Primary & Secondary Market Research
Primary market research.
Primary market research is market research that is done by a firm for its own use. A business can tailor this research to their own exact needs.


Examples of primary market research
- For example, a firm may use questionnaires, surveys or interviews to carry out primary research.
- Firms often do this without the customer thinking about it.
- A key benefit of primary research is that it is tailored exactly to the needs of the business.

The likert scale
- At airports, firms like Ferrovial, which owns Heathrow often ask what your service was like at security clearance queues.
- This is known as a likert scale, which is a form of market research that firms use to try to understand and gauge what customers think of their product or service.
Secondary Market Research
Secondary market research happens when firms collect information on research that has been performed by other organisations or people. Secondary market research is particularly useful for information about an entire market rather than a specific target market. It is often cheap.

Government reports
- For example, market research done by governments contained in reports like the Family Expenditure Survey, newspaper articles and research reports written by independent organisations.
1 Enterprise & Entrepreneurship
1.1 The Dynamic Nature of Businesses
1.1.1 The Dynamic Nature of Businesses
1.1.2 Risk & Reward
1.1.3 The Role of Business Enterprise
1.1.4 The Role of Business Enterprise 2
1.1.5 The Role of the Entrepreneur
1.1.6 End of Topic Test - Dynamic Nature of Business
1.1.7 Grade 9 - Dynamic Nature of Business
1.2 Spotting a Business Opportunity
1.2.1 Customer Needs
1.2.2 Market Research
1.2.3 Market Segmentation
1.2.4 The Competitive Environment
1.2.5 Primary & Secondary Market Research
1.2.6 End of Topic Test - Business Opportunities
1.2.7 Application Questions - Business Opportunities
1.2.8 Exam-Style Questions - Market Segmentation
1.3 Putting a Business Idea into Practice
1.3.1 Business Aims
1.3.2 Business Objectives
1.3.3 Business Revenues & Costs
1.3.4 Costs - Calculations
1.3.5 Revenue - Calculations
1.3.6 Business Profits & Break-Even Analysis
1.3.7 Profits & Losses - Calculations
1.3.8 Interest - Calculations
1.3.9 Cash & Cash Flow
1.3.10 Cash & Cash Flow 2
1.3.11 Cash Flow - Calculations
1.3.12 Sources of Business Finance
1.3.13 End of Topic Test - Business in Practice
1.3.14 Grade 9 - Business in Practice
1.3.15 Exam-Style Questions - Business in Practice
1.4 Making the Business Effective
1.4.1 The Options for Start-Up & Small Businesses
1.4.2 Limited Liability
1.4.3 Franchising & Not-For-Profits
1.4.4 Business Location
1.4.5 The Marketing Mix
1.4.6 Business Plans
1.4.7 End of Topic Test - Effective Business
1.4.8 Application Questions - Effective Business
1.4.9 Exam-Style Questions - Business Plans
1.5 Business Stakeholders
1.5.1 Business Stakeholders
1.5.2 Technology & Business
1.5.3 Legislation & Business
1.5.4 Legislation & Business 2
1.5.5 The Economy & Business
1.5.6 External Influences
1.5.7 End of Topic Test - Business Stakeholders
1.5.8 Grade 9 - Business Stakeholders
2 Building a Business
2.1 Growing the Business
2.1.1 Business Growth
2.1.2 Finance
2.1.3 Changes in Business Aims & Globalisation
2.1.4 Ethics & Business
2.1.5 The Environment & Business
2.1.6 End of Topic Test - Growing a Business
2.1.7 Application Questions - Growing a Business
2.1.8 Exam-Style Questions - Business Growth
2.2 Making Marketing Decisions
2.2.1 Product
2.2.2 Product Life Cycle
2.2.3 Price
2.2.4 Pricing Methods
2.2.5 End of Topic Test - Product & Price
2.2.6 Grade 9 - Product & Price
2.2.7 Promotion & Advertising
2.2.8 PR & Sales Promotions
2.2.9 Sponsorship & Product Placement
2.2.10 Promotional Mix
2.2.11 End of Topic Test - Promotion
2.2.12 Application Questions - Promotion
2.2.13 Exam-Style Questions - Promotional Mix
2.2.14 Place & Wholesalers
2.2.15 Direct to Consumer
2.2.16 E-commerce & M-commerce
2.3 Making Operational Decisions
2.3.1 Job Production
2.3.2 Batch & Flow Production
2.3.3 Working with Suppliers
2.3.4 Effective Supply Chains
2.3.5 Just In Time & Just In Case
2.3.6 Managing Quality
2.3.7 Total Quality Management
2.3.8 The Sales Process
2.3.9 End of Topic Test - Operational Decisions
2.3.10 Grade 9 - Operational Decisions
2.3.11 Exam-Style Questions - Managing Stock
2.4 Making Financial Decisions
2.4.1 Gross Profit & Net Profit - Definitions
2.4.2 Gross Profit - Calculations
2.4.3 Net Profit - Calculations
2.4.4 Rate of Return
2.4.5 Rate of Return - Calculations
2.4.6 Research & Financial Data
2.4.7 Marketing Data
2.4.8 Percentage Change - Calculations
2.5 Making Human Resource Decisions
2.5.1 Organisational Structures
2.5.2 Organisational Structures 2
2.5.3 Recruitment
2.5.4 Effective Recruitment
2.5.5 Training a Workforce
2.5.6 Motivating a Workforce
2.5.7 End of Topic Tests - Human Resources
2.5.8 Application Questions - Human Resources
2.5.9 Exam-Style Questions - Human Resources
Jump to other topics

