Certificate in Advanced Education Leadership (CAEL)


Additional Resources
- Request More Information
The Certificate in Advanced Education Leadership (CAEL) provides current and aspiring education leaders with the opportunity to deepen their knowledge and skills while working to address current problems of practice.
Additional details
Request more information.
Modules begin in February, May, and September.
AASA members are eligible for an exclusive membership discount on this program. Please visit AASA's website for details.
In pre-K-12 education, we need transformational leaders whose passion for education quality and equity is matched by a knowledge of learning and development, the organizational management skills to translate visionary ideas into real-world success, and a firm grasp of the role of context and politics in shaping leadership.
Based on the groundbreaking Doctor of Education Leadership program, the Certificate in Advanced Education Leadership (CAEL) provides current and aspiring education leaders with the opportunity to deepen their knowledge and skills while working to address current problems of practice.
Certificate Details
A practice-based learn, apply, reflect model.
CAEL was designed not only to build the foundation knowledge necessary for visionary, system-wide leadership but to give participants the time and opportunity to step back from, assess, and address a pressing problem in their own practice. The first 4-5 weeks of each module center on in-depth learning on the focused topic area. During weeks 6 and 7, participants identify a problem they are working to solve and apply their learning to it. Weeks 8-12 are about pushing deeper on knowledge acquisition while demonstrating mastery in a project. Participants work in small learning groups, supported by an experienced facilitator, to deepen and extend their thinking and leadership skills.
A Rigorous, Flexible Experience
- 60 clock hours per module
- Asynchronous activities: choose when to complete them within a given week
- Direct support from an online learning facilitator and peer learning group
- Option for team-based enrollment and participation
- Certificate of mastery – it is highly facilitated, and you will have the opportunity to demonstrate your mastery through a project.
Led by HGSE faculty members, CAEL offers five distinct 12-week online modules that build competencies in self-, team-, and systemic leadership. Each of the five modules may be taken separately. A certificate of mastery is offered to those completing four of the five modules.
- Leading Learning: A CAEL Module
- Developing Myself: A CAEL Module
- Driving Change: A CAEL Module
Learn how to manage the change process to drive better outcomes.
- Leading for Excellence & Equity: A CAEL Module
- Managing Evidence: A CAEL Module
Faculty Chair
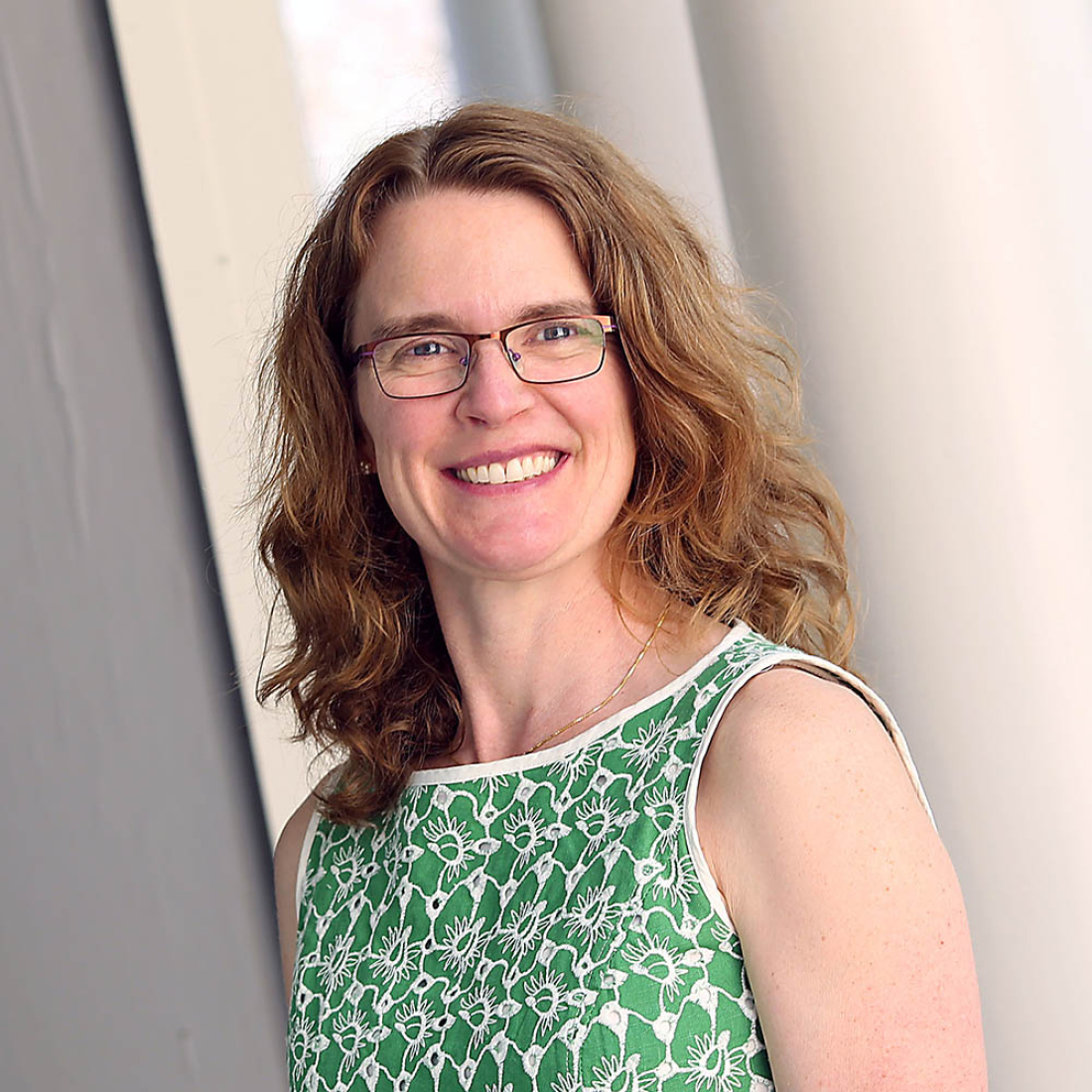

Elizabeth City
Through work on strategy, instructional improvement, and the future of learning, Liz City develops leaders with the skills, imagination, and collaboration necessary to build and re-build systems that serve each and every child well.
Who Should Attend
CAEL is ideal for current and aspiring preK-12 leaders:
- Superintendents and district-level administrators
- Directors of charter management organizations
- Administrators at state agencies
- Experienced principals and teachers who aspire to system-level roles
- Teams of education leaders seeking to strengthen their skills and collaborative capabilities
- Educators are encouraged to apply as teams to increase their impact
How to Participate
Taking cael modules as a team.
When you take one or more CAEL modules as a school, district, or organization-level team, you create a collective impact on learning in your system. Enrolling in CAEL as a team allows you to identify unified goals and objectives and apply what you learn together. Your team will work on a single, shared problem of practice across the 12 weeks, submitting a single midterm and final project that represents your collective effort. Along the way, you will also have the chance to submit individual assignments focused on personal learning.
Earning the Certificate
A Certificate in Advanced Education Leadership will be awarded to participants who complete four of the five modules, including Leading Learning and a final reflective assignment. All four courses must be taken within two years of starting. Please visit the application pages for each CAEL module below:
Pursuing HGSE Graduate Credit
Participants admitted to complete CAEL modules for graduate credit will complete a specialized version of the final activities during weeks 9-12. Participants should estimate an additional five hours of study during that period.
How to Apply
This program welcomes applications from both individuals and teams. First-time applicants need to create a Professional Education account to apply.
Individuals : Click the "Apply" button at the top of this page to log into your Professional Education account and access the application page. Proceed with the individual form until submission.
Step 1: Designate one participant or an administrative staff member as the Coordinator .
- The Coordinator should click the "Apply" button at the top of this page to log into their Professional Education account and access the application page.
- Proceed with the team form, including providing the name, email address, and job title of each participant in your team.
- The Coordinator can choose to receive a team invoice.
- Contact us if you need to make any changes to your team after submitting the form.
Step 2: Upon the submission of the team application, all team members will receive an email notification with a link to their personal application form. Team members should complete their forms promptly. Once all team members submit their forms, the application is considered complete and ready for review by the Admissions Committee.
Invoices: Invoices will only be available upon your acceptance.
Tuition Assistance
Tuition assistance is available for the programs in this certificate on a need and application basis. Tuition assistance is granted based on participant and institutional needs. Requests for tuition assistance do not affect an applicant's prospects for admission. You may access the tuition assistance application after you have submitted your program application. Tuition assistance applications should be submitted at least one month prior to the final application deadline.
Considering this program?
Related news, unlearning toward a fresh perspective.

Professional education alumnus pushes the boundaries of Italian academia
- Career and Lifelong Learning
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Global Education
- Higher Education Leadership
The Many Types of Education Degrees: How to Pick Your Path
Education degrees aren't just for classroom teachers.
Education Degrees: Picking Your Path

