Blog > Effective Feedback for Presentations - digital with PowerPoint or with printable sheets

Effective Feedback for Presentations - digital with PowerPoint or with printable sheets
10.26.20 • #powerpoint #feedback #presentation.
Do you know whether you are a good presenter or not? If you do, chances are it's because people have told you so - they've given you feedback. Getting other's opinions about your performance is something that's important for most aspects in life, especially professionally. However, today we're focusing on a specific aspect, which is (as you may have guessed from the title): presentations.

The importance of feedback
Take a minute to think about the first presentation you've given: what was it like? Was it perfect? Probably not. Practise makes perfect, and nobody does everything right in the beginning. Even if you're a natural at speaking and presenting, there is usually something to improve and to work on. And this is where feedback comes in - because how are you going to know what it is that you should improve? You can and should of course assess yourself after each and every presentation you give, as that is an important part of learning and improvement. The problem is that you yourself are not aware of all the things that you do well (or wrong) during your presentation. But your audience is! And that's why you should get audience feedback.
Qualities of good Feedback
Before we get into the different ways of how you can get feedback from your audience, let's briefly discuss what makes good feedback. P.S.: These do not just apply for presentations, but for any kind of feedback.
- Good feedback is constructive, not destructive. The person receiving feedback should feel empowered and inspired to work on their skills, not discouraged. You can of course criticize on an objective level, but mean and insulting comments have to be kept to yourself.
- Good feedback involves saying bot what has to be improved (if there is anything) and what is already good (there is almost always something!)
- After receiving good feedback, the recipient is aware of the steps he can and should take in order to improve.
Ways of receiving / giving Feedback after a Presentation
1. print a feedback form.

Let's start with a classic: the feedback / evaluation sheet. It contains several questions, these can be either open (aka "What did you like about the presentation?") or answered on a scale (e.g. from "strongly disagree" to "strongly agree"). The second question format makes a lot of sense if you have a large audience, and it also makes it easy to get an overview of the results. That's why in our feedback forms (which you can download at the end of this post), you'll find mainly statements with scales. This has been a proven way for getting and giving valuable feedback efficiently for years. We do like the feedback form a lot, though you have to be aware that you'll need to invest some time to prepare, count up and analyse.
- ask specifically what you want to ask
- good overview of the results
- anonymous (people are likely to be more honest)
- easy to access: you can just download a feedback sheet online (ours, for example, which you'll find at the end of this blog post!)
- analysing the results can be time-consuming
- you have to print out the sheets, it takes preparation
2. Online: Get digital Feedback
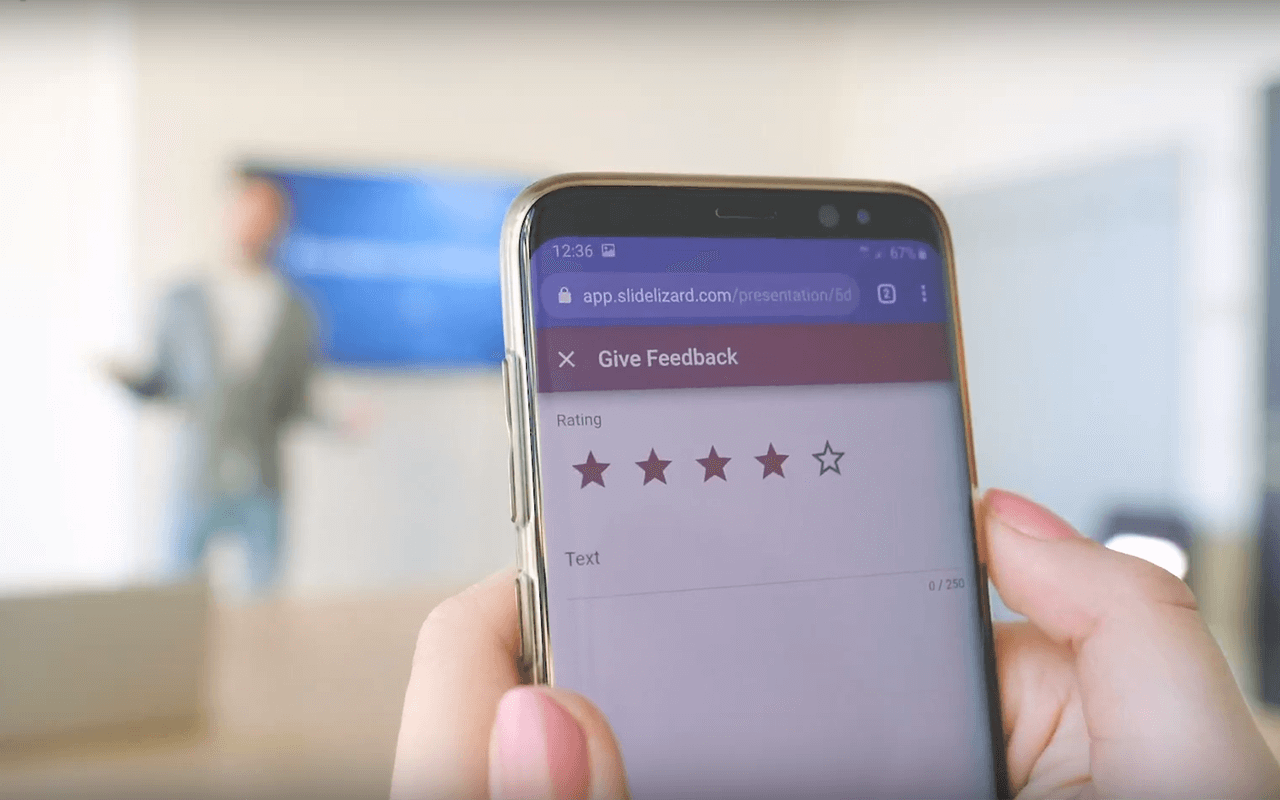
In the year 2020, there's got to be a better way of giving feedback, right? There is, and you should definitely try it out! SlideLizard is a free PowerPoint extension that allows you to get your audience's feedback in the quickest and easiest way possible. You can of course customize the feedback question form to your specific needs and make sure you get exactly the kind of feedback you need. Click here to download SlideLizard right now, or scroll down to read some more about the tool.
- quick and easy to access
- easy and fast export, analysis and overview of feedback
- save feedback directly on your computer
- Participants need a working Internet connection (but that usually isn't a problem nowadays)
3. Verbal Feedback

"So, how did you like the presentation?", asks the lecturer. A few people in the audience nod friendly, one or two might even say something about how the slides were nice and the content interesting. Getting verbal feedback is hard, especially in big groups. If you really want to analyse and improve your presentation habits and skills, we recommend using one of the other methods. However, if you have no internet connection and forgot to bring your feedback sheets, asking for verbal feedback is still better than nothing.
- no prerequisites
- open format
- okay for small audiences
- not anonymous (people might not be honest)
- time consuming
- no detailed evaluation
- no way to save the feedback (except for your memory)
- not suitable for big audiences
Feedback to yourself - Self Assessment

I've mentioned before that it is incredibly important to not only let others tell you what went well and what didn't in your presentation. Your own impressions are of huge value, too. After each presentation you give, ask yourself the following questions (or better yet, write your answers down!):
- What went wrong (in my opinion)? What can I do in order to avoid this from happening next time?
- What went well? What was well received by the audience? What should I do more of?
- How was I feeling during this presentation? (Nervous? Confident? ...)
Tip: If you really want to actively work on your presentation skills, filming yourself while presenting and analysing the video after is a great way to go. You'll get a different view on the way you talk, move, and come across.

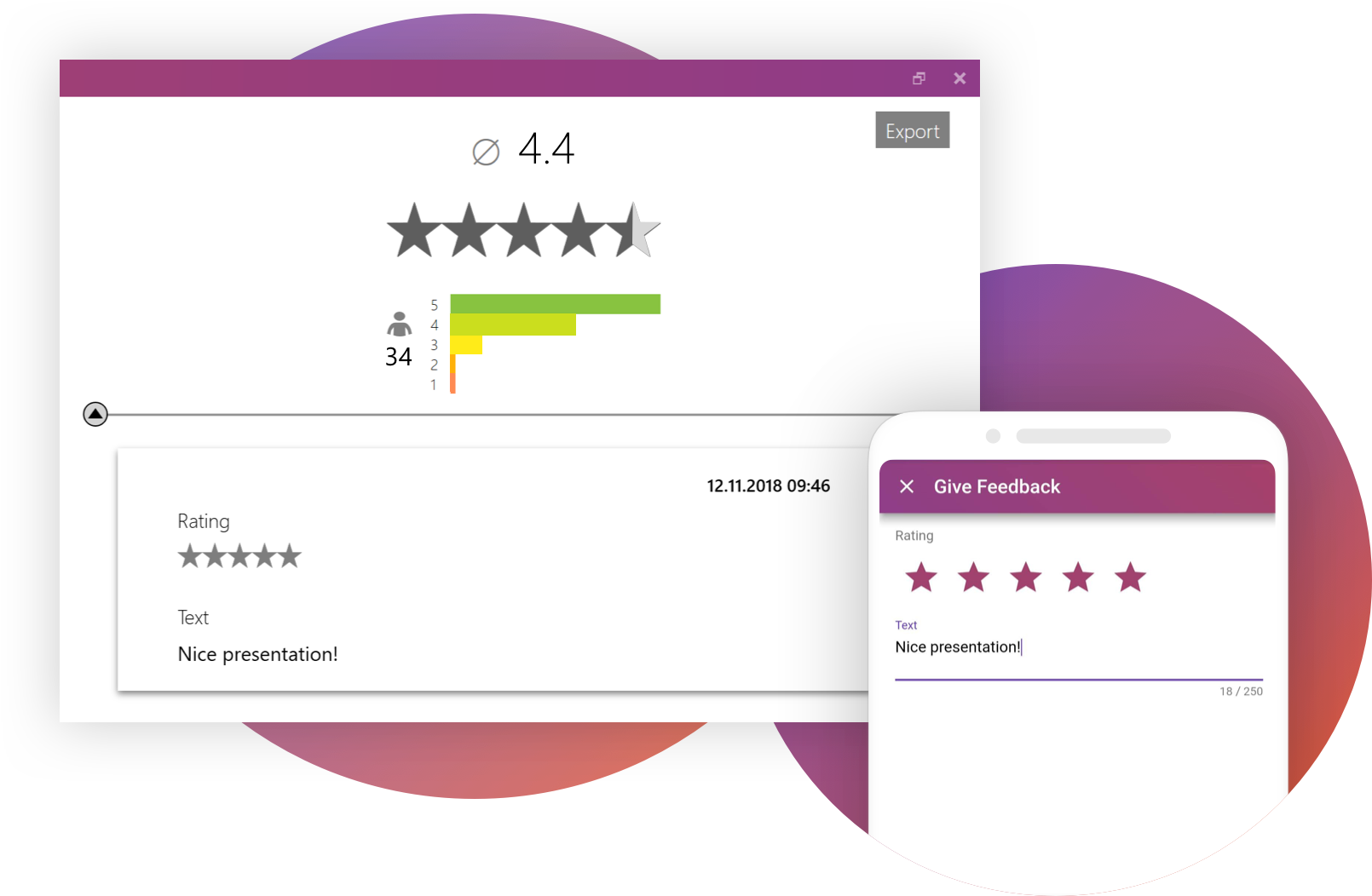
Digital Feedback with SlideLizard
Were you intrigued by the idea of easy Online-feedback? With SlideLizard your attendees can easily give you feedback directly with their Smartphone. After the presentation you can analyze the result in detail.
- type in your own feedback questions
- choose your rating scale: 1-5 points, 1-6 points, 1-5 stars or 1-6 stars;
- show your attendees an open text field and let them enter any text they want
Note: SlideLizard is amazing for giving and receiving feedback, but it's definitely not the only thing it's great for. Once you download the extension, you get access to the most amazing tools - most importantly, live polls and quizzes, live Q&A sessions, attendee note taking, content and slide sharing, and presentation analytics. And the best thing about all this? You can get it for free, and it is really easy to use, as it is directly integrated in PowerPoint! Click here to discover more about SlideLizard.
Free Download: Printable Feedback Sheets for Business or School Presentations
If you'd rather stick with the good old paper-and-pen method, that's okay, too. You can choose between one of our two feedback sheet templates: there is one tailored to business presentations and seminars, and one that is created specifically for teachers assessing their students. Both forms can be downloaded as a Word, Excel, or pdf file. A lot of thought has gone into both of the forms, so you can benefit as much as possible; however, if you feel like you need to change some questions in order to better suit your needs, feel free to do so!
Feedback form for business
Template as PDF, Word & Excel - perfect for seminars, trainings,...
Feedback form for teachers (school or university)
Template as PDF, Word & Excel - perfect for school or university,...
Where can I find a free feedback form for presentations?
There are many templates available online. We designed two exclusive, free-to-download feedback sheets, which you can get in our blog article
What's the best way to get feedback for presentations?
You can get feedback on your presentations by using feedback sheets, asking for feedback verbally, or, the easiest and fastest option: get digital feedback with an online tool
Related articles
About the author.

Pia Lehner-Mittermaier
Pia works in Marketing as a graphic designer and writer at SlideLizard. She uses her vivid imagination and creativity to produce good content.
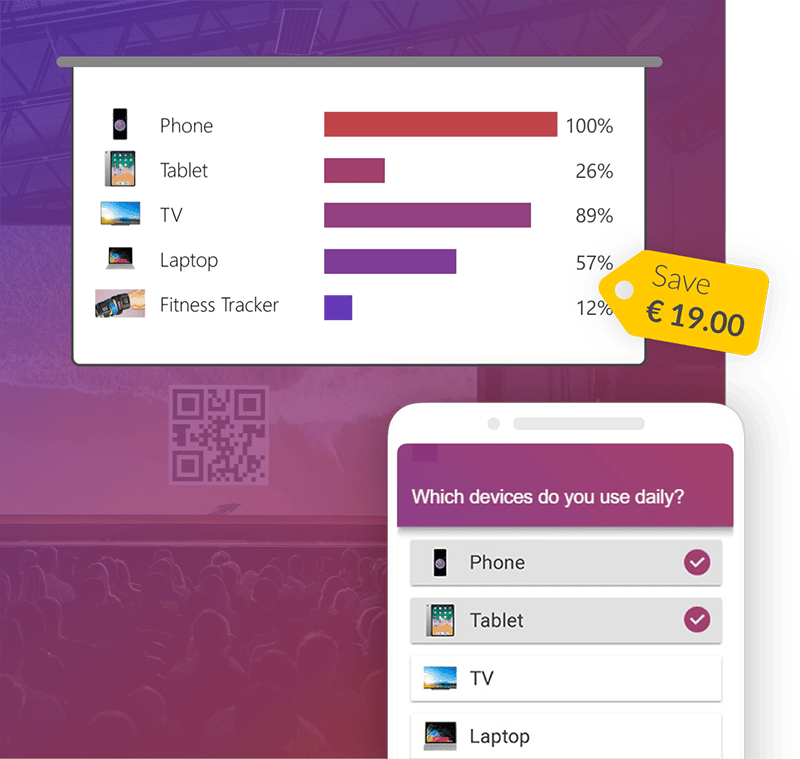
Get 1 Month for free!
Do you want to make your presentations more interactive.
With SlideLizard you can engage your audience with live polls, questions and feedback . Directly within your PowerPoint Presentation. Learn more

Top blog articles More posts

Tips for good PowerPoint Presentations

A Guide to PowerPoint-Karaoke
Get started with Live Polls, Q&A and slides
for your PowerPoint Presentations
The big SlideLizard presentation glossary
Co-located audience.
Co-located Audience means that the speaker talks to the audience in person. It is used verbal and non-verbal methods to communicate a message. The speaker makes gestures with their hands, changes their face expression and shows images.
Keynote is a programme which, like PowerPoint, is used to create digital screen presentations. It is mainly used by Apple users.
External Communication
External communication is the exchange of information between two organisations. For example, it can be an exchange with customers, clients or traders. Feedback from a customer also counts as external communication.
PowerPoint Online
PowerPoint Online is the web version of PowerPoint. You can present and edit your PowerPoint presentation with it, without having PowerPoint installed on your computer. It's only necessary to have a Microsoft - or a Microsoft 365 account.
Be the first to know!
The latest SlideLizard news, articles, and resources, sent straight to your inbox.
- or follow us on -
We use cookies to personalize content and analyze traffic to our website. You can choose to accept only cookies that are necessary for the website to function or to also allow tracking cookies. For more information, please see our privacy policy .
Cookie Settings
Necessary cookies are required for the proper functioning of the website. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information about the number of visitors, etc.
Home Blog Education Presentation Skills 101: A Guide to Presentation Success
Presentation Skills 101: A Guide to Presentation Success
Getting the perfect presentation design is just a step toward a successful presentation. For the experienced user, building presentation skills is the answer to elevating the power of your message and showing expertise on any subject. Still, one can ask: is it the same set of skills, or are they dependable on the type of presentation?
In this article, we will introduce the different types of presentations accompanied by the skillset required to master them. The purpose, as always, is to retain the audience’s interest for a long-lasting and convincing message.

Table of Contents
The Importance of Presentation Skills
Persuasive presentations, instructional presentations, informative presentations, inspirational presentations, basic presentation skills, what are the main difficulties when giving a presentation, recommendations to improve your presentation skills, closing statement.
Effective communication is the answer to reaching business and academic goals. The scenarios in which we can be required to deliver a presentation are as diverse as one can imagine. Still, some core concepts apply to all presentations.
We define presentation skills as a compendium of soft skills that directly affect your presentation performance and contribute to creating a great presentation. These are not qualities acquired by birth but skills you ought to train and master to delve into professional environments.
You may ask: is it really that evident when a presenter is not prepared? Here are some common signs people can experience during presentations:
- Evasive body language: Not making eye contact with the audience, arms closed tightly to the body, hands in pockets all the time.
- Lack of interest in the presenter’s voice: dull tone, not putting an effort to articulate the topics.
- Doubting when asked to answer a question
- Irksome mood
The list can go on about common presenter mistakes , and most certainly, it will affect the performance of any presented data if the lack of interest by the presenter is blatantly obvious. Another element to consider is anxiety, and according to research by the National Institute of Mental Health, 73% of the population in the USA is affected by glossophobia , which is the fear of public speaking, judgment, or negative evaluation by other people.
Therefore, presentation skills training is essential for any business professional who wants to achieve effective communication . It will remove the anxiety from presentation performance and help users effectively deliver their message and connect with the audience.
Archetypes of presentations
Persuasive presentations aim to convince the audience – often in short periods – to acquire a product or service, adhere to a cause, or invest in a company. For business entrepreneurs or politicians, persuasive presentations are their tool for the trade.
Unless you aim to be perceived as an imposter, a proper persuasive presentation has the elements of facts, empathy, and logic, balanced under a well-crafted narrative. The central pillar of these presentations is to identify the single factor that gathered your audience: it could be a market need, a social cause, or a revolutionary concept for today’s society. It has to be something with enough power to gather critiques – both good and bad.
That single factor has to be backed up by facts. Research that builds your hypothesis on how to solve that problem. A deep understanding of the target audience’s needs , concerns, and social position regarding the solution your means can offer. When those elements are in place, building a pitch becomes an easy task.
Graphics can help you introduce information in a compelling format, lowering the need for lengthy presentations. Good presentation skills for persuasive presentations go by the hand of filtering relevant data and creating the visual cues that resonate with what your audience demands.
One powerful example of a persuasive presentation is the technique known as the elevator pitch . You must introduce your idea or product convincingly to the audience in a timeframe between 30 seconds and less than 2 minutes. You have to expose:
- What do you do
- What’s the problem to solve
- Why is your solution different from others
- Why should the audience care about your expertise

For that very purpose, using engaging graphics with contrasting colors elevates the potential power of your message. It speaks professionalism, care for details, and out-of-the-box thinking. Knowing how to end a presentation is also critical, as your CTAs should be placed with care.
Therefore, let’s resume the requirements of persuasive presentations in terms of good presentation skills:
- Identifying problems and needs
- Elaborating “the hook” (the element that grabs the audience’s attention)
- Knowing how to “tie” your audience (introducing a piece of information related to the hook that causes an emotional impact)
- Broad knowledge of body language and hand gestures to quickly convey your message
- Being prepared to argue a defense of your point of view
- Handling rejection
- Having a proactive attitude to convert opportunities into new projects
- Using humor, surprise, or personal anecdotes as elements to sympathize with the audience
- Having confidence
- Be able to summarize facts and information in visually appealing ways

You can learn more about persuasive presentation techniques by clicking here .
In the case of instructional presentations, we ought to differentiate two distinctive types:
- Lecture Presentations : Presentations being held at universities or any other educative institution. Those presentations cover, topic by topic, and the contents of a syllabus and are created by the team of teachers in charge of the course.
- Training Presentations : These presentations take place during in-company training sessions and usually comprise a good amount of content that is resumed into easy-to-take solutions. They are aimed to coach employees over certain topics relevant to their work performance. The 70-20-10 Model is frequently used to address these training situations.
Lecture presentations appeal to the gradual introduction of complex concepts, following a structure set in the course’s syllabus. These presentations often have a similar aesthetic as a group of professors or researchers created to share their knowledge about a topic. Personal experience does tell that course presentations often rely on factual data, adequately documented, and on the theoretical side.
An example of a presentation that lies under this concept is a Syllabus Presentation, used by the teaching team to introduce the subject to new students, evaluation methods, concepts to be learned, and expectations to pass the course.

On the other hand, training presentations are slide decks designed to meet an organization’s specific needs in the formal education of their personnel. Commonly known as “continuous education,” plenty of companies invest resources in coaching their employees to achieve higher performance results. These presentations have the trademark of being concise since their idea is to introduce the concepts that shall be applied in practice sessions.
Ideally, the training presentations are introduced with little text and easy-to-recognize visual cues. Since the idea is to summarize as much as possible, these are visually appealing for the audience. They must be dynamic enough to allow the presenter to convey the message.

Those key takeaways remind employees when they revisit their learning resources and allow them to ruminate on questions that fellow workers raise.
To sum up this point, building presentation skills for instructional presentations requires:
- Ability to put complex concepts into simpler words
- Patience and a constant learning mindset
- Voice training to deliver lengthy speeches without being too dense
- Ability to summarize points and note the key takeaways
- Empathizing with the audience to understand their challenges in the learning process

The informative presentations take place in business situations, such as when to present project reports from different departments to the management. Another potential usage of these presentations is in SCRUM or other Agile methodologies, when a sprint is completed, to discuss the advance of the project with the Product Owner.
As they are presentations heavily dependent on data insights, it’s common to see the usage of infographics and charts to express usually dense data in simpler terms and easy to remember.

Informative presentations don’t just fall into the business category. Ph.D. Dissertation and Thesis presentations are topics that belong to the informative presentations category as they condense countless research hours into manageable reports for the academic jury.

Since these informational presentations can be perceived as lengthy and data-filled, it is important to learn the following professional presentation skills:
- Attention to detail
- Be able to explain complex information in simpler terms
- Creative thinking
- Powerful diction
- Working on pauses and transitions
- Pacing the presentation, so not too much information is divulged per slide

The leading inspirational platform, TEDx, comes to mind when talking about inspirational presentations. This presentation format has the peculiarity of maximizing the engagement with the audience to divulge a message, and due to that, it has specific requirements any presenter must meet.
This presentation format usually involves a speaker on a stage, either sitting or better standing, in which the presenter engages with the audience with a storytelling format about a life experience, a job done that provided a remarkable improvement for society, etc.

