What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.

What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
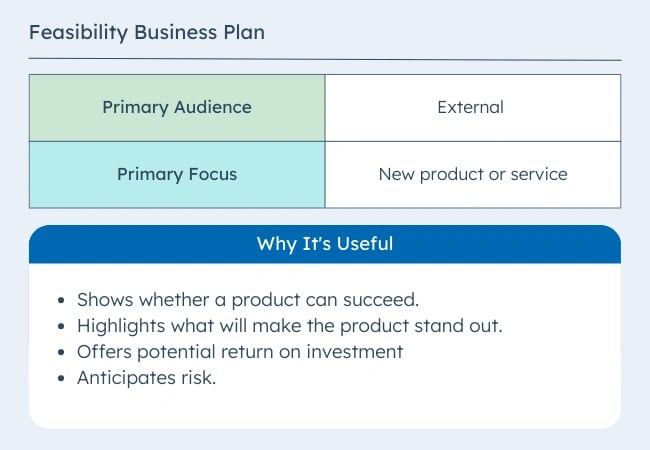
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![discuss what is business plan How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]
20 Free & Paid Small Business Tools for Any Budget

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2024
![discuss what is business plan 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![discuss what is business plan The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

What is a business plan? Definition, Purpose, and Types
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies , and financial projections. Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.
As a business plan writer and consultant , I’ve crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse range of businesses. In this article, I’ll be sharing my wealth of experience about what a business plan is, its purpose, and the step-by-step process of creating one. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how to develop a robust business plan that can drive your business to success.
What is a business plan?
Purposes of a business plan, what are the essential components of a business plan, executive summary, business description or overview, product and price, competitive analysis, target market, marketing plan, financial plan, funding requirements, types of business plan, lean startup business plans, traditional business plans, how often should a business plan be reviewed and revised, what are the key elements of a lean startup business plan.
- What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?
A business plan is a roadmap for your business. It outlines your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. It’s a living document that you can update as your business grows and changes.
Looking for someone to write a business plan?
Find professional business plan writers for your business success.
These are the following purpose of business plan:
- Attract investors and lenders: If you’re seeking funding for your business , a business plan is a must-have. Investors and lenders want to see that you have a clear plan for how you’ll use their money to grow your business and generate revenue.
- Get organized and stay on track: Writing a business plan forces you to think through all aspects of your business, from your target market to your marketing strategy. This can help you identify any potential challenges and opportunities early on, so you can develop a plan to address them.
- Make better decisions: A business plan can help you make better decisions about your business by providing you with a framework to evaluate different options. For example, if you’re considering launching a new product, your business plan can help you assess the potential market demand, costs, and profitability.

The executive summary is the most important part of your business plan, even though it’s the last one you’ll write. It’s the first section that potential investors or lenders will read, and it may be the only one they read. The executive summary sets the stage for the rest of the document by introducing your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
The business description section of your business plan should introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way. It should include your business name, years in operation, key offerings, positioning statement, and core values (if applicable). You may also want to include a short history of your company.
In this section, the company should describe its products or services , including pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other relevant information could include production and manufacturing processes, patents, and proprietary technology.
Every industry has competitors, even if your business is the first of its kind or has the majority of the market share. In the competitive analysis section of your business plan, you’ll objectively assess the industry landscape to understand your business’s competitive position. A SWOT analysis is a structured way to organize this section.
Your target market section explains the core customers of your business and why they are your ideal customers. It should include demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic information about your target market.
Marketing plan describes how the company will attract and retain customers, including any planned advertising and marketing campaigns . It also describes how the company will distribute its products or services to consumers.
After outlining your goals, validating your business opportunity, and assessing the industry landscape, the team section of your business plan identifies who will be responsible for achieving your goals. Even if you don’t have your full team in place yet, investors will be impressed by your clear understanding of the roles that need to be filled.
In the financial plan section,established businesses should provide financial statements , balance sheets , and other financial data. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years, and may also request funding.
Since one goal of a business plan is to secure funding from investors , you should include the amount of funding you need, why you need it, and how long you need it for.
- Tip: Use bullet points and numbered lists to make your plan easy to read and scannable.
Access specialized business plan writing service now!
Business plans can come in many different formats, but they are often divided into two main types: traditional and lean startup. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) says that the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
Lean startup business plans are short (as short as one page) and focus on the most important elements. They are easy to create, but companies may need to provide more information if requested by investors or lenders.
Traditional business plans are longer and more detailed than lean startup business plans, which makes them more time-consuming to create but more persuasive to potential investors. Lean startup business plans are shorter and less detailed, but companies should be prepared to provide more information if requested.
Need Guidance with Your Business Plan?
Access 14 free business plan samples!
A business plan should be reviewed and revised at least annually, or more often if the business is experiencing significant changes. This is because the business landscape is constantly changing, and your business plan needs to reflect those changes in order to remain relevant and effective.
Here are some specific situations in which you should review and revise your business plan:
- You have launched a new product or service line.
- You have entered a new market.
- You have experienced significant changes in your customer base or competitive landscape.
- You have made changes to your management team or organizational structure.
- You have raised new funding.
A lean startup business plan is a short and simple way for a company to explain its business, especially if it is new and does not have a lot of information yet. It can include sections on the company’s value proposition, major activities and advantages, resources, partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?

- Unrealistic assumptions: Business plans are often based on assumptions about the market, the competition, and the company’s own capabilities. If these assumptions are unrealistic, the plan is doomed to fail.
- Lack of focus: A good business plan should be focused on a specific goal and how the company will achieve it. If the plan is too broad or tries to do too much, it is unlikely to be successful.
- Poor execution: Even the best business plan is useless if it is not executed properly. This means having the right team in place, the necessary resources, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Unforeseen challenges: Every business faces challenges that could not be predicted or planned for. These challenges can be anything from a natural disaster to a new competitor to a change in government regulations.
What are the benefits of having a business plan?
- It helps you to clarify your business goals and strategies.
- It can help you to attract investors and lenders.
- It can serve as a roadmap for your business as it grows and changes.
- It can help you to make better business decisions.
How to write a business plan?
There are many different ways to write a business plan, but most follow the same basic structure. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Executive summary.
- Company description.
- Management and organization description.
- Financial projections.
How to write a business plan step by step?
Start with an executive summary, then describe your business, analyze the market, outline your products or services, detail your marketing and sales strategies, introduce your team, and provide financial projections.
Why do I need a business plan for my startup?
A business plan helps define your startup’s direction, attract investors, secure funding, and make informed decisions crucial for success.
What are the key components of a business plan?
Key components include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, products or services, marketing and sales strategy, management and team, financial projections, and funding requirements.
Can a business plan help secure funding for my business?
Yes, a well-crafted business plan demonstrates your business’s viability, the use of investment, and potential returns, making it a valuable tool for attracting investors and lenders.
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated May 7, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Home > Business > Business Startup
How To Write a Business Plan

We are committed to sharing unbiased reviews. Some of the links on our site are from our partners who compensate us. Read our editorial guidelines and advertising disclosure .

Starting a business is a wild ride, and a solid business plan can be the key to keeping you on track. A business plan is essentially a roadmap for your business — outlining your goals, strategies, market analysis and financial projections. Not only will it guide your decision-making, a business plan can help you secure funding with a loan or from investors .
Writing a business plan can seem like a huge task, but taking it one step at a time can break the plan down into manageable milestones. Here is our step-by-step guide on how to write a business plan.
Table of contents
- Write your executive summary
- Do your market research homework
- Set your business goals and objectives
- Plan your business strategy
- Describe your product or service
- Crunch the numbers
- Finalize your business plan

