try to work through problems yourself before asking for hints or explanations.
- Write down homework assignments in your planner right when your teacher gives them so you don't forget details later. Knowing exactly what work you need to do keeps you from being surprised.
- Break big assignments down into smaller pieces that feel more manageable. Taking things step-by-step makes big tasks feel less overwhelming, and helps you stay motivated.

- Never leave unfinished homework for the next day because you might have other homework to do and you will have to do both. Thanks Helpful 24 Not Helpful 0
- If you forget your homework, your teacher might not accept late work or may even give you more homework. Thanks Helpful 7 Not Helpful 1
Things You'll Need
- Writing equipment, such as pencils, rulers, and erasers.
- Resources that may help you work faster.
- A comfy place to sit while doing homework.
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.warnerpacific.edu/5-tips-for-dealing-with-too-much-homework/
- ↑ https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/mental-wealth/201206/10-tips-make-homework-time-less-painful
- ↑ Ronitte Libedinsky, MS. Academic Tutor. Expert Interview. 26 May 2020.
- ↑ https://bigfuture.collegeboard.org/plan-for-college/college-prep/stay-motivated/take-control-of-homework
- ↑ https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/homework.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/understanding-assignments/
- ↑ https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/homework.html
- ↑ http://kidshealth.org/teen/school_jobs/school/homework.html#a_Create_a_Homework_Plan
- ↑ https://tutorial.math.lamar.edu/Extras/StudyMath/Homework.aspx
- ↑ https://learningcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/studying-101-study-smarter-not-harder/
- ↑ https://kidshealth.org/en/kids/homework-help.html
About This Article

If you need to do homework, find a quiet, comfortable spot where you won’t be distracted. Turn off any electronics, like your TV, phone, or radio, and gather all of the supplies you’ll need before you get started. Work on the most important or hardest assignments first to get them out of the way, and if you have a homework assignment that actually seems fun, save it for last to motivate you to finish your other work faster. Keep reading to learn how to find extra time to get your homework done, like working on it on the way home from school! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Margaret Wessex
Dec 2, 2017
Did this article help you?
Doris Fasanya
Oct 25, 2017
May 27, 2017
Shibapriya Mukhopadhyay
Jun 3, 2017
Sep 13, 2021