Unlock your full potential with GoStudent tutoring
Affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of your home
Tutors are matched to your specific learning needs
30+ school subjects covered
The Competitive Environment
End of Topic Test - Business Opportunities

Methods of market research

In this post
In order to make sure that it is doing the right things, a business will carry out market research. Now that we have looked at the purpose of this research, we will move on to explore how to carry out this research and the various methods that may be used. The two main types of research are primary and secondary, with the majority of businesses using a combination of the two in order to plan new activity.
Primary market research
Primary research is when you collect information yourself. It is called primary because it has not been collected previously by someone else . Types of primary research include:
- Observations – businesses will record the interactions they have with customers and look at ways that these can be improved. They may also observe the methods of other businesses and look for ways that they can work with customers in order to meet their needs.
- Surveys and questionnaires – asking existing or potential customers their opinion is very important when carrying out market research on customers’ needs. This will require the business to ask specific questions and gather feedback that will inform its decisions in the future.

- Focus groups – focus groups are small groups of people that are invited to discuss a potential new product or service. The researcher will then record the responses of each individual in order to understand if the product is understood and will be popular with the intended customer
- Experimentation and testing – testing and experiments are most popular as a form of research with innovative products. A small batch of goods might be created (these are called ‘prototypes’) which are then tested in a variety of situations. Products might be tested for their quality, durability, safety or features
Primary research can have many different advantages. Firstly, it can be done in any manner that the business sees as appropriate with questions and analysis specifically designed to test the individual products that a company offers. Some of the drawbacks are that it can be expensive, time-consuming and hard to ensure that answers are gathered fairly. Since a business is biased when it comes to its own products, questionnaires can often contain leading answers, focus groups made up of people that do not cover the whole population and observations interpreted in a way that is good for the business. All of these things can lead to research that is unreliable and expensive.
Secondary market research
Secondary research (also known as desk research) is when data that has already been collected is used to inform a decision. This means that information is gathered from sources (these can be inside the business or outside) that has been collected previously for a different purpose. This information has not been collected specifically for the market research currently being carried out but can still be vital when making decisions. Typical types of secondary research include:
- Using resources to gather data – the internet is one of the main resources now used in secondary research. This allows a business to research what is already on the market, the demand for products, what its competitors offer and the key features of other products or services. Some other resources that can be used include business directories, magazines, newspapers or reviews by customers
- Market reports – finding reports that contain information on different markets can be great sources of data. These can be free but can also be purchased and will help a business to understand the demand for goods and what companies already operate in the market.
- Financial data – information can be gathered about running and manufacturing costs for new ventures, returns that other companies have seen and the prices that are charged for similar items
- Information the business already has – many businesses will carry out primary research. In the future, this research may be used again for another purpose. Since the data was not specifically collected for this new purpose, it is now secondary research. However, this information can still be very useful to inform business decisions