Empathizing with the audience is the key ingredient for these inspirational presentations. Still, creativity is what shapes the outcome of your performance as people are constantly looking for different experiences – not the same recipe rephrased with personal touches. The human factor is what matters here, way above data and research. What has your experience to offer to others? How can it motivate another human being to pursue a similar path or discover their true calling?
To achieve success in terms of communication skills presentation, these inspirational presentations have the following requirements:
- Focus on the audience (engage, consider their interests, and make them a part of your story)
- Putting ego aside
- Creative communication skills
- Storytelling skills
- Body language knowledge to apply the correct gestures to accompany your story
- Voice training
- Using powerful words

After discussing the different kinds of presentations we can come across at any stage of our lives, a group of presentation skills is standard in any type of presentation. See below what makes a good presentation and which skills you must count on to succeed as a presenter.
Punctuality
Punctuality is a crucial aspect of giving an effective presentation. Nothing says more about respect for your audience and the organization you represent than delivering the presentation on time . Arriving last minute puts pressure on the tech team behind audiovisuals, as they don’t have enough preparation to test microphones, stage lights, and projector settings, which can lead to a less powerful presentation Even when discussing presentations hosted in small rooms for a reduced audience, testing the equipment becomes essential for an effective presentation.
A solution for this is to arrive at least 30 minutes early. Ideally, one hour is a sweet spot since the AV crew has time to check the gear and requirements for your presentation. Another benefit of this, for example, in inspirational presentations, is measuring the previous presenter’s impact on the audience. This gives insights about how to resonate with the public, and their interest, and how to accommodate your presentation for maximum impact.
Body Language
Our bodies can make emotions transparent for others, even when we are unaware of such a fact. Proper training for body language skills reduces performance anxiety, giving the audience a sense of expertise about the presented topic.
Give your presentation and the audience the respect they deserve by watching over these potential mistakes:
- Turning your back to the audience for extended periods : It’s okay to do so when introducing an important piece of information or explaining a graph, but it is considered rude to give your back to the audience constantly.
- Fidgeting : We are all nervous in the presence of strangers, even more, if we are the center of attention for that moment. Instead of playing with your hair or making weird hand gestures, take a deep breath to center yourself before the presentation and remember that everything you could do to prepare is already done. Trust your instincts and give your best.
- Intense eye contact : Have you watched a video where the presenter stared at the camera the entire time? That’s the feeling you transmit to spectators through intense eye contact. It’s a practice often used by politicians to persuade.
- Swearing : This is a no-brainer. Even when you see influencers swearing on camera or in podcasts or live presentations, it is considered an informal and lousy practice for business and academic situations. If you have a habit to break when it comes to this point, find the humor in these situations and replace your swear words with funny alternatives (if the presentation allows for it).
Voice Tone plays a crucial role in delivering effective presentations and knowing how to give a good presentation. Your voice is a powerful tool for exposing your ideas and feelings . Your voice can articulate the message you are telling, briefing the audience if you feel excited about what you are sharing or, in contrast, if you feel the presentation is a burden you ought to complete.
Remember, passion is a primary ingredient in convincing people. Therefore, transmitting such passion with a vibrant voice may help gather potential business partners’ interest.
But what if you feel sick prior to the presentation? If, by chance, your throat is sore minutes before setting foot on the stage, try this: when introducing yourself, mention that you are feeling a bit under the weather. This resonates with the audience to pay more attention to your efforts. In case you don’t feel comfortable about that, ask the organizers for a cup of tea, as it will settle your throat and relax your nerves.
Tech Skills
Believe it or not, people still feel challenged by technology these days. Maybe that’s the reason why presentation giants like Tony Robbins opt not to use PowerPoint presentations . The reality is that there are plenty of elements involved in a presentation that can go wrong from the tech side:
- A PDF not opening
- Saving your presentation in a too-recent PowerPoint version
- A computer not booting up
- Mac laptops and their never-ending compatibility nightmare
- Not knowing how to change between slides
- Not knowing how to use a laser pointer
- Internet not working
- Audio not working
We can come up with a pretty long list of potential tech pitfalls, and yet more than half of them fall in presenters not being knowledgeable about technology.
If computers aren’t your thing, let the organization know about this beforehand. There is always a crew member available to help presenters switch between slides or configure the presentation for streaming. This takes the pressure off your shoulders, allowing you to concentrate on the content to present. Remember, even Bill Gates can get a BSOD during a presentation .
Presentations, while valuable for conveying information and ideas, can be daunting for many individuals. Here are some common difficulties people encounter when giving presentations:
Public Speaking Anxiety
Glossophobia, the fear of public speaking, affects a significant portion of the population. This anxiety can lead to nervousness, trembling, and forgetfulness during a presentation.
Lack of Confidence
Many presenters struggle with self-doubt, fearing that they may not be knowledgeable or skilled enough to engage their audience effectively.
Content Organization
Organizing information in a coherent and engaging manner can be challenging. Presenters often grapple with how to structure their content to make it easily digestible for the audience. Artificial Intelligence can help us significantly reduce the content arrangement time when you work with tools like our AI Presentation Maker (made for presenters by experts in presentation design).
Audience Engagement
Keeping the audience’s attention and interest throughout the presentation can be difficult. Distractions, disengaged attendees, or lack of interaction can pose challenges.
Technical Issues
Technology glitches, such as malfunctioning equipment, incompatible file formats, or poor internet connectivity, can disrupt presentations and increase stress.
Time Management
Striking the right balance between providing enough information and staying within time limits is a common challenge. Going over or under the allotted time can affect the effectiveness of the presentation.
Handling Questions and Challenges
Responding to unexpected questions, criticism, or challenges from the audience can be difficult, especially when presenters are unprepared or lack confidence in their subject matter.
Visual Aids and Technology
Creating and effectively using visual aids like slides or multimedia can be a struggle for some presenters. Technical competence is essential in this aspect.
Language and Articulation
Poor language skills or unclear articulation can hinder effective communication. Presenters may worry about stumbling over words or failing to convey their message clearly.
Maintaining appropriate and confident body language can be challenging. Avoiding nervous habits, maintaining eye contact, and using gestures effectively requires practice.
Overcoming Impersonal Delivery
In virtual presentations, maintaining a personal connection with the audience can be difficult. The absence of face-to-face interaction can make it challenging to engage and read the audience.
Cultural and Diversity Awareness
Presenting to diverse audiences requires sensitivity to cultural differences and varying levels of familiarity with the topic.
In this section, we gathered some tips on how to improve presentation skills that can certainly make an impact if applied to your presentation skills. We believe these skills can be cultivated to transform into habits for your work routine.
Tip #1: Build a narrative
One memorable way to guarantee presentation success is by writing a story of all the points you desire to cover. This statement is based on the logic behind storytelling and its power to connect with people .
Don’t waste time memorizing slides or reading your presentation to the audience. It feels unnatural, and any question that diverts from the topic in discussion certainly puts you in jeopardy or, worse, exposes you as a fraud in the eyes of the audience. And before you ask, it is really evident when a presenter has a memorized speech.
Build and rehearse the presentation as if telling a story to a group of interested people. Lower the language barrier by avoiding complex terms that maybe even you aren’t fully aware of their meaning. Consider the ramifications of that story, what it could lead to, and which are the opportunities to explore. Then, visualize yourself giving the presentation in a natural way.
Applying this technique makes the presentation feel like second nature to you. It broadens the spectrum in which you can show expertise over a topic or even build the basis for new interesting points of view about the project.
Tip #2: Don’t talk for more than 3 minutes per slide
It is a common practice of presenters to bombard the audience with facts and information whilst retaining the same slide on the screen. Why can this happen? It could be because the presenter condensed the talk into very few slides and preferred to talk. The reality is that your spectators won’t retain the information you are giving unless you give visual cues to help that process.
Opt to prepare more slides and pace your speech to match the topics shown on each slide. Don’t spend more than 3 minutes per slide unless you have to introduce a complex piece of data. Use visual cues to direct the spectators about what you talk about, and summarize the principal concepts discussed at the end of each section.
Tip #3: Practice meditation daily
Anxiety is the number one enemy of professional presenters. It slowly builds without you being aware of your doubts and can hinder your performance in multiple ways: making you feel paralyzed, fidgeting, making you forget language skills or concepts, affecting your health, etc.
Meditation is an ancient practice taken from Buddhist teachings that train your mind to be here in the present. We often see the concepts of meditation and mindfulness as synonyms, whereas you should be aware that meditation is a practice that sets the blocks to reach a state of mindfulness. For presenters, being in the here and now is essential to retain focus, but meditation techniques also teach us to control our breathing and be in touch with our body signals when stress builds up.
The customary practice of meditation has an impact on imagination and creativity but also helps to build patience – a skill much needed for connecting with your audience in instructional presentations.
Having the proper set of presentation skills can be quite subjective. It goes beyond presentation tips and deepens into how flexible we can be in our ability to communicate ideas.
Different presentations and different audiences shape the outcome of our efforts. Therefore, having a basic understanding of how to connect, raise awareness, and empathize with people can be key ingredients for your career as a presenter. A word of advice: success doesn’t happen overnight. It takes dedication and patience to build communication skills . Don’t condition your work to believe you will be ready “someday”; it’s best to practice and experience failure as part of the learning process.

Like this article? Please share
Business Presentations, Presentation Approaches, Presentation Skills Filed under Education
Related Articles

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • May 22nd, 2024
How to Translate Google Slides
Whereas Google Slides doesn’t allow to natively translate slides, such process is possible thanks to third-party add-ons. Learn how to translate Google Slides with this guide!
Filed under PowerPoint Tutorials • May 22nd, 2024
How to Rotate a Picture in PowerPoint
Sometimes, one has the perfect picture for a presentation that seems to be crooked or needs to be rotated to correct its alignment. At other moments, one might want to rotate an image to present a different perspective before an audience. Luckily, it would be best not to waste time using an image editor to […]

Filed under Design • May 22nd, 2024
Exploring the 12 Different Types of Slides in PowerPoint
Become a better presenter by harnessing the power of the 12 different types of slides in presentation design.
Leave a Reply
.css-1qrtm5m{display:block;margin-bottom:8px;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:14px;line-height:1.5714285714285714;-webkit-letter-spacing:-0.35px;-moz-letter-spacing:-0.35px;-ms-letter-spacing:-0.35px;letter-spacing:-0.35px;font-weight:300;color:#606F7B;}@media (min-width:600px){.css-1qrtm5m{font-size:16px;line-height:1.625;-webkit-letter-spacing:-0.5px;-moz-letter-spacing:-0.5px;-ms-letter-spacing:-0.5px;letter-spacing:-0.5px;}} Best Practices Become a better presenter -- with a little help from your friends
by TED Masterclass Team • May 12, 2020

Getting useful feedback can be a critical step in developing an effective presentation - it can also be harder to find than you might expect. Honest feedback calls on you to be vulnerable, and forces your feedback partner to sometimes deliver difficult constructive criticism. The good news is that this type of deep and authentic feedback can encourage personal growth and a willingness to take creative risks.
Get high-quality feedback that elevates your presentation skills by putting in a little extra preparation and focus.
First, decide who to ask for feedback
Feedback can feel personally risky if it’s coming from a close friend or colleague. Because these relationships are so important to us, honest feedback can end up feeling critical. In these situations, it can become tempting to give non-critical feedback, but that’s not helpful.
The person you work with to give you feedback should be someone:
- You want to learn from, who pushes you to think creatively
- With a different perspective - it can help to look beyond the people you spend a lot of time with personally or professionally
- Who shares your enthusiasm for acquiring new skills and is excited for you to become a better presenter
Then, prepare to receive feedback
Just as important as deciding who will be giving you feedback, is creating an environment and mindset where giving and receiving constructive feedback is easy.
- Create a distraction-free time and space for getting feedback. Ideally both of you should be present, focused, and open. If we’re feeling stressed or pressed for time, it’s hard to be a good feedback partner. That’s why it’s wise to tune in to how you’re feeling before you schedule a session.
- Remind the person that you’re looking for honest feedback to be the best presenter you can be.
- Before getting started, tell the person if there are any specific aspects of your idea or talk that you’d like them to focus feedback on.
Finally, ask the right questions
Giving feedback can be overwhelming for your partner if they don’t know what they should be focusing on. Decide on these areas ahead of time, and let your partner know. Then follow up with questions that will help them hone in on the most helpful feedback points for you.
Get overall feedback using these three questions:
- What works?
- What needs work?
- What’s a suggestion for one thing I might try?
Get specific feedback using these questions:
- Delivery: How is it landing for you overall? Are there places where your attention is wandering? What’s distracting?
- Content: Do you get this - will the audience? What questions do you have? Where are you engaged? Surprised? Moved? Is there a clear takeaway for the audience? Do you have any clarifying questions?
Good feedback is a gift that can really elevate your presentation skills. Make the most of your feedback opportunities with a little preparation.
© 2024 TED Conferences, LLC. All rights reserved. Please note that the TED Talks Usage policy does not apply to this content and is not subject to our creative commons license.
- Self Confidence
- Public Speaking
- Communication
Boost your self-confidence for quick thinking and adaptability.
Improve your public speaking for better communication., enhance your communication skills for stronger relationships..
- Communication Skills
LEARNER STORIES
- Kanhaiya Sharma
- Ashfaq Sorathia
- Prateek Chawla
OTHER TOOLS
- Comparative Analysis
Learner Stories
Other tools, featured blogs, top 10 best leadership development programs for corporates & management [2024], how to overcome fear of public speaking, how to improve communication skills in the workplace.
On This Page
Ever wondered what sets a great presentation apart? It’s more than just the words you use. Think about this, voice modulation, or how you say things, plays a substantial role at 38%. Your body language like hand gestures or eye contact, or how you carry yourself, takes a commanding lead at 55%.
Surprisingly, the content—the words you speak—only contributes 7% to a successful presentation. This interesting fact reveals that being an impressive presenter is like having a special recipe. It’s not just about what you say but how you present yourself.
In this blog, we’ll dive into the world of presentation skills, and here’s the exciting part—we’ll make the learning process enjoyable by exploring games and activities that can transform you into an outstanding communicator even in front of a large group. Let’s explore the elements that can make you a standout presenter on your professional journey!
Importance of Presentation Skills
In the professional world, the ability to deliver a compelling presentation goes beyond sharing information; it’s about creating a memorable impact on your audience.
Here’s why presentation skills are important:

1. Communication Mastery
Presentation skills are at the forefront of effective communication. It’s not just about what you say; it’s how you say it. A well-delivered presentation ensures your message is heard and understood, fostering clear and meaningful communication.
2. Professional Credibility
A skilled presenter commands professional credibility. The ability to articulate ideas with clarity and confidence instils trust and respect from colleagues, superiors, and stakeholders. Credibility is a cornerstone for career advancement and building strong professional relationships.
3. Influence and Persuasion
Presentations are powerful tools for influencing and persuading others. Whether pitching a proposal, leading a team meeting, or advocating for a project, effective presentation skills enable you to sway opinions, gain support, and drive initiatives forward.
4. Career Advancement
Professionals with polished presentation skills often find themselves on a fast track to career advancement. The capacity to deliver compelling presentations positions you as a valuable asset to the organisation, setting the stage for leadership roles.
5. Confidence Building
Mastering presentation skills significantly contributes to building confidence. The more skilled you become at presenting, the more confident you feel in expressing your ideas. Confidence is contagious and can inspire confidence in others, creating a positive and dynamic work culture.
Now that we understand the pivotal role presentation skills play in professional success, let’s dive into engaging activities that can serve as effective tools for improvement.
Activities To Enhance Presentation Skills
These activities go beyond traditional training methods, offering a dynamic and enjoyable way to refine your presentation prowess.
Explore the following activities to elevate your skills:
Activity 1: Pecha Kucha
Pecha Kucha is a unique presentation style that challenges individuals to communicate their message with precision and impact. Originating from Japan, the term “Pecha Kucha” translates to “chit-chat” in English, and the format was first introduced in 2003 by architects Astrid Klein and Mark Dytham . Here’s how Pecha Kucha works:

20 Slides, 20 Seconds Each:
Presenters create a slideshow with precisely 20 slides. The catch? Each slide is displayed for only 20 seconds. This strict time constraint adds an element of urgency, compelling presenters to deliver their message succinctly.
Concise and Focused Content
With only 20 seconds per slide, presenters must convey their content in the most essential and impactful points. This format discourages information overload and encourages a clear and focused presentation.
To excel in creating a Pecha Kucha presentation, consider the following tips:
Thematic Consistency: Maintain a consistent theme or message throughout your 20 slides to ensure coherence and a unified presentation.
Powerful Visuals: Prioritise impactful images, diagrams, or concise text on each slide to enhance the visual appeal and complement your spoken content.
Scripted Timing: Practise your presentation to synchronise with the 20-second time limit per slide. This ensures a smooth and well-timed delivery during the actual presentation.
Succinct Messaging: Craft concise and memorable messages for each slide, focusing on the main points to avoid overwhelming the formal audience with information.
Engaging Transitions: Plan smooth transitions between slides to keep the audience engaged. The rapid pace should feel natural and purposeful.
Feedback Seeking: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to gather insights on your Pecha Kucha presentation’s clarity, impact, and effectiveness.
Activity 2: Gush About Something You Don’t Like
In this unconventional activity, participants are tasked with passionately speaking about something they don’t like. The challenge lies in transforming a negative subject into a positive and engaging presentation.
The objective is not to dwell on criticism but to practise the art of constructive communication and find positive aspects even in seemingly unfavourable situations.

Key Elements of the Activity:
Positive Framing: Participants must employ positive framing, emphasising constructive aspects or potential solutions related to a disliked subject. This requires creative thinking and the ability to reframe perspectives.
Expressive Communication: The activity encourages a person to maintain a passionate and expressive tone while discussing a disliked topic. This helps develop spontaneity and enthusiasm, key elements of engaging communication.
Audience Engagement: Engaging the audience is crucial in this activity, which also acts as an ice breaker. Participants must capture attention by injecting humour or providing relatable anecdotes, ensuring the presentation remains interesting despite the negative subject.
Improvisation Skills: The unpredictability of this activity fosters improvisation skills. Participants must think on their feet, respond to potential audience questions or objections, and navigate the presentation with adaptability.
Benefits of Gushing About Something You Don’t Like:
Participating in this activity provides several benefits. It cultivates the ability to find positives in challenging situations, fostering a constructive mindset. Expressive communication skills are honed through the challenge of maintaining enthusiasm, even when discussing a disliked topic. Engaging the audience under these circumstances enhances overall presentation skills, and the fun exercise sharpens improvisation skills by navigating unexpected turns.
Ultimately, this activity transforms negativity into an opportunity for growth, allowing participants to develop a positive and adaptable approach to communication challenges.
Activity 3: Photo Story
The Photo Story storytelling activity is a creative and engaging way to enhance presentation skills by incorporating visual storytelling. Participants are tasked with creating a presentation using a series of carefully selected photos as visual aids.
Each image becomes a piece of the narrative puzzle, and the presenter must seamlessly articulate the story, connecting each photo to the overarching message.

Visual Narrative Building: Participants select a sequence of photos telling a story. The challenge is to ensure that each image contributes meaningfully to the narrative, creating a cohesive and interactive visual journey.
Storytelling Skills: The activity focuses on developing storytelling skills. Presenters must describe the images and weave them into a compelling story. This enhances the ability to convey messages in a narrative format, making presentations more memorable.
Emphasis on Visual Communication: Photo Story underscores the importance of visual communication. Participants learn to use visuals effectively, recognising the impact of images in conveying emotions, themes, and key points. This skill is transferable to other aspects of presentation design.
Audience Engagement through Imagery: Engaging the audience is achieved through the power of imagery. Participants must captivate their audience by explaining the significance of each photo, fostering a deeper connection between the audience and the presented content.
Benefits of Photo Story:
Engaging in the Photo Story activity yields numerous benefits. It enhances storytelling capabilities, making presentations more engaging and memorable. The emphasis on visual communication contributes to creating visually appealing presentations in various professional contexts.
Additionally, the activity cultivates the ability to structure information coherently and captivate audiences through compelling visuals and narrative elements.
Overall, Photo Story is a versatile tool that improves presentation skills and promotes creativity and effective visual communication.
Activity 4: 30 Seconds Without Filler Words
The “30 Seconds Without Filler Words” activity is a great exercise designed to enhance public speaking skills by promoting clarity, coherence, and the elimination of filler words. Participants are challenged to speak on a random topic for 30 seconds without using common filler words such as “um,” “uh,” or “like.”
This activity aims to sharpen communication skills, encourage mindful expression, and minimise distractions to create a more impactful and engaging presentation style.

Elimination of Filler Words: The primary focus is on eliminating filler words that often diminish a presentation’s impact. Participants are encouraged to speak fluently and confidently, avoiding unnecessary pauses or distractions.
Mindful Communication: The activity cultivates mindful communication by prompting participants to recognise their speech patterns. This heightened awareness contributes to more intentional expression.
Pacing and Time Management: Participants must effectively manage their time within the 30-second limit, emphasising the importance of pacing in public speaking. This skill is transferable to various presentation scenarios where time constraints are a factor.
Enhanced Message Impact: Presenters create a more polished and professional impression for the whole room by eliminating filler words. The message becomes clearer, and the overall impact of the presentation is heightened, contributing to a more effective communication style.
Benefits of 30 Seconds Without Filler Words:
Engaging in this activity yields several benefits. It fosters an awareness of speech patterns, enabling participants to identify and eliminate filler words from their presentations. The emphasis on fluent and coherent expression enhances overall public speaking skills along with nonverbal communication, making presentations more impactful and engaging.
Moreover, the activity instils valuable lessons in time management and pacing, crucial elements in delivering concise and effective presentations. Ultimately, “30 Seconds Without Filler Words” is a targeted exercise that empowers participants to refine their communication style and deliver presentations with increased clarity and confidence.
The Power of Presentation Skills Training
Starting a presentation skills training course is like discovering a secret weapon for professional success. A skilled trainer can guide you through the intricacies of effective communication, helping you harness the true power of your voice.
Practice speaking under the guidance of experts allows you to refine your delivery, build confidence, and captivate your audience with every presentation.
Most people may underestimate the impact of a well-delivered presentation, but with the right training, you can elevate your skills to new heights.
In a presentation skills training course, you’ll discover the art of engaging an audience through various mediums. A seasoned trainer will train you on different types of presentations, teaching you to adapt your approach based on the context and audience.
Whether you write a speech, deliver a pitch, or participate in a video conference, the course equips you with the skills to excel and make your presentation successful.
A great trainer understands that effective communication goes beyond words. They emphasise the importance of non-verbal cues, teaching you to read and respond to your audience in the session. For example, when you actively listen, you can tailor your presentation to address the specific interests of your audience, ensuring they not only listen but also relate to your message.
Good presentation involves understanding these two truths: the significance of non-verbal communication and the importance of audience engagement.
In presentation skills training, every session is an opportunity to refine your abilities and unlock your full potential as a communicator.
So, if you’re interested in making a lasting impression and mastering the art of persuasive communication, a presentation skills training course is your pathway to success, offering opportunities for public speaking activities and discussion.
By Rishabh Bhandari
Presentation skill appraisal comments: crafting self-assessment and performance evaluation, training for effective leadership: presentation skills for managers, enhancing personal impact: presentation skills and personality development.
Kapable © 2024
- TERMS OF USE
- PRIVACY POLICY
- Fast, Fluent & Structured Thinking
- Confident Communication and Public Speaking
- Leadership & Team Management
- Power Presentation & Storytelling
- Negotiation and Persuasion
- Influence and Charisma
Ideas and insights from Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning

Powerful and Effective Presentation Skills: More in Demand Now Than Ever

When we talk with our L&D colleagues from around the globe, we often hear that presentation skills training is one of the top opportunities they’re looking to provide their learners. And this holds true whether their learners are individual contributors, people managers, or senior leaders. This is not surprising.
Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way.
For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget, or explain a new product to a client or prospect. Or you may want to build support for a new idea, bring a new employee into the fold, or even just present your achievements to your manager during your performance review.
And now, with so many employees working from home or in hybrid mode, and business travel in decline, there’s a growing need to find new ways to make effective presentations when the audience may be fully virtual or a combination of in person and remote attendees.
Whether you’re making a standup presentation to a large live audience, or a sit-down one-on-one, whether you’re delivering your presentation face to face or virtually, solid presentation skills matter.
Even the most seasoned and accomplished presenters may need to fine-tune or update their skills. Expectations have changed over the last decade or so. Yesterday’s PowerPoint which primarily relied on bulleted points, broken up by the occasional clip-art image, won’t cut it with today’s audience.
The digital revolution has revolutionized the way people want to receive information. People expect presentations that are more visually interesting. They expect to see data, metrics that support assertions. And now, with so many previously in-person meetings occurring virtually, there’s an entirely new level of technical preparedness required.
The leadership development tools and the individual learning opportunities you’re providing should include presentation skills training that covers both the evergreen fundamentals and the up-to-date capabilities that can make or break a presentation.
So, just what should be included in solid presentation skills training? Here’s what I think.
The fundamentals will always apply When it comes to making a powerful and effective presentation, the fundamentals will always apply. You need to understand your objective. Is it strictly to convey information, so that your audience’s knowledge is increased? Is it to persuade your audience to take some action? Is it to convince people to support your idea? Once you understand what your objective is, you need to define your central message. There may be a lot of things you want to share with your audience during your presentation, but find – and stick with – the core, the most important point you want them to walk away with. And make sure that your message is clear and compelling.
You also need to tailor your presentation to your audience. Who are they and what might they be expecting? Say you’re giving a product pitch to a client. A technical team may be interested in a lot of nitty-gritty product detail. The business side will no doubt be more interested in what returns they can expect on their investment.
Another consideration is the setting: is this a formal presentation to a large audience with questions reserved for the end, or a presentation in a smaller setting where there’s the possibility for conversation throughout? Is your presentation virtual or in-person? To be delivered individually or as a group? What time of the day will you be speaking? Will there be others speaking before you and might that impact how your message will be received?
Once these fundamentals are established, you’re in building mode. What are the specific points you want to share that will help you best meet your objective and get across your core message? Now figure out how to convey those points in the clearest, most straightforward, and succinct way. This doesn’t mean that your presentation has to be a series of clipped bullet points. No one wants to sit through a presentation in which the presenter reads through what’s on the slide. You can get your points across using stories, fact, diagrams, videos, props, and other types of media.
Visual design matters While you don’t want to clutter up your presentation with too many visual elements that don’t serve your objective and can be distracting, using a variety of visual formats to convey your core message will make your presentation more memorable than slides filled with text. A couple of tips: avoid images that are cliched and overdone. Be careful not to mix up too many different types of images. If you’re using photos, stick with photos. If you’re using drawn images, keep the style consistent. When data are presented, stay consistent with colors and fonts from one type of chart to the next. Keep things clear and simple, using data to support key points without overwhelming your audience with too much information. And don’t assume that your audience is composed of statisticians (unless, of course, it is).
When presenting qualitative data, brief videos provide a way to engage your audience and create emotional connection and impact. Word clouds are another way to get qualitative data across.
Practice makes perfect You’ve pulled together a perfect presentation. But it likely won’t be perfect unless it’s well delivered. So don’t forget to practice your presentation ahead of time. Pro tip: record yourself as you practice out loud. This will force you to think through what you’re going to say for each element of your presentation. And watching your recording will help you identify your mistakes—such as fidgeting, using too many fillers (such as “umm,” or “like”), or speaking too fast.
A key element of your preparation should involve anticipating any technical difficulties. If you’ve embedded videos, make sure they work. If you’re presenting virtually, make sure that the lighting is good, and that your speaker and camera are working. Whether presenting in person or virtually, get there early enough to work out any technical glitches before your presentation is scheduled to begin. Few things are a bigger audience turn-off than sitting there watching the presenter struggle with the delivery mechanisms!
Finally, be kind to yourself. Despite thorough preparation and practice, sometimes, things go wrong, and you need to recover in the moment, adapt, and carry on. It’s unlikely that you’ll have caused any lasting damage and the important thing is to learn from your experience, so your next presentation is stronger.
How are you providing presentation skills training for your learners?
Manika Gandhi is Senior Learning Design Manager at Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning. Email her at [email protected] .
Let’s talk
Change isn’t easy, but we can help. Together we’ll create informed and inspired leaders ready to shape the future of your business.
© 2024 Harvard Business School Publishing. All rights reserved. Harvard Business Publishing is an affiliate of Harvard Business School.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Information
- Terms of Use
- About Harvard Business Publishing
- Higher Education
- Harvard Business Review
- Harvard Business School
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience. By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Cookie and Privacy Settings
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
Click on the different category headings to find out more. You can also change some of your preferences. Note that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our websites and the services we are able to offer.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refusing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
We also use different external services like Google Webfonts, Google Maps, and external Video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data like your IP address we allow you to block them here. Please be aware that this might heavily reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will take effect once you reload the page.
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Map Settings:
Google reCaptcha Settings:
Vimeo and Youtube video embeds:
You can read about our cookies and privacy settings in detail on our Privacy Policy Page.
📞 Call Now 800.403.6598 Contact Us - Get Started

