103 Tuberculosis Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best tuberculosis topic ideas & essay examples, 💡 interesting topics to write about tuberculosis, ⭐ good essay topics on tuberculosis, 📌 simple & easy tuberculosis essay titles.
- 🥇 Most Tuberculosis Abortion Topics to Write about
- Tuberculosis as a Global Health Issue Over the years, the bacteria strain that causes tuberculosis has developed a lot of resistance mainly as a result of a lack of compliance to treatment on the part of the patient.
- The History of Tuberculosis To prove the contagiousness of the infection, the French doctor Jean-Antoine Villemain collected the sputum of the infected and placed it in a container with guinea pigs.
- The Misinformation Associated With Tuberculosis Diagnosis The head of HR should also be interviewed to assess how workers’ data is being stored and whether the method is secure.
- The Concepts of Epidemiology and Nursing Research to Tuberculosis A typical sign of tuberculosis of the spine is back pain, but a sign of TB of the kidneys is blood in the urine.
- Tuberculosis: Epidemiology, Prevention, and Control Approximately 920,000 cases of TB and HIV coinfection were accounted for in 2017, representing 9% of the total TB cases observed.
- Strategy Against Tuberculosis in US Children Tuberculosis in children and adolescents in the US remains a serious medico-biological and social problem, the significance of which has significantly increased in the conditions of the tuberculosis epidemic.
- Tuberculosis Presentation Supplement As a result, policies for the prevention and control of tuberculosis are still in use and are vital for the population.
- Tuberculosis in the Late 19th Century Tuberculosis became a dangerous challenge for the society of the Gilded Age and was inscribed in the public culture through the works of art.
- Tuberculosis: Transmission, Clinical Manifestations and Treatment When inhaled, the Tubercle bacilli are carried to the alveolar, where they cause infection. LTBI patients do not manifest any symptoms and are unable to spread the infection.
- Tuberculosis in Older Adults: Epidemiological Analysis Despite the decrease in TB cases, the number of older adults affected by it remains stable throughout the years, signifying that the current measures need to be tailored for this specific group.
- The Tuberculosis Medication: Patient Compliance Various methods have been used to ensure patient compliance during TB treatment; most of the methods have focused on: home based care and hospital based care where the health officials have developed mechanisms to ensure […]
- Discussion of Tuberculosis Epidemiology These two sources offer relevant and credible information about smoking patterns in the area and causes leading to the emergence of new addicted people.
- The Problem of Co-Morbidity: Alcohol and Tuberculosis The problem of alcohol abuse as one of the main factors for the emergence and amplification of tuberculosis is widely discussed in medical circles and social organizations as well.
- Tuberculosis: Symptoms and Treatment The development of the disease is gradual with only an eighth of those infected with the mild form of the disease developing secondary infection.
- Tuberculosis: Diagnosis, X-Ray Radiography Tuberculosis is among the disease category of rare bone diseases, and the problem is estimated to occur in the range of 1 to 3 %.
- Reduction of Tuberculosis in Brockton, Massachusetts The other objectives include reduction of infections of contagious diseases and development of vaccinations through an increase in the number of people vaccinated for these disorders. The social and economic statuses of the disadvantaged people […]
- Tuberculosis: Causes and Prevention For women between the ages of 14 and 45, TB infection is the leading cause of death. Poverty is a localized environmental factor that directly aggravates the onset and development of TB.
- Tuberculosis: Demographics & Epidemiological Triangle The primary source of the bacteria is the sputum emanating from the larynx or the lungs of untreated tuberculosis patients. During the treatment of tuberculosis, the first step is to isolate the patients in a […]
- Respiratory Isolation Teaching for Tuberculosis The patients and their family members should be provided with the right information and guidelines on how to organize the appropriate isolation rooms and maintain the patient in order to prevent the spread of the […]
- Recognizing Health Care Worker With Tuberculosis in the Workplace On the other hand, workers that are aware of the health policies do not understand them because of the complex language, and terminologies used in the health documents.
- Pharmacology of the Tuberculosis Epidemic With over a third of the global population contracting TB infections, paradigmatic questions, such as the origin of TB, its treatment, demographics and frequency remain unexplored in-depth.
- Epidemiology: Tuberculosis in India The health status of a nation is one of the key indicators of the level of growth or the economic status of a given nation since a healthy nation automatically results to a wealthy nation.
- Peter Crosta: What Is Tuberculosis? What Causes Tuberculosis? The name of the bacterium causing tuberculosis is Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. The article also discusses the various treatment options that can be used to treat patients infected with tuberculosis.
- Prevalence of Tuberculosis and Malaria in Africa and Middle East Globally the epidemiological distribution of Malaria and Tuberculosis disease worldwide is greatly skewed with majority of the cases occurring in Africa; 90% of all malaria related deaths for instance take place in Africa which is […]
- Tuberculosis Surveillance Program: Evaluation Design Participation of the users and the application of the information in guiding future prevention, research and control programs will be adhered to.
- The Global Impact of Tuberculosis and Malaria Again the whole of Africa shows the maximum incidence when compared to the rest of the world. The HAART therapy in HIV infections allows the treatment period to be free of TB infection.
- Pathophysiology and Management of Tuberculosis Infection This, though, is in sharp contrast to the limited development of BCG in the first two decades of the 20th century.
- The Problem of Tuberculosis in South Africa Consequently, high treatment interruption rates, the HIV epidemic, low cure rates have contributed to the emergence of multi drug resistance tuberculosis in South Africa; this has been blamed on the adoption of inappropriate treatment programmes […]
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Intervention As a BSN-prepared community health nurse, Debbie needs to implement measures that reduce the danger of a tuberculosis outbreak in the community.
- Tuberculosis Control and Prevention in Prisons It is widely accepted that the overall conditions in the US correction facilities, along with the background lifestyles of some inmates, lead to a dramatic disease rate in cells.
- HR Department Steps to Provide Health Information: Tuberculosis The first step, or lecturing, should include the causes and conditions for the occurrence of pulmonary diseases with the emphasis on tuberculosis, as well as the results and consequences of treatment.
- Tuberculosis: Health Behaviors, Surveillance System, and Risk Communication In the case of TB, risk communication, especially between ordinary people, is essential, since some people may be ashamed of their disease and even prefer not to treat it rather than make it known.
- Tuberculosis: History and Current State of a Disease A breakthrough in understanding the nature of tuberculosis occurred in the XIX century. The recent figures indicate quite a high level of disease spread in Georgia.
- Tuberculosis as the Health Problem in New Jersey New Jersey has a health policy that postulates the actions of physicians and medical personnel in cases of new cases of tuberculosis.
- Communicable Diseases: Tuberculosis The explication following herein describes tuberculosis as an infectious disease including details such as the disease’s incidence in the World and in Cobb County, GA, agent characteristics, environmental characteristics, signs and symptoms, treatment, and how […]
- Culture and Disease: Tuberculosis and African Americans In this paper we will discuss in details about tuberculosis and why the African Americans have been thinking of the disease and how different treatment options, cultural beliefs and values have been impacting on the […]
- An Overview of Tuberculosis The coming into existence of deadly diseases and the escalation of the already existing epidemics, to name but a few, are some of the key characteristics of this century.
- Tuberculosis: The Symptoms, Pathogenesis, and Treatment The cell wall is however, due to the presence of concentration of lipids, thought to be the main contributor for the virulence of the bacterium.
- Tuberculosis Treatment in Clinical Practice This paper briefly discusses the agent and environmental characteristics of the disease, its signs, symptoms, and treatment, providing a basis for the public health nurse’s clinical practice.
- Tuberculosis and How to Prevent Its Dissemination Due to an easy way of spreading and the gravity of the consequences, it is necessary to prevent the dissemination of tuberculosis.
- Tuberculosis Employee Assistance Program As a part of them, TB tests, training for employees about tuberculosis and other infections, and HR policies should help to prevent such situations in the future.
- Tuberculosis: Epidemiology and Health Statistics Nevertheless, access to health care and the quality of treatment are not the only factors contributing to the resurgence of TB. As compared to the worldwide statistics, the U.S.is not included in the list of […]
- Descriptive and Analytical Epidemiology: Tuberculosis and HIV The establishment of trends in the epidemic process for the rapid introduction of adjustments helps optimize preventive and anti-epidemic measures alongside the evaluation of the effectiveness of the activities.
- Descriptive and Analytical Epidemiology: Tuberculosis in Pennsylvania To obtain a comprehensive picture of the issue, it is necessary to identify the main categories of the population at risk.
- Tuberculosis in Nigeria: Policy Brief Considering this, the present policy brief will discuss the nature of the infection, its risk factors and the populations it affects most, the scope of infection spread in Nigeria, and the consequences of the problem […]
- Examining Chest X-Rays of a Tuberculosis Patient This microbial infection of the respiratory parts of the lung proceeds with the development of intraalveolar exudation and inflammatory infiltration of the pulmonary parenchyma, fever, and productive cough with mucopurulent sputum.
- Tuberculosis and Human Immunodeficiency Coinfection Moreover, TB is a sensitive illness because the improper medication is dangerous as it can result in the illness becoming resistant to drugs to both the patient and the person to who the patient transmits […]
- Tuberculosis: Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment In this case, it means that the incubation period will be counted from the introduction of the ‘causal’ microbe, as opposed to the initial infection.
- Tuberculosis Epidemiology Worldwide in 2015 Despite multiple attempts to eliminate the most dangerous diseases and improve the epidemiologic situation, there are many illnesses or other health issues that deteriorate the health of the nation and result in the appearance of […]
- EFI Testing to Detect Drug Resistance of Tuberculosis The article that was selected for the review introduces the problem of antibiotics resistance and the causes of it in humans.
- Tuberculosis Outbreak Investigation When investigating whether a disease is a cluster, a researcher should gather adequate information, which will help him/her to make a conclusion. When investigating whether a disease is an outbreak, a good researcher should gather […]
- Tuberculosis: Community and National Response Most commonly, three or four antibiotics are taken during the initial months of the treatment, and the number is decreased to two for the rest of the process.
- Tuberculosis Statistics Among Cigarette Smokers The proposal outlines the statistical applications of one-way ANOVA, the study participants, the variables, study methods, expected results and biases, and the practical significance of the expected results.
- Tuberculosis and Infectious Disease Slogan The level of awareness about sexually transmitted diseases among people is higher compared to that of tuberculosis, owing to the fact the risk factors of the latter are hard to identify. The risk population of […]
- Epidemiological Studies of Tuberculosis The United States The prevalence rate of tuberculosis in the United States is the lowest when compared to the prevalence rates in Sub-Saharan Africa and Asia.
- Prevention and Treatment of Tuberculosis Although a strong immune system can contain the pathogen, in an immunosuppressed individual, the MTB is capable of multiplying and rupturing the host’s macrophages, resulting in the destruction of the body’s primary line of defense […]
- Control of Tuberculosis in Swaziland This is a programme plan for controlling the TB epidemic in Swaziland as one of the developing countries with highest prevalence of TB infections in the world.
- The Problem of Tuberculosis in the American Local Community The public health ministry is in charge of curtailing the effects of the disease, but it is reluctant to liaise with the community to resolve the issue.
