- Visualizing Your To-Do List
- 30-60-90 Day Plan
- Work Plan Template
- Weekly Planner Template
- Task Analysis Examples
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts for Planning
- Inventory Management Tecniques
- Inventory Templates
- Six Sigma DMAIC Method
- Visual Process Improvement
- Value Stream Mapping
- Creating a Workflow
- Fibonacci Scale Template
- Supply Chain Diagram
- Kaizen Method
- Procurement Process Flow Chart
- Guide to State Diagrams
- UML Activity Diagrams
- Class Diagrams & their Relationships
- Visualize flowcharts for software
- Wire-Frame Benefits
- Applications of UML
- Selecting UML Diagrams
- Create Sequence Diagrams Online
- Activity Diagram Tool
- Archimate Tool
- Class Diagram Tool
- Graphic Organizers
- Social Work Assessment Tools
- Using KWL Charts to Boost Learning
- Editable Timeline Templates
- Kinship Diagram Guide
- Power of Visual Documentation
- Graphic Organizers for Teachers & Students
- Visual Documentation Techniques
- Visual Tool for Visual Documentation
- Conducting a Thematic Analysis
- Visualizing a Dichotomous Key
- 5 W's Chart
- Circular Flow Diagram Maker
- Cladogram Maker
- Comic Strip Maker
- Course Design Template
- AI Buyer Persona
- AI Data Visualization
- AI Diagrams
- AI Project Management
- AI SWOT Analysis
- Best AI Templates
- Brainstorming AI
- Pros & Cons of AI
- AI for Business Strategy
- Using AI for Business Plan
- AI for HR Teams
- BPMN Symbols
- BPMN vs UML
- Business Process Analysis
- Business Process Modeling
- Capacity Planning Guide
- Case Management Process
- How to Avoid Bottlenecks in Processes
- Innovation Management Process
- Project vs Process
- Solve Customer Problems
- Spaghetti Diagram
- Startup Templates
- Streamline Purchase Order Process
- What is BPMN
- Approval Process
- Employee Exit Process
- Iterative Process
- Process Documentation
- Process Improvement Ideas
- Risk Assessment Process
- Tiger Teams
- Work Instruction Templates
- Workflow Vs. Process
- Process Mapping
- Business Process Reengineering
- Meddic Sales Process
- SIPOC Diagram
- What is Business Process Management
- Process Mapping Software
- Business Analysis Tool
- Business Capability Map
- Decision Making Tools and Techniques
- Operating Model Canvas
- Mobile App Planning
- Product Development Guide
- Product Roadmap
- Timeline Diagrams
- Visualize User Flow
- Sequence Diagrams
- Flowchart Maker
- Online Class Diagram Tool
- Organizational Chart Maker
- Mind Map Maker
- Retro Software
- Agile Project Charter
- Critical Path Software
- Brainstorming Guide
- Brainstorming Tools
- Visual Tools for Brainstorming
- Brainstorming Content Ideas
- Brainstorming in Business
- Brainstorming Questions
- Brainstorming Rules
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Brainstorming Workshop
- Design Thinking and Brainstorming
- Divergent vs Convergent Thinking
- Group Brainstorming Strategies
- Group Creativity
- How to Make Virtual Brainstorming Fun and Effective
- Ideation Techniques
- Improving Brainstorming
- Marketing Brainstorming
- Rapid Brainstorming
- Reverse Brainstorming Challenges
- Reverse vs. Traditional Brainstorming
- What Comes After Brainstorming
- Flowchart Guide
- Spider Diagram Guide
- 5 Whys Template
- Assumption Grid Template
- Brainstorming Templates
- Brainwriting Template
- Innovation Techniques
- 50 Business Diagrams
- Business Model Canvas
- Change Control Process
- Change Management Process
- Macro Environmental Analysis
- NOISE Analysis
- Profit & Loss Templates
- Scenario Planning
- What are Tree Diagrams
- Winning Brand Strategy
- Work Management Systems
- Balanced Scorecard
- Developing Action Plans
- Guide to setting OKRS
- How to Write a Memo
- Improve Productivity & Efficiency
- Mastering Task Analysis
- Mastering Task Batching
- Monthly Budget Templates
- Program Planning
- Top Down Vs. Bottom Up
- Weekly Schedule Templates
- Kaizen Principles
- Opportunity Mapping
- Strategic-Goals
- Strategy Mapping
- T Chart Guide
- Business Continuity Plan
- Developing Your MVP
- Incident Management
- Needs Assessment Process
- Product Development From Ideation to Launch
- Value-Proposition-Canvas
- Visualizing Competitive Landscape
- Communication Plan
- Graphic Organizer Creator
- Fault Tree Software
- Bowman's Strategy Clock Template
- Decision Matrix Template
- Communities of Practice
- Goal Setting for 2024
- Meeting Templates
- Meetings Participation
- Microsoft Teams Brainstorming
- Retrospective Guide
- Skip Level Meetings
- Visual Documentation Guide
- Weekly Meetings
- Affinity Diagrams
- Business Plan Presentation
- Post-Mortem Meetings
- Team Building Activities
- WBS Templates
- Online Whiteboard Tool
- Communications Plan Template
- Idea Board Online
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Genograms in Social Work Practice
- Conceptual Framework
- How to Conduct a Genogram Interview
- How to Make a Genogram
- Genogram Questions
- Genograms in Client Counseling
- Understanding Ecomaps
- Visual Research Data Analysis Methods
- House of Quality Template
- Customer Problem Statement Template
- Competitive Analysis Template
- Creating Operations Manual
- Knowledge Base
- Folder Structure Diagram
- Online Checklist Maker
- Lean Canvas Template
- Instructional Design Examples
- Genogram Maker
- Work From Home Guide
- Strategic Planning
- Employee Engagement Action Plan
- Huddle Board
- One-on-One Meeting Template
- Story Map Graphic Organizers
- Introduction to Your Workspace
- Managing Workspaces and Folders
- Adding Text
- Collaborative Content Management
- Creating and Editing Tables
- Adding Notes
- Introduction to Diagramming
- Using Shapes
- Using Freehand Tool
- Adding Images to the Canvas
- Accessing the Contextual Toolbar
- Using Connectors
- Working with Tables
- Working with Templates
- Working with Frames
- Using Notes
- Access Controls
- Exporting a Workspace
- Real-Time Collaboration
- Notifications
- Meet Creately VIZ
- Unleashing the Power of Collaborative Brainstorming
- Uncovering the potential of Retros for all teams
- Collaborative Apps in Microsoft Teams
- Hiring a Great Fit for Your Team
- Project Management Made Easy
- Cross-Corporate Information Radiators
- Creately 4.0 - Product Walkthrough
- What's New

Understanding the S Curve: A Comprehensive Guide for Project Managers
One of the hardest aspects of project management is accurately estimating whether things are going according to plan. Access to the right information at the right time is what allows you to make minor adjustments along the way to make sure you hit your project milestones. A tool like an S-curve allows you to manage projects more effectively, overcome obstacles, and avert possible obstacles.
What is An S Curve
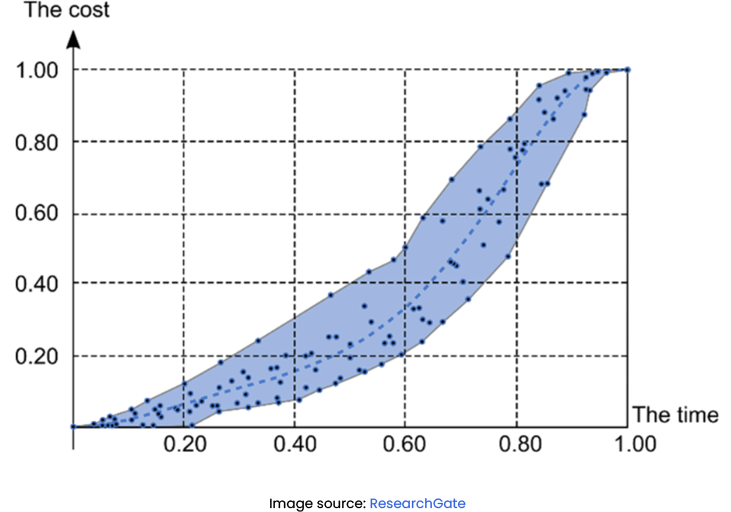
An S curve is a tool used to monitor and visualize the progress of project activities over time, helping project managers to assess whether the project is progressing as planned, identify potential bottlenecks or delays, and forecast future performance. The graph, shaped like a stretched ‘S’, is a reflection of cumulative costs, labor hours, or other measurable units against the project timeline. Here’s why the S curve is indispensable in the project manager’s toolkit:
Visual Representation of Progress : The S curve graph provides a snapshot of where the project currently stands in relation to its planned schedule and budget. It’s a clear, visual representation that helps in quickly assessing project health.
Tracking Milestones : By mapping out the project’s milestones on the S curve, managers can easily see if the project is on track to meet its critical deadlines or if adjustments need to be made.
Performance Monitoring : The S curve allows for a comparison between planned progress and actual progress, enabling project managers to identify variances and take corrective actions promptly.
The S curve in project management is not just a reporting tool; it’s a strategic asset for forecasting, planning, and communicating the project’s trajectory. With tools like Creately, project managers can visually plot their S curve on an infinite canvas, ensuring that all relevant data is captured and easily accessible for real-time collaboration and decision-making.
Understanding the S-Curve in Project Management:
The S curve in project management is a powerful visual tool that graphically represents the relationship between time and project cost or work. Understanding the three distinct phases of the S curve—initial, middle, and late—is crucial for project managers to effectively monitor and steer project progress. This helps you better contend with scenario planning .
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

Initial Phase : This is where the project kicks off, and activities are gradually ramping up. Costs and work output are relatively low as the project team is in the process of mobilizing and setting up operations. The S curve graph is shallow here, indicating slow progress.
Middle Phase : As the project gains momentum, this phase shows a steep increase in the S curve graph. It represents a period of high productivity and resource utilization, where the bulk of the project work is being executed. This is often where the most critical and time-sensitive tasks occur, and the curve’s steepness reflects the acceleration of project activities.
Late Phase : Approaching project completion, the S curve starts to plateau, indicating a deceleration in work. The tasks are now focused on finalizing and closing out the project. Costs may still be high, but the rate of work completion slows down as the project nears its end.
The S curve’s role in highlighting project acceleration and deceleration is invaluable for project managers. It allows them to anticipate changes in resource allocation and manage the pace of work to ensure timely delivery. By visualizing these phases on a platform like Creately, managers can plot their project’s S curve on an infinite canvas, drag and drop tasks, and collaborate in real time to adjust their strategies as the project evolves. This visual approach not only tracks project progress but also predicts resource utilization, manages stakeholder expectations, and plans for different schedule scenarios.
Exploring the Different Types of S Curves in Project Management
Understanding the nuances of cost, schedule, and manpower S curves is pivotal for project managers to effectively monitor and steer their projects. Each type of S curve graph serves a unique purpose and offers insights specific to its domain.
Cost S Curve : This graph represents the financial spend over time. It’s crucial for tracking the budget and ensuring that the project remains financially viable. During the initial phases, costs are typically low as planning and design take precedence. As the project progresses into execution, costs rise sharply, reflecting material purchases and labor costs. In the final stages, costs taper off as the project nears completion.
Schedule S Curve : The schedule S curve is a visual representation of project progress against the planned timeline. It helps in identifying whether the project is on track, ahead, or behind schedule. In the planning phase, the curve is relatively flat, but as milestones are reached and tasks are completed, the curve ascends steeply, indicating progress. Any deviations from the plan are easily spotted, allowing for timely corrective actions.
Manpower S Curve : This graph illustrates the workforce allocation throughout the project’s lifecycle. It’s essential for managing human resources and predicting when the project will require more or fewer personnel. The curve typically starts low, rises to a peak during the peak of project activity, and then declines as the project winds down and fewer hands are needed.
Comparing these S curves side by side can provide a comprehensive analysis of the project’s health. For instance, if the cost S curve is advancing faster than the scheduled S curve, it may indicate that the project is over budget for the work completed. Conversely, if the manpower S curve is lagging, it could suggest potential delays due to insufficient staffing. By leveraging a tool like Creately, project managers can visually plot these S curves on an infinite canvas, enabling real-time collaboration and a holistic view of project dynamics. This integration of visual data aids in making informed decisions, ensuring resource optimization, and maintaining stakeholder satisfaction.
How S-Curves Help in Strategic Decision-Making
S-curves serve as a pivotal tool for scenario planning, enabling managers to make informed and proactive adjustments. By visualizing the trajectory of project progress, S-curves allow for a clear comparison between planned performance and actual performance. This comparison is crucial for identifying deviations early on and implementing corrective measures.
Key ways S-curves contribute to scenario planning include:
- Predictive Analysis : S-curves help in forecasting future project performance based on current trends, allowing managers to allocate resources efficiently and prepare for upcoming demands.
- Risk Mitigation : By highlighting potential bottlenecks and risks, S-curves enable managers to devise contingency plans, ensuring that the project remains on track despite unforeseen challenges.
- Decision Support : S-curves provide a visual representation of different project scenarios, supporting strategic decision-making by illustrating the impact of potential changes in project variables.
Through the use of tools like Creately, which offers features such as an infinite canvas and real-time collaboration, project managers can plot S-curves with ease, gather all relevant data, and make proactive adjustments in a visually intuitive environment. This not only enhances the accuracy of scenario planning but also fosters a collaborative approach to managing project uncertainties.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating S Curves for Your Projects
Creating an S-curve in project management is a strategic way to visualize project progress and forecast potential outcomes. To begin, you’ll need to gather all relevant project data, which typically includes timeframes, budget allocations, resource availability, and project milestones. Here’s how you can use a tool like Creately to plot an effective S-curve:
- Visually plot your S-curve : Utilize Creately’s infinite canvas to draw your S-curve graph. This visual representation will help you track project progress against time.
- Gather all relevant data : Input your collected project data into Creately, ensuring that every detail from your project plan is accounted for.
- Centralize all project information : Keep all your project details in one place, making it easier to update and manage changes.
- Assign, manage and track project progress visually : With real-time collaboration features, you can assign tasks and track progress with your team in a visually engaging way.
To ensure accuracy and reliability in your S-curve representation, regularly update the curve with actual project data, and compare it against your initial projections. This will help you identify any discrepancies early on and make necessary adjustments. Remember, an accurate S-curve can be a powerful tool for predicting resource utilization and managing stakeholder expectations, enabling you to plan for different schedule scenarios effectively.
Best Practices for Utilizing S Curves in Project Management
In the dynamic realm of project management, S-curves are not just static graphs; they are living indicators of project health and progress. To harness their full potential, consider these best practices:
Regularly Update S-Curves : As projects evolve, so should your S-curves. Regular updates ensure that the S-curve graph reflects the most current data, allowing for accurate tracking and forecasting. This dynamic approach to the S curve in project management can highlight trends and deviations early, enabling proactive adjustments.
Integrate with Other Tools : S-curves should not exist in isolation. Integrate them with other project management tools to gain a holistic view of your project. This integration can provide insights into how changes in one area, such as resource allocation, might impact the overall project timeline and costs.
Educate Your Team : An S-curve graph is only as useful as the team’s ability to interpret it. Training your project team on what is an S-curve, how to read it, and what actions to take based on its shape can empower them to make informed decisions and contribute to the project’s success.
Leverage Software Solutions : Utilize software like Creately to visually plot your S-curve, gather all relevant data on a visual canvas, and manage project information centrally. Creately’s features, such as real-time collaboration and visual kanban project management, can enhance the utility of S-curves by making them more interactive and accessible to the entire team.
By following these best practices, project managers can ensure that their project S-curves are not just a formality but a vital tool for steering projects towards successful completion. Remember, an S-curve in project management is more than a graph; it’s a roadmap to project success.
The S curve emerges as more than a mere project management tool; it embodies the essence of adaptability and foresight. By enabling dynamic adjustments and proactive decision-making, it serves as a strategic asset in navigating the complexities of project execution. The S curve’s visual narrative offers not just a reflection of progress but a roadmap for resilience, guiding teams toward successful project outcomes amidst uncertainty and change.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
Chiraag George is a communication specialist here at Creately. He is a marketing junkie that is fascinated by how brands occupy consumer mind space. A lover of all things tech, he writes a lot about the intersection of technology, branding and culture at large.