No products in the cart.
Collecting Presentation Feedback to Improve Your Skills
Why is getting presentation feedback so important.
Collecting presentation feedback is probably low on your list of priorities, especially if you’re terrified of public speaking and not making a fool of yourself in front of a group of people is your biggest concern. But having some sort of response system in place so your audience can provide you with feedback on your presentation is an incredibly useful (not to mention inexpensive) way to improve your public speaking skills and become an even better presenter.
Why is getting presentation feedback so important?
For starters, when people provide you with feedback—even if it’s negative—you know they were paying attention. They were listening and watching, and by telling you what they thought of your presentation, they’re giving you input on your overall message, from what you said to how you said it .
That’s powerful information; it’s the best way for you to know if your presentation is doing what you want it to, whether that’s to inform, persuade, or motivate other people. Who better to tell you than the people in your audience?
Choose The Right Response System
Despite its usefulness, speakers continue to pass up the opportunity to poll audiences to get their feedback on a presentation. Certainly, no one wants to feel rejected or be told their presentation was terrible, but wouldn’t you rather be told your presentation missed the mark, than to continue delivering bad presentations that don’t engage audiences?
Not only that, but without presentation feedback, a speaker is forced to self-evaluate. Some will be overly-critical while others will be self-congratulatory—neither of which are beneficial or inspire the speaker to get better.
Offer a Presentation Feedback Form
In our Presentation Skills Training workshops, we talk about the importance of making a connection with the audience, and that connection doesn’t need to end with the presentation.
An immediate response system, such as providing your audience with a presentation feedback form to fill in and return at the end of the presentation is one way to gauge your performance. You can also encourage audience members to use other methods to provide feedback, such as directly to you through temp email , on social media, or online on Google or Yelp. This way, they’re not only helping you by rating your presentation, but their positive reviews will bolster your reputation, which will encourage others to work with you. And they’re staying connected with you beyond the presentation.
If the thought of having people “judge” your presentation frightens you, think about how getting positive feedback will make you feel. If you’re someone who lacks confidence or tends to be self-critical of your performance, hearing others tell you your presentation was inspiring or enjoyable can go a long way to helping you overcome your feelings of inadequacy.
Using Presentation Feedback to Achieve Your Goals
Whatever the situation that’s brought you to the podium—whether you’re a keynote speaker at a fundraiser or delivering a sales pitch—getting presentation feedback can be energizing. Consider how you feel when a manager or co-worker congratulates you on a job well done. You feel invigorated and motived to continue doing a good job that gets recognized.
The same is true of positive presentation feedback: When you know you’ve achieved your goal of connecting with an audience , you’re motivated to keep making those connections—and make them even better.
So what should your presentation feedback form (or other response system) look like? That’s up to you. But however you decide to collect presentation feedback, use the comments you receive to:
- Assess what you are doing well and where you need to improve
- Understand how your message is being received by others
- Direct you toward achieving your goals (e.g., increase your number of sales)
Not All Feedback is Bad
The term ‘feedback’ has earned a bad rap with some people. They hear it and run because they’re afraid someone will say something negative about them.
Not all feedback is negative, and not all of it is positive. But it should always be constructive, and as a public speaker you should want to hear it all. It’s the best way to know what your audience is getting from your presentation so you can improve your public speaking skills.
Do you provide opportunities for your audiences to give feedback? Tell us about it in the comment section or find us on social media and bring the conversation there. We’re on Facebook , Twitter , Google+ and LinkedIn .
16 Comments
I joined Toastmasters a year ago and have had some good feedback and some not so good. Some of the members were in my shoes, really not sure how to evaluate my presentations very well. Feedback is great but I guess it depends on the person giving the feedback.
Self evaluation is always hard to do. I’m a firm believer in having another person critique your work- it’s an opportunity to learn more about yourself!
Good post! I also had a bad feeling about the feedback until I read this post. I’ll be definitely using feedback form next time. I might still feel a bit uneasy, though.
I would like to get some professional feedback on my delivery. I think I will have someone video my presentation and send it to you guys to evaluate it.
I am a corporate trainer and give presentation feedback to our managers. Most of our folks really appreciate having good feedback so they can make their next presentations better.
Soliciting feedback is scary but necessary if you want to improve and I do…very scary though. Good article
Since I have written feedback forms for companies myself, I know how they work.But reading this blog set me thinking as to how it helps the presenter. I agree with the author that feedback, whether good or bad, definitely helps us in evaluating oneself.
Yes. I agree with everyone who says feedback can be scary-but it can also be helpful. The key is getting people to use constructive criticism. You are also going to have to get used to the occasional remarks from someone who is just being spiteful. Learn to recognize constructive criticism and take it to heart.
I used to take all feedback as negative. I wasn’t able to differentiate “bad” from “constructive”. This greatly hurt me in the workforce and I actually lost my first job fresh from college over it. I have come a long way but I am still learning and things like this help me a lot. Public speaking on any level has never been easy for me but I have always been way too hard on myself. I see that now.
I have never had anybody give me any feedback on my presentations.
One of the cardinal characters of people who want to succeed is the courage to accept valid criticism. Feedbacks must not be good but it is a necessity that will help to know if you rea making progress
Great feedback is absolutely essential to one’s ability to polish one’s skills even as an experienced speaker. Without it, we are unable to assess our strengths and growth opportunities along the way. Who wants to fall into a rut and never improve when called upon to speak? I would say no one which is why feedback is a must for both amateur and experienced speakers.
Good article. Very knowledgeable and informative. I would like to read new articles related to this! I Would also like you to read our articles related personality development and mental health.
Good article. Very knowledgeable and informative.
Your article provides helpful tips on how to collect feedback to improve our presentation skills.
good bro. Thx!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Special Offer! Get 25% off
Your exclusive code is ready! Copy it now!
DETROIT, JUNE 20-21 PUBLIC SPEAKING CLASS IS ALMOST FULL! RESERVE YOUR SPOT NOW

- Public Speaking Classes
- Corporate Presentation Training
- Online Public Speaking Course
- Northeast Region
- Midwest Region
- Southeast Region
- Central Region
- Western Region
- Presentation Skills
- 101 Public Speaking Tips
- Fear of Public Speaking
How to Collect Feedback on a Presentation

How, exactly do we collect feedback on a presentation? Are there ways to solicit feedback that will help us grow as speakers? The answer is, absolutely, YES! However, the way that you typically ask for feedback may not be the best way to gain confidence as a speaker. In fact, many traditional feedback techniques can actually make you more nervous. In addition, speakers will sometimes make adjustments to their delivery based on anecdotal issues. This can start a snowball effect that leads to terrible presentation skills.
A Funny Example of How Feedback Can Throw You Off Your Game.
A few years after I started The Leaders Institute ®, I was asked to be a keynote speaker at a quarterly meeting. The group loved my presentation so much, they hired me to come back in the next quarter as well. After the second speech, members of the group came to the front of the room and thanked me. They shook my hand and complimented me over and over. I felt really good about the presentation. The last woman to speak to me, though, was the founder of the association. She was long retired from the industry, but since she was the founder, she was still quite involved in the meetings. Just like the other attendees, she started with a nice compliment.
She said, “I really enjoyed your speech! The group had so much fun listening to you. Do you mind if I give you some critical feedback, though?”
I nodded, so she continued. “I’ve noticed that a few times during the speech, you ‘double-clutched.’ My Toastmasters group can probably help you with that.”
I smiled and thanked her for the feedback. However, I didn’t change anything that I was doing as a speaker as a result of the comment. There were over 100 people in the audience. Dozens of these people told me how great the presentation was. The group liked my delivery so much that they paid a fee for me to speak to them… TWICE. And, I got a single, anecdotal, comment to make a change. Most speakers would make a change because of the comment. I didn’t.
Traditional Ways to Collect Feedback on a Presentation
- Printed Exit Survey from the Audience

In the early days of our presentation skills class , we surveyed every graduate. I used the surveys as a way to measure instructor effectiveness.
Out of the blue, I got a phone call from a class member who wanted a partial tuition refund. When I asked him to clarify, he said, “Well, the instructor let us out of class 30 minutes early each day. I want a refund for the missed time.” It was a weird request, so I did some investigating.
I looked at past surveys from this guy’s instructor. The exit surveys for the instructor were all top-notch. I decided to set up an audit of this instructor’s next class. Turns out that the instructor wasn’t following our instructor guidelines. His class members weren’t getting the massive reduction in public speaking fear that we promised. However, they had no way of knowing this. They liked the instructor, so they gave him high marks on the surveys. The results they received were subpar, though.
- Collect Feedback on a Presentation from Friends or Coworkers

For instance, if a speaker talks faster when he/she is nervous, a friend might suggest to slow down. However, this is a symptom of nervousness. Slowing down will just make the person more conscious of the nervousness. So, the nervousness will likely show up in a multitude of additional symptoms.
An analogy for this would be if your “Check Engine” light comes on. You can crawl under the dashboard and snip the electric wire to the light. The light will go off. The problem with the engine will still be there.
It is better to ask these friends for more specific feedback. “Did what I say make sense?” or “Was what I said easy to understand?”
- Self-Criticism from Video Presentation Feedback
This final type of feedback is the most detrimental. We are our own worst critic. So, I would never encourage you to video yourself as a way to improve your presentation performance. You will knit-pick every negative thing that you see about yourself. When we conduct video feedback in our presentation seminars, we focus on the positive. If you focus on your natural strengths, you will grow as a speaker. If you focus on your weaknesses, they will grow.
How to Collect Feedback on a Presentation that Will Increase Your Presentation Skills
If you want better feedback on your presentation skills, here are a few that work every time!
- The Way Your Audience Reacts to You Is a Much Better Way to Judge Your Effectiveness

Are audience members on their cellphones? If so, you are likely less interesting to them than what they are looking at. You should change something.
Are people getting up and leaving the room. If so, you have likely spoken too long without giving them a break.
Are they looking at you and nodding when you speak? If so, you are probably doing really well. They are agreeing with you and paying attention.
- Visual Feedback from Friends or Coworkers.
Although the verbal feedback from friends and coworkers can throw you off, the visual feedback can be helpful. One of the tips we give folks in our classes is to practice your presentation with a partner. (We do this in our classes before most presentations.) As you run through your presentation with another person, you get to see how they react. When you say things that they understand, they nod in agreement. When you say something confusing, their facial expressions will change. This allows you to alter and adapt your delivery. If you practice alone, you don’t get this important feedback on a presentation.
- Get Feedback on a Presentation from a Professional Coach.
Eventually, you may get to a point where you want some professional help with presentations. Investing in a good presentation can be a wise decision. If you have a big presentation where a lot is on the line, feedback from an independent third-party can help.
This is the way that I began helping companies with “shortlist” presentations. A company in Houston had a series of high-level sales presentations which amounted to millions of dollars. They wanted someone outside of their company to help them deliver the best presentations possible. After helping them with a few of these, I got better and better as a coach. In fact, we went on a run where we won about 12 of these presentations in a row.
People who attend our presentation training classes often come for this type of coaching as well. They have a big presentation coming up and want to do their best. So a class can be a good way to get access to a professional coach without the expense of one-on-one coaching.
Good Feedback Helps You Improve. Bad Feedback Can Stunt Your Growth

Free Public Speaking Tips , Podcasts
View More Posts By Category: Free Public Speaking Tips | leadership tips | Online Courses | Past Fearless Presentations ® Classes | Podcasts | presentation skills | Uncategorized
How to Give Feedback on Presentation (Step by Step Guide)

Presentations can be a powerful tool to inform, persuade, or inspire. But let's be honest, they can also be nerve-wracking experiences. You pour your heart and soul into crafting the content, but the real test lies in how it resonates with your audience.
Did your message land? Were you able to communicate key points effectively? The answer often hinges on one crucial element: presentation feedback.
Here's the thing: Feedback isn't just about pointing out flaws. It's a double-edged sword that can elevate your presentation skills and drive you towards becoming a confident and impactful presenter.
Constructive feedback provides valuable insights that can help you refine your delivery, strengthen your content, and connect with your audience on a deeper level. Presentation feedback acts as a mirror, reflecting our strengths and weaknesses and empowering us to continuously hone our craft.
But how do you ensure you're giving and receiving feedback that's truly helpful? This blog will equip you with the tools to navigate the feedback process effectively.
Characteristics of Effective Feedback
Not all feedback is created equal. Effective feedback is a carefully crafted message that provides clear direction for improvement while fostering a positive learning environment.
Here are the key characteristics that define effective feedback on presentations:
(1) Specific
Ditch vague comments like "good job" or "it needs work" . Instead, pinpoint specific aspects of the presentation that were strong and areas where improvement is possible.
For example, "Instead of saying 'your slides were a bit crowded,' you could offer: 'The information on slide 5 seems overwhelming. Consider breaking it down into two slides or using bullet points to improve readability.'"
Another example of effective feedback might be: "The data you presented on target audience demographics was clear and well-organized (positive note).
However, consider briefly explaining how this data will be used to tailor the campaign message for different audience segments (actionable suggestion)."
(2) Actionable
Good feedback goes beyond simply identifying issues. It provides concrete suggestions for improvement.
Instead of saying, "Your body language seemed stiff," offer actionable advice like "Focusing on maintaining eye contact with different audience members can help project confidence and connect with the audience on a more personal level."
(3) Respectful
Remember, the goal is to provide constructive criticism, not tear someone down. Maintain a respectful and encouraging tone.
Phrase your feedback in a way that focuses on the presentation itself, not the presenter's personality.
(4) Future-Oriented
Effective feedback should be focused on something other than past mistakes. Frame your suggestions in a way that guides the presenter towards future presentations.
(5) Balanced
While constructive criticism is important, don't neglect to acknowledge the presenter's strengths.
A positive note at the beginning or end of your feedback can create a more receptive environment and reinforce positive behaviors.
Giving Feedback Like a Pro: A Step-By-Step Guide
So, you're ready to provide effective feedback on a presentation, but where do you begin?
This step-by-step guide will equip you with the tools to deliver clear, actionable feedback that is ultimately well-received.
Step 1: Preparation
Before diving headfirst into feedback, take a moment to familiarize yourself with the context of the presentation. Review the presentation material beforehand, focusing on the topic, objectives, and key messages the presenter aimed to convey.
Understanding the presenter's goals allows you to tailor your feedback for maximum impact.
Step 2: Active Observation
Shift your mindset from passive observer to active listener. Pay close attention to the presenter's delivery, both verbal and nonverbal.
This includes:
- Content: Is the information clear, concise, and well-organized? Does it effectively support the key points ?
- Delivery: Is the pace appropriate? Does the presenter use vocal variety to keep the audience engaged?
- Visual Aids: Are the slides visually appealing and easy to understand? Do they complement the spoken content or create distractions?
- Body Language: Does the presenter maintain good posture and eye contact with the audience? Does their body language convey confidence and enthusiasm?
Step 3: The Feedback Framework
Now for the heart of the matter: delivering your feedback!
Here's a framework to ensure your message is clear and constructive:
(1) Set the Stage
Briefly acknowledge the topic and objectives of the presentation. This helps the presenter understand the context within which you're providing feedback.
(2) Specificity is Crucial
Avoid vague comments. Instead, highlight specific aspects of the presentation that were effective and areas for improvement.
For example, "The opening story did a great job of grabbing the audience's attention (positive note). However, some of the technical terminology on the following slides might have been confusing for a non-specialist audience (actionable suggestion)."
(3) The Positive Sandwich
Frame your feedback with a positive note. Compliment the presenter on something they did well before offering constructive criticism. This creates a more receptive environment for feedback.
(4) Open-Ended Questions
Don't just tell; prompt discussion. Use open-ended questions to encourage the presenter to reflect on their delivery and explore potential improvements.
For example, "How did you feel the audience responded to that particular statistic?"
(5) Focus on the Future
Instead of dwelling on what went wrong, frame your feedback in a way that guides the presenter towards future presentations.
For example, "Consider adding a real-world example to illustrate that point for your next audience."
(6) Delivery Matters
Remember, even the most valuable feedback can fall flat if delivered poorly. Maintain a respectful and encouraging tone, and avoid accusatory language.
Focus on providing helpful suggestions for improvement.
(7) Consider the Audience
Tailoring your feedback to the audience can also be beneficial. If you're providing feedback to a colleague for a client presentation, your focus might be on the clarity and persuasiveness of the message.
For internal presentations, you might emphasize the organization and flow of the content.
Receiving Feedback Gracefully: A Practical Guide
So you've just delivered a presentation, and now comes the feedback.
While constructive criticism can feel daunting, it's actually a gift – a valuable opportunity to identify areas for improvement and elevate your presentation skills. But how do you ensure you receive feedback with grace and a growth mindset?
Here are some practical tips to help you navigate the process effectively:
(1) Maintain a Positive Attitude
It's natural to feel defensive when receiving feedback, especially if it's critical. However, resist the urge to get discouraged.
Remember, the goal is to learn and grow. Approach the feedback session with an open mind and a willingness to listen. Thank the person for their time and effort, and express your genuine interest in their insights.
(2) Active Listening is Key
Don't just hear the feedback; actively listen. Pay close attention to the specific points being raised. Ask clarifying questions if needed to ensure you fully understand the feedback.
Taking notes can also be helpful to remember key points for later reflection. If taking notes manually feels distracting and difficult, consider utilizing AI note-taking assistants like Wudpecker .
Wudpecker's AI features automatically transcribe meetings and generate summaries, capturing key points and decisions. This will free you from the burden of note-taking, allowing you to fully engage in the discussion.
(3) Separate Feedback from Emotion
It's easy to take feedback personally. However, try to separate the feedback from your own emotions.
Focus on the content of the message, not the delivery. Remember, the feedback is about the presentation, not you as a person.
(4) Identify Actionable Items
As you listen to the feedback, identify specific, actionable items you can work on to improve your future presentations.
This might involve refining your content structure, incorporating new visual aids, or practicing your delivery techniques.
(5) Don't Try to Defend Yourself
The urge to defend your choices is understandable but resist it. Instead, acknowledge the feedback and take time to process it later.
You can always ask follow-up questions for clarification, but avoid getting into a defensive debate.
(6) Express Gratitude
Thank the person for their feedback, regardless of whether it's positive or critical. Their willingness to share their insights is a valuable asset to your growth as a presenter.
(7) Reflect and Refine
Once you've received the feedback, take some time to reflect on it. Consider which points resonate most and identify areas where you can make improvements.
Develop a plan to incorporate the actionable items into your presentation skills development strategy.
Enhancing Presentation Skills Through Feedback
We've established that presentation feedback is a powerful tool for improvement. But how exactly can you leverage this feedback to enhance your presentation skills and become a more confident and impactful communicator?
Here are some ways to turn feedback into action:
Self-Evaluation and Targeted Feedback
Seeking feedback doesn't have to be a one-time event. Develop a habit of self-evaluation after each presentation. Consider areas where you felt strong and areas where you could improve.
Based on your self-assessment, identify specific aspects you'd like to get targeted feedback on from colleagues or mentors. This targeted approach allows you to delve deeper into specific skills and receive focused insights.
Embrace Diverse Feedback Sources
Don't limit yourself to feedback from just one or two people. Seek feedback from a diverse audience whenever possible.
This could include colleagues, managers, clients, or even friends and family who witnessed your presentation.
Each person will have a unique perspective, offering valuable insights into how your message resonated with different audience members.
Leverage Technology
Technology can be a powerful tool for gathering feedback. Consider using online feedback forms or survey tools to collect anonymous feedback from a wider audience.
You can also record your presentations and watch them back to identify areas for improvement in areas like pacing, body language, and vocal variety.
Practice Makes Progress
Once you've identified areas for improvement based on feedback, it's time to put that knowledge into action!
Practice your delivery with a focus on the specific skills you're working on.
Role-play with a colleague, record yourself practicing, or join a public speaking group to gain experience and refine your presentation style.
Consistency Is Key
Remember, presentation skills don't develop overnight. The key to becoming a confident and impactful presenter lies in consistent effort and dedication.
Integrate feedback into your ongoing development plan, actively seek opportunities to present, and continuously strive to refine your craft.
Presentations can be powerful tools for informing, persuading, and inspiring, but mastering the art of delivery takes dedication and continuous improvement.
This blog has equipped you with the knowledge to harness the power of presentation feedback. You've learned how to provide clear, actionable feedback that empowers presenters, and you've explored strategies for receiving feedback with grace and a growth mindset.
Remember, the journey to becoming a captivating presenter is an ongoing process. Embrace the power of feedback, actively seek opportunities to practice, and never stop refining your skills.
By consistently seeking improvement, you'll transform those nervous presentation jitters into the confidence and clarity needed to deliver truly impactful presentations that resonate with any audience.
What Is an Example of Feedback on a Presentation?
Scenario: You listened to a presentation on the benefits of switching to a new project management software.
Here's how you could provide constructive feedback:
Positive Aspects:
- Clear Introduction: "The introduction did a great job of grabbing the audience's attention by highlighting the common pain points associated with traditional project management methods. It effectively set the stage for the presentation."
Areas for Improvement:
- Visual Aids: "The slides felt a bit text-heavy at times. Consider incorporating more visuals like charts, graphs, or even screenshots to illustrate the features and benefits of the new software."
- Content Depth: "While you covered the key features of the software, it might be beneficial to delve deeper into how it addresses specific challenges faced by different user groups within the company (e.g., project managers vs. team members)."
Actionable Suggestions:
- "For your next presentation, you could try including a short demo of the software in action to showcase its user-friendliness."
- "Consider adding a slide that compares the new software to existing options, highlighting its unique advantages."
How Do You Comment on a Good Presentation?
Here are some ways to comment on a good presentation:
Highlight Specific Strengths:
- Content: "The information you presented was clear, concise, and well-organized. It was easy to follow and understand." (focuses on clarity and structure)
- Oral Presentation: "You delivered the presentation with great enthusiasm and confidence. Your use of vocal variety kept the audience engaged." (highlights delivery skills)
- Visual Aids: "The slides were visually appealing and effectively complemented your spoken points. They were easy to read and understand." (focuses on visuals)
- Structure: "The flow of the presentation was logical and well-paced. You transitioned smoothly between topics and kept the audience engaged throughout." (highlights structure and audience engagement)
Focus on Impact:
- "Your presentation was very informative and insightful. I learned a lot about [topic]."
- "You did a great job capturing the audience's attention and keeping them engaged throughout the presentation."
- "Your presentation was well-organized and easy to follow. I felt like I had a clear understanding of the key points."
- "I particularly enjoyed [specific aspect of the presentation, e.g., the real-world example you used, the humor you incorporated]."
Positive and Encouraging Tone:
- "Overall, it was a very impressive presentation. Well done!"
- "I can tell you put a lot of effort into this presentation, and it showed. Great job!"
- "Thank you for sharing your insights with us. It was a very informative presentation."
- "I look forward to seeing more presentations from you in the future."
- Be genuine and specific in your compliments. Make sure you are giving constructive feedback.
- Tailor your comments to the presenter and the presentation content.
- Focus on both the delivery and the content itself.
- End with a positive feedback and encouraging note.
How Do You Give Peer Feedback to a Presentation?
Here are some things to keep in mind when giving peer feedback on presentation:
Before the Feedback:
- Preparation: Review the presentation topic and objectives beforehand (if available) to understand the presenter's goals.
- Mindset: Approach the feedback with a positive and helpful attitude.
Delivering the Feedback:
- Start Positive: Start by acknowledging the presenter's effort and highlighting your observed strength.
- Specificity is Key: Focus on specific aspects of the presentation, both positive and areas for improvement. Avoid vague comments.
- Actionable Suggestions: Don't just point out problems; offer suggestions for improvement. Use "I" statements to frame your feedback (e.g., "I found the opening story engaging. Perhaps adding a visual element could enhance it further").
- Respectful Tone: Maintain a respectful and encouraging tone throughout the feedback session.
- Focus on the Future: Frame your suggestions in a way that guides the presenter towards future presentations.
- Open-Ended Questions: Consider asking open-ended questions to encourage discussion and reflection (e.g., "How did you feel the audience responded to that statistic?").
Here’s an Example of How You Might Structure Your Feedback:
"Thanks for the presentation, [presenter's name]. I really enjoyed the way you [positive aspect, e.g., explained the technical details clearly and concisely]. I noticed that [area for improvement, e.g., some of the slides seemed text-heavy]. Perhaps you could consider [actionable suggestion, e.g., using bullet points or visuals to break up the text]."
Additional Tips for Constructive Feedback:
- Tailor Your Feedback: Consider the audience and purpose of the presentation when providing feedback.
- Be Mindful of Time: Keep your feedback concise and focused on the most important points.
- Offer to Help: If you have specific skills or resources that could benefit the presenter, offer your help.
- Welcome Questions: Encourage the presenter to ask clarifying questions or seek further feedback.
How to Get a Meeting Summary with Zoom IQ (4 Steps)
.png)
27 Must-Ask Client Interview Questions for Building Strong Relationships (With Examples)
.png)
How to Run a Weekly Touch Base Meeting (+ Template)