- The Role of Vitamin D for Tuberculosis Treatment This study investigates the use of vitamin D for the deterrence and cure of tuberculosis and other contagious infections. The unearthing of vitamin D as a therapeutic agent begins with the detection of rickets as […]
- The Evolutionary Genetics of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis The aim of the study was to define the prevalence of the various genotypes, drug resistance isolates and cluster patterns of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Taipei in order to present information on the possible methods and […]
- The Impact of Tuberculosis on the Work of Anton Chekhov
- The Second Greatest Cause of Death Due to a Single Infectious Agent: Tuberculosis
- Tuberculosis: The Most Common Bacterial Infection Worldwide
- The Differences and Similarities of Pneumonia and Tuberculosis
- Modern Methods of Tuberculosis Diagnosis
- Prevention of the Tuberculosis Epidemic
- Global Tuberculosis Testing Market Finds Encouragement in Growing Healthcare Efforts
- Risk-Based Disease Management in the Fight Against to Bovine Tuberculosis
- People Centered Tuberculosis Care Verses Standard Directly
- The Signs, Symptoms and Treatment of Tuberculosis
- The Diagnosis of Cancer, Pulmonary Tuberculosis, and HIV AIDS
- Living in the Shadow of Death Tuberculosis and the Social Experience of Illness in American History
- The Pathogenesis of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
- Tuberculosis: Most Lethal Bacterial Pathogen
- The Relationship Between Cystic Fibrosis and Tuberculosis
- Tuberculosis Vaccine May Help Stop Multiple Sclerosis Development
- The Role of Race and Economic Disadvantage in the Incidence of Tuberculosis
- Factors Influencing the Perceived Priority of Tuberculosis in India
- Why Is Tuberculosis Coming Back With a Vengeance
- Immigrants and the Spread of Tuberculosis in the United States: A Hidden Cost of Immigration

🥇 Most Interesting Tuberculosis Topics to Write about
- Innovation Dynamics in Tuberculosis Control in India: The Shift to New Partnerships
- Tuberculosis: Infectious Disease and Health Care Facilities
- What Is Tuberculosis, and How Serious Is This Disease
- The Background of Common Infection, Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- The Development of The Tuberculosis Vaccine
- The Effects of Tuberculosis on the Health and Lives of Humans
- The Spread of Tuberculosis in Ancient Egypt and Europe
- The Success of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
- Ontology With SVM Based Diagnosis of Tuberculosis and Statistical Analysis
- The Causes and Treatment of the Disease of Tuberculosis
- Techniques Used for the Diagnostic of Ancient Tuberculosis Remains
- Positive Tuberculosis Blood Test as a Predictor of Health Status Among HIV-Infected Persons
- The Incidence of Tuberculosis Among Low Income People
- The History of the Tuberculosis and Research on Its Vaccine
- Performance-Based Incentives for Health: A Way to Improve Tuberculosis Detection and Treatment Completion
- Historians Blamed Columbus for Spreading Tuberculosis to the World
- Tuberculosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- MDR Tuberculosis in Georgia: Problem in Prevention and Control
- Evolution of Drug Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
- Investigation of Bovine Tuberculosis in Rangpur Division of Bangladesh
- HPLC: Techniques Used for the Diagnostic of Ancient Tuberculosis Remains
- Impacts of Tuberculosis and AIDS on Society
- Ethics Ideas
- Infection Essay Ideas
- Hygiene Essay Topics
- SARS Topics
- Vaccination Research Topics
- Immunization Paper Topics
- Viruses Research Topics
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 13). 103 Tuberculosis Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/tuberculosis-essay-topics/
"103 Tuberculosis Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 13 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/tuberculosis-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '103 Tuberculosis Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 13 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "103 Tuberculosis Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 13, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/tuberculosis-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "103 Tuberculosis Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 13, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/tuberculosis-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "103 Tuberculosis Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 13, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/tuberculosis-essay-topics/.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Tuberculosis articles from across Nature Portfolio
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by strains of bacteria known as mycobacteria. The disease most commonly affects the lungs and can be fatal if not treated. However, most infected individuals show no disease symptoms. One third of the worlds population is thought to have been infected with TB.
Latest Research and Reviews
Chest ultrasound is better than CT in identifying septated effusion of patients with pleural disease
- Linhui Yang
Mycobacterium tuberculosis suppresses host antimicrobial peptides by dehydrogenating L-alanine
In this work, authors mechanistically investigate the reduced induction of antimicrobial peptides in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infected macrophages.
- Yuanna Cheng
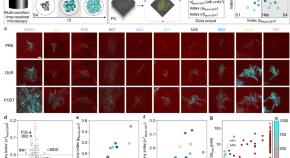
Dynamic microfluidic single-cell screening identifies pheno-tuning compounds to potentiate tuberculosis therapy
Tuberculosis is a major global health threat. Here, the authors develop a single-cell drug discovery approach and identify a compound that tunes bacterial phenotypic variation. This enhances the activity of anti-tubercular drugs against the pathogen.
- Maxime Mistretta
- Mena Cimino
- Giulia Manina
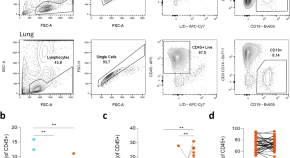
B cell heterogeneity in human tuberculosis highlights compartment-specific phenotype and functional roles
Using flow cytometry and transcriptomic analyses, the authors characterize the functional diversity of B cell subsets in the lungs of patients with tuberculosis.
- Robert Krause
- Paul Ogongo
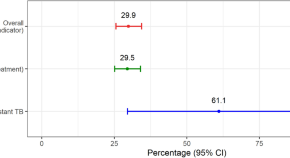
Catastrophic costs incurred by tuberculosis affected households from Thailand’s first national tuberculosis patient cost survey
- Sitaporn Youngkong
- Phalin Kamolwat
- Takuya Yamanaka

Mortality among extrapulmonary tuberculosis patients in the HIV endemic setting: lessons from a tertiary level hospital in Mbeya, Tanzania
- Erlend Grønningen
- Marywinnie Nanyaro
- Tehmina Mustafa
News and Comment
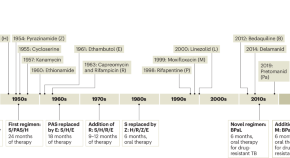
Restocking the tuberculosis drug arsenal
After many lean years, important progress has been made in updating the anti-tuberculosis drug armamentarium; a new drug that targets bacterial protein synthesis is one of several that could help transform the treatment of this neglected and deadly disease.
- Eric L. Nuermberger
- Richard E. Chaisson
Digital intervention improves tuberculosis treatment outcomes
An intervention that incorporates electronic pill boxes and remote adherence monitoring improved treatment success in patients with tuberculosis in Tibet — making this a promising strategy for low-resource settings.
- Karen O’Leary

A spotlight on the tuberculosis epidemic in South Africa
Tuberculosis is the leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, with over 25% of these occurring in the African region. Multi-drug resistant strains which do not respond to first-line antibiotics continue to emerge, putting at risk numerous public health strategies which aim to reduce incidence and mortality. Here, we speak with Professor Valerie Mizrahi, world-leading researcher and former director of the Institute of Infectious Disease and Molecular Medicine at the University of Cape Town, regarding the tuberculosis burden in South Africa. We discuss the challenges faced by researchers, the lessons that need to be learnt and current innovations to better understand the overall response required to accelerate progress.
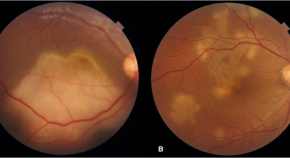
Presumed ocular tuberculosis – need for caution before considering anti-tubercular therapy
- Rohan Chawla
- Urvashi B. Singh
- Pradeep Venkatesh
Transforming tuberculosis diagnosis
Diagnosis is the weakest aspect of tuberculosis (TB) care and control. We describe seven critical transitions that can close the massive TB diagnostic gap and enable TB programmes worldwide to recover from the pandemic setbacks.
- Madhukar Pai
- Puneet K. Dewan
- Soumya Swaminathan
B cells and T follicular helper-like cells within lung granulomas are required for TB control
We show a crucial protective function for T follicular helper (T FH )-like cells localized within granuloma-associated lymphoid tissue for Mycobacterium tuberculosis control in mouse models of tuberculosis. Antigen-specific B cells contribute to this strategic localization and the maturation of cytokine-producing T FH -like cells.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Help | Advanced Search
Electrical Engineering and Systems Science > Image and Video Processing
Title: phd thesis. computer-aided assessment of tuberculosis with radiological imaging: from rule-based methods to deep learning.
Abstract: Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb.) that produces pulmonary damage due to its airborne nature. This fact facilitates the disease fast-spreading, which, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2021 caused 1.2 million deaths and 9.9 million new cases. Fortunately, X-Ray Computed Tomography (CT) images enable capturing specific manifestations of TB that are undetectable using regular diagnostic tests. However, this procedure is unfeasible to process the thousands of volume images belonging to the different TB animal models and humans required for a suitable (pre-)clinical trial. To achieve suitable results, automatization of different image analysis processes is a must to quantify TB. Thus, in this thesis, we introduce a set of novel methods based on the state of the art Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Computer Vision (CV). Initially, we present an algorithm to assess Pathological Lung Segmentation (PLS). Next, a Gaussian Mixture Model ruled by an Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm is employed to automatically. Chapter 3 introduces a model to automate the identification of TB lesions and the characterization of disease progression. Chapter 4 extends the classification of TB lesions. Namely, we introduce a computational model to infer TB manifestations present in each lung lobe of CT scans by employing the associated radiologist reports as ground truth. In Chapter 5, we present a DL model capable of extracting disentangled information from images of different animal models, as well as information of the mechanisms that generate the CT volumes. To sum up, the thesis presents a collection of valuable tools to automate the quantification of pathological lungs. Chapter 6 elaborates on these conclusions.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

Research Topics

Return to main research page
Adherence to treatment
Arts and humanities, behavioural research, biology of host and pathogen, capacity development & training, clinical management, clinical trials, computational genomics, diagnostics, digital health, drug development, drug-resistant tb, gene regulation, host-directed therapies, latent and sub-clinical tb, migrant tb / tb in mobile populations, non-tuberculous mycobacterial disease (ntms), pharmacology, whole genome sequencing.
Developing effective drug regimens is just one part of effective TB treatment. The course of treatment is long, may cause side effects, and non-adherence can lead to new antibiotic resistance. The same is true of treating latent TB, when individuals have no symptoms. Supporting people in taking their full course of treatment, and understanding reasons for non-adherence, are therefore important.
Example outputs:
- All nonadherence is equal but is some more equal than others? Tuberculosis in the digital era. (2020) Stagg, H. R. et al. ERJ Open Res 6(4) https://doi.org/10.1183/23120541.00315-2020
- IMPACT study on intervening with a manualised package to achieve treatment adherence in people with tuberculosis: protocol paper for a mixed-methods study, including a pilot randomised controlled trial. (2019) Stagg, H. R. et al. BMJ Open 9(12): e032760 https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2019-032760
- Measuring and reporting treatment adherence: What can we learn by comparing two respiratory conditions? (2020) Tibble, H. et al . Br J Clin Pharmacol https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.14458
- Protocol for a systematic review of treatment adherence for HIV, hepatitis C and tuberculosis among homeless populations. (2020) Johnson, L. et al . Syst Rev 9(1): 211 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-020-01470-y
The IMPACT study - Voices from the Front Line: Presentation for World TB Day 2020 ( Slideshare )
Projects: IMPACT , RID-TB
People: Ibrahim Abubakar , Amy Clarke , Marcia Darvell , Rob Horne , Annie Jones , Marc Lipman , Lele Rangaka
Return to main research page | top
TB is an ancient disease, and also immensely significant in our more recent history. New DNA and lipid technologies allow TB disease to be identified in archaeological samples.
- Oldest evidence of tuberculosis in Argentina: A multidisciplinary investigation in an adult male skeleton from Saujil, Tinogasta, Catamarca (905-1030 CE). (2020) Luna, L. H. et al. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 125: 101995 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tube.2020.101995
Verification of tuberculosis infection among Vac mummies (18th century CE, Hungary) based on lipid biomarker profiling with a new HPLC-HESI-MS approach. (2020) Varadi, O. A. et al . Tuberculosis (Edinb) 126: 102037 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tube.2020.102037
People: Helen Donoghue
TB has been part of the fabric of life in the UK for many centuries, and therefore has a presence in our culture, which we are keen to explore.
People: John Mullan
Example outputs:
People: Amy Clarke , Rob Horne , Annie Jones
See also: Adherence to treatment
See sub-themes: Computational Genomics ; Drug Development, Gene regulation ; Immunology ; Pharmacology
People: Kristine Arnvig , Francois Balloux , Sanjib Bhakta , Frank Kloprogge , Camus Nimmo , Gillian Tomlinson , Lucy van Dorp
The body is complex, and infection and our immune response to it are complex processes that we only partly understand. However, we can now collect enormous amounts of information about the activity going on in our bodies, and use computers to identify signatures that are found (for example) in a group of people with known disease, but not in people we know not to be infected. These signatures can then be used as biomarkers for disease in people of unknown status. For example, this approach is analysing mRNA expression in the blood for biomarker signatures that identify people who don’t yet have clinical TB, but in whom TB bacteria that were latent/inactive have now become active. In addition, we are investigating TB-specific cytokine profiles that may aid to distinguish between latent and active TB, as well as functional T cell profiling.