Secondary research is usually easy to carry out and cheap (often it is free) for a business. The time taken to collect this type of research is often much less than with primary research. There are several drawbacks to consider though – one of the main ones being reliability. Because the research has not been conducted by the researcher personally, it is hard to know if the data is accurate, as there could be other factors that had an influence over results. Businesses can also run into issues with secondary research as the data that is needed might not be available. This will mean that the company might be unable to carry out this method of research or that it has to use data that is not right for the situation.
Collecting and using data
Data comes in many different styles. Understanding the types of data and how each should be used is key to getting the most from information that is gathered.
Qualitative and quantitative data
All data can be split down into two categories: qualitative and quantitative. The difference between the two is that qualitative data is information that cannot necessarily be counted. It includes opinions and attitudes that are hard to count and focuses on finding trends, since a number cannot be assigned to this type of information.
Quantitative data can be counted easily. This type of data will include a lot of numbers such as the number of people who answered ‘yes’ to a question, the breaking point of a prototype during product testing or the number of potential customers in a market. This type of data can be used to create graphs and charts; making it easier to spot trends and form opinions.
Customer contact when collecting data
When collecting data, a business must work with customers to ensure that information collected is accurate. It is customers that keep a business making money so they must be fully understood to ensure products are desirable. The way that customers work with companies changes over time and the rise of social media has changed the way data is collected massively. Using social media sites, businesses can generate reviews and collect data in a way that is quick and easy for customers. Doing this means that the amount of data collected is much wider and people are more likely to be honest since data is not collected face to face. However, since younger people use social media more, data collected can be skewed and not reflect the full range of customers that a company has.
Data reliability
When information is collected by a company, it simply must be accurate . If data is unreliable then business decisions could be made based on this information with catastrophic consequences. Basing a business decision on incorrect data will dramatically decrease the chances of the change being a success. Incorrect data that influences a business decision may include:
- Opinions from customers that have not been truthful
- Poor estimations of financial data
- Not accounting for all costs or possible earnings
- Using a data collection method that is biased
- Using data from secondary research that is incorrectly collected
All information that is collected should be thoroughly checked by a business to ensure it is valid. Many businesses have made errors in the past due to information being incorrect and invested heavily in something that seems like a good idea, only to find out later that the information they initially collected was incorrect.

Interested in business?
We offer a GCSE Business course that covers Methods of market research
Learn more about our GCSE business course
Read another one of our posts
Understanding dementia: types, symptoms, and care needs.

A Comprehensive Guide to Health and Social Care Training

Understanding and Supporting Mental Health Conditions

The Role of Diet in Managing Chronic Diseases

Effective Communication Skills in Health and Social Care

Understanding Animal Training – Positive Reinforcement Techniques

Key Skills for Successful Care Home Management

Save your cart?
This website works best with JavaScript switched on. Please enable JavaScript
- Centre Services
- Associate Extranet
- All About Maths
GCSE Business
- Specification
- Planning resources
- Teaching resources
- Assessment resources
- Introduction
- Specification at a glance
- 3.1 Business in the real world
- 3.2 Influences on business
- 3.3 Business operations
- 3.4 Human resources
- 3.5 Marketing
- 3.6 Finance
- Scheme of assessment
- General administration
- Appendix: quantitative skills in business

3.5.3 The purpose and methods of market research
Market Research
- Market research is a systematic method of gathering, analysing, and interpreting information about a market, including its customers and competitors.
- It is crucial for businesses to better understand the needs and wants of their target audience, competition, and market trends, helping them to make more informed and effective decisions.
- Primary research or field research involves fresh data collected for a specific purpose. This includes techniques such as surveys, interviews, questionnaires, focus groups, and observations.
- Secondary research or desk research involves using existing data that has been collected by another entity for a different purpose. This includes internal business records, government statistics, newspapers, industry reports, and academic studies.
- Qualitative research provides in-depth understanding and explores attitudes, behaviour, and experiences. It often uses small sample sizes and includes methods such as personal interviews and focus groups.
- Quantitative research involves numerically oriented data, such as statistics or percentages. Generally speaking, it uses larger sample sizes and includes methods such as surveys and questionnaires.
- Market segmentation divides a market into distinct groups with different needs, characteristics, or behaviour who might require distinct products or marketing approaches. Common factors for segmentation include geographical location, demographics (age, gender, occupation, etc), psychographics (lifestyle, values, personality, etc), and behaviour (brand loyalty, usage rate, etc).
- A market map or perceptual map is a diagram that visually represents the perceptions of customers or potential customers about specific attributes of a business or product compared to its competitors. It helps businesses identify market gaps and opportunities.
- Sampling is a process used in statistical analysis in which a predetermined number of observations are taken from a larger population. There are different sampling methods including random, stratified, cluster, and convenience.
- The purpose of market research is to help a business reduce risks by making effective and strategic decisions about product design, pricing, promotions, distribution, and growth opportunities.
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Market Research - Lesson 1/3 - Primary & Secondary Marketing Research - GCSE Business Studies
Subject: Business and finance
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Other
Last updated
14 June 2022
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

