Qualitative Research: Characteristics, Design, Methods & Examples
Lauren McCall
MSc Health Psychology Graduate
MSc, Health Psychology, University of Nottingham
Lauren obtained an MSc in Health Psychology from The University of Nottingham with a distinction classification.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on gathering and analyzing non-numerical data to gain a deeper understanding of human behavior, experiences, and perspectives.
It aims to explore the “why” and “how” of a phenomenon rather than the “what,” “where,” and “when” typically addressed by quantitative research.
Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on gathering and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis, qualitative research involves researchers interpreting data to identify themes, patterns, and meanings.

Qualitative research can be used to:
- Gain deep contextual understandings of the subjective social reality of individuals
- To answer questions about experience and meaning from the participant’s perspective
- To design hypotheses, theory must be researched using qualitative methods to determine what is important before research can begin.
Examples of qualitative research questions include:
- How does stress influence young adults’ behavior?
- What factors influence students’ school attendance rates in developed countries?
- How do adults interpret binge drinking in the UK?
- What are the psychological impacts of cervical cancer screening in women?
- How can mental health lessons be integrated into the school curriculum?
Characteristics
Naturalistic setting.
Individuals are studied in their natural setting to gain a deeper understanding of how people experience the world. This enables the researcher to understand a phenomenon close to how participants experience it.
Naturalistic settings provide valuable contextual information to help researchers better understand and interpret the data they collect.
The environment, social interactions, and cultural factors can all influence behavior and experiences, and these elements are more easily observed in real-world settings.
Reality is socially constructed
Qualitative research aims to understand how participants make meaning of their experiences – individually or in social contexts. It assumes there is no objective reality and that the social world is interpreted (Yilmaz, 2013).
The primacy of subject matter
The primary aim of qualitative research is to understand the perspectives, experiences, and beliefs of individuals who have experienced the phenomenon selected for research rather than the average experiences of groups of people (Minichiello, 1990).
An in-depth understanding is attained since qualitative techniques allow participants to freely disclose their experiences, thoughts, and feelings without constraint (Tenny et al., 2022).
Variables are complex, interwoven, and difficult to measure
Factors such as experiences, behaviors, and attitudes are complex and interwoven, so they cannot be reduced to isolated variables , making them difficult to measure quantitatively.
However, a qualitative approach enables participants to describe what, why, or how they were thinking/ feeling during a phenomenon being studied (Yilmaz, 2013).
Emic (insider’s point of view)
The phenomenon being studied is centered on the participants’ point of view (Minichiello, 1990).
Emic is used to describe how participants interact, communicate, and behave in the research setting (Scarduzio, 2017).
Interpretive analysis
In qualitative research, interpretive analysis is crucial in making sense of the collected data.
This process involves examining the raw data, such as interview transcripts, field notes, or documents, and identifying the underlying themes, patterns, and meanings that emerge from the participants’ experiences and perspectives.
Collecting Qualitative Data
There are four main research design methods used to collect qualitative data: observations, interviews, focus groups, and ethnography.
Observations
This method involves watching and recording phenomena as they occur in nature. Observation can be divided into two types: participant and non-participant observation.
In participant observation, the researcher actively participates in the situation/events being observed.
In non-participant observation, the researcher is not an active part of the observation and tries not to influence the behaviors they are observing (Busetto et al., 2020).
Observations can be covert (participants are unaware that a researcher is observing them) or overt (participants are aware of the researcher’s presence and know they are being observed).
However, awareness of an observer’s presence may influence participants’ behavior.
Interviews give researchers a window into the world of a participant by seeking their account of an event, situation, or phenomenon. They are usually conducted on a one-to-one basis and can be distinguished according to the level at which they are structured (Punch, 2013).
Structured interviews involve predetermined questions and sequences to ensure replicability and comparability. However, they are unable to explore emerging issues.
Informal interviews consist of spontaneous, casual conversations which are closer to the truth of a phenomenon. However, information is gathered using quick notes made by the researcher and is therefore subject to recall bias.
Semi-structured interviews have a flexible structure, phrasing, and placement so emerging issues can be explored (Denny & Weckesser, 2022).
The use of probing questions and clarification can lead to a detailed understanding, but semi-structured interviews can be time-consuming and subject to interviewer bias.
Focus groups
Similar to interviews, focus groups elicit a rich and detailed account of an experience. However, focus groups are more dynamic since participants with shared characteristics construct this account together (Denny & Weckesser, 2022).
A shared narrative is built between participants to capture a group experience shaped by a shared context.
The researcher takes on the role of a moderator, who will establish ground rules and guide the discussion by following a topic guide to focus the group discussions.
Typically, focus groups have 4-10 participants as a discussion can be difficult to facilitate with more than this, and this number allows everyone the time to speak.
Ethnography
Ethnography is a methodology used to study a group of people’s behaviors and social interactions in their environment (Reeves et al., 2008).
Data are collected using methods such as observations, field notes, or structured/ unstructured interviews.
The aim of ethnography is to provide detailed, holistic insights into people’s behavior and perspectives within their natural setting. In order to achieve this, researchers immerse themselves in a community or organization.
Due to the flexibility and real-world focus of ethnography, researchers are able to gather an in-depth, nuanced understanding of people’s experiences, knowledge and perspectives that are influenced by culture and society.
In order to develop a representative picture of a particular culture/ context, researchers must conduct extensive field work.
This can be time-consuming as researchers may need to immerse themselves into a community/ culture for a few days, or possibly a few years.
Qualitative Data Analysis Methods
Different methods can be used for analyzing qualitative data. The researcher chooses based on the objectives of their study.
The researcher plays a key role in the interpretation of data, making decisions about the coding, theming, decontextualizing, and recontextualizing of data (Starks & Trinidad, 2007).
Grounded theory
Grounded theory is a qualitative method specifically designed to inductively generate theory from data. It was developed by Glaser and Strauss in 1967 (Glaser & Strauss, 2017).
This methodology aims to develop theories (rather than test hypotheses) that explain a social process, action, or interaction (Petty et al., 2012). To inform the developing theory, data collection and analysis run simultaneously.
There are three key types of coding used in grounded theory: initial (open), intermediate (axial), and advanced (selective) coding.
Throughout the analysis, memos should be created to document methodological and theoretical ideas about the data. Data should be collected and analyzed until data saturation is reached and a theory is developed.
Content analysis
Content analysis was first used in the early twentieth century to analyze textual materials such as newspapers and political speeches.
Content analysis is a research method used to identify and analyze the presence and patterns of themes, concepts, or words in data (Vaismoradi et al., 2013).
This research method can be used to analyze data in different formats, which can be written, oral, or visual.
The goal of content analysis is to develop themes that capture the underlying meanings of data (Schreier, 2012).
Qualitative content analysis can be used to validate existing theories, support the development of new models and theories, and provide in-depth descriptions of particular settings or experiences.
The following six steps provide a guideline for how to conduct qualitative content analysis.
- Define a Research Question : To start content analysis, a clear research question should be developed.
- Identify and Collect Data : Establish the inclusion criteria for your data. Find the relevant sources to analyze.
- Define the Unit or Theme of Analysis : Categorize the content into themes. Themes can be a word, phrase, or sentence.
- Develop Rules for Coding your Data : Define a set of coding rules to ensure that all data are coded consistently.
- Code the Data : Follow the coding rules to categorize data into themes.
- Analyze the Results and Draw Conclusions : Examine the data to identify patterns and draw conclusions in relation to your research question.
Discourse analysis
Discourse analysis is a research method used to study written/ spoken language in relation to its social context (Wood & Kroger, 2000).
In discourse analysis, the researcher interprets details of language materials and the context in which it is situated.
Discourse analysis aims to understand the functions of language (how language is used in real life) and how meaning is conveyed by language in different contexts. Researchers use discourse analysis to investigate social groups and how language is used to achieve specific communication goals.
Different methods of discourse analysis can be used depending on the aims and objectives of a study. However, the following steps provide a guideline on how to conduct discourse analysis.
- Define the Research Question : Develop a relevant research question to frame the analysis.
- Gather Data and Establish the Context : Collect research materials (e.g., interview transcripts, documents). Gather factual details and review the literature to construct a theory about the social and historical context of your study.
- Analyze the Content : Closely examine various components of the text, such as the vocabulary, sentences, paragraphs, and structure of the text. Identify patterns relevant to the research question to create codes, then group these into themes.
- Review the Results : Reflect on the findings to examine the function of the language, and the meaning and context of the discourse.
Thematic analysis
Thematic analysis is a method used to identify, interpret, and report patterns in data, such as commonalities or contrasts.
Although the origin of thematic analysis can be traced back to the early twentieth century, understanding and clarity of thematic analysis is attributed to Braun and Clarke (2006).
Thematic analysis aims to develop themes (patterns of meaning) across a dataset to address a research question.
In thematic analysis, qualitative data is gathered using techniques such as interviews, focus groups, and questionnaires. Audio recordings are transcribed. The dataset is then explored and interpreted by a researcher to identify patterns.
This occurs through the rigorous process of data familiarisation, coding, theme development, and revision. These identified patterns provide a summary of the dataset and can be used to address a research question.
Themes are developed by exploring the implicit and explicit meanings within the data. Two different approaches are used to generate themes: inductive and deductive.
An inductive approach allows themes to emerge from the data. In contrast, a deductive approach uses existing theories or knowledge to apply preconceived ideas to the data.
Phases of Thematic Analysis
Braun and Clarke (2006) provide a guide of the six phases of thematic analysis. These phases can be applied flexibly to fit research questions and data.
Template analysis
Template analysis refers to a specific method of thematic analysis which uses hierarchical coding (Brooks et al., 2014).
Template analysis is used to analyze textual data, for example, interview transcripts or open-ended responses on a written questionnaire.
To conduct template analysis, a coding template must be developed (usually from a subset of the data) and subsequently revised and refined. This template represents the themes identified by researchers as important in the dataset.
Codes are ordered hierarchically within the template, with the highest-level codes demonstrating overarching themes in the data and lower-level codes representing constituent themes with a narrower focus.
A guideline for the main procedural steps for conducting template analysis is outlined below.
- Familiarization with the Data : Read (and reread) the dataset in full. Engage, reflect, and take notes on data that may be relevant to the research question.
- Preliminary Coding : Identify initial codes using guidance from the a priori codes, identified before the analysis as likely to be beneficial and relevant to the analysis.
- Organize Themes : Organize themes into meaningful clusters. Consider the relationships between the themes both within and between clusters.
- Produce an Initial Template : Develop an initial template. This may be based on a subset of the data.
- Apply and Develop the Template : Apply the initial template to further data and make any necessary modifications. Refinements of the template may include adding themes, removing themes, or changing the scope/title of themes.
- Finalize Template : Finalize the template, then apply it to the entire dataset.
Frame analysis
Frame analysis is a comparative form of thematic analysis which systematically analyzes data using a matrix output.
Ritchie and Spencer (1994) developed this set of techniques to analyze qualitative data in applied policy research. Frame analysis aims to generate theory from data.
Frame analysis encourages researchers to organize and manage their data using summarization.
This results in a flexible and unique matrix output, in which individual participants (or cases) are represented by rows and themes are represented by columns.
Each intersecting cell is used to summarize findings relating to the corresponding participant and theme.
Frame analysis has five distinct phases which are interrelated, forming a methodical and rigorous framework.
- Familiarization with the Data : Familiarize yourself with all the transcripts. Immerse yourself in the details of each transcript and start to note recurring themes.
- Develop a Theoretical Framework : Identify recurrent/ important themes and add them to a chart. Provide a framework/ structure for the analysis.
- Indexing : Apply the framework systematically to the entire study data.
- Summarize Data in Analytical Framework : Reduce the data into brief summaries of participants’ accounts.
- Mapping and Interpretation : Compare themes and subthemes and check against the original transcripts. Group the data into categories and provide an explanation for them.
Preventing Bias in Qualitative Research
To evaluate qualitative studies, the CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme) checklist for qualitative studies can be used to ensure all aspects of a study have been considered (CASP, 2018).
The quality of research can be enhanced and assessed using criteria such as checklists, reflexivity, co-coding, and member-checking.
Co-coding
Relying on only one researcher to interpret rich and complex data may risk key insights and alternative viewpoints being missed. Therefore, coding is often performed by multiple researchers.
A common strategy must be defined at the beginning of the coding process (Busetto et al., 2020). This includes establishing a useful coding list and finding a common definition of individual codes.
Transcripts are initially coded independently by researchers and then compared and consolidated to minimize error or bias and to bring confirmation of findings.
Member checking
Member checking (or respondent validation) involves checking back with participants to see if the research resonates with their experiences (Russell & Gregory, 2003).
Data can be returned to participants after data collection or when results are first available. For example, participants may be provided with their interview transcript and asked to verify whether this is a complete and accurate representation of their views.
Participants may then clarify or elaborate on their responses to ensure they align with their views (Shenton, 2004).
This feedback becomes part of data collection and ensures accurate descriptions/ interpretations of phenomena (Mays & Pope, 2000).
Reflexivity in qualitative research
Reflexivity typically involves examining your own judgments, practices, and belief systems during data collection and analysis. It aims to identify any personal beliefs which may affect the research.
Reflexivity is essential in qualitative research to ensure methodological transparency and complete reporting. This enables readers to understand how the interaction between the researcher and participant shapes the data.
Depending on the research question and population being researched, factors that need to be considered include the experience of the researcher, how the contact was established and maintained, age, gender, and ethnicity.
These details are important because, in qualitative research, the researcher is a dynamic part of the research process and actively influences the outcome of the research (Boeije, 2014).
Reflexivity Example
Who you are and your characteristics influence how you collect and analyze data. Here is an example of a reflexivity statement for research on smoking. I am a 30-year-old white female from a middle-class background. I live in the southwest of England and have been educated to master’s level. I have been involved in two research projects on oral health. I have never smoked, but I have witnessed how smoking can cause ill health from my volunteering in a smoking cessation clinic. My research aspirations are to help to develop interventions to help smokers quit.
Establishing Trustworthiness in Qualitative Research
Trustworthiness is a concept used to assess the quality and rigor of qualitative research. Four criteria are used to assess a study’s trustworthiness: credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability.
Credibility in Qualitative Research
Credibility refers to how accurately the results represent the reality and viewpoints of the participants.
To establish credibility in research, participants’ views and the researcher’s representation of their views need to align (Tobin & Begley, 2004).
To increase the credibility of findings, researchers may use data source triangulation, investigator triangulation, peer debriefing, or member checking (Lincoln & Guba, 1985).
Transferability in Qualitative Research
Transferability refers to how generalizable the findings are: whether the findings may be applied to another context, setting, or group (Tobin & Begley, 2004).
Transferability can be enhanced by giving thorough and in-depth descriptions of the research setting, sample, and methods (Nowell et al., 2017).
Dependability in Qualitative Research
Dependability is the extent to which the study could be replicated under similar conditions and the findings would be consistent.
Researchers can establish dependability using methods such as audit trails so readers can see the research process is logical and traceable (Koch, 1994).
Confirmability in Qualitative Research
Confirmability is concerned with establishing that there is a clear link between the researcher’s interpretations/ findings and the data.
Researchers can achieve confirmability by demonstrating how conclusions and interpretations were arrived at (Nowell et al., 2017).
This enables readers to understand the reasoning behind the decisions made.
Audit Trails in Qualitative Research
An audit trail provides evidence of the decisions made by the researcher regarding theory, research design, and data collection, as well as the steps they have chosen to manage, analyze, and report data.
The researcher must provide a clear rationale to demonstrate how conclusions were reached in their study.
A clear description of the research path must be provided to enable readers to trace through the researcher’s logic (Halpren, 1983).
Researchers should maintain records of the raw data, field notes, transcripts, and a reflective journal in order to provide a clear audit trail.
Discovery of unexpected data
Open-ended questions in qualitative research mean the researcher can probe an interview topic and enable the participant to elaborate on responses in an unrestricted manner.
This allows unexpected data to emerge, which can lead to further research into that topic.
The exploratory nature of qualitative research helps generate hypotheses that can be tested quantitatively (Busetto et al., 2020).
Flexibility
Data collection and analysis can be modified and adapted to take the research in a different direction if new ideas or patterns emerge in the data.
This enables researchers to investigate new opportunities while firmly maintaining their research goals.
Naturalistic settings
The behaviors of participants are recorded in real-world settings. Studies that use real-world settings have high ecological validity since participants behave more authentically.
Limitations
Time-consuming .
Qualitative research results in large amounts of data which often need to be transcribed and analyzed manually.
Even when software is used, transcription can be inaccurate, and using software for analysis can result in many codes which need to be condensed into themes.
Subjectivity
The researcher has an integral role in collecting and interpreting qualitative data. Therefore, the conclusions reached are from their perspective and experience.
Consequently, interpretations of data from another researcher may vary greatly.
Limited generalizability
The aim of qualitative research is to provide a detailed, contextualized understanding of an aspect of the human experience from a relatively small sample size.
Despite rigorous analysis procedures, conclusions drawn cannot be generalized to the wider population since data may be biased or unrepresentative.
Therefore, results are only applicable to a small group of the population.
Extraneous variables
Qualitative research is often conducted in real-world settings. This may cause results to be unreliable since extraneous variables may affect the data, for example:
- Situational variables : different environmental conditions may influence participants’ behavior in a study. The random variation in factors (such as noise or lighting) may be difficult to control in real-world settings.
- Participant characteristics : this includes any characteristics that may influence how a participant answers/ behaves in a study. This may include a participant’s mood, gender, age, ethnicity, sexual identity, IQ, etc.
- Experimenter effect : experimenter effect refers to how a researcher’s unintentional influence can change the outcome of a study. This occurs when (i) their interactions with participants unintentionally change participants’ behaviors or (ii) due to errors in observation, interpretation, or analysis.
What sample size should qualitative research be?
The sample size for qualitative studies has been recommended to include a minimum of 12 participants to reach data saturation (Braun, 2013).
Are surveys qualitative or quantitative?
Surveys can be used to gather information from a sample qualitatively or quantitatively. Qualitative surveys use open-ended questions to gather detailed information from a large sample using free text responses.
The use of open-ended questions allows for unrestricted responses where participants use their own words, enabling the collection of more in-depth information than closed-ended questions.
In contrast, quantitative surveys consist of closed-ended questions with multiple-choice answer options. Quantitative surveys are ideal to gather a statistical representation of a population.
What are the ethical considerations of qualitative research?
Before conducting a study, you must think about any risks that could occur and take steps to prevent them. Participant Protection : Researchers must protect participants from physical and mental harm. This means you must not embarrass, frighten, offend, or harm participants. Transparency : Researchers are obligated to clearly communicate how they will collect, store, analyze, use, and share the data. Confidentiality : You need to consider how to maintain the confidentiality and anonymity of participants’ data.
What is triangulation in qualitative research?
Triangulation refers to the use of several approaches in a study to comprehensively understand phenomena. This method helps to increase the validity and credibility of research findings.
Types of triangulation include method triangulation (using multiple methods to gather data); investigator triangulation (multiple researchers for collecting/ analyzing data), theory triangulation (comparing several theoretical perspectives to explain a phenomenon), and data source triangulation (using data from various times, locations, and people; Carter et al., 2014).
Why is qualitative research important?
Qualitative research allows researchers to describe and explain the social world. The exploratory nature of qualitative research helps to generate hypotheses that can then be tested quantitatively.
In qualitative research, participants are able to express their thoughts, experiences, and feelings without constraint.
Additionally, researchers are able to follow up on participants’ answers in real-time, generating valuable discussion around a topic. This enables researchers to gain a nuanced understanding of phenomena which is difficult to attain using quantitative methods.
What is coding data in qualitative research?
Coding data is a qualitative data analysis strategy in which a section of text is assigned with a label that describes its content.
These labels may be words or phrases which represent important (and recurring) patterns in the data.
This process enables researchers to identify related content across the dataset. Codes can then be used to group similar types of data to generate themes.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative research?
Qualitative research involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data in order to understand experiences and meanings from the participant’s perspective.
This can provide rich, in-depth insights on complicated phenomena. Qualitative data may be collected using interviews, focus groups, or observations.
In contrast, quantitative research involves the collection and analysis of numerical data to measure the frequency, magnitude, or relationships of variables. This can provide objective and reliable evidence that can be generalized to the wider population.
Quantitative data may be collected using closed-ended questionnaires or experiments.
What is trustworthiness in qualitative research?
Trustworthiness is a concept used to assess the quality and rigor of qualitative research. Four criteria are used to assess a study’s trustworthiness: credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability.
Credibility refers to how accurately the results represent the reality and viewpoints of the participants. Transferability refers to whether the findings may be applied to another context, setting, or group.
Dependability is the extent to which the findings are consistent and reliable. Confirmability refers to the objectivity of findings (not influenced by the bias or assumptions of researchers).
What is data saturation in qualitative research?
Data saturation is a methodological principle used to guide the sample size of a qualitative research study.
Data saturation is proposed as a necessary methodological component in qualitative research (Saunders et al., 2018) as it is a vital criterion for discontinuing data collection and/or analysis.
The intention of data saturation is to find “no new data, no new themes, no new coding, and ability to replicate the study” (Guest et al., 2006). Therefore, enough data has been gathered to make conclusions.
Why is sampling in qualitative research important?
In quantitative research, large sample sizes are used to provide statistically significant quantitative estimates.
This is because quantitative research aims to provide generalizable conclusions that represent populations.
However, the aim of sampling in qualitative research is to gather data that will help the researcher understand the depth, complexity, variation, or context of a phenomenon. The small sample sizes in qualitative studies support the depth of case-oriented analysis.
Boeije, H. (2014). Analysis in qualitative research. Sage.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative research in psychology , 3 (2), 77-101. https://doi.org/10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
Brooks, J., McCluskey, S., Turley, E., & King, N. (2014). The utility of template analysis in qualitative psychology research. Qualitative Research in Psychology , 12 (2), 202–222. https://doi.org/10.1080/14780887.2014.955224
Busetto, L., Wick, W., & Gumbinger, C. (2020). How to use and assess qualitative research methods. Neurological research and practice , 2 (1), 14-14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42466-020-00059-z
Carter, N., Bryant-Lukosius, D., DiCenso, A., Blythe, J., & Neville, A. J. (2014). The use of triangulation in qualitative research. Oncology nursing forum , 41 (5), 545–547. https://doi.org/10.1188/14.ONF.545-547
Critical Appraisal Skills Programme. (2018). CASP Checklist: 10 questions to help you make sense of a Qualitative research. https://casp-uk.net/images/checklist/documents/CASP-Qualitative-Studies-Checklist/CASP-Qualitative-Checklist-2018_fillable_form.pdf Accessed: March 15 2023
Clarke, V., & Braun, V. (2013). Successful qualitative research: A practical guide for beginners. Successful Qualitative Research , 1-400.
Denny, E., & Weckesser, A. (2022). How to do qualitative research?: Qualitative research methods. BJOG : an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology , 129 (7), 1166-1167. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.17150
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (2017). The discovery of grounded theory. The Discovery of Grounded Theory , 1–18. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203793206-1
Guest, G., Bunce, A., & Johnson, L. (2006). How many interviews are enough? An experiment with data saturation and variability. Field Methods, 18 (1), 59-82. doi:10.1177/1525822X05279903
Halpren, E. S. (1983). Auditing naturalistic inquiries: The development and application of a model (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Indiana University, Bloomington.
Hammarberg, K., Kirkman, M., & de Lacey, S. (2016). Qualitative research methods: When to use them and how to judge them. Human Reproduction , 31 (3), 498–501. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dev334
Koch, T. (1994). Establishing rigour in qualitative research: The decision trail. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 19, 976–986. doi:10.1111/ j.1365-2648.1994.tb01177.x
Lincoln, Y., & Guba, E. G. (1985). Naturalistic inquiry. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Mays, N., & Pope, C. (2000). Assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ, 320(7226), 50–52.
Minichiello, V. (1990). In-Depth Interviewing: Researching People. Longman Cheshire.
Nowell, L. S., Norris, J. M., White, D. E., & Moules, N. J. (2017). Thematic Analysis: Striving to Meet the Trustworthiness Criteria. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 16 (1). https://doi.org/10.1177/1609406917733847
Petty, N. J., Thomson, O. P., & Stew, G. (2012). Ready for a paradigm shift? part 2: Introducing qualitative research methodologies and methods. Manual Therapy , 17 (5), 378–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2012.03.004
Punch, K. F. (2013). Introduction to social research: Quantitative and qualitative approaches. London: Sage
Reeves, S., Kuper, A., & Hodges, B. D. (2008). Qualitative research methodologies: Ethnography. BMJ , 337 (aug07 3). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.a1020
Russell, C. K., & Gregory, D. M. (2003). Evaluation of qualitative research studies. Evidence Based Nursing, 6 (2), 36–40.
Saunders, B., Sim, J., Kingstone, T., Baker, S., Waterfield, J., Bartlam, B., Burroughs, H., & Jinks, C. (2018). Saturation in qualitative research: exploring its conceptualization and operationalization. Quality & quantity , 52 (4), 1893–1907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-017-0574-8
Scarduzio, J. A. (2017). Emic approach to qualitative research. The International Encyclopedia of Communication Research Methods, 1–2 . https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118901731.iecrm0082
Schreier, M. (2012). Qualitative content analysis in practice / Margrit Schreier.
Shenton, A. K. (2004). Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Education for Information, 22 , 63–75.
Starks, H., & Trinidad, S. B. (2007). Choose your method: a comparison of phenomenology, discourse analysis, and grounded theory. Qualitative health research , 17 (10), 1372–1380. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732307307031
Tenny, S., Brannan, J. M., & Brannan, G. D. (2022). Qualitative Study. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
Tobin, G. A., & Begley, C. M. (2004). Methodological rigour within a qualitative framework. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 48, 388–396. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2004.03207.x
Vaismoradi, M., Turunen, H., & Bondas, T. (2013). Content analysis and thematic analysis: Implications for conducting a qualitative descriptive study. Nursing & health sciences , 15 (3), 398-405. https://doi.org/10.1111/nhs.12048
Wood L. A., Kroger R. O. (2000). Doing discourse analysis: Methods for studying action in talk and text. Sage.
Yilmaz, K. (2013). Comparison of Quantitative and Qualitative Research Traditions: epistemological, theoretical, and methodological differences. European journal of education , 48 (2), 311-325. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejed.12014
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples
- Privacy Policy

Home » Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Table of Contents

Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people’s beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis.
Qualitative research aims to uncover the meaning and significance of social phenomena, and it typically involves a more flexible and iterative approach to data collection and analysis compared to quantitative research. Qualitative research is often used in fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, and education.
Qualitative Research Methods

Qualitative Research Methods are as follows:
One-to-One Interview
This method involves conducting an interview with a single participant to gain a detailed understanding of their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. One-to-one interviews can be conducted in-person, over the phone, or through video conferencing. The interviewer typically uses open-ended questions to encourage the participant to share their thoughts and feelings. One-to-one interviews are useful for gaining detailed insights into individual experiences.
Focus Groups
This method involves bringing together a group of people to discuss a specific topic in a structured setting. The focus group is led by a moderator who guides the discussion and encourages participants to share their thoughts and opinions. Focus groups are useful for generating ideas and insights, exploring social norms and attitudes, and understanding group dynamics.
Ethnographic Studies
This method involves immersing oneself in a culture or community to gain a deep understanding of its norms, beliefs, and practices. Ethnographic studies typically involve long-term fieldwork and observation, as well as interviews and document analysis. Ethnographic studies are useful for understanding the cultural context of social phenomena and for gaining a holistic understanding of complex social processes.
Text Analysis
This method involves analyzing written or spoken language to identify patterns and themes. Text analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative text analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Text analysis is useful for understanding media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
This method involves an in-depth examination of a single person, group, or event to gain an understanding of complex phenomena. Case studies typically involve a combination of data collection methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case. Case studies are useful for exploring unique or rare cases, and for generating hypotheses for further research.
Process of Observation
This method involves systematically observing and recording behaviors and interactions in natural settings. The observer may take notes, use audio or video recordings, or use other methods to document what they see. Process of observation is useful for understanding social interactions, cultural practices, and the context in which behaviors occur.
Record Keeping
This method involves keeping detailed records of observations, interviews, and other data collected during the research process. Record keeping is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data, and for providing a basis for analysis and interpretation.
This method involves collecting data from a large sample of participants through a structured questionnaire. Surveys can be conducted in person, over the phone, through mail, or online. Surveys are useful for collecting data on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, and for identifying patterns and trends in a population.
Qualitative data analysis is a process of turning unstructured data into meaningful insights. It involves extracting and organizing information from sources like interviews, focus groups, and surveys. The goal is to understand people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations
Qualitative Research Analysis Methods
Qualitative Research analysis methods involve a systematic approach to interpreting and making sense of the data collected in qualitative research. Here are some common qualitative data analysis methods:
Thematic Analysis
This method involves identifying patterns or themes in the data that are relevant to the research question. The researcher reviews the data, identifies keywords or phrases, and groups them into categories or themes. Thematic analysis is useful for identifying patterns across multiple data sources and for generating new insights into the research topic.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing the content of written or spoken language to identify key themes or concepts. Content analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative content analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Content analysis is useful for identifying patterns in media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
Discourse Analysis
This method involves analyzing language to understand how it constructs meaning and shapes social interactions. Discourse analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as conversation analysis, critical discourse analysis, and narrative analysis. Discourse analysis is useful for understanding how language shapes social interactions, cultural norms, and power relationships.
Grounded Theory Analysis
This method involves developing a theory or explanation based on the data collected. Grounded theory analysis starts with the data and uses an iterative process of coding and analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data. The theory or explanation that emerges is grounded in the data, rather than preconceived hypotheses. Grounded theory analysis is useful for understanding complex social phenomena and for generating new theoretical insights.
Narrative Analysis
This method involves analyzing the stories or narratives that participants share to gain insights into their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. Narrative analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as structural analysis, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis. Narrative analysis is useful for understanding how individuals construct their identities, make sense of their experiences, and communicate their values and beliefs.
Phenomenological Analysis
This method involves analyzing how individuals make sense of their experiences and the meanings they attach to them. Phenomenological analysis typically involves in-depth interviews with participants to explore their experiences in detail. Phenomenological analysis is useful for understanding subjective experiences and for developing a rich understanding of human consciousness.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing and contrasting data across different cases or groups to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can be used to identify patterns or themes that are common across multiple cases, as well as to identify unique or distinctive features of individual cases. Comparative analysis is useful for understanding how social phenomena vary across different contexts and groups.
Applications of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has many applications across different fields and industries. Here are some examples of how qualitative research is used:
- Market Research: Qualitative research is often used in market research to understand consumer attitudes, behaviors, and preferences. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with consumers to gather insights into their experiences and perceptions of products and services.
- Health Care: Qualitative research is used in health care to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education: Qualitative research is used in education to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. Researchers conduct classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work : Qualitative research is used in social work to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : Qualitative research is used in anthropology to understand different cultures and societies. Researchers conduct ethnographic studies and observe and interview members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : Qualitative research is used in psychology to understand human behavior and mental processes. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy : Qualitative research is used in public policy to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
How to Conduct Qualitative Research
Here are some general steps for conducting qualitative research:
- Identify your research question: Qualitative research starts with a research question or set of questions that you want to explore. This question should be focused and specific, but also broad enough to allow for exploration and discovery.
- Select your research design: There are different types of qualitative research designs, including ethnography, case study, grounded theory, and phenomenology. You should select a design that aligns with your research question and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Recruit participants: Once you have your research question and design, you need to recruit participants. The number of participants you need will depend on your research design and the scope of your research. You can recruit participants through advertisements, social media, or through personal networks.
- Collect data: There are different methods for collecting qualitative data, including interviews, focus groups, observation, and document analysis. You should select the method or methods that align with your research design and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Analyze data: Once you have collected your data, you need to analyze it. This involves reviewing your data, identifying patterns and themes, and developing codes to organize your data. You can use different software programs to help you analyze your data, or you can do it manually.
- Interpret data: Once you have analyzed your data, you need to interpret it. This involves making sense of the patterns and themes you have identified, and developing insights and conclusions that answer your research question. You should be guided by your research question and use your data to support your conclusions.
- Communicate results: Once you have interpreted your data, you need to communicate your results. This can be done through academic papers, presentations, or reports. You should be clear and concise in your communication, and use examples and quotes from your data to support your findings.
Examples of Qualitative Research
Here are some real-time examples of qualitative research:
- Customer Feedback: A company may conduct qualitative research to understand the feedback and experiences of its customers. This may involve conducting focus groups or one-on-one interviews with customers to gather insights into their attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
- Healthcare : A healthcare provider may conduct qualitative research to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education : An educational institution may conduct qualitative research to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. This may involve conducting classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work: A social worker may conduct qualitative research to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : An anthropologist may conduct qualitative research to understand different cultures and societies. This may involve conducting ethnographic studies and observing and interviewing members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : A psychologist may conduct qualitative research to understand human behavior and mental processes. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy: A government agency or non-profit organization may conduct qualitative research to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. This may involve conducting focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
Purpose of Qualitative Research
The purpose of qualitative research is to explore and understand the subjective experiences, behaviors, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research aims to provide in-depth, descriptive information that can help researchers develop insights and theories about complex social phenomena.
Qualitative research can serve multiple purposes, including:
- Exploring new or emerging phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring new or emerging phenomena, such as new technologies or social trends. This type of research can help researchers develop a deeper understanding of these phenomena and identify potential areas for further study.
- Understanding complex social phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring complex social phenomena, such as cultural beliefs, social norms, or political processes. This type of research can help researchers develop a more nuanced understanding of these phenomena and identify factors that may influence them.
- Generating new theories or hypotheses: Qualitative research can be useful for generating new theories or hypotheses about social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data about individuals’ experiences and perspectives, researchers can develop insights that may challenge existing theories or lead to new lines of inquiry.
- Providing context for quantitative data: Qualitative research can be useful for providing context for quantitative data. By gathering qualitative data alongside quantitative data, researchers can develop a more complete understanding of complex social phenomena and identify potential explanations for quantitative findings.
When to use Qualitative Research
Here are some situations where qualitative research may be appropriate:
- Exploring a new area: If little is known about a particular topic, qualitative research can help to identify key issues, generate hypotheses, and develop new theories.
- Understanding complex phenomena: Qualitative research can be used to investigate complex social, cultural, or organizational phenomena that are difficult to measure quantitatively.
- Investigating subjective experiences: Qualitative research is particularly useful for investigating the subjective experiences of individuals or groups, such as their attitudes, beliefs, values, or emotions.
- Conducting formative research: Qualitative research can be used in the early stages of a research project to develop research questions, identify potential research participants, and refine research methods.
- Evaluating interventions or programs: Qualitative research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions or programs by collecting data on participants’ experiences, attitudes, and behaviors.
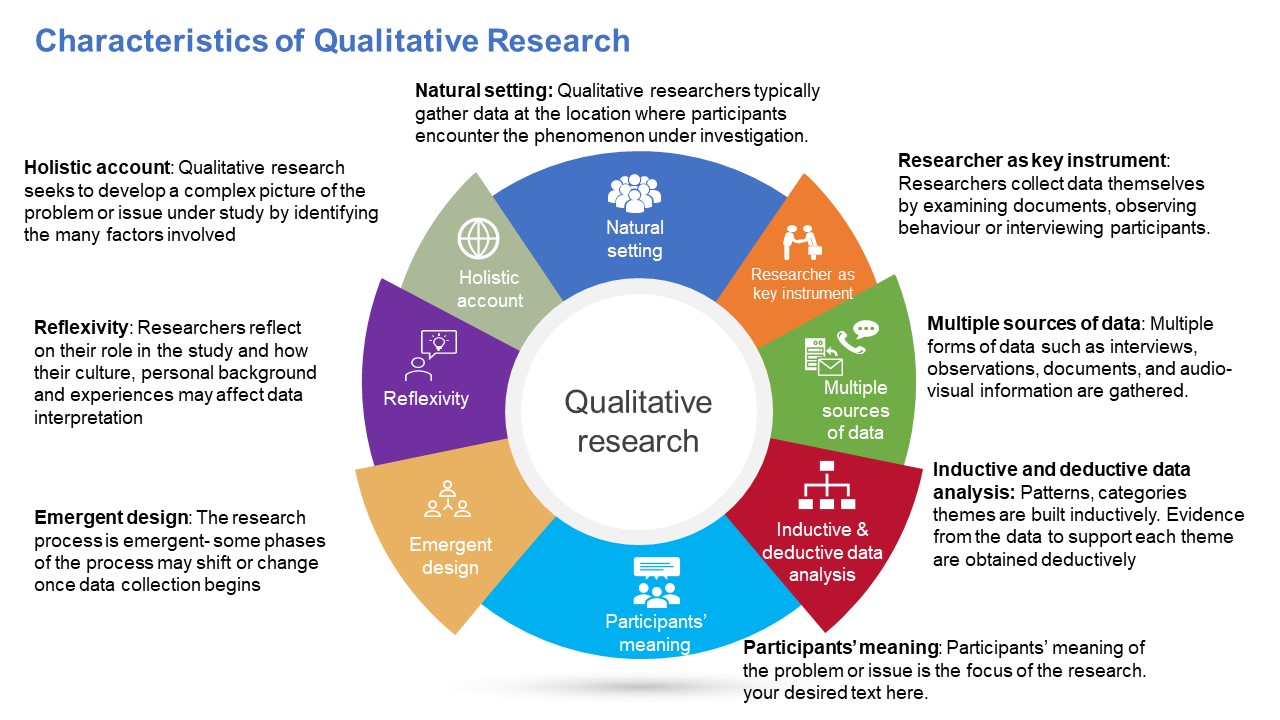
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is characterized by several key features, including:
- Focus on subjective experience: Qualitative research is concerned with understanding the subjective experiences, beliefs, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Researchers aim to explore the meanings that people attach to their experiences and to understand the social and cultural factors that shape these meanings.
- Use of open-ended questions: Qualitative research relies on open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed, in-depth responses. Researchers seek to elicit rich, descriptive data that can provide insights into participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Sampling-based on purpose and diversity: Qualitative research often involves purposive sampling, in which participants are selected based on specific criteria related to the research question. Researchers may also seek to include participants with diverse experiences and perspectives to capture a range of viewpoints.
- Data collection through multiple methods: Qualitative research typically involves the use of multiple data collection methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation. This allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data from multiple sources, which can provide a more complete picture of participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Inductive data analysis: Qualitative research relies on inductive data analysis, in which researchers develop theories and insights based on the data rather than testing pre-existing hypotheses. Researchers use coding and thematic analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data and to develop theories and explanations based on these patterns.
- Emphasis on researcher reflexivity: Qualitative research recognizes the importance of the researcher’s role in shaping the research process and outcomes. Researchers are encouraged to reflect on their own biases and assumptions and to be transparent about their role in the research process.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers several advantages over other research methods, including:
- Depth and detail: Qualitative research allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data that provides a deeper understanding of complex social phenomena. Through in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation, researchers can gather detailed information about participants’ experiences and perspectives that may be missed by other research methods.
- Flexibility : Qualitative research is a flexible approach that allows researchers to adapt their methods to the research question and context. Researchers can adjust their research methods in real-time to gather more information or explore unexpected findings.
- Contextual understanding: Qualitative research is well-suited to exploring the social and cultural context in which individuals or groups are situated. Researchers can gather information about cultural norms, social structures, and historical events that may influence participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Participant perspective : Qualitative research prioritizes the perspective of participants, allowing researchers to explore subjective experiences and understand the meanings that participants attach to their experiences.
- Theory development: Qualitative research can contribute to the development of new theories and insights about complex social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data and using inductive data analysis, researchers can develop new theories and explanations that may challenge existing understandings.
- Validity : Qualitative research can offer high validity by using multiple data collection methods, purposive and diverse sampling, and researcher reflexivity. This can help ensure that findings are credible and trustworthy.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research also has some limitations, including:
- Subjectivity : Qualitative research relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers, which can introduce bias into the research process. The researcher’s perspective, beliefs, and experiences can influence the way data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
- Limited generalizability: Qualitative research typically involves small, purposive samples that may not be representative of larger populations. This limits the generalizability of findings to other contexts or populations.
- Time-consuming: Qualitative research can be a time-consuming process, requiring significant resources for data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Resource-intensive: Qualitative research may require more resources than other research methods, including specialized training for researchers, specialized software for data analysis, and transcription services.
- Limited reliability: Qualitative research may be less reliable than quantitative research, as it relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers. This can make it difficult to replicate findings or compare results across different studies.
- Ethics and confidentiality: Qualitative research involves collecting sensitive information from participants, which raises ethical concerns about confidentiality and informed consent. Researchers must take care to protect the privacy and confidentiality of participants and obtain informed consent.
Also see Research Methods
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide
Qualitative Research : Definition
Qualitative research is the naturalistic study of social meanings and processes, using interviews, observations, and the analysis of texts and images. In contrast to quantitative researchers, whose statistical methods enable broad generalizations about populations (for example, comparisons of the percentages of U.S. demographic groups who vote in particular ways), qualitative researchers use in-depth studies of the social world to analyze how and why groups think and act in particular ways (for instance, case studies of the experiences that shape political views).
Events and Workshops
- Introduction to NVivo Have you just collected your data and wondered what to do next? Come join us for an introductory session on utilizing NVivo to support your analytical process. This session will only cover features of the software and how to import your records. Please feel free to attend any of the following sessions below: April 25th, 2024 12:30 pm - 1:45 pm Green Library - SVA Conference Room 125 May 9th, 2024 12:30 pm - 1:45 pm Green Library - SVA Conference Room 125
- Next: Choose an approach >>
- Choose an approach
- Find studies
- Learn methods
- Getting Started
- Get software
- Get data for secondary analysis
- Network with researchers

