- Block access to a list of URLs
Define a list of sites, based on URL patterns, that are blocked (your users can't load them). Format the URL pattern according to https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2095322. You can define exceptions in the 'URLAllowlist' (Define a list of allowed URLs) policy. These policies are limited to 1000 entries; subsequent entries are ignored. Note that blocking internal 'edge://*' URLs isn't recommended - this may lead to unexpected errors. This policy doesn't prevent the page from updating dynamically through JavaScript. For example, if you block 'contoso.com/abc', users might still be able to visit 'contoso.com' and click on a link to visit 'contoso.com/abc', as long as the page doesn't refresh. If you don't configure this policy, no URLs are blocked. Example value: contoso.com https://ssl.server.com hosting.com/bad_path https://server:8080/path .exact.hostname.com file://* custom_scheme:* *


Administrative Templates (Computers)
- Register protocol handlers
- Configure the new tab page search box experience
- Default search provider encodings
- Default search provider keyword
- Default search provider name
- Default search provider search URL
- Default search provider URL for suggestions
- Enable the default search provider
- Parameters for an image URL that uses POST
- Specifies the search-by-image feature for the default search provider
- Allow users to be alerted if their passwords are found to be unsafe
- Enable Password reveal button
- Enable saving passwords to the password manager
- Enable startup boost
- Print headers and footers
- Set the system default printer as the default printer
- Block Sleeping Tabs on specific sites
- Configure Sleeping Tabs
- Set the background tab inactivity timeout for Sleeping Tabs
- Configure Microsoft Defender SmartScreen
- Configure Microsoft Defender SmartScreen to block potentially unwanted apps
- Force Microsoft Defender SmartScreen checks on downloads from trusted sources
- Action to take on startup
- Configure the home page URL
- Configure the Microsoft Edge new tab page experience (deprecated)
- Configure the new tab page URL
- Enable preload of the new tab page for faster rendering
- Set new tab page quick links
- Set the new tab page as the home page
- Show Home button on toolbar
- Sites to open when the browser starts
- Allow download restrictions
- Allow importing of autofill form data
- Allow importing of browser settings
- Allow importing of browsing history
- Allow importing of Cookies
- Allow importing of extensions
- Allow importing of favorites
- Allow importing of open tabs
- Allow importing of payment info
- Allow importing of saved passwords
- Allow importing of search engine settings
- Allow importing of shortcuts
- Allow suggestions from local providers
- Block third party cookies
- Clear browsing data when Microsoft Edge closes
- Clear cached images and files when Microsoft Edge closes
- Continue running background apps after Microsoft Edge closes
- Disable synchronization of data using Microsoft sync services
- Enable AutoFill for addresses
- Enable AutoFill for credit cards
- Enable favorites bar
- Enable network prediction
- Enable resolution of navigation errors using a web service
- Enable search suggestions
- Enable Translate
- Manage Search Engines
- Redirect incompatible sites from Internet Explorer to Microsoft Edge
- Set application locale
- Set download directory
- Shopping in Microsoft Edge Enabled
- Show Microsoft Rewards experiences
- Suggest similar pages when a webpage can't be found
- Application Guard Container Proxy
- Enable Google Cast
- Show the cast icon in the toolbar
- Allow cookies on specific sites
- Allow images on these sites
- Allow insecure content on specified sites
- Allow JavaScript on specific sites
- Allow notifications on specific sites
- Allow pop-up windows on specific sites
- Allow read access via the File System API on these sites
- Allow the Adobe Flash plug-in on specific sites (obsolete)
- Allow WebUSB on specific sites
- Allow write access to files and directories on these sites
- Automatically select client certificates for these sites
- Block cookies on specific sites
- Block images on specific sites
- Block insecure content on specified sites
- Block JavaScript on specific sites
- Block notifications on specific sites
- Block pop-up windows on specific sites
- Block read access via the File System API on these sites
- Block the Adobe Flash plug-in on specific sites (obsolete)
- Block WebUSB on specific sites
- Block write access to files and directories on these sites
- Choose whether users can receive customized background images and text, suggestions, notifications, and tips for Microsoft services
- Configure cookies
- Control use of insecure content exceptions
- Control use of the File System API for reading
- Control use of the File System API for writing
