- Library FAQs

Q. How can I add my publications to my Google Scholar profile?
- 9 Academic Integrity Module
- 19 Borrowing
- 27 Copyright licensing
- 9 Creative Commons Licence
- 4 Document Delivery
- 6 e-journal
- 58 General Library
- 32 Higher Degree Research (HDR)
- 23 Information
- 2 Library fees
- 3 My Library and Off Campus Access Login
- 5 Newspapers
- 15 Off-Campus Access
- 8 Open Access
- 32 Open Educational Resources (OER)
- 28 Open Scholarship
- 31 Open Textbooks
- 1 Peer Review
- 7 Printing and Photocopying
- 11 Publications
- 2 Reading Lists
- 24 Referencing
- 104 Research
- 10 Research Data Management
- 6 Research Metrics
- 18 Researcher Profiles
- 39 Resources
- 3 Studiosity
- 2 Study Smart
- 3 Study Smart Librarian
- 15 Textbooks
- 30 Turnitin for students
- 24 Western Open Books
- 8 Western Sydney University Digital Theses
Answered By: The Library Last Updated: Aug 02, 2022 Views: 55774
- 'SIGN IN' to your Google Scholar profile
- Click on 'My profile'
- To add publications, click on the + button and select from the list of the following options:
a) Add article groups : Articles will be grouped together by name. Use the check box to select and add a group of articles under your name
b) Add articles : Lists articles individually. Tick the check box to select and add the articles you have authored
c) Add article manually : If the article cannot be found you can create an entry manually. First choose the publication type at the top of the form then fill in as many fields as possible
NOTE: Archiving your publication to ResearchDirect (Western’s Institutional Repository) or personal web page will help Google Scholar find your publication. Remember to check which version of your paper you are permitted to archive and always link to an Open Access URL if available.
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 55 No 114
Comments (0)
Related topics.
- Researcher Profiles
How to Add Papers in Google Scholar: A Guide

Incorporating publications into Google Scholar and learning how to add papers in google scholar can be an excellent strategy for R&D and innovation teams to enhance their presence in the scholarly community. It can help optimize your profile, make it easier to find relevant information quickly, and provide insight into trends in the industry. With some tips on how to add papers in google scholar, you’ll be able to take advantage of this powerful tool with ease. In this blog post we will discuss what is Google Scholar; adding papers; optimizing your profile; using it effectively; and troubleshooting common issues associated with it. Get ready for insights that will help you maximize the potential of how to add papers in google scholar today.
Table of Contents
What is Google Scholar?
Adding papers to google scholar, optimizing your profile on google scholar, tips for using google scholar effectively, keeping track of new research developments, utilizing advanced search features, troubleshooting common issues with google scholar, faqs in relation to how to add papers in google scholar, how do i add a paper to google scholar, does google scholar automatically add papers, why is google scholar not showing my paper, how do i import publications into google scholar.
Google Scholar is a powerful search engine for finding scholarly literature. Google Scholar grants access to a wealth of academic documents, periodicals, books, and other resources from all corners of the globe. With Google Scholar, researchers can quickly find relevant research materials related to their field of study or research topic. Google Scholar offers an advantage over regular search engines like Google or Bing in that it can quickly locate hard-to-find, peer-reviewed sources, and scientific data.
Google Scholar’s advanced search features, such as author name, publication date, subject area, and language preferences filtering make finding the right information a breeze. Moreover, its citation indexing allows users to quickly trace references made by authors in their own work without having to review each source individually – an invaluable time-saver for complex research projects. With comprehensive coverage across all disciplines and the inclusion of both open-access publications and subscription-based content from various publishers worldwide, Google Scholar is undoubtedly one of the best tools for locating scholarly material.
Google Scholar is an invaluable tool for researchers and academics, providing access to scholarly literature from around the world. With its ability to teach you how to add papers in google scholar, it allows users to create a comprehensive profile of their research work. Next, we will look at how one can use Google Scholar in order to effectively manage their publications.
Key Takeaway: Google Scholar is a one-stop shop for finding scholarly literature, offering researchers advanced search features and comprehensive coverage of both open access publications and subscription-based content from around the world. Its citation indexing makes tracking references in research projects a breeze – making it an invaluable tool for any researcher.
Google Scholar is a great tool for research and innovation teams to stay on top of the latest developments in their field. It allows users to easily search for relevant publications and how to add papers in google scholar, track citations and impact, create profiles to showcase their work, and even collaborate with other researchers. Adding papers to Google Scholar can be done quickly and efficiently by following these steps.
To get started in boosting the visibility of your work, one must first generate a profile on Google Scholar. To create your profile, go to scholar.google.com/citations and click “Create Profile” at the top right corner of the page, providing all required information including name and affiliation (if applicable) before clicking “Save & Continue”. Once you have created your profile, you can begin adding publications associated with it by clicking “Add Publications” under your profile picture or name in your Google Scholar dashboard.
Once all authors have been listed properly along with any co-authors who made significant contributions, titles of articles included, journal names (if applicable), and volume numbers (where available), click “Add Publication” to instantly add the publication to your list of published works. Make sure to include keywords throughout the citation in order to maximize visibility when searching through databases such as PubMed or Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC). A couple of clicks can allow you to demonstrate your research achievements and make them visible for discovery.

Checking back on each paper’s citation count via the “My Citations” tab located under the “Tools” section in the left sidebar menu regularly is important to ensure accuracy and manage publications correctly, allowing others to access them without difficulty. If there appear to be discrepancies between the actual number of citations versus what is displayed here, contact support immediately for further investigation as it could be due to duplicate entries or typos/errors during the entry process. Keywords such as ‘accuracy’, ‘difficulty’, and ‘investigation’ should be used throughout this text while ensuring proper grammar, spelling, punctuation, and avoiding exclamation points are all adhered to.
Utilizing Google Scholar’s advanced search features, especially with the knowledge on how to add papers in google scholar can help you stay current with new research in your field, saving time and effort. These features allow users to narrow down searches using keyword phrases related to specific topics, making more efficient use of time when looking for relevant materials quickly and easily.
The implementation of how to add papers in google scholar can increase the visibility and impact of your publications. Additionally, optimizing your profile on Google Scholar will help ensure accuracy in citations and track the overall performance of each publication.
Key Takeaway Adding papers to Google Scholar can be done quickly and efficiently by creating a profile, adding publications with the correct authorship details, checking citation count regularly for accuracy, and utilizing advanced search features. By taking these steps you’ll have your research accomplishments on full display in no time.
It can help you enhance the visibility of your publications, improve the accuracy of citations, and track the impact of your work. To maximize the benefits of Google Scholar, here are some ways to optimize your profile.
To enhance the visibility of your publications on Google Scholar, make sure that all relevant information about them is included in the metadata – such as authors’ names, titles, abstracts, etc. This will ensure that they appear more prominently in search results and are easier to find by other researchers. Additionally, it’s important to keep up with any changes or updates made to existing papers so that these show up correctly in searches too.
Improving the accuracy of citations for your publications can also help boost their visibility on Google Scholar. Make sure that all references used are properly cited and formatted according to academic standards; this will ensure that other researchers can easily locate them when searching for related topics or materials online. Additionally, adding keywords associated with each paper can also help increase its relevance in searches conducted by others within the field. # Papers #google #googlescholars #publications Click To Tweet
Finally, tracking citations and the impact of your publications is essential if you want to maximize their reach across various platforms like Google Scholar or other databases like PubMed Central (PMC). Keeping an eye out for new articles citing yours helps identify potential opportunities for collaboration as well as areas where further research may be needed; both key elements when it comes to staying ahead in today’s competitive landscape. To do this effectively use tools such as Publish or Perish which allows users to monitor citation counts over time using data from sources including PMC and Web Of Science (WoS).
By optimizing your profile on Google Scholar, you can enhance the visibility of your publications and track their citations and impact. By utilizing the advanced search capabilities of Google Scholar, you can stay abreast of recent research developments, quickly and effortlessly uncover pertinent materials, and make the most out of this potent tool.
Key Takeaway Additionally, citing references properly and adding keywords associated with each paper will help improve accuracy of citations. Finally tracking citation counts over time using tools like Publish or Perish helps identify potential opportunities for collaboration within a competitive landscape.
To maximize the use of Google Scholar and how to add papers in google scholar here are some tips to keep in mind.
To keep up with new research, set up an alert on Google Scholar. This will notify you whenever new papers related to your interests are published. You can also use Google’s advanced search feature to narrow down results by date or topic so that only relevant articles show up in your alerts.
Finding Relevant Research Materials Quickly and Easily: Using keywords, phrases, authors, journals or other criteria can make it easier for you to find what you need quickly and easily without wasting time sifting through irrelevant results. Try using Boolean operators such as AND/OR/NOT when searching multiple terms at once; this allows you to focus more precisely on exactly what it is that you’re looking for.
The advanced search feature offers a variety of options that allow users greater control over their searches including limiting by language or publication type (e.g., peer-reviewed journals). It also provides sorting options such as relevance or date range so that users can customize their searches even further according to their needs. Additionally, if needed, users can save their searches for future reference making it easy for them to access previously used queries without having to start from scratch each time they want information about a particular topic area or author, etc.
These tips should help R&D and innovation teams maximize the potential offered by Google Scholar, allowing them to stay informed about current trends and developments in their field quickly and efficiently. This will give them more time to spend on actual work instead of researching.
By following the tips outlined above, researchers can easily and effectively utilize Google Scholar to keep up with new research developments, find relevant materials quickly and take advantage of its advanced search features. Additionally, troubleshooting common issues such as duplicate entries in your profile or incorrect citation counts is essential for ensuring accurate results when using Google Scholar.
Key Takeaway Google Scholar is a powerful research tool for R&D and innovation teams, offering numerous features to help keep up with the latest developments in your field. With its advanced search feature, users can easily find relevant materials quickly by utilizing keywords and Boolean operators as well as sorting options such as relevance or date range. This will save time on researching so that teams have more of it to spend on actual work.
Troubleshooting issues with Google Scholar necessitates comprehending the source of each difficulty and how to manage them effectively. Resolving duplicate entries in your profile is one of the most common problems encountered when using Google Scholar. This can be caused by different versions of a publication being uploaded or incorrect metadata for an existing entry. Search Google Scholar for the paper you are trying to add and delete any duplicates that don’t belong to you before adding your own version. If there are, delete any that don’t belong to you before adding your own version of the paper.
Another issue you may encounter is incorrect citation counts. Citations should accurately reflect how often a particular work has been cited in other publications over time, but sometimes they can be inaccurate due to errors or outdated data from third-party sources such as Crossref or Web Of Science Core Collection (WOSCC). To ensure accuracy, check all citations against those found on reputable databases like WOSCC and manually update any discrepancies if necessary.
Key Takeaway Troubleshooting common issues with Google Scholar, such as duplicate entries and incorrect citation counts, can be a tricky task. Before adding your own version of the paper, ensure that any duplicates not belonging to you are deleted by searching for it on Google Scholar. Additionally, double-check citations against reputable databases like WOSCC in order to ensure accuracy.
To add a paper to Google Scholar, start by signing into your Google account. Go to ‘My Citations’ page, click the ‘Add Article’ button, and enter paper details. Enter the details of your paper including its title, author names, journal name, and year published. Finally hit submit for it to be added. It’s important that you ensure all information is accurate and you have a google scholar profile before submitting as incorrect data can lead to inaccurate citations being displayed in search results. how to add papers in google scholar is a great topic under this specific session of google scholar.
No, Google Scholar does not automatically add papers. Users can employ Google Scholar to search and acquire scholarly material from multiple sources, including educational publishers, universities, preprint repositories, and professional organizations. Users must manually upload their own documents or articles for indexing in the system.
Google Scholar is a search engine that indexes scholarly literature from around the world. It may not be showing your paper because it has yet to index it or because the content does not meet its criteria for inclusion in its database. To ensure visibility of your work, make sure you are submitting papers to reputable journals and following all guidelines for publication. Additionally, you can use tools such as Google Alerts to monitor when new research on topics related to yours is published so that you can cite them in your own work and maximize visibility of both parties’ works.
To import publications into Google Scholar, you must first create a profile and upload your publication list. Once uploaded, the platform will automatically detect citations and match them to existing works. You can also manually add new papers or edit information about existing ones. Additionally, you may use citation management tools such as EndNote or Zotero to quickly transfer data from other sources into Google Scholar for easy access and analysis.
Maximizing the exposure of R&D and innovation teams’ efforts can be achieved through learning on how to add papers in google scholar. By optimizing your profile, utilizing tips for effective use, and troubleshooting common issues with Google Scholar you can ensure that your research is being seen by the right people. With careful attention given to these details, you will be able to make sure that adding papers to google scholar yields maximum results.
Take control of your research with Cypris and quickly add papers to Google Scholar for faster insights. Streamline the way you manage data sources and make better decisions today!
Similar insights you might enjoy

