Indirect Assignment of Roles
We know how roles are assigned directly to user id via SU01 tcode. This is called direct assignment of roles to the user.
There is one more way by which roles can be assigned. This is done by assigning roles to a Position and then assignment of that position to the user id. This advantage of using this process is that it helps in reducing the overhead of assignment or removal of roles from user if he/she changes position. This process is referred to as indirect role assignment or position based role assignment.
Suppose a user A is assigned to position P1 and after some time moves to a different position P2 (due to promotion or change in responsibility or change in department etc). He automatically loses all his previous roles which was meant for position P1 and he gets new roles for position P2 (since he has been assigned to position P2 now).
** Point to be noted – For this indirect role assignment to work, some prerequisite needs to be taken care of. The Infotype 0105 (Communication) and subtype 001 contain a relationship among user id, user position and personnel number. This relationship (record) needs to be maintained. If this is not maintained, indirect role assignment will not work.**
Steps for indirect assignment of roles:
Assignment of position to user id:
Go to PFCG -> Goto -> Settings
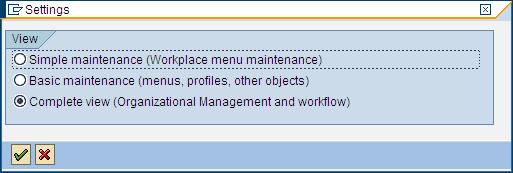
Under User tab, there is a button “Organizational Mgmt”:
You will get this screen:
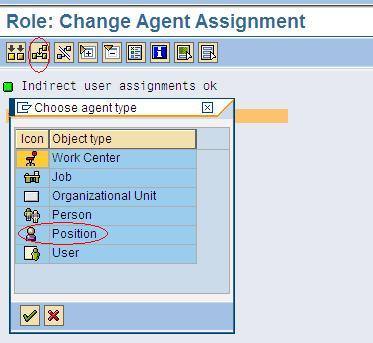
Select Position from the list (as shown in the above screenshot).
Assigning Role to Position :
Infotype 1001 Subtype B 007 record is created between Position (S) and Role (AG). For creating relationship between Position(S) and Role(AG), tcodes PP01, PP02 or PO13 can be used.
Steps using PP01 tcode:
- Execute transaction PP01 and select the Object type as Position.
- Provide the object id as Position Id.
- Select “Relationships” and click on create button. It will take you to the next screen.
- Select Relationship type as B 007 and Type of Related object as Role.
- ID of the related object is the Role name which needs to be assigned to the position.
- Kale by LyraThemes.com.

Sap Security Pages
Learn SAP Security & Authorizations Concepts
Indirect Role Assignment via OM
We have come across the Organizational Management (OM) component while talking about SAP HCM. The OM component in SAP is used to map the Organizational Hierarchy of an enterprise by means of HR objects and Relationships between these objects. In this post we will discuss about the possibility of using OM to simplify some of the user-role assignments tasks that need to be handled by a security administrator.
Lets start with an sample org hierarchy created in PPOME transaction as shown below. We start with a root org unit ( HR obj O) “IDES Root” with “IDES India” and “IDES Bangalore” under it. ” IDES India” includes the position (HR obj S) of “Director – India” which is also set as the Line Manager for it. The position is filled by person (HR obj P) “Mister Director”. We make the basic assumption that the SAP access for a user corresponds to his position in the org structure of the enterprise.
