
Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.

How to Structure your Presentation, with Examples
August 3, 2018 - Dom Barnard
For many people the thought of delivering a presentation is a daunting task and brings about a great deal of nerves . However, if you take some time to understand how effective presentations are structured and then apply this structure to your own presentation, you’ll appear much more confident and relaxed.
Here is our complete guide for structuring your presentation, with examples at the end of the article to demonstrate these points.
Why is structuring a presentation so important?
If you’ve ever sat through a great presentation, you’ll have left feeling either inspired or informed on a given topic. This isn’t because the speaker was the most knowledgeable or motivating person in the world. Instead, it’s because they know how to structure presentations – they have crafted their message in a logical and simple way that has allowed the audience can keep up with them and take away key messages.
Research has supported this, with studies showing that audiences retain structured information 40% more accurately than unstructured information.
In fact, not only is structuring a presentation important for the benefit of the audience’s understanding, it’s also important for you as the speaker. A good structure helps you remain calm, stay on topic, and avoid any awkward silences.
What will affect your presentation structure?
Generally speaking, there is a natural flow that any decent presentation will follow which we will go into shortly. However, you should be aware that all presentation structures will be different in their own unique way and this will be due to a number of factors, including:
- Whether you need to deliver any demonstrations
- How knowledgeable the audience already is on the given subject
- How much interaction you want from the audience
- Any time constraints there are for your talk
- What setting you are in
- Your ability to use any kinds of visual assistance
Before choosing the presentation’s structure answer these questions first:
- What is your presentation’s aim?
- Who are the audience?
- What are the main points your audience should remember afterwards?
When reading the points below, think critically about what things may cause your presentation structure to be slightly different. You can add in certain elements and add more focus to certain moments if that works better for your speech.

What is the typical presentation structure?
This is the usual flow of a presentation, which covers all the vital sections and is a good starting point for yours. It allows your audience to easily follow along and sets out a solid structure you can add your content to.
1. Greet the audience and introduce yourself
Before you start delivering your talk, introduce yourself to the audience and clarify who you are and your relevant expertise. This does not need to be long or incredibly detailed, but will help build an immediate relationship between you and the audience. It gives you the chance to briefly clarify your expertise and why you are worth listening to. This will help establish your ethos so the audience will trust you more and think you’re credible.
Read our tips on How to Start a Presentation Effectively
2. Introduction
In the introduction you need to explain the subject and purpose of your presentation whilst gaining the audience’s interest and confidence. It’s sometimes helpful to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped to help filter down your topic:
- Introduce your general topic
- Explain your topic area
- State the issues/challenges in this area you will be exploring
- State your presentation’s purpose – this is the basis of your presentation so ensure that you provide a statement explaining how the topic will be treated, for example, “I will argue that…” or maybe you will “compare”, “analyse”, “evaluate”, “describe” etc.
- Provide a statement of what you’re hoping the outcome of the presentation will be, for example, “I’m hoping this will be provide you with…”
- Show a preview of the organisation of your presentation
In this section also explain:
- The length of the talk.
- Signal whether you want audience interaction – some presenters prefer the audience to ask questions throughout whereas others allocate a specific section for this.
- If it applies, inform the audience whether to take notes or whether you will be providing handouts.
The way you structure your introduction can depend on the amount of time you have been given to present: a sales pitch may consist of a quick presentation so you may begin with your conclusion and then provide the evidence. Conversely, a speaker presenting their idea for change in the world would be better suited to start with the evidence and then conclude what this means for the audience.
Keep in mind that the main aim of the introduction is to grab the audience’s attention and connect with them.
3. The main body of your talk
The main body of your talk needs to meet the promises you made in the introduction. Depending on the nature of your presentation, clearly segment the different topics you will be discussing, and then work your way through them one at a time – it’s important for everything to be organised logically for the audience to fully understand. There are many different ways to organise your main points, such as, by priority, theme, chronologically etc.
- Main points should be addressed one by one with supporting evidence and examples.
- Before moving on to the next point you should provide a mini-summary.
- Links should be clearly stated between ideas and you must make it clear when you’re moving onto the next point.
- Allow time for people to take relevant notes and stick to the topics you have prepared beforehand rather than straying too far off topic.
When planning your presentation write a list of main points you want to make and ask yourself “What I am telling the audience? What should they understand from this?” refining your answers this way will help you produce clear messages.
4. Conclusion
In presentations the conclusion is frequently underdeveloped and lacks purpose which is a shame as it’s the best place to reinforce your messages. Typically, your presentation has a specific goal – that could be to convert a number of the audience members into customers, lead to a certain number of enquiries to make people knowledgeable on specific key points, or to motivate them towards a shared goal.
Regardless of what that goal is, be sure to summarise your main points and their implications. This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there.
Follow these steps:
- Signal that it’s nearly the end of your presentation, for example, “As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…”
- Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation – “In this speech I wanted to compare…”
- Summarise the main points, including their implications and conclusions
- Indicate what is next/a call to action/a thought-provoking takeaway
- Move on to the last section
5. Thank the audience and invite questions
Conclude your talk by thanking the audience for their time and invite them to ask any questions they may have. As mentioned earlier, personal circumstances will affect the structure of your presentation.
Many presenters prefer to make the Q&A session the key part of their talk and try to speed through the main body of the presentation. This is totally fine, but it is still best to focus on delivering some sort of initial presentation to set the tone and topics for discussion in the Q&A.

Other common presentation structures
The above was a description of a basic presentation, here are some more specific presentation layouts:
Demonstration
Use the demonstration structure when you have something useful to show. This is usually used when you want to show how a product works. Steve Jobs frequently used this technique in his presentations.
- Explain why the product is valuable.
- Describe why the product is necessary.
- Explain what problems it can solve for the audience.
- Demonstrate the product to support what you’ve been saying.
- Make suggestions of other things it can do to make the audience curious.
Problem-solution
This structure is particularly useful in persuading the audience.
- Briefly frame the issue.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it ‘s such a problem. Use logos and pathos for this – the logical and emotional appeals.
- Provide the solution and explain why this would also help the audience.
- Call to action – something you want the audience to do which is straightforward and pertinent to the solution.
Storytelling
As well as incorporating stories in your presentation , you can organise your whole presentation as a story. There are lots of different type of story structures you can use – a popular choice is the monomyth – the hero’s journey. In a monomyth, a hero goes on a difficult journey or takes on a challenge – they move from the familiar into the unknown. After facing obstacles and ultimately succeeding the hero returns home, transformed and with newfound wisdom.
Storytelling for Business Success webinar , where well-know storyteller Javier Bernad shares strategies for crafting compelling narratives.
Another popular choice for using a story to structure your presentation is in media ras (in the middle of thing). In this type of story you launch right into the action by providing a snippet/teaser of what’s happening and then you start explaining the events that led to that event. This is engaging because you’re starting your story at the most exciting part which will make the audience curious – they’ll want to know how you got there.
- Great storytelling: Examples from Alibaba Founder, Jack Ma
Remaining method
The remaining method structure is good for situations where you’re presenting your perspective on a controversial topic which has split people’s opinions.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it’s such a problem – use logos and pathos.
- Rebut your opponents’ solutions – explain why their solutions could be useful because the audience will see this as fair and will therefore think you’re trustworthy, and then explain why you think these solutions are not valid.
- After you’ve presented all the alternatives provide your solution, the remaining solution. This is very persuasive because it looks like the winning idea, especially with the audience believing that you’re fair and trustworthy.
Transitions
When delivering presentations it’s important for your words and ideas to flow so your audience can understand how everything links together and why it’s all relevant. This can be done using speech transitions which are words and phrases that allow you to smoothly move from one point to another so that your speech flows and your presentation is unified.
Transitions can be one word, a phrase or a full sentence – there are many different forms, here are some examples:
Moving from the introduction to the first point
Signify to the audience that you will now begin discussing the first main point:
- Now that you’re aware of the overview, let’s begin with…
- First, let’s begin with…
- I will first cover…
- My first point covers…
- To get started, let’s look at…
Shifting between similar points
Move from one point to a similar one:
- In the same way…
- Likewise…
- Equally…
- This is similar to…
- Similarly…
Internal summaries
Internal summarising consists of summarising before moving on to the next point. You must inform the audience:
- What part of the presentation you covered – “In the first part of this speech we’ve covered…”
- What the key points were – “Precisely how…”
- How this links in with the overall presentation – “So that’s the context…”
- What you’re moving on to – “Now I’d like to move on to the second part of presentation which looks at…”
Physical movement
You can move your body and your standing location when you transition to another point. The audience find it easier to follow your presentation and movement will increase their interest.
A common technique for incorporating movement into your presentation is to:
- Start your introduction by standing in the centre of the stage.
- For your first point you stand on the left side of the stage.
- You discuss your second point from the centre again.
- You stand on the right side of the stage for your third point.
- The conclusion occurs in the centre.
Key slides for your presentation
Slides are a useful tool for most presentations: they can greatly assist in the delivery of your message and help the audience follow along with what you are saying. Key slides include:
- An intro slide outlining your ideas
- A summary slide with core points to remember
- High quality image slides to supplement what you are saying
There are some presenters who choose not to use slides at all, though this is more of a rarity. Slides can be a powerful tool if used properly, but the problem is that many fail to do just that. Here are some golden rules to follow when using slides in a presentation:
- Don’t over fill them – your slides are there to assist your speech, rather than be the focal point. They should have as little information as possible, to avoid distracting people from your talk.
- A picture says a thousand words – instead of filling a slide with text, instead, focus on one or two images or diagrams to help support and explain the point you are discussing at that time.
- Make them readable – depending on the size of your audience, some may not be able to see small text or images, so make everything large enough to fill the space.
- Don’t rush through slides – give the audience enough time to digest each slide.
Guy Kawasaki, an entrepreneur and author, suggests that slideshows should follow a 10-20-30 rule :
- There should be a maximum of 10 slides – people rarely remember more than one concept afterwards so there’s no point overwhelming them with unnecessary information.
- The presentation should last no longer than 20 minutes as this will leave time for questions and discussion.
- The font size should be a minimum of 30pt because the audience reads faster than you talk so less information on the slides means that there is less chance of the audience being distracted.
Here are some additional resources for slide design:
- 7 design tips for effective, beautiful PowerPoint presentations
- 11 design tips for beautiful presentations
- 10 tips on how to make slides that communicate your idea
Group Presentations
Group presentations are structured in the same way as presentations with one speaker but usually require more rehearsal and practices. Clean transitioning between speakers is very important in producing a presentation that flows well. One way of doing this consists of:
- Briefly recap on what you covered in your section: “So that was a brief introduction on what health anxiety is and how it can affect somebody”
- Introduce the next speaker in the team and explain what they will discuss: “Now Elnaz will talk about the prevalence of health anxiety.”
- Then end by looking at the next speaker, gesturing towards them and saying their name: “Elnaz”.
- The next speaker should acknowledge this with a quick: “Thank you Joe.”
From this example you can see how the different sections of the presentations link which makes it easier for the audience to follow and remain engaged.
Example of great presentation structure and delivery
Having examples of great presentations will help inspire your own structures, here are a few such examples, each unique and inspiring in their own way.
How Google Works – by Eric Schmidt
This presentation by ex-Google CEO Eric Schmidt demonstrates some of the most important lessons he and his team have learnt with regards to working with some of the most talented individuals they hired. The simplistic yet cohesive style of all of the slides is something to be appreciated. They are relatively straightforward, yet add power and clarity to the narrative of the presentation.
Start with why – by Simon Sinek
Since being released in 2009, this presentation has been viewed almost four million times all around the world. The message itself is very powerful, however, it’s not an idea that hasn’t been heard before. What makes this presentation so powerful is the simple message he is getting across, and the straightforward and understandable manner in which he delivers it. Also note that he doesn’t use any slides, just a whiteboard where he creates a simple diagram of his opinion.
The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout – by Rick Rigsby
Here’s an example of a presentation given by a relatively unknown individual looking to inspire the next generation of graduates. Rick’s presentation is unique in many ways compared to the two above. Notably, he uses no visual prompts and includes a great deal of humour.
However, what is similar is the structure he uses. He first introduces his message that the wisest man he knew was a third-grade dropout. He then proceeds to deliver his main body of argument, and in the end, concludes with his message. This powerful speech keeps the viewer engaged throughout, through a mixture of heart-warming sentiment, powerful life advice and engaging humour.
As you can see from the examples above, and as it has been expressed throughout, a great presentation structure means analysing the core message of your presentation. Decide on a key message you want to impart the audience with, and then craft an engaging way of delivering it.
By preparing a solid structure, and practising your talk beforehand, you can walk into the presentation with confidence and deliver a meaningful message to an interested audience.
It’s important for a presentation to be well-structured so it can have the most impact on your audience. An unstructured presentation can be difficult to follow and even frustrating to listen to. The heart of your speech are your main points supported by evidence and your transitions should assist the movement between points and clarify how everything is linked.
Research suggests that the audience remember the first and last things you say so your introduction and conclusion are vital for reinforcing your points. Essentially, ensure you spend the time structuring your presentation and addressing all of the sections.

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 10 min read
How to Structure a Presentation
Choosing the best format for your audience.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Have you ever sat through a rambling, disorganized presentation? If so, you probably found it hard to follow what the speaker was saying.
When presentations don't flow well, it's easy for audiences to get lost. This is why it's important to think carefully about the structure and organization of your presentation.
In this article, we'll explore some common structures that you can use next time you speak in front of other people.
The Importance of Structure
Without a defined structure, your audience may not be able to follow your presentation. When this happens, your opportunity is lost, the communication fails, and your reputation takes a hit. For example, if your aim is to persuade people, you'll want to use a different approach from the one you'd use if you wanted to demonstrate how a product works.
Many factors can influence your choice of structure, but the most important consideration is your presentation's purpose or goal. You need to identify what you want to achieve – do you want to inspire, motivate, inform, persuade, or entertain people?
Your audience's needs also affect the structure you choose. For example, those who are new to your topic need more background information than people with more expertise and experience. So, in this case, you'd want to choose an approach that gives you ample time to explain the context of your subject, as well as to reinforce your main points.
Structures to Consider
Below, we outline several structures that you can use to organize your presentation.
1. Open – Body – Conclusion
The Open – Body – Conclusion approach is one of the most practical structures you can use for presentations. (Click here to download a worksheet that helps you use it.)
People often call it the "tell 'em" approach, because you:
- Tell audience members what you're going to tell them (introduction).
- Tell them (body).
- Tell them what you told them (conclusion).
This structure is simple, effective and easy to remember. Its repetitive nature allows you to reinforce your points, which helps others remember them. It is also flexible: you can adjust the introduction and body to persuade, motivate, educate, or entertain them.
One downside, however, is that repetition can quickly bore people. The approach is also "old hat" to many, which can cause them to lose interest. If you choose to use it, balance repetition with plenty of interesting facts, images, anecdotes, or stories to hold your audience's interest.
Let's look at each stage of the Open – Body – Conclusion structure in detail and discuss the elements that you need to include in each. We'll start with the body, rather than the introduction, because the rest of your presentation will be based on that.
The body of your presentation needs to contain your key points. You should present these in a logical order, so that your audience can follow them easily.
Keep in mind that the body should comprise a limited number of ideas: the more you try to include, the fewer people will remember. A good guide is to cover three to five main points, but no more.
When organizing your ideas, use the chunking principle to put the information into specific units. This will make the concepts easier to grasp, and help people remember what you have told them.
Make sure that you back up your main points with facts. Use good information-gathering strategies in your research, and consider citing the sources that you use. To add credibility to your presentation, consider using the following information to support your ideas:
- Data, facts or statistics.
- Images or diagrams.
- Stories and examples.
- Quotes or testimonials from experts or industry leaders.
Reliable sources will strengthen your credibility , and build trust with your audience.
Your opening, or introduction, has two main purposes: to grab your audience's attention, and to cover the key points that you intend to talk about.
Instead of telling people what you plan to say, you can use a different approach and explain why they are there. What will they learn from your presentation, and how will the content benefit them?
It's also important to get their attention right from the beginning. You can do this in several ways:
- Tell a story.
- Ask a rhetorical question.
- Play a short video.
- Make a strong or unexpected statement.
- Challenge your audience.
- Use a quotation or example.
- Appeal to people's self-interest.
- Request a specific action.
- Use suspense.
If you plan to answer questions at the end of your presentation, it's a good idea to mention this in the introduction, so people don't interrupt you mid-flow.
Many presenters overlook the importance of a conclusion – but the statements you finish with are what many audience members will remember best.
With the "tell 'em" approach, your conclusion summarizes the main points in the body of your presentation. If you want people to take action, be specific about what you want them to do.
Think carefully about how you want them to feel once you've finished; your conclusion is a great opportunity to reinforce this. Why not inspire them with a great story, a quote or a compelling call to action?
2. The Sandwich Approach
The Sandwich Approach is a variation of the Open – Body – Conclusion structure. This three-part structure covers:
- Advantages and/or benefits of your message or idea.
- Risks and concerns.
- How the benefits manage or eliminate those risks.
This approach is effective when you want to persuade audience members, or change their minds.
Having evidence to support your position is critical. However, factual data and reams of spreadsheets and charts are not highly persuasive. What people respond to is "vivid" evidence that brings your concept or argument to life.
To brush up on your persuasion skills, look at The Rhetorical Triangle . This tool asks you to consider your communication from three perspectives: those of the writer, the audience and the context. It's a method that builds credibility, and helps you ensure that your arguments are logical.
3. Monroe's Motivated Sequence
Monroe's Motivated Sequence is another good structure to use when you need to motivate or persuade. This sequence consists of five key steps:
- Getting your audience's attention – Use an interesting "hook" or opening point, such as a shocking statistic. Be provocative and stimulating, not boring and unemotional.
- Creating a need – Convince the audience there's a problem, explain how it affects them. Persuade them that things need to change.
- Defining your solution – Explain what you think needs to be done.
- Describing a detailed picture of success (or failure) – Give people a vision; something they can see, hear, taste, and touch.
- Asking the audience to do something straight away – Get them involved right from the start. If you do this, it's then much easier to keep them engaged and active in your cause.
4. Demonstration Structure
Use a simple demonstration structure when you are unveiling a new product or service.
Start by explaining why the product or service is so good. What makes it special? What problem will it solve for people?
Next, demonstrate what it does. How you do this will depend on your product but, whatever you do, make sure it works! Bring any important points to the audience's attention and provide helpful tips, where appropriate. Show them the results, and finish by giving them useful information, a good understanding of your topic, and something to remember.
Don't get too wrapped up in the detail; remember to keep it simple. Your presentation will be more powerful and your audience will remember more if you highlight just a few of the most important features. This will whet their appetite, and leave them wanting to know more.
5. Opportunity, Benefits, Numbers Structure
The Opportunity, Benefits, Number (OBN) structure is useful when you face busy people who want to hear what you have to say in the shortest time possible.
To use this structure, give audience members a quick summary of the opportunity that they need to consider, and outline the benefits that they can expect. Then, show them the numbers that back up your claims. [1]
For example, imagine you are explaining why your company should implement a new performance management system. First, you might give some background on the proposal – for example, you want to drive a high-performance culture. Then, you could explain the benefits, such as improving organizational performance and profits. Finally, you could compare the cost of bringing the system in with the predicted return on investment, based on a similar system at another organization.
Presentations that lack a clear flow are confusing and ineffective. This is why it's important to pay careful attention when choosing the most appropriate structure.
Different structures fulfill different purposes. Before you begin, think about why you are giving your presentation. Do you want to inform, persuade, inspire, or entertain your audience?
The most common structure for presentations is Open – Body – Conclusion. This is often effective because it gives you the opportunity to repeat your key points a number of times. However, other structures can be more appropriate, depending on the circumstances, such as when you're trying to persuade an audience, demonstrate a product, or provide information in the most time-efficient way.
Download Worksheet
[1] Martinuzzi, B. (2013). '11 Ways to Structure a Knockout Presentation,' from American Express OPEN Forum [online]. Available here . [Accessed 7 August 2014.]
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Expert Interviews
So Good They Can't Ignore You
Cal Newport
Monitoring and Evaluating the Outcomes of Change
How To Measure the Outcomes of Change to See If Your Objectives Have Been Met
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 30% off your first year of Mind Tools
Great teams begin with empowered leaders. Our tools and resources offer the support to let you flourish into leadership. Join today!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Starting a New Job