Upcoming Webinar: Overview of ScheduleReader and ScheduleCleaner | 27 June, 10 - 11 AM GMT

S Curves for Monitoring and Reporting Project Progress – Definitive Guide
What is an “s curve”.
An S curve , named due to the S form-shaped shape of a curve, is a management tool that depicts a mathematical graph of relevant cumulative data over time.
S-Curves are widely used in projects, as well as in production organizations to record, monitor, analyze and control various performances by measuring parameters over time. They provide a quick overview of projects’ current status, comparisons between the baseline or targets, as well as the forecast for future periods.
For the projects of significantly longer time frame such as infrastructure development or construction of an industrial plant, the data is populated every week or on monthly basis, whereas for smaller projects where each day is critical to monitor such as in plant turnarounds and shutdowns, this graph is updated every day to reflect the current as well as the historical status of the project.
Inputs for S-Curve
S Curves are developed using a monitoring parameter and a time interval.
Monitoring parameters are the numbers that need to be updated, monitored, presented, analyzed, controlled, and forecasted such as Cost, Progress, Labor Units (Man hours), number of deliverables, and so on.
The time interval is the frequency at which these parameters need to be monitored and are normally expressed in days, weeks or months.
Monitoring parameters are normally plotted on the vertical axis while time is on the horizontal.
What is the S-Curve Used for?
In today’s advanced business climate, ensuring the project is on schedule and under or on a budget is paramount to its success and S Curves are widely used for this purpose.
Here are some of the common uses of S Curves in projects management organizations;
1 – Schedule Analysis & Leveling:
During the early stages of a project, when planning processes are happening, this graph is used to finalize the baseline schedule.
Data (mainly in the form of man-hours and cost) is taken from the resource-loaded schedule and the S Curve is plotted to review and analyze the planned performance.
Any ups and downs as highlighted in the S Curve are then leveled and adjusted back into the schedule using various techniques (such as fast-tracking or crashing) to come to a uniform and realistic S-Shaped trend.
This is an important step during schedule development as any unexplained peaks and downs can result in irregular mobilization and demobilization of resources which is not viable and practical as well as put a massive financial burden on the project budget.
A uniform S Curve generated from the resource leveled schedule is also an indication of optimum utilization of resources and cash flows.
2 – Performance Evaluations & Comparisons
S Curves are also used for performance evaluations and comparison purposes: Comparison of actual and planned parameters.
During the planning phase of the project cycle, the project schedule is developed and a baseline is frozen. Resultantly all the monitoring parameters are plotted on the basis of the baseline schedule in the form of S Curve.
This is the initial curve stated as the planned curve.
As the actual work is performed during the execution phase of the project, all the actual data is reported at a set frequency and plotted on a relevant S Curve as the actual one.
The curve then clearly indicates any positive or negative variance of actual and what was planned during the planning phase and this comparison allows the projects managers and team members to see the overall status of parameters and further decision makings.
Some of the parameters which are mainly generated and monitored with the S Curves are listed below;
- Planned Progress Vs Actual Progress
- Planned Man hours Vs Actual Man-hours
- Planned Cost Vs Actual Cost
- Planned Quantity Vs Actual Quantity
Progress, Man-hours, and Cost are normally plotted to see the overall status of the project whereas the quantities are plotted at individual discipline level to see the details of each discipline contributing to the overall status of the project.
Examples of quantities that are normally monitored in the form of S Curve at construction projects are listed as below;
- Engineering deliverables
- Concrete pouring
- Steel installations
- Equipment installation
- Piping installation
- Cable laying
- Cable terminations
3 – Forecasting
Another use of the S Curve is found in forecasting purposes.
As the project continues and the S-curve grows with the data populated at a regular frequency, the graph will turn into a historical representation.
This is used to predict future trends based on historical performance.
Progress and cash flow forecasting and resource mobilization or demobilization planning is important in this context based on work front availability and historical performance to have a clear picture of future status and requirement for the project and thus taking any preventive control measures before it gets worse.
Interpretation of S Curve
Interpretation of the S Curve is important for the team members as it helps to identify the actual performance of any monitoring parameter with the set target (baseline).
As the S Curve is plotted with the cumulative numbers, if the actual curve is above the planned curve, it is a positive variance meaning the actual performance is higher than the planned one and the project is ahead of the baseline schedule.
While on the other hand, if the actual curve is progressing below the planned one i.e. negative variance, this is a sign of further analyzing the performance and looking into more details of work, and taking necessary corrective actions to bring the project on track.
As the project progresses, there can be ups and downs in the actual performance compared with the planned one. As the S Curve is the reflection of what is being done actually, this data must be communicated with the project manager and the discipline team members to put the timely efforts to maintain or to improve the project performance.
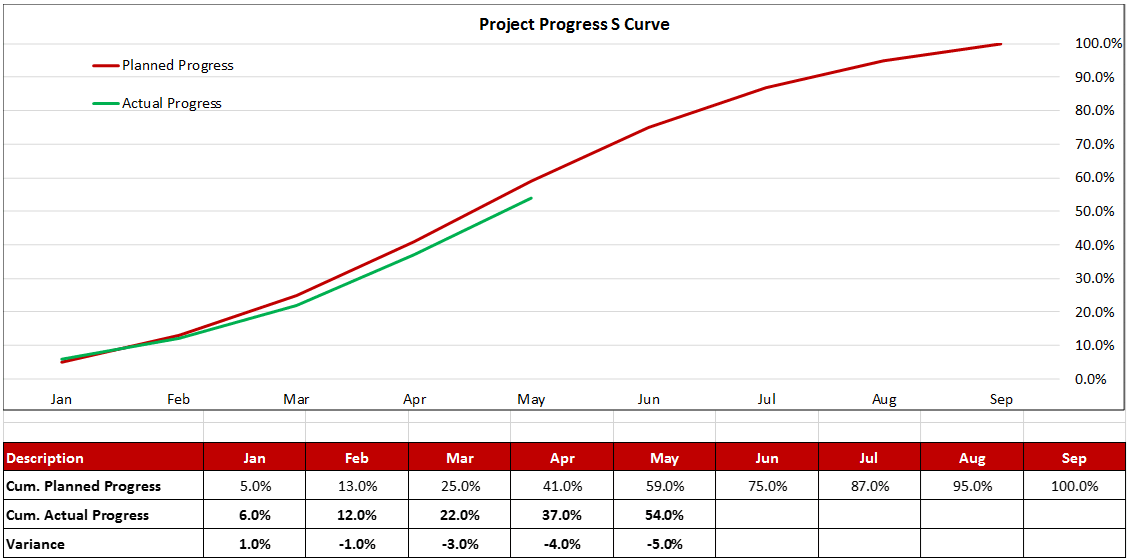
The pictures below illustrate a projects’ typical progress S Curve. Figure-1 can be seen where the actual progress line is above the planned curve with a positive variance of 7.0% (Ahead of Schedule) while Figure-II shows the actual progress curve below the planned curve with a negative variance of 5.0% (Behind Schedule).
S Curve Development Tools
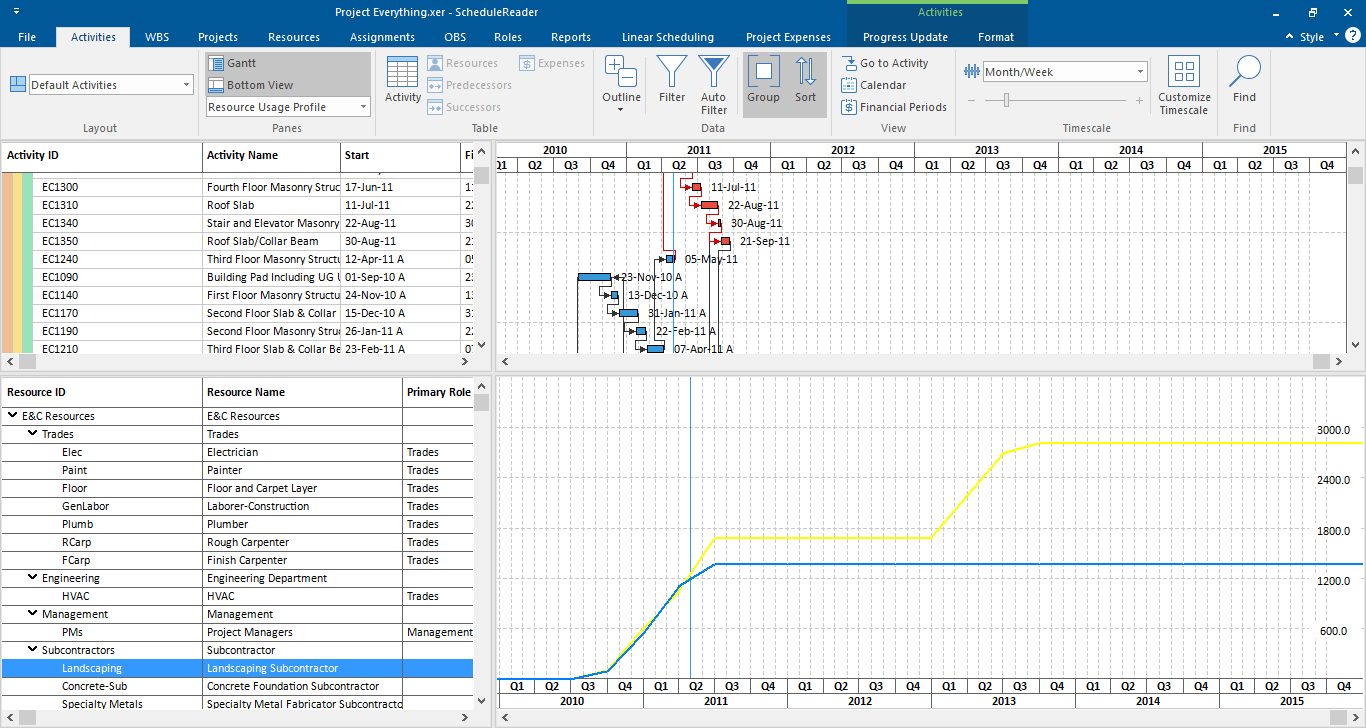
S-Curve can be generated in Primavera P6 from the resource loaded schedule as well as the schedule resource data can be taken out and S Curve could be generated in Microsoft Excel for better and customized graphical formatting.
ScheduleReader is also an important tool in this context and can be used to present primavera S Curves in a better and presentable format for team members as well as executive management.
The software is capable of showing the S-curves for the following data: units and costs .
To apply the s-curves into the Resource Usage Profile view, do the following steps:
- In the Activities Format menu, select the Options feature from the Resource Usage Profile group.
- Select any check-box from the Cumulative column (for example: Budget or Actual).
You will get a plot of the S-curve as shown in the image below.
Types of S-Curves in P6
In Primavera P6, S Curve is plotted for several parameters against the time interval to see the comparison.
These parameters are listed below;
- Labor Units
- Non-Labor Units
- Non-Labor Cost
- Material Cost
From the above list, units can be plotted either labor or non-labor at one time however cost can be plotted as an individual or the total of all costs associated with the activities.
Moreover from the above list of parameters, various types of S Curves could be generated in Primavera P6 which are listed below and can be chosen by the project manager and team members to reflect the appropriate one at any given time.
- Baseline Curve
- Budgeted Curve
- Actual Curve
- Remaining Early Curve
- Remaining Late Curve
In addition to the above types, Earned value curves can also be reflected in Primavera P6 which are used for earned value analysis of the project and are mentioned below;
- Planned Value Cost Curve
- Earned Value Cost Curve
- Estimate at Completion Cost Curve
How to Use S-Curves for Monitoring and Reporting Project Progress
An S-curve is a representation of the cost, resource, or any other unit consumed plotted against the time taken. The S-curve can be created for any value you want, depending on the need of the hour. You can plot different S-curves for different values and then compare them to get important information about the project’s life-cycle or the project’s current status. It is an essential tool used by project managers to check the cumulative budget, actual budget, and remaining budget for the project at any given time. It helps in monitoring the success of the project.
The graph is termed “S-curve” because of its nature to form a sort of S. The graph is flat at the start, gets steeper in the middle, and gets flat again at the end. This S-shaped formation of the graph is similar to almost all projects. The resources and costs ramp up at the start, get steady in the middle, and then gradually wind down during the end days.
How to Create an S-Curve in Primavera P6
Although it’s possible to plot an S-curve by hand or manually, it would be a lot of hassle. It would be prone to human errors, calculation errors, or errors in data management. One of the best and most efficient methods would be to use Primavera P6 to create an S-curve.
Primavera P6 has its own standard function of generating S-curves. There are two ways to create S-curves in Primavera:
- Resource Usage
- Tracking View
One of the first things to keep in mind before creating an S-curve in Primavera is that your input data should be complete and correct. Let’s talk about an S-curve with resources or cost against time. Since the S-curve greatly depends upon the cost/resources, your resource data should be accurate.
When you create a resource, the two most important things to keep in mind are the “max unit per time” and the “standard rate.” These factors determine how much work a laborer or machinery can do in a day. Carefully plan all resources to use in a specific activity. After you create all the resources, start assigning them to each activity.
After you properly assign resources to each activity, the software automatically calculates the total cost. The software calculates this by multiplying the “max unit per time” and the “standard rate.” The software calculates the total cost of all activities on its own. Now for the S-curve generation. There are two ways to go about this.
You can view the S-curve through the Resource Usage Profile Bottom Layout. On the top layout bar, there is a button labeled “Resource Usage Profile.”
When you click on the button, a histogram shows up. A histogram differs from an S-curve because it shows periodic data according to the period you have provided it. On the other hand, the S-curve shows cumulative data, and its graph rises at every point, showing the accumulation of resources and cost. To view the S-curve instead of the histogram, right-click on the histogram and select “resource usage profile options.”
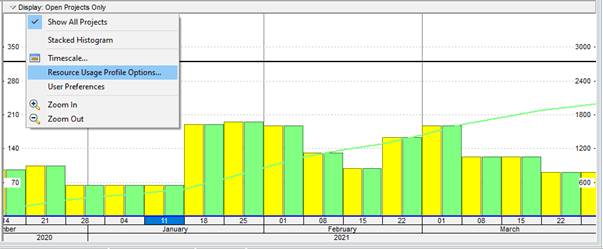
A pop-up menu appears, containing different settings for the resource usage profile. Untick the “By date” option and tick on the “Cumulative” Option. Change the color of the budgeted and actual bars to differentiate between both easily.
The second method to generate an S-curve is through the “Tracking” option. On the topmost toolbar, click on “Enterprise” and then “Tracking.” This option shows us an Aggregated S-Curve of the project.
The result is as follows:
So, what’s the difference between both methods? The “Resource Usage Profile” method, by default, shows you what is happening for a single resource. It does not tell you about the entire project as a whole. One resource may be going well for the project, but some other resources may not show favorable results. However, you can hold the Ctrl button and select all the resources individually to show the entire picture.