By signing up I agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Step 1: Write your executive summary
Though this will be the first page of your business plan , we recommend you actually write the executive summary last. That’s because an executive summary highlights what’s to come in the business plan but in a more condensed fashion.
An executive summary gives stakeholders who are reading your business plan the key points quickly without having to comb through pages and pages. Be sure to cover each successive point in a concise manner, and include as much data as necessary to support your claims.
You’ll cover other things too, but answer these basic questions in your executive summary:
- Idea: What’s your business concept? What problem does your business solve? What are your business goals?
- Product: What’s your product/service and how is it different?
- Market: Who’s your audience? How will you reach customers?
- Finance: How much will your idea cost? And if you’re seeking funding, how much money do you need? How much do you expect to earn? If you’ve already started, where is your revenue at now?
Step 2: Do your market research homework
The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research . This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to gather this information. Your method may be formal or more casual, just make sure that you’re getting good data back.
This research will help you to understand the needs of your target market and the potential demand for your product or service—essential aspects of starting and growing a successful business.
Step 3: Set your business goals and objectives
Once you’ve completed your market research, you can begin to define your business goals and objectives. What is the problem you want to solve? What’s your vision for the future? Where do you want to be in a year from now?
Use this step to decide what you want to achieve with your business, both in the short and long term. Try to set SMART goals—specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound benchmarks—that will help you to stay focused and motivated as you build your business.
Step 4: Plan your business strategy
Your business strategy is how you plan to reach your goals and objectives. This includes details on positioning your product or service, marketing and sales strategies, operational plans, and the organizational structure of your small business.
Make sure to include key roles and responsibilities for each team member if you’re in a business entity with multiple people.
Step 5: Describe your product or service
In this section, get into the nitty-gritty of your product or service. Go into depth regarding the features, benefits, target market, and any patents or proprietary tech you have. Make sure to paint a clear picture of what sets your product apart from the competition—and don’t forget to highlight any customer benefits.
Step 6: Crunch the numbers
Financial analysis is an essential part of your business plan. If you’re already in business that includes your profit and loss statement , cash flow statement and balance sheet .
These financial projections will give investors and lenders an understanding of the financial health of your business and the potential return on investment.
You may want to work with a financial professional to ensure your financial projections are realistic and accurate.
Step 7: Finalize your business plan
Once you’ve completed everything, it's time to finalize your business plan. This involves reviewing and editing your plan to ensure that it is clear, concise, and easy to understand.
You should also have someone else review your plan to get a fresh perspective and identify any areas that may need improvement. You could even work with a free SCORE mentor on your business plan or use a SCORE business plan template for more detailed guidance.
Compare the Top Small-Business Banks
Data effective 1/10/23. At publishing time, rates, fees, and requirements are current but are subject to change. Offers may not be available in all areas.
The takeaway
Writing a business plan is an essential process for any forward-thinking entrepreneur or business owner. A business plan requires a lot of up-front research, planning, and attention to detail, but it’s worthwhile. Creating a comprehensive business plan can help you achieve your business goals and secure the funding you need.
Related content
- 5 Best Business Plan Software and Tools in 2023 for Your Small Business
- How to Get a Business License: What You Need to Know
- What Is a Cash Flow Statement?
Best Small Business Loans
5202 W Douglas Corrigan Way Salt Lake City, UT 84116
Accounting & Payroll
Point of Sale
Payment Processing
Inventory Management
Human Resources
Other Services
Best Inventory Management Software
Best Small Business Accounting Software
Best Payroll Software
Best Mobile Credit Card Readers
Best POS Systems
Best Tax Software
Stay updated on the latest products and services anytime anywhere.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Disclaimer: The information featured in this article is based on our best estimates of pricing, package details, contract stipulations, and service available at the time of writing. All information is subject to change. Pricing will vary based on various factors, including, but not limited to, the customer’s location, package chosen, added features and equipment, the purchaser’s credit score, etc. For the most accurate information, please ask your customer service representative. Clarify all fees and contract details before signing a contract or finalizing your purchase.
Our mission is to help consumers make informed purchase decisions. While we strive to keep our reviews as unbiased as possible, we do receive affiliate compensation through some of our links. This can affect which services appear on our site and where we rank them. Our affiliate compensation allows us to maintain an ad-free website and provide a free service to our readers. For more information, please see our Privacy Policy Page . |
© Business.org 2024 All Rights Reserved.

The Business Planning Process: 6 Steps To Creating a New Plan
In this article, we will define and explain the basic business planning process to help your business move in the right direction.
What is Business Planning?
Business planning is the process whereby an organization’s leaders figure out the best roadmap for growth and document their plan for success.
The business planning process includes diagnosing the company’s internal strengths and weaknesses, improving its efficiency, working out how it will compete against rival firms in the future, and setting milestones for progress so they can be measured.
The process includes writing a new business plan. What is a business plan? It is a written document that provides an outline and resources needed to achieve success. Whether you are writing your plan from scratch, from a simple business plan template , or working with an experienced business plan consultant or writer, business planning for startups, small businesses, and existing companies is the same.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
The best business planning process is to use our business plan template to streamline the creation of your plan: Download Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template and finish your business plan & financial model in hours.
The Better Business Planning Process
The business plan process includes 6 steps as follows:
- Do Your Research
- Calculate Your Financial Forecast
- Draft Your Plan
- Revise & Proofread
- Nail the Business Plan Presentation
We’ve provided more detail for each of these key business plan steps below.
1. Do Your Research
Conduct detailed research into the industry, target market, existing customer base, competitors, and costs of the business begins the process. Consider each new step a new project that requires project planning and execution. You may ask yourself the following questions:
- What are your business goals?
- What is the current state of your business?
- What are the current industry trends?
- What is your competition doing?
There are a variety of resources needed, ranging from databases and articles to direct interviews with other entrepreneurs, potential customers, or industry experts. The information gathered during this process should be documented and organized carefully, including the source as there is a need to cite sources within your business plan.
You may also want to complete a SWOT Analysis for your own business to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and potential risks as this will help you develop your strategies to highlight your competitive advantage.

2. Strategize
Now, you will use the research to determine the best strategy for your business. You may choose to develop new strategies or refine existing strategies that have demonstrated success in the industry. Pulling the best practices of the industry provides a foundation, but then you should expand on the different activities that focus on your competitive advantage.
This step of the planning process may include formulating a vision for the company’s future, which can be done by conducting intensive customer interviews and understanding their motivations for purchasing goods and services of interest. Dig deeper into decisions on an appropriate marketing plan, operational processes to execute your plan, and human resources required for the first five years of the company’s life.
3. Calculate Your Financial Forecast
All of the activities you choose for your strategy come at some cost and, hopefully, lead to some revenues. Sketch out the financial situation by looking at whether you can expect revenues to cover all costs and leave room for profit in the long run.
Begin to insert your financial assumptions and startup costs into a financial model which can produce a first-year cash flow statement for you, giving you the best sense of the cash you will need on hand to fund your early operations.
A full set of financial statements provides the details about the company’s operations and performance, including its expenses and profits by accounting period (quarterly or year-to-date). Financial statements also provide a snapshot of the company’s current financial position, including its assets and liabilities.
This is one of the most valued aspects of any business plan as it provides a straightforward summary of what a company does with its money, or how it grows from initial investment to become profitable.
4. Draft Your Plan
With financials more or less settled and a strategy decided, it is time to draft through the narrative of each component of your business plan . With the background work you have completed, the drafting itself should be a relatively painless process.
If you have trouble writing convincing prose, this is a time to seek the help of an experienced business plan writer who can put together the plan from this point.
5. Revise & Proofread
Revisit the entire plan to look for any ideas or wording that may be confusing, redundant, or irrelevant to the points you are making within the plan. You may want to work with other management team members in your business who are familiar with the company’s operations or marketing plan in order to fine-tune the plan.
Finally, proofread thoroughly for spelling, grammar, and formatting, enlisting the help of others to act as additional sets of eyes. You may begin to experience burnout from working on the plan for so long and have a need to set it aside for a bit to look at it again with fresh eyes.
6. Nail the Business Plan Presentation
The presentation of the business plan should succinctly highlight the key points outlined above and include additional material that would be helpful to potential investors such as financial information, resumes of key employees, or samples of marketing materials. It can also be beneficial to provide a report on past sales or financial performance and what the business has done to bring it back into positive territory.
Business Planning Process Conclusion
Every entrepreneur dreams of the day their business becomes wildly successful.
But what does that really mean? How do you know whether your idea is worth pursuing?
And how do you stay motivated when things are not going as planned? The answers to these questions can be found in your business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs make better decisions and avoid common pitfalls along the way.
Business plans are dynamic documents that can be revised and presented to different audiences throughout the course of a company’s life. For example, a business may have one plan for its initial investment proposal, another which focuses more on milestones and objectives for the first several years in existence, and yet one more which is used specifically when raising funds.
Business plans are a critical first step for any company looking to attract investors or receive grant money, as they allow a new organization to better convey its potential and business goals to those able to provide financial resources.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink business plan consultants can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
Sign up for our newsletter for product updates, new blog posts, and the chance to be featured in our Small Business Spotlight!