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
- Raising Kids
What School Subjects Do You Need in High School?
The subjects you study in high school should allow you to graduate, but you’ll also want classes that will prepare you for college and for life as an adult.
- Subjects Offered in High School
- Subjects Needed to Graduate
- Subjects for College Preparation
Picking high school courses is an exciting process. Core high school subjects like math, science, and language arts are required, but a range of others can be selected. Finally being given more of a choice in what a student studies can be freeing, but also may feel overwhelming, confusing, or stressful.
What courses are best? There's no one right path. First, consider what is needed to graduate. Then, take a look at your options.
Parents and teens can work together to choose school subjects that not only engage their interests but also have their future plans and goals in mind.
For example, students who want to go to college may be required to take more years of a foreign language or other classes required by the schools they are interested in. A student who is interested in pursuing a career in construction may want to take an industrial arts class.
Read on to learn more about selecting courses in high school.
Parents / Nusha Ashjaee
What School Subjects Are Offered in High School?
Most high schools offer the same basic school subjects: Math, language arts, foreign language, science, social studies, health, and physical education (PE).
However, the exact courses may vary dramatically from school to school. Different high schools—even within the same district—often have different course offerings or special programs. If possible, choose the local high school that provides the programs and classes that best suit your needs and passions.
Below is a list of the most common school subjects. However, individual schools may offer a range of specialized classes, such as mindfulness or engineering.
High School Subjects
- Literature or Language Arts
- Speech and Debate
- Writing or Composition
- Trigonometry or Calculus
- Biology (typically has advanced class options)
- Chemistry (typically has advanced class options)
- Earth or Space Sciences
- Physics (typically has advanced class options)
- US Government
- World History
- Foreign Language, such as Spanish, French, Japanese, Chinese, Arabic, and German
- Physical Education and Health
- Arts, such as Music, Photography, Drawing, or Ceramics
- Computer Applications, Graphic Design, or Web Design
- Cooking and other life skills
- Physical Education
- Trade field studies such as Auto Mechanics, Woodworking, or Nursing
- Personal Finance
School Subjects You Need to Graduate
Ideally, teens should start high school with a basic plan of the classes they will need to take to graduate. Every state has different requirements for obtaining a high school diploma, and each school varies greatly in what it offers to give kids a chance to fulfill them. Different schools also vary in the number of classes students take each year.
The school's guidance department can help students understand the graduation requirements and how their coursework aligns with them.
English language arts
Studying the English language and literature is an important part of high school for every student, regardless of their post-school plans. In addition to studying important pieces of literature, English classes teach teens about writing, reading, and speaking.
Most states require four years of English or language arts classes. Colleges require four years of English for admission. The main English classes in high school include:
Mathematics
In high school, students dig into several different types of math . Algebra and geometry are required at most high schools, and students may choose to take advanced math classes if they are offered.
Most states require three or four years of math coursework in high school. The main math classes in high school include:
Basic life sciences (biology) and physical sciences (chemistry and physics) are required at most high schools. These classes often include lab components that allow students to perform hands-on experiments.
Most states require two to three years of science coursework in high school. These may include:
- Biology (typically has advanced class options)
- Chemistry (typically has advanced class options)
- Earth or Space sciences
Social studies and history
Understanding the past and how the world works is important for young adults. In high school, students will study history and government and learn about how social studies affects their lives.
Most states require three to four years of social studies coursework in high school, including:
Foreign languages
Learning a second language is important in today's global world. While many high schools offer foreign language courses, only 11 states require students to take a foreign language course.
High school students can fill these requirements by learning the basics of at least one foreign language. They may also be able to choose to take advanced classes to learn more.
Common languages offered in high school include:
- Mandarin Chinese
Other possible language offerings include Russian, Latin, American Sign Language, Arabic, and German.
Physical education and health
Physical education and health classes can teach high schoolers how to care for their bodies' fitness, health, and nutritional needs. These courses often touch on the following:
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Making healthy choices about drugs, alcohol, and nicotine.
Many states require at least one unit of PE and health to graduate. Other states offer these subjects as electives.
School Subjects for College Preparation
Students planning to go to college should consider how colleges will look at their courses during the application process. Grade point average (GPA) is important, but coursework should also demonstrate academic rigor.
When planning, it can be helpful to balance standard high school courses with some that are more challenging. Additionally, students can do this—and even get a head start on college—by taking advanced placement (AP) or college-level classes.
AP classes are more rigorous courses that teach subjects at an introductory college level. Some of the most common AP courses that are available include:
- Calculus AB
- English Literature
- African American Studies
Students who take AP classes have the option to take an AP test in the spring. If they get a certain score, they can get credit for the course at many colleges.
College credit courses
Many high schools offer opportunities to gain college credit through various programs. Your child's academic advisor, teachers, or counseling department can inform them about such offerings.
These may be online or in-person classes through programs offered by colleges and universities, and a professor or a high school teacher may teach them. Dual-credit programs allow students to fulfill their high school requirements while obtaining some college credits free of charge.
School Subject Electives
In addition to the basic classes, there are usually plenty of opportunities to take electives in various areas of study. These can not only broaden a student's academic knowledge but also teach them valuable life skills and inspire their career aspirations .
In some cases, a student may be given the freedom to choose one class from a select group of options required in the school's curriculum. In others, a student may have room in their schedule to choose to study something simply based on their interests and goals.
Examples of elective classes may include:
- Arts, such as music, photography, fashion design, painting, theater, dance, or ceramics
- Computer applications, graphic design, or web design
- Student government
- Forensic science
- Physical education
- Sports medicine
- Trade field studies such as auto mechanics, welding, or nursing
- Personal finance or business
Students on a vocational track may be able to gain some hands-on learning in fields such as metalworks and woodworking. Many schools even offer the opportunity to gain certificates or licenses that will help them in their future careers .
Key Takeaways
Choosing high school classes requires planning both as a student enters school and throughout their high school experience. The right classes are challenging and engaging but not unrealistically rigorous or overwhelming.
An ideal schedule can help a student succeed, enjoy learning, and have a good academic experience while preparing them for their future plans , whatever they may be. Have your teen set up a meeting with their school counselor if they need any help.
The association between neighbourhoods and educational achievement, a systematic review and meta-analysis . J Hous Built Environ . 2016.
50-state comparison . Education Commission of the States . 2019.
High school classes required for college admission . National Association for College Admission Counseling . n.d.
The national K-16 foreign language enrollment survey report . American Councils for International Education . 2017.
Program summary report . College Board. 2019.
Related Articles
- A Medical School That Looks More Like California
- Measuring Meals
- Clinical Trial Offers Hope for Spina Bifida Cure
When Should You Neuter or Spay Your Dog?
Updated guidelines to decrease risk of certain cancers, joint disorders.
- by Trina Wood
- May 28, 2024