A nice lesson on a market research - lesson 1 of 3 of my marketing research lessons. The presentation covers market research. The lesson looks at both primary and secondary research and the pros and cons of primary research. There are a number of tasks throughout the lesson. I have also included a really fun starter where students need to underline / highlight all the mistakes on a very poorly made questionnaire - the student who finds the most mistakes wins a prize. I have also included a nice gap fill and exam style question worksheet. The lesson finishes with students asked to create their own questionnaire for Walkers Crisps. Perfect for GCSE Business Studies.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Get this resource as part of a bundle and save up to 33%
A bundle is a package of resources grouped together to teach a particular topic, or a series of lessons, in one place.
Market Research Lesson Bundle - GCSE Business Studies
This bundle includes three lessons that cover marketing research in a lot of detail. The lessons include key theory, tasks and examples. Lessons in bundle: 1\. Market Research - Primary Marketing Research 2\. Market Research - Secondary Marketing Research 3\. Market Research - Quantitative & Qualitative Marketing Research
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
GCSE Business Studies/Market Research
- 1 Why do firms conduct market research?
- 2 Methods of market research
- 3 Types of data
- 4.1 Writing a questionnaire
- 4.2.1 Random sampling
- 4.2.2 Quota sampling
- 4.2.3 Target sampling
- 4.3 Advantages
- 4.4 Disadvantages
- 5.1 Advantages
- 5.2 Disadvantages
Why do firms conduct market research? [ edit | edit source ]
Some reasons that firms conduct market research are:
- Finding out if customers like their existing products.
- Finding out if customers would be prepared to buy a new product.
If businesses do not conduct market research, they risk producing a product that customers are not interested in. Their marketing will not be effective, and the business will be unsuccessful.
Methods of market research [ edit | edit source ]
There are two methods of market research:
- Primary (Field) Research involves collecting information directly.
- Secondary (Desk) Research involves looking at information that has already been collected and published.
The advantages for desk research is that it saves more time also it has no cost.
Types of data [ edit | edit source ]
You can find out two types of information through market research.
- Quantitative information is anything that you can measure or reduce to a number. For example, asking "How many chocolate bars do you buy each week?" will give a numerical answer, so this is quantitative data.
- Qualitative information is anything about people's opinions. For example, asking "What do you think of this chocolate bar?" will give an answer in words, so this is qualitative data.
Quantitative data is easy to analyse and compare, whereas qualitative data is more difficult, because it is hard to compare people's opinions. However, good market research will use both types of information.
Primary research [ edit | edit source ]
Primary research involves things like questionnaires, surveys, product testing, and using consumer groups.
Writing a questionnaire [ edit | edit source ]
With questionnaires in particular, it is important to communicate to your respondent exactly what you want them to do. This ensures the information you get is reliable and easy to compare.
- Decide what information you want to find out.
- Decide what questions you can ask to find out each piece of information that you want to know.
- Use both open and closed questions. Closed questions only allow specific answers, e.g."How many bottles of orange juice do you drink each week?". Open questions allow a more detailed answer to be given, e.g. "How do you feel about organic juice drinks?".
- Write the questions in an unambiguous way.
- Allow the respondent to give their answer. Make sure that they are given an option that reflects their opinion.
- Avoid misleading questions. For instance, don't ask "How much do you prefer drinking organic juice to ordinary juice?". Instead, ask which they prefer.
- Test the questionnaire first (called a pilot ). This gives you the chance to rewrite the questions.
Sample choice [ edit | edit source ]
Instead of asking the whole population questions, a business will question a smaller group, known as the sample, that will be representative of the whole population.
Random sampling [ edit | edit source ]
With random sampling, the total population is known, and names of people are selected from a list (such as the electoral register) at random. This effectively means that everyone in the population has an equal chance of being selected. This gives a true sample of the population, but is more expensive and time-consuming to conduct.
Quota sampling [ edit | edit source ]
With quota sampling, the interviewers will select people who meet certain criteria. They may, for example, choose to interview 100 men and 100 women. This is easier and cheaper than random sampling, but it is not truly random. For example, if the interviewers were asking passers-by in the street, the people there would not necessarily be representative of the whole population - some people would not be there at the time of day that the interviews were being conducted.
Target sampling [ edit | edit source ]
With target sampling, the interviewers only want to sample a particular group of the population. This might be because its products are only bought by a particular market segment.