The importance of a business plan

Business plans are like road maps: it’s possible to travel without one, but that will only increase the odds of getting lost along the way.
Owners with a business plan see growth 30% faster than those without one, and 71% of the fast-growing companies have business plans . Before we get into the thick of it, let’s define and go over what a business plan actually is.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a 15-20 page document that outlines how you will achieve your business objectives and includes information about your product, marketing strategies, and finances. You should create one when you’re starting a new business and keep updating it as your business grows.
Rather than putting yourself in a position where you may have to stop and ask for directions or even circle back and start over, small business owners often use business plans to help guide them. That’s because they help them see the bigger picture, plan ahead, make important decisions, and improve the overall likelihood of success.
Why is a business plan important?
A well-written business plan is an important tool because it gives entrepreneurs and small business owners, as well as their employees, the ability to lay out their goals and track their progress as their business begins to grow. Business planning should be the first thing done when starting a new business. Business plans are also important for attracting investors so they can determine if your business is on the right path and worth putting money into.
Business plans typically include detailed information that can help improve your business’s chances of success, like:
- A market analysis : gathering information about factors and conditions that affect your industry
- Competitive analysis : evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors
- Customer segmentation : divide your customers into different groups based on specific characteristics to improve your marketing
- Marketing: using your research to advertise your business
- Logistics and operations plans : planning and executing the most efficient production process
- Cash flow projection : being prepared for how much money is going into and out of your business
- An overall path to long-term growth
What is the purpose of a business plan?
A business plan is like a map for small business owners, showing them where to go and how to get there. Its main purposes are to help you avoid risks, keep everyone on the same page, plan finances, check if your business idea is good, make operations smoother, and adapt to changes. It's a way for small business owners to plan, communicate, and stay on track toward their goals.
10 reasons why you need a business plan
I know what you’re thinking: “Do I really need a business plan? It sounds like a lot of work, plus I heard they’re outdated and I like figuring things out as I go...”.
The answer is: yes, you really do need a business plan! As entrepreneur Kevin J. Donaldson said, “Going into business without a business plan is like going on a mountain trek without a map or GPS support—you’ll eventually get lost and starve! Though it may sound tedious and time-consuming, business plans are critical to starting your business and setting yourself up for success.
To outline the importance of business plans and make the process sound less daunting, here are 10 reasons why you need one for your small business.
1. To help you with critical decisions
The primary importance of a business plan is that they help you make better decisions. Entrepreneurship is often an endless exercise in decision making and crisis management. Sitting down and considering all the ramifications of any given decision is a luxury that small businesses can’t always afford. That’s where a business plan comes in.
Building a business plan allows you to determine the answer to some of the most critical business decisions ahead of time.
Creating a robust business plan is a forcing function—you have to sit down and think about major components of your business before you get started, like your marketing strategy and what products you’ll sell. You answer many tough questions before they arise. And thinking deeply about your core strategies can also help you understand how those decisions will impact your broader strategy.
Send invoices, estimates, and other docs:
- via links or PDFs
- automatically, via Wave
*While subscribed to Wave’s Pro Plan, get 2.9% + $0 (Visa, Mastercard, Discover) and 3.4% + $0 (Amex) per transaction for the first 10 transactions of each month of your subscription, then 2.9% + $0.60 (Visa, Mastercard, Discover) and 3.4% + $0.60 (Amex) per transaction. Discover processing is only available to US customers. See full terms and conditions for the US and Canada . See Wave’s Terms of Service for more information.
Send invoices, get paid, track expenses, pay your team, and balance your books with our financial management software.
2. To iron out the kinks
Putting together a business plan requires entrepreneurs to ask themselves a lot of hard questions and take the time to come up with well-researched and insightful answers. Even if the document itself were to disappear as soon as it’s completed, the practice of writing it helps to articulate your vision in realistic terms and better determine if there are any gaps in your strategy.
3. To avoid the big mistakes
Only about half of small businesses are still around to celebrate their fifth birthday . While there are many reasons why small businesses fail, many of the most common are purposefully addressed in business plans.
According to data from CB Insights , some of the most common reasons businesses fail include:
- No market need : No one wants what you’re selling.
- Lack of capital : Cash flow issues or businesses simply run out of money.
- Inadequate team : This underscores the importance of hiring the right people to help you run your business.
- Stiff competition : It’s tough to generate a steady profit when you have a lot of competitors in your space.
- Pricing : Some entrepreneurs price their products or services too high or too low—both scenarios can be a recipe for disaster.
The exercise of creating a business plan can help you avoid these major mistakes. Whether it’s cash flow forecasts or a product-market fit analysis , every piece of a business plan can help spot some of those potentially critical mistakes before they arise. For example, don’t be afraid to scrap an idea you really loved if it turns out there’s no market need. Be honest with yourself!
Get a jumpstart on your business plan by creating your own cash flow projection .
4. To prove the viability of the business
Many businesses are created out of passion, and while passion can be a great motivator, it’s not a great proof point.
Planning out exactly how you’re going to turn that vision into a successful business is perhaps the most important step between concept and reality. Business plans can help you confirm that your grand idea makes sound business sense.

A critical component of your business plan is the market research section. Market research can offer deep insight into your customers, your competitors, and your chosen industry. Not only can it enlighten entrepreneurs who are starting up a new business, but it can also better inform existing businesses on activities like marketing, advertising, and releasing new products or services.
Want to prove there’s a market gap? Here’s how you can get started with market research.
5. To set better objectives and benchmarks
Without a business plan, objectives often become arbitrary, without much rhyme or reason behind them. Having a business plan can help make those benchmarks more intentional and consequential. They can also help keep you accountable to your long-term vision and strategy, and gain insights into how your strategy is (or isn’t) coming together over time.
6. To communicate objectives and benchmarks
Whether you’re managing a team of 100 or a team of two, you can’t always be there to make every decision yourself. Think of the business plan like a substitute teacher, ready to answer questions any time there’s an absence. Let your staff know that when in doubt, they can always consult the business plan to understand the next steps in the event that they can’t get an answer from you directly.
Sharing your business plan with team members also helps ensure that all members are aligned with what you’re doing, why, and share the same understanding of long-term objectives.
7. To provide a guide for service providers
Small businesses typically employ contractors , freelancers, and other professionals to help them with tasks like accounting , marketing, legal assistance, and as consultants. Having a business plan in place allows you to easily share relevant sections with those you rely on to support the organization, while ensuring everyone is on the same page.
8. To secure financing
Did you know you’re 2.5x more likely to get funded if you have a business plan?If you’re planning on pitching to venture capitalists, borrowing from a bank, or are considering selling your company in the future, you’re likely going to need a business plan. After all, anyone that’s interested in putting money into your company is going to want to know it’s in good hands and that it’s viable in the long run. Business plans are the most effective ways of proving that and are typically a requirement for anyone seeking outside financing.
Learn what you need to get a small business loan.
9. To better understand the broader landscape
No business is an island, and while you might have a strong handle on everything happening under your own roof, it’s equally important to understand the market terrain as well. Writing a business plan can go a long way in helping you better understand your competition and the market you’re operating in more broadly, illuminate consumer trends and preferences, potential disruptions and other insights that aren’t always plainly visible.
10. To reduce risk
Entrepreneurship is a risky business, but that risk becomes significantly more manageable once tested against a well-crafted business plan. Drawing up revenue and expense projections, devising logistics and operational plans, and understanding the market and competitive landscape can all help reduce the risk factor from an inherently precarious way to make a living. Having a business plan allows you to leave less up to chance, make better decisions, and enjoy the clearest possible view of the future of your company.
Business plan FAQs
How does having a business plan help small business owners make better decisions.
Having a business plan supports small business owners in making smarter decisions by providing a structured framework to assess all parts of their businesses. It helps you foresee potential challenges, identify opportunities, and set clear objectives. Business plans help you make decisions across the board, including market strategies, financial management, resource allocation, and growth planning.
What industry-specific issues can business plans help tackle?
Business plans can address industry-specific challenges like regulatory compliance, technological advancements, market trends, and competitive landscape. For instance, in highly regulated industries like healthcare or finance, a comprehensive business plan can outline compliance measures and risk management strategies.
How can small business owners use their business plans to pitch investors or apply for loans?
In addition to attracting investors and securing financing, small business owners can leverage their business plans during pitches or loan applications by focusing on key elements that resonate with potential stakeholders. This includes highlighting market analysis, competitive advantages, revenue projections, and scalability plans. Presenting a well-researched and data-driven business plan demonstrates credibility and makes investors or lenders feel confident about your business’s potential health and growth.
Understanding the importance of a business plan
Now that you have a solid grasp on the “why” behind business plans, you can confidently move forward with creating your own.
Remember that a business plan will grow and evolve along with your business, so it’s an important part of your whole journey—not just the beginning.
Related Posts
Now that you’ve read up on the purpose of a business plan, check out our guide to help you get started.
The information and tips shared on this blog are meant to be used as learning and personal development tools as you launch, run and grow your business. While a good place to start, these articles should not take the place of personalized advice from professionals. As our lawyers would say: “All content on Wave’s blog is intended for informational purposes only. It should not be considered legal or financial advice.” Additionally, Wave is the legal copyright holder of all materials on the blog, and others cannot re-use or publish it without our written consent.