The Role of a Facilitator
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Decision-making mistakes and how to avoid them.
Explore some common decision-making mistakes and how to avoid them with this Skillbook
Using Decision Trees
What decision trees are, and how to use them to weigh up your options
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Influence maps.
Uncovering Where the Power Lies in Your Projects
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
Home Blog Business Presentation Structure Guidelines for Effective Communication
Presentation Structure Guidelines for Effective Communication

In the business world, a presentation is so much more than just a bunch of slides or points—it’s a golden opportunity. It can sway decisions, propel change, or bring people together. How you structure your presentation is absolutely critical in getting your ideas across clearly and compellingly.
When you’ve got a structured presentation just right, it’s like you’re taking your audience by the hand and guiding them through your thoughts, making sure they pick up all the important bits along the way. Moreover, it speaks of your degree of professionalism and how much knowledge you bear on the topic in question.
Therefore, nailing your presentation structure isn’t just helpful; it’s downright necessary to get the results you’re after. Whether you’re pitching a new concept to the investors, sharing the latest findings with your team, or taking the stage at a conference, how you lay out your content becomes the language you use to interact with your audience. Get to know all that’s required to create a powerful presentation structure that will guarantee success in business meetings, academic dissertations, or motivational talks .
Table of Contents
What is a Presentation Structure
Introduction, techniques to structure your presentation, common mistakes to avoid when designing a presentation structure, final words.
Let’s compare a presentation structure to a business plan . Just as a business plan is essential for guiding a company’s strategy and ensuring all aspects of the business are aligned toward common goals, a presentation structure is crucial for organizing the content and delivery of your talk.
The presentation structure lays out a clear and logical sequence of information, akin to the sections of a business plan that outline the company’s mission , market analysis , and financial projections. This clear sequence ensures that your audience can easily follow and understand your message, maximizing the impact your speech can deliver and influencing your target audience.
Key Elements of a Presentation Structure
The easiest way to study a presentation structure is to subdivide it into sections. Basically, every presentation has a structure that follows this formula: Introduction > Body > Conclusion.
The introduction is the first section of the presentation and sets the tone for the rest of the presentation. It should be attention-grabbing and make the audience want to listen to the rest of the presentation.
When defining how to start a presentation , these are the best tips we recommend you implement.
Start with a Hook
Kick off your introduction with a strong hook that grabs your audience’s attention. This could be an intriguing fact, a thought-provoking question, or a compelling story related to your topic. A captivating opening will make your audience want to listen and engage with your presentation.
Clearly State Your Topic
Be clear and concise when stating your topic. Your audience should immediately understand what your presentation is about and what they can expect to learn. A clear statement of your topic sets the stage and provides a roadmap for the rest of your presentation.
Establish Credibility
Take a moment to establish your credibility by briefly sharing your qualifications or experience related to the topic. This helps to build trust and rapport with your audience, and it shows that you are knowledgeable and well-prepared.
Engage Your Audience
Make your audience part of the presentation by engaging them from the start. Ask a question, encourage participation, or invite them to think about how the topic relates to their own experiences. Engagement helps to create a connection between you and your audience. Using a surprise factor is an alternative if you feel the topic you’re about to present may not fully resonate with the target audience.
Preview Main Points
End your introduction by briefly previewing the main points you will cover in your presentation. This provides a clear structure for your audience to follow and helps them understand what to expect in the body of your presentation. An agenda slide is the perfect tool for this purpose.

The body is the main part of the presentation and provides the content and information that the audience came to hear. It should feature the main points and details supporting your presentation’s objective. Depending on your topic, this could include data, arguments, case studies, examples, or demonstrations. Each main point should be clear and distinct, with evidence or examples substantiating it. The content should be tailored to your audience’s level of knowledge and interest.
Different presentations call for various structures. For example, a Product Presentation ’s structure should start by dividing the content into clear sections or headings. For instance, if presenting a new software tool, sections could include its features, benefits, and user feedback.

On the other hand, a Persuasive Presentation begins with stating the current situation or problem, followed by proposed solutions, evidence supporting those solutions, and the benefits of adopting your proposition.

Workshop or Training Presentations begin with an overview of what will be taught, followed by step-by-step instructions, examples, demonstrations, and summaries or quizzes after each major section.

One essential aspect is to plan the multimedia elements to include in your presentation, including audio, images, and video, depending on the presentation style you aim to deliver. Through our expertise, we want to share some tips on how to plan this kind of content:
- Using relevant content: Each image should be related to its accompanying content. Avoid using images just for decoration. If using videos, dedicate an entire slide to them rather than sticking them to a corner of your slide. Plan a powerful hook to connect your thoughts with these visual aids.
- Quality: Ensure all images are of high resolution and can be clearly viewed, even from a distance. Avoid pixelated or distorted images.
- Simplicity: Infographics and diagrams should be easy to understand. If presenting data, use simple charts or graphs instead of complex tables. Limit the amount of text on each slide to ensure clarity. This rule of simplicity also applies to written content and the structure of your speech. Use the Feynman Technique as a time-saver approach to simplify content to reach any knowledgeable audience.
- Consistency: A common cause of presentation failures is to distract the audience with an unprofessional look. Maintain a consistent style and color scheme for all images to give your presentation a polished and professional feel.
Along the path of creating these media elements, you can rethink your strategy for disclosing content. In general lines, you should present your points in a logical order, often from the most to least important or in a chronological sequence. This helps the audience follow along and build understanding step by step. Well-known practices like the storytelling technique follow this approach to maximize audience engagement.
Transition smoothly between points. Phrases like “moving on,” “in addition,” or “on the other hand” can guide your audience through your narrative. Break up long sections of spoken content with anecdotes, questions, or short videos. Such an approach adds variety and keeps the audience engaged.
A well-structured conclusion is the linchpin that holds your presentation together, reinforcing your main points and leaving a lasting impression on your audience. It is your final opportunity to communicate your message and encourage audience engagement. So, before you consider how to end a presentation , here are some powerful tips to ensure you conclude your presentation with impact.
End with a Strong Statement or Quote
This technique is commonly used in motivational presentations, where the speaker leaves the audience with a slide containing a quote related to the topic of the presentation, something that evokes inner reflection about the topic discussed.

Conclude your presentation with a strong, memorable statement or a powerful quote that ties back to your main message. This adds weight to your argument and leaves a lasting impression on your audience. If you aim to surprise your audience, silence can also be a strong statement if your presentation has to raise awareness about a problem.
Incorporate a Call-to-Action
Clearly communicate to your audience what you want them to do next. Whether it’s to adopt a new perspective, take specific action, or continue the conversation outside of the presentation, a clear call to action drives engagement and encourages your audience to act upon your message.
Ask Thought-Provoking Questions
Pose thought-provoking questions that stimulate reflection and discussion. This opens the door for audience participation and engagement and allows you to interact with the audience in a Q&A session, or reach after your presentation concluded to network.

Additional Resources and Contact Info
Offer resources such as articles, websites, or books for those interested in exploring your topic further. This not only adds value to your presentation but also encourages the audience to engage with the content beyond the presentation itself.
Consider the way you leave a communication channel open with your audience. This can be in the format of a deliverable, writing down your contact data in the “Thank You” slide , or simply via speech to inform where they can know more about you and your work.
We already discussed the basic Introduction-Body-Conclusion framework for a presentation, but there are alternative approaches that can help you structure your talk.
Problem-Solution Framework
The Problem-Solution Framework is a compelling method to structure presentations, particularly when aiming to persuade or inform an audience about addressing specific challenges. The framework operates on a simple yet impactful premise: initially, highlight a problem or challenge that needs addressing and subsequently propose a viable solution or set of solutions.

Starting with the problem establishes a context, engages the audience by highlighting pain points or challenges they may recognize, and creates a desire for resolution. It sets the stage for the solution to be perceived as necessary and valuable.
The solution phase offers that much-needed resolution. By presenting a clear, actionable solution or set of recommendations, the presenter provides a pathway to overcome the identified challenge. This structure is not only logical but also highly persuasive, as it appeals to the audience’s desire for resolution and improvement. In essence, the Problem-Solution Framework is both a guide for content organization and a psychological tool for persuasion.
Chronological Structure
The Chronological Structure is an intuitive and organized approach to presenting information based on a sequence of events or a progression in time. Whether recounting historical events, outlining the stages of a project, or narrating a personal story, this structure follows a clear beginning, middle, and end sequence. By presenting details in the order they occurred, the audience can easily follow the narrative, making connections between events and understanding causality.

This structure is especially effective when the timeline of events is crucial to the narrative or when showcasing developments, evolutions, or growth over time. It provides clarity and eliminates confusion that might arise from a non-linear presentation. Moreover, by anchoring information on a timeline, the Chronological Structure aids memory retention, as the audience can mentally “map out” the journey of events. In sum, this method offers clarity and a compelling narrative arc, ensuring audience engagement from start to finish.
Comparative Structure
The Comparative Structure is a strategic approach to presentations that hinges on juxtaposing two or more elements, ideas, or solutions side by side. By examining similarities and differences, this method illuminates unique qualities, advantages, or drawbacks inherent in each element. Often employed in business scenarios like product comparisons, market analysis, or debates, the comparative structure helps audiences critically analyze options and make informed decisions.
Presenters utilizing this structure typically start by introducing the elements for comparison. They then delve into detailed analysis, often using criteria or metrics to maintain objective evaluations. Visual aids like Venn diagrams or comparison charts can enhance clarity and visual appeal.

The strength of the Comparative Structure lies in its ability to foster critical thinking. By directly contrasting items, audiences are engaged, encouraged to weigh pros and cons, and ultimately arrive at a deeper understanding or more nuanced perspective on the subject matter.
Matrix Structure
The Matrix Structure offers an approach to organizing presentations by segmenting information into distinct categories or sections, akin to a grid or matrix. Instead of a linear flow, topics are grouped by themes, criteria, or any relevant classification, allowing for simultaneous exploration of multiple facets of a subject. Think of it as viewing a topic through various lenses concurrently.
For instance, in a business setting, a product might be examined in terms of design, functionality, market positioning, and customer feedback. Each of these constitutes a segment in the matrix.
Visually, the matrix can be represented using tables, grids, or quadrant charts, making the content easily digestible and engaging. A key advantage of this structure is its flexibility; presenters can delve deep into one segment or provide a broader overview of all areas, depending on the audience’s needs. Ultimately, the Matrix Structure ensures a comprehensive and multifaceted examination of a topic, providing depth and breadth in analysis.
Modular Structure
The final model we will study is the Modular Structure. It takes content and packs it into modules, which can be arranged at any other the presenter requires them to be. Each module addresses a specific topic or idea and is designed to be self-contained, ensuring clarity even if presented independently or in a different order. This adaptability makes the modular approach especially valuable in dynamic settings, such as workshops or conferences, where audience feedback or time constraints might necessitate adjustments on the fly.
For example, in a corporate training session, different modules could cover distinct skills or topics. Based on the attendees’ prior knowledge or the session’s time limit, the presenter can prioritize, omit, or rearrange modules without compromising the integrity of each segment.
By adopting the Modular Structure, presenters gain flexibility without sacrificing depth. This approach fosters a responsive presentation style, allowing speakers to tailor content in real-time, ensuring maximum relevance and engagement for their audience.
Even well-seasoned presenters can fall prey to these common mistakes in terms of presentation structure. Let’s learn how to prevent them.
Overloading with Information
It’s tempting to include every bit of knowledge you have on a topic. Still, information overload can quickly disengage an audience. Prioritize key points and leave out extraneous details. As famous architect, Mies van der Rohe famously coined, “Less is More.”
Weak Transitions
Jumping abruptly from one point to another can disrupt the flow and confuse listeners. Ensure smooth transitions between sections, signaling shifts in topics or ideas to keep the narrative cohesive.
Dull Design
While content is king, visual appeal matters. Relying solely on walls of text or bland slides can lose your audience’s interest. Incorporate engaging visuals, charts, and multimedia elements to enhance your message and retain attention.
Ignoring the Call to Action
Concluding your presentation without guiding the audience on the next steps or what’s expected of them can be a missed opportunity. Whether it’s seeking feedback, prompting a discussion, or encouraging an action, always have a clear call to action.
Good communication is all about making your point clear, especially in presentations. We’ve talked about how the right structure can keep your audience hooked. But there’s more to it. Think about your presentation. Is it telling your story the way you want? Is it reaching your audience? Take a step back and really look at how you’re laying it out. Don’t just go with the flow – choose your format wisely. Remember, every presentation tells a story, and how you set it up matters a lot.

Like this article? Please share
Design, Presentation Approaches Filed under Business
Related Articles

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • April 23rd, 2024
How to Align Objects in Google Slides
Optimize your layouts by learning how to align objects in Google Slides presentations. Step-by-step guide with screenshots.

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 29th, 2024
How to Make a Fundraising Presentation (with Thermometer Templates & Slides)
Meet a new framework to design fundraising presentations by harnessing the power of fundraising thermometer templates. Detailed guide with examples.
Leave a Reply
Presentation Structures: Everything You Need to Organize Your Talk
Hrideep barot.
- Presentation , Public Speaking , Speech Writing

A presentation structure includes an introduction, context, main body, conclusion, and scope for questions. Depending on the type of presentation you’re doing, this format can change. The article discusses various considerations for each section of a presentation structure.
For presentations to be understood and create a good impression, they can’t be haphazard. It has to have some sort of pre-planned presentation structure that is both logical and simple enough. Depending on the type of presentation you’re doing, there are likely some basic frameworks available that people tend to follow. Before we delve into the format, let’s consider key points to consider when planning a presentation.
How do you structure and plan a presentation?
We plan a presentation by considering the type of presentation, who our audience is, ideating the purpose, and formulating subtopics through research.
Consider the type of presentation
This leads to understanding the ideal flow to convey your content best. For instance, for persuasive presentations, you could use creative ways to convey what is best about a product, such as starting with a story about how it has helped many people achieve something.
On the other hand, for a progress presentation at your workplace, you might have conventions about what is expected, which must be followed precisely.
A few other types of presentations include:
- Informative presentations
- Instructive presentations
- Motivational presentations
- Analytical presentations
You might also want to consider if you want audience interaction and put that into the structure accordingly. While some allow questions mid-presentation for smaller audiences, it is typically left towards the end.
Consider your audience’s knowledge level and interests
This will determine if you can assume a particular knowledge base and not include it in your presentation structure or if you have to start off with basics and build up on that.
For instance, if you’re teaching 1st-year students about something, you might start with basics. But for graduates, a similar format would be unnecessary as they might have already learned about it.
Similarly, if your purpose is to deliver something entertaining, knowing about the interests and values of your audience helps a ton.
The most simple way is demographics. It’s typically quite easy to find out the expected age group, gender, etc of the audience. This information can help you have a basic idea of the sort of experiences they go through, which helps formulate an understanding.
Consider the purpose of your presentation
While this may seem obvious, many of us lose track of the main purpose and spend too much time on remotely related content. This diverts attention from the topic and might even cause boredom.
For example, if you’re advocating for some social action, it would be beneficial to stay on the topic itself, like the pros, cons, what can be done practically, etc. Instead, if the presenters spend more time criticizing others, the presentation will fall short of its purpose.
Few other examples of different purposes your presentation could have:
- Entertainment
- Providing information
- Telling your story
- Proposing ideas
- Discussing future plans for the company
Research your topic and start noting down the subtopics
Skip this if you already know exactly what needs to be a part of your presentation, and plan to include just that. While looking up your topic, you’ll discover the various sub-topics within that field. After you start noting them down, you can organize later what comes under which to build a structure.
Here is a guide on short presentations that you might be interested in.
So with these three considerations and subtopics in mind, we’re good to go over to decide our final structure.