Advantages [ edit | edit source ]
- It is up to date.
- Can be kept private by the company.
- It is relevant and specific to what the company needs to find out.
- Gives the company an advantage over competitors, since they have more insight into the market.
Disadvantages [ edit | edit source ]
- Expensive and time-consuming to collect.
- Needs a large sample to be accurate, takes time.
- The data often has to be analysed by experts to reach meaningful conclusions.
Secondary research [ edit | edit source ]
Secondary research involves things like market research reports, government publications, and newspaper and magazine articles.
- Usually significantly cheaper, to obtain than primary research.
- Can be easily found and usually instantly available.
- Useful for looking at the whole market, and analysing past trends.
- Not always relevant to what the company wants to find out.
- Not specifically about the company's products.
- May be out of date.
- Other companies have access to it as well, so it does not give the company an advantage.
- Book:GCSE Business Studies
Navigation menu

- TOP CATEGORIES
- AS and A Level
- University Degree
- International Baccalaureate
- Uncategorised
- 5 Star Essays
- Study Tools
- Study Guides
- Meet the Team
- Business Studies
- Marketing and Markets
primary and secondary research
This is a preview of the whole essay

Document Details
- Word Count 1921
- Subject Business Studies
Related Essays

Maketing - Primary research

The aim of my coursework is to: Firstly undertake market research: such as,...

Secondary Research

In this assignment I will carry out both primary and secondary research to...
Live revision! Join us for our free exam revision livestreams Watch now →
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Business news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Business Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
Study Notes
Marketing: Primary Market Research (GCSE)
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
There are various methods of primary research:
Observation
Watching how consumers behave provides many insights, but can leave questions unanswered. Observation works well in retail markets; sit outside a shop and watch how many people walk by, look at the window display etc.
Postal surveys
Sent to the address of potential customers who complete the form and send back in a pre-paid envelope. Relatively cheap, a postal survey can cover a wide geographical area and avoids the potential for interviewer bias. However, response rates (the proportion of people sending back a completed survey) are often very low and it can take be a long time before enough surveys are returned
Telephone interviews
Not to be confused with "telesales" (which is a method of selling), the telephone interview allow quicker feedback than a postal survey. However, potential customers are often wary of being called and may be reluctant to give anything other than short answers
Online surveys
Increasingly popular and relatively low cost, online surveys are widely used by small businesses as a way of capturing the views of existing and potential customers
Face-to-face surveys
Personal interviews conducted face-to-face. A costly, but good way to get detailed insights from an individual
Focus groups
Groups of potential customers are brought together to discuss their feelings about a product or market. Focus groups are a good way of getting detailed information about customer tastes and preferences
Test marketing
This involves selling a new product in a small section of the market in order to assess customer reaction. For example, a start-up could start by selling to a limited local area in order to iron-out product issues. Software firms often test-market their products by offering "beta" versions for testing by a small group of potential customers. Test marketing can be a good predictor of how a new product or service will be received by the larger market (provided that it can be kept secret from competitors!)
- Marketing research
- Primary research
- Focus group
You might also like
Research & development & new products, marketing planning (overview), marketing: quantitative and qualitative research (gcse), data mining, market mapping (positioning).
Topic Videos
The Prisoner’s Solution – Podcast and Question Sheet
22nd January 2017
Market Research and New Product Sales | AQA Q1.5, Paper 2 2019
Exam Support
Technology & Marketing Decision Making
Our subjects.
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Take action
- Report an antitrust violation
- File adjudicative documents
- Find banned debt collectors
- View competition guidance
- Competition Matters Blog
New HSR thresholds and filing fees for 2024
View all Competition Matters Blog posts
We work to advance government policies that protect consumers and promote competition.
View Policy
Search or browse the Legal Library
Find legal resources and guidance to understand your business responsibilities and comply with the law.
Browse legal resources
- Find policy statements
- Submit a public comment