- Small Business
- How to Start a Business
How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
Building an effective business launch plan
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Conducting Market Research
Crafting a business plan, reviewing funding options, understanding legal requirements, implementing marketing strategies, the bottom line.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Headshot-4c571aa3d8044192bcbd7647dd137cf1.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps CURRENT ARTICLE
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
Starting a business in the United States involves a number of different steps spanning legal considerations, market research, creating a business plan, securing funding, and developing a marketing strategy. It also requires decisions about a business’ location, structure, name, taxation, and registration. Here are the key steps involved in starting a business, as well as important aspects of the process for entrepreneurs to consider.
Key Takeaways
- Entrepreneurs should start by conducting market research to understand their industry space, competition, and target customers.
- The next step is to write a comprehensive business plan, outlining the company’s structure, vision, and strategy.
- Securing funding in the form of grants, loans, venture capital, and/or crowdfunded money is crucial if you’re not self-funding.
- When choosing a venue, be aware of local regulations and requirements.
- Design your business structure with an eye to legal aspects, such as taxation and registration.
- Make a strategic marketing plan that addresses the specifics of the business, industry, and target market.
Before starting a business, entrepreneurs should conduct market research to determine their target audience, competition, and market trends. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) breaks down common market considerations as follows:
- Demand : Is there a need for this product or service?
- Market size : How many people might be interested?
- Economic indicators : What are the income, employment rate, and spending habits of potential customers?
- Location : Are the target market and business well situated for each other?
- Competition : What is the market saturation ? Who and how many are you going up against?
- Pricing : What might a customer be willing to pay?
Market research should also include an analysis of market opportunities, barriers to market entry, and industry trends, as well as the competition’s strengths, weaknesses, and market share .
There are various methods for conducting market research, and these will vary depending on the nature of the industry and potential business. Data can come from a variety of places, including statistical agencies, economic and financial institutions, and industry sources, as well as direct consumer research through focus groups, interviews, surveys, and questionnaires.
A comprehensive business plan is like a blueprint. It lays the foundation for business development and affects decision-making, day-to-day operations, and growth. Potential investors or partners may want to review and assess it in advance of agreeing to work together. Financial institutions often request business plans as part of an application for a loan or other forms of capital.
Business plans will differ according to the needs and nature of the company and should only include what makes sense for the business in question. As such, they can vary in length and structure. They can generally be divided into two formats: traditional and lean start-up. The latter is less common and more useful for simple businesses or those that expect to rework their traditional business plan frequently. It provides a vivid snapshot of the company through a small number of elements.
The process of funding a business depends on its needs and the vision and financial situation of its owner. The first step is to calculate the start-up costs . Identify a list of expenses and put a dollar amount to each of them through research and requesting quotes. The SBA has a start-up costs calculator for small businesses that includes common types of business expenses.
The next step is to determine how to get the money. Common methods include:
- Self-funding , also known as “ bootstrapping ”
- Finding investors willing to contribute to your venture capital
- Raising money online by crowdfunding
- Securing a business loan from a bank, an online lender, or a credit union
- Winning a business grant from a donor, usually a government, foundation, charity, or corporation
Different methods suit different businesses, and it’s important to consider the obligations associated with any avenue of funding. For example, investors generally want a degree of control for their money, while self-funding puts business owners fully in charge. Of course, investors also mitigate risk; self-funding does not.
Availability is another consideration. Loans are easier to get than grants, which don’t have to be paid back. Additionally, the federal government doesn’t provide grants for the purposes of starting or growing a business, although private organizations may. However, the SBA does guarantee several categories of loans , accessing capital that may not be available through traditional lenders. No matter the funding method(s), it’s essential to detail how the money will be used and lay out a future financial plan for the business, including sales projections and loan repayments .
Businesses operating in the U.S. are legally subject to regulations at the local, county, state, and federal level involving taxation, business IDs, registrations, and permits.
Choosing a Business Location
Where a business operates will dictate such things as taxes, zoning laws (for brick-and-mortar locations), licenses, and permits. Other considerations when choosing a location might include:
- Human factors : These include target audience and the preferences of business owners and partners regarding convenience, knowledge of the area, and commuting distance.
- Regulations : Government at every level will assert its authority.
- Regionally specific expenses : Examples are average salaries (including required minimum wages), property or rental prices, insurance rates, utilities, and government fees and licensing.
- The tax and financial environment : Tax types include income, sales, corporate, and property, as well as tax credits; available investment incentives and loan programs may also be geographically determined.
Picking a Business Structure
The structure of a business should reflect the desired number of owners, liability characteristics, and tax status. Because these have legal and tax compliance implications , it’s important to understand them fully. If necessary, consult a business counselor, a lawyer, and/or an accountant.
Common business structures include:
- Sole proprietorship : A sole proprietorship is an unincorporated business that has just one owner, who pays personal income tax on its profits.
- Partnership : Partnership options include a limited partnership (LP) and a limited liability partnership (LLP) .
- Limited liability company (LLC) : An LLC protects its owners from personal responsibility for the company’s debts and liabilities.
- Corporation : The different types of corporations include C corp , S corp , B corp , closed corporation , and nonprofit .
Getting a Tax ID Number
A tax ID number is the equivalent of a Social Security number for a business. Whether or not a state and/or federal tax ID number is required will depend on the nature of the business and the location in which it’s registered.
A federal tax ID, also known as an employer identification number (EIN) , is required if a business:
- Operates as a corporation or partnership
- Pays federal taxes
- Has employees
- Files employment, excise, alcohol, tobacco, or firearms tax returns
- Has a Keogh plan
- Withholds taxes on non-wage income to nonresident aliens
- Is involved with certain types of organizations, including trusts, estates, real estate mortgage investment conduits, nonprofits, farmers’ cooperatives, and plan administrators
An EIN can also be useful if you want to open a business bank account, offer an employer-sponsored retirement plan, or apply for federal business licenses and permits. You can get one online from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) . State websites will do the same for a state tax ID.
Registering a Business
How you register a business will depend on its location, nature, size, and business structure. For example, a small business may not require any steps beyond registering its business name with local and state governments, and business owners whose business name is their own legal name might not need to register at all.
That said, registration can provide personal liability protection, tax-exempt status, and trademark protection, so it can be beneficial even if it’s not strictly required. Overall registration requirements, costs, and documentation will vary depending on the governing jurisdictions and business structure.
Most LLCs, corporations, partnerships, and nonprofits are required to register at the state level and will need a registered agent to file on their behalf. Determining which state to register with can depend on factors such as:
- Whether the business has a physical presence in the state
- If the business often conducts in-person client meetings in the state
- If a large portion of business revenue comes from the state
- Whether the business has employees working in the state
If a business operates in more than one state, it may need to file for foreign qualification in other states in which it conducts business. In this case the business would register in the state in which it was formed (this would be considered the domestic state) and file for foreign qualification in any additional states.
Obtaining Permits
Filing for the applicable government licenses and permits will depend on the industry and nature of the business and might include submitting an application to a federal agency, state, county, and/or city. The SBA lists federally regulated business activities alongside the corresponding license-issuing agency, while state, county, and city regulations can be found on the official government websites for each region.
Every business should have a marketing plan that outlines an overall strategy and the day-to-day tactics used to execute it. A successful marketing plan will lay out tactics for how to connect with customers and convince them to buy what the company is selling.
Marketing plans will vary according to the specifics of the industry, target market, and business, but they should aim to include descriptions of and strategies for the following:
- A target customer : Including market size, demographics, traits, and relevant trends
- Value propositions or business differentiators : An overview of the company’s competitive advantage with regard to employees, certifications, and offerings
- A sales and marketing plan : Including methods, channels, and a customer’s journey through interacting with the business
- Goals : Should cover different aspects of the marketing and sales strategy, such as social media follower growth, public relations opportunities, and sales targets
- An execution plan : Should detail tactics and break down higher-level goals into specific actions
- A budget : Detailing how much different marketing projects and activities will cost
How Much Does It Cost to Start a Business?
Business start-up costs will vary depending on the industry, business activity, and product or service offered. Home-based online businesses will usually cost less than those that require an office setting to meet with customers. The estimated cost can be calculated by first identifying a list of expenses and then researching and requesting quotes for each one. Use the SBA’s start-up costs calculator for common types of expenses associated with starting a small business.
What Should I Do Before Starting a Business?
Entrepreneurs seeking to start their own business should fully research and understand all the legal and funding considerations involved, conduct market research, and create marketing and business plans. They will also need to secure any necessary permits, licenses, funding, and business bank accounts.
What Types of Funding Are Available to Start a Business?
Start-up capital can come in the form of loans, grants, crowdfunding, venture capital, or self-funding. Note that the federal government does not provide grant funding for the purposes of starting a business, although some private sources do.
Do You Need to Write a Business Plan?
Business plans are comprehensive documents that lay out the most important information about a business. They reference its growth, development, and decision-making processes, and financial institutions and potential investors and partners generally request to review them in advance of agreeing to provide funding or to collaborate.
Starting a business is no easy feat, but research and preparation can help smooth the way. Having a firm understanding of your target market, competition, industry, goals, company structure, funding requirements, legal regulations, and marketing strategy, as well as conducting research and consulting experts where necessary, are all things that entrepreneurs can do to set themselves up for success.
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Market Research and Competitive Analysis .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Write Your Business Plan .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Calculate Your Startup Costs ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Fund Your Business .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Grants .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Loans .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Pick Your Business Location .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Choose a Business Structure .”
Internal Revenue Service. “ Do You Need an EIN? ”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Get Federal and State Tax ID Numbers .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Register Your Business .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Apply for Licenses and Permits .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Marketing and Sales .”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1421562920-d5cf7a5a92204c579da450389c6b01a5.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