Getty Images
Though some education degree programs focus on teacher training, others concentrate on education administration, policy or technology. Some education majors explore the unique challenges faced by rural or urban schools.
One common misconception about education degrees is that they're only useful for future classroom teachers.
However, education degrees can lead to all sorts of careers: They're often held by education administrators, policymakers, researchers, technologists, curriculum designers, learning scientists, school counselors or psychologists , standardized test-makers and textbook authors. Staffers at education-oriented government agencies at the local, state and federal level – such as the U.S. Department of Education – frequently have academic degrees in education as well, and the same is true for representatives of education-related charities and nonprofit organizations.
Here's what you need to know about the hierarchy of education degrees and how to choose the right one.
How to Tell if an Education Degree Is a Good Fit
An interest in helping others learn and a desire to work with children are common and compelling reasons for studying education, says Daniel A. Domenech, the executive director of AASA, The School Superintendents Association. Education majors tend to earn less than people who receive a comparable level of training in other fields, so a majority of people who become educators do so for non-financial reasons, he adds.
According to an August 2022 report from the Economic Policy Institute, a Washington, D.C.-based think tank that analyzes working conditions for low-income and middle-income workers in the U.S., the pay disparity between teachers and similarly educated professionals reached an all-time high in 2021, when teachers received 23.5% lower wages on average relative to other workers with comparable credentials.
However, some education occupations typically lead to six-figure salaries. For example, the median salary among U.S. school district superintendents, the majority of whom have doctorates, was $147,000 in 2022, according to a recent report from AASA.
Laura W. Perna, vice provost for faculty at the University of Pennsylvania Graduate School of Education , says education degree recipients can use their degree to do good work and benefit society. "If we think about the important problems that need to be addressed in our world, you know, so much of the answer comes down to education," Perna says.
Stacey Ludwig Johnson, senior vice president and executive dean of the school of education at Western Governors University , an online university, emphasizes that schools and school districts aren't the only places where education degree recipients can use their skills. For instance, an educator can work as a corporate trainer, helping a business to increase the skills of its workforce, she says.
The Many Kinds of Education Majors
Among teaching degree programs, some focus on a particular level of education, such as preschool, elementary, middle or high school. Teaching degree programs may also hone in on how to teach a particular subject, or they can emphasize teaching methods that work well with a specific student population, such as adult learners, multi-lingual learners or individuals with disabilities.
When comparing education degree specializations, keep in mind that the earning potential of educators varies widely depending on which part of the education system they are trained for and what credential their job usually requires. For example, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median salary among U.S. high school teachers, who typically had a bachelor's degree, was about $61,820 in May 2021. That's about twice the median salary of preschool teachers, who usually had an associate degree and earned $30,210. The median salary among principals, who usually had a master's degree, was $98,420.
Sometimes educators with the same level of education earn different amounts depending on their area of focus. For instance, BLS data reveals that though teachers who specialize in basic adult education generally had the same amount of training as high school teachers – a bachelor's degree – their 2021 median salary was roughly $2,100 lower.
Education Degree Levels and How to Find the Right Tier
Leadership roles in the education sector generally require graduate education . The more training educators have, the higher their salaries tend to be. For example, according to PayScale, a compensation data company, the average base salary for U.S. workers with a Bachelor of Education , or B.Ed. degree, was $57,000, whereas the average annual base salary among those with a Doctor of Education, or Ed.D. degree, was $80,000.
Prospective education students should analyze the resumes of people who have jobs they are interested in to figure out the highest level of education to pursue, experts say.
Associate Degrees
Many preschool teaching jobs require at least a two-year associate degree in early childhood education. Teachers' assistants or paraprofessionals usually need at least two years of college coursework or an associate degree to work in public school classrooms.
Bachelor's Degrees
A bachelor's is the minimum amount of education needed for an entry-level K-12 teaching position at a U.S. public school.
Master's Degrees
A few states require teachers to begin pursuing a master's degree within several years of beginning teaching to maintain their license. Teachers may also move up the pay scale with a master's. According to the National Center for Education Statistics, 58% of U.S. public school teachers who taught during the 2017-18 school year had a more advanced degree than a bachelor's.
Instructional coordinators or curriculum specialists, the educational administrators who oversee curricula, standards, teaching materials and often assessments, usually have a master's, and their median salary was $63,740 in May 2021, BLS data shows.
College and university administrators, who earned a median annual salary of $96,910 in May 2021, also typically have master's degrees, according to the BLS. Work in education policy typically requires a master's degree as well.
Master's degrees in education usually require two years of coursework.
College faculty who research and teach about education typically have Doctor of Philosophy, or Ph.D., degrees, and they sometimes have Ed.D. degrees. According to PayScale, the average salary for a worker with a Ph.D. in education was $87,000. Doctoral programs in education usually last at least three years and often take longer to finish.
School district administration positions sometimes require doctoral education, and certain managerial roles at government agencies and nonprofit organizations are reserved for individuals with doctorates. Education researchers frequently have doctorates, and so do school psychologists.
Guidance on Figuring Out How Much Schooling You Need
When deciding how high of a degree they should aim for, education students should think about the level of expertise and the kinds of skills that their desired job requires, says Carol Basile, dean of Arizona State University's Mary Lou Fulton Teachers College . "As you continue to move up in any education organization, there begins to be more of a requirement for a doctorate," she says.
Searching for a grad school? Get our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
Grad Degree Jobs With $100K+ Salaries

Tags: education , education policy , education graduate school , teachers , careers , students
You May Also Like
Get accepted to multiple top b-schools.
Anayat Durrani May 16, 2024

Premeds and Emerging Medical Research
Zach Grimmett May 14, 2024

How to Get a Perfect Score on the LSAT
Gabriel Kuris May 13, 2024

Premeds Take 5 Public Health Courses
Rachel Rizal May 7, 2024

Fortune 500 CEOs With a Law Degree
Cole Claybourn May 7, 2024

Why It's Hard to Get Into Med School
A.R. Cabral May 6, 2024

Pros, Cons of Unaccredited Law Schools
Gabriel Kuris May 6, 2024

An MBA and Management Consulting
Sammy Allen May 2, 2024

Med School Access for Minority Students
Cole Claybourn May 2, 2024

Different jobs with med degree
Jarek Rutz April 30, 2024


What is a Graduate Degree?