Vision and Priorities
Memo from Chair Lina M. Khan to commission staff and commissioners regarding the vision and priorities for the FTC.
Technology Blog
Consumer facing applications: a quote book from the tech summit on ai.
View all Technology Blog posts
Advice and Guidance
Learn more about your rights as a consumer and how to spot and avoid scams. Find the resources you need to understand how consumer protection law impacts your business.
- Report fraud
- Report identity theft
- Register for Do Not Call
- Sign up for consumer alerts
- Get Business Blog updates
- Get your free credit report
- Find refund cases
- Order bulk publications
- Consumer Advice
- Shopping and Donating
- Credit, Loans, and Debt
- Jobs and Making Money
- Unwanted Calls, Emails, and Texts
- Identity Theft and Online Security
- Business Guidance
- Advertising and Marketing
- Credit and Finance
- Privacy and Security
- By Industry
- For Small Businesses
- Browse Business Guidance Resources
- Business Blog
Servicemembers: Your tool for financial readiness
Visit militaryconsumer.gov
Get consumer protection basics, plain and simple
Visit consumer.gov
Learn how the FTC protects free enterprise and consumers
Visit Competition Counts
Looking for competition guidance?
- Competition Guidance
News and Events
Latest news, razer, inc. to pay more than $1.1 million for misrepresenting the performance and efficacy of supposed “n95-grade” zephyr face masks.
View News and Events
Upcoming Event
Older adults and fraud: what you need to know.
View more Events
Sign up for the latest news
Follow us on social media
--> --> --> --> -->

Playing it Safe: Explore the FTC's Top Video Game Cases
Learn about the FTC's notable video game cases and what our agency is doing to keep the public safe.
Latest Data Visualization
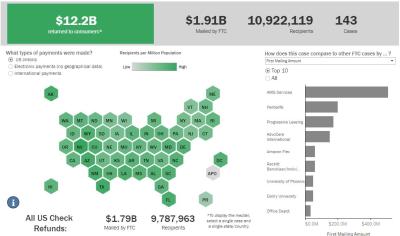
FTC Refunds to Consumers
Explore refund statistics including where refunds were sent and the dollar amounts refunded with this visualization.
About the FTC
Our mission is protecting the public from deceptive or unfair business practices and from unfair methods of competition through law enforcement, advocacy, research, and education.
Learn more about the FTC