Researchers at the University of California, Davis, have updated their guidelines on when to neuter 40 popular dog varieties by breed and sex. Their recent paper in Frontiers in Veterinary Science adds five breeds to a line of research that began in 2013 with a study that suggested that early neutering of golden retrievers puts them at increased risk of joint diseases and certain cancers.
That initial study set off a flurry of debate about the best age to neuter other popular breeds . Professors Lynette and Benjamin Hart of the School of Veterinary Medicine, the study’s lead authors, set out to add more breed studies by examining more than a decade of data from thousands of dogs treated at the UC Davis veterinary hospital. Their goal was to provide owners with more information to make the best decision for their animals.
They specifically looked at the correlation between neutering or spaying a dog before 1 year of age and a dog’s risk of developing certain cancers. These include cancers of the lymph nodes, bones, blood vessels or mast cell tumors for some breeds; and joint disorders such as hip or elbow dysplasia, or cranial cruciate ligament tears. Joint disorders and cancers are of particular interest because neutering removes male and female sex hormones that play key roles in important body processes such as closure of bone growth plates.
For the most recent study , they focused on German short/wirehaired pointer, mastiff, Newfoundland, Rhodesian ridgeback and Siberian husky. Data was collected from the UC Davis veterinary hospital’s records that included more than 200 cases for each of these five breeds weighing more than 20 kg (or 44 pounds), spanning January 2000 through December 2020.
The Harts said their updated guidelines emphasize the importance of personalized decisions regarding the neutering of dogs, considering the dog’s breed, sex and context. A table representing guidelines reflecting the research findings for all 40 breeds that have been studied, including the five new breeds, can be found here .
Health risks different among breeds
“It’s always complicated to consider an alternate paradigm,” said Professor Lynette Hart. “This is a shift from a long-standing model of early spay/neuter practices in the U.S. and much of Europe to neuter by 6 months of age, but important to consider as we see the connections between gonadal hormone withdrawal from early spay/neuter and potential health concerns.”
The study found major differences among these breeds for developing joint disorders and cancers when neutered early. Male and female pointer breeds had elevated joint disorders and increased cancers; male mastiff breeds had increased cranial cruciate ligament tears and lymphoma; female Newfoundland breeds had heightened risks for joint disorders; female Ridgeback breeds had heightened risks for mast cell tumors with very early neutering; and Siberian huskies showed no significant effects on joint disorders or cancers.
“We’re invested in making contributions to people’s relationship with their animals,” said Benjamin Hart, distinguished professor emeritus. “This guidance provides information and options for veterinarians to give pet owners, who should have the final decision-making role for the health and well-being of their animal.”
Their combined research studies will soon be available with others in the open access journal, Frontiers of Veterinary Science, as a free e-book, Effective Options Regarding Spay or Neuter of Dogs .
Other researchers on this UC Davis study include: Abigail Thigpen, Maya Lee, Miya Babchuk, Jenna Lee, Megan Ho, Sara Clarkson and Juliann Chou with the School of Veterinary Medicine; and Neil Willits with the Department of Statistics.
The research received a small amount of funding from the Center for Companion Animal Health, but was primarily conducted by the above authors as volunteers.
Media Resources
Media Contacts:
- Lynette Hart, School of Veterinary Medicine, [email protected]
- Trina Wood, School of Veterinary Medicine, [email protected]
- Amy Quinton, News and Media Relations, [email protected]
Primary Category
Secondary categories.