6 Leadership Communication Styles for Team Success [With Examples]

10 Project Meetings to Prepare Your Project Management Team

How to Have a Successful Touchpoint Meeting (Tips for Manager)

How to Record Teams Meeting as a Participant

How to Make Your Meetings Inclusive

How to Draft a Perfect Pre-Meeting Email Template

Agenda Approval During Board Meetings and How to Do It Right
.png)
How to Write the Notice of Meeting (With Template)

16 Best Cold Call Opening Lines for Sales Reps
How to Run a Project Premortem in 6 Steps

12 Creative Agenda Templates for Common Team Meetings
.png)
How to Draft a Winning Post-Sales Handoff (With Template)
Sign up for wudpecker. it's free..
Join professionals and teams supercharging their productivity with Wudpecker.
How to Give Effective Presentation Feedback
A conversation with sam j. lubner, md, facp.
Giving an effective scientific presentation, like all public speaking, is an acquired skill that takes practice to perfect. When delivered successfully, an oral presentation can be an invaluable opportunity to showcase your latest research results among your colleagues and peers. It can also promote attendee engagement and help audience members retain the information being presented, enhancing the educational benefit of your talk, according to Sam J. Lubner, MD, FACP , Associate Professor of Medicine and Program Director, Hematology-Oncology Fellowship, at the University of Wisconsin Carbone Cancer Center, and a member of ASCO’s Education Council.

Sam J. Lubner, MD, FACP
In 2019, the Education Council launched a pilot program to provide a group of selected speakers at the ASCO Annual Meeting with feedback on their presentations. Although some of the reviewers, which included members of the Education Council and Education Scholars Program, as well as ASCO’s program directors, conveyed information to the presenters that was goal-referenced, tangible, transparent, actionable, specific, and personalized—the hallmarks of effective feedback—others provided comments that were too vague to improve the speaker’s performance, said Dr. Lubner. For example, they offered comments such as “Great session” or “Your slides were too complicated,” without being specific about what made the session “great” or the slides “too complicated.”
“Giving a presentation at a scientific meeting is different from what we were trained to do. We’re trained to take care of patients, and while we do have some training in presentation, it usually centers around how to deliver clinical information,” said Dr. Lubner. “What we are trying to do with the Education Council’s presentation feedback project is to apply evidence-based methods for giving effective feedback to make presentations at ASCO’s Annual Meeting, international meetings, symposia, and conferences more clinically relevant and educationally beneficial.”
GUEST EDITOR
The ASCO Post talked with Dr. Lubner about how to give effective feedback and how to become a more effective presenter.
Defining Effective Feedback
Feedback is often confused with giving advice, praise, and evaluation, but none of these descriptions are exactly accurate. What constitutes effective feedback?
When I was looking over the literature on feedback to prepare myself on how to give effective feedback to the medical students and residents I oversee, I was amazed to find the information is largely outdated. For example, recommendations in the 1980s and 1990s called for employing the “sandwich” feedback method, which involves saying something positive, then saying what needs to be improved, and then making another positive remark. But that method is time-intensive, and it feels disingenuous to me.
What constitutes helpful feedback to me is information that is goal-referenced, actionable, specific, and has immediate impact. It should be constructive, descriptive, and nonjudgmental. After I give feedback to a student or resident, my next comments often start with a self-reflective question, “How did that go?” and that opens the door to further discussion. The mnemonic I use to provide better feedback and achieve learning goals is SMART: specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and timely, as described here:
- Specific: Avoid using ambiguous language, for example, “Your presentation was great.” Be specific about what made the presentation “great,” such as, “Starting your presentation off with a provocative question grabbed my attention.”
- Measurable: Suggest quantifiable objectives to meet so there is no uncertainty about what the goals are. For example, “Next time, try a summary slide with one or two take-home points for the audience.”
- Achievable: The goal of the presentation should be attainable. For example, “Trim your slides to no more than six lines per slide and no more than six words per line; otherwise, you are just reading your slides.”
- Realistic: The feedback you give should relate to the goal the presenter is trying to achieve. For example, “Relating the research results back to an initial case presentation will solidify the take-home point that for cancer x, treatment y is the best choice.”
- Timely: Feedback given directly after completion of the presentation is more effective than feedback provided at a later date.
The ultimate goal of effective feedback is to help the presenter become more adept at relaying his or her research in an engaging and concise way, to maintain the audience’s attention and ensure that they retain the information presented.
“Giving a presentation at a scientific meeting is different from what we were trained to do.” — Sam J. Lubner, MD, FACP Tweet this quote
Honing Your Communication Skills
What are some specific tips on how to give effective feedback?
There are five tips that immediately come to mind: (1) focus on description rather than judgment; (2) focus on observation rather than inference; (3) focus on observable behaviors; (4) share both positive and constructive specific points of feedback with the presenter; and (5) focus on the most important points to improve future presentations.
Becoming a Proficient Presenter
How can ASCO faculty become more proficient at delivering their research at the Annual Meeting and at ASCO’s thematic meetings?
ASCO has published faculty guidelines and best practices to help speakers immediately involve an audience in their presentation and hold their attention throughout the talk. They include the following recommendations:
- Be engaging. Include content that will grab the audience’s attention early. For example, interesting facts, images, or a short video to hold the audience’s focus.
- Be cohesive and concise. When preparing slides, make sure the presentation has a clear and logical flow to it, from the introduction to its conclusion. Establish key points and clearly define their importance and impact in a concise, digestible manner.
- Include take-home points. Speakers should briefly summarize key findings from their research and ensure that their conclusion is fully supported by the data in their presentation. If possible, they should provide recommendations or actions to help solidify their message. Thinking about and answering this question—if the audience remembers one thing from my presentation, what do I want it to be?—will help speakers focus their presentation.
- When it comes to slide design, remember, less is more. It’s imperative to keep slides simple to make an impact on the audience.
Another method to keep the audience engaged and enhance the educational benefit of the talk is to use the Think-Pair ( ± Share) strategy, by which the speaker asks attendees to think through questions using two to three steps. They include:
- Think independently about the question that has been posed, forming ideas.
- Pair to discuss thoughts, allowing learners to articulate their ideas and to consider those of others.
- Share (as a pair) the ideas with the larger group.
The value of this exercise is that it helps participants retain the information presented, encourages individual participation, and refines ideas and knowledge through collaboration.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR SLIDE DESIGN
- Have a single point per line.
- Use < 6 words per line.
- Use < 6 lines per slide.
- Use < 30 characters per slide.
- Use simple words.
- When using tables, maintain a maximum of 6 rows and 6 columns.
- Avoid busy graphics or tables. If you find yourself apologizing to the audience because your slide is too busy, it’s a bad slide and should not be included in the presentation.
- Use cues, not full thoughts, to make your point.
- Keep to one slide per minute as a guide to the length of the presentation.
- Include summary/take-home points per concept. We are all physicians who care about our patients and believe in adhering to good science. Highlight the information you want the audience to take away from your presentation and how that information applies to excellent patient care.
Speakers should also avoid using shorthand communication or dehumanizing language when describing research results. For example, do not refer to patients as a disease: “The study included 250 EGFR mutants.” Say instead, “The study included 250 patients with EGFR -mutant tumors.” And do not use language that appears to blame patients when their cancer progresses after treatment, such as, “Six patients failed to respond to [study drug].” Instead say, “Six patients had tumors that did not respond to [study drug].”
We all have respect for our patients, families, and colleagues, but sometimes our language doesn’t reflect that level of respect, and we need to be more careful and precise in the language we use when talking with our patients and our colleagues.
ASCO has developed a document titled “The Language of Respect” to provide guidance on appropriate respectful language to use when talking with patients, family members, or other health-care providers and when giving presentations at the Annual Meeting and other ASCO symposia. Presenters should keep these critical points in mind and put them into practice when delivering research data at these meetings. ■
DISCLOSURE: Dr. Lubner has been employed by Farcast Biosciences and has held a leadership role at Farcast Biosciences.
Osimertinib for Patients With Locally Advanced EGFR-Mutated NSCLC A New Standard of Care
Perioperative chemotherapy vs neoadjuvant chemoradiation in esophageal cancer, consolidation therapy with durvalumab for limited-stage sclc, t-dxd improves progression-free survival in patients with breast cancer previously treated with endocrine therapy, telehealth shown to be effective for palliative care delivery in patients with advanced lung cancer.

- Editorial Board
- Advertising
- Disclosures
- Privacy Policy

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
6 presentation skills and how to improve them

Jump to section
What are presentation skills?
The importance of presentation skills, 6 presentation skills examples, how to improve presentation skills.
Tips for dealing with presentation anxiety
Learn how to captivate an audience with ease
Capturing an audience’s attention takes practice.
Over time, great presenters learn how to organize their speeches and captivate an audience from start to finish. They spark curiosity, know how to read a room , and understand what their audience needs to walk away feeling like they learned something valuable.
Regardless of your profession, you most likely use presentation skills on a monthly or even weekly basis. Maybe you lead brainstorming sessions or host client calls.
Developing effective presentation skills makes it easier to contribute ideas with confidence and show others you’re someone to trust. Although speaking in front of a crowd sometimes brings nerves and anxiety , it also sparks new opportunities.
Presentation skills are the qualities and abilities you need to communicate ideas effectively and deliver a compelling speech. They influence how you structure a presentation and how an audience receives it. Understanding body language , creating impactful visual aids, and projecting your voice all fall under this umbrella.
A great presentation depends on more than what you say. It’s about how you say it. Storytelling , stage presence, and voice projection all shape how well you express your ideas and connect with the audience. These skills do take practice, but they’re worth developing — especially if public speaking makes you nervous.
Engaging a crowd isn’t easy. You may feel anxious to step in front of an audience and have all eyes and ears on you.
But feeling that anxiety doesn’t mean your ideas aren’t worth sharing. Whether you’re giving an inspiring speech or delivering a monthly recap at work, your audience is there to listen to you. Harness that nervous energy and turn it into progress.
Strong presentation skills make it easier to convey your thoughts to audiences of all sizes. They can help you tell a compelling story, convince people of a pitch , or teach a group something entirely new to them. And when it comes to the workplace, the strength of your presentation skills could play a part in getting a promotion or contributing to a new initiative.
To fully understand the impact these skills have on creating a successful presentation, it’s helpful to look at each one individually. Here are six valuable skills you can develop:
1. Active listening
Active listening is an excellent communication skill for any professional to hone. When you have strong active listening skills, you can listen to others effectively and observe their nonverbal cues . This helps you assess whether or not your audience members are engaged in and understand what you’re sharing.
Great public speakers use active listening to assess the audience’s reactions and adjust their speech if they find it lacks impact. Signs like slouching, negative facial expressions, and roaming eye contact are all signs to watch out for when giving a presentation.
2. Body language
If you’re researching presentation skills, chances are you’ve already watched a few notable speeches like TED Talks or industry seminars. And one thing you probably noticed is that speakers can capture attention with their body language.
A mixture of eye contact, hand gestures , and purposeful pacing makes a presentation more interesting and engaging. If you stand in one spot and don’t move your body, the audience might zone out.

3. Stage presence
A great stage presence looks different for everyone. A comedian might aim for more movement and excitement, and a conference speaker might focus their energy on the content of their speech. Although neither is better than the other, both understand their strengths and their audience’s needs.
Developing a stage presence involves finding your own unique communication style . Lean into your strengths, whether that’s adding an injection of humor or asking questions to make it interactive . To give a great presentation, you might even incorporate relevant props or presentation slides.
4. Storytelling
According to Forbes, audiences typically pay attention for about 10 minutes before tuning out . But you can lengthen their attention span by offering a presentation that interests them for longer. Include a narrative they’ll want to listen to, and tell a story as you go along.
Shaping your content to follow a clear narrative can spark your audience’s curiosity and entice them to pay careful attention. You can use anecdotes from your personal or professional life that take your audience along through relevant moments. If you’re pitching a product, you can start with a problem and lead your audience through the stages of how your product provides a solution.
5. Voice projection
Although this skill may be obvious, you need your audience to hear what you’re saying. This can be challenging if you’re naturally soft-spoken and struggle to project your voice.
Remember to straighten your posture and take deep breaths before speaking, which will help you speak louder and fill the room. If you’re talking into a microphone or participating in a virtual meeting, you can use your regular conversational voice, but you still want to sound confident and self-assured with a strong tone.
If you’re unsure whether everyone can hear you, you can always ask the audience at the beginning of your speech and wait for confirmation. That way, they won’t have to potentially interrupt you later.
Ensuring everyone can hear you also includes your speed and annunciation. It’s easy to speak quickly when nervous, but try to slow down and pronounce every word. Mumbling can make your presentation difficult to understand and pay attention to.

6. Verbal communication
Although verbal communication involves your projection and tone, it also covers the language and pacing you use to get your point across. This includes where you choose to place pauses in your speech or the tone you use to emphasize important ideas.
If you’re giving a presentation on collaboration in the workplace , you might start your speech by saying, “There’s something every workplace needs to succeed: teamwork.” By placing emphasis on the word “ teamwork ,” you give your audience a hint on what ideas will follow.
To further connect with your audience through diction, pay careful attention to who you’re speaking to. The way you talk to your colleagues might be different from how you speak to a group of superiors, even if you’re discussing the same subject. You might use more humor and a conversational tone for the former and more serious, formal diction for the latter.
Everyone has strengths and weaknesses when it comes to presenting. Maybe you’re confident in your use of body language, but your voice projection needs work. Maybe you’re a great storyteller in small group settings, but need to work on your stage presence in front of larger crowds.
The first step to improving presentation skills is pinpointing your gaps and determining which qualities to build upon first. Here are four tips for enhancing your presentation skills:
1. Build self-confidence
Confident people know how to speak with authority and share their ideas. Although feeling good about your presentation skills is easier said than done, building confidence is key to helping your audience believe in what you’re saying. Try practicing positive self-talk and continuously researching your topic's ins and outs.
If you don’t feel confident on the inside, fake it until you make it. Stand up straight, project your voice, and try your best to appear engaged and excited. Chances are, the audience doesn’t know you’re unsure of your skills — and they don’t need to.
Another tip is to lean into your slideshow, if you’re using one. Create something colorful and interesting so the audience’s eyes fall there instead of on you. And when you feel proud of your slideshow, you’ll be more eager to share it with others, bringing more energy to your presentation.
2. Watch other presentations
Developing the soft skills necessary for a good presentation can be challenging without seeing them in action. Watch as many as possible to become more familiar with public speaking skills and what makes a great presentation. You could attend events with keynote speakers or view past speeches on similar topics online.
Take a close look at how those presenters use verbal communication and body language to engage their audiences. Grab a notebook and jot down what you enjoyed and your main takeaways. Try to recall the techniques they used to emphasize their main points, whether they used pauses effectively, had interesting visual aids, or told a fascinating story.

3. Get in front of a crowd
You don’t need a large auditorium to practice public speaking. There are dozens of other ways to feel confident and develop good presentation skills.
If you’re a natural comedian, consider joining a small stand-up comedy club. If you’re an avid writer, participate in a public poetry reading. Even music and acting can help you feel more comfortable in front of a crowd.
If you’d rather keep it professional, you can still work on your presentation skills in the office. Challenge yourself to participate at least once in every team meeting, or plan and present a project to become more comfortable vocalizing your ideas. You could also speak to your manager about opportunities that flex your public speaking abilities.
4. Overcome fear
Many people experience feelings of fear before presenting in front of an audience, whether those feelings appear as a few butterflies or more severe anxiety. Try grounding yourself to shift your focus to the present moment. If you’re stuck dwelling on previous experiences that didn’t go well, use those mistakes as learning experiences and focus on what you can improve to do better in the future.
Tips for dealing with presentation anxiety
It’s normal to feel nervous when sharing your ideas. In fact, according to a report from the Journal of Graduate Medical Education, public speaking anxiety is prevalent in 15–30% of the general population .
Even though having a fear of public speaking is common, it doesn’t make it easier. You might feel overwhelmed, become stiff, and forget what you were going to say. But although the moment might scare you, there are ways to overcome the fear and put mind over matter.
Use these tactics to reduce your stress when you have to make a presentation:
1. Practice breathing techniques
If you experience anxiety often, you’re probably familiar with breathing techniques for stress relief . Incorporating these exercises into your daily routine can help you stop worrying and regulate anxious feelings.
Before a big presentation, take a moment alone to practice breathing techniques, ground yourself, and reduce tension. It’s also a good idea to take breaths throughout the presentation to speak slower and calm yourself down .
2. Get organized
The more organized you are, the more prepared you’ll feel. Carefully outline all of the critical information you want to use in your presentation, including your main talking points and visual aids, so you don’t forget anything. Use bullet points and visuals on each slide to remind you of what you want to talk about, and create handheld notes to help you stay on track.
3. Embrace moments of silence
It’s okay to lose your train of thought. It happens to even the most experienced public speakers once in a while. If your mind goes blank, don’t panic. Take a moment to breathe, gather your thoughts, and refer to your notes to see where you left off. You can drink some water or make a quick joke to ease the silence or regain your footing. And it’s okay to say, “Give me a moment while I find my notes.” Chances are, people understand the position you’re in.

4. Practice makes progress
Before presenting, rehearse in front of friends and family members you trust. This gives you the chance to work out any weak spots in your speech and become comfortable communicating out loud. If you want to go the extra mile, ask your makeshift audience to ask a surprise question. This tests your on-the-spot thinking and will prove that you can keep cool when things come up.
Whether you’re new to public speaking or are a seasoned presenter, you’re bound to make a few slip-ups. It happens to everyone. The most important thing is that you try your best, brush things off, and work on improving your skills to do better in your next presentation.
Although your job may require a different level of public speaking than your favorite TED Talk , developing presentation skills is handy in any profession. You can use presentation skills in a wide range of tasks in the workplace, whether you’re sharing your ideas with colleagues, expressing concerns to higher-ups, or pitching strategies to potential clients.
Remember to use active listening to read the room and engage your audience with an interesting narrative. Don’t forget to step outside your comfort zone once in a while and put your skills to practice in front of a crowd. After facing your fears, you’ll feel confident enough to put presentation skills on your resume.
If you’re trying to build your skills and become a better employee overall, try a communications coach with BetterUp.
Elevate your communication skills
Unlock the power of clear and persuasive communication. Our coaches can guide you to build strong relationships and succeed in both personal and professional life.
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
The 11 tips that will improve your public speaking skills
The importance of good speech: 5 tips to be more articulate, learn types of gestures and their meanings to improve your communication, what’s my earning potential determining the right salary, why it's good to have a bff at work and how to find one, why is there a labor shortage 5 ways it could impact you, what is a career path definition, examples, and steps for paving yours, why we need to reframe potential into readiness, member story: developing communication skills and owning the spotlight, similar articles, how to write a speech that your audience remembers, 8 tip to improve your public speaking skills, 30 presentation feedback examples, your guide to what storytelling is and how to be a good storyteller, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, 8 clever hooks for presentations (with tips), how to make a presentation interactive and exciting, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences

Evaluating Business Presentations: A Six Point Presenter Skills Assessment Checklist
Posted by Belinda Huckle | On April 18, 2024 | In Presentation Training, Tips & Advice
In this Article...quick links
For many business people, speaking in front of clients, customers, their bosses or even their own large team is not a skill that comes naturally. So it’s likely that within your organisation, and indeed within your own team, you’ll find varying levels of presenting ability. Without an objective way to assess the presenter skills needed to make a good presentation, convincing someone that presentation coaching could enhance their job performance (benefiting your business), boost their promotion prospects (benefiting their career) and significantly increase their self confidence (benefiting their broader life choices) becomes more challenging.