10 Simple Tips to Write a Successful Business Plan
"The absolute biggest business plan mistake you can make is to not plan at all." So writes Noah Parsons in his helpful blog post 17 Key Business Plan Mistakes to Avoid in 2023 . But how does one pull together all of the necessary components of a cohesive plan? It can feel overwhelming.
Eric Butow, CEO of online marketing ROI improvement firm Butow Communications Group, has teamed up with Entrepreneur Media to update the second edition of our best-selling book Write Your Business Plan to provide you with a simple, step-by-step process for creating a successful business plan. In the following excerpt, he gives ten tips to gather all of the critical information you will need to succeed.
1. Know your competition.
You need to name them and point out what makes you different from (and better than) each of them. But do not disparage your competition.
2. Know your audience.
You may need several versions of your business plan. For example, you may need one for bankers or venture capitalists, one for individual investors, and one for companies that may want to do a joint venture with you rather than fund you.
3. Have proof to back up every claim you make.
If you expect to be the leader in your field in six months, you have to say why you think that is. If you say your product will take the market by storm, you have to support this statement with facts. If you say your management team is fully qualified to make the business a success, be sure staff resumes demonstrate their experience.
Order Write Your Own Business Plan Now and Get 1 Month of Free Access to Business Planning Software Liveplan Premium
- Easy step-by-step business plan generator
- Built-in financial calculators
- 500+ sample plans and templates
4. Be conservative in all financial estimates and projections.
If you feel certain you'll capture 50 percent of the market in the first year, you can say why you think so and hint at what those numbers may be. But make your financial projections more conservative. For example, a 10 percent market share is much more credible.
5. Be realistic with time and resources available.
If you're working with a big company before you buy a business, you may think things will happen faster than they will once you have to buy the supplies, write the checks, and answer the phones yourself. Being overly optimistic with time and resources is a common error entrepreneurs make. Being realistic is important because it lends credibility to your presentation. Always assume things will take 20 percent longer than you anticipated. Therefore, twenty weeks is now twenty-four weeks.
6. Be logical.
Think like a banker and write what they would want to see.
7. Have a strong management team.
Make sure it has good credentials and expertise. Your team members don't have to have worked in the field. However, you need to draw parallels between what they've done and the skills needed to make your venture succeed. Don't have all the skills you need? Consider adding an advisory board of people skilled in your field and include their resumes.
Write Your Own Business Plan is available now at Entrepreneur Bookstore | Barnes & Noble | Amazon
8. Document why your idea will work.
Have others done something similar that was successful? Have you made a prototype? Include all the variables that can have an impact on the result or outcome of your idea. Show why some of the variables don't apply to your situation or explain how you intend to overcome them or make them better.
9. Describe your facilities and location for performing the work.
That includes equipment you use to create your products and/or services. If you'll need to expand, discuss when, where, and why.
10. Discuss payout options for the investors.
Some investors want a hands-on role. Some want to put associates on your board of directors. Some don't want to be involved in day-to-day activities at all. All investors want to know when they can get their money back and at what rate of return. Most want out within three to five years. Provide a brief description of options for investors, or at least mention that you're ready to discuss options with any serious prospect.
To dig deeper, buy Write Your Own Business Plan and get 1 month of free access to business planning software Liveplan Premium.

General election latest: Minister hangs up on Sky's Sam Coates after being told poll has predicted he'll lose his seat
A YouGov poll has predicted an enormous majority for Labour - and several big names Tories to lose their seats. One of them, Grant Shapps, hung up on our deputy political editor Sam Coates after being told live on the phone.
Monday 3 June 2024 22:23, UK
- General Election 2024
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
Election news
- Bulletin: Catch up on the main news from the campaign trail
- Labour set for biggest majority in 100 years - YouGov poll
- Minister predicted to be voted out hangs up live on Sky News
- The top Tories under threat | Why this poll is a big deal | '31 days to save Tory party'
- Farage to stand at general election | Taking over as Reform leader
- Be in the audience for our election leaders event
- Live reporting by Tim Baker and Brad Young
Expert analysis
- Jon Craig: Grim record aside, Farage has made a canny choice
- Rob Powell: Farage U-turn is a really significant development
- Adam Boulton: 'Starmtroopers' are purging Labour
Election essentials
- Trackers: Who's leading polls? | Is PM keeping promises?
- Follow Sky's politics podcasts: Electoral Dysfunction | Politics At Jack And Sam's
- Read more: Who is standing down? | Key seats to watch | How to register to vote | What counts as voter ID? | Check if your constituency is changing | Your essential guide to election lingo | Sky's election night plans
Sir Keir Starmer could be heading to Downing Street with a majority of 194 seats, bigger than what Tony Blair achieved in 1997, according to the first polling projection by YouGov of the campaign.
The projection shows a historic Labour landslide, with the party getting the highest number of seats of any party at an election in history.
At the same time, the Tories are trying to boost ratings by talking about culture wars while Labour is talking about real wars in terms of what they would do for defence. And Nigel Farage has announced he's standing for Reform UK.
On the Sky News Daily, Niall Patterson talks to Sky's chief political correspondent Jon Craig about the poll and today's developments, and to Scarlett Maguire, director of the polling organisation JL Partners.
Click to subscribe to the Sky News Daily wherever you get your podcasts
We're winding up here for the day - the clock has gone ten and we'll be off to bed soon.
Today felt like a day that could be an inflection point in the election for a number of reasons.
We had big announcements from numerous parties, and a megapoll predicting a historic result.
If you want a fuller rundown, here is today's main news:
- A YouGov poll predicted Labour will win a supermajority of 194 seats - with the Conservatives routed to just 140 MPs;
- Tory ministers are among those who could lose their seat - including the defence secretary, Grant Shapps, who hung up on our deputy political editor Sam Coates when he was told live on air ;
- As chief political correspondent Jon Craig writes, panic will be spread through Tory ranks ;
- Meanwhile, Sky election analyst Professor Michael Thrasher said Rishi Sunak has 31 days to save the Conservative Party ;
- Twelve big Conservative beasts face losing their seats - and political correspondent Tamara Cohen has a despatch from one such constituency .
- Just before this poll was published, Nigel Farage announced he was standing to be an MP for Reform UK - U-turning on his previous stance of not contesting;
- As political correspondent Rob Powell says, Mr Farage doesn't just have his eye on this election but the years ahead ;
- And political correspondent Gurpreet Narwan says the news will send shivers down Tory spines;
- This morning, Labour was pitching itself as the "party of defence" as it pledged to build new nuclear submarines;
- And the Conservatives were campaigning on reforming the Equalities Act, including wanting to protect single sex toilets;
- Equalities minister Kemi Badenoch also said trans athletes may have to compete with their biological sex ;
- In slightly lighter news, the prime minister revealed his preferred Nando's order - with a surprise inclusion in the sides .
- Elsewhere, the SNP said there was no need for the UK to have a nuclear deterrent , in response to the Labour announcement;
- The Liberal Democrats sabotaged Rishi Sunak as he held a campaign event;
- Meanwhile, political correspondent Serena Barker-Singh outlined the difficulties facing Sir Keir Starmer over Jeremy Corbyn.
Here are a couple of other stories that may interest you:
Our essential political podcast, Politics At Jack And Sam's , is going out every week day through the election campaign to bring a short burst of everything you need to know about the day ahead as this election unfolds - here is today's edition .
Tap here to follow Politics At Jack At Sam's wherever you get your podcasts .
Stick with us for all the latest throughout the afternoon.
Today's poll suggests that in the Conservative heartlands, voters are about to turn on the governing party like never before, Tarama Cohen writes from Godalming, Surrey .
Chancellor Jeremy Hunt is running in Godalming and Ash, one of the country's most affluent areas.
Conservative since its creation, Mr Hunt's majority - on different boundaries - was down to 8,817 at tzhe 2019 election, ahead of the Liberal Democrats. YouGov's seat by seat poll predicts it could be overturned altogether.
It could be a significant moment of election night - compared with cabinet minister Michael Portillo losing his seat in 1997.
Mortgage rates are a key issue for many voters in this commuter town, and switchers were not hard to find.
Sam and Fi Hayward, who have three children under five, previously voted Conservative but will now back the Lib Dems.
Finance worker Sam - who's natural home is with Conservatives - will be changing who he backs, saying "different issues on our radar now we have a young family".
He is also unimpressed with the government's performance, putting it down to "general incompetence, Brexit hasn't gone their way, COVID hasn't helped".
Fi is also switching, saying "I think it would be better for our family".
At the Godalming Delights sweet shop, new mum Felicity is also switching away from the Tories.
"We're living on savings to pay a massive mortgage", she said, and they've taken their older child out of nursery due to the costs.
Retired teacher Jean said the impact of COVID is still on her mind - including a friend who died "while [politicians] were partying".
She's also concerned about children's mental health, a subject the Lib Dems are campaigning on.
But there was still support for the Conservatives here - and lack of enthusiasm for the alternative.
Retired railway worker Robert Jones said: "I like Jeremy Hunt and Rishi Sunak. I like his apprenticeship scheme, my children's children need a job and all our heavy industries are going."
He was not impressed with the National Service idea - and does worry about Labour.
"Diane Abbott was in, and now she's out. The left always worry me, and the unions - although I was a union man for years - having their sway," he says.
Some voters felt Mr Hunt personally had worked hard as an MP. "He's moderate, and I'm a moderate", said Tory party member David Cooper.
But he was worried about a severe defeat.
This corner of southwest Surrey, a constituency held by former cabinet minister Virginia Bottomley and now the chancellor, has never deserted the Tories, even at the height of New Labour.
If the tide turns here on election night, it will be a sign the once unshakeable Blue Wall is really tumbling down.
The candidates for Godalming and Ash are:
- Graham Drage, Reform UK;
- Paul Follows, Liberal Democrats;
- Jeremy Hunt, Conservatives;
- James Walsh, Labour;
- Steve Williams; Greens.
By Jon Craig , chief political correspondent
The findings of the SkyNews/YouGov MRP poll are a disaster for the Conservatives, a worry for Labour and good news for the Lib Dems and Reform UK.
The forecast of a Tory near wipeout will spread panic among Conservative candidates and potentially spark a fresh bout of mutiny against Rishi Sunak from the right of his party.
For Labour, the suggestion that Sir Keir Starmer is heading for a landslide even bigger than Tony Blair won in 1997 will alarm those in the party already fearing complacency.
But for the Lib Dems, the projection that Sir Ed Davey's party is heading for a result to match the heady days of Paddy Ashdown and Charles Kennedy will be a massive confidence boost.
However, the party that will be really delighted is Reform UK - already newly energised with Nigel Farage replacing Richard Tice as leader - who will claim that with Labour on course to win, Tory supporters can vote for them.
There will also be consternation in the Tory high command at the forecast that so many of the party's big beasts - led by Chancellor Jeremy Hunt - are at risk of losing their seat.
Mr Hunt is fighting the new constituency of Godalming and Ash - in his favour it's in a part of the affluent Surrey stockbroker belt represented by Conservative MPs since 1910.
But the cabinet minsters who are vulnerable are in seats held by Labour in the Blair and Brown years or the Liberal Democrats in the Ashdown, Kennedy or Nick Clegg years.
Read Jon's full analysis below:
By Gurpreet Narwan , political correspondent
We've just witnessed what is probably the most dramatic moment of the general election campaign so far - Nigel Farage, a figure of fear for the Tories, is entering the fray ( read more here ).
All eyes will now turn to the polls, where Reform UK is performing at around 12%.
It hasn't made any major breakthroughs so far - and this vote share will not translate into a seat.
However, speaking to Sky News after the announcement, Mr Farage was adamant the party would now ascend and win more than the 3.9 million votes UKIP took in 2015.
It was at that election that Douglas Carswell - after defecting from the Tories - won a seat for UKIP. It is in this seat that Farage is now bidding to be an MP after seven failed attempts to enter the Commons.
Clacton will be viewed as a soft target for Reform. This was a strong Leave voting area and the Conservative candidate, Giles Watling, is a Remainer.
Reform UK is polling above the national average in this seaside town - YouGov and Sky News' MRP poll puts its share here at 19.5%. But the "Farage factor" cannot be underestimated. He could really win here.
All of this will send shivers down the spines of those in Tory HQ, but Sir Keir Starmer may be rubbing his hands with glee.
Polling already suggests that Reform could cost the Tories 100 seats by splitting the right wing vote across the Red Wall and Essex. It explains why the Tories were pushing the message hard that "a vote for Reform is a vote for Labour".
Farage has turned that on its head. The election is a foregone conclusion and the Tories are too divided to be serious in opposition, he says.
Instead, given the Tories have already lost, Farage argues that a vote for the Tories is the real wasted vote.
That's his pitch to voters who he is now inviting to join his "political takeover".
It was a week ago that the government was announcing its plans to reintroduce national service - after a fashion - if they won the election.
The idea is for all 18-year-olds to volunteer at least once a month, and some to join the military for the year.
Since then, pollsters at JL Partners have asked the country for their opinions on the policy.
As part of its survey, it asked 2,013 people to check boxes against answers for which statements they agreed with.
People could tick as many boxes as they want.
Some 32% of people - a total of 651 of the 2,013 - ticked the box saying it made them feel more negative about the Tories.
Meanwhile, 23% - 467 people of the 2,013 - said it made them feel better about the Conservatives.
To break that down, that's 184 more responses that thought badly of the Conservatives after the national service announcement than thought better of it - a nine point gap.
And then 24% of people - 479 - ticked the box saying it made no difference to their views.
Some 12% - 236 - said it made them feel better about Labour, while 3% - 51 - said it made them feel worse about Sir Keir Starmer's party.
And 12% - 243 - said they did not know.
Read more about the national service announcement below.
Nick Thomas-Symonds is a shadow minister for Labour.
He is asked by Sophy about the major victory estimated for Sir Keir Starmer by YouGov today.
Mr Thomas-Symonds says: "Not a single vote has been cast in this general election - it hasn't been cast by post, and obviously no votes will be cast on the day until 4 July.
"Now, of course we are confident - but we are most certainly not complacent.
"I've been out all day today, my colleagues are out in their own constituencies and around the country.
"And we will continue to fight hard for every single vote until the close of polls at 10pm on 4 July.
"We will never take the voters for granted."
Grant Shapps says a vote for Reform is a vote for Keir Starmer.
The Tory minister's comments come after Nigel Farage announced he was standing for parliament a little earlier today.
The only possible outcomes on 5 July are either Keir Starmer or Rishi Sunak become prime minister, Mr Shapps says.
On backing Reform, he says the party's voters would only end up with the Labour leader "being handed more power to do things you really don't want him to do with this country".
One of the cabinet ministers predicted to lose his seat by today's YouGov poll is Grant Shapps .
Speaking to Sophy Ridge , Mr Shapps says he has "always thought of it as being marginal".
Mr Shapps was the MP for Welwyn Hatfield before parliament was dissolved, and is contesting the seat again.
He says that polling in his seat that took place recently had him down as winning it.
But Mr Shapps deploys one of the most well-worn of political phrases - that "the only poll that matters is the one on election day".
But he admits knowing it is one that is oft deployed, saying he is trying not to sound "too much like a politician".
Mr Shapps is asked about what happened earlier, when he rang Sky deputy political editor Sam Coates live on air.
The defence secretary says he was presented with an "opportunity to go live on air" that "was not entirely planned" - but was pleased to "come on anyway" once Sophy's show began.
You can watch the earlier moment below:
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free