- Blood transcriptional biomarkers for active pulmonary tuberculosis in a high-burden setting: a prospective, observational, diagnostic accuracy study. (2020) Turner, C. T. et al. Lancet Respir Med 8(4): 407-419 https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30469-2
- Blood transcriptomic biomarkers for tuberculosis screening: time to redefine our target populations? (2021) Gupta, R.K. and M. Noursadeghi. Lancet Glob Health https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00088-7
- Blood transcriptomic stratification of short-term risk in contacts of tuberculosis. (2020) Roe, J. et al. Clin Infect Dis 70(5): 731-737 https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciz252
- Concise whole blood transcriptional signatures for incipient tuberculosis: a systematic review and patient-level pooled meta-analysis. (2020) Gupta, R. K. et al. Lancet Respir Med 8(4): 395-406 https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30282-6
- Mycobacteria-Specific Mono- and Polyfunctional CD4+ T Cell Profiles in Children With Latent and Active Tuberculosis: A Prospective Proof-of-Concept Study. (2019) Tebruegge, M. et al. Front Immunol 10: 431 https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00431 .
People: Ibrahim Abubakar , Rishi Gupta , Isobella Honeyborne , Maddy Noursadeghi , Marc Tebruegge
Most TB is found in the Global South, where overall scientific infrastructure and support is most insecure for multiple historical and economic reasons. We strongly support the idea that these countries should be enabled to develop high quality science with highly trained workforces. We are both part of large programmes explicitly aiming to improve capacity development, and we also bring capacity development into other work wherever we can. As a university, we see the importance of academic and practical education, and have expertise in delivering it. This includes supporting individuals to visit UCL for varying periods of time, carrying out workshops in London and abroad, training laboratory workers in diagnostic laboratories, and being part of bigger capacity development programmes.
Projects: PanACEA ; UK-Korean partnership for a TB cohort
People: Frank Kloprogge , Tim McHugh , Ali Zumla
Although standard treatments are published for patients with TB, working with individual patients to apply those treatments is a long process that is often far from smooth. TB as a disease is different in every patient in terms of where the infection is active, whether the bacteria are resistant to any antibiotics, how the patient responds to drugs they are given, their personal situation, and other complicating conditions or factors. Treatment is long, and many of these factors may change, while stopping the treatment early may lead to new drug resistance developing. All this happens in the context of a changing NHS and Social Services with limited resources. Clinical management is therefore never routine, and developing processes that are flexible and robust enough is challenging.
People: Helen Booth , Hanif Esmail , Marc Lipman , Maddy Noursadeghi , Jacqui White
The way we can improve treatment for TB, and be confident that it will be safe and effective, is through stringent clinical trials. For TB, which is a disease that can be slow to develop and to treat, where the drug resistance patterns are changing, and manifests most in the poorest parts of the world, these trials are particularly challenging. They involve a large team of people with different skills over a long period of time, so are costly, and those we run have to be carefully selected. The MRC Clinical Trials Unit at UCL – which formed originally as the MRC Tuberculosis Research Unit in 1948 has an unprecedented track record in TB trials. As well as their leadership, management, statistical and analysis expertise, they work with others at UCL who carry out TB microbiology and train and monitor participating laboratories, and an army of people throughout the world who recruit and work with the trial participants. UCL also works with other trial sponsors such as the Global TB Alliance, and the University of Stellenbosch.
Sub-themes: Clinical trial design
Projects: SimpliciTB , STREAM 2.0 , TB-CHAMP , TB-PRACTECAL , ZeNix ; ( MRC-CTU TB project page )
People: Suzanne Anderson , Robindra Basu Roy , Angela Crook , Hanif Esmail , Diana Gibb , Ruth Goodall , Tim McHugh , Sarah Meredith , Andrew Nunn , Lele Rangaka , Anna Turkova , Conor Tweed
Studying the spread of M. tuberculosis strains can identify local outbreaks, identify sub-strains with particular properties, inform on genotypic predictors of disease pathology, tell us how drug resistance develops and spreads, and inform us about human history. Computational genomics relies on the ability to differentiate isolates based on their evolutionary relatedness, typically employing the fields of phylogenetics and population genomics. These days, this is mostly done through Whole Genome Sequencing .
- Dynamics of within-host Mycobacterium tuberculosis diversity and heteroresistance during treatment. (2020) Nimmo, C. et al. EBioMedicine 55: 102747 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102747
- Population-level emergence of bedaquiline and clofazimine resistance-associated variants among patients with drug-resistant tuberculosis in southern Africa: a phenotypic and phylogenetic analysis. (2020) Nimmo, C. et al. Lancet Microbe 1(4): e165-e174 https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30031-8
People: Francois Balloux , Camus Nimmo , Lucy van Dorp
Despite many technical advances in diagnostics in the last two decades diagnosing TB is often challenging, especially in children. Existing tests have suboptimal sensitivity, which means that many TB patients have false-negative results. Diagnosing TB in children has additional challenges, as collecting adequate samples is often difficult and most children have paucibacillary disease (meaning that few mycobacteria are present in their clinical samples, making it hard to detect them). We are conducting studies on existing immune-based TB tests, including the tuberculin skin test and interferon-gamma release assays, and are working towards designing novel immunological TB tests that perform better across all age groups.
- Diagnostic accuracy of QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus assays in children and adolescents with tuberculosis disease. (2020) Soler-Garcia, A. et al. J Pediatr 223: 212-215 e211 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.02.025
- Tuberculosis disease in children and adolescents on therapy with antitumor necrosis factor-a agents: A collaborative, multicenter Paediatric Tuberculosis Network European Trials Group (ptbnet) study. (2020) Noguera-Julian, A. et al . Clin Infect Dis 71(10): 2561-2569 https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciz1138
- TB-PRACTECAL
- Comparison of Cepheid Xpert MTB/XDR and GenoScreen Deeplex Myc-TB for MDR and XDR M. tuberculosis (Giovanni Satta).
People: Tim McHugh , Giovanni Satta , Marc Tebruegge
Return to main research page | top
- Knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors on utilizing mobile health technology for TB in Indonesia: A qualitative pilot study. (2020) Aisyah, D. N. et al . Front Public Health 8: 531514 https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2020.531514
- Management and control of tuberculosis control in socially complex groups: a research programme including three RCTs. (2020) Story, A., et al. Programme Grants for Applied Research 8(9) https://doi.org/http://doi.org/10.3310/pgfar08090
- TB Mentor app for clinical decision support
People: Hanif Esmail , Andrew Hayward , Patty Kostkova , Al Story
After the success of early drugs against TB, starting in the 1940s with streptomycin, there was a long period where no new antibiotics were developed, due to lower priority, cost and time to develop these, and lack of biological understanding. The rise of antibiotic resistance has shown this to be short-sighted, and at last there is a renewed pipeline of drugs, some of which have moved into clinical use. We are looking for novel drugs, coming both from the biology, and also from direction of large collections of chemical derivatives.
- Analogues of Disulfides from Allium stipitatum Demonstrate Potent Anti-tubercular Activities through Drug Efflux Pump and Biofilm Inhibition. (2018) Danquah, C. A. et al. . Sci Rep 8(1): 1150 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18948-w
- Carprofen elicits pleiotropic mechanisms of bactericidal action with the potential to reverse antimicrobial drug resistance in tuberculosis. (2020) Maitra, A. et al. J Antimicrob Chemother 75(11): 3194-3201 https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkaa307
- Cell wall peptidoglycan in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: An Achilles' heel for the TB-causing pathogen. (2019) Maitra, A., T. Munshi, J. Healy, L. T. Martin, W. Vollmer, N. H. Keep and S. Bhakta. FEMS Microbiol Rev 43(5): 548-575 https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuz016
- Characterization of the MurT/GatD complex in Mycobacterium tuberculosis towards validating a novel anti-tubercular drug target. (2021) Maitra, A., S. Nukala, R. Dickman, L. T. Martin, T. Munshi, A. Gupta, A. J. Shepherd, K. B. Arnvig, A. B. Tabor, N. H. Keep and S. Bhakta. JAC Antimicrob Resist 3(1): dlab028 https://doi.org/10.1093/jacamr/dlab028
- Ertapenem and Faropenem against Mycobacterium tuberculosis : in vitro testing and comparison by macro and microdilution. (2020) Gonzalo, X. et al. BMC Microbiol 20(1): 271 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-020-01954-w
- Improving the potency of N-Aryl-2,5-dimethylpyrroles against multidrug-resistant and intracellular mycobacteria. (2020) Touitou, M. et al. ACS Med Chem Lett 11(5): 638-644 https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00515
- Polymersomes eradicating intracellular bacteria. (2020) Fenaroli, F. et al. ACS Nano 14(7): 8287-8298 https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c01870
- Role of whole-genome sequencing in characterizing the mechanism of action of para-aminosalicylic acid and its resistance. (2020) Satta, G. et al . Antimicrob Agents Chemother 64(9) https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00675-20
- See also Tuberculomucin in 'Host-directed therapies', below
- Inhibitors of cell-wall peptidoglycan as novel anti-TB drugs
People: Sanjib Bhakta , Dimitris Evangelopoulos , Tim McHugh , Mat Todd
Return to main research page | top
Antibiotics are one of the cornerstones of the modern world, curing once-fatal diseases, and this is true for TB. Yet resistance to these antibiotics develops - in the case of M. tuberculosis , through the bacteria acquiring mutations in their chromosomes one at a time. Reducing the risk of this happening is one major reason that TB is always treated with combination drug therapy. With TB the problem is worsened by the long period of treatment and side effects of drugs, which can lead to patients not completing their full courses. It is an aspect of TB that affects almost everything else: diagnosis, clinical management, and drug development to name a few.
People and sub-themes:
- Clinical management of patients ( Marc Lipman )
- Clinical trials ( MRC CTU at UCL , Angela Crook , Diana Gibb , Tim McHugh , Andrew Nunn )
- Development and spread of resistance ( Francois Balloux , Camus Nimmo , Lucy van Dorp )
- Monitoring resistance of isolates in clinical trials for new drug combinations ( Tim McHugh )
- Repurposing Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs to Reverse Drug resistance in TB ( Sanjib Bhakta )
- Bedaquiline resistance in drug-resistant tuberculosis HIV co-infected patients. (2020) Nimmo, C. et al . Eur Respir J 55(6) https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.02383-2019
- Carprofen elicits pleiotropic mechanisms of bactericidal action with the potential to reverse antimicrobial drug resistance in tuberculosis. (2020) Maitra, A. et al. J Antimicrob Chemother 75(11): 3194-3201 https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkaa307
Projects: SimpliciTB , STREAM 2.0 , TB-CHAMP , TB-PRACTECAL , ZeNix
Although we have known the genetic structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis for over 20 years, much of its biology relates to how and when genes are switched on and off, but our understanding of the underlying mechanisms remains incomplete. The development of high-throughput sequencing (HTS) techniques, has revealed the abundance and importance of regulatory RNAs such as small RNAs and so-called riboswitches in bacterial gene expression control, and we can now monitor expression of all genes in an effort to understand their role in different activity states and in different locations within the host.
- Coupling of peptidoglycan synthesis to central metabolism in mycobacteria: Post-transcriptional control of CwlM by aconitase. (2020) Bancroft, P. J. et al. Cell Rep 32(13): 108209 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108209
- Riboswitches: choosing the best platform. (2019) Arnvig, K. B. Biochem Soc Trans 47(4): 1091-1099 https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20180507
People: Kristine Arnvig
Classically we think of treating bacterial disease with antibiotics – molecules that kill or damage the bacteria, and ideally don’t affect the patient at all. A complementary approach is to use molecules that modulate the host’s immune response. An effective immune response aims to kill pathogen but not its own cells. Pathology caused by infectious agents can either be a direct effect of the pathogen, or arise indirectly from an inappropriate immune response that causes damage. Host-directed therapies, therefore, can both be developed to stimulate the immune response, and dampen autoimmune damage depending on what is needed.