So, how do you evaluate the presenting skills of your people to find out, objectively, where the skill gaps lie? Well, you work out your presentation skills evaluation criteria and then measure/assess your people against them.
To help you, in this article we’re sharing the six crucial questions we believe you need to ask to not only make a professional assessment of your people’s presenting skills, but to showcase what makes a great presentation. We use them in our six-point Presenter Skills Assessment checklist ( which we’re giving away as a free download at the end of this blog post ). The answers to these questions will allow you to identify the presenter skills strengths and weaknesses (i.e. skills development opportunities) of anyone in your team or organisation, from the Managing Director down. You can then put presenter skills training or coaching in place so that everyone who needs it can learn the skills to deliver business presentations face-to-face, or online with confidence, impact and purpose.
Read on to discover what makes a great presentation and how to evaluate a presenter using our six-point Presenter Skills Assessment criteria so you can make a professional judgement of your people’s presenting skills.
1. Ability to analyse an audience effectively and tailor the message accordingly
If you ask most people what makes a great presentation, they will likely comment on tangible things like structure, content, delivery and slides. While these are all critical aspects of a great presentation, a more fundamental and crucial part is often overlooked – understanding your audience . So, when you watch people in your organisation or team present, look for clues to see whether they really understand their audience and the particular situation they are currently in, such as:
- Is their content tight, tailored and relevant, or just generic?
- Is the information pitched at the right level?
- Is there a clear ‘What’s In It For Them’?
- Are they using language and terminology that reflects how their audience talk?
- Have they addressed all of the pain points adequately?
- Is the audience focused and engaged, or do they seem distracted?
For your people, getting to know their audience, and more importantly, understanding them, should always be the first step in pulling together a presentation. Comprehending the challenges, existing knowledge and level of detail the audience expects lays the foundation of a winning presentation. From there, the content can be structured to get the presenter’s message across in the most persuasive way, and the delivery tuned to best engage those listening.
2. Ability to develop a clear, well-structured presentation/pitch that is compelling and persuasive

Flow and structure are both important elements in a presentation as both impact the effectiveness of the message and are essential components in understanding what makes a good presentation and what makes a good speech. When analysing this aspect of your people’s presentations look for a clear, easy to follow agenda, and related narrative, which is logical and persuasive.
Things to look for include:
- Did the presentation ‘tell a story’ with a clear purpose at the start, defined chapters throughout and a strong close?
- Were transitions smooth between the ‘chapters’ of the presentation?
- Were visual aids, handouts or audience involvement techniques used where needed?
- Were the challenges, solutions and potential risks of any argument defined clearly for the audience?
- Were the benefits and potential ROI quantified/explained thoroughly?
- Did the presentation end with a clear destination/call to action or the next steps?
For the message to stick and the audience to walk away with relevant information they are willing to act on, the presentation should flow seamlessly through each part, building momentum and interest along the way. If not, the information can lose impact and the presentation its direction. Then the audience may not feel equipped, inspired or compelled to implement the takeaways.
3. Ability to connect with and maintain the engagement of the audience
Connecting with your audience and keeping them engaged throughout can really be the difference between giving a great presentation and one that falls flat. This is no easy feat but is certainly a skill that can be learned. To do it well, your team need a good understanding of the audience (as mentioned above) to ensure the content is on target. Ask yourself, did they cover what’s relevant and leave out what isn’t?
Delivery is important here too. This includes being able to build a natural rapport with the audience, speaking in a confident, conversational tone, and using expressive vocals, body language and gestures to bring the message to life. On top of this, the slides need to be clear, engaging and add interest to the narrative. Which leads us to point 4…
4. Ability to prepare effective slides that support and strengthen the clarity of the message
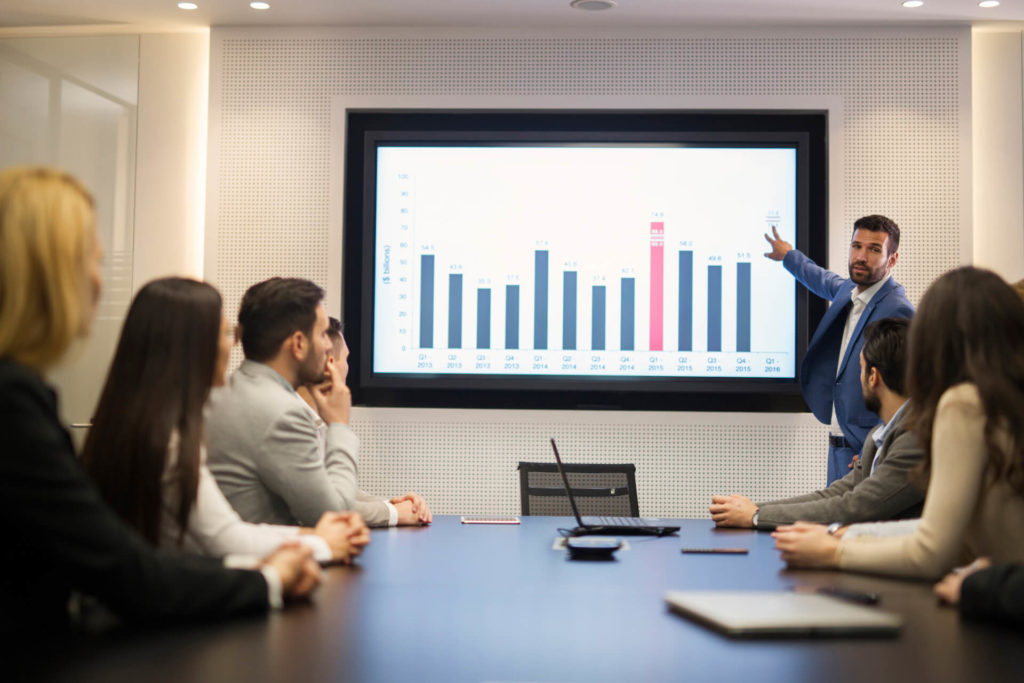

It’s not uncommon for slides to be used first and foremost as visual prompts for the speaker. While they can be used for this purpose, the first priority of a slide (or any visual aid) should always be to support and strengthen the clarity of the message. For example, in the case of complex topics, slides should be used to visualise data , reinforcing and amplifying your message. This ensures that your slides are used to aid understanding, rather than merely prompting the speaker.
The main problem we see with people’s slides is that they are bloated with information, hard to read, distracting or unclear in their meaning.
The best slides are visually impactful, with graphics, graphs or images instead of lines and lines of text or bullet points. The last thing you want is your audience to be focused on deciphering the multiple lines of text. Instead your slides should be clear in their message and add reinforcement to the argument or story that is being shared. How true is this of your people’s slides?
5. Ability to appear confident, natural and in control
Most people find speaking in front of an audience (both small and large) at least a little confronting. However, for some, the nerves and anxiety they feel can distract from their presentation and the impact of their message. If members of your team lack confidence, both in their ideas and in themselves, it will create awkwardness and undermine their credibility and authority. This can crush a presenter and their reputation.
This is something that you will very easily pick up on, but the good news is that it is definitely an area that can be improved through training and practice. Giving your team the tools and training they need to become more confident and influential presenters can deliver amazing results, which is really rewarding for both the individual and the organisation.
6. Ability to summarise and close a presentation to achieve the required/desired outcome

No matter how well a presentation goes, the closing statement can still make or break it. It’s a good idea to include a recap on the main points as well as a clear call to action which outlines what is required to achieve the desired outcome.
In assessing your people’s ability to do this, you can ask the following questions:
- Did they summarise the key points clearly and concisely?
- Were the next steps outlined in a way that seems achievable?
- What was the feeling in the room at the close? Were people inspired, motivated, convinced? Or were they flat, disinterested, not persuaded?
Closing a presentation with a well-rounded overview and achievable action plan should leave the audience with a sense that they have gained something out of the presentation and have all that they need to take the next steps to overcome their problem or make something happen.

Effective Presentation Skills are Essential to Growth
It’s widely accepted that effective communication is a critical skill in business today. On top of this, if you can develop a team of confident presenters, you and they will experience countless opportunities for growth and success.
Once you’ve identified where the skill gaps lie, you can provide targeted training to address it. Whether it’s feeling confident presenting to your leadership team or answering unfielded questions , understanding their strengths and weaknesses in presenting will only boost their presenting skills. This then creates an ideal environment for collaboration and innovation, as each individual is confident to share their ideas. They can also clearly and persuasively share the key messaging of the business on a wider scale – and they and the business will experience dramatic results.
Tailored Training to Fill Your Presentation Skill Gaps
If you’re looking to build the presentation skills of your team through personalised training or coaching that is tailored to your business, we can help. For nearly 20 years we have been Australia’s Business Presentation Skills Experts , training & coaching thousands of people in an A-Z of global blue-chip organisations. All our programs incorporate personalised feedback, advice and guidance to take business presenters further. To find out more, click on one of the buttons below:
And follow us on social media for some more great presentation tips:
Don’t Forget To Download Our Presenter Skills Assessment Form
- Work Email Address * Please enter your email address and then click ‘download’ below

Written By Belinda Huckle
Co-Founder & Managing Director
Belinda is the Co-Founder and Managing Director of SecondNature International. With a determination to drive a paradigm shift in the delivery of presentation skills training both In-Person and Online, she is a strong advocate of a more personal and sustainable presentation skills training methodology.
Belinda believes that people don’t have to change who they are to be the presenter they want to be. So she developed a coaching approach that harnesses people’s unique personality to build their own authentic presentation style and personal brand.
She has helped to transform the presentation skills of people around the world in an A-Z of organisations including Amazon, BBC, Brother, BT, CocaCola, DHL, EE, ESRI, IpsosMORI, Heineken, MARS Inc., Moody’s, Moonpig, Nationwide, Pfizer, Publicis Groupe, Roche, Savills, Triumph and Walmart – to name just a few.
A total commitment to quality, service, your people and you.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Crush Your Next Virtual Presentation

A little prep can go a long way.
While virtual communication platforms help keep remote teams connected, they’re not always the ideal venue for delivering engaging presentations. It’s difficult (or impossible) to read your audience’s nonverbal cues over video and audio — if you’ve lost them, you might not even realize it. You’re also up against the many distractions inherent to working from home. Delivering effective presentations over video requires a little extra preparation. Ask a few people you trust to help you out before and after the meeting by being ready to participate when called on and by giving you actionable feedback afterward. Learn about your audience in advance and build in a short, relevant personal story that will make them feel included. Above all, be concise and clear.
My coaching client, an engineer named Carlos, is a magnificent in-person storyteller. He talks with his hands and tells lengthy, animated stories replete with humorous metaphors and plot twists. His wit and warmth used to be received positively.
- GS Gia Storms is a leadership coach and member of The Boda Group. She facilitates team and executive coaching from Los Angeles.
Partner Center
Presentation Skills: 40 Useful Performance Feedback Phrases
Presentation Skills: Use these sample phrases to craft meaningful performance evaluations, drive change and motivate your workforce.
Presentation Skills are useful in getting your message or opinion out there in many aspects of life and work, though they are mostly used in businesses, sales, teaching, lecturing, and training.
Presentation Skills: Exceeds Expectations Phrases
- Always prepares well before making any form of presentation whether formal or non-formal.
- Gives a clear and well-structured delivery when making a presentation.
- Exhibits excellent skill when it comes to expressing ideas and opinions with clarity.
- Knows the audience well enough to use proper language and terms.
- Engages well with audiences before, during and after delivering a presentation.
- Gives the audiences ample and appropriate time to ask questions.
- Creates a very lively and positive outlook when delivering a presentation.
- Adjusts very well to the new surrounding and exudes a great aura of confidence.
- Knows how to get and maintain the attention of the audience.
- Responds well to questions and issues raised by the audience.
Presentation Skills: Meets Expectations Phrases
- Organizes a good, balanced and dynamic presentation with high impact results.
- Demonstrates good ability to use visual aids most appropriately during presentations.
- Speaks in a good speech rate not so fast and at the same time not too slow.
- Explains each point to the fullest and only tries to emphasize the key points.
- Demonstrates a good logical order when presenting ideas not to confuse the audience.
- Uses non-verbal forms of communication such as facial expressions in a good way.
- Does proper research on the topic to be presented to gather all updated facts and figures.
- Delivers short and powerful presentations that create interest and excitement.
- Knows how to use true stories in between the presentation to pass across a point or to grab the audience's attention.
- Makes good eye contact with the audience from the start of the presentation to the end.
Presentation Skills: Needs Improvement Phrases
- Does not make good and consistent eye contact with the audience.
- Has minimal movement on stage and does not walk around the presentation room.
- Does not talk in a very engaging and positive way something that creates a dull presentation.
- Does not exude confidence and poise when delivering a presentation.
- Uses old facts and figures when presenting as a result of not doing enough research.
- Gives long presentations and does little to get the attention of the audience.
- Does not use the visual aids to help deliver a powerful conversation.
- Does not know the audience well and uses hard words that they do not understand.
- Does not give audiences ample time to raise questions and to seek clarification if need be.
- Presents ideas in a non-logical manner that creates confusion to the audience.
Presentation Skills: Self Evaluation Questions
- Have you ever gone for presentation without preparing well? How did the presentation go?
- How frequently do you engage your audience during any presentation?
- What was the highest score or reviews you received for any presentation that you have made so far?
- Give an instance your presentation backfired and what was your backup plan?
- How do you normally conclude your presentations and how can you rate it?
- How well do you deal with questions and issues raised by the audience?
- When it comes to nervousness, how do you manage or deal with it before hand?
- How can you rate your experience level when it comes to giving presentations?
- What do you like or dislike most about giving presentations?
- What presentation method do you like and why do you like it?
These articles may interest you
Recent articles.
- Good Employee Performance Feedback: Senior Clinical Data Specialist
- Outstanding Employee Performance Feedback: Research Greenhouse Supervisor
- Poor Employee Performance Feedback: Tax Auditor
- Employee Engagement Ideas For Managers
- 20 Critical Decision-Making Interview Questions
- Employee Performance Goals Sample: Oracle/Sybase Database Administrator
- Poor Employee Performance Feedback: Claims Quality Assurance Auditor
- Good Employee Performance Feedback: Database Administration Manager
- Top 10 Employee Productivity Metrics Explained
- Good Employee Performance Feedback: Accounting Compliance Officer
- Outstanding Employee Performance Feedback: Auxiliary Engineer
- Employee Selection Definition, Formula And Examples
- Employee Performance Goals Sample: Quality Assurance Director
- Top Employee Performance Questions
- Poor Employee Performance Feedback: Forensic Accounting Manager

- Tips & Tricks
- PowerPoint Templates
- Training Programs
- Free E-Courses
Presentation Skills Training
Home > Presentation Tips > Presentation Skills Training Video Evaluation
You video recorded your participants making their presentations. Now, what parameters should you use to evaluate them? Learn the 3 parameters on which you should evaluate your participants in your Presentation skills training programs.
Your presentation skills training evaluation parameters reinforce your lessons:
The parameters you use to evaluate your participants will primarily depend on the lessons you covered in your program. With that said, there are certain parameters that are worth including in your presentation rubric to make your evaluation complete.
These are the parameters we use in our Presentation skills training programs.
Criteria for deciding the evaluation parameters:
Many trainers make the mistake of evaluating videos only for obvious aspects like negative body language or distracting mannerisms of the presenters. Since these aspects stick out like sore thumb it is easy to harp on these forever.
When you highlight the negatives, participants object to having their videos shared with others.
A good evaluation draws participant’s attention to subtler aspects that are normally missed. That is why our evaluation parameters give equal emphasis on the clarity of message and the effectiveness of delivery.
Download the Presentation Skills Training Video Evaluation sheet
Evaluation Parameters:
Video analysis is primarily used to evaluate the delivery aspects of the presentations. Over the years, we’ve seen that the effectiveness of delivery is a good indicator of the strength of the underlying content.
Thus, the parameters for presentation evaluation may be classified into 3 main categories. They are
- Presentation Structure
- Method of Delivery and
- Style of Delivery
Let us understand the parameters in detail.
A) Presentation Structure
1. story flow:.
This parameter is used to evaluate the flow structure chosen to build the presentation. The structure could be anything from – ‘Problem – cause- solution’ to ‘Goal – path- challenges’. The evaluation is based on clarity and logic of the argument.
2. Message clarity in slides:
The questions to evaluate this parameter are:
- Do the PowerPoint slides serve as teleprompter for the presenter or do they help the audience understand the information better?
- Can the audience derive a clear message from each slide?
- Are the assertions supported with credible data, pictures or diagrams?
Related: Evaluating PowerPoint Presentations
3. Visual representation of ideas:
Did the presenter use charts, diagrams and images to explain the ideas clearly? Are the slides clean, without any unnecessary information? Has the presenter used meaningful animation to present ideas in stages?
B) Method of Delivery
4. Effective opening:
The 2 questions used to consider the effectiveness of opening are –
- Was the opening strong enough to grab the audience attention?
- Did the opening help the presenter to establish credibility?
5. Audience engagement:
Did the presenter engage the audience by asking questions or eliciting views? Did s/he acknowledge the comments and questions of the audience?
6. Verbal transitions between slides:
Did the presenter consistently summarize the current slide and give a preview of the next slide, before showing the next slide?
Verbal transition ensures that the audience stays connected with the story. It indicates that the presenter has built the slide structure based on a strong presentation outline. When a presenter uses verbal transition consistently, it shows that he/she has sufficiently rehearsed the presentation.
C) Style of Delivery
7. eye contact:.
Did the presenter maintain sufficient eye contact with the audience? Did he/she give equal attention to everyone in the room?
8. Voice clarity:
Could the last person in the audience clearly hear the voice of the presenter? Was there sufficient modulation in the voice?
9. Hand gestures:
Were there nervous hand gestures? Was the hand movement used to emphasize key points in the speech? Were there any distracting hand gestures like jangling of coins, clutching the marker etc?
10. Movement:
Did the presenter seek the comfort of the podium or move around freely? Did s/he pace the room nervously or commit other body language blunders? Did the presenter move away from the audience when faced with uncomfortable questions? Did he/she step forward when asking for a decision from the audience?
Conclusion:
These 10 parameters help you effectively evaluate the video recordings of your participants in Presentation skill training workshop.
Related Downloads
Related Article: Creative Presentation Evaluation Ideas to keep your participants focused.
Return to Top of Presentation Skills Training Evaluation Page
Share these tips & tutorials
Get 25 creative powerpoint ideas mini course & members-only tips & offers. sign up for free below:.
7 Presentation Skills to Wow Your Audience

We’ve all been there, sitting in a presentation or speech, struggling to keep our eyes open as the presenter drones on. Maybe the content is interesting, but the delivery is lacklustre. Or maybe the delivery is fantastic, but the content is disorganised or hard to follow. Whatever the reason, there’s no denying that effective presentation skills are critical to captivating and inspiring your audience.
So, whether you’re a seasoned speaker or a novice presenter, it’s always a good idea to brush up on your skills. That’s why in this blog post, we’ll be covering seven effective presentation skills that are sure to wow your audience. From knowing your audience to engaging with them, these skills will help you deliver powerful presentations that leave a lasting impact.
So, let’s dive in and explore these seven effective presentation skills that will take your speaking abilities to the next level. And to help you hone these skills, we’d like to introduce you to our specialised effective presentation skills training programs.
Skill 1: Knowing Your Audience
One of the most effective presentation skills is knowing your audience. Understanding your audience helps you tailor your presentation to their needs, interests, and expectations.
Knowing your audience allows you to focus on the topics that are most relevant to them and speak in a language they can understand. Failure to know your audience can lead to a disengaged and uninterested audience, which can ultimately derail your presentation.
Tips for Identifying and Understanding Your Audience
When it comes to delivering a presentation, understanding your audience is essential. Identifying their needs, interests, and expectations can help you tailor your presentation to keep them engaged and interested throughout. Here are some tips to help you better identify and understand your audience:
1. Research your audience
Before your presentation, research your audience to understand their demographics, interests, and expectations. This can be done through social media, surveys, or by asking the event organisers for details about the attendees.
2. Ask questions
During your presentation, ask questions that engage the audience and help you understand their needs and interests. This can help you tailor your presentation to meet their expectations.
3. Analyse non-verbal cues
Pay attention to non-verbal cues, such as facial expressions and body language. This can help you gauge the audience's level of engagement and adjust your presentation accordingly.
4. Consider the occasion
The type of event can affect the expectations of your audience. If you're presenting at a formal event, your audience may expect a more polished and structured presentation. On the other hand, if you're presenting at a more casual event, your audience may appreciate a more relaxed and conversational tone.
5. Use social media
Social media can be a great tool for understanding your audience. Look for groups or hashtags related to your topic to see what people are saying about it. You can also use social media to ask questions and get feedback from your audience.
Skill 2: Storytelling
Storytelling is a powerful tool that can make your presentation stand out from the rest. It can help you engage your audience emotionally and make your message more memorable.
A well-crafted story can take your audience on a journey, creating a connection between you and them. In a world where attention spans are short, storytelling can be an effective way to hold the attention of your audience and keep them engaged.
Tips for crafting a compelling story for your presentation
Crafting a compelling story for your presentation takes some effort, but the result can be powerful. Here are some tips to help you create a story that resonates with your audience:
1. Start with a clear message
Before you begin crafting your story, identify the key message you want to convey. This will help you structure your story around the central idea and ensure that it aligns with your overall goal.
2. Use a simple structure
A simple structure can help you keep your story focused and easy to follow. Consider using a traditional story arc, which includes an introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution.
3. Create relatable characters
Characters are an important part of any story. Create characters that your audience can relate to, and make them feel human and believable. This will help your audience connect with your story on an emotional level.
4. Use sensory language
Sensory language can help bring your story to life. Use descriptive words to paint a picture in the minds of your audience. This can help them better understand and remember your story.
5. Incorporate humour
Humour can be an effective way to engage your audience and create a memorable presentation. However, be sure to use humour that is appropriate, relevant and not sexist, ageist or ableist.
Skill 3: Visual Aids
Visual aids can be a powerful tool to enhance your presentation and improve its effectiveness. They can help you convey complex information in an easy-to-understand way and make your presentation more engaging and memorable.
The human brain processes visual information much faster than text, so incorporating visual aids in your presentation can help your audience understand your message more quickly and effectively.
Tips for creating effective visual aids
Now that we've covered the importance of visual aids, here are some tips for effective presentation skills :
1. Keep it simple
Visual aids should be simple and easy to understand. Avoid cluttered or complicated images, and use clear and concise language. Your audience should be able to quickly and easily understand the information you are presenting.
2. Use high-quality images
Low-quality images can be distracting and detract from your message. Use high-quality images that are relevant to your message and enhance the overall tone of your presentation.
3. Avoid too much text
Visual aids should be used to support your message, not replace them. Avoid using too much text on your slides or graphs, and instead, use bullet points or brief phrases to convey your message.
4. Use colour strategically
Colour can be a powerful tool to help emphasise important information, but it should be used strategically. Avoid using too many colours or bright colours that can be distracting.
5. Incorporate multimedia
Videos and audio can be effective tools to help engage your audience and make your presentation more interactive. Just be sure to use multimedia that is relevant to your message and supports the overall tone of your presentation.
Skill 4: Body Language
Body language is a critical aspect of effective communication skills for presentation , especially in a presentation setting. The way you use your body can have a significant impact on how your message is received by your audience.
Your body language can convey confidence, interest, enthusiasm, and many other emotions and attitudes that can affect how your audience perceives you and your message.
Tips for using effective body language
Here are some tips for effective presentation skills :
1. Stand up straight
Good posture is key to projecting confidence and authority. Stand up straight with your shoulders back and your feet shoulder-width apart.
2. Make eye contact
Eye contact is a powerful way to connect with your audience and build trust. Try to make eye contact with different members of your audience throughout your presentation.
3. Use hand gestures
Appropriate hand gestures can help emphasise your message and make your presentation more engaging. However, be careful not to overdo it or use gestures that are distracting or inappropriate.
4. Avoid fidgeting
Fidgeting can be distracting and convey nervousness or anxiety. Try to stand still and avoid pacing, tapping your feet, or playing with objects.
5. Use facial expressions
Your facial expressions can convey a wide range of emotions and attitudes, from enthusiasm and interest to boredom and disengagement. Use appropriate facial expressions to match the tone of your message.
Skill 5: Voice and Tone
The way you use your voice can have a significant impact on how your presentation is perceived by your audience.
Your voice and tone can convey a range of emotions and attitudes, such as confidence, authority, enthusiasm, and interest. Your tone can also indicate the level of importance or urgency of your message.
Tips for using effective voice and tone
Now that we understand the impact that voice and tone can have on a presentation, let's explore some tips for effective presentation skills:
1. Practice speaking with intention
Before your presentation, take some time to practice your speaking with intention. Think about the key messages you want to convey and how you want your audience to feel while listening to your presentation. This will help you deliver your message with a clear and purposeful voice and tone.
2. Vary your pace
Varying your pace can help keep your audience engaged and interested in your presentation. Slow down during important or complex points, and speed up during lighter or more exciting parts. By varying your pace, you can also create a sense of urgency or importance in your message.
3. Use pitch to convey emotion
Varying the pitch of your voice can help convey different emotions and attitudes in your presentation. For example, a higher pitch can convey excitement, while a lower pitch can convey seriousness or importance.
4. Pay attention to your volume
Be sure to project your voice so that everyone in the room can hear you. However, be careful not to speak too loudly, which can be distracting or overwhelming for your audience.
5. Pause for emphasis
Pausing at strategic moments can help emphasise important points and give your audience time to process your message. Take a breath and pause before making an important point to give it more weight.
Skill 6: Engaging Your Audience
One of the most important aspects of giving a presentation is engaging your audience. Without audience engagement, your presentation can quickly become boring, forgettable, or even frustrating for your listeners. Engaging your audience is a crucial skill that can help you build rapport, gain trust, and effectively communicate your message through your communication skills for presentation .
Tips for engaging your audience throughout your presentation
Engaging your audience is a crucial skill that can help you build rapport, gain trust, and effectively communicate your message using your communication skills for presentation . In this section, we will explore some tips for effective presentation skills .
1. Use storytelling
Storytelling is a powerful tool that can help you capture your audience's attention and keep them engaged. Use personal stories, anecdotes, or case studies to illustrate your points and make your presentation more relatable.
Asking questions can help you create a dialogue with your audience and make them feel like they are part of the conversation. Use open-ended questions to encourage participation and discussion.
3. Use humour
Appropriate humour can help lighten the mood and create a sense of rapport with your audience. Use jokes, puns, or funny anecdotes to break up the monotony of your presentation and keep your audience engaged.
4. Use visual aids
Visual aids, such as graphs, charts, or videos, can help illustrate your points and make your presentation more dynamic. Use them strategically to support your message and keep your audience engaged.
5. Use audience participation
Incorporating interactive elements, such as polls, quizzes, or games, can help keep your audience engaged and create a sense of excitement or competition. Use them strategically to break up your presentation and keep your audience engaged.
Skill 7: Handling Questions and Feedback
Handling questions and feedback is a critical skill that can make or break a presentation. It provides an opportunity to demonstrate your knowledge, address any concerns, and show your audience that you value their input.
Tips for handling questions and feedback effectively
Handling questions and feedback can be daunting, but with some practice, it can become an opportunity to showcase your expertise and engage with your audience. Here are some tips on how to handle questions and feedback effectively:
1. Listen carefully
Listen carefully to the question or feedback, and take a moment to think about your response. This shows that you respect the person asking the question and value their input.
2. Repeat or rephrase the question
This ensures that you have understood the question correctly, and it also helps the audience hear the question clearly. Rephrasing the question can also help clarify any misunderstandings or confusion.
3. Be concise
Keep your answers concise and to the point. Avoid giving long-winded answers that might confuse or bore the audience.
4. Use real-life examples
Using examples or stories can help illustrate your points and make them more relatable to the audience. It can also help keep the audience engaged.
5. Be honest
If you don't know the answer to a question, it's okay to say so. You can offer to follow up with the person after the presentation or suggest resources where they can find more information.
Wrapping It Up
In conclusion, effective presentation skills are an essential part of being a successful communicator. Knowing your audience, storytelling, using visual aids, body language, voice, and tone, engaging your audience, and handling questions and feedback are all key skills that can help you deliver a powerful and impactful presentation.
By following the tips and strategies we've shared, you can improve your communication skills for presentation and leave a lasting impression on your audience. And if you're looking to take your skills to the next level, some.Education provides presentation skills training that can help you develop and hone these skills.
Remember, a great presentation isn't just about the content - it's also about the delivery. By mastering these skills, you can engage your audience, build your credibility, and leave a lasting impression. So go out there and wow your audience!
Useful Resources : 10 importance of speech communication | Communication skills presentation | Grapevine communication
Recent Blogs

What is Social Learning Theory? How to Adopt It in The Workplace
Explore the transformative power of social learning theory in the OB. If you're curious about what social learning theory is and how it can revolutionize your workplace,...
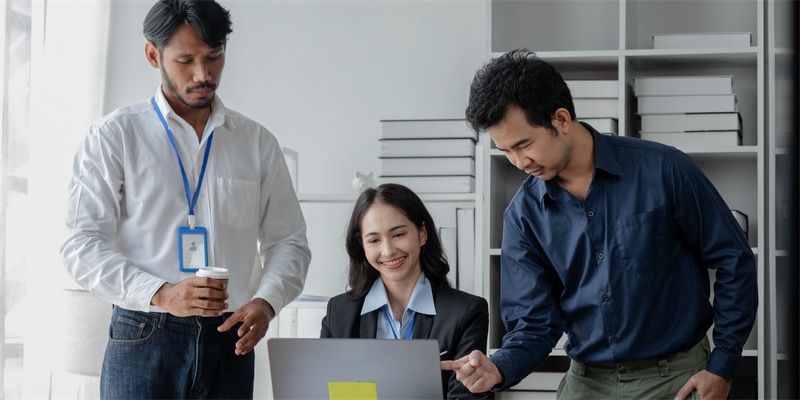

Why Are Employees Your Greatest Asset and How to Mentor Them
In the dynamic landscape of modern businesses, employees are the most valuable asset of any organisation. Their skills, knowledge, creativity, and dedication fuel an organisation's...