- Développer son business
- Success stories
- Générateur de nom d’entreprise
- Générateur de slogan
- Calcul d’audience dropshipping
Créez votre business et vivez votre meilleure vie - le tout à portée de clics
- © 2015-2024 Oberlo
- | Conditions d’utilisation

Comment rédiger un business plan en 2022 : le guide complet
Vous souhaitez lancer votre business ou vous tentez de décrocher un prêt pour votre entreprise ? Dans les deux cas, vous allez devoir rédiger un business plan. Si l’opération semble rébarbative, sachez que faire un business plan est un excellent moyen d’analyser votre idée de projet et de repérer d’éventuels problèmes que vous n’auriez pas vu. C’est l’opportunité d’étudier en profondeur tous les aspects de votre idée d’entreprise.
Cet article vous apprendra comment faire un business plan efficace pour votre projet d’entreprise. Nous aborderons les sujets suivants :
- Qu’est-ce qu’un business plan ?
Comment faire un business plan ?
- Comment construire un business plan et les éléments qui doivent y figurer
- Business plan : exemple pour vous inspirer et modèle de business plan gratuit
- Des suggestions de logiciel business plan gratuit
Tout savoir sur comment faire un business plan, c’est parti !
Business plan : définition
Qu’est-ce qu’un business plan ? Il s’agit d’un document formel qui présente vos objectifs de développement et la stratégie pour les atteindre. Les études montrent que les entrepreneurs qui se lancent avec un business plan fondent des entreprises ayant plus de succès. C’est la clé d’une croissance équilibrée, vous guidant à travers les étapes de votre développement, limitant les risques et vous aidant à sécuriser des apports financiers (entre autres avantages). On parle parfois de plan d’affaire en français.
Faire un business plan : objectifs
La plupart des banques et institutions financières exigent que vous leur transmettiez un business plan détaillé pour obtenir des fonds . Puisque les business en dropshipping demandent peu de budget pour démarrer, vous n’avez peut-être pas besoin d’apport financier et ne voyez pas l’intérêt de faire un business plan.
Cependant, vous pourriez en avoir besoin pour enlever une limite un peu trop stricte sur votre carte de crédit alors que votre entreprise grandit, ou même pour ouvrir un compte bancaire. Cela varie d’une banque à l’autre.
Si vous développez votre entreprise, faire un business plan vous servira pour augmenter votre capital, créer une stratégie de croissance, trouver de nouvelles opportunités et limiter les risques. Il a été démontré que faire un business plan donne deux fois plus de chances d’obtenir des fonds et même de réussir.
Si vous démarrez une entreprise, utilisez votre business plan pour identifier les forces et les faiblesses de votre projet, communiquer votre vision aux autres et établir des prévisions justes.
Le business plan concerne tous les types d’entreprises. Il est ainsi possible de faire un business plan auto-entrepreneur.