- Last Updated: May 23, 2024 1:27 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.stanford.edu/qualitative_research

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
4.2 Definitions and Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research aims to uncover the meaning and understanding of phenomena that cannot be broken down into measurable elements. It is based on naturalistic, interpretative and humanistic notions. 5 This research method seeks to discover, explore, identify or describe subjective human experiences using non-statistical methods and develops themes from the study participants’ stories. 5 Figure 4.1 depicts major features/ characteristics of qualitative research. It utilises exploratory open-ended questions and observations to search for patterns of meaning in collected data (e.g. observation, verbal/written narrative data, photographs, etc.) and uses inductive thinking (from specific observations to more general rules) to interpret meaning. 6 Participants’ voice is evident through quotations and description of the work. 6 The context/ setting of the study and the researcher’s reflexivity (i.e. “reflection on and awareness of their bias”, the effect of the researcher’s experience on the data and interpretations) are very important and described as part of data collection. 6 Analysis of collected data is complex, often involves inductive data analysis (exploration, contrasts, specific to general) and requires multiple coding and development of themes from participant stories. 6
Reflexivity- avoiding bias/Role of the qualitative researcher
Qualitative researchers generally begin their work with the recognition that their position (or worldview) has a significant impact on the overall research process. 7 Researcher worldview shapes the way the research is conducted, i.e., how the questions are formulated, methods are chosen, data are collected and analysed, and results are reported. Therefore, it is essential for qualitative researchers to acknowledge, articulate, reflect on and clarify their own underlying biases and assumptions before embarking on any research project. 7 Reflexivity helps to ensure that the researcher’s own experiences, values, and beliefs do not unintentionally bias the data collection, analysis, and interpretation. 7 It is the gold standard for establishing trustworthiness and has been established as one of the ways qualitative researchers should ensure rigour and quality in their work. 8 The following questions in Table 4.1 may help you begin the reflective process. 9
Table 4.1: Questions to aid the reflection process
Philosophical underpinnings to qualitative research
Qualitative research uses an inductive approach and stems from interpretivism or constructivism and assumes that realities are multiple, socially constructed, and holistic. 10 According to this philosophical viewpoint, humans build reality through their interactions with the world around them. 10 As a result, qualitative research aims to comprehend how individuals make sense of their experiences and build meaning in their lives. 10 Because reality is complex/nuanced and context-bound, participants constantly construct it depending on their understanding. Thus, the interactions between the researcher and the participants are considered necessary to offer a rich description of the concept and provide an in-depth understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. 11
An Introduction to Research Methods for Undergraduate Health Profession Students Copyright © 2023 by Faith Alele and Bunmi Malau-Aduli is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on 4 April 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 30 January 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analysing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, and history.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organisation?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography, action research, phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasise different aims and perspectives.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves ‘instruments’ in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analysing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organise your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorise your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analysing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasise different concepts.
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analysing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analysing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalisability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalisable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labour-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organisation to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organise your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, January 30). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 27 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/introduction-to-qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Qualitative Methods
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The word qualitative implies an emphasis on the qualities of entities and on processes and meanings that are not experimentally examined or measured [if measured at all] in terms of quantity, amount, intensity, or frequency. Qualitative researchers stress the socially constructed nature of reality, the intimate relationship between the researcher and what is studied, and the situational constraints that shape inquiry. Such researchers emphasize the value-laden nature of inquiry. They seek answers to questions that stress how social experience is created and given meaning. In contrast, quantitative studies emphasize the measurement and analysis of causal relationships between variables, not processes. Qualitative forms of inquiry are considered by many social and behavioral scientists to be as much a perspective on how to approach investigating a research problem as it is a method.
Denzin, Norman. K. and Yvonna S. Lincoln. “Introduction: The Discipline and Practice of Qualitative Research.” In The Sage Handbook of Qualitative Research . Norman. K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, eds. 3 rd edition. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005), p. 10.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Below are the three key elements that define a qualitative research study and the applied forms each take in the investigation of a research problem.
- Naturalistic -- refers to studying real-world situations as they unfold naturally; non-manipulative and non-controlling; the researcher is open to whatever emerges [i.e., there is a lack of predetermined constraints on findings].
- Emergent -- acceptance of adapting inquiry as understanding deepens and/or situations change; the researcher avoids rigid designs that eliminate responding to opportunities to pursue new paths of discovery as they emerge.
- Purposeful -- cases for study [e.g., people, organizations, communities, cultures, events, critical incidences] are selected because they are “information rich” and illuminative. That is, they offer useful manifestations of the phenomenon of interest; sampling is aimed at insight about the phenomenon, not empirical generalization derived from a sample and applied to a population.
The Collection of Data
- Data -- observations yield a detailed, "thick description" [in-depth understanding]; interviews capture direct quotations about people’s personal perspectives and lived experiences; often derived from carefully conducted case studies and review of material culture.
- Personal experience and engagement -- researcher has direct contact with and gets close to the people, situation, and phenomenon under investigation; the researcher’s personal experiences and insights are an important part of the inquiry and critical to understanding the phenomenon.
- Empathic neutrality -- an empathic stance in working with study respondents seeks vicarious understanding without judgment [neutrality] by showing openness, sensitivity, respect, awareness, and responsiveness; in observation, it means being fully present [mindfulness].
- Dynamic systems -- there is attention to process; assumes change is ongoing, whether the focus is on an individual, an organization, a community, or an entire culture, therefore, the researcher is mindful of and attentive to system and situational dynamics.
The Analysis
- Unique case orientation -- assumes that each case is special and unique; the first level of analysis is being true to, respecting, and capturing the details of the individual cases being studied; cross-case analysis follows from and depends upon the quality of individual case studies.
- Inductive analysis -- immersion in the details and specifics of the data to discover important patterns, themes, and inter-relationships; begins by exploring, then confirming findings, guided by analytical principles rather than rules.
- Holistic perspective -- the whole phenomenon under study is understood as a complex system that is more than the sum of its parts; the focus is on complex interdependencies and system dynamics that cannot be reduced in any meaningful way to linear, cause and effect relationships and/or a few discrete variables.
- Context sensitive -- places findings in a social, historical, and temporal context; researcher is careful about [even dubious of] the possibility or meaningfulness of generalizations across time and space; emphasizes careful comparative case study analysis and extrapolating patterns for possible transferability and adaptation in new settings.
- Voice, perspective, and reflexivity -- the qualitative methodologist owns and is reflective about her or his own voice and perspective; a credible voice conveys authenticity and trustworthiness; complete objectivity being impossible and pure subjectivity undermining credibility, the researcher's focus reflects a balance between understanding and depicting the world authentically in all its complexity and of being self-analytical, politically aware, and reflexive in consciousness.
Berg, Bruce Lawrence. Qualitative Research Methods for the Social Sciences . 8th edition. Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon, 2012; Denzin, Norman. K. and Yvonna S. Lincoln. Handbook of Qualitative Research . 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2000; Marshall, Catherine and Gretchen B. Rossman. Designing Qualitative Research . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1995; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research: A Guide to Design and Implementation . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 2009.
Basic Research Design for Qualitative Studies
Unlike positivist or experimental research that utilizes a linear and one-directional sequence of design steps, there is considerable variation in how a qualitative research study is organized. In general, qualitative researchers attempt to describe and interpret human behavior based primarily on the words of selected individuals [a.k.a., “informants” or “respondents”] and/or through the interpretation of their material culture or occupied space. There is a reflexive process underpinning every stage of a qualitative study to ensure that researcher biases, presuppositions, and interpretations are clearly evident, thus ensuring that the reader is better able to interpret the overall validity of the research. According to Maxwell (2009), there are five, not necessarily ordered or sequential, components in qualitative research designs. How they are presented depends upon the research philosophy and theoretical framework of the study, the methods chosen, and the general assumptions underpinning the study. Goals Describe the central research problem being addressed but avoid describing any anticipated outcomes. Questions to ask yourself are: Why is your study worth doing? What issues do you want to clarify, and what practices and policies do you want it to influence? Why do you want to conduct this study, and why should the reader care about the results? Conceptual Framework Questions to ask yourself are: What do you think is going on with the issues, settings, or people you plan to study? What theories, beliefs, and prior research findings will guide or inform your research, and what literature, preliminary studies, and personal experiences will you draw upon for understanding the people or issues you are studying? Note to not only report the results of other studies in your review of the literature, but note the methods used as well. If appropriate, describe why earlier studies using quantitative methods were inadequate in addressing the research problem. Research Questions Usually there is a research problem that frames your qualitative study and that influences your decision about what methods to use, but qualitative designs generally lack an accompanying hypothesis or set of assumptions because the findings are emergent and unpredictable. In this context, more specific research questions are generally the result of an interactive design process rather than the starting point for that process. Questions to ask yourself are: What do you specifically want to learn or understand by conducting this study? What do you not know about the things you are studying that you want to learn? What questions will your research attempt to answer, and how are these questions related to one another? Methods Structured approaches to applying a method or methods to your study help to ensure that there is comparability of data across sources and researchers and, thus, they can be useful in answering questions that deal with differences between phenomena and the explanation for these differences [variance questions]. An unstructured approach allows the researcher to focus on the particular phenomena studied. This facilitates an understanding of the processes that led to specific outcomes, trading generalizability and comparability for internal validity and contextual and evaluative understanding. Questions to ask yourself are: What will you actually do in conducting this study? What approaches and techniques will you use to collect and analyze your data, and how do these constitute an integrated strategy? Validity In contrast to quantitative studies where the goal is to design, in advance, “controls” such as formal comparisons, sampling strategies, or statistical manipulations to address anticipated and unanticipated threats to validity, qualitative researchers must attempt to rule out most threats to validity after the research has begun by relying on evidence collected during the research process itself in order to effectively argue that any alternative explanations for a phenomenon are implausible. Questions to ask yourself are: How might your results and conclusions be wrong? What are the plausible alternative interpretations and validity threats to these, and how will you deal with these? How can the data that you have, or that you could potentially collect, support or challenge your ideas about what’s going on? Why should we believe your results? Conclusion Although Maxwell does not mention a conclusion as one of the components of a qualitative research design, you should formally conclude your study. Briefly reiterate the goals of your study and the ways in which your research addressed them. Discuss the benefits of your study and how stakeholders can use your results. Also, note the limitations of your study and, if appropriate, place them in the context of areas in need of further research.
Chenail, Ronald J. Introduction to Qualitative Research Design. Nova Southeastern University; Heath, A. W. The Proposal in Qualitative Research. The Qualitative Report 3 (March 1997); Marshall, Catherine and Gretchen B. Rossman. Designing Qualitative Research . 3rd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1999; Maxwell, Joseph A. "Designing a Qualitative Study." In The SAGE Handbook of Applied Social Research Methods . Leonard Bickman and Debra J. Rog, eds. 2nd ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2009), p. 214-253; Qualitative Research Methods. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Yin, Robert K. Qualitative Research from Start to Finish . 2nd edition. New York: Guilford, 2015.
Strengths of Using Qualitative Methods
The advantage of using qualitative methods is that they generate rich, detailed data that leave the participants' perspectives intact and provide multiple contexts for understanding the phenomenon under study. In this way, qualitative research can be used to vividly demonstrate phenomena or to conduct cross-case comparisons and analysis of individuals or groups.
Among the specific strengths of using qualitative methods to study social science research problems is the ability to:
- Obtain a more realistic view of the lived world that cannot be understood or experienced in numerical data and statistical analysis;
- Provide the researcher with the perspective of the participants of the study through immersion in a culture or situation and as a result of direct interaction with them;
- Allow the researcher to describe existing phenomena and current situations;
- Develop flexible ways to perform data collection, subsequent analysis, and interpretation of collected information;
- Yield results that can be helpful in pioneering new ways of understanding;
- Respond to changes that occur while conducting the study ]e.g., extended fieldwork or observation] and offer the flexibility to shift the focus of the research as a result;
- Provide a holistic view of the phenomena under investigation;
- Respond to local situations, conditions, and needs of participants;
- Interact with the research subjects in their own language and on their own terms; and,
- Create a descriptive capability based on primary and unstructured data.
Anderson, Claire. “Presenting and Evaluating Qualitative Research.” American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education 74 (2010): 1-7; Denzin, Norman. K. and Yvonna S. Lincoln. Handbook of Qualitative Research . 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2000; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research: A Guide to Design and Implementation . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 2009.
Limitations of Using Qualitative Methods
It is very much true that most of the limitations you find in using qualitative research techniques also reflect their inherent strengths . For example, small sample sizes help you investigate research problems in a comprehensive and in-depth manner. However, small sample sizes undermine opportunities to draw useful generalizations from, or to make broad policy recommendations based upon, the findings. Additionally, as the primary instrument of investigation, qualitative researchers are often embedded in the cultures and experiences of others. However, cultural embeddedness increases the opportunity for bias generated from conscious or unconscious assumptions about the study setting to enter into how data is gathered, interpreted, and reported.
Some specific limitations associated with using qualitative methods to study research problems in the social sciences include the following:
- Drifting away from the original objectives of the study in response to the changing nature of the context under which the research is conducted;
- Arriving at different conclusions based on the same information depending on the personal characteristics of the researcher;
- Replication of a study is very difficult;
- Research using human subjects increases the chance of ethical dilemmas that undermine the overall validity of the study;
- An inability to investigate causality between different research phenomena;
- Difficulty in explaining differences in the quality and quantity of information obtained from different respondents and arriving at different, non-consistent conclusions;
- Data gathering and analysis is often time consuming and/or expensive;
- Requires a high level of experience from the researcher to obtain the targeted information from the respondent;
- May lack consistency and reliability because the researcher can employ different probing techniques and the respondent can choose to tell some particular stories and ignore others; and,
- Generation of a significant amount of data that cannot be randomized into manageable parts for analysis.
Research Tip
Human Subject Research and Institutional Review Board Approval
Almost every socio-behavioral study requires you to submit your proposed research plan to an Institutional Review Board. The role of the Board is to evaluate your research proposal and determine whether it will be conducted ethically and under the regulations, institutional polices, and Code of Ethics set forth by the university. The purpose of the review is to protect the rights and welfare of individuals participating in your study. The review is intended to ensure equitable selection of respondents, that you have met the requirements for obtaining informed consent , that there is clear assessment and minimization of risks to participants and to the university [read: no lawsuits!], and that privacy and confidentiality are maintained throughout the research process and beyond. Go to the USC IRB website for detailed information and templates of forms you need to submit before you can proceed. If you are unsure whether your study is subject to IRB review, consult with your professor or academic advisor.
Chenail, Ronald J. Introduction to Qualitative Research Design. Nova Southeastern University; Labaree, Robert V. "Working Successfully with Your Institutional Review Board: Practical Advice for Academic Librarians." College and Research Libraries News 71 (April 2010): 190-193.
Another Research Tip
Finding Examples of How to Apply Different Types of Research Methods
SAGE publications is a major publisher of studies about how to design and conduct research in the social and behavioral sciences. Their SAGE Research Methods Online and Cases database includes contents from books, articles, encyclopedias, handbooks, and videos covering social science research design and methods including the complete Little Green Book Series of Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences and the Little Blue Book Series of Qualitative Research techniques. The database also includes case studies outlining the research methods used in real research projects. This is an excellent source for finding definitions of key terms and descriptions of research design and practice, techniques of data gathering, analysis, and reporting, and information about theories of research [e.g., grounded theory]. The database covers both qualitative and quantitative research methods as well as mixed methods approaches to conducting research.
SAGE Research Methods Online and Cases
NOTE : For a list of online communities, research centers, indispensable learning resources, and personal websites of leading qualitative researchers, GO HERE .
For a list of scholarly journals devoted to the study and application of qualitative research methods, GO HERE .
- << Previous: 6. The Methodology
- Next: Quantitative Methods >>
- Last Updated: May 25, 2024 4:09 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Qualitative Research Methods: Types, Analysis + Examples
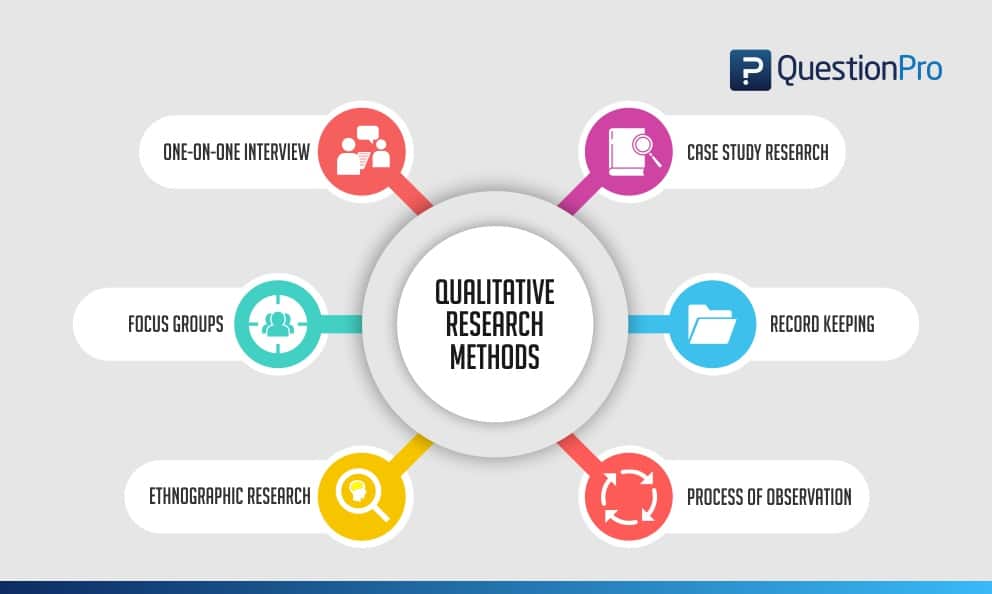
Qualitative research is based on the disciplines of social sciences like psychology, sociology, and anthropology. Therefore, the qualitative research methods allow for in-depth and further probing and questioning of respondents based on their responses. The interviewer/researcher also tries to understand their motivation and feelings. Understanding how your audience makes decisions can help derive conclusions in market research.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is defined as a market research method that focuses on obtaining data through open-ended and conversational communication .
This method is about “what” people think and “why” they think so. For example, consider a convenience store looking to improve its patronage. A systematic observation concludes that more men are visiting this store. One good method to determine why women were not visiting the store is conducting an in-depth interview method with potential customers.
For example, after successfully interviewing female customers and visiting nearby stores and malls, the researchers selected participants through random sampling . As a result, it was discovered that the store didn’t have enough items for women.
So fewer women were visiting the store, which was understood only by personally interacting with them and understanding why they didn’t visit the store because there were more male products than female ones.
Gather research insights
Types of qualitative research methods with examples
Qualitative research methods are designed in a manner that helps reveal the behavior and perception of a target audience with reference to a particular topic. There are different types of qualitative research methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, ethnographic research, content analysis, and case study research that are usually used.
The results of qualitative methods are more descriptive, and the inferences can be drawn quite easily from the obtained data .
Qualitative research methods originated in the social and behavioral research sciences. Today, our world is more complicated, and it is difficult to understand what people think and perceive. Online research methods make it easier to understand that as it is a more communicative and descriptive analysis .
The following are the qualitative research methods that are frequently used. Also, read about qualitative research examples :

1. One-on-one interview
Conducting in-depth interviews is one of the most common qualitative research methods. It is a personal interview that is carried out with one respondent at a time. This is purely a conversational method and invites opportunities to get details in depth from the respondent.
One of the advantages of this method is that it provides a great opportunity to gather precise data about what people believe and their motivations . If the researcher is well experienced, asking the right questions can help him/her collect meaningful data. If they should need more information, the researchers should ask such follow-up questions that will help them collect more information.
These interviews can be performed face-to-face or on the phone and usually can last between half an hour to two hours or even more. When the in-depth interview is conducted face to face, it gives a better opportunity to read the respondents’ body language and match the responses.
2. Focus groups
A focus group is also a commonly used qualitative research method used in data collection. A focus group usually includes a limited number of respondents (6-10) from within your target market.
The main aim of the focus group is to find answers to the “why, ” “what,” and “how” questions. One advantage of focus groups is you don’t necessarily need to interact with the group in person. Nowadays, focus groups can be sent an online survey on various devices, and responses can be collected at the click of a button.
Focus groups are an expensive method as compared to other online qualitative research methods. Typically, they are used to explain complex processes. This method is very useful for market research on new products and testing new concepts.
3. Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research is the most in-depth observational research method that studies people in their naturally occurring environment.
This method requires the researchers to adapt to the target audiences’ environments, which could be anywhere from an organization to a city or any remote location. Here, geographical constraints can be an issue while collecting data.
This research design aims to understand the cultures, challenges, motivations, and settings that occur. Instead of relying on interviews and discussions, you experience the natural settings firsthand.
This type of research method can last from a few days to a few years, as it involves in-depth observation and collecting data on those grounds. It’s a challenging and time-consuming method and solely depends on the researcher’s expertise to analyze, observe, and infer the data.
4. Case study research
T he case study method has evolved over the past few years and developed into a valuable quality research method. As the name suggests, it is used for explaining an organization or an entity.
This type of research method is used within a number of areas like education, social sciences, and similar. This method may look difficult to operate; however , it is one of the simplest ways of conducting research as it involves a deep dive and thorough understanding of the data collection methods and inferring the data.
5. Record keeping
This method makes use of the already existing reliable documents and similar sources of information as the data source. This data can be used in new research. This is similar to going to a library. There, one can go over books and other reference material to collect relevant data that can likely be used in the research.
6. Process of observation
Qualitative Observation is a process of research that uses subjective methodologies to gather systematic information or data. Since the focus on qualitative observation is the research process of using subjective methodologies to gather information or data. Qualitative observation is primarily used to equate quality differences.
Qualitative observation deals with the 5 major sensory organs and their functioning – sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing. This doesn’t involve measurements or numbers but instead characteristics.
Explore Insightfully Contextual Inquiry in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research: data collection and analysis
A. qualitative data collection.
Qualitative data collection allows collecting data that is non-numeric and helps us to explore how decisions are made and provide us with detailed insight. For reaching such conclusions the data that is collected should be holistic, rich, and nuanced and findings to emerge through careful analysis.
- Whatever method a researcher chooses for collecting qualitative data, one aspect is very clear the process will generate a large amount of data. In addition to the variety of methods available, there are also different methods of collecting and recording the data.
For example, if the qualitative data is collected through a focus group or one-to-one discussion, there will be handwritten notes or video recorded tapes. If there are recording they should be transcribed and before the process of data analysis can begin.
- As a rough guide, it can take a seasoned researcher 8-10 hours to transcribe the recordings of an interview, which can generate roughly 20-30 pages of dialogues. Many researchers also like to maintain separate folders to maintain the recording collected from the different focus group. This helps them compartmentalize the data collected.
- In case there are running notes taken, which are also known as field notes, they are helpful in maintaining comments, environmental contexts, environmental analysis , nonverbal cues etc. These filed notes are helpful and can be compared while transcribing audio recorded data. Such notes are usually informal but should be secured in a similar manner as the video recordings or the audio tapes.
B. Qualitative data analysis
Qualitative data analysis such as notes, videos, audio recordings images, and text documents. One of the most used methods for qualitative data analysis is text analysis.
Text analysis is a data analysis method that is distinctly different from all other qualitative research methods, where researchers analyze the social life of the participants in the research study and decode the words, actions, etc.
There are images also that are used in this research study and the researchers analyze the context in which the images are used and draw inferences from them. In the last decade, text analysis through what is shared on social media platforms has gained supreme popularity.
Characteristics of qualitative research methods

- Qualitative research methods usually collect data at the sight, where the participants are experiencing issues or research problems . These are real-time data and rarely bring the participants out of the geographic locations to collect information.
- Qualitative researchers typically gather multiple forms of data, such as interviews, observations, and documents, rather than rely on a single data source .
- This type of research method works towards solving complex issues by breaking down into meaningful inferences, that is easily readable and understood by all.
- Since it’s a more communicative method, people can build their trust on the researcher and the information thus obtained is raw and unadulterated.
Qualitative research method case study
Let’s take the example of a bookstore owner who is looking for ways to improve their sales and customer outreach. An online community of members who were loyal patrons of the bookstore were interviewed and related questions were asked and the questions were answered by them.
At the end of the interview, it was realized that most of the books in the stores were suitable for adults and there were not enough options for children or teenagers.
By conducting this qualitative research the bookstore owner realized what the shortcomings were and what were the feelings of the readers. Through this research now the bookstore owner can now keep books for different age categories and can improve his sales and customer outreach.
Such qualitative research method examples can serve as the basis to indulge in further quantitative research , which provides remedies.
When to use qualitative research
Researchers make use of qualitative research techniques when they need to capture accurate, in-depth insights. It is very useful to capture “factual data”. Here are some examples of when to use qualitative research.
- Developing a new product or generating an idea.
- Studying your product/brand or service to strengthen your marketing strategy.
- To understand your strengths and weaknesses.
- Understanding purchase behavior.
- To study the reactions of your audience to marketing campaigns and other communications.
- Exploring market demographics, segments, and customer care groups.
- Gathering perception data of a brand, company, or product.
LEARN ABOUT: Steps in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research methods vs quantitative research methods
The basic differences between qualitative research methods and quantitative research methods are simple and straightforward. They differ in:
- Their analytical objectives
- Types of questions asked
- Types of data collection instruments
- Forms of data they produce
- Degree of flexibility
LEARN MORE ABOUR OUR SOFTWARE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Trend Report: Guide for Market Dynamics & Strategic Analysis
May 29, 2024

Cannabis Industry Business Intelligence: Impact on Research
May 28, 2024
Top 10 Dynata Alternatives & Competitors
May 27, 2024
What Are My Employees Really Thinking? The Power of Open-ended Survey Analysis
May 24, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
CRO Platform
Test your insights. Run experiments. Win. Or learn. And then win.
eCommerce Customer Analytics Platform
Acquisition matters. But retention matters more. Understand, monitor & nurture the best customers.
- Case Studies
- Ebooks, Tools, Templates
- Digital Marketing Glossary
- eCommerce Growth Stories
- eCommerce Growth Show
- Help & Technical Documentation
CRO Guide > Chapter 3.1
Qualitative Research: Definition, Methodology, Limitation & Examples
Qualitative research is a method focused on understanding human behavior and experiences through non-numerical data. Examples of qualitative research include:
- One-on-one interviews,
- Focus groups, Ethnographic research,
- Case studies,
- Record keeping,
- Qualitative observations
In this article, we’ll provide tips and tricks on how to use qualitative research to better understand your audience through real world examples and improve your ROI. We’ll also learn the difference between qualitative and quantitative data.
Table of Contents
Marketers often seek to understand their customers deeply. Qualitative research methods such as face-to-face interviews, focus groups, and qualitative observations can provide valuable insights into your products, your market, and your customers’ opinions and motivations. Understanding these nuances can significantly enhance marketing strategies and overall customer satisfaction.
What is Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a market research method that focuses on obtaining data through open-ended and conversational communication. This method focuses on the “why” rather than the “what” people think about you. Thus, qualitative research seeks to uncover the underlying motivations, attitudes, and beliefs that drive people’s actions.
Let’s say you have an online shop catering to a general audience. You do a demographic analysis and you find out that most of your customers are male. Naturally, you will want to find out why women are not buying from you. And that’s what qualitative research will help you find out.
In the case of your online shop, qualitative research would involve reaching out to female non-customers through methods such as in-depth interviews or focus groups. These interactions provide a platform for women to express their thoughts, feelings, and concerns regarding your products or brand. Through qualitative analysis, you can uncover valuable insights into factors such as product preferences, user experience, brand perception, and barriers to purchase.
Types of Qualitative Research Methods
Qualitative research methods are designed in a manner that helps reveal the behavior and perception of a target audience regarding a particular topic.
The most frequently used qualitative analysis methods are one-on-one interviews, focus groups, ethnographic research, case study research, record keeping, and qualitative observation.
1. One-on-one interviews
Conducting one-on-one interviews is one of the most common qualitative research methods. One of the advantages of this method is that it provides a great opportunity to gather precise data about what people think and their motivations.
Spending time talking to customers not only helps marketers understand who their clients are, but also helps with customer care: clients love hearing from brands. This strengthens the relationship between a brand and its clients and paves the way for customer testimonials.
- A company might conduct interviews to understand why a product failed to meet sales expectations.
- A researcher might use interviews to gather personal stories about experiences with healthcare.
These interviews can be performed face-to-face or on the phone and usually last between half an hour to over two hours.
When a one-on-one interview is conducted face-to-face, it also gives the marketer the opportunity to read the body language of the respondent and match the responses.
2. Focus groups
Focus groups gather a small number of people to discuss and provide feedback on a particular subject. The ideal size of a focus group is usually between five and eight participants. The size of focus groups should reflect the participants’ familiarity with the topic. For less important topics or when participants have little experience, a group of 10 can be effective. For more critical topics or when participants are more knowledgeable, a smaller group of five to six is preferable for deeper discussions.
The main goal of a focus group is to find answers to the “why”, “what”, and “how” questions. This method is highly effective in exploring people’s feelings and ideas in a social setting, where group dynamics can bring out insights that might not emerge in one-on-one situations.
- A focus group could be used to test reactions to a new product concept.
- Marketers might use focus groups to see how different demographic groups react to an advertising campaign.
One advantage that focus groups have is that the marketer doesn’t necessarily have to interact with the group in person. Nowadays focus groups can be sent as online qualitative surveys on various devices.
Focus groups are an expensive option compared to the other qualitative research methods, which is why they are typically used to explain complex processes.
3. Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research is the most in-depth observational method that studies individuals in their naturally occurring environment.
This method aims at understanding the cultures, challenges, motivations, and settings that occur.
- A study of workplace culture within a tech startup.
- Observational research in a remote village to understand local traditions.
Ethnographic research requires the marketer to adapt to the target audiences’ environments (a different organization, a different city, or even a remote location), which is why geographical constraints can be an issue while collecting data.
This type of research can last from a few days to a few years. It’s challenging and time-consuming and solely depends on the expertise of the marketer to be able to analyze, observe, and infer the data.
4. Case study research
The case study method has grown into a valuable qualitative research method. This type of research method is usually used in education or social sciences. It involves a comprehensive examination of a single instance or event, providing detailed insights into complex issues in real-life contexts.
- Analyzing a single school’s innovative teaching method.
- A detailed study of a patient’s medical treatment over several years.
Case study research may seem difficult to operate, but it’s actually one of the simplest ways of conducting research as it involves a deep dive and thorough understanding of the data collection methods and inferring the data.
5. Record keeping
Record keeping is similar to going to the library: you go over books or any other reference material to collect relevant data. This method uses already existing reliable documents and similar sources of information as a data source.
- Historical research using old newspapers and letters.
- A study on policy changes over the years by examining government records.
This method is useful for constructing a historical context around a research topic or verifying other findings with documented evidence.
6. Qualitative observation
Qualitative observation is a method that uses subjective methodologies to gather systematic information or data. This method deals with the five major sensory organs and their functioning, sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing.
- Sight : Observing the way customers visually interact with product displays in a store to understand their browsing behaviors and preferences.
- Smell : Noting reactions of consumers to different scents in a fragrance shop to study the impact of olfactory elements on product preference.
- Touch : Watching how individuals interact with different materials in a clothing store to assess the importance of texture in fabric selection.
- Taste : Evaluating reactions of participants in a taste test to identify flavor profiles that appeal to different demographic groups.
- Hearing : Documenting responses to changes in background music within a retail environment to determine its effect on shopping behavior and mood.
Below we are also providing real-life examples of qualitative research that demonstrate practical applications across various contexts:
Qualitative Research Real World Examples
Let’s explore some examples of how qualitative research can be applied in different contexts.
1. Online grocery shop with a predominantly male audience
Method used: one-on-one interviews.
Let’s go back to one of the previous examples. You have an online grocery shop. By nature, it addresses a general audience, but after you do a demographic analysis you find out that most of your customers are male.
One good method to determine why women are not buying from you is to hold one-on-one interviews with potential customers in the category.
Interviewing a sample of potential female customers should reveal why they don’t find your store appealing. The reasons could range from not stocking enough products for women to perhaps the store’s emphasis on heavy-duty tools and automotive products, for example. These insights can guide adjustments in inventory and marketing strategies.
2. Software company launching a new product
Method used: focus groups.
Focus groups are great for establishing product-market fit.
Let’s assume you are a software company that wants to launch a new product and you hold a focus group with 12 people. Although getting their feedback regarding users’ experience with the product is a good thing, this sample is too small to define how the entire market will react to your product.
So what you can do instead is holding multiple focus groups in 20 different geographic regions. Each region should be hosting a group of 12 for each market segment; you can even segment your audience based on age. This would be a better way to establish credibility in the feedback you receive.
3. Alan Pushkin’s “God’s Choice: The Total World of a Fundamentalist Christian School”
Method used: ethnographic research.
Moving from a fictional example to a real-life one, let’s analyze Alan Peshkin’s 1986 book “God’s Choice: The Total World of a Fundamentalist Christian School”.
Peshkin studied the culture of Bethany Baptist Academy by interviewing the students, parents, teachers, and members of the community alike, and spending eighteen months observing them to provide a comprehensive and in-depth analysis of Christian schooling as an alternative to public education.
The study highlights the school’s unified purpose, rigorous academic environment, and strong community support while also pointing out its lack of cultural diversity and openness to differing viewpoints. These insights are crucial for understanding how such educational settings operate and what they offer to students.
Even after discovering all this, Peshkin still presented the school in a positive light and stated that public schools have much to learn from such schools.
Peshkin’s in-depth research represents a qualitative study that uses observations and unstructured interviews, without any assumptions or hypotheses. He utilizes descriptive or non-quantifiable data on Bethany Baptist Academy specifically, without attempting to generalize the findings to other Christian schools.
4. Understanding buyers’ trends
Method used: record keeping.
Another way marketers can use quality research is to understand buyers’ trends. To do this, marketers need to look at historical data for both their company and their industry and identify where buyers are purchasing items in higher volumes.
For example, electronics distributors know that the holiday season is a peak market for sales while life insurance agents find that spring and summer wedding months are good seasons for targeting new clients.
5. Determining products/services missing from the market
Conducting your own research isn’t always necessary. If there are significant breakthroughs in your industry, you can use industry data and adapt it to your marketing needs.
The influx of hacking and hijacking of cloud-based information has made Internet security a topic of many industry reports lately. A software company could use these reports to better understand the problems its clients are facing.
As a result, the company can provide solutions prospects already know they need.
Real-time Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) Benchmark Report
See where your business stands compared to 1,000+ e-stores in different industries.
Qualitative Research Approaches
Once the marketer has decided that their research questions will provide data that is qualitative in nature, the next step is to choose the appropriate qualitative approach.
The approach chosen will take into account the purpose of the research, the role of the researcher, the data collected, the method of data analysis , and how the results will be presented. The most common approaches include:
- Narrative : This method focuses on individual life stories to understand personal experiences and journeys. It examines how people structure their stories and the themes within them to explore human existence. For example, a narrative study might look at cancer survivors to understand their resilience and coping strategies.
- Phenomenology : attempts to understand or explain life experiences or phenomena; It aims to reveal the depth of human consciousness and perception, such as by studying the daily lives of those with chronic illnesses.
- Grounded theory : investigates the process, action, or interaction with the goal of developing a theory “grounded” in observations and empirical data.
- Ethnography : describes and interprets an ethnic, cultural, or social group;
- Case study : examines episodic events in a definable framework, develops in-depth analyses of single or multiple cases, and generally explains “how”. An example might be studying a community health program to evaluate its success and impact.
How to Analyze Qualitative Data
Analyzing qualitative data involves interpreting non-numerical data to uncover patterns, themes, and deeper insights. This process is typically more subjective and requires a systematic approach to ensure reliability and validity.
1. Data Collection
Ensure that your data collection methods (e.g., interviews, focus groups, observations) are well-documented and comprehensive. This step is crucial because the quality and depth of the data collected will significantly influence the analysis.
2. Data Preparation
Once collected, the data needs to be organized. Transcribe audio and video recordings, and gather all notes and documents. Ensure that all data is anonymized to protect participant confidentiality where necessary.
3. Familiarization
Immerse yourself in the data by reading through the materials multiple times. This helps you get a general sense of the information and begin identifying patterns or recurring themes.
Develop a coding system to tag data with labels that summarize and account for each piece of information. Codes can be words, phrases, or acronyms that represent how these segments relate to your research questions.
- Descriptive Coding : Summarize the primary topic of the data.
- In Vivo Coding : Use language and terms used by the participants themselves.
- Process Coding : Use gerunds (“-ing” words) to label the processes at play.
- Emotion Coding : Identify and record the emotions conveyed or experienced.
5. Thematic Development
Group codes into themes that represent larger patterns in the data. These themes should relate directly to the research questions and form a coherent narrative about the findings.
6. Interpreting the Data
Interpret the data by constructing a logical narrative. This involves piecing together the themes to explain larger insights about the data. Link the results back to your research objectives and existing literature to bolster your interpretations.
7. Validation
Check the reliability and validity of your findings by reviewing if the interpretations are supported by the data. This may involve revisiting the data multiple times or discussing the findings with colleagues or participants for validation.
8. Reporting
Finally, present the findings in a clear and organized manner. Use direct quotes and detailed descriptions to illustrate the themes and insights. The report should communicate the narrative you’ve built from your data, clearly linking your findings to your research questions.
Limitations of qualitative research
The disadvantages of qualitative research are quite unique. The techniques of the data collector and their own unique observations can alter the information in subtle ways. That being said, these are the qualitative research’s limitations:
1. It’s a time-consuming process
The main drawback of qualitative study is that the process is time-consuming. Another problem is that the interpretations are limited. Personal experience and knowledge influence observations and conclusions.
Thus, qualitative research might take several weeks or months. Also, since this process delves into personal interaction for data collection, discussions often tend to deviate from the main issue to be studied.
2. You can’t verify the results of qualitative research
Because qualitative research is open-ended, participants have more control over the content of the data collected. So the marketer is not able to verify the results objectively against the scenarios stated by the respondents. For example, in a focus group discussing a new product, participants might express their feelings about the design and functionality. However, these opinions are influenced by individual tastes and experiences, making it difficult to ascertain a universally applicable conclusion from these discussions.
3. It’s a labor-intensive approach
Qualitative research requires a labor-intensive analysis process such as categorization, recording, etc. Similarly, qualitative research requires well-experienced marketers to obtain the needed data from a group of respondents.
4. It’s difficult to investigate causality
Qualitative research requires thoughtful planning to ensure the obtained results are accurate. There is no way to analyze qualitative data mathematically. This type of research is based more on opinion and judgment rather than results. Because all qualitative studies are unique they are difficult to replicate.
5. Qualitative research is not statistically representative
Because qualitative research is a perspective-based method of research, the responses given are not measured.
Comparisons can be made and this can lead toward duplication, but for the most part, quantitative data is required for circumstances that need statistical representation and that is not part of the qualitative research process.
While doing a qualitative study, it’s important to cross-reference the data obtained with the quantitative data. By continuously surveying prospects and customers marketers can build a stronger database of useful information.

Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research
Image source
Quantitative and qualitative research are two distinct methodologies used in the field of market research, each offering unique insights and approaches to understanding consumer behavior and preferences.
As we already defined, qualitative analysis seeks to explore the deeper meanings, perceptions, and motivations behind human behavior through non-numerical data. On the other hand, quantitative research focuses on collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and statistical relationships.
Let’s explore their key differences:
Nature of Data:
- Quantitative research : Involves numerical data that can be measured and analyzed statistically.
- Qualitative research : Focuses on non-numerical data, such as words, images, and observations, to capture subjective experiences and meanings.
Research Questions:
- Quantitative research : Typically addresses questions related to “how many,” “how much,” or “to what extent,” aiming to quantify relationships and patterns.
- Qualitative research: Explores questions related to “why” and “how,” aiming to understand the underlying motivations, beliefs, and perceptions of individuals.
Data Collection Methods:
- Quantitative research : Relies on structured surveys, experiments, or observations with predefined variables and measures.
- Qualitative research : Utilizes open-ended interviews, focus groups, participant observations, and textual analysis to gather rich, contextually nuanced data.
Analysis Techniques:
- Quantitative research: Involves statistical analysis to identify correlations, associations, or differences between variables.
- Qualitative research: Employs thematic analysis, coding, and interpretation to uncover patterns, themes, and insights within qualitative data.
Do Conversion Rate Optimization the Right way.
Explore helps you make the most out of your CRO efforts through advanced A/B testing, surveys, advanced segmentation and optimised customer journeys.
If you haven’t subscribed yet to our newsletter, now is your chance!
Like what you’re reading?
Join the informed ecommerce crowd.
We will never bug you with irrelevant info.
By clicking the Button, you confirm that you agree with our Terms and Conditions .
Continue your Conversion Rate Optimization Journey
- Last modified: January 3, 2023
- Conversion Rate Optimization , User Research
Valentin Radu
We’re a team of people that want to empower marketers around the world to create marketing campaigns that matter to consumers in a smart way. Meet us at the intersection of creativity, integrity, and development, and let us show you how to optimize your marketing.
Our Software
- > Book a Demo
- > Partner Program
- > Affiliate Program
- Blog Sitemap
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy & Security
- Cookies Policy
- REVEAL Terms and Conditions
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Grad Med Educ
- v.3(4); 2011 Dec
Qualities of Qualitative Research: Part I
Many important medical education research questions cry out for a qualitative research approach: How do teacher characteristics affect learning? Why do learners choose particular specialties? How is professionalism influenced by experiences, mentors, or the curriculum? The medical paradigm, the “hard” science most often taught in medical schools, usually employs quantitative approaches. 1 As a result, clinicians 5 be less familiar with qualitative research or its applicability to medical education questions. For these why types of questions, qualitative or mixed qualitative and quantitative approaches 5 be more appropriate and helpful. 2 Thus, we wish to encourage submissions to the Journal of Graduate Medical Education that are for qualitative purposes or use qualitative methods.
This editorial is the first in a series of two, and it will provide an introduction to qualitative approaches and compare features of quantitative and qualitative research. The second editorial will review in more detail the approaches for selecting participants, analyzing data, and ensuring rigor and study quality in qualitative research. The aims of the editorials are to enhance readers' understanding of articles using this approach and to encourage more researchers to explore qualitative approaches.
Theory and Methodology
Good research follows from a reasonable starting point, a theoretical concept or perspective. Quantitative research uses a positivist perspective in which evidence is objectively and systematically obtained to prove a causal model or hypothesis; what works is the focus. 3 Alternatively, qualitative approaches focus on how and why something works, to build understanding. 3 In the positivist model, study objects (eg, learners) are independent of the researchers, and knowledge or facts are determined through direct observations. Also, the context in which the observations occur is controlled or assumed to be stable. In contrast, in a qualitative paradigm researchers might interact with the study objects (learners) to collect observations, which are highly context specific. 3
Qualitative research has often been differentiated from quantitative as hypothesis generating rather than hypothesis testing . 4 Qualitative research methods “explore, describe, or generate theory, especially for uncertain and ‘immature’ concepts; sensitive and socially dependent concepts; and complex human intentions and motivations.” 4 In education, qualitative research strives to understand how learning occurs through close study of small numbers of learners and a focus on the individual. It attempts to explain a phenomenon or relationship. Typically, results from qualitative research have been assumed to apply only to the small groups studied, such that generalizability of the results to other populations is not expected. For this reason, qualitative research is considered to be hypothesis generating, although some experts dispute this limitation. 5 table 1 presents a comparison of qualitative and quantitative approaches.
Quantitative Versus Qualitative Research

When Qualitative Studies Make Sense
Qualitative studies are helpful to understand why and how; quantitative studies focus on cause and effect, how much, and numeric correlations. Qualitative approaches are used when the potential answer to a question requires an explanation, not a straightforward yes/no. Generally, qualitative research is concerned with cases rather than variables, and understanding differences rather than calculating the mean of responses. 4 In-depth interviews, focus groups, case studies, and open-ended questions are often employed to find these answers. A qualitative study is concerned with the point of view of the individual under study. 6
For example, the changes in duty hours for residents in 2003 have generated many quantitative research articles, which have counted and correlated the changes in numbers of procedures, patient safety parameters, resident test results, and resident sleep hours. However, to determine why residents still sleep about the same number of hours since 2003, one could start from a qualitative framework in order to understand residents' decisions regarding sleep. Similarly, to understand how residents perceive the influence of resident work hour restrictions on aspects of professionalism, a qualitative study would start with the learners rather than by measuring and correlating scores on professionalism assessments. Because learning takes place in social environments characterized by complex interactions, the quantitative “cause and effect” model is often too simplistic. 7
A variety of ways to collect information are available to researchers, such as observation, field notes, reflexive journals, interviews, focus groups, and analysis of documents and materials; table 2 provides examples of these methods. Interviews and focus groups are usually audiorecorded and transcribed for analysis, whereas observations are recorded in field notes by the observer.
Potential Data Sources for Qualitative Research 8

After data collection, accepted methods are employed to interpret the data. Researchers review the observations and report their impressions in a structured format, with subsequent analysis also standardized. table 3 provides one example of an analysis plan. Strategies to ensure rigor in data collection and trustworthiness of the data and data analysis will be discussed in the second editorial in the series.
Iterative Team Process to Interpret Data 8

In contrast to quantitative methods, subjective responses are critical findings, both in participant responses and observer reactions. The unique or outlier response has value in contributing to understanding the experience of others, and thus individual responses are not lost in the aggregation of findings or in the development of research group consensus. 2 , 4 Qualitative methods acknowledge the “myth of objectivity” between researcher and subjects of study. 7 In fact, the researcher is unlikely to be a purely detached observer.
Ethical Issues
As qualitative researchers usually attempt to study subjects and interactions in their “natural settings,” ethical issues frequently arise. Because of the sensitive nature of some discussions as well as the relationship between researchers and participants, informed consent is often required. The very reason for doing qualitative research—to discover why and how, particularly for thorny topics—can lead to potential exposure of sensitive opinions, feelings, and personal information. Thus, consideration of how to protect participants from harm is essential from the very onset of the study.
Quality Assessment
Qualitative researchers need to show that their findings are credible. As with quantitative approaches, a strong research project starts with a basic review of existing knowledge: a solid literature search. However, in contrast to quantitative approaches, most qualitative paradigms do not look to find a single “truth,” but rather multiple views of a context-specific “reality.” The concepts of validity and reliability originally evolved from the quantitative tradition, and therefore their accepted definitions are considered inadequate for qualitative research. Instead, concepts of precision, credibility, and transferability are key aspects of evaluating a qualitative study. 9
Although some experts find that reliability has little relevance to qualitative studies, others propose the term “dependability” as the analogous metric for this type of research. Dependability is gained though consistency of data, which is evaluated through transparent research steps and research findings. 9 , 10 Trustworthiness and rigor are terms used to establish credible findings. One technique often used to enhance trustworthiness and rigor is triangulation, in which multiple data sources (eg, observation, interviews, and recordings), multiple analytic methods, or multiple researchers are used to study the question. 9 The overall goal is to minimize and understand potential bias while ensuring the researcher's “truthfulness” of interpretation. 9
A potentially helpful appraisal checklist for qualitative studies, developed by Coté and Turgeon, 11 is found in table 4 . This appraisal checklist has not been examined systematically. table 5 includes a list of terms commonly used in qualitative research. Approaches to ensure rigor and trustworthiness in qualitative research will be addressed in greater detail in Part 2.
Sample Quality Appraisal Checklist for Qualitative Studies 11 , a

Commonly Used Terms in Qualitative Research 8

Both quantitative and qualitative approaches have strengths and weaknesses; medical education research will benefit from each type of inquiry. The best approach will depend on the kind of question asked, and the best methods will be those most appropriate to the question. 4 To learn more about this topic, the references below are a useful start, as is talking to colleagues engaged in qualitative research at your institution or in your specialty.
Gail M. Sullivan, MD, MPH, is Editor-in-Chief, Journal of Graduate Medical Education; and Joan Sargeant, PhD, is Professor in the Division of Medical Education, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada.
- Open access
- Published: 27 May 2024
Challenges to the implementation of a multi-level intervention to reduce mistreatment of women during childbirth in Iran: a qualitative study using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research
- Marjan Mirzania 1 ,
- Elham Shakibazadeh 1 ,
- Meghan A. Bohren 2 ,
- Sedigheh Hantoushzadeh 3 ,
- Abdoljavad Khajavi 4 &
- Abbas Rahimi Foroushani 5
Reproductive Health volume 21 , Article number: 70 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Mistreatment during childbirth is a growing concern worldwide, especially in developing countries, such as Iran. In response, we launched a comprehensive implementation research (IR) project to reduce mistreatment during childbirth and enhance positive birth experiences in birth facilities. This study identified the challenges of implementing a multi-level intervention to reduce mistreatment of women during childbirth using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR).
An exploratory qualitative study, involving 30 in-depth interviews, was conducted between July 2022 and February 2023. Participants included a purposive sample of key stakeholders at different levels of the health system (macro: Ministry of Health and Medical Education; meso: universities of medical sciences and health services; and micro: hospitals) with sufficient knowledge, direct experience, and/or collaboration in the implementation of the studied interventions. Interviews were transcribed verbatim and coded using directed qualitative content analysis (CFIR constructs) in MAXQDA 18.
The identified challenges were: (1) individual level (childbirth preparation classes: e.g., adaptability, design quality and packaging, cosmopolitanism; presence of birth companions: e.g., patient needs and resources, structural characteristics, culture); (2) healthcare provider level (integrating respectful maternity care into in-service training: e.g., relative priority, access to knowledge and information, reflecting and evaluating); (3) hospital level (evaluating the performance of maternity healthcare providers: e.g., executing, external policies and incentives); and (4) national health system level (implementation of pain relief during childbirth guidelines: e.g., networks and communications, patient needs and resources, executing, reflecting and evaluating).
Conclusions
This study provides a clear understanding of the challenges of implementing a multi-level intervention to reduce mistreatment of women during childbirth and highlights potential implications for policy makers and practitioners of maternal health programs. We encourage them to take the lessons learned from this study and revise their current programs and policies regarding the quality of maternity care by focusing on the identified challenges.
Plain English summary
Evidence suggests that mistreatment during childbirth is a growing concern worldwide, especially in developing countries, such as Iran. In this qualitative study, through 30 in-depth interviews with key stakeholders at different levels of the health system (macro: Ministry of Health and Medical Education; meso: universities of medical sciences and health services; and micro: hospitals), we identified the challenges of implementing a multi-level intervention to reduce mistreatment of women during childbirth using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR). The data were analyzed using directed content analysis and a deductive approach in MAXQDA 18 software. The identified challenges were: (1) individual level (childbirth preparation classes: e.g., adaptability; presence of birth companions: e.g., patient needs and resources); (2) healthcare provider level (integrating respectful maternity care into in-service training: e.g., relative priority); (3) hospital level (evaluating the performance of maternity healthcare providers: e.g., executing, external policies and incentives); and (4) national health system level (implementation of pain relief childbirth guidelines: e.g., networks and communications). This study provides a clear understanding of the challenges of implementing a multi-level intervention to reduce mistreatment of women during childbirth; and highlights potential implications for policy makers and practitioners of maternal health programs.
Peer Review reports
Despite the recognition of every woman's right to enjoy the highest attainable standard of health, including the right to dignified and respectful care [ 1 ], evidence shows that mistreatment during childbirth is a common experience among women worldwide [ 2 , 3 ]. It is increasingly recognized as an urgent public health priority and a poor quality of care index [ 1 , 4 ], and is a critical determinant of women's decisions regarding place of birth, mode of birth, lactation, mother-child bonding, and childbirth experiences [ 5 , 6 ]. The prevalence of mistreatment among women seeking maternity care varies across different settings, from 43% in Latin America and the Caribbean [ 7 ] to 76.3% in Europe (Germany and the Netherlands) [ 8 ]. The prevalence in Iran is likewise high, reported as 75.7% [ 9 ] and 100% [ 10 ]. Women in Iran have experienced verbal abuse, frequent and painful vaginal examinations, lack of continuity of care, empathy, participation in decision-making, choice of preferred birth position, privacy, and birth companions [ 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 ].
In recent years, some interventions have been developed, implemented, and showed promising results on reducing mistreatment and promoting respectful care for all women [ 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 ]. The Heshima project reported reductions in most forms of disrespect and abuse (D&A) in 13 health facilities in Kenya [ 15 ]. A study by Kujawski et al. (2017) in two hospitals in Tanzania (Staha project) showed a 66% reduction in the odds of women experiencing D&A after the intervention [ 17 ]. Asfa et al.'s (2020) study in Ethiopia showed that the intervention led to an 18% reduction in the number of mistreatment components [ 18 ].
In Iran, the Ministry of Health and Medical Education (MOHME) has developed a list of programs and practices to ensure maternal dignity during childbirth, such as the mother's bill of rights, maternal dignity training package, maternal dignity seminars for maternity healthcare providers (MHCPs) [ 19 , 20 ], and emphasis on respectful maternity care (RMC) in the national guidelines for normal childbirth [ 21 ]. However, these actions did not make effective changes in the maternity quality of care. It seems that the programs implemented by the MOHME were not developed using context- and evidence-based approaches. There were also lacks of precise guidance on their effective implementation. Furthermore, the available research evidence on respectful/disrespectful maternity care in Iran has focused on the prevalence [ 9 , 10 ], development and psychometrics of instruments [ 22 , 23 ], and descriptions of women and healthcare providers’ experiences [ 24 , 25 ], and few interventional studies have been conducted to reduce D&A or promote RMC, including workshops for midwives [ 26 , 27 ]. It seems that healthcare providers training alone is not a sufficient solution [ 28 ]. In response, we launched a comprehensive implementation research (IR) project to reduce mistreatment during childbirth and enhance positive birth experiences in health facilities.
Prior to implementing any evidence-based intervention/innovation (EBI), it is important to identify the factors affecting its implementation in “real-world” settings to increase its adoption, scale-up, and sustainability [ 29 ]. It has been shown that many interventions that were effective in “in-vitro” and controlled conditions or small-scale fail in the real world due to contextual factors that acted against the implementation [ 30 , 31 ]. Implementation science (IS) helps to identify factors that can support or inhibit implementation and to optimize intervention implementation. Therefore, although it is necessary to prove the effectiveness of interventions in trials, this is not sufficient to ensure successful implementation at scale. Therefore, it is necessary to understand why intervention works, how, for whom, and in what settings, and what strategies are needed to improve its implementation [ 32 , 33 ].
In recent years, several models, theories, and implementation frameworks have been developed. The Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) [ 31 ] was developed by combining 19 theories on dissemination, innovation, implementation, organizational change, knowledge translation, and research uptake [ 34 ]. The CFIR is a “determinant framework” that consists of five domains, including the intervention characteristics (key features of an intervention), outer setting (features of the external context such as economic, political, and social environments of the intervention), inner setting (features of the organization such as structural, political, and cultural environments), characteristics of individuals involved (features of implementers such as cultural, organizational, and professional norms), and process of implementation (strategies or tactics that might influence the success of implementation) with 39 constructs/sub-constructs [ 34 , 35 ] (Additional file 1 : CFIR).
Despite attention to intervention studies to promote RMC or prevent mistreatment during childbirth, few studies have examined the implementation process of such interventions, and there is little insight into how the contextual conditions surrounding the implementation of these interventions contribute to their success or failure. To address this gap, we chose a qualitative method to obtain the experiences and perspectives of key stakeholders on the challenges of implementing a multi-level intervention to reduce mistreatment of women during childbirth in Iran using CFIR. Qualitative research methods are appropriate when seeking an in-depth understanding of participants' perspectives.
This qualitative study was part of a larger implementation research project focusing on the development and implementation of a context-specific intervention to reduce disrespectful maternity care and evaluation of strategies to improve implementation. The project was initiated in October 2021 in five public teaching hospitals in Tehran, Iran, and consists of five phases: (1) needs assessment (to assess knowledge, attitudes and practices of maternity healthcare providers about mistreatment of women during labour and childbirth, and the manifestations of mistreatment and its influencing factors), (2) identifying interventions to reduce mistreatment of women during childbirth, (3) identifying the implementation challenges of interventions, (4) designing implementation strategies for the intervention, and (5) testing implementation strategies in a real-life setting. The findings of phase 1 of the project are described elsewhere [ 11 , 36 ].
Identifying interventions to reduce mistreatment of women during childbirth
Based on the findings of phase 1 of the project, we created a logical model of the mistreatment problem based on the PRECEDE health-planning model [ 37 ]. According to the determinants of mistreatment based on the model, multi-level intervention was identified to address mistreatment drivers (Fig. 1 ). In this phase 3 of the project, we selected interventions from each level (individual, healthcare provider, hospital, and national health system) that are currently being implemented in Iran's health system to gain in-depth understanding of the challenges that affect proper implementation. Interventions implemented at each level are presented in Table 1 . This study investigated the implementation challenges of these interventions.
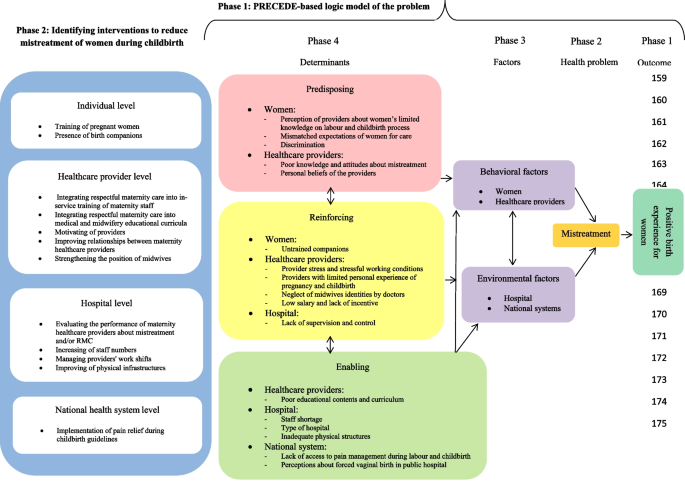
Logic model of the study
Study design and participants
We conducted an exploratory qualitative study consisting of individual in-depth interviews between July 2022 and February 2023 in Tehran, Iran. Participants included key stakeholders at different levels of the health system (including healthcare providers, managers, experts, policy makers, and decision makers) with sufficient knowledge, direct experience, and/or collaboration in the implementation of each of the studied interventions. We selected participants using purposive sampling to obtain diverse perspectives and experiences and then used the snowball method to recruit more participants. We aimed for maximum variation among participants according to age, education, organizational role, and work experience. Key stakeholders were selected from three levels: macro (Ministry of Health and Medical Education (MOHME): four participants), meso (universities of medical sciences and health services: 12 participants), and micro (hospitals: 14 participants). These individuals were invited to participate by phone calls and/or in-person. The eligibility criteria for this study were familiarity and/or executive responsibility in any of the studied interventions and having at least five years of work experience.
Data collection
We developed the initial semi-structured interview guide based on sample interviews at http://cfirguide.org [ 42 ]. Damschroder et al. (2009) recommend that researchers try to select constructs from CFIR that are most related to their study setting [ 34 ]. Therefore, the interview guide was revised using study-related constructs (Additional file 2 : interview guide). We then pilot-tested this by conducting two initial interviews, which were not analyzed. Interviews were conducted in Persian by the lead author (M.M.), a female PhD candidate in Health Education and Promotion with previous experience in qualitative studies who had no prior interactions with the participants. To prepare participants for the interview, interview guide questions were sent to them in advance via email. Additionally, at the beginning of the interviews, the purpose of the study, guarantee of confidentiality and anonymity of information, nature of voluntary participation, and the possibility of withdrawing from the study at any time were explained to the participants. All participants provided written informed consent and permission for audio recordings. The interviews were conducted in participants' workplaces (in a private room) and during their preferred accommodation. The duration of the interviews ranged from 40 to 60 min, during which the interviewer made field notes. The demographic characteristics of the participants (including age, gender, education, organizational role, and number of years of work experience) were recorded at the end of each interview. The interviews continued until data saturation was reached. Saturation was obtained after the 28th interview; however, to ensure that no new information emerged, data collection continued until the 30th interview. All the invited individuals participated in the interviews, and no repeat interviews were conducted.
Data analysis
Data analysis was conducted simultaneously with data collection, using directed content analysis [ 43 ] and a deductive approach. After each interview, M.M. listened to the recorded audios several times, transcribed verbatim in Persian, and returned to the participants for comments and/or corrections. E.Sh. (female professor in Health Education and Promotion; an experienced qualitative researcher) checked the transcripts for accuracy and consistency. Prior to coding the data, a categorization matrix was developed based on the interview guide (i.e., CFIR constructs). Next, two authors (M.M. and E.Sh.) independently analyzed the data. We marked and color-coded the significant segments of the text. We put those color-coded text segments together and gave codes. We categorized the codes according to their differences and similarities, and linked them to pre-specified categorizations in sub-themes and themes. If disagreements arose in coding, the authors discussed until consensus was reached. The MAXQDA 18 software was used to manage the data [ 44 ]. We translated selected quotes into English to support the themes developed throughout the analysis.
The trustworthiness of this study was tested based on the four criteria of Lincoln and Guba [ 45 ]. The credibility of the data was ensured through prolonged engagement with the data, applying a sampling technique with maximum variation, multiple data sources (including field notes, audio recordings, and transcripts), and providing initial codes to the three participants for approval. To enhance the transferability of the data, we conducted interviews with participants who had the most experience and knowledge of each of the studied interventions. Furthermore, dependability was obtained by analyzing the data separately by the two members of the research team. To assess confirmability, a qualitative research specialist, who did not participate in this study, confirmed the data analysis process. This paper was reported in accordance with the consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ) checklist [ 46 ] (Additional file 3 : COREQ Checklist).
Characteristics of participants
Thirty in-depth interviews were conducted with the key stakeholders. The mean age of the participants was 49.5 years (range: 35-65 years). Most participants (73.4%) held an MD or PhD degree. Four participants worked in MOHME, 12 in medical universities, and 14 in hospitals; more than half had over 20 years of work experience (Table 2 ).
The identified challenges
The challenges of implementing each intervention (currently implemented in the system) were identified and categorized using the domains and constructs/sub-constructs of the CFIR (Table 3 ).
Individual-level interventions
At the individual level, two interventions were listed according to the determinants of mistreatment based on the model: childbirth preparation classes and the presence of birth companions (Fig. 1 ). Both interventions are implemented in the system; however, there were serious challenges in the settings, as outline below.
Training of pregnant women about the process of labour and childbirth, respectful care and their rights during childbirth
In our study, participants shared opinions about the challenges of implementing childbirth preparation classes in five CFIR domains (intervention characteristics, outer setting, inner setting, characteristics of individuals involved, and process of implementation).
Intervention characteristics
Adaptability.
The level of adaptability of the intervention (childbirth preparation classes) was described as a key barrier to its implementation by most participants. They believed that non-compliance of the conditions and facilities of maternity hospitals with the educational content of the classes, improper timing of the start of classes (from the 20th week of pregnancy), and poor announcements can weaken the implementation of the intervention. The participants suggested that for effective childbirth preparation classes, the situations of facilities of maternity hospitals can be tailored and refined according to the educational content of the classes. Additionally, classes should be held in the early phases of pregnancy and widely announced.
“The training that women receive in classes is different from that implemented in maternity hospitals. For example, we teach that they can move during labour, take their preferred position during childbirth, and have a chosen companion. However, in practice, this has not been implemented in maternity hospitals ...” (Reproductive Health Specialist, University level) “Announcing about childbirth preparation classes in hospitals and health centers is poor. Only 18% of the pregnant women participated in classes. We did not announce them correctly…” (Health Policy Specialist, MOHME level)
Design quality and packaging
Weakness in the design quality and packaging of childbirth preparation classes prevent their successful implementation. Some participants (obstetricians) reported a lack of a multidisciplinary team in holding classes as a barrier to implementation. They believed that classes should be managed by a team and should not be exclusive to midwives. However, the midwives stated that the content of the classes was such that it could be handled by them, but the presence of a psychologist in some sessions could play an important role in the success of the classes.
“We must accept that midwives cannot cover all sessions. Psychologists, nutritionists, and obstetricians can be used in these classes.” (Obstetrician, Hospital level)
Outer setting
Patient needs and resources.
Lack of training about RMC was also considered a fundamental factor. Most participants highlighted that women do not understand respectful care principles and their rights during childbirth, and this should be integrated into the content of childbirth preparation classes.
“… They should be aware of their rights during childbirth. This should be integrated into the content of the childbirth preparation classes.” (Obstetrician, MOHME level)
Cosmopolitanism
A crucial factor affecting childbirth preparation class implementation was the poor collaboration of the private sector to hold classes. Participants reported that since most pregnant women receive their care from the private sector (obstetricians and/or midwives' offices), there is a need to establish efficient mechanisms for more support and collaboration of these sectors in holding classes.
“Participation of the private sector is essential because 70% of pregnant women receive their care from obstetricians and midwives.” (Midwife, University level)
Inner setting
Organizational incentives and rewards.
A few participants expressed concerns about the poor implementation of childbirth preparation classes following the low participation of pregnant women in classes. They believed that setting enough incentives could affect women’s degree of engagement and commitment to participate in classes.
“Between 9-10% of pregnant women attend our classes (health centers), and this rate is very low ... If incentives are provided, they are more motivated to participate.” (Reproductive Health Specialist, University level)
Available resources
Participants reported that poor physical environment and staff shortages were barriers to implementing childbirth preparation classes.
“In some hospitals, there is no standard space to hold classes, especially in private hospitals.” (Midwife, Hospital level) “Dedicated instructors should be considered in these classes. Here, they appoint one person as an instructor, and at the same time, she has to work shifts in the maternity hospital because they do not have staff.” (Midwife, Hospital level)
Characteristics of individuals involved
Other personal attributes.
Instructors’ skill and interest was another challenge that was highlighted by some participants: “Unfortunately, some of our midwives (as instructors of classes) are rarely interested in training or do not have enough skills …” (Reproductive Health Specialist, Hospital level)
Process of implementation
Poor execution of childbirth preparation classes, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, was an important challenge discussed by participants. They also believed that focusing on quantity and neglecting the quality of the classes made them not have the proper efficiency, and their goal was rarely reached: “The classes are implemented, but they are not implemented according to plan and properly ... Unfortunately, we focused on the quantity of the classes, for example, the forms we have to complete and the statistics we have to give to the MOHME.” (Reproductive Health Specialist, University level)
Reflecting and evaluating
Supervising implementation and continuous evaluation were crucial factors emphasized by the participants. They acknowledged that the MOHME should supervise the implementation of childbirth preparation classes in hospitals and health centers through regular inspections. In addition, evaluate the progress and quality of their implementation through an external evaluation.
“I think the biggest challenge of childbirth preparation classes is that there is no supervision of their implementation … There should be a monitoring and auditing system.” (Reproductive Health Specialist, MOHME level)
Presence of birth companions
In this study, the challenges of implementing birth companions in four CFIR domains (outer setting, inner setting, characteristics of individuals involved, and process of implementation) were discussed by the participants.
According to the participants, the lack of knowledge of companions could be a barrier to their attendance at maternity hospitals. Some participants believed that a person going to be a birth companion should be required to participate in childbirth preparation classes and receive training:
“Companions have limited knowledge. I think birth companions should be required to participate in childbirth preparation classes because those who are trained in these classes are helpful to both labouring women and us providers.” (Reproductive Health Specialist, Hospital level)
Structural characteristics
The lack of physical space in some maternity hospitals was another factor that some participants stated: “Some of our maternity hospitals do not have a standard structure, for example, Hospital X, which is a hall with 12 beds and set up some extra beds because of the high visits, so there will be no place for the presence of a birth companion.” (Health Policy Specialist, MOHME level)
The participants also reported cultural issues as barriers to the implementation of birth companions. They noted that most of the time, if the companion is a partner, due to the feminine environment of maternity hospitals and female providers’ unwillingness to be accompanied by men in the delivery room; they are not allowed to be accompanied.
“The companion is not allowed to enter the maternity hospital; why? Because my colleague (midwife or doctor) does not like a man to be in the labour room, she says, 'No, sir, you go out and let a woman come.” (Reproductive Health Specialist, MOHME level)
Compatibility
One potential barrier to implementation was concern about the compatibility of the presence of birth companions with the existing workflows of maternity staff. The participants agreed that the interference of birth companions in the clinical duties of staff was a major factor for not allowing a companion.
“As a midwife who worked in a maternity hospital for several years and was strongly against the presence of birth companions, I say that our main challenge was the interference of companions. For example, when a labouring woman's serum runs out, the companion comes many times and warns …” (Midwife, University level)
Some participants believed that the unwillingness of staff was an important barrier. They mentioned that staff prevents the presence of birth companions because of the perception that the companion is witnessing their performance as an advocate for the woman, which may cause them to expect more attention to labouring women.
“The companion is like an advocate; it is like a hidden camera. Why do some staff members not like companions to enter maternity hospitals? This is because it controls their performance …” (Obstetrician, Hospital level)
Another factor was related to lack of supervision. The participants highlighted the need for continuous supervision of the implementation of birth companion guidelines in hospitals: “The presence of birth companions has a guideline that has been communicated to all hospitals, but in many hospitals, especially public hospitals, it is not implemented because it is not supervising ...” (Obstetrician, University level)
Healthcare provider-level intervention
At this level, five interventions were listed according to the determinants of mistreatment based on the model (Fig. 1 ). However, one of them (integrating RMC into the in-service training of maternity staff) is implemented in the system. The challenges of this intervention were identified as follows:
Integrating RMC into in-service training of maternity staff
Participants in this study reported intervention implementation challenges in the four CFIR domains (outer setting, inner setting, characteristics of individuals involved, and process of implementation).
External policies and incentives
Regulations and guidelines related to in-service training of staff affect the quality and efficiency of courses. Weakness in some regulations and guidelines has caused staff to be given a quantitative view, which means that many of them participate in the training course to obtain a certificate, rather than improve their knowledge, skills, and behavior, and/or increase the organization's productivity.
“… Unfortunately, our regulations and guidelines are quantitative; that is, they dictate that if a person spends X hours in a year, it will be included in his/her evaluation and career promotion. Therefore, staff members only participate in courses to complete their duty hours and obtain a certificate.” (Midwife, University level)
Relative priority
Obtaining a license to hold an in-service training course was one of the challenges mentioned by some of the participants. They expressed the belief that the necessity of holding a respectful care training course should be clarified in the steering committee of training and empowerment of human resources in such a way that the course is included in the specialized and mandatory training of employees, not general and optional; thus, it is effective in their career development and they have sufficient motivation to participate in the course.
“One of the challenges is to obtain a license to hold the course. You must justify the necessity of holding a respectful care training course in such a way that the course is included in the job description of the maternity staff.” (Public Health- related manager, University level)
Allocation of an insufficient budget for staff training was an important challenge reported by some participants. They found that staff participation in training courses required more financial support: “Unfortunately, the investment in training staff is very low. The per capita education budget for healthcare staff training this year is 800,000 Iranian rials (IRR), is very small.” (Public Health- related manager, MOHME level)
Similarly, the lack of experienced instructors is considered a challenge. When the instructor of an in-service training course does not have specialized knowledge and teaching ability, the course does not have the necessary efficiency and is not welcomed.
Access to knowledge and information
The participants also believed that informing the staff about the value and importance of the training course played an important role in its successful implementation. They highlighted that information and materials about the importance of RMC should already be provided to the maternity staff. A participant said: “First, it clarifies the importance of respectful care training for the maternity staff. They need to know how much their behavior with labouring women can affect their mental health status as well as their decisions for future pregnancies.” (Health Services Management Specialist, University level)
Knowledge and beliefs about the intervention
Managers do not believe in in-service training for staff, and lack of support for them has caused the need for this training to not be included in the organization's plans and priorities.
“Some managers do not support participation in training courses, and they do not believe that these courses have many benefits for the individual and organization.” (Public Health- related manager, University level)
Another major challenge was the weakness of evaluating the effectiveness of the training courses. The participants acknowledged that, although the evaluation of the effectiveness of courses is done using Kirkpatrick's model [ 47 ], it is often incomplete or limited to the first two levels of this model, and the third and fourth levels are not done because of problems and complexity.
“... Our current evaluation method is flawed, and we do not evaluate almost any of our courses at the level of behavior; therefore, we cannot be sure if the person who participated in the course acquired the expected capabilities.” (Reproductive Health Specialist, University level)
Hospital-level intervention
At the hospital level, four interventions were listed based on the model (Fig. 1 ). Of these, the evaluation of the performance of MHCPs is implemented in the system. The identified challenges for this intervention were as follows:
Evaluating the performance of MHCPs about mistreatment and/or RMC
In our study, participants discussed the intervention implementation challenges in two CFIR domains (outer setting and process of implementation).
Some participants complained of weakness in laws and regulations. They stated that to supervise the performance of MHCPs in laws and regulations (including the Support of Family and Youth Population Act), the merit pay of providers dependent on the satisfaction of pregnant women is defined. However, they are not included in the payment systems of all MHCPs. Furthermore, participants expressed concern that these laws (such as reducing merit pay or warnings) were not very effective in supervising the performance of the providers.
“Currently, in the Support of Family and Youth Population Act, merit pay of the providers depends on the satisfaction of pregnant women, but unfortunately not for all providers (including obstetricians or residents). We are pursuing this to be modified.” (Health Policy Specialist, MOHME level)
Poor execution of the intervention (mother’s satisfaction questionnaire) was considered important. Participants stated that, although all hospitals were required to implement and provide feedback to the MOHME, the providers often completed the questionnaire. To solve this problem, an electronic satisfaction questionnaire is currently being designed, whose links will be sent to women, and their satisfaction reports will be registered in the Ministry of Health's portal. However, owing to the poor support of the Information Technology (IT) unit, it has not yet been implemented.
“… Unfortunately, the questionnaires were completed by the providers, without the mother being informed. Currently, an electronic questionnaire is designed, the report of which will be registered in the Ministry of Health's portal, but it has not yet been implemented.” (Reproductive Health Specialist, Hospital level)
National health system-level intervention
At the national health system level, the implementation of pain relief during childbirth guidelines was listed based on the model (Fig. 1 ). This intervention is implemented in the system, and its challenges were as follows:
Implementation of pain relief during childbirth guidelines
In this study, the participants identified implementation challenges in the four CFIR domains (outer setting, inner setting, characteristics of individuals involved, and process of implementation).
Participants mentioned the lack of knowledge of pregnant women as an important challenge in implementing pain relief during childbirth. They believed that most women are unaware of the option of pain relief during childbirth. Pregnancy is an important time to inform and prepare women about pain relief options during childbirth; however, women are unaware of this right and do not demand it.
“… Pregnant women do not have sufficient information regarding pain relief during childbirth … so they do not demand ... Information about this should be provided during pregnancy (for example, in childbirth preparation classes), but when labouring women come to the maternity hospital, we have to go and explain … I think that this is not the right time for training.” (Anesthesiologist, Hospital level)
Some participants also pointed out that a large number of their clients are Afghan women who refuse pain relief, because they do not have insurance coverage and would be required to pay out-of-pocket.
“... Most of our clients are Afghan women. They do not have insurance and have to pay for it. Therefore, they do not do (pain relief during childbirth).” (Obstetrician, Hospital level)
The presence of good networking and relationships with external organizations, such as insurance organizations, to modify pain relief during childbirth tariffs and motivate staff was described by participants as an effective factor in implementation.
“The support of insurance organizations is also crucial for the implementation of pain relief during childbirth; tariffs should be revised, but unfortunately, they do not collaborate.” (Obstetrician, MOHME level)
MOHME policies and support were critical for the successful implementation of pain relief during childbirth. Some participants believed that being free of charge for pain relief during childbirth in public hospitals was one of the factors facilitating its implementation. However, the participants reported that some measures of the MOHME, including the absence of on-call anesthesiologists in hospitals were another challenge for the implementation of the program.
“... The hospital should have an on-call anesthetist, which unfortunately the MOHME took it away ... Therefore; we do not have the possibility of pain relief during childbirth at night because we there is not have an on-call anesthesiologist. There is an aesthesia resident, but it is normal that she/he does not spend X hours on pain relief during childbirth and quickly performs a caesarean section.” (Obstetrician, Hospital level)
Networks and communications
Poor working relationships between obstetricians and anesthesiologists were key barriers. Some participants believed that obstetricians are the primary decision-makers for pain relief during childbirth, and if they approve, labouring woman will be referred to anesthesiologists, but unfortunately, they do not collaborate enough in this regard. A participant stated:
“Obstetricians should select labouring women based on the criteria and then refer to them. Unfortunately, they do not collaborate with us …” (Anesthesiologist, Hospital level)
The availability of resources during the implementation process was critical for success. The participants complained about the low tariff allocated to pain relief during childbirth and considered it a fundamental barrier to non-collaboration of anesthesiologists in the implementation of the program. Furthermore, the lack of staff (anesthesiologists and nurse anesthetists) to offer top-ups and continuous monitoring adds to this factor.
“Pain relief during childbirth is a time-consuming process, but the tariff is so low that the anesthesiologist does not want to perform it. However, there is a shortage of anesthesiologists and nurse anesthetists in most hospitals.” (Anesthesiologist, Hospital level)
Similarly, limited access to knowledge and information about pain relief during childbirth for the provider team was considered another challenge. The participants identified a lack of adequate training for providers prior to implementing the program as a contributing factor.
“Prior to the implementation of this program (pain relief during childbirth), sufficient training should have been provided to all team members (including anesthesiologists, obstetricians, and midwifes), and the purpose and importance of the program were well introduced. We were not justified at all as to why we wanted to do this program ...” (Obstetrician, Hospital level)
Another challenge was the lack of knowledge and misconceptions of providers (obstetricians and midwives) regarding pain relief during childbirth. For example, it is believed that pain relief during childbirth is associated with an increased risk of prolonged labour, poor maternal and infant outcomes, and an increased chance of cesarean section. The participants believed that there was a serious need to spread awareness and cultivate a positive attitude among providers about the benefits of pain relief during childbirth and eliminate misconceptions by holding training courses.
“I think the most important challenge is misconceptions. Still, many obstetricians do not agree with pain relief during childbirth; it is believed that it prolongs the labour process or may have complications for the mother and/or the infant; all this is due to lack of knowledge. This belief needs to be corrected.” (Anesthesiologist, Hospital level)
According to most participants, the lack of expertise and skills of anesthesiologists was another barrier to implementation. They acknowledged that pain relief during childbirth is one of the important abilities that anesthesia residents should acquire, which has not been considered in their educational curriculum. Anesthesiology residents spend a short period of one month in the maternity ward, so they do not acquire enough skills.
“Pain relief during childbirth requires expertise and skill ... However, it has not been considered an important topic in the educational curriculum of anesthesiologists.” (Midwife, University level)
Some participants felt that pain relief during childbirth had not been implemented according to the implementation plan. They emphasized the identification of program problems and the importance of proper planning: “At first, the process of pain relief during childbirth in our hospitals was increasing; for example, in our hospital, we had about 500 pain relief during childbirths per month, but currently we do not have four ... We were weak in execution; we have implemented the program since 2014, but unfortunately, I can say that we have been unsuccessful thus far.” (Anesthesiologist, Hospital level)
In addition, supervising the implementation of pain relief during childbirth in hospitals was another factor mentioned by some participants. They stated that internal and external inspections should be used to supervise the performance of the team in providing pain relief during childbirth.
“There must be supervision ... If it is not done (pain relief during childbirth), it is not supervised that why was it not done? The mother did not request or you (providers) did not?” (Health Education and Promotion Specialist, University level)
In this study, using the CFIR, we identified perspectives of key stakeholders from different levels of the health system regarding the challenges of implementing a multi-level intervention to reduce mistreatment of women during childbirth in Iran. Overall, the findings showed that through the lens of CFIR domains (intervention characteristics, outer setting, inner setting, characteristics of individuals involved, and process of implementation), there are several challenges to successfully implementing current interventions. Documenting the findings of such studies can help formulate appropriate strategies to improve the implementation of interventions to reduce mistreatment during childbirth as well as the development of high-quality maternity care guidelines in similar settings.
In our study, the most identified challenges to successfully implementing the interventions were related to the outer- and inner-setting domains. The key role of the outer setting [ 48 , 49 ] and inner setting [ 50 ], which emphasize the external influences on the intervention and characteristics of the implementing organization, has been highlighted in other studies for successful implementation. Our findings showed that all proposed interventions were influenced by factors from the outer setting. Patients’ needs and resources could challenge the implementation of childbirth preparation classes, birth companionship, and pain relief during childbirth. Participants reported that women were not trained in childbirth preparation classes about respectful care principles and their rights during childbirth, birth companions were not trained, and most women were unaware of pain relief during childbirth. Previous studies are in agreement with our findings and reflect the need for respectful care education for women [ 51 , 52 ], the presence of a trained birth companion [ 25 , 53 ], and training programs to increase women's awareness of pain relief options during childbirth [ 54 ]. In this study, poor collaboration with external organizations was also identified as a barrier to the implementation of childbirth preparation classes and pain relief during childbirth. The Heshima project in Kenya showed that participatory design of interventions at the policy, facility, and community levels played a significant role in the public acceptance of maternity care and health rights; therefore, the successful implementation and sustainability of the RMC intervention requires the formation of partnerships with external organizations [ 55 ]. Furthermore, our findings showed that external policies (including weakness in regulations and guidelines) challenge the implementation of interventions (including integrating RMC into in-service training, evaluating the performance of MHCPs, and pain relief during childbirth). Similar to our findings, Warren et al. (2017) reported that the free maternity care policy in Kenya affected the quality of care by increasing the demand for health facilities, delays in financing, augmented provider workloads and shortages, and posed challenges to the implementation of RMC [ 55 ]. In another study (2021), the existing policy in the West Bank to prevent the presence of birth companions in public facilities was reported by participants as a factor for mistreatment during childbirth [ 56 ].
Inner setting factors that affected the implementation of interventions were structural characteristics, networks and communications, culture, compatibility, relative priority, organizational incentives and rewards, and readiness for implementation (available resources and access to knowledge and information). Participants acknowledged that structural characteristics (including a lack of physical space), cultural issues, and incompatibility can act as barriers to birth companion intervention. Studies support the findings of our study that the limitations of the physical structure of hospitals make it difficult to allow birth companions [ 28 , 57 ]. In addition, in our study, as in some cultures, the presence of male partners was not socially acceptable, especially during childbirth [ 58 ], and there were concerns about the interference of birth companions in healthcare providers’ medical decisions [ 58 ]. Moreover, in this study, participants stressed the importance of holding a respectful care training course for providers. Healthcare providers have been shown to have a negative attitude toward respectful care [ 59 ], which is often less important than other aspects of care [ 60 ]. Poor working relationships between providers were another factor affecting implementation. Similarly, poor teamwork among obstetricians, midwives, and anesthesiologists was highlighted as an important barrier to implementing labour analgesia in Wu et al.'s study [ 61 ]. Moreover, in our study, lack of resources (including physical space, human resources, money, and training) was described as a potential barrier to readiness for implementation. In addition, limited access to knowledge and information about the intervention was another barrier to readiness for implementation. Our findings are consistent with previous studies that have examined how inner setting characteristics such as readiness for implementation [ 55 ] and organizational rewards and incentives [ 62 ] influence implementation.
The intervention characteristics domain, which emphasizes the importance of the need to adapt the intervention to enhance its fit with the context [ 63 ], is a critical determinant of the success of implementation [ 34 , 64 , 65 ]. In our study, adaptability and design quality and packaging were seen as important factors in the implementation of childbirth preparation classes. The findings showed that the situations of facilities of maternity hospitals do not adapt the content of the classes, the timing of the start of the classes are not appropriate, and they are not announced correctly. Previous studies have assessed the factors influencing childbirth preparation classes; for example, a study conducted by Otogara (2017) reported the need for the presence of a psychologist consultant as well as appropriate timing and information for successful implementation of classes [ 66 ].
The domain of the characteristics of individuals involved in the intervention is also crucial to ensure the success of implementation [ 34 ]. Our findings showed that the personal attributes of individuals within the organization (such as interest, skills, and expertise), as well as their knowledge and beliefs about the intervention, are other key factors that can hinder implementation. Other studies have similarly shown that competent, skilled, and motivated service providers are important for RMC provision [ 67 ]. Moreover, providers' knowledge and understanding of RMC are reported to be important in designing interventions to address mistreatment in maternity care [ 68 ]. In Mexico, training and enabling healthcare providers to promote respectful delivery care have been noted [ 69 ].
In our study, the implementation process domain was identified as a key factor in the implementation of all the studied interventions. Participants noted suboptimal execution, lack of supervision, and weakness in evaluating posed challenges for implementing interventions. Previous studies have revealed the key role of monitoring and evaluation interventions in the success of RMC implementation [ 15 , 70 ]. This was implemented in the Hashima project by applying mechanisms to report cases of disrespect, such as customer service desks, suggestion boxes and supervisory visits at the facility level [ 15 ].
Overall, our study has potential implications for practice and research. This study highlights practical benefits for policy makers and practitioners of maternal health programs in Iran and other contexts. We suggest that they consider the findings of this study when implementing their current programs and policies regarding the quality of maternity care. Moreover, intervention studies focusing on RMC and/or mistreatment during childbirth appear to be relatively limited in high-income countries (HICs), and research and implementation efforts in these settings must continue. The implementation process of these interventions has been inadequately explored, thus affecting their comparability. Using the CFIR, this study provides important insights into how the contextual conditions surrounding the implementation of multi-level interventions to reduce mistreatment during childbirth contribute to their success or failure. Therefore, the findings of this study can provide evidence for formulating effective strategies with the potential to increase the positive experiences of childbirth for women.
Strengths and limitations
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to identify the challenges of implementing a multi-level intervention to reduce mistreatment of women during childbirth in Iran and provides important insights into the contextual conditions around the implementation of each of the interventions. Our findings can be useful for other developing countries (LMICs) in similar contexts, especially those in the Eastern Mediterranean region. Reflecting the perspectives of key stakeholders from the micro- to macro-level of the health system was another strength of our study. Furthermore, the use of CFIR as the most common framework in IS allowed us to comprehensively identify the effective factors in the implementation of each intervention. However, given that the interviews were conducted with key stakeholders involved in the interventions, there is a possibility of a social desirability bias (underreporting of actual experiences and challenges due to their roles). We tried to mitigate this limitation by guaranteeing the confidentiality and anonymity of information as well as, conducting interviews in a private room. Also, this study focused on the interventions that are currently implemented in Iran's health system; and further research is needed to explore the implementation challenges of other interventions intended to reduce mistreatment during childbirth.
Our findings revealed potential challenges for implementing a multi-level intervention to reduce mistreatment of women during childbirth in the domains of intervention characteristics, outer setting, inner setting, characteristics of individuals involved, and process of implementation of the CFIR. Addressing these challenges is necessary to improve the implementation of interventions to reduce mistreatment during childbirth in Iran.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to privacy restrictions of the participants but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Disrespect and Abuse
Respectful Maternity Care
Evidence-Based Intervention/Innovation
Implementation Science
Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research
Ministry of Health and Medical Education
Maternity Healthcare Providers
Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research
Iranian Rials
Information Technology
High-Income Countries
Low and Middle Income Countries
World Health Organization. WHO Statement: The Prevention and Elimination of Disrespect and Abuse During Facility-based Childbirth: Geneva: World Health Organization; 2014.
Shemelis D, Gelagay AA, Boke MM. Prevalence and risk factor for mistreatment in childbirth: In health facilities of Gondar city Ethiopia. Plos One. 2022;17:e0268014. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268014 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Tello HJ, Téllez DJ, Gonzales JE. Identifying obstetric mistreatment experiences in US birth narratives: Application of internationally informed mistreatment typologies. MCN Am J Maternal/Child Nurs. 2022;47:138–46.
Article Google Scholar
Sando D, Ratcliffe H, McDonald K, Spiegelman D, Lyatuu G, Mwanyika-Sando M, Emil F, Wegner MN, Chalamilla G, Langer A. The prevalence of disrespect and abuse during facility-based childbirth in urban Tanzania. BMC Pregn Childb. 2016;16:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-016-1019-4 .
Hajizadeh K, Vaezi M, Meedya S. Mohammad Alizadeh Charandabi S, Mirghafourvand M: Respectful maternity care and its related factors in maternal units of public and private hospitals in Tabriz: a sequential explanatory mixed method study protocol. Reprod Health. 2020;17:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-020-0863-x .
Padmanaban S, Udayakumar JR, Sironmani V. Respectful maternity care initiative-beneficiaries interview-in KMC hospital Chennai. Int J Clinical Obstet Gynaecol. 2021;5:214–7.
Tobasía-Hege C, Pinart M, Madeira S, Guedes A, Reveiz L, Valdez-Santiago R, Pileggi V, Arenas-Monreal L, Rojas-Carmona A, Piña-Pozas M. Irrespeto y maltrato durante el parto y el aborto en América Latina: revisión sistemática y metaanálisis. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2019;43:e36. https://doi.org/10.26633/RPSP.2019.36 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Reuther ML. Prevalence of Obstetric Violence in Europe: Exploring Associations with trust, and care-Seeking Intention. Bachelor's thesis, University of Twente. 2021.
Hajizadeh K, Vaezi M, Meedya S, Mohammad AlizadehCharandabi S, Mirghafourvand M. Prevalence and predictors of perceived disrespectful maternity care in postpartum Iranian women: a cross-sectional study. BMC Pregn Childb. 2020;20:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-020-03124-2 .
Shakibazadeh E, Taherkhani F, Yekaninejad MS, Shojaeizadeh D, Tajvar M. Prevalence of disrespectful maternity care in hospitals affiliated with TUMS and its associated factors. HAYAT. 2021;27:262–77.
Google Scholar
Mirzania M, Shakibazadeh E, Bohren MA, Hantoushzadeh S, Babaey F, Khajavi A, Foroushani AR. Mistreatment of women during childbirth and its influencing factors in public maternity hospitals in Tehran, Iran: a multi-stakeholder qualitative study. Reprod Health. 2023;20:79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-023-01620-0 .
Gholipour R, Shahoei R, Ghader Khani G. The quality of midwifery care from the perspective of healthcare service recipients using the SERVQUAL model in Sanandaj comprehensive health centers in 2018. J Clin Nurs Midw. 2019;8:337–46.
Mirlohi V, Ehsanpour S, Kohan S. Health providers’ compliance with pregnant women’s Bill of Rights in labor and delivery in Iran. Iran J Nurs Midw Res. 2015;20:565–9. https://doi.org/10.4103/1735-9066.164503 .
Tabrizi JS, Askari S, Fardiazar Z, Koshavar H, Gholipour K. Service quality of delivered care from the perception of women with caesarean section and normal delivery. Health Promot Perspect. 2014;4:137–43. https://doi.org/10.5681/hpp.2014.018 .
Abuya T, Ndwiga C, Ritter J, Kanya L, Bellows B, Binkin N, Warren CE. The effect of a multi-component intervention on disrespect and abuse during childbirth in Kenya. BMC Pregn Childb. 2015;15:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-015-0645-6 .
Ratcliffe HL, Sando D, Lyatuu GW, Emil F, Mwanyika-Sando M, Chalamilla G, Langer A, McDonald KP. Mitigating disrespect and abuse during childbirth in Tanzania: an exploratory study of the effects of two facility-based interventions in a large public hospital. Reprod Health. 2016;13:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-016-0187-z .
Kujawski SA, Freedman LP, Ramsey K, Mbaruku G, Mbuyita S, Moyo W, Kruk ME. Community and health system intervention to reduce disrespect and abuse during childbirth in Tanga region, Tanzania: a comparative before-and-after study. Plos Med. 2017;14:e1002341. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002341 .
Asefa A, Morgan A, Gebremedhin S, Tekle E, Abebe S, Magge H, Kermode M. Mitigating the mistreatment of childbearing women: evaluation of respectful maternity care intervention in Ethiopian hospitals. BMJ Open. 2020;10:e038871. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-038871 .
Safaee M, Golmakani N, Abedian Z. Respect to the bill of mothers rights in labor and delivery by midwife responsible for delivery through 360° evaluation in training maternities affiliated to Mashhad University of medical science in 2014. Iran J Obstetr Gynecol Infertil. 2017;20:43–51. https://doi.org/10.22038/IJOGI.2017.8623 .
Vosogh Moghadam A, Rostamina Goran N, Babaey F, Turkestani F, Mazaheripour Z. Promoting normal childbirth with the focus on maternal dignity. Islamic Republic of Iran, Tehran: Ministry of Health and Medical Education; 2017.
Ministry of Health and Medical Education. National guidelines for normal delivery. Islamic Republic of Iran, Tehran: Ministry of Health and Medical Education; 2019.
Hajizadeh K, AsghariJafarabadi M, Vaezi M, Meedya S, Mohammad Alizadeh-Charandabi S, Mirghafourvand M. The psychometric properties of the respectful maternity care (RMC) for an Iranian population. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-05729-x .
Esmkhani M, Namadian M, Nooroozy A, Korte JE. Psychometric properties of a Persian version of respectful maternity care questionnaire. BMC Pregn Childb. 2021;21:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-021-03693-w .
Taghizadeh Z, Ebadi A, Jaafarpour M. Childbirth violence-based negative health consequences: a qualitative study in Iranian women. BMC Pregn Child. 2021;21:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-021-03986-0 .
Moridi M, Pazandeh F, Hajian S, Potrata B. Midwives’ perspectives of respectful maternity care during childbirth: a qualitative study. Plos One. 2020;15:e0229941. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0229941 .
Abdollahpour S, Bayrami R, Ghasem Zadeh N, Alinezhad V. Investigating the effect of implementation of respecting pregnant women traning workshop on knowledge and performance of midwives. Nurs Midw J. 2023;21:334–42.
Alipour S: Effectiveness of Educational Intervention of Midwives Working in Hospitals of Tehran University of Medical Sciences on Providing Respectful Care for Mothers. Tehran: Tehran University of Medical Sciences; 2021.
Asefa A, Morgan A, Bohren MA, Kermode M. Lessons learned through respectful maternity care training and its implementation in Ethiopia: an interventional mixed methods study. Reprod Health. 2020;17:103. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-020-00953-4 .
Peters DH, Adam T, Alonge O, Agyepong IA, Tran N: Implementation research: what it is and how to do it. BMJ 2013;347. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f6753
Theobald S, Brandes N, Gyapong M, El-Saharty S, Proctor E, Diaz T, Wanji S, Elloker S, Raven J, Elsey H. Implementation research: new imperatives and opportunities in global health. Lancet. 2018;392:2214–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32205-0 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Damschroder LJ, Reardon CM, Widerquist MAO, Lowery J. The updated consolidated framework for implementation research based on user feedback. Implement Sci. 2022;17:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-022-01245-0 .
Ridde V. Need for more and better implementation science in global health. BMJ Special J. 2016;1:e000115.
Nilsen P. Making sense of implementation theories, models, and frameworks. Implement Sci. 2015;10:53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-015-0242-0 .
Damschroder LJ, Aron DC, Keith RE, Kirsh SR, Alexander JA, Lowery JC. Fostering implementation of health services research findings into practice: a consolidated framework for advancing implementation science. Implement Sci. 2009;4:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-4-50 .
Keith RE, Crosson JC, O’Malley AS, Cromp D, Taylor EF. Using the consolidated framework for implementation research (CFIR) to produce actionable findings: a rapid-cycle evaluation approach to improving implementation. Implement Sci. 2017;12:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-017-0550-7 .
Mirzania M, Shakibazadeh E, Bohren MA, Babaey F, Hantoushzadeh S, Khajavi A, Rahimi Foroushani A: Knowledge, attitude and practice of healthcare providers on mistreatment of women during labour and childbirth: a cross-sectional study in Tehran, Iran, 2021, under review. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1806039/v1 .
Green L, Kreuter M. Health Program Planning: An Educational and Ecological Approach. 4th ed. New York: McGraw Hill; 2005.
Masoumi SZ, Kazemi F, Oshvandi K, Jalali M, Esmaeili-Vardanjani A, Rafiei H. Effect of training preparation for childbirth on fear of normal vaginal delivery and choosing the type of delivery among pregnant women in Hamadan, Iran: a randomized controlled trial. J Fam Reprod Health. 2016;10:115.
Halil H, Benti A, Zeleke Y, Abdo R. Mistreatment and its associated factors among women during labor and delivery in hospitals of Silte Town, Southern Ethiopia. J Midw Reprod Health. 2020;8:2342–9. https://doi.org/10.22038/jmrh.2020.43343.1512 .
Maung TM, Show KL, Mon NO, Tunçalp Ö, Aye NS, Soe YY, Bohren MA. A qualitative study on acceptability of the mistreatment of women during childbirth in Myanmar. Reprod Health. 2020;17:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-020-0907-2 .
Azizi M, Kamali M, Elyasi F, Shirzad M. Fear of childbirth in Iran: a systematic review of psychological intervention research. Int J Reprod BioMed. 2021;19:401. https://doi.org/10.18502/ijrm.v19i5.9250 .
Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research: .Available from: http://www.cfirguide.org/ . Assessed on 10 May 2022.
Hsieh H-F, Shannon SE. Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qual Health Res. 2005;15:1277–88. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732305276687 .
VERBI Software. MAXQDA Qualitative Data Analysis Software. Marburg: VERBI Software; 2018.
Lincoln Y, Guba E. Naturalistic inquiry: Newbury Park. CA: Sage; 1985.
Book Google Scholar
Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007;19:349–57. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzm042 .
Kirkpatrick DL. Techniques for evaluating training programs. Train Dev J. 1979;33:78–92.
Bruns EJ, Parker EM, Hensley S, Pullmann MD, Benjamin PH, Lyon AR, Hoagwood KE. The role of the outer setting in implementation: associations between state demographic, fiscal, and policy factors and use of evidence-based treatments in mental healthcare. Implement Sci. 2019;14:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-019-0944-9 .
Aarons GA, Hurlburt M, Horwitz SM. Advancing a conceptual model of evidence-based practice implementation in public service sectors. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2011;38:4–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10488-010-0327-7 .
Varsi C, Ekstedt M, Gammon D, Ruland CM. Using the consolidated framework for implementation research to identify barriers and facilitators for the implementation of an internet-based patient-provider communication service in five settings: a qualitative study. J Med Internet Res. 2015;17:e5091. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.5091 .
Hajizadeh K, Vaezi M, Meedya S, Mohammad AlizadehCharandabi S, Mirghafourvand M. Respectful maternity care and its relationship with childbirth experience in Iranian women: a prospective cohort study. BMC Pregn Childb. 2020;20:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-020-03118-0 .
Bayrami R, Baghaei R. Exploring the barriers to pregnant women’s engagement in the childbirth process from Iranian midwives’ point of view: A qualitative study. Proc Singapore Healthc. 2022;31:20101058221089990. https://doi.org/10.1177/20101058221089990 .
Lathwal P, Vyas H, Singh P, Deviga T. Knowledge, attitude, and factors affecting implementation of birth companionship during labor among obstetricians, nurses and pregnant women at a tertiary care teaching hospital. J Public Health Prim Care. 2022;3:15. https://doi.org/10.4103/jphpc.jphpc_17_21 .
Moradi F, Hashemian M, Hosseini F, Shafiei S, Alidousti K: Knowledge, perception, and desire for pain relief in labor among Iranian pregnant women. Res Square. 2022. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2313039/v1
Warren CE, Ndwiga C, Sripad P, Medich M, Njeru A, Maranga A, Odhiambo G, Abuya T. Sowing the seeds of transformative practice to actualize women’s rights to respectful maternity care: reflections from Kenya using the consolidated framework for implementation research. BMC Womens Health. 2017;17:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-017-0425-8 .
Dwekat IMM, Ismail TAT, Ibrahim MI, Ghrayeb F. Exploring factors contributing to mistreatment of women during childbirth in West Bank Palestine. Women Birth. 2021;34:344–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wombi.2020.07.004 .
Ige WB, Cele WB. Barriers to the provision of respectful maternity care during childbirth by midwives in South-West, Nigeria: Findings from semi-structured interviews with midwives. Int Afr Nurs Sci. 2022;17:100449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijans.2022.100449 .
Kabakian-Khasholian T, Portela A. Companion of choice at birth: factors affecting implementation. BMC Pregn Childb. 2017;17:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-017-1447-9 .
Berhe H, Berhe H, Bayray A, Godifay H, Beedemariam G. Status of caring, respectful and compassionate health care practice in Tigrai regional state: patients’ perspective. Int J Caring Sci. 2017;10:1119.
Jemal K, Hailu D, Mekonnen M, Tesfa B, Bekele K, Kinati T. The importance of compassion and respectful care for the health workforce: a mixed-methods study. J Public Health. 2021;31:167–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-021-01495-0 .
Wu J, Ling K, Song W, Yao S. Perspective on the low labor analgesia rate and practical solutions for improvement in China. Chin Med J. 2020;133:606–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/CM9.0000000000000660 .
Washio Y. Incentive use for improving maternal health: perspective from behavioral science. Psychol Rep. 2018;121:42–7. https://doi.org/10.1177/0033294117720937 .
Moore G, Campbell M, Copeland L, Craig P, Movsisyan A, Hoddinott P, Littlecott H, O’Cathain A, Pfadenhauer L, Rehfuess E. Adapting interventions to new contexts—the ADAPT guidance. BMJ. 2021;374:n1679. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n1679 .
Fixsen DL, Blase KA. Active Implementation Frameworks. In Handbook on Implementation Science: Edward Elgar Publishing; 2020.
Harvey G, Kitson A. Promoting Action on Research Implementation in Health Services: The Integrated-PARIHS Framework. In Handbook on Implementation Science: Edward Elgar Publishing; 2020.
Otogara M, Karimi-Shahanjarini A, Hazavehei SMM, Poorolajal J, Radnia N, Akrami F, Bagheri F. Exploring perceptions of instructors about childbirth preparation training courses: a qualitative study. Electr Phys. 2017;9:4215–24. https://doi.org/10.19082/4215 .
Wilson-Mitchell K, Marowitz A, Lori JR. Midwives’ perceptions of barriers to respectful maternity care for adolescent mothers in Jamaica: a qualitative study. Int J Childbirth. 2018;8:18–34.
D-zomeku VM, Mensah BAB, Nakua EK, Agbadi P, Lori JR, Donkor P. Exploring midwives’ understanding of respectful maternal care in Kumasi, Ghana: qualitative inquiry. Plos One. 2020;15:e0220538. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220538 .
Nigenda G, Montaño M, Aranda Z, Aristizabal P, Ortiz F, Ortega S, Juárez A, Macías V, Zárate-Grajales RA, Flores H: Achievements and challenges in the development of a respectful delivery care model provided by partners in health in rural Mexico: a mixed methods analysis. 2022. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1570068/v1 .
Reis V, Deller B, Catherine Carr C, Smith J. Respectful Maternity Care: Country Experiences. Washington DC: USAID; 2012.
Download references
Acknowledgments
This study was part of a PhD dissertation. We thank the Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS) and the Health Information Management Research Center, TUMS for their financial support. We appreciate the sincere collaboration of all participants who provided valuable information in the interviews.
This study received funding from the Deputy for Education at Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS) (9811108001) and Health Information Management Research Center, TUMS (1401-3-208-62407). The role of the funders is to monitor the corresponding study planning and progression.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Health Education and Promotion, School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Marjan Mirzania & Elham Shakibazadeh
Gender and Women’s Health Unit, Nossal Institute for Global Health, School of Population and Global Health, University of Melbourne, Carlton, VIC, Australia
Meghan A. Bohren
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, School of Medicine, Vali-E-Asr Reproductive Health research Center, Family Health Research Institute, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Sedigheh Hantoushzadeh
Department of Social Medicine, School of Medicine, Gonabad University of Medical Sciences, Gonabad, Iran
Abdoljavad Khajavi
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Abbas Rahimi Foroushani
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
E.Sh. and M.M. conceived and designed the project with input from all authors. M.M. developed the interview guide, conducted the interviews, coded and analyzed the data, and drafted the manuscript. E.Sh. contributed to the development of the interview guide, coding and analysis the data, and drafting of the manuscript. M.B., S.H., A.Kh., and A.RF. participated in the revision of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Elham Shakibazadeh .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences (code number: IR.TUMS.SPH.REC.1400.169). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to the interviews. This study was performed in accordance with the principles set out in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., supplementary material 2., supplementary material 3., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Mirzania, M., Shakibazadeh, E., Bohren, M.A. et al. Challenges to the implementation of a multi-level intervention to reduce mistreatment of women during childbirth in Iran: a qualitative study using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research. Reprod Health 21 , 70 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-024-01813-1
Download citation
Received : 10 May 2023
Accepted : 14 May 2024
Published : 27 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-024-01813-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Maternity care
- Mistreatment
- Multi-level intervention
- Implementation research
- Qualitative study
Reproductive Health
ISSN: 1742-4755
- General enquiries: [email protected]
What is Qualitative in Qualitative Research
- Open access
- Published: 27 February 2019
- Volume 42 , pages 139–160, ( 2019 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Patrik Aspers 1 , 2 &
- Ugo Corte 3
603k Accesses
292 Citations
24 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
What is qualitative research? If we look for a precise definition of qualitative research, and specifically for one that addresses its distinctive feature of being “qualitative,” the literature is meager. In this article we systematically search, identify and analyze a sample of 89 sources using or attempting to define the term “qualitative.” Then, drawing on ideas we find scattered across existing work, and based on Becker’s classic study of marijuana consumption, we formulate and illustrate a definition that tries to capture its core elements. We define qualitative research as an iterative process in which improved understanding to the scientific community is achieved by making new significant distinctions resulting from getting closer to the phenomenon studied. This formulation is developed as a tool to help improve research designs while stressing that a qualitative dimension is present in quantitative work as well. Additionally, it can facilitate teaching, communication between researchers, diminish the gap between qualitative and quantitative researchers, help to address critiques of qualitative methods, and be used as a standard of evaluation of qualitative research.
Similar content being viewed by others

Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach
Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review

Qualitative Research: Ethical Considerations
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
If we assume that there is something called qualitative research, what exactly is this qualitative feature? And how could we evaluate qualitative research as good or not? Is it fundamentally different from quantitative research? In practice, most active qualitative researchers working with empirical material intuitively know what is involved in doing qualitative research, yet perhaps surprisingly, a clear definition addressing its key feature is still missing.
To address the question of what is qualitative we turn to the accounts of “qualitative research” in textbooks and also in empirical work. In his classic, explorative, interview study of deviance Howard Becker ( 1963 ) asks ‘How does one become a marijuana user?’ In contrast to pre-dispositional and psychological-individualistic theories of deviant behavior, Becker’s inherently social explanation contends that becoming a user of this substance is the result of a three-phase sequential learning process. First, potential users need to learn how to smoke it properly to produce the “correct” effects. If not, they are likely to stop experimenting with it. Second, they need to discover the effects associated with it; in other words, to get “high,” individuals not only have to experience what the drug does, but also to become aware that those sensations are related to using it. Third, they require learning to savor the feelings related to its consumption – to develop an acquired taste. Becker, who played music himself, gets close to the phenomenon by observing, taking part, and by talking to people consuming the drug: “half of the fifty interviews were conducted with musicians, the other half covered a wide range of people, including laborers, machinists, and people in the professions” (Becker 1963 :56).
Another central aspect derived through the common-to-all-research interplay between induction and deduction (Becker 2017 ), is that during the course of his research Becker adds scientifically meaningful new distinctions in the form of three phases—distinctions, or findings if you will, that strongly affect the course of his research: its focus, the material that he collects, and which eventually impact his findings. Each phase typically unfolds through social interaction, and often with input from experienced users in “a sequence of social experiences during which the person acquires a conception of the meaning of the behavior, and perceptions and judgments of objects and situations, all of which make the activity possible and desirable” (Becker 1963 :235). In this study the increased understanding of smoking dope is a result of a combination of the meaning of the actors, and the conceptual distinctions that Becker introduces based on the views expressed by his respondents. Understanding is the result of research and is due to an iterative process in which data, concepts and evidence are connected with one another (Becker 2017 ).
Indeed, there are many definitions of qualitative research, but if we look for a definition that addresses its distinctive feature of being “qualitative,” the literature across the broad field of social science is meager. The main reason behind this article lies in the paradox, which, to put it bluntly, is that researchers act as if they know what it is, but they cannot formulate a coherent definition. Sociologists and others will of course continue to conduct good studies that show the relevance and value of qualitative research addressing scientific and practical problems in society. However, our paper is grounded in the idea that providing a clear definition will help us improve the work that we do. Among researchers who practice qualitative research there is clearly much knowledge. We suggest that a definition makes this knowledge more explicit. If the first rationale for writing this paper refers to the “internal” aim of improving qualitative research, the second refers to the increased “external” pressure that especially many qualitative researchers feel; pressure that comes both from society as well as from other scientific approaches. There is a strong core in qualitative research, and leading researchers tend to agree on what it is and how it is done. Our critique is not directed at the practice of qualitative research, but we do claim that the type of systematic work we do has not yet been done, and that it is useful to improve the field and its status in relation to quantitative research.
The literature on the “internal” aim of improving, or at least clarifying qualitative research is large, and we do not claim to be the first to notice the vagueness of the term “qualitative” (Strauss and Corbin 1998 ). Also, others have noted that there is no single definition of it (Long and Godfrey 2004 :182), that there are many different views on qualitative research (Denzin and Lincoln 2003 :11; Jovanović 2011 :3), and that more generally, we need to define its meaning (Best 2004 :54). Strauss and Corbin ( 1998 ), for example, as well as Nelson et al. (1992:2 cited in Denzin and Lincoln 2003 :11), and Flick ( 2007 :ix–x), have recognized that the term is problematic: “Actually, the term ‘qualitative research’ is confusing because it can mean different things to different people” (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :10–11). Hammersley has discussed the possibility of addressing the problem, but states that “the task of providing an account of the distinctive features of qualitative research is far from straightforward” ( 2013 :2). This confusion, as he has recently further argued (Hammersley 2018 ), is also salient in relation to ethnography where different philosophical and methodological approaches lead to a lack of agreement about what it means.
Others (e.g. Hammersley 2018 ; Fine and Hancock 2017 ) have also identified the treat to qualitative research that comes from external forces, seen from the point of view of “qualitative research.” This threat can be further divided into that which comes from inside academia, such as the critique voiced by “quantitative research” and outside of academia, including, for example, New Public Management. Hammersley ( 2018 ), zooming in on one type of qualitative research, ethnography, has argued that it is under treat. Similarly to Fine ( 2003 ), and before him Gans ( 1999 ), he writes that ethnography’ has acquired a range of meanings, and comes in many different versions, these often reflecting sharply divergent epistemological orientations. And already more than twenty years ago while reviewing Denzin and Lincoln’ s Handbook of Qualitative Methods Fine argued:
While this increasing centrality [of qualitative research] might lead one to believe that consensual standards have developed, this belief would be misleading. As the methodology becomes more widely accepted, querulous challengers have raised fundamental questions that collectively have undercut the traditional models of how qualitative research is to be fashioned and presented (1995:417).
According to Hammersley, there are today “serious treats to the practice of ethnographic work, on almost any definition” ( 2018 :1). He lists five external treats: (1) that social research must be accountable and able to show its impact on society; (2) the current emphasis on “big data” and the emphasis on quantitative data and evidence; (3) the labor market pressure in academia that leaves less time for fieldwork (see also Fine and Hancock 2017 ); (4) problems of access to fields; and (5) the increased ethical scrutiny of projects, to which ethnography is particularly exposed. Hammersley discusses some more or less insufficient existing definitions of ethnography.
The current situation, as Hammersley and others note—and in relation not only to ethnography but also qualitative research in general, and as our empirical study shows—is not just unsatisfactory, it may even be harmful for the entire field of qualitative research, and does not help social science at large. We suggest that the lack of clarity of qualitative research is a real problem that must be addressed.
Towards a Definition of Qualitative Research
Seen in an historical light, what is today called qualitative, or sometimes ethnographic, interpretative research – or a number of other terms – has more or less always existed. At the time the founders of sociology – Simmel, Weber, Durkheim and, before them, Marx – were writing, and during the era of the Methodenstreit (“dispute about methods”) in which the German historical school emphasized scientific methods (cf. Swedberg 1990 ), we can at least speak of qualitative forerunners.
Perhaps the most extended discussion of what later became known as qualitative methods in a classic work is Bronisław Malinowski’s ( 1922 ) Argonauts in the Western Pacific , although even this study does not explicitly address the meaning of “qualitative.” In Weber’s ([1921–-22] 1978) work we find a tension between scientific explanations that are based on observation and quantification and interpretative research (see also Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 ).
If we look through major sociology journals like the American Sociological Review , American Journal of Sociology , or Social Forces we will not find the term qualitative sociology before the 1970s. And certainly before then much of what we consider qualitative classics in sociology, like Becker’ study ( 1963 ), had already been produced. Indeed, the Chicago School often combined qualitative and quantitative data within the same study (Fine 1995 ). Our point being that before a disciplinary self-awareness the term quantitative preceded qualitative, and the articulation of the former was a political move to claim scientific status (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 ). In the US the World War II seem to have sparked a critique of sociological work, including “qualitative work,” that did not follow the scientific canon (Rawls 2018 ), which was underpinned by a scientifically oriented and value free philosophy of science. As a result the attempts and practice of integrating qualitative and quantitative sociology at Chicago lost ground to sociology that was more oriented to surveys and quantitative work at Columbia under Merton-Lazarsfeld. The quantitative tradition was also able to present textbooks (Lundberg 1951 ) that facilitated the use this approach and its “methods.” The practices of the qualitative tradition, by and large, remained tacit or was part of the mentoring transferred from the renowned masters to their students.
This glimpse into history leads us back to the lack of a coherent account condensed in a definition of qualitative research. Many of the attempts to define the term do not meet the requirements of a proper definition: A definition should be clear, avoid tautology, demarcate its domain in relation to the environment, and ideally only use words in its definiens that themselves are not in need of definition (Hempel 1966 ). A definition can enhance precision and thus clarity by identifying the core of the phenomenon. Preferably, a definition should be short. The typical definition we have found, however, is an ostensive definition, which indicates what qualitative research is about without informing us about what it actually is :
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives. (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 :2)
Flick claims that the label “qualitative research” is indeed used as an umbrella for a number of approaches ( 2007 :2–4; 2002 :6), and it is not difficult to identify research fitting this designation. Moreover, whatever it is, it has grown dramatically over the past five decades. In addition, courses have been developed, methods have flourished, arguments about its future have been advanced (for example, Denzin and Lincoln 1994) and criticized (for example, Snow and Morrill 1995 ), and dedicated journals and books have mushroomed. Most social scientists have a clear idea of research and how it differs from journalism, politics and other activities. But the question of what is qualitative in qualitative research is either eluded or eschewed.
We maintain that this lacuna hinders systematic knowledge production based on qualitative research. Paul Lazarsfeld noted the lack of “codification” as early as 1955 when he reviewed 100 qualitative studies in order to offer a codification of the practices (Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 :239). Since then many texts on “qualitative research” and its methods have been published, including recent attempts (Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ) similar to Lazarsfeld’s. These studies have tried to extract what is qualitative by looking at the large number of empirical “qualitative” studies. Our novel strategy complements these endeavors by taking another approach and looking at the attempts to codify these practices in the form of a definition, as well as to a minor extent take Becker’s study as an exemplar of what qualitative researchers actually do, and what the characteristic of being ‘qualitative’ denotes and implies. We claim that qualitative researchers, if there is such a thing as “qualitative research,” should be able to codify their practices in a condensed, yet general way expressed in language.
Lingering problems of “generalizability” and “how many cases do I need” (Small 2009 ) are blocking advancement – in this line of work qualitative approaches are said to differ considerably from quantitative ones, while some of the former unsuccessfully mimic principles related to the latter (Small 2009 ). Additionally, quantitative researchers sometimes unfairly criticize the first based on their own quality criteria. Scholars like Goertz and Mahoney ( 2012 ) have successfully focused on the different norms and practices beyond what they argue are essentially two different cultures: those working with either qualitative or quantitative methods. Instead, similarly to Becker ( 2017 ) who has recently questioned the usefulness of the distinction between qualitative and quantitative research, we focus on similarities.
The current situation also impedes both students and researchers in focusing their studies and understanding each other’s work (Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 :239). A third consequence is providing an opening for critiques by scholars operating within different traditions (Valsiner 2000 :101). A fourth issue is that the “implicit use of methods in qualitative research makes the field far less standardized than the quantitative paradigm” (Goertz and Mahoney 2012 :9). Relatedly, the National Science Foundation in the US organized two workshops in 2004 and 2005 to address the scientific foundations of qualitative research involving strategies to improve it and to develop standards of evaluation in qualitative research. However, a specific focus on its distinguishing feature of being “qualitative” while being implicitly acknowledged, was discussed only briefly (for example, Best 2004 ).
In 2014 a theme issue was published in this journal on “Methods, Materials, and Meanings: Designing Cultural Analysis,” discussing central issues in (cultural) qualitative research (Berezin 2014 ; Biernacki 2014 ; Glaeser 2014 ; Lamont and Swidler 2014 ; Spillman 2014). We agree with many of the arguments put forward, such as the risk of methodological tribalism, and that we should not waste energy on debating methods separated from research questions. Nonetheless, a clarification of the relation to what is called “quantitative research” is of outmost importance to avoid misunderstandings and misguided debates between “qualitative” and “quantitative” researchers. Our strategy means that researchers, “qualitative” or “quantitative” they may be, in their actual practice may combine qualitative work and quantitative work.
In this article we accomplish three tasks. First, we systematically survey the literature for meanings of qualitative research by looking at how researchers have defined it. Drawing upon existing knowledge we find that the different meanings and ideas of qualitative research are not yet coherently integrated into one satisfactory definition. Next, we advance our contribution by offering a definition of qualitative research and illustrate its meaning and use partially by expanding on the brief example introduced earlier related to Becker’s work ( 1963 ). We offer a systematic analysis of central themes of what researchers consider to be the core of “qualitative,” regardless of style of work. These themes – which we summarize in terms of four keywords: distinction, process, closeness, improved understanding – constitute part of our literature review, in which each one appears, sometimes with others, but never all in the same definition. They serve as the foundation of our contribution. Our categories are overlapping. Their use is primarily to organize the large amount of definitions we have identified and analyzed, and not necessarily to draw a clear distinction between them. Finally, we continue the elaboration discussed above on the advantages of a clear definition of qualitative research.
In a hermeneutic fashion we propose that there is something meaningful that deserves to be labelled “qualitative research” (Gadamer 1990 ). To approach the question “What is qualitative in qualitative research?” we have surveyed the literature. In conducting our survey we first traced the word’s etymology in dictionaries, encyclopedias, handbooks of the social sciences and of methods and textbooks, mainly in English, which is common to methodology courses. It should be noted that we have zoomed in on sociology and its literature. This discipline has been the site of the largest debate and development of methods that can be called “qualitative,” which suggests that this field should be examined in great detail.
In an ideal situation we should expect that one good definition, or at least some common ideas, would have emerged over the years. This common core of qualitative research should be so accepted that it would appear in at least some textbooks. Since this is not what we found, we decided to pursue an inductive approach to capture maximal variation in the field of qualitative research; we searched in a selection of handbooks, textbooks, book chapters, and books, to which we added the analysis of journal articles. Our sample comprises a total of 89 references.
In practice we focused on the discipline that has had a clear discussion of methods, namely sociology. We also conducted a broad search in the JSTOR database to identify scholarly sociology articles published between 1998 and 2017 in English with a focus on defining or explaining qualitative research. We specifically zoom in on this time frame because we would have expect that this more mature period would have produced clear discussions on the meaning of qualitative research. To find these articles we combined a number of keywords to search the content and/or the title: qualitative (which was always included), definition, empirical, research, methodology, studies, fieldwork, interview and observation .
As a second phase of our research we searched within nine major sociological journals ( American Journal of Sociology , Sociological Theory , American Sociological Review , Contemporary Sociology , Sociological Forum , Sociological Theory , Qualitative Research , Qualitative Sociology and Qualitative Sociology Review ) for articles also published during the past 19 years (1998–2017) that had the term “qualitative” in the title and attempted to define qualitative research.
Lastly we picked two additional journals, Qualitative Research and Qualitative Sociology , in which we could expect to find texts addressing the notion of “qualitative.” From Qualitative Research we chose Volume 14, Issue 6, December 2014, and from Qualitative Sociology we chose Volume 36, Issue 2, June 2017. Within each of these we selected the first article; then we picked the second article of three prior issues. Again we went back another three issues and investigated article number three. Finally we went back another three issues and perused article number four. This selection criteria was used to get a manageable sample for the analysis.
The coding process of the 89 references we gathered in our selected review began soon after the first round of material was gathered, and we reduced the complexity created by our maximum variation sampling (Snow and Anderson 1993 :22) to four different categories within which questions on the nature and properties of qualitative research were discussed. We call them: Qualitative and Quantitative Research, Qualitative Research, Fieldwork, and Grounded Theory. This – which may appear as an illogical grouping – merely reflects the “context” in which the matter of “qualitative” is discussed. If the selection process of the material – books and articles – was informed by pre-knowledge, we used an inductive strategy to code the material. When studying our material, we identified four central notions related to “qualitative” that appear in various combinations in the literature which indicate what is the core of qualitative research. We have labeled them: “distinctions”, “process,” “closeness,” and “improved understanding.” During the research process the categories and notions were improved, refined, changed, and reordered. The coding ended when a sense of saturation in the material arose. In the presentation below all quotations and references come from our empirical material of texts on qualitative research.
Analysis – What is Qualitative Research?
In this section we describe the four categories we identified in the coding, how they differently discuss qualitative research, as well as their overall content. Some salient quotations are selected to represent the type of text sorted under each of the four categories. What we present are examples from the literature.
Qualitative and Quantitative
This analytic category comprises quotations comparing qualitative and quantitative research, a distinction that is frequently used (Brown 2010 :231); in effect this is a conceptual pair that structures the discussion and that may be associated with opposing interests. While the general goal of quantitative and qualitative research is the same – to understand the world better – their methodologies and focus in certain respects differ substantially (Becker 1966 :55). Quantity refers to that property of something that can be determined by measurement. In a dictionary of Statistics and Methodology we find that “(a) When referring to *variables, ‘qualitative’ is another term for *categorical or *nominal. (b) When speaking of kinds of research, ‘qualitative’ refers to studies of subjects that are hard to quantify, such as art history. Qualitative research tends to be a residual category for almost any kind of non-quantitative research” (Stiles 1998:183). But it should be obvious that one could employ a quantitative approach when studying, for example, art history.
The same dictionary states that quantitative is “said of variables or research that can be handled numerically, usually (too sharply) contrasted with *qualitative variables and research” (Stiles 1998:184). From a qualitative perspective “quantitative research” is about numbers and counting, and from a quantitative perspective qualitative research is everything that is not about numbers. But this does not say much about what is “qualitative.” If we turn to encyclopedias we find that in the 1932 edition of the Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences there is no mention of “qualitative.” In the Encyclopedia from 1968 we can read:
Qualitative Analysis. For methods of obtaining, analyzing, and describing data, see [the various entries:] CONTENT ANALYSIS; COUNTED DATA; EVALUATION RESEARCH, FIELD WORK; GRAPHIC PRESENTATION; HISTORIOGRAPHY, especially the article on THE RHETORIC OF HISTORY; INTERVIEWING; OBSERVATION; PERSONALITY MEASUREMENT; PROJECTIVE METHODS; PSYCHOANALYSIS, article on EXPERIMENTAL METHODS; SURVEY ANALYSIS, TABULAR PRESENTATION; TYPOLOGIES. (Vol. 13:225)
Some, like Alford, divide researchers into methodologists or, in his words, “quantitative and qualitative specialists” (Alford 1998 :12). Qualitative research uses a variety of methods, such as intensive interviews or in-depth analysis of historical materials, and it is concerned with a comprehensive account of some event or unit (King et al. 1994 :4). Like quantitative research it can be utilized to study a variety of issues, but it tends to focus on meanings and motivations that underlie cultural symbols, personal experiences, phenomena and detailed understanding of processes in the social world. In short, qualitative research centers on understanding processes, experiences, and the meanings people assign to things (Kalof et al. 2008 :79).
Others simply say that qualitative methods are inherently unscientific (Jovanović 2011 :19). Hood, for instance, argues that words are intrinsically less precise than numbers, and that they are therefore more prone to subjective analysis, leading to biased results (Hood 2006 :219). Qualitative methodologies have raised concerns over the limitations of quantitative templates (Brady et al. 2004 :4). Scholars such as King et al. ( 1994 ), for instance, argue that non-statistical research can produce more reliable results if researchers pay attention to the rules of scientific inference commonly stated in quantitative research. Also, researchers such as Becker ( 1966 :59; 1970 :42–43) have asserted that, if conducted properly, qualitative research and in particular ethnographic field methods, can lead to more accurate results than quantitative studies, in particular, survey research and laboratory experiments.
Some researchers, such as Kalof, Dan, and Dietz ( 2008 :79) claim that the boundaries between the two approaches are becoming blurred, and Small ( 2009 ) argues that currently much qualitative research (especially in North America) tries unsuccessfully and unnecessarily to emulate quantitative standards. For others, qualitative research tends to be more humanistic and discursive (King et al. 1994 :4). Ragin ( 1994 ), and similarly also Becker, ( 1996 :53), Marchel and Owens ( 2007 :303) think that the main distinction between the two styles is overstated and does not rest on the simple dichotomy of “numbers versus words” (Ragin 1994 :xii). Some claim that quantitative data can be utilized to discover associations, but in order to unveil cause and effect a complex research design involving the use of qualitative approaches needs to be devised (Gilbert 2009 :35). Consequently, qualitative data are useful for understanding the nuances lying beyond those processes as they unfold (Gilbert 2009 :35). Others contend that qualitative research is particularly well suited both to identify causality and to uncover fine descriptive distinctions (Fine and Hallett 2014 ; Lichterman and Isaac Reed 2014 ; Katz 2015 ).
There are other ways to separate these two traditions, including normative statements about what qualitative research should be (that is, better or worse than quantitative approaches, concerned with scientific approaches to societal change or vice versa; Snow and Morrill 1995 ; Denzin and Lincoln 2005 ), or whether it should develop falsifiable statements; Best 2004 ).
We propose that quantitative research is largely concerned with pre-determined variables (Small 2008 ); the analysis concerns the relations between variables. These categories are primarily not questioned in the study, only their frequency or degree, or the correlations between them (cf. Franzosi 2016 ). If a researcher studies wage differences between women and men, he or she works with given categories: x number of men are compared with y number of women, with a certain wage attributed to each person. The idea is not to move beyond the given categories of wage, men and women; they are the starting point as well as the end point, and undergo no “qualitative change.” Qualitative research, in contrast, investigates relations between categories that are themselves subject to change in the research process. Returning to Becker’s study ( 1963 ), we see that he questioned pre-dispositional theories of deviant behavior working with pre-determined variables such as an individual’s combination of personal qualities or emotional problems. His take, in contrast, was to understand marijuana consumption by developing “variables” as part of the investigation. Thereby he presented new variables, or as we would say today, theoretical concepts, but which are grounded in the empirical material.
Qualitative Research
This category contains quotations that refer to descriptions of qualitative research without making comparisons with quantitative research. Researchers such as Denzin and Lincoln, who have written a series of influential handbooks on qualitative methods (1994; Denzin and Lincoln 2003 ; 2005 ), citing Nelson et al. (1992:4), argue that because qualitative research is “interdisciplinary, transdisciplinary, and sometimes counterdisciplinary” it is difficult to derive one single definition of it (Jovanović 2011 :3). According to them, in fact, “the field” is “many things at the same time,” involving contradictions, tensions over its focus, methods, and how to derive interpretations and findings ( 2003 : 11). Similarly, others, such as Flick ( 2007 :ix–x) contend that agreeing on an accepted definition has increasingly become problematic, and that qualitative research has possibly matured different identities. However, Best holds that “the proliferation of many sorts of activities under the label of qualitative sociology threatens to confuse our discussions” ( 2004 :54). Atkinson’s position is more definite: “the current state of qualitative research and research methods is confused” ( 2005 :3–4).
Qualitative research is about interpretation (Blumer 1969 ; Strauss and Corbin 1998 ; Denzin and Lincoln 2003 ), or Verstehen [understanding] (Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 ). It is “multi-method,” involving the collection and use of a variety of empirical materials (Denzin and Lincoln 1998; Silverman 2013 ) and approaches (Silverman 2005 ; Flick 2007 ). It focuses not only on the objective nature of behavior but also on its subjective meanings: individuals’ own accounts of their attitudes, motivations, behavior (McIntyre 2005 :127; Creswell 2009 ), events and situations (Bryman 1989) – what people say and do in specific places and institutions (Goodwin and Horowitz 2002 :35–36) in social and temporal contexts (Morrill and Fine 1997). For this reason, following Weber ([1921-22] 1978), it can be described as an interpretative science (McIntyre 2005 :127). But could quantitative research also be concerned with these questions? Also, as pointed out below, does all qualitative research focus on subjective meaning, as some scholars suggest?
Others also distinguish qualitative research by claiming that it collects data using a naturalistic approach (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 :2; Creswell 2009 ), focusing on the meaning actors ascribe to their actions. But again, does all qualitative research need to be collected in situ? And does qualitative research have to be inherently concerned with meaning? Flick ( 2007 ), referring to Denzin and Lincoln ( 2005 ), mentions conversation analysis as an example of qualitative research that is not concerned with the meanings people bring to a situation, but rather with the formal organization of talk. Still others, such as Ragin ( 1994 :85), note that qualitative research is often (especially early on in the project, we would add) less structured than other kinds of social research – a characteristic connected to its flexibility and that can lead both to potentially better, but also worse results. But is this not a feature of this type of research, rather than a defining description of its essence? Wouldn’t this comment also apply, albeit to varying degrees, to quantitative research?
In addition, Strauss ( 2003 ), along with others, such as Alvesson and Kärreman ( 2011 :10–76), argue that qualitative researchers struggle to capture and represent complex phenomena partially because they tend to collect a large amount of data. While his analysis is correct at some points – “It is necessary to do detailed, intensive, microscopic examination of the data in order to bring out the amazing complexity of what lies in, behind, and beyond those data” (Strauss 2003 :10) – much of his analysis concerns the supposed focus of qualitative research and its challenges, rather than exactly what it is about. But even in this instance we would make a weak case arguing that these are strictly the defining features of qualitative research. Some researchers seem to focus on the approach or the methods used, or even on the way material is analyzed. Several researchers stress the naturalistic assumption of investigating the world, suggesting that meaning and interpretation appear to be a core matter of qualitative research.
We can also see that in this category there is no consensus about specific qualitative methods nor about qualitative data. Many emphasize interpretation, but quantitative research, too, involves interpretation; the results of a regression analysis, for example, certainly have to be interpreted, and the form of meta-analysis that factor analysis provides indeed requires interpretation However, there is no interpretation of quantitative raw data, i.e., numbers in tables. One common thread is that qualitative researchers have to get to grips with their data in order to understand what is being studied in great detail, irrespective of the type of empirical material that is being analyzed. This observation is connected to the fact that qualitative researchers routinely make several adjustments of focus and research design as their studies progress, in many cases until the very end of the project (Kalof et al. 2008 ). If you, like Becker, do not start out with a detailed theory, adjustments such as the emergence and refinement of research questions will occur during the research process. We have thus found a number of useful reflections about qualitative research scattered across different sources, but none of them effectively describe the defining characteristics of this approach.
Although qualitative research does not appear to be defined in terms of a specific method, it is certainly common that fieldwork, i.e., research that entails that the researcher spends considerable time in the field that is studied and use the knowledge gained as data, is seen as emblematic of or even identical to qualitative research. But because we understand that fieldwork tends to focus primarily on the collection and analysis of qualitative data, we expected to find within it discussions on the meaning of “qualitative.” But, again, this was not the case.
Instead, we found material on the history of this approach (for example, Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 ; Atkinson et al. 2001), including how it has changed; for example, by adopting a more self-reflexive practice (Heyl 2001), as well as the different nomenclature that has been adopted, such as fieldwork, ethnography, qualitative research, naturalistic research, participant observation and so on (for example, Lofland et al. 2006 ; Gans 1999 ).
We retrieved definitions of ethnography, such as “the study of people acting in the natural courses of their daily lives,” involving a “resocialization of the researcher” (Emerson 1988 :1) through intense immersion in others’ social worlds (see also examples in Hammersley 2018 ). This may be accomplished by direct observation and also participation (Neuman 2007 :276), although others, such as Denzin ( 1970 :185), have long recognized other types of observation, including non-participant (“fly on the wall”). In this category we have also isolated claims and opposing views, arguing that this type of research is distinguished primarily by where it is conducted (natural settings) (Hughes 1971:496), and how it is carried out (a variety of methods are applied) or, for some most importantly, by involving an active, empathetic immersion in those being studied (Emerson 1988 :2). We also retrieved descriptions of the goals it attends in relation to how it is taught (understanding subjective meanings of the people studied, primarily develop theory, or contribute to social change) (see for example, Corte and Irwin 2017 ; Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 :281; Trier-Bieniek 2012 :639) by collecting the richest possible data (Lofland et al. 2006 ) to derive “thick descriptions” (Geertz 1973 ), and/or to aim at theoretical statements of general scope and applicability (for example, Emerson 1988 ; Fine 2003 ). We have identified guidelines on how to evaluate it (for example Becker 1996 ; Lamont 2004 ) and have retrieved instructions on how it should be conducted (for example, Lofland et al. 2006 ). For instance, analysis should take place while the data gathering unfolds (Emerson 1988 ; Hammersley and Atkinson 2007 ; Lofland et al. 2006 ), observations should be of long duration (Becker 1970 :54; Goffman 1989 ), and data should be of high quantity (Becker 1970 :52–53), as well as other questionable distinctions between fieldwork and other methods:
Field studies differ from other methods of research in that the researcher performs the task of selecting topics, decides what questions to ask, and forges interest in the course of the research itself . This is in sharp contrast to many ‘theory-driven’ and ‘hypothesis-testing’ methods. (Lofland and Lofland 1995 :5)
But could not, for example, a strictly interview-based study be carried out with the same amount of flexibility, such as sequential interviewing (for example, Small 2009 )? Once again, are quantitative approaches really as inflexible as some qualitative researchers think? Moreover, this category stresses the role of the actors’ meaning, which requires knowledge and close interaction with people, their practices and their lifeworld.
It is clear that field studies – which are seen by some as the “gold standard” of qualitative research – are nonetheless only one way of doing qualitative research. There are other methods, but it is not clear why some are more qualitative than others, or why they are better or worse. Fieldwork is characterized by interaction with the field (the material) and understanding of the phenomenon that is being studied. In Becker’s case, he had general experience from fields in which marihuana was used, based on which he did interviews with actual users in several fields.
Grounded Theory
Another major category we identified in our sample is Grounded Theory. We found descriptions of it most clearly in Glaser and Strauss’ ([1967] 2010 ) original articulation, Strauss and Corbin ( 1998 ) and Charmaz ( 2006 ), as well as many other accounts of what it is for: generating and testing theory (Strauss 2003 :xi). We identified explanations of how this task can be accomplished – such as through two main procedures: constant comparison and theoretical sampling (Emerson 1998:96), and how using it has helped researchers to “think differently” (for example, Strauss and Corbin 1998 :1). We also read descriptions of its main traits, what it entails and fosters – for instance, an exceptional flexibility, an inductive approach (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :31–33; 1990; Esterberg 2002 :7), an ability to step back and critically analyze situations, recognize tendencies towards bias, think abstractly and be open to criticism, enhance sensitivity towards the words and actions of respondents, and develop a sense of absorption and devotion to the research process (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :5–6). Accordingly, we identified discussions of the value of triangulating different methods (both using and not using grounded theory), including quantitative ones, and theories to achieve theoretical development (most comprehensively in Denzin 1970 ; Strauss and Corbin 1998 ; Timmermans and Tavory 2012 ). We have also located arguments about how its practice helps to systematize data collection, analysis and presentation of results (Glaser and Strauss [1967] 2010 :16).
Grounded theory offers a systematic approach which requires researchers to get close to the field; closeness is a requirement of identifying questions and developing new concepts or making further distinctions with regard to old concepts. In contrast to other qualitative approaches, grounded theory emphasizes the detailed coding process, and the numerous fine-tuned distinctions that the researcher makes during the process. Within this category, too, we could not find a satisfying discussion of the meaning of qualitative research.
Defining Qualitative Research
In sum, our analysis shows that some notions reappear in the discussion of qualitative research, such as understanding, interpretation, “getting close” and making distinctions. These notions capture aspects of what we think is “qualitative.” However, a comprehensive definition that is useful and that can further develop the field is lacking, and not even a clear picture of its essential elements appears. In other words no definition emerges from our data, and in our research process we have moved back and forth between our empirical data and the attempt to present a definition. Our concrete strategy, as stated above, is to relate qualitative and quantitative research, or more specifically, qualitative and quantitative work. We use an ideal-typical notion of quantitative research which relies on taken for granted and numbered variables. This means that the data consists of variables on different scales, such as ordinal, but frequently ratio and absolute scales, and the representation of the numbers to the variables, i.e. the justification of the assignment of numbers to object or phenomenon, are not questioned, though the validity may be questioned. In this section we return to the notion of quality and try to clarify it while presenting our contribution.
Broadly, research refers to the activity performed by people trained to obtain knowledge through systematic procedures. Notions such as “objectivity” and “reflexivity,” “systematic,” “theory,” “evidence” and “openness” are here taken for granted in any type of research. Next, building on our empirical analysis we explain the four notions that we have identified as central to qualitative work: distinctions, process, closeness, and improved understanding. In discussing them, ultimately in relation to one another, we make their meaning even more precise. Our idea, in short, is that only when these ideas that we present separately for analytic purposes are brought together can we speak of qualitative research.
Distinctions
We believe that the possibility of making new distinctions is one the defining characteristics of qualitative research. It clearly sets it apart from quantitative analysis which works with taken-for-granted variables, albeit as mentioned, meta-analyses, for example, factor analysis may result in new variables. “Quality” refers essentially to distinctions, as already pointed out by Aristotle. He discusses the term “qualitative” commenting: “By a quality I mean that in virtue of which things are said to be qualified somehow” (Aristotle 1984:14). Quality is about what something is or has, which means that the distinction from its environment is crucial. We see qualitative research as a process in which significant new distinctions are made to the scholarly community; to make distinctions is a key aspect of obtaining new knowledge; a point, as we will see, that also has implications for “quantitative research.” The notion of being “significant” is paramount. New distinctions by themselves are not enough; just adding concepts only increases complexity without furthering our knowledge. The significance of new distinctions is judged against the communal knowledge of the research community. To enable this discussion and judgements central elements of rational discussion are required (cf. Habermas [1981] 1987 ; Davidsson [ 1988 ] 2001) to identify what is new and relevant scientific knowledge. Relatedly, Ragin alludes to the idea of new and useful knowledge at a more concrete level: “Qualitative methods are appropriate for in-depth examination of cases because they aid the identification of key features of cases. Most qualitative methods enhance data” (1994:79). When Becker ( 1963 ) studied deviant behavior and investigated how people became marihuana smokers, he made distinctions between the ways in which people learned how to smoke. This is a classic example of how the strategy of “getting close” to the material, for example the text, people or pictures that are subject to analysis, may enable researchers to obtain deeper insight and new knowledge by making distinctions – in this instance on the initial notion of learning how to smoke. Others have stressed the making of distinctions in relation to coding or theorizing. Emerson et al. ( 1995 ), for example, hold that “qualitative coding is a way of opening up avenues of inquiry,” meaning that the researcher identifies and develops concepts and analytic insights through close examination of and reflection on data (Emerson et al. 1995 :151). Goodwin and Horowitz highlight making distinctions in relation to theory-building writing: “Close engagement with their cases typically requires qualitative researchers to adapt existing theories or to make new conceptual distinctions or theoretical arguments to accommodate new data” ( 2002 : 37). In the ideal-typical quantitative research only existing and so to speak, given, variables would be used. If this is the case no new distinction are made. But, would not also many “quantitative” researchers make new distinctions?
Process does not merely suggest that research takes time. It mainly implies that qualitative new knowledge results from a process that involves several phases, and above all iteration. Qualitative research is about oscillation between theory and evidence, analysis and generating material, between first- and second -order constructs (Schütz 1962 :59), between getting in contact with something, finding sources, becoming deeply familiar with a topic, and then distilling and communicating some of its essential features. The main point is that the categories that the researcher uses, and perhaps takes for granted at the beginning of the research process, usually undergo qualitative changes resulting from what is found. Becker describes how he tested hypotheses and let the jargon of the users develop into theoretical concepts. This happens over time while the study is being conducted, exemplifying what we mean by process.
In the research process, a pilot-study may be used to get a first glance of, for example, the field, how to approach it, and what methods can be used, after which the method and theory are chosen or refined before the main study begins. Thus, the empirical material is often central from the start of the project and frequently leads to adjustments by the researcher. Likewise, during the main study categories are not fixed; the empirical material is seen in light of the theory used, but it is also given the opportunity to kick back, thereby resisting attempts to apply theoretical straightjackets (Becker 1970 :43). In this process, coding and analysis are interwoven, and thus are often important steps for getting closer to the phenomenon and deciding what to focus on next. Becker began his research by interviewing musicians close to him, then asking them to refer him to other musicians, and later on doubling his original sample of about 25 to include individuals in other professions (Becker 1973:46). Additionally, he made use of some participant observation, documents, and interviews with opiate users made available to him by colleagues. As his inductive theory of deviance evolved, Becker expanded his sample in order to fine tune it, and test the accuracy and generality of his hypotheses. In addition, he introduced a negative case and discussed the null hypothesis ( 1963 :44). His phasic career model is thus based on a research design that embraces processual work. Typically, process means to move between “theory” and “material” but also to deal with negative cases, and Becker ( 1998 ) describes how discovering these negative cases impacted his research design and ultimately its findings.
Obviously, all research is process-oriented to some degree. The point is that the ideal-typical quantitative process does not imply change of the data, and iteration between data, evidence, hypotheses, empirical work, and theory. The data, quantified variables, are, in most cases fixed. Merging of data, which of course can be done in a quantitative research process, does not mean new data. New hypotheses are frequently tested, but the “raw data is often the “the same.” Obviously, over time new datasets are made available and put into use.
Another characteristic that is emphasized in our sample is that qualitative researchers – and in particular ethnographers – can, or as Goffman put it, ought to ( 1989 ), get closer to the phenomenon being studied and their data than quantitative researchers (for example, Silverman 2009 :85). Put differently, essentially because of their methods qualitative researchers get into direct close contact with those being investigated and/or the material, such as texts, being analyzed. Becker started out his interview study, as we noted, by talking to those he knew in the field of music to get closer to the phenomenon he was studying. By conducting interviews he got even closer. Had he done more observations, he would undoubtedly have got even closer to the field.
Additionally, ethnographers’ design enables researchers to follow the field over time, and the research they do is almost by definition longitudinal, though the time in the field is studied obviously differs between studies. The general characteristic of closeness over time maximizes the chances of unexpected events, new data (related, for example, to archival research as additional sources, and for ethnography for situations not necessarily previously thought of as instrumental – what Mannay and Morgan ( 2015 ) term the “waiting field”), serendipity (Merton and Barber 2004 ; Åkerström 2013 ), and possibly reactivity, as well as the opportunity to observe disrupted patterns that translate into exemplars of negative cases. Two classic examples of this are Becker’s finding of what medical students call “crocks” (Becker et al. 1961 :317), and Geertz’s ( 1973 ) study of “deep play” in Balinese society.
By getting and staying so close to their data – be it pictures, text or humans interacting (Becker was himself a musician) – for a long time, as the research progressively focuses, qualitative researchers are prompted to continually test their hunches, presuppositions and hypotheses. They test them against a reality that often (but certainly not always), and practically, as well as metaphorically, talks back, whether by validating them, or disqualifying their premises – correctly, as well as incorrectly (Fine 2003 ; Becker 1970 ). This testing nonetheless often leads to new directions for the research. Becker, for example, says that he was initially reading psychological theories, but when facing the data he develops a theory that looks at, you may say, everything but psychological dispositions to explain the use of marihuana. Especially researchers involved with ethnographic methods have a fairly unique opportunity to dig up and then test (in a circular, continuous and temporal way) new research questions and findings as the research progresses, and thereby to derive previously unimagined and uncharted distinctions by getting closer to the phenomenon under study.
Let us stress that getting close is by no means restricted to ethnography. The notion of hermeneutic circle and hermeneutics as a general way of understanding implies that we must get close to the details in order to get the big picture. This also means that qualitative researchers can literally also make use of details of pictures as evidence (cf. Harper 2002). Thus, researchers may get closer both when generating the material or when analyzing it.
Quantitative research, we maintain, in the ideal-typical representation cannot get closer to the data. The data is essentially numbers in tables making up the variables (Franzosi 2016 :138). The data may originally have been “qualitative,” but once reduced to numbers there can only be a type of “hermeneutics” about what the number may stand for. The numbers themselves, however, are non-ambiguous. Thus, in quantitative research, interpretation, if done, is not about the data itself—the numbers—but what the numbers stand for. It follows that the interpretation is essentially done in a more “speculative” mode without direct empirical evidence (cf. Becker 2017 ).
Improved Understanding
While distinction, process and getting closer refer to the qualitative work of the researcher, improved understanding refers to its conditions and outcome of this work. Understanding cuts deeper than explanation, which to some may mean a causally verified correlation between variables. The notion of explanation presupposes the notion of understanding since explanation does not include an idea of how knowledge is gained (Manicas 2006 : 15). Understanding, we argue, is the core concept of what we call the outcome of the process when research has made use of all the other elements that were integrated in the research. Understanding, then, has a special status in qualitative research since it refers both to the conditions of knowledge and the outcome of the process. Understanding can to some extent be seen as the condition of explanation and occurs in a process of interpretation, which naturally refers to meaning (Gadamer 1990 ). It is fundamentally connected to knowing, and to the knowing of how to do things (Heidegger [1927] 2001 ). Conceptually the term hermeneutics is used to account for this process. Heidegger ties hermeneutics to human being and not possible to separate from the understanding of being ( 1988 ). Here we use it in a broader sense, and more connected to method in general (cf. Seiffert 1992 ). The abovementioned aspects – for example, “objectivity” and “reflexivity” – of the approach are conditions of scientific understanding. Understanding is the result of a circular process and means that the parts are understood in light of the whole, and vice versa. Understanding presupposes pre-understanding, or in other words, some knowledge of the phenomenon studied. The pre-understanding, even in the form of prejudices, are in qualitative research process, which we see as iterative, questioned, which gradually or suddenly change due to the iteration of data, evidence and concepts. However, qualitative research generates understanding in the iterative process when the researcher gets closer to the data, e.g., by going back and forth between field and analysis in a process that generates new data that changes the evidence, and, ultimately, the findings. Questioning, to ask questions, and put what one assumes—prejudices and presumption—in question, is central to understand something (Heidegger [1927] 2001 ; Gadamer 1990 :368–384). We propose that this iterative process in which the process of understanding occurs is characteristic of qualitative research.
Improved understanding means that we obtain scientific knowledge of something that we as a scholarly community did not know before, or that we get to know something better. It means that we understand more about how parts are related to one another, and to other things we already understand (see also Fine and Hallett 2014 ). Understanding is an important condition for qualitative research. It is not enough to identify correlations, make distinctions, and work in a process in which one gets close to the field or phenomena. Understanding is accomplished when the elements are integrated in an iterative process.
It is, moreover, possible to understand many things, and researchers, just like children, may come to understand new things every day as they engage with the world. This subjective condition of understanding – namely, that a person gains a better understanding of something –is easily met. To be qualified as “scientific,” the understanding must be general and useful to many; it must be public. But even this generally accessible understanding is not enough in order to speak of “scientific understanding.” Though we as a collective can increase understanding of everything in virtually all potential directions as a result also of qualitative work, we refrain from this “objective” way of understanding, which has no means of discriminating between what we gain in understanding. Scientific understanding means that it is deemed relevant from the scientific horizon (compare Schütz 1962 : 35–38, 46, 63), and that it rests on the pre-understanding that the scientists have and must have in order to understand. In other words, the understanding gained must be deemed useful by other researchers, so that they can build on it. We thus see understanding from a pragmatic, rather than a subjective or objective perspective. Improved understanding is related to the question(s) at hand. Understanding, in order to represent an improvement, must be an improvement in relation to the existing body of knowledge of the scientific community (James [ 1907 ] 1955). Scientific understanding is, by definition, collective, as expressed in Weber’s famous note on objectivity, namely that scientific work aims at truths “which … can claim, even for a Chinese, the validity appropriate to an empirical analysis” ([1904] 1949 :59). By qualifying “improved understanding” we argue that it is a general defining characteristic of qualitative research. Becker‘s ( 1966 ) study and other research of deviant behavior increased our understanding of the social learning processes of how individuals start a behavior. And it also added new knowledge about the labeling of deviant behavior as a social process. Few studies, of course, make the same large contribution as Becker’s, but are nonetheless qualitative research.
Understanding in the phenomenological sense, which is a hallmark of qualitative research, we argue, requires meaning and this meaning is derived from the context, and above all the data being analyzed. The ideal-typical quantitative research operates with given variables with different numbers. This type of material is not enough to establish meaning at the level that truly justifies understanding. In other words, many social science explanations offer ideas about correlations or even causal relations, but this does not mean that the meaning at the level of the data analyzed, is understood. This leads us to say that there are indeed many explanations that meet the criteria of understanding, for example the explanation of how one becomes a marihuana smoker presented by Becker. However, we may also understand a phenomenon without explaining it, and we may have potential explanations, or better correlations, that are not really understood.
We may speak more generally of quantitative research and its data to clarify what we see as an important distinction. The “raw data” that quantitative research—as an idealtypical activity, refers to is not available for further analysis; the numbers, once created, are not to be questioned (Franzosi 2016 : 138). If the researcher is to do “more” or “change” something, this will be done by conjectures based on theoretical knowledge or based on the researcher’s lifeworld. Both qualitative and quantitative research is based on the lifeworld, and all researchers use prejudices and pre-understanding in the research process. This idea is present in the works of Heidegger ( 2001 ) and Heisenberg (cited in Franzosi 2010 :619). Qualitative research, as we argued, involves the interaction and questioning of concepts (theory), data, and evidence.
Ragin ( 2004 :22) points out that “a good definition of qualitative research should be inclusive and should emphasize its key strengths and features, not what it lacks (for example, the use of sophisticated quantitative techniques).” We define qualitative research as an iterative process in which improved understanding to the scientific community is achieved by making new significant distinctions resulting from getting closer to the phenomenon studied. Qualitative research, as defined here, is consequently a combination of two criteria: (i) how to do things –namely, generating and analyzing empirical material, in an iterative process in which one gets closer by making distinctions, and (ii) the outcome –improved understanding novel to the scholarly community. Is our definition applicable to our own study? In this study we have closely read the empirical material that we generated, and the novel distinction of the notion “qualitative research” is the outcome of an iterative process in which both deduction and induction were involved, in which we identified the categories that we analyzed. We thus claim to meet the first criteria, “how to do things.” The second criteria cannot be judged but in a partial way by us, namely that the “outcome” —in concrete form the definition-improves our understanding to others in the scientific community.
We have defined qualitative research, or qualitative scientific work, in relation to quantitative scientific work. Given this definition, qualitative research is about questioning the pre-given (taken for granted) variables, but it is thus also about making new distinctions of any type of phenomenon, for example, by coining new concepts, including the identification of new variables. This process, as we have discussed, is carried out in relation to empirical material, previous research, and thus in relation to theory. Theory and previous research cannot be escaped or bracketed. According to hermeneutic principles all scientific work is grounded in the lifeworld, and as social scientists we can thus never fully bracket our pre-understanding.
We have proposed that quantitative research, as an idealtype, is concerned with pre-determined variables (Small 2008 ). Variables are epistemically fixed, but can vary in terms of dimensions, such as frequency or number. Age is an example; as a variable it can take on different numbers. In relation to quantitative research, qualitative research does not reduce its material to number and variables. If this is done the process of comes to a halt, the researcher gets more distanced from her data, and it makes it no longer possible to make new distinctions that increase our understanding. We have above discussed the components of our definition in relation to quantitative research. Our conclusion is that in the research that is called quantitative there are frequent and necessary qualitative elements.
Further, comparative empirical research on researchers primarily working with ”quantitative” approaches and those working with ”qualitative” approaches, we propose, would perhaps show that there are many similarities in practices of these two approaches. This is not to deny dissimilarities, or the different epistemic and ontic presuppositions that may be more or less strongly associated with the two different strands (see Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ). Our point is nonetheless that prejudices and preconceptions about researchers are unproductive, and that as other researchers have argued, differences may be exaggerated (e.g., Becker 1996 : 53, 2017 ; Marchel and Owens 2007 :303; Ragin 1994 ), and that a qualitative dimension is present in both kinds of work.
Several things follow from our findings. The most important result is the relation to quantitative research. In our analysis we have separated qualitative research from quantitative research. The point is not to label individual researchers, methods, projects, or works as either “quantitative” or “qualitative.” By analyzing, i.e., taking apart, the notions of quantitative and qualitative, we hope to have shown the elements of qualitative research. Our definition captures the elements, and how they, when combined in practice, generate understanding. As many of the quotations we have used suggest, one conclusion of our study holds that qualitative approaches are not inherently connected with a specific method. Put differently, none of the methods that are frequently labelled “qualitative,” such as interviews or participant observation, are inherently “qualitative.” What matters, given our definition, is whether one works qualitatively or quantitatively in the research process, until the results are produced. Consequently, our analysis also suggests that those researchers working with what in the literature and in jargon is often called “quantitative research” are almost bound to make use of what we have identified as qualitative elements in any research project. Our findings also suggest that many” quantitative” researchers, at least to some extent, are engaged with qualitative work, such as when research questions are developed, variables are constructed and combined, and hypotheses are formulated. Furthermore, a research project may hover between “qualitative” and “quantitative” or start out as “qualitative” and later move into a “quantitative” (a distinct strategy that is not similar to “mixed methods” or just simply combining induction and deduction). More generally speaking, the categories of “qualitative” and “quantitative,” unfortunately, often cover up practices, and it may lead to “camps” of researchers opposing one another. For example, regardless of the researcher is primarily oriented to “quantitative” or “qualitative” research, the role of theory is neglected (cf. Swedberg 2017 ). Our results open up for an interaction not characterized by differences, but by different emphasis, and similarities.
Let us take two examples to briefly indicate how qualitative elements can fruitfully be combined with quantitative. Franzosi ( 2010 ) has discussed the relations between quantitative and qualitative approaches, and more specifically the relation between words and numbers. He analyzes texts and argues that scientific meaning cannot be reduced to numbers. Put differently, the meaning of the numbers is to be understood by what is taken for granted, and what is part of the lifeworld (Schütz 1962 ). Franzosi shows how one can go about using qualitative and quantitative methods and data to address scientific questions analyzing violence in Italy at the time when fascism was rising (1919–1922). Aspers ( 2006 ) studied the meaning of fashion photographers. He uses an empirical phenomenological approach, and establishes meaning at the level of actors. In a second step this meaning, and the different ideal-typical photographers constructed as a result of participant observation and interviews, are tested using quantitative data from a database; in the first phase to verify the different ideal-types, in the second phase to use these types to establish new knowledge about the types. In both of these cases—and more examples can be found—authors move from qualitative data and try to keep the meaning established when using the quantitative data.
A second main result of our study is that a definition, and we provided one, offers a way for research to clarify, and even evaluate, what is done. Hence, our definition can guide researchers and students, informing them on how to think about concrete research problems they face, and to show what it means to get closer in a process in which new distinctions are made. The definition can also be used to evaluate the results, given that it is a standard of evaluation (cf. Hammersley 2007 ), to see whether new distinctions are made and whether this improves our understanding of what is researched, in addition to the evaluation of how the research was conducted. By making what is qualitative research explicit it becomes easier to communicate findings, and it is thereby much harder to fly under the radar with substandard research since there are standards of evaluation which make it easier to separate “good” from “not so good” qualitative research.
To conclude, our analysis, which ends with a definition of qualitative research can thus both address the “internal” issues of what is qualitative research, and the “external” critiques that make it harder to do qualitative research, to which both pressure from quantitative methods and general changes in society contribute.
Åkerström, Malin. 2013. Curiosity and serendipity in qualitative research. Qualitative Sociology Review 9 (2): 10–18.
Google Scholar
Alford, Robert R. 1998. The craft of inquiry. Theories, methods, evidence . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Alvesson, Mats, and Dan Kärreman. 2011. Qualitative research and theory development. Mystery as method . London: SAGE Publications.
Book Google Scholar
Aspers, Patrik. 2006. Markets in Fashion, A Phenomenological Approach. London Routledge.
Atkinson, Paul. 2005. Qualitative research. Unity and diversity. Forum: Qualitative Social Research 6 (3): 1–15.
Becker, Howard S. 1963. Outsiders. Studies in the sociology of deviance . New York: The Free Press.
Becker, Howard S. 1966. Whose side are we on? Social Problems 14 (3): 239–247.
Article Google Scholar
Becker, Howard S. 1970. Sociological work. Method and substance . New Brunswick: Transaction Books.
Becker, Howard S. 1996. The epistemology of qualitative research. In Ethnography and human development. Context and meaning in social inquiry , ed. Jessor Richard, Colby Anne, and Richard A. Shweder, 53–71. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Becker, Howard S. 1998. Tricks of the trade. How to think about your research while you're doing it . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Becker, Howard S. 2017. Evidence . Chigaco: University of Chicago Press.
Becker, Howard, Blanche Geer, Everett Hughes, and Anselm Strauss. 1961. Boys in White, student culture in medical school . New Brunswick: Transaction Publishers.
Berezin, Mabel. 2014. How do we know what we mean? Epistemological dilemmas in cultural sociology. Qualitative Sociology 37 (2): 141–151.
Best, Joel. 2004. Defining qualitative research. In Workshop on Scientific Foundations of Qualitative Research , eds . Charles, Ragin, Joanne, Nagel, and Patricia White, 53-54. http://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2004/nsf04219/nsf04219.pdf .
Biernacki, Richard. 2014. Humanist interpretation versus coding text samples. Qualitative Sociology 37 (2): 173–188.
Blumer, Herbert. 1969. Symbolic interactionism: Perspective and method . Berkeley: University of California Press.
Brady, Henry, David Collier, and Jason Seawright. 2004. Refocusing the discussion of methodology. In Rethinking social inquiry. Diverse tools, shared standards , ed. Brady Henry and Collier David, 3–22. Lanham: Rowman and Littlefield.
Brown, Allison P. 2010. Qualitative method and compromise in applied social research. Qualitative Research 10 (2): 229–248.
Charmaz, Kathy. 2006. Constructing grounded theory . London: Sage.
Corte, Ugo, and Katherine Irwin. 2017. “The Form and Flow of Teaching Ethnographic Knowledge: Hands-on Approaches for Learning Epistemology” Teaching Sociology 45(3): 209-219.
Creswell, John W. 2009. Research design. Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed method approaches . 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Davidsson, David. 1988. 2001. The myth of the subjective. In Subjective, intersubjective, objective , ed. David Davidsson, 39–52. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Denzin, Norman K. 1970. The research act: A theoretical introduction to Ssociological methods . Chicago: Aldine Publishing Company Publishers.
Denzin, Norman K., and Yvonna S. Lincoln. 2003. Introduction. The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In Collecting and interpreting qualitative materials , ed. Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, 1–45. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Denzin, Norman K., and Yvonna S. Lincoln. 2005. Introduction. The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In The Sage handbook of qualitative research , ed. Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, 1–32. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Emerson, Robert M., ed. 1988. Contemporary field research. A collection of readings . Prospect Heights: Waveland Press.
Emerson, Robert M., Rachel I. Fretz, and Linda L. Shaw. 1995. Writing ethnographic fieldnotes . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Esterberg, Kristin G. 2002. Qualitative methods in social research . Boston: McGraw-Hill.
Fine, Gary Alan. 1995. Review of “handbook of qualitative research.” Contemporary Sociology 24 (3): 416–418.
Fine, Gary Alan. 2003. “ Toward a Peopled Ethnography: Developing Theory from Group Life.” Ethnography . 4(1):41-60.
Fine, Gary Alan, and Black Hawk Hancock. 2017. The new ethnographer at work. Qualitative Research 17 (2): 260–268.
Fine, Gary Alan, and Timothy Hallett. 2014. Stranger and stranger: Creating theory through ethnographic distance and authority. Journal of Organizational Ethnography 3 (2): 188–203.
Flick, Uwe. 2002. Qualitative research. State of the art. Social Science Information 41 (1): 5–24.
Flick, Uwe. 2007. Designing qualitative research . London: SAGE Publications.
Frankfort-Nachmias, Chava, and David Nachmias. 1996. Research methods in the social sciences . 5th ed. London: Edward Arnold.
Franzosi, Roberto. 2010. Sociology, narrative, and the quality versus quantity debate (Goethe versus Newton): Can computer-assisted story grammars help us understand the rise of Italian fascism (1919- 1922)? Theory and Society 39 (6): 593–629.
Franzosi, Roberto. 2016. From method and measurement to narrative and number. International journal of social research methodology 19 (1): 137–141.
Gadamer, Hans-Georg. 1990. Wahrheit und Methode, Grundzüge einer philosophischen Hermeneutik . Band 1, Hermeneutik. Tübingen: J.C.B. Mohr.
Gans, Herbert. 1999. Participant Observation in an Age of “Ethnography”. Journal of Contemporary Ethnography 28 (5): 540–548.
Geertz, Clifford. 1973. The interpretation of cultures . New York: Basic Books.
Gilbert, Nigel. 2009. Researching social life . 3rd ed. London: SAGE Publications.
Glaeser, Andreas. 2014. Hermeneutic institutionalism: Towards a new synthesis. Qualitative Sociology 37: 207–241.
Glaser, Barney G., and Anselm L. Strauss. [1967] 2010. The discovery of grounded theory. Strategies for qualitative research. Hawthorne: Aldine.
Goertz, Gary, and James Mahoney. 2012. A tale of two cultures: Qualitative and quantitative research in the social sciences . Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Goffman, Erving. 1989. On fieldwork. Journal of Contemporary Ethnography 18 (2): 123–132.
Goodwin, Jeff, and Ruth Horowitz. 2002. Introduction. The methodological strengths and dilemmas of qualitative sociology. Qualitative Sociology 25 (1): 33–47.
Habermas, Jürgen. [1981] 1987. The theory of communicative action . Oxford: Polity Press.
Hammersley, Martyn. 2007. The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research & Method in Education 30 (3): 287–305.
Hammersley, Martyn. 2013. What is qualitative research? Bloomsbury Publishing.
Hammersley, Martyn. 2018. What is ethnography? Can it survive should it? Ethnography and Education 13 (1): 1–17.
Hammersley, Martyn, and Paul Atkinson. 2007. Ethnography. Principles in practice . London: Tavistock Publications.
Heidegger, Martin. [1927] 2001. Sein und Zeit . Tübingen: Max Niemeyer Verlag.
Heidegger, Martin. 1988. 1923. Ontologie. Hermeneutik der Faktizität, Gesamtausgabe II. Abteilung: Vorlesungen 1919-1944, Band 63, Frankfurt am Main: Vittorio Klostermann.
Hempel, Carl G. 1966. Philosophy of the natural sciences . Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Hood, Jane C. 2006. Teaching against the text. The case of qualitative methods. Teaching Sociology 34 (3): 207–223.
James, William. 1907. 1955. Pragmatism . New York: Meredian Books.
Jovanović, Gordana. 2011. Toward a social history of qualitative research. History of the Human Sciences 24 (2): 1–27.
Kalof, Linda, Amy Dan, and Thomas Dietz. 2008. Essentials of social research . London: Open University Press.
Katz, Jack. 2015. Situational evidence: Strategies for causal reasoning from observational field notes. Sociological Methods & Research 44 (1): 108–144.
King, Gary, Robert O. Keohane, S. Sidney, and S. Verba. 1994. Designing social inquiry. In Scientific inference in qualitative research . Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Chapter Google Scholar
Lamont, Michelle. 2004. Evaluating qualitative research: Some empirical findings and an agenda. In Report from workshop on interdisciplinary standards for systematic qualitative research , ed. M. Lamont and P. White, 91–95. Washington, DC: National Science Foundation.
Lamont, Michèle, and Ann Swidler. 2014. Methodological pluralism and the possibilities and limits of interviewing. Qualitative Sociology 37 (2): 153–171.
Lazarsfeld, Paul, and Alan Barton. 1982. Some functions of qualitative analysis in social research. In The varied sociology of Paul Lazarsfeld , ed. Patricia Kendall, 239–285. New York: Columbia University Press.
Lichterman, Paul, and Isaac Reed I (2014), Theory and Contrastive Explanation in Ethnography. Sociological methods and research. Prepublished 27 October 2014; https://doi.org/10.1177/0049124114554458 .
Lofland, John, and Lyn Lofland. 1995. Analyzing social settings. A guide to qualitative observation and analysis . 3rd ed. Belmont: Wadsworth.
Lofland, John, David A. Snow, Leon Anderson, and Lyn H. Lofland. 2006. Analyzing social settings. A guide to qualitative observation and analysis . 4th ed. Belmont: Wadsworth/Thomson Learning.
Long, Adrew F., and Mary Godfrey. 2004. An evaluation tool to assess the quality of qualitative research studies. International Journal of Social Research Methodology 7 (2): 181–196.
Lundberg, George. 1951. Social research: A study in methods of gathering data . New York: Longmans, Green and Co..
Malinowski, Bronislaw. 1922. Argonauts of the Western Pacific: An account of native Enterprise and adventure in the archipelagoes of Melanesian New Guinea . London: Routledge.
Manicas, Peter. 2006. A realist philosophy of science: Explanation and understanding . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Marchel, Carol, and Stephanie Owens. 2007. Qualitative research in psychology. Could William James get a job? History of Psychology 10 (4): 301–324.
McIntyre, Lisa J. 2005. Need to know. Social science research methods . Boston: McGraw-Hill.
Merton, Robert K., and Elinor Barber. 2004. The travels and adventures of serendipity. A Study in Sociological Semantics and the Sociology of Science . Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Mannay, Dawn, and Melanie Morgan. 2015. Doing ethnography or applying a qualitative technique? Reflections from the ‘waiting field‘. Qualitative Research 15 (2): 166–182.
Neuman, Lawrence W. 2007. Basics of social research. Qualitative and quantitative approaches . 2nd ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
Ragin, Charles C. 1994. Constructing social research. The unity and diversity of method . Thousand Oaks: Pine Forge Press.
Ragin, Charles C. 2004. Introduction to session 1: Defining qualitative research. In Workshop on Scientific Foundations of Qualitative Research , 22, ed. Charles C. Ragin, Joane Nagel, Patricia White. http://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2004/nsf04219/nsf04219.pdf
Rawls, Anne. 2018. The Wartime narrative in US sociology, 1940–7: Stigmatizing qualitative sociology in the name of ‘science,’ European Journal of Social Theory (Online first).
Schütz, Alfred. 1962. Collected papers I: The problem of social reality . The Hague: Nijhoff.
Seiffert, Helmut. 1992. Einführung in die Hermeneutik . Tübingen: Franke.
Silverman, David. 2005. Doing qualitative research. A practical handbook . 2nd ed. London: SAGE Publications.
Silverman, David. 2009. A very short, fairly interesting and reasonably cheap book about qualitative research . London: SAGE Publications.
Silverman, David. 2013. What counts as qualitative research? Some cautionary comments. Qualitative Sociology Review 9 (2): 48–55.
Small, Mario L. 2009. “How many cases do I need?” on science and the logic of case selection in field-based research. Ethnography 10 (1): 5–38.
Small, Mario L 2008. Lost in translation: How not to make qualitative research more scientific. In Workshop on interdisciplinary standards for systematic qualitative research, ed in Michelle Lamont, and Patricia White, 165–171. Washington, DC: National Science Foundation.
Snow, David A., and Leon Anderson. 1993. Down on their luck: A study of homeless street people . Berkeley: University of California Press.
Snow, David A., and Calvin Morrill. 1995. New ethnographies: Review symposium: A revolutionary handbook or a handbook for revolution? Journal of Contemporary Ethnography 24 (3): 341–349.
Strauss, Anselm L. 2003. Qualitative analysis for social scientists . 14th ed. Chicago: Cambridge University Press.
Strauss, Anselm L., and Juliette M. Corbin. 1998. Basics of qualitative research. Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
Swedberg, Richard. 2017. Theorizing in sociological research: A new perspective, a new departure? Annual Review of Sociology 43: 189–206.
Swedberg, Richard. 1990. The new 'Battle of Methods'. Challenge January–February 3 (1): 33–38.
Timmermans, Stefan, and Iddo Tavory. 2012. Theory construction in qualitative research: From grounded theory to abductive analysis. Sociological Theory 30 (3): 167–186.
Trier-Bieniek, Adrienne. 2012. Framing the telephone interview as a participant-centred tool for qualitative research. A methodological discussion. Qualitative Research 12 (6): 630–644.
Valsiner, Jaan. 2000. Data as representations. Contextualizing qualitative and quantitative research strategies. Social Science Information 39 (1): 99–113.
Weber, Max. 1904. 1949. Objectivity’ in social Science and social policy. Ed. Edward A. Shils and Henry A. Finch, 49–112. New York: The Free Press.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Financial Support for this research is given by the European Research Council, CEV (263699). The authors are grateful to Susann Krieglsteiner for assistance in collecting the data. The paper has benefitted from the many useful comments by the three reviewers and the editor, comments by members of the Uppsala Laboratory of Economic Sociology, as well as Jukka Gronow, Sebastian Kohl, Marcin Serafin, Richard Swedberg, Anders Vassenden and Turid Rødne.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Sociology, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
Patrik Aspers
Seminar for Sociology, Universität St. Gallen, St. Gallen, Switzerland
Department of Media and Social Sciences, University of Stavanger, Stavanger, Norway
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Patrik Aspers .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Aspers, P., Corte, U. What is Qualitative in Qualitative Research. Qual Sociol 42 , 139–160 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11133-019-9413-7
Download citation
Published : 27 February 2019
Issue Date : 01 June 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11133-019-9413-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Epistemology
- Philosophy of science
- Phenomenology
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Open access
- Published: 28 May 2024
Current status of electronic health literacy among pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and their perceptions of online health information: a mixed-methods study
- Jingqi Xu 1 na1 ,
- Yujia Chen 1 na1 ,
- Jing Zhao 1 na1 ,
- Jiarun Wang 1 ,
- Jianfei Chen 1 ,
- Xinlong Pan 1 ,
- Wei Zhang 1 ,
- Jin Zheng 2 ,
- Zhijie Zou 1 ,
- Xiaoli Chen 1 &
- Yingzi Zhang 3
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth volume 24 , Article number: 392 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus often rely on internet-based health information for managing their condition. This study aims to investigate the present state of electronic health literacy among women with gestational diabetes mellitus, analyze the influencing factors, and explore their experiences regarding accessing, comprehending, evaluating, and applying online health information pertinent to gestational diabetes mellitus.
A sequential explanatory mixed methods research design was adopted in this study. Initially, 235 women with gestational diabetes mellitus participated in a cross-sectional survey. The research tools included general information and the Chinese version of the electronic Health Literacy Scale (eHEALS). Descriptive analyses were conducted to describe the characteristics of the sample, and multiple linear regression analyses were used to explore the factors influencing electronic health literacy among women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Secondly, 11 women with gestational diabetes mellitus joined semi-structured in-depth interviews to obtain their perceptions about online health information. The data were analyzed using inductive content analysis to develop themes.
The median score of eHEALS in the Chinese version among 235 women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus was 29 (interquartile range [IQR], 26 to 32). Factors influencing electronic health literacy among these women included accessing health information from medical professionals (β = 0.137, p = 0.029) and utilizing health information from applications (β = 0.159, p = 0.013). From the qualitative phase of the study, four thematic categories emerged: reasons and basis for accessing health information from the Internet; address barriers to accessing and applying online health information; desires for a higher level of online health information services; outcomes of accessing and applying online health information.
The electronic health literacy of women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus remains suboptimal and warrants improvement. The sources of access to health information affect electronic health literacy in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Moreover, women facing gestational diabetes encounter numerous impediments when attempting to access health-related information online, underscoring the necessity for enhanced online health information services to meet their needs.
Peer Review reports
Gestational diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder occurring during pregnancy [ 1 ], primarily resulting from insulin resistance and the progressive dysfunction of pancreatic β-cell [ 2 ]. Symptoms of gestational diabetes mellitus often manifest insidiously, making detection challenging. Diagnosis typically occurs through the oral glucose tolerance test administered between the 24th and 28th weeks of gestation [ 3 ]. Although there have been some advancements in monitoring the fetal health of women with gestational diabetes [ 4 , 5 ], gestational diabetes mellitus remains one of the most important causes of adverse perinatal outcomes [ 6 , 7 ], which may also have a negative impact on maternal mental health [ 8 ]. To mitigate these adverse effects, a collaborative multidisciplinary approach is typically employed, with lifestyle and behavioral management serving as the preferred method of intervention [ 9 ]. Lifestyle and behavioral management strategies for gestational diabetes mellitus encompass a diverse array of medical knowledge, spanning medical nutrition therapy, physical activity recommendations, weight management strategies, and more [ 10 ]. Therefore, to effectively manage gestational diabetes mellitus, women typically require access to extensive health information regarding lifestyle and behavioral management strategies.
In recent years, with the development of information and communication technologies, electronic resources have been increasingly used in healthcare. The Internet, in particular, has emerged as a popular platform for accessing health information among women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus [ 11 ]. However, despite the convenience afforded by the Internet for accessing health information, it is essential to acknowledge the challenges associated with online health information and services. These challenges include content duplication, the presence of unregulated information sources, inadequate quality control measures, and difficulty in verifying the credibility of information sources [ 12 ]. Therefore, for women managing gestational diabetes mellitus, discerning the most reliable and credible health information from the vast array of online resources is paramount.
According to Norman and Skinner, the ability of individuals to access reliable and credible health information from electronic resources hinges on their electronic health literacy, an extension of traditional health literacy within the digital realm [ 13 ]. Unlike traditional health literacy, which primarily emphasizes individual access to and understanding of health information [ 14 ], electronic health literacy focuses on the individual comprehensive ability to access, understand, and assess health information from electronic resources, and apply health information available online to address health issues or make health-related decisions [ 15 ]. Evidence suggests that individual electronic health literacy is positively associated with one’s health behaviors and health outcomes, including a higher level of medication adherence, psychosocial well-being, and quality of life, as well as adopting adaptive health behaviors [ 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 ]. Therefore, to enhance the health behaviors and outcomes of women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus, a thorough understanding of their electronic health literacy is indispensable.
Most of the existing studies on electronic health literacy focus on adolescents, college students, and the elderly [ 20 , 21 , 22 ]. In recent years, a few researchers have explored electronic health literacy in people with chronic diseases and their caregivers, including cancer patients and their caregivers [ 23 , 24 ], individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus, and those diagnosed with diabetes [ 25 ]. To the best of our knowledge, there is relatively limited research on the electronic health literacy of pregnant women, and currently, no studies have investigated the electronic health literacy of women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Through a review of studies on electronic health literacy in other populations, it was found that demographic characteristics, pregnancy-related features, and sources of health information acquisition may influence the electronic health literacy of women with gestational diabetes mellitus, including factors such as age, education level, employment status, household income, residential location, gestational age, number of pregnancies, and online health information searching [ 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 ]. In addition, research on electronic health literacy is primarily quantitative, while comprehensive studies on the experience and needs related to electronic health information remain insufficient. Taking these factors into consideration, this study adopted a mixed-methods approach to investigate electronic health literacy among women with gestational diabetes mellitus. It thoroughly explored the factors that influence electronic health literacy in this population, while also delving into their experiences of accessing, comprehending, evaluating, and applying online health information. Based on the literature review above, before the study began, we hypothesized that demographic characteristics, pregnancy-related factors, and sources of health information acquisition are associated with the electronic health literacy of pregnant women with gestational diabetes.
A sequential explanatory mixed-methods research design was employed to investigate the current status of electronic health literacy and cognition of online health information among women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus. This study is divided into two parts. The first part discusses the current status and influencing factors of electronic health literacy among women with gestational diabetes mellitus through quantitative analysis. In the second part, qualitative research was conducted to explore the perception and cognition of women with gestational diabetes mellitus on online health information.
Quantitative phase—questionnaire survey
Study design and setting.
The quantitative phase is a cross-sectional study conducted through questionnaire surveys. During this phase, we recruited pregnant women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus from the obstetrics department of a tertiary maternity hospital in Wuhan City using a convenience sampling method. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) aged 18 years old and above; (2) diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus according to the International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups (IADPSG) criteria; (3) native Chinese speakers or non-native Chinese speakers who could understand Chinese well; (4) no cognitive impairment and normal mental state; (5) signed informed consent. Exclusion criteria included the inability to complete the questionnaire due to poor physical condition.
The sample size for studies on variable influencing factors should be determined according to the requirements of statistical variable analysis, typically recommended to be at least 5 to 10 times the number of variables [ 32 ]. In this study, based on 19 variables (16 independent variables and the 3 dimensions of the electronic health literacy scale), the estimated sample size ranged from 95 to 190. Considering a 20% invalid questionnaire rate, this section ultimately included 235 participants.
Data collection
Data were obtained through a self-completed questionnaire between July 20, 2022 and September 10, 2022. The questionnaire included the collection of independent and dependent variable information. The collection of independent variable information was based on a review of previous studies, covering general data related to demographic characteristics, pregnancy features, and sources of obtaining healthcare information. The instrument for collecting dependent variable information is the Chinese version of the eHEALS.
The eHEALS is the original and most frequently used instrument for investigating electronic health literacy [ 33 ]. It was initially developed by Norman and Skinner in 2006 [ 34 ]. The Cronbach alpha coefficient of the original English version of eHEALS is 0.88. The Chinese version of eHEALS was translated by Guo in 2013 [ 35 ]. It consists of 3 dimensions with 8 items, scored on a 5-point Likert scale. The score of each item ranges from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree), with higher scores indicating greater electronic health literacy. The Chinese version of eHEALS demonstrates good reliability and validity. Regarding reliability, the Cronbach’s α coefficient is 0.913 [ 35 ]. For validity, exploratory factor analysis reveals a KMO coefficient of 0.875 and a significant Bartlett’s test of sphericity with a χ2 value of 544.000 (df = 28); confirmatory factor analysis indicates factor loadings ranging from 0.692 to 0.869 [ 35 ]. In our study, the Cronbach’s alpha coefficient for eHEALS was 0.937.
Data analysis
IBM SPSS Statistics was employed for statistical analysis. Demographic and pregnancy characteristics of participants were presented using descriptive statistics. Continuous variables were described by means and standard deviations, or medians and interquartile, depending on the normality of the data. Categorical variables were described by frequencies and percentages. To investigate the correlation between general data and e-health literacy among pregnant women, univariate analysis was performed. Due to the non-normal distribution of the data, either the Mann-Whitney U test or Kruskal-Wallis H test was utilized. Subsequently, the general data of women with gestational diabetes mellitus ( p < 0.05) from the univariate analysis were included as independent variables in a multiple linear regression model, with e-health literacy as the dependent variables, to explore the influencing factors of e-health literacy.
Qualitative phase—in-depth interviews
Study design and sample.
Qualitative data was collected through semi-structured in-depth interviews between September 1, 2022, and October 3, 2022. The sample size was determined based on the saturation principle, which means that sample recruitment continued until no new codes emerged [ 36 ]. Ultimately, a total of 11 participants were enrolled. Among these, four participants took part in both the qualitative and quantitative segments of the study, while the remaining seven exclusively contributed to the qualitative phase.
Before the interviews began, a survey was conducted on the personal basic information and electronic health literacy status of all 11 participants involved in the interviews.
The semi-structured interview instrument comprised 10 questions (Supplementary 1 ). The interview location was a quiet and clean reception room for pregnant women at the obstetrics clinic, which ensured the privacy of the interviews. Two researchers were involved: one recorded environmental information, interviewees’ non-verbal communication, and facial expressions, while the other conducted the interviews with pregnant women. Midway through the study, owing to the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers conducted interviews with pregnant women via online video calls. All interviews were audio-recorded and transcribed verbatim.
The qualitative data from 11 interview transcripts were coded using NVivo 11.0, and analyzed using the inductive content analysis method described by Elo and Kyngäs [ 37 ]. The process of inductive content analysis comprises three phases. Open coding (Phases 1): researchers immersed themselves in the text data, generating numerous notes and headings to capture the content comprehensively. Subsequently, the researchers organized the headings into coding sheets and freely generated categories. Creating categories (Phases 2): the researchers amalgamated akin or disparate categories into higher-order categories for reducing the number of categories. Abstraction (Phases 3): the researchers delineated research topics through the utilization of generalized descriptions, thereby shaping the themes.
Quantitative results
Description of the sample.
The eHEALS score in the Chinese version, obtained from 235 women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus, spanned from 8 to 40, with a median score of 29 (IQR, 26 to 32). The median age of these participants was 31 (IQR, 29 to 34) years and their median gestational age was 34 (IQR, 32 to 36) weeks. All individuals involved in the study identified as Han Chinese. Further demographic and pregnancy characteristics of participants are shown in Table 1 .
Influencing factors of electronic health literacy in women with gestational diabetes mellitus
The results of single factor analysis indicated that educational status ( p = 0.003), experience of accessing health information from clinicians or nurses ( p = 0.022), experience of accessing health information from social forums or WeChat official accounts ( p = 0.018), experience of accessing health information from applications ( p = 0.016), experience of accessing health information from Internet pages ( p = 0.046), and satisfaction with health information on the Internet ( p = 0.002) had a statistically significant difference in electronic health literacy scores of women with gestational diabetes mellitus. The results are shown in Table 1 . Additionally, correlation analysis of gestational weeks and electronic health literacy scores showed that gestational weeks and electronic health literacy were not correlated in women with gestational diabetes mellitus ( p = 0.346).
In the multiple linear regression analysis, the eHEALS score served as the dependent variable, while the statistically significant factors identified in the univariate analysis were considered independent variables. P < 0.05 indicates statistical significance. Results showed that women with gestational diabetes mellitus who accessed health information from clinicians or nurses scored higher on the eHEALS than those who did not (β = 0.137, p = 0.029). Similarly, women with gestational diabetes mellitus who accessed health information from applications demonstrated higher eHEALS scores than those who did not do (β = 0.159, p = 0.013). These results are shown in Table 2 .
Qualitative findings
A total of 11 women with gestational diabetes mellitus participated in the interviews, designated with identifiers P1 to P11 based on the interview sequence. All interviewees were married and of Han nationality. Their age ranged from 27 to 36 years, with an average age of approximately 31 years. Three participants were in their second trimester, while the remaining were in their third trimester. Notably, only one interviewee, identified as P1, had prior pregnancy experience and already had one child. Furthermore, the ninth participant possessed a medical background and resided in a rural area. Among the participants, five individuals scored 32 points or more on the Chinese version of eHEALS (The score of eHEALS range from 26 to 40). The general information about the participants is presented in Supplementary 2 .
Based on the results of the interviews, a total of 4 themes and 12 sub-themes were identified. Supplementary 3 presents excerpts of selected quotes corresponding to each theme.
Reasons and basis for accessing health information from the internet
This theme revealed why and how women with gestational diabetes mellitus access health information from the Internet. They access information pertaining to maintaining a healthy pregnancy, managing their condition, monitoring fetal growth and development, and ensuring a successful delivery by utilizing Internet searches or subscribing to popular medical science articles disseminated via WeChat official accounts and pregnancy-related applications. The preference for electronic media among women with gestational diabetes mellitus is influenced by factors such as their previous information-seeking habits, recommendations from friends, and insights derived from data analysis. These information-seeking behaviors are motivated by concerns regarding health risks associated with disease exposure and perceived barriers to effective doctor-patient communication.
Reasons for accessing health information from the internet
The majority of interviewees reported actively seeking or passively receiving health information from the Internet. Their motivations included encountering abnormal prenatal examination results, experiencing personal or family physical discomfort, and lacking sufficient knowledge about various medical conditions.
Furthermore, some interviewees highlighted communication barriers between healthcare providers and patients, including distrust of doctors, dissatisfaction with their performance, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, as factors prompting them to resort to the Internet for health information.
Basis for selecting electronic media providing health information
The interviewees utilize diverse electronic media platforms like Baidu, Little Red Book, and Baby Tree for accessing health information. Their choices are frequently influenced by previous preferences, recommendations from acquaintances, and the promotion of big data.
Address barriers to accessing and applying online health information
Many barriers impede women with gestational diabetes mellitus in accessing and applying health information available online, including advertising, inappropriate medical depth of health information, redundant and cluttered health information, conflicting opinions on the same health issue, wide period and content span for health information update, and difficulties in evaluating the quality, sources, and safety of online health information. In response, they adopted strategies to address these barriers, including asking for help, exploring and practicing independently, and assessing the credentials of health information providers.
Barriers abound
During the interviews, women with gestational diabetes mellitus indicated that they encountered many barriers in accessing information. Two interviewees noted excessive hidden advertisements in online health information. Additionally, two interviewees pointed out that the medical depth of the health information available online was inappropriate and they expressed that this health information was insufficient to address their health concerns. Furthermore, three interviewees expressed difficulty in making decisions due to the plethora of conflicting opinions encountered online regarding the same health issue. Two respondents highlighted that the frequency and scope of updates to online health information posed obstacles to their access. Three respondents expressed apprehensions regarding the quality, source, and safety of the information available online.
Respond to barriers
Whenever women with gestational diabetes mellitus encounter difficulties accessing valuable health information online or have doubts about the reliability of the information they find, they tend to seek guidance from individuals with more expertise or experience, such as hospital doctors, online healthcare professionals, and peers who have similar experiences. They said that if they did not know whether health information available online was credible, they would try to practice it personally and judge the truth of health information based on their health changes. In addition, they expressed that they would try to retrieve health information through multiple online sources, compare the information content, and finally trust the highly overlapping parts. Furthermore, they also evaluate the credibility of online health information by assessing the credentials of information providers.
Desires for a higher level of online health information services
Women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus often turn to the Internet as a supplementary resource for obtaining health-related information, yet deficiencies persist within current online health information platforms. Their expressed aspirations for enhanced online health services manifest across four key dimensions, as outlined below.
Desires for online transmission media with simple design and easy-to-use search function
Women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus express a preference for online health information platforms that prioritize user-friendly design and enhanced searchability. Such features streamline software navigation, thereby facilitating their information retrieval process.
Desires for diversified online transmission forms of health information
Women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus expressed a clear preference for online health information dissemination to encompass not only simple textual descriptions but also incorporate videos and images, thereby enhancing the comprehensibility and appeal of the content.
Desires for online information platforms containing real cases and experience sharing
Women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus articulated the wish for web-based platforms to feature shared experiences from pregnant women and real-life cases. This inclusion is seen as instrumental in fostering confidence in recovery, accessing credible health information, and gaining deeper insights into pregnancy-related matters.
Desires for online information platforms with strong interactivity and personalized health information push services
Women with gestational diabetes mellitus expressed their desire for the personalized push service of health information provided by the web-based platforms, preferably sending health information according to their pregnancy duration. They also seek increased interaction with medical professionals on web-based platforms to receive more personalized and relevant advice and guidance.
Outcomes of accessing and applying online health information
Women with gestational diabetes mellitus noted that applying and accessing online health information could not only enhance their health literacy but also foster greater awareness of adopting a healthy lifestyle and encourage increased involvement from their spouses. However, they also acknowledged potential adverse effects, such as heightened anxiety stemming from the treatment experiences shared by others.
Popularization of health knowledge
Women with gestational diabetes mellitus point out that accessing online health information has improved their health knowledge and helps them effectively control blood sugar levels.
Emotional feedback
Some women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus remarked that the severity of the condition was often exaggerated on the Internet, leading to heightened anxiety. Furthermore, encountering accounts of successful disease management shared by others sometimes evoked feelings of self-doubt regarding their own ability to manage the condition, consequently causing stress and anxiety. Conversely, one woman with gestational diabetes mellitus expressed that upon encountering individuals facing similar health challenges online, she found solace in the shared experience of others facing similar struggles.
Increased awareness about adapting healthy lifestyles
Women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus emphasized that their awareness of adopting healthy lifestyles had been heightened through their exploration of health information accessible on the Internet.
Increased husband’s sense of involvement and experience
Women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus noted that their husbands also have the opportunity to access online health information, thereby enabling them to gain a deeper understanding of the pregnancy experience.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate electronic health literacy among women with gestational diabetes mellitus through a mixed-methods design. Our study indicates that the electronic health literacy of women with gestational diabetes warrants improvement. Additionally, we delved into reasons for seeking health information online, barriers encountered, aspirations for improved online health services, and the impacts of utilizing online health information.
In terms of the influencing factors on electronic health literacy, our results indicated that women with gestational diabetes mellitus who accessed health information from medical personnel scored higher on electronic health literacy compared to those who did not, which was inconsistent with Kim et al.‘s finding that there was no difference in electronic health literacy scores between those with type 2 diabetes who relied on health professionals for health information and those who did not [ 38 ]. One possible explanation for this discrepancy is the variation in disease self-management capabilities. The majority of people with type 2 diabetes surveyed had managed their diabetes for 1–10 years, while participants in our study were diagnosed with gestational diabetes for a maximum of three months. The duration of illness positively correlates with the level of self-management [ 39 ]. This suggests that gestational diabetes patients may have weaker disease self-management abilities compared to type 2 diabetes patients, leading to a greater need for healthcare professionals’ assistance in addressing more health issues and facilitating gestational diabetes women’s understanding and application of online health information [ 40 ]. Additionally, the reason for this outcome in our study may be attributed to inadequate communication between healthcare professionals and patients [ 41 ]. Evidence suggests that individuals turn to the internet for information when their health concerns are not addressed by healthcare providers during consultations [ 41 ]. In the qualitative portion of our study, some patients reported that their issues were not fully resolved after communication with healthcare providers or that new uncertainties arose from these interactions. Consequently, women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus turn to the internet as an additional resource for health information, thereby augmenting their level of electronic health literacy [ 42 ].
The control of blood sugar levels is crucial for women with gestational diabetes mellitus, and continuous blood sugar monitoring, along with maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle, is key to controlling blood sugar [ 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 ]. Our research findings indicate that by accessing online health information, women with gestational diabetes mellitus can gain a deeper understanding of information related to blood sugar control, thereby effectively managing their blood sugar levels. Amr Jamal et al. have also noted that patients who engage in online health information queries have a better understanding of diabetes-related knowledge and demonstrate stronger blood sugar management capabilities compared to those who do not [ 47 ]. Therefore, future research should continue to explore the impact of this online health information on blood sugar management among women with gestational diabetes mellitus, thus effectively improving the management and prognosis of the disease.
Studies have demonstrated that precise health guidance aids in both treating gestational diabetes and preventing its development in high-risk pregnant women [ 48 , 49 ]. Although the qualitative results of this study indicate that online health information searches play a role in health guidance, this depends on the quality of the information obtained. Accurate online medical information can assist patients in comprehending their condition and guide them toward suitable treatment options [ 50 ]. However, inaccurate or misleading information can result in confusion and treatment delays [ 51 ]. The results of our qualitative study showed that women with gestational diabetes mellitus were not competent in discerning the quality of health information available online. Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate the quality of online health information. Presently, several tools have been developed to assess the quality of websites providing health information, including DISCERN, HONcode, and CRAAP [ 52 ]. However, current investigations into the quality of online health information primarily focus on cancer patients [ 53 , 54 , 55 ], with relatively limited research on the quality of online health information for gestational diabetes. Future studies could address this gap to assist gestational diabetes women in better selecting online health information. Additionally, the authority of online health information publishers has a positive impact on the credibility of health information [ 56 ]. Medical professionals have traditionally been the primary source of health information for individuals, being widely regarded as the most authoritative [ 57 ]. In our study, participants expressed a greater willingness to trust online health information published by certified healthcare professionals. These indications suggest the necessity of encouraging healthcare professionals to take responsibility for providing online guidance and support to women with gestational diabetes, thereby facilitating their access to and utilization of high-quality online healthcare information.
In terms of the design of online health platforms, interviewees expressed desires for easy access to health information, receiving personalized push services of health information, and increased interaction with medical personnel through these platforms, aligning with findings by Nijland et al. [ 58 ]. These implied that at the outset of developing online health information platforms, platform designers need to consider how to deliver health information to users in an understandable and accessible manner, as well as how to tailor health information to users’ needs [ 59 ].
Due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, we chose to conduct online video interviews with some participants. Compared to traditional offline interviews, online interviews offer more convenience in terms of time and space, but they also present some challenges [ 60 ]. Firstly, there are issues with internet connectivity, as online video interviews may be affected by network interruptions, thus disrupting the smooth progress of the interviews [ 61 ]. Secondly, online video interviews lack the emotional connection and interpersonal interaction of face-to-face communication, which may affect the richness of the information provided by the interviewees [ 62 ]. Lastly, due to issues with image quality and angles, online video interviews may not accurately capture the facial expressions and body language of the interviewees, thereby impacting the understanding and interpretation of the interview information [ 63 ]. The epidemic has sparked increased interest in video interviews, but video interviews should not be seen solely as expedient measures in response to the pandemic, but rather as an opportunity for long-term methodological advancement. Future research should further optimize the process of online video interviews to facilitate the development of virtual qualitative research methods.
Limitations
Some limitations needed to be reported. Firstly, the quantitative study utilized a self-assessment scale as the research instrument. Participants may have either exaggerated or minimized certain information to obtain more favorable results, potentially introducing reporting bias. Secondly, all participants were sourced from a single hospital, potentially impacting the generalizability of the findings. Lastly, participants who engaged in both quantitative and qualitative phases of the study appeared more prepared at qualitative interviews compared to those solely involved in the qualitative phase. This discrepancy may introduce bias into their responses.
Conclusions
Women with gestational diabetes mellitus have a low level of electronic health literacy and insufficient ability to assess online health information, and the source of health information could influence their electronic health literacy. They often accessed health information from the Internet due to perceived disease threats and blocked doctor-patient communication. Furthermore, they highlighted numerous barriers to accessing electronic health information and expressed a desire for enhanced quality in online information services. It is recommended to enhance doctor-patient communication and encourage medical staff to take on a guiding and supportive role to facilitate access to valuable information. Additionally, the development of assessment tools tailored to online health information suitable for women with gestational diabetes mellitus is proposed. Furthermore, improvements to online health information platforms are suggested to better align with user needs, thereby enhancing the electronic health literacy of women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus.
Data availability
Owing to the confidentiality of the information, the datasets generated and analyzed in this study are not publicly available. Nevertheless, upon reasonable request, they can be made accessible through the corresponding author.
Choudhury AA, Devi Rajeswari V. Gestational diabetes mellitus - A metabolic and reproductive disorder. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;143:112183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112183 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Plows JF, Stanley JL, Baker PN, Reynolds CM, Vickers MH. The pathophysiology of gestational diabetes Mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113342 .
International association of D, pregnancy study groups consensus P, Metzger BE, Gabbe SG, Persson B, Buchanan TA, et al. International association of diabetes and pregnancy study groups recommendations on the diagnosis and classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(3):676–82. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-1848 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Sirico A, Raffone A, Maruotti GM, Travaglino A, Paciullo C, Diterlizzi A, et al. Third trimester myocardial performance index in fetuses from women with hyperglycemia in pregnancy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Ultraschall Med. 2023;44(2):e99–107. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1499-7265 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Sirico A, Rizzo G, Maruotti GM, Aiello E, Morlando M, Arduini D, et al. Does fetal macrosomia affect umbilical artery doppler velocity waveforms in pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes? J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;29(20):3266–70. https://doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2015.1121479 .
Kariniemi K, Vaarasmaki M, Mannisto T, Mustaniemi S, Kajantie E, Etelainen S, et al. Neonatal outcomes according to different glucose threshold values in gestational diabetes: a register-based study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024;24(1):271. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-024-06473-4 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Zhang Q, Lai S, Zhang Y, Ye X, Wu Y, Lin T, et al. Associations of elevated glucose levels at each time point during OGTT with fetal congenital heart diseases: a cohort study of 72,236 births. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023;23(1):837. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-023-06152-w .
Ouyang H, Chen B, Abdulrahman A-M, Li L, Wu N. Associations between gestational diabetes and anxiety or depression: a systematic review. J Diabetes Res. 2021;2021(9959779). https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9959779 .
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice C. 15. Management of diabetes in pregnancy: standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S232–43. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc22-S015 .
Article Google Scholar
Brennan L, Teede H, Skouteris H, Linardon J, Hill B, Moran L. Lifestyle and behavioral management of polycystic ovary syndrome. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2017;26(8):836–48. https://doi.org/10.1089/jwh.2016.5792 .
Sayakhot P, Carolan-Olah M. Sources of information on gestational diabetes Mellitus, satisfaction with diagnostic process and information provision. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016;16(1):287. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-016-1067-9 .
Hou X, Chen J, Zhao W, J C J O H I, Management. Qual Anal Public Med Health Inform Internet. 2014;11(1):38–42.
Google Scholar
Norman CD, Skinner HA. eHealth literacy: Essential Skills for Consumer Health in a Networked World. J Med Internet Res. 2006;8(2):e9. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.8.2.e9 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Nutbeam D, Lloyd JE. Understanding and responding to Health Literacy as a Social Determinant of Health. Annu Rev Public Health. 2021;42:159–73. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-publhealth-090419-102529 .
Campanozzi LL, Gibelli F, Bailo P, Nittari G, Sirignano A, Ricci G. The role of digital literacy in achieving health equity in the third millennium society: a literature review. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1109323. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1109323 .
Filabadi ZR, Estebsari F, Milani AS, Feizi S, Nasiri M. Relationship between electronic health literacy, quality of life, and self-efficacy in Tehran, Iran: a community-based study. J Educ Health Promot. 2020;9:175. https://doi.org/10.4103/jehp.jehp_63_20 .
Lin CY, Ganji M, Griffiths MD, Bravell ME, Brostrom A, Pakpour AH. Mediated effects of insomnia, psychological distress and medication adherence in the association of eHealth literacy and cardiac events among Iranian older patients with heart failure: a longitudinal study. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2020;19(2):155–64. https://doi.org/10.1177/1474515119873648 .
Mitsutake S, Shibata A, Ishii K, Oka K. Associations of eHealth literacy with Health Behavior among adult internet users. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18(7):e192. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.5413 .
Yang SC, Luo YF, Chiang CH. The associations among individual factors, eHealth Literacy, and Health-promoting lifestyles among College Students. J Med Internet Res. 2017;19(1):e15. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.5964 .
Cui GH, Li SJ, Yin YT, Chen LJ, Li JQ, Liang FY, et al. The relationship among social capital, eHealth literacy and health behaviours in Chinese elderly people: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2021;21(1):45. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-10037-4 .
Giger JT, Barnhart S, Feltner F, Slone M, Lawler MJ, Windsor L, et al. Validating the eHealth literacy scale in rural adolescents. J Rural Health. 2021;37(3):504–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/jrh.12509 .
Tubaishat A, Habiballah L. eHealth literacy among undergraduate nursing students. Nurse Educ Today. 2016;42:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2016.04.003 .
Hoogland AI, Mansfield J, Lafranchise EA, Bulls HW, Johnstone PA, Jim HSL. eHealth literacy in older adults with cancer. J Geriatr Oncol. 2020;11(6):1020–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgo.2019.12.015 .
Moore C, Hassett D, Dunne S. Health literacy in cancer caregivers: a systematic review. J Cancer Surviv. 2021;15(6):825–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-020-00975-8 .
Guo SH, Hsing HC, Lin JL, Lee CC. Relationships between Mobile eHealth literacy, diabetes Self-care, and glycemic outcomes in Taiwanese patients with type 2 Diabetes: cross-sectional study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2021;9(2):e18404. https://doi.org/10.2196/18404 .
Xie T, Zhang N, Mao Y, Zhu B. How to predict the electronic health literacy of Chinese primary and secondary school students? Establishment of a model and web nomograms. BMC Public Health. 2022;22(1):1048. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-13421-4 .
Alhuwail D, Abdulsalam Y. Assessing Electronic Health Literacy in the state of Kuwait: survey of internet users from an arab state. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(5):e11174. https://doi.org/10.2196/11174 .
Rezakhani Moghaddam H, Ranjbaran S, Babazadeh T. The role of e-health literacy and some cognitive factors in adopting protective behaviors of COVID-19 in Khalkhal residents. Front Public Health. 2022;10:916362. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.916362 .
Rahdar S, Montazeri M, Mirzaee M, Ahmadian L. The relationship between e-health literacy and information technology acceptance, and the willingness to share personal and health information among pregnant women. Int J Med Informatics. 2023;178:105203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2023.105203 .
Korkmaz Aslan G, Kılınç İşleyen E, Kartal A, Koştu N. The relation between eHealth literacy and healthy lifestyle behaviours in pregnant women. Health Promot Int. 2024;39(2). https://doi.org/10.1093/heapro/daae022 .
Demir Y, Dağ E, Özpinar S. The relationship of E-health Literacy with Cyberchondria: a cross-sectional study on pregnant women. J Health Lit. 2024;89–101. https://doi.org/10.22038/jhl.2024.76171.1501 .
Ni P, Chen J, Liu N. The sample size estimation in quantitative nursing research. Chin J Nurs. 2010;45(4):378e80.
Lee J, Lee EH, Chae D. eHealth Literacy Instruments: systematic review of Measurement Properties. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23(11):e30644. https://doi.org/10.2196/30644 .
Norman CD, Skinner HA. eHEALS: the eHealth literacy scale. J Med Internet Res. 2006;8(4):e27. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.8.4.e27 .
Guo S, Yu X, Sun Y, Et, Nie D, Li X, Wang L. Adaptation and evaluation of Chinese version of eHEALS and its usage among senior high school students. Chin J Health Educ. 2013;29(2):106–8.
Bradshaw C, Atkinson S, Doody O. Employing a qualitative description approach in health care research. Global Qualitative Nurs Res. 2017;4:2333393617742282. https://doi.org/10.1177/2333393617742282 .
Elo S, Kyngäs H. The qualitative content analysis process. Journal of advanced nursing. 2008, 62(1): 107 – 15. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04569.x .
Kim KA, Kim YJ, Choi M. Association of electronic health literacy with health-promoting behaviors in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Comput Inf Nurs. 2018;36(9):438–47. https://doi.org/10.1097/CIN.0000000000000438 .
Lan X, Lu X, Yi B, Chen X, Jin S. Factors associated with self-management behaviors of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Jpn J Nurs Sci. 2022;19(1):e12450. https://doi.org/10.1111/jjns.12450 .
Wah YYE, Mcgill M, Wong J, Ross GP, Harding A-J, Krass I. Self-management of gestational diabetes among Chinese migrants: a qualitative study. Women Birth. 2019;32(1):e17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wombi.2018.03.001 .
Li N, Orrange S, Kravitz RL, Bell RA. Reasons for and predictors of patients’ online health information seeking following a medical appointment. Fam Pract. 2014;31(5):550–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/fampra/cmu034 .
Wong DK-K, Cheung M-K. Online health information seeking and eHealth literacy among patients attending a primary care clinic in Hong Kong: a cross-sectional survey. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(3):e10831. https://doi.org/10.2196/10831 .
Scott EM, Murphy HR, Myers J, Saravanan P, Poston L, Law GR. MAGIC (maternal glucose in pregnancy) understanding the glycemic profile of pregnancy, intensive CGM glucose profiling and its relationship to fetal growth: an observational study protocol. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023;23(1):563. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-023-05824-x .
Tartaglione L, Di Stasio E, Sirico A, Di Leo M, Caputo S, Rizzi A, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring in women with normal OGTT in pregnancy. J Diabetes Res. 2021;2021(9987646). https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9987646 .
/Nielsen-Bohlman L, Panzer AM, Kindig DA. Health Literacy: A Prescription to End Confusion. Washington (DC). 2004.
Le DC, Vu TB, Tran TN, Nguyen TL, Nguyen TB, Nguyen DC, et al. The effectiveness of Lifestyle Changes in Glycemic Control among pregnant women with gestational diabetes Mellitus. Med (Kaunas). 2023;59(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091587 .
Jamal A, Khan SA, Alhumud A, Al-Duhyyim A, Alrashed M, Bin Shabr F, et al. Association of Online Health Information-Seeking Behavior and self-care activities among type 2 Diabetic patients in Saudi Arabia. J Med Internet Res. 2015;17(8):e196. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.4312 .
Lin C-L, Huang L-C, Chang Y-T, Chen R-Y, Yang S-H. Effectiveness of Health Coaching in Diabetes Control and Lifestyle Improvement: a randomized-controlled trial. Nutrients. 2021;13(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113878 .
Mohammadian F, Delavar MA, Behmanesh F, Azizi A, Esmaeilzadeh S. The impact of health coaching on the prevention of gestational diabetes in overweight/obese pregnant women: a quasi-experimental study. BMC Womens Health. 2023;23(1):619. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-023-02750-0 .
Li Y, Zhou X, Zhou Y, Mao F, Shen S, Lin Y, et al. Evaluation of the quality and readability of online information about breast cancer in China. Patient Educ Couns. 2021;104(4):858–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2020.09.012 .
Hartzband P, Groopman J. Untangling the Web–patients, doctors, and the internet. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(12):1063–6. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp0911938 .
Portillo IA, Johnson CV, Johnson SY. Quality Evaluation of Consumer Health Information Websites Found on Google using DISCERN, CRAAP, and HONcode. Med Ref Serv Q. 2021;40(4):396–407. https://doi.org/10.1080/02763869.2021.1987799 .
Yang W, Li B, Liu M, Tong D, Zou Y, Li X, et al. Quality evaluation of health information about breast cancer treatment found on WeChat public accounts. Archives Public Health. 2023;81(1):170. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-023-01184-2 .
Arif N, Ghezzi P. Quality of online information on breast cancer treatment options. Breast. 2018;37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2017.10.004 .
Sobota A, Ozakinci G. The quality and readability of online consumer information about gynecologic cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2015;25(3):537–41. https://doi.org/10.1097/IGC.0000000000000362 .
Sbaffi L, Rowley J. Trust and credibility in web-based Health Information: a review and agenda for Future Research. J Med Internet Res. 2017;19(6):e218. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.7579 .
Almaazmi MA, Samara KA, Jarai M, Majeed H, Barqawi HJ. The usage and Trustworthiness of Various Health Information Sources in the United Arab Emirates: an Online National Cross-sectional Survey. Healthc (Basel). 2023;11(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11050663 .
Nijland N, Van Gemert-Pijnen J, Boer H, Steehouder MF, Seydel ER. Evaluation of internet-based technology for supporting self-care: problems encountered by patients and caregivers when using self-care applications. J Med Internet Res. 2008;10(2):e13. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.957 .
Eysenbach G, Jadad AR. Evidence-based patient choice and consumer health informatics in the internet age. J Med Internet Res. 2001;3(2):E19. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.3.2.e19 .
Rupert DJ, Poehlman JA, Hayes JJ, Ray SE, Moultrie RR. Virtual Versus In-Person focus groups: comparison of costs, recruitment, and Participant Logistics. J Med Internet Res. 2017;19(3):e80. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.6980 .
Ullman SE. Conducting virtual interviews with sexual assault survivors and their informal supports during COVID-19 and beyond. J Interpers Violence. 2024;39(7–8). https://doi.org/10.1177/08862605231207619 . 1398 – 420.
Irvine A, Drew P, Sainsbury R, ‘Am. I not answering your questions properly?’Clarification, adequacy and responsiveness in semi-structured telephone and face-to-face interviews. Qualitative Res. 2013;13(1):87–106. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468794112439086 .
Keen S, Lomeli-Rodriguez M, Joffe H. From challenge to opportunity: virtual qualitative research during COVID-19 and Beyond. Int J Qual Methods. 2022;21:16094069221105075. https://doi.org/10.1177/16094069221105075 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the pregnant women who participated in our study.
The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities [grant number 2021PT073] supported this research.
Author information
Jingqi Xu, Yujia Chen and Jing Zhao are considered as co-first authors.
Authors and Affiliations
School of Nursing, Wuhan University, No. 115, Donghu Road, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071, China
Jingqi Xu, Yujia Chen, Jing Zhao, Jiarun Wang, Jianfei Chen, Xinlong Pan, Wei Zhang, Zhijie Zou & Xiaoli Chen
Hospital of Stomatology, Wuhan University, 237 Luoyu Road, Wuhan, Hubei, 430079, China
Magnet Program & Nursing Research Department, UT Southwestern Medical Center, 8200 Brookriver Dr, Dallas, TX, 75247, USA
Yingzi Zhang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JX: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing - Original Draft; YC: Methodology, Validation, Writing - Original Draft; JZ: Methodology, Investigation, Writing - Original Draft; JW: Methodology, Validation, Investigation; JC: Investigation, Data Curation; XP: Investigation, Data Curation; WZ: Validation, Data Curation; JZ: Conceptualization, Writing - Review & Editing, Supervision; ZZ: Conceptualization, Writing - Review & Editing, Supervision; XC: Conceptualization, Writing - Review & Editing, Supervision, Project administration; YZ: Validation, Data Curation.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Jin Zheng , Zhijie Zou or Xiaoli Chen .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was conducted in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants provided signed informed consent to participate in the study. Ethical approval for the study was granted by the Medical Ethics Committee of Wuhan University (2021YF0048).
Consent for publication
Participants were notified, at the time of signing their informed consent, that their data (including questionnaire information and audio recordings) would be encoded and utilized for the purpose of drafting and publishing the paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Xu, J., Chen, Y., Zhao, J. et al. Current status of electronic health literacy among pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and their perceptions of online health information: a mixed-methods study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 24 , 392 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-024-06594-w
Download citation
Received : 24 January 2024
Accepted : 20 May 2024
Published : 28 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-024-06594-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Gestational diabetes mellitus
- Electronic health literacy
- Online health information
- Pregnant women
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth
ISSN: 1471-2393
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 28 May 2024
Maternal employment characteristics as a structural social determinant of breastfeeding after return to work in the European Region: a scoping review
- Pauline Brugaillères 1 ,
- Séverine Deguen 1 ,
- Sandrine Lioret 2 ,
- Sahar Haidar 3 ,
- Corinne Delamaire 3 ,
- Emilie Counil 4 , 5 &
- Stéphanie Vandentorren 1 , 3
International Breastfeeding Journal volume 19 , Article number: 38 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
The European Region has the lowest rate of exclusive breastfeeding at 6 months worldwide. Improving work-related breastfeeding issues is important given that women may have difficulties combining work and breastfeeding, especially those in precarious working situations, which adds to their adversity. This scoping review overviews research on the maternal employment characteristics that support breastfeeding continuation after return to work in the European Region.
Studies published from 2013 to 2023 were collected from Scopus, PubMed, and PsycInfo. Quantitative and qualitative studies published in English or French that explored the association between maternal employment characteristics and any breastfeeding status, duration, or experience were included. Participants included were mothers of healthy children who continued breastfeeding after resuming work. The main determinants were work-related factors that can lead to socially differentiated working conditions, including type of employment (e.g., occupation, employed/self-employed status, type of contract, working time, occupational prestige), working conditions (e.g., work schedule, decision latitude, latitude to organize worktime), and work environment (e.g., occupational exposure, family-friendly workplace policy, social support). The geographic area encompassed countries included in the World Health Organization European Region.
Of the 693 single studies retrieved and screened, 13 were included in the review. Eight studies focused on combining work and breastfeeding, while the others had a broader spectrum by investigating breastfeeding determinants. The represented countries were Spain ( n = 4), France ( n = 4), UK ( n = 2), Ireland ( n = 2), and the Netherlands ( n = 1). Results highlighted the heterogeneity of measures, time frames, and fields of inquiry, thus revealing a lack of conceptual framework regarding the links between work, breastfeeding, and social health inequalities. Nonetheless, being self-employed, working in a non-manual profession with time flexibility, having lactation rooms at work, being supported by co-workers, and having a breastfeeding workplace policy were salient factors that supported breastfeeding in working mothers.
Conclusions
Supporting working mothers who choose to breastfeed is important given the myriad of adverse factors faced by mothers and their children. These results advocate for targeted actions at the workplace such as time flexibility, breastfeeding facilities, and the promotion of breastfeeding-friendly policies.
Breastfeeding rates remain relatively low in high-income countries, particularly in the WHO European Region, which has the lowest rates of exclusive breastfeeding in infants aged 6 months compared with other regions, standing at about 25% [ 1 ]. Breastfeeding practices vary substantially across high-income countries and within the European Region [ 2 ]. As revealed by a survey comparing data from 11 European countries, between 56% (Ireland) and 98% (Norway) of infants were reported to receive any human milk after birth; at 6 months, 38% (Italy) to 71% (Norway) of infants were continuing breastfed, while 13% (Denmark) to 39% (Netherlands) were exclusively breastfed [ 3 ]. These cross-national variations in breastfeeding practices may be partially explained by the various social policies in place. Maternity leave regulations differ substantially across the European Region: countries like Sweden, Finland, and Portugal, which offer lengthy and well-compensated maternity leave and have greater uptake, flexibility, and division of leave between parents, show better breastfeeding outcomes in terms of initiation and duration [ 4 ].
Indeed, policy attributes are one of the five types of determinants for successful breastfeeding, together with community, health care-related, psycho-social, and sociodemographic attributes [ 4 ]. According to the conceptual model proposed by the 2016 Lancet Breastfeeding Series, breastfeeding determinants operate from the most distal levels – i.e., sociocultural context, formula milk industry, health system, family or community, and workplace or employment – to the most proximal levels – i.e., individual factors such as mother and infant attributes and mother-infant relationship [ 5 ]. From a socioecological perspective, regulations play the most crucial role in breastfeeding initiation and duration rates such as the existence of baby-friendly hospitals, the international code of marketing for breast-milk substitutes, and maternal, paternal, and parental leave [ 5 , 6 ]. In the workplace, employers have legal obligations toward lactating mothers, although public policies are still needed for working women to effectively support their choice to breastfeed. Moreover, employment is sometimes conceptualized as the relationship between a woman’s productive and reproductive work; because breastfeeding is sex-specific, it challenges the feminist principle of gender-neutral child rearing [ 7 ]. Indeed, the socioecological framework does not take into account how gender is inherently connected with breastfeeding at the structural, cultural, and personal levels such as the place of motherhood in women’s lives, the sexualization versus maternal function of their bodies, and the issue of personal choice [ 4 , 8 ].
Returning to work while still breastfeeding remains the main challenge faced by lactating mothers [ 5 , 9 , 10 ]. Work-related factors include working full-time, not having access to a suitable place to express and store breast milk, not being supported by co-workers, and returning to work earlier, which all impair breastfeeding intention and practices, including initiation and duration [ 5 ]. Removing work-related breastfeeding barriers is especially important given women’s active participation in the labor force. Furthermore, it has been shown that supporting breastfeeding reduces sick leave due to child illness [ 11 ]. In contemporary Western societies, even though breastfeeding is praised particularly for its health benefits, there is considerable cultural stigmatization around the current practice of breastfeeding [ 12 ], and women may face many difficulties when trying to combine work and breastfeeding. This is especially true for women experiencing socioeconomic disadvantage. Indeed, women with low education level are frequently in low-skilled or precarious employment, characterized by non-supportive breastfeeding environments (e.g., manual labor, full-time, lack of flexibility) [ 13 , 14 ].
The macro-theoretical framework proposed by the WHO Commission on Social Determinants of Health gives some insight into the relations between employment and health inequalities [ 15 ] (Additional file 1 ). From this, and with the aim of better supporting working women who choose to breastfeed, the present study proposes a deeper understanding of the work-related factors that may hinder this personal/family choice and that may, in turn, worsen social inequalities in maternal and child health. To our knowledge, no study to date has reviewed the structural social determinants of breastfeeding in Europe such as maternal employment in light of the social inequalities in breastfeeding practices after return to work. To fill this gap, the present scoping review aims to identify the maternal employment characteristics that support any breastfeeding continuation after resuming work in the European Region.
This scoping review was guided by the Joanna Briggs Institute’s approach to scoping reviews [ 16 ] and compliant with the PRISMA-ScR checklist [ 17 ].
Inclusion criteria
Full-text peer-reviewed articles using quantitative and/or qualitative methods and published in English or French between 2013 and 2023 were included according to the following inclusion criteria: (1) Population: mothers of a healthy child with an experience of breastfeeding after resuming work; (2) Outcomes: any breastfeeding duration (i.e., exclusive, predominant, or partial), breastfeeding status, or breastfeeding experience after returning to work; (3) Main determinants: any maternal employment factors that can lead to socially differentiated working conditions, including organizational aspects such as work type, work schedule, worktime flexibility, or type of contract as well as environmental factors like occupational exposure, arduousness, or social support at work; (4) Geographic coverage of the study: countries in the WHO European Region.
Exclusion criteria