On the other hand, the “Tracking view” method groups all the resources in a WBS or the entire project and shows them as an Aggregated S-curve.
Monitoring the Project Progress Using the S-Curve
Now that we know how to create an S-curve, why and how do we use it? Before that, let’s discuss the predictability of a project’s progress. Construction projects rarely go in accordance with our plans. The project manager needs to keep track of the changes in the project from the original plan. He has to identify the variations in costs and schedule from the planned cost and schedule. This process is called Monitoring and Control. Even if there are changes in activities outside the critical path, it can affect other activities and create a domino effect.
One of the most common ways to monitor the project is to compare the Actual Performed Progress with the Planned or Baseline schedule. In order to perform this task, you use the project envelope or the S-curve. S-curves are utilized in various Earned Value Management techniques to evaluate the project’s status. The three most important factors to consider in EVM are:
- Planned Value
- Actual Value
- Earned Value
These factors are compared with the planned S-curve to evaluate the current or future status of the project. The results tell you if a project is under budget, over budget, behind schedule, or ahead of schedule. Earned Value Management calculations can be done manually, but it is done automatically in Primavera P6.
Project Managers also use the S-curve to predict or plan cashflows. Cashflows are the inflow and outflow of cash in a project or company during any period of time. Using the S-curve can help determine when there is a need for cash inflow and when the outflow or payment is overdue.
Project Managers often create a planned S-curve using baseline values before the project starts. This allows them to plot the actual S-curve along with it and monitor any changes in the planned schedule.
One of the most important components of the S-curve is its ability to show different possibilities for the project. The S-curve envelope shows you the early schedule curve and the late schedule curve. The early schedule curve shows data according to the early start dates and the late schedule curve shows data according to the late start dates. The project manager can use these curves to see if the project’s S-curve is going inside the envelope or not.
Reporting of S-Curve
Now that you have an S-curve in your hand, you have to formally document it in a report to show it to your superiors or in charge.
So, the next step is to print the S-curve.
- Click on File and select Page Setup
- In the pop-up dialogue, select the Options menu
- Untick all the options and only select Profile
- The Print Preview option shows you the S-curve. You can print it on any desired page.
The S-curve reporting is a crucial part of the process. Even an accurately drawn S-curve can show the project’s lousy image if not reported or displayed well.
Often, your superior would ask you for more details or changes in the schedule. Printing each variation or detail can be a hassle. On the other hand, not everyone has expertise in Primavera and can load the .xer file. So you cannot simply give him the .xer file either. In this case, the best option is to use a third-party tool like ScheduleReader.
ScheduleReader is a standalone software that you can use to open and read .xer, .xml, and .xls files exported from Primavera P6. It is an independent software, and unlike Primavera P6, you do not have to connect it to any database. This allows people with no expertise in Primavera to quickly open any project schedule on their PCs. It also saves you the trouble of saving a PDF file every time. One of its best advantages is its cost-effectiveness. They provide you with custom licensing options according to your business.
A few uses and benefits of using ScheduleReader for S-curve reporting are:
- The presentation of the S-Curve drastically affects how the project manager perceives the report. E.g., light-colored or less visible lines often confuse people as it makes them wonder what it depicts. ScheduleReader uses vibrant and warm colors to display all stats and progress of your project.
- The S-curve in ScheduleReader shows the entire summary of the project in the shape of graphs. The graphs show the cost used, resources used, cumulative budget, the project’s status, etc. This saves the project manager time of going through different types of reports.
- Through ScheduleReader, the project manager can assess the S-curve of a single resource as well. This lets him evaluate which resources are affecting the S-curve the most.
S-Curves in ScheduleReader
ScheduleReader allows its users to perform a quick analysis of the schedule, apply filters, group activities. It also has the ability to draw S-curves for both Costs and Units.
There are numerous S-curves used in project management, but this software supports the following:
- Man Hours versus Time S-curve
- Cost versus Time S-curve
- Actual S-curve.
To create S-curves in SchedulerReader, just go to the Activity tab and click on “Bottom View.”
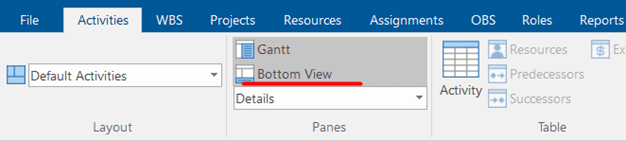
The drop-down menu will show you several options that will appear in the bottom view. These are Trace Logic, Resource Usage Profile, Stacked Histogram, and Activity Usage Profile.
First, we will show the S-curves generated from the Resource Usage Profile. Select the Resource Usage Profile.
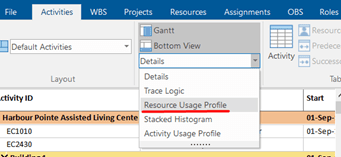
Then, in the Activity Format ribbon, choose whether you want to see the s-curves By Resource or By Role.
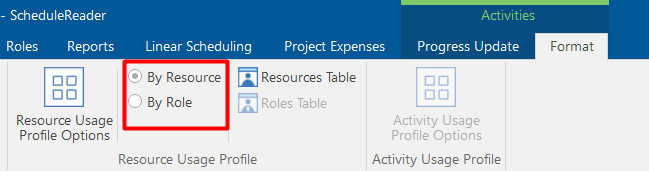
The project plan presented in the examples is created with resources, and because of it, the images that follow will be shown By Resources. The steps are exactly the same as a project plan that includes roles.
After you have chosen between By Resource or By Role, click on the Resource Usage Profile Option.
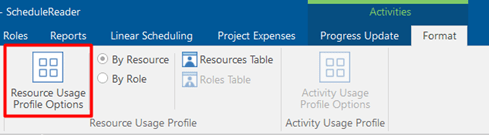
A new dialog pop-up window will open. In this window you may select any check-box from the Cumulative column including Budgeted, Actual, Remaining, and/or Remaining Late. Choose the ones you want to track, and they will appear in the bottom view. An interesting feature in ScheduleReader is that the software allows you to customize the look of the curves by color, and to make combinations of the cumulative curves. Plus, you may add Additional Data such as Legend, Overtime, Overllocation, and/or Limit.
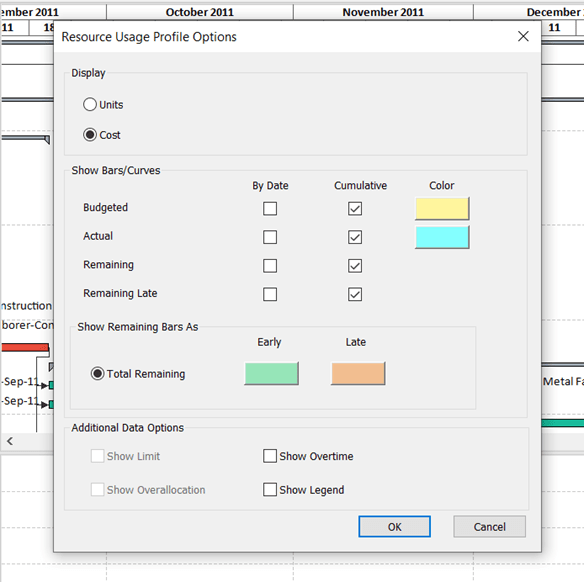
After arranging the fields you need, when you click OK, and the S-curves will appear in the Bottom View like this:
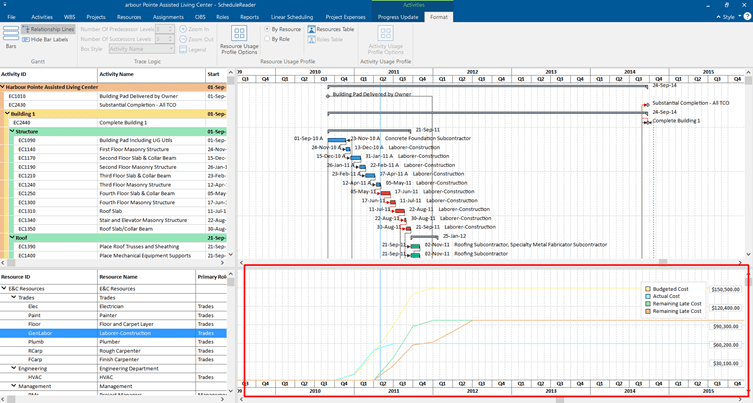
This example presents you with only one way to draw S-curves in ScheduleReader. It shows you only the S-curves for a selected resource.
But, if we select the Activity Usage Profile from the Activity tab under the Bottom View, we will get a different view of the S-curves:
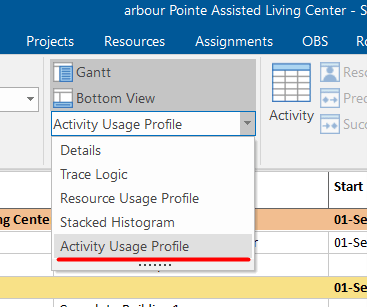
This view shows us the S-curves for the entire resources in the project plan.
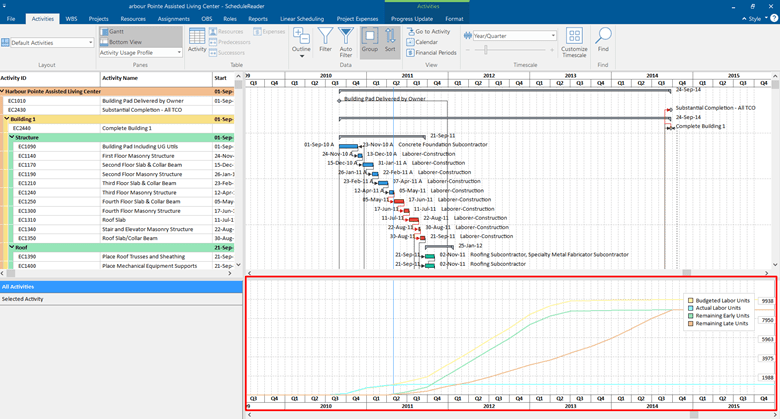
If we click on the Activity Format ribbon, again we have the possibility to open Activity Usage Profile Options that gives us an extra option from the Resource Usage Profile.
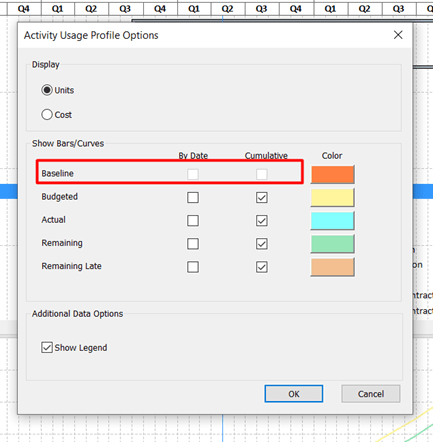
As you can see from the dialog we have the same options to draw S-curves by Units or Costs. The same Cumulative curves are there, but now we have the option to check Baseline. This will allow us to compare the project plans.
Moreover, we can navigate a selected activity and see its S-curves from the Activity Usage Profile in the left chart. See the image below:
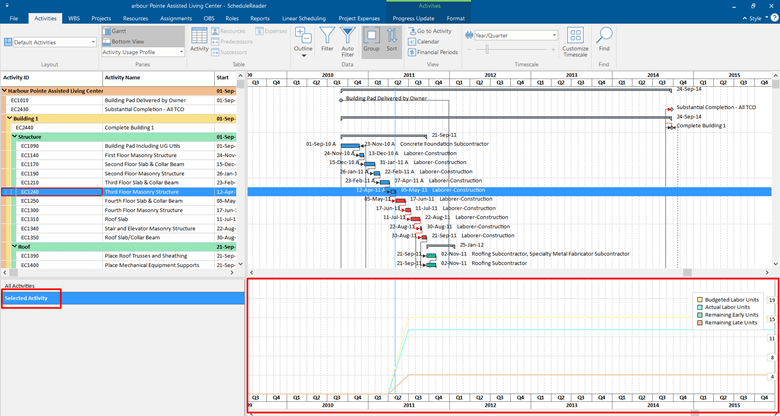
You can choose a specific resource, and in the Bottom View, you will see its S-curves.
The possibility to navigate the S-curves on the Selected Activity and All Activities from the same place allows us to analyze, monitor, track, and report all changes of the project with ease. It will save time, but most importantly we will be able to see every change in the schedule and take the needed actions.
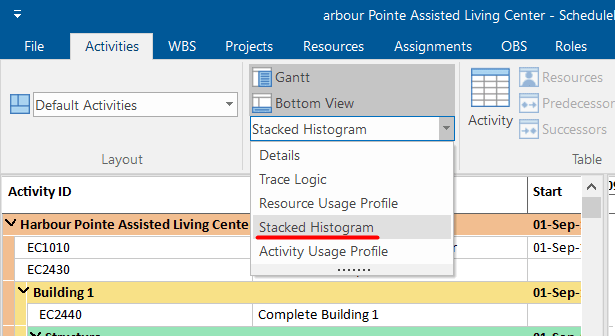
Finally, we have the S-curves in the Stacked Histogram. Users can view the S-curves for each resource separately, or the S-curves for all resources that are assigned to the project plan.
To draw these S-curves, go in the Activity ribbon tab, select the bottom view option, and in the drop-down menu click Stacked Histogram.
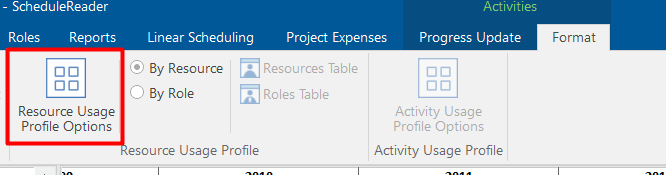
Then, click on the Activity Format ribbon, and open the Resource Usage Profile Options.
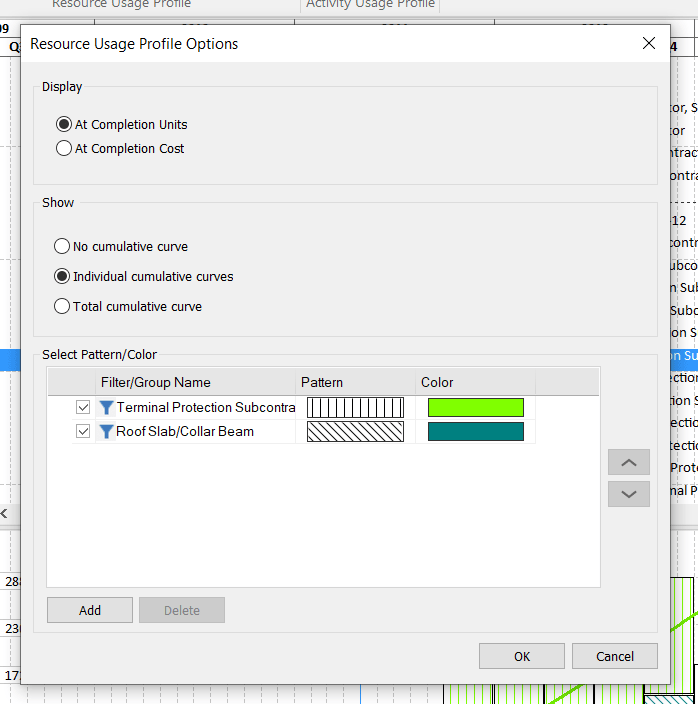
This dialog will give you many possibilities. You may choose between two parameters At Completion Units or At Completion Cost. Also, you have options to choose how you want to see the bars: with Individual cumulative curves, with No cumulative curve or to see the Total cumulative curve. The curves presented in the Bottom View are the S-curves. It is important to mention that you are able to create your own filters, to choose patterns and colors. You have the ability to customize the look of the bars. For this example, we created two filters:
The presentation of the S-curves in Stacked Histogram are shown like this:
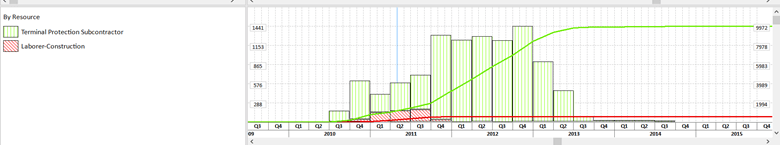
This view shows us the combination of bars and S-curves for two different resources. But, we also have the possibility to see the Total cumulative Curve, by selecting the check-box in the Resource Usage Profile Options dialog. For these filters, the Total Cumulative Curve is shown like this:
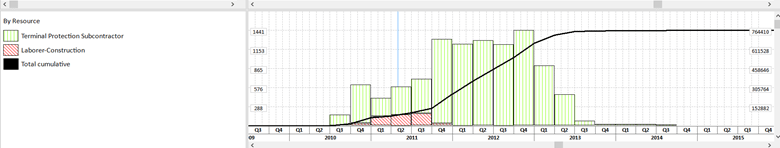
One of the benefits of using ScheduleReader is that the software provides the possibility to print out not only the entire plan but also just the Bottom View. In this way, you will get a printed document from the S-curves.
To print out the Bottom View, click File and select Print.
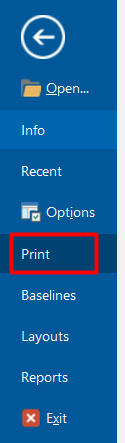
After clicking Print, numerous printing options along with Print Preview will appear. By default, the entire project shows up in the Print Preview. Under Settings, you may specify which pages you want to print out. For a better view and copy, we selected the A4 format and a Landscape Orientation.
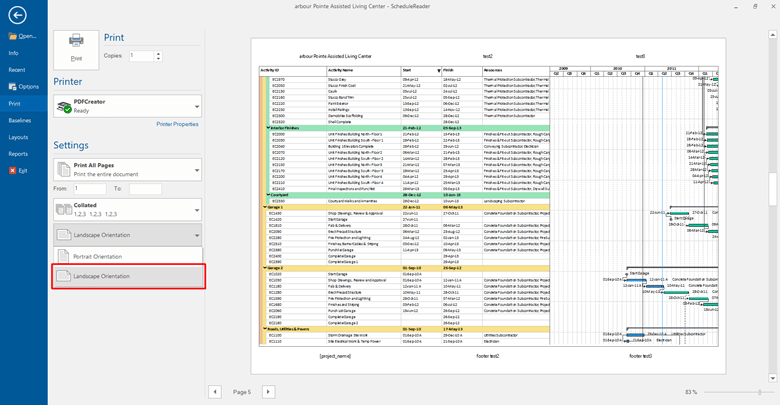
To print out just the Bottom View, select Page Setup.
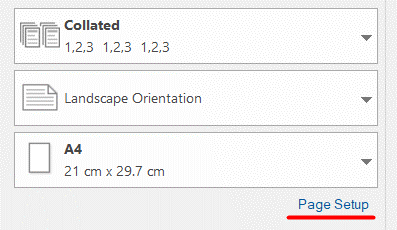
In this dialog, you can customize the time period, margins, scaling, page header, and footer.
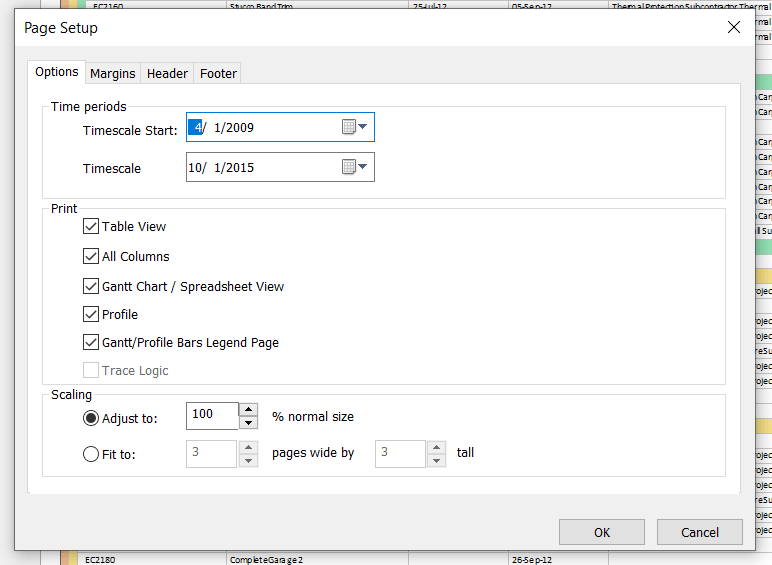
To print out only the Bottom View uncheck the boxes for Table View, All Columns, Gantt Chart/Spreadsheet View, and Gantt/Profile Bars Legend Page. Leave only Profile.
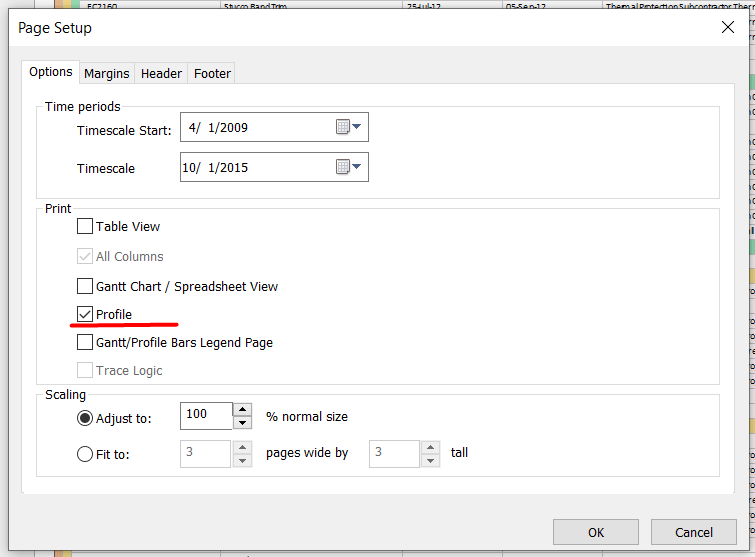
After clicking OK, in the Print Preview section, you will see only the Bottom View. In our case, S-curves in Stacked Histogram are ready to be printed out.
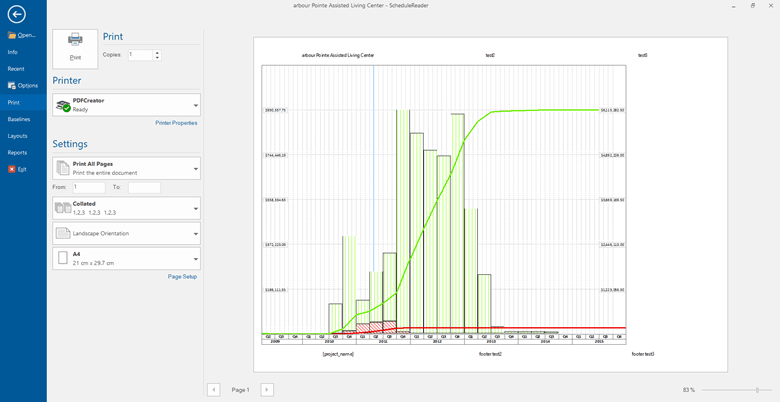
It is important to point out that in this way you get a better view of separate details of the project schedule, plus you save on paper.
Final Thoughts
S Curve is an important and widely used management tool across project management and project control.
It helps the project team and project controls professionals monitor the various forms of performance outputs, identify any cracks and take preventive and corrective control measures to ensure on schedule and under budget completion of projects.
The S Curves of completed projects also become part of the lesson learned document for organizations as guidance for future similar projects.
The S-curve representation and the ability to view variations are much more manageable in ScheduleReader than in Primavera P6. The primary benefit of using this program would be to create a fast-paced environment with smooth communication and coordination between stakeholders. The intuitive and dynamic overview of the project detail and the customization also make you feel comfortable and reduces miscommunications.
Privacy Overview
- Google Analytics
- LinkedIn tag
- Facebook pixel
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
Guide to using S-curves in project management