Gallium Nitride Innovation Pulse

Carbon Capture & Storage Innovation Pulse

Sodium-Ion Batteries Innovation Pulse
Thomas Vanhoutte
Personal website and blog
Submit academic research paper to Google Scholar
You have worked many months to complete your thesis or academic paper and you have relied on existing knowledge to finalize your research. Now you want to make your work available to the public. Here is how to properly include your academic research (journal article, thesis, book, ) in the Google Scholar search engine.
Create your Google Scholar profile
From this page, you can create your Google Scholar profile page. Include as much information as possible, such as a profile picture, your website, affiliation and areas of interest. I would also recommend you to make your profile public.
Once your profile looks good, we can move on to actually adding your academic writings. From here on, you have two options:
- You have only one or a few documents you want to submit, go for option 1
- You have many articles you want to add and are planning on writing even more in the future, go for option 2
Option 1 – Adding one by one
If you only want to include one document (let’s say, your master’s thesis), you can do so manually. Here are the steps:
- Go to this page to start adding a document manually.
- Choose the type of document (journal, conference, chapter, book, thesis, patent, court case or other).
- Fill in all the details about your article (title, author(s), publication date(s), volume, publisher, institution).
Click save and if you filled in everything correctly, you will see the message ‘Added article to your profile’. Congratulations!
Option 2 – Submit a website with all your work
In case you have an academic career and you have a list of work on your (academic or personal) website, option 2 is more suitable for you.
Google has guidelines to help you index your website that contains your academic work. Here are the steps you should follow to successfully include all of your work at once:
- Go to this page and pick the type of website you are submitting. In my case, I choose ‘Personal publications’.
- Read and check the check-boxes that apply to you, such as ‘My inclusion request is for my personal publications’.
- Fill in the requested details, whereby the your webpage with academic articles should be filled in by ‘List of publications page’.
- Lastly, you are asked to include one or more article examples. So, paste the direct link to on or more of your PDFs there.
click submit and you are greeted with this message
Thanks for submitting your website to Google Scholar. Our crawl team is working hard to add new content as quickly as possible, and we appreciate your assistance. Please keep in mind that bibliographic data is extracted from your pages by automatic software. If you aren’t satisfied with the accuracy of your listings, please refer to our technical guidelines at http://scholar.google.com/intl/en/scholar/inclusion.html for ways to provide more accurate bibliographic data. An email detailing your submission has been sent to [email protected] . If your content meets our guidelines, you can generally expect to find it included within the Google Scholar results within 4-6 weeks.
Be patient, because as the message says, it can take up to a month or more before your articles are indexed. You will also receive an e-mail from [email protected] with the data you just submitted.
Follow your own profile
Here is a great tip: follow your own Google Scholar profile!
Go to your own profile and at the top right, choose ‘follow’. Enter your e-mail and create the alert. If Google adds a new article to your profile, or a new citation, you will receive an e-mail alert.
This is an excellent way to receive a heads up if another researcher or student has cited your work in their academic writings. Maybe you can even reach out to the author(s) and talk about their research; a great way to expand your network.
Join the conversation
17 Comments
What are good open alternatives or extensions for Google Scholar and Microsoft Academic Search?
Mate is it equivalent to journal publishings.
Thanks a lot Mr. Thomas. I am much benefited by your informative article. The way and simplicity gave me enourament to read all and actually helped me to solve my problem. God bless you.
I like to add my journal in indexing of google scholar
Thanks Thomas for the link to “Submit a website with all your work”, that was a great tip.
I am genuinely happy to read this webpage posts which carries lots of valuable information, thanks for providing such statistics.
RESPECTED SIR, HOW CAN I UPLOAD MY ARTICLE WHICH IS NOT PUBLISHED ANYWHERE TO GOOGLE SCHOLAR, AS I AM A PHD SCHOLAR, THERE IS NO PROVISION TO UPLOAD AND SAVE OPTION IN MY SCHOLAR ACCOUNT. I JUST OPENED AN ACCOUNT SIR. PLS GUIDE ME IN THIS REGARD. THANK YOU SIR
how to add pdf file to google scholars?
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Name Course Professor Institution City and State location The Date
TABLE OF CONTENT 1. Introduction…………………………………………………..4 1.1 Background Information………………………………….4 1.2 Definition of Corporate Governance……………………4 1.3 Importance of Corporate Governance…………………..4 1.4 Corporate Governance Theories………………………….5 1.5 Corporate Governance Codes……………………………5 2. Corporate Governance Mechanism………………………….6 2.1 Corporate boards………………………………………….7 2.1.1 Corporate board Structure……………………………7 2.1.2 Role of corporate board……………………………..8 2.2 Institutional Investors……………………………………9 2.2.1 Role of Institutional Investors ……………………..9 2.3 Other Corporate Governance Mechanisms……………10 3. Case Studies…………………………………………………10 3.1 Enron…………………………………………………….10 3.1.1 Background………………………………………..10 3.1.2 Enron’s Failure of Corporate Governance………..11 3.2 Reckitt Benckiser………………………………………12 3.2.1 Background………………………………………..12 3.2.2 Failure of Corporate Governance…………………12 3.3 Satyam………………………………………………….13 3.3.1 Background………………………………………..13 3.3.2 Failure of Corporate Governance ………………..13 3.4 WorldCom……………………………………………..14 3.4.1 Background……………………………………….14 3.4.2 Failure of Corporate Governance…………………14
4 Recommendations…………………………………………15 5 Conclusion…………………………………………………17 6 References…………………………………………………18 Introduction 1.1 Background Many scholars, economists, and other professions consider 2007- 2009 global financial crisis as the worst financial crisis ever since the great depression of 1930. The period characterized by the collapse of many financial institutions, massive bailouts, the economic downturn and finally the great recession was primarily attributed to the failure of corporate governance. As much as this was a low point in corporate governance, it also showed its importance not only to individual firms but to the world economy as a whole (Tricker & Tricker 2015). Never before has the notion that corporate boards and institutional investors are the most important corporate governance mechanisms in the firms with important implications for the sustainable long-term success of the firm been so vividly seen. From time immemorial as humans, we have always learned from our mistakes and the 2007-2009 was an eye opener especially to corporate governance. Before I can explain further on the notion, it is important to learn the basic aspects of corporate governance. 1.2 Definition of Corporate Governance Corporate governance in simple terms refers to the set of rules, processes, and practice through which a company is controlled and directed with (Solomon 2007). It involves balancing the interests of the organization with the interests of other parties such as the government, investors, lenders, suppliers, the community etc. 1.3 Importance of Corporate Governance When executed properly, corporate governance can help a company avoid certain risks such as lawsuits, fraud, and misappropriation of funds. In addition to that, good corporate governance helps in boosting the organization’s brand and reputation to the media, investors, suppliers, customers and the society as the whole. Furthermore, cooperate governance protects the financial interests of the individuals involved with the company such as the shareholders and the employees as explained by (Vitez, 2017).
1.4 Theories of Corporate Governance Corporate governance can be defined in many ways but when it comes to analyzing it, we do it through a framework of different theories. One of those theories is the agency theory which looks at the shareholders as the principals and the executives that have been hired to run the business as their agents. Another theory is the stewardship theory which looks at the executive as the stewards of the shareholders with both parties sharing the same goals. In addition to that, we have the resource dependent theory which considers the board as to be in existence so as to provide resources to the management with the aim of achieving the overall objectives of the business. Stakeholder theory comes from the assumptions that it is not just the shareholders who have an interest in the company but other parties too such as suppliers, the government, creditors among others (Farrar 2008). This means that this parties too can be affected by the success or failure of the business. Other theories of cooperate governance include transaction cost theory, political theory, and ethical related theories. 1.5 Corporate Governance Codes Introduction The code of governance over the years have originated for various reasons or in response to various circumstances. The first major release was in 1992 by Sir Adrian Cadbury popularly referred to ‘Cadbury Code’ titled “the Financial Aspects of Corporate Governance”. Following serious revisions over the years, the code is nowadays administered by the Financial Reporting Council. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) developed the first internationally influential codes back in 1999 following a business advisory committee that was led by Irra Milstein. Boards that govern companies are influenced by several documents which include but not limited to articles of incorporation, by-laws, corporate governance guidelines, committee charters, and codes of conduct. When it comes to the United States, various federals laws such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Act, federal laws as well as federal security laws in addition to regulations, rules, and guidance from SEC are used. These documents are meant to be used for the purpose of best practices and flexible working standards to safeguard the various parties that have an interest in the organization. In short, they basically outline the interaction between the board and management outlining the structure and the behavior of the board. The codes are normally contributed to by various individuals including investors, accounting firms, regulators, banks, corporate governance interest organizations, academics, and stock exchanges, among others.