- Host-directed therapies and holistic care for tuberculosis. (2020) Zumla, A. et al. Lancet Respir Med 8(4): 337-340 https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30078-3
- Tuberculomucin - a substance first developed by Dr Friedrich Weleminsky in the early part of the 20th century (Friedrich Weleminsky, Ueber die Bildung von Elweiss und Mucin durch Tuberkelbacillen, Berliner klinische Wochenschr 28 (1912): 1-8. Translated by Stephanie Eichberg (SE)). Long term TB culture following his protocol has resulted in a product similar in characteristics to that described by Weleminsky and testing of its efficacy is planned. Reeves, CA; Tuberculomucin: a forgotten treatment for tuberculosis, (2014) The Transactions of the Medical Society of London 131 pp. 106-112, available at UCL Discovery
People: Ali Zumla , Judy Weleminsky , Dimitris Evangelopoulos
- Analysis tools to quantify dissemination of pathology in zebrafish larvae. (2020) Stirling, D. R. et al. Sci Rep 10(1): 3149 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59932-1
People: David Lowe , Gillian Tomlinson
When people are infected with M. tuberculosis, if not cleared by the immune response, the bacteria will most often stay in the body – often the lungs – in a quiescent state. At some point, which could be soon after infection or many years later, it can reactivate to cause disease. Only 10% of infections move to disease, so most infection is latent. Identifying people with latent infection, and those where the bacteria are starting to reactivate but not yet clinically apparent, is an important part of controlling disease. However this is not only technically difficult, but it also raises issues of what is appropriate to do, and often requires engaging with particular at-risk communities.
- Discovery and validation of a personalized risk predictor for incident tuberculosis in low transmission settings. (2020) Gupta, R. K. et al. Nat Med 26(12): 1941-1949 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-1076-0
- Exaggerated IL-17A activity in human in vivo recall responses discriminates active tuberculosis from latent infection and cured disease. (2021) Pollara, G. et al. Sci Transl Med 13(592) https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abg7673
- The relationship between social risk factors and latent tuberculosis infection among individuals residing in England: a cross-sectional study. (2020) Lule, S. A. et al . BMJ Glob Health 5(12) https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjgh-2020-003550
- Subclinical tuberculosis disease - a review and analysis of prevalence surveys to inform definitions, burden, associations and screening methodology. (2020) Frascella, B. et al . Clin Infect Dis https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa1402
Projects: RID-TB
People: Ibrahim Abubakar , Hanif Esmail , Rishi Gupta , Marc Lipman , Maddy Noursadegh i , Gabriele Pollara , Lele Rangaka , Ali Zumla
Like most infectious diseases, TB is more prevalent in populations who have fewer resources, less access to good and stable healthcare. Furthermore, the long periods needed for treatment means that mobile populations of all sorts are less likely to enter a treatment programme, or are liable to default, while migrants are more likely to come from countries where TB is endemic. Yet lack of adequate treatment not only affects those individuals, but their communities and the wider public. We have been working to support different mobile populations, such as migrants, the homeless, and people in prison.
- Integrated screening of migrants for multiple infectious diseases: Qualitative study of a city-wide programme. (2020) Eborall, H. et al . EClinicalMedicine 21: 100315 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100315
People: Ibrahim Abubakar , Rob Aldridge , Andrew Hayward , Lele Rangaka , Al Story
Although TB, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other highly related organisms in what is called the M. tuberculosis complex, may be considered the most important disease caused by mycobacteria, other mycobacteria do cause significant human disease. These are grouped essentially as ‘everything that is not tuberculosis or leprosy: non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTMs). These mycobacteria, such as M. abscessus and M. avium , survive in the environment or other animals, and disease in humans is usually opportunistic. However these infections are increasingly common and are seen in people who are generally not thought of as being at risk of such infections. NTM infections can be debilitating, and hard to diagnose and treat. Our work looks at both at how these bacteria (including M. abscessus , M. avium , M. marinum and M. ulcerans ) cause disease, and how infections can be effectively managed in patients.
- Cross-transmission is not the source of new Mycobacterium abscessus infections in a multicenter cohort of cystic fibrosis patients. (2020) Doyle, R. M. et al. Clin Infect Dis 70(9): 1855-1864 https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciz526
- Current and future management of non-tuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease (NTM-PD) in the UK. (2020) Lipman, M. et al. BMJ Open Respir Res 7(1) https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjresp-2020-000591
- Engineered bacteriophages for treatment of a patient with a disseminated drug-resistant Mycobacterium abscessus . (2019) Dedrick, R. M. et al. Nat Med 25(5): 730-733 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0437-z
- Interferon-Gamma release assays differentiate between Mycobacterium avium complex and tuberculous lymphadenitis in children. (2021) Martinez-Planas, A. et al. J Pediatr 236: 211-218 e212 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2021.05.008
- Mycobacterium ulcerans -specific immune response after immunisation with bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine. (2021) Pittet, L. F. et al. Vaccine 39(4): 652-657 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.11.045
- The mycobactin biosynthesis pathway: A prospective therapeutic target in the battle against tuberculosis . (2021) Shyam, M. et al. J Med Chem 64(1): 71-100 https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01176
- Mycobactin Analogues with Excellent Pharmacokinetic Profile Demonstrate Potent Antitubercular Specific Activity and Exceptional Efflux Pump Inhibition. (2022) Shyam, M. et al . J Med Chem 65(1): 234-256 https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01349
- Cell-wall and Iron-acquisition mechanisms in Mycobacterium abscessus (Sanjib Bhakta)
- European Non-tuberculouS Mycobacterial Lymphadenitis in childrEn (ENSeMBLE) study (Marc Tebruegge)
- Evolution of mycobacterial drug resistance (Naomi Fuller, Tim McHugh)
- M. abscessus rapid diagnosis of resistance with whole genome sequencing (Giovanni Satta, Garth Dixon)
- M. abscessus new treatment options, including bacteriophages (Giovanni Satta)
- Post-transcriptional regulation in M. abscessus (Kristine Arnvig)
- The Hollow-Fibre Model of M. abscessus disease to test new antibiotics and combination therapy (Steve Morris-Jones, Giovanni Satta)
People: Ibrahim Abubakar , Kristine Arnvig , Sanjib Bhakta , Helen Booth , Hanif Esmail , Naomi Fuller , Frank Kloprogge , David Lowe , Marc Lipman , Tim McHugh , Rob Miller , Steve Morris-Jones , Giovanni Satta , Helen Spencer , Marc Tebruegge , Gillian Tomlinson , Jacqui White
Determining the best combinations and levels of drugs for TB treatment to effectively kill bacteria, and minimise side effects, is challenging. By investigating the relationship between how much drug is used and how effective they are (the pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationships), we can optimise the combinations of drugs that we use to treat TB. We use two approaches: the first is the hollow-fibre laboratory model, in which we investigate drug effects of treatment combinations against M. tuberculosis in a controlled way by mimicking antibiotic profiles to human conditions. A second approach is to evaluate antibiotic effects of drug combinations in the context of the whole body and immune system using data from patients.
- Can phenotypic data complement our understanding of antimycobacterial effects for drug combinations? (2019) Kloprogge, F. et al. J Antimicrob Chemother 74(12): 3530-3536 https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkz369
- Emergence of phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . (2022) Kloprogge, F. et al. Sci Rep 12(1): 21429 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-25827-6
- Exploring a combined biomarker for tuberculosis treatment response: protocol for a prospective observational cohort study. (2021) Kloprogge, F et al. . BMJ Open 11(7): e052885 https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-052885
- Longitudinal pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic biomarkers correlate with treatment outcome in drug-sensitive pulmonary tuberculosis: A population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis. (2020) Kloprogge, F., et al . Open Forum Infect Dis 7(7): ofaa218 https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofaa218
- Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of investigational regimens' drugs in the TB-PRACTECAL clinical trial (the PRACTECAL-PKPD study): a prospective nested study protocol in a randomised controlled trial. (2021) Nyang'wa, B. T., F. Kloprogge, D. A. J. Moore, A. Bustinduy, I. Motta, C. Berry and G. R. Davies. BMJ Open 11(9): e047185 https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047185
- Exploring a combined bio-marker for tuberculosis treatment response
- Exploring a biomarker for phenotypic variants of TB to map antimicrobial response
People: Frank Kloprogge , Arundhati Maitra , Zahra Sadouki
Sequencing the entire genome of M. tuberculosis has in recent years changed from a major enterprise, to being quick and a fraction of the previous cost. Knowing the genome sequence allows the spread of the bacteria to be studied, the success of clinical trials to be measured, and genetic changes that lead to antibiotic resistance to be identified.
- Association between bacterial homoplastic variants and radiological pathology in tuberculosis. (2020) Grandjean, L. et al. Thorax 75(7): 584-591 https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2019-213281
- From Theory to Practice: Translating Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS) into the Clinic. (2018) Balloux, F. et al . Trends Microbiol 26(12): 1035-1048 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2018.08.004
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis and whole-genome sequencing: how close are we to unleashing its full potential? (2018) Satta, G. et al. Clin Microbiol Infect 24(6): 604-609 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2017.10.030 .
People: Francois Balloux , Louis Grandjean , Tim McHugh , Giovanni Satta , Lucy van Dorp
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Rev Soc Bras Med Trop


Thesis and dissertations examining tuberculosis in Brazil between 2013 and 2019: an overview
Ana júlia reis.
1 Universidade Federal do Rio Grande, Faculdade de Medicina, Núcleo de Pesquisa em Microbiologia Médica, Rio Grande, RS, Brasil.
Juliana Lemos Dal Pizzol
Rúbia gattelli.
2 Universidade Federal do Rio Grande, Biblioteca Setorial da Área Acadêmica da Saúde, Rio Grande, RS, Brasil.
Andrea von Groll
Daniela fernandes ramos, ivy bastos ramis, afrânio kritski.
3 Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Faculdade de Medicina, Programa Acadêmico de Tuberculose, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brasil.
José Roberto Lapa e Silva
Pedro eduardo almeida da silva.
Authors' contribution: AJR, JLDP, RG, IBR, PEAS: Paper conception and planning, as well as the evidence interpretation; AJR, JLDP, RG, AvG, DFR, IBR, AK, JRLS, PEAS: Writing and/or reviewing the preliminary and definitive versions; AJR, JLDP, RG, AvG, DFR, IBR, AK, JRLS, PEAS: Final version approval.
Background:
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a serious public health problem, with approximately 10 million new cases reported annually. Knowledge about the quantitative evolution of theses and dissertations (T&Ds) examining human TB in Brazil can contribute to generating strategic planning for training professionals in this field and disease control. Therefore, this study highlights the role of T&Ds on TB in national scientific disclosures.
An integrative review related to TB was performed, including T&Ds produced in Brazil and completed between 2013 and 2019.
A total of 559,457 T&Ds were produced, of which 1,342 were associated with TB, accounting for 0.24% of the total number of T&Ds in Brazil. This was evidenced by a predominance of themes such as attention/health care, epidemiology, and TB treatment, and 80.2% of the T&Ds on TB were related to the large areas of health and biological sciences. Only 19.7% of T&Ds were associated with groups of patients considered at risk for TB, and 50.9% were produced in southeastern Brazil. The 1,342 T&Ds on TB were developed in 416 postgraduate programs linked to 121 higher education institutions (HEIs). We highlight that 72.7% of T&Ds on TB were produced in federal HEIs, 27.4% in state HEIs, and 8.5% in private HEIs.
Conclusions:
Strategic themes, such as TB control, require public policies that aim to increase the number of doctors and masters with expertise in TB, with geographic uniformity, and in line with the priorities for disease control.
INTRODUCTION
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a serious public health problem and is responsible for approximately 10 million new cases and 1.5 million deaths annually. Moreover, it is one of the main causes of death caused by a single infectious agent. Brazil is a priority country for this public health problem 1 , with approximately 90,000 new cases per year and a TB/human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) coinfection proportion of 11% 2 .
At the World Health Assembly in 2014, the World Health Organization approved the End Tuberculosis Strategy. Their main objectives were to reduce 90% of TB cases and 95% of TB deaths by 2035. In addition, the strategy aims to eliminate or minimize the economic impact on families affected by TB 3 . In the following year, the United Nations launched the Sustainable Development Goals, which included a 90% reduction in deaths caused by TB by 2030 4 , 5 .