The S-curve is a widely used project management tool across multiple industries. Most commonly, is used to track and analyze a project’s progress over time.

Understanding the S-curve helps product and project managers identify potential issues quickly and make decisions to get the team back on track before it’s too late. It also aids in predicting the adjusted completion date based on progress made over time.
What are S-curves?
An S-curve is a graph that represents the progress of a project over time. As the name suggests, it forms a loose S shape:
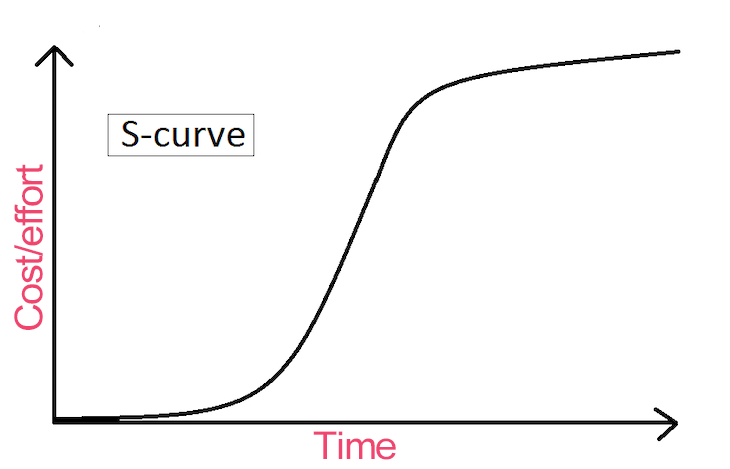
When an S-curve is used in product and project management to track progress, man-hours or effort/cost is plotted on the y-axis against time, which is plotted on the x-axis.
Initially, when the project starts, the team spends a significant amount of time researching the tasks at hand. This the lower part of the S to increase slowly over time. Once the team starts working intensively on the project, a rapid acceleration in progress forms the middle part of the S.
This point of maximum growth is called the ‘point of inflection’. After this stage, the project enters a mature phase, and the upper part of the S-curve begins to plateau as the team wraps up the final touches.
An S-curve has the following characteristics:
- In the initial stages, the curve starts slowly due to the gradual progress of the project
- As the team overcomes the learning curve, productivity increases, leading to a steep increase in output
- Toward the end of the project, progress slows as the team completes the final tasks and adds finishing touches
- At the peak of the curve, the project is fully completed
How are S-curves used in project management?
The S-curve displays the cumulative progress of a project over time. Comparing this graph with the projected timeline helps product and project managers determine whether the project is running behind or ahead of schedule.
S-curves can also assist project managers in identifying potential risks and obstacles, which helps them get the project back on track by making the right decisions at the right time.
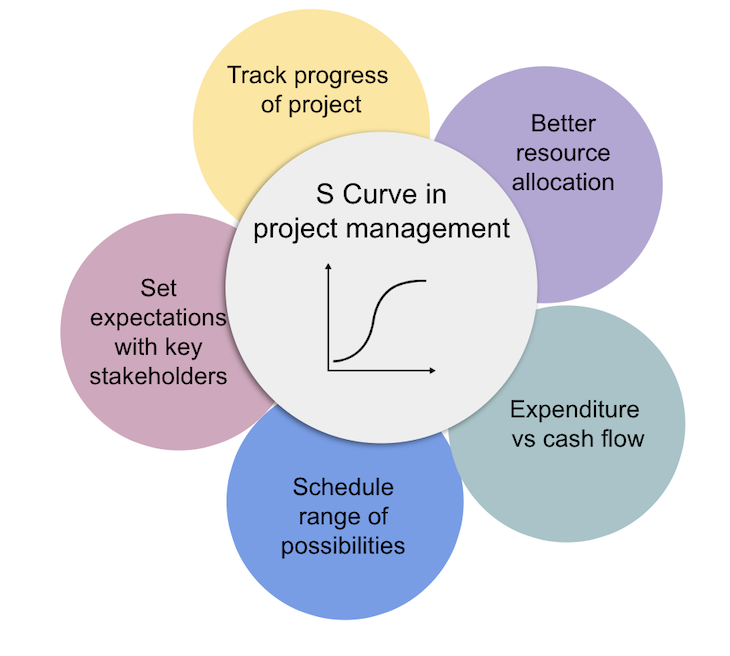
The S-curve is for activities including but not limited to:
Tracking project progress
Setting expectations with stakeholders, allocating resources, comparing expenditure vs. cash flow, scheduling a range of possibilities.
To track the progress of a project, plot the projected progress against available resources and time, which creates a baseline curve.
Once the project starts, plot the actual resources consumed over time. Comparing the two graphs can help you determine whether you are on track, lagging, or ahead of schedule.
If the project is falling behind, you’ll need to make crucial decisions at this point, such as increasing the size of your team or fast-tracking activities to get the project back on track.
Being aware of the project’s progress compared to the baseline, along with potential issues or challenges, can help you prepare before communicating the project’s status to stakeholders. Presenting the S-curve to stakeholders provides a platform to explain the current status of the project and present it visually.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
The S-curve can help you identify the optimal time to allocate the required resources to different stages of the project.
By analyzing the S-curve, you can ensure that the necessary resources are available at each phase, reducing the risk of timeline delays. As a result, resources are optimized and not wasted or lacking.
Typically, project budgets are released in phases. In addition to indicating the cost needed for the project over time, the budget release can also be displayed over time.
This provides a visual representation of the comparison between the cost required at each phase and the funding available at that phase. In this way, project managers can gain a complete view of any potential risks of running low on cash flow throughout the project’s timeline.
A banana curve can be created by generating two overlapping S-curves. The first S-curve is created using the early start date and early finish date, while the second S-curve is created by inputting the late start and finish dates. This generates a graph that looks like a banana by joining these two S-curves.
Project managers often use this ‘banana curve’ to estimate the earliest and latest start times for tasks within the schedule, without impacting the overall project timeline. This displays the flexibility that can be allowed in the schedule during project execution. If the actual progress of the project aligns more with the lower S-curve, which includes late start and finish dates, it is time to look into steps that can be taken to correct the project’s progress path.
3 types of S-curves
Depending on what you are trying to monitor, there are different types of S-curves you can use. The types of S-curves most commonly used in product and project management are:
Cost S-curve
Effort s-curve, baseline s-curve.
The cost S-curve is a graphical representation of the planned and actual costs of a project over time.
More great articles from LogRocket:
- How to implement issue management to improve your product
- 8 ways to reduce cycle time and build a better product
- What is a PERT chart and how to make one
- Discover how to use behavioral analytics to create a great product experience
- Explore six tried and true product management frameworks you should know
- Advisory boards aren’t just for executives. Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
A cost S-curve is useful for projects involving labor, non-labor, and material costs, capturing the cumulative cost of the project against the planned cost. It is helpful in determining the project’s total cost and cash flow.
An effort S-curve displays the cumulative effort required against the planned effort for a project. Also known as the man-hours-vs.-time S-curve, the effort S-curve is ideal for labor-intensive projects.
The curve shows the actual effort below the planned effort if the actual effort is less. If the actual effort is more than the planned effort, then the actual effort line is above the planned effort line.
Every project has a planned timetable defining the required resource allocation and schedule of activities as the project progresses with time.
This optimal progress of the project, aligned with the planned activities needed to finish the project within a predetermined timeline, is called a baseline S-curve. It is created based on projections before a project begins.
How to create an S-curve graph
Now that we understand the importance of S-curves in project management and how they can help you make the right decisions at the right time, let’s delve into the steps to create an S-curve:
- Determine the scope and timeline
- Identify the critical path and duration
- Calculate the percentage of completion
- Plot the S-curve
1. Determine the scope and timeline
The first step is to identify the project’s scope — i.e., what needs to be covered as part of the project. Clearly outline any items as descoped or out of scope to avoid confusion. This will help set the right expectations with your team and key stakeholders and avoid ambiguity regarding the project’s scope.
Once the scope is identified, list all the activities covered under the scope and the duration required for each activity.
2. Identify the critical path and duration
Determine the sequence of activities that must be completed on time to ensure the project is finished within the required timeline. This sequence of activities, which is used to lay down the optimal or baseline S-curve, is the critical path.
To determine the baseline S-curve, you will also need to determine the duration of each activity. This information will help capture the project’s progress over time.
3. Calculate the percentage of completion
The next step is to calculate the percentage of completion for each activity — i.e., indicate how much a project has progressed since it started after completing a set of activities.
This information will help capture the project’s progress over time in terms of percentage until it is completed or reaches 100 percent.
4. Plot the S-curve
By this step, you should have all the information required to plot the S-curve using the percentage of completion and the duration of the project.
You can use the baseline S-curve, plotting the planned activities’ effort and duration before the project begins. Then compare the cumulative graph of the actual activities against the baseline S-curve to gauge the project’s progress.
Tools for creating an S-curve
There are several tools, both free and paid, you can use to create an S-curve graph. Some of the most common types of solutions include:
Microsoft Excel and other spreadsheet tools
Project management software.
Microsoft Excel has various built-in functions that can be used to calculate the cumulative man-hours or cost and the duration of a project to plot the S-curve.
Functions like SUM, COUNT, and AVERAGE can be used for basic calculations, while more advanced functions like VLOOKUP and INDEX can help with retrieving and organizing data from different sources. Excel also provides charting tools that can be used to visualize the S-curve.
These operations can also be carried out using alternative spreadsheet tools such as Google Sheets , which offers similar functions to Excel. Google Sheets has the added benefit of being cloud-based, which allows for real-time collaboration among team members.
Other alternatives, such as LibreOffice Calc and Apache OpenOffice Calc , provide similar functionalities that can be used to create S-curves as well.
Many project management software offerings have built-in features to calculate the percentage of effort completion or cost incurred and plot an S-curve accordingly. Some popular paid tools include:
- Microsoft Project
- Primavera P6
These tools often provide advanced features for tracking progress, managing resources, and generating reports.
There are also some free tools that provide S-curve functionality, such as GanttProject and ProjectLibre . These tools may have fewer features compared to their paid counterparts, but they can still be helpful for small projects or teams with limited budgets. At the very least, you can create Gantt charts and track project progress using S-curves, making these open-source tools suitable for basic project management tasks and even some advanced use cases.
Disadvantages and challenges
Before you start using S-curves to make decisions you should understand its limitations.
The S-curve indicates any project timeline deviation from the planned timeline, but does not provide insight into the causes of such deviations. Identifying the causes of any deviations might require more effort and time.
The project’s scope may change over time, so you’ll need to adjust the S-curve accordingly.
The S-curve is beneficial only if the data is entered and analyzed frequently. Additionally, the data entered to calculate the plot must be accurate to represent the project’s actual progress. Any data manipulation will not present an accurate picture.
As a result, using a S-curve graph might not be the most suitable technique for complex projects or projects with a high degree of uncertainty in terms of scope, timeline, or resources.
Key takeaways
A S-curve graph can be a valuable tool to help you track, analyze, and predict project progress. Understanding the various types of S-curves, how to create them, and the tools available can significantly enhance your ability to make informed decisions and improve product outcomes.
While there are some disadvantages and limitations to using S-curves, being aware of them can help ensure that the technique is used effectively and in appropriate situations.
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #project management