Corporate Governance Mechanism Policies, control, and guidelines are vital for an adequate corporate governance mechanisms. An effective corporate governance mechanism will consist of a number of various mechanisms. The first level consists of internal mechanisms which monitor the business from within and take corrective measures when the business stray away from its set objectives. They include reporting lines that are clearly defined, systems that measure performance and systems for the smooth operation of the business. The next level is the external mechanisms which are controlled by those outside the business and serve the objectives of outsiders such as the regulators, government, financial institutions, and trade unions among others. The objectives of the external mechanism include proper debt management and legal compliance by the company in question. The last level consists of an audit of the entity’s financial statements by an independent auditor who generally works to serve both the internal and external parties that are involved with an organization to ensure that their interests are guided and that the management is doing everything properly. They also act as a second opinion to back up what the management is saying. 2.1 Corporate Boards The board generally consist of groups of individuals elected or nominated by shareholders in the annual general meeting. The board of directors normally act as a bridge between the company and the shareholders -it decides as a fiduciary with the aim of protecting the latter’s interests. This is the norm with a Public company even though nowadays most non-profit making organizations and private companies also have a board. Their main mandate is to make policies for corporate management and also to make decisions on major issues that affect the company. 2.1.1 Corporate Board Structure The structure of the board of directors is mainly guided by the company’s bylaws which sets out the structure, number of members, how often they meet etc. The most important element is that it should be able to balance both the interests of the management and Shareholders. The duties are regulated by the statutory laws, federal statutory laws, listing standards, common law and shareholder activism and litigation. The membership of the board normally constitutes independent directors, senior company executives, non-independent directors such as former senior executives of the company among others. Nasdaq rules require the majority of the board members to be independent and in they constitute up to 75% or more of the boards in 93 of the top 100 US companies. Most boards consist of 8 to 15 members. There are no age and nationality restrictions although in recent years gender balance has been emphasized. 2.1.2 Roles of the Corporate Boards The board’s primary role as discussed earlier is the fiduciary duty to safeguard the finances and the legal requirements of the entity. They do this by ensuring that the entity in questions does all that is required of it by the law, and the funds are properly used. Another role of the board of directors is setting up the mission and vision of the organization. In addition to that, they ensure that the management adheres and work towards achieving them. Over sighting the activities of members of the organization such as executives is another role of the corporate board. The board ensures that the management adheres to rules and regulations and do their work as prescribed. Other roles of the board of directors come up in the annual meetings where-by, they announce the annual dividends, oversee the appointment of key executives and amend the by-laws where it is necessary (Dimopoulos & Wagner, 2016). Other roles of the corporate board include setting up the strategy for the company for long-term survival, short-term gains and future exploration of opportunities that are likely to arise. This might also include setting up the structure of the company to ensure efficiency. The board, however, does not take part in the day to day running of the organization and thus serve another role of delegating the duties to the management. The board should also monitor, control functions and set up compensation plans for the executives. Last but definitely not least, the board helps in acquiring resources for the organization while ensuring continuity. With great power comes great responsibilities. The board must always use their powers for the right reason and do what is required of them by the shareholders of the company. The board must always carry out whatever they do in the full interest of the company, and in case there is a conflict of interest then the interests of the company should always come first. They must also carry out their task with due care minding the interests of both the shareholders and that of the employees. Other responsibilities of the board include acting as the court of appeal in case there are disputes, accessing the performance of the firm and enhancing the organization’s overall public image and brand name. 2.2 Institutional Investors An institutional investor is a person, persons or organization that pools money or provides funds to purchase securities, other investment assets, property or originate loans. They include financial institutions such as banks, Insurance companies, pension and hedge firms, investment advisors, commercial trusts and mutual funds. For a firm to grow, it requires resources inform of money which is provided by these institutional investors who get profits and interests as compensation for their troubles in taking the risk. The returns should exceed the fees and expenses of the investments and is compared against treasury bills which are considered to be risk-free. 2.2.1 Roles and Responsibilities of Institutional investors The best thing about institutional investors is the fact that they have expertise and knowledge to monitor the health and progress of the business. With this knowledge, they can provide the best advice the organization and also control the tendency of the management to put their interests first as opposed to the interests of the company. This active monitoring helps reduce misappropriation of funds and other forms of fraud (Gillan & Starks 2002, pp. 275-305) The institutional investors can act as a source of stability in hard times as was the case in the coal crisis in India recently. By offering additional funds, the institutional investors increase their stake and say in the company thus can push for better corporate governance. Another aspect related to this is the fact the institutional investors have a louder voice compared to minority investors. Most of the time when minority shareholders raise their concerns on corporate governance, they will rarely get addressed or at times get thwarted by the minorities which are not the case with institutional investors. 2.3 Other Corporate Governance Mechanism Other parties that are involved in corporate governance include the shareholders themselves who have the biggest interests as the main contributors of capital, the employees who get their incomes and job security from the good governance of the company, the government which gets taxes from the organization and the society as a whole which benefits from job creation, income distribution, corporate social responsibility activities of the firm among other benefits. Case Studies 3.1 Enron 3.1.1 Background The story of Enron was not only the largest bankruptcy case at the time but also the biggest audit failure. This was cited by many as the biggest corporate governance failure especially on the part of corporate boards and institutional investors. Enron was founded in 1985 by Kenneth Lay who also triples up as the chairman and chief executive officer. This was after merging Houston Natural gas and Intermonth. Other key people involved with Enron included: Jeffrey Skiing who was the C.O.O, Andrew Fastow who was the CFO and Rebecca Mark-Jusbasche who was the once a vice chairman. From 1995 to 2000 Enron was in fact named America most innovative company by Fortune. In the mid-2000s at its peak, the shares of Enron were trading at $90.75 per share. By the end of November 2001, they were trading at less than $1 per share. This was when the shareholders filed a $40 billion lawsuit. Enron filed for bankruptcy on December second, 2001 with assets worth $63.4 billion making it the biggest bankruptcy scandal ever in American history at the time. At this stage, the shares were going at $0.26 per share. 3.1.2 Failure of Corporate Governance in Enron Lack of due care and skill from the board was one of the reasons why Enron failed. As submitted by S.Watkins, Kenneth Lay who was Enron’s chair, could not get what was being said to him in regards to the company having questionable accounting practices. This also showed lack of proper communication between the board and the executives. This was further elaborated by Jeffrey McMahon, the new Enron’s president who said it was virtually impossible to challenge the authorities at Enron. A culture of intimidation had also developed at the company with the likes of Ms. Watkins fearing to lose their jobs. The board literally failed in its role of directing. This showed some sort of conflict of interests where they were more than happy to receive high compensations without asking serious questions which would have led to a decrease in their personal bonuses. The management who carried out the day to running of the Enron misrepresented information by allocating Enron’s debts to its dubious partners. This also showed the lack of proper internal controls at Enron (Carberry & Zajac 2017, p.15134). The corporate investors also failed to properly supervise the company and advice accordingly. For example, according to an economist at Enron, it was important it was all mind games as it was important for the employees, investors, and analysts to believe that the stock will bounce back. Other corporate investors such as the two trustees of Enron’s 401(k) plan failed in their duties as they did not warn the plan participants despite a memo detailing the accounting malpractices. The institutional investors also had all the knowledge and expertise but failed to utilize them- they just sat back and believed whatever they were told. 3.2 Reckitt Benckiser 3.2.1 Background Reckitt Benckiser is a British multinational that produces consumer goods to do with hygien, health, and home products. The name comes from the merging of a United Kingdom company Reckitt & Coleman and Benckiser NV that was based in the Netherlands back in 1999. The most well-known products worldwide include Dettol and Strepsil. Reckitt Benckiser acquired Korean Oxy brand in 2001 which had been using polyhexamethathylene guanidine (PHMG) in a product since 1996. In 2011, PHMG was banned by the Korea Centers for Disease Control and prevention after a published report showed a link to lung damage and report. Several reports also came out supporting the Korean report, and at the height of this in 2016 a coalition of consumer groups came out for the total boycott of Reckitt Benckiser products after it had been linked to more than 500 deaths from a BBC report. 