For those considering graduate school , it’s important to take the time to understand what an advanced degree program entails. Read on to learn about the different types of graduate programs, the time commitment, cost, and enrollment conditions required, and what students should expect at this level of advanced study.
An undergraduate degree —either a bachelor’s or associate degree—is considered a baseline educational requirement in many professions. As such, the pursuit of this degree has become commonplace among high school graduates. As of 2018, 69 percent of students chose to complete their undergraduate degree immediately after earning their high school diploma.
A graduate degree —including master’s degrees , doctorates , and PhDs —provides an advanced understanding of a specific topic or field, and demonstrates a commitment to lifelong learning that many employers value. Those who choose to enroll in graduate school often do so with a series of focused, career-oriented goals in mind, which sets the stage for a substantially different type of learning environment than one might experience during an undergraduate career.
Interested in earning an advanced degree?
Explore Northeastern’s 200+ programs to find the one that will best help you achieve your goals.
FIND YOUR PROGRAM
Types of Graduate Degrees
Students embarking on graduate school should begin by determining if an academic or professional degree is right for them.
Students who desire a career in a specific field (such as law, pharmaceuticals, medicine, or education) may opt to pursue a professional degree . These programs emphasize hands-on learning and often require students to obtain substantial real-world experience prior to graduation.
Academic (or research) degrees align with a single, specific area of study or field. Students in pursuit of these degrees are required to develop an in-depth understanding of their subject area and complete a thesis or capstone project to demonstrate their knowledge.
Learn More: Professional Degree Vs. Academic Degree: What’s the Difference?
Master’s Degree
Although master’s degrees may be the most common form of graduate study, there are various professional and academic graduate-level degrees that students should consider. Some of the most common include:
- Master of Arts Degree (MA): An MA is a type of academic master’s degree that correlates most directly with humanities-based subject areas such as communications, teaching, languages, and more. Classes in these programs are primarily discussion-based and might require fieldwork, a thesis, or a capstone project prior to graduation. Some common MA programs include Homeland Security , English , and Elementary Education .
- Master of Science Degree (MS) : An MS is another type of academic master’s degree which typically correlates with advanced study in fields that relate to science and mathematics. Courses in these programs often require extensive lab work or research and culminate with thesis or capstone projects, as well. Some common MS programs include Cybersecurity , Corporate & Organizational Communication , Leadership , and Project Management .
- Master of Fine Arts (MFA): An MFA is a professional degree for artists in fields such as graphic design, music, theater, film, and more. Alongside a practical and abstract exploration of their art, graduates of these programs often receive the credentials necessary to teach at the undergraduate level. Some common MFA programs include Information Design & Visualization , Creative Writing, and Acting.
- Master of Professional Studies (MPS) : An MPS is an interdisciplinary degree focused on a single area of professional study. Unlike MA or MS degrees, these programs are typically more hands-on in nature and require an internship, work-study, or co-op experience prior to graduation. Some common MPS programs include Analytics , Informatics , and Digital Media .
Professional Doctorate
A professional doctorate is focused on the advanced practice of knowledge and skills, making it a degree for those who are more professionally oriented. While these programs also help to develop research skills, the main focus is to apply knowledge to industry to solve new and emerging problems.
- Juris Doctor (JD): This degree provides students with the practical skills and expansive knowledge needed to practice law in America. While JD programs share some commonalities with other graduate-level law degrees, such as a Master of Legal Studies or a Master of Laws , there are key differences between the three.
- Doctor of Education (EdD): This is another professional doctorate degree not to be confused with a PhD in Education . This type of program is for educators and professionals who want to direct and implement change within their organizations. These degrees are designed to prepare students to become leaders in their communities.
- Doctor of Medicine (MD): Students hoping to pursue a career in medicine or surgery pursue this professional doctorate degree.
- Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) : Individuals pursuing a career in the pharmaceutical industry must obtain a PharmD. These programs include components of research, teaching, and clinical practice.
Learn More: Why Earn a Professional Doctoral Degree?
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD)
A PhD is a postgraduate doctoral degree based on extensive research in a given field. Students can earn a PhD in areas such as technology, humanities, social sciences, and more. Individuals who complete their PhDs often pursue a career in academia, though some may continue on to complete similar research for the remainder of their career. Some common PhD programs include Counseling Psychology , Bioengineering , and Pharmacology . PhDs are not to be confused with professional/clinical doctorates , which are designed to provide students with the practical skills needed to excel in their career.
How Long Does it Take to Earn a Graduate Degree
The timeline for completion of a graduate degree will vary depending on three factors:
- The type of degree you pursue.
- Your desired subject area.
- The specific institution at which you are studying.
On average, however, those enrolled in a master’s program full-time will likely complete their degree within one-and-a-half to three years. Individuals who pursue their master’s degree part-time might take longer than three years to complete it, depending on how many credits they enroll in each semester.
Most PhD and professional doctoral candidates will finish their degrees in five to six years, though the time commitment may vary depending on the subject area. Some more intensive degree programs, like an MD, can take up to eight years to complete.
Learn More: How Long Does It Take to Earn a Master’s Degree?
Graduate Degree Requirements
Requirements for different graduate programs vary greatly depending on the subject, institution, and whether or not it is a culminating degree. The most common requirement, however, is an undergraduate degree, as this acts as a base for advanced learning.
Other application requirements for specific graduate programs might include:
- A statement of purpose
- Your educational transcripts
- A portfolio of your work
- Professional/academic recommendations
- Any additional written assignments
You may also need to take and submit your scores for a subject-specific exam (e.g. LSAT, MCAT, etc.) or for the general Graduate Record Examination (GRE) , which is a requirement for many graduate programs globally.
The Cost of A Graduate Degree
The cost of a graduate degree will also vary greatly depending on what program and what institution you are considering. Yet, many people make incorrect assumptions about the price of graduate school based on their knowledge of undergraduate costs.
“Many of us have in our heads the sticker price of $30,000 to $40,000 per year for undergraduate education,” Sean Gallagher , executive director of the Center for the Future of Higher Education and Talent Strategy at Northeastern told U.S. News & Report in 2017. “So we say, ‘OK, it’s two years for a graduate degree, so it’s going to cost me $70,000 to $80,000 or more.’ And while there are certainly programs at that price point, there are many programs where you can get the entire graduate degree for between $20,000 and $40,000.”
No matter the program, graduate school will be both an educational and financial investment in your career. As such, institutions like Northeastern have adopted a variety of financial aid options for students to help hedge the cost of graduate studies. Students can utilize scholarships, grants, and even tuition reimbursement programs through their employers to help pay for their advanced education.
Learn More: Paying for Grad School: Where and How to Start
5 Characteristics of a Strong Graduate Program
#1) flexible learning options.
In most universities, graduate programs are designed to accommodate the needs of working professionals and are thus offered in a variety of exceedingly flexible formats.
Firstly, students at the graduate level can choose to enroll in either a part-time or full-time capacity. A part-time graduate program offers working professionals the opportunity to take on only as many classes as they can handle per semester, and work toward finishing their degree at their own speed. Full-time students, on the other hand, must be enrolled in a specific number of credit hours per semester as determined by the university, and will work toward completing their program in a linear manner. At Northeastern, for example, full-time students must be enrolled in nine quarter hours of graduate credits per semester.
Universities like Northeastern also offer a variety of graduate programs in online , on-ground, and hybrid formats to best fit the needs of any given students. Taking online or hybrid courses is an effective way for students who are already working in their field to balance their coursework with their other professional commitments, as well.
For those who aren’t ready to commit to an entire graduate program, some universities also offer graduate certificates in many in-demand areas of study. Certificate programs provide either a condensed understanding of basic advanced principles as they relate to an area of study, or a very niche look at a specific aspect of the subject. Though the amount of knowledge attained in a certificate program is vastly less than that of a full graduate degree, some prefer this condensed format of study for its reduced cost and shorter time commitment.
#2) A Focused Curriculum
By the time a student reaches graduate school, they are likely no longer in the exploring phase of their education. Instead, these students have often experienced life as a working professional, determined which area of study best aligns with their passions, and have made the educated decision to become an expert on that topic through the pursuit of a graduate degree.
For this reason, many graduate programs offer students a far more unified educational experience than at the undergraduate level. Often, this will be reflected in a common curriculum that all students within a single program must follow. While they may still be able to pick the specific topics that most interest them off this predetermined list of classes, each course will relate back to their base area of study. This is done in an effort to give students a much more in-depth exploration of that specific topic rather than a surface-level understanding of many, unrelated ones.
Students in graduate school still have the opportunity to customize their education to best fit their needs, however. In fact, programs like those at Northeastern recognize that one of the most impactful offerings they can give their students is the chance to declare a concentration within their degree and tailor their studies in a way that aligns with their professional aspirations.
#3) Opportunities for Hands-On Learning
Northeastern University is known for its emphasis on experiential learning at all phases of a student’s educational journey, offering opportunities for real-world, hands-on learning through internships, work-study, co-ops, and more. There are also a variety of graduate-specific experiential learning opportunities for students, such as Northeastern’s Experiential Network (XN) initiative.
A Closer Look: Northeastern’s XN initiative offers students the opportunity to participate in six-week-long, virtual projects for active organizations within the university’s expansive network. These projects align with students’ academic work, allowing them to apply what they learn in the classroom to these real-world scenarios. Following the format of gig-economy work experiences, students spend 30-40 hours on each project and, in that time, practice making decisions and completing work that will have a genuine impact on these organizations’ success.
In general, graduate degrees tend to be research- or capstone-oriented in nature, meaning that, depending on a student’s area of study, they will be frequently honing their practical abilities alongside their theoretical skills. Graduate programs emphasize this type of learning in an effort to develop well-rounded professionals in each field. These hands-on learning opportunities also offer students unparalleled exposure to different facets of their industry—as well as different types of workplaces—which can then be used to help them make an educated employment decision after graduation.
#4) An Industry-Aligned Network
Students have a unique advantage when it comes to networking in grad school . Between the opportunities to make connections in the classroom, at university-hosted events, and even in the professional world through hands-on learning experiences, these students are in the ideal setting to build their network.
Connecting with Classmates
Your classmates in grad school will likely be equally as driven and passionate about the exact same area of study as you are. You will also have the opportunity to grow together throughout your time in the program, resulting in a slew of common experiences and relationships that will help to keep you connected with and looking out for one another throughout your career. Although they may start out as your classmates, these individuals have the potential to become powerful players in the professional industry post-graduation, as well.
Connecting with Professors
Smaller class sizes and a more collaborative learning environment allow students to develop more personal connections with their professors during grad school than in their undergraduate studies. These relationships can be some of the most important in regards to your career, as professors at top universities like Northeastern are industry leaders and have connections that can be used to make introductions or open doors to potential employment opportunities after graduation.
Connecting with Industry Professionals
Given the emphasis on hands-on learning in grad school, students have the chance to develop their professional networks in their region and with organizations that they may be able to work with post-graduation. Having these types of industry-aligned connections is vital in today’s competitive job market, especially since a connection that has worked with you first-hand in a professional environment can speak to your qualifications in a far more concrete and impactful way than those who are only able to speak to your abilities abstractly.
Students who take the time to develop their professional network while in graduate school — whether online or on-ground —have the potential to see the positive impact of those connections for the remainder of their professional career.
#5) Substantial Impact on Your Career
Many students pursue graduate degrees to advance their careers. Whether that means getting a promotion, increasing their current salary, or even transitioning fields, these students are looking to make a positive change by showing employers the extent of their knowledge, network, and exposure to experiential learning.
While these goals are often achieved during the pursuit of a graduate degree, students’ careers can be impacted by graduate study in more ways than one. The overall career outlook for graduate degree holders, for instance, is incredibly positive compared to those with only a bachelor’s or associate degree.
For example, the current jobless rate for individuals with a master’s degree or higher is 12.5 percent lower than those who only hold a bachelor’s degree. Similarly, in regard to salary, those with a graduate degree earn 28 percent more than those with just an undergraduate degree on average. These individuals will also make over a million dollars more than those with just a high school diploma in their lifetime.
What’s more, graduates of advanced degree programs are some of the most in-demand within organizations today. When it comes to applying for a new role, 61 percent of employers are finding that the skills required for their open positions have evolved to require a higher education among applicants. By 2022, it is also expected that 18 percent of all jobs will require a graduate degree. Earning an advanced degree will help improve your skills and demonstrate your commitment to career development—two of the best ways to stand out in today’s competitive job market .
Explore Your Options at Northeastern
Ready to take the leap? Consider advancing your career with a graduate degree from Northeastern, a top-40 university . Evaluate the personal and professional benefits of a graduate degree, then explore Northeastern’s 200+ master’s , doctorate , and certificate programs to find the one that best aligns with your career goals.
Browse the Grad School Tips & Advice category of the Northeastern Graduate blog for more content like this from Northeastern University Graduate Programs .

Subscribe below to receive future content from the Graduate Programs Blog.
About shayna joubert, related articles.

Why Earn a Professional Doctoral Degree?

5 Tips to Get the Most out of Grad School

Is Earning a Graduate Certificate Worth It?
Did you know.
Advanced degree holders earn a salary an average 25% higher than bachelor's degree holders. (Economic Policy Institute, 2021)
Northeastern University Graduate Programs
Explore our 200+ industry-aligned graduate degree and certificate programs.
Most Popular:
Tips for taking online classes: 8 strategies for success, public health careers: what can you do with an mph, 7 international business careers that are in high demand, edd vs. phd in education: what’s the difference, 7 must-have skills for data analysts, in-demand biotechnology careers shaping our future, the benefits of online learning: 8 advantages of online degrees, how to write a statement of purpose for graduate school, the best of our graduate blog—right to your inbox.
Stay up to date on our latest posts and university events. Plus receive relevant career tips and grad school advice.
By providing us with your email, you agree to the terms of our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
Keep Reading:

Should I Go To Grad School: 4 Questions to Consider

Grad School or Work? How to Balance Both

7 Networking Tips for Graduate Students
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
How Technology Is Changing the Future of Higher Education
Labs test artificial intelligence, virtual reality and other innovations that could improve learning and lower costs for Generation Z and beyond.