What is the best presentation form?
The best presentation format is one that includes the introduction, context, main body, conclusion, and questions.
Here, we will discuss a template or structure for a typical presentation.
Introduction
- Greet the audience and introduce yourself, e.g., what you do and why you’re here
- The purpose of your presentation
- The flow or outline gives a sense of what they can expect
- Depending on the topic and audience, you might have to provide more or less context about your topic
- This could include a brief history, terminologies, the current market status, the current status of the field, etc.
- Includes the full depth of the primary purpose of the presentation
- All major chunks of data, including examples, evidence like research studies, etc, are included here
- Care needs to be taken at times to ensure that your introduction and context are not taking up so much time that the main body isn’t receiving enough attention. Ever wonder if a presentation can be too short? Check out this article .
- Bring emphasis to the main takeaways
- Thank your audience if they have been a good one
- Take questions and encourage healthy discussion
- End with sharing ways they can address their questions later
To make sure that the structure works out, it is important that you practice your presentation. This will also tell you if you’re falling within the time constraints. Here is a guide on how you can go about practicing your presentation.
5 Ways to Structure Your Presentation
The five ways include ordered, problem-solution, comparative, storytelling, and demonstrating structures.
1. Ordered Structure
The presentation follows a logical sequence starting with an introduction, main points, and then conclusions. This is what this article has focused on, as it’s the most straightforward method and tends to be very clear for the audience. However, for presentations that do not follow a clear progression, this may not be useful.
2. Problem-Solution Structure
This is useful when persuading the audience. You explain the problem (+ its importance and impact) and then provide a solution that motivates the audience to take it. This could be in the form of a product, a particular method of communication, some technical thing, etc. There should be a decent amount of time spent on the benefits of the solution as well as the exact “How?” to implement it to make the audience convinced. It helps to address any questions or barriers you expect them to have during the speech itself.
3. Comparative Method
This is useful when you want to highlight the benefits of something over alternatives . It is ideal to first fully address the alternatives by talking about their benefits and limitations. Then you lastly talk about the solution that you possess that effectively addresses the other limitations or is in some way a better choice than others, based on your arguments.
Alternatively, if you do not want to highlight the benefits of something particular and just form a comparison that demonstrates the pros and cons of different subjects in an unbiased manner, this technique is still used. For instance, how the main benefit of a product is practically useful for the consumer in comparison to the main benefit of another product can be discussed.
4. Storytelling Structure
This is useful when your goal is just to tell a story. This could be to explain the context or history of a company. It could also serve to talk about yourself and how you got there. A story will typically have an introduction, a complicating factor that introduces some challenges, and then an ending that highlights the importance of some action or belief.
You may also go in a timewise order when explaining a story. This might take away from the thrill but is useful nonetheless when it is required for the audience to properly understand what is being conveyed. Storytelling can be done in various ways, so feel free to find your own structure.
5. Demonstration Structure
This is useful when demonstrating products or services . The benefits of the product/service are highlighted and it is demonstrated showing those capabilities. The goal should be on persuading the audience that it is useful to them for their needs.
How to structure a scientific presentation?
Structuring a scientific presentation typically includes an introduction, methods, results, and discussion.
This typically follows the below format, but depending on the university/conference guidelines, you’ll have to adjust accordingly. The rest of the sub-topics revolves around these sections.
- Introduction/Background
- Literature review (if applicable)
- Acknowledgments (often optional)
After this, time is given to take questions.
How do you structure a presentation script?
The presentation never includes the full extent of the information. It’s just a concise version of what you’re speaking that adds as a visual aid at times while also highlighting major points.
The script is where the major content lies. The structure remains the same, but the content is greater in depth .
Sample Presentation Script
To make it easier for you to understand how you can structure your presentation script, here is a sample script for a presentation on the topic: Importance of Public Speaking.
This follows the same flow introduced earlier- introduction, context, main body, conclusion, and questions.
Title: Importance of Public Speaking
Slide 1: Why is Public Speaking Important?
Greetings, ladies, and gentlemen. Today, I will be exploring the importance of public speaking. My name is John, and I’m thrilled to discuss with you how improving our public speaking abilities may make a significant difference in our quality of life in the personal, social, and professional domains.
Slide 2: Introduction
Public speaking involves persuading an audience with a well-organized message. It is an essential part of our daily lives. We use it when we make conversation in social groups as well as when we address enormous crowds at social gatherings. It is a highly multifaceted and effective tool.
I will start off by giving some information about the context, moving on to its benefits, which is the main crux of our presentation, and then we will spend some time concluding.
Slide 3: Context
Effective communication is essential in our globally interconnected society. Speaking in front of an audience enables us to express our views and thoughts clearly and firmly. It facilitates the development of solid bonds and influences others, and acts as a catalyst for constructive change. Public speaking may open doors of opportunity and propel achievement for anyone, whether they are a student, professional, or member of the community.
Slide 4: Personal Development
Public speaking increases self-esteem and confidence, which are quite rudimentary to our self-efficacy. Effective communication skills help us to be more assertive and feel more in control of our lives. Research suggests that having an internal locus of control (i.e., feeling in control) leads to better outcomes in our personal lives as well as greater mental health. As we organize our ideas and arguments through public speaking, it improves critical thinking and organizational abilities. Furthermore, as we interact with others during talks and Q&A sessions, public speaking also enhances our listening abilities.
Slide 5: Professional Advancement
The ability to speak in front of an audience effectively is highly essential in most workplaces.
You ask Why? Well, it is because we are better able to communicate our qualifications and worth to potential employers, which enhances our performance in job interviews. Secondly, our influence within organizations grows when we can make a strong case for our points in meetings and conferences.
Next, for leadership positions, where success depends on inspiring and motivating others, public speaking is critical. And in general, you’ll need public speaking in any meeting or any talk you would typically deliver in front of a bunch of people.
Slide 6: Conclusion
Public speaking is a sought-after, multifaceted, and handy skill across many settings. It gives us the ability to inspire others, tell our stories, and make a lasting impression. Strong public speaking abilities help us communicate clearly and lead with influence in many facets of our lives.
Slide 7: Questions
I appreciate everyone here for being a great audience and cooperating wonderfully throughout the presentation. Now I will be taking any questions you all have. Feel free to discuss this now or reach out to me after the session is over.
Slide 8: Thank you
I want to thank you all for being here today.
I hope that the presentation did well to emphasize the importance of public speaking and perhaps motivated at least some of you to work on improving your abilities. We will end here.
[End of presentation]
Here are some tips for delivering an effective presentation.
We considered a few key points for presentation structure and the typical format that can be followed. We also covered five ways you can structure your presentation and the format for a scientific presentation. Lastly, we covered a sample script for presentations.
Public speaking coaching is a great way to increase your skills and get better at presentations as well.
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

Lost Voice? Here’s How to Recover Sore Throat and Speak Again

7 Keys to Emcee Like a Pro: Unlock Your Hosting Potential

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.

How to make a great presentation
Stressed about an upcoming presentation? These talks are full of helpful tips on how to get up in front of an audience and make a lasting impression.

The secret structure of great talks

The beauty of data visualization

TED's secret to great public speaking

How to speak so that people want to listen

How great leaders inspire action
- Search entire site
- Search for a course
- Browse study areas
Analytics and Data Science
- Data Science and Innovation
- Postgraduate Research Courses
- Business Research Programs
- Undergraduate Business Programs
- Entrepreneurship
- MBA Programs
- Postgraduate Business Programs
Communication
- Animation Production
- Business Consulting and Technology Implementation
- Digital and Social Media
- Media Arts and Production
- Media Business
- Media Practice and Industry
- Music and Sound Design
- Social and Political Sciences
- Strategic Communication
- Writing and Publishing
- Postgraduate Communication Research Degrees
Design, Architecture and Building
- Architecture
- Built Environment
- DAB Research
- Public Policy and Governance
- Secondary Education
- Education (Learning and Leadership)
- Learning Design
- Postgraduate Education Research Degrees
- Primary Education
Engineering
- Civil and Environmental
- Computer Systems and Software
- Engineering Management
- Mechanical and Mechatronic
- Systems and Operations
- Telecommunications
- Postgraduate Engineering courses
- Undergraduate Engineering courses
- Sport and Exercise
- Palliative Care
- Public Health
- Nursing (Undergraduate)
- Nursing (Postgraduate)
- Health (Postgraduate)
- Research and Honours
- Health Services Management
- Child and Family Health
- Women's and Children's Health
Health (GEM)
- Coursework Degrees
- Clinical Psychology
- Genetic Counselling
- Good Manufacturing Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Speech Pathology
- Research Degrees
Information Technology
- Business Analysis and Information Systems
- Computer Science, Data Analytics/Mining
- Games, Graphics and Multimedia
- IT Management and Leadership
- Networking and Security
- Software Development and Programming
- Systems Design and Analysis
- Web and Cloud Computing
- Postgraduate IT courses
- Postgraduate IT online courses
- Undergraduate Information Technology courses
- International Studies
- Criminology
- International Relations
- Postgraduate International Studies Research Degrees
- Sustainability and Environment
- Practical Legal Training
- Commercial and Business Law
- Juris Doctor
- Legal Studies
- Master of Laws
- Intellectual Property
- Migration Law and Practice
- Overseas Qualified Lawyers
- Postgraduate Law Programs
- Postgraduate Law Research
- Undergraduate Law Programs
- Life Sciences
- Mathematical and Physical Sciences
- Postgraduate Science Programs
- Science Research Programs
- Undergraduate Science Programs
Transdisciplinary Innovation
- Creative Intelligence and Innovation
- Diploma in Innovation
- Transdisciplinary Learning
- Postgraduate Research Degree
Structure of a presentation

Supporting Study
Your go-to for support options, study resources, fun stuff and general help with being a student at UTS.
Get uni sorted now
A presentation:
- has an introduction, body and conclusion
- may include visual aids
- is usually followed by questions and discussions
- may also have a handout for the audience to take away.
Introduction
- The introduction should orient the audience to your subject and purpose. To capture interest and set up rapport, it should tell the audience what to expect.
- Be sure to carefully define the central point (or thesis) that is the basis of your talk and ensure that your supporting argument or information relates closely to it.
- If you are not proceeding from an already written assignment, it might help to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped, with the content coming out of the funnel. See the diagram below:
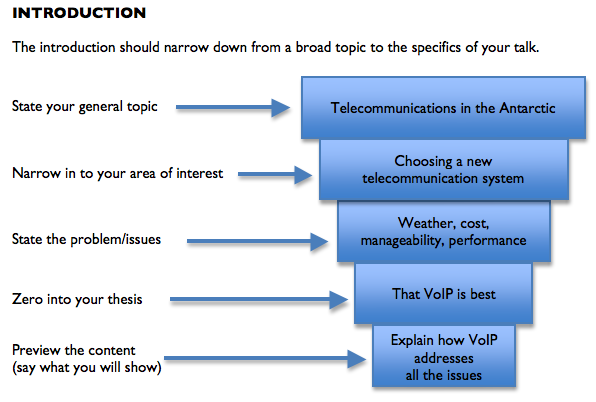
Useful language for presentations
Staging the introduction.
The body of the presentation should meet the promises of purpose and information made in the introduction.
The structure of the presentation is crucial.
Whether you organise:
- chronologically,
- by priority,
the body of your talk must proceed logically. The main points should be brought out one by one, with concise and relevant supportive evidence, statistics or examples and verbal ‘signposting’ of your progress through your argument or report.
You could present each important idea or point several times in different ways, because a listening audience needs several opportunities to fully absorb meaning.
You need to state clearly the links between your ideas and always signal when the next point is coming. If you think something is particularly important, say so and why.
If you don’t have a written assignment, it will help to think of your main points as paragraph topic sentences, each of which needs to be followed by supporting sentences and a conclusion.
Staging the body of your talk
Group presentations.
It may be that you are making a presentation as part of a group. Essentially the same information applies to group presentations as individual ones. It is important that they are logical and well structured as well as professional and meaningful. It is also doubly important that the group rehearse and practise together several times to ensure the presentation runs smoothly on the day.
Handing over to a co-presenter
Your talk may involve several speakers in your group presentation. You need to manage the handover smoothly and professionally, for example:
“I would like to conclude my discussion/report at this point and hand over to my partner/colleague XYZ who will examine/discuss/report the area/topic/perspective of…”
Similar to a written assignment, the conclusion again states your main points and what has been learned or shown but you also may raise implications inherent in the findings and offer creative recommendations.
Staging the conclusion
Back to top
UTS acknowledges the Gadigal people of the Eora Nation, the Boorooberongal people of the Dharug Nation, the Bidiagal people and the Gamaygal people, upon whose ancestral lands our university stands. We would also like to pay respect to the Elders both past and present, acknowledging them as the traditional custodians of knowledge for these lands.

- Directories
Structuring your presentation
Having worked out your key message and main points, the next stage is to structure the content of your presentation. Just like other forms of academic writing, a presentation can be divided into three parts: an introduction detailing the purpose and structure of the talk; a body covering the main points; and a conclusion summarising and highlighting the significance of your talk. A template for your talk is given in the Presentations structure document.
Introduction
You may wish to capture the audience's interest and attention with a story or commentary on a current development that raises an important question / problem / dilemma. Or, you may first wish to frame your talk with brief context / background, and then swiftly transition into a concise explantion of the issue / problem or debate that your key message addresses. In either case, the next step in your introduction is to clearly state the purpose or key message of the talk, for example using the following prompts.
- 'Today I would like to talk about a highly contested issue...'
- 'This question is central to understanding...'
- 'I will make the case that...'
If necessary, limit the scope of the presentation:
- 'Although there are several theories, this talk will only focus on two ...'
- 'focuses only on the private sector as opposed to the public sector ...'
- 'Implementation, rather than policy formation, will be considered ...'
Signpost the structure/approach of the talk:
- 'My case is based on three main points. Firstly...The second point is that...This will then lead me to...Finally...'
This part of the talk provides the support for your main message. You should discuss each of your main points in a clear and logical order. As you do, be sure to explain how these points relate to each other and your key message:
- 'Turning to the next point...'
- 'Another important consideration is that...'
- 'Having examined...I'd now like to talk about...'
All necessary concepts and terms need to be defined and explained before being used. Examples can be used to effectively illustrate your points.
Signpost that you have reached the end of the talk:
- 'In conclusion...'
- 'I'd like to finish by...'
Summarise the key points covered. In the process, remind the audience of the significance of the topic, the aims of your talk and demonstrate how you have met the aims. Thank the audience for their attention and invite them to comment or ask questions.
Acknowledging others ideas
As with all academic work, if you use other people's ideas, images, data etc, then you must appropriately acknowledge it in your presentation. You do this through your spoken words or supply references on your visual aids. In text references can be kept brief to enable the audience to read. You should also include a reference list slide at the end of your presentation. See referencing resources for more information.
Working with visual aids >>
Presentations
Working with visual aids
Delivering the presentation
Reference Documents
- Simple presentation template (DOCX, 64.34 KB)
- Detailed presentation template (DOCX, 66.58 KB)
Use contact details to request an alternative file format.
- ANU Library Academic Skills
- +61 2 6125 2972
👀 Turn any prompt into captivating visuals in seconds with our AI-powered design generator ✨ Try Piktochart AI!
- Piktochart Visual
- Video Editor
- AI Design Generator
- Infographic Maker
- Banner Maker
- Brochure Maker
- Diagram Maker
- Flowchart Maker
- Flyer Maker
- Graph Maker
- Invitation Maker
- Pitch Deck Creator
- Poster Maker
- Presentation Maker
- Report Maker
- Resume Maker
- Social Media Graphic Maker
- Timeline Maker
- Venn Diagram Maker
- Screen Recorder
- Social Media Video Maker
- Video Cropper
- Video to Text Converter
- Video Views Calculator
- AI Brochure Maker
- AI Document Generator
- AI Flyer Generator
- AI Infographic
- AI Instagram Post Generator
- AI Newsletter Generator
- AI Report Generator
- AI Timeline Generator
- For Communications
- For Education
- For eLearning
- For Financial Services
- For Healthcare
- For Human Resources
- For Marketing
- For Nonprofits
- Brochure Templates
- Flyer Templates
- Infographic Templates
- Newsletter Templates
- Presentation Templates
- Resume Templates
- Business Infographics
- Business Proposals
- Education Templates
- Health Posters
- HR Templates
- Sales Presentations
- Community Template
- Explore all free templates on Piktochart
- Course: What is Visual Storytelling?
- The Business Storyteller Podcast
- User Stories
- Video Tutorials
- Need help? Check out our Help Center
- Earn money as a Piktochart Affiliate Partner
- Compare prices and features across Free, Pro, and Enterprise plans.
- For professionals and small teams looking for better brand management.
- For organizations seeking enterprise-grade onboarding, support, and SSO.
- Discounted plan for students, teachers, and education staff.
- Great causes deserve great pricing. Registered nonprofits pay less.
How to Structure a Great Presentation

Today, visual communication is more important than ever. The time we spend in a home-office is rapidly growing . Not only that, but the interaction between us changed significantly in the last couple of years.
It’s completely normal to work with somebody for a long time, but never meet them in person. You can get customers, suppliers, investors anywhere on the globe—without the actual need to travel there personally.
Webinars have been with us for quite some time, but we can all agree that the number of webinar events is unprecedented. With those comes a variety of webinar services , so nowadays you are presenting through MS Teams, later participating in Google Hangouts, and tomorrow you are invited to a Webinarjam event.
Even personal meetings are becoming fast-paced. Everybody has a lot to do. It is critical to communicate in a clear an simple way.
This is why visual presentation is now more important than ever. It is not difficult to lay out an idea in 50 slides and give a two-hour presentation. But in the modern world, it is not possible to have such long interactions.
A challenge is to put an idea on a few presentation slides and get your message across in five minutes. While this is an extreme example, in most cases this is what the presenter should strive for.
In this post, we will go over the main tips on structuring an informative, clear, and short presentation.
You could also learn on the go by creating an account on Piktochart for free. Select one of our presentation templates to get started.
Considerations Before Structuring Your Presentation.
Before we dive into actionable tips to get your presentation going, first let’s clarify some of the main points.
What is the goal of your presentation?
Making posters , infographics, or presentations; whatever your visual medium, you need to ask yourself what is its purpose. Is the main objective of your presentation to pitch investors ? Get new customers? Discuss an idea with your colleagues?
Never do the presentation just because “it has to be done”. Your whole pitch will be much more efficient when you know exactly why you are doing it and where you need to get your audience to.
Who is your audience?
As for every marketing endeavor, the same goes for presentations —know your audience. It does not have to be exact research, but you must know the overall information.
Age, profession, interests—the more you connect with your audience the more memorable will your presentation be.
No matter the goal of the presentation, during your pitch, the audience is your client. And as a famous saying goes, “know your client”.
What are the main points?
Right at the beginning, establish the main points that you want your audience to remember. If I would ask one of the presentation participants in a week what was your pitch about—what would he/she answer?
Presentation style
There are many ways how you can style (structure) your presentation. Which approach you will choose hugely depends on what is required from you. Let’s go over some of the most popular styles of the presentation:
- Short Presentation
If you are one of many presenters that day, you will have a very limited amount of time to present your idea. In addition to that, you may be speaking after many people. So at this point, the audience is already tired and it is important for you to stand out.
In this situation, you must compress your ideas to as few points as possible. Your presentation will probably not have more than 3-5 slides. On these slides, only the main points will be included.
Piktochart has many great templates that will help you create a pitch deck (or a quick presentation) in no time! Sign up for free to create a visual.
- Guest Presenter
If you are one of the main participants of the program, you will have more time to present. Though it may not seem so, it is much easier to prepare for a longer presentation than for a short one.
In this case, you may add more points to each slide, and speak more freely on the topic.
- Problem Solving
You may see this approach frequently on TED. Presenters briefly talk about themselves, then they describe the problem that exists there.
To emphasize its importance, they also describe the possible impacts of the problem not being solved. After the stage is set, they describe how they would solve it.
- Storytelling
We frequently see this approach in various motivational presentations. Storytelling is a great way to emotionally connect with the audience. All the stories start with an underdog. Why? Because everybody can relate.
They go through struggles, setbacks, problems. Again—everyone can relate. They end with catharsis in a form of success or justice. For the last part, not many can relate but they can emotionally resonate with it as they too would like such an outcome for themselves.
- Demonstration
We all remember the presentation of the iPhone by Steve Jobs in 2007:

Or the unveiling of the Tesla 3 model by Elon Musk:
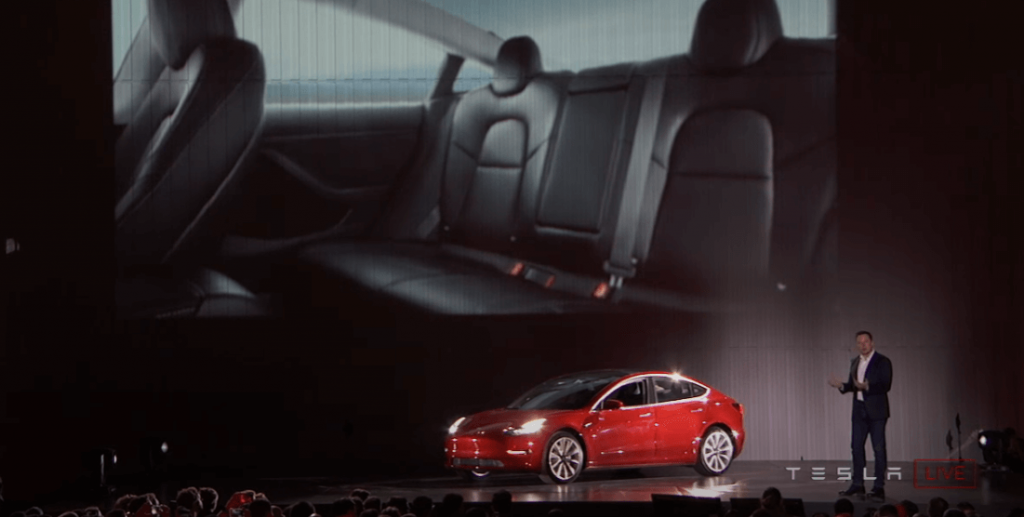

Rather than the speaker, the center stage is given to the product. This is what good demonstration-presentation should look like.
The main topic becomes the product, so all the tips that we will discuss in this post must be related to it.
There are many other niche styles of the presentation, but most of the ones you see (and do) will fall into one of the described categories.
So since we established the main presentation styles, let’s dive a bit deeper into the way a good presentation would be structured.
Presentation Structure
While in the previous section we established what and to who we will be presenting. In this section, we will go over the main flow of your presentation.
In this section, I will use some examples. All of them come from Piktochart, and they are of course done for illustration purposes only—so please do not judge my creations too critically.
Also, for each section, I will be using a different visual template. Your presentation should of course be coherent in terms of style!
- Cover Slide
Through your presentation, you are telling a story and all good stories start at the beginning. Cover slides look professional when you present and they are a must when you are printing or sending.
Nothing too complicated. Brief and to the point. The cover slide is there to establish the topic (or that audience knows that they are in the right room) and set an overall tone to the presentation.
If you have a longer presentation, an agenda slide should be included. Sure, if you are going with a 5-minute sales pitch—skip this, but it is good to let your audience know what you will cover and how much time it will take.
- Profile Slide
It is important to establish authority with your audience. Why should they listen to you? What qualifications or experiences do you have?
The profile slide is a great tool to establish your background and also to connect a bit.