3.2.1 Failure of Corporate Governance Mechanism in Reckitt Benckiser In the case of corporate governance, the management and directors fail as a whole in doing their duty of due care and skill when acquiring the Korean Oxy brand. They had a duty to investigate and know what is in the product. They put the company’s financial interests before the safety of the consumers. In addition to that, several attempts were made by the board and management to suppress investigations instead of taking corrective measures. Even though this was mostly a failure by the management and board, institutional investors also had the power to ask questions. Despite the various reports, they were silent till there was outrage in the mass media. 3.3 Satyam 3.3.1 Background Satyam was India’s fourth largest computer service company in India which has a population of over 1 billion. It was even listed on New York Stock exchange in 2001 with revenues exceeding $1 billion. The founder, M. Raju Ramalinga who was also the chair was a highly regarded person in the business often gracing all the major corporate events. In 2008 Satyam won the coveted prize of the Golden Peacock Award for compliance issues and Risk Management in corporate governance. In 2009, M. Raju confessed that the company’s accounts had been falsified by a massive $1.47 billion (Bhasin 2005). In the same year, Satyam stock was banned from trading on the New York Stock Exchange, and the Golden Peacock Award stripped off. Mr. Raju was later convicted together with other senior members. 3.3.2 Failure of Corporate Governance Mechanisms The board at Satyam failed in their primary duty of due care and monitoring the activity of the business as they did not notice the discrepancy. This was so evident that the first order was to appoint a temporary board. The board also put their interests first at the expense of the company for financial gains as confessed by their chairman. Despite the amount that falsified being that large, the auditors who were Price Water House Coopers failed in their auditing duties as they did not report anything amiss despite having all the expertise and experience. They were even fined $6 million by the US stock exchange for not following the code of conduct and auditing standards in when offering their services to Satyam. Institutional investors also failed to raise questions or properly examine the financial statements. Furthermore, with their expertise, they should have pushed for compliance with the corporate code of governance. 3.4 Worldcom 3.4.1 Background Before filing for bankruptcy protection in 2002, WorldCom was the second largest long distance phone company in the United States. With assets totaling over $104 billion, $30 billion in revenues and over 60,000 employees WorldCom filed for bankruptcy protection on July 1, 2002. The company later wrote down more than 75% of the total assets with over 17,000 of the workers losing their jobs. Over the period between 1999-2002, WorldCom had deliberately overstated their income before tax by over $7 billion which was the main reason behind the falling from grace to grass. It is currently known as Verizon business or Verizon enterprise solution after being acquired by Verizon Communications and is slowly rebuilding and being integrated into the parent company. 3.4.2 Failure of corporate Mechanism in WorldCom The biggest failure of WorldCom was the fact that the board had failed in its structuring role. Over the years, it had acquired a lot of companies with even one accountant confessing that they would get calls from people they did not even know existed. The departments were also not even properly structured for efficient working and were very decentralized. For example, the finance department was in Mississippi; the network operations were in Texas, the human resource in Florida and the legal department in Washington DC. This provided a challenge of communication as each department developed their ways of doing things. Apart from that, the difference in management style and the culture that was developed of not questioning seniors was a discouragement for employees who wanted to correct any issues that arose. In fact, there was a deliberate attempt by the management to hide vital financial issues as explained by Buddy Yates, the director of general accounting who was told he would be thrown outside the window in case he had shown the numbers to the auditors by Gene Morse, a senior manager. The employees also put their self-interests above the interest of the company as loyal employees were often compensated above the company’s approved salaries and bonus packages by Ebbers and Sullivan. The biggest failure was the board however as they failed terribly in all their roles and responsibilities including due care, supervision, bridging the gap between management and shareholder among others. In the case of institutional investors, they also failed terribly. No one raised a question on the structure of the firm or why the firm was highly decentralized. The increase in the salaries and compensation for the ‘loyal’ employees in the finance and accounting department should also have raised questions. Institutional investors should have also used their expertise to confirm the information that was being provided to them. Recommendations on Improving the Quality Of Corporate Governance Corporates Boards Should Meet Regularly: The corporates boards do not take part in the day to day running of the business, but they have a supervisory role. To carry out the tasks effectively, they need to meet more often (Christensen et al 2015, pp.133-164) Division of Responsibilities: The duties and responsibilities of a firm should be properly defined and allocated within an organization. This will help in reducing conflicts and also knowing who is liable and for what. This will also help enhance effective communication within an organization. Stronger Internal Controls: Controls in an organization should start from within for effective corporate governance. The controls include the supervision of seniors, physical controls, controls among others. Transparency: Corporate governance is all about transparency. Transparency does not mean revealing the companies but being honest in its activities. In case there is a loss it should be stated and corrective measures to correct it taken, Proper succession planning: One of the best attributes is that its life is not limited to that of the owners or directors. A proper succession plan should, therefore, be set in place to ensure that the values of the company that encourages proper corporate governance are passed from one generation to the other within the company Proper training of directors: The directors of the company are the eyes of the society and shareholders in the business. They need to be properly trained to carry out their tasks effectively as is required of them. Another option is to select a board of directors that is highly qualified in the different fields that the business is engaged in. Independent members increase: Any organization that is interested in improving its corporate governance should try as much as possible to increase the list of independent parties in its running. The independent parties with no direct relation can view the business from a better neutral point (Klapper & Love 2002, pp.703-728) Conclusion It is crystal clear from the discussions above that the corporate governance mechanisms such as corporate boards and institutional boards are the backbone for the survival of any company. From the cases discussed above, we can see the consequences of bad corporate governance and the fact that it does not matter how big the company is. In addition to that, there is a failure the many bodies that are meant to supervise corporate governance. Corporate governance board needs to do more than just take the words of corporations. It is an understatement to say that corporate governance should be a priority, it should actually be a prerequisite (Lebedeva et al 2016).
References Bhasin, M.L., 2015. Corporate accounting fraud: A case study of Satyam Computers Limited. Carberry, E. and Zajac, E., 2017, January. How US Corporations Changed Executive Compensation after Enron: Substance and Symbol. In Academy of Management Proceedings (Vol. 2017, No. 1, p. 15134). Academy of Management Christensen, J., Kent, P., Routledge, J. and Stewart, J., 2015. Do corporate governance recommendations improve the performance and accountability of small listed companies?. Accounting & Finance, 55(1), pp.133-164. Dimopoulos, T. and Wagner, H.F., 2016. Corporate Governance and CEO Turnover Decisions. Farrar, J., 2008. Corporate governance: theories, principles and practice. Oxford University Press Gillan, S.L. and Starks, L.T., 2000. Corporate governance proposals and shareholder activism: The role of institutional investors. Journal of financial Economics, 57(2), pp.275-305. Ilya, P., 2015. inc. [Online] Available at: http://www.inc.com/ilya-pozin/14-highly-effective-ways-to-motivate-employees.html [Accessed 27 January 2018].
Klapper, L.F. and Love, I., 2004. Corporate governance, investor protection, and performance in emerging markets. Journal of corporate Finance, 10(5), pp.703-728. Lebedeva, T.E., Akhmetshin, E.M., Dzagoyeva, M.R., Kobersy, I.S. and Ikoev, S.K., 2016. Corporate governance issues and control in conditions of unstable capital risk. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 6(1S). Solomon, J., 2007. Corporate governance and accountability. John Wiley & Sons. Tricker, R.B. and Tricker, R.I., 2015. Corporate governance: Principles, policies, and practices. Oxford University Press, USA. Vitez, O., 2017. Bizfluent. [Online] Available at: https://bizfluent.com/facts-6884459-importance-corporate governance.html [Accessed 21 February 2018].
Hi, we have the scientific journal: https://journal.scsa.ge/
we are submitting it to google scholar manually already for one year, but it is not indexed still in scholar.
What can we do?
Hi, how to upload my thesis into google or share
hello, how to upload my thesis into google or share .
An impressive share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a friend who was doing a little research on this. And he actually bought me breakfast simply because I found it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending time to discuss this subject here on your web site.
I am interested to publish my articles on Goodle scholar but I have know clear idea about the steps to follow. Please link me
Thanks, Thomas your article help me to explore google scholar differently thanks a lots.
Thanks, friend. I wanted to publish my marketing papers over there. Your article helped. Thanks again.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Leave a comment