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
Creating a consumer behavior playbook for your product
Consumer behavior is complex, but you can break down key elements or levers to give you insights.

Leader Spotlight: Encouraging design thinking workshops, with Tamara Pluviose
Tamara Pluviose discusses her approach to design thinking workshops that promote problem-solving, brainstorming, and customer-centricity.

Crafting a successful product launch strategy: Key tips and steps
A launch strategy builds anticipation, maximizes initial sales, and establishes a strong market presence early on.
Leader Spotlight: Having a bias for action, with Anish Chadda
Anish Chadda discusses the importance of having a “bias for action” — iterating quickly instead of focusing on creating a perfect prototype.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Project Management
See It in Action: How to Create and Use S-Curves in Project Management

Max 7 min read

Click the button to start reading
Wanna enjoy the ride to project success?
Discover the tool that helps you spot the twists, turns, and potential bottlenecks every step of the way.
Join us as we explore what an S-curve is and how to use it in project management . Along the way, you’ll find quick examples and advanced tips to get started.
Let’s dive in!
What Is an S-Curve in Project Management?
An S-curve is a term for a graph that shows how a project is progressing over time. It helps you visualize this journey, showing you where you started, how far you’ve come, and how close you are to the finish line.
S-curves can be used in any type of project, no matter how big or small. They’re flexible and adaptable to different industries and sectors. Obviously, this makes them useful for tracking progress and continuously improving projects .
It’s called an S-curve because it looks like the letter “S” when you plot your project’s data points on a graph.
Take this sample graph for illustration:
The S-curve is also referred to as the “sigmoid curve”. The term “sigmoid” comes from the Greek word “sigma,” which means “S-shaped.” By the way, the sigmoid curve is a mathematical function. It shares a similar shape to the S-curve, with gradual growth, acceleration, and eventual leveling off.
What Does an S-Curve Graph Show?
An S-curve in project management shows what was planned and helps to compare it with what actually happened. Here’s what the S-curve depicts:
Time: On the graph, you have a horizontal line that represents time. It could be weeks, months, or whatever time units you’re using for your project.
Progress: Then, you have a vertical line that represents progress. It could be things like the work completed, the money spent, or any other measure of progress you want to track.
Planned Curve: You start by drawing a line that shows how you planned the project to progress over time. This line represents your initial estimates and expectations.
Actual Curve: As your project unfolds, you collect real data and plot it on the graph. This shows how your project is actually progressing compared to the plan.
Below you see the area of the S-curve of budgeted costs. It indicates the portion of the S-curve that represents the total planned costs for the project.
S-Curve in Project Management: How It Works
Now, let’s see a quick example of how an s-curve works:
Getting Started: Imagine you’re starting a project. At the beginning, the S-curve starts with a gentle slope. This means progress is a bit slower because you’re setting things up and getting organized.
Picking Up Speed: As your project gains momentum, the S-curve starts to go up more steeply. This is the exciting part where things really start moving! You’re completing tasks, hitting milestones, and making progress.
Reaching the Peak: The S-curve reaches its highest point when progress is at its maximum. This is when you’re firing on all cylinders and reaching milestones right on schedule. Your actual progress should be closely aligned with your plan during this peak phase.
Slowing Down: After reaching the peak, the S-curve starts to level off. Progress becomes a bit slower. It’s like taking a breather after a sprint! This could be because you’ve finished big tasks or run into unexpected challenges. During this phase, your actual progress might be a bit behind your plan.
Finishing Strong: The S-curve approaches a plateau as the project nears completion. Progress slows down even more as you wrap up the final tasks. It’s like crossing the finish line with a big smile!
Common Uses of the S-Curve in Project Management
You may wonder why you should use S-curves in project management. Well, take these statistics.
Typically, big IT projects go over budget by about 45% and take longer than expected. What’s more, they end up delivering only 56% of the value originally predicted.
But the good news is – you can steer clear of the common setbacks that lead to poor project outcomes. In fact, an S-curve tells you a lot about your project. Next, let’s discover how the S-curve is used in project management.
Spotting Deviations
You can compare the planned curve with the actual curve to find any differences or changes in project progress. If your actual progress consistently falls below the planned curve, it’s a sign that something might be off-track. It could be delays or issues you need to address.
Communicating with Stakeholders
S-curves are great for sharing project progress with stakeholders. So, are things going well? Are there any challenges to overcome? These graphs provide a clear visual representation that everyone can understand. You can share them in reports, presentations, or meetings to keep stakeholders in the loop.
Dealing with Risks
If the actual curve deviates from the planned curve, be attentive. It may indicate underlying issues or risks that need to be addressed. By keeping an eye on the S-curve in project management, you can spot warning signs early and make decisions to mitigate risks.
Planning for the Future
The S-curve helps with forecasting and planning. Here’s how. You can extend the curve into the future and estimate the project’s completion and resource needs. This will help you make decisions about project timelines, resources, and stakeholder expectations.

Creating an S-Curve: What Do You Need to Make an S-Curve?
Making an S-curve is as easy as plotting points on a graph. You take the planned progress and the actual progress of the project and plot them against time.
Here’re the prerequisites you’ll need in place.
Project Schedule: You need a clear plan that shows what needs to be done and when.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Next, you need to break down the project into smaller tasks with specific start and end dates. This helps track progress and generate accurate S-curves.
Baseline Plan: Set a starting point for your project by creating a baseline plan that represents the original schedule. It helps compare actual progress to the planned curve.
Data Collection: Collect information on completed tasks and the percentage of work done for ongoing tasks. This data is crucial for creating meaningful S-curves.
Regular Updates: Provide regular updates on completed tasks and the percentage of work done. This ensures the S-curves reflect the actual progress.

Mastering S-Curves in Project Management: Advanced Tips and Expert Advice.
Keep your baseline updated.
As your project progresses, make sure to review and update your baseline regularly. For example, adjust the planned curve to reflect any changes in the project’s scope, schedule, or resource allocation. If you keep your baseline up to date, your S-curve will remain a reliable reference point for tracking performance.
Combine S-Curves with Earned Value Management
Consider using Earned Value Management (EVM) alongside S-curves for a more comprehensive analysis. EVM combines cost, schedule, and work performance data to give you a well-rounded view of project progress. By integrating EVM metrics with S-curves, you can gain deeper insights into a number of metrics. For example, you’ll be able to estimate completion dates and monitor project performance .
Use S-Curves as an Early Warning System
S-curves can act as an early warning system for project risks or performance issues. By comparing the actual curve with the planned curve, you can spot patterns that indicate potential problems. Use this information to take timely corrective actions. Plus, adjust project plans and mitigate risks before they become significant issues.
Integrate S-Curves with Other Tools
Combine S-curves with other project management tools and techniques to enhance their effectiveness. For example, integrate S-curves with different scheduling methods or Monte Carlo simulations . This will allow you to manage project risks , track critical activities, and schedule for uncertainties.
Use Advanced Reporting and Visualization
Need to share information about project progress and information? Explore visualization techniques to present S-curves in a more meaningful way. Use dashboards, interactive charts, and graphical representations to get your message through faster.
Compare Different Scenarios
Make several S-curves for different project situations. Try alternative schedules or resource plans. Eventually, see how choices affect project performance and make smarter decisions.
Use Tools to Create Graphs for Your Project
Microsoft Excel is a widely available and easy-to-use tool for creating S-curves. You can create a simple graph by plotting your planned and actual data points against time. If you prefer a cloud-based solution, Google Sheets is another free and user-friendly tool.
Besides, many project management software tools include built-in features for creating various graphs. All-in-one platforms, such as Teamly , can help you generate templates and graphs based on your project data. Alternatively, you can check for integrations with third-party apps that allow you to create S-curves on the platform you’re using now.
To sum up, with S-curves, you can stay one step ahead, spot deviations, and make smart decisions. Say goodbye to project headaches and hello to streamlined success. Use S-curves in project management and let them guide you towards project triumph with ease!
#ezw_tco-2 .ez-toc-title{ font-size: 120%; ; ; } #ezw_tco-2 .ez-toc-widget-container ul.ez-toc-list li.active{ background-color: #ededed; } Table of Contents
Manage your remote team with teamly. get your 100% free account today..

PC and Mac compatible

Teamly is everywhere you need it to be. Desktop download or web browser or IOS/Android app. Take your pick.
Get Teamly for FREE by clicking below.
No credit card required. completely free.
Teamly puts everything in one place, so you can start and finish projects quickly and efficiently.
Keep reading.

The 11 Essential Books on Communication Every Project Manager Should Read
The 11 Essential Books on Communication Every Project Manager Should ReadImagine this: you’re in the middle of a project and you’ve just realized that you and your team are not on the same page. Miscommunication has led to lost time, and wasted effort, and now you’re scrambling to get everyone back on track. If only …
Continue reading “The 11 Essential Books on Communication Every Project Manager Should Read”
Max 9 min read

8 Powerful Tips to Help You With Organizing Your Business
8 Powerful Tips to Help You With Organizing Your BusinessIs your business set up for maximum productivity and free of anything that could cause you stress or anxiety? If you can honestly answer yes, then this article isn’t for you. However, if you’re answer is no, that’s okay. There are plenty of things you can …
Continue reading “8 Powerful Tips to Help You With Organizing Your Business”
Max 5 min read


The Best Practices, Tools & Softwares to Simplify Change in Your Organization
The Best Practices, Tools & Softwares to Simplify Change in Your OrganizationIf you’ve spent any time as a project manager, you’ve experienced plenty of resistance to change. Maybe the requirements change midway through a project, and then key players throw up their hands and quit in fits of frustration. Or a project’s timeline gets cut …
Continue reading “The Best Practices, Tools & Softwares to Simplify Change in Your Organization”
Max 14 min read
Project Management Software Comparisons
Asana vs Wrike

Basecamp vs Slack

Smartsheet vs Airtable

Trello vs ClickUp

Monday.com vs Jira Work Management
Trello vs asana.
Get Teamly for FREE Enter your email and create your account today!
You must enter a valid email address
You must enter a valid email address!

S-Curve in Project Management: Examples with Definitions
Fahad Usmani, PMP
October 5, 2022

Today we will discuss the s-curve in project management and provide you with its definitions and examples.
S-curve is a graph that shows the relevant cumulative data for your project. The data can be costs, person-hours, etc.
S-curve is a good communication tool and helps project managers communicate project progress to project stakeholders .
Let’s dive in deeper.
Project management has become complex nowadays, and you need to track many parameters to monitor status and progress.
You will require some tools to learn your processes and identify issues.
One such project management tool is the s-curve graph which uncovers crucial data about your project.
An s-curve is a mathematical graph that represents the aggregate data for a project. This information can be the project cost or the number of person-hours against time.
The curve is termed an s-curve because of the graph’s s-shape.
Note that the graph’s shape depends on the type of project, and it can be different from the usual s-curve.
Typically, the s-curve tracks work progress, forecasts cash flow, and assesses performance. The s-curve’s ability to display real-time cumulative data and compare it with the planned progress is the key reason for its popularity.
What is the “S” in S-Curve?
The ‘s’ shape isn’t imposed; it is simply the shape made by the graph from the project initiation to the end.
As time progresses, growth begins to accelerate. This growth is represented by the middle section of the ‘s’ in the graph, which shows this rapid rise.
The inflection point is the point where the change occurs. These are crucial areas of the curve since they show a change in growth.
The growth hits a plateau after it has passed through the inflection point, forming the upper half of the s-curve. In this stage, the project is matured.
This maturity is attributable to the fact that most project work is now complete and in the process of being wound down.
Prerequisites for S-Curves
You need monitoring parameters and time intervals to draw an s-curve.
Some monitoring parameters are cost, number of deliverables , labor units (person-hours), etc.
The time interval can be indicated in weeks, days, or months; it is the frequency with which certain metrics must be examined. The vertical axis is used to plot monitoring parameters, whereas the horizontal axis represents time.
Types of S-Curves
The s-curve can be of many types, such as:
- Baseline S-curve
- Target S-curve
- Costs Vs Time S-curve
- Value and Percentage S-curve
- Man-Hours versus Time S-curve
- Actual S-curve
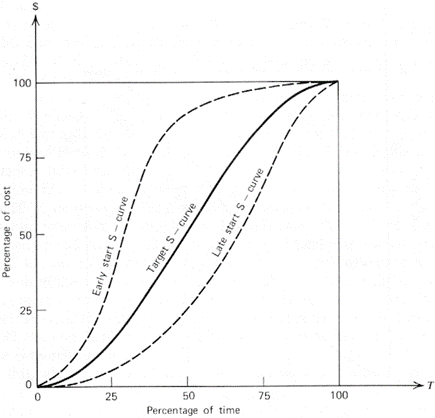
Baseline S-Curve
Before the project starts, a schedule is created to outline the anticipated resource allocation and task sequencing. The schedule is called the baseline schedule; the s-curve drawn from this schedule is known as a baseline s-curve.
This s-curve shows the project’s anticipated progress. The baseline schedule can be revised if project parameters, such as duration, scope, etc., change.