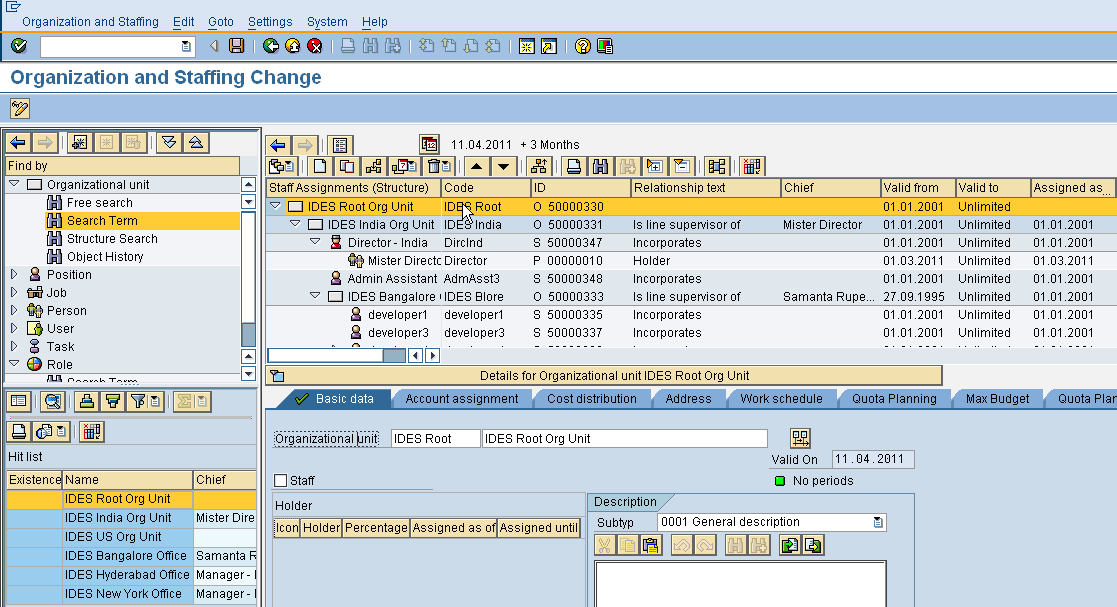
Consider the access for “Mister Director”. In the case of direct role assignment, any role would be assigned to the user id for “Mister Director” through SU01 or PFCG. Now lets consider, that “Mister Director” get promoted to be the CEO of “IDES Root” and a new person comes to take his place. However, since the roles for the India Director were directly assigned to his user id, he will continue to keep his old access even in his new position. Also the new person filling the position of “Director – India” will have to be manually assigned with enough access to enable him to do his job. This same situation will repeat for every transfer, promotion, demotion (and most other org changes in general) that takes place in an enterprise. For an enterprise with more than a few thousand employees, the effort involved in keeping user access in sync with the org hierarchy is substantial. In addition to the monetary cost of the effort, their is a time penalty as users would need to wait for the User Admin team to adjust their security before they can start using SAP. Indirect role assignment comes to the rescue in such situation and if configured correctly can reduce the routine maintenance effort appreciably. In indirect assignment, instead o directly assigning the roles to user id for “Mister Director” we assign the roles to the position “Director India” (The standard SAP configuration allows role assignments to the OM objects – Position, Org Unit, Work Center, Task and can be used depending on business cases) such that any user occupying the position would automatically get the access needed for “Director India”.
There are four technical prerequisites for the use of indirect role assignment through Org Mgmt
- An active planning version must be defined in the system. Roles/profiles are assigned to the OM objects defined in the active plan.
- The User and Personnel masters are linked via the IT 0105 (communication) subtype 0001 (system id). This translates to maintaining the SAP user id for a user in IT 0105, 0001 for the user’s personnel number with an active validity date.
- The HR_ORG_ACTIVE customizing switch is set to YES in the PRGN_CUST table either as the default value or as an entry in the table.
- The evaluation path US_ACTGR is defined and suitably adjusted in the system. The evaluation path is actually used by SAP to assign roles to the users during user comparison and is the last and the most vital cog in the wheel. The screen-shot below shows the default definition of the evaluation path in OOAW.
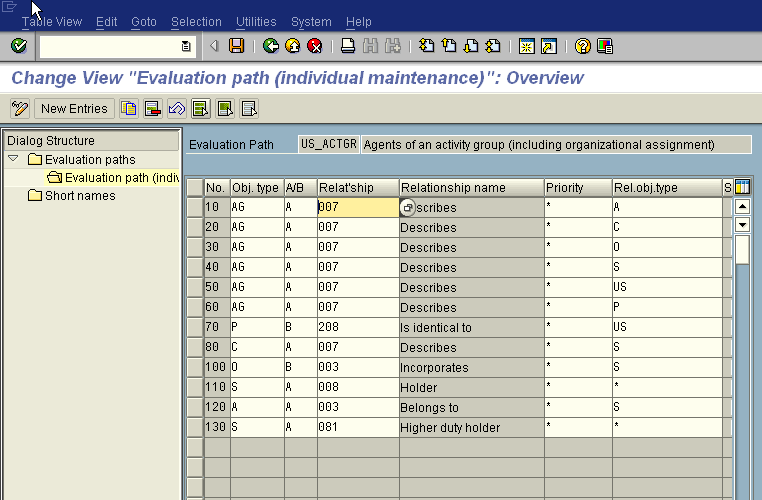
Once the above prerequisites are met, we can just go ahead and create indirect role assignments between roles and HR objects. Indirect role assignment through PFCG can be accessed through the “Organization Management” button shown below. The blue lines correspond to indirect role assignments.