Creating and Managing Google Scholar Profiles
These instructions were adapted under a CC-BY 4.0 license from UC Davis College of Biological Sciences' Create and Manage a Google Scholar Profile.
Step 1: Create your basic profile
- Log on to scholar.google.com and click the “My Profile” link at the top of the page to get your account setup started.
- On the first screen, add your affiliation information and university email address so Google Scholar can confirm your account. Add keywords that are relevant to your research interests so others can find you when browsing a subject area. Provide a link to your faculty page.
- Click “Next Step,” and--that’s it! Your basic profile is done. Now, let’s add some publications to it.
Step 2: Add publications
Google has likely already been indexing your work for some time now as part of their mission as a scholarly search engine. However, keep in mind that Google Scholar does not index everything .
Google Scholar will provide you with a list of publications they think belong to you. You’ll need to read through the list of publications that it suggests as yours and select which ones you want to add to your profile.
Beware--if you have a common name, it’s likely there’s some publications in this list that don’t belong to you. And there’s also possibly content that you don’t want on your profile because it’s not a scholarly article, or is not representative of your current research path, and so on.
Read through the publications list and deselect any that you do not want to add to your profile (like the below newsletter item that Google Scholar thinks is a scholarly article).
Click the grey “Add” button at the top of your profile.

Confirm you want Google to automatically add new publications to your profile in the future. If you’ve got a very common name, note that this might add publications you didn’t author to your profile. But if you’re a prolific author, it can be worth it for the time it saves you approving new articles every month.
Your profile is now almost complete! Two more steps: add a photo by clicking the “Change Photo” link on your profile homepage, and set your private profile to “Public.”
Step 3: Make your profile public
Your profile is private if you’ve just created it. Change your profile visibility by clicking the link to "Make it public" under your name and title. You can also make your profile public by clicking the Edit button and selecting the box next to the words "Make my profile public."
Step 4: Add missing articles
You might have articles that Google Scholar didn’t automatically add to your profile. If that’s the case, you’ll need to add it manually.
Click the “Add” icon button (looks like a plus) in the grey toolbar within your profile.
Select "Add articles manually."
Complete the form for each new paper to add to your profile. Include as much information as possible so that Google Scholar can find citations to yoru work.
Click "Save" after filling out the form and repeat as needed.
Step 5: Clean up your Google Scholar Profile data
Thanks to Google Scholar Profiles’ “auto add” functionality, your Profile might include some articles you didn’t author.
If that’s the case, you can remove them in one of two ways:
- Click on the title of each offending article to get to the article’s page, and then clicking the “Delete” button a the top of the page.
- From the main Profile page, tick the boxes next to each incorrect article and click the “Delete” button in the top grey bar.
Google Scholar will automatically populate your profile (to the best of its abilities).
- Last Updated: Feb 13, 2024 3:54 PM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.wm.edu/GSprofiles

Scholarly Publications: Creating a Google Scholar Citations Account: Adding Publications
- Getting Started
- Adding Publications

Adding publications to your Google Scholar Citations profile

Suggested Guides
- Scholarly Publications: Creating and Maintaining a ResearchGate Profile by Nicholas Cummins Last Updated Apr 4, 2023 1787 views this year
- Scholarly Publications: Creating and Maintaining a SSRN Account by Nicholas Cummins Last Updated Sep 28, 2021 587 views this year
- Scholarly Publications: Posting Journal Articles Online by Nicholas Cummins Last Updated May 20, 2021 111 views this year
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Last Updated: Aug 29, 2023 8:33 PM
- URL: https://darden.libguides.com/googlescholarcitations
Darden Camp Library, First Floor, 100 Darden Blvd., Darden Business School, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA 22903 Mailing Address: Darden Camp Library, PO Box 6550, Charlottesville, VA 22906-6550 Google Map with Darden Library Email: [email protected] Phone: (434) 924-7321 FAX: (434) 924-3533
Darden Portal | Darden Homepage | UVA Homepage
Manage Your Research Identity: How to add missing publications to a Google Scholar profile?
- Why manage your researcher identity?
- Researcher ID options
- What is ORCID?
- Why get an ORCID?
- How to create an ORCID iD?
- How to develop an ORCID iD?
- How to add publications to an ORCID profile?
- Can I delegate ORCID maintenance to someone else?
- Helpful tips
- What is Google Scholar profile?
- Why get a Google Scholar profile?
- How to sign up for a Google Scholar profile?
- How to add missing publications to a Google Scholar profile?
- What is Scopus Author ID?
- How to find an author's Scopus ID?
- How to merge multiple Scopus IDs?
- How to import Scopus Author ID and publications into an ORCID profile?
- How can the library help?
- Help us improve, take this survey
To add missing publications to your profile:
Go to google scholar page and click on 'my profile' at the top left corner of the window..

On your Google Scholar Citations profile, click on the '+' icon above your list of articles. There are three ways to add articles from here. 'Add article groups' and 'Add articles' offer suggestions based on your profile and you can check the articles you want to add to your profile. 'Add article manually' allows you to input the citation information for articles that don't appear in the automatic options.

To add articles manually, you need to add the citation information for each document. Select the type of publication from the options given and fill out the form with the needed information.

In addition to adding publications to your profile, there are also options for you to merge, delete and export records on your Google Scholar profile.
Add / Reorder
- << Previous: How to sign up for a Google Scholar profile?
- Next: Helpful tips >>
- Last Updated: Mar 26, 2024 1:54 PM
- URL: https://aub.edu.lb.libguides.com/researchID
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Google Scholar: the ultimate guide

What is Google Scholar?
Why is google scholar better than google for finding research papers, the google scholar search results page, the first two lines: core bibliographic information, quick full text-access options, "cited by" count and other useful links, tips for searching google scholar, 1. google scholar searches are not case sensitive, 2. use keywords instead of full sentences, 3. use quotes to search for an exact match, 3. add the year to the search phrase to get articles published in a particular year, 4. use the side bar controls to adjust your search result, 5. use boolean operator to better control your searches, google scholar advanced search interface, customizing search preferences and options, using the "my library" feature in google scholar, the scope and limitations of google scholar, alternatives to google scholar, country-specific google scholar sites, frequently asked questions about google scholar, related articles.
Google Scholar (GS) is a free academic search engine that can be thought of as the academic version of Google. Rather than searching all of the indexed information on the web, it searches repositories of:
- universities
- scholarly websites
This is generally a smaller subset of the pool that Google searches. It's all done automatically, but most of the search results tend to be reliable scholarly sources.
However, Google is typically less careful about what it includes in search results than more curated, subscription-based academic databases like Scopus and Web of Science . As a result, it is important to take some time to assess the credibility of the resources linked through Google Scholar.
➡️ Take a look at our guide on the best academic databases .
One advantage of using Google Scholar is that the interface is comforting and familiar to anyone who uses Google. This lowers the learning curve of finding scholarly information .
There are a number of useful differences from a regular Google search. Google Scholar allows you to:
- copy a formatted citation in different styles including MLA and APA
- export bibliographic data (BibTeX, RIS) to use with reference management software
- explore other works have cited the listed work
- easily find full text versions of the article
Although it is free to search in Google Scholar, most of the content is not freely available. Google does its best to find copies of restricted articles in public repositories. If you are at an academic or research institution, you can also set up a library connection that allows you to see items that are available through your institution.
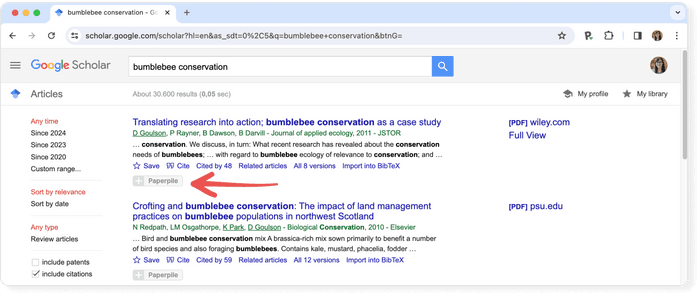
The Google Scholar results page differs from the Google results page in a few key ways. The search result page is, however, different and it is worth being familiar with the different pieces of information that are shown. Let's have a look at the results for the search term "machine learning.”
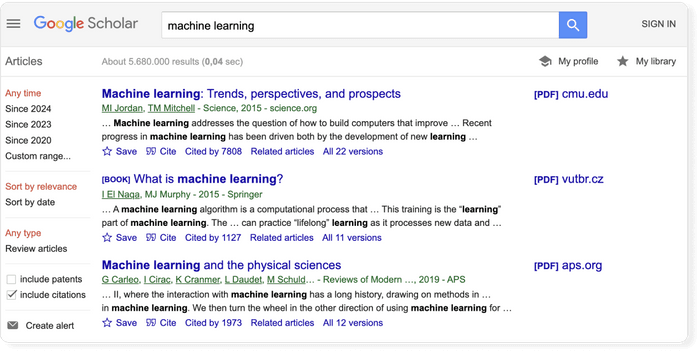
- The first line of each result provides the title of the document (e.g. of an article, book, chapter, or report).
- The second line provides the bibliographic information about the document, in order: the author(s), the journal or book it appears in, the year of publication, and the publisher.
Clicking on the title link will bring you to the publisher’s page where you may be able to access more information about the document. This includes the abstract and options to download the PDF.