The voice in your head may help you recall and process words. But what if you don’t have one?
Professor, School of Psychology, The University of Queensland
Disclosure statement
Derek Arnold has received funding from the Australian Research Council.
University of Queensland provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
Can you imagine hearing yourself speak? A voice inside your head – perhaps reciting a shopping list or a phone number? What would life be like if you couldn’t?
Some people, including me, cannot have imagined visual experiences. We cannot close our eyes and conjure an experience of seeing a loved one’s face, or imagine our lounge room layout – to consider if a new piece of furniture might fit in it. This is called “ aphantasia ”, from a Greek phrase where the “a” means without, and “phantasia” refers to an image. Colloquially, people like myself are often referred to as having a “blind mind”.
While most attention has been given to the inability to have imagined visual sensations, aphantasics can lack other imagined experiences. We might be unable to experience imagined tastes or smells. Some people cannot imagine hearing themselves speak.
A recent study has advanced our understanding of people who cannot imagine hearing their own internal monologue. Importantly, the authors have identified some tasks that such people are more likely to find challenging.
What the study found
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark and at the University of Wisconsin-Madison in the United States recruited 93 volunteers . They included 46 adults who reported low levels of inner speech and 47 who reported high levels.
Both groups were given challenging tasks: judging if the names of objects they had seen would rhyme and recalling words. The group without an inner monologue performed worse. But differences disappeared when everyone could say words aloud.
Importantly, people who reported less inner speech were not worse at all tasks. They could recall similar numbers of words when the words had a different appearance to one another. This negates any suggestion that aphants (people with aphantasia) simply weren’t trying or were less capable.

A welcome validation
The study provides some welcome evidence for the lived experiences of some aphants, who are still often told their experiences are not different, but rather that they cannot describe their imagined experiences. Some people feel anxiety when they realise other people can have imagined experiences that they cannot. These feelings may be deepened when others assert they are merely confused or inarticulate.
In my own aphantasia research I have often quizzed crowds of people on their capacity to have imagined experiences.
Questions about the capacity to have imagined visual or audio sensations tend to be excitedly endorsed by a vast majority, but questions about imagined experiences of taste or smell seem to cause more confusion. Some people are adamant they can do this, including a colleague who says he can imagine what combinations of ingredients will taste like when cooked together. But other responses suggest subtypes of aphantasia may prove to be more common than we realise.
The authors of the recent study suggest the inability to imagine hearing yourself speak should be referred to as “anendophasia”, meaning without inner speech. Other authors had suggested anauralia (meaning without auditory imagery). Still other researchers have referred to all types of imagined sensation as being different types of “imagery”.
Having consistent names is important. It can help scientists “talk” to one another to compare findings. If different authors use different names, important evidence can be missed.

We have more than 5 senses
Debate continues about how many senses humans have, but some scientists reasonably argue for a number greater than 20 .
In addition to the five senses of sight, smell, taste, touch and hearing, lesser known senses include thermoception (our sense of heat) and proprioception (awareness of the positions of our body parts). Thanks to proprioception, most of us can close our eyes and touch the tip of our index finger to our nose. Thanks to our vestibular sense, we typically have a good idea of which way is up and can maintain balance.
It may be tempting to give a new name to each inability to have a given type of imagined sensation. But this could lead to confusion. Another approach would be to adapt phrases that are already widely used. People who are unable to have imagined sensations commonly refer to ourselves as “aphants”. This could be adapted with a prefix, such as “audio aphant”. Time will tell which approach is adopted by most researchers.
Why we should keep investigating
Regardless of the names we use, the study of multiple types of inability to have an imagined sensation is important. These investigations could reveal the essential processes in human brains that bring about a conscious experience of an imagined sensation.
In time, this will not only lead to a better understanding of the diversity of humans, but may help uncover how human brains can create any conscious sensation. This question – how and where our conscious feelings are generated – remains one of the great mysteries of science.
- Neuroscience
- proprioception
- Sensory perception
- Auditory processing