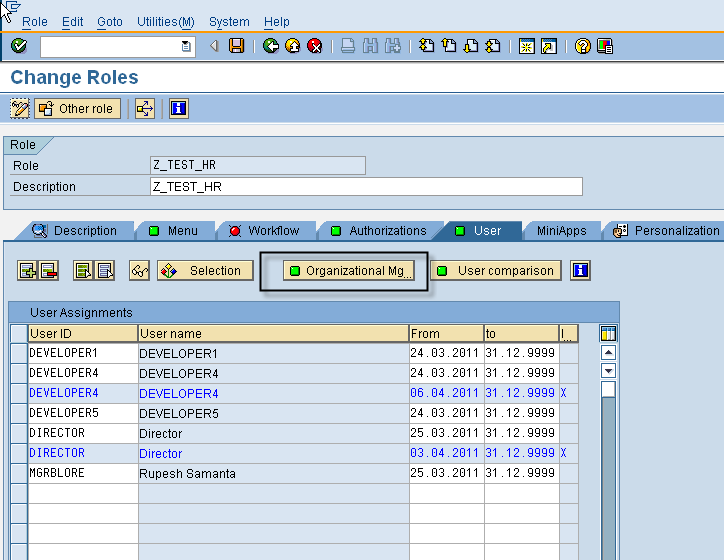
Clicking the Org Mgmt button opens the below screen where we can check the existing assignments for the role (both direct and indirect). New role assignments can e created using the highlighted button
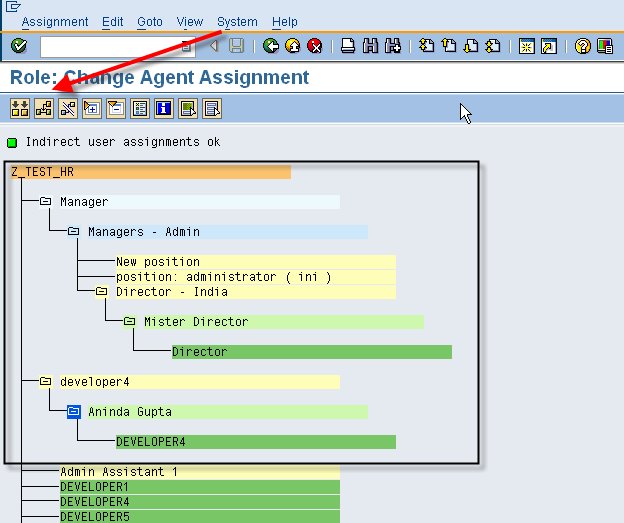
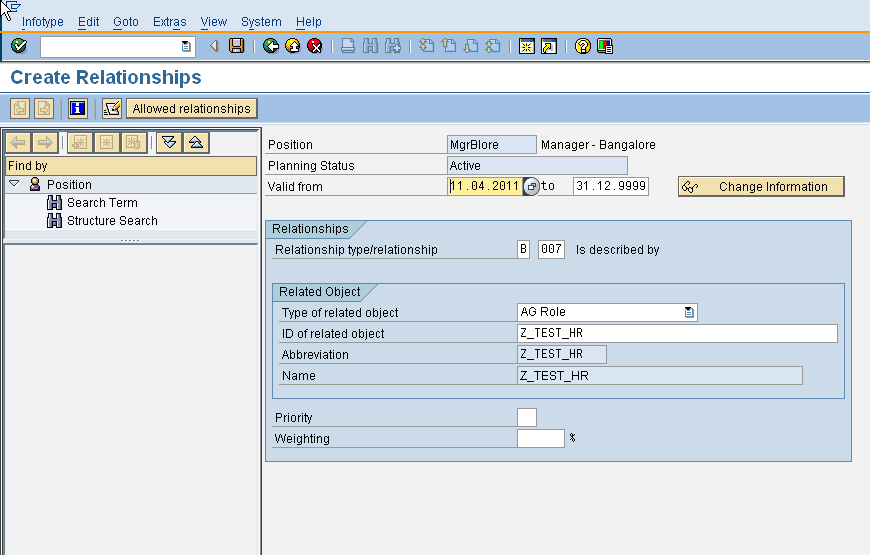
Roles can also be assigned through PP01. An indirect role assignment is a relationship between object type AG (Activity Group or Role) and HR objects like positions, org units, etc. Below screen shows a new assignment (relationship B007) between the users’ position and the role object (object type AG)
The final step in the process of indirect role assignment is to copy the roles from the HR objects to the users. One of the most common way to achieve this is to execute the PFUD transaction with the option for HR reconciliation checked. In productive systems, this program is normally scheduled to run everyday at midnight to sync user access with a changing org structure.