Brazil's National Tuberculosis Control Program has used several strategies to control the disease, most of which are consistent with scientific evidence and guidelines recommended by the World Health Organization. This effort has resulted in improvements in epidemiological indicators, such as a reduction in the incidence and mortality of TB 6 , 7 . However, there are still many challenges, such as TB in prisons, TB/HIV coinfection, drug-resistant TB, other comorbidities (e.g., diabetes mellitus, mental health disorder, alcohol, illicit drugs, and tobacco use), a high proportion of treatment abandonment, low adherence to directly observed treatment, low contact evaluation, latent TB diagnosis and treatment, low coverage of rapid molecular diagnosis, and a low proportion of patients and family members who receive social protection 6 , 8 .
The success of actions that support global and national TB control and elimination strategies depends on qualified professionals generating, evaluating, and correctly using scientific knowledge. In Brazil, doctors and masters (D&M) are formed within the National Postgraduate System, whose Postgraduate Programs (PGPs) are accredited and periodically evaluated using the Coordination of Higher-level Personnel Improvement (CAPES) evaluation system 9 .
Knowledge about the quantitative evolution of theses and dissertations (T&Ds) produced in the area of human TB, as well as information about the spatiotemporal, thematic, and institutional distribution and its relationship with the TB burden in different populations and regions of Brazil, can contribute to generating strategic planning for the training of professionals in this theme. In addition, this study highlights the essential role of T&Ds in national scientific disclosures.
An integrative review was performed, including T&Ds related to TB, completed between January 1, 2013 and December 31, 2019, and made available in the CAPES database. This study was carried out based on the principles of scientometrics, which consist of “Quantitative assessment and analysis of intercomparisons of activity, productivity, and scientific progress 10 . ”
T&Ds identification and classification were performed independently by two researchers using the T&Ds catalog made available using the CAPES (Ministry of Education, Federal Government, Brazil) in Portuguese at https://dadosabertos.capes.gov.br/dataset.
The search for T&Ds was performed using the following Portuguese terms: Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacteria , antituberculostatics, isoniazid, and rifampicin. In addition, authorized descriptors in Portuguese, synonyms/alternative terms, related terms, and generic terms were used (DeCS/MeSH Health Sciences Descriptors - https://decs.bvsalud.org/) ( Supplementary Material Table 1S ). T&Ds that had any of these terms in the title, abstract, or keywords I were selected.
After the initial screening, the selected T&Ds were individually analyzed by two researchers, and those that mentioned any of the terms used in the search ( Supplementary Material Table 1S ) but whose work content was not associated with TB were excluded. The data were analyzed considering each thesis and dissertation equivalent to a doctorate and master's degree (professional and academic), respectively. In addition, the following variables were evaluated: T&Ds theme, the total number of T&Ds on TB produced in Brazil, period of time for D&M academic formation, CAPES assessment area, CAPES large knowledge areas, CAPES knowledge areas, subareas, risk groups for TB included in T&Ds, and T&Ds geographic and institutional distribution.
According to the CAPES, the assessment areas are grouped into a large knowledge area, which in turn are grouped into knowledge areas and subareas (first level: large knowledge area: gathering of different knowledge areas, due to the affinity of their objects, cognitive methods, instrumental resources, and reflecting specific sociopolitical contexts; second level: knowledge area: set of interrelated knowledge, collectively constructed, gathered according to the nature of the investigation object, and for the purposes of teaching, research, and practical applications; and third level: subarea: segmentation of the knowledge area established according to the object of study and recognized and widely used methodological procedures) 11 .
T&Ds were classified into the following themes: attention/health care, biochemistry, diagnosis, drugs, epidemiology, genetics, immunology, resistance, and treatment. The classification was performed by searching for keyword II in Portuguese associated with different themes ( Supplementary Material List 1S ). For T&Ds related to more than one theme, the main theme and its associated themes were independently defined by two researchers.
Data were tabulated in Microsoft Excel and analyzed using International Business Machine (IBM) Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software version 20.0 (International Business Machines Corporation - IBM - Armonk - New York - USA). The absolute and relative frequencies were determined.
Between 2013 and 2019, considering all PGPs and knowledge areas, 559,457 T&Ds were produced in Brazil, of which 2,665 were initially selected as being associated with TB using the terms described in the Supplementary Material Table 1S . After an individual analysis, 1,342 T&Ds were selected for their association with TB, accounting for 0.24% of the total number of T&Ds produced in Brazil, of which 31.8% (427/1,342) were theses and 68.2% (915/1,342) were dissertations.
The total number of completed T&Ds in Brazil increased by 38.7% between 2013 and 2019, while the number of T&Ds on TB was proportionally reduced annually, beginning in 2014. When comparing 2013 and 2019, there was a 24.5% reduction in academic dissertations associated with TB, whereas the number of theses increased by 26%. Despite this, the number of theses concluded showed a 9% reduction between 2018 (the year with the greatest production) and 2019 ( Table 1 ).
* Total production and percentage of each production type per year in Brazil. ** Total productions and percentage of each type of production per year, associated with TB.
Between 2013 and 2019, there was a 77% increase in the number of professional dissertations. In 2016, professional master’s degrees represented 20.7% (41/198) of the T&Ds on TB produced in Brazil ( Table 1 ). Of these, 48.8% (20/41) were carried out in Rio de Janeiro, with 85% (17/20) linked to the PGP of Family Health and Epidemiology in public health, coordinated by the Fundação Oswaldo Cruz (Fiocruz); 29.3% (12/41) were carried out in the state of Pernambuco, with 66.7% (8/12) linked to the PGP of public health of the Fiocruz.
When evaluating the necessary time to complete the postgraduate course, only approximately half of the T&Ds - doctorate 52.5% (224/427), academic master's degree 52.5% (404/770), and professional master's degree 48.3% (70/145) - were completed within 48 (doctorate) and 24 (master’s) months, the periods expected for presenting T&Ds in Brazil.
Regarding the large knowledge areas, among the 1,342 T&Ds produced during the study period, 67.9% and 12.3% were related to health sciences and biological sciences, respectively. The remaining T&Ds (19.8%) were multidisciplinary (8.4%), exact and earth sciences (6.8%), engineering (1.3%), applied social sciences (1.0%), human sciences (1.1%), agricultural sciences (1.0%), and linguistics, letters, and arts (0.3%).
When the knowledge areas were evaluated, 67.4% of the T&Ds associated with TB were concentrated in medicine (27.8%), public health (16.7%), and nursing (13.5%) ( Table 2 ).
*administration (0.1% - 02/1,342); agronomy (0.4% - 06/1,342); botany (0.1% - 01/1,342); computer science (0.2% - 03/1,342); information science (0.1% - 02/1,342); food science and technology (0.1% - 01/1,342); political science (0.1% - 01/1,342); communication (0.1% - 01/1,342); ecology (0.1% - 01/1,342); economy (0.4% - 05/1,342); education (0.1% - 01/1,342); biomedical engineering (0.1% - 01/1,342); materials and metallurgical engineering (0.1% - 02/1,342); production engineering (0.1% - 02/1,342); mechanical engineering (0.1% - 01/1,342); nuclear engineering (0.1% - 01/1,342); chemical engineering (0.1% - 01/1,342); physics (0.3% - 04/1,342); geography (0.4% - 05/1,342); history (0.4% - 06/1,342); language (0.2% - 03/1,342); linguistics (0.1% - 01/1,342); mathematics (0.1% - 01/1,342); materials (0.4% - 05/1,342); veterinary medicine (0.4% - 05/1,342); morphology (0.1% - 01/1,342); nutrition (0.1% - 01/1,342); odontology (0.4% - 06/1,342); urban and regional planning (0.1% - 02/1,342); social service (0.1% - 01/1,342); sociology (0.1% - 02/1,342); zootechnics (0.1% - 01/1,342). **public and business administration, accounting science and tourism (0.1% - 02/1,342); astronomy/physics (0.3% - 04/1,342); biodiversity (0.1% - 02/1,342); computer science (0.2% - 03/1,342); food science (0.1% - 01/1,342); political science and international relations (0.1% - 01/1,342); agrarian sciences I (0,4% - 06/1342); biological sciences II (0.1% - 01/1,342); communication and information (0.2% - 03/1,342); economy (0.4% - 05/1,342); education (0.1% - 01/1,342); engineering II (0.3% - 04/1,342); engineering III (0.2% - 03/1,342); engineering IV (0.1% - 01/1,342,); geography (0.4% - 05/1,342); history (0.4% - 06/1,342); language/linguistics (0.1% - 01/1,342); linguistics and literature (0.2% - 03/1,342); mathematics/probability and statistics (0.1% - 01/1,342); materials (0.4% - 05/1,342); veterinary medicine (0.4% - 05/1,342); nutrition (0.1% - 01/1,342); odontology (0.4% - 06/1,342); urban and regional planning/demography (0.1% - 02/1,342); social service (0.1% - 01/1,342); sociology (0.1% - 02/1,342); zootechnics/fishing resources (0.1% - 01/1,342).
Almost all T&Ds within the knowledge area of medicine were related to the assessment areas of Medicine I and II. In the Medicine II assessment area, 209 T&Ds were concluded, with 38.8% on the infectious and parasitic diseases or tropical and infectious disease subareas. In the Medicine I assessment area, 162 T&Ds were concluded, with 53.7% distributed among the subareas of pulmonology, infectious diseases, and pneumological sciences. In addition to the subareas mentioned above, 26 other subareas were observed in the assessment area of Medicine I and 38 in Medicine II.
Thematic classification
T&Ds on TB were developed within a wide range of themes. Although 50.3% (675/1,342) of T&Ds could be classified as a single theme, 49.7% (667/1,342) were related to more than one theme, which was named “associated themes” in this study. With a predominance of themes, such as attention/health care, epidemiology, and treatment ( Supplementary Material Table 2S ), the association frequency between the main and associated themes was evaluated ( Figure 1 ).

T&Ds on TB were also classified according to the type of study, with 50.1% related to basic research (drugs, genetics, immunology, resistance, and biochemistry), 33.9% to translational research (attention/healthcare), 30.5% to epidemiological research, 26.7% to TB treatment, and 19.4% to TB diagnosis.
T&Ds associated with groups of patients at risk for tuberculosis development
Only 19.7% (264/1,342) of T&Ds cases were associated with groups of patients considered at risk for TB development ( Table 3 ), with 5.7% (15/264) associated with more than one risk group.
Source: National Congress, Federal Government. BRASIL, 1990: According to the Child and Teenagers Statute, were considered children those aged up to 12 years and teenagers those aged up to 18 years. Source: National Congress, Federal Government. BRASIL, 2003: According to the Elderly Statute, all patients aged > 60 years were considered. & Source: SINAN, 2021. Calculation based on the average per year of all TB cases in Brazil between 2013 and 2019 (89,104): # 12 children and teenagers (< 1 year, 1-4, 5-9, 10-14, and 15-19 years); * 13 and older adults (60-64, 65-69, 70-79, and ≥ 80 years).
T&Ds geographical and institutional distribution
The 1,342 T&Ds on TB were produced in 416 PGPs and linked to 121 higher education institutions (HEIs) ( Figure 2 ): 48.8% were federal, 19.8% were state, and 31.4% were private HEIs. Although approximately 1/3 (31.4%) of the HEIs were private, only 8.5% of the T&Ds on TB were produced in this type of institution, while 72.7% were in federal HEIs, and 27.4% were in state HEIs.

Overall, 50.9% of T&Ds on TB are produced in southeast Brazil. The state of Rio de Janeiro was responsible for 23% of T&Ds on TB produced in Brazil between 2013 and 2019, and 17.6% of T&Ds were produced in southern Brazil. Rio Grande do Sul produced 10% and 55.9% of T&Ds on TB in the country and southern Brazil, respectively. Finally, 16.8% and 8.2% of T&Ds were produced in the northeast and northern Brazil, respectively ( Supplementary Material Table S3 ).
Between 2013 and 2019, 0.24% of T&Ds produced in Brazil were associated with TB. According to a previous study, Brazil ranked sixth among countries that published the most on TB between 2007 and 2016, representing 3.8% of global publications associated with this theme 15 .