Comment faire un business plan : les grandes étapes
Un business plan passe par 5 grandes étapes : établir des objectifs, rechercher des données, comprendre sa cible, choisir un format et rédiger.
Faire un business plan étape 1 : établir des objectifs
Il y a deux questions clés à se poser ici :
- Qu’espérez-vous accomplir avec votre business ?
- Qu’espérez-vous accomplir avec votre business plan ?
Aborder votre business plan dans cette perspective vous aidera à vous concentrer sur l’objectif final à travers le processus de rédaction. Cela guidera votre manière d’orienter votre business plan. C’est aussi un moyen d’établir des critères d’évaluation de votre succès.
Faire un business plan étape 2 : la recherche de données
Avant de rédiger votre business plan, rassemblez les informations et données dont vous aurez besoin. Cela comprend des informations sur votre marché et votre industrie – et notamment les chiffres clés et les grandes tendances
Ce sera beaucoup plus facile de démarrer avec toutes les informations à disposition, plutôt que de faire les recherches au fur et à mesure de votre progression.
Par exemple, si vous voulez lancer un business e-commerce, étudiez les chiffres e-commerce France . Votre business plan doit démontrer votre parfaite connaissance du marché.
Faire un business plan étape 3 : comprendre votre audience
Parce que les business plans peuvent servir différents objectifs, vous ne le présenterez pas forcément à la même audience. Il est important de s’adapter aux personnes qui vont le lire, de penser à ce que vous souhaitez obtenir d’elles et aux doutes que ces personnes pourraient avoir.
Ainsi, vous pouvez adapter votre business plan en fonction de ces différents objectifs. Votre audience détermine donc le type ou le format de business plan à utiliser. Ce qui nous amène au point suivant…
Faire un business plan étape 4 : choisir un format
Il existe actuellement deux types de business plans :
- Le business plan traditionnel s’adresse aux entrepreneurs qui veulent créer un business plan détaillé pour eux-mêmes ou pour trouver des financements.
- Le business plan simplifié, concerne les entrepreneurs qui veulent pitcher leurs projets et tient en une seule page. Il est très utilisé par les start-ups.
Si le business plan ne concerne que vous-même et vos collaborateurs, faites un business plan simplifié ou une version personnalisée de la version traditionnelle, avec seulement les sections dont vous avez besoin.
Si vous en avez besoin pour trouver des fonds ou pour d’autres objectifs, choisissez la version traditionnelle et complétez soigneusement toutes les parties en prêtant une attention particulière aux projections financières.
Faire un business plan étape 5 : rédiger !
Une fois vos objectifs bien définis, le marché analysé et votre cible identifiée, vous pouvez commencer à rédiger !
Alors, comment rédiger un business plan ? Un business plan contient généralement les information suivantes, dans un ordre qui peut varier :
Résumé du projet
Description de l’entreprise.
- Produit et service
Étude de marché
Analyse swot.
- Marketing et sales
Management et organisation
- Apport financier
- Projection financière
Pour vous aider à faire votre business plan, nous allons détailler chacun de ces éléments, avant de nous pencher sur les ressources pour trouver un exemple de business plan et un modèle business plan, notamment un modèle de business plan gratuit PowerPoint.
Avant cela, une remarque : tandis que vous rédigez votre business plan, prenez le temps non seulement d’analyser votre idée de business, mais également vous-même. Posez-vous les questions suivantes pour vous aider à faire le point sur votre entreprise au fur et à mesure :
- Pourquoi je veux lancer ou développer une/mon entreprise ?
- Est-ce que mes objectifs (personnels et professionnels) et valeurs correspondent à mon idée de business ?
- De quels revenus ai-je besoin de gagner pour moi-même ?
- Quelles éducation, expérience et compétences dois-je apporter à mon business ?
Faire un business plan : les différentes parties
Voici comment rédiger chaque partie de votre business plan, avec les informations à inclure.
Le résumé du projet est la première partie de votre business plan, c’est là que vous devez accrocher le lecteur. Chaque business plan débute de cette façon, même les plus basiques. Résumez tout votre business plan en une page, en soulignant les détails qui éveilleront la curiosité de vos investisseurs et soutiens potentiels.
Expliquez l’objectif de votre business, votre marché cible, ce qui vous différencie de la concurrence, dites-en un peu à votre sujet et sur les personnes au cœur de votre entreprise et présentez des projections réalistes sur le succès potentiel de votre entreprise.
Bien que cette partie soit la première de votre business plan, rédigez-la après avoir écrit tout le reste. Ce sera beaucoup plus facile parce que vous n’aurez plus qu’à ressortir les sections les mieux écrites pour les agencer dans votre première partie.
Cette partie devrait comprendre des détails basiques tels que :
- Statut juridique (micro-entreprise, société ou autreetc…)
- Numéro SIRET
- Date de création
- Responsable légal
- Nombre de salariés
Le concept de votre entreprise, votre philosophie et vos valeurs, votre vision, vos objectifs à court et long terme et les étapes de développement, ainsi qu’une rapide présentation de votre industrie, du marché, des perspectives et de vos concurrents devraient aussi être inclus dans la description de votre entreprise.
Produits et services
La section produits et services détaille ce que vous prévoyez de vendre aux consommateurs. Dans le cas d’un business plan dédié au dropshipping, cette section devrait expliquer quels produits tendance vous comptez vendre, le problème que ce produit résout pour vos clients, comment vous déterminez vos prix par rapport à vos concurrents, la marge commerciale attendue, les informations liées à la production et à la livraison.
Rappelez-vous d’inclure la proposition commerciale unique pour chaque produit ou catégorie de produits, comme les accords exclusifs avec des fournisseurs, la capacité d’obtenir des produits rares ou très demandés grâce à vos relations un service client personnalisé ou d’autres avantages.
Pour les business en dropshipping vendant des centaines voire des milliers de produits, détaillez les catégories principales de produits et le nombre d’articles que vous prévoyez de proposer dans chaque catégorie. De cette façon, il sera plus facile de visualiser l’ensemble de votre offre et de déterminer si vous avez besoin de plus de produits dans telle ou telle catégorie.
La section étude de marché de votre business plan vous permet de partager les recherches effectuées pour en apprendre plus sur votre clientèle, les acheteurs potentiels ou vos produits.
Votre audience voudra savoir si vous avez de solides connaissances sur votre industrie, le paysage concurrentiel et ceux qui devraient devenir vos clients.
Il est important de démontrer que le marché est assez dynamique pour accueillir vos produits, pour être compétitif et/ou faire un bon retour sur investissement .
Pour compléter la section étude de marché de votre business plan, vérifiez les ressources suivantes de votre industrie, de votre secteur et des recherches économiques locales :
L’ union des Français de l’étranger propose des ressources pour les gens qui souhaitent lancer une entreprise dans un pays étranger.
Les ambassades françaises de la plupart des pays disposent d’une section entreprise avec des informations pour les personnes souhaitant vendre à l’étranger. Cette section comportera un guide basique de démarrage, des liens vers des rapports ou des données économiques, des évènements professionnels et d’autres liens utiles pour une région en particulier.
Statista propose aussi des statistiques gratuites et payantes, ainsi que des études de plus de 18 000 ressources, incluant des rapports d’industrie, des rapports nationaux, des études de marché, des rapports prévisionnels et d’autres études de consommateurs.
Utilisez ces sites et d’autres pour en apprendre plus sur les projections de développement de votre industrie et de son potentiel. Vous pourrez aussi utiliser les réseaux sociaux tels que Facebook audience insights pour estimer la taille de votre marché cible sur le plus grand réseau social.
Un autre moyen de faire des recherches sur votre marché et vos produits consiste à utiliser Google Trends . Cet outil gratuit vous permet de voir à quelle fréquence sur une période donnée, les gens recherchent les produits que votre entreprise propose. Assurez-vous d’expliquer clairement comment votre business prévoit de capitaliser sur ces tendances.
Certains business plans comprennent également une analyse SWOT. Il s’agit d’une page qui résume les forces, les faiblesses, les opportunités et les menaces. Les forces et les faiblesses seront internes, tandis que les opportunités et les menaces seront externes.
En fonction de ce que révèle cette section, vous déciderez si oui ou non, vous souhaitez intégrer cette analyse dans votre business plan.
Marketing et ventes
Connaître son marché cible, c’est déjà la moitié du travail fait. Dans la section marketing et ventes, expliquez comment vous comptez atteindre votre cible et lui vendre vos produits. Présentez les stratégies marketing et communication que vous comptez utiliser pour faire connaître votre produit auprès de clients potentiels, le marketing de référencement, le marketing de réseaux sociaux , le marketing de contenu , l’ email marketing et les canaux publicitaires.
Si vous ne savez pas vraiment comment promouvoir vos produits, analysez vos concurrents pour trouver un peu d’inspiration. Étudiez les stratégies marketing de vos concurrents vous aidera à concevoir les vôtres pour développer une base clients et ainsi pousser votre business au niveau supérieur.
Faites une recherche Google avec les noms de vos concurrents pour trouver leurs sites Internet, leurs comptes sociaux et le contenu qu’ils ont créé pour promouvoir leurs produits. Regardez comment ils utilisent chaque canal pour attirer de nouveaux clients vers leur boutique en ligne.
Insérez dans votre business plan une description de la façon dont vous comptez convertir ces cibles en clients réels, grâce à vos messages marketing et de communication. Pour les boutiques en dropshipping, les conversions se passeront typiquement sur votre site Internet lorsque les visiteurs achètent vos produits.