Dealing with difficult employees: An employer's guide
In any workplace, you're likely to encounter a variety of personalities and work styles. While most employees are cooperative and contribute positively to the team, there may be in...

How to stop being self-conscious: Strategies to feel more confident
In a world where self-confidence reigns supreme, it's all too easy to feel self-conscious. But what does it really mean to be self-conscious?And why does it have such a profound im...

How to prepare your team to handle negotiations?
In the dynamic business world, the ability to negotiate effectively and deliver persuasive pitches can be the key differentiator between triumph and failure. Whether you're seeking...

Effective Communication skills can improve your self-confidence and boost career growth
In today's fast-paced and competitive professional world, self-confidence is a valuable asset that can significantly impact your career growth and success. Whether you're seeking a...

Difference between KRA and KPI
In the realm of performance management and goal setting, the terms KRA (Key Result Area) and KPI (Key Performance Indicator) are frequently used, but they serve distinct purposes i...

What is the difference between a boss and a leader?
In the world of management and leadership, the terms "boss" and "leader" are often used interchangeably. However, they represent distinct approaches to managing and inspiring a tea...

How to interview for a job when you have no work experience?
Landing your first job can be both exciting and nerve-wracking, especially when you lack work experience. However, with the right approach and preparation, you can ace your job int...

9 steps for improving collaboration between teams
In today's rapidly evolving workplace, effective team collaboration is more critical than ever. Whether you're in a traditional office, a remote team, or a hybrid work environment,...

How being intentional can advance your career?
In a world filled with constant distractions and fast-paced living, the concept of being intentional stands out as a beacon of purpose and direction. But what does it mean to...

How to improve your problem solving skills?
Problem solving is a critical skill that permeates various aspects of life, from personal challenges to professional endeavors. The ability to tackle issues, make decisions, and fi...

Complete Guide to Debating: Improve your Debating Skills
In the world of communication and persuasion, mastering the art of debate is a skill that can truly set you apart. Whether you're a student, a professional, or simply someone who w...

Experimentation brings innovation: An experimental workplace
Experimentation is the lifeblood of innovation, breathing new life into stagnant routines and sparking transformative ideas. Organisations that embrace a culture of experimentation...

How to Build a Healthy Workplace Environment?
In today's highly competitive work landscape, the importance of cultivating a healthy workplace environment cannot be overstated. A positive work environment not only contributes t...

How Would You Define Success?
Success, a word that carries different meanings for different individuals, is a universal aspiration.The concept of what is success in life has captivated minds for centuries, fuel...

Why is Networking Important
The importance of networking has never been more evident. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting out, building and nurturing a strong professional network can be t...
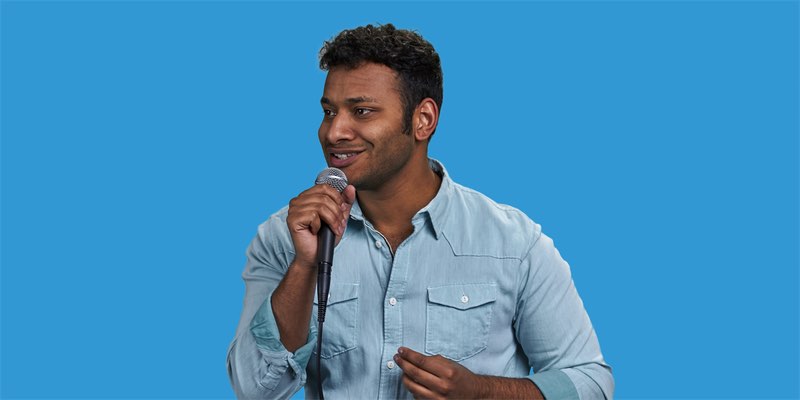

Guide to Choosing a Successful Speech Topic
Effective communication skills have become more crucial in today's rapidly changing world. Whether you're a student, a professional, or someone simply looking to enhance your publi...

The Importance of Storytelling in Business, with Examples
In the dynamic world of business, where information is abundant, and attention spans are fleeting, storytelling has emerged as a powerful tool that captivates audiences and leaves...

10 Best Practices for Giving a Remote Presentation
After COVID, with more companies embracing the WFH hybrid model of working, virtual presentations have become a fundamental part of professional communication. Whether you're an ex...
Your success. Powered by the Six Cs.
Knowledge centre.
Copyright © School Of Meaningful Experiences private limited, Privacy Policy, Cookie Policy and Terms of Use | Sitemap
Chat with us now
Your account has been created.
Join our team
Interact with our admission team, download brochure.
OTP has been sent, Please check your E-mail
Resend OTP in:
Verify Your Details
- Open access
- Published: 24 February 2015
Tools and evaluation methods for discussion and presentation skills training
- Katashi Nagao 1 ,
- Mehrdad Panahpour Tehrani 2 &
- Jovilyn Therese B Fajardo 3
Smart Learning Environments volume 2 , Article number: 5 ( 2015 ) Cite this article
14k Accesses
4 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Our university is currently developing an advanced physical-digital learning environment that can train students to enhance their discussion and presentation skills. The environment guarantees an efficient discussion among users with state-of-the-art technologies such as touch panel discussion tables, digital posters, and an interactive wall-sized whiteboard. It includes a data mining system that efficiently records, summarizes, and annotates discussions held inside our facility. We also developed a digital poster authoring tool, a novel tool for creating interactive digital posters displayed using our digital poster presentation system. Evaluation results show the efficiency of using our facilities: the data mining system and the digital poster authoring tool. In addition, our physical-digital learning environment will be further enhanced with a vision system that will detect interactions with the digital poster presentation system and the different discussion tools enabling a more automated skill evaluation and discussion mining.
Introduction
Recently, a lot of attention has been paid to evidence-based research, such as life-logging Sellen and Whittaker (2010 ) or big data applications Armstrong (2014 ), that proposes techniques to raise the quality of human life by storing and analyzing data of daily activities in large quantities. This technique has been applied in the education sector but a key method has not been found yet because it is generally hard to record intellectual activities, accumulate and analyze data in a large scale, and compare it with a person’s physical activities, position, movement information, and the like. Although there are some recent studies on the automated recording of intellectual activities in more detail, their techniques are not sufficient to be applied to an automated evaluation of a person’s intellectual activities. Thus, this study aims to develop a new environment to empower the skills of students not only in real-time but also offline based on the abundant presentation and discussion data analyses.
Our study focuses on the new graduate leading program of Nagoya University that aims to cultivate future industrial science leaders. This leading graduate program has a new physical-digital environment for facilitating presentations and discussions among the selected students of the program. In particular, the presentations and discussions of the students are recorded in detail, and the mechanism for knowledge emergence is analyzed based on a discussion mining system. Furthermore, we have evaluated the performance of some students with respect to their skill in creating a digital poster using our recently developed tool.
Related work and motivation
This section has two parts: discussion evaluation and presentation evaluation. For each evaluation system, there are also two parts based on the type of system: a fully-automatic system and a semi-automatic system. A fully-automatic system calculates the scores of discussion or presentation quality in an automated fashion while a semi-automatic system supports the people in evaluating the discussion or presentation with some evidential data.
Discussion evaluation
Fully-automatic.
With the abundant data in discussions, there is difficulty in searching for good quality posts. An automatic rating of postings in online discussion forums was presented based on a set of metrics Wanas et al. (2008 ). This set of metrics was used to assess the value of a post and includes the following: relevance, originality, forum-specific features, surface features, and posting-component features. With these metrics used to train a non-linear support vector machine classifier, the posts were then categorized to their corresponding levels (High, Medium, or Low).
Another system called Auto-Assessor used natural language processing tools to assess the responses of students to short-answer questions Cutrone et al. (2011 ). The system utilized a component-based architecture with a text pre-processing phase and a word/synonym matching phase to automate the marking process. In their system evaluation, they compared the assessment results of the Auto-Assessor and Human Graders to verify the possibility of applying the proposed system in practical situations.
However, these fully-automatic systems still have some drawbacks. Some methods are language independent resulting in a poor performance in relevance and originality Wanas et al. (2008 ) thus, other additional techniques should be employed in their assessment of discussions. Also, even with additional NLP techniques, the weights given to words are not varied Cutrone et al. (2011 ) hindering the system from identifying words that are more significant than others.
Semi-automatic
Aside from fully-automatic systems, some studies employed a semi-automatic approach. One such study is the implementation of a group discussion evaluation method and a discussion evaluation support system that focused on ex post evaluation Omori et al. (2006 ). The system provided a Web-based interface to display the evaluation item and the evaluation criteria so that users can easily make a score to each of the discussion remarks based on clearness of remarks, proposal of issues, and logicality of remarks. Results confirmed the effectiveness of both their evaluation method and support system.
With the above-mentioned systems, there was no mention about one problem in discussions, which is the difficulty in getting students to actively participate. Thus, a gamification framework was integrated to a discussion support system for enhancing and sustaining motivation in student discussions Ohira et al. (2014 ). Besides sustaining student motivation, the system also evaluates and visualizes improvement of the students’ capacity to discuss. It also supports the users to evaluate the quality of each discussion statement.
However, with the two semi-automatic systems, more experiments are needed to determine the effect of teachers’ feedback to the students Omori et al. (2006 ) and its performance in real-world settings.
Presentation evaluation
A presentation training system called Presentation Sensei was implemented to observe a presentation rehearsal and give presentation feedback to the speaker Kurihara et al. (2007 ). The system is equipped with a microphone and camera to analyze the presentation by combining speech and image processing techniques. Based on the results of the analysis, the system provides the speaker with recommendations for improving presentation delivery such as speed and audience engagement. During the presentation, the system can alert the speaker when some of the indices: speaking rate, eye contact with the audience, and timing, exceed predefined warning thresholds. After the presentation, the system generates summaries of the analysis results for the user’s self-examination. Although this system focuses on self-training, it still needs to be tested in a real presentation environment.
Another presentation training system called PitchPerfect was implemented to develop confidence in presentations Trinh et al. (2014 ). From interviews with presenters, the authors uncovered mismatches between best rehearsal practices as recommended in the presentation literature, the actual rehearsal practices, and support for rehearsal in conventional presentation tool. Thus, they developed the proposed system, an integrated rehearsal environment that supports users to evaluate their presentation performance during preparation for structured presentation in PowerPoint. Their user study with 12 participants demonstrated that PitchPerfect led to small but significant improvements in perceived presentation quality and coverage of prepared content after a single hour of use, arising from more effective support for the presenter’s content mastery, time management, and confidence building.
In the initial phase of our research, we select a semi-automatic approach to evaluate the discussion and presentation. However, our proposed system can acquire several kinds of student activity-related data so as to make evaluation automated in the near future. We understand that current technologies to analyze human activity data fully-automated are still insufficient to realize our purposes so we focus on data acquisition by using our new environment for discussion and presentation.
Leaders’ Saloon: a new physical-digital learning environment
The Leaders’ Saloon shown in Figure 1 is capable of creating discussion contents using the discussion tables, the digital poster panels, and the interactive wall-size whiteboard.
Leaders’ Saloon environment.
Discussion table
Each student uses a tablet to connect with the facilities including the discussion table shown in Figure 2 . The content and operation history of the discussion table are automatically transferred and shared to the server, the meeting cloud . Previous table contents can be easily retrieved and any texts or images can be reused. Such reference and quotation operations are recorded and analyzed to discover semantic relationships between discussions. Furthermore, a software that analyzes temporal changes of table contents with the corresponding users is also being developed.
Students using the discussion table.
Digital poster panel
For poster presentations, a digital poster panel system, shown in Figure 3 , is used for content and operation analyses. The system helps the users create digital posters and analyze their creation process. The system also supports the retrieval of previously presented posters and allows users to annotate them. Annotations are automatically sent to the author and are analyzed by the system to evaluate the quality of the poster. Poster presentations as well as the regular slide-based presentations are also broadcasted by streaming on the Web. The system collects and analyzes the feedbacks based on comments and reviews given by Internet viewers (e.g., Twitter users can associate their tweet messages with any scenes from the presentation based on the starting and ending timestamps).
Poster presentation using the digital poster panel system.
Interactive wall-sized whiteboard
As shown in Figure 4 , our facility houses a wall-sized whiteboard. Unlike the traditional whiteboards, we are able to physically and digitally write on the whiteboard. We use a special projector equipped with an infrared sensor to detect the location of the digital pen with respect to the wall. The writings and interaction on the whiteboard can then be recorded by cameras. The captured data using the camera can identify the physical interaction in combination with the given digital interaction information. This system is under development and we are working on proposing a new evaluation system that can enhance the presentation and discussion performance of students using this system.
Capturing data using the interactive wall-sized whiteboard.
Discussion mining system
The discussion mining system generates knowledge discovery from discussion contents during face-to-face meetings. This previously developed system Nagao et al. (2005 ), shown in Figure 5 , generates structured minutes for meetings semi-automatically and links them with audiovisual data. This system summarizes discussions using a personal device, which captures information, called the discussion commander . The created content is then viewed using the discussion browser mentioned later, which provides a search function that lets users browse the discussion details.
System overview of discussion mining.
Recording and structuring discussions
Discussions in our meetings are automatically recorded and these meeting records are composed of structured multimedia contents including texts and videos. In the contents, meeting scenes are segmented based on discussion chunks. The segments of contents are connected with visual and auditory data corresponding to the segmented meeting scenes.
Previous studies on structuring discussions and supporting discussions by referring past structured discussion contents include IBIS and gIBIS Conklin and Begeman (1988 ) that consider semantic discussion structures. However, most studies that provide technology for discussions and minutes generations have focused on automatic recognition techniques for auditory and visual data. For example, Lee et al. ( 2002 ) proposed a method that records the participants’ actions using cameras and microphones and then produces indexed minutes using automatic recognition techniques. Chiu et al. ( 2001 ) integrated audio-visual information and information for presentation materials.
We analyze meetings not only with natural language processing to support the comprehension of arguments in a discussion but also form diversified perspectives using auditory and visual information in slides as well as other presentation content. We also use metadata to deal with discussion content. Overall, our discussion mining system supports the creation of minutes for face-to-face meetings, records the meeting environment with cameras and microphones, and generates meta-information that relates elements in the contents.
In addition, the system can graphically display the structure of a discussion to facilitate understanding of the minutes and encourage effective statements. Our discussion commander has some functionality for discussion facilitation such as pointing/highlighting some areas and underlining some texts in the presentation slides displayed on the main screen. We also developed a method to define visual referents in the presentation slides that are pointed and referred by meeting participants.
Our method can handle sharing and re-referring the visual referents. This method then contributes to finding central topics of the discussion chunks. A discussion chunk has a tree structure and it consists of participants’ utterances and relationships between two utterances. An utterance has one of two types: start-up and follow-up . The start-up type is assigned to the utterance when it introduces a new topic while the follow-up type is assigned when the utterance inherits the predecessor’s topic. The discussion content of a meeting has several discussion chunks that have tree structures of utterances as shown in Figure 6 .
Discussion structure.
The summarization of discussion content is performed as follows:
Based on common visual referents in utterances included in discussion chunks, a graph structure is generated. Spreading activation is applied to the graph structure where external inputs are assigned based on marking agreeable/disagreeable utterances which are decided by using discussion commander . Highly activated utterances are selected as more significant elements of the content. The discussion browser allows the users to adjust some parameters such as the ratio of summary and the weight of marking. The whole system provides functions of generating and publishing multimedia meeting records and their in-depth search and summarization.
On-time visualization of discussion structures and histories of visual referents contributes to the facilitation of current discussion and modification of discussion structures by changing parent nodes of follow-up utterances and by re-referring previous visual referents. Such modification is performed using each participant’s discussion commander . The discussion commander also works for annotating agree or disagree attributes to the current utterance by pressing + or - buttons. The time of pressing the buttons, the user who pressed the buttons, and the target utterance are recorded and used for summarization. The target utterance of the agree annotation has a high-valued external input when spreading activation is performed.
Since our main mission is to train students’ discussion skills, the previous system was extended and new functions were added in order to obtain user-specific data such as the quality of statements and level of understanding the discussions, which led to the creation of the Leaders’ Saloon (Section ‘ Leaders’ Saloon: a new physical-digital learning environment ’).
Discussion browser
The information accumulated by the discussion mining system is presented synchronously in the discussion browser shown in Figure 7 . This system consists of a video view, a slide view, a discussion view, a search menu, and a layered seek bar.
Discussion browser interface.
The discussion browser provides the function of searching and browsing discussion details in correspondence to the users’ requests. For example, when the participant of the meeting wants to refer to certain important previous discussions, the participant will search for the statements using keywords or the speakers’ names, and then browse the details of the statements in the search results. Users who did not participate in the meeting can search and browse the important meeting elements displayed in the layered seek bar by inquiring into discussions containing statements that form agreements by using the discussion commanders, or by surveying the frequency distributions of keywords.
The video view provides recorded videos of the meeting, including the participants, presenter, and screen. The participant video shows the scene of the speaker if the speaker is not a presenter or the whole span of the meeting room if the speaker is the presenter.
Discussion view
The discussion view consists of text forms, in which the contents of the discussion primarily constitute of information inputted by a secretary and relation links, which visualize the structure of the discussion. This view supports the understanding of the contents of the discussion, because the users can survey the structure of the discussion. The user can also tag the meeting contents for searching by selecting accurate tags from a tag cloud containing tags extracted from the text of statements and presentation materials.
Search menu
In the search menu, three types of search queries are available: speaker name, the target of the search (either the contents of the slide or the statement, or both), and keywords. The users will search for the necessary information using combined queries. The search results are shown in the layered seek bar (matched elements in the timeline are highlighted) and in the discussion view (discussions where the matched elements appear are highlighted).
Layered seek bar
The elements that compose a meeting content are displayed in the layered seek bar. Various bars are generated according to each type of element and it also presents the details. The left edge of each bar corresponds to the start time of the meeting, and the right edge corresponds to the end time. The discussion browser enables effective reuse of meeting contents. Additionally, summarization is possible by acquiring relevant discussion from links between statements. The entire operation history of the discussion media browser is saved in the database. This history is used for the personalization of meeting contents.
Importing discussion mining system into Leaders’ Saloon
We developed an extended version of the discussion mining system working at the Leaders’ Saloon. The discussion tables are used to operate and visualize discussion structures. The users also use discussion commanders and the previously described discussion mining system.
In this section, we explain two systems implemented on the discussion tables to visualize real information recorded by the discussion mining system: (1) discussion visualizer, a system to visualize the structure of an ongoing discussion, and (2) discussion reminder, a system to retrieve and visualize past discussions.
Discussion visualizer
The discussion visualizer shown in Figure 8 is a system to visualize the structure of meeting discussions shown in the discussion table (Section ‘ Discussion table ’). This visualizer consists of a meeting view, a slide list, a discussion segment view, and a discussion segment list.
Discussion visualizer interface and sample content.
The meeting view provides a preview of camera records showing the participants, a list of all attendances, and elapsed time of presentation. A list of slide thumbnails displayed in the presentation is also shown and the thumbnail of the currently displayed slide is emphasized in the slide list. Speakers can operate the slide show by selecting the thumbnail in this view using the touch panel.