The total number of T&Ds in Brazil increased by 38.7% between 2013 and 2019, while the number of T&Ds on TB was proportionally reduced annually beginning in 2014, showing a reduction in the generation of D&M. This reduced formation of human capital in this area could put Brazilian TB control efforts at risk, harming the promotion, assistance, management, research, development, and innovation related to TB.
It is important to emphasize that the number of professional master's degree dissertations showed significant growth during the study period, which may be related to the fact that this is the newest modality of stricto sensu postgraduate study in recent years. For example, in 2016, the number of professional master's degrees represented 20.7% of the T&Ds on TB produced in Brazil, with a 77% increase when comparing 2013 and 2019.
In general, professional and academic master's degrees differ primarily in the formation of professionals who meet specific needs and have immediate applicability of the generated knowledge (professional) from those who will follow an academic career with a doctorate as their next goal (academic).
Regarding scholarships offered by the CAPES, there was an 11% increase in master's scholarships between 2011 and 2017 and a 23% increase in doctorate scholarships between 2010 and 2014 16 . Although there is a dissociation between the number of T&Ds on TB and the increase in scholarship offerings, the ratio between academic dissertations and theses decreased from 2.3 to 1.5 between 2013 and 2019, while the ratio between academic and professional dissertations decreased from 8.8 to 4.1 during the same period. These results indicate a policy to encourage the development of doctors and professional masters in relation to academic masters.
Although the CAPES recommended (before the coronavirus disease 2019 [COVID-19] pandemic) a maximum time for the training of masters and doctors of 24 and 48 months, respectively, only approximately half of the T&Ds on TB were completed within this time. Even though there is not necessarily a direct relationship between the deadline to complete the postgraduate course and the quality of T&Ds or the formation process, the time to complete a doctorate could be reduced through the implementation of strategies such as reducing the time for a master's degree to 1 year, as was recently proposed to the CAPES 17 .
As mentioned above, TB remains a serious public health problem in Brazil, with a high number of cases, a high proportion of TB/HIV coinfection, underreporting of cases (10-20% of undetected and/or untreated cases), high proportions of treatment abandonment, and a high incidence in vulnerable populations 1 , 6 , 18 . In this demanding scenario of needs and questions, T&Ds on TB were developed within a wide range of themes. There was a greater association between different themes, indicating an important multi-disciplinarity in the formation of D&M in the area of TB. This combination of themes boosts the formation of D&M with diverse skills and a broader view of problems.
Furthermore, according to previous studies 19 , 20 , T&Ds on TB were classified according to the type of study, with 50.1% related to basic research, 33.9% to translational research, 30.5% to epidemiological research, 26.7% to TB treatment, and 19.4% to TB diagnosis. A study evaluating publications on TB from BRICS countries (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) indicated that 29.6% of publications were associated with epidemiological research, 33.8% with basic research, 13.1% with operational research, 10.1% with TB diagnosis, and 6.6% with TB treatment 15 .
When the groups of patients considered at risk for TB development were evaluated, we observed that only 19.7% of the T&Ds on TB were associated with these groups of patients, with 5.7% being associated with more than one risk group. Among the priority groups for TB control are people with positive serology for HIV (HIV+), prisoners, children/teenagers, indigenous individuals, health professionals, patients with diabetes mellitus, older adults, homeless populations, alcohol, drugs, and tobacco users 2 , 18 , only 8.2%, 2.9%, 2.5%, 1.6%, 1.5%, 1.3%, 0.8%, and 0.8% of T&Ds on TB were associated with these groups of patients, respectively. This dissonance between the main risk groups for TB development and the production of scientific knowledge, as well as the formation of professionals related to these essential issues, shows a precarious balance between academic needs and solutions, limiting the transfer of scientific benefits to the society. A significant number of TB cases in Brazil are among HIV+ patients, prisoners, children/teenagers, elderly people, and patients with diabetes mellitus 6 ; however, only 16% of the T&Ds on TB were associated with these groups of patients.
Brazil is a continental country with profound inter- and intra-regional social, economic, educational, and public health asymmetries. This diversity of scenarios is also observed in relation to the T&Ds produced within the TB theme. Most T&Ds were concentrated in southeastern and southern Brazil and were produced in PGPs from public HEIs, particularly federal HEIs. The necessary impetus for the formation of D&M in regions such as northern and northeastern Brazil can be facilitated by public policies using connections established by the Brazilian Tuberculosis Research Network (REDE-TB) 21 .
In southeast Brazil, where 45.2% of TB cases occur, with a prevalence of 45.9 cases per 100,000 inhabitants, which is higher than that of the overall prevalence in Brazil (41.9 cases per 100,000 inhabitants), 50.9% of T&Ds on TB were produced. The state of Rio de Janeiro, with a TB prevalence of 79.5 cases per 100,000 inhabitants, was responsible for 23% of T&Ds on TB produced between 2013 and 2019. In southern Brazil, where 12.7% of TB cases occurred, with a TB prevalence of 37.4 cases per 100,000 inhabitants, 17.6% of T&Ds on TB were produced. Interestingly, 26% of T&Ds produced in southern Brazil were associated with private HEIs. The state of Rio Grande do Sul has approximately 50% of the HEIs and PGPs in southern Brazil and produces 10% and 55.9% of T&Ds on TB in the country and southern region, respectively 2 , 14 .
Northeast Brazil, which was home to 26.3% of TB cases in Brazil between 2013 and 2019, produced 16.8% of T&Ds on TB. Despite having 10.9% of TB cases with a prevalence of 51.6 cases per 100,000 inhabitants, Northern Brazil produced only 8.2% of the T&Ds on TB. Finally, we highlight the state of Amazonas, which has the highest TB prevalence in Brazil, with 81.2 cases per 100,000 inhabitants, and produces only 3.1% of the T&Ds on TB. In both regions, northeast and northern Brazil, unlike in southeast and southern Brazil, there is a dissonance between the TB burden and the number of D&M formed in the TB theme, which is likely related to the lowest number of PGPs in these regions 2 , 14 .
D&M can act in government institutions and civil society, both public and private, as a protagonist in the promotion, production, evaluation, and implementation of scientific knowledge. Scientific knowledge generation, which is necessary to overcome the challenges faced by society, depends on investments in infrastructure, the provision of money for research, and the formation of human capital. Furthermore, strategic themes, such as disease control, including TB, should be prioritized. Therefore, it is necessary to create public policies that can integrate PGPs, public health agencies, and entities representing civil society, among others, aiming for an expansion in the number of D&M with expertise in TB as well as a greater geographic uniformity in D&M formation, in line with the priorities for TB control.
Despite this, we highlight that a limitation of this study is related to the number and themes of T&Ds associated with TB may not reflect the quality of the research and product generation in Brazil, as this is evaluated through article impact factors and patent registration.
Finally, the development, evaluation, and implementation of new diagnostic platforms, more effective vaccines, new antimicrobials, evaluation of new therapies, and management strategies are essential and constitute the pillar of research and innovation in the End Tuberculosis Strategy. Despite this, the formation of D&M in knowledge areas with a technological profile that can meet the technological demands of the Brazilian Unified Health System has decreased, not exceeding 1/5 of the titled D&M. This scenario puts efforts for TB control at risk and jeopardizes technological sovereignty promotion, foreign exchange savings, and the universalization of academic knowledge benefits 22 .
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL.
LIST S1: KEYWORDS USED TO CLASSIFY THESES AND DISSERTATIONS IN THEMES.
ATTENTION/HEALTH CARE: healthcare access; assistance; attention to the person with tuberculosis; attitudes and practices; basic health care; basic health indicators; basic health unit/units; brief intervention; capacity building; collective health; committee methods; communicators; community councils; community health agent; comprehensive health care; contacts; control measures; control program; cost/costs; cost-effectiveness; disease control; educational material/materials; educational technology; interventions effectiveness; family health; fight against tuberculosis; healthcare promotion; healthcare; health communication; health conditions analysis; health education; health evaluation; health policies; health service/services; health surveillance; health teaching; health training; health unic system; health unit/units; home contact; home visit; income; inequalities/inequality; infection control; information source; information system/systems; integrated management; knowledge about tuberculosis; knowledge evaluation; living condition/conditions; management; meanings and experiences; medical education; nurses' actions/appointment; nursing practice; health professionals' performance; permanent education; pharmaceutical attention; post-discharge management; prevention and control; primary health care; public health; public health policies; service qualification; life quality; information quality; reference center/laboratory/unit; referral hospital/service; referral outpatient clinic; respiratory symptomatic; route; sanitary service; social condition/conditions; social determinants; social development; social indicators; social inequity; social mobilization; social protection; social representations; social security; social support; stigma; trajectories/trajectory; tuberculosis control; tuberculosis indicators; undernotification; vulnerability.
BIOCHEMISTRY: acetyltransferase/acetyltransferases; ATP: biochemicals; biochemistry; cathepsin; enzymatic; enzyme/enzymes; glycation; leptina; lipid mediators; metalloproteinase/metalloproteinases; oxidative stress; phospholipase; protease; proteolysis; reductase/reductases; shikimate; transferase; transpeptidase/transpeptidase.
DIAGNOSIS: accuracy; bacilloscopy/BAAR; biomarker/biomarkers; clinical decision; clinical laboratory; detection; diagnosis; diagnoses/diagnosis; GeneXPERT/XPERT; signs and symptoms identification; IGRA; immunodiagnostic; molecular rapid test; mpt64; multiplex/multiplex PCR; mycobacteria identification; point-of-care; quantiferon/quantiferon-TB; radiography; screening exam; tomographic features; tuberculin proof; tuberculin test/skin test; X-ray.
EPIDEMIOLOGY: age/age and sex effects; associated determinants/factors; association measures; case analysis; case-control; clinical and laboratory profile; clinical-epidemiological; determinant factors; epidemiological; epidemiology; genotyping; geoepidemiological; geographic aspects; health geography; hospitalization time; incidence; lethality; MIRU/MIRU-VNTR; molecular characterization; morbidity; mortality; notification; notified; pharmacoepidemiological; prevalence; probabilistic correlation; related factors; risk factor/factors; score; spatial analysis/distribution; spatio-temporal; sociodemographic; socioeconomic; spoligotyping; survival; systematic review; temporal analysis.
GENETICS: alleles; beijing; chemogenomics; epigenetic/epigenetics; gene/genes; gene expression; gene transcription; genetic/genetics; genome; genotype/genotypes; hemeproteins; lineage/lineages; metabolomics; microRNA; mutation/mutations; polymorphism/polymorphisms; protein/proteins; protein subunit; proteomics; transcriptional regulation; transcriptional repressor; sequencing; sub-lineage.
IMMUNOLOGY: antibodies; antigen/antigens; apolipoprotein; BCG; CD cells; cytokine/cytokines; dendritic cells; epitopes; granuloma; HLA; humoral response; IFN; immune; immunodiagnostic; immunological; immunomodulation; immunomodulator/immunomodulators; immunomodulatory; immunopathogenesis; immunopathology; inflammatory markers; inflammasome/inflammasomes; interleukin/IL; interferon; lymphocyte/lymphocytes; lysosome; macrophage; monocytes; neutrophils; T-cells; toll-like; tumor necrosis factor/TNF; vaccine/vaccines.
DRUGS: activity evaluation; anti- Mycobacterium tuberculosis activity/activities; antimicrobial action/activity/potential; antimycobacterial activity/potential; antituberculosis activity; biocomposites; biological activity/activities; biological evaluation; biological prospecting; bioprospecting; biosynthesis; chemical and biological study; computational modeling; computational simulation; cytotoxicity; cytotoxicity; cytotoxicological evaluation; drug development; drug planning; extract/extracts; formulation/formulation development; inhibitor development; medicine innovation; microparticles; nanocarriers; nanocomposite/nanocomposites; nanofibers; nanomaterials; nanoparticle/nanoparticles; nanoreservoir; new derivatives; new drugs/molecules; obtaining and characterization; pharmaceutical excipient; pharmaceutical innovations; pharmacokinetic studies; pharmacophore; pharmacophoric; phytochemical study; physical stability; physicochemical characterization; potential action; potential activity; randomized clinical trial; rational drug design; molecule reuse; secondary metabolites; solubility; drug structural characterization; structure activity; synthesis; synthetic and antimicrobial potential; tuberculostatic activity.