By Jon Marcus
This article is part of our latest Learning special report . We’re focusing on Generation Z, which is facing challenges from changing curriculums and new technology to financial aid gaps and homelessness.
MANCHESTER, N.H. — Cruising to class in her driverless car, a student crams from notes projected on the inside of the windshield while she gestures with her hands to shape a 3-D holographic model of her architecture project.
It looks like science fiction, an impression reinforced by the fact that it is being demonstrated in virtual reality in an ultramodern space with overstuffed pillows for seats. But this scenario is based on technology already in development.
The setting is the Sandbox ColLABorative, the innovation arm of Southern New Hampshire University, on the fifth floor of a downtown building with panoramic views of the sprawling red brick mills that date from this city’s 19th-century industrial heyday.
It is one of a small but growing number of places where experts are testing new ideas that will shape the future of a college education, using everything from blockchain networks to computer simulations to artificial intelligence, or A.I.
Theirs is not a future of falling enrollment, financial challenges and closing campuses. It’s a brighter world in which students subscribe to rather than enroll in college, learn languages in virtual reality foreign streetscapes with avatars for conversation partners, have their questions answered day or night by A.I. teaching assistants and control their own digital transcripts that record every life achievement.
The possibilities for advances such as these are vast. The structure of higher education as it is still largely practiced in America is as old as those Manchester mills, based on a calendar that dates from a time when students had to go home to help with the harvest, and divided into academic disciplines on physical campuses for 18- to 24-year-olds.
Universities may be at the cutting edge of research into almost every other field, said Gordon Jones, founding dean of the Boise State University College of Innovation and Design. But when it comes to reconsidering the structure of their own, he said, “they’ve been very risk-averse.”
Now, however, squeezed by the demands of employers and students — especially the up and coming Generation Z — and the need to attract new customers, some schools, such as Boise State and Southern New Hampshire University, are starting labs to come up with improvements to help people learn more effectively, match their skills with jobs and lower their costs.
More than 200 have added senior executives whose titles include the words “digital” or “innovation,” the consulting firm Entangled Solutions found; many were recruited from the corporate and tech sectors. M.I.T. has set up a multimillion-dollar fund to pay for faculty to experiment with teaching innovations .
Some colleges and universities are collaborating on such ideas in groups including the University Innovation Alliance and the Marvel Universe-worthy HAIL Storm — it stands for Harvesting Academic Innovation for Learners — a coalition of academic innovation labs.
If history is a guide, the flashiest notions being developed in workshops in these places won’t get far. University campuses are like archaeological digs of innovations that didn’t fulfill their promises. Even though the biggest leap forward of the last few decades, for example — delivering courses online — appears to have lowered costs , the graduation rates of online higher education remain much lower than those of programs taught in person .
“One of the most important things we do here is disprove and dismantle ideas,” said William Zemp, chief strategy and innovation officer at Southern New Hampshire University.
“There’s so much white noise out there, you have to be sort of a myth buster.”
But some ambitious concepts are already being tested.
College by Subscription
One of these would transform the way students pay for higher education. Instead of enrolling, for example, they might subscribe to college; for a monthly fee, they could take whatever courses they want, when they want, with long-term access to advising and career help.
The Georgia Institute of Technology is one of the places mulling a subscription model, said Richard DeMillo, director of its Center for 21st Century Universities. It would include access to a worldwide network of mentors and advisers and “whatever someone needs to do to improve their professional situation or acquire a new skill or get feedback on how things are going.”
Boise State is already piloting this concept. Its Passport to Education costs $425 a month for six credit hours or $525 for nine in either of two online bachelor’s degree programs. That’s 30 percent cheaper than the in-state, in-person tuition.
Paying by the month encourages students to move faster through their educations, and most are projected to graduate in 18 months, Mr. Jones said. The subscription model has attracted 47 students so far, he said, with another 94 in the application process.
However they pay for it, future students could find other drastic changes in the way their educations are delivered.
Your Teacher Is a Robot
Georgia Tech has been experimenting with a virtual teaching assistant named Jill Watson, built on the Jeopardy-winning IBM Watson supercomputer platform. This A.I. answers questions in a discussion forum alongside human teaching assistants; students often can’t distinguish among them, their professor says. More Jill Watsons could help students get over hurdles they encounter in large or online courses. The university is working next on developing virtual tutors, which it says could be viable in two to five years .
S.N.H.U., in a collaboration with the education company Pearson, is testing A.I. grading. Barnes & Noble Education already has an A.I. writing tool called bartleby write , named for the clerk in the Herman Melville short story, that corrects grammar, punctuation and spelling, searches for plagiarism and helps create citations.
At Arizona State University, A.I. is being used to watch for signs that A.S.U. Online students might be struggling, and to alert their academic advisers.
“If we could catch early signals, we could go to them much earlier and say, ‘Hey you’re still in the window’ ” to pass, said Donna Kidwell, chief technology officer of the university’s digital teaching and learning lab, EdPlus.
Another harbinger of things to come sits on a hillside near the Hudson River in upstate New York, where an immersion lab with 15-foot walls and a 360-degree projection system transports Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute language students to China , virtually.
The students learn Mandarin Chinese by conversing with A.I. avatars that can recognize not only what they say but their gestures and expressions, all against a computer-generated backdrop of Chinese street markets, restaurants and other scenes.
Julian Wong, a mechanical engineering major in the first group of students to go through the program, “thought it would be cheesy.” In fact, he said, “It’s definitely more engaging, because you’re actively involved with what’s going on.”
Students in the immersion lab mastered Mandarin about twice as fast as their counterparts in conventional classrooms, said Shirley Ann Jackson, the president of Rensselaer.
Dr. Jackson, a physicist, was not surprised. The students enrolling in college now “grew up in a digital environment,” she said. “Why not use that to actually engage them?”
Slightly less sophisticated simulations are being used in schools of education, where trainee teachers practice coping with simulated schoolchildren. Engineering students at the University of Michigan use an augmented-reality track to test autonomous vehicles in simulated traffic.
A Transcript for Life
The way these kinds of learning get documented is also about to change. A race is underway to create a lifelong transcript.
Most academic transcripts omit work or military histories, internships, apprenticeships and other relevant experience. And course names such as Biology 301 or Business 102 reveal little about what students have actually learned.
“The learner, the learning provider and the employer all are speaking different languages that don’t interconnect,” said Michelle Weise, chief innovation officer at the Strada Institute for the Future of Work.
A proposed solution: the “interoperable learning record,” or I.L.R. (proof that, even in the future, higher education will be rife with acronyms and jargon).
The I.L.R. would list the specific skills that people have learned — customer service, say, or project management — as opposed to which courses they passed and majors they declared. And it would include other life experiences they accumulated.
This “digital trail” would remain in the learner’s control to share with prospective employers and make it easier for a student to transfer academic credits earned at one institution to another.
American universities, colleges and work force training programs are now awarding at least 738,428 unique credentials , according to a September analysis by a nonprofit organization called Credential Engine, which has taken on the task of translating these into a standardized registry of skills.
Unlike transcripts, I.L.R.s could work in two directions. Not only could prospective employees use them to look for jobs requiring the skills they have; employers could comb through them to find prospective hires with the skills they need.
“We’re trying to live inside this whole preindustrial design and figure out how we interface with technology to take it further,” said Dr. Kidwell of Arizona State. “Everybody is wrangling with trying to figure out which of these experiments are really going to work.”
This story was produced in collaboration with The Hechinger Report , a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education.
- Utility Menu
Certificate in Advanced Education Leadership
Project Objectives
Tll engagement, related blog posts.
Setting a new bar for online higher education
The education sector was among the hardest hit by the COVID-19 pandemic. Schools across the globe were forced to shutter their campuses in the spring of 2020 and rapidly shift to online instruction. For many higher education institutions, this meant delivering standard courses and the “traditional” classroom experience through videoconferencing and various connectivity tools.
The approach worked to support students through a period of acute crisis but stands in contrast to the offerings of online education pioneers. These institutions use AI and advanced analytics to provide personalized learning and on-demand student support, and to accommodate student preferences for varying digital formats.
Colleges and universities can take a cue from the early adopters of online education, those companies and institutions that have been refining their online teaching models for more than a decade, as well as the edtechs that have entered the sector more recently. The latter organizations use educational technology to deliver online education services.
To better understand what these institutions are doing well, we surveyed academic research as well as the reported practices of more than 30 institutions, including both regulated degree-granting universities and nonregulated lifelong education providers. We also conducted ethnographic market research, during which we followed the learning journeys of 29 students in the United States and in Brazil, two of the largest online higher education markets in the world, with more than 3.3 million 1 Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System, 2018, nces.ed.gov. and 2.3 million 2 School Census, Censo Escolar-INEP, 2019, ensobasico.inep.gov.br. online higher education students, respectively.
We found that, to engage most effectively with students, the leading online higher education institutions focus on eight dimensions of the learning experience. We have organized these into three overarching principles: create a seamless journey for students, adopt an engaging approach to teaching, and build a caring network (exhibit). In this article, we talk about these principles in the context of programs that are fully online, but they may be just as effective within hybrid programs in which students complete some courses online and some in person.
Create a seamless journey for students
The performance of the early adopters of online education points to the importance of a seamless journey for students, easily navigable learning platforms accessible from any device, and content that is engaging, and whenever possible, personalized. Some early adopters have even integrated their learning platforms with their institution’s other services and resources, such as libraries and financial-aid offices.
1. Build the education road map
In our conversations with students and experts, we learned that students in online programs—precisely because they are physically disconnected from traditional classroom settings—may need more direction, motivation, and discipline than students in in-person programs. The online higher education programs that we looked at help students build their own education road map using standardized tests, digital alerts, and time-management tools to regularly reinforce students’ progress and remind them of their goals.
Brazil’s Cogna Educação, for instance, encourages students to assess their baseline knowledge at the start of the course. 3 Digital transformation: A new culture to shape our future , Kroton 2018 Sustainability Report, Kroton Educacional, cogna.com.br. Such up-front diagnostics could be helpful in highlighting knowledge gaps and pointing students to relevant tools and resources, and may be especially helpful to students who have had unequal educational opportunities. A web-based knowledge assessment allows Cogna students to confirm their mastery of certain parts of a course, which, according to our research, can potentially boost their confidence and allow them to move faster through the course material.
At the outset of a course, leaders in online higher education can help students clearly understand the format and content, how they will use what they learn, how much time and effort is required, and how prepared they are for its demands.
The University of Michigan’s online Atlas platform, for instance, gives students detailed information about courses and curricula, including profiles of past students, sample reports and evaluations, and grade distributions, so they can make informed decisions about their studies. 4 Atlas, Center for Academic Innovation, University of Michigan, umich.edu. Another provider, Pluralsight, shares movie-trailer-style overviews of its course content and offers trial options so students can get a sense of what to expect before making financial commitments.
Meanwhile, some of the online doctoral students we interviewed have access to an interactive timeline and graduation calculator for each course, which help students understand each of the milestones and requirements for completing their dissertations. Breaking up the education process into manageable tasks this way can potentially ease anxiety, according to our interviews with education experts.
2. Enable seamless connections
Students may struggle to learn if they aren’t able to connect to learning platforms. Online higher education pioneers provide a single sign-on through which students can interact with professors and classmates and gain access to critical support services. Traditional institutions considering a similar model should remember that because high-speed and reliable internet are not always available, courses and program content should be structured so they can be accessed even in low-bandwidth situations or downloaded for offline use.
The technology is just one element of creating seamless connections. Since remote students may face a range of distractions, online-course content could benefit them by being more engaging than in-person courses. Online higher education pioneers allow students to study at their own pace through a range of channels and media, anytime and anywhere—including during otherwise unproductive periods, such as while in the waiting room at the doctor’s office. Coursera, for example, invites students to log into a personalized home page where they can review the status of their coursework, complete unfinished lessons, and access recommended “next content to learn” units. Brazilian online university Ampli Pitagoras offers content optimized for mobile devices that allows students to listen to lessons, contact tutors for help, or do quizzes from wherever they happen to be.
Adopt an engaging approach to teaching
The pioneers in online higher education we researched pair the “right” course content with the “right” formats to capture students’ attention. They incorporate real-world applications into their lesson plans, use adaptive learning tools to personalize their courses, and offer easily accessible platforms for group learning.
3. Offer a range of learning formats
The online higher education programs we reviewed incorporate group activities and collaboration with classmates—important hallmarks of the higher education experience—into their mix of course formats, offering both live classes and self-guided, on-demand lessons.
The Georgia Institute of Technology, for example, augments live lessons from faculty members in its online graduate program in data analytics with a collaboration platform where students can interact outside of class, according to a student we interviewed. Instructors can provide immediate answers to students’ questions via the platform or endorse students’ responses to questions from their peers. Instructors at Zhejiang University in China use live videoconferencing and chat rooms to communicate with more than 300 participants, assign and collect homework assignments, and set goals. 5 Wu Zhaohui, “How a top Chinese university is responding to coronavirus,” World Economic Forum, March 16, 2020, weforum.org.
The element of personalization is another area in which online programs can consider upping their ante, even in large student groups. Institutions could offer customized ways of learning online, whether via digital textbook, podcast, or video, ensuring that these materials are high quality and that the cost of their production is spread among large student populations.
Some institutions have invested in bespoke tools to facilitate various learning modes. The University of Michigan’s Center for Academic Innovation embeds custom-designed software into its courses to enhance the experience for both students and professors. 6 “Our mission & principles,” University of Michigan Center for Academic Innovation, ai.umich.edu. The school’s ECoach platform helps students in large classes navigate content when one-on-one interaction with instructors is difficult because of the sheer number of students. It also sends students reminders, motivational tips, performance reviews, and exam-preparation materials. 7 University of Michigan, umich.edu. Meanwhile, Minerva University focuses on a real-time online-class model that supports higher student participation and feedback and has built a platform with a “talk time” feature that lets instructors balance class participation and engage “back-row students” who may be inclined to participate less. 8 Samad Twemlow-Carter, “Talk Time,” Minerva University, minervaproject.com.
4. Ensure captivating experiences
Delivering education on digital platforms opens the potential to turn curricula into engaging and interactive journeys, and online education leaders are investing in content whose quality is on a par with high-end entertainment. Strayer University, for example, has recruited Emmy Award–winning film producers and established an in-house production unit to create multimedia lessons. The university’s initial findings show that this investment is paying off in increased student engagement, with 85 percent of learners reporting that they watch lessons from beginning to end, and also shows a 10 percent reduction in the student dropout rate. 9 Increased student engagement and success through captivating content , Strayer Studios outcomes report, Strayer University, studios.strategiced.com.
Other educators are attracting students not only with high-production values but influential personalities. Outlier provides courses in the form of high-quality videos that feature charismatic Ivy League professors and are shot in a format that reduces eye strain. 10 Outlier online course registration for Calculus I, outlier.org. The course content follows a storyline, and each course is presented as a crucial piece in an overall learning journey.
5. Utilize adaptive learning tools
Online higher education pioneers deliver adaptive learning using AI and analytics to detect and address individual students’ needs and offer real-time feedback and support. They can also predict students’ requirements, based on individuals’ past searches and questions, and respond with relevant content. This should be conducted according to the applicable personal data privacy regulations of the country where the institution is operating.
Cogna Educação, for example, developed a system that delivers real-time, personalized tutoring to more than 500,000 online students, paired with exercises customized to address specific knowledge gaps. 11 Digital transformation , 2018. Minerva University used analytics to devise a highly personalized feedback model, which allows instructors to comment and provide feedback on students’ online learning assignments and provide access to test scores during one-on-one feedback sessions. 12 “Maybe we need to rethink our assumptions about ‘online’ learning,” Minerva University, minervaproject.com. According to our research, instructors can also access recorded lessons during one-on-one sessions and provide feedback on student participation during class.
6. Include real-world application of skills
The online higher education pioneers use virtual reality (VR) laboratories, simulations, and games for students to practice skills in real-world scenarios within controlled virtual environments. This type of hands-on instruction, our research shows, has traditionally been a challenge for online institutions.
Arizona State University, for example, has partnered with several companies to develop a biology degree that can be obtained completely online. The program leverages VR technology that gives online students in its biological-sciences program access to a state-of-the-art lab. Students can zoom in to molecules and repeat experiments as many times as needed—all from the comfort of wherever they happen to be. 13 “ASU online biology course is first to offer virtual-reality lab in Google partnership,” Arizona State University, August 23, 2018, news.asu.edu. Meanwhile, students at Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas are using 3-D games to find innovative solutions to real-world problems—for instance, designing the post-COVID-19 campus experience. 14 Cleofé Vergara, “Learn by playing with Minecraft Education,” Innovación Educativa, July 13, 2021, innovacioneducativa.upc.edu.pe.
Some institutions have expanded the real-world experience by introducing online internships. Columbia University’s Virtual Internship Program, for example, was developed in partnership with employers across the United States and offers skills workshops and resources, as well as one-on-one career counseling. 15 Virtual Internship Program, Columbia University Center for Career Education, columbia.edu.
Create a caring network
Establishing interpersonal connections may be more difficult in online settings. Leading online education programs provide dedicated channels to help students with academic, personal, technological, administrative, and financial challenges and to provide a means for students to connect with each other for peer-to-peer support. Such programs are also using technologies to recognize signs of student distress and to extend just-in-time support.
7. Provide academic and nonacademic support
Online education pioneers combine automation and analytics with one-on-one personal interactions to give students the support they need.
Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU), for example, uses a system of alerts and communication nudges when its digital platform detects low student engagement. Meanwhile, AI-powered chatbots provide quick responses to common student requests and questions. 16 “SNHU turns student data into student success,” Southern New Hampshire University, May 2019, d2l.com. Strayer University has a virtual assistant named Irving that is accessible from every page of the university’s online campus website and offers 24/7 administrative support to students, from recommending courses to making personalized graduation projections. 17 “Meet Irving, the Strayer chatbot that saves students time,” Strayer University, October 31, 2019, strayer.edu.
Many of these pioneer institutions augment that digital assistance with human support. SNHU, for example, matches students in distress with personal coaches and tutors who can follow the students’ progress and provide regular check-ins. In this way, they can help students navigate the program and help cultivate a sense of belonging. 18 Academic advising, Southern New Hampshire University, 2021, snhu.edu. Similarly, Arizona State University pairs students with “success coaches” who give personalized guidance and counseling. 19 “Accessing your success coach,” Arizona State University, asu.edu.
8. Foster a strong community
The majority of students we interviewed have a strong sense of belonging to their academic community. Building a strong network of peers and professors, however, may be challenging in online settings.
To alleviate this challenge, leading online programs often combine virtual social events with optional in-person gatherings. Minerva University, for example, hosts exclusive online events that promote school rituals and traditions for online students, and encourages online students to visit its various locations for in-person gatherings where they can meet members of its diverse, dispersed student population. 20 “Join your extended family,” Minerva University, minerva.edu. SNHU’s Connect social gateway gives online-activity access to more than 15,000 members, and helps them interact within an exclusive university social network. Students can also join student organizations and affinity clubs virtually. 21 SNHU Connect, Southern New Hampshire University, snhuconnect.com.