The discussion segment view shows the information about the discussion segment, which contains the current statement. The texts of the start-up statement, which was the trigger of the discussion, and the parent statement of the current statement (if it is a follow-up statement) are shown at the upper side of this view. The structure of the discussion segment is shown at the bottom side of this view. Users can also make corrections of parent statements. Participants confirm the stream of discussion at the meeting through the discussion segment list. In this list, the nodes representing main topics are shown as rectangle nodes while the subtopics are shown as circle nodes. These discussion segment topics are displayed as a chain structure in the middle, the keywords of multiple discussion segments are displayed on the left, and the keywords of the main topics or subtopics are displayed on the right. Moreover, the nodes that involve questions and answers are represented by the specific character Q . The amount of agreements on the statements inputted by the discussion commanders is represented as a density of the color of the nodes. The icons are displayed next to the node containing the statements marked by discussion commanders. Therefore, it enables participants to confirm when important discussions occur.
There are various kinds of discussion segments created by the discussion mining system. For example, short segments with only comments on the presentation and long segments that contain a lot of statements as a result of a hot debate. There is also a possibility that the long discussion segments have follow-up statements whose content derives from the topic of the start statement. Thus, we think that the start statement is the root node of the discussion segment and some subtopics derive from this root node.
Discussion reminder
A review and sharing of previous discussion contents lead to a uniformed knowledge level among all participants, wherein low-level participants can make remarks actively. This will also prevent redundant discussion. From here, we can then think about topics from a new point of view and figure out solutions to problems that have not been solved due to lack of technology. Therefore, we develop a system to retrieve and browse past discussions on time, called discussion reminder.
There are two concerning issues in the development of the discussion reminder. One is an accurate understanding of discussion contents, and another issue is the quick retrieval of discussion contents preventing any disruption in the ongoing discussion. Unclear and inadequate sharing of discussion contents will inhibit the achievement of a uniformed knowledge level and will lead to misunderstandings and confusion. Thus, the discussion reminder provides a function to browse videos of past discussions for accurate understanding.
However, all of the participants need to interrupt the ongoing discussion for a review of discussion contents, thus it is desirable to finish the review in no time using the above method to find the things required in the audiovisual information. For an efficient review, the discussion reminder provides an interface to narrow down the browsing information, such as discussion content matched with queries, slides matched discussion content, and statements associated with matched slide, and to retrieve cooperatively by participants. A participant who notices the existence of the discussion, which he/she wants to review, inputs queries to the discussion reminder. Various types of information, such as names of presenters, dates of meetings, and keywords, are available as queries. The contents of retrieved results are displayed on the discussion table as shown in Figure 9 .
Result contents of the discussion reminder.
Participants conduct various operations using the touch panel in this interface. This interface consists of a discussion content list, a slide list, and a discussion segment view. The discussion content list displays titles of the discussion contents, which contains the discussion matched queries. When a participant selects a title using the touch panel, slide thumbnails comprised in the selected discussion content are shown at the bottom of the slide list. Participants can preview the larger slide thumbnail at the top of the slide list.
The discussion segment view shows information about the discussion segments associated with the slide selected in the slide list. Examples of discussion segment information include structures of discussion segments, speaker’s ID, keywords of statement, and so on. In the discussion segment view, full text of the statement can also be previewed. Participants can browse videos in the video view displayed on the table from the start time of the selected statement in the discussion segment view.
Employing machine learning techniques
In this study, machine learning techniques are employed to obtain deep structures of presentation and discussion contents. Techniques like deep neural networks Bengio (2009 ) integrate several context information such as operation histories of users. By integrating the results of subject experiments on presentations and discussions, different methods to evaluate the quality of students’ intellectual activities and to increase their skills are discovered. The system tries to perform some consensus-building processes to make evaluation results appropriate for each student.
Digital poster presentation system
The digital poster presentation system consists of an authoring tool for digital posters, an interactive presentation system with digital posters, and an online sharing system for digital posters. Poster presentations can be considered as a close communication with the audience, and is also ideal for training in discussion not only for presentation. The digital poster presentation system makes the poster presentation easier. Tools such as PowerPoint slides can be integrated into the poster presentation. Additionally, the system will be extended for an interactive data acquisition. Hence, we believe that this system would significantly change the way of poster presentations.
Digital posters vs. regular posters
A digital poster is an interactive multimodal version of regular papers. The advantage of digital posters includes retrieval and reuse of contents. However, one of the biggest problems is portability since a digital poster needs a special hardware such as a digital poster panel and these devices cannot be carried elsewhere. Perhaps, in the near future, large and thin film-type screen devices, such as organic electro-luminescence displays, will be available and tools for digital posters will be commodities and easily acquired.
Authoring digital posters
Authoring of digital posters is very simple but some preparation is needed. The users should prepare resources such as images, videos, and slides in advance. We also developed an online resource management system for memos, images, videos, and slides. The digital poster authoring tool can import any resources submitted or shared in the resource management system.
The digital poster authoring tool shown in Figure 10 has three parts: the main menu, the resources menu, and the poster field.
Main screen of the digital poster authoring tool.
The main menu provides the basic functionalities of the tool such as creating, opening, and saving of poster files, setting up the desired preferences, and choosing different creation modes. The digital authoring tool is also able to create both portrait and landscape orientation posters as needed.
The resources menu shown in Figure 11 lets the users add different types of blocks to the poster field. Each block automatically downloads a certain type of resource depending on the selected block from the online resource management system, except for the layout and text blocks. Selecting an image block will automatically scan for images in the resource management system while selecting a video block will automatically scan for videos in the resource management system. For the slide block, existing PowerPoint slides will be selected.
Detailed view of the resources menu.
When the user taps a block in the resource menu, a list of thumbnail images is displayed in the window that appears from the right edge of the screen as shown in Figure 12 . The user can easily arrange the layout of the poster using a layout block and interactively change a position of a block’s borderline. When the user wants to place any resource in the block, he/she should just drag and drop the thumbnail image from the resource list to the target block as shown in Figure 13 .
Image resource menu window.
Image resource placement in the layout block.
Other resources, such as videos and slides, are inserted in the blocks in a similar way. An example of a created poster using the described authoring tool is shown in Figure 14 . When the user finished editing the digital poster, the final poster can be stored in the online poster sharing system. It can be used for presentations by searching the digital poster at any time. During presentation time, the enlargement of images and the playback of videos and slides in the poster can be done.
Example of a digital poster.
Data acquisition from interactions with digital posters
Digital posters are not only for a presenter to make a presentation but also for an audience to view in detail by interacting with the poster. Posters are unlike slides, where the complete content is summarized in one piece, which is more suitable to understand the content quickly. At the Leaders’ Saloon, visitors can easily retrieve and view the digital posters using the digital poster panel whenever they like. Interaction histories when visitors have interacted with the posters are recorded automatically. The number and time of poster views, views of the elements in the poster, and data such as browsing the order of the poster elements can be obtained by this system. These data are used to evaluate the posters and the skills of the poster author.
Skill evaluation methods
The focus of this study is the students of the new Graduate Leading Program at Nagoya University, which aims to nurture future global leaders. To achieve this goal, improving the communication skills of the students has to be addressed. In this study, we focus on developing the discussion and presentation skills of the students and this section describes in detail the evaluation method for the discussion and presentation skills of the students.
- Discussion skill
Data acquired by the discussion mining system includes participant types (presenter, secretary, and others), number of start-up/follow-up statements of each participant, and scores of quality of each statement. The scores of quality are calculated by the agreement/disagreement data inputted by each participant’s discussion commander during discussions. For each statement, one point is added if someone agrees with it, one point is subtracted if someone disagrees, and then the score is determined. Results of the aggregate data of multiple students in three months are shown in Table 1 .
The discussion skill of a student is evaluated using the score calculated by the following processes. First, the weight values for every behavior are determined. These weights are going to be rationally determined in the future using machine learning, but for now, the values were decided intuitively based on the difficulty of execution.
Number of participants: 3
Number of presentations: 10
Number of secretary acts: 5
Start-up statements except presenter’s cases: 3
Follow-up statements except presenter’s cases: 2
Quality (sum of agreement/disagreement values): 4
Let the score be the value of the sum after having applied such weight to the number of each behavior. Additionally, the evaluation of statement quality is also calculated. For the discussion skill score calculation, the presenter’s cases are excluded by start-up and follow-up statements of the students. This is because the situations when the presenters must answer the question from other participants occur naturally and they should not be treated the same way as cases in which participants of the discussion make remarks spontaneously.
The students can judge their status for this evaluation as reference, and can analyze their weak points. The student performance increases if the student makes many statements when he/she is not the presenter and many of the other participants also agree with these statements. It is then possible that these data be a basis to improve a student’s discussion skills. It can also be confirmed that the discussion skill is improved by making high quality statements, that is, a lot of agreements obtained from many participants.
- Presentation skill
A study on developing oral presentations skills embedded oral presentations and assessment to their curriculum Kerby and Romine (2009 ). In their case study, they included at least one oral presentation in three of their courses and used a rubric to assess the oral presentations. Their results indicate that students better understood their weaknesses, strengths, and areas for improvement with their presentations. In our study, we also implemented the same design to improve the presentation skills of our students. We conducted two poster presentation sessions with two groups of students to evaluate their presentation skills. We used the poster presentation format instead of the regular oral presentations because of the interactivity of poster presentations. In poster presentations, the students are able to engage in conversation with people, giving them more opportunities to improve their communication skills. Also, poster presentations enliven the student presentations because students interact with each other more instead of just passively observing like in formal presentations.
Poster presentation session I
In this poster presentation session, twenty four (24) inexperienced students were divided into six (6) groups and each group was asked to create a digital poster using the authoring tool discussed in Section ‘ Digital poster presentation system ’. Each group presented their posters in the allotted time of fifteen (15) minutes while members of the other groups and spectators of the poster session evaluated each poster presentation. The evaluation sheet used for this poster presentation session is shown in Table 2 .
Evaluators fill up the feedback form shown in Table 2 for each presentation. The evaluation criteria include Content , Organization , and Impact . The said criteria are based on the common themes in Brownlie’s 2007 bibliography Hess et al. (2009 ). For scoring results, the numerical values for the different ratings are as follows: Bad is 1, Poor is 2, Fair is 3, Good is 4, and Excellent is 5. The average scores of all the evaluators for all group presentations are shown in Table 3 .
In addition, the scores and standard deviations of all groups are shown in Figure 15 . Since the standard deviations are not too large, this metric is not far off from human intuition for evaluation. Histories of interactions with digital posters are not analyzed yet. We are planning to combine human metrics and accumulated data such as access counts of posters and their internal elements in the near future.
Scores and standard deviations of all groups.
However, there were major drawbacks in the evaluation sheet that we used for this session. First, we failed in evaluating the presentation delivery of the students. Second, the evaluators found it hard to judge a certain criteria based on the ratings. Thus, for the next poster presentation session, we made a number of changes in our evaluation sheet.
Poster presentation session II
In this poster presentation session, five (5) students were asked to create and present five digital posters using the authoring tool discussed in Section ‘ Digital poster presentation system ’. Spectators of the poster session were asked to evaluate each poster presentation.
We improved our evaluation criteria based on the encountered problems in the former trial. Based on feedback from the evaluators, one major drawback in the previous evaluation sheet shown in Table 2 is that there are not enough details for the ratings (Bad, Poor, Fair, Good, and Excellent) under a certain criteria. Thus, the evaluation sheet was modified to a rubric with concrete descriptions for each score and criteria. The new evaluation sheet is shown in Table 4 . Using this rubric-style of evaluation, the evaluation criteria were clearer and evaluation time were faster for the spectators. Aside from changing the evaluation format, the sets of criteria were also modified. We added two main sets of criteria: impact and presentation. We added Impact to determine how the poster is able to attract the attention of spectators. It consists of the criteria for evaluating the poster’s title, overall appearance, and interest. We also added Presentation , another set of criteria for evaluating the students’ poster presentation skills. It consists of the ability to communicate properly to their audience and the ability to answer questions confidently. Adding these new sets of criteria provided a more effective and complete digital poster evaluation.
Using the new evaluation sheet, the score results of the second round of poster presentations are shown in Table 5 . The evaluation scores of the professors (P) and students (S) were calculated. With these results, we were able to determine the weakness of each poster based on the criteria. For example, with Poster III, its content and organization needed a lot of improvement thus for feedback, the author needs to focus on these sets of criteria when he/she modifies the said poster.
Future features of the new learning environment
The current training environment contains a 2D interactive system, such as touch panel discussion tables, digital poster panels, and an interactive wall-sized whiteboard, facilitating the interactions of users with the system. However, to further enhance the performance of the current learning environment, a vision system will be incorporated to increase the interaction dimension to 3D. The system will consist of a multi-camera system or Kinect that has a camera and range sensor device. Moreover, given an intelligent system that recognizes the users by robust face detection algorithm, user interaction will be smooth, and annotations will be automated and personalized, thereby creating a more advanced learning environment. An automated evaluation and facilitation of intellectual activities will also be applied to confirm whether the skills of the students improve, and whether their created contents obtain a higher evaluation than previous ones.
The current criteria does not evaluate body movement, gestures, posture, etc., which is common in evaluating presentations. However, it is difficult to evaluate these criteria and we will be incorporating evaluating these movements through the planned vision system. In order to improve the evaluation criteria presented in previous section, the automated system is expected to receive real-time evaluation from the audience and to provide the presenter with the relative score. The registered audience can input their score to an online sheet with a tablet while attending the poster session. The audio-visual system is also expected to record the visual and audio interactions between the presenter and each audience. The system will be able to match the provided online score by each spectator and his/her interaction with the presenter. We hope to understand the relation between the audio/visual information and the provided online score to train the system. Our eventual goal is to introduce a nearly automatic evaluation system that is regularly trained by the audience.
A novel physical-digital learning environment for discussion and presentation skills training has been developed at our university under the leading graduate program. By using state-of-the-art technologies, the selected students of the program will achieve an effective, interactive, and smooth discussion with the discussion mining system simultaneously summarizing and annotating the ongoing discussion. The discussion contents are available to the community or to the faculty for evaluation, feedback, and follow-up activities.
Moreover, the students of the program also have opportunities to improve their presentation skills with our digital poster presentation system. A presentation evaluation system has been adopted to our physical-digital learning environment that will be capable of evaluating each presentation and/or discussion based on audiences online feedback, recorded audio-visual data, and interaction with the facilities. The developed interactive presentation system has been initially evaluated and proven to be effective, not only for our novel physical-digital learning environment, but also for any other users equipped at least with an interactive display.
Evaluations were done to help the students in overcoming their weak points during their discussions and presentations. With this prototype environment, a new education system may emerge promoting an efficient and advanced learning.
Written informed consent was obtained from the students for the publication of this report and any accompanying images.
Armstrong, K, Big data: a revolution that will transform how we live, work, and think. Inf. Commun. Soc. 17(10), 1300–1302 2014.
Bengio, Y, Learning deep architectures for ai. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2(1), 1–127 2009.
Chiu, P, J Boreczky, A Girgensohn, D Kimber, in Proceedings of the Tenth World Wide Web Conference. WWW10 . LiteMinutes: An Internet-based system for multimedia meeting minutes (ACMNew York, NY, USA, 2001), pp. 140–149.
Conklin, J, ML Begeman, gibis: A hypertext tool for exploratory policy discussion. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 6(4), 303–331 1988.
Cutrone, L, M Chang, Kinshuk, in Technology for Education (T4E), 2011 IEEE International Conference On . Auto-assessor: Computerized assessment system for marking student’s short-answers automatically (IEEE Computer Society, Los AlamitosCA, USA, 2011), pp. 81–88 isbn = 978-0-7695-4534-9.
Hess, GR, KW Tosney, LH Liegel, Creating effective poster presentations: Amee guide no. 40. Med. Teach. 31(4), 319–321 2009.
Kerby, D, J Romine, Develop oral presentation skills through accounting curriculum design and course-embedded assessment. J. Educ. Bus. 85(3), 172–179 2009.
Kurihara, K, M Goto, J Ogata, Y Matsusaka, T Igarashi, in Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Multimodal Interfaces. ICMI ’07 . Presentation sensei: a presentation training system using speech and image processing (ACMNew York, NY, USA, 2007), pp. 358–365.
Lee, D-S, B Erol, J Graham, JJ Hull, N Murata, in Proceedings of the Tenth ACM International Conference on Multimedia. MULTIMEDIA ’02 . Portable meeting recorder (ACMNew York, NY, USA, 2002), pp. 493–502.
Nagao, K, K Kaji, D Yamamoto, H Tomobe, in Advances in Multimedia Information Processing - PCM 2004. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 3331 , ed. by K Aizawa, Y Nakamura, and S Satoh. Discussion mining: Annotation-based knowledge discovery from real world activities (Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2005), pp. 522–531. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-30541-5_64 .
Ohira, S, K Kawanishi, K Nagao, in Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality. TEEM ’14 . Assessing motivation and capacity to argue in a gamified seminar setting (ACMNew York, NY, USA, 2014), pp. 197–204.
Omori, Y, K Ito, S Nishida, T Kihira, in Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 2006. SMC ’06. IEEE International Conference On, vol. 3 . Study on supporting group discussions by improving discussion skills with expost evaluation (IEEE, 2006), pp. 2191–2196.
Sellen, AJ, S Whittaker, Beyond total capture: a constructive critique of lifelogging. Commun. ACM. 53(5), 70–77 2010.
Trinh, H, K Yatani, D Edge, in Proceedings of the 32nd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. CHI ’14 . Pitchperfect: Integrated rehearsal environment for structured presentation preparation (ACMNew York, NY, USA, 2014), pp. 1571–1580.
Wanas, N, M El-Saban, H Ashour, W Ammar, in Proceedings of the 2Nd ACM Workshop on Information Credibility on the Web. WICOW ’08 . Automatic scoring of online discussion posts (ACMNew York, NY, USA, 2008), pp. 19–26.
Download references
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Real-World Data Circulation Leaders’ Graduate Program of Nagoya University.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Media Science, Graduate School of Information Science, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan
Katashi Nagao
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Graduate School of Engineering, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan
Mehrdad Panahpour Tehrani
Department of Information Engineering, Graduate School of Information Science, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan
Jovilyn Therese B Fajardo
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Katashi Nagao .
Additional information
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
KN, MPT, and JTF conducted research activities on development of an advanced physical-digital learning environment that can train students to enhance their discussion and presentation skills, and drafted the results in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0 ), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Nagao, K., Tehrani, M.P. & B Fajardo, J.T. Tools and evaluation methods for discussion and presentation skills training. Smart Learn. Environ. 2 , 5 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-015-0011-1
Download citation
Received : 09 September 2014
Accepted : 21 January 2015
Published : 24 February 2015
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-015-0011-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Learning environment
- Skill training
- Discussion mining
- Digital poster