RESISTANCE: antibiofilm; biofilm/biofilm; drug resistant; efflux; MDR-TB: minimal inhibitory concentration; modulatory effect: monoresistant; multidrug resistant/resistance; multi-resistant; resistance to drugs; sensitivity test/tests.
TREATMENT: abandonment; acetylation; adverse reactions; anti-tuberculosis drugs; anti-tuberculosis therapy; anti-tuberculosis regimens; bacteriological conversion; blood concentrations; case outcomes; chemoprevention; chemoprophylaxis; clinical/clinical and therapeutic evolution; combined therapy; cure; directly observed therapy; drug exposure; drug interaction/interactions; drug therapy; fixed combined dose; hepatotoxicity; isoniazid; quadruple scheme; plasmatic concentrations; post-treatment; medicines rational use; retreatment; rifampicin; serum concentrations; therapeutic adherence; therapeutic effect; therapeutic intervention; therapeutic itinerary/itineraries; therapeutic outcomes; therapeutic scheme; treaties; treatment; tuberculosis therapy.
Supplementary Material Table 1S:
Supplementary material table 2s:.
* Based on total T&D. ** T&D not classified in any of the themes.
Supplementary Material Table 3S:
I = Keywords of T&D; II = Keywords used to classify T&D by theme.
132 Tuberculosis Essay Topics
🏆 best essay topics on tuberculosis, ✍️ tuberculosis essay topics for college, 👍 good tuberculosis research topics & essay examples, 🎓 most interesting tuberculosis research titles, 💡 simple tuberculosis essay ideas, ❓ research questions on tuberculosis.
- Tuberculosis, Health Determinants and Nurse’s Role
- Tuberculosis and Epidemiologic Triangle
- Tuberculosis, Its Causes and Symptoms
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Causes and Treatment
- Tuberculosis: Desciption and Role of Nursing
- The Characteristics of Tuberculosis
- Epidemiology and Communicable Diseases: Tuberculosis
- Tuberculosis as Global Health Risk The global annual TB cases are falling at a rate of 2 percent, which could be increased to 4 percent to address this problem in line with End TB Strategy milestones.
- Tuberculosis Infections and Healthcare in Brunei Tuberculosis infections are a major health concern in Brunei, just like is the case for other South Asian countries. This paper discusses the aspects of the problem.
- Tuberculosis: Diagnostics and Treatment This disease is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is a pathogenic bacteria belonging to the order Actinomycetales, family Mycobacteriaceae, and genus Mycobacterium.
- Tuberculosis: Family Medicine and Disease Prevention This essay focuses on tuberculosis infection, prevention and control, surveillance, epidemiology, and significant events.
- Tuberculosis and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Tuberculosis is a common infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis is now a significant problem in many countries around the world.
- Tuberculosis Under Epidemiological Analysis Tuberculosis is a highly contagious disease, and it has airborne transmission. Due to its rapid spread, it remains a global problem nowadays, and humanity cannot cope with it.
- Tuberculosis and Preventive Measures in India This paper aims to develop, propose, and describe several measures to prevent the TB epidemic in India during the COVID-19 crisis.
- Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Strains As with any other infectious disease, TB exhibits specific signs and symptoms that help distinguish it from other illnesses.
- Tuberculosis Transmission, Manifestations and Social Concerns The paper states that Tuberculosis is preventable and curable and individuals should seek immediate medical attention when they feel they are infected.
- The U.S. Government and the Global Fund: Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria The United States participates in a range of international health programs, in particular, and contributes financially to the Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria.
- Tuberculosis as an Infectious Disease The paper discusses tuberculosis. It is an infectious disease because it spreads through tiny droplets when released through coughs and sneezes.
- Tuberculosis: Diagnostics, Prevention, and Management Nurses play an essential role in the diagnostics and treatment of tuberculosis patients: doing the screening, reporting the cases, acting prompt with diagnosis establishment, etc.
- Tuberculosis Desease: Symptoms and Prevention This paper seeks to explore one of the re-emerging infectious diseases the world faces. Tuberculosis (TB) is a re-emerging infectious disease affecting the world’s population.
- Tuberculosis: Control of Non-Endemic Communicable Diseases Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that is traditionally considered a disease of poverty. It influences mainly adults of the productive age.
- Diabetes and Tuberculosis: Review of Articles in Nursing This paper discusses articles in nursing about different issues related to diabetes, trends in prevalence and control, and also about tuberculosis treatment.
- Antimicrobial Resistance in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: A Review Antimicrobial resistance is a factor that steadily nullifies the efforts put into the attempts to triumph over tuberculosis.
- Epidemiology. Tuberculosis as Communicable Disease This paper aims to investigate TB’s core properties, as it still presents a substantial danger for human health with several issues not fully resolved by contemporary researchers.
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Pathogenesis and Epidemiology This paper discusses M. tuberculosis with a special focus on its structure and physiology, pathogenesis, epidemiology of the disease, treatment, and prevention of the infection.
- Researching the Issue of Tuberculosis Disease in the World Tuberculosis (TB) is among the serious infectious diseases reported in countries across the world. It mainly affects individuals’ lungs.
- Global Health Issues, Tuberculosis Tuberculosis is often latent and reveals itself when the immune system is weak. The TB incidence rates in Southeast Asia and Africa remain the highest in the world.
- Tuberculosis: Risks, Implications, and Prevention The research question is: What are the key risk factors, health implications, and appropriate prevention strategies for TB infections?
- Tuberculosis and Control Programs The present paper offers an overview of tuberculosis and reviews the recommendations and guidelines of effective disease control programs.
- Tuberculosis Education and Cooperation in Mumbai This paper discusses tuberculosis causes with specific regard to the current achievements and challenges observed in Mumbai, the west coast of India.
- Tuberculosis Education in Mumbai, India In this paper, the promotion of healthy living through the reduction of epidemic cases of tuberculosis (TB) will be discussed with specific regard to the current achievements and challenges.
- Tuberculosis as a Highly Contagious Infection The purpose of this paper is to explain the elements that influence the infectiousness of a tuberculosis patient.
- AIDS, Tuberculosis, Hepatitis in Miami Community AIDS, tuberculosis, and hepatitis have been marked as the most dangerous in the list of the most spread communicable illnesses that citizens of Miami suffer from.
- Tuberculosis, Mumps, Influenza in Miami The recent events of Hurricane Irma created an increasingly unhealthy environment for Miami. The three diseases that require containment are tuberculosis, mumps, and influenza.
- Malaria, AIDS, and Tuberculosis in Miami, Florida The paper will discuss and analyze AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria and how they influence the community in Miami, Florida.
- Tuberculosis: Case Study Assessment This paper gives an assessment of the case study Jose and Jill that concern tuberculosis, how its transmitted, prevention strategies and barriers, and their elimination.
- Influenza, Tuberculosis, AIDS Prevention in Miami Three population-based communicable illnesses have been chosen for analysis: influenza, tuberculosis, and AIDS.
- Tuberculosis Rates and Related Issues in Miami Although tuberculosis is not a new threat to patients’ well-being, it remains a tangible threat to U.S. communities, the one in Miami, FL not being an exception.
- Tuberculosis, AIDS, and Influenza A Virus in Miami The communicable diseases, which strongly affect the life of the population of the Miami-Dade County community are tuberculosis, AIDS, and influenza A virus.
- HIV, Gonorrhea, and Tuberculosis in Miami HIV, STDs such as gonorrhea, and tuberculosis are among those diseases that have the highest rates and thus the most influence on the community life in Miami.
- Tuberculosis Epidemiology in Global Public Health Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the most widespread infectious diseases all over the world. More than 95% of TB deaths happen in low- and middle-income countries.
- Tuberculosis, Its Description and Epidemiology Tuberculosis (abbreviated as TB) is one of the common communicable diseases in different parts of the world. This disease affects the human lungs.
- Tuberculosis, Influenza A, AIDS in Healthy People 2020 This discussion explains how HIV/AIDS, influenza A, and tuberculosis affect Miami city. The paper also describes how the community deals with these communicable illnesses.
- The Nurse-Patient Ratios: Tuberculosis in Elderly The main purpose of the paper is to discuss the nurse-patient ratios as the aspect for the concern and highlight the reasons elder people are at the highest risk for tuberculosis.
- Analysis of Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis: Characteristics, Treatment and Prevention Tuberculosis is one of the most contagious diseases. This paper gives a detailed analysis of Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis.
- Nurse-Patient Ratio and Tuberculosis A drop in the number of nurses and increase in the number of the patients presupposes the quality of the services declines correspondingly.
- Macrophage Polarization: Convergence Point Targeted by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and HIV
- Tuberculosis and Compliance With Medical Protocols
- HPLC: Techniques Used for the Diagnostic of Ancient Tuberculosis Remains
- Anti-tuberculosis Drug-induced Liver Injury (ATLI) Effects
- Morphoproteomic-guided Host-directed Therapy for Tuberculosis
- Tuberculosis Market Share, Trends, H2 2016
- The Causes and Treatment of the Disease of Tuberculosis
- Advancing Immunotherapeutic Vaccine Strategies Against Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- The Zebrafish Breathes New Life Into the Study of Tuberculosis
- Tuberculosis: Most Lethal Bacterial Pathogen
- Diagnosis for Latent Tuberculosis Infection: New Alternatives
- Multidrug Resistant Tuberculosis
- South Africa and Tuberculosis
- Monocyte Subsets: Phenotypes and Function in Tuberculosis Infection
- The Differences and Similarities of Pneumonia and Tuberculosis
- Challenging the Drug-Likeness Dogma for New Drug Discovery in Tuberculosis
- Tuberculosis: Infectious Disease and TB Patients
- Tuberculosis and New Tuberculosis Vaccines
- Fair Regulates Fatty Acid Biosynthesis and Is Essential for Virulence of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
- Clinical Presentations and Outcomes Related to Tuberculosis in Children Younger Than 2 Years of Age in Catalonia
- Tuberculosis: Immune System and Ongoing Research
- Artificial Neural Networks for Prediction of Tuberculosis Disease
- Epidemiology, Tuberculosis, and the Homeless Population
- Drug Resistance Rising Among Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
- Tuberculosis Among Native Americans
- Gut Dysbiosis Thwarts the Efficacy of Vaccine Against Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
- BCG Vaccination and Who’s Global Strategy for Tuberculosis Control 1948-1983
- Tuberculosis Vaccine May Help Stop Multiple Sclerosis Development
- Aid and the Control of Tuberculosis in Papua New Guinea: Is Australia’s Assistance Cost-effective
- Tuberculosis: Infectious Disease and Health Care Facilities
- Tuberculosis and Its Pathogenic Processes
- Examining Mycobacterium Tuberculosis, Its Spread, and Effect
- Tuberculosis and Its Effects on the Body System
- Host Antimicrobial Peptides: The Promise of New Treatment Strategies Against Tuberculosis
- United States Constitution and TB Patients
- Tuberculosis and New Types of Testing
- HIV and Tuberculosis Infection in Sub- Saharan Africa
- Reassessing Twenty Years of Vaccine Development Against Tuberculosis
- Tuberculosis and Its Effects on the Lungs
- Wild Animal Tuberculosis: Stakeholder Value Systems and Management of Disease
- Relationship Between Traveling and Infections of Tuberculosis
- Foam Cells Control Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection
- Examining the Complex Relationship Between Tuberculosis and Other Infectious Diseases in Children
- Extra-pulmonary Tuberculosis (EPTB) Treatment
- Host-directed Therapeutic Strategies for Tuberculosis
- Tuberculosis and Its Treatment
- Cost-Effectiveness and Addressing Tuberculosis
- Tuberculosis and Its Severity
- Harnessing the mTOR Pathway for Tuberculosis Treatment
- Tuberculosis, Important Determinants, and the Health System
- Historians Blamed Columbus for Spreading Tuberculosis to the World
- Tuberculosis and New Mexico
- Public Health Disease Management of Tuberculosis
- Factors Influencing the Perceived Priority of Tuberculosis in India
- Current and Novel Approaches to Vaccine Development Against Tuberculosis
- Tuberculosis and Its Effects on Society
- Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Virulence
- Tuberculosis and Antibiotic Resistance
- Animal Models for Tuberculosis in Translational and Precision Medicine
- Granulomas and Inflammation: Host-directed Therapies for Tuberculosis
- What Are the Organs Not Affected in Tuberculosis?