Getting started: Designing the online journey
Building a distinctive online student experience requires significant time, effort, and investment. Most institutions whose practices we reviewed in this article took several years to understand student needs and refine their approaches to online education.
For those institutions in the early stages of rethinking their online offerings, the following three steps may be useful. Each will typically involve various functions within the institution, including but not necessarily limited to, academic management, IT, and marketing.
The diagnosis could be performed through a combination of focus groups and quantitative surveys, for example. It’s important that participants represent various student segments, which are likely to have different expectations, including young-adult full-time undergraduate students, working-adult part-time undergraduate students, and graduate students. The eight key dimensions outlined above may be helpful for structuring groups and surveys, in addition to self-evaluation of institution performance and potential benchmarks.
- Set a strategic vision for your online learning experience. The vision should be student-centric and link tightly to the institution’s overarching manifesto. The function leaders could evaluate the costs/benefits of each part of the online experience to ensure that the costs are realistic. The online model may vary depending on each school’s market, target audience, and tuition price point. An institution with high tuition, for example, is more likely to afford and provide one-on-one live coaching and student support, while an institution with lower tuition may need to rely more on automated tools and asynchronous interactions with students.
- Design the transformation journey. Institutions should expect a multiyear journey. Some may opt to outsource the program design and delivery to dedicated program-management companies. But in our experience, an increasing number of institutions are developing these capabilities internally, especially as online learning moves further into the mainstream and becomes a source of long-term strategic advantage.
We have found that leading organizations often begin with quick wins that significantly raise student experiences, such as stronger student support, integrated technology platforms, and structured course road maps. In parallel, they begin the incremental redesign of courses and delivery models, often focusing on key programs with the largest enrollments and tapping into advanced analytics for insights to refine these experiences.
Finally, institutions tackle key enabling factors, such as instructor onboarding and online-teaching training, robust technology infrastructure, and advanced-analytics programs that enable the institutions to understand which features of online education are performing well and generating exceptional learning experiences for their students.
The question is no longer whether the move to online will outlive the COVID-19 lockdowns but when online learning will become the dominant means for delivering higher education. As digital transformation accelerates across all industries, higher education institutions will need to consider how to develop their own online strategies.
Felipe Child is a partner in McKinsey’s Bogotá office, Marcus Frank is a senior practice expert in the São Paulo office, Mariana Lef is an associate in the Buenos Aires office, and Jimmy Sarakatsannis is a partner in the Washington, DC, office.
References to specific products, companies, or organizations are solely for information purposes and do not constitute any endorsement or recommendation.
This article was edited by Justine Jablonska, an editor in the New York office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