To the far right of the entry are more direct options for obtaining the full text of the document. In this example, Google has also located a publicly available PDF of the document hosted at umich.edu . Note, that it's not guaranteed that it is the version of the article that was finally published in the journal.
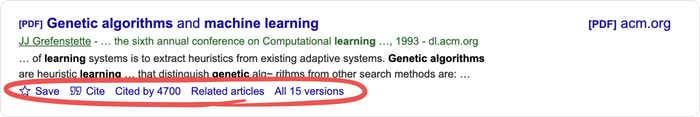
Below the text snippet/abstract you can find a number of useful links.
- Cited by : the cited by link will show other articles that have cited this resource. That is a super useful feature that can help you in many ways. First, it is a good way to track the more recent research that has referenced this article, and second the fact that other researches cited this document lends greater credibility to it. But be aware that there is a lag in publication type. Therefore, an article published in 2017 will not have an extensive number of cited by results. It takes a minimum of 6 months for most articles to get published, so even if an article was using the source, the more recent article has not been published yet.
- Versions : this link will display other versions of the article or other databases where the article may be found, some of which may offer free access to the article.
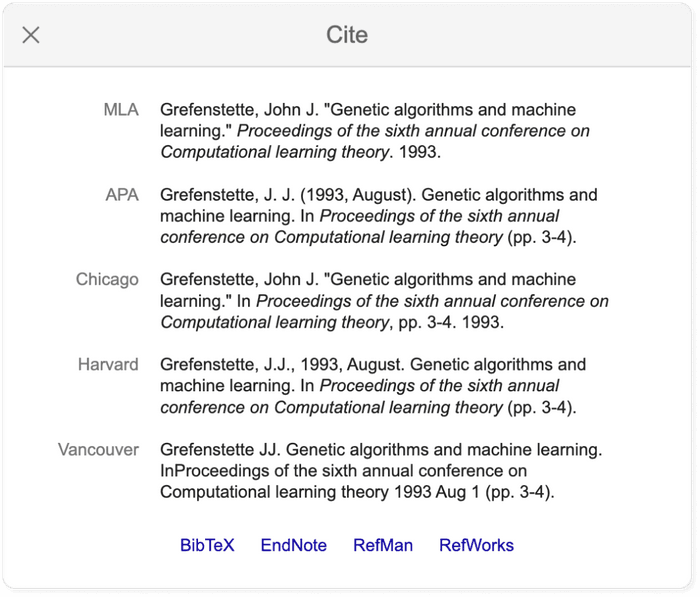
- Quotation mark icon : this will display a popup with commonly used citation formats such as MLA, APA, Chicago, Harvard, and Vancouver that may be copied and pasted. Note, however, that the Google Scholar citation data is sometimes incomplete and so it is often a good idea to check this data at the source. The "cite" popup also includes links for exporting the citation data as BibTeX or RIS files that any major reference manager can import.
Pro tip: Use a reference manager like Paperpile to keep track of all your sources. Paperpile integrates with Google Scholar and many popular academic research engines and databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons and later cite them in thousands of citation styles:
Although Google Scholar limits each search to a maximum of 1,000 results , it's still too much to explore, and you need an effective way of locating the relevant articles. Here’s a list of pro tips that will help you save time and search more effectively.
You don’t need to worry about case sensitivity when you’re using Google scholar. In other words, a search for "Machine Learning" will produce the same results as a search for "machine learning.”
Let's say your research topic is about self driving cars. For a regular Google search we might enter something like " what is the current state of the technology used for self driving cars ". In Google Scholar, you will see less than ideal results for this query .
The trick is to build a list of keywords and perform searches for them like self-driving cars, autonomous vehicles, or driverless cars. Google Scholar will assist you on that: if you start typing in the search field you will see related queries suggested by Scholar!
If you put your search phrase into quotes you can search for exact matches of that phrase in the title and the body text of the document. Without quotes, Google Scholar will treat each word separately.
This means that if you search national parks , the words will not necessarily appear together. Grouped words and exact phrases should be enclosed in quotation marks.
A search using “self-driving cars 2015,” for example, will return articles or books published in 2015.
Using the options in the left hand panel you can further restrict the search results by limiting the years covered by the search, the inclusion or exclude of patents, and you can sort the results by relevance or by date.
Searches are not case sensitive, however, there are a number of Boolean operators you can use to control the search and these must be capitalized.
- AND requires both of the words or phrases on either side to be somewhere in the record.
- NOT can be placed in front of a word or phrases to exclude results which include them.
- OR will give equal weight to results which match just one of the words or phrases on either side.
➡️ Read more about how to efficiently search online databases for academic research .
In case you got overwhelmed by the above options, here’s some illustrative examples:
Tip: Use the advanced search features in Google Scholar to narrow down your search results.
You can gain even more fine-grained control over your search by using the advanced search feature. This feature is available by clicking on the hamburger menu in the upper left and selecting the "Advanced search" menu item.

Adjusting the Google Scholar settings is not necessary for getting good results, but offers some additional customization, including the ability to enable the above-mentioned library integrations.
The settings menu is found in the hamburger menu located in the top left of the Google Scholar page. The settings are divided into five sections:
- Collections to search: by default Google scholar searches articles and includes patents, but this default can be changed if you are not interested in patents or if you wish to search case law instead.
- Bibliographic manager: you can export relevant citation data via the “Bibliography manager” subsection.
- Languages: if you wish for results to return only articles written in a specific subset of languages, you can define that here.
- Library links: as noted, Google Scholar allows you to get the Full Text of articles through your institution’s subscriptions, where available. Search for, and add, your institution here to have the relevant link included in your search results.
- Button: the Scholar Button is a Chrome extension which adds a dropdown search box to your toolbar. This allows you to search Google Scholar from any website. Moreover, if you have any text selected on the page and then click the button it will display results from a search on those words when clicked.
When signed in, Google Scholar adds some simple tools for keeping track of and organizing the articles you find. These can be useful if you are not using a full academic reference manager.
All the search results include a “save” button at the end of the bottom row of links, clicking this will add it to your "My Library".
To help you provide some structure, you can create and apply labels to the items in your library. Appended labels will appear at the end of the article titles. For example, the following article has been assigned a “RNA” label:
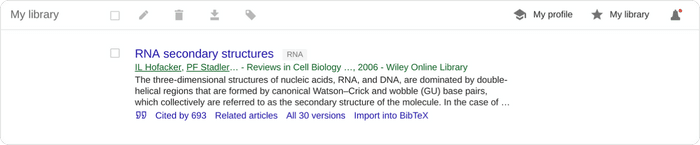
Within your Google Scholar library, you can also edit the metadata associated with titles. This will often be necessary as Google Scholar citation data is often faulty.
There is no official statement about how big the Scholar search index is, but unofficial estimates are in the range of about 160 million , and it is supposed to continue to grow by several million each year.
Yet, Google Scholar does not return all resources that you may get in search at you local library catalog. For example, a library database could return podcasts, videos, articles, statistics, or special collections. For now, Google Scholar has only the following publication types:
- Journal articles : articles published in journals. It's a mixture of articles from peer reviewed journals, predatory journals and pre-print archives.
- Books : links to the Google limited version of the text, when possible.
- Book chapters : chapters within a book, sometimes they are also electronically available.
- Book reviews : reviews of books, but it is not always apparent that it is a review from the search result.
- Conference proceedings : papers written as part of a conference, typically used as part of presentation at the conference.
- Court opinions .
- Patents : Google Scholar only searches patents if the option is selected in the search settings described above.
The information in Google Scholar is not cataloged by professionals. The quality of the metadata will depend heavily on the source that Google Scholar is pulling the information from. This is a much different process to how information is collected and indexed in scholarly databases such as Scopus or Web of Science .
➡️ Visit our list of the best academic databases .
Google Scholar is by far the most frequently used academic search engine , but it is not the only one. Other academic search engines include:
- Science.gov
- Semantic Scholar
- scholar.google.fr : Sur les épaules d'un géant
- scholar.google.es (Google Académico): A hombros de gigantes
- scholar.google.pt (Google Académico): Sobre os ombros de gigantes
- scholar.google.de : Auf den Schultern von Riesen
➡️ Once you’ve found some research, it’s time to read it. Take a look at our guide on how to read a scientific paper .
No. Google Scholar is a bibliographic search engine rather than a bibliographic database. In order to qualify as a database Google Scholar would need to have stable identifiers for its records.
No. Google Scholar is an academic search engine, but the records found in Google Scholar are scholarly sources.
No. Google Scholar collects research papers from all over the web, including grey literature and non-peer reviewed papers and reports.
Google Scholar does not provide any full text content itself, but links to the full text article on the publisher page, which can either be open access or paywalled content. Google Scholar tries to provide links to free versions, when possible.
The easiest way to access Google scholar is by using The Google Scholar Button. This is a browser extension that allows you easily access Google Scholar from any web page. You can install it from the Chrome Webstore .

Faculty and researchers : We want to hear from you! We are launching a survey to learn more about your library collection needs for teaching, learning, and research. If you would like to participate, please complete the survey by May 17, 2024. Thank you for your participation!