Meet the Chair
Lina M. Khan was sworn in as Chair of the Federal Trade Commission on June 15, 2021.
Chair Lina M. Khan
Looking for legal documents or records? Search the Legal Library instead.
- Cases and Proceedings
- Premerger Notification Program
- Merger Review
- Anticompetitive Practices
- Competition and Consumer Protection Guidance Documents
- Warning Letters
- Consumer Sentinel Network
- Criminal Liaison Unit
- FTC Refund Programs
- Notices of Penalty Offenses
- Advocacy and Research
- Advisory Opinions
- Cooperation Agreements
- Federal Register Notices
- Public Comments
- Policy Statements
- International
- Office of Technology Blog
- Military Consumer
- Consumer.gov
- Bulk Publications
- Data and Visualizations
- Stay Connected
- Commissioners and Staff
- Bureaus and Offices
- Budget and Strategy
- Office of Inspector General
- Careers at the FTC
FTC Announces Rule Banning Noncompetes
- Competition
- Office of Policy Planning
- Bureau of Competition
Today, the Federal Trade Commission issued a final rule to promote competition by banning noncompetes nationwide, protecting the fundamental freedom of workers to change jobs, increasing innovation, and fostering new business formation.
“Noncompete clauses keep wages low, suppress new ideas, and rob the American economy of dynamism, including from the more than 8,500 new startups that would be created a year once noncompetes are banned,” said FTC Chair Lina M. Khan. “The FTC’s final rule to ban noncompetes will ensure Americans have the freedom to pursue a new job, start a new business, or bring a new idea to market.”
The FTC estimates that the final rule banning noncompetes will lead to new business formation growing by 2.7% per year, resulting in more than 8,500 additional new businesses created each year. The final rule is expected to result in higher earnings for workers, with estimated earnings increasing for the average worker by an additional $524 per year, and it is expected to lower health care costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade. In addition, the final rule is expected to help drive innovation, leading to an estimated average increase of 17,000 to 29,000 more patents each year for the next 10 years under the final rule.
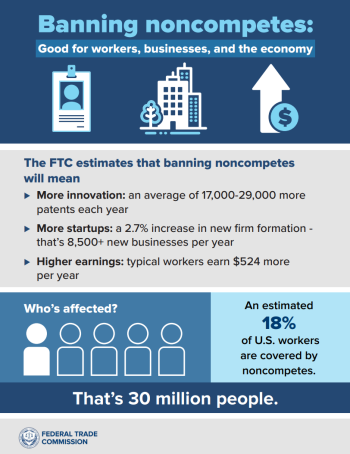
Noncompetes are a widespread and often exploitative practice imposing contractual conditions that prevent workers from taking a new job or starting a new business. Noncompetes often force workers to either stay in a job they want to leave or bear other significant harms and costs, such as being forced to switch to a lower-paying field, being forced to relocate, being forced to leave the workforce altogether, or being forced to defend against expensive litigation. An estimated 30 million workers—nearly one in five Americans—are subject to a noncompete.
Under the FTC’s new rule, existing noncompetes for the vast majority of workers will no longer be enforceable after the rule’s effective date. Existing noncompetes for senior executives - who represent less than 0.75% of workers - can remain in force under the FTC’s final rule, but employers are banned from entering into or attempting to enforce any new noncompetes, even if they involve senior executives. Employers will be required to provide notice to workers other than senior executives who are bound by an existing noncompete that they will not be enforcing any noncompetes against them.
In January 2023, the FTC issued a proposed rule which was subject to a 90-day public comment period. The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on the proposed rule, with over 25,000 comments in support of the FTC’s proposed ban on noncompetes. The comments informed the FTC’s final rulemaking process, with the FTC carefully reviewing each comment and making changes to the proposed rule in response to the public’s feedback.
In the final rule, the Commission has determined that it is an unfair method of competition, and therefore a violation of Section 5 of the FTC Act, for employers to enter into noncompetes with workers and to enforce certain noncompetes.
The Commission found that noncompetes tend to negatively affect competitive conditions in labor markets by inhibiting efficient matching between workers and employers. The Commission also found that noncompetes tend to negatively affect competitive conditions in product and service markets, inhibiting new business formation and innovation. There is also evidence that noncompetes lead to increased market concentration and higher prices for consumers.
Alternatives to Noncompetes
The Commission found that employers have several alternatives to noncompetes that still enable firms to protect their investments without having to enforce a noncompete.
Trade secret laws and non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) both provide employers with well-established means to protect proprietary and other sensitive information. Researchers estimate that over 95% of workers with a noncompete already have an NDA.
The Commission also finds that instead of using noncompetes to lock in workers, employers that wish to retain employees can compete on the merits for the worker’s labor services by improving wages and working conditions.
Changes from the NPRM
Under the final rule, existing noncompetes for senior executives can remain in force. Employers, however, are prohibited from entering into or enforcing new noncompetes with senior executives. The final rule defines senior executives as workers earning more than $151,164 annually and who are in policy-making positions.
Additionally, the Commission has eliminated a provision in the proposed rule that would have required employers to legally modify existing noncompetes by formally rescinding them. That change will help to streamline compliance.
Instead, under the final rule, employers will simply have to provide notice to workers bound to an existing noncompete that the noncompete agreement will not be enforced against them in the future. To aid employers’ compliance with this requirement, the Commission has included model language in the final rule that employers can use to communicate to workers.
The Commission vote to approve the issuance of the final rule was 3-2 with Commissioners Melissa Holyoak and Andrew N. Ferguson voting no. Commissioners Rebecca Kelly Slaughter , Alvaro Bedoya , Melissa Holyoak and Andrew N. Ferguson each issued separate statements. Chair Lina M. Khan will issue a separate statement.
The final rule will become effective 120 days after publication in the Federal Register.
Once the rule is effective, market participants can report information about a suspected violation of the rule to the Bureau of Competition by emailing [email protected] .
The Federal Trade Commission develops policy initiatives on issues that affect competition, consumers, and the U.S. economy. The FTC will never demand money, make threats, tell you to transfer money, or promise you a prize. Follow the FTC on social media , read consumer alerts and the business blog , and sign up to get the latest FTC news and alerts .
Press Release Reference
Contact information, media contacts.
Victoria Graham Office of Public Affairs