The critical success factor for indirect role assignment is to understand how correctly your org hierarchy mirrors the roles/ responsibilities of your users. Some of the questions that need to be discussed with your business owners, functional consultants and security team are
- What is the correlation between the roles/responsibilities users and their position in the org structure?
- Who will be responsible for maintaining the org structure and how frequently?
- Will users need their old access even if they move to a new position?
- How will contractors be given access? Contractors are normally not part of the org structure and don’t occupy a position. So do you continue to directly assign roles to contractors or do you link them to the org structure in some way (for example through positions/jobs/tasks)?
- Are you only concerned about a central ECC system or are there other systems in the landscape (BW, CRM, SRM, APO, etc)? Will the roles assigned in these other systems also be determined by the users’ positions in ECC?
- Parent & Derived Roles
- Profile Assignment via OM
13 thoughts on “ Indirect Role Assignment via OM ”
I want to implement 0Employee Level Security. Can you please suggest me what needs to be done on this?
Hi Prakash,
Sorry, but you need to be more specific than this. By 0EMPLOYEE, I think you are working on BI security for HR data. In such a case please go through the posts on BW security in my blog. They should help to get you started.
Regards, Aninda
can Please explain how the organizational units , managers,employees are created in the hirarchy and the transactions that are used in a step by step manner.
I am trying to test the structral autorizations but i am struck whith creating the structure correctly.
HI Aninda, We are having a default position ie 99999999 in the organisation structure. Any user who is not assigned to any postion will be automatically gets assigned to this default position. i want to add a role to this position but system says position does not exist. Can you please advice
Hi Parveen,
I have never actually tried doing this but I believe the system will not allow you to add roles to the default position as this is not really an actual position in the org structure. Since these people on 99999….. position are not actually part of the org structure, indirect role assignment probably would not work for them.
I think you are trying to set default access for all users? One way of handling this to add the default access when the user masters for new users are actually being created.
HI Aninda we have a requirement that when the users leave the organisation all the roles should be taken from them and a new role should be added for ESS – Separated employees. Since when the users will leave the organisation they will be removed from the position in organisation structure and they will automatically get default position assigned to them. So if by any way i can add the role ESS – Separated employees to the default position user will get it automatically.
Let me know if you have any other suggestion for automatically assigning roles to the user when they leave the organisation
Sorry, I must have missed the original comment. Can not think of a standard functionality which will handle this. However, you can probably develop a simple program which runs in the background each day, which evaluates the employees leaving the company on that day and replaces their existing roles with the single role. I don’t think indirect assignment through OM will work as the employees in question belong to the default position.
The question mentioned above – “Will users need their old access even if they move to a new position?” How do we achieve this, do we map a single pernr/object ID to more than one position? When a person changes position, wouldn’t the roles associated with prev. position assignment (which doesn’t exist anymore for the user) get auto-removed by system?
The indirect position role assignment will remove the access once a person moves to a new position. I am yet to see a standard way to achieve this without significant amount of coding.