How to transform higher-education institutions for the long term

Higher education in the post-COVID world

Reimagining higher education in the United States
Learning & Education
Bringing Gemini to Google Workspace for Education
May 16, 2024
[[read-time]] min read
We’re bringing Gemini for Google Workspace to education communities with two new paid add-ons and adding more data protections for schools using Gemini, free of charge.
- General summary
Google Workspace for Education now offers Gemini, an AI-powered tool that enhances teaching and learning experiences. Gemini integrates with Docs, Gmail, Slides, and more, helping educators create lesson plans, summarize emails, and generate original images for presentations. Gemini also provides access to chat with AI safely and securely, with enterprise-grade data protection. Additional features like OpenStax and Data Commons extensions, guided practice quizzes, and added data protection for users 18 and older are coming soon. Gemini is a valuable tool that can save time, inspire creativity, and promote confident learning.
- Bullet points
- Gemini for Google Workspace brings powerful generative AI to education users 18 and older.
- Gemini add-ons provide access to advanced AI features in Docs, Gmail, Slides, and more.
- New Gemini features include OpenStax and Data Commons extensions, and guided practice quizzes.
- Added data protection for Gemini users 18 and older with school accounts, free of charge.
- Gemini is a helpful tool to enhance and enrich teaching and learning experiences.
Explore other styles:

At Google for Education, we believe AI has the potential to help students, educators and education communities save time, create captivating learning experiences, inspire creativity and learn with confidence.
Today, designed together with education experts and institutions, we’re bringing Gemini for Google Workspace to education users 18 years and older with two new paid add-ons, introducing a new and powerful way of working, teaching and learning with generative AI. We’re also adding new functionality to our flagship Gemini conversational experience to help everyone learn confidently. And soon, we’ll introduce additional data protection for Gemini users 18 years and older logged into their Workspace for Education school accounts, free of charge.
Bringing Gemini for Google Workspace to more education institutions
Gemini for Google Workspace provides access to our most capable generative AI models widely available today across your favorite apps, like Docs, Gmail, Slides and more. Starting May 23rd, education institutions can add Gemini for Google Workspace to their existing Workspace for Education edition for users 18 years and older by purchasing one of the following add-ons:
- Gemini Education is a lower price offering to help education institutions get started with generative AI in Workspace, with a monthly usage limit. Through the Admin console, Admins can learn more about how people in their domain are trending towards their usage limits.
- Gemini Education Premium includes everything in Gemini Education, plus additional advanced features like AI-powered note taking and summaries in Meet, AI-enhanced data loss prevention and more coming soon. This add-on provides full access and usage of generative AI tools in Workspace.
In early testing, we heard from educators that they loved having Gemini integrated into the Workspace tools they use every day. For example, they used Gemini to:
- Go from a blank page to a lesson plan template, grant proposal or job description in Docs
- Summarize a long email thread with key takeaways and next steps in Gmail
- Create an agenda for an upcoming professional development session in Sheets
- Bring a presentation to life or illustrate a topic in class by creating an original image in Slides
We're also piloting Gemini in Classroom with new lesson planning features that are informed by LearnLM , our new family of models fine-tuned for learning, based on Gemini and grounded in educational research.
Gemini for Google Workspace also provides access to chat with Gemini safely and securely at gemini.google.com with enterprise-grade data protection and Google’s most capable generative AI models widely available today. Gemini can help you speed up time-consuming tasks, from conducting research about IT security best practices to creating an alumni outreach plan. It can be your collaborative thought partner helping you get fresh ideas and make learning more personal for your students, like re-leveling content or creating class exercises or assignments based on their interests.
Gemini in Docs lesson plan template
Gemini in Gmail email thread
Gemini in Sheets agenda
Gemini in Slides image
Gemini chat experience
Gemini in Classroom lesson planning pilot
The Gemini Education add-ons don't have a minimum purchase requirement, so institutions can buy as few or as many licenses as they need with any existing Workspace for Education edition. Learn more about available pricing and discounts .
Learn with confidence using new Gemini features
Because learning is among the most popular ways people are using Gemini, we’re announcing OpenStax and Data Commons extensions, and guided practice quizzes to help people learn more confidently and with trusted sources. Coming soon, here are a few ways you’ll be able to try these out:
- Type in something like “@OpenStax how does the Moon's distance and orbital path influence the type of solar eclipse we see?” to pull in accurate, trustworthy responses based on Rice University’s OpenStax educational resources — including citations and links to relevant peer-reviewed textbook content.
- Visualize data about complex topics like climate change, jobs, economics and health by typing "@Data Commons” and asking something like “show me a breakdown of business types in Florida" for a response from authoritative sources.
- Test your knowledge with guided practice quizzes that walk you through a series of questions and provide conversational feedback on each of your responses. For example, ask Gemini “quiz me on the periodic table of elements.”
Providing additional data protection in Gemini when using your school account, free of charge
Coming soon, educators and students 18 years and older will have added data protection when accessing Gemini at gemini.google.com with their school accounts, free of charge. With added data protection, your data is not reviewed by anyone, it’s not used to train artificial intelligence models, or shared with other users or institutions. This experience will use our 1.0 Pro model and be available in 40+ languages. Gemini is currently not available to people under 18 while using their Workspace for Education account. AI can never replace the expertise, knowledge, or creativity of an educator, but it can be a helpful tool to enhance and enrich teaching and learning experiences. While we’re encouraged by the widespread excitement around generative AI, it’s still early days for this technology. That’s why it’s always important to review information that’s presented as fact, and when in doubt, double check it with Google Search. Gemini makes this easy with its double-check feature, which uses Google Search to find content that’s likely similar to or different from statements generated by Gemini.
Keeping your data private and secure
Google for Education provides industry-leading education technology that helps create a safer digital learning environment for every school, every classroom, and every student. We’ve long shared robust privacy commitments that outline how we protect user data and prioritize privacy. Generative AI reaffirms these commitments. Gemini for Google Workspace is covered under your Google Workspace for Education Terms of Service . Learn more about how we're protecting your Google Workspace data in the era of generative AI.
Get started with Gemini today
Get started with Gemini for Workspace today by contacting your existing Google Workspace for Education reseller or a Google for Education sales specialist . Gemini with added data protection will be available free of charge for education users 18 years and older, soon. Join us for a webinar on May 23 to learn more about how to use these new tools.
*Education institutions that have already purchased Gemini Enterprise will have the choice to transition to either Gemini Education or Gemini Education Premium.
**In order for users to access Gemini for Workspace they need a license assigned to them.
Related stories

New support for AI advancement in Central and Eastern Europe

8 new accessibility updates across Lookout, Google Maps and more

How we’re building accessibility into our Chromebooks around the world

Four new ways we’re partnering with the disability community

100 things we announced at I/O 2024

How Google’s AI model Gemini got its name
Let’s stay in touch. Get the latest news from Google in your inbox.
Saskatchewan
Advanced education student portal, welcome to the advanced education student portal.
- Portal Account Login
- Security Statement
- Create Portal Account
- Forgot User Name
- Forgot Password
Share your feedback to improve saskatchewan.ca
Meet Gemini Education: Three ways Google is equipping students and educators with AI

Google's Gemini assistant can optimize nearly every step of a user's workflow, including emails, presentations, documents, and more.
Also: 3 reasons to upgrade to Gemini Advanced, from Google I/O 2024
On Thursday, Google introduced new plan add-ons, protections, and features, so educational institutions, teachers, and students can also take advantage of Gemini's perks.
1. Gemini Education
Initially announced in February, Gemini Education is an add-on that educational institutions can sign up for to access AI features in Google Workspace. The add-on includes extra protections and features that make it a better fit for academic needs.
The add-on is being offered in two different tiers: Gemini Education, a lower-price offering with a monthly usage limit, and Gemini Education Premium, which provides users with full access to generative AI tools in Workspace and more advanced features like AI-powered note-taking, summaries in Meet, and more.
Also: This subtle (but useful) AI feature was my favorite Google I/O 2024 announcement
The Gemini Education add-ons do not have a minimum purchasing requirement, making it possible for educational institutions to personalize their subscriptions to suit their needs. However, both tiers are only available for users 18 years or older. Interested educators can visit the Workspace for Education page for pricing information.
Google said educators found assistance during testing from Google Workspace on all sorts of tasks, including putting together lesson plan templates, grant proposals, or job descriptions, summarizing long email threads, creating agendas for development sessions, and generating engaging images in Slides.
2. School account users get free data protection
All educators and students over 18 with school accounts will soon have access to added data protection when they access Gemini at no additional cost. These extra protections ensure educators' and students' data is not reviewed by anyone else, used to train artificial intelligence models, or shared with other institutions or users, according to Google.
This new level of protection is important because it addresses concerns about academic integrity. Students can have peace of mind knowing that if they input an essay for proofreading, it won't be used to train models and potentially appear in an AI-generated answer for the same topic.
Also: 5 ways AI can help you study for finals - for free
There is no additional information on when to expect the feature other than that it is coming soon.
3. New Chat with Gemini features
Google is also "soon" adding two new extensions to Chat with Gemini and a new guided practice quiz feature to enhance users' learning experiences.
An OpenStax extension will allow Gemini to pull information from Rice University's OpenStax educational resources by typing "@OpenStax" in the chat, followed by a query.
As seen in the video above, the responses from Gemini include citations and links to "relevant peer-reviewed textbook content", according to Google. These citations help address a significant pain point for users when they use generative AI models -- the trustworthiness of an answer.
Also: Google Glass vs. Project Astra: Sergey Brin on AI wearables and his top use case
A Data Commons extension allows users to visualize data about complex topics by typing in "@Data-Commons", followed by the subject they'd like to learn more about. The responses will come from "authoritative sources", according to Google.
Lastly, students can prepare for exams with the new guided practice quizzes feature. This feature allows Gemini to test students' knowledge of a subject and provide feedback on their responses. All a student has to do is type in "Quiz me on", followed by the topic.
Artificial Intelligence
3 reasons to upgrade to gemini advanced, from google i/o 2024, is openai sweating 9 google features announced for gemini, search, android, and more, 5 exciting android features google just announced at i/o 2024.