- Control use of the Web Bluetooth API
- Control use of the WebUSB API
- Default Adobe Flash setting (obsolete)
- Default geolocation setting
- Default images setting
- Default JavaScript setting
- Default notification setting
- Default pop-up window setting
- Enable default legacy SameSite cookie behavior setting
- Grant access to specific sites to connect to specific USB devices
- Limit cookies from specific websites to the current session
- Revert to legacy SameSite behavior for cookies on specified sites
- Allow specific extensions to be installed
- Blocks external extensions from being installed
- Configure allowed extension types
- Configure extension and user script install sources
- Configure extension management settings
- Control which extensions are installed silently
- Control which extensions cannot be installed
- Allow Basic authentication for HTTP
- Allow cross-origin HTTP Authentication prompts
- Configure list of allowed authentication servers
- Disable CNAME lookup when negotiating Kerberos authentication
- Include non-standard port in Kerberos SPN
- Specifies a list of servers that Microsoft Edge can delegate user credentials to
- Supported authentication schemes
- Configure address bar editing for kiosk mode public browsing experience
- Delete files downloaded as part of kiosk session when Microsoft Edge closes
- Allow user-level native messaging hosts (installed without admin permissions)
- Configure native messaging block list
- Control which native messaging hosts users can use
- Configure password protection warning trigger
- Configure the change password URL
- Configure the list of enterprise login URLs where the password protection service should capture salted hashes of a password
- Default printer selection rules
- Default printing page size
- Disable printer types on the deny list
- Enable printing
- Print using system print dialog
- Configure address or URL of proxy server (deprecated)
- Configure proxy bypass rules (deprecated)
- Configure proxy server settings (deprecated)
- Proxy settings
- Set the proxy .pac file URL (deprecated)
- Configure the list of domains for which Microsoft Defender SmartScreen won't trigger warnings
- Prevent bypassing Microsoft Defender SmartScreen prompts for sites
- Prevent bypassing of Microsoft Defender SmartScreen warnings about downloads
- Configure the background types allowed for the new tab page layout
- Hide the default top sites from the new tab page
- Set new tab page company logo (obsolete)
- Ads setting for sites with intrusive ads
- Allow access to sensors on specific sites
- Allow access to the Enterprise Mode Site List Manager tool
- Allow certificates signed using SHA-1 when issued by local trust anchors (deprecated)
- Allow default search provider context menu search access
- Allow file selection dialogs
- Allow freezing of background tabs
- Allow full screen mode
- Allow Google Cast to connect to Cast devices on all IP addresses
- Allow importing of home page settings
- Allow Internet Explorer mode testing
- Allow launching of local files in Internet Explorer mode
- Allow legacy TLS/DTLS downgrade in WebRTC (deprecated)
- Allow managed extensions to use the Enterprise Hardware Platform API
- Allow media autoplay for websites
- Allow or block audio capture
- Allow or block video capture
- Allow or deny screen capture
- Allow pages to send synchronous XHR requests during page dismissal (deprecated)
- Allow personalization of ads, search and news by sending browsing history to Microsoft
- Allow Pin to taskbar wizard
- Allow queries to a Browser Network Time service
- Allow QUIC protocol
- Allows a page to show popups during its unloading (obsolete)
- Allows the AppCache feature to be re-enabled, even if it's turned off by default
- Allow surf game
- Allows users to edit favorites
- Allow the audio sandbox to run
- Allow the Serial API on specific sites
- Allow the Web widget at Windows startup
- Allow user feedback
- Allow users to configure Family safety
- Allow users to open files using the ClickOnce protocol
- Allow users to open files using the DirectInvoke protocol
- Allow users to proceed from the HTTPS warning page
- Allow WebDriver to Override Incompatible Policies (deprecated)
- Allow websites to query for available payment methods
- Always open PDF files externally
- Ask where to save downloaded files
- Automatically import another browser's data and settings at first run
- Block access to a specified list of services and export targets in Collections
- Block access to sensors on specific sites
- Block all ads on Bing search results
- Block the Serial API on specific sites
- Block tracking of users' web-browsing activity
- Browser sign-in settings
- Configure automatic sign in with an Active Directory domain account when there is no Azure AD domain account
- Configure Do Not Track