Thanks for all the useful knowledge that you are sharing, I am looking for a solution to mass in-direct role assignment i.e. ‘X’ number of users/positions are getting assigned ‘Y’ number of roles (different user & different role combinations). Rather than opening one role at a time and assigning it to one position, is there any SU10 equivalent method to assign en mass. Regards, Sean
Thank you very much for the useful information, but I have a couple of questions. Do we need to maintain all the entries as you have maintained them in ooaw or simply maintaing a single entry for AG? Also what will the relating object be? I am assuming it would be Position (S). Secondly I would like to have indirect role assignment ONLY for MSS access. I do not want any other indirect role assignments. Do you think I need to be careful of it compromising some other functionality? Looking forward to your response.
The default definition of the evaluation path should already be provided by SAP and for assigning access to positions like in the case of MSS should work without you having to update this at all. You just assign the MSS role to the manager positions and run PFUD checking the options for org assignment. You don’t need to use indirect assignment of roles for all roles or positions.
Thanks, Aninda
How can we get change documents for Indirect role assignment(Role assigned to position).
Thanks & Regards, Sreeknath
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

10 SAP Role Design Best Practices
If you're looking for best practices around SAP role design, this article has you covered. From using standard roles to keeping things organized, you'll find everything you need to know here.
SAP role design is an important part of any SAP implementation. It is the process of creating roles and assigning them to users in order to control access to the system. It is important to design roles that are secure, efficient, and easy to maintain.
In this article, we will discuss 10 best practices for SAP role design. We will cover topics such as role naming conventions, role hierarchy, and role authorization. Following these best practices will help ensure that your SAP roles are secure, efficient, and easy to maintain.
1. Use the SAP standard roles as a starting point
SAP standard roles are pre-defined and tested by SAP, so they provide a good foundation for your role design. They also contain the most up-to-date security settings, which can help you ensure that your users have access to only the data and functions they need.
When using SAP standard roles as a starting point, it’s important to remember that these roles may not meet all of your organization’s needs. You’ll likely need to customize them to fit your specific requirements. This could include adding or removing certain transactions, changing authorization objects, or creating new custom roles.
2. Avoid using generic roles
Generic roles are those that have access to a wide range of functions and data, which can be dangerous if they fall into the wrong hands.
Instead, it’s best practice to create specific roles for each user or group of users. This way, you can ensure that only the necessary functions and data are available to them. You should also consider using authorization objects to further restrict access to certain areas within SAP.
By following these best practices, you can help protect your organization from potential security risks and ensure that all users have the appropriate level of access to perform their job duties.
3. Make sure your role names are meaningful and descriptive
When you create a role, it’s important to give it a name that accurately describes the purpose of the role. This makes it easier for users to understand what they can and cannot do with the role. It also helps administrators quickly identify roles when assigning them to users or making changes to existing roles.
Additionally, having meaningful and descriptive role names makes it easier to audit user access rights. If an auditor sees a role called “Admin” or “Superuser,” they may not know exactly what permissions are associated with that role. However, if the role is named something like “Accounting Manager” or “HR Administrator,” then it’s much easier to determine which users have access to certain areas of the system.
4. Keep it simple
Complex roles can be difficult to maintain and manage, as they require more time and effort. Additionally, complex roles are prone to errors due to the sheer number of objects that need to be configured correctly.
To keep your SAP role design simple, start by breaking down the user’s job into its core tasks. Then, create a role for each task, making sure to include only the necessary authorizations. This will help ensure that users have access to only what they need, while also reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Finally, make sure to review and test the roles regularly to ensure accuracy.
5. Don’t create too many roles
Having too many roles can lead to confusion and complexity, making it difficult for users to understand which role they should use. It also increases the risk of security breaches as there are more opportunities for someone to gain access to sensitive data or functions that they shouldn’t have access to.
To avoid this problem, try to create fewer roles with broader permissions. This will make it easier for users to understand their roles and responsibilities, while still ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to the necessary information and functions.
6. Create an approval process for new roles
When creating a new role, it’s important to ensure that the access rights and privileges associated with the role are appropriate for the user. An approval process helps to ensure that all roles are reviewed by an experienced SAP security professional before they are assigned to users. This review can help identify any potential risks or vulnerabilities associated with the role, as well as ensuring that the role is designed in accordance with organizational policies and procedures.