40 Facts About Elektrostal
Written by Lanette Mayes
Modified & Updated: 17 May 2024
Reviewed by Jessica Corbett

Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to captivate you.
This article will provide you with 40 fascinating facts about Elektrostal, giving you a better understanding of why this city is worth exploring. From its origins as an industrial hub to its modern-day charm, we will delve into the various aspects that make Elektrostal a unique and must-visit destination.
So, join us as we uncover the hidden treasures of Elektrostal and discover what makes this city a true gem in the heart of Russia.
Key Takeaways:
- Elektrostal, known as the “Motor City of Russia,” is a vibrant and growing city with a rich industrial history, offering diverse cultural experiences and a strong commitment to environmental sustainability.
- With its convenient location near Moscow, Elektrostal provides a picturesque landscape, vibrant nightlife, and a range of recreational activities, making it an ideal destination for residents and visitors alike.
Known as the “Motor City of Russia.”
Elektrostal, a city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia, earned the nickname “Motor City” due to its significant involvement in the automotive industry.
Home to the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Elektrostal is renowned for its metallurgical plant, which has been producing high-quality steel and alloys since its establishment in 1916.
Boasts a rich industrial heritage.
Elektrostal has a long history of industrial development, contributing to the growth and progress of the region.
Founded in 1916.
The city of Elektrostal was founded in 1916 as a result of the construction of the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Located approximately 50 kilometers east of Moscow.
Elektrostal is situated in close proximity to the Russian capital, making it easily accessible for both residents and visitors.
Known for its vibrant cultural scene.
Elektrostal is home to several cultural institutions, including museums, theaters, and art galleries that showcase the city’s rich artistic heritage.
A popular destination for nature lovers.
Surrounded by picturesque landscapes and forests, Elektrostal offers ample opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, and birdwatching.
Hosts the annual Elektrostal City Day celebrations.
Every year, Elektrostal organizes festive events and activities to celebrate its founding, bringing together residents and visitors in a spirit of unity and joy.
Has a population of approximately 160,000 people.
Elektrostal is home to a diverse and vibrant community of around 160,000 residents, contributing to its dynamic atmosphere.
Boasts excellent education facilities.
The city is known for its well-established educational institutions, providing quality education to students of all ages.
A center for scientific research and innovation.
Elektrostal serves as an important hub for scientific research, particularly in the fields of metallurgy, materials science, and engineering.
Surrounded by picturesque lakes.
The city is blessed with numerous beautiful lakes, offering scenic views and recreational opportunities for locals and visitors alike.
Well-connected transportation system.
Elektrostal benefits from an efficient transportation network, including highways, railways, and public transportation options, ensuring convenient travel within and beyond the city.
Famous for its traditional Russian cuisine.
Food enthusiasts can indulge in authentic Russian dishes at numerous restaurants and cafes scattered throughout Elektrostal.
Home to notable architectural landmarks.
Elektrostal boasts impressive architecture, including the Church of the Transfiguration of the Lord and the Elektrostal Palace of Culture.
Offers a wide range of recreational facilities.
Residents and visitors can enjoy various recreational activities, such as sports complexes, swimming pools, and fitness centers, enhancing the overall quality of life.
Provides a high standard of healthcare.
Elektrostal is equipped with modern medical facilities, ensuring residents have access to quality healthcare services.
Home to the Elektrostal History Museum.
The Elektrostal History Museum showcases the city’s fascinating past through exhibitions and displays.
A hub for sports enthusiasts.
Elektrostal is passionate about sports, with numerous stadiums, arenas, and sports clubs offering opportunities for athletes and spectators.
Celebrates diverse cultural festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal hosts a variety of cultural festivals, celebrating different ethnicities, traditions, and art forms.
Electric power played a significant role in its early development.
Elektrostal owes its name and initial growth to the establishment of electric power stations and the utilization of electricity in the industrial sector.
Boasts a thriving economy.
The city’s strong industrial base, coupled with its strategic location near Moscow, has contributed to Elektrostal’s prosperous economic status.
Houses the Elektrostal Drama Theater.
The Elektrostal Drama Theater is a cultural centerpiece, attracting theater enthusiasts from far and wide.
Popular destination for winter sports.
Elektrostal’s proximity to ski resorts and winter sport facilities makes it a favorite destination for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter activities.
Promotes environmental sustainability.
Elektrostal prioritizes environmental protection and sustainability, implementing initiatives to reduce pollution and preserve natural resources.
Home to renowned educational institutions.
Elektrostal is known for its prestigious schools and universities, offering a wide range of academic programs to students.
Committed to cultural preservation.
The city values its cultural heritage and takes active steps to preserve and promote traditional customs, crafts, and arts.
Hosts an annual International Film Festival.
The Elektrostal International Film Festival attracts filmmakers and cinema enthusiasts from around the world, showcasing a diverse range of films.
Encourages entrepreneurship and innovation.
Elektrostal supports aspiring entrepreneurs and fosters a culture of innovation, providing opportunities for startups and business development.
Offers a range of housing options.
Elektrostal provides diverse housing options, including apartments, houses, and residential complexes, catering to different lifestyles and budgets.
Home to notable sports teams.
Elektrostal is proud of its sports legacy, with several successful sports teams competing at regional and national levels.
Boasts a vibrant nightlife scene.
Residents and visitors can enjoy a lively nightlife in Elektrostal, with numerous bars, clubs, and entertainment venues.
Promotes cultural exchange and international relations.
Elektrostal actively engages in international partnerships, cultural exchanges, and diplomatic collaborations to foster global connections.
Surrounded by beautiful nature reserves.
Nearby nature reserves, such as the Barybino Forest and Luchinskoye Lake, offer opportunities for nature enthusiasts to explore and appreciate the region’s biodiversity.
Commemorates historical events.
The city pays tribute to significant historical events through memorials, monuments, and exhibitions, ensuring the preservation of collective memory.
Promotes sports and youth development.
Elektrostal invests in sports infrastructure and programs to encourage youth participation, health, and physical fitness.
Hosts annual cultural and artistic festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal celebrates its cultural diversity through festivals dedicated to music, dance, art, and theater.
Provides a picturesque landscape for photography enthusiasts.
The city’s scenic beauty, architectural landmarks, and natural surroundings make it a paradise for photographers.
Connects to Moscow via a direct train line.
The convenient train connection between Elektrostal and Moscow makes commuting between the two cities effortless.
A city with a bright future.
Elektrostal continues to grow and develop, aiming to become a model city in terms of infrastructure, sustainability, and quality of life for its residents.
In conclusion, Elektrostal is a fascinating city with a rich history and a vibrant present. From its origins as a center of steel production to its modern-day status as a hub for education and industry, Elektrostal has plenty to offer both residents and visitors. With its beautiful parks, cultural attractions, and proximity to Moscow, there is no shortage of things to see and do in this dynamic city. Whether you’re interested in exploring its historical landmarks, enjoying outdoor activities, or immersing yourself in the local culture, Elektrostal has something for everyone. So, next time you find yourself in the Moscow region, don’t miss the opportunity to discover the hidden gems of Elektrostal.
Q: What is the population of Elektrostal?
A: As of the latest data, the population of Elektrostal is approximately XXXX.
Q: How far is Elektrostal from Moscow?
A: Elektrostal is located approximately XX kilometers away from Moscow.
Q: Are there any famous landmarks in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to several notable landmarks, including XXXX and XXXX.
Q: What industries are prominent in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal is known for its steel production industry and is also a center for engineering and manufacturing.
Q: Are there any universities or educational institutions in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to XXXX University and several other educational institutions.
Q: What are some popular outdoor activities in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal offers several outdoor activities, such as hiking, cycling, and picnicking in its beautiful parks.
Q: Is Elektrostal well-connected in terms of transportation?
A: Yes, Elektrostal has good transportation links, including trains and buses, making it easily accessible from nearby cities.
Q: Are there any annual events or festivals in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal hosts various events and festivals throughout the year, including XXXX and XXXX.
Elektrostal's fascinating history, vibrant culture, and promising future make it a city worth exploring. For more captivating facts about cities around the world, discover the unique characteristics that define each city . Uncover the hidden gems of Moscow Oblast through our in-depth look at Kolomna. Lastly, dive into the rich industrial heritage of Teesside, a thriving industrial center with its own story to tell.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:
Two anti-LGBTQ bills advanced by Louisiana Senate’s education committee