- University of Massachusetts Lowell
- University Libraries
Google Scholar Search Strategies
- About Google Scholar
- Manage Settings
- Enable My Library
- Google Scholar Library
- Cite from Google Scholar
- Tracking Citations
- Add Articles Manually
- Refine your Profile Settings

Using Google Scholar for Research
Google Scholar is a powerful tool for researchers and students alike to access peer-reviewed papers. With Scholar, you are able to not only search for an article, author or journal of interest, you can also save and organize these articles, create email alerts, export citations and more. Below you will find some basic search tips that will prove useful.
This page also includes information on Google Scholar Library - a resource that allows you to save, organize and manage citations - as well as information on citing a paper on Google Scholar.
Search Tips
- Locate Full Text
- Sort by Date
- Related Articles
- Court Opinions
- Email Alerts
- Advanced Search
Abstracts are freely available for most of the articles and UMass Lowell holds many subscriptions to journals and online resources. The first step is make sure you are affiliated with the UML Library on and off campus by Managing your Settings, under Library Links.
When searching in Google Scholar here are a few things to try to get full text:
- click a library link, e.g., "Full-text @ UML Library", to the right of the search result;
- click a link labeled [PDF] to the right of the search result;
- click "All versions" under the search result and check out the alternative sources;
- click "More" under the search result to see if there's an option for full-text;
- click "Related articles" or "Cited by" under the search result to explore similar articles.

Your search results are normally sorted by relevance, not by date. To find newer articles, try the following options in the left sidebar:

- click "Sort by date" to show just the new additions, sorted by date; If you use this feature a lot, you may also find it useful to setup email alerts to have new results automatically sent to you.
- click the envelope icon to have new results periodically delivered by email.
Note: On smaller screens that don't show the sidebar, these options are available in the dropdown menu labeled "Any time" right below the search button .
The Related Articles option under the search result can be a useful tool when performing research on a specific topic.
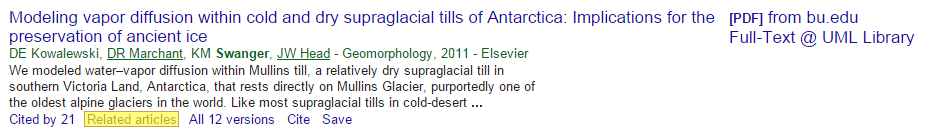
After clicking you will see articles from the same authors and with the same keywords.

You can select the jurisdiction from either the search results page or the home page as well; simply click "select courts". You can also refine your search by state courts or federal courts.
To quickly search a frequently used selection of courts, bookmark a search results page with the desired selection.
How do I sign up for email alerts?
Do a search for the topic of interest, e.g., "M Theory"; click the envelope icon in the sidebar of the search results page; enter your email address, and click " Create alert ". Google will periodically email you newly published papers that match your search criteria. You can use any email address for this; it does not need to be a Google Account.
If you want to get alerts from new articles published in a specific journal; type in the name of this journal in the search bar and create an alert like you would a keyword.
How do I get notified of new papers published by my colleagues, advisors or professors?

First, do a search for your their name, and see if they have a Citations profile. If they do, click on it, and click the "Follow new articles" link in the right sidebar under the search box.
If they don't have a profile, do a search by author, e.g., [author:s-hawking], and click on the mighty envelope in the left sidebar of the search results page. If you find that several different people share the same name, you may need to add co-author names or topical keywords to limit results to the author you wish to follow.
How do I change my alerts?
If you created alerts using a Google account, you can manage them all on the "Alerts" page .

From here you can create, edit or delete alerts. Select cancel under the actions column to unsubscribe from an alert.

This will pop-open the advanced search menu

Here you can search specific words/phrases as well as for author, title and journal. You can also limit your search results by date.
- << Previous: Enable My Library
- Next: Google Scholar Library >>
- Last Updated: Feb 14, 2024 2:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uml.edu/googlescholar
Indexing Policies
- Other Policies
Publisher Support
Google Scholar can boost the worldwide visibility and accessibility of your content. We work with publishers of scholarly information to index peer-reviewed papers, theses, preprints, abstracts, and technical reports from all disciplines of research and make them searchable on Google and Google Scholar.
This section provides policy and technical information for scholarly publishers and societies. Detailed technical inclusion guidelines for webmasters can be found here .
Multiple versions of a work are grouped to improve its ranking
In many research areas versions of a work may appear as preprints and conference papers before being published as a journal article. These preliminary versions of a work are often cited in addition to the authoritative journal version. The number of citations to a particular work is an important part of determining its rank in the Google Scholar search results. Grouping versions allows us to collect all citations to all versions of a work. In practice, this can significantly improve the position of an article in the search results.
Publisher's full-text, if indexed, is the primary version
When multiple versions of a work are indexed, we select the full and authoritative text from the publisher as the primary version. We can only do this if we are able to successfully identify, crawl and process the full text of the publisher's version.
Publishers have control over access to their articles
We work with publishers to preserve their control over access to their content and only cache articles and papers that don't have access restrictions. Publishers can help us by identifying the regions of their sites that have access restrictions.
Google users must see at least the complete abstract or the first full page
This is a necessary component of our indexing program. For papers with access restrictions, all users clicking on search results must see at least the full author-written abstract or the first full page of the article without requiring to login or click on additional links.
We will respond to complaints regarding copyright infringement
Our policy is to respond to all notices of alleged copyright infringement that comply with the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. For directions and more information, please click here .
Subscriber Links Policies
Google's use of electronic holdings information
We will use electronic holdings information for generating per article links in our search results to publisher servers. We will not share this information with third parties or use it for marketing purposes.
Electronic holdings usage information
We will not share information with third parties on the usage of your electronic holdings or on aggregate usage based on institutional characteristics or profiles.
Publishers can withdraw electronic holdings information
Once the electronic holdings information is no longer available to our search robots, we will stop using it within 30 days.
General Questions
We would love to work with you. As noted in the policies, an abstract (at least) of each work must be available to non-subscribers who come from Google and Google Scholar. Please configure your website according to our technical inclusion guidelines .
Maybe. Google Scholar indexes mostly scholarly articles. For textbooks and monographs, we recommend Google Book Search. Google Scholar automatically includes scholarly works from Google Book Search.
Since users click through to your website, your web server logs should have all the usage statistics.
It is our policy to respond to notices of alleged infringement that comply with the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. For directions and more information, please click here .
Technical Questions
Yes. We can index PDF articles as long as they're searchable and as long as their size doesn't exceed 5MB. For larger documents and for scanned images that require OCR, we recommend Google Book Search.
Open the file in Adobe Acrobat Reader. Click 'Find' (look for the binocular icon), and confirm that you can search for and find several words on the page.
Alas, we can't. We can index only one file per article at the moment.
Refer to Google webmaster help .
Add the following robots meta-tag to the <head> section of your webpage:
If we're showing 'Cached' links for your restricted-access content, please email us specific examples of where the links appear. Display of cached links for restricted-access content isn't intentional, but may happen if our methodical crawlers accidentally discover a forgotten alternative interface to your content. You'll need to tell us of all such interfaces, because crawlers can go places where you least expect them. Please email us and we'll look into it.
If you believe another site is infringing your copyright, please see our directions on the DMCA process .
If we're showing unwanted Quick Abstracts for your restricted-access content, please email us specific examples of where the abstracts appear. Display of unwanted Quick Abstracts for restricted-access content isn't intentional, but may happen if our methodical crawlers accidentally discover a forgotten alternative interface to your content. You'll need to tell us of all such interfaces, because crawlers can go places where you least expect them. Please email us and we'll look into it.
Indeed you can. Our indexing algorithms automatically extract bibliographic data, citations and other information from articles and use it for ranking purposes. Providing authoritative metadata about your articles can help facilitate this and can increase the likelihood of identifying all the citations to your articles. We strongly recommend this approach. Please refer to the following technical inclusion guidelines for the details of how to implement it.
Yes. Gaps in coverage are certainly not intentional; but they could be caused by a number of different technical issues in the automatic processing of your website by our search robots. The troubleshooting section in our technical inclusion guidelines describes ways to identify and fix common coverage issues. We encourage you to take a look.
- Privacy & Terms
Exploring the Importance of Google Scholar Citations for Researchers
What Are Google Scholar Citations?
Google Scholar Citations are one way to gauge a research paper’s influence. They are determined by tracking how frequently a particular paper is cited in other academic works.

Citations are distinct from references in that the former are the sources acknowledged inside a publication, while the latter is how other writers acknowledge a work.
What Are the Benefits of Google Scholar Citations?
Tracking research effect and influence, finding pertinent research and collaborators, building academic reputation and credibility, and influencing funding and tenure decisions are just a few advantages of using Google Scholar citations.
Google Scholar indexes full-text journal articles , technical reports, preprints, theses, books, and other publications and lets users search for digital or hard versions of articles online or in libraries.