Having an approval process also ensures that roles are properly documented and tracked. This makes it easier to audit roles and make changes when necessary. It also allows organizations to keep track of who has access to what data and resources, which is essential for maintaining compliance with industry regulations.
7. Organize roles into groups or categories
By grouping roles into categories, you can easily identify which roles are related to each other and how they interact with one another. This makes it easier for users to understand the different roles and their responsibilities within the system.
Additionally, organizing roles into groups or categories helps ensure that all of the necessary permissions are assigned correctly. For example, if a user needs access to certain data, but not all of it, then creating separate roles for each type of data will help ensure that only the appropriate data is accessible.
Finally, organizing roles into groups or categories also makes it easier to manage changes in the future. If new roles need to be added or existing roles need to be modified, it’s much simpler to do so when roles are organized into categories.

8. Consider how to handle access requests that don’t fit any of your existing roles
When designing SAP roles, it’s important to consider how you will handle access requests that don’t fit any of your existing roles. This is because if a user needs access to something that isn’t covered by an existing role, they may be denied access or given too much access. To avoid this, create a process for handling these types of requests and ensure that all users are aware of the process.
For example, you could create a form where users can submit their request and explain why they need access to certain data or functions. Then, have a designated team review the request and decide whether or not to grant access. This way, you can make sure that only those who truly need access get it, while also ensuring that no one gets more access than necessary.
9. Assign roles based on business function, not job title
When roles are assigned based on job title, it can lead to a lack of flexibility in the system. For example, if someone with a certain job title is given access to a particular function, then all people with that same job title will have access to that same function regardless of whether or not they actually need it. This can create security risks and make it difficult for users to find what they need quickly.
By assigning roles based on business function instead, you ensure that only those who need access to a particular function get it. This makes the system more secure and easier to use. It also allows for greater flexibility when changes occur within an organization, as roles can be easily adjusted to reflect new responsibilities.
10. Review your roles regularly
As your business changes, so do the roles and responsibilities of your employees. As a result, their access to SAP systems needs to be updated accordingly.
Regularly reviewing your roles ensures that users have the right level of access to perform their job duties. It also helps you identify any potential security risks or compliance issues. Additionally, it can help you optimize user performance by ensuring they only have access to the data and functions they need.
10 AWS S3 Folder Structure Best Practices
10 internal domain name best practices, you may also be interested in..., 10 spark etl best practices, 10 sql server numa nodes best practices, 10 .net core caching best practices, 10 production environment best practices.
Automatic Role Assignment in the Background
On the initial screen of transaction WP3R, you can automate role assignment for the Assign Authorization Roles function by selecting the option Assign Automatically and Update Immediately .
If this option is selected, the transaction assigns and saves the role without any further interaction.
Automatic assignment only works if there is only one authorization role per portal role. See also Assigning Roles .
Messages are output in a list and not in the message window.
This function should be used to schedule regular updates of the role assignments in the background. You must redistribute the role-user assignments of the portal in the SAP System if needed so that the information about the current role-user assignments in the portal is available in the WP3R.
If you are using central user administration with global role assignment, the background job should first execute report WP3ROLELIST_GET_CLIENT_ROLES to read the current role data of the client systems and only then execute report WP3ROLELIST.
Executing report WP3ROLELIST_GET_CLIENT_ROLES corresponds to the function Read roles from client systems .
/support/notes/service/sap_logo.png)
2541730 - How to add a field to Dynamic Role Assignment when setting up a Dynamic Role
How to add fields to the Dynamic Role Assignment object to be able to use more filters in the Dynamic Role configuration
Image/data in this KBA is from SAP internal systems, sample data, or demo systems. Any resemblance to real data is purely coincidental.
Environment
- SAP SuccessFactors HXM Suite
- SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central
It is possible to add Foundation Object and Generic Object fields to the Dynamic Role Assignment object (dynamicRoleAssignment) in the Corporate Data Model. When adding the filed, you must reference "jobInfo". See the example below -:
<hris-element id="dynamicRoleAssignment"> ..... <hris-field id="jobInfo.custom-string8" visibility="both"> <label>Sub Division</label> </hris-field>
The field configuration is inherited from the Succession Data Model so the field in the Corporate data model must have the same visibility that is configured in the Succession Data Model.