Senior Research Fellow - Women's Health Services

Data Manager

Director, Social Policy

Communications Coordinator

Head, School of Psychology
When should you neuter or spay your dog?
Updated guidelines to decrease risk of certain cancers, joint disorders.
Researchers at the University of California, Davis, have updated their guidelines on when to neuter 40 popular dog varieties by breed and sex. Their recent paper in Frontiers in Veterinary Science adds five breeds to a line of research that began in 2013 with a study that suggested that early neutering of golden retrievers puts them at increased risk of joint diseases and certain cancers.
That initial study set off a flurry of debate about the best age to neuter other popular breeds. Professors Lynette and Benjamin Hart of the School of Veterinary Medicine, the study's lead authors, set out to add more breed studies by examining more than a decade of data from thousands of dogs treated at the UC Davis veterinary hospital. Their goal was to provide owners with more information to make the best decision for their animals.
They specifically looked at the correlation between neutering or spaying a dog before 1 year of age and a dog's risk of developing certain cancers. These include cancers of the lymph nodes, bones, blood vessels or mast cell tumors for some breeds; and joint disorders such as hip or elbow dysplasia, or cranial cruciate ligament tears. Joint disorders and cancers are of particular interest because neutering removes male and female sex hormones that play key roles in important body processes such as closure of bone growth plates.
For the most recent study, they focused on German short/wirehaired pointer, mastiff, Newfoundland, Rhodesian ridgeback and Siberian husky. Data was collected from the UC Davis veterinary hospital's records that included more than 200 cases for each of these five breeds weighing more than 20 kg (or 44 pounds), spanning January 2000 through December 2020.
The Harts said their updated guidelines emphasize the importance of personalized decisions regarding the neutering of dogs, considering the dog's breed, sex and context. A table representing guidelines reflecting the research findings for all 40 breeds that have been studied, including the five new breeds, can be found here.
Health risks different among breeds
"It's always complicated to consider an alternate paradigm," said Professor Lynette Hart. "This is a shift from a long-standing model of early spay/neuter practices in the U.S. and much of Europe to neuter by 6 months of age, but important to consider as we see the connections between gonadal hormone withdrawal from early spay/neuter and potential health concerns."
The study found major differences among these breeds for developing joint disorders and cancers when neutered early. Male and female pointer breeds had elevated joint disorders and increased cancers; male mastiff breeds had increased cranial cruciate ligament tears and lymphoma; female Newfoundland breeds had heightened risks for joint disorders; female Ridgeback breeds had heightened risks for mast cell tumors with very early neutering; and Siberian huskies showed no significant effects on joint disorders or cancers.
"We're invested in making contributions to people's relationship with their animals," said Benjamin Hart, distinguished professor emeritus. "This guidance provides information and options for veterinarians to give pet owners, who should have the final decision-making role for the health and well-being of their animal."
Their combined research studies will soon be available with others in the open access journal, Frontiers of Veterinary Science, as a free e-book, Effective Options Regarding Spay or Neuter of Dogs .
Other researchers on this UC Davis study include: Abigail Thigpen, Maya Lee, Miya Babchuk, Jenna Lee, Megan Ho, Sara Clarkson and Juliann Chou with the School of Veterinary Medicine; and Neil Willits with the Department of Statistics.
The research received a small amount of funding from the Center for Companion Animal Health, but was primarily conducted by the above authors as volunteers.
- Veterinary Medicine
- Mating and Breeding
- Behavioral Science
- Agriculture and Food
- Dog skin disorders
- Mixed-breed dog
- Companion dog
- Dog hybrids and crossbreeds
- African Wild Dog
Story Source:
Materials provided by University of California - Davis . Original written by Trina Wood. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Lynette Arnason Hart, Abigail Paige Thigpen, Benjamin L. Hart, Neil H. Willits, Maya Lee, Miya M. Babchuk, Jenna Lee, Megan Ho, Sara T. Clarkson, Juliann W. Chou. Assisting decision-making on age of neutering for German Short/Wirehaired Pointer, Mastiff, Newfoundland, Rhodesian Ridgeback, Siberian Husky: associated joint disorders, cancers, and urinary incontinence . Frontiers in Veterinary Science , 2024; 11 DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1322276
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Computer Vision, Machine Learning Aid Driving
- Most Distant Known Galaxy
- A New Dinosaur from Zimbabwe
- The Case of the Missing Black Holes
- Adjusting Sunglasses for Your Windows
- Novel Gene-Editing Tool Created
- How Hummingbirds Hover With Such Accuracy
- Complete X and Y Chromosomes of Great Apes
- Moonlets Stuck Together Orbit 'Dinky' Asteroid
- Orchids Aid Seedlings Through Fungal Networks
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.
- Weird But True
- Sex & Relationships
- Viral Trends
- Human Interest
- Fashion & Beauty
- Food & Drink
trending now in Lifestyle

Here's the real reason why flight attendants greet passengers...