Why Are Google Scholar Citations Important for Researchers?
Researchers should value Google Scholar citations because they can gauge their work’s effect and influence, find relevant studies and collaborators, build academic credibility, and influence choices about financing and tenure.
Maintaining a record of citations aids scholars in staying current, participating in the broader academic discourse, and locating possible partners.
How Do You Boost Your Google Scholar Citations?
Make your study more visible and accessible if you want to increase the number of citations it receives from Google Scholar. Ensure Google Scholar correctly indexes your papers by setting up a profile and confirming your authorship.
To reach a wider audience, collaborate with other scholars, present at conferences, and post your work on academic networks. Ensure your articles are optimized with pertinent keywords, and consider publishing them in an open-access manner to boost your chances of being mentioned.
How Do I Maximize Google Scholar?
Google Scholar citations and maximize your impact by creating a thorough and current profile, confirming your authorship and ensuring your citation counts are correct. Add co-authors and claim and merge duplicate profiles to improve the visibility of your collaboration.
Update your publication list frequently and use keywords and abstracts to improve discoverability. Use Google Scholar’s citation monitoring and alerts to keep tabs on relevant research and track the influence of your work .
To sum up, Google Scholar citations are an essential indicator for academics that show the reputation, impact, and influence of their work. Citations are necessary, but so are careful use and interpretation.
Scholars should prioritize quality over quantity, consider the context of citations, and refrain from manipulation. You can use citations to promote academic integrity and quality by doing this.
https://unimelb.libguides.com/researcher_profiles/googlescholar#:~:text=Considerations%20and%20Risks-,What%20is%20Google%20Scholar%20Citations%3F,automatically%20or%20update%20them%20yourself. https://libguides.tulane.edu/citation_tools/google_scholar
Header Title image: Exploring the Importance of Google Scholar Citations for Researchers
Image briefing: 1. Background Image:
- A clean and modern academic setting, such as a well-organized study desk with a laptop open to Google Scholar, stacks of research papers , and a few open books.
- Alternatively, a visual representation of a researcher’s digital workspace with charts and graphs depicting citation metrics.
- Main Visual Elements:
- A prominent Google Scholar logo, either in the center or subtly integrated into the background.
- Icons or graphics representing various aspects of citations, such as upward-trending graphs, citation marks (quotation marks) , or a cluster of books and academic journals.
- Title Text:
- Place the title “Exploring the Importance of Google Scholar Citations for Researchers” prominently across the top or center of the image.
- Use a professional and modern font, with a color that contrasts well with the background for readability (e.g., white text on a dark background or vice versa).
- Supporting Text:
- Include a brief tagline or subtitle under the main title, such as “Enhance your academic impact and visibility with effective citation management.”
- Use a slightly smaller font size for the supporting text to distinguish it from the main title.
- Visual Cues:
- Incorporate subtle arrows or lines pointing to different elements within the image, guiding the viewer’s eye from the title to key aspects like the Google Scholar logo and citation metrics.
- Use icons representing citation metrics, such as a citation graph or a list of citations, to visually emphasize the topic.
- Color Scheme:
- Use a color palette that aligns with academic and professional themes, such as blues, grays, and whites, ensuring a clean and trustworthy look.
- Ensure the colors used for text and icons stand out against the background for maximum readability.
- Branding Elements:
- Include a small, unobtrusive ManuscriptEdit logo or watermark in one of the corners to subtly brand the image without distracting from the main content.
- Ensure the branding aligns with the overall aesthetic and color scheme of the image.
- Call-to-Action (Optional):
- If space allows, add a small call-to-action at the bottom of the image, such as “Learn more in our latest blog post!” with an arrow or icon indicating further engagement.
Image References:
https://www.greyb.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/featured-images-1.png
https://libapps-ca.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/142800/images/Google_Scholar_Profile.png
!Google Scholar Infographic reference image: https://img.freepik.com/premium-vector/risk-management-infographic_23-2148607942.jpg?w=826
- Familiar Interface : Google Scholar’s simple and intuitive design makes it easy to use, similar to regular Google searches.
- Diverse Materials : It allows users to find a wide variety of scholarly materials, including articles, theses, books, and conference proceedings.
- Related Articles and Citations : Google Scholar provides related articles, citation counts, and information on who cited a particular article.
- Library Links : It can display links to articles and books available through university libraries.
- Save Feature : Users can save citations and articles for later reading.
Remember that Google Scholar is a powerful tool for researchers, offering both simplicity and depth in accessing scholarly literature 1 2
1scholar.google.com 2scholar.google.com 3drupal.org 4scholar.google.com.ec
Exploring the Importance of Google Scholar Citations for Researchers Google Scholar Citations play a crucial role in the research community, providing a valuable platform for researchers to showcase their work and enhance their visibility. By accurately tracking citations, Google Scholar helps researchers measure the impact and reach of their publications, enabling them to establish their credibility and influence in their respective fields. Moreover, Google Scholar Citations also facilitate collaborations and networking opportunities among researchers with similar research interests, fostering a dynamic and interconnected scholarly community. Don’t miss out on the benefits that Google Scholar Citations can offer to elevate your research profile.
Related Posts
Increasing visibility of research paper using simple seo tricks.
What is SEO? Search Engine Optimization (SEO) refers to the process of ensuring that your manuscript is found by search engines such as Google or PubMed. After all, you’ve spent a lot of time on your research and would want to share your findings with those interested. For this, you need to ensure that readers […]
HOW TO REUSE OLD ACADEMIC PAPERS
While pursuing a career or academic research and publication, it is only natural to expect academicians to develop on their previous works or pursue a set line of investigation. More often than not, research or experimental investigation spans over years and researchers may indulge in multiple publications on the matter which builds on their previous […]
Most Common Reasons for Journal Editors Rejecting Paper
Rejection is unpleasant for everyone since it is demotivating. Even top scientists have encountered rejection in their carrier. Academic publishing, on the other hand, is rife with rejection. Any script could be rejected for multiple causes, which could be grouped into two categories: technical and editorial. Technical reasons Fragmented information, like narrow sample size or […]
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn how to easily add your published research paper to Google Scholar in just a few simple steps! Watch this tutorial to ensure your work gets the recognit...
To add publications, click on the + button and select from the list of the following options: a) Add article groups: Articles will be grouped together by name. Use the check box to select and add a group of articles under your name. b) Add articles: Lists articles individually. Tick the check box to select and add the articles you have authored.
Questions. Google Scholar Profiles. Google Scholar Profiles provide a simple way for authors to showcase their academic publications. You can check who is citing your articles, graph citations over time, and compute several citation metrics. You can also make your profile public, so that it may appear in Google Scholar results when people ...
To add a paper to Google Scholar, start by signing into your Google account. Go to 'My Citations' page, click the 'Add Article' button, and enter paper details. Enter the details of your paper including its title, author names, journal name, and year published. Finally hit submit for it to be added.
When adding articles after Google Scholar profile set-up, you have the option to add articles manually. Select the third option on the left navigation panel "Add article manually". You will see a screen similar to this. Start by selecting the type of resource first (journal, conference, book, thesis, etc). ...
Here are the steps: Go to this page to start adding a document manually. Choose the type of document (journal, conference, chapter, book, thesis, patent, court case or other). Fill in all the details about your article (title, author (s), publication date (s), volume, publisher, institution). Click save and if you filled in everything correctly ...
Step 3: Click on the "Add article" button. On the top menu bar of the Google Scholar homepage, you will find a button labeled "Add article." Click on this button to proceed. Step 4: Fill in the ...
Search Help. Get the most out of Google Scholar with some helpful tips on searches, email alerts, citation export, and more. Your search results are normally sorted by relevance, not by date. To find newer articles, try the following options in the left sidebar: click the envelope icon to have new results periodically delivered by email.
Do you want to showcase your publications on Google Scholar and ORCID, two popular platforms for researchers and academics? Watch this video to learn how to add your publications to both sites and ...
Log on to scholar.google.com and click the "My Profile" link at the top of the page to get your account setup started.; On the first screen, add your affiliation information and university email address so Google Scholar can confirm your account. Add keywords that are relevant to your research interests so others can find you when browsing a subject area.
To add publications, click on the + button and select from the list of the following options: c) Add article manually: If the article cannot be found you can create an entry manually. First choose the publication type at the top of the form then fill in as many fields as possible. Then, you can merge the manually-added article with the preprint.
There are three ways to add articles from here. Add article groups and Add articles offer suggestions based on your profile.Add article manually allows you to input the citation information for articles that don't appear in the automatic options. In the Add article groups option, check the box(es) next to the group(s) containing your articles. In the Add articles option, check the boxes the ...
This tutorial is primarily for all who would like to create a Google Scholar Profile to showcase their publications on online platforms. This video systemati...
On your Google Scholar Citations profile, click on the '+' icon above your list of articles. There are three ways to add articles from here. 'Add article groups' and 'Add articles' offer suggestions based on your profile and you can check the articles you want to add to your profile. 'Add article manually' allows you to input the citation ...
Google Scholar searches are not case sensitive. 2. Use keywords instead of full sentences. 3. Use quotes to search for an exact match. 3. Add the year to the search phrase to get articles published in a particular year. 4. Use the side bar controls to adjust your search result.
The first step is make sure you are affiliated with the UML Library on and off campus by Managing your Settings, under Library Links. When searching in Google Scholar here are a few things to try to get full text: click a library link, e.g., "Full-text @ UML Library", to the right of the search result; click a link labeled [PDF] to the right of ...
The Neotia University. Open google scholar and then login with your ID and password. There is a option with + symbol. Click on that and then click on add mannually and then fill about your ...
It can also help to clarify that a source you are considering really meets your needs. 2. Search in incognito mode for better results. When you search in standard mode, Google helpfully remembers previous searches, the links you have clicked in the past, and several other bits of information.
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
To add or import a single work, or individual works one by one, use one of the following two options: Add DOI / Add PubMed ID. Import the work by entering its DOI or PMID. For detailed instructions, see Add works using an Identifier. Add manually. If your work doesn't have a DOI or PMID, you can manually add its information.
Questions. Publisher Support. Google Scholar can boost the worldwide visibility and accessibility of your content. We work with publishers of scholarly information to index peer-reviewed papers, theses, preprints, abstracts, and technical reports from all disciplines of research and make them searchable on Google and Google Scholar. This ...
Google Scholar Citations are one way to gauge a research paper's influence. They are determined by tracking how frequently a particular paper is cited in other academic works. Citations are distinct from references in that the former are the sources acknowledged inside a publication, while the latter is how other writers acknowledge a work.