Dans la partie management et organisation de votre business plan, décrivez la structure de votre entreprise. La plupart du temps, les entreprises sont déclarées sous forme demicro -entreprise (un fondateur), une société (deux ou plusieurs fondateurs) ou des coopératives.
Rédigez une présentation courte de chacun des membres clés de votre entreprise. Si vous êtes auto-entrepreneur, ajoutez les éléments de votre parcours professionnel qui vous aideront à gérer votre entreprise. Si vous avez un ou plusieurs partenaires et salariés, faites de même pour eux.
Pensez à cet exercice comme un excellent moyen d’évaluer les forces de chaque personne dirigeant votre entreprise. Lors de cette auto-évaluation, vous serez capable d’identifier les aspects de votre business qui seront faciles à gérer pour vous et ceux que vous feriez mieux de déléguer à des freelances , des partenaires, des employés ou des services sous-traitants. C’est aussi un bon moyen d’optimiser les forces de l’entreprise pour maximiser sa croissance.
Apports financiers
Dans le cas d’une start-up en dropshipping, il y a peu de chance que vous ayez besoin de trouver des fonds puisque l’attrait de ce modèle économique est justement le peu de fonds requis pour se lancer. Cela dit, si vous cherchez un prêt, c’est dans cette section que vous indiqueriez le montant souhaité, comment vous prévoyez de l’investir et comment vous voyez votre retour sur investissement.
Un autre moyen d’exploiter cette section consiste à analyser l’investissement que vous avez ou comptez obtenir lors du lancement ou du développement de votre entreprise. Cela devrait inclure tous les éléments : des ordinateurs pour gérer le site Internet aux frais mensuels pour d’autres services marketing ou commerciaux.
Projections financières
Dans les projections financières, partagez les prévisions de revenus et charges pour les cinq premières années de votre entreprise. L’idée ici est de montrer que le revenu escompté permettra d’atteindre rapidement un retour sur investissement, qu’il s’agisse de vos finances personnelles ou d’un apport au capital.

Si vous êtes à la recherche de fonds, vous aurez besoin de rentrer dans les détails concernant vos revenus, le budget prévisionnel, l’état des flux de trésorerie et les budgets d’investissement. Si vous n’avez pas besoin de fonds, vous ne perdrez pas votre temps à créer ce type de projections financières, qui vous permettront de faire des prévisions réalistes pour le futur de votre entreprise.
L’annexe de votre business plan doit comprendre tout document supplémentaire que vous jugerez nécessaire, en fonction de votre business plan. Cela peut inclure, mais n’est pas limité à :
- Historique de crédits
- Brochures de produits
- Documents légaux
- Contacts fournisseurs
Si vous soumettez votre business plan dans le but d’obtenir des financements, contactez le prêteur pour connaître la documentation requise pour votre demande.

Business plan : exemple et modèle de business plan gratuit
Pour faire un business plan, le plus simple est souvent de se baser sur un exemple de business plan création d’entreprise ou un modèle de business plan gratuit. Alors, où trouver un business plan en ligne ? Quel site propose un business plan exemple concret ?
Voici quelques ressources très utiles pour faire un business plan, pour ne pas partir de zéro :
- La Chambre de Commerce et d’Industrie de Paris (CCI) a développé une plateforme gratuite qui permet de construire son business plan en ligne. Sur CCI Business Builder , vous pourrez construire un business plan pas à pas, à partir d’un modèle de business plan.
- Le site creerentreprise.fr offre un modèle de business plan gratuit Powerpoint pour start-up. Vous pourrez compléter le document directement.
- BPI France a créé un modèle de business plan gratuit / modèle de présentation de projet pour aider les entrepreneurs qui se lancent. Le template se présente sous forme d’un guide PDF à télécharger.
- Le magazine L’Express propose plus de 150 modèles de business plan à télécharger. Vous êtes sûr de trouver un exemple de business plan gratuit pour vos besoins !
- Shopify met aussi à disposition un modèle de business plan gratuit, en anglais. Ce business plan à télécharger se présente sous la forme d’un document Word, avec les grandes parties du business plan.
Logiciel business plan gratuit

Autre approche pour faire un business plan : utiliser un logiciel business plan gratuit. Si la plupart des logiciels de création de business plan sont payants, nous avons trouvé pour vous 2 solutions gratuites :
- Montpellier Business Plan est un logiciel de business plan gratuit à télécharger. Il permet de construire un business plan pas à pas et de construire un prévisionnel en testant plusieurs scénarios.
- Bpi France propose une application gratuite pour faire son business plan en ligne, dans le cadre de son offre Pass Entrepreneur. Vous devrez créer un compte pour pouvoir y accéder.
Ces 2 options de logiciel business plan gratuit devraient répondre à vos besoins.
Comme vous pouvez le voir, rédiger un business plan pour votre entreprise de dropshipping est un très bon moyen de valider votre idée d’entreprise, de percevoir les forces et les faiblesses de votre projet et de mettre toutes les chances de votre côté pour réussir votre aventure en tant qu’entrepreneur. Si vous ne l’avez pas déjà fait, prenez le temps de créer un business plan pour lancer ou développer votre business dropshipping en 2022 !
Découvrez d'autres conseils utiles sur comment faire un business plan dans cet article de Shopify.
- Rédiger un résumé de son projet
- Inclure une description de l’entreprise
- Présenter ses produits et services
- Faire une étude de marché
- Réaliser une analyse SWOT
- Détailler sa stratégie marketing et ventes
- Présenter le management et l’organisation
- Indiquer ses apports financiers
- Réaliser une projection financière
- Préparer les annexes
Vous souhaitez en savoir plus ?
- Nom d’entreprise : Générateur de nom d’entreprise
- Que vendre sur Internet ? Comment trouver des produits dropshipping
- Les 20 avantages et inconvénients de l’e-commerce à connaître
- La signification des couleurs en communication et marketing

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture. 2. Feasibility Business Plan. This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business. But the reality can be more nuanced - it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written. Ideal times to write a business plan include: When you have an idea for a ...
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
It's the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you'll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance. A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and ...
This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections. Whether you're starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool. As a business plan writer and consultant, I've crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse ...
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Step 2: Do your market research homework. The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research. This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to ...
Traditional business plans use some combination of these nine sections. Executive summary. Briefly tell your reader what your company is and why it will be successful. Include your mission statement, your product or service, and basic information about your company's leadership team, employees, and location.
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan: Section 1: Executive Summary. Present the company's mission. Describe the company's product and/or service offerings. Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
Sell your business and explain why it matters. Additionally, supplement your sell with a high level summary of your plan and operating model. However, don't go over one or two pages. Feel free to include the following as well: Business Name. Key Employees. Address.
A business plan is an executive document that acts as a blueprint or roadmap for a business. It is quite necessary for new ventures seeking capital, expansion activities, or projects requiring additional capital. It is also important to remind the management, employees, and partners of what they represent. You are free to use this image on your ...
What is a business plan? A business plan is a guide for a company that identifies its goals and outlines the steps for achieving those goals. Business plans help pinpoint a company's priorities and metrics while also holding employees accountable in their roles. When companies develop business plans, it allows employees at all levels to see the company as a whole enterprise.
A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a business, ... For example, a business plan for a non-profit might discuss the fit between the business plan and the organization's mission. Banks are quite concerned about defaults, so a business plan for a bank loan will build a convincing case for the organization's ...
Above all, the numbers should help answer why your business can do it better. 4. Competitive Analysis. A good business plan will present a clear comparison of your business vs your direct and indirect competitors. This is where you prove your knowledge of the industry by breaking down their strengths and weaknesses.
The Better Business Planning Process. The business plan process includes 6 steps as follows: Do Your Research. Strategize. Calculate Your Financial Forecast. Draft Your Plan. Revise & Proofread. Nail the Business Plan Presentation. We've provided more detail for each of these key business plan steps below.
The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs. Purposes of a Business Plan. A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
To outline the importance of business plans and make the process sound less daunting, here are 10 reasons why you need one for your small business. 1. To help you with critical decisions. The primary importance of a business plan is that they help you make better decisions. Entrepreneurship is often an endless exercise in decision making and ...
A business plan is essential as an entrepreneur. It helps you set clear goals and guidelines for how you will manage your business. A business plan may also be needed to set employee goals, obtain funding or even to sell your business one day. In this article, we discuss the importance of a business plan for entrepreneurs, as well as a few main ...
The best way to accomplish any business or personal goal is to write out every possible step it takes to achieve the goal. Then, order those steps by what needs to happen first. Some steps may ...
The first step is to calculate the start-up costs. Identify a list of expenses and put a dollar amount to each of them through research and requesting quotes. The SBA has a start-up costs ...
1. Know your competition. You need to name them and point out what makes you different from (and better than) each of them. But do not disparage your competition. Continue reading. 2. Know your ...
The project management lifecycle is a step-by-step framework of best practices used to shepherd a project from its beginning to its end. This project management process generally includes four phases: initiating, planning, executing, and closing. Some may also include a fifth "monitoring and controlling" phase between the executing and ...
Learn the client's expectations up front and meet them. Discuss openly and plan ahead for cost considerations. Know the client's priorities and goals, and the relative importance of a case. Litigators spend countless hours trying to position themselves to land a case with a large corporate client. As hard as that process may seem, getting ...
We spoke a short while ago to Kate Forbes, MSP and deputy first minister of Scotland, and we asked why the SNP thinks Labour's plan to create GB Energy - a publicly owned energy company ...
Comment faire un business plan : les grandes étapes. Un business plan passe par 5 grandes étapes : établir des objectifs, rechercher des données, comprendre sa cible, choisir un format et rédiger. Faire un business plan étape 1 : établir des objectifs. Il y a deux questions clés à se poser ici :