Important Information:
- Foundation Object and Generic Object fields are the only types of fields supported by Dynamic Roles - available field for FO and GO can be found on our implementation guide .
- Legacy Picklists are not supported
- Fields with type="worker" are not supported
FAQ - Additional Information
Q) Where can I get information on this from the guide?
A) Guide: Employee Central Workflows: Implementation and Administration
Chapter: Chapter: Creating a Dynamic Group and Creating a Dynamic Role
- 2838785 - Dynamic Role assignment behavior for Custom Foundation Object
- 2541730 - How to add a field to Dynamic Role Assignment when setting up a Dynamic Role
- 2753871 - How to Add Custom Field to a Foundation Object
Dynamic role, Dynamic Role assignment, corporate data model, succession data model, Create, Dynamic Role Filter, dynamicRoleAssignment, ECT-113382, FOO , Foundation object, custom field, application error, error : Invalid file format specified. Please ensure the imported file is in XML format. org.xml.sax.SAXException: cust_GO_OrgUnit1 is not a supported type for hris field jobInfo.custom-string2 in dynamicRoleAssignment HRIS Element , KBA , LOD-SF-EC-RBP , Roles & Permissions (EC Core only) , LOD-SF-EC-WFL , Workflows - Configuration, Tools, Objects & Rules , LOD-SF-EC-FOO , Foundation Objects (Organisation, Pay and Job Structures) , How To
Privacy | Terms of use | Legal Disclosure | Copyright | Trademark
Reviewing the Position Information of Employees
After completing this lesson, you will be able to:
- Identify the Position Fields available in the Employee File
Describe the Job Information HRIS-Element (jobInfo)
As you learned in the prerequisite THR81 - SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central Core Academy training, the Employee File structure includes Person and Employment objects (HRIS-Elements), including Home Address, Biographical Information, Job Information or Job Relationships, to name a few.
This structure is defined in the Succession Data Model, and the admin tool to view the structure of the Employee File is Manage Business Configuration UI.
One of the most important HRIS-Elements in Employee Central is the Job Information ( jobInfo ) where we store the Job, Organizational and Position Information details of the employee.
When Position Management is enabled, one of the prerequisites is to enable the position field, which will be used to assign a specific position to the employee being hired, or when an employee changes their position.
A data propagation might occur when position is assigned, to auto-populate other fields in the Job Information, like Employee Class, Regular/Temporary, Cost Center, Department or Pay Grade, based on the attributes from the Position. A business rule will ensure that the data coming from the Position will synchronize to the employee's Job Information.
Describe the organization of the fields in Job Information
Since the position field ( hris-field ) that needs to be enabled is a prerequisite in Position Management to assign a position to the employee, it will play an important role in the Job Information.
The jobInfo or Job Information HRIS-Element organizes the fields in HRIS Sections. As a standard, the Position related fields will be displayed in the Position Information section, so while they are part of the whole Job Information, the system organizes the fields in this manner.
With this same logic, the Foundation Objects related to Organization, like Legal Entity, Division, Department or Location, are placed in a section called Organizational Information and those fields related to the Job, like Job Classification, Job Title or FTE, will be visible in the Job Information section. Ultimately, everything belongs to the same HRIS-Element jobInfo .


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
understands security and the use and maintenance of organizational. management is a huge advantage in implementing indirect role assignment with. organizational objects. Greg Robinette, CISM. 757-407-7683 or 434-263-6942. We would like to implement Position-based security - assigning roles ""indirectly"" to positions using the HR-ORG model.
2. If we implement structural authorizations and position based role mapping in a single system, then do we need to assign the role to the chief position or it would automatically have the authorizations which are assigned to the users below chief position. 3. First step do we need to create the users in SU01 / SU10 or can we create the entries ...