Featured Resource
Why hiv prevention, we are not on track..
Despite progress in several countries, we are still not on track to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030. In 2022, about 4000 adults and children acquired HIV each day — a total of 1.3 million new HIV infections. Lifesaving antiretroviral therapy can also prevent HIV by suppressing the virus in a person’s blood to an untransmissible level, but 9.2 million people living with AIDS did not receive ART in 2022.
Intensive effort is needed to reach the global target of fewer than 370,000 new HIV infections annually by 2025.
Accelerating progress in HIV prevention is particularly important in the GPC focus countries where three out of four new HIV infections occur.
Learn About the GPC
1.3 million new HIV infections
39 million people living with hiv, 630,000 people died of aids related illnesses, global search.

Assess HIV prevention efforts in your country
The Global HIV Prevention Coalition and partners in HIV prevention have developed tools to facilitate country-led planning of prevention programmes. Tools are available for use in GPC and non-GPC countries for each of the thematic “pillars” of HIV prevention.
Upcoming Events
South-to-south learning network webinar: sexual and reproductive health and prevention of mother-to-child transmission, south-to-south learning network webinar: hiv prevention self-assessment tools, global key populations hiv prevention pre-conference.
- Open access
- Published: 31 May 2024
Freely available, online videos to support neurological physiotherapists and students in task-specific training skill acquisition: a scoping review
- Nicola C.M. Towersey 1 ,
- Kelvin Sasse 1 ,
- Verna Stavric 1 ,
- Gemma Alder 1 &
- Nicola L. Saywell 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 603 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
20 Accesses
Metrics details
Videos to support learning of clinical skills are effective; however, little is known about the scope and educational quality of the content of freely available online videos demonstrating task-specific training (TST). This review aimed to determine the extent, characteristics of freely available online videos, and whether the content is suitable to guide skill acquisition of task-specific training for neurological physiotherapists and students.
A scoping review was conducted. Google video and YouTube were searched in December 2022. Videos that met our eligibility criteria and were explicitly designed for (TST) skill acquisition were included in the report.
Ten videos met the inclusion criteria and were difficult to find amongst the range of videos available. Most were presented by physiotherapists or occupational therapists, originated from the USA, featured stroke as the condition of the person being treated, and involved a range of interventions (upper limb, constraint induced movement therapy, balance, bicycling). Most videos were created by universities or private practices and only two used people with a neurological condition as the participant. When the content of videos and their presentation (instruction and/or demonstration), was assessed against each key component of TST (practice structure, specificity, repetition, modification, progression, feedback), five of the videos were rated very suitable and five moderately suitable to guide skill acquisition. Most videos failed to demonstrate and provide instruction on each key component of TST and were missing at least one component, with feedback most frequently omitted.
Conclusions
There are many freely available online videos which could be described as demonstrating TST; very few are suitable to guide skill acquisition. The development of a standardised and validated assessment tool, that is easy to use and assesses the content of TST videos is required to support learners to critically evaluate the educational quality of video content. Guidelines based on sound teaching theory and practice are required to assist creators of online videos to provide suitable resources that meet the learning needs of neurological physiotherapists and students.
Peer Review reports
Task-specific training (TST) is a common rehabilitation strategy used and taught by a wide range of allied health professionals including physiotherapists, occupational therapists, speech language therapists and academic institutions. It involves goal directed practice, repetition, progressive challenge, and positive reinforcement to optimise motor learning [ 1 ]. TST has been shown to be effective at inducing cortical reorganization, decreasing disability and improving functional outcomes for people with neurological conditions such as stroke, Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injury and cerebral palsy [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 ]. TST is referred to in the literature by a range of terms, including ‘repetitive functional task practice’, ‘repetitive task practice’ [ 3 ], ‘task-orientated therapy’ [ 1 ] and ‘task-related training’ [ 9 ]. For this review, it will be referred to as task-specific training (TST).
The widespread use of the internet has extended traditional education by enabling users to search for, watch, and share a large variety of freely available online videos to supplement their learning. The use of online videos has grown in popularity over the past decade with ease of access and low cost making them one of the most frequently used self-learning resources for health professionals and students [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. Videos have been shown to significantly improve learning outcomes [ 13 ], however, mechanisms for controlling the content within online videos are limited. The results of internet searches are determined by an algorithm using likes, views, and popularity rather than an assessment of whether the content is suitable to guide skill acquisition [ 14 , 15 ] and previous studies have found online videos often omit key learning points and are of variable educational quality [ 14 , 16 , 17 , 18 ].
Freely available online videos may be useful to guide skill acquisition and reinforce learning for neurological physiotherapists and students. However, there is a need to evaluate the quality of the content of these videos to ensure that they are based on best practice. To our knowledge, there has been no research exploring the extent, characteristics, and educational quality of freely available online videos for the skill acquisition of TST. In this scoping review, our aim was to determine the extent, characteristics, and whether the content of freely available online videos is suitable to guide skill acquisition of TST.
A scoping review was conducted and carried out according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and meta-analysis for scoping reviews (PRISMA- ScR), adapting the five stages suggested by Arksey and O’Malley and the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) for evidence synthesis [ 21 , 22 , 23 ]. An a priori protocol was developed to guide this review prior to undertaking it.
Identifying relevant videos
A detailed search plan outlining the search terms, sources, eligibility criteria, and delimiters was established based on suggestions by Godin et al. [ 24 ], and in consultation with a senior librarian. The JBI; Population, Concept and Context (PCC) elements were used to formulate a combination of search terms to maintain transparency, ensure organised search methods, and reduce the risk of bias [ 23 ]. The population included neurological physiotherapy, the condition of interest or intended audience, were left open. The concept was the demonstration and instruction of TST that a novice could use for skill acquisition. The context included rehabilitation. Refer to Table 1 for the initial search terms.
The inclusion criteria included videos with the stated purpose to teach TST and included an element of physical skill demonstration and instruction. Videos had to be freely available online via a device with internet capabilities, in English, without subscription requirements to access, and within the scope of neurological physiotherapy practice [ 25 ]. There were no restrictions on the rehabilitation setting, date of upload, duration of video, or country of origin (Table 2 ).
A pilot search was carried out as suggested by the JBI guidelines [ 23 ] and following discussion between authors; search terms and the eligibility criteria were refined to reduce ambiguity regarding the definition of TST, and the level of instruction required for the video. For this review, TST included practice of meaningful tasks. Tasks were considered part-task if they were linked to a whole-task reconstruction; virtual reality involving the upper limb was considered part-task as it lacked the manipulation of physical objects and were included. Instructions needed to be provided during TST with sufficient detail to allow a novice to apply it. These could have been in the form of subtitles, voice-over, or directly to the camera.
Google video search engine and YouTube were searched due to their high use, free access and relevancy ordered results [ 26 ]. YouTube has 2,562 million active users, while Google is the dominant global search engine, with an 84.08% worldwide market share [ 26 , 27 ]. Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and being logged into Google accounts have been found to contribute 11.7% to variation in results [ 19 ]. Therefore, searches were performed with personalised search off, in Google Chrome incognito browser, with relevancy sorting on, to improve the consistency of the search results. To reduce the effect of algorithmic searching, all preliminary searches were conducted on the Firefox search engine, with official searches performed in Google incognito, from the same IP address, on a single day in Auckland, New Zealand.
The searches were conducted from Auckland, New Zealand (NZ), on the 16th of December 2022 by KS. The complete search strategy used in Google video search engine and YouTube is in Appendix 1 . Ten searches were conducted on each search engine with the first 10 pages of each search (representing 100 results) screened for relevance. This number was chosen to capture a wide range of the most relevant results, while still being feasible to screen [ 24 ]. Potentially relevant videos were bookmarked in a folder named after the search engine and in a subfolder with the search terms used [ 24 ]. If a video was embedded within a website, it was followed to its source and then bookmarked, to reduce duplicates.
Finally, a series of YouTube channels were hand searched to identify missed videos. Consistency was maintained by the same reviewer (KS), using the same IP address, applying the same method as the primary searches, on a single day (22nd December 2022).
Video selection
Videos were selected using the following process. Duplicates were removed and KS screened all the videos against the eligibility criteria. A second reviewer (NT) independently cross-checked 20% of videos, to check for consistency and appropriate application of the selection criteria. Any discrepancies were referred to NLS to be resolved by consensus.
Data charting
Data charting was used to synthesise and interpret the data [ 21 ]. KS and NT independently viewed the selected videos and summarised the data in a Microsoft (MS) Excel spreadsheet, based on the JBI guidelines [ 22 , 23 ]. The data extracted for this review were the video title, upload date, duration, number of views, likes/ dislikes, the presenter(s), the participant(s), source, country of origin, intervention, the key components of TST (practice structure, specificity, repetition, modification, progression, feedback) and how they were presented (instruction and/or demonstration).
Summarising and reporting results
To address the extent and characteristics of the selected videos, we identified trends using data analysing tools and pivot tables in MS Excel and presented the data descriptively.
Scoring of videos
The suitability of videos to guide skill acquisition was assessed using a pragmatic scoring system developed for this scoping review. Although previous studies have developed scoring systems to evaluate online material [ 28 , 29 ], none were appropriate for the purpose of this study. The scoring system was developed after reviewing pertinent literature [ 30 , 31 ] and seeking expert opinion. It evaluated video content against the agreed key components of TST for motor learning (practice structure, specificity, repetition, modification, progression, feedback) and whether demonstration and instruction were provided on each component. Videos were scored from 0 to 2 for each of the six TST components for a total possible score of 12. Components scored 2 if both demonstration and instruction were provided, 1 if they provided either one, or 0 for a missing component. Those videos scoring 0–4 were considered unsuitable, 5–8 moderately suitable and 9–12 very suitable to guide skill acquisition. Data analysis was conducted by KS, and NT and NSW, physiotherapists with extensive clinical and teaching experience in neurological physiotherapy.
Identification and selection of material
Google Video and YouTube searches resulted in 2,000 videos. After initial screening of titles and thumbnails, 179 were bookmarked as potentially relevant. Hand-searching YouTube channels identified an additional 12 videos, resulting in 191 videos being manually inputted into a MS Excel spreadsheet.
All 191 videos were screened against the eligibility criteria by KS, with NT cross-checking 20% between January 11th, 2023, and January 13th, 2023. The agreement between reviewers was high (95%), exceeding the PRISMA-ScR guidelines requirements of 70–80% agreement [ 22 ]. A third reviewer (NLS) adjudicated any discrepancies (7%) with reference to the definition of TST and the inclusion criteria. Of the181 rejected videos, seven were duplicates, four were unavailable in English, 74 did not meet our definition for TST, 47 did not explicitly state that the purpose of the video was to teach TST, six had no skills demonstration in the video and 43 did not have sufficient instruction to allow a novice to repeat. Only ten videos fulfilled the eligibility criteria (0.4% of videos identified, 5% of videos bookmarked) and were included in the review, as represented in Fig. 1 .
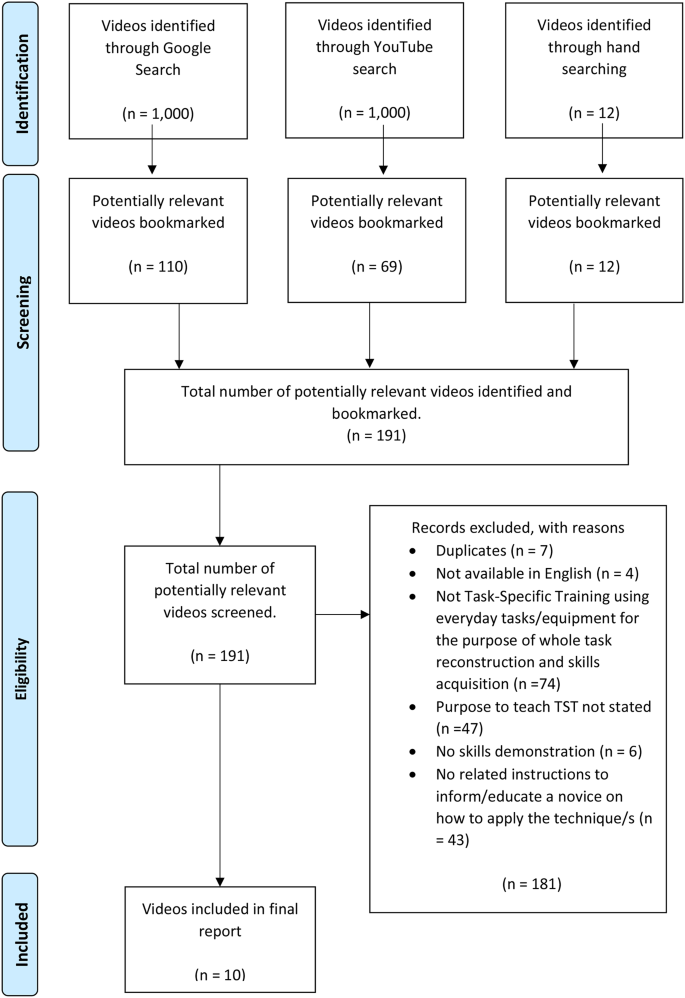
PRISMA flow diagram
Description of included videos
Videos had been uploaded to the platform a median of 30 months prior to our search date (range: 7–79 months). The median length of videos was 5.32 min (range: 3–20 min), with a median of 1386.5 views (range: 181–21950). The median number of likes for a video was 11.5 (range: 2–581), and the number of dislikes for all videos was 0. Occupational therapists were presenters in five of the videos, physiotherapists in two and the professional status of the presenter was unidentified in three videos. The focus of most videos was stroke rehabilitation (9) with cerebral palsy rehabilitation presented in one. Only two of the videos included people with the selected condition as participants. Seven videos were uploaded by universities, two by clinicians in a private practice and one by an unidentified contributor. Most videos were created in the United States of America (USA) with one each from Australia and India. A range of interventions were presented including upper limb training (7), bicycle training (1), constraint induced movement therapy (1), and balance training (1). A summary of the characteristics of the included videos is provided in Table 3 .
Only 10 videos explicitly stated that the purpose of the video was to teach TST and therefore had their content assessed for its suitability to guide skill acquisition. The videos were assessed in relation to the key components of TST (practice structure, specificity, repetition, modification, progression, feedback) and how they were presented (with instruction and/or demonstration). All videos included demonstration and instruction about manipulating practice structure to promote motor learning. Specificity was demonstrated in all videos using physical objects relevant to the task, while only three videos provided instruction in addition to demonstration. Nine of the videos provided demonstration and instruction on the use of repetition, with one video providing instruction only. Five videos provided demonstration and instruction on how to modify the activity, three provided instructions only and two failed to provide modification. Seven videos provided demonstration and instruction on progressions, with two videos providing instruction only, and one failing to demonstrate or provide instruction on any form of progression. None of the videos demonstrated the provision of feedback to promote motor learning and only one video provided instruction on how to provide feedback. The scores for videos ranged from 6 to 9/12 with five videos being considered moderately suitable and five very suitable to guide skill acquisition. Only one video included all the key components of TST and none of the videos provided demonstration and instruction on each component. A breakdown of the TST components and suitability scores is detailed in Table 4 .
This review was the first, to our knowledge, to examine the extent, characteristics, and suitability of freely available online videos that guide skill acquisition of TST for neurological physiotherapists and students. Despite a wide and comprehensive search strategy, only ten videos met the eligibility criteria. This suggests that despite over 2000 videos being available, there is a lack of suitable material to address the skill acquisition of TST for neurological physiotherapists and students.
This review highlights a fundamental problem when searching for educational videos online. Namely, it is difficult to find the few suitable videos amongst the array of videos of variable educational quality. It is unlikely that everyday internet users would be prepared to screen so many videos to find those ones related to TST which provide adequate information for training skill acquisition. Several authors have suggested mechanisms to improve the identification of educational videos. The use of a domain based ranking system, that ranks videos from trusted sources (universities or health organisations) higher up in the search results may make identification easier [ 32 ]. The use of inbuilt educational filters, with a strict criterion for labelling content as educational, might also improve identification [ 32 , 33 ]. In addition, organisations with an interest in educating physiotherapists could identify and disseminate existing online videos that are suitable to guide skill acquisition.
During our review of the characteristics of videos, we noticed that physiotherapists and occupational therapists created the majority of TST videos using a range of interventions, mainly featuring the upper limb, and the condition of stroke. None of the videos demonstrated the use of TST during walking, which would be particularly useful for neurological physiotherapists and students, as this is often their focus in rehabilitation. People with a neurological condition used as participants were found in only two of the videos. One of the strengths of video is that it can depict authentic, real-world experiences of people with neurological conditions during rehabilitation sessions. The lack of involvement of people who have real impairments means subtleties in using TST skills for people with a neurological condition will be overlooked. Time constraints and ethical considerations may have been factors in the reduced involvement of people with neurological conditions, however, overcoming these issues to include people with real impairments would enhance the learning experience.
The suitability of videos to guide skill acquisition was assessed in relation to the key components of TST and how they were presented (with demonstration and/ or instructions) and were found to be variable. None of the videos provided demonstration and instruction for each component of TST, and only one video included all the key components. The use of instruction and demonstration has been found to optimise skill acquisition [ 34 , 35 ], therefore, its omission would impact users’ understanding of the components and their ability to perform TST effectively. Feedback was omitted in all but one video, which was concerning as feedback is essential for motor learning and an integral component of TST [ 36 , 37 ]. These results support the findings of previous studies, which found videos created for health professions to be of low educational quality and missing key information. Videos on surface anatomy omitted key aspects related to upper and lower limb anatomy, such as vessels, nerves, cubital fossa, wrists, and hands [ 28 ]. Videos by physiotherapists on shoulder joint mobilisation techniques failed to describe or illustrate vital aspects of techniques such as patient and therapist position, force of application and dosage [ 17 ]. Online videos have also frequently been found to contain inaccurate, contradictory, or misleading information [ 28 , 32 , 38 , 39 ] with no reference to sources or evidence; this is in part due to the lack of peer review processes to monitor quality [ 38 ]. This highlights, that users need to critically evaluate the content of videos, and that improvements need to be made before they can be recommended as a valuable learning resource.
It has been suggested that the quality of video content for education can be filtered by evaluating variables such as the uploading source, video duration or the subjective estimation by viewers, expressed as likes/dislikes. The uploading source in particular has been found to be valuable for discriminating and predicting the quality of video content. Those uploaded by professionals, professional associations, and credible health care organisations are often of higher quality and are more suitable for education than those uploaded by individuals [ 38 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 ]. In contrast, video duration and the likes/dislikes ratio were found to be unreliable as a predictor of quality [ 14 , 40 , 42 , 43 ]. These results are consistent with the findings from our study which found that the videos sourced from educational institutions or private clinics were more suitable to guide skill acquisition. Neurological physiotherapists and students should consider the source of online videos to assist them to assess the educational quality of video resources.
This review highlights the importance of evaluating the content within freely available online videos. There are several tools available for assessing the quality, flow, and user friendliness of websites [ 44 ], evaluating health information on the internet, and the credibility of websites [ 45 ]. Although these tools are somewhat useful, they do not assess the content of the video in sufficient detail to help users determine if they are a suitable learning resource to guide skill acquisition. The development of content specific quality tools is required to assist learners to critically evaluate the quality of video content. In addition, guidelines based on sound teaching theory and practice are required to assist creators of online videos to create high quality resources that meet the needs of neurological physiotherapists and students.
This study was the first, to our knowledge, to examine the extent, characteristics of freely available online videos, and whether the content is suitable to guide skill acquisition of TST for neurological physiotherapists and students. Previous studies [ 38 , 39 ] have evaluated the quality of online videos using various gross assessment tools [ 44 , 45 , 46 ]. However, these tools do not evaluate the video content; our study assessed whether the content of freely available online TST videos is suitable to guide skill acquisition. This review has identified difficulties neurological physiotherapists and students face in sourcing relevant videos of good educational quality without subscriptions to specialised domains. Attempts were made throughout the searches to reduce the impacts of search engine personalisation; and consistent reporting of the search strategy and methods, maintained rigour and transparency.
Limitations
The criteria used to evaluate the suitability of the video content for skill acquisition was developed by the authors, was subjective, and may have been affected by observer bias. To reduce the risk of bias, two authors (KS, NT) assessed each video independently. The use of American spelling was used as it resulted in the most search results however, it may have influenced the identification of videos and resulted in the higher prevalence of videos from the USA. Forty-seven videos were excluded as they did not fit our inclusion criteria of explicitly stating that the purpose was the teach. It is acknowledged that some of these videos may have been videos teaching TST.
There are very few suitable online videos that are freely available and specifically designed to support neurological physiotherapists and students in the skill acquisition of TST. The development of a standardised and validated assessment tool, that is easy to use and assesses the content of TST videos is required to support learners to critically evaluate the educational quality of video content. Guidelines based on sound teaching theory and practice are required to assist creators of online videos to provide suitable resources that meet the needs of neurological physiotherapists and students.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Task-specific training
United States of America
Constraint Induced Movement Therapy
Joanna Briggs Institute
New Zealand
Internet protocol
Population, Concept, Context
Winstein CJ, Wolf SL, Dromerick AW, Lane CJ, Nelsen MA, Lewthwaite R, et al. Effect of a Task-oriented Rehabilitation Program on Upper Extremity Recovery following Motor Stroke: the ICARE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2016;315(6):571–81.
Article Google Scholar
English C, Hillier SL, Lynch EA. Circuit class therapy for improving mobility after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;6(6):Cd007513.
Google Scholar
French B, Thomas LH, Coupe J, McMahon NE, Connell L, Harrison J, et al. Repetitive task training for improving functional ability after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;11(11):Cd006073.
Hornby TG, Reisman DS, Ward IG, Scheets PL, Miller A, Haddad D, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline to improve locomotor function following chronic stroke, incomplete spinal cord Injury, and Brain Injury. J Neurol Phys Ther. 2020;44(1):49–100.
Kwakkel G, Veerbeek JM, van Wegen EE, Wolf SL. Constraint-induced movement therapy after stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(2):224–34.
Lin SH, Dionne TP. Interventions to Improve Movement and Functional outcomes in Adult Stroke Rehabilitation: review and evidence Summary. J Participat Med. 2018;10(1).
Ni M, Hazzard JB, Signorile JF, Luca C. Exercise guidelines for Gait function in Parkinson’s Disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2018;32(10):872–86.
Sakzewski L, Gordon A, Eliasson A-C. The state of the evidence for intensive Upper Limb Therapy approaches for Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. J Child Neurol. 2014;29(8):1077–90.
Bayona NA, Bitensky J, Salter K, Teasell R. The role of task-specific training in rehabilitation therapies. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2005;12(3):58–65.
Pearson Education. Beyond Millennials: The Next Generation of Learners. 2018.
Rapp AK, Healy MG, Charlton ME, Keith JN, Rosenbaum ME, Kapadia MR. YouTube is the most frequently used Educational Video Source for Surgical Preparation. J Surg Educ. 2016;73(6):1072–6.
Ventola CL. Social media and health care professionals: benefits, risks, and best practices. P t. 2014;39(7):491–520.
Noetel M, Griffith S, Delaney O, Sanders T, Parker P, del Pozo Cruz B, et al. Video improves learning in higher education: a systematic review. Rev Educ Res. 2021;91(2):204–36.
Frongia G, Mehrabi A, Fonouni H, Rennert H, Golriz M, Günther P. YouTube as a potential training resource for laparoscopic fundoplication. J Surg Educ. 2016;73(6):1066–71.
Srinivasa K, Chen Y, Henning MA. The role of online videos in teaching procedural skills to post-graduate medical learners: a systematic narrative review. Med Teach. 2020;42(6):689–97.
Derakhshan A, Lee L, Bhama P, Barbarite E, Shaye D. Assessing the educational quality of ‘YouTube’ videos for facelifts. Am J Otolaryngol. 2019;40(2):156–9.
Shah S, Patel R, Patel N, Patel I. Low educational quality and trustworthiness of YouTube videos by physiotherapists on shoulder joint mobilization techniques: a descriptive study. J Man Manip Ther. 2022;30(6):334–41.
Küçükakkaş O, İnce B. Can YouTube be used as an educational tool in lymphedema rehabilitation? Arch Physiother. 2022;12(1):5.
Hannák A, Sapiezynski P, Kakhki AM, Krishnamurthy B, Lazer D, Mislove A et al. Measuring personalization of web search. Proceedings of the 22nd international conference on World Wide Web. 2013.
Bianchi T. Worldwide desktop market share of leading search engines from January 2015 to December 2022: Statista; 2023 January 6 Available from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/216573/worldwide-market-share-of-search-engines/ .
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA Extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Peters MDJ, Marnie C, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Munn Z, Alexander L, et al. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid Synth. 2020;18(10):2119–26.
Godin K, Stapleton J, Kirkpatrick SI, Hanning RM, Leatherdale ST. Applying systematic review search methods to the grey literature: a case study examining guidelines for school-based breakfast programs in Canada. Syst Reviews. 2015;4(1):138.
Lennon S. Physical Management in Neurological Rehabilitation. 2 ed2004.
Bianchi T. Global search engine desktop market share 2022: Statista; 2023, January 6 Available from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/216573/worldwide-market-share-of-search-engines/ .
Kemp SD. 2022: Global Overview Report: Data Reportal - Global Digital Insights; 2022, May 4 Available from: https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2022-global-overview-report .
Azer SA. Can “YouTube” help students in learning surface anatomy? Surg Radiol Anat. 2012;34(5):465–8.
Murugiah K, Vallakati A, Rajput K, Sood A, Challa NR. YouTube as a source of information on cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Resuscitation. 2011;82(3):332–4.
Hubbard IJ, Parsons MW, Neilson C, Carey LM. Task-specific training: evidence for and translation to clinical practice. Occup Ther Int. 2009;16(3–4):175–89.
Kleim JA, Jones TA. Principles of experience-dependent neural plasticity: implications for rehabilitation after brain damage. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2008;51(1):S225–39.
Sunderland N, Camm CF, Glover K, Watts A, Warwick G. A quality assessment of respiratory auscultation material on YouTube. Clin Med (Lond). 2014;14(4):391–5.
Camm CF, Sunderland N, Camm AJ. A quality assessment of cardiac auscultation material on YouTube. Clin Cardiol. 2013;36(2):77–81.
Preston E, Ada L, Dean CM, Stanton R, Waddington G, Canning C. The Physiotherapy eSkills Training Online resource improves performance of practical skills: a controlled trial. BMC Med Educ. 2012;12:119.
Dong C, Goh PS. Twelve tips for the effective use of videos in medical education. Med Teach. 2015;37(2):140–5.
Levin MF, Demers M. Motor learning in neurological rehabilitation. Disabil Rehabil. 2021;43(24):3445–53.
Maier M, Ballester BR, Verschure P. Principles of Neurorehabilitation after Stroke based on Motor Learning and Brain plasticity mechanisms. Front Syst Neurosci. 2019;13:74.
Madathil KC, Rivera-Rodriguez AJ, Greenstein JS, Gramopadhye AK. Healthcare information on YouTube: a systematic review. Health Inf J. 2015;21(3):173–94.
Erdem MN, Karaca S. Evaluating the Accuracy and Quality of the information in kyphosis videos Shared on YouTube. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(22):E1334–9.
Lee JS, Seo HS, Hong TH. YouTube as a potential training method for laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2015;89(2):92–7.
Lee H, Choi A, Jang Y, Lee JI. YouTube as a learning tool for four shoulder tests. Prim Health Care Res Dev. 2018;20:e70.
Ajumobi AB, Malakouti M, Bullen A, Ahaneku H, Lunsford TN. YouTube™ as a source of Instructional Videos on Bowel Preparation: a content analysis. J Cancer Educ. 2016;31(4):755–9.
Desai T, Shariff A, Dhingra V, Minhas D, Eure M, Kats M. Is content really king? An objective analysis of the public’s response to medical videos on YouTube. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(12):e82469.
Bernard A, Langille M, Hughes S, Rose C, Leddin D, Veldhuyzen van Zanten S. A systematic review of patient inflammatory bowel disease information resources on the world wide web. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102(9):2070–7.
Silberg WM, Lundberg GD, Musacchio RA. Assessing, controlling, and assuring the quality of medical information on the internet: Caveant Lector et viewor–let the reader and viewer beware. JAMA. 1997;277(15):1244–5.
Team HON. Health On the Net 2020 updated March 2020; cited 2023 May 13. Available from: https://www.hon.ch/en/ .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Melanie Grant (Senior librarian) contributed to the design of the search strategy.
Kelvin Sasse was funded as part of a student summer scholarship funded by the School of Clinical Sciences, Physiotherapy Department, Auckland University of Technology. Auckland, New Zealand.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Clinical Sciences, Department of Physiotherapy, Health and Rehabilitation Research Institute, Auckland University of Technology, Northshore Campus, Private Bag 92006, Auckland, 1142, New Zealand
Nicola C.M. Towersey, Kelvin Sasse, Verna Stavric, Gemma Alder & Nicola L. Saywell
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
NT, NLS, GA and VS conceived and designed the study and contributed to manuscript preparation. KS collected, collated, analysed the data, and contributed to the writing of the manuscript. NT, NLS, GA and VS also contributed to data collection and analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nicola C.M. Towersey .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Towersey, N., Sasse, K., Stavric, V. et al. Freely available, online videos to support neurological physiotherapists and students in task-specific training skill acquisition: a scoping review. BMC Med Educ 24 , 603 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05545-5
Download citation
Received : 21 June 2023
Accepted : 09 May 2024
Published : 31 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05545-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Search engine
- Neurological rehabilitation
- Physiotherapy
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
3. Create dialogue (and listen carefully) Feedback is never a one-way street. Without the opportunity for dialogue, you're already shutting down and not listening to the other person. Make sure you're creating space for dialogue and active listening. Invite questions — or, even better, feedback.
Create a checklist or use these presentation evaluation examples to make tracking strengths and areas for improvement easier. Tips for giving effective presentation feedback. Just like presenting, giving feedback is a skill that takes practice to master. Because every presentation is different, the specific feedback you give will vary, but the ...
With SlideLizard your attendees can easily give you feedback directly with their Smartphone. After the presentation you can analyze the result in detail. type in your own feedback questions. choose your rating scale: 1-5 points, 1-6 points, 1-5 stars or 1-6 stars; show your attendees an open text field and let them enter any text they want.
Tip #1: Build a narrative. One memorable way to guarantee presentation success is by writing a story of all the points you desire to cover. This statement is based on the logic behind storytelling and its power to connect with people. Don't waste time memorizing slides or reading your presentation to the audience.
Create a distraction-free time and space for getting feedback. Ideally both of you should be present, focused, and open. If we're feeling stressed or pressed for time, it's hard to be a good feedback partner. That's why it's wise to tune in to how you're feeling before you schedule a session. Remind the person that you're looking ...
Feedback Seeking: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to gather insights on your Pecha Kucha presentation's clarity, impact, and effectiveness. ... The Power of Presentation Skills Training. Starting a presentation skills training course is like discovering a secret weapon for professional success. A skilled trainer can guide you through the ...
This is not surprising. Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way. For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget ...
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images. You'll make presentations at various ...
In our Presentation Skills Training workshops, we talk about the importance of making a connection with the audience, and that connection doesn't need to end with the presentation. An immediate response system, such as providing your audience with a presentation feedback form to fill in and return at the end of the presentation is one way to ...
Traditional Ways to Collect Feedback on a Presentation. Printed Exit Survey from the Audience. The most common way to solicit feedback is through a survey. As a professional speaker, though, I have found that this technique is the least helpful. Surveys basically tell you if your audience liked you.
Tip #4: Focus on your presentation design. Tip #5: Visualize boring numbers and data. Tip #6: Practice in front of a live audience. Tip #7: Meet your audience before presenting. Tip #8: Channel nervous energy into enthusiastic energy. Tip #9: Use proper and confident body language.
Step 1: Preparation. Before diving headfirst into feedback, take a moment to familiarize yourself with the context of the presentation. Review the presentation material beforehand, focusing on the topic, objectives, and key messages the presenter aimed to convey. Understanding the presenter's goals allows you to tailor your feedback for maximum ...
Achievable: The goal of the presentation should be attainable. For example, "Trim your slides to no more than six lines per slide and no more than six words per line; otherwise, you are just reading your slides.". Realistic: The feedback you give should relate to the goal the presenter is trying to achieve. For example, "Relating the ...
To fully understand the impact these skills have on creating a successful presentation, it's helpful to look at each one individually. Here are six valuable skills you can develop: 1. Active listening. Active listening is an excellent communication skill for any professional to hone.
Presentation Skills Training: Choosing the Right Feedback Technique. Feedback Sandwich: Give balanced feedback with positive comments before and after constructive criticism. Adult to Adult: Express feedback based on feelings rather than actions to avoid defensiveness. 360-Degree Feedback: Gather feedback from diverse sources to provide a ...
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
1. Ability to analyse an audience effectively and tailor the message accordingly. If you ask most people what makes a great presentation, they will likely comment on tangible things like structure, content, delivery and slides. While these are all critical aspects of a great presentation, a more fundamental and crucial part is often overlooked ...
HBR Learning's online leadership training helps you hone your skills with courses like Presentation Skills. Earn badges to share on LinkedIn and your resume. Access more than 40 courses trusted ...
Presentation Skills: Exceeds Expectations Phrases. Always prepares well before making any form of presentation whether formal or non-formal. Gives a clear and well-structured delivery when making a presentation. Exhibits excellent skill when it comes to expressing ideas and opinions with clarity. Knows the audience well enough to use proper ...
A) Presentation Structure. 1. Story flow: This parameter is used to evaluate the flow structure chosen to build the presentation. The structure could be anything from - 'Problem - cause- solution' to 'Goal - path- challenges'. The evaluation is based on clarity and logic of the argument.
About the For-Credit Version of this course • 10 minutes. About Successful Presentation • 15 minutes. Kuskin's Top Ten Best Practices • 15 minutes. Keith Code's Twist of the Wrist • 10 minutes. Successful Presentation Assignment, Part 1: Telling a Two-Minute Story • 70 minutes. 1 quiz • Total 25 minutes.
2. Ask questions. During your presentation, ask questions that engage the audience and help you understand their needs and interests. This can help you tailor your presentation to meet their expectations. 3. Analyse non-verbal cues. Pay attention to non-verbal cues, such as facial expressions and body language.
Presentation evaluation Fully-automatic. A presentation training system called Presentation Sensei was implemented to observe a presentation rehearsal and give presentation feedback to the speaker Kurihara et al. (2007). The system is equipped with a microphone and camera to analyze the presentation by combining speech and image processing ...
Assess HIV prevention efforts in your country. The Global HIV Prevention Coalition and partners in HIV prevention have developed tools to facilitate country-led planning of prevention programmes. Tools are available for use in GPC and non-GPC countries for each of the thematic "pillars" of HIV prevention.
Videos to support learning of clinical skills are effective; however, little is known about the scope and educational quality of the content of freely available online videos demonstrating task-specific training (TST). This review aimed to determine the extent, characteristics of freely available online videos, and whether the content is suitable to guide skill acquisition of task-specific ...