BATON ROUGE, La. ( Louisiana Illuminator ) - Two anti-LGBTQ+ bills advanced Wednesday (May 15) from the Louisiana Senate’s education committee, putting them one step away from final legislative approval.
The committee advanced House Bill 121 by Rep. Raymond Crews (R-Bossier City), which prohibits the use of transgender and nonbinary youth’s chosen names and pronouns in public K-12 schools without parental permission.
House Bill 122 by Rep. Dodie Horton (R-Haugton), which limits discussion of gender and sexuality in public K-12 schools, was also approved.
Both bills were advanced without objection. Sen. Katrina Jackson-Andrews (D-Monroe) was the only Democrat present.
The legislature approved both bills last year. Then-Gov. John Bel Edwards, a Democrat, vetoed them, and Republicans were unable to overturn his action. Lance Maxwell, a legislative liaison for Republican Gov. Jeff Landry, attended the committee meeting in support of Crews’ and Horton’s bills.
Wednesday’s emotional hearing marked the latest step for an advancing culture-war agenda, once held back under a Democratic governor. With the support of an ultra-conservative in the governor’s mansion, a slew of anti-LGBTQ+ proposals are rapidly advancing toward enactment.
“I don’t know how y’all continue to hear things from us about our pain and our trauma, and just still pass bills,” said Peyton Rose Michelle, executive director of Louisiana Trans Advocates. “I don’t know how y’all sit through these things, and you don’t break down.”
Crews’ bill would require teachers and other school personnel to use a student’s given name and pronouns that align with their birth sex, unless a student has permission from their parents to use their chosen name. The proposal has been promoted as a “parental rights” bill.
“This bill is a grave violation of parental rights by prioritizing the moral objections of others over the fundamental rights of transgender students to be recognized by their chosen names, pronouns and identities,” said SarahJane Guidry, executive director of LGBTQ+ rights group Forum For Equality. “This legislation sets a dangerous and discriminatory precedent.
“This relentless focus on legislating the lives of a small, vulnerable population diverts precious time, money and energy away from addressing real educational issues.”
Under Crews’ bill, teachers would be allowed to disregard a parent’s choice to respect their transgender or nonbinary child’s name and pronouns if they have religious opposition to doing so.
In an interview, Crews said that while his bill supports parental rights, parents should not be able to eclipse somebody else’s religious rights.
His bill does not have an exception for those who have a religious opposition to deadnaming or misgendering students. Deadnaming is when someone uses a transgender or nonbinary person’s birth name or “dead name” against their wishes. Misgendering occurs when someone refers to an individual by a gender to which they do not identify.
While the bill would allow parents to request a classroom change if a teacher disregards their permission for their transgender or nonbinary child to use their name or pronouns, it does not require this change to take place. Advocates have argued such classroom changes might not be feasible in smaller schools.
Jacob Newsom, an Ascension Parish public school teacher, said disregarding students’ names and pronouns would make them uncomfortable, which he believes would hamper their learning environment.
“How am I going to reach this child? How am I going to effectively teach this child?” Newsom said.
“There is an undeniable correlation between feeling safe and secure and being able to learn,” added Megan Sheehan-Dean, a child education expert.
At the core of Crews’ proposal is his belief that parents have the right to know whether their children are transgender. Advocates for the LGBTQ+ community say the bill would force transgender youth to out themselves to their parents or else be deadnamed and misgendered at school. They have raised concerns about what happens when parents find out and don’t approve.
A survey from the Trevor Project found 38% of transgender women, 39% of transgender men and 35% of nonbinary youth have experienced homelessness as a result of parental rejection.
Horton’s bill is similar to a Florida law referred to by critics as a “Don’t Say Gay” bill. Her proposal is much broader and would apply to K-12 grades, whereas Florida’s law applies only to early grade students.
Florida recently settled a lawsuit over the law filed by civil rights activists. As part of the agreement, students and teachers are permitted to discuss gender and sexuality as long as it is not part of classroom instruction.
Horton said she didn’t believe teachers should discuss their “lifestyle choices” with students.
“Having sexualized personal discussions between educators and students in our classrooms are not appropriate, and they can rob our children of their innocence while imposing suggested influence over their developing young minds,” Horton said.
Horton’s bill would not just apply to classroom instruction. It also prohibits “covering the topics of sexual orientation or gender identity” during any extracurricular and athletics events, meaning it could potentially hinder student chapters of the Gay-Straight Alliance (GSA) and other LGBTQ+ student organizations.
When asked by committee Chair Sen. Rick Edmonds (R-Central), Horton agreed that heterosexuality falls under “sexual orientation” and is also not appropriate for classroom discussion.
The bills will next be discussed in the state Senate.
This story was produced by Fox 8′s news partner The Louisiana Illuminator, part of of States Newsroom , the nation’s largest state-focused nonprofit news organization.
See a spelling or grammar error in our story? Click Here to report it. Please include the headline.
Subscribe to the Fox 8 YouTube channel .
Copyright 2024 WVUE. All rights reserved.

‘Heinous, gruesome, horrific;’ Couple accused of sexually abusing, burning and shooting 15-year-old girl

Cold Case: Hurricane Katrina victim identified nearly two decades later

Stream news and weather 24/7

New Orleans woman ordered to stay away from Mayor Cantrell over stalking allegations

3 dead after plane that departed Gonzales crashes in TN
Latest news.

Biden administration proposes a reclassification of marijuana

Gov. Landry drumming up support for bill that would use tax dollars to send students to private schools

La. bill seeks to better inform the public about discounts for fortified roofs

‘It’s being abused’: People, businesses react to bill banning retail sale of nitrous oxide

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Discover thousands of offerings — from free courses to full degrees — delivered by world-class partners like Harvard, Google, Amazon and more.
Overview of Advanced Education Degrees. Advanced education degrees are found at both the master's and doctoral levels. Individuals pursue these degrees for several reasons, including changing careers, expanding professional skills, or as a condition of license renewal or attainment. Programs are varied, and concentrations of study can range ...
A report by the National Working Group on Advanced Education offers recommendations for how to improve advanced learning opportunities for students from marginalized backgrounds. It addresses the challenges and controversies of gifted education, honors courses, and selective schools in the U.S.
Learn how to lead for excellence and equity in K-12 education with Harvard Graduate School of Education. The CAEL program offers four modules that cover developing self, driving change, leading learning, and managing evidence.
JHU offers part-time graduate degree programs for adults seeking flexibility, career advancement, and personal enrichment. Learn from world-renowned faculty and experts in various fields of study, online or at the Washington, D.C. or Baltimore Homewood locations.
If an advanced degree is required to meet job qualifications, a student may want to consider an accelerated combined degree program, often known as 4+1 programs - an option to earn both a ...
According to the National Center for Education Statistics, 58% of U.S. public school teachers who taught during the 2017-18 school year had a more advanced degree than a bachelor's.
As of 2018, 69 percent of students chose to complete their undergraduate degree immediately after earning their high school diploma. A graduate degree—including master's degrees, doctorates, and PhDs—provides an advanced understanding of a specific topic or field, and demonstrates a commitment to lifelong learning that many employers value.
To pursue an advanced degree in education you must take several admissions tests, depending on the degree program they've selected. Plan on taking the Graduate Record Exam (GRE) near the end of your junior year if it is required for the programs to which you are planning to apply. Credentialing programs do test for knowledge of specific ...
That's 30 percent cheaper than the in-state, in-person tuition. Paying by the month encourages students to move faster through their educations, and most are projected to graduate in 18 months ...
Here are five specific and sequential guidelines for decisionmakers to realize the potential of education technology to accelerate student learning. 1. Take stock of how your current schools ...
Education Technologies for Meaningful and Transformative Learning. The University of Michigan School of Education Advanced Education Technology Certificate (AETP) is a growth-based teacher certification that aligns with the ISTE Standards for Educators (internationally recognized standards in P-16 teaching with technology).
MIT Open Learning is exploring an agile, continuous education (ACE) model that, Prof. Breazeal explained, will give learners more pathways to advance their education at their own pace. The ACE model, which MIT ReACT adopted for its Computer and Data Science certificate program, combines online, in-person, and at-work learning modalities that ...
Overview. The Certificate in Advanced Education Leadership (CAEL), based upon the ground-breaking Doctor of Education Leadership (Ed.L.D.) Program at HGSE, is an online certificate program comprised of 12-week modules led by HGSE faculty and offered on rotation throughout the year.
Our responsibilities. Prepares Albertans for lifelong success through education by: approving programs of study. funding public post-secondary institutions and other adult learning providers. providing financial aid for learners. registering and certifying apprentices. supporting academic research and innovation.
2008 - 2012 Bachelor's Degree or Higher (5-year estimate) by County (percent) The educational attainment of the U.S. population refers to the highest level of education completed. The educational attainment of the U.S. population is similar to that of many other industrialized countries with the vast majority of the population having completed secondary education and a rising number of college ...
We advance scientific discovery & inventions that further students' brilliance and transform PreK-12 education futures. Our Advanced Inclusive Research and Development (R&D) Approach We design, measure, and evaluate learning solutions for breakthroughs in US PreK-12 education. We study the evidence behind these solutions that could unlock new capabilities and insights for teaching and ...
Colleges and universities can take a cue from the early adopters of online education, which use AI and advanced analytics to provide personalized learning and on-demand student support. ... The education sector was among the hardest hit by the COVID-19 pandemic. Schools across the globe were forced to shutter their campuses in the spring of ...
Shutterstock. (TNS) — Syracuse University announced this morning a $20 million investment to launch the SU Center for Advanced Semiconductor Manufacturing. The center will include experts in ...
Bringing Gemini to Google Workspace for Education. Gemini for Google Workspace brings powerful generative AI to education users 18 and older. Gemini add-ons provide access to advanced AI features in Docs, Gmail, Slides, and more. New Gemini features include OpenStax and Data Commons extensions, and guided practice quizzes.
Welcome to the Advanced Education Student Portal. Portal Account Login. Security Statement. Create Portal Account. Forgot User Name. Forgot Password. Share your feedback to improve saskatchewan.ca.
On Thursday, Google introduced new plan add-ons, protections, and features, so educational institutions, teachers, and students can also take advantage of Gemini's perks. 1. Gemini Education ...
In conclusion, Elektrostal is a fascinating city with a rich history and a vibrant present. From its origins as a center of steel production to its modern-day status as a hub for education and industry, Elektrostal has plenty to offer both residents and visitors. With its beautiful parks, cultural attractions, and proximity to Moscow, there is ...
Its a city in the Moscow region. As much effort they take in making nice flags, as low is the effort in naming places. The city was founded because they built factories there.
Course Description. Advanced Life Support in Obstetrics (ALSO®) is an evidence-based, interprofessional, and multidisciplinary training program that equips the entire maternity care team with skills to effectively manage obstetric emergencies. This comprehensive course encourages a standardized team-based approach amongst physicians, residents ...
12. Offer advanced courses in as many subjects as possible in grades 6-12 13. Automatically enroll students participating in elementary school advanced education programs in subsequent advanced learning opportunities in middle and/or high school 14. Intentionally recruit underrepresented and underserved students for external advanced learning
Alliance. 1 review. #1 of 1 small hotel in Zheleznodorozhny. Gidrogorodok St., 3, Zheleznodorozhny 143982 Russia. Write a review. Check availability. Have you been to Alliance?
596K subscribers in the vexillology community. A subreddit for those who enjoy learning about flags, their place in society past and present, and…
IIT Madras has released the JEE Advanced 2024 admit cards on May 17th, available on the official website jeeadv.ac.in. The exam, set for May 26th, includes two three-hour papers covering Physics ...
Two bills targeting LGBTQ youth and how they are to be accepted and taught in public schools were advanced Wednesday (May 15) out of the Louisiana Senate's education committee, putting them one ...