Steps for indirect assignment of roles: Assignment of position to user id: Go to PFCG -> Goto -> Settings. Under User tab, there is a button "Organizational Mgmt": Click on Organizational Mgmt button. This will take you to the next screen. Click on icon or execute F5 to create assignment. You will get this screen:
PFCG - Indirect Role Assignment through OM. Clicking the Org Mgmt button opens the below screen where we can check the existing assignments for the role (both direct and indirect). New role assignments can e created using the highlighted button. PFCG - Indirect Role Assignment through OM 2. Roles can also be assigned through PP01.
The user ID (US) of the user is stored using the infotype 0105. At the same time, the role (AG) is also assigned to the position. From this indirect role assignment, the user master comparison generates the direct role assignment to the user. See the following graphic. OM Model with the Organizational Object Type Employee
Cloud implementation will have more standardised business roles (SAP provided). ... Manager had been proficient in SAP ways of working and understood what "position-based role assignment ...
The Dynamic Role based on Position can only be used in workflows for MDF Position objects, and the system uses the changed position information to determine the dynamic role assignment. For example, you have moved a position from US to Canada.
Its pretty simple. In the RDS solution of IDM, There are predefined tasks for Rule Management. You have to use the following. 1. Create a dynamic group. In this you will create a dynamic group with your rule criteria. Say if the position of an employee is Delivery manager", Assign XYZ role.
SAP Community is moving in January 2024! Hereâ s what you need to know to prepare. ... Search Questions and Answers . 0. Former Member . Dec 27, 2008 at 11:44 AM E-Recruiting - Position Role Assignment. 26 Views . Follow ... RSS Feed Hello, Has anybody tried to implement the position based role assignment for E-Recruiting. Did it work ...
Select roles on the Roles tab. Make the required entries. To assign a role to a user for a limited time, specify a date in the Valid from or the Valid to column. Use the input help calendar to help you. Note. To assign more authorizations to a user, you can also assign a reference user. For more information, (see Logon Data Tab.
The Roles with Assigned Tasks area displays how much work is planned for each role and how much of this work has already been assigned. You can assign the total work to one task or distribute it over various tasks. Save your data. You are in the Details subview of the Resources view and have selected the Tasks tab:. In the Roles screen area on the left, select the role to which you want to ...
Learn how to assign a person to a position in SAP OM using PPOME or infotype 0000, and how to handle different personnel areas and relationships.
Following these best practices will help ensure that your SAP roles are secure, efficient, and easy to maintain. 1. Use the SAP standard roles as a starting point. SAP standard roles are pre-defined and tested by SAP, so they provide a good foundation for your role design. They also contain the most up-to-date security settings, which can help ...
You can configure the role attributes whose values you specified when defining the role. During the configuration, you determine values for each attribute and then assign or input the defined attributes when you create a role. This includes attributes, such as: Role type. Role name (naming rules) Business process. Business subprocess.
On the initial screen of transaction WP3R, you can automate role assignment for the Assign Authorization Roles function by selecting the option Assign Automatically and Update Immediately . If this option is selected, the transaction assigns and saves the role without any further interaction. Caution. Automatic assignment only works if there is ...
Learn how to enable position under resolver type for dynamic role in Manage Organization, Pay and Job Structure in SAP SuccessFactors. This article explains the steps and prerequisites to configure and use dynamic role for position management and workflow approval.
It is possible to add Foundation Object and Generic Object fields to the Dynamic Role Assignment object (dynamicRoleAssignment) in the Corporate Data Model. When adding the filed, you must reference "jobInfo". See the example below -:
The ability to assign a defined function to other roles. An example would be a business role that is mapped to many component system roles. role mapping in SAP - Everything you need to know about role mapping; definition, explanation, tcodes, tables, wiki, relevant SAP documents, PDFs, and useful links.
Create a new business rule to propagate data from the Job Classification into the Position. Navigate to Configure Business Rules using Action Search.. Select the + to Create New Rule. In the rule scenario category list, expand Metadata Framework and click on Rules for MDF Based Objects rule scenario. In the Rule Name, type Propagate_Job_Classification_to_Position and leave the Rule ID with the ...
Since the position field (hris-field) that needs to be enabled is a prerequisite in Position Management to assign a position to the employee, it will play an important role in the Job Information.. The jobInfo or Job Information HRIS-Element organizes the fields in HRIS Sections. As a standard, the Position related fields will be displayed in the Position Information section, so while they are ...