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn about and revise how market research can influence the products or services a business offers with BBC Bitesize GCSE Business - Edexcel. ... Methods of market research - secondary research.
Government reports. For example, market research done by governments contained in reports like the Family Expenditure Survey, newspaper articles and research reports written by independent organisations. Primary market research is market research that is done by a firm for its own use. A business can tailor this research to their own exact needs.
Learn about and revise how market research can influence the products or services a business offers with BBC Bitesize GCSE Business - Edexcel. ... Methods of market research - secondary research.
Secondary Market Research. Secondary market research uses data that already exists and has been collected by someone else for another purpose. Sources of secondary data can come from within the firm itself - this is known as internal secondary data. External secondary data, on the other hand, is data that has been published by other ...
In this video for students revising for GCSE Business exams, we investigate the methods of secondary market research that entrepreneurs and managers might us...
Revision notes on 1.2.2 Market Research for the Edexcel GCSE Business syllabus, written by the Business experts at Save My Exams. ... primary and secondary research; Primary research is the process of gathering information directly from consumers in the target market using field research methods such as surveys, ...
Learn about and revise how market research can influence the products or services a business offers with BBC Bitesize GCSE Business - Edexcel. ... Methods of market research - secondary research;
Secondary Research. Secondary research involves the use of existing data, or data gathered by someone other than the user. This includes reports, studies, internet research, and statistical data. It's a less costly method which provides a broad background view. Quantitative Research. Quantitative research develops numerical data and can be ...
This short revision video explains what is meant by secondary market research. ... Business news, insights and enrichment. Collections. ... Marketing: Quantitative and Qualitative Research (GCSE) Study Notes. Marketing: Primary Market Research (GCSE) Study Notes ...
Primary market research. Secondary market research. Collecting and using data. Qualitative and quantitative data. Customer contact when collecting data. Data reliability. In order to make sure that it is doing the right things, a business will carry out market research. Now that we have looked at the purpose of this research, we will move on to ...
Students should understand why businesses conduct market research, such as to identify market opportunities and to get a better insight into their customers and competitors. Methods of market research to include primary and secondary: questionnaires. surveys. interviews. focus groups. internet research.
Advantages of Secondary Research. Typically involves less time and cost compared to primary research. Easy access to a large amount of data which can provide a broad understanding of a market. Provides a good foundation to establish the need for primary research. Limitations of Secondary Research. The data is not exclusive to the business and ...
This lesson focuses on secondary research and what it is/entails, as well as its advantages and disadvantages. It includes a research activity which will encourage students to investigate and judge whether a business idea would be successful, using secondary market research methods. 1. Define what secondary market research is, using examples. 2.
GCSE Business OCR View topics (31) Topics. Business Activity Business Growth ; ... Market research is a systematic method of gathering, analysing, and interpreting information about a market, including its customers and competitors. ... Secondary research or desk research involves using existing data that has been collected by another entity ...
Watch this video if you want to understand the role of Secondary Market Research in Business and the common methods used. SUBSCRIBE: https://www.youtube.com...
Diagram of Secondary Research Sources. Businesses can consult a wide range of secondary sources to gather market research data. Government Publications: National governments and trading blocs such as the EU publish reports and statistics on topics such as the economy, demographics, industry trends and consumer behaviour.
Market Research Lesson Bundle - GCSE Business Studies. This bundle includes three lessons that cover marketing research in a lot of detail. The lessons include key theory, tasks and examples. Lessons in bundle: 1\. Market Research - Primary Marketing Research 2\. Market Research - Secondary Marketing Research 3\.
Methods of market research. There are two methods of market research: Primary (Field) Research involves collecting information directly. Secondary (Desk) Research involves looking at information that has already been collected and published. The advantages for desk research is that it saves more time also it has no cost.
Learn about and revise how market research can influence the products or services a business offers with BBC Bitesize GCSE Business - Edexcel. ... Methods of market research - secondary ...
Method. Explanation. Surveys. The most widely used method of gathering primary research. A questionnaire is used to ask a series of questions to a certain number of people (respondents) The results from the 'sample' are used to to make inferences, in which the results of the sample are extrapolated to be true for the wider population.
Primary research methods ü Questionnaires, interviews, trials, focus groups Secondary research methods ü Newspapers and magazines, census, websites, internal data How appropriate different methods and sources of market research are for different business purposes ü Make recommendations in different contexts as to which method
Primary Research. There are many different methods for Primary research, such as: * Focus Groups. * Face to Face Interviews. * Postal surveys. * Telephone Interviews. Focus Groups. Focus groups are an economical method of obtaining useful qualitative information from consumers. There are some advantages and disadvantages for focus groups, such as:
Marketing: Primary Market Research (GCSE) There are various methods of primary research: Observation. Watching how consumers behave provides many insights, but can leave questions unanswered. Observation works well in retail markets; sit outside a shop and watch how many people walk by, look at the window display etc. Postal surveys.
Today, the Federal Trade Commission issued a final rule to promote competition by banning noncompetes nationwide, protecting the fundamental freedom of workers to change jobs, increasing innovation, and fostering new business formation. "Noncompete clauses keep wages low, suppress new ideas, and rob the American economy of dynamism, including from the more than 8,500 new startups that would ...