- Configure enhanced hang detection for Internet Explorer mode
- Configure favorites
- Configure InPrivate mode availability
- Configure Internet Explorer integration
- Configure list of force-installed Web Apps
- Configure Online Text To Speech
- Configures availability of a vertical layout for tabs on the side of the browser
- Configure Speech Recognition
- Configure the default paste format of URLs copied from Microsoft Edge, and determine if additional formats will be available to users
- Configure the Enterprise Mode Site List
- Configure the list of names that will bypass the HSTS policy check
- Configure the list of sites for which Microsoft Edge will attempt to establish a Token Binding with
- Configure the list of types that are excluded from synchronization
- Configure the Share experience
- Configure tracking prevention exceptions for specific sites
- Configure whether a user always has a default profile automatically signed in with their work or school account
- Configure whether Microsoft Edge should automatically select a certificate when there are multiple certificate matches for a site configured with "AutoSelectCertificateForUrls"
- Control communication with the Experimentation and Configuration Service
- Control the IntensiveWakeUpThrottling feature
- Control the mode of DNS-over-HTTPS
- Control use of the Serial API
- Control where developer tools can be used
- Control where security restrictions on insecure origins apply
- Default sensors setting
- Define a list of allowed URLs
- Define a list of protocols that can launch an external application from listed origins without prompting the user
- Delete old browser data on migration
- Disable Certificate Transparency enforcement for a list of legacy certificate authorities
- Disable Certificate Transparency enforcement for a list of subjectPublicKeyInfo hashes
- Disable Certificate Transparency enforcement for specific URLs
- Disable download file type extension-based warnings for specified file types on domains
- Disable saving browser history
- Disable support for 3D graphics APIs
- Disable taking screenshots
- DNS interception checks enabled
- Do not set window.opener for links targeting _blank
- Enable Ambient Authentication for InPrivate and Guest profiles
- Enable a TLS 1.3 security feature for local trust anchors (obsolete)
- Enable component updates in Microsoft Edge
- Enable deleting browser and download history
- Enable Domain Actions Download from Microsoft (obsolete)
- Enable ending processes in the Browser task manager
- Enable full-tab promotional content
- Enable globally scoped HTTP auth cache
- Enable guest mode
- Enable Microsoft Search in Bing suggestions in the address bar
- Enable Native Window Occlusion
- Enable online OCSP/CRL checks
- Enable Proactive Authentication (deprecated)
- Enable profile creation from the Identity flyout menu or the Settings page
- Enable renderer code integrity
- Enables background updates to the list of available templates for Collections and other features that use templates
- Enable scrolling to text specified in URL fragments
- Enable security warnings for command-line flags
- Enable Signed HTTP Exchange (SXG) support
- Enable site isolation for every site
- Enable site isolation for specific origins
- Enable specific spellcheck languages
- Enable spellcheck
- Enable stricter treatment for mixed content (deprecated)
- Enable the Collections feature
- Enable the User-Agent Client Hints feature (deprecated)
- Enable the Web widget
- Enable usage and crash-related data reporting (deprecated)
- Enable use of ephemeral profiles
- Enable using roaming copies for Microsoft Edge profile data
- Enable warnings for insecure forms
- Enable web capture feature in Microsoft Edge
- Enforce Bing SafeSearch
- Enforce Google SafeSearch
- Extend Adobe Flash content setting to all content (obsolete)
- Force direct intranet site navigation instead of searching on single word entries in the Address Bar
- Force disable spellcheck languages
- Force minimum YouTube Restricted Mode
- Force networking code to run in the browser process (obsolete)
- Force synchronization of browser data and do not show the sync consent prompt
- Hide the First-run experience and splash screen
- Hide the one-time redirection dialog and the banner on Microsoft Edge
- Intranet Redirection Behavior
- Limits the number of user data snapshots retained for use in case of emergency rollback
- List of file types that should be automatically opened on download
- Manage exposure of local IP addressess by WebRTC
- Maximum number of concurrent connections to the proxy server
- Minimum TLS version enabled
- Notify a user that a browser restart is recommended or required for pending updates
- Open local files in Internet Explorer mode file extension allow list
- Prevent install of the BHO to redirect incompatible sites from Internet Explorer to Microsoft Edge
- Re-enