
Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research

How to Write a Research Proposal as an Undergrad
As I just passed the deadline for my junior independent work (JIW), I wanted to explore strategies that could be helpful in composing a research proposal. In the chemistry department, JIW usually involves lab work and collecting raw data. However, this year, because of the pandemic, there is limited benchwork involved and most of the emphasis has shifted to designing a research proposal that would segue into one’s senior thesis. So far, I have only had one prior experience composing a research proposal, and it was from a virtual summer research program in my department. For this program, I was able to write a proposal on modifying a certain chemical inhibitor that could be used in reducing cancer cell proliferation. Using that experience as a guide, I will outline the steps I followed when I wrote my proposal. (Most of these steps are oriented towards research in the natural sciences, but there are many aspects common to research in other fields).
The first step is usually choosing a topic . This can be assigned to you by the principal investigator for the lab or a research mentor if you have one. For me, it was my research mentor, a graduate student in our lab, who helped me in selecting a field of query for my proposal. When I chose the lab I wanted to be part of for my summer project (with my JIW and senior thesis in mind) , I knew the general area of research I wanted to be involved in. But, usually within a lab, there are many projects that graduate students and post-docs work on within that specific area. Hence, it is important to identify a mentor with specific projects you want to be involved in for your own research. Once you choose a mentor, you can talk to them about formulating a research proposal based on the direction they plan to take their research in and how you can be involved in a similar project. Usually, mentors assign you one to three papers related to your research topic – a review paper that summarizes many research articles and one to two research articles with similar findings and methodology. In my case, the papers involved a review article on the role of the chemical inhibitor I was investigating along with articles on inhibitor design and mechanism of action.
The next step is to perform a literature review to broadly assess previous work in your research topic, using the articles assigned by your mentor. At this stage, for my proposal, I was trying to know as much about my research area from these papers as well as the articles cited in them. Here, it is helpful to use a reference management software such as Zotero and Mendeley to organize your notes along with all the articles you look into for a bibliography.
After going through your literature review, you can start thinking about identifying questions that remain to be answered in that field. For my JIW, I found some good ideas in the discussion section of the papers I had read where authors discussed what could be done in future research projects. One discussion section, for example, suggested ways to complement in-vitro experiments (outside of a living organism) with in-vivo ones (inside a living organism) . Reviewing the discussion section is a relatively straightforward way to formulate your own hypothesis. Alternatively, you could look at the papers’ raw data and find that the authors’ conclusions need to be revisited (this might require a critical review of the paper and the supplementary materials) or you could work on improving the paper’s methodology and optimizing its experiments. Furthermore, you might think about combining ideas from different papers or trying to reconcile differing conclusions reached by them.
The next step is developing a general outline ; deciding on what you want to cover in your proposal and how it is going to be structured. Here, you should try hard to limit the scope of your proposal to what you can realistically do for your senior thesis. As a junior or a senior, you will only be working with your mentor for a limited amount of time. Hence, it is not possible to plan long term experiments that would be appropriate for graduate students or post-docs in the lab. (For my summer project, there was not a follow up experiment involved, so I was able to think about possible experiments without the time or equipment constraints that would need to be considered for a JIW). Thus, your proposal should mostly focus on what you think is feasible given your timeline.
Below are two final considerations. It is important that your research proposal outlines how you plan to collect your own data , analyze it and compare it with other papers in your field. For a research project based on a proposal, you need only establish if your premises/hypotheses are true or false. To do that, you need to formulate questions you can answer by collecting your own data, and this is where experiments come in. My summer project had three specific aims and each one was in the form of a question.
It is important to keep in mind in your proposal the experiments you can perform efficiently on your own – the experimental skills you want to master as an undergraduate. In my view, it is better to learn one to two skills very well than having surface-level knowledge of many. This is because the nature of research has been very specialized in each field that there is limited room for broad investigations. This does not mean your proposal should be solely based on things you can test by yourself (although it might be preferable to put more emphasis there). If your proposal involves experiments beyond what you can learn to do in a year or two, you can think of asking for help from an expert in your lab.
A research proposal at the undergraduate level is an engaging exercise on coming up with your own questions on your chosen field. There is much leeway as an undergraduate to experiment within your field and think out of the box. In many ways, you will learn how to learn and how to formulate questions for any task you encounter in the future. Whether or not you want to be involved in research, it is an experience common to all Princeton students that you take with you after graduation.
In this post, I have described the basic elements of a natural science research proposal and my approach to writing one. Although the steps above are not comprehensive, I am hopeful they offer guidance you can adapt when you write your own proposal in the future.
— Yodahe Gebreegziabher, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

Writing a Project Proposal
Main navigation, a good proposal describes....
- what you hope to accomplish
- why those objectives are important to your academic or artistic field
- how you intend to achieve your objectives
Your original project proposal is the core of your grant application.
Detailed Proposal Requirements
- General guidelines for all grant proposals
- Additional specific guidelines for Research, Arts/Design, and Senior Synthesis project proposals -- please follow carefully!
- Ways to turn your good proposal into a great one
- Sample Project Proposals : Check out exemplars of past student project proposals.
Connect with Faculty Mentors and UADs
- Faculty Mentors should meet required eligibility criteria .
- Students should schedule a meeting with their Undergraduate Advising Director (UAD) as they write their proposal. UADs are well-versed with all VPUE Undergraduate Research Grants!
Watch a 3-minute overview of the VPUE Student Grant application process.
Watch a 2-minute video on how to write the critical dialogue section of a creative arts project proposal.
PROPOSAL WRITING
The writing required for a research proposal is not like other, more familiar, forms of writing. In particular, it does not work like an essay where you weave your ideas in and out of the different sections. Grant proposals are very segmented; each section is its own little pod. In general, you complete the section and never revisit the content in it – you simply move on to the next argument you have to make.
OUR runs a number of different grant programs. Our core proposal writing advice is connected to the Undergraduate Research Grant programs, where students apply to do independent research and/or creative projects in the summer or academic year. What follows is a brief rundown of a basic research grant proposal, and we encourage you to use our URG Proposal Writing Guide for a fuller exploration of what we want to see. We also have lots of Sample Grant Proposals across a range of fields to help you. Finally, OUR offers one-on-one advising for students applying to our programs, and we regularly review and provide feedback on multiple drafts.
We also have two other programs which use slightly modified proposal formats, and their guides can be found here (plus we have advisors for them too).
- Undergraduate Language Grant Proposal Guide
- Circumnavigators Travel-Study Grant Proposal Guide
RESEARCH GRANT PROPOSAL BASICS
Introduction.
A proposal introduction is part abstract for your entire project and part movie trailer pitching its value. A good introduction tell us what the topic/issue is, why it is significant to study, and what you specifically propose to do about it. Grant proposals are an ask for money, so if they don’t know what you are asking for money to do (aka your actual project, not just its subject), we are in trouble! You are setting the frame for the entire proposal, so make it clear, compelling, and free of jargon. We recommend that you wait to write the intro until you are finished drafting the rest of the proposal because it is much easier to summarize a proposal once you know what it actually says!
WHY IS THIS PROJECT NEEDED? YOUR LIT REVIEW
Your first main argument needs to justify that the topic warrants the work you intend to do. What is currently known/explored about your topic, and why is your project needed/what value will it add? It is not enough to say that something hasn’t been done before; you also have to show that it should! This section focuses on citations and quotations; use the words of experts to craft your argument about why this project is needed in your field. Focus on making an argument for your project, not just listing a bunch of citations. The goal of this section to reveal your research question as the logical choice to make in the field. Make your lit review a funnel that leads clearly to your intended research question, so the reader will see that this project 1) needs to be done and 2) needs to be done that way you intend.
WHAT'S THE PLAN? YOUR METHODOLOGY
Now that the reader believes that this project should be done, you now need to show them how you will do it. Take them step by step through the process you will follow. This section is the beating heart of your proposal, so focus on specifics. Think through (with your faculty) the full trajectory of the project and outline the steps and processes involved. Remember to not stop at research collection; they will want to know how you plan to analyze the data you collect, whether that is interviews, literary analysis, or scientific procedures. At the end of this section, the reader should be believe that you have a viable plan – if you follow these steps, then you should be able to answer the question at the end of the lit review.
CAN YOU DO IT? YOUR QUALIFICATIONS
We don’t need a list of everything you have ever accomplished in your life. Instead, we want to see that you have the specific skills needed to do what you describe. In this way, this argument needs to be based upon the methodology you laid out in the previous section. If you lack a critical skills, don’t worry (we know you don’t have a PhD!), but demonstrate how you will fill that gap, i.e. I will do this training course or my faculty will work with me on preparatory interviews… Finally, end the proposal (there is no formal conclusion) telling the reader how this project will help you achieve your academic and professional goals. They want to know that this project makes sense for you.
THE KEYS TO SUCCESS
- Start early! Writing a good proposal takes time.
- Read examples of successful proposals.
- Get lots of feedback. From your faculty, and also from the advisors at the OUR , who are happy to read through drafts.
- Be prepared to write multiple drafts.
- If you are struggling with jargon, try this nifty resource!
Prepare your proposal
Use these tips and our sample proposal sections to develop a strong proposal and increase your chances of being awarded.
Jump to writing resources, proposal examples and workshop info.

Proposal writing tips
- Manage your time – Know the deadlines and plan ahead to obtain requirements like transcripts and recommendations.
- Follow directions carefully – Applications that are missing elements or submitted incorrectly are usually removed from consideration. Double check the requirements before submitting.
- Use simple language – Keep in mind that many members of the panel will not be experts in your field. Your proposal should be intelligible to someone with little to no background in your subject matter.
Outline for a proposal
- In simple language provide a very brief overview of your project.
- Start with one or two sentences about the issue.
- State the objective of what you plan to do.
- Finish the abstract by two or three sentences about how you will conduct the research/creative work.
- Introduction
- This is the place to tell us what your research is all about.
- Clearly state the problem you are addressing.
- Point out why your research or study is necessary or important.
- Discuss the research of others pertaining to your topic.
- Identify any gaps in previous work that your research would fill.
- The objectives should be stated very specifically.
- Bulleting or numbering the objectives is a useful way to stay on track and clearly present the aims of your project.
- Include study questions or hypothesis as appropriate
- Explain the purpose of what you want to do
Plans for research/creative work
- Remember that many members of the review panel will not be experts in your field.
- Spell out the tasks of your project step by step. Use numbers or bullets if appropriate.
- Clearly explain how to accomplish your objectives.
- Discuss in detail how your research will address gaps in previous research on your topic.
- Be realistic about how much you can accomplish in the timeframe provided. Reviewers will be looking to see if your project is feasible.
- Explain how you will accomplish the steps in your research plan.
- A chart may be a helpful aid in this section.
Plans for dissemination of results
- Demonstrate who will benefit from the work you have done and how you will share it with the public, other students, and the academic community.
- Sharing your results is very important to the review panel.
- State whether you ultimately will be preparing a paper, report, or a presentation for a conference.
- This section allows you to justify the expense of your project.
- Provide a specific list of items required for your project.
- Provide justification for each item in your budget.
- Hosting is not permitted in your budget.
Human subjects or vertebrate animals
- If your study includes human subjects or vertebrate animals, your application must include documentation.
- Visit the Research Integrity & Security website for more information about studies with human subjects.
- Visit the Animal Resources website for more information on studies with vertebrate animals.
Campus assistance for proposal writing
The University Writing Center offers services dedicated to proposal writing.
Visit the University Writing Center
Sample application sections
- Budget & justification
Proposal writing workshops
We have partnered with the Writing Center to provide you with research, scholarship and creative activity writing workshops.
Check the workshop schedule
- Utility Menu
GA4 tracking code

- CARAT (Opportunities Database)
- URAF Application Instructions
- URAF Calendar
Writing Research Proposals
The research proposal is your opportunity to show that you—and only you!—are the perfect person to take on your specific project. After reading your research proposal, readers should be confident that…
- You have thoughtfully crafted and designed this project;
- You have the necessary background to complete this project;
- You have the proper support system in place;
- You know exactly what you need to complete this project and how to do so; and
- With this funding in hand, you can be on your way to a meaningful research experience and a significant contribution to your field.
Research proposals typically include the following components:
- Why is your project important? How does it contribute to the field or to society? What do you hope to prove?
- This section includes the project design, specific methodology, your specific role and responsibilities, steps you will take to execute the project, etc. Here you will show the committee the way that you think by explaining both how you have conceived the project and how you intend to carry it out.
- Please be specific in the project dates/how much time you need to carry out the proposed project. The scope of the project should clearly match the timeframe in which you propose to complete it!
- Funding agencies like to know how their funding will be used. Including this information will demonstrate that you have thoughtfully designed the project and know of all of the anticipated expenses required to see it through to completion.
- It is important that you have a support system on hand when conducting research, especially as an undergraduate. There are often surprises and challenges when working on a long-term research project and the selection committee wants to be sure that you have the support system you need to both be successful in your project and also have a meaningful research experience.
- Some questions to consider are: How often do you intend to meet with your advisor(s)? (This may vary from project to project based on the needs of the student and the nature of the research.) What will your mode of communication be? Will you be attending (or even presenting at) lab meetings?
Don’t be afraid to also include relevant information about your background and advocate for yourself! Do you have skills developed in a different research experience (or leadership position, job, coursework, etc.) that you could apply to the project in question? Have you already learned about and experimented with a specific method of analysis in class and are now ready to apply it to a different situation? If you already have experience with this professor/lab, please be sure to include those details in your proposal! That will show the selection committee that you are ready to hit the ground running!
Lastly, be sure to know who your readers are so that you can tailor the field-specific language of your proposal accordingly. If the selection committee are specialists in your field, you can feel free to use the jargon of that field; but if your proposal will be evaluated by an interdisciplinary committee (this is common), you might take a bit longer explaining the state of the field, specific concepts, and certainly spelling out any acronyms.
- Getting Started
- Application Components
- Interviews and Offers
- Building On Your Experiences
- Applying FAQs
Secondary Menu
- Events & Workshops
- Join our Listserv!
Writing Research Proposals
Summer research funding: writing successful proposals.
Applying for a fellowship or grant for a summer research project? Read the guidelines below and attend information sessions and workshops to help you write a winning proposal!
Sponsored by the Undergraduate Research Support Office and the Thompson Writing Program .
Guidelines for Writing Research Proposals
- General Proposal Guidelines
- Slides: Writing Successful Research Proposals
- Writing Rubric for Summer Funding Proposals .
- See the Undergraduate Research Grant Writing Support site for examples, advice from students, and other resources.
- Get feedback from the Duke Reader Project or the Writing Studio .
Information Sessions and Workshops
Session 1: what is a successful research grant proposal, tues, feb 2nd, 4:00-5:00 pm, perkins 218.
In order to help you understand how to write a good first draft, we will discuss what’s expected in a proposal. This session will provide answers to these questions: What is a research grant proposal? What are the most essential elements? What makes a proposal likely to get funded? Why are some proposals unlikely to get funded? We will look at some proposals from prior years that got funded, and some that didn't.
Session 2: Revising your proposal to make it successful. Wed, Feb 24th, 3:30-5:30 pm, Perkins 218 or Thurs, Feb 25th, 12:30-2:30 pm, Breedlove Meeting Rm (2nd Fl, Rubenstein Library)
If you want a good shot at getting your research funded, you’ll need to get feedback on your draft and then do some serious revision. We will begin by discussing the strengths and weaknesses of sample proposals. Then we’ll break up into guided groups so everyone can get some feedback on 2-3 of the most important aspects of their proposals. Attendees must bring 3 copies of their proposal draft.
- Getting Started in Research
- Guide to Undergraduate Research at Duke
- Undergrad Research Calendar
- Honors Theses
- Explore Research by Department
- Compensation for International Students
- Research Abroad: Safety Considerations
- Human Subjects: Institutional Review Board
- Responsible Conduct of Research Training and Tutorials
- Frequently Asked Questions
- URS Academic Term Grants
- Program II Research Funds
- Duke Opportunities
- Opportunities Database
- Non-Duke Opportunities
- Resources for Presentations
- Undergraduate Research Journals
- Student Team Grants
- Eligibility & Requirements
- Application Instructions
- Background & Facts
- Duke ASP Faculty Mentors
- Duke ASP Scholars
- Financial Support
- Contact the Amgen Scholars Program
- PRIME-Cancer Research Program Mentors
- Student Stories
- Student Advisory Council
- Annual Undergraduate Research Symposium
- 2024 Symposium Abstract Booklets
- Previous Abstract Books
- 301 Academic Skills Centre
- Study skills online
How to write a research proposal
Advice and guidance on writing a proposal for a student research project.

Purpose of a Research Proposal
A research proposal should describe what you will investigate, why it is important to the discipline and how you will conduct your research.
Simply put, it is your plan for the research you intend to conduct. All research proposals are designed to persuade someone about how and why your intended project is worthwhile.
In your proposal you will need to explain and defend your choices. Always think about the exact reasons why you are making specific choices and why they are the best options available to you and your project.
Your research proposal aims should be centred on:
- Relevance - You want to convince the reader how and why your research is relevant and significant to your field and how it is original. This is typically done in parts of the introduction and the literature review.
- Context - You should demonstrate that you are familiar with the field, you understand the current state of research on the topic and your ideas have a strong academic basis (i.e., not simply based on your instincts or personal views). This will be the focus of your introduction and literature review.
- Approach - You need to make a case for your methodology, showing that you have carefully thought about the data, tools and procedures you will need to conduct the research. You need to explicitly defend all of your choices. This will be presented in the research design section.
- Feasibility - You need to demonstrate clearly that your project is both reasonable and feasible within the practical constraints of the course, timescales, institution or funding. You need to make sure you have the time and access to resources to complete the project in a reasonable period.
301 Recommends:
Our Research Writing workshop will look at some of the main writing challenges associated with writing a large-scale research project and look at strategies to manage your writing on a day-to-day basis. It will identify ways to plan, organise and map out the structure of your writing to allow you to develop an effective writing schedule and make continuous progress on your dissertation project.
Proposal format
The format of a research proposal varies between fields and levels of study but most proposals should contain at least these elements: introduction, literature review, research design and reference list.
Generally, research proposals can range from 500-1500 words or one to a few pages long. Typically, proposals for larger projects such as a PhD dissertation or funding requests, are longer and much more detailed.
Remember, the goal of your research proposal is to outline clearly and concisely exactly what your research will entail and accomplish, how it will do so and why it is important. If you are writing to a strictly enforced word count, a research proposal can be a great test of your ability to express yourself concisely!
Introduction
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project, so make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why. In other words, this is where you answer the reader’s “so what?” It should typically include: introducing the topic , outlining your problem statement and research question(s) and giving background and context. Some important questions to shape your introduction include:
- Who has an interest in the topic (e.g. scientists, practitioners, policymakers, particular members of society)?
- How much is already known about the problem and why is it important?
- What is missing from current knowledge and why?
- What new insights will your research contribute?
- Why is this research worth doing?
If your proposal is very long, you might include separate sections with more detailed information on the background and context, problem statement, aims and objectives, and importance of the research.
Literature Review
It’s important to show that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review convinces the reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory (i.e. how it relates to established research in the field).
Your literature review will also show that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said. This is also where you explain why your research is necessary. You might want to consider some of the following prompts:
- Comparing and contrasting: what are the main theories, methods, debates and controversies?
- Being critical: what are the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches?
- Showing how your research fits in: how will you build on, challenge or synthesise the work of others?
- Filling a gap in the existing body of research: why is your idea innovative?
Research design and methods
Following the literature review, it is a good idea to restate your main objectives, bringing the focus back to your own project. The research design/ methodology section should describe the overall approach and practical steps you will take to answer your research questions. You also need to demonstrate the feasibility of the project keeping in mind time and other constraints.
You should definitely include:
- Qualitative vs quantitative research? Combination?
- Will you collect original data or work with primary/secondary sources?
- Is your research design descriptive, correlational or experimental? Something completely different?
- If you are undertaking your own study, when and where will you collect the data? How will you select subjects or sources? Ethics review? Exactly what or who will you study?
- What tools and procedures will you use (e.g. systematic reviews, surveys, interviews, observation, experiments, bibliographic data) to collect your data?
- What tools/methods will you use to analyse your data?
- Why are these the best methods to answer your research question(s)? This is where you should justify your choices.
- How much time will you need to collect the data?
- How will you gain access to participants and sources?
- Do you foresee any potential obstacles and if so, how will you address them?
Make sure you are not simply compiling a list of methods. Instead, aim to make an argument for why this is the most appropriate, valid and reliable way to approach answering your question. Remember you should always be defending your choices!
Implications and Contributions to Knowledge
To ensure you finish your proposal on a strong note, it is a good idea to explore and/or emphasise the potential implications of the research. This means: what do you intend to contribute to existing knowledge on the topic?
Although you cannot know the results of your research until you have actually done the work, you should be going into the project with a clear idea of how your work will contribute to your field. This section might even be considered the most critical to your research proposal’s argument because it expresses exactly why your research is necessary.
You should consider covering at least some of the following topics:
- Ways in which your work can challenge existing theories and assumptions in your field.
- How your work will create the foundation for future research and theory.
- The practical value your findings will provide to practitioners, educators and other academics in your field.
- The problems or issues your work can potentially help to resolve.
- Policies that could be impacted by your findings.
- How your findings can be implemented in academia or other settings and how this will improve or otherwise transform these settings.
This part is not about stating the specific results that you expect to obtain but rather, this is the section where you explicitly state how your findings will be valuable.
This section is where you want to wrap it all up in a nice pretty bow. It is just like the concluding paragraph that you would structure and craft for a typical essay. You should briefly summarise your research proposal and reinforce your research purpose.
Reference List or Bibliography
Your research proposal MUST include proper citations for every source you have used and full references. Please consult your departmental referencing styles to ensure you are citing and referencing in an appropriate way.
Common mistakes to avoid
Try and avoid these common pitfalls when you are writing your research proposal:
- Being too wordy: Remember formal does not mean flowery or pretentious. In fact, you should really aim to keep your writing as concise and accessible as possible. The more economically you can express your goals and ideas, the better.
- Failing to cite relevant information/sources: You are adding to the existing body of knowledge on the subject you are covering. Therefore, your research proposal should reference the main research pieces in your field (while referencing them correctly!) and connect your proposal to these works in some way. This does not mean just communicating the relevance of your work, it should explicitly demonstrate your familiarity with the field.
- Focusing too much on minor issues: Your research is most likely important for so many great reasons. However, they do not all need to be listed in your research proposal. Generally, including too many questions and issues in your research proposal can serve as a red flag and detract from your main purpose(s). This will in turn weaken your proposal. Only involve the main/key issues you plan to address.
- Failing to make a strong argument for your research: This is the simplest way to undermine your proposal. Your proposal is a piece of persuasive and critical writing . This means that, although you are presenting your proposal in an academic and hopefully objective manner, the goal is to get the reader to say ‘yes’ to your work.
- Not polishing your writing : If your proposal has spelling or grammatical errors, an inconsistent or inappropriate tone or even just awkward phrasing it can undermine your credibility. Check out some of these resources to help guide you in the right direction: Manchester Academic Phrasebank , Proofreading Guide , Essay Checklist and Grammar Guide . Remember to double and triple check your work.
Links and Resources
You might also need to include a schedule and/or a budget depending on your requirements. Some tools to help include:
- Manchester University Academic Phrasebank
- Leeds Beckett Assignment Calculator
- Calendarpedia
Related information
Dissertation planning
Writing a literature review
Research methods

Be the first to hear about our new and upcoming workshops!
The 301 Academic Skills Centre newsletter is a fortnightly email for study skills, mathematics and statistics.
Be the first to find out about our:
- new and upcoming workshops,
- special events and programmes, and
- new and relevant online materials and resources.
How To Write A Research Proposal
A Straightforward How-To Guide (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | August 2019 (Updated April 2023)
Writing up a strong research proposal for a dissertation or thesis is much like a marriage proposal. It’s a task that calls on you to win somebody over and persuade them that what you’re planning is a great idea. An idea they’re happy to say ‘yes’ to. This means that your dissertation proposal needs to be persuasive , attractive and well-planned. In this post, I’ll show you how to write a winning dissertation proposal, from scratch.
Before you start:
– Understand exactly what a research proposal is – Ask yourself these 4 questions
The 5 essential ingredients:
- The title/topic
- The introduction chapter
- The scope/delimitations
- Preliminary literature review
- Design/ methodology
- Practical considerations and risks
What Is A Research Proposal?
The research proposal is literally that: a written document that communicates what you propose to research, in a concise format. It’s where you put all that stuff that’s spinning around in your head down on to paper, in a logical, convincing fashion.
Convincing is the keyword here, as your research proposal needs to convince the assessor that your research is clearly articulated (i.e., a clear research question) , worth doing (i.e., is unique and valuable enough to justify the effort), and doable within the restrictions you’ll face (time limits, budget, skill limits, etc.). If your proposal does not address these three criteria, your research won’t be approved, no matter how “exciting” the research idea might be.
PS – if you’re completely new to proposal writing, we’ve got a detailed walkthrough video covering two successful research proposals here .

How do I know I’m ready?
Before starting the writing process, you need to ask yourself 4 important questions . If you can’t answer them succinctly and confidently, you’re not ready – you need to go back and think more deeply about your dissertation topic .
You should be able to answer the following 4 questions before starting your dissertation or thesis research proposal:
- WHAT is my main research question? (the topic)
- WHO cares and why is this important? (the justification)
- WHAT data would I need to answer this question, and how will I analyse it? (the research design)
- HOW will I manage the completion of this research, within the given timelines? (project and risk management)
If you can’t answer these questions clearly and concisely, you’re not yet ready to write your research proposal – revisit our post on choosing a topic .
If you can, that’s great – it’s time to start writing up your dissertation proposal. Next, I’ll discuss what needs to go into your research proposal, and how to structure it all into an intuitive, convincing document with a linear narrative.
The 5 Essential Ingredients
Research proposals can vary in style between institutions and disciplines, but here I’ll share with you a handy 5-section structure you can use. These 5 sections directly address the core questions we spoke about earlier, ensuring that you present a convincing proposal. If your institution already provides a proposal template, there will likely be substantial overlap with this, so you’ll still get value from reading on.
For each section discussed below, make sure you use headers and sub-headers (ideally, numbered headers) to help the reader navigate through your document, and to support them when they need to revisit a previous section. Don’t just present an endless wall of text, paragraph after paragraph after paragraph…
Top Tip: Use MS Word Styles to format headings. This will allow you to be clear about whether a sub-heading is level 2, 3, or 4. Additionally, you can view your document in ‘outline view’ which will show you only your headings. This makes it much easier to check your structure, shift things around and make decisions about where a section needs to sit. You can also generate a 100% accurate table of contents using Word’s automatic functionality.

Ingredient #1 – Topic/Title Header
Your research proposal’s title should be your main research question in its simplest form, possibly with a sub-heading providing basic details on the specifics of the study. For example:
“Compliance with equality legislation in the charity sector: a study of the ‘reasonable adjustments’ made in three London care homes”
As you can see, this title provides a clear indication of what the research is about, in broad terms. It paints a high-level picture for the first-time reader, which gives them a taste of what to expect. Always aim for a clear, concise title . Don’t feel the need to capture every detail of your research in your title – your proposal will fill in the gaps.
Need a helping hand?
Ingredient #2 – Introduction
In this section of your research proposal, you’ll expand on what you’ve communicated in the title, by providing a few paragraphs which offer more detail about your research topic. Importantly, the focus here is the topic – what will you research and why is that worth researching? This is not the place to discuss methodology, practicalities, etc. – you’ll do that later.
You should cover the following:
- An overview of the broad area you’ll be researching – introduce the reader to key concepts and language
- An explanation of the specific (narrower) area you’ll be focusing, and why you’ll be focusing there
- Your research aims and objectives
- Your research question (s) and sub-questions (if applicable)
Importantly, you should aim to use short sentences and plain language – don’t babble on with extensive jargon, acronyms and complex language. Assume that the reader is an intelligent layman – not a subject area specialist (even if they are). Remember that the best writing is writing that can be easily understood and digested. Keep it simple.

Note that some universities may want some extra bits and pieces in your introduction section. For example, personal development objectives, a structural outline, etc. Check your brief to see if there are any other details they expect in your proposal, and make sure you find a place for these.
Ingredient #3 – Scope
Next, you’ll need to specify what the scope of your research will be – this is also known as the delimitations . In other words, you need to make it clear what you will be covering and, more importantly, what you won’t be covering in your research. Simply put, this is about ring fencing your research topic so that you have a laser-sharp focus.
All too often, students feel the need to go broad and try to address as many issues as possible, in the interest of producing comprehensive research. Whilst this is admirable, it’s a mistake. By tightly refining your scope, you’ll enable yourself to go deep with your research, which is what you need to earn good marks. If your scope is too broad, you’re likely going to land up with superficial research (which won’t earn marks), so don’t be afraid to narrow things down.
Ingredient #4 – Literature Review
In this section of your research proposal, you need to provide a (relatively) brief discussion of the existing literature. Naturally, this will not be as comprehensive as the literature review in your actual dissertation, but it will lay the foundation for that. In fact, if you put in the effort at this stage, you’ll make your life a lot easier when it’s time to write your actual literature review chapter.
There are a few things you need to achieve in this section:
- Demonstrate that you’ve done your reading and are familiar with the current state of the research in your topic area.
- Show that there’s a clear gap for your specific research – i.e., show that your topic is sufficiently unique and will add value to the existing research.
- Show how the existing research has shaped your thinking regarding research design . For example, you might use scales or questionnaires from previous studies.
When you write up your literature review, keep these three objectives front of mind, especially number two (revealing the gap in the literature), so that your literature review has a clear purpose and direction . Everything you write should be contributing towards one (or more) of these objectives in some way. If it doesn’t, you need to ask yourself whether it’s truly needed.
Top Tip: Don’t fall into the trap of just describing the main pieces of literature, for example, “A says this, B says that, C also says that…” and so on. Merely describing the literature provides no value. Instead, you need to synthesise it, and use it to address the three objectives above.

Ingredient #5 – Research Methodology
Now that you’ve clearly explained both your intended research topic (in the introduction) and the existing research it will draw on (in the literature review section), it’s time to get practical and explain exactly how you’ll be carrying out your own research. In other words, your research methodology.
In this section, you’ll need to answer two critical questions :
- How will you design your research? I.e., what research methodology will you adopt, what will your sample be, how will you collect data, etc.
- Why have you chosen this design? I.e., why does this approach suit your specific research aims, objectives and questions?
In other words, this is not just about explaining WHAT you’ll be doing, it’s also about explaining WHY. In fact, the justification is the most important part , because that justification is how you demonstrate a good understanding of research design (which is what assessors want to see).
Some essential design choices you need to cover in your research proposal include:
- Your intended research philosophy (e.g., positivism, interpretivism or pragmatism )
- What methodological approach you’ll be taking (e.g., qualitative , quantitative or mixed )
- The details of your sample (e.g., sample size, who they are, who they represent, etc.)
- What data you plan to collect (i.e. data about what, in what form?)
- How you plan to collect it (e.g., surveys , interviews , focus groups, etc.)
- How you plan to analyse it (e.g., regression analysis, thematic analysis , etc.)
- Ethical adherence (i.e., does this research satisfy all ethical requirements of your institution, or does it need further approval?)
This list is not exhaustive – these are just some core attributes of research design. Check with your institution what level of detail they expect. The “ research onion ” by Saunders et al (2009) provides a good summary of the various design choices you ultimately need to make – you can read more about that here .
Don’t forget the practicalities…
In addition to the technical aspects, you will need to address the practical side of the project. In other words, you need to explain what resources you’ll need (e.g., time, money, access to equipment or software, etc.) and how you intend to secure these resources. You need to show that your project is feasible, so any “make or break” type resources need to already be secured. The success or failure of your project cannot depend on some resource which you’re not yet sure you have access to.
Another part of the practicalities discussion is project and risk management . In other words, you need to show that you have a clear project plan to tackle your research with. Some key questions to address:
- What are the timelines for each phase of your project?
- Are the time allocations reasonable?
- What happens if something takes longer than anticipated (risk management)?
- What happens if you don’t get the response rate you expect?
A good way to demonstrate that you’ve thought this through is to include a Gantt chart and a risk register (in the appendix if word count is a problem). With these two tools, you can show that you’ve got a clear, feasible plan, and you’ve thought about and accounted for the potential risks.
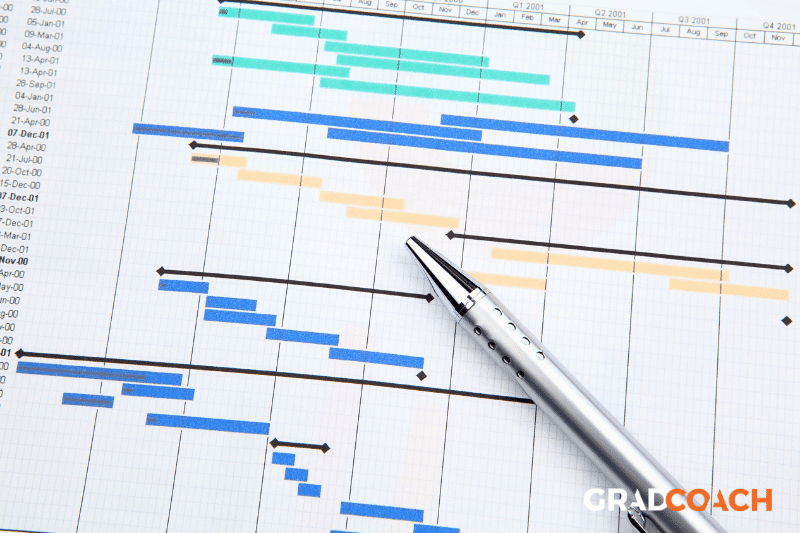
Tip – Be honest about the potential difficulties – but show that you are anticipating solutions and workarounds. This is much more impressive to an assessor than an unrealistically optimistic proposal which does not anticipate any challenges whatsoever.
Final Touches: Read And Simplify
The final step is to edit and proofread your proposal – very carefully. It sounds obvious, but all too often poor editing and proofreading ruin a good proposal. Nothing is more off-putting for an assessor than a poorly edited, typo-strewn document. It sends the message that you either do not pay attention to detail, or just don’t care. Neither of these are good messages. Put the effort into editing and proofreading your proposal (or pay someone to do it for you) – it will pay dividends.
When you’re editing, watch out for ‘academese’. Many students can speak simply, passionately and clearly about their dissertation topic – but become incomprehensible the moment they turn the laptop on. You are not required to write in any kind of special, formal, complex language when you write academic work. Sure, there may be technical terms, jargon specific to your discipline, shorthand terms and so on. But, apart from those, keep your written language very close to natural spoken language – just as you would speak in the classroom. Imagine that you are explaining your project plans to your classmates or a family member. Remember, write for the intelligent layman, not the subject matter experts. Plain-language, concise writing is what wins hearts and minds – and marks!
Let’s Recap: Research Proposal 101
And there you have it – how to write your dissertation or thesis research proposal, from the title page to the final proof. Here’s a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- The purpose of the research proposal is to convince – therefore, you need to make a clear, concise argument of why your research is both worth doing and doable.
- Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper.
- Title – provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms
- Introduction – explains what you’ll be researching in more detail
- Scope – explains the boundaries of your research
- Literature review – explains how your research fits into the existing research and why it’s unique and valuable
- Research methodology – explains and justifies how you will carry out your own research
Hopefully, this post has helped you better understand how to write up a winning research proposal. If you enjoyed it, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog . If your university doesn’t provide any template for your proposal, you might want to try out our free research proposal template .

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

30 Comments
Thank you so much for the valuable insight that you have given, especially on the research proposal. That is what I have managed to cover. I still need to go back to the other parts as I got disturbed while still listening to Derek’s audio on you-tube. I am inspired. I will definitely continue with Grad-coach guidance on You-tube.
Thanks for the kind words :). All the best with your proposal.
First of all, thanks a lot for making such a wonderful presentation. The video was really useful and gave me a very clear insight of how a research proposal has to be written. I shall try implementing these ideas in my RP.
Once again, I thank you for this content.
I found reading your outline on writing research proposal very beneficial. I wish there was a way of submitting my draft proposal to you guys for critiquing before I submit to the institution.
Hi Bonginkosi
Thank you for the kind words. Yes, we do provide a review service. The best starting point is to have a chat with one of our coaches here: https://gradcoach.com/book/new/ .
Hello team GRADCOACH, may God bless you so much. I was totally green in research. Am so happy for your free superb tutorials and resources. Once again thank you so much Derek and his team.
You’re welcome, Erick. Good luck with your research proposal 🙂
thank you for the information. its precise and on point.
Really a remarkable piece of writing and great source of guidance for the researchers. GOD BLESS YOU for your guidance. Regards
Thanks so much for your guidance. It is easy and comprehensive the way you explain the steps for a winning research proposal.
Thank you guys so much for the rich post. I enjoyed and learn from every word in it. My problem now is how to get into your platform wherein I can always seek help on things related to my research work ? Secondly, I wish to find out if there is a way I can send my tentative proposal to you guys for examination before I take to my supervisor Once again thanks very much for the insights
Thanks for your kind words, Desire.
If you are based in a country where Grad Coach’s paid services are available, you can book a consultation by clicking the “Book” button in the top right.
Best of luck with your studies.
May God bless you team for the wonderful work you are doing,
If I have a topic, Can I submit it to you so that you can draft a proposal for me?? As I am expecting to go for masters degree in the near future.
Thanks for your comment. We definitely cannot draft a proposal for you, as that would constitute academic misconduct. The proposal needs to be your own work. We can coach you through the process, but it needs to be your own work and your own writing.
Best of luck with your research!
I found a lot of many essential concepts from your material. it is real a road map to write a research proposal. so thanks a lot. If there is any update material on your hand on MBA please forward to me.
GradCoach is a professional website that presents support and helps for MBA student like me through the useful online information on the page and with my 1-on-1 online coaching with the amazing and professional PhD Kerryen.
Thank you Kerryen so much for the support and help 🙂
I really recommend dealing with such a reliable services provider like Gradcoah and a coach like Kerryen.
Hi, Am happy for your service and effort to help students and researchers, Please, i have been given an assignment on research for strategic development, the task one is to formulate a research proposal to support the strategic development of a business area, my issue here is how to go about it, especially the topic or title and introduction. Please, i would like to know if you could help me and how much is the charge.
This content is practical, valuable, and just great!
Thank you very much!
Hi Derek, Thank you for the valuable presentation. It is very helpful especially for beginners like me. I am just starting my PhD.
This is quite instructive and research proposal made simple. Can I have a research proposal template?
Great! Thanks for rescuing me, because I had no former knowledge in this topic. But with this piece of information, I am now secured. Thank you once more.
I enjoyed listening to your video on how to write a proposal. I think I will be able to write a winning proposal with your advice. I wish you were to be my supervisor.
Dear Derek Jansen,
Thank you for your great content. I couldn’t learn these topics in MBA, but now I learned from GradCoach. Really appreciate your efforts….
From Afghanistan!
I have got very essential inputs for startup of my dissertation proposal. Well organized properly communicated with video presentation. Thank you for the presentation.
Wow, this is absolutely amazing guys. Thank you so much for the fruitful presentation, you’ve made my research much easier.
this helps me a lot. thank you all so much for impacting in us. may god richly bless you all
How I wish I’d learn about Grad Coach earlier. I’ve been stumbling around writing and rewriting! Now I have concise clear directions on how to put this thing together. Thank you!
Fantastic!! Thank You for this very concise yet comprehensive guidance.
Even if I am poor in English I would like to thank you very much.
Thank you very much, this is very insightful.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Find an Opportunity
- Student Stories
- For Faculty
- Fulbright Week 2024
Research Proposal
- Research Symposium
- Humanities Research Scholars Program
- Laidlaw Scholarship
- How to Apply
- MMUF Fellows and Alumni
- Current Rabi Scholars
- Publications
- Rabi Faculty Committee
- Current Science Research Fellows
- C.P. Davis Scholars
- Egleston Scholars
- Program for Academic Leadership and Service (PALS)
- Research Ambassadors and Peer Advisors
- Help & Advice
A research proposal is generally required for any research opportunity that you wish to pursue. This document is a clear account of the research that you plan to undertake. It is your chance to explain what you want to study and its significance. It is also an occasion to show the expertise you already have in the field.
Your research proposal describes the who, what, where, when, and why of your project. It should:
- establish your research question;
- explain why the research is important to your field;
- say where you and with whom you will work;
- describe how you will answer your question; and
- discuss the wider impact of your research.
Research is almost never done in a vacuum. Plan to talk with your professors and other students about your questions and plans.
Leave enough time to write several drafts of the research proposal. Show it to your professors, other students, and URF advisers for constructive feedback. Having a range of opinions is useful since review committees for fellowships are not always made up of specialists in your field. How your work impacts the wider world is important.
Related Articles
- Applying as an International Student
- Personal Statement
- Resume or CV
- Letters of Recommendation
- Applying for a Research Opportunity

Search Utah State University:
Types of research proposals.
In all sectors (academe, government, and the private sector), research scientists typically seek and obtain competitive funding for their research projects by writing and submitting research proposals for consideration by the funding source. There are two kinds of research proposals:
Solicited proposals are those that are written and submitted in response to the issuance of a “Request for Proposals” (RFP), a document that identifies a specific research problem of interest to the funding agency for which they are specifically seeking a solution. The interested investigator then submits a “concept” or “white paper” briefly outlining their proposed solution to the problem. If the funding agency or company is interested, they may then request that the investigator submit a full proposal for consideration of funding.
- Unsolicited
Unsolicited proposals are those proposals that are submitted by an investigator in response to a “general call” for proposals that is issued by a funding agency or company in a field or area of study. The majority of funding agencies issue calls for proposals which have firmly established deadlines and for which the format of the proposals is fairly well defined. Thus, it is vitally important at the outset after you have identified a funding source that you obtain all of the relevant information on the specific grant program and its requirements. Today most funding agencies have searchable websites where they post detailed information concerning their grant programs.
- Purpose of a Research Proposal
The purpose of a proposal is to sell your idea to the funding agency. This means that the investigator must convince the funding agency that:
- The problem is significant and worthy of study
- The technical approach is novel and likely to yield results
- The investigator and his/her research team is/are the right group of individuals to carry out and accomplish the work described in the research proposal
- Typical Proposal Format
The title of your proposal should be short, accurate, and clear. A single sentence containing ten or fewer words is best. Don’t use acronyms and technical jargon as your reviewers may not come from your technical specialty. For example, “Web-GURU: Web-based Guide to Research for Undergraduates.”
As in a technical paper, the proposal abstract should “abstract” the project for the reader. It should be a brief (100 – 200 words), tightly worded summary of the project, its objectives, the problem’s significance, the project’s scope, the methods that will be employed, the identity and relevant technical expertise of the research team, and the results that are expected to result. Be sure to write this section last so that its content indeed abstracts your proposal.
Introduction
The introduction section should introduce the research problem, its significance, and the technical approach your work will take to investigate/solve the problem. It should introduce the research team that will carry out the work.
This section should present a concise review of the primary literature relevant to your proposed research efforts. As such it should:
- Cite the key literature sources
- Be up to date
- Critically appraise the literature
- Take science in a bold new direction?
- Build on the prior work of others (whose?) in the field
- Address flaws in previous work (again, whose?)
- Develop infrastructure (instrumentation, methodology, collaborations) that will take science in exciting new directions
Preliminary Studies
If the project builds on past studies from your laboratory, then you should include a brief section outlining what you have already accomplished and explain how these results relate to the work outlined in the present proposal. If the ideas you are proposing are novel, then it is especially important to include this section and to present evidence supporting the probable success of your project.
Research Methodology
This section should outline your plan of attack. Specific information that should be contained in this section includes information on the research team and its technical expertise as it relates to the project, a realistic timeline, description of the specific experiments that will be accomplished together with alternate plans in case of potential difficulties/challenges. If more than one person will do the work described in the proposal then a division of labor should be provided together with an explanation of why each person is best qualified to do the work described. The timeline should define the length of the project and provide a schedule of who will do what specific tasks approximately when during the project period. Problems always arise in research. Things never go as anticipated. So, it is important to provide the reviewer with enough information to give them confidence that when problems arise, as they inevitably will, that you will be able to handle them in such a way that meaningful science results.
The budget should identify the anticipated cost for everything (salaries, materials, instrumentation, travel costs, etc.) that will be required in order to accomplish the research project. Usually budgets are prepared and submitted as tables with prescribed format. A budget justification typically accompanies the budget request. The budget justification is simply an explanation, item-by-item, stating why you must spend the money requested in order to carry out the experiments planned.
The most important point in preparing a budget is to make sure that you ask for what you really need. Some people underestimate the importance of working through a budget in advance of writing the actual grant proposal. This is really important because most grant programs provide grants with a certain set monetary value. It is critical to ask for the amount you really need because if you don’t ask for what you need you simply won’t be able to do the work and if you can’t carry out your project, it is highly unlikely that you will ever be able to obtain funding from that funding agency again in the near future. At the same time, it is important not to go overboard in padding your budgetary request. A thoughtful budget demonstrates that your project is well conceived and likely to yield quality results. If the reviewers feel that your budget is naïve or over-inflated, that can work against you – your project could be funded at a lower rate or certain items requested might simply be eliminated from the budget by the funding agency – so be sure to think through your budget requests carefully and make sure that all requests are thoughtfully justified.
There are two major components in a budget:
Direct costs are the costs that you incur that are directly attributable to the project. Examples of direct costs include personnel salary, fringe benefits, materials and supplies, major instrumentation, and travel costs. We will briefly examine each of these:
Direct Costs
- Personnel Salary. An important budget request in most grants is the salary for the personnel who will carry out the research on the project. Salary is usually requested for the principal investigator, postdoctoral students, graduate and undergraduate students. Some funding agencies will provide secretarial support. Academic faculty, who usually receive academic year ( 9-mos typically) salary from their institutions, often supplement their salary (summer salary) by carrying out external research programs.
- Fringe benefits refers to the costs incurred by your institution/employer in providing group health insurance, retirement, unemployment, workers compensation, FICA (Medicare), etc. Undergraduate salaries are not normally assessed fringe benefits when the student is supported during the academic year.
- Materials and supplies include a wide range of items such as laboratory supplies, chemical reagents, research animals, computer software and supplies, etc.
- Major Instrumentation. A purchase is typically identified as major instrumentation rather than materials and supplies when the cost of the instrument exceeds a thousand dollars and when the device has an anticipated lifespan of more than a year. Examples of major instrumentation purchases include laptops (cost typically $2k), UV-vis instruments, desktop centrifuges, etc. When requesting major instrumentation it is important to specify the manufacturer and model of the specific instrument that you wish to purchase and to indicate what if any features this model has that make it uniquely required in order to accomplish your proposed work. If you do require a specific instrument, it is wise to obtain a quotation from the manufacturer. Since it may be six months or more before you begin your project be sure to inquire what the anticipated cost of the instrument will be at the time you anticipate purchasing it (i.e., allow for inflation).
- Travel Costs. If you intend to attend a professional meeting in order to present the results of your research, you may include the anticipated cost of traveling to and attending the meeting in your budget request. You may include the cost of a round-trip coach class fare airplane ticket, meeting registration, hotel, ground transportation (taxi, car rental, etc.), and food. Many funding sources place strict limitations on travel so be sure to research this carefully before making your request.
- Subcontractor Costs. If you are working on a collaborative project with an investigator at another institution, then you will need to include the costs that they will incur in carrying out the proposed work. Your collaborator is viewed as a subcontractor in terms of the grant proposal. Their institution may assess its own indirect costs and those will also need to be included in your budget request to the funding agency.
Indirect Costs
Indirect costs are the facilities and administrative costs that are incurred by your institution/employer in support of your research activities. These are typically assessed as a percentage of the direct costs for the project. Indirect costs are often assessed on either a modified total direct costs basis (MTDC) or a total direct costs basis (TDC). MTDC rates do not include the costs of major instrumentation, student tuition, or subcontractors in the total for the direct costs on which the indirect costs are assessed while TDC includes all costs when assessing the indirect costs for the project. The MTDC and TDC rates are set by your institution so be sure to check with them to determine what the current rates are.
Cirriculum Vitae for Principal Investigators
Most funding agencies require the principal investigator(s) to include some form of curriculum vitae. Curriculum vitae are the academic-version (extended) of a resume. They provide useful information on the education, technical expertise, and research productivity of the principal investigator. In an effort to ensure the brevity and uniformity of the information provided, many funding agencies require that this information be provided according to a specific format. Be sure to include only the information requested. Do not embellish your accomplishments.
This ancillary section should be used only to provide secondary information that is relevant to the research project. For example, if you are collaborating with another investigator, it is appropriate to obtain a letter from him/her indicating his/her willingness to collaborate and detailing what specific support (personnel, equipment, research materials, results, etc.) they are willing to provide for the research project. Some funding programs do not allow investigators to submit appendices so be sure to find out in advance whether or not you can submit supporting materials and what if any limitations there may be concerning these materials (content, page limits, etc.).

Human and Animal Subjects
If your project involves experimentation on either animals or people, you will need to obtain approval for your project through your institution’s office of Institutional Compliance.
- General Suggestions
- Don’t be afraid to ask your advisor or other scientists if you can read copies of their successfully funded proposals.
- There is no substitute for a good idea. This means the idea should be important and technically sound. If the idea is of interest to you, it is likely going to be of interest to others. Your job is to clearly make the case that this is work worth funding by the particular funding agency and program to which you have applied. In terms of the work being technically sound, make sure that you research it before you begin writing. This may mean doing some preliminary experiments in order to obtain data that clearly demonstrate that your ideas will work. This is particularly important if your ideas are truly novel.
- Before you begin writing, map out your project. Identify the key experiments you will need to do. Determine who and what you will need in order to carry out these experiments and figure out how much it will cost to do the actual work (i.e., work out the budget). Be sure that the anticipated cost of your project fits the scope of the funding agency’s program.
- Read the application instructions thoroughly and follow them carefully. If you have any questions telephone or e-mail and ask. Don’t make any implicit assumptions about your reviewers including their technical expertise, what they know about you and your work, the conditions under which they will read your proposal, etc. If you don’t follow the directions, don’t be surprised if your proposal is returned to you un-reviewed.
- Write your proposal to address all of the review criteria of the grant program.
- Start writing your proposal well in advance of the deadline for submission.
- Presentation and written expression count. Think about the reviewer’s workload (see “The Review Process”). Don’t use a lot of technical jargon. Write simply and clearly. Use the spell checker and grammar checker. Don’t fault the reviewers for equating a poorly written and poorly proofed proposal with evidence of a sloppy scientist likely incapable of carrying out a quality project if funded.
- Ask your advisor, a friend, and/or colleague to review your proposal (be sure to provide them with a copy of the funding agency’s review criteria) before submitting it and when you receive their feedback modify your proposal accordingly.
- If your proposal is not funded, seek feedback. Don’t take the rejection of your proposal personally. Learn from it! Modify your proposal accordingly, and resubmit it. Perseverance is everything when it comes to research funding – just about everyone has submitted a proposal that didn’t get funded.
Source: WebGuru
Research Proposals
- Enroll & Pay
- Getting Started in Research
- Undergraduate Research Awards
- Fall Research Showcase
- Student Workshops
UGRA Proposal Guidelines
NOTICE: The proposal format requirements have changed slightly since last semester.
Your UGRA proposal will be evaluated using one of the following rubrics provided to faculty reviewers: Research Project Rubric (.docx) or Creative Project Rubric (.docx) We recommend that you read over the appropriate rubric and use it while revising your proposal.
Your proposal should:
- be no more than 5 total pages, including your text content (~2000 words), figures, images, image captions, references, footnotes, appendices, etc.
- be single-spaced and typed using Times New Roman 12 point font for main content. Additional text can be used as needed to support figures, images, captions, footnotes, etc.
- have 1 inch margins top, bottom, right, and left.
- have a title at the top of the first page. Please do not include your name.
- include the following sections: abstract/summary, background and introduction, methods and approach, applicant's preparation, conclusion, and references. Optional content may include figures, charts, and images.
- be saved as a PDF with file name LastnameProposal.PDF. For example, SmithProposal.PDF
***Proposals not meeting the criteria outlined above may not be considered for review.
Guidelines for:
- Students working in groups: Students applying as part of a group need to each submit their own proposal. Proposals should not be written together and, therefore, should not share written content (ie, identical sentences or paragraphs). Reviewers must be able to see that each student has a full understanding of the project since each student will receive an individual scholarship.
- Students who have previously received a UGRA: If applying for a second award, students should submit a full proposal even when continuing on the same project. This proposal needs to include a brief update on their progress either in the Background and Introduction section or the Methods and Approach section. The Methods and Approach should then describe the next steps of the project. Much of your proposal may stay the same, but be sure to include any newly relevant background information if the project has shifted directions or new information was published.
Your UGRA proposal is required to include the following sections:
1. Abstract/Summary
Purpose : In one paragraph, summarize your proposal. Give the reader a general sense of the field, the problem or idea your work will address, and how you will accomplish this project.
Guiding Questions
- Why will you do this work?
- What will you do (think broadly for this section)?
- And how will you do it?
- This is your chance to make a good first impression on your readers; it should clearly convey what your project is and why it is important enough to fund.
- Connect your project to the big picture.
- This section is a summary of your entire proposal, so write it last.
- For tips on writing research proposals, see The Professor Is In blog's " Foolproof Research Grant Template ," as well as posts on how to talk about the big issue in your project and the contribution to the literature .
- Visit the KU Writing Center’s webpage .
2. Background and Introduction
Purpose: This section has two goals: 1) summarize the work that’s been done in your area and 2) explain how your work will contribute to this field of study. In many fields, this section is referred to as the literature review. It must include citations of previous research or creative work related to your topic.
- What is already known or has been done in this area?
- For creative projects: Which artists have done similar work or explored similar themes?
- How will this project add to what is already known or has been done?
- For creative projects: What is your creative vision for the project? What is the inspiration for your project?
- This section is commonly referred to as a literature review. The purpose is to position your project within the academic conversation about your topic.
- You must cite the published work that you review in this section and list it in the References section. Proposals that do not cite other works in this section and include them in the References section will not be funded.
- Focus on the key publications needed to outline the current state of the field; typical UGRA proposals include 5-10 sources.
- Be sure to synthesize your sources; this section should read more like a story than a list. Avoid direct quotes; they make it harder for you to synthesize multiple works into a story. Show how your project continues the story by explaining your contribution.
- Watch this video about the B.E.A.M. system for organizing sources for some tips.
3. Methods and Approach
Purpose: Describe what you will actually do for your project and why you will take this approach. You need to include a timeline that clearly details the work that you will complete during the semester of the award.
- What will you actually do? What data will you be using? How will you collect it? How will you analyze it? What materials or resources will you need?
- What are the major steps to complete this project?
- How will the results of these methods allow you to address your original question?
- Is the project that you’ve outlined feasible in one semester?
- Will you work with human subjects? If so, how will you meet the requirements of the KU Human Subjects Committee (HSCL)? Consult your mentor for help with this process.
- For creative projects: How will you approach and get feedback on your work?
- Why did you select the particular methods/techniques you’ve described?
- Be specific to show the reviewer that you have thought through the process and are prepared to begin your project.
- Relevant details you might mention (depending on project type) include: descriptions of methods and rationale for choosing them, any software or equipment you’ll use and why, a description of your creative process, and/or controls for proposed experiments.
- Explain the choices you have made in designing your project. Why are you choosing this method over another? Are there other studies that have used a similar approach? Show the reviewer that you understand not just what you are doing for your project, but why you are doing it.
- Use the timeline to help you and the reviewers ensure that you are proposing a feasible project for one semester. A chart or table is an easy way to provide the timeline.
- If the project is part of a larger research program or a long-term interest, make clear what part of the larger project will be completed during the one semester term of the grant.
- Cite your method's origin paper or other work using this technique to show that your approach is standard in the field.
- Use a first person narrative here, especially when you are working as part of a research group. Reviewers will have a better idea of what you are doing versus what others will do.
- Don't forget to describe your data analysis plan, especially any statistical methods you plan to use, and how this analysis will tie back to the original question you set out to address. This is a common mistake that reviewers catch.
- If you are working on a multi-semester project, be sure to provide the most details about the award period that you are applying for. The reviewer will want to see what work would be funded if you had the award.
4. Applicant's Preparation
Purpose : Describe your preparation and qualifications to complete this project.
- What experiences, coursework, or training have you done that will give you the needed background knowledge and skills to undertake the project?
- Did you complete coursework that is relevant? What specific skills or background information did you learn in these classes that prepared you for your project?
- Did you learn a language, technique, or laboratory skill that you’ll use?
- Or have you already been doing faculty mentored research or independent study on this topic?
- Do not skimp on this section; be sure to write at least one paragraph here to make the case that you can complete this project. The reviewer needs to be able to see whether you have the skills and background knowledge needed to complete the project.
- Rather than telling the reviewer that you are qualified, show them. Saying "I am prepared to do this research project" is not as convincing as saying "I used X technique in my BIOL 123 class, earned an A in my BIOL 456 course, and have already begun preparations to do Y procedure in my work in Prof. Z's lab this semester."
- Keep in mind that UGRA reviewers will not be viewing your transcripts as part of your UGRA application, so if you have taken relevant courses you should mention them, what grade you received in those classes, and how they will help you complete the proposed project.
- If you do not already have a skill that you will need to complete the project, be sure to address how you will get that knowledge or training.
5. Conclusion
Purpose: Show a clear connection between the different parts of your proposal. Summarize key points of your proposal for one final reminder of what you’re doing, how you’ll do it, and why. This is your final sales pitch to the reviewer and a good time to return to how your project relates to the big picture.
- How will the results and outcomes of your proposed work tie back to your original intent? In other words, explain how and why your proposed approach will help you achieve your goal.
- How will you disseminate your work?
- What criteria will you use to evaluate your success?
- Clearly show the reviewer the connections between your initial intent, proposed work, and anticipated outcomes. You want to convince your reviewer that the overall goals of your project are important, and that the plan you’ve outlined will move you toward those goals.
6. References
Purpose: List the materials you are citing in your proposal.
- Did you list every source you cited in the text?
- Did you include the most important and relevant sources for your project?
- Use the citation style most commonly used in your discipline for both the in-text citations and the reference list.
- Your references do not count towards your 2,000 word limit.
- You should not include any references that are not cited in the text of the proposal.
7. (Optional) Figures, Charts, and Images
Purpose: You may include any figures, charts, images, etc. that are helpful in explaining your work, either as an appendix or within the body of your work.
- Is there an idea you’re trying to communicate in words that would be easier to understand in picture form?
- Do you have portfolio pieces that will demonstrate the type of artwork or product you are proposing to create?
- Do you have a survey or interview tool you’d like to reference as an appendix?
- Do you have preliminary data showing that a new technique works?
- Keep it simple. Only include information that is needed to understand the proposal. Don’t include a figure or image just to have one.
- Any figures, charts, images, and examples of artwork need to be referred to within the text of the proposal. Without explanation, the reader does not know why you are including them.
- Label any figures, charts, and images with a descriptive title, caption, and/or legend for easy reference.
- Prepare to Apply
- Proposal Guidelines
- Courtwright Award
Student Links
- Get Started
- Fund your Research
- Share your Research
- Instructional Videos
- Volunteer Opportunities
Connect With Us
Quick links.
- Getting Started
30+ SAMPLE Undergraduate Research Proposal in PDF
Undergraduate research proposal, 30+ sample undergraduate research proposal, what is an undergraduate research proposal, parts of an undergraduate research proposal, how to write a comprehensive undergraduate research proposal, how long is an undergraduate research proposal, what is the appropriate format for an undergraduate research proposal, what do you keep in mind when writing an undergraduate research proposal.

Undergraduate Research Proposal Format

Undergraduate Research Project Proposal

Undergraduate Research by Engineering Students Proposal

Undergraduate Research Program Academic Proposal

Undergraduate Research Proposal in PDF

Undergraduate Research Proposal Form
Undergraduate Research Conference Proposal

Undergraduate Research Thesis Proposal

Undergraduate Research Fund Proposal

Undergraduate Research Grants Proposal

Undergraduate Research Proposal Cover Sheet

Undergraduate Student Research Funding Proposal

Basic Undergraduate Research Proposal
Office of Undergraduate Research Summer Proposal Evaluation Form

Faculty Submitting Undergraduate Research Proposal

Undergraduate Research Proposal Example
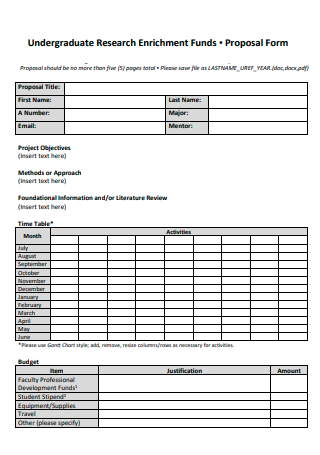
Undergraduate Research Enrichment Funds Proposal Form

Undergraduate Students Independent Study Proposal Form

Undergraduate Research Forum Proposal
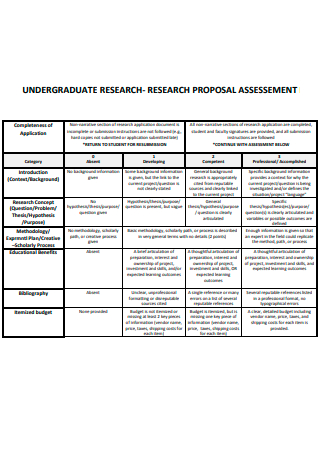
Undergraduate Research Proposal Assessment

Undergraduate Research Course Designation Work Proposal

College Undergraduate Research and Creative Project Proposal

Printable Undergraduate Research Proposal

Standard Undergraduate Research Proposal

Sample Undergraduate Research Proposal

Undergraduate Research and Creative Opportunity Proposal

Economics Undergraduate Research Assistant Program Proposal

Undergraduate Research Proposal Template

Undergraduate Student Research Committee Proposal
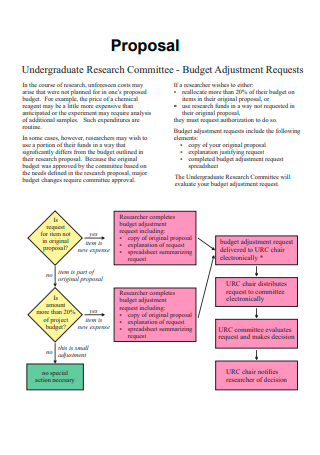
Undergraduate Research Committee Proposal

Undergraduate Student and Research Cost Program For Faculty Proposal
Step 1: determine the research topic and perform literature reviews, step 2: list the gaps in literature and frame the purpose of the study, step 3: construct the introduction, hypothesis, and research questions to guide the study, step 4: outline the investigation methods and research design, step 5: indicate the sample size, including its characteristics, step 6: outline the necessary procedures for data collection and analysis, share this post on your network, file formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 25+ sample construction company proposal in ms word.
Navigating the intricate world of construction demands a seasoned company with a proven track record. Our comprehensive guide on the Construction Company Proposal is your blueprint to understanding the…
8+ SAMPLE Drama Proposal in PDF

Julia Child said: “Drama is very important in life: You have to come on with a bang. You never want to go out with a whimper. Everything can have…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
- UC Berkeley
- Letters & Science
Undergraduate Research & Scholarships
Haas scholars program, proposal format, haas scholars program: guidelines for your project proposal.
Please review these guidelines and policies before beginning to write your Haas Scholars proposal. We recommended using this research proposal worksheet to prepare your proposal. For more suggestions on how to approach each section, visit the proposal-writing resources page on the OURS website and/or attend a “How to Write a Proposal” workshop (times/dates here ). You may also review a video recording of the Research Proposal Workshop linked here . Note: you will need to be signed into you BMail account (@berkeley.edu) in order to access the linked resources above.
Your proposal should contain the following five sections:
- Research Statement (Project Summary)
- Background and Rationale
- Research Plan (Methodologies and Timeline)
- Qualifications and Affiliations
- Bibliography
Note : You will need to number any supplementary materials (graphics, images, charts) that you refer to in your application and upload them as a single PDF.
Research Statement (Project Summary) (max. 1,000 characters, approx. 175 words)
Provide an overview of your project, addressing the following questions:
- What specific question does your research ask. and why is it important?
- How will your project potentially contribute new knowledge to the field?
A good research statement acts as an abstract of your project – it is your sales pitch. It should:
- Provide a hook or snapshot of your specific topic
- Introduce a hypothesis or intervention in the field, stating your research question
- Briefly contextualize your proposal in current conversations in the field
- Describe the potential impact or implication(s) of the project
- Make a claim about how this project is relevant
- Convince the reader that this project is exciting, innovative, and meaningful!
Background and Rationale (max. 4,000 characters, approx. 750 words)
Contextualize your research project within existing literature and make a case for why this research matters. Although you may use in-text citations to refer to sources that have informed your research, full citations of these sources should be included in the bibliography section. Be sure to address the following questions:
- What is already known about the research topic you will be working on?
- How does your project align with or depart from the existing scholarship?
- How will this research contribute to the wider field?
This section builds on the project overview you provided in the Research Statement section. In it, you will situate your research project within existing literature. This is where you will cite the sources included in the bibliography!
- Situate your research question within the broader field, summarizing the key findings of scholarship that shaped your thinking
- Indicate how your project will contribute new knowledge
- Identify questions your research will answer
Research Plan (Methodologies and Timeline) (max. 3,000 characters, approx. 500 words)
Describe your research plan. Provide an account of the methodologies that will inform your process and outline the timeline of your project. Be sure to address the following questions:
- Describe your summer research plan in chronological order, using either a week-by-week timeline or phases approach. Each week/phase should specify goals, action items, and methods.
- How are your chosen research methods appropriate for addressing these issues?
- Are there constraints or anticipated challenges associated with any particular elements of your research process?
This section details the how, when, where, and what of your project, describing how you will tackle the research objectives. It should identify the components of this research and your organizational approach. Be clear about the nature of your research (e.g., bibliographic, labwork, experiments, interviews, documentation). Describe your project as a process that can be broken down into rational, discrete phases:
- What will your first step be? What is entailed in this step? What will your questioning look like? How long will it take?
- How does step 1 prepare you for step 2? How does step 2 prepare you for step 3? etc.
- Are there benchmarks that will define your process?
Qualifications and Affiliations (max. 1,200 characters, approx. 200 words)
Describe your qualifications to conduct this research. Reference not only any relevant coursework and germane research experience but also personal experiences that make the project meaningful to you. If your research requires an external affiliation or permission to access particular resources, provide evidence that you have secured these. Be sure to address the following:
- What academic and personal experiences have prepared you to carry out this research project?
- Does your project depend on access to people and/or institutions or particular resources (i.e., interviewing subjects, partnering with institutions, traveling to archives or museums)? If so, please describe the affiliations, permissions, and agreements you have established.
In this section, you are convincing the committee that you are prepared to undertake this research. You are providing a personal statement about why this research matters to you. Here’s what to include:
- A narrative account of what you learned
- Previous research experience
- Planned training in the coming semester or early summer
- Any external affiliations secured (archives, labs, community groups)
- Relevant leadership or extracurricular activities
- Demonstration of passion for the proposed project
Bibliography (max. 4,000 characters)
Provide a short bibliography that has informed your thinking. Include full citations of any sources you mentioned elsewhere in this proposal.
- Ten most important sources
- e.g., Chicago, MLA, APA, etc.
Previously Successful Research Proposals
To view examples of research proposals, you can visit the SURF L&S Resources page linked here .
Note: The proposals will be listed by Major(s), Fellow, and Title of Project. To access the files linked, you must be logged into a valid UC Berkeley email address.
Department of Biological Sciences

Examples of Undergraduate Research Projects
Fall 2021 projects, previous projects.
- Enroll & Pay
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Degree Programs
Undergraduate Research Furthers Students’ Goals
The opportunity for KUEC undergraduates to conduct and publish their research escalates their skills and their career opportunities.

Randy Logan, director of the biotechnology program at the KU Edwards Campus, and Jack Treml, assistant director, designed the program to provide a hands-on education. The students still take some traditional lecture courses, but their time is primarily focused on developing and implementing a capstone research project.
“Capstones are year-long research projects where students really learn to do science,” Treml says. “Obviously, faculty are available to them, but for the most part they're working alone, and it is primarily their responsibility to figure things out.”
Students fine-tune their primary research questions and design a research project with coaching from Logan and Treml during the fall semester of their senior year. Once their topics are in place, they present their project proposals during the ‘Biotech Day’ event to approximately 300 attending high school and collegiate underclassmen from the Kansas City metropolitan region.
In the spring, they complete the research and are required to submit a paper to the KU-based research journal, Midwestern Journal of Undergraduate Sciences, a new research journal Treml launched to publish undergraduate research . Students then present their results at the end of the semester, which hosts professionals in the field who are eager to recruit new talent.
“They are not guaranteed publication in the journal,” Treml says. “It’s open to undergraduate students and their mentors around the world and we only publish the best.”
The most recent edition includes research from recent graduates Cinthia Moncada, Ambreen Niaman, Guenaele Raphael, and Kaityn Sy. Sy’s research paper is titled “ Partners in Crime: Synergistic Anti-apoptotic Effects of HCMV Gene Products in Infected Cells .” Sy was in the Honors Program at the University of Kansas Edwards Campus. She is starting medical school in the fall.
The opportunity to do undergraduate research is furthering Sy’s knowledge and her career. She says the research skills she learned at KU, her summer internships, and the mentorship she’s received, have provided valuable opportunities.
“The research skills I gained from the KU Honors Program and summer research internship equipped me to tackle a real-world research question,” Sy says. “Ultimately, our research led us to some intriguing findings. We will be presenting our work at two conferences this month and are drafting a manuscript for publication.”
Treml says that providing the opportunity for students to gain research experience is satisfying.
“We make a point to accept or reject articles at the journal before the end of the academic year, so that the students who will be published can take it to a job interview. We’re doing this so that our students gain experience and have published work of which they are really proud.”
The current edition of the Midwestern Journal of Undergraduate Sciences is online now .
This blog was authored by Patricia O’Dell.

Get Insights from KU Graduates
Download this report filled with statistical and qualitative feedback from more than 500 alumni to help you decide if the KU Edwards Campus is right for you.
Download report

Get started at the KU Edwards Campus
Download your guide for a successful start on your KU Edwards Campus undergraduate or graduate program, including information on financial aid, academic advising and more.

Maximize Your Financial Aid
Download your guide for making the most of financial aid at KU Edwards Campus.

An Adult Learner’s Guide to Choosing the Right KC University
Helpful tips to choosing the right university in Kansas City.

Putting off your academic pursuits?
Download our eBook that addresses and debunks 7 of the biggest concerns adult learners have about returning to school.
Download ebook

Find the right online program for you
Download your guide for tips and questions to ask when researching online learning options.
Getting Over Going Back
Fill out the form to download an ebook detailing the 7 of the biggest concerns adult learners have about returning to school.
9 Undergraduate Research Projects That Wowed Us This Year
The telegraph. The polio vaccine. The bar code. Light beer. Throughout its history, NYU has been known for innovation, with faculty and alumni in every generation contributing to some of the most notable inventions and scientific breakthroughs of their time. But you don’t wind up in the history books—or peer-reviewed journals—by accident; academic research, like any specialized discipline, takes hard work and lots of practice.
And at NYU, for students who are interested, that training can start early—including during an undergraduate's first years on campus. Whether through assistantships in faculty labs, summer internships, senior capstones, or independent projects inspired by coursework, undergrad students have many opportunities to take what they’re learning in the classroom and apply it to create original scholarship throughout their time at NYU. Many present their work at research conferences, and some even co-author work with faculty and graduate students that leads to publication.
As 2023-2024 drew to a close, the NYU News team coordinated with the Office of the Provost to pull together a snapshot of the research efforts that students undertook during this school year. The nine featured here represent just a small fraction of the impressive work we encountered in fields ranging from biology, chemistry, and engineering to the social sciences, humanities, and the arts.
These projects were presented at NYU research conferences for undergrads, including Migration and Im/Mobility , Pathways for Discovery: Undergraduate Research and Writing Symposium , Social Impact: NYU’s Applied Undergraduate Research Conference , Arts-Based Undergraduate Research Conference , Gallatin Student Research Conference , Dreammaker’s Summit , Tandon’s Research Excellence Exhibit , and Global Engagement Symposium . Learn more about these undergrad research opportunities and others.
Jordan Janowski (CAS '24)
Sade Chaffatt (NYU Abu Dhabi '24)
Elsa Nyongesa (GPH, CAS ’24 )
Anthony Offiah (Gallatin ’26)
Kimberly Sinchi (Tandon ’24) and Sarah Moughal (Tandon ’25)
Rohan Bajaj (Stern '24)
Lizette Saucedo (Liberal Studies ’24)
Eva Fuentes (CAS '24)
Andrea Durham (Tandon ’26)
Jordan Janowski (CAS ’24) Major: Biochemistry Thesis title: “Engineering Chirality for Functionality in Crystalline DNA”
Jordan Janowski (CAS '24). Photo by Tracey Friedman
I work in the Structural DNA Nanotechnology Lab, which was founded by the late NYU professor Ned Seeman, who is known as the father of the field. My current projects are manipulating DNA sequences to self-assemble into high order structures.
Essentially, we’re using DNA as a building material, instead of just analyzing it for its biological functions. It constantly amazes me that this is possible.
I came in as a pre-med student, but when I started working in the lab I realized that I was really interested in continuing my research there. I co-wrote a paper with postdoc Dr. Simon Vecchioni who has been a mentor to me and helped me navigate applying to grad school. I’m headed to Scripps Research in the fall. This research experience has led me to explore some of the molecules that make up life and how they could be engineered into truly unnatural curiosities and technologies.
My PI, Prof. Yoel Ohayon , has been super supportive of my place on the NYU women’s basketball team, which I’m a member of. He’s been coming to my games since sophomore year, and he’ll text me with the score and “great game!”— it’s been so nice to have that support for my interests beyond the lab.
Anthony Offiah (Gallatin ’26) Concentration: Fashion design and business administration MLK Scholars research project title: “project: DREAMER”
Anthony Offiah (Gallatin '26). Photo by Tracey Friedman
In “project: DREAMER,” I explored how much a person’s sense of fashion is a result of their environment or societal pressures based on their identity. Certain groups are pressured or engineered to present a certain way, and I wanted to see how much of the opposing force—their character, their personality—affected their sense of style.
This was a summer research project through the MLK Scholars Program . I did ethnographic interviews with a few people, and asked them to co-design their ideal garments with me. They told me who they are, how they identify, and what they like in fashion, and we synthesized that into their dream garments. And then we had a photo shoot where they were empowered to make artistic choices.
Some people told me they had a hard time conveying their sense of style because they were apprehensive about being the center of attention or of being dissimilar to the people around them. So they chose to conform to protect themselves. And then others spoke about wanting to safeguard the artistic or vulnerable—or one person used the word “feminine”—side of them so they consciously didn’t dress how they ideally would.
We ended the interviews by stating an objective about how this co-designing process didn’t end with them just getting new clothes—it was about approaching fashion differently than how they started and unlearning how society might put them in a certain box without their approval.
My concentration in Gallatin is fashion design and business administration. In the industry some clothing is critiqued and some clothing is praised—and navigating that is challenging, because what you like might not be well received. So doing bespoke fashion for just one person is freeing in a sense because you don’t have to worry about all that extra stuff. It’s just the art. And I like being an artist first and thinking about the business second.
Lizette Saucedo (Global Liberal Studies ’24) Major: Politics, rights, and development Thesis title: “Acknowledging and Remembering Deceased Migrants Crossing the U.S.-Mexican Border”
Lizette Saucedo (Global Liberal Studies '24). Photo by Tracey Friedman
My thesis project is on commemorating migrants who are dying on their journey north to cross the U.S.–Mexican border. I look at it through different theoretical lenses, and one of the terms is necropolitics—how politics shapes the way the State governs life and especially death. And then of the main issues aside from the deaths is that a lot of people in the U.S. don’t know about them, due to the government trying to eschew responsibility for migrant suffering. In the final portion of the thesis, I argue for presenting what some researchers call “migrant artifacts”—the personal belongings left behind by people trying to cross over—to the public, so that people can become aware and have more of a human understanding of what’s going on.
This is my senior thesis for Liberal Studies, but the idea for it started in an International Human Rights course I took with professor Joyce Apsel . We read a book by Jason De León called The Land of the Open Graves , which I kept in the back of my mind. And then when I studied abroad in Germany during my junior year, I noticed all the different memorials and museums, and wondered why we didn’t have the equivalent in the U.S. My family comes from Mexico—my parents migrated—and ultimately all of these interests came together.
I came into NYU through the Liberal Studies program and I loved it. It’s transdisciplinary, which shaped how I view my studies. My major is politics, rights, and development and my minor is social work, but I’ve also studied museum studies, and I’ve always loved the arts. The experience of getting to work one-on-one on this thesis has really fortified my belief that I can combine all those things.
Sade Chaffatt (Abu Dhabi ’24) Major: Biology Thesis title: “The Polycomb repressive component, EED in mouse hepatocytes regulates liver homeostasis and survival following partial hepatectomy.”
Sade Chaffatt (NYU Abu Dhabi '24). Photo courtesy of NYUAD
Imagine your liver as a room. Within the liver there are epigenetic mechanisms that control gene expression. Imagine these epigenetic mechanisms as a dimmer switch, so that you could adjust the light in the room. If we remove a protein that is involved in regulating these mechanisms, there might be dysregulation—as though the light is too bright or too dim. One such protein, EED, plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression. And so my project focuses on investigating whether EED is required in mouse hepatocytes to regulate liver homeostasis and to regulate survival following surgical resection.
Stepping into the field of research is very intimidating when you’re an undergraduate student and know nothing. But my capstone mentor, Dr. Kirsten Sadler , encourages students to present their data at lab meetings and to speak with scientists. Even though this is nerve-wracking, it helps to promote your confidence in communicating science to others in the field.
If you’d asked 16-year-old me, I never would’ve imagined that I’d be doing research at this point. Representation matters a lot, and you often don't see women—especially not Black women—in research. Being at NYUAD has really allowed me to see more women in these spaces. Having had some experience in the medical field through internships, I can now say I’m more interested in research and hope to pursue a PhD in the future.
Kimberly Sinchi (Tandon ’24) Major: Computer Science Sarah Moughal (Tandon ’25) Major: Computer Science Project: Robotic Design Team's TITAN
Sarah Moughal (Tandon '25, left) and Kimberly Sinchi (Tandon '24). Photo by Tracey Friedman
Kimberly: The Robotic Design Team has been active at NYU for at least five years. We’re 60-plus undergrad and grad students majoring in electrical engineering, mechanical engineering, computer science, and integrated design. We’ve named our current project TITAN because of how huge it is. TITAN stands for “Tandon’s innovation in terraforming and autonomous navigation.”
Sarah: We compete in NASA’s lunatics competition every year, which means we build a robot from scratch to be able to compete in lunar excavation and construction. We make pretty much everything in house in the Tandon MakerSpace, and everyone gets a little experience with machining, even if you're not mechanical. A lot of it is about learning how to work with other people—communicating across majors and disciplines and learning how to explain our needs to someone who may not be as well versed in particular technologies as we are.
Kimberly: With NYU’s Vertically Integrated Project I’ve been able to take what I was interested in and actually have a real world impact with it. NASA takes notes on every Rover that enters this competition. What worked and what didn’t actually influences their designs for rovers they send to the moon and to Mars.
Eva Fuentes (CAS ’24) Major: Anthropology Thesis title: “Examining the relationship between pelvic shape and numbers of lumbar vertebrae in primates”
Eva Fuentes (CAS '24). Photo by Tracey Friedman
I came into NYU thinking I wanted to be an art history major with maybe an archeology minor. To do the archeology minor, you have to take the core classes in anthropology, and so I had to take an intro to human evolution course. I was like, this is the coolest thing I’ve learned—ever. So I emailed people in the department to see if I could get involved.
Since my sophomore year, I’ve been working in the Evolutionary Morphology Lab with Scott Williams, who is primarily interested in the vertebral column of primates in the fossil record because of how it can inform the evolution of posture and locomotion in humans.
For my senior thesis, I’m looking at the number of lumbar vertebrae—the vertebrae that are in the lower back specifically—and aspects of pelvic shape to see if it is possible to make inferences about the number of lumbar vertebrae a fossil may have had. The bones of the lower back are important because they tell us about posture and locomotion.
I committed to a PhD program at Washington University in St. Louis a few weeks ago to study biological anthropology. I never anticipated being super immersed in the academic world. I don’t come from an academic family. I had no idea what I was doing when I started, but Scott Williams, and everyone in the lab, is extremely welcoming and easy to talk to. It wasn't intimidating to come into this lab at all.
Elsa Nyongesa (GPH, CAS ’24 ) Major: Global Public Health and Biology Project: “Diversity in Breast Oncological Studies: Impacts on Black Women’s Health Outcomes”
Elsa Nyongesa (GPH, CAS '24). Photo by Tracey Friedman
I interned at Weill Cornell Medicine through their Travelers Summer Research Fellowship Program where I worked with my mentor, Dr. Lisa Newman, who is the head of the International Center for the Study of Breast Cancer Subtypes. I analyzed data on the frequency of different types of breast cancer across racial and ethnic groups in New York. At the same time, I was also working with Dr. Rachel Kowolsky to study minority underrepresentation in clinical research.
In an experiential learning course taught by Professor Joyce Moon Howard in the GPH department, I created a research question based on my internship experience. I thought about how I could combine my experiences from the program which led to my exploration of the correlation between minority underrepresentation in breast oncological studies, and how it affects the health outcomes of Black women with breast cancer.
In my major, we learn about the large scope of health disparities across different groups. This opportunity allowed me to learn more about these disparities in the context of breast cancer research. As a premedical student, this experience broadened my perspective on health. I learned more about the social, economic, and environmental factors influencing health outcomes. It also encouraged me to examine literature more critically to find gaps in knowledge and to think about potential solutions to health problems. Overall, this experience deepened my philosophy of service, emphasizing the importance of health equity and advocacy at the research and clinical level.
Rohan Bajaj (Stern ’24) Major: Finance and statistics Thesis title: “Measuring Socioeconomic Changes and Investor Attitude in Chicago’s Post-Covid Economic Recovery”
Rohan Bajaj (Stern '24). Photo by Tracey Friedman
My thesis is focused on understanding the effects of community-proposed infrastructure on both the socioeconomic demographics of cities and on fiscal health. I’m originally from Chicago, so it made a lot of sense to pay tribute back to the place that raised me. I’m compiling a list of characteristics of infrastructure that has been developed since 2021 as a part of the Chicago Recovery Plan and then assessing how neighborhoods have changed geographically and economically.
I’m looking at municipal bond yields in Chicago as a way of evaluating the fiscal health of the city. Turns out a lot of community-proposed infrastructure is focused in lower income areas within Chicago rather than higher income areas. So that makes the research question interesting, to see if there’s a correlation between the proposed and developed infrastructure projects, and if these neighborhoods are being gentrified alongside development.
I kind of stumbled into the impact investing industry accidentally from an internship I had during my time at NYU. I started working at a renewable energies brokerage in midtown, where my main job was collecting a lot of market research trends and delivering insights on how these different energy markets would come into play. I then worked with the New York State Insurance Fund, where I helped construct and execute their sustainable investment strategy from the ground up.
I also took a class called “Design with Climate Change” with Peter Anker in Gallatin during my junior year, and a lot of that class was focused on how to have climate resilient and publicly developed infrastructure, and understanding the effects it has on society. It made me start thinking about the vital role that physical surroundings play in steering communities.
In the short term I want to continue diving into impact-focused investing and help identify urban planners and city government to develop their communities responsibly and effectively.
Andrea Durham (Tandon, ’26) Major: Biomolecular science Research essay title: “The Rise and Fall of Aduhelm”
Andrea Durham (Tandon '26). Photo by Tracey Friedman
This is an essay I wrote last year in an advanced college essay writing class with Professor Lorraine Doran on the approval of a drug for Alzheimer’s disease called Aduhelm—a monoclonal antibody therapy developed by Biogen in 2021, which was described as being momentous and groundbreaking. But there were irregularities ranging from the design of its clinical trials to government involvement that led to the resignation of three scientists on an advisory panel, because not everybody in the scientific community agreed that it should be approved.
When I was six years old, my grandmother was diagnosed. Seeing the impact that it had over the years broke my heart and ignited a passion in me to pursue research.
When I started at NYU, I wasn’t really sure what I was going to do in the future, or what opportunities I would go after. This writing class really gave me an opportunity to reflect on the things that were important to me in my life. The September after I wrote this paper, I started volunteering in a lab at Mount Sinai for Alzheimer's disease research, and that’s what I’m doing now—working as a volunteer at the Center for Molecular Integrative Neuroresilience under Dr. Giulio Pasinetti. I have this opportunity to be at the forefront, and because of the work I did in my writing class I feel prepared going into these settings with an understanding of the importance of conducting ethical research and working with integrity.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Sample Project Proposals. Check out a few sample grant proposals below. Read ones annotated with reviewer notes (even if the topic is outside your area of interest) to learn what reviewers look for. You can also see also how resubmitted proposals respond to reviewer comments. Please note that these proposals serve as exemplars for students ...
A research proposal at the undergraduate level is an engaging exercise on coming up with your own questions on your chosen field. There is much leeway as an undergraduate to experiment within your field and think out of the box. In many ways, you will learn how to learn and how to formulate questions for any task you encounter in the future.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of ...
VPUE Project Proposal Writing Guide. (link is external) : Read this document carefully and follow the guidelines based on the project you envision to pursue. In this guide, you will find: General guidelines for all grant proposals. Additional specific guidelines for Research, Arts/Design, and Senior Synthesis project proposals -- please follow ...
The basic purposes of all research proposals are to. convince. the reader that: (a) the research project has clear objectives; (b) the research project is worth doing (it is significant. / important in some sense and will make an original. contribution to knowledge / understanding in the. field)
Do not submit a first draft: These sample proposals went through multiple rounds of revisions with feedback from both Office of Undergraduate Research advisors and the student's faculty mentor.First, it helps to learn about grant structure and proposal writing techniques before you get started. Then, when you begin drafting, it's normal to make lots of changes as the grant evolves.
Our core proposal writing advice is connected to the Undergraduate Research Grant programs, where students apply to do independent research and/or creative projects in the summer or academic year. What follows is a brief rundown of a basic research grant proposal, and we encourage you to use our URG Proposal Writing Guide for a fuller ...
Proposal writing tips. Manage your time - Know the deadlines and plan ahead to obtain requirements like transcripts and recommendations. Follow directions carefully - Applications that are missing elements or submitted incorrectly are usually removed from consideration. Double check the requirements before submitting.
Writing Research Proposals. The research proposal is your opportunity to show that you—and only you!—are the perfect person to take on your specific project. After reading your research proposal, readers should be confident that…. You have thoughtfully crafted and designed this project; You have the necessary background to complete this ...
We will look at some proposals from prior years that got funded, and some that didn't. Session 2: Revising your proposal to make it successful. Wed, Feb 24th, 3:30-5:30 pm, Perkins 218. or. Thurs, Feb 25th, 12:30-2:30 pm, Breedlove Meeting Rm (2nd Fl, Rubenstein Library) If you want a good shot at getting your research funded, you'll need to ...
The format of a research proposal varies between fields and levels of study but most proposals should contain at least these elements: introduction, literature review, research design and reference list. Generally, research proposals can range from 500-1500 words or one to a few pages long. Typically, proposals for larger projects such as a PhD ...
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
1 of 5. Research Proposals. Writing a research proposal is the first step for a research project. Before you can work on your research, it must be approved, whether that is by a professor, thesis advisor, or supervisor. It is essential to make your proposal as strong as possible; if your proposal is denied, you may not get the funding you need ...
A Sample Research Proposal with Comments A research project or thesis will take at least two semesters to complete. Prior to starting a research, i.e. enrolling in the first semester research course, students must go through the proposal stage, during which students will develop their proposal and have it reviewed by his/her research advisor. ...
Your research proposal describes the who, what, where, when, and why of your project. It should: discuss the wider impact of your research. Research is almost never done in a vacuum. Plan to talk with your professors and other students about your questions and plans. Leave enough time to write several drafts of the research proposal.
The Office of Research at Utah State University provides a summary of the types of research proposals for undergraduate students as they seek funding for their research. ... This ancillary section should be used only to provide secondary information that is relevant to the research project. For example, if you are collaborating with another ...
Your UGRA proposal will be evaluated using one of the following rubrics provided to faculty reviewers: Research Project Rubric (.docx) or Creative Project Rubric (.docx) We recommend that you read over the appropriate rubric and use it while revising your proposal. Your proposal should: be single-spaced and typed using Times New Roman 12 point ...
The grants awarded by the Office of Undergraduate Research (OUR) are intended to promote research and scholarly activities for the undergraduate students of the University of Toledo. This document provides the template and instructions for submitting a proposal to any of the OUR grant opportunities. Content Guidelines - see Template for more ...
Step 1: Determine the Research Topic and Perform Literature Reviews. Identify the general topic of your research to investigate. The research proposal centers around the student or students' chosen research topic that the rest of the content follows. The research topics are either assigned by professors or advisers.
For an undergraduate student, the size of the research proposal varies with the requirements of universities. As a thumb-rule, an undergraduate research proposal should be 4-6 pages long with double-spaced line spacing. The specified page limit does not include the list of references, figures, tables, or any other add-ons.
The University Digital Conservancy holds 79,180 open access articles, university documents, dissertations, UROP projects, student & faculty research, data sets, & more. Digital Conservancy. Lists of Previous Projects by College Twin Cities Campus College of Biological Sciences past projects Carlson School of Management past projects.
Your proposal should contain the following five sections: Research Statement (Project Summary) Background and Rationale. Research Plan (Methodologies and Timeline) Qualifications and Affiliations. Bibliography. Budget. Note: You will need to number any supplementary materials (graphics, images, charts) that you refer to in your application and ...
Examples of Undergraduate Research Projects Fall 2021 Projects. Student Research Proposal; Whitney Brown: Characterizing the role of FOXP3 in ccRCC: Ziche Chen: Intereations between LANA and Super-enhancers: Anna Eberwein: Synaptic Dysfunction in the Drosophila Niemann Pick Type C Disease Model:
Students fine-tune their primary research questions and design a research project with coaching from Logan and Treml during the fall semester of their senior year. Once their topics are in place, they present their project proposals during the 'Biotech Day' event to approximately 300 attending high school and collegiate underclassmen from ...
Many present their work at research conferences, and some even co-author work with faculty and graduate students that leads to publication. As 2023-2024 drew to a close, the NYU News team coordinated with the Office of the Provost to pull together a snapshot of the research efforts that students undertook during this school year.