Articles based on interventional studies, opinion pieces, editorials, case studies, or any types of reviews were excluded. Since we focused on mothers choosing to combine breastfeeding and work, studies that only reported associations between breastfeeding practices and maternity leave duration or return to work timeframe were excluded. For the same reason, we also excluded studies focusing solely on breastfeeding intention or initiation, which are events that occur upstream of the return to work. Finally, we excluded studies that only investigated employment as a dichotomous variable (i.e., working vs not working).
Search strategy
Three electronic databases were used, including Scopus, PubMed, and PsycInfo for relevant articles published in the past 10 years (database searches were conducted on October 22, 2022, and updated on March 20, 2023). The search strategy was first developed in Scopus using proximity operators (e.g., W/3 means that two keywords of interest must be within a maximum distance of three words) and was as follows: (TITLE (Breastf* OR "Breast F*" OR (mother* W/3 milk) OR "Infant Feeding") AND (TITLE-ABS-KEY(((*employ* OR work* OR occupation* OR Job) W/3 (mother OR maternal OR women)) OR "work related" OR "Occupation* related" OR Workplace OR ((parental OR matern* OR Mother OR Breastf* OR "Breast F*") W/3 leave) OR ((job OR Work* OR *employ* OR Occupation*) W/3 (characteristic OR Status OR condition OR Schedule)) OR Shift-work* OR Shiftwork OR "return* to work" OR self-employed) OR KEY("Women Working"))). This search was then adapted to each of the different databases (Additional file 2 ).
After eliminating duplicates, P.B. screened all titles and abstracts using a priori eligibility criteria (e.g., type of paper, country, targeted population, breastfeeding outcome). Then P.B. read the full-text articles of the remaining references to confirm their eligibility; a double-check was carried out at 20% by S.D. ( n = 17/87; 89% agreement), with any conflicts being resolved by a third reviewer (S.V.).
Data synthesis and analysis
For each study, data were extracted and summarized in several tables. The following information was reported:
General information concerning the author’s name, country, and study date;
Main study characteristics: study design, period, location, statistical methods, and population size;
Participant characteristics including information on confounders;
Work-related factors considered to support (or not) breastfeeding when returning to work;
Outcome definitions including any, exclusive, or predominant breastfeeding;
Main findings concerning assessments of association, including odds ratios (ORs), hazard ratios (HRs), relative risks (RRs), and other metrics measuring the strength of association of maternal employment characteristics with breastfeeding duration, employment status after returning to work, and experience of breastfeeding as reported in qualitative studies (e.g., work-related barriers and facilitators).
When several measures of association were available for a given outcome, we reported those from the fully adjusted models.
Description of maternal work-related variables
We grouped the work-related variables into three main dimensions described as follows:
Type of employment refers to the terms that govern the organization of work, generally stated in the contract between the employer and employee, and includes the occupation, work status (employed/self-employed), type of contract (permanent/fixed-term/temporary), working time (part-time/full-time) and occupational prestige (manual/non-manual).
Working conditions refers to the constraint level to which workers are subject and includes work schedule (atypical/regular shift), decision latitude, and latitude to organize worktime (onsite/teleworking/hybrid/flexible hours).
Work environment is generally not defined by the contract but includes occupational exposure and hazards (e.g., chemical, physical), family-friendly breastfeeding workplace policies such as workplace facilities (e.g., lactation room, childcare system) and social network characteristics (e.g., parity, social support from manager or colleagues).
Study selection
A total of 856 articles were selected from the three databases (Fig. 1 ). After removing duplicates ( n = 163), 693 articles were screened for possible relevance based on their title and abstract. A total of 87 studies met our inclusion criteria and were subject to a full-text review, with 13 articles meeting the eligibility criteria and being included in this scoping review.
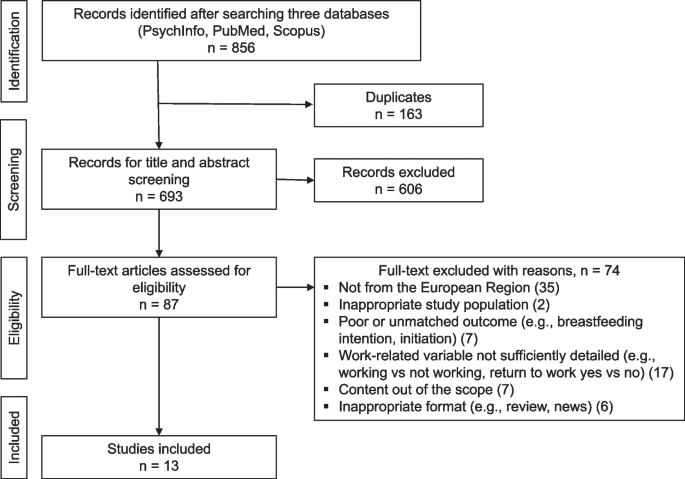
PRISMA flow diagram of study selection
Characteristics of the included studies
Table 1 provides an overview of the included studies: in eight of the articles, the relation between maternal work and breastfeeding practices was main objective [ 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 ], while the remaining five investigated a broader spectrum of determinants [ 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 ]. The majority of studies were conducted in Spain ( n = 4) and France ( n = 4), followed by the UK ( n = 2), Ireland ( n = 2), and the Netherlands ( n = 1). Eight studies were conducted on mothers sampled from the general population, whereas the others targeted mothers working at a university ( n = 3) or immigrant mothers (Latina [ n = 1] or Chinese [ n = 1]). Eight studies were quantitative, and five were qualitative. There was thus substantial heterogeneity between the available studies.
Factors related to the type of employment
A previous study revealed that compared with managers, self-employed mothers were twice as likely to combine breastfeeding and work (OR 95% CI 2.2 (1.1, 4.5)), while intermediate professionals (OR 95% CI 0.6 (0.4, 0.8)) and manual workers (OR 95% CI 0.5 (0.3, 0.9)) were less likely to combine breastfeeding and work [ 22 ]. Accordingly, Villar et al. observed higher rates of predominant breastfeeding at 13 or 16 weeks in non-manual working mothers (59 and 52%, respectively) compared with their manual counterparts (48 and 41%, respectively). However, the likelihood of breastfeeding cessation did not differ between manual and non-manual workers in the fully adjusted model (not adjusted for child’s age) [ 27 ]. Inconsistent results were found concerning the association between working time and breastfeeding. Data from a French birth cohort revealed that working part-time during the first year postpartum was associated with longer breastfeeding duration [ 19 ]. This was especially true for primiparous mothers who were more likely to breastfeed for at least 9 months compared with an intermediate duration of 3 to < 6 months when they shifted from full-time work during pregnancy to part-time work in the first year postpartum (OR 95% CI 1.8 (1.2, 2.7)). However, other studies did not observe significant differences in breastfeeding duration [ 23 , 24 ] or breastfeeding rate at 4 months [ 21 ] depending on the work schedules (part-time vs full-time).
Factors related to the work conditions
Zilanawala et al. investigated maternal nonstandard work schedules and breastfeeding duration: no differences in the odds of breastfeeding duration patterns (i.e., less than 2 months, between 2 and 4 months, more than 4 months) were shown in terms of mothers’ nonstandard working schedules (i.e., working evenings, nights, or weekend shifts) in the fully adjusted models [ 25 ]. Lack of time or flexibility to express milk at work was cited by mothers as a barrier to breastfeeding in several qualitative studies [ 20 , 23 , 30 ] but also discussed as a potential explanatory factor of deleterious breastfeeding outcomes in other studies, which nevertheless did not measure lack of time or flexibility [ 18 , 19 , 21 , 22 ]. Only two studies [ 18 , 24 ] targeting Spanish mothers working at universities have quantitatively measured the ‘Break Time’ dimension using the Workplace Breastfeeding Support Scale (WBSS) [ 31 ]. This dimension measures, for example, mothers’ perception of the frequency and duration of their break time (e.g., “My breaks are frequent/long enough for breastfeeding or pumping breast milk”) but also their time flexibility (“I can adjust my break schedule in order to breastfeed or pump breast milk”) on a 7-point Likert scale. Both studies showed that compared with administrative staff, faculty members took more breastfeeding breaks and were able to organize their breaks more easily. Faculty members were also more likely to continue breastfeeding after returning to work [ 24 ]. However, in these studies, the ‘Break Time’ dimension was not assessed according to breastfeeding outcomes.
Factors related to the work environment
Working environment factors were systematically highlighted in qualitative studies exploring nursing mothers’ experiences [ 20 , 23 , 26 , 29 , 30 ]. The cited breastfeeding facilitators were mostly related to the possibility and ease for mothers to express milk during working hours: availability of adequate breastfeeding facilities (i.e., quiet lactation room with cleaning and storage facilities) [ 18 , 23 , 29 ] or the existence of childcare near the workplaces [ 30 ]. In their quantitative study, Leon-Larios et al. showed that compared with administrative staff, faculty members had easier access to quiet places to pump breast milk and breastfed for longer (association between access to pumping room and breastfeeding duration not assessed) [ 24 ]. Broadly, the workplace breastfeeding policy seems to play a major role: as reported by a French study, women were more likely to breastfeed for more than 4 months when their workplace had implemented a breastfeeding-friendly policy (OR 95% CI 1.8 (1.1, 2.8)), fully adjusted model) compared with those which did not [ 28 ]. When comparing breastfeeding duration between two universities with contrasting breastfeeding policies, Cervera-Gasch et al. highlighted that the factors associated with longer breastfeeding were the university having a breastfeeding support policy and special breastfeeding facilities; participating in breastfeeding support groups; intending to continue breastfeeding after returning to work; knowing the occupational legislation in force; and having a female supervisor [ 18 ]. In line with the latter, the negative attitude of managers and colleagues, the perceived lack of support from them, the difficulty of asking for time to express in the workplace, especially in male-dominated environments, and the stress caused by male gazing were all breastfeeding barriers identified by working mothers [ 20 , 26 ].
This scoping review aimed to identify maternal employment characteristics that support any breastfeeding continuation when returning to work in the WHO European Region. To better highlight the characteristics of employment that can lead to social inequalities, we proposed a classification through three main dimensions: type of employment, working conditions, and work environment. While these dimensions are interrelated, our review highlights that no study to date has combined all three dimensions in their measured variables. Furthermore, there is a large heterogeneity of measured work-related and breastfeeding variables, time frames, and fields of inquiry, thus revealing the lack of a conceptual framework for the links between work, breastfeeding, and social health inequalities. Nevertheless, it appears that being self-employed or working in a non-manual occupation with time flexibility, the availability of breastfeeding facilities at work, the support of co-workers, and the existence of a breastfeeding workplace policy are salient factors that promote breastfeeding among working mothers. These results are interpreted in Fig. 2 .
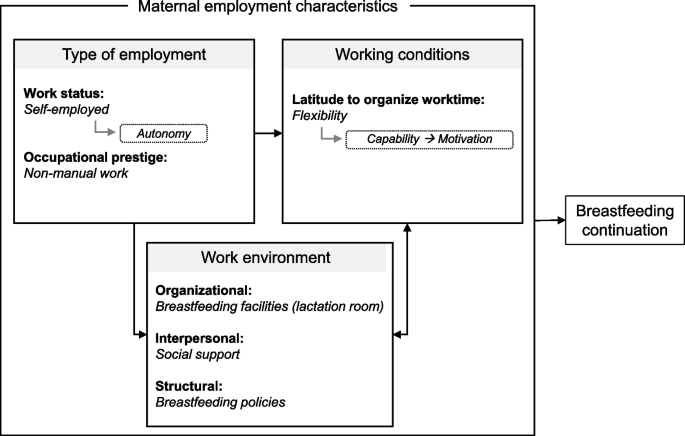
Maternal employment characteristics that support any breastfeeding continuation when returning to work in European countries. Maternal employment characteristics were grouped into three main dimensions. The type of employment dimension refers to the terms that govern the organization of work, generally stated in the contract between the employer and employee. The working conditions dimension refers to the level of constraints to which workers are subjected. The work environment dimension pertains to factors generally not defined by the contract (e.g., family-friendly breastfeeding workplace policies, occupational exposure, social network)
Being self-employed implies a high level of autonomy with an early return to work. This work status was associated with longer breastfeeding duration in France [ 22 ]. As emphasized by authors, the autonomy inherent in the self-employed status can be seen as a factor favoring flexibility and thus the continuation of breastfeeding. Nevertheless, it also implies a greater dedication to work and less institutional support, which would affect the initiation of breastfeeding. A longitudinal Australian cohort study illustrated this duality by showing that women in occupations with higher levels of autonomy and limited hazards (e.g., exposure to extreme noise, temperature levels, chemicals) were more likely to intend to breastfeed and initiate it [ 32 ]. Unfortunately, in the articles identified by this scoping review, occupational exposure was neither measured nor investigated. Finally, it appears that non-manual jobs positively influence breastfeeding [ 28 , 33 ]. These working mothers from socially advantaged backgrounds and with higher education levels probably have a higher degree of health awareness, better health literacy, greater autonomy over their work schedule, more resources to seek help, and better compliance with the existing recommendations [ 33 , 34 ]. In agreement, breastfeeding surveys conducted in 19 European countries showed that a low education level is associated with a lower initiation of breastfeeding and earlier weaning [ 35 ]. As underlined by several European studies, the promotion, protection, and support of breastfeeding should be provided to all breastfeeding mothers, with specific interventions tailored to the more disadvantaged groups such as young and less educated mothers [ 23 , 33 , 35 , 36 ]. Alternative explanations could be that manual working mothers are more likely to stop breastfeeding when resuming work than their non-manual counterparts, so as not to add to the stress or fatigue of their already physically demanding job. As stressed by Rollins et al., the impact of work on breastfeeding is multidimensional, including fatigue and practicality [ 5 ]. A French survey conducted on 1,000 women showed that breast pain, fatigue, and back pain were the main difficulties encountered during breastfeeding [ 37 ].
In terms of the work conditions dimension, the qualitative studies show that worktime flexibility is a major facilitator of breastfeeding continuation. Having the freedom to organize their own working time can potentially increase breastfeeding mothers’ capability, which refers to whether people have the knowledge, skills, and abilities required to engage in a particular behavior. Based on the framework of behavior change by Michie et al., capability influences motivation, which plays a major role in breastfeeding practices [ 38 , 39 , 40 ]. A recent Spanish study showed, for example, that women who decided to opt for exclusive breastfeeding and maintain it “as long as I can” were five times more likely to meet their expectations than women who set less ambitious expectations concerning exclusive breastfeeding duration [ 41 ]. Overall, these results highlight that employment may influence the entire breastfeeding process from intention to continuation. Indeed, breastfeeding intention – which is the strongest predictor of breastfeeding initiation and duration – is formed during pregnancy [ 39 , 42 ]. The mother’s choice could be influenced by the anticipation of their expected work-life balance after resuming work [ 43 , 44 ].
Regarding the work environment dimension, the studies summarized here identified a key feature, namely the importance of a set of underlying conditions: organizational (i.e., presence of adequate lactation room, childcare close to the workplace), structural (i.e., breastfeeding policies in the workplace), and even interpersonal conditions (i.e., support from co-workers), which must coexist to allow mothers to express their milk. In line with the interpersonal dimension, it was underlined that female-dominated environments were perceived to be more positive and supportive, thus enhancing breastfeeding practices [ 18 , 23 , 24 ]. A female environment would facilitate communication and shared experiences [ 23 ]. Findings from a study in the US showed that compared with female coworkers, males were more stigmatizing to lactating colleagues, had more responses of disgust, had a poorer perception of the fairness of the additional break time accorded for pumping breast milk, and showed less support [ 45 ]. Recent literature reviews and meta-analysis unanimously pointed out the lack of research on the effectiveness of interventions to support breastfeeding in the workplace in high-income countries, specifically in the European Region [ 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 ]. As demonstrated in 2022 by Tomori et al. in their review of reviews, inadequate attention is given to interventions addressing policy and structural factors, and only 9% addressed workplace intervention settings [ 48 ].
Our results should also be considered according to different national parental leave and return-to-work policies that play a crucial role in influencing breastfeeding practices. The five countries represented in our corpus (i.e., Spain, France, UK, Ireland and the Netherland) have different statutory well-paid maternity leaves durations that vary from 16 weeks (Spain, France and the Netherland) to 39 weeks (UK) whilst paternity leaves durations vary from 1 week (UK and The Netherland) to 16 weeks (Spain) [ 50 ]. Additional parental leaves are generally low or unpaid, inflexible, and not evenly distributed between fathers and mothers, because of the conservative division of gender roles predominant in these countries [ 4 , 51 ]. Conversely, Sweden, which has one of the most generous, supportive and equitable parental leave programs in the world provides some insights into the integration of breastfeeding and women’s employment [ 52 ]. A cross sectional study among Swedish families revealed that a longer period of shared parental leave was associated with an extended duration of breastfeeding [ 53 ]. Thus, from national policy directives to sociocultural attitudes and values, maternal employment conditions play a crucial role to improve breastfeeding.
This study has several limitations. Inherent to the design of scoping reviews, we did not assess the methodological quality of the included papers, and so we only discuss general, albeit, limited findings regarding breastfeeding and maternal employment. This work lacks representativeness, since only five of the 53 countries included in the WHO European Region were represented in our study selection with an exclusive representation of the countries in North-West and Southern Europe. Finally, from a methodological point of view, we observed heterogeneity in the description and analysis of maternal work-related variables, thus making comparisons difficult across studies. As underlined by some authors, data on work characteristics were often limited [ 22 ], and job title classifications should be homogenized throughout the European Region [ 54 ]. While not investigated in our corpus, we may assume that other stressor factors such as job insecurity, occupational exposure to chemicals, and physical strain may also affect breastfeeding practices. Given that some studies from our corpus did not specifically aim to assess the associations between breastfeeding and maternal work, the infant’s age at the time of breastfeeding cessation was not always reported or considered in the adjusted models: this made it difficult to interpret the reason for breastfeeding cessation (e.g., work-related, meeting expectations, duration regarded as sufficient). The strength of this scoping review lies in its innovative approach by considering maternal employment characteristics in light of social inequalities. Broadly, and as conceptualized by the WHO [ 15 ], employment conditions can lead to social health inequalities through numerous behavioral, psychosocial, and physio-pathological pathways: employment conditions (e.g., full-time work, precarious employment) influence working conditions (e.g., physical and chemical hazards, ergonomics, psychosocial), and both are affected by social and family networks, health system, material deprivation, and economic inequalities. The scoping review methodology allowed us to apply a broad research question and iterative search strategy to gain a comprehensive overview of the current literature on maternal work characteristics and breastfeeding as a major public health outcome. Additionally, we considered the association between maternal work characteristics and any types of breastfeeding, without restricting the analysis to exclusive breastfeeding. We believe that this inclusive approach is relevant given the beneficial effects of breastfeeding, even partial, compared with not breastfeeding [ 55 , 56 ].
This review highlights that the pursuit of breastfeeding after returning to work is associated with various work characteristics that act at different interrelated dimensions (i.e., type of employment, working conditions, and work environment). Supporting disadvantaged working mothers who choose to breastfeed is all the more important given the myriad of adverse factors to which underprivileged mother and child dyads are exposed. Results from our review suggest the need for policy directives or workplace interventions to improve employment quality in order to favor work-life balance: targeting low skilled or precarious jobs by increasing flexibility and reorganizing manual work posts to be less stressful could be a relevant perspective to reduce social health inequalities broadly, and in particular, in relation to breastfeeding practices. Widely, promoting work-life balance at this crucial moment of child arrival must address the issue of gender inequalities in domestic labor. This work also advocates for actions at a more macroscopic level with the implementation of well-paid, flexible and equitable parental leave regulations between both parents in Europe. From a methodological perspective, there is an additional need for a rigorous and homogenous assessment of maternal employment characteristics in studies in order to better understand the specificities that mothers face in the workplace – including potential stressors like job insecurity, occupational exposure to chemicals, or physical strain – and to identify targeted actions. Furthermore, better quantifying worktime flexibility in studies could be of interest, since this aspect seems to play a major role in the pursuit of breastfeeding after returning to work. The new working practices adopted since the COVID-19 pandemic have challenged this link between work-life balance and social health inequalities, since precarious employees, including manual workers, are less likely to work from home.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Bagci Bosi A, Eriksen K, Sobko T, Wijnhoven T, Breda J. Breastfeeding practices and policies in WHO European region member states. Public Health Nutr. 2016;19(4):753–64. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980015001767 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Ibanez G, Martin N, Denantes M, Saurel-Cubizolles MJ, Ringa V, Magnier AM. Prevalence of breastfeeding in industrialized countries. Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 2012;60(4):305–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respe.2012.02.008 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Theurich M, Davanzo R, Busck-Rasmussen M, Díaz-Gómez N, Brennan C, Kylberg E, et al. Breastfeeding rates and programs in europe: A survey of 11 national breastfeeding committees and representatives. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2019;68(3):400–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000002234 .
Vanderlinden K, Buffel V, Van de Putte B, Van de Velde S. Motherhood in Europe: An examination of parental leave regulations and breastfeeding policy influences on breastfeeding initiation and duration. Soc Sci. 2020;9(12):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci9120222 .
Article Google Scholar
Rollins NC, Bhandari N, Hajeebhoy N, Horton S, Lutter CK, Martines JC, et al. Why invest, and what it will take to improve breastfeeding practices? Lancet. 2016;387(10017):491–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01044-2 .
Rollins N, Piwoz E, Baker P, Kingston G, Mabaso KM, McCoy D, et al. Marketing of commercial milk formula: a system to capture parents, communities, science, and policy. Lancet. 2023;401(10375):486–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01931-6 .
Van Esterik P. Breastfeeding and feminism. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 1994;47:S41-54. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7292(94)02233-o .
Risman BJ. Gender as a social structure: Theory wrestling with activism. Gend Soc. 2011;18(4):429–50. https://doi.org/10.1177/0891243204265349 .
Fein SB, Mandal B, Roe BE. Success of strategies for combining employment and breastfeeding. Pediatrics. 2008;122(suppl 2):S56-62. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2008-1315g .
Standish KR, Parker MG. Social determinants of breastfeeding in the United States. Clin Ther. 2022;44(2):186–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.11.010 .
Murtagh L, Moulton AD. Working mothers, breastfeeding, and the law. Am J Public Health. 2011;101(2):217–23. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2009.185280 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Tomori C, Palmquist AE, Dowling S. Contested moral landscapes: Negotiating breastfeeding stigma in breastmilk sharing, nighttime breastfeeding, and long-term breastfeeding in the US and the UK. Soc Sci Med. 2016;168:178–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2016.09.014 .
Gojard S. L’allaitement : Une pratique socialement différenciée [Breastfeeding: A socially differentiated practice]. Rech Prévisions. 1988;53(1):23–34. https://doi.org/10.3406/caf.1998.1823 .
Kimbro RT. On-the-job moms: work and breastfeeding initiation and duration for a sample of low-income women. Matern Child Health J. 2006;10:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-005-0058-7 .
Benach J, Muntaner C, Santana V. Benach J, Muntaner C, Santana V. Employment conditions knowledge network (EMCONET). Employ. Cond. Heal. inequalities. Final Rep. to WHO Comm. Soc. Determ. Heal. 2007. Available from: https://repository.mdx.ac.uk/item/8328x .
Peters MD, Marnie C, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Munn Z, Alexander L, et al. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid Synth. 2020;18(10):2119–26. https://doi.org/10.11124/JBIES-20-00167 .
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73. https://doi.org/10.7326/M18-0850 .
Cervera-Gasch Á, Mena-Tudela D, Leon-Larios F, Felip-Galvan N, Rochdi-Lahniche S, Andreu-Pejó L, et al. Female employees’ perception of breastfeeding support in the workplace, public universities in Spain: A multicentric comparative study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(17):6402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176402 .
de Lauzon-Guillain B, Thierry X, Bois C, Bournez M, Davisse-Paturet C, Dufourg MN, et al. Maternity or parental leave and breastfeeding duration: Results from the ELFE cohort. Matern Child Nutr. 2019;15(4):e12872. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.12872 .
Desmond D, Meaney S. A qualitative study investigating the barriers to returning to work for breastfeeding mothers in Ireland. Int Breastfeed J. 2016;11:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13006-016-0075-8 .
Bonet M, Marchand L, Kaminski M, Fohran A, Betoko A, Charles MA, et al. Breastfeeding duration, social and occupational characteristics of mothers in the French ‘EDEN mother-child’ cohort. Matern Child Health J. 2013;17(4):714–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-012-1053-4 .
Castetbon K, Boudet-Berquier J, Salanave B. Combining breastfeeding and work: Findings from the Epifane population-based birth cohort. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020;20:110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-020-2801-x .
Hentges M, Pilot E. Making it ‘work’: Mothers’ perceptions of workplace breastfeeding and pumping at Dutch universities. Int Breastfeed J. 2021;16:87. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13006-021-00433-w .
Leon-Larios F, Pinero-Pinto E, Arnedillo-Sanchez S, Ruiz-Ferron C, Casado-Mejia R, Benitez-Lugo M. Female employees’ perception of breastfeeding-friendly support in a public university in Spain. Public Health Nurs. 2019;36(3):370–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/phn.12590 .
Zilanawala A. Maternal nonstandard work schedules and breastfeeding behaviors. Matern Child Health J. 2017;21(6):1308–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-016-2233-4 .
Jackson JE, Hallam JL. ‘It’s quite a taboo subject’: An investigation of mother’s experiences of breastfeeding beyond infancy and the challenges they face. Women Health. 2021;61(6):572–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/03630242.2021.1938790 .
Villar M, Santa-Marina L, Murcia M, Amiano P, Gimeno S, Ballester F, et al. Social factors associated with non-initiation and cessation of predominant breastfeeding in a mother-child cohort in Spain. Matern Child Health J. 2018;22(5):725–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-018-2441-1 .
Huet F, Maigret P, Elias-Billon I, Allaert FA. Identifying clinical, sociological, economic and regional determinants of the duration of maternal breastfeeding. J Pediatr Pueric. 2016;29(4):177–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpp.2016.04.010 .
Iglesias-Rosado B, Leon-Larios F. Breastfeeding experiences of Latina migrants living in Spain: A qualitative descriptive study. Int Breastfeed J. 2021;16:76. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13006-021-00423-y .
Zhou Q, Chen H, Younger KM, Cassidy TM, Kearney JM. ‘I was determined to breastfeed, and I always found a solution’: Successful experiences of exclusive breastfeeding among Chinese mothers in Ireland. Int Breastfeed J. 2020;15:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13006-020-00292-x .
Bai DL, Fong DYT, Tarrant M. Factors associated with breastfeeding duration and exclusivity in mothers returning to paid employment postpartum. Matern Child Health J. 2015;19(5):990–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-014-1596-7 .
Spitzmueller C, Zhang J, Thomas CL, Wang Z, Fisher GG, Matthews RA, et al. Identifying job characteristics related to employed women’s breastfeeding behaviors. J Occup Health Psychol. 2018;23(4):457–70. https://doi.org/10.1037/ocp0000119 .
Magnanosan Lio R, Maugeri A, La Rosa MC, Cianci A, Panella M, Giunta G, et al. The impact of socio-demographic factors on breastfeeding: Findings from the ‘Mamma & bambino’ cohort. Medicina. 2021;57(2):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57020103 .
Dominguez Folgueras M. Des politiques d’allaitement déconnectées de la réalité [Breastfeeding policies out of touch with reality]. SciencesPo. 2020 [cited 2023 Mar 20]; Available from: https://www.sciencespo.fr/research/cogito/home/des-politiques-dallaitement-deconnectees-de-la-realite/ .
Sarki M, Parlesak A, Robertson A. Comparison of national cross-sectional breast-feeding surveys by maternal education in Europe (2006–2016). Public Health Nutr. 2019;22(5):848–61. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980018002999 .
Yngve A, Sjstrm M. Breastfeeding determinants and a suggested framework for action in Europe. Public Health Nutr. 2001;4(2b):729–39. https://doi.org/10.1079/PHN2001164 .
Delamaire C. L’allaitement maternel: Vécu et opinions des mères en 2009 [Breastfeeding: Experiences and opinions of mothers in 2009]. Santé Homme. 2010;409:50–1.
Google Scholar
Michie S, Van Stralen MM, West R. The behaviour change wheel: A new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions. Implement Sci. 2011;6(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-6-42 .
Meedya S, Fahy K, Kable A. Factors that positively influence breastfeeding duration to 6 months: A literature review. Women Birth. 2010;23(4):135–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wombi.2010.02.002 .
Lau CYK, Lok KYW, Tarrant M. Breastfeeding duration and the theory of planned behavior and breastfeeding self-efficacy framework: A systematic review of observational studies. Matern Child Health J. 2018;22(3):327–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-018-2453-x .
Santacruz-Salas E, Aranda-Reneo I, Segura-Fragoso A, Cobo-Cuenca AI, Laredo-Aguilera JA, Carmona-Torres JM. Mothers’ expectations and factors influencing exclusive breastfeeding during the first 6 months. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(1):3–5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010077 .
Arora S, McJunkin C, Wehrer J, Kuhn P. Major factors influencing breastfeeding rates: Mother’s perception of father’s attitude and milk supply. Pediatrics. 2000;106(5):e67. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.106.5.e67 .
Oosterhoff A, Hutter I, Haisma H. It takes a mother to practise breastfeeding: Women’s perceptions of breastfeeding during the period of intention. Women Birth. 2014;27(4):e43-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wombi.2014.08.003 .
Al-Sagarat AY, Yaghmour G, Moxham L. Intentions and barriers toward breastfeeding among Jordanian mothers—A cross sectional descriptive study using quantitative method. Women Birth J Aust Coll Midwives. 2017;30(4):e152–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wombi.2016.11.001 .
Zhuang J, Bresnahan M, Zhu Y, Yan X, Bogdan-Lovis E, Goldbort J, et al. The impact of coworker support and stigma on breastfeeding after returning to work. J Appl Commun Res. 2018;46(4):491–508. https://doi.org/10.1080/00909882.2018.1498981 .
Vilar-Compte M, Hernández-Cordero S, Ancira-Moreno M, Burrola-Méndez S, Ferre-Eguiluz I, Omaña I, et al. Breastfeeding at the workplace: A systematic review of interventions to improve workplace environments to facilitate breastfeeding among working women. Int J Equity Health. 2021;20:110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-021-01432-3 .
Tang X, Patterson P, MacKenzie-Shalders K, Van Herwerden LA, Bishop J, Rathbone E, et al. Workplace programmes for supporting breast-feeding: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Public Health Nutr. 2021;24(6):1501–13. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980020004012 .
Tomori C, Hernández-Cordero S, Busath N, Menon P, Pérez-Escamilla R. What works to protect, promote and support breastfeeding on a large scale: A review of reviews. Matern Child Nutr. 2022;18(suppl 3):e13344. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.13344 .
Lioret S, Harrar F, Boccia D, Hesketh KD, Kuswara K, Van Baaren C, et al. The effectiveness of interventions during the first 1,000 days to improve energy balance-related behaviors or prevent overweight/obesity in children from socio-economically disadvantaged families of high-income countries: A systematic review. Obes Rev. 2023;24(1):e13524. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.13524 .
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Employment: Length of maternity, parental and home care leave, and paid father-specific leave. Available from: https://stats.oecd.org/index.aspx?queryid=54760 . Accessed 1 Feb 2023.
Ciccia R, Verloo M. Parental leave regulations and the persistence of the male breadwinner model: Using fuzzy-set ideal type analysis to assess gender equality in an enlarged Europe. J Eur Soc Policy. 2012;22(5):507–28. https://doi.org/10.1177/0958928712456576 .
Galtry J. The impact on breastfeeding of labour market policy and practice in Ireland, Sweden, and the USA. Soc Sci Med. 2003;57(1):167–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0277-9536(02)00372-6 .
Grandahl M, Stern J, Funkquist EL. Longer shared parental leave is associated with longer duration of breastfeeding: A cross-sectional study among Swedish mothers and their partners. BMC Pediatr. 2020;20:159. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-020-02065-1 .
Tijdens KG, De Ruijter E, De Ruijter J. Comparing tasks of 160 occupations across eight European countries. Empl Relat. 2014;36(2):110–27. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-05-2013-0046 .
Lamberti LM, Fischer Walker CL, Noiman A, Victora C, Black RE. Breastfeeding and the risk for diarrhea morbidity and mortality. BMC Public Health. 2011;11(suppl 3):S15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-11-S3-S15 .
Brahm P, Valdés V. The benefits of breastfeeding and associated risks of replacement with baby formulas. Rev Chil Pediatría. 2017;88(1):7–14. https://doi.org/10.4067/s0370-41062017000100001 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Edwige Bertrand for her help in the bibliographic search strategy.
This study was funded by the French National Research Agency (ANR-19-CE36-0006).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Bordeaux Population Health Research Center, U1219, Inserm, University of Bordeaux, 146 Rue Léo Saignat, Bordeaux, France
Pauline Brugaillères, Séverine Deguen & Stéphanie Vandentorren
Center for Research in Epidemiology and StatisticS (CRESS), Université Paris Cité and Université Sorbonne Paris Nord, Inserm, INRAE, Paris, France
Sandrine Lioret
Santé Publique France, Saint-Maurice, France
Sahar Haidar, Corinne Delamaire & Stéphanie Vandentorren
Institut National d’études Démographiques (INED), Aubervilliers, France
Emilie Counil
Institute of Interdisciplinary Research On Social Issues (IRIS), UMR8156 CNRS, EHESS, U997 Inserm, SPN, Aubervilliers, France
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
P.B., S.D., and S.V. conceived the study. P.B. designed the search strategy, conducted the database search, and screened the records. P.B. and S.D. screened the full texts. P.B. completed all data extraction. P.B. drafted the full manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved final submission. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pauline Brugaillères .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Research ethics approval was not required due to the nature of the study methodology.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
13006_2024_643_moesm1_esm.docx.
Additional file 1. Macro-theoretical framework of employment relations and health inequalities from the WHO Commission on Social Determinants of Health (CSDH) Employment Conditions Knowledge Network (EMCONET), Final Report, 20 September 2007.
Additional file 2. Literature Search Strategy.
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Brugaillères, P., Deguen, S., Lioret, S. et al. Maternal employment characteristics as a structural social determinant of breastfeeding after return to work in the European Region: a scoping review. Int Breastfeed J 19 , 38 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13006-024-00643-y
Download citation
Received : 06 July 2023
Accepted : 10 May 2024
Published : 28 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13006-024-00643-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Working mother
- Infant and young child feeding practice
- Social determinants of health
International Breastfeeding Journal
ISSN: 1746-4358
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative research is a method of inquiry used in various disciplines, including social sciences, education, and health, to explore and understand human behavior, experiences, and social phenomena. It focuses on collecting non-numerical data, such as words, images, or objects, to gain in-depth insights into people's thoughts, feelings, motivations, and perspectives.
Qualitative Research. Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people's beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus ...
Qualitative research methods. Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods.These are some of the most common qualitative methods: Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes. Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations. Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among ...
Since then many texts on "qualitative research" and its methods have been published, ... We believe that the possibility of making new distinctions is one the defining characteristics of qualitative research. It clearly sets it apart from quantitative analysis which works with taken-for-granted variables, albeit as mentioned, meta-analyses ...
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems.[1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervening or introducing treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypothenar to further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences ...
INTRODUCTION. Qualitative research methods refer to techniques of investigation that rely on nonstatistical and nonnumerical methods of data collection, analysis, and evidence production. Qualitative research techniques provide a lens for learning about nonquantifiable phenomena such as people's experiences, languages, histories, and cultures.
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
Qualitative research is the naturalistic study of social meanings and processes, using interviews, observations, and the analysis of texts and images. In contrast to quantitative researchers, whose statistical methods enable broad generalizations about populations (for example, comparisons of the percentages of U.S. demographic groups who vote in particular ways), qualitative researchers use ...
qualitative methods to address questions about people's ways of organizing, relating to, and interacting with the world. Despite the interdisciplinary recognition of the value of "qualitative research" (or perhaps because of it), qualitative research is not a unified field of theory and practice. On the contrary, a plethora of viewpoints ...
Qualitative research is a 'big tent' that encompasses various schools of thoughts. There is a general consensus that qualitative research is best used to answer why and howresearch questions, but not how much or to what extent questions. The word 'how can Footnote 5 ' is also frequently used in the research question of a qualitative research; this typically requires open-ended vs ...
Qualitative researchers generally begin their work with the recognition that their position (or worldview) has a significant impact on the overall research process. 7 Researcher worldview shapes the way the research is conducted, i.e., how the questions are formulated, methods are chosen, data are collected and analysed, and results are reported.
Fundamental Criteria: General Research Quality. Various researchers have put forward criteria for evaluating qualitative research, which have been summarized in Table 3.Also, the criteria outlined in Table 4 effectively deliver the various approaches to evaluate and assess the quality of qualitative work. The entries in Table 4 are based on Tracy's "Eight big‐tent criteria for excellent ...
Qualitative research methods. Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods.These are some of the most common qualitative methods: Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes. Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations. Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among ...
Characteristics of Qualitative Research. Below are the three key elements that define a qualitative research study and the applied forms each take in the investigation of a research problem. ... Some specific limitations associated with using qualitative methods to study research problems in the social sciences include the following:
Qualitative research is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting non-numerical data. (Image by rawpixel.com on Freepik) Qualitative research is a type of method that researchers use depending on their study requirements. Research can be conducted using several methods, but before starting the process, researchers should understand the different methods available to decide the ...
Qualitative research is defined as an exploratory method that aims to understand complex phenomena, often within their natural settings, by examining subjective experiences, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical measurements and statistical analysis, qualitative research employs a range of ...
Abstract. This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions ...
Broadly defined, ethnography is a qualitative research method consisting of the observation, in-depth analysis, and thick description of a group of people, their culture, and their way of life (Atkinson and Hammersley, 1994 ). Whereas the case study focuses on a single case, ethnographic studies use the group or community as their unit of analysis.
Characteristics of qualitative research methods Qualitative research methods usually collect data at the sight, where the participants are experiencing issues or research problems . These are real-time data and rarely bring the participants out of the geographic locations to collect information.
Qualitative research seeks to gain insights and understand people's experiences and perspectives by studying social organizations and human behavior. Data in qualitative studies focuses on people's beliefs and emotional responses. Qualitative data is especially helpful when a company wants to know how customers feel about a product or ...
Qualitative research is a market research method that focuses on obtaining data through open-ended and conversational communication. This method focuses on the "why" rather than the "what" people think about you. Thus, qualitative research seeks to uncover the underlying motivations, attitudes, and beliefs that drive people's actions.
Qualitative research is a method used mainly in the social sciences to study human phenomena that require complex analysis for their understanding. ... Characteristics of a qualitative research : Qualitative research is an approach to research that focuses on understanding the subjective experiences, perspectives, and meanings of individuals ...
Papers were included if they used qualitative research methods about the barriers, facilitators, perceptions, experiences, and attitudes toward community reintegration from prison or secure care for MCoSO. ... The characteristics from the 79 qualitative papers are presented in the Supplemental Material. All the papers included male participants ...
Theory and Methodology. Good research follows from a reasonable starting point, a theoretical concept or perspective. Quantitative research uses a positivist perspective in which evidence is objectively and systematically obtained to prove a causal model or hypothesis; what works is the focus. 3 Alternatively, qualitative approaches focus on how and why something works, to build understanding ...
Qualitative research methods are appropriate when seeking an in-depth understanding of participants' perspectives. Methods This qualitative study was part of a larger implementation research project focusing on the development and implementation of a context-specific intervention to reduce disrespectful maternity care and evaluation of ...
What is qualitative research? If we look for a precise definition of qualitative research, and specifically for one that addresses its distinctive feature of being "qualitative," the literature is meager. In this article we systematically search, identify and analyze a sample of 89 sources using or attempting to define the term "qualitative." Then, drawing on ideas we find scattered ...
A sequential explanatory mixed methods research design was adopted in this study. Initially, 235 women with gestational diabetes mellitus participated in a cross-sectional survey. ... Descriptive analyses were conducted to describe the characteristics of the sample, and multiple linear regression analyses were used to explore the factors ...
This scoping review was guided by the Joanna Briggs Institute's approach to scoping reviews [] and compliant with the PRISMA-ScR checklist [].Inclusion criteria. Full-text peer-reviewed articles using quantitative and/or qualitative methods and published in English or French between 2013 and 2023 were included according to the following inclusion criteria: (1) Population: mothers of a ...
Using qualitative and quantitative methods, the study identifies key components of mutual aid, explores the relationship between mutual aid behaviors and spatial composition, and outlines strategies for designing community environments that support mutual aid. ... The study categorizes mutual aid activities and behavior characteristics, and ...