Target S-Curve
Modifications to the baseline schedule frequently occur after the project is started. This modified schedule is known as the production schedule. In the beginning, the production schedule is the same as the baseline schedule, but it changes as the project progresses.
The production schedule represents the project’s progress to date and all adjustments.
A target s-curve can be produced from the production schedule, and it represents the project’s ideal progress as though the actual progress is the same as planned progress. In a perfect world where a project is on budget and on time, the target s-curve would intersect the baseline s-curve at the project’s conclusion.
It would conclude below and to the left of the baseline s-curve if the project is ahead of schedule and under budget. In reality, the target s-curve frequently concludes above and to the right of the baseline s-curve since projects are often delayed and over budget.

Costs Vs Time S-Curve
The costs vs time s-curve is useful for projects that include labor and non-labor costs such as subcontracting, hiring, and supplying materials. It shows the total cost incurred throughout the project life cycle and can be used to calculate the project cost and cash flow.

Value and Percentage S-Curves
S-curves can be plotted as absolute quantities such as values vs time or costs or person-hours vs time. Value s-curves can be used to calculate the number of man-hours or amount spent so far, as well as the number of person-hours or costs needed to finish the project.
Percentage s-curves can be used to compare the project’s planned vs actual completion in a percentage, the project’s percentage growth, contraction, etc.
Man-Hours Vs Time S-Curve
The man-hours vs time s-curve is suitable for labor-intensive projects and shows the number of man-hours spent on the project over time. The man-hours is the sum of the manpower needed and the number of hours to execute the task.

Actual S-Curve
Throughout the project lifecycle, the production schedule is revised regularly. These revisions include the data from the completed work, and you can build an actual s-curve with this data.
This s-curve shows the actual progress, but it can be used to compare progress with the target baseline s-curve to compare the performance.
The actual s-curve ends at the project’s cut-off date, which is the last day that the production schedule is updated. The actual s-curve meets the target s-curve at the end of the project.

Understanding the Lines in an S-Curve
Front-loaded s-curve.
A front-loaded s-curve begins sharply and gradually flattens off. It has a speedy start. Here, more time and resources are spent at the initial stage of the project.
This might happen with projects that have a lot of repetition and require minimal planning and preparation time. Front-loaded curves are used in projects that have been rushed from the start.

Back-Loaded S-Curve
Back-loaded s-curves begin with a lesser slope and gradually increase in steepness as the project progresses, with most resources expected to be utilized later in the project.
A back-loaded s-curve suggests extensive planning and design at the start of the project and a shortened development time.

Uses of the S-Curve in Project Management
Performance and progress evaluation.
S-curves help assess the project’s progress and performance using earned value management (EVM) .
To determine the project’s current status, progress, and future projections, you need to identify the following parameters: actual cost, earned value, and planned value .
Each of these elements must be compared with the designed s-curve. These comparisons help you see whether a project is over/under budget or ahead of/behind schedule.
The difference between the target s-curve and the actual s-curve shows the project’s progress over time. For most projects, the actual s-curve will be lower than the target s-curve because of many factors, such as update delays in the production schedule. The curves only intersect near the end of the project.

Growth Determination
When the baseline and target s-curves are compared, you can see if the project’s scope has changed.
A scope change may require extra resources with a possibility of contract variation. If the project has fixed resources, you may require a project extension.

Determining Slippage
The duration that a task is pushed back from its schedule is referred to as slippage. It is the difference between a task’s scheduled start or its finish date and the baseline start and finish dates.
Slippage occurs when a baseline schedule is established and the actual dates are ahead of the baseline schedule.
You can see the slippage instantly when comparing the baseline and target s-curves, as the target s-curve terminates to the right of the baseline s-curve.
You may have to allocate extra resources to avoid slippage. If avoiding slippage is not possible, you will raise a change request to update the schedule baseline.

Forecasting Cash Flows
Cash flow refers to the flow of cash and its timing.
A cash flow curve allows you to assess the requirement for money and the precise time when payments are due.
In project management, you have to track many parameters, and the s-curve is very helpful in such a scenario. It is a fantastic tool to track costs in connection to man-hours and other aspects.
If you are into project management, you will find s-curves useful.
Please share your experience with using s-curves in your projects.
Note: this topic is crucial from a PMP exam point of view.

I am Mohammad Fahad Usmani, B.E. PMP, PMI-RMP. I have been blogging on project management topics since 2011. To date, thousands of professionals have passed the PMP exam using my resources.
PMP Question Bank
This is the most popular Question Bank for the PMP Exam. To date, it has helped over 10,000 PMP aspirants prepare for the exam.
PMP Training Program
This is a PMI-approved 35 contact hours training program and it is based on the latest exam content outline applicable in 2024.
Similar Posts

Verification Vs Validation
Validation and verification are two important terms in project management; they seem very similar, and it’s easy to get them confused.
These are important concepts and any PMP aspirants needs to understand them well. I will explain these terms fully, so you will have a better understanding of them when you finish this blog post.
This topic is not very important from the PMP exam point of view. However, as a project manager, you must know the difference between these terms.

What is an Action Plan? (Template and Example Included)
An action plan makes easier to achieve your goal using a planned approach. It does not matter whether you manage a project or a department; an action plan will provide you with a path that you can follow to success. Action plans also help you achieve goals in your personal life. It helps you or…

5 Conflict Resolution Techniques in Project Management
In project management, the work environment is dynamic and stressful, unlike a functional environment where it is very stable. Conflict is a common occurrence in this field.
Whenever two or more stakeholders have different opinions or interests, conflict can occur. According to the American Management Association, managers spend 24% of their time managing conflicts.
Conflicts happen due to many reasons, such as schedule priorities, scarce resources, technical reasons, and personal issues.
Don’t panic, it’s usually not as bad as you think. If appropriately managed, conflict resolution can build trust and sometimes bring new ideas and opportunities. Proper conflict resolution can make the difference between a positive and negative outcome, and an incorrect resolution can negatively affect a project.

Quality Assurance Vs Quality Control (QA Vs QC)
Quality assurance and quality control are most important processes for any project, as the project’s success depends on these processes.
Every project has a quality control section to take care of these functions. The quality assurance function usually stays with the organization and the quality control section has to communicate with the organization to coordinate between these two processes.
Since these processes are connected and work in coordination, many professionals, especially those working in small and medium sized organizations, do not understand their differences.
This reminds me of one interaction when I was in my ISO 9001 training course a few years back. I met with many professionals involved in quality management. These people were all from different backgrounds and were working in various fields.

Work Performance Information (WPI) vs Work Performance Measurements (WPM)
This blog post was based on the 4th edition of the PMBOK Guide, and from the 5th edition of the PMBOK Guide, the PMI has changed the definitions of terms used in this blog post; therefore, this post is now obsolete.
I have re-written this blog post based on the current version of the PMBOK Guide (6th edition). Please visit: Work Performance Data and Work Performance Information. I am leaving this post in case someone wants to review the old post under the PMBOK Guide (4th edition).
Management is always interested in the status and progress of the project. They want to know:

What is the Best Power of the Project Manager?
A project’s environment is much like a startup company’s environment. There is continuous pressure to perform with a limited budget and a fixed schedule. More importantly, you will always have new team members.
In this situation, you will have to manage your team and motivate them to perform their best.
This is not an easy task, and you will have to use your soft and hard skills to push team members continuously.
As a project manager, you can have many powers. The sixth edition of the PMBOK Guide recognizes the following fourteen powers:
One Comment
Thank you Could you please illustrate regarding banana curve?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- [email protected]
- United States