Mom influencer ripped for asking for donations — after spending...

Men keep hitting on me at the gym, then I turn around and they...

Dear Abby: I've been dating my boyfriend for 6 years and he...

Single mom who went viral sobbing while baking her own birthday...

Mom melts down after first-grade son snubbed at award ceremony:...

Experts warn of dangerous weight loss drug side effect: reckless...

Gen Zers boycotting ‘hard’ 9-5 jobs for their 'mental energy'
Breaking news, seniors in nursing homes should have sex if they want to, researchers say.
- View Author Archive
- Email the Author
- Follow on X
- Get author RSS feed
Contact The Author
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
Age is just a number.
New research suggests that older people should be encouraged to have sex.
The University of Sheffield’s Sexual Rights Charter has developed new training that aims to minimize the stigma that surrounds seniors and sex.

Older adults are more likely to experience discrimination when it comes to sexual health and well-being, such as not being taken seriously when bringing difficulties to medical professionals, the study found.
They also have trouble managing sexual expression in nursing homes due to a lack of privacy and staff attitudes.
The UK’s first Sexual Rights Charter was designed to encourage discussions surrounding sex in order to provide proper support to older adults.

“In adult social care, it is important to have an open culture towards sexuality so the charter helps create that,” Professor Sharron Hinchliff, lead researcher on the project and professor of psychology and health at the University’s School of Allied Health Professions, Nursing and Midwifery, said in a statement .
“The resources we are developing will be a key step in giving care home staff the guidance and understanding they need to better support residents,” she continued, noting that the information would treat seniors “with the dignity and respect they deserve.”
“We’re also exploring ways to expand the literature in terms of transgender and diverse sexual identities to make the charter even more inclusive.”

The charter was created by researchers at the University’s Healthy Lifespan Institute in collaboration with Age-friendly Sheffield and launched in 2022 to “break down barriers” and “help tackle the silence.”
Now, it’s being used to co-design, develop and roll out training to more than 60 UK care homes, with the hope that the training will be officially established in facilities later this year.
“This piece of work will help older adults living in care homes across the city and region to live the lives they want to, and this is great to see,” said Councillor Angela Argenzio, chair of the Adult Health and Social Care Policy Committee at Sheffield City Council.
When asked if they learned anything during training, an anonymous attendee shared: “It has given me confidence in understanding what problems are and why — and how to approach it with patients, and where to signpost.”
Share this article:

Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A 2006 study found that "homework had no association with achievement gains" when measured by standardized tests results or ... Your Kid Is Right, Homework Is Pointless. Here's What You Should Do Instead.," cnn.com, Jan. 28, 2020: 28. Jeanne Fratello, "Survey: Homework Is Biggest Source of Stress for Mira Costa Students," digmb.com ...
A majority of studies on homework's impact - 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another - showed that take home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. ... I just feel like this site is one-sided and you should include what the students of today think of spending four hours every night completing 6-8 classes worth of ...
As young children begin school, the focus should be on cultivating a love of learning, and assigning too much homework can undermine that goal. And young students often don't have the study skills to benefit fully from homework, so it may be a poor use of time (Cooper, 1989; Cooper et al., 2006; Marzano & Pickering, 2007). A more effective ...
It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student. 5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time.
For high schoolers, Cooper's research suggests that two hours per night is optimal. If teens have more than two hours of homework a night, their academic success flatlines. But less is not better. The average high school student doing homework outperformed 69 percent of the students in a class with no homework.
In a recent study of Spanish students, Rubén Fernández-Alonso, PhD, and colleagues found that students who were regularly assigned math and science homework scored higher on standardized tests. But when kids reported having more than 90 to 100 minutes of homework per day, scores declined ( Journal of Educational Psychology , 2015).
Too much homework may diminish its effectiveness. While research on the optimum amount of time students should spend on homework is limited, there are indications that for high school students, 1½ to 2½ hours per night is optimum. Middle school students appear to benefit from smaller amounts (less than 1 hour per night).
Their study found that too much homework is associated with: ... "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills ...
A TIME cover in 1999 read: "Too much homework! How it's hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.". The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push ...
Pro 1: Homework Helps to Improve Student Achievement. Homework teaches students various beneficial skills that they will carry with them throughout their academic and professional life, from time management and organization to self-motivation and autonomous learning. Homework helps students of all ages build critical study abilities that help ...
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein, co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work ...
In 2007, a study from the National Center for Education Statistics found that, on average, high school students spent around seven hours a week on homework. A similar study in 1994 put the average ...
Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary. "Every child should be doing homework, but the ...
A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can't ...
The best study spot is one that is quiet, well-lit, and in a low-traffic area. Make sure there is a clear workspace to study and write on. Everyone's needs are different, so it is important you find a spot that works for you. Study in short bursts. For every 30 minutes you study, take a short 10-15 minute break to recharge.
"Ideally homework should be about taking something home, spending a few curious and interesting moments in which children might engage with parents, and then getting that project back to school — an organizational triumph," she says. ... According to a recent University of Michigan study, daily homework for six- to eight-year-olds increased ...
Active engagement is the process of constructing meaning from text that involves making connections to lectures, forming examples, and regulating your own learning (Davis, 2007). Active studying does not mean highlighting or underlining text, re-reading, or rote memorization. Though these activities may help to keep you engaged in the task ...
Here's how it works: first, set a timer for 25 minutes. This is going to be your work time. During this 25 minutes, all you can do is work on whatever homework assignment you have in front of you. No email, no text messaging, no phone calls—just homework. When that timer goes off, you get to take a 5 minute break.
Instead, you should use a proven study strategy that will help you think through the material and retain the information. Strategy #1 - SQ3R Method. With the SQ3R approach to reading, you'll learn to think critically about a text. ... For each class, you can enter meeting times and homework assignments, and you can keep track of your grades ...
Here are some key reasons why homework is valuable: Reinforces Learning: Homework helps reinforce what was taught in class, allowing students to practice and apply knowledge, ensuring a deeper understanding and retention of the material. Promotes Discipline and Time Management: Regular homework assignments teach students to manage their time ...
The Day Studier. For students who have more energy earlier in the day, studying in the morning may work best, when the brain is better able to focus. Students who study during the day benefit from a refreshed and energized mind after a good night's sleep. This energy makes it easier to focus on what is being learned, and absorb the ...
8 Reasons why homework should be banned. When looking for arguments to support our stance, we stopped at eight. They are as follows: Increased stress. Less time for family. Lack of equality among students. Poor sleep schedules. No time for after-school development. Questionable academic benefit.
At Brainscape, we know there are two types of study breaks. You can either: Take the right kind of break, and get back to studying with more energy and a sharper brain, or, Get sidetracked, realizing four hours later that it's 11:30 pm, and you've wasted most of your study time Googling cat memes. Here's the important bit: there are good ...
Write out your daily homework in a list. You should have a section of your notes dedicated specifically to homework, to make it easy-to-find and convenient. ... In public, the library is a great place to study and do homework. At all libraries, it's a rule that you have to be quiet, and you won't have any of the distractions of home. ...
The subjects you study in high school should allow you to graduate, but you'll also want classes that will prepare you for college and for life as an adult. By Staff Author Published on May 14, 2024
The study analyzed data on over 415,000 people ages 40 to 69 participating in the UK Biobank, a longitudinal study of the health of people in the United Kingdom.
They specifically looked at the correlation between neutering or spaying a dog before 1 year of age and a dog's risk of developing certain cancers. These include cancers of the lymph nodes, bones, blood vessels or mast cell tumors for some breeds; and joint disorders such as hip or elbow dysplasia, or cranial cruciate ligament tears.
This question - how and where our conscious feelings are generated - remains one of the great mysteries of science. Neuroscience. Senses. proprioception. Sensory perception. Aphantasia ...
A new study updates guidelines for when you should neuter or spay your dog to prevent increased risk of cancer or joint disorders. Researchers at the University of California, Davis, have updated ...
00:01. 01:22. Age is just a number. New research suggests that older people should be encouraged to have sex. The University of Sheffield's Sexual Rights Charter has developed new training that ...