I am not a big fan of jokes in presentations. Particularly when speaking to a bigger audience. What may seem like a witty joke to you, may be taken as not funny or even insulting by your audience.
But if I would be considering a small joke, it would be in the profile slide. Do not overdo it, or don’t it at all if you are not sure about it.
- The Problem
The common pleasantries are behind us and now we are getting to the main part of a good presentation. It opens with The Problem.
For this post, I will not be explaining how to present a quarterly financial report (you may find plenty of report presentations here). But (as you may have noticed) we are rather having a look at how a sales deck, investment pitch, or product presentation may look like.

The problem slide will set out the main point of the presentation. This is when you are trying to seriously connect with your audience.
In the case of a pitch—you are trying to present the problem in such a way that many people can relate to it. If nobody can relate—nobody will be interested.
If you are just doing a presentation on the topic (not a sales pitch), you might want to draft this in a way that will explain the overall environment of the topic that you are to tell about—to set the tone of the whole presentation.
The Solution
After the tone of the presentation is set, or in the case of a pitch—the problem is explained, it is time to deliver what everybody is here for. For the pitch it would be the solution, for the overall presentation—it would be just an explanation of things (or possibly your personal view on the matter).

As with everything else, the provided solution/explanation must be as simple as possible. It must directly tackle the problem/the tone of the presentation that you‘ve set in the earlier slide.
The Conclusion Slide
After the main talk is done, close the presentation with the final slide. One of the teachings of leadership books (or pseudo-teachings) is that even if you are silent for the whole meeting, but in the end, you recap all that was said by others—you will be seen as a leader.
Closing statement matters. Ending with a properly chosen inspirational quote is something that worked well for me.

Of course, it will depend on the overall theme and tone of your presentation. But first and last impressions matter. So make sure you close on a strong note.
Right before the closing slide, it is good to set up a “stop slide” which will remind you that now is a good time to take some questions.

You may start with a couple of pre-written questions to get the discussion going and then see if there are some questions from the public.
Closing Slide
The final slide of your presentation will be the one with Thank You note and contact information.

Make sure that you include the contact information, so you make it easier for everyone to find you.
That is it. While it may seem like a lot of work, with Piktochart templates you will be much quicker. The brief slides that you see above took me a couple of minutes to make.
So while we have the main structure of the presentation behind us, let’s have a look at some actionable tips that you should think of when preparing for your event or a webinar.
Presentation Tips
No matter what type of presentation awaits you, here are some presentation tips that will hopefully help you as much as they helped me:
- When designing your presentation, make sure to leave space on the left or upper side. This will serve you well if you have to print and bind your presentation.
- Font type matters . It sets the tone for your presentation. Piktochart has lots of great combinations to choose from, but when in doubt, Helvetica and possibly Verdana will always look good. For tables with lots of numbers, Arial will be both readable and will fit the cells.
- This will force you to put less text on the slide.
- Always imagine that you are a 50+ investor sitting in a back row. How readable is your presentation for him/her?
- In small groups, take questions as you go . It will help you develop the topic and better feel out what your listeners are thinking about (worried about).
- In bigger groups, leave the Q&A to the end of the presentation . Otherwise, it will be too messy and you will constantly get interrupted.
- The presentation podium is an enemy . It will make you stand in one spot, with no movement, and monotonously monolog through your presentation. Do not do it.
- Use your voice . It is said that to get into the meditative state of trance, you have to hum on the same low frequency. You do not want that to happen to your listeners right? Do not be overly dramatic or emotional, but do not be afraid to give a rhetorical question or to give color to your presentation with the proper use of your voice.
- Do not read from your presentation . Your slides are there just so you can keep track of where you are in your story. Pay attention to the audience, not the presentation.
- If possible, do not give out your presentation in advance . Your audience will read through it, make their conclusion about it and you will have no chance to explain all the nuances.
The hardest part of a presentation is to start. When you are staring at a blank slide, it seems like it just can’t be done. You do not know where to put the pictures, how the titles should be, how the text will be laid out.
Here is where Piktochart’s online presentation maker comes to the rescue. Create an account for free and choose the design that seems to work for your topic and just start filling the blanks. As you will progress, the path will be much clearer.
Hopefully these tips on how to structure a presentation and how to present it will help you achieve your goal!
Other Posts

How to Make a Presentation (2023 Guide With Tips & Templates)

How to Nail Your Brand Presentation: Examples and Pro Tips
Presentation Design: A Step-by-Step Guide
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides How To Make a Good Presentation [A Complete Guide]
How To Make a Good Presentation [A Complete Guide]
Written by: Krystle Wong Jul 20, 2023

A top-notch presentation possesses the power to drive action. From winning stakeholders over and conveying a powerful message to securing funding — your secret weapon lies within the realm of creating an effective presentation .
Being an excellent presenter isn’t confined to the boardroom. Whether you’re delivering a presentation at work, pursuing an academic career, involved in a non-profit organization or even a student, nailing the presentation game is a game-changer.
In this article, I’ll cover the top qualities of compelling presentations and walk you through a step-by-step guide on how to give a good presentation. Here’s a little tip to kick things off: for a headstart, check out Venngage’s collection of free presentation templates . They are fully customizable, and the best part is you don’t need professional design skills to make them shine!
These valuable presentation tips cater to individuals from diverse professional backgrounds, encompassing business professionals, sales and marketing teams, educators, trainers, students, researchers, non-profit organizations, public speakers and presenters.
No matter your field or role, these tips for presenting will equip you with the skills to deliver effective presentations that leave a lasting impression on any audience.
Click to jump ahead:
What are the 10 qualities of a good presentation?
Step-by-step guide on how to prepare an effective presentation, 9 effective techniques to deliver a memorable presentation, faqs on making a good presentation, how to create a presentation with venngage in 5 steps.
When it comes to giving an engaging presentation that leaves a lasting impression, it’s not just about the content — it’s also about how you deliver it. Wondering what makes a good presentation? Well, the best presentations I’ve seen consistently exhibit these 10 qualities:
1. Clear structure
No one likes to get lost in a maze of information. Organize your thoughts into a logical flow, complete with an introduction, main points and a solid conclusion. A structured presentation helps your audience follow along effortlessly, leaving them with a sense of satisfaction at the end.
Regardless of your presentation style , a quality presentation starts with a clear roadmap. Browse through Venngage’s template library and select a presentation template that aligns with your content and presentation goals. Here’s a good presentation example template with a logical layout that includes sections for the introduction, main points, supporting information and a conclusion:

2. Engaging opening
Hook your audience right from the start with an attention-grabbing statement, a fascinating question or maybe even a captivating anecdote. Set the stage for a killer presentation!
The opening moments of your presentation hold immense power – check out these 15 ways to start a presentation to set the stage and captivate your audience.
3. Relevant content
Make sure your content aligns with their interests and needs. Your audience is there for a reason, and that’s to get valuable insights. Avoid fluff and get straight to the point, your audience will be genuinely excited.
4. Effective visual aids
Picture this: a slide with walls of text and tiny charts, yawn! Visual aids should be just that—aiding your presentation. Opt for clear and visually appealing slides, engaging images and informative charts that add value and help reinforce your message.
With Venngage, visualizing data takes no effort at all. You can import data from CSV or Google Sheets seamlessly and create stunning charts, graphs and icon stories effortlessly to showcase your data in a captivating and impactful way.

5. Clear and concise communication
Keep your language simple, and avoid jargon or complicated terms. Communicate your ideas clearly, so your audience can easily grasp and retain the information being conveyed. This can prevent confusion and enhance the overall effectiveness of the message.
6. Engaging delivery
Spice up your presentation with a sprinkle of enthusiasm! Maintain eye contact, use expressive gestures and vary your tone of voice to keep your audience glued to the edge of their seats. A touch of charisma goes a long way!
7. Interaction and audience engagement
Turn your presentation into an interactive experience — encourage questions, foster discussions and maybe even throw in a fun activity. Engaged audiences are more likely to remember and embrace your message.
Transform your slides into an interactive presentation with Venngage’s dynamic features like pop-ups, clickable icons and animated elements. Engage your audience with interactive content that lets them explore and interact with your presentation for a truly immersive experience.

8. Effective storytelling
Who doesn’t love a good story? Weaving relevant anecdotes, case studies or even a personal story into your presentation can captivate your audience and create a lasting impact. Stories build connections and make your message memorable.
A great presentation background is also essential as it sets the tone, creates visual interest and reinforces your message. Enhance the overall aesthetics of your presentation with these 15 presentation background examples and captivate your audience’s attention.
9. Well-timed pacing
Pace your presentation thoughtfully with well-designed presentation slides, neither rushing through nor dragging it out. Respect your audience’s time and ensure you cover all the essential points without losing their interest.
10. Strong conclusion
Last impressions linger! Summarize your main points and leave your audience with a clear takeaway. End your presentation with a bang , a call to action or an inspiring thought that resonates long after the conclusion.
In-person presentations aside, acing a virtual presentation is of paramount importance in today’s digital world. Check out this guide to learn how you can adapt your in-person presentations into virtual presentations .
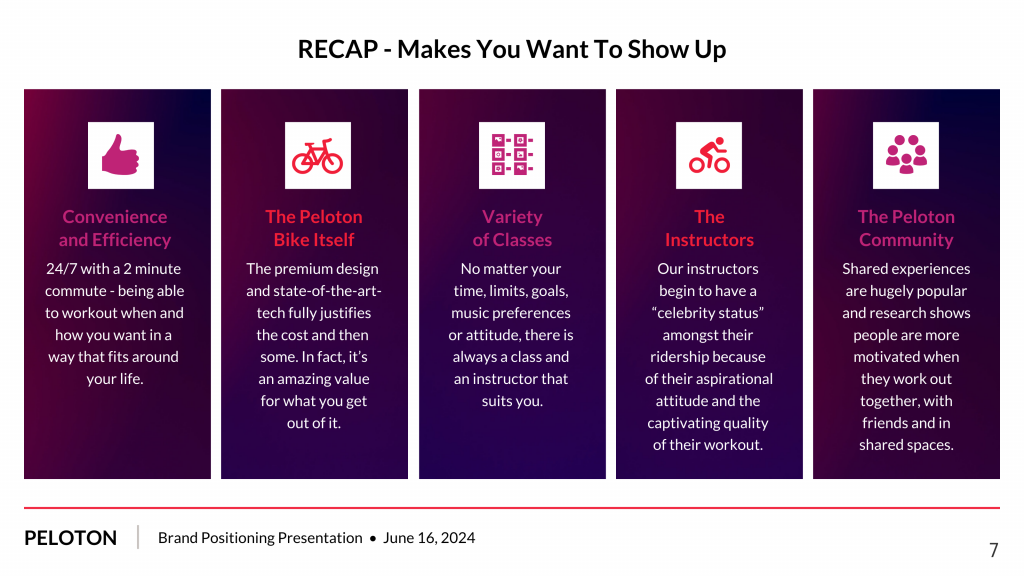
Preparing an effective presentation starts with laying a strong foundation that goes beyond just creating slides and notes. One of the quickest and best ways to make a presentation would be with the help of a good presentation software .
Otherwise, let me walk you to how to prepare for a presentation step by step and unlock the secrets of crafting a professional presentation that sets you apart.
1. Understand the audience and their needs
Before you dive into preparing your masterpiece, take a moment to get to know your target audience. Tailor your presentation to meet their needs and expectations , and you’ll have them hooked from the start!

2. Conduct thorough research on the topic
Time to hit the books (or the internet)! Don’t skimp on the research with your presentation materials — dive deep into the subject matter and gather valuable insights . The more you know, the more confident you’ll feel in delivering your presentation.
3. Organize the content with a clear structure
No one wants to stumble through a chaotic mess of information. Outline your presentation with a clear and logical flow. Start with a captivating introduction, follow up with main points that build on each other and wrap it up with a powerful conclusion that leaves a lasting impression.
Delivering an effective business presentation hinges on captivating your audience, and Venngage’s professionally designed business presentation templates are tailor-made for this purpose. With thoughtfully structured layouts, these templates enhance your message’s clarity and coherence, ensuring a memorable and engaging experience for your audience members.
Don’t want to build your presentation layout from scratch? pick from these 5 foolproof presentation layout ideas that won’t go wrong.

4. Develop visually appealing and supportive visual aids
Spice up your presentation with eye-catching visuals! Create slides that complement your message, not overshadow it. Remember, a picture is worth a thousand words, but that doesn’t mean you need to overload your slides with text.
Well-chosen designs create a cohesive and professional look, capturing your audience’s attention and enhancing the overall effectiveness of your message. Here’s a list of carefully curated PowerPoint presentation templates and great background graphics that will significantly influence the visual appeal and engagement of your presentation.
5. Practice, practice and practice
Practice makes perfect — rehearse your presentation and arrive early to your presentation to help overcome stage fright. Familiarity with your material will boost your presentation skills and help you handle curveballs with ease.
6. Seek feedback and make necessary adjustments
Don’t be afraid to ask for help and seek feedback from friends and colleagues. Constructive criticism can help you identify blind spots and fine-tune your presentation to perfection.
With Venngage’s real-time collaboration feature , receiving feedback and editing your presentation is a seamless process. Group members can access and work on the presentation simultaneously and edit content side by side in real-time. Changes will be reflected immediately to the entire team, promoting seamless teamwork.
7. Prepare for potential technical or logistical issues
Prepare for the unexpected by checking your equipment, internet connection and any other potential hiccups. If you’re worried that you’ll miss out on any important points, you could always have note cards prepared. Remember to remain focused and rehearse potential answers to anticipated questions.
8. Fine-tune and polish your presentation
As the big day approaches, give your presentation one last shine. Review your talking points, practice how to present a presentation and make any final tweaks. Deep breaths — you’re on the brink of delivering a successful presentation!
In competitive environments, persuasive presentations set individuals and organizations apart. To brush up on your presentation skills, read these guides on how to make a persuasive presentation and tips to presenting effectively .

Whether you’re an experienced presenter or a novice, the right techniques will let your presentation skills soar to new heights!
From public speaking hacks to interactive elements and storytelling prowess, these 9 effective presentation techniques will empower you to leave a lasting impression on your audience and make your presentations unforgettable.
1. Confidence and positive body language
Positive body language instantly captivates your audience, making them believe in your message as much as you do. Strengthen your stage presence and own that stage like it’s your second home! Stand tall, shoulders back and exude confidence.
2. Eye contact with the audience
Break down that invisible barrier and connect with your audience through their eyes. Maintaining eye contact when giving a presentation builds trust and shows that you’re present and engaged with them.
3. Effective use of hand gestures and movement
A little movement goes a long way! Emphasize key points with purposeful gestures and don’t be afraid to walk around the stage. Your energy will be contagious!
4. Utilize storytelling techniques
Weave the magic of storytelling into your presentation. Share relatable anecdotes, inspiring success stories or even personal experiences that tug at the heartstrings of your audience. Adjust your pitch, pace and volume to match the emotions and intensity of the story. Varying your speaking voice adds depth and enhances your stage presence.

5. Incorporate multimedia elements
Spice up your presentation with a dash of visual pizzazz! Use slides, images and video clips to add depth and clarity to your message. Just remember, less is more—don’t overwhelm them with information overload.
Turn your presentations into an interactive party! Involve your audience with questions, polls or group activities. When they actively participate, they become invested in your presentation’s success. Bring your design to life with animated elements. Venngage allows you to apply animations to icons, images and text to create dynamic and engaging visual content.
6. Utilize humor strategically
Laughter is the best medicine—and a fantastic presentation enhancer! A well-placed joke or lighthearted moment can break the ice and create a warm atmosphere , making your audience more receptive to your message.
7. Practice active listening and respond to feedback
Be attentive to your audience’s reactions and feedback. If they have questions or concerns, address them with genuine interest and respect. Your responsiveness builds rapport and shows that you genuinely care about their experience.

8. Apply the 10-20-30 rule
Apply the 10-20-30 presentation rule and keep it short, sweet and impactful! Stick to ten slides, deliver your presentation within 20 minutes and use a 30-point font to ensure clarity and focus. Less is more, and your audience will thank you for it!
9. Implement the 5-5-5 rule
Simplicity is key. Limit each slide to five bullet points, with only five words per bullet point and allow each slide to remain visible for about five seconds. This rule keeps your presentation concise and prevents information overload.
Simple presentations are more engaging because they are easier to follow. Summarize your presentations and keep them simple with Venngage’s gallery of simple presentation templates and ensure that your message is delivered effectively across your audience.

1. How to start a presentation?
To kick off your presentation effectively, begin with an attention-grabbing statement or a powerful quote. Introduce yourself, establish credibility and clearly state the purpose and relevance of your presentation.
2. How to end a presentation?
For a strong conclusion, summarize your talking points and key takeaways. End with a compelling call to action or a thought-provoking question and remember to thank your audience and invite any final questions or interactions.
3. How to make a presentation interactive?
To make your presentation interactive, encourage questions and discussion throughout your talk. Utilize multimedia elements like videos or images and consider including polls, quizzes or group activities to actively involve your audience.
In need of inspiration for your next presentation? I’ve got your back! Pick from these 120+ presentation ideas, topics and examples to get started.
Creating a stunning presentation with Venngage is a breeze with our user-friendly drag-and-drop editor and professionally designed templates for all your communication needs.
Here’s how to make a presentation in just 5 simple steps with the help of Venngage:
Step 1: Sign up for Venngage for free using your email, Gmail or Facebook account or simply log in to access your account.
Step 2: Pick a design from our selection of free presentation templates (they’re all created by our expert in-house designers).
Step 3: Make the template your own by customizing it to fit your content and branding. With Venngage’s intuitive drag-and-drop editor, you can easily modify text, change colors and adjust the layout to create a unique and eye-catching design.
Step 4: Elevate your presentation by incorporating captivating visuals. You can upload your images or choose from Venngage’s vast library of high-quality photos, icons and illustrations.
Step 5: Upgrade to a premium or business account to export your presentation in PDF and print it for in-person presentations or share it digitally for free!
By following these five simple steps, you’ll have a professionally designed and visually engaging presentation ready in no time. With Venngage’s user-friendly platform, your presentation is sure to make a lasting impression. So, let your creativity flow and get ready to shine in your next presentation!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

Structuring a Slide Presentation
Defining your structure is charting the path that the audience will take through your presentation. A poor structure is disorienting and leaves the audience wondering how they will get to their destination (or what the destination even is). Invest time in defining your central message and present your results as the evidence to support it. Don’t forget to tailor how much context you provide in your introduction and conclusion to the audience you are presenting to.
1. Before you start
Put away PowerPoint, Google Slides, and any software you’re tempted to open up. The first step to an effective presentation is clarifying your objectives, your audience, and your central (takeaway) message.
1.1. Identify your purpose
What do you want your audience to do, think, or feel after hearing your talk? Goals such as “update my audience” are short-sighted, but can be developed further. For instance, it could become “update my audience so they can appreciate all the promising work I’ve done and they’ll want to renew our grant.” Helpful goals are audience-centric and can inform what to include in your presentation.