The Philosophy Behind S-curves
- June 11, 2017
- Shohreh Ghorbani
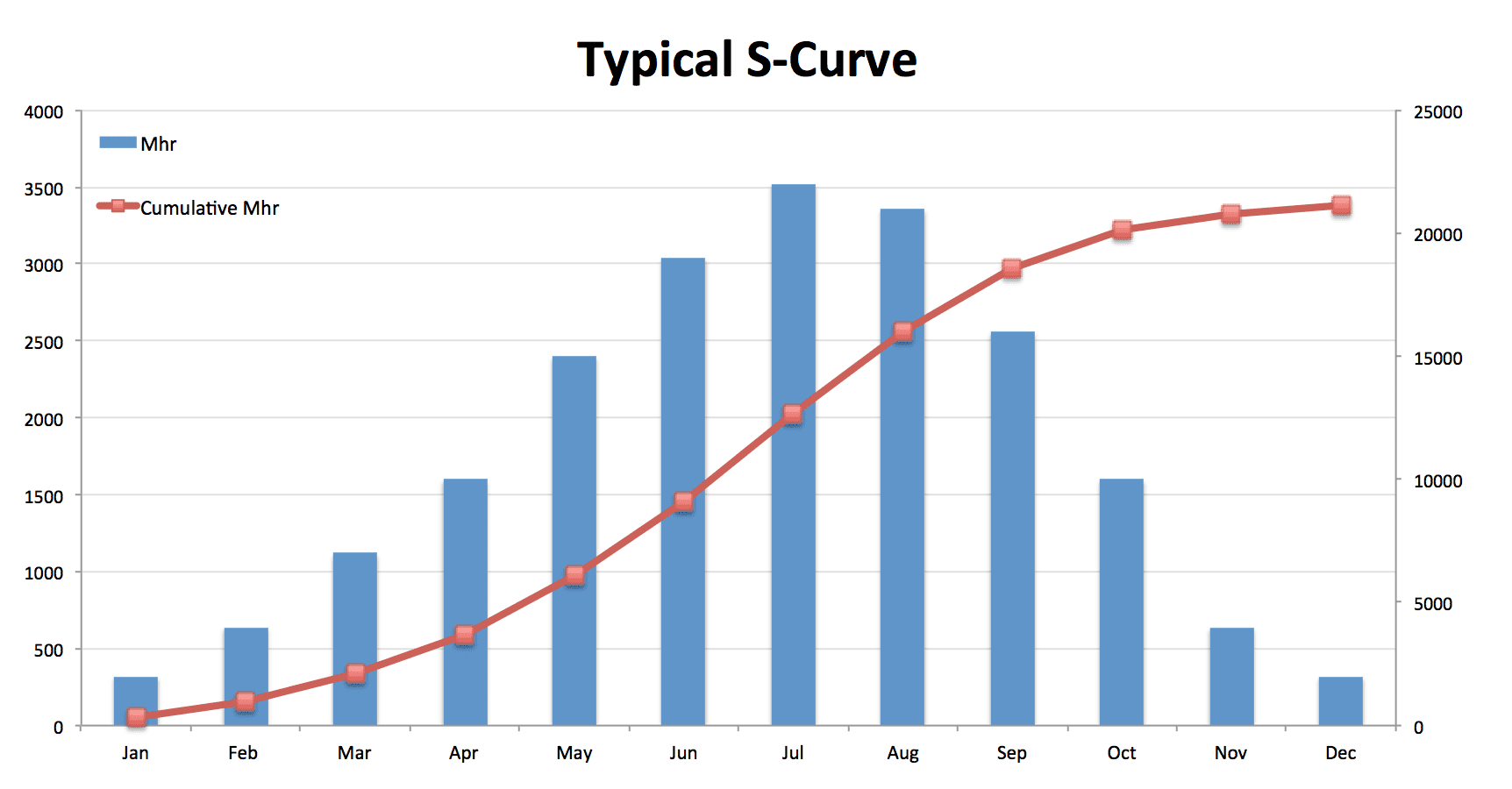
Have you ever wondered what an s-curve is in projects?
Do you know why Project Managers are interested in seeing s-curves in project reports?
Well, an s-curve is a project management graphical tool that displays cumulative data ( e.g. project’s costs, hours, progress, or quantities) against time.
The term S-Curve denotes the tendency of the cumulative curve to form a shallow ‘S’ shape; flatter at the start, steeper in the middle, and flattening off again towards the end.
Although the s-curve drives from the S-like shape of the curve, don’t be surprised if your s-curve is not in the shape of an “S”. The shape of an s-curve depends on the nature of your project.
Watch this video to learn more about the philosophy behind s-curves and get crystal clear on the concept of s-curves.
Download the free audio mp3 podcast of this episode on iTunes .
Like this episode? Please share it so others can also benefit from it.
Want more training? Subscribe to Project Control Academy to receive complimentary training videos and resources delivered to your mailbox.
Project Control Quotes to Consider: Join Project Control Academy on Instagram for tons of great quotes .
Video Transcript:
S-curve! Hum, what on earth is an s-curve?!
Is it a curve with the shape of “S”? …… What kind of curve is an s-curve anyway?
Why are Project Managers interested in seeing s-curves in reports? Tell me, what is the use of an s-curve?
These were my questions when I first got exposed to the term “s-curve” in projects. I didn’t know what an s-curve was until I started populating s-curves in almost every single project cost or schedule report that I issued. I realized how this simple graphical report is useful in briefing the stakeholders on project status and trends in a quick and intuitive manner.
In this training, I am going to open up the concept of s-curves for you, so you are crystal clear on the philosophy behind s-curves and their use.
What is an s-curve?
An s-curve is a graphical display of cumulative man-hours, cost, progress, or other quantities plotted against time.
An s-curve aims to represent the utilization of resources over the proposed time of the project.
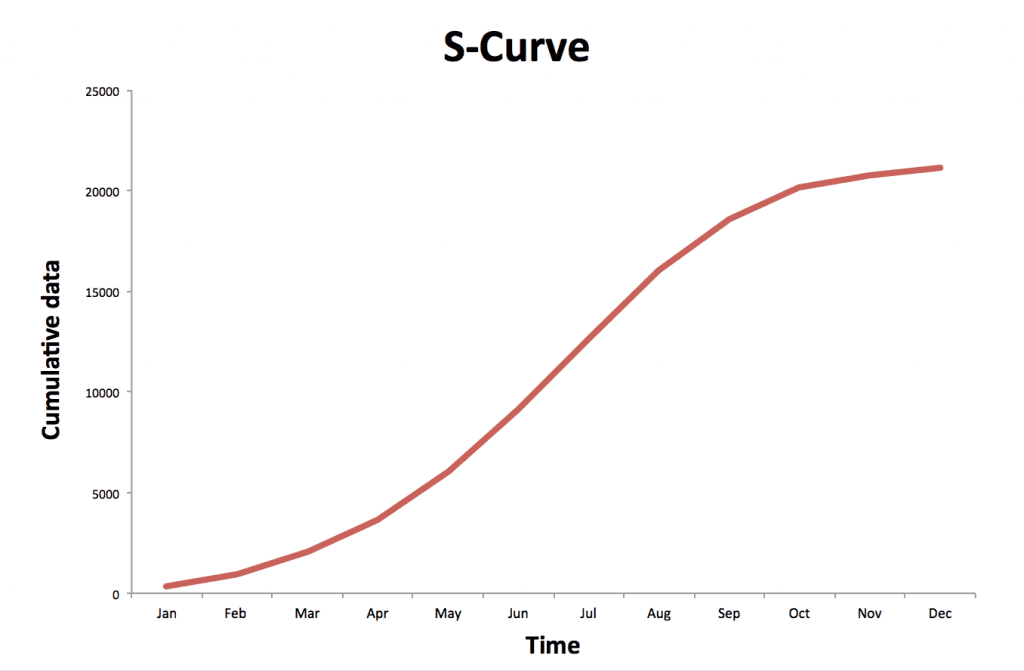
S-curves are also called, “s-plots”, “cumulative distribution charts”, “velocity diagrams”, and “Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB).”
The shape of the s-curve reveals information about the project
This shape is typical for most projects as they start slowly, ramp up during the main execution phase, and then wind down again towards the project’s completion, as productivity declines and work runs out.
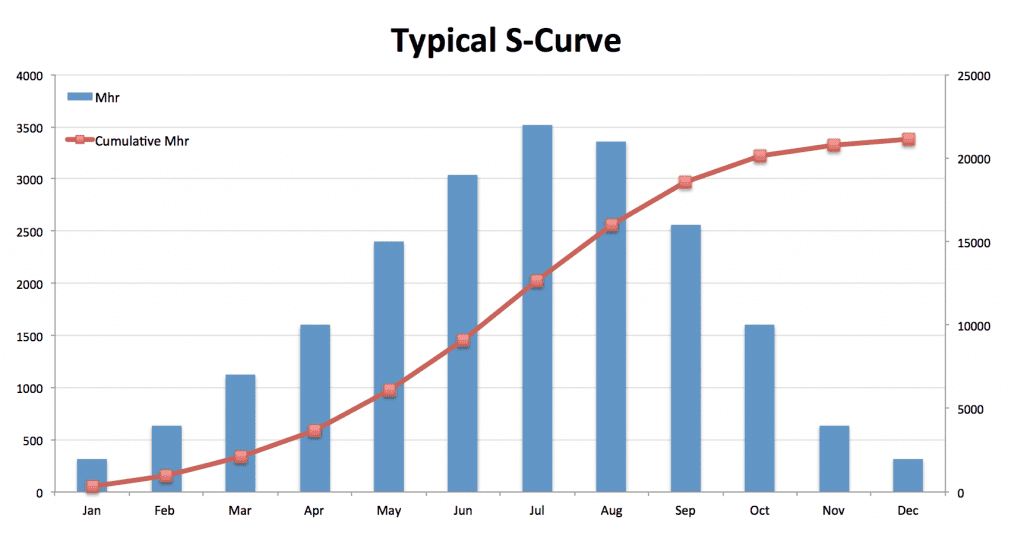
Although the s-curve drives from the S-like shape of the curve, don’t be surprised if your s-curve is not in the shape of an “S”. The shape of an s-curve depends on the nature of your project:
Front-Loaded S-Curves
You may find a front-loaded s-curve, where the curve starts up steeply and then flatten out.
The graph below illustrates how a front loaded s-curve may look like:
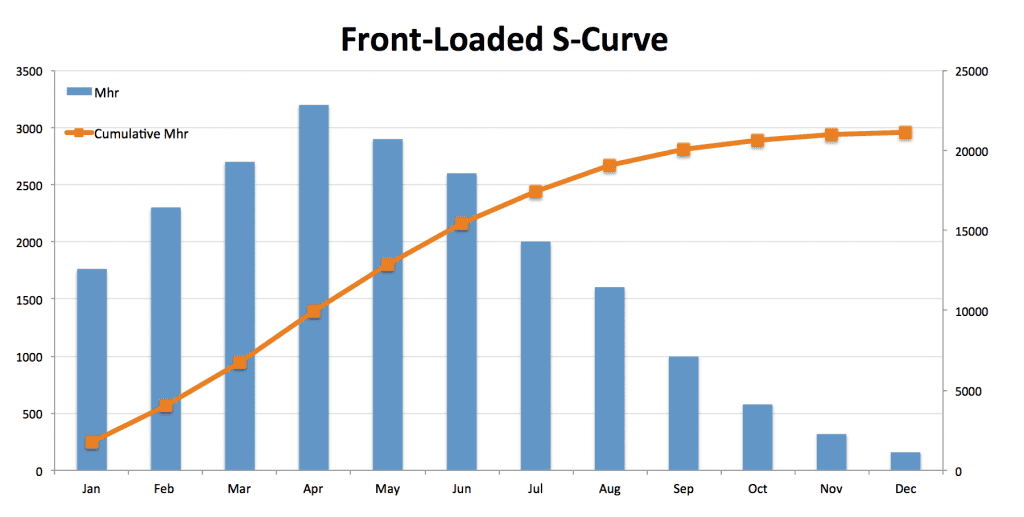
As demonstrated here, front loaded curves have a rapid start. More resources assumed to be consumed early in the project. This may happen for repetitive projects that need little planning and preparation time. Other examples of front loaded curves are for projects that have been accelerated from the beginning, or projects that need urgent repair of damage early on. Mobilization costs and deposits will also lean toward a front-loading s-curve.
The questions that need to be asked on front loaded curves are what the basis for this plan is and whether the resources are available.
Back-Loaded S-Curves
Curves that start out with a lower slope and increasingly steep towards the end of the project are typically back-loaded.
In the back-loaded curves, most resources assumed to be consumed late in the project.
A back loaded s-curve could indicate a large planning or design in the beginning and a reduced construction time.
Here is an example of a back-loaded project:
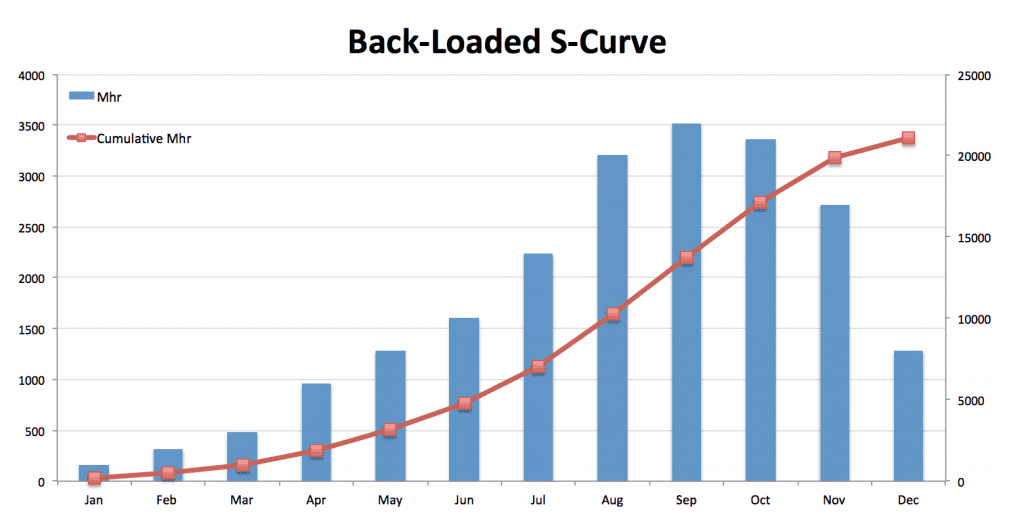
To give you a perspective of a front-loaded and back-loaded s-curve vs. a typical s-curve, I have put all three curves in one graph:
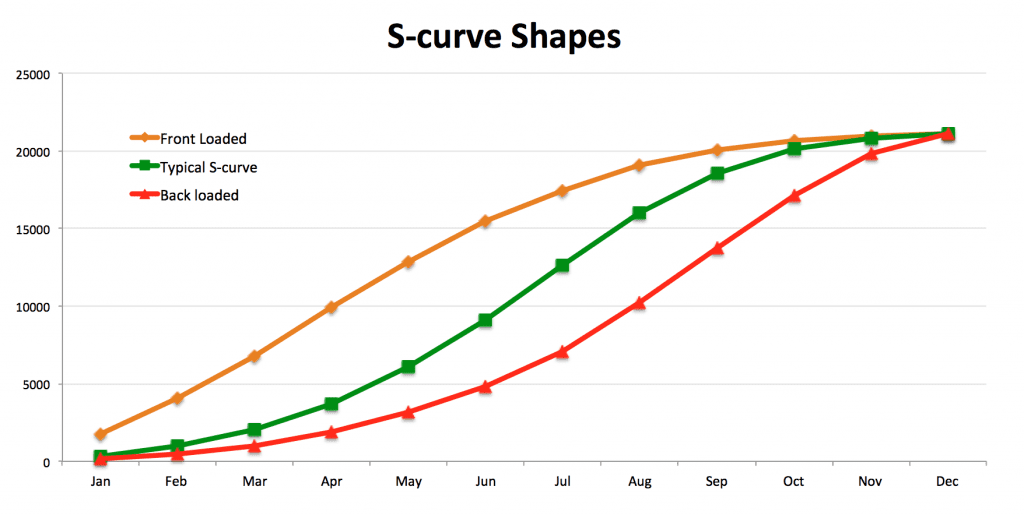
You need to be careful with either front-loaded or back-loaded curves. You should verify the basis of the project plan and ensure both the schedule and the available resources are realistic.
With the understanding of s-curves and their various shapes, now the question is “what kind of information are plotted in an s-curve?”
Well, the x-axis is “time”. The time unit should coincide with the project status update intervals (e.g. monthly, bi-weekly, or even weekly). The smaller the time unit, the “smoother” the s-curve will be and easier to use for analyzing trends.
The y-axis of an s-curve varies according to the information that you like to plot. It might be the cost ($), man-hours (Mhrs), manpower (FTE), progress (%), quantities, resources, etc.
Common Types of S-curves
The most common types of S-curves are man-hours vs. time and cost vs. time. The cost vs. time S-curves are useful for developing project’s overall “cash flow”.
Another common type of S-curves is the ones generated using units/quantities vs. time. These kinds of s-curves are useful for comparison.
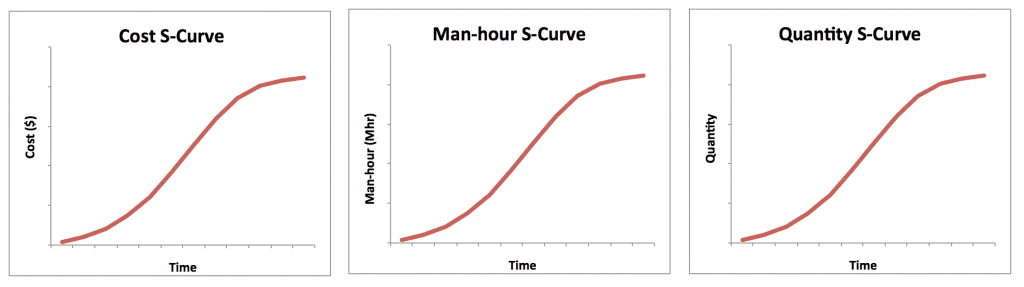
Now, are you clear on the philosophy behind S-curves, their shapes, and types?
Going back to the question I asked earlier, “Why Project Managers are interested in seeing s-curves in reports?”, do you know what the use of s-curves is? Do you know who the developer of s-curves is in a project? And how s-curves are developed?
This will be the topic of my next post in this series, “ The Common Use & Utilization of S-curves in Projects ”.
In summary,
An s-curve is a project management graphical tool that displays cumulative data ( e.g. project’s costs, hours, progress, or quantities) against time.
About the Author, Shohreh Ghorbani

Shohreh is a licensed project management professional (PMP) recognized by Project Management Institute (PMI) and holds a Master of Science in Industrial Engineering.
Connect with Shohreh via Facebook , Linkedin , Google+ , Instagram , iTunes , YouTube

Recent Blog Posts


< Go back to Login
Forgot Password
Please enter your registered email ID. You will receive an email message with instructions on how to reset your password.

S Curve PowerPoint Template

Product Description:
S curve presentation template.
Use this S Curve PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds.
The S Curve PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey your message clearly with our unique set of editable infographics, icons, images, fonts, and presentation backgrounds. Download now and stand out in your next presentation with S Curve PowerPoint and Google Slides template.
Ask us to modify or edit any specific element of the S Curve template as per your need with our custom slides services. Lets collaborate to blend your ideas with our S Curve template and get the final product delivered within 24 hours.
We can also help you and your team create full-fledged presentations from scratch with our presentation services . Explore now!
Features of this PowerPoint Template And Google Slides Theme:
- 100% editable with easy-to-use features.
- Contains 4:3 and 16:9 aspect ratio suitable for all types of screens.
- Includes icons, images, graphics, and infographics to capture audience’s attention.
- Compatible with both Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint.
- S Curve PowerPoint Template - 4x3 – $4.99
- S Curve PowerPoint Template - 16x9 – $4.99
You May Also Like
- Product RoadMap S Curve - 4x3 – $4.99
- Product RoadMap S Curve - 16x9 – $4.99

Product RoadMap S Curve PowerPoint Template
Product RoadMap S Curve Presentation Template Use this Product RoadMap S Curve PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds. The Product RoadMap S Curve PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey your message clearly... read more
- Product Roadmap S Curve1 - 4x3 – $6.99
- Product Roadmap S Curve1 - 16x9 – $6.99

Product Roadmap S Curve1 PowerPoint Template
Product Roadmap S Curve1 Presentation Template Use this Product Roadmap S Curve1 PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds. The Product Roadmap S Curve1 PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey your message clearly... read more
- Normal Distribution Curve For Powerpoint - 4x3 – $4.99
- Normal Distribution Curve For Powerpoint - 16x9 – $4.99

Normal Distribution Curve PowerPoint Template
Normal Distribution Curve Presentation Template Use this Normal Distribution Curve PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds. The Normal Distribution Curve PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey your message clearly with our unique... read more
- Product Planning Launch Bell Curve - 4x3 – $6.99
- Product Planning Launch Bell Curve - 16x9 – $6.99
Product Planning Launch Bell Curve PowerPoint Template
Product Planning Launch Bell Curve Presentation Template Use this Product Planning Launch Bell Curve PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds. The Product Planning Launch Bell Curve PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey... read more
- Products Bell Curve Comparison - 4x3 – $4.99
- Products Bell Curve Comparison - 16x9 – $4.99

Products Bell Curve Comparison PowerPoint Template
Products Bell Curve Comparison Presentation Template Use this Products Bell Curve Comparison PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds. The Products Bell Curve Comparison PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey your message clearly... read more
- Product Analysis Bell Curve - 4x3 – $4.99
- Product Analysis Bell Curve - 16x9 – $4.99

Product Analysis Bell Curve PowerPoint Template
Product Analysis Bell Curve Presentation Template Use this Product Analysis Bell Curve PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds. The Product Analysis Bell Curve PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey your message clearly... read more
- Inflection-Curve-PowerPoint-Template - 4x3 – $4.99
- Inflection-Curve-PowerPoint-Template - 16x9 – $4.99
Inflection Curve PowerPoint Template
Inflection Curve Presentation Template Use this Inflection Curve PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds. The Inflection Curve PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey your message clearly with our unique set of editable... read more
- Bell Curve PowerPoint Template 2 - 4x3 – $4.99
- Bell Curve PowerPoint Template 2 - 16x9 – $4.99

Bell Curve 2 PowerPoint Template
Bell Curve 2 Presentation Template Use this Bell Curve 2 PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds. The Bell Curve 2 PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey your message clearly with our unique... read more
Recommended for you
- Bell Curve PowerPoint Template 3 - 4x3 – $4.99
- Bell Curve PowerPoint Template 3 - 16x9 – $4.99

Bell Curve 3 PowerPoint Template
Bell Curve 3 Presentation Template Use this Bell Curve 3 PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds. The Bell Curve 3 PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey your message clearly with our unique... read more
- Bell Curve PowerPoint Template - 4x3 – $4.99
- Bell Curve PowerPoint Template - 16x9 – $4.99

Bell Curve PowerPoint Template
Bell Curve Presentation Template Use this Bell Curve PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds. The Bell Curve PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey your message clearly with our unique set of editable... read more
- Bell Curve PowerPoint Template 1 - 4x3 – $6.99
- Bell Curve PowerPoint Template 1 - 16x9 – $6.99

Bell Curve PowerPoint Template 1
This Bell Curve PowerPoint Template is an incredible, eye-catching template that helps you categorize your customers among Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, Laggards and showcase it in a data-driven curve graph. The template gives a user a better understanding of their target customers and the expected performance of their product/ service in the market. Using a professional color... read more
- Product Launch Timeline Map PowerPoint Template - 4x3 – $4.99
- Product Launch Timeline PowerPoint - 16x9 – $4.99

Product Launch Timeline Map Template for PowerPoint and Google Slides
Product Launch Timeline Map Template for PowerPoint and Google Slides The Product Launch Timeline Map Template is designed to illustrate the timeline of a product launch, showing the different stages of the process visually. The template has a map with specific states highlighted to indicate areas of focus for the launch. Below the map is a timeline for different years,... read more
- Inflection-Point-PowerPoint-Template - 4x3 – $4.99
- Inflection-Point-PowerPoint-Template - 16x9 – $4.99
Inflection Point PowerPoint Template
Inflection Point Presentation Template Use this Inflection Point PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds. The Inflection Point PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey your message clearly with our unique set of editable... read more
- Bell Curve Graph PowerPoint Template-4x3 – $4.99
- Bell Curve Graph PowerPoint Template-16x9 – $4.99

Bell Curve Graph PowerPoint Template
Bell Curve Graph Presentation Template Use this Bell Curve Graph PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds. The Bell Curve Graph PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey your message clearly with our unique... read more
- Product-Market-Fit-1-PowerPoint-Template - 4x3 – $4.99
- Product-Market-Fit-1-PowerPoint-Template - 16x9 – $4.99
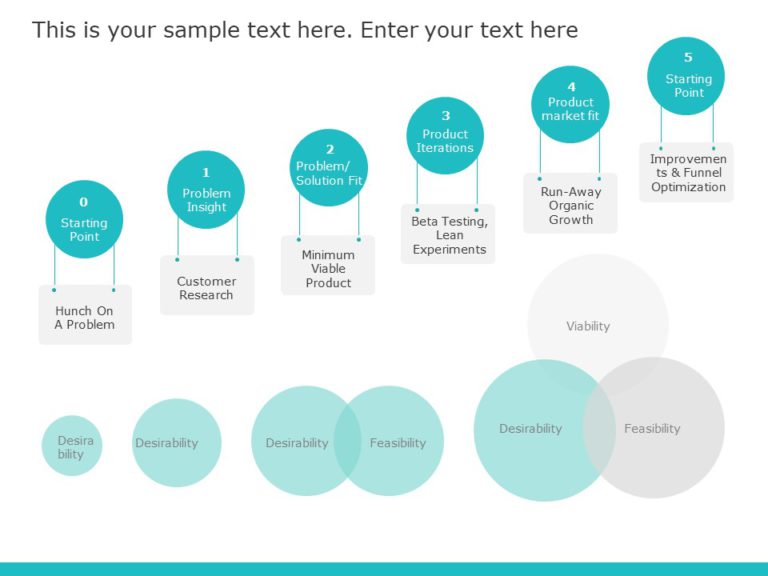
Product Market Fit 1 PowerPoint Template
Product Market Fit 1 Presentation Template Use this Product Market Fit 1 PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds. The Product Market Fit 1 PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey your message clearly... read more
- Product Strategy Planning Template - 4x3 – $4.99
- Product Strategy Planning Template - 16x9 – $4.99
Product Strategy Planning PowerPoint Template
Product Strategy Planning Presentation Template Use this Product Strategy Planning PowerPoint template to create visually appealing presentations in any professional setting. Its minimalistic design and ready-to-use features enhance your presentation slides ten folds. The Product Strategy Planning PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience’s attention. Convey your message clearly with our unique... read more
Forgot Password?
Join the SlideUpLift Discount Club- A Lifetime Value

Benefits never expire and apply to the whole SlideUplift library including future additions.
Upon paying a one time fee, you will remain a Discount Clubber for a lifetime and enjoy 20% discounts on all products that you purchase à la carte from SlideUpLift.com
Privacy Overview
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. It is mandatory to procure user consent prior to running these cookies on your website.
Home PowerPoint Templates Curves & Lines Doble S Curve Template for PowerPoint
Doble S Curve Template for PowerPoint
Doble S Curve Template for PowerPoint is a presentation template containing the Double S curve model and available as a PowerPoint presentation file. In the S-curve every product goes through three different environments on the way to market acceptance. At the beginning the growth is slow but then there is a rush by the mass market. Finally in the S shaped curve, there is a peak of acceptance where replacements become the norm. S-Curve is also used as a forecasting tool and for strategy management as a strategic innovation tool for established companies.
This double S curve model for PowerPoint was created drawing a Bezier curve and you can easily edit the points in Microsoft PowerPoint to adjust the slope. Alternatively you can download other S-Curve PowerPoint designs as well as other popular curves for PowerPoint presentations .
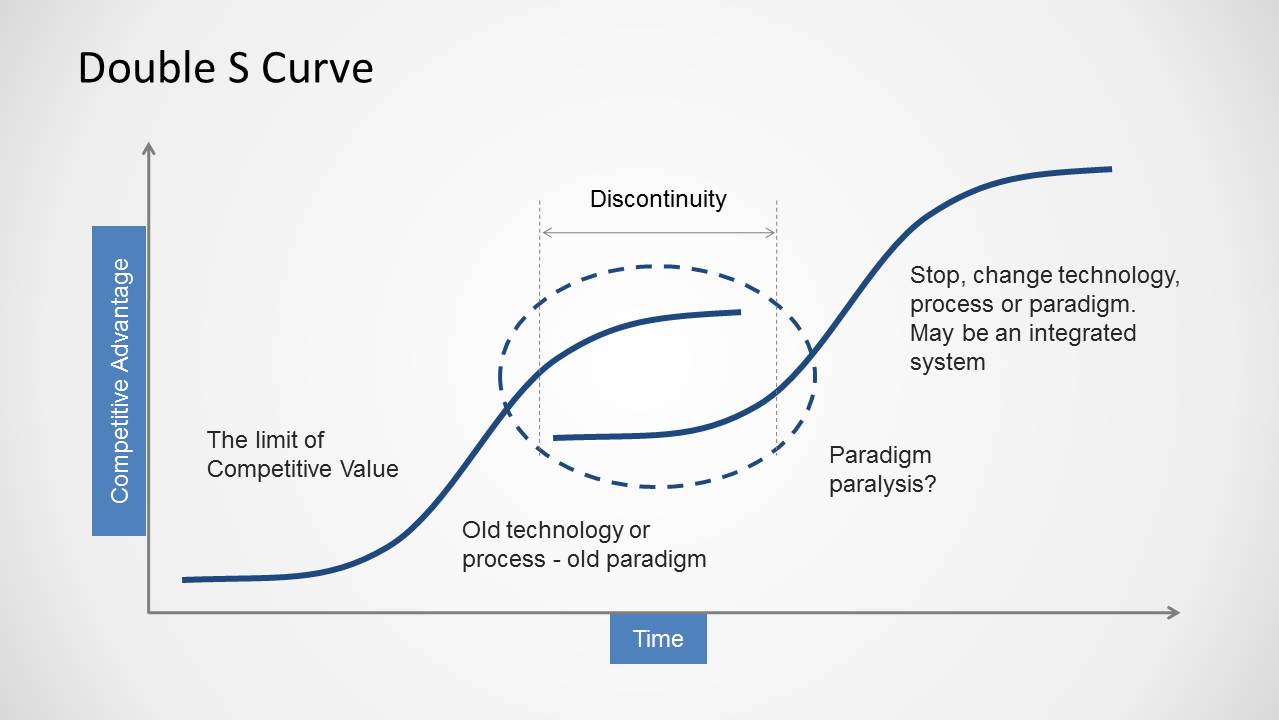
You must be logged in to download this file.
Favorite Add to Collection
Details ( slide)

Subscribe today and get immediate access to download our PowerPoint templates.
Related PowerPoint Templates
VUCA vs BANI PowerPoint Template

Change Kaleidoscope PowerPoint Template
SPACE Matrix PowerPoint Template

3-Item Futuristic Slide Template for PowerPoint

- Customer Favourites
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

- You're currently reading page 1

Stages // require(['jquery'], function ($) { $(document).ready(function () { //removes paginator if items are less than selected items per page var paginator = $("#limiter :selected").text(); var itemsPerPage = parseInt(paginator); var itemsCount = $(".products.list.items.product-items.sli_container").children().length; if (itemsCount ? ’Stages’ here means the number of divisions or graphic elements in the slide. For example, if you want a 4 piece puzzle slide, you can search for the word ‘puzzles’ and then select 4 ‘Stages’ here. We have categorized all our content according to the number of ‘Stages’ to make it easier for you to refine the results.
Category // require(['jquery'], function ($) { $(document).ready(function () { //removes paginator if items are less than selected items per page var paginator = $("#limiter :selected").text(); var itemsperpage = parseint(paginator); var itemscount = $(".products.list.items.product-items.sli_container").children().length; if (itemscount.
- Business Slides (187)
- Circular (8)
- Complete Decks (3)
- Concepts 1 (8)
- Diagrams (191)
- Essentials 1 (18)
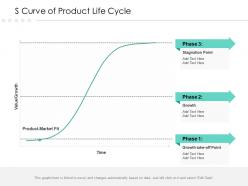

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The S curve in project management is a powerful visual tool that graphically represents the relationship between time and project cost or work. Understanding the three distinct phases of the S curve—initial, middle, and late—is crucial for project managers to effectively monitor and steer project progress.
S-Curve for PowerPoint is an editable diagram template which makes it easy to create a custom S-Curve for PowerPoint presentations. With this template you can easily and accurately display an S-Curve diagram for depicting a growth of a variable, by simply editing the existing model with little effort. For making curves and diagrams for other ...
3. What is the "S" in S-Curve? The 's' shape isn't imposed; it is simply the shape made by the graph from the project initiation to the end. As time progresses, growth begins to accelerate. This growth is represented by the middle section of the 's' in the graph, which shows this rapid rise. The inflection point is the point where the change occurs.
The presentation of the S-curves in Stacked Histogram are shown like this: This view shows us the combination of bars and S-curves for two different resources. But, we also have the possibility to see the Total cumulative Curve, by selecting the check-box in the Resource Usage Profile Options dialog.
An S-curve is a graph that represents the progress of a project over time. As the name suggests, it forms a loose S shape: When an S-curve is used in product and project management to track progress, man-hours or effort/cost is plotted on the y-axis against time, which is plotted on the x-axis. Initially, when the project starts, the team ...
An S curve is a project management analysis that illustrates the relevant cumulative data (cost or the number of hours worked compared against time) for a project or task. Project managers use S-curves to record, monitor, analyze and control various performances by measuring variables over time. With an S-curve, the project team can clearly see ...
Use Tools to Create Graphs for Your Project. Microsoft Excel is a widely available and easy-to-use tool for creating S-curves. You can create a simple graph by plotting your planned and actual data points against time. If you prefer a cloud-based solution, Google Sheets is another free and user-friendly tool.
An S-curve is a mathematical graph that shows the progress of a project over time. Its name comes from its "S" shape. While the S-curve starts off slow initially and looks like a straight line ...
October 5, 2022. Today we will discuss the s-curve in project management and provide you with its definitions and examples. S-curve is a graph that shows the relevant cumulative data for your project. The data can be costs, person-hours, etc. S-curve is a good communication tool and helps project managers communicate project progress to project ...
An s-curve is a graphical display of cumulative man-hours, cost, progress, or other quantities plotted against time. An s-curve aims to represent the utilization of resources over the proposed time of the project. S-curves are also called, "s-plots", "cumulative distribution charts", "velocity diagrams", and "Performance ...
The S-Curve is also known as Sigmoid curve and it can help to create a relationship between two different attributes or parameters. This shape is sometimes associated with potential business growth in revenue and it is not only used for complex Math formulas and statistics but also in other presentation topics, including sales, business ...
So, what is S-curve analysis in project management? This two-minute video will show you everything you need to implement S-curve analysis in your next assign...
S-Curves for PowerPoint is a presentation template that you can download to model a S-Curve in a slide design. The sample diagrams in the given slides can be comprehensively edited to adjust the curve to depict and accurate representation of your S-Curve. You can also perform major customizations to your slides by making use of the given ...
Here are the stages of an S-curve in business: 1. Initial slow growth. In the first stage, as a business experiences slow growth and gains little market share, the slope of the S-curve is a slight increase. This stage is critical for building the foundations of a company's operations.
A S Curve PowerPoint template is a ready-made presentation template that provides a structured framework for creating professional S Curve presentations. The S Curve PPT presentation template includes design elements, layouts, and fonts that you can customize to fit your content and brand.
L Curve for PowerPoint and Google Slides. Sigmoid curve, or commonly known as the "S curve" refers to a special case of the logistics function. Usually, it defines the relationship between two parameters having real values and how a positive derivative takes place between the two of them at various points. Due to its peculiar shape, it is often ...
The S Curve Template for powerpoint presentation will display relevant cumulative data for a project, including cost and man-hours that will have taken to complete a task. It is called S curve because of the shape of the graph. It typically forms a thin "S." it is used to track the project's progress with the help of a mathematical chart.
S curve can be used in defining the growth of any system, like business, product development, costing etc. The horizontal axis indicate time frame of the product, and the vertical axis represent performance of the system, or product, or technology. Also Vertical axis represent the maturity value or the performance of system, which are measured ...
Presenting this set of slides with name s curve for cost quantity and time anaysis ppt powerpoint presentation template pdf. The topics discussed in these slides are a typical s curve, time, manhours, cost, quantity. This is a completely editable PowerPoint presentation and is available for immediate download.
The S Curve PPT template is professionally designed with the principles of vision sciences to capture your audience's attention. Convey your message clearly with our unique set of editable infographics, icons, images, fonts, and presentation backgrounds. Download now and stand out in your next presentation with S Curve PowerPoint and Google ...
Slide 1 of 14. S Curve Mapping Powerpoint PPT Template Bundles. Deliver a lucid presentation by utilizing this S Curve Mapping Powerpoint PPT Template Bundles. Use it to present an overview of the topic with the right visuals, themes, shapes, and graphics. This is an expertly designed complete deck that reinforces positive thoughts and actions.
Doble S Curve Template for PowerPoint is a presentation template containing the Double S curve model and available as a PowerPoint presentation file. In the S-curve every product goes through three different environments on the way to market acceptance. At the beginning the growth is slow but then there is a rush by the mass market. Finally in ...
Bar graph with s curve flat powerpoint design. Slide 1 of 2. S curve measuring man power on a project. Slide 1 of 2. S curve for progress of project plan. Slide 1 of 5. S curve showing launch growth and decline. Slide 1 of 7. S Curve Mapping To Show Original Set 2 Innovation Product Development.