- What Is Bone Tuberculosis and What Is the Cure of Bone Tuberculosis?
- Why Is the Tuberculosis Epidemic So Hard to Stop?
- How Long Can Tuberculosis Patients Survive Without Treatment?
- Why Does Tuberculosis Appear in the Upper Lung?
- What Should Be the Diet for Someone With Tuberculosis Meningitis?
- Why Is There an Evening Rise of Temperature in Cases of Tuberculosis?
- Is It Possible That Tuberculosis Medication Cause Skin Problem?
- Will Intestinal Tuberculosis Spread From One Person to Another?
- What Are the Factors Responsible for the Re-Emergence of Tuberculosis?
- Is Tuberculosis Considered to Be Hereditary?
- Can Tuberculosis Happen Twice, Even if It Was Properly Cured Earlier?
- What’s the Link Between Tuberculosis and COVID-19?
- Is There Anyone Who Is Suffering From Lymph Nodes Tuberculosis?
- Is There Any Permanent Way to Eradicate Tuberculosis by Any Vaccines?
- Is There Any Ayurvedic Medicine to Cure Tuberculosis Completely?
- Does a Tuberculosis Patient on Treatment for a Month Infect Others With Tuberculosis?
- What Are the Different Types of Tuberculosis?
- What Are Causes, Symptoms, Signs and Treatment for Tuberculosis?
- Did Doctors Burn the Hearts of Tuberculosis Vitctims in the Late 1800s?
- What Killed More People Last Century: War, Tuberculosis or Influenza?
- Is It Possible to Get Tuberculosis a Second Time?
- Without Access to Antibiotics, What’s the Best Treatment for Tuberculosis?
- Is It That Tuberculosis Follows Pneumonia or Pneumonia Follows Tuberculosis?
- Is the Tuberculosis Blood Test the Same as the Tuberculosis Skin Test?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, March 1). 132 Tuberculosis Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/tuberculosis-essay-topics/
"132 Tuberculosis Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 1 Mar. 2022, studycorgi.com/ideas/tuberculosis-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) '132 Tuberculosis Essay Topics'. 1 March.
1. StudyCorgi . "132 Tuberculosis Essay Topics." March 1, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/tuberculosis-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "132 Tuberculosis Essay Topics." March 1, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/tuberculosis-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "132 Tuberculosis Essay Topics." March 1, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/tuberculosis-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Tuberculosis were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on December 27, 2023 .
- Frontiers in Microbiology
- Antimicrobials, Resistance and Chemotherapy
- Research Topics
New Approaches Against Drug-Resistant M. tuberculosis
Total Downloads
Total Views and Downloads
About this Research Topic
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious and deadly disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus, which has reached pandemic proportions. About 1.7 billion people (23% of the world’s population) are estimated to have a latent TB infection, and are thus at risk of developing active TB disease during ...
Keywords : Tuberculosis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, drug target, drug resistance, antitubercular drugs
Important Note : All contributions to this Research Topic must be within the scope of the section and journal to which they are submitted, as defined in their mission statements. Frontiers reserves the right to guide an out-of-scope manuscript to a more suitable section or journal at any stage of peer review.
Topic Editors
Topic coordinators, recent articles, submission deadlines.
Submission closed.
Participating Journals
Total views.
- Demographics
No records found
total views article views downloads topic views
Top countries
Top referring sites, about frontiers research topics.
With their unique mixes of varied contributions from Original Research to Review Articles, Research Topics unify the most influential researchers, the latest key findings and historical advances in a hot research area! Find out more on how to host your own Frontiers Research Topic or contribute to one as an author.
The DHS Program
- Childhood Mortality
- Family Planning
- Maternal Mortality
- Wealth Index
- MORE TOPICS
- Alcohol and Tobacco
- Child Health
- Fertility and Fertility Preferences
- Household and Respondent Characteristics
- Male Circumcision
- Maternal Health
- Tuberculosis

What is tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis, or TB, is an infectious bacterial disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which most commonly affects the lungs. It is transmitted from person to person via droplets from the throat and lungs of people with the active respiratory disease. But people infected with TB bacilli will not necessarily become sick with the disease. The immune system "walls off" the TB bacilli which, protected by a thick waxy coat, can lie dormant for years. When someone's immune system is weakened, the chances of becoming sick are greater.
- Overall, one-third of the world's population is currently infected with the TB bacillus.
- 5-10% of people who are infected with TB bacilli (but who are not infected with HIV) become sick or infectious at some time during their life.
- People with HIV and TB infection are much more likely to develop TB.
- TB is the leading killer of people who are HIV infected.
If properly treated, tuberculosis caused by drug-susceptible strains is curable in virtually all cases. If untreated, more than half the cases may be fatal within five years.
What data does DHS collect about TB?
The DHS collects data on women's and men's knowledge and attitudes concerning TB. Over 90 surveys have included TB questions.
What are the DHS indicators related to TB knowledge and attitudes?
- Percentage who have heard of TB
- Percentage who report that TB is spread through the air by coughing
- Percentage who believe that TB can be cured
- Percentage who would want a family member's TB kept secret
What data does SPA collect about TB?
The Service Provision Assessment ( SPA ) survey collects data on TB diagnostic services, TB treatment, and/or follow-up services and facilities following DOTS (Directly-observed Treatment, Short-course) strategy and any treatment other than DOTS strategy.
Photo credit: © 2008 Anil Gulati, Courtesy of Photoshare. Wall paintings on a TB hospital in Nowgaon, District Chhatarpur, Madhya Pradesh, India, illustrate DOTS tuberculosis medication therapy.
- Stop TB Partnership - resources page
- WHO - TB indicators
- The Lancet - special series on TB
- WHO - Status of the global TB epidemic
- WHO - Stop TB Strategy
- World Bank - TB data by country
- CDC - Find TB Resources
- US Global Health Policy (data by topic: TB)
- Tuberculosis Control Assistance Program (2005-2010) toolbox

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes tuberculosis (TB), infects approximately a third of the global population [1,2]. M. tuberculosis is transmitted through the air via droplets when an infectious individual talks, sings [3], or coughs [4,5]. Tuberculosis infections can be classified as either "latent" (non-transmissible TB
A typical sign of tuberculosis of the spine is back pain, but a sign of TB of the kidneys is blood in the urine. Tuberculosis: Epidemiology, Prevention, and Control. Approximately 920,000 cases of TB and HIV coinfection were accounted for in 2017, representing 9% of the total TB cases observed.
Introduction. Tuberculosis (TB) continues to pose a major threat to global health , and research is a key component of the Global Plan to Stop TB2011-2015 .Research is particularly critical for developing new tools and approaches needed for eliminating TB by 2050 .Recognizing this, the Stop TB Partnership and the World Health Organization's (WHO) Stop TB Department have launched the TB ...
Tuberculosis is the leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, with over 25% of these occurring in the African region. Multi-drug resistant strains which do not respond to first-line ...
INTRODUCTION. Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the most ancient diseases of mankind and has co-evolved with humans for many thousands of years or perhaps for several million years.[] The oldest known molecular evidence of TB was detected in a fossil of an extinct bison (Pleistocene bison), which was radiocarbon dated at 17,870±230 years[] ; and in 9000, year old human remains which were recovered ...
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the most common infectious diseases worldwide [1,2,3].It is estimated that about 10 million people were infected with TB in 2017 with 1.3 million deaths among HIV negative people and an additional 350,000 deaths among HIV positive [4, 5].Tuberculosis incidence rates in Africa have been decreasing at a rate of 4% per year between 2013 and 2017, however, TB ...
Tuberculosis (TB) is a communicable infectious disease affecting around one quarter of the world's population [].The 'BRICS' countries of Brazil , Russia, India, China, and South Africa account for 47% of the total number of TB cases annually [1,2,3].Caused by the bacillus Mycobacterium tuberculosis, around 5-10% of those infected will develop active disease.
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb.) that produces pulmonary damage due to its airborne nature. This fact facilitates the disease fast-spreading, which, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2021 caused 1.2 million deaths and 9.9 million new cases. Fortunately, X-Ray Computed Tomography (CT) images enable capturing specific ...
Although TB, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other highly related organisms in what is called the M. tuberculosis complex, may be considered the most important disease caused by mycobacteria, other mycobacteria do cause significant human disease. These are grouped essentially as 'everything that is not tuberculosis or leprosy: non ...
This qualitative market research study was conducted between July 2020 and February 2021. Eight TB patients from each country (n = 40) completed health questionnaires, video/telephone interviews, and diaries regarding their experiences of TB. Additionally, 52 household members were interviewed.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) epidemiology, particularly in Southern Africa where, by any measure, tuberculosis (TB) is out of control(1,2). A particular focus of the work is my wish to better locate transmission. If we better understood where MTB transmission occurs, TB control programmes might be better targeted(3). The thesis
I would like to express my gratitude to Dr. Srikanta Banerjee, dissertation chair, Dr. Debo I. Awosika-Olumo, dissertation committee member, Dr. Muazzam Nasrullah, university research reviewer, and Dr. Laura J. McCormick, dissertation editor, for being instrumental in my success with completing this dissertation project. I would also like to
7. TB research and innovation. Tuberculosis (TB) research and innovation is essential to achieve the global TB targets of the United Nations (UN) Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the World Health Organization (WHO) End TB Strategy. The SDG target is to "end the epidemic" by 2030; more specific targets for 2030 set in the End TB ...
The total number of completed T&Ds in Brazil increased by 38.7% between 2013 and 2019, while the number of T&Ds on TB was proportionally reduced annually, beginning in 2014. When comparing 2013 and 2019, there was a 24.5% reduction in academic dissertations associated with TB, whereas the number of theses increased by 26%.
Abstract. Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the deadliest infectious diseases responsible for millions of deaths annually across the world. In this paper we present a general overview of TB ...
High-quality research evidence is critical for improving global health and health equity, and for achieving the World Health Organization (WHO)'s objective of the attainment of the highest possible level of health by all peoples [1]. This need is most apparent when responding to complex epidemics such as tuberculosis (TB). TB is the leading killer among diseases caused by an infectious agent ...
About this Research Topic. Submission closed. The emergence and spread of drug-resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) threatens global efforts to control tuberculosis (TB), an airborne disease which remains among the biggest infectious killers globally. Treatment of drug-susceptible TB with the four-drug combination of isoniazid (INH), ...
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that is traditionally considered a disease of poverty. It influences mainly adults of the productive age. The paper describes Tuberculosis -causes, symptoms, mode of transmission, complications, treatment, and the demographic (mortality, morbidity, incidence, and prevalence).
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious and deadly disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus, which has reached pandemic proportions. About 1.7 billion people (23% of the world's population) are estimated to have a latent TB infection, and are thus at risk of developing active TB disease during their lifetime. According to the World Health Organization, in 2018 it was estimated that ...
Preface: Tuberculosis research in The Netherlands: Innovation to accelerate global tuberculosis elimination 2 By Mario C. Raviglione, Director Global TB Programme, WHO, Geneva 2 Executive summary 4 1. Rationale and justification 6 2. Major hurdles in TB control and elimination 8 3. Elimination of TB requires massive step-up in research 10
Tuberculosis was reported to be curable by 74.6% of the subjects and 67.9% knew that there are medications for treatment of tuberculosis, while 11.5% knew the duration of treatment. Conclusion.
Thesis(MPH)-University of Ghana,2015: dc.description.abstract: Tuberculosis threatens public health all over the world and affects persons mostly in their productive lives. The proportion of cases with successful treatment outcome is a key indicator to assess the effectiveness and performance of any Tuberculosis Control Programme. Effective ...
Tuberculosis, or TB, is an infectious bacterial disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which most commonly affects the lungs. It is transmitted from person to person via droplets from the throat and lungs of people with the active respiratory disease. But people infected with TB bacilli will not necessarily become sick with the disease.