1.2 Understand your audience
Think about who will be in attendance and tailor your talk to them. Determine your audience’s
- reason for attending your talk
- prior knowledge about your field or your work
- interests and motivations.
Understanding your audience will help you gauge how much background and technical detail to include. It will also help you motivate your work.
1.3 Craft a central message
Effective talks leave the audience with a clear take-away message. Based on your goal for the talk and the interests of your audience, create a single-sentence message that you would deliver to your audience. If an audience member thinks back about your talk and remembers a single thing, what should that be?

Also, make sure you understand the format and constraints of your talk, including how much time you will have, how your slides will be shown (large projector vs. small TV screen), and how many people will attend and how they will participate (questions during vs. after).
Return to Contents
2. Developing your content
Your technical presentation should follow an hourglass-shaped narrative: start broadly with an issue that your audience cares about, lead into the specifics of your work, then open up again with what your results mean and how they link back to the bigger picture. When you structure your talk, however, start at the narrowest part of the hourglass—your results. Your central message will emerge from here.
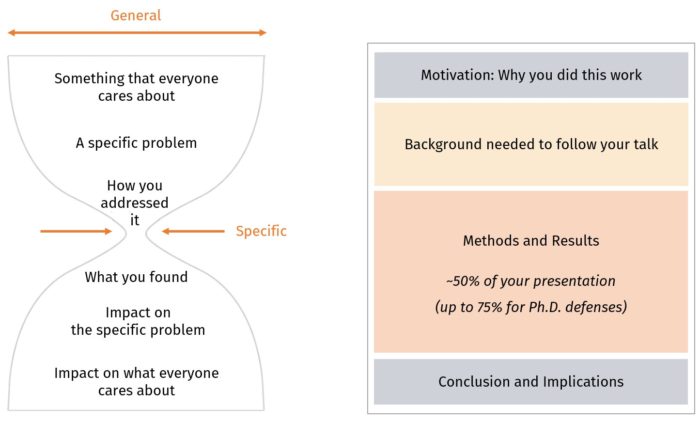
2.1. Interpret your results
The most important part of your talk to the majority of your audience is not your results themselves, but the message they support. Start planning your talk by looking at your results and deciding what main points you can draw from them.
Carefully group your results , not by how you performed the experiments, but by the main points they support. Aim for 2-4 groupings that each lead to a single main point. These 2-4 main points should form the evidence for the main message of your talk.
Filter out less relevant results based on how well they support your main points. You often just can’t fit everything into one talk, so be selective about what you include to maximize your impact.
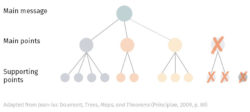
Evaluate your argument based on how well your results support your conclusions, and how well your conclusions support your main message. Look for logical holes in your argument, and address them or modify your main message to better fit your conclusions.
2.2 Explain your methods
Describe what you did to get to your results. Give your audience the information they need to understand your results (how you set up your experiment, simulation, etc.). Be selective about what information you include to keep focus on your central message.

2.3 Motivate your work
Explicitly tell your audience why they should invest time listening to your talk
Start with something your whole audience cares about. For expert audiences, this could be a specific problem, where for uninformed audiences it should be a more general goal for your field.
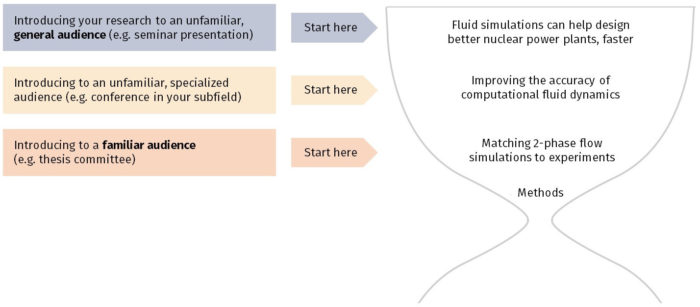
2.4 Describe the impact
How did your work address the needs from your motivation? Look forward to the future and describe the difference made by your work.
Start with the most direct impact of your work. What is at least one thing that your work directly accomplishes? What next steps does your work motivate?
Connect back to your motivation. Describe how you see your project evolving to have a larger impact. Explain how your (and your group’s/colleague’s/field’s) work is coming together to meet a larger goal. End by connecting back to the thing the whole audience cares about, not a “Questions?” “Thank you!” or “backups” slide.
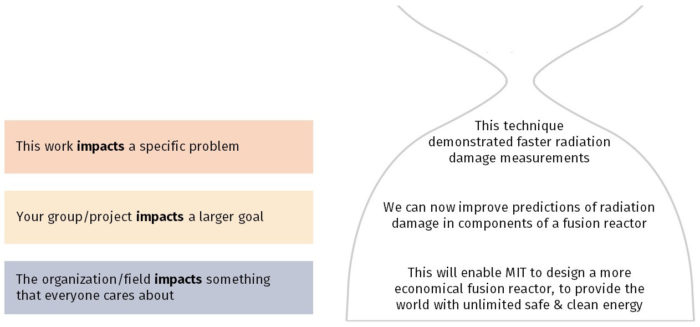
3. Putting it together
Build a slide list based on the information you gathered. Take your motivation, methods, results, and impact, and turn them into a series of sentences, each representing a single slide. These sentences will become your slide titles, and together they should form a coherent story.
Fill out your outline from your slide list. Plan out what evidence you’ll need to support each slide title.
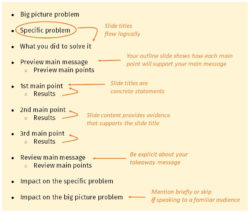
Now you can start creating slides !
4. Quick tips
- You can write, sketch, or storyboard your narrative to discover and develop your story. Just make sure that there is a clear logical flow leading from one point to the next.
- Do not focus on how many slides you should have. Especially in technical presentations, some of the content will be complex enough that animations will be needed, which will throw off your slide count. Instead, focus on constraints such as time limits and your audience’s capacity to understand your message.
- If you are recycling slides from a previous talk, take a moment to still go through the “ Before you start ” section. This will help ensure that you have a solid foundation for your new talk.
Additional resources
- Jean-luc Doumont, Trees, Maps, and Theorems (Principiae, 2009), specifically the “Designing the Presentation” chapter. You can borrow a copy from the NSE Communication Lab.
- Jean-luc Doumont’s one-page guide
To get started or receive feedback on your draft, make an appointment with us. We’d love to help!
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Structure Your Presentation Like a Story
- Nancy Duarte

To win people over, create tension between the status quo and a better way.
After studying hundreds of speeches, I’ve found that the most effective presenters use the same techniques as great storytellers: By reminding people of the status quo and then revealing the path to a better way, they set up a conflict that needs to be resolved.
- ND Nancy Duarte is a best-selling author with thirty years of CEO-ing under her belt. She’s driven her firm, Duarte, Inc., to be the global leader behind some of the most influential messages and visuals in business and culture. Duarte, Inc., is the largest design firm in Silicon Valley, as well as one of the top woman-owned businesses in the area. Nancy has written six best-selling books, four have won awards, and her new book, DataStory: Explain Data and Inspire Action Through Story , is available now. Follow Duarte on Twitter: @nancyduarte or LinkedIn .
Partner Center
Blog > English Presentation Structure (Introduction, Closing) & useful Phrases
English Presentation Structure (Introduction, Closing) & useful Phrases
02.21.20 • #powerpoint #presentation #english.
When giving a presentation in english, there are certain guidelines you should follow. Maybe you haven't got a lot of experience presenting - or you would simply like to refresh your already existing knowledge - we're here to teach you the basics about presenting and provide you with a free list of useful phrases and the basic structure you can in your presentation!
1. Structure
The general structure of a presentation is the following:
- Introduction
It is up to you to design these three parts. Using videos or everyday-examples can be a great way to introduce the audience to the topic. The important thing is that you capture the audience's attention from the beginning by making an interesting introduction. The main part is where you present your topic, ideally divided into sections. You can be creative with it - incorporate images, videos, stories or interactive polls . We generally recommend using different kinds of elements, as that makes the presentation more lively. Make sure your main part is well structured, so your audience can follow. In the conclusion, you should give a short summary of the points you made without adding any new information. You can also make an appeal to your audience in the end.
2. Useful Phrases
Here you'll find several phrases that you'll need in every presentation. Of course, you should adapt them and use them in a context that is suitable for your setting. The phrases are divided into subcategories so you can find what you're looking for more easily.

Starting your Presentation
In your introduction, you should:
Welcome your audience
Good morning/afternoon/evening everyone!
Ladies and gentlemen, I welcome you to my presentation about...
Introduce yourself
I am ... (from company ...) and today I would like to introduce you to the topic of ...
My name is ... and I am going to talk about ... today.
Icebreakers (for audience engagement)
Icebreaker polls are an amazing way to engage your audience instantly. They function as a fun and playful element at the beginning, giving you the perfect start you need to give a successful presentation. Click here to read our detailed post about icebreaker polls!
Mention the presentation topic and the reason for giving the presentation
I am grateful to be here today and tell you you about...
I would like to take this opportunity to talk about ...
I am here today to talk to you about ...
The reason why I am here today to talk about ... is ...
The purpose of this presentation is to ...
My goal today is to ...
Hopefully, by the end of the presentation, you will all know more about ...
Give a short overview of the content
To make it as understandable as possible, I divided my presentation into ... parts. In the first part, I will concentrate on ..., the second part will be about ..., ...
First of all, I will give you a short introduction, then we will move on to ...
... and finally, I will give you some insights to ...

Here are a few phrases that you could use during the whole presentation, but especially in the main part.
Engage your audience
In order to raise the audience's attention and improve their engagement, it is extremely important to make contact with them. A great way to do so is by adding interactive elements such as polls. If you would like to know more about this topic, read our article on How To Boost Audience Engagement . You can also use a software like SlideLizard , which allows you to conduct live polls, do Q&A sessions with your audience, share your resources and many more benefits that take your presentation to the next level.
Please raise your hand if you ...
Have you ever thought about ... ?
I would like to do a poll about ...
Please ask any questions as soon as they arrive.
On one hand, … on the other hand…
Comparing … with …, we can see that…
Clearly, … makes more sense than …
Whereas Option A is …, Option B is …
Making new points
Firstly,… Secondly,…
What also has to be mentioned is…
Next, I would like to bring up the topic of…
That being said, now we are going to take a look at…
Let's move on to the next topic.
On the next slide,…
The last thing I would like to mention is…

We made a whole blog post about how to pose questions in your presentation: The Right Way to do a Question Slide .
Talking about images or videos
In this image you can clearly see that ...
We are now going to take a look at a picture/video of ...
I'm going to show you a video by ... about ... now.
I've prepared a video about ...
Talking about statistics and charts
I am now addressing this graph that refers to the results of study XY.
In the graph on this slide, you can see that ...
The average is at ...
This graph clearly shows that the majority ...
According to this graph, the focus should be on ...
What that study tells us for practice is that we should ...
Emphasizing
I would like to emphasize the importance of ...
Moreover, it has to be said that ...
I want to stress the importance of ...
We always have to remember that ...
This is of high significance because ...
That part is especially important because ...
When something goes wrong
I am sorry, but it seems like the projector isn't working.
Could someone please help me with ...?
Is anybody here who knows how to ...?
Could someone give me a hand with ...
I would like to apologize for ...
I apologize for the technical problems, we are going to continue in a minute.
I am sorry for the inconvenience.
End of Presentation
In the conclusion, you should...
Sum up the main points
In conclusion I can say that…
To sum up the main points,…
With all mentioned aspects taken into consideration, I can say that…
Make an appeal
So please, in the future, try to be conscious about...
Please take a moment to think about...
I would like to encourage you to...
Thank your audience and say goodbye
It was a pleasure being here today.
Thank you for listening and goodbye.
Thank you for being such a great, engaged audience. Goodbye.
Thank you so much for listening, see you next time.
What is the structure of a presentation?
Your presentations should always have an Introduction, a Main part and a Conclusion.
What is a good way to begin a presentation?
You can start by introducing yourself, giving an overview of your topic, telling a little story or showing the audience an introductory video or image.
What are good phrases to use in English presentations?
There are many phrases that will make your presentation a lot more professional. Our blog post gives you a detailed overview.
Related articles
About the author.

Pia Lehner-Mittermaier
Pia works in Marketing as a graphic designer and writer at SlideLizard. She uses her vivid imagination and creativity to produce good content.
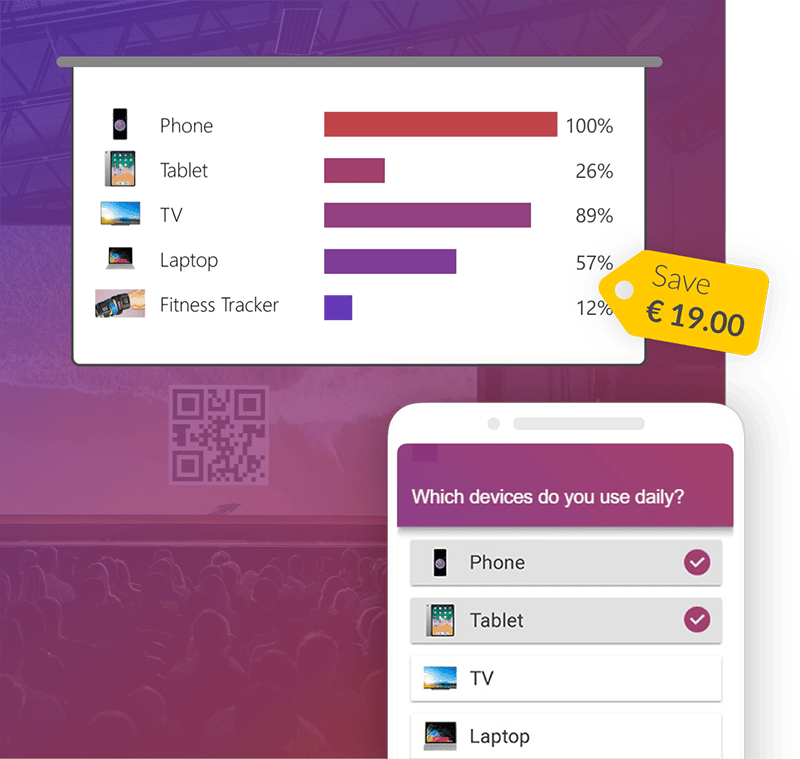
Get 1 Month for free!
Do you want to make your presentations more interactive.
With SlideLizard you can engage your audience with live polls, questions and feedback . Directly within your PowerPoint Presentation. Learn more

Top blog articles More posts

Modern mountains - Free PowerPoint Template

Best Sources of free Images to use in PowerPoint Presentations
Get started with Live Polls, Q&A and slides
for your PowerPoint Presentations
The big SlideLizard presentation glossary
Internal preview.
An Internal Preview is a statement, which is made in the body of the speech, so that the audience knows what the speaker is going to discuss next.
Informal Communication
informal communication can be used when talking to your friends or your family
Master view
In the master view in PowerPoint you can edit the Slide Master.
Multimedia Presentation
A multmedia presentation is a speech in which several types of visual and audio aids are combined in the same speech with the help of computer software. .
Be the first to know!
The latest SlideLizard news, articles, and resources, sent straight to your inbox.
- or follow us on -
We use cookies to personalize content and analyze traffic to our website. You can choose to accept only cookies that are necessary for the website to function or to also allow tracking cookies. For more information, please see our privacy policy .
Cookie Settings
Necessary cookies are required for the proper functioning of the website. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information about the number of visitors, etc.
You’re using an older browser version. Update to the latest version of Google Chrome , Safari , Mozilla Firefox , or Microsoft Edge for the best site experience.
- eLearning Blog
- eLearning Basics
- Instructional Design
- Corporate Training
- Course Selling
- Manufacturing
- Products iSpring Suite iSpring Learn
- Use Cases Onboarding Compliance Training Induction Training Product Training Channel Partner Training Sales Training Microlearning Mobile Learning
- Company About Us Case Studies Customers Partnership Course Development Contact Us
- Knowledge Hub Knowledge Hub Academy Webinars Articles Guides Experts on iSpring
- Language EN English Français Deutsch Español Italiano Nederlands Português Polski 中文 日本語 العربية Indonesia
- Shopping Cart
How to Structure a PowerPoint Presentation

Table of Contents

This is the main part of your presentation, which should keep the promises you made in the introduction. This is where you explain your topic and present all your information.
Depending on the nature of your presentation, divide it into segments/points. Arrange your points in a logical order and then provide information to support each of them. There are many different ways to organize your key points, for example:
- Number your points according to their priority (1, 2, 3, …)
- Place the points in a time frame (past, present, future)
- Use narration (tell a story from beginning to end)
- Present the points with a problem-solution dynamic (state a problem, describe its impact, offer ways to solve the issue)
A good conclusion summarizes the key points you made or highlights what the audience should have learned. It clarifies the general purpose of your presentation and reinforces the reason for viewing it. Here are the slides you may want to include:
- Summary. List what goals your audience have achieved, what knowledge they got, and how this information can help them in the future.
- Conclusion. Here you can thank your audience for viewing the presentation.
Tips for Structuring a Presentation in PowerPoint
Now that you know which parts a typical presentation should consist of, let’s see how to structure it in PowerPoint.
1. Combine slides into sections
When working with a large PowerPoint presentation (PPT), you can create sections that can be collapsed and expanded. This will help you keep presentation slides organized and facilitate navigation in editing mode. To do that, follow these steps:

- To shift a section, right-click on its name and use the Move Section Up and Move Section Down options.
- To collapse or expand a certain section, click on the collapse icon to the left of the section name. You can also minimize and maximize all sections at once by right-clicking on the section name and choosing Collapse All or Expand All .
As well, you can access these settings by choosing Slide Sorter under the VIEW tab.

This kind of segmentation is a great way to overview the logical flow of your slides all at once and see if there are any changes required. For example, you may decide to break one slide into two or three, or the other way around.
2. Use the Outline View
One other way to structure a PowerPoint presentation in the editing mode is to use Outline View . You can choose it from the VIEW tab.

This view doesn’t display sections, but it shows the title and main text of each slide, which can give you a quick overview of the presentation contents. Here you can go through the entire text and edit it instantly. You can also work with text (on the left) and slides (on the right) simultaneously, as the latter is shown on the right side of your screen.
Note that, to be displayed in an outline, text needs to be typed in a text placeholder, not a text box . A text placeholder is a box with the words “Click to add text” or “Click to add title”, and it appears when you choose a standard layout.
You can also use Outline View to promote bullet text to titles and the other way around. To do that, right-click on a relevant title or text and select the Promote or Demote options.

Be attentive about demoting a title, as this will delete the original slide and move its title and text to the adjacent slide.
PowerPoint only allows users to promote and demote text, not entire slides. Therefore, there’s no possibility to change the hierarchical order of slides.
3. Create a table of contents
All the aforementioned tips help you organize a presentation when formatting it. However, it’s crucial that your viewers can easily navigate through entire presentation too. One sure way to provide them with this opportunity is to create an interactive and structured table of contents.
Though there’s no native automatic outline in PowerPoint, it can be created manually:

- Press Ctrl+A to select all the names, and Ctrl+C to copy them.
- Then Press Ctrl+V to paste the copied titles on the desired slide. In case there are too many titles and they don’t fit onto a single page, you can divide the table of contents into two columns or place it on two slides.

You’ll need to repeat this procedure to link all the chapters to corresponding slides. For more information, read this step-by-step guide on how to add a hyperlink in PowerPoint .
Now all the chapters can be accessed from a single table of contents, which is very convenient. However, you will also need to link them back to that unifying page. You can do this by inserting an Action Button on every slide of your presentation in Slide Master mode:

Now there is a single page from which all the other pages can be easily accessed. As well, it’s possible to go back to the table of contents at any time with the intuitive Home button.
Depending on the size of your presentation, the time it takes to create an interactive outline may vary, as you will need to add hyperlinks to every chapter manually. Be aware that if you rename a slide or simply delete it, these changes will not be automatically registered in the table of contents. For example, if you delete a slide, its title will still be displayed in the table of contents, but clicking on it won’t lead the viewer to another point in the presentation.
This is what our sample presentation looks like:

A Better Way to Structure a PowerPoint Presentation
Creating a table of contents manually might be fine for a small presentation, but if you have 122 slides, it would require too much time and energy to do so. That’s why, instead of manually creating a table of contents, we took advantage of iSpring Suite and simply enabled the automatic outline.
iSpring Suite
Fully-stocked eLearning authoring toolkit for PowerPoint. No training required to start!

Note: iSpring Suite turns slides into HTML5 format, so your audience can view them online, right in their browsers.

As you can see, the new presentation has a pop-up outline and a navigation panel, which make it possible to move to any slide at any time without leaving the slide show mode.
How to set up navigation
To create navigation in your presentation, follow these simple steps:
- Get a free trial of iSpring Suite.

- When you’ve configured the Slide Properties settings, click on Save & Close in the upper-left corner.
How to configure an outline
Whereas PowerPoint requires the outline to be designed manually, iSpring Suite has already prepared it for you. At the same time, you don’t have to stick with the standard outline template, as you can easily customize the player’s final look and feel:

We recommend leaving Enable Search marked, as this will allow viewers to search for any content at any time, including the texts on the slides. This is especially useful for large presentations with a lot of text.
If you have previously arranged slides into multiple levels in the Slide Properties, then leave Multilevel outline marked. That way, the outline will display the nesting structure of the presentation, facilitating navigation. You can learn more about the other outline options here .

- When you have finished configuring the player, click on Apply & Close in the upper-left corner.
- Now you can publish your enhanced presentation either to HTML5, to make it easily accessible via browser on any device, or MP4 video format. If you’re going to upload your presentation to an LMS, you can publish it to any eLearning format: SCORM, AICC, Tin Can, or cmi5.
While a standard PowerPoint slideshow is straightforward and limited, iSpring Suite saves viewers from having to follow a strict slide order. An interactive and searchable outline allows non-linear navigation, where any information can be accessed at any time at a glance.
Also read : → How to Convert PowerPoint to MP4 Video
Also read : → How To Record Presentations With Audio
Another perk
iSpring Suite comes with Content Library , which provides a great collection of presentation templates and allows you to create professional-looking presentations in a matter of minutes. Each template includes basic course elements: a title slide, a table of contents, chapters, a timeline, and info slides. Organize them in the order you prefer, populate them with your texts and images, and your presentation is ready to go.

We hope this article will help you develop an ideal structure for your PowerPoint presentation and do this quickly and easily. Captivate your audience with a powerful and persuasive presentation!
Do you have any other insights on how to simplify PowerPoint slides design? Please share them in the comment section. We’d like to hear from you.
Fast course authoring toolkit
Create online courses and assessments in record time.

Content creator:
Helen Colman
She enjoys combining in-depth research with expert knowledge of the industry. If you have eLearning insights that you’d like to share, please get in touch .
You might also like this

Subscribe to our blog
Stay tuned to get our latest eLearning tips and tricks!
By clicking “Subscribe”, you agree to our Privacy Policy . All emails include an unsubscribe link, so that you can opt-out at any time.
We use cookies to give you the best possible experience on our website and also for analytics and marketing purposes. You can enable or disable optional cookies as desired. See our Cookie Policy for more details.
Manage your cookies
Essential cookies are always on. You can turn off other cookies if you wish.
Essential cookies
Analytics cookies
Social media cookies

Presentation structure: Tips & examples for the perfect presentation structure
A well-structured presentation is crucial to engaging your audience and getting your message across effectively. A clear presentation structure allows the audience to follow your thoughts and arguments easily and remember the information presented better. In this article, we give you a comprehensive guide to the perfect presentation structure and offer you helpful tips and examples to make your presentation a success.
The start of the presentation: raising interest and providing orientation
The beginning of your presentation is of great importance as it sets the tone for the entire talk and should arouse the interest of your audience. Start with a powerful introduction that introduces the topic and grabs the audience's attention. For example, you can use a relevant quote, an anecdote or a provocative question to arouse the audience's curiosity. Further tips and examples for presentation introductions. After you have aroused interest, you should give your audience a clear orientation by introducing the main points of your presentation. List the main points you will cover and make sure they are well structured. A guiding question can help you maintain the thread of your presentation and get your message across at the end.
The main part: An in-depth look at the topic
The main part of your presentation should take up most of your speaking time and cover the topic in depth. Here you have the opportunity to present your specialist knowledge and shed light on the topic from different perspectives. Structure the main part logically and use clear transitions to allow the audience to move smoothly between topics. Use verifiable arguments, valid facts and supporting examples to back up your statements. Graphics, images and diagrams can also be used to visually represent complex information and make it easier to understand. Make sure that your presentation slides are not overloaded and focus on the most important points.
The end: Summary and call to action
The end of your presentation is just as important as the beginning. Use this section to summarize the key points again and ensure that the key messages stick in your audience's mind. A clear conclusion gives your audience a final understanding of the topic. You can also use the conclusion to ask your listeners to take action. For example, if your topic is intended to draw attention to a problem, you can encourage your listeners to take action and do something. Offer them a simple invitation to take action and make it effective. Here are 7 examples of the perfect way to end your presentation.
An example of a good presentation structure
To give you a better idea of a successful presentation structure, here is an example of how you could organize your presentation:
1. Introduction
- Arouse interest
- Provide orientation
- Ask the key question
2.Main section
- Summary of the key points
- Request for action
Find more tips for the optimal structure of a presentation here.
Creating a presentation - choosing the right tool
Choosing the right tool to create and deliver your presentation can make a big difference. Nowadays, there are a variety of technologies and platforms specifically designed to make presentations easier and more effective. One such tool that comes highly recommended is Collaboard. Collaboard is an online whiteboard that not only offers the ability to create engaging and interactive presentations, but also offers a variety of collaboration and interactivity features.
Here you will find detailed instructions on how to create a presentation with Collaboard. With Collaboard, you can visually organize your thoughts and ideas, highlight parts of your presentation and even collaborate with others in real time. Plus, technical issues can be avoided as the software is cross-platform and runs in the cloud, meaning you can access it from anywhere and on any device. So, when you're planning your next presentation, remember: choosing the right tool can help you get your message across more effectively and make your presentation a success.
The role of visualizations in building the presentation
Visualizations are a powerful tool in any presentation. Not only do they serve to make your presentation more visually appealing, but they can also help simplify complex information and make it easier for the audience to understand. Infographics, diagrams, images or even videos can be used to illustrate data, trends and correlations that would otherwise be difficult to convey. In addition, a well-designed visualization can help to keep the interest and attention of your audience. But be careful: make sure that your visualizations are not overloaded and present the content clearly and simply. They should support your message and not distract from it. Remember that a good visualization is worth a thousand words, and use it wisely to take your presentation to the next level.
Presentation structure: Your guide to success through clear structure and effective message delivery
A well-structured presentation is the key to success. By having a clear and logical presentation structure, you can ensure that your message is conveyed effectively and that your audience can understand your presentation more easily. Use the tips and examples in this article to make your next presentation a success.
Presentation structure - Frequently asked questions & answers
What is the best way to start my presentation.
An effective way to start a presentation is to include an interesting hook such as an amazing statistic, a personal story or a provocative question to grab the audience's attention.
How long should the presentation last?
The ideal length of a presentation depends on the context, but a good rule of thumb is that it should last no longer than 20-30 minutes to keep the audience's attention.
How many slides should I use for my presentation?
There is no hard and fast rule for the number of slides, but a common approach is to plan one slide per minute of presentation time. However, the most important rule is that each slide should have a clear purpose.
How can I ensure that my message is communicated effectively?
Make sure that your presentation is clearly structured and that every point you make contributes directly to your main message. Visualizations and examples can also help to get your message across more effectively.
What do I do if I feel nervous during my presentation?
It's normal to be nervous before a presentation. Take a deep breath, speak more slowly and remind yourself that you are the expert on your topic. Practice and preparation can also help to reduce nervousness.
How do I deal with questions or objections during my presentation?
Be open to questions and objections and see them as an opportunity to better understand your audience and cover your topic in more detail. Prepare in advance for possible questions and take time to answer each question carefully.
Which technology should I use for my presentation?
The choice of technology depends on your needs and the context. A good online tool like Collaboard can help you design and deliver your presentation effectively.
Recent Posts from Blog
150 ice breaker questions.
Find here the ultimate guide to icebreaker questions. Whether you’re looking to foster engagement in a meeting, lighten the mood...
The 5-Why method » The most important things at a glance!
In companies and in everyday life, we often face problems that at first glance appear to be solvable using simple methods....
Best questions in retrospective. These methods can help your team move forward
In many work and project environments, retrospective methods are among the key tools for improving processes. In a good...
Stay up to date with the latest collaboration tips and news.
The Best Presentation Structure: Tips & Tricks!
The name PowerPoint says it all – a powerful tool for visualizing expressive content. With the right presentation structure, PowerPoint helps add weight to your ideas and statements through visual impact.
Are you looking for the perfect presentation structure that provides lots of opportunities to inspire your audience? Not exactly sure where to start? Keep reading for a detailed guide that will guarantee success.
As a rule, a presentation needs a topic and a specific reason for presenting it.
Here are some examples:
- A sales presentation to a customer to introduce products or services
- Presenting company figures to management
- An onboarding presentation to inform new colleagues about the most important company information
- A presentation for your company’s anniversary
- Presentations for school or university
- A presentation of research results for a science conference
Regardless of the topic or occasion, you need a clear and well-thought-out presentation structure. Without that, your audience will have a tough time following and your presentation will fall short of its goal, like attracting a new customer.
Give yourself enough time
Give yourself enough time to prepare your PowerPoint presentation. As soon as you know when you’re presenting, create a schedule. Spend 30 minutes a day preparing your upcoming presentation. Allow enough time to research the material, too. Use the rule of thirds as a guideline: If you have twelve days until the presentation, devote four days to researching and collecting information.
Take the time to thoroughly research your presentation topic. Take notes, collect ideas and thoughts. Use something you always have with you; a small notebook, a tablet or your smartphone is all you need. Keep your notes short – just enough information to get your creative juices flowing.
Organize your notes

Once you have enough material, it’s time to organize and structure it. Now is the time to form your basic presentation framework. Remember to allot enough time for this (think about the 3/3 rule).
Use your notes to develop your presentation. Ask yourself this: What’s the goal of my presentation? For example, do you want to impress investors with your startup or present an innovative marketing plan for the coming fiscal year? Answering this question will help you develop a core thesis.
Here’s something else to ask yourself: What do you want from your audience? Do you want to prompt an action (e.g., buy a product) or kick-start a discussion?
The go-to PowerPoint structure
Now that you’re prepared, it’s time to think about the right PowerPoint presentation structure . Here’s a general guide:
- Introduction
- Topic component 1
- Topic component 2
- Topic component 3
Remember to balance the various parts of your presentation. As a rule, the introduction shouldn’t be more than two slides. The topic slides form the body and should make up about 70% of your PowerPoint presentation. As simple as this may sound, it can be difficult to know which stylistic devices or elements to use to keep your audience’s attention. What should you focus on in each section of the presentation?
Take a look at this chart outlining a presentation:
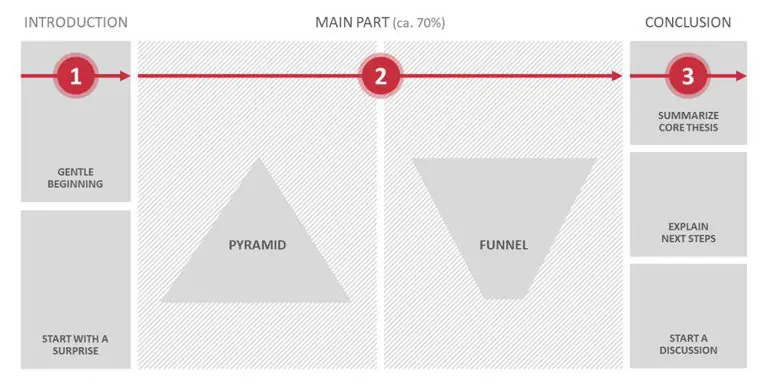
So, what does this mean for each part of the presentation structure?
1. The introduction: Pique curiosity
An intro is an important part of any presentation structure. It has to awaken the audience’s interest and ideally, create a rapport. There are several ways to start the presentation.
- The soft intro
With this type of introduction, you meet the audience at their level and gradually get to the core content of your presentation. Your first slides should be simple and not introduce too much new content. The audience should be able to understand and agree with all points until you finally get to the main topic. The first step is to describe the current situation , the second step to describe the challenge and the third step to discuss how to respond to the challenge .
- The “element of surprise” intro

With this introduction, the element of surprise is on your side. Start the presentation with a statement that shocks or surprises your audience. Bold statements or results from studies are excellent ways to do this. With this kind of intro, you also describe the current situation and what has happened or could happen. You outline the potential consequences and ask how it should be handled. Make sure these statements are true and relevant to your audience. If they aren’t, you’ll come off as less credible.
2. The body of the presentation: The heart of the matter
The body should make up about 70% of your presentation structure. This is where you flesh out your presentation topic. Put yourself in your audience’s shoes; how you would like a presenter to address you? Are their arguments valid? This is a great time to actively involve your audience in a question-and-answer scenario. This is called a dialogue-oriented presentation. Involving your audience this way guarantees their full attention.
There are two ways to organize the main part of the presentation:
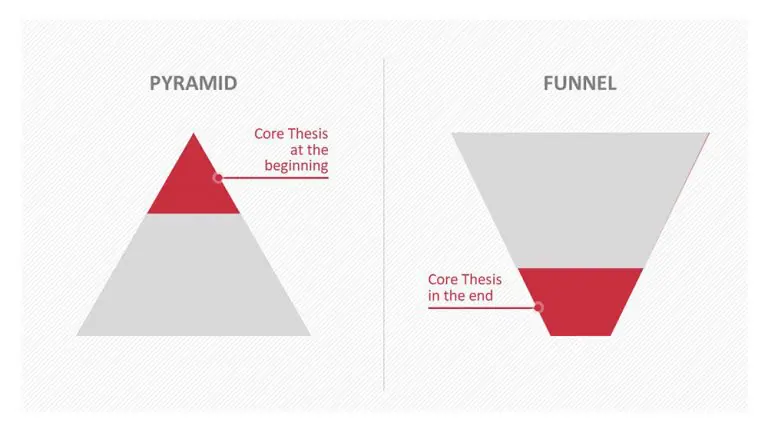
- As a pyramid
With this structure, the core message is introduced at the beginning of the presentation’s main section. Presenting the core message early will have your audience wanting to hear more. This is exactly the right time to start the question-and-answer scenario to hold their attention and get them involved.
- As a funnel
The funnel introduces the core message towards the end of the presentation . This structure does have a few drawbacks. It doesn’t lend itself well to a dialogue-oriented presentation and by waiting until the end to deliver your core message, your audience may not make the connection with earlier key statements. To avoid this, it always helps to revisit those earlier statements and reinforce the core message.
It’s also a more challenging presentation structure to pull off, especially if you don’t have that much experience with presenting. The funnel can be effective with controversial and/or highly emotional topics. Controversial core messages that are brought up at the very beginning of a presentation can lead to discussions that veer off and are hard to control. In these cases, the funnel structure is the better option.
3. The conclusion: crossing the finish line
The final part of your presentation structure may seem like the easiest. You’ve presented all your content, so the hard part is over, right? Never underestimate the importance of your conclusion . It gives you the perfect opportunity to reiterate your key points. Use it to summarize your insights, draw a conclusion and finally, discuss what needs to be done next.
It’s also a great opportunity to initiate an open discussion. If you want to open the floor to comments and questions at the end, give your audience a heads-up at the beginning of your presentation. That will give them a chance to take notes as you go along. You could also encourage the audience to ask questions during the presentation. Do this only if you know you won’t get thrown off track and you can quickly shift gears while presenting. You can find more helpful tips for a successful end of presentation here.
How to apply these tips now and create a presentation from scratch can be found in this tutorial .
The right presentation structure: It’s not just about content
Don’t forget that content alone is not enough to convince your audience. A well thought-out and rehearsed presentation is also counts as part of a presentation’s structure. The right delivery supports your slides and opens the door to communicating with your audience. You can find many helpful tips on giving a presentation in these articles:
- Why a good presentation intro is so important
- Tips for closing out a presentation
- Using the right body language while presenting
- Public speaking skills
- How to handle mistakes and slip-ups while presenting
- Using humor in presentations
Pro tip: Use notes
Is your presentation ready? Now it is time to prepare for your delivery. A short script may help . Just make sure you provide additional information and don’t simply read the slides aloud.
You can choose any note-taking tool you like. You can either use classic index cards with keywords or the Notes function in PowerPoint. You can read more about this here .
Most importantly, practice your presentation . Speaking freely and confidently is key to your presentation’s success. As great a tool as it is, PowerPoint can’t do it all for you; it can only visually support your key messages. So, take the time to make sure you are as well prepared as possible.
Impress your audience: Deliver a strong presentation with the perfect structure!
PowerPoint gives so many advantages to you and your presentation. PowerPoint is so easy to use, even beginners can master it in just a few simple steps.
Follow our tips on the right presentation structure – you’ll be amazed at how easy it is to create a professional and cohesive PowerPoint presentation!
If you need help developing the right presentation structure or building your presentation, let us put our expertise to work and help you create the perfect presentation. Feel free to contact us here for a no-obligation estimate or email us at: [email protected] .
Are you looking for professionally designed slide templates for your presentation? Then take a look at our shop . We have templates on a diverse selection of business topics and design themes for you to download. For example, these:

These articles might also interest you:
- Create a PowerPoint presentation
- How to create a PowerPoint table of contents
- Notes in PowerPoint
- A solid presentation conclusion
- Why the start of a presentation is so important
- The right body language while presenting
Share this post
- share
- save

Design Thinking: Problem Solving with a Difference

Why Corporate Mission Statements Are So Important

7 Tips & Learnings from the Apple Keynote
How to structure a presentation

A compelling presentation basically tells a story. It may not seem like it, but successful presentations all use the basic structure associated with stories. They have a beginning, a middle and an end. Planning with this in mind will help clarify what you wish to say, when you should say it, and how to tie the threads of your presentation together.
The beginning
The beginning shapes the rest of the presentation and serves two main purposes:
1. To grab the attention of your audience.
2. To calm the elevated levels of adrenaline racing through your bloodstream, so that you can relax into your presentation.
Of course, experienced presenters will know how to deal with pre-show nerves. But beginners should start their presentation with something that they feel confident will draw the audience’s attention. Don’t take any risks with your opening lines if you are already in unfamiliar territory. The audience’s reaction to your beginning could make or break the rest of the presentation. A good opener will put you, and the audience, at ease. A bad one may be misunderstood, and no matter how thick-skinned you may be it is hard to present when members of the audience look uninterested.
There is no definitive right or wrong attention-grabber – simply begin with something that you are comfortable with, and which seems to work. Here are a few suggestions:
1. A funny story, if you feel able to deliver one with humour. Avoid religious, sexual, sexist or racist jokes.
2. A short video clip – make sure that it is less than 60 seconds.
3. Unusual or interesting statistics about your industry or about your audience. These should be well-researched. Members of the audience may know more than you. Getting the statistics wrong would make you look amateur.
4. A short animation. Cartoon-like shorts can be created easily with various graphic design programs or by professional designers. Alternatively, animations are available online ready for use.
5. A touch of suspense. For example, walk on with a cardboard box and place it in the middle of the stage – but don’t tell people what it is there for. This option is probably best if practised beforehand with a trial audience of friends or colleagues. They will ensure that your prop doesn’t just confuse people.
The rule of three is a good technique for the middle section of a presentation.
The rule of three is based on the idea that three is the optimum number of points to form a pattern of information that sticks in the memory. In oratory it comes up all the time. Here are some examples:
“Friends, Romans, countrymen”
“The good, the bad and the ugly”
“Blood, sweat and tears”
Think about it – if there are only three points that you would like to leave the audience with, what would they be? These three points should form the middle of the presentation.
All you now have to do is to think of ways of illustrating these points and then you have the bulk of the structure of the presentation.
The end is more important than the beginning. This is because of the recency factor – put simply, people are likely to remember the last thing they are told much more than the points made earlier in a presentation. This particularly applies to lists.
So a good ending to the presentation is essential. There are a number of techniques that can work well, but they should link in to the main structure of the presentation.
Relating the end back to the beginning can be effective. If you opened with a funny story, remind the audience of the punchline and the point you sought to illustrate in telling it. If you brought an unusual object on stage to create suspense, then tell the audience why it is there.
If you are really struggling for ideas and want to play it safe, you could simply recap the three main concepts that you put forward in the middle section.
In many business settings a presentation ending would also benefit from a call to action. Tell the audience where they can find out more about you or your business. Offer contact details so that anyone with a question or enquiry can easily get in touch. If the audience has enjoyed your story, they may well want to hear more.
Recommended Pages

i thnink it was very good and detailes it made scence and it gave me a better perspective on hoew to do homework it gave me an fantastic picture on things and all the information could be absorbed easilly but i think if the writing was was broken up in to little bits such as bullet points it would have been much easir to read and
Nice article, but you need to provide real world example structures.
Thanks for this. Great little article and very concise. Like the stage prop the idea and the rule of three.
- All Templates
- Persuasive Speech Topics
- Informative
- Architecture
- Celebration
- Educational
- Engineering
- Food and Drink
- Subtle Waves Template
- Business world map
- Filmstrip with Countdown
- Blue Bubbles
- Corporate 2
- Vector flowers template
- Editable PowerPoint newspapers
- Hands Template
- Red blood cells slide
- Circles Template on white
- Maps of America
- Light Streaks Business Template
- Zen stones template
- Heartbeat Template
- Web icons template

- Scientific Biographies
Francis Crick, Rosalind Franklin, James Watson, and Maurice Wilkins
These four scientists—Crick, Franklin, Watson, and Wilkins—codiscovered the double-helix structure of DNA, which formed the basis for modern biotechnology.

At King’s College London, Rosalind Franklin obtained images of DNA using X-ray crystallography, an idea first broached by Maurice Wilkins. Franklin’s images allowed James Watson and Francis Crick to create their famous two-strand, or double-helix, model.
In 1962 Watson (b. 1928), Crick (1916–2004), and Wilkins (1916–2004) jointly received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their 1953 determination of the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Wilkins’s colleague Franklin (1920–1958), who died from cancer at the age of 37, was not so honored. The reasons for her exclusion have been debated and are still unclear. There is a Nobel Prize stipulation that states “in no case may a prize amount be divided between more than three persons.” The fact she died before the prize was awarded may also have been a factor, although the stipulation against posthumous awards was not instated until 1974.
Discovering the Structure of DNA
The molecule that is the basis for heredity, DNA, contains the patterns for constructing proteins in the body, including the various enzymes. A new understanding of heredity and hereditary disease was possible once it was determined that DNA consists of two chains twisted around each other, or double helixes, of alternating phosphate and sugar groups, and that the two chains are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of organic bases—adenine (A) with thymine (T), and guanine (G) with cytosine (C). Modern biotechnology also has its basis in the structural knowledge of DNA—in this case the scientist’s ability to modify the DNA of host cells that will then produce a desired product, for example, insulin.
The background for the work of the four scientists was formed by several scientific breakthroughs: the progress made by X-ray crystallographers in studying organic macromolecules; the growing evidence supplied by geneticists that it was DNA, not protein, in chromosomes that was responsible for heredity; Erwin Chargaff’s experimental finding that there are equal numbers of A and T bases and of G and C bases in DNA; and Linus Pauling ’s discovery that the molecules of some proteins have helical shapes—arrived at through the use of atomic models and a keen knowledge of the possible disposition of various atoms.

Rosalind Franklin
Of the four DNA researchers, only Rosalind Franklin had any degrees in chemistry. She was born into a prominent London banking family, where all the children—girls and boys—were encouraged to develop their individual aptitudes. She attended Newnham College, one of the women’s colleges at Cambridge University. She completed her degree in 1941 in the middle of World War II and undertook graduate work at Cambridge with Ronald Norrish, a future Nobel laureate.
She resigned her research scholarship in just one year to contribute to the war effort at the British Coal Utilization Research Association. There she performed fundamental investigations on the properties of coal and graphite. She returned briefly to Cambridge, where she presented a dissertation based on this work and was granted a PhD in physical chemistry.
After the war, through a French friend, she gained an appointment at the Laboratoire Centrale des Services Chimiques de l’Etat in Paris, where she was introduced to the technique of X-ray crystallography and rapidly became a respected authority in this field. In 1951 she returned to England to King’s College London, where her charge was to upgrade the X-ray crystallographic laboratory there for work with DNA.
Maurice Wilkins
Already at work at King’s College was Maurice Wilkins, a New Zealand–born but Cambridge-educated physicist. As a new PhD he worked during World War II on the improvement of cathode-ray tube screens for use in radar and then was shipped out to the United States to work on the Manhattan Project.
Like many other nuclear physicists, he became disillusioned with his subject when it was applied to the creation of the atomic bomb; he turned instead to biophysics, working with his Cambridge mentor, John T. Randall—who had undergone a similar conversion—first at the University of St. Andrews in Scotland and then at King’s College London.
It was Wilkins’s idea to study DNA by X-ray crystallographic techniques, which he had already begun to implement when Franklin was appointed by Randall. The relationship between Wilkins and Franklin was unfortunately a poor one and probably slowed their progress.
James Watson and Francis Crick
Meanwhile, in 1951, 23-year-old James Watson, a Chicago-born American, arrived at the Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge. Watson had two degrees in zoology: a bachelor’s degree from the University of Chicago and a doctorate from Indiana University, where he became interested in genetics. He had worked under Salvador E. Luria at Indiana on bacteriophages, the viruses that invade bacteria in order to reproduce—a topic for which Luria received a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1969.
Watson went to Denmark for postdoctoral work, to continue studying viruses and to remedy his relative ignorance of chemistry. At a conference in the spring of 1951 at the Zoological Station at Naples, Watson heard Wilkins talk on the molecular structure of DNA and saw his recent X-ray crystallographic photographs of DNA. He was hooked.
Watson soon moved to the Cavendish Laboratory, where several important X-ray crystallographic projects were in progress. Under the leadership of William Lawrence Bragg, Max Perutz was investigating hemoglobin and John Kendrew was studying myoglobin, a protein in muscle tissue that stores oxygen. (Perutz and Kendrew received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their work in the same year that the prize was awarded to the DNA researchers—1962.)

Working under Perutz was Francis Crick, who had earned a bachelor’s degree in physics from University College London and had helped develop radar and magnetic mines during World War II. Crick, another physicist in biology, was supposed to be writing a dissertation on the X-ray crystallography of hemoglobin when Watson arrived, eager to recruit a colleague for work on DNA.
Inspired by Pauling’s success in working with molecular models, Watson and Crick rapidly put together several models of DNA and attempted to incorporate all the evidence they could gather. Franklin’s excellent X-ray photographs, to which they had gained access without her permission, were critical to the correct solution. The four scientists announced the structure of DNA in articles that appeared together in the same issue of Nature .
Separate Career Paths
Then they moved off in different directions. Franklin went to Birkbeck College, London, to work in J. D. Bernal’s laboratory, a much more congenial setting for her than King’s College. Before her untimely death from cancer she made important contributions to the X-ray crystallographic analysis of the structure of the tobacco mosaic virus, a landmark in the field.
By the end of her life she had become friends with Francis Crick and his wife and had moved her laboratory to Cambridge, where she undertook dangerous work on the poliovirus. Wilkins applied X-ray techniques to the structural determination of nerve cell membranes and of ribonucleic acid (RNA)—a molecule that is associated with chemical synthesis in the living cell—while rising in rank and responsibility at King’s College.
Watson’s subsequent career eventually took him to the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) of Quantitative Biology on Long Island, New York, where as director from 1968 onward he led it to new heights as a center of research in molecular biology. From 1988 to 1992 he headed the National Center for Human Genome Research at the National Institutes of Health. Afterward he returned to CSHL as chancellor. Watson’s racist remarks about the intelligence of Africans in 2007 led the CSHL to force him into retirement, though the Lab named him an emeritus professor and honorary trustee.
When Watson doubled down on his racist views in a 2018 documentary, the lab revoked these honors and severed ties with Watson. Watson’s fame as a discoverer of the structure of DNA also made his continued public expression of sexist views on women in science and his previous eugenicist comments on homosexuality particularly harmful during the first decades of the 21st century.
The information contained in this biography was last updated on July 28, 2022.
Featured image: Rosalind Franklin in Paris, ca. 1949. Vittorio Luzzati.
Browse more biographies

Leonor Michaelis

Eugene Houdry

Friedrich Wöhler
Copy the above HTML to republish this content. We have formatted the material to follow our guidelines, which include our credit requirements. Please review our full list of guidelines for more information. By republishing this content, you agree to our republication requirements.
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

11 templates

20 templates

holy spirit
36 templates

9 templates

25 templates

memorial day
12 templates
Organizational Structure Project Proposal
It seems that you like this template, organizational structure project proposal presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
Download the Organizational Structure Project Proposal presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. A well-crafted proposal can be the key factor in determining the success of your project. It's an opportunity to showcase your ideas, objectives, and plans in a clear and concise manner, and to convince others to invest their time, resources, and support in your vision. Think of it as your chance to make a case for your project and to motivate others to join you on your journey. Well, that journey begins here, with our editable template for Google Slides and PowerPoint presentations. Download it and start working on your proposal.
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- Different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Register for free and start editing online

Postdoctoral Research Associate-College of Science and Engineering
- College of Science & Engineering
- Professional Staff
- Opening at: May 9 2024 at 13:10 CDT
Job Summary:
The Postdoctoral Research Associate is responsible for performing independent research on virtual screening of beyond-rule-of-five therapeutics.
Duties & Essential Job Functions:
1. Implements computational workflows for conformational sampling, continuum solvation, and density functional theory (DFT) prediction of molecular structure and properties. 2. Implements in the workflows alternative hypotheses bridging multiple code bases, including commercial and open-source electronic structure packages. 3. Benchmarks computational workflows from published SAMPL physical properties competitions 4. Prepares validated computational workflows as entries to new upcoming SAMPL physical properties competitions 5. Communicates research findings and results through oral and written presentation. 6. Assists in the preparation of manuscripts based on research findings. 7. Works collaboratively with graduate student researchers and assist with mentoring undergraduate researchers. 8. Performs other related duties as assigned.
Required Education & Experience:
• Ph.D. in Chemistry
Preferred Education & Experience:
• Experience with electronic structure simulation in high-performance computing environments. • Experience writing, validating, and releasing open-source or commercial molecular simulation software. • Experience simulating drug docking, pKa, solubility, and/or other properties relevant to pharmaceutical virtual screening. Experience with previous SAMPL blind challenges is especially desired. • Proven record with communicating and publishing research results.
Required Licensure/Certification/Specialized Training:
Preferred licensure, certification, and/or specialized training:, knowledge, skills & abilities:.
• Knowledge of Linux environments. • Knowledge of Python and/or Perl. • Knowledge of at least one open or commercial electronic structure simulation package. • Ability to perform research and document results. • Ability to communicate effectively. • Ability to work both independently and collaboratively as part of a team. • Ability to mentor undergraduate researchers.
TCU Core Competencies:
University Core Competencies definitions may be found on the Human Resources website and in the staff performance management system.
Physical Requirements (With or Without Accommodations):
• Visual acuity to read information from computer screens, forms, and other printed materials and information. • Able to speak (enunciate) clearly in conversation and general communication. • Hearing ability for verbal communication/conversation/responses via telephone, telephone systems, and face-to-face interactions. • Manual dexterity for typing, writing, standing and reaching, flexibility, body movement for bending, crouching, walking, kneeling and prolonged sitting. • Lifting and moving objects and equipment up to 10 lbs.
Work Environment:
• Work is indoors and sedentary and is subject to schedule changes and/or variable work hours. • This role is an on campus, in-person position. • There are no harmful environmental conditions present for this job. • The noise level in this work environment is usually moderate.
AA/EEO Statement:
As an AA/EEO employer, TCU recruits, hires, and promotes qualified persons in all job classifications without regard to age, race, color, religion, sex, sexual orientation, gender, gender identity, gender expression, national origin, ethnic origin, disability, genetic information, covered veteran status, or any other basis protected by law.
TCU Annual Security Report & Fire Safety Report Notice of Availability
Texas Christian University is committed to assisting all members of the campus community in providing for their own safety and security. TCU’s Annual Security Report and Fire Safety Report is published in compliance with the Jeanne Clery Disclosure of Campus Security Policy & Campus Crime Statistics Act (Clery Act) and the Higher Education Opportunity Act. This report includes statistics for the previous three calendar years concerning reported crimes that occurred on campus, in certain off-campus buildings owned or controlled by the University, and on public property within, or immediately adjacent to and accessible from the campus. The statements of policy contained within this report address institutional policies, procedures, and programs concerning campus security, alcohol and drug use, crime prevention, the reporting of crimes, emergency notifications and timely warning of crimes, sexual and interpersonal violence, and personal safety at TCU. Additionally, this report outlines fire safety systems, policies and procedures for on-campus housing facilities, as well as residence hall fire statistics.
The Annual Security Report and Fire Safety Report can be found on the TCU Police Department website at https://police.tcu.edu/annual-security-report , or a paper copy of the report may be obtained by contacting the TCU Police Department at 817-257-7930, or via email at [email protected] .
Sign Up for Job Alerts!
Want to share this job.
We've sent an email!
Recently Posted Jobs
Climbing wall attendant-temporary, assistant director for athletics communications, music prep instructor-temporary, ready to apply, before you hop away, take the leap and register to be a part of our horned frog talent community.
Thank you for your interest in a career at TCU!

TCU uses "cookies" (i.e., a small text file that is sent to your browser from the Site) to improve your return access and visits to the Site. TCU may use cookies to customize content, to analyze Site activity and user behavior, including, without limitation, through Google Analytics Demographics and Interest Reporting, and for advertising and promotional purposes (further discussed in "Interest-based Advertising" below). TCU reserves the right to use cookies in the future in conjunction with new or extended functionalities.
Privacy Policy
Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, what's the general structure of the ap seminar course and exam.
I'm considering taking AP Seminar next year, but I'd like to know more about the course structure and exam format. Can anyone give a brief overview of what to expect in this course and how the exam works? Thanks!
AP Seminar is a unique course that focuses on developing students' research, analytical, and interdisciplinary thinking skills. It's part of the AP Capstone™ program, which also includes AP Research, and is designed to help prepare students for college-level research and academic success.
Course Structure:
In AP Seminar, you will undertake several major projects and participate in regular class discussions throughout the year. The course includes exploring various topics, themes, and viewpoints by critically analyzing varied sources. You will work individually and in teams to research, discuss, and synthesize different perspectives, creating evidence-based arguments to demonstrate your understanding. Students will develop and present research projects, honing their oral communication skills too.
Exam Format:
The AP Seminar exam is divided into three main components:
1. Team Project and Presentation (Team PTP): This component constitutes 20% of the overall AP Seminar score. You and your teammates will collaborate on a research project, selecting a theme and crafting a team question or problem based on that theme. You'll then divide the work and carry out research individually before coming together to create a team presentation, addressing various perspectives and implications.
2. Individual Research Report (IRR): Making up 35% of the AP Seminar score, the IRR is a 2,000-word research paper, developed by each student individually. The paper should delve into a topic related to the team project, providing evidence-based arguments and analysis while demonstrating critical thinking and research skills.
3. End-of-Course Exam: The last component, which constitutes 45% of the overall score, is a 2-hour exam typically taken in May. The exam has two main sections, both involving reading, analyzing, and responding to stimulus material, such as articles, infographics, and data sets.
Section 1 (Short Answer Responses): In this section, you'll analyze various sources and write three short, focused responses to questions provided. You'll need to examine, evaluate and synthesize the given information to form evidence-based arguments.
Section 2 (Essay Question): Here, you'll be asked to develop a well-reasoned argument with a strong thesis statement based on provided stimulus material. You'll need to synthesize the information into a coherent essay, incorporating evidence to support your position.
In conclusion, AP Seminar offers a diverse learning experience that diverges from the typical content-specific AP courses. It focuses on honing research, analytical, and presentation skills, which are valuable for college and beyond. Assessments will challenge you to conduct research, work collaboratively, and develop strong arguments through various mediums such as reports, presentations, and timed exams. Good luck!
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.
Trends in serotype distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of invasive Haemophilus influenzae isolates from Brazil, 2009–2021
- Published: 15 May 2024
Cite this article

- Rosemeire Cobo Zanella 1 ,
- Sérgio Bokermann 1 ,
- Marta Galhardo 1 ,
- Caroline Gava 2 ,
- Samanta Cristine Grassi Almeida 1 ,
- Gabriela Andrade Pereira 2 &
- Ana Paula Silva de Lemos 1
Introduction
Invasive Haemophilus influenzae (Hi) disease poses a significant global health challenge. With the relaxation of COVID-19 pandemic measures and declining H. influenzae serotype b (Hib) vaccination coverage, there is concern about a potential increase in Hi cases worldwide.
Methodology
This study analyzed 1437 invasive Hi isolates in Brazil over 13 years, determining capsular serotypes, antimicrobial susceptibility, and genetic relatedness through multilocus sequence typing.
The primary source of isolation for these invasive H. influenzae isolates was blood (54.4%), followed by cerebrospinal fluid (37.1%) and lung specimens (8.5%), respectively. Consequently, bacteremia (47%) was the most common clinical presentation, followed by meningitis (39.6%) and pneumonia (13.4%). Non-encapsulated Hi (NTHi) predominated among the isolates (51.4%), along with serotype a (22%) and serotype b (21.5%) among the encapsulated isolates. The majority of the encapsulated isolates were isolated from children under 14 years of age (76.7%), while NTHi isolates were identified in patients older than 15 years, particularly those ≥ 60 years old (40%). Ampicillin resistance was observed in 17.1% of cases, displaying β-lactamase production as the principal resistance mechanism. MLST revealed a diverse NTHi population, whereas the encapsulated isolates presented a clonal structure.
This study describes the prevalence of NTHi isolates circulating in Brazil after two decades of the Hib vaccine immunization program. Continuous universal surveillance is crucial for implementing prompt public health measures to prevent and control invasive Hi disease and monitor changes in antibiotic resistance profiles.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Data Availability
The data presented in the study are available upon request to the corresponding author. The new sequences type (ST) described in this study are available in the MLST website available at https://pubmlst.org/organisms/haemophilus-influenzae .
Abbreviations
Adolfo Lutz Institute
Haemophilus influenzae Type a
Haemophilus influenzae Type b
Haemophilus influenzae Type c
Haemophilus influenzae Type d
Haemophilus influenzae Type e
Haemophilus influenzae Type f
Non-capsulate Haemophilus influenzae
Pentavalent conjugated vaccine
National Immunization Program
Minimum inhibitory concentration
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute
Chloramphenicol
Ceftriaxone
Azithromycin
Ciproflaxin
β-Lactamase negative ampicillin resistant
Multilocus sequence typing
Sequence type
Bertran M, D’Aeth JC, Hani E, Amin-Chowdhury Z, Fry NK, Ramsay ME, Litt DJ, Ladhani SN (2023) Trends in invasive Haemophilus influenzae serotype a disease in England from 2008–09 to 2021–22: a prospective national surveillance study. Lancet Infect Dis 23:1197–1206. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00188-3
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bokermann S, Zanella RC, Lemos AP, de Andrade AL, Brandileone MCC (2003) Evaluation of methodology for serotyping invasive and nasopharyngeal isolates of Haemophilus influenzae in the going surveillance in Brazil. J Clin Microbiol 12:5546–5550. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.41.12.5546-5550.2003
Article Google Scholar
Carrera-Salinas A, Gonzalez-Diaz A, Calatayud L, Mercado-Maza J, Puig C, Berbeli D, Camara J, Tubau F, Grau I, Dominguez MA, Ardanuy C, Marti S (2021) Epidemiology and population structure of Haemophilus influenzae causing invasive disease. Microb Genomics 7:000723. https://doi.org/10.1099/mgen.0.000723
Article CAS Google Scholar
Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI) (2021) Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing 31 th ed. CLSI Suplement M100
Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI) (2018) Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically, 11 th ed. CLSI standard M07
Cohen R, Ashmana M, Taha M, Varonh E, Angoulvant F, Levya C, Rybaka A, Ouldali N, Guisol N, Grimprel E (2021) Pediatric Infectious Disease Group (GPIP) position paper on the immune debt of the COVID-19 pandemic in childhood, how can we fill the immunity gap? Infect Dis Now 51:418–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idnow.2021.05.004
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Efron A, Nápoli D, Neyro S, Juárez MV, Moscoloni M, Eluchans NS, Regueira M, Lavayén S, Argentinean H. influenzae Working Group, Faccone D, Santos M (2022) Laboratory surveillance of invasive Haemophilus influenzae disease in Argentina, 2011–2019. Rev Argen Microbiol S0325–7541(22):00062–00071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ram.2022.08.002
Falla TJ, Crook DW, Brophy LN, Maskell D, Kroll JS, Moxon ER (1994) PCR for capsular typing of Haemophilus influenzae . J Clin Microbiol 10:2382–2386
Heliodoro CIM, Bettencourt CR, Bajanca-Lavado MP, Portuguese Group for the Study of Haemophilus influenzae invasive infection (2020) Molecular epidemiology of invasive Haemophilus influenzae disease in Portugal: an update of the post-vaccine, period 2011–2018. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 39:1471–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-020-03865-0
Ledeboer NA, Doern GV (2011) Haemophilus . In: Versalovic J, Carroll KC, Funke G, Jorgensen JH, Landry ML, Warnock DW (eds) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 10th edn. American Society for Microbiology Press, Washington, DC, pp 588–602
Chapter Google Scholar
Léon M, Kawabata A, Nagai M, Rojas L, Chamorro G, Zárate N, Gómez G, Leguizamón M, Irala J, Franco R, Segovia N (2021) Studio epidemiológico de Haemophilus influenzae causante de enfermedad invasiva y no invasiva em Paraguay (1999–2017). Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin 39:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eimc.2020.02.020
McElligott M, Meyler K, Bennett D, Mulhall R, Drew RJ, Cunney R (2020) Epidemiology of Haemophilus influenzae in the Republic of Ireland, 2010–2018. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 39:2335–2344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-020-03971-z
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
McNeil JC, Sommer LM, Dunn JJ, Hulten KG, Kaplan SL, Vallejo JG (2021) Molecular epidemiology of contemporary invasive Haemophilus influenzae isolates in Texas children. Pediatric Infect Dis J 40:852–855. https://doi.org/10.1097/INF.0000000000003188
Meats E, Feil EJ, Stringer S, Cody AJ, Goldstein R, Kroll JS, Popovic T, Spratt BG (2003) Characterization of encapsulated and non-encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae and determination of phylogenetic relationships by multilocus sequence typing. J Clin Microbiol 41:1623–1636. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.41.4.1623-1636.2003
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ministério da Saúde BR (2012) Informe técnico da vacina pentavalente. Publishing Physics Web. https://www.saude.go.gov.br/images/imagens_migradas/upload/arquivos/2012-06/informe-tecnico-vacina-pentavalente.pdf . Accessed 05 May 2023
Ministério da Saúde BR (2019) Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde. Vigilância em Saúde no Brasil 2003–2019: da Criação da Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde aos Dias Atuais. Bol Epidemiol (Internet) 50:1–154. Disponível em: http://www.saude.gov.br/boletins-epidemiologicos . Accessed 05 May 2023
Ministério da Saúde BR (2023) Sistema de Informação do Programa Nacional de Imunizações (SI-PNI/CGPNI/DEIDT/SVS/MS). Publishing PhysicsWeb. http://pni.datasus.gov.br . Accessed 26 May 2023
Nørskov-Lauritsen N, Pedersen N, Lam JUH, Nielsen HL, Kobel CM, Hansen DS, ODiD Consortium (2021) Haemophilus influenzae one day in Denmark: prevalence, circulating clones, and dismal resistance to aminopenicillins. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 40:2077–2085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-021-04247-w
O’Callaghan CH, Morris A, Jirby SM, Shingler AH (1972) Novel method for detection of beta-lactamase by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 4:283–288
Oliver SE,Rubis AB,Soeters HM,Reingold A, Barnes M, Petit S, Farley MM, Harrison LH, Como-Sabetti K, Khanlian SA, Wester R, Thomas A, Schaffner W, Marjuki H, Wang X, Hariri S (2023) Epidemiology of invasive nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae disease-United States, 2008–2019. Clin Infect Dis ciad054. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciad054
Peltola H (2000) Worldwide Haemophilus influenzae type b disease at the beginning of the 21st century: global analysis of the disease burden 25 years after the use of the polysaccharide vaccine and a decade after the advent of conjugates. Clin Microbiol Rev 13:302–317. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.13.2.302
Pitmann M (1931) Variation and type specificity in the bacterial species Haemophilus influenzae . J Exp Med 53:471–492
Potts CC, Topaz N, Rodriguez-Rivera LD, Hu F, Chang HY, Whaley MJ, Schmink S, Retchless AC, Chen A, Ramos E, Doho GH, Wang X (2019) Genomic characterization of Haemophilus influenzae: a focus on the capsule locus. BMC Genomics 20:733. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-6145-8
Rodriguez M, Agudelo C, Duarte C (2015) Aislamentos invasivos de Haemophilus influenzae en menores de 5 años: distribuición de lós serotypes y de La sensibilidade antimicrobiana, SIREVA II, Colombia 2002–2013. Infectio 19:67–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infect.2014.12.005.17
Russo DO, Torres BR, Romanelli RMC, Rocha FSV, Viegas ECC, Diniz LMO (2022) Haemophilus influenzae serotype a as a cause of meningitis in children in Brazil. Pediatr Infect Dis J 41:108–111. https://doi.org/10.1097/INF.0000000000003391
Slack MPE (2021) Long term impact of conjugate vaccines on Haemophilus influenzae meningitis: narrative review. Microorganisms 9:886. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9050886
Tonnessen R, Garcia I, Debech N, Lindstrom JC, Wester AL, Skaare D (2022) Molecular epidemiology and antibiotic resistance profiles of invasive Haemophilus influenzae from Norway 2017–2021. Front Microbiol 13:973257. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.973257
Topaz N, Tsang R, Deghmane A, Claus H, Lâm T, Litt D, Bajanca-Lavado MP, Pérez-Vázquez M, Vestrheim D, Giufrè M, Van Der Ende A, Gaillot O, Kuch A, McElligott M, Taha M, Wang X (2022) Phylogenetic structure and comparative genomics of multi-national invasive Haemophilus influenzae serotype a isolates. Front Microbiol 13:856884. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.856884
Tsang RSW, Ulanova M (2017) The changing epidemiology of inavise Haemophilus influenzae disease: emergence and global presence of serotype a strain that may require a new vaccine for control. Vaccine 35:4270–4275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.06.001
Ulanova M, Tsang RS (2009) Invasive Haemophilus influenzae disease: changing epidemiology and host-parasite interactions in the 21st century. Infect Genet Evol 9:594–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meedgid.2009.03.001
Wen S, Feng D, Chen D, Yang L, Xu Z (2020) Molecular epidemiology and evolution of Haemophilus influenzae . Infect Genet Evol 80:104205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104205
Whittaker R, Economopoulo A, Dias JG, Bancroft E, Ramliden M, Celentano LP, European Center for Disease Prevention and Control County Experts for invasive Haemophilusinfluenzae Disease (2017) Epidemiology of invasive Haemophilus influenzae disease, Europe, 2007–2014. Emerg Infect Dis 23:396–404. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2303.161552
Zanella RC, Bokermann S, Andrade ALSS, Flannery B, Brandileone MCC (2011) Changes in serotype distribution of Haemophilus influenzae meningitis isolates identified through laboratory-based surveillance following routine childhood vaccination against H. influenzae type b in Brazil. Vaccine 29:8937–8942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.09.53
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all microbiologists who provided isolates and Marta Galhardo for her assistance in conducting the microbiological tests at IAL. We are thankful to Dr. Raymond Tsang and Kathleen Whyte from the National Microbiology Laboratory (NML) of Canada, Monique St-Laurent from the Public Health Agency of Canada’s Center for Immunization and Respiratory Infectious Diseases, and Gloria J. Rey-Benito and Lúcia de Oliveira from the Pan American Health Organization’s VPD Lab Network (OPAS) for providing the Multilocus Sequencing Typing data. We also thank the Brazilian Ministry of Health, SINAN/SVS/MS, for providing the epidemiological data. This publication made use of the Haemophilus influenzae Multi Locus Sequence Typing website ( https://pubmlst.org/organisms/haemophilus-influenzae _seqdef) at the University of Oxford (Jolley et al. Welcome Open Res 3:124).
This study was conducted as part of our routine work.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Center of Bacteriology, Adolfo Lutz Institute, Av. Dr. Arnaldo, 355, São Paulo, State of São Paulo, CEP 01246-902, Brazil
Rosemeire Cobo Zanella, Sérgio Bokermann, Marta Galhardo, Samanta Cristine Grassi Almeida & Ana Paula Silva de Lemos
Secretary of Health Surveillance, Ministry of Health, Brasília, Distrito Federal, Brazil
Caroline Gava & Gabriela Andrade Pereira
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors attest they meet the ICMJE criteria for authorship.
Conceptualization: Rosemeire Cobo Zanella.
Data curation: Rosemeire Cobo Zanella.
Investigation: Rosemeire Cobo Zanella, Sérgio Bokermann, Samanta Cristine Grassi Almeida, and Ana Paula Silva de Lemos.
Methodology: Rosemeire Cobo Zanella, Sérgio Bokermann, Marta Galhardo, Carolina Gava, Gabriela Andrade Pereira.
Writing—original draft: Rosemeire Cobo Zanella, Ana Paula Silva de Lemos.
Writing—review and editing: Rosemeire Cobo Zanella, Sérgio Bokermann, Marta Galhardo, Caroline Gava, Samanta Cristine Grassi Almeida, Gabriela Andrade Pereira, and Ana Paula Silva de Lemos.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rosemeire Cobo Zanella .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 21 KB)
Supplementary file2 (docx 20 kb), supplementary file3 (docx 20 kb), supplementary file4 (docx 21 kb), rights and permissions.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Zanella, R.C., Bokermann, S., Galhardo, M. et al. Trends in serotype distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of invasive Haemophilus influenzae isolates from Brazil, 2009–2021. Int Microbiol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-024-00535-5
Download citation
Received : 27 February 2024
Revised : 03 May 2024
Accepted : 10 May 2024
Published : 15 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-024-00535-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Haemophilus influenzae disease
- Invasive Hi disease
- Haemophilus influenzae b
- Haemophilus influenzae NT
- Antimicrobial susceptibility
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The way you structure your introduction can depend on the amount of time you have been given to present: a sales pitch may consist of a quick presentation so you may begin with your conclusion and then provide the evidence. Conversely, a speaker presenting their idea for change in the world would be better suited to start with the evidence and ...
Let's look at each stage of the Open - Body - Conclusion structure in detail and discuss the elements that you need to include in each. We'll start with the body, rather than the introduction, because the rest of your presentation will be based on that. Body. The body of your presentation needs to contain your key points.
Length and Structure. The main part should make up about 70% of the presentation and also include a clear structure. Explain your ideas in detail and build them up logically. It should be organized chronologically, by priority or by topic. There should be a smooth transition between the individual issues.
The presentation structure lays out a clear and logical sequence of information, akin to the sections of a business plan that outline the company's mission, market analysis, and financial projections. This clear sequence ensures that your audience can easily follow and understand your message, maximizing the impact your speech can deliver and ...
Here is a guide on how you can go about practicing your presentation. 5 Ways to Structure Your Presentation. The five ways include ordered, problem-solution, comparative, storytelling, and demonstrating structures. 1. Ordered Structure. The presentation follows a logical sequence starting with an introduction, main points, and then conclusions ...
Hook, Meat and Payoff. This presentation structure, like The Drama, is deeply founded in the art of storytelling. While the Hero's Journey is more of a literary technique, Hook, Meat and Payoff is more like a spoken-word progression. Source. Create your own graphics with this drag-and-drop tool.
The secret structure of great talks. From the "I have a dream" speech to Steve Jobs' iPhone launch, many great talks have a common structure that helps their message resonate with listeners. In this talk, presentation expert Nancy Duarte shares practical lessons on how to make a powerful call-to-action. 18:00.
The body of the presentation should meet the promises of purpose and information made in the introduction. The structure of the presentation is crucial. Whether you organise: chronologically, by priority, or theme. the body of your talk must proceed logically. The main points should be brought out one by one, with concise and relevant ...
If you want your audience to stay engaged, you need to structure your ideas as a well-crafted story. Follow these three steps to clearly define your narrative before you start creating your slides ...
Presentation template. Having worked out your key message and main points, the next stage is to structure the content of your presentation. Just like other forms of academic writing, a presentation can be divided into three parts: an introduction detailing the purpose and structure of the talk; a body covering the main points; and a conclusion ...
In this situation, you must compress your ideas to as few points as possible. Your presentation will probably not have more than 3-5 slides. On these slides, only the main points will be included. Piktochart has many great templates that will help you create a pitch deck (or a quick presentation) in no time!
This structure is usually used in a presentation to inform the new ways of doing things in a company. One example of an explanation structure presentation is a TED talk from American social psychologist Amy Cuddy. The Essential Elements of a Presentation Structure. An excellent presentation has a story to tell.
1. Clear structure. No one likes to get lost in a maze of information. Organize your thoughts into a logical flow, complete with an introduction, main points and a solid conclusion. A structured presentation helps your audience follow along effortlessly, leaving them with a sense of satisfaction at the end.
Defining your structure is charting the path that the audience will take through your presentation. A poor structure is disorienting and leaves the audience wondering how they will get to their destination (or what the destination even is). Invest time in defining your central message and present your results as the evidence to support it.
Structure Your Presentation Like a Story. by. Nancy Duarte. October 31, 2012. PM Images/Getty Images. After studying hundreds of speeches, I've found that the most effective presenters use the ...
The Explanation. Our second presentation structure is the explanation. The explanation's purpose is to inform about a process, create a plan to fix a problem or even to learn something new. This is typically used by consultants or sales people trying to create new master plans. You start at the bottom with the lay of the land.
Here is a quick look at how this structure looks like: The Wind Up - A summary of the current scenario. The Hurdle - The problem/issue that needs to be resolved. The Vision - A quick glimpse into the main idea on how the problem/issue can be solved. The Options - Illustrates two different options to solve the problem.
The general structure of a presentation is the following: It is up to you to design these three parts. Using videos or everyday-examples can be a great way to introduce the audience to the topic. The important thing is that you capture the audience's attention from the beginning by making an interesting introduction.
2. Use the Outline View. One other way to structure a PowerPoint presentation in the editing mode is to use Outline View. You can choose it from the VIEW tab. This view doesn't display sections, but it shows the title and main text of each slide, which can give you a quick overview of the presentation contents.
An example of a good presentation structure. To give you a better idea of a successful presentation structure, here is an example of how you could organize your presentation: 1. Introduction. Arouse interest. Provide orientation. Ask the key question. 2.Main section.
Delivering a great presentation sounds like a daunting task - but really, it's all about how you structure it. Learning these presentation skills and structu...
The funnel can be effective with controversial and/or highly emotional topics. Controversial core messages that are brought up at the very beginning of a presentation can lead to discussions that veer off and are hard to control. In these cases, the funnel structure is the better option. 3.
A compelling presentation basically tells a story. It may not seem like it, but successful presentations all use the basic structure associated with stories. They have a beginning, a middle and an end. Planning with this in mind will help clarify what you wish to say, when you should say it, and how to tie the threads of your presentation together.
These four scientists—Crick, Franklin, Watson, and Wilkins—codiscovered the double-helix structure of DNA, which formed the basis for modern biotechnology. At King's College London, Rosalind Franklin obtained images of DNA using X-ray crystallography, an idea first broached by Maurice Wilkins. Franklin's images allowed James Watson and ...
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. Download the Organizational Structure Project Proposal presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. A well-crafted proposal can be the key factor in determining the success of your project. It's an opportunity to showcase your ideas, objectives, and plans in a clear and concise manner, and to ...
Structure of the Presentation Introduction page - indicating the name of the company you are analyzing and group member's name and task completed by each member. 1. Brief overview of the company, the industry, and its strategic purpose (mission, vision) 2. Sustainability challenges - (Issue identification) 3.
2. A new understanding of the Einstein tensor (gravity +. secondary int eractions) has the potential t o solve the. mys tery of Dark Matter. 3. Gravity in the system arises naturally, as a result ...
Job Summary: The Postdoctoral Research Associate is responsible for performing independent research on virtual screening of beyond-rule-of-five therapeutics. Duties & Essential Job Functions: 1. Implements computational workflows for conformational sampling, continuum solvation, and density functional theory (DFT) prediction of molecular structure and properties. 2. Implements in the ...
The AP Seminar exam is divided into three main components: 1. Team Project and Presentation (Team PTP): This component constitutes 20% of the overall AP Seminar score. You and your teammates will collaborate on a research project, selecting a theme and crafting a team question or problem based on that theme.
Study design and bacterial isolates. Since 1982, laboratories across the country have submitted isolates of invasive H. influenzae (Hi) to the National Reference Laboratory for Meningitis at the Adolfo Lutz Institute (IAL) in São Paulo for species confirmation, serotyping, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing. This is a retrospective observational study on the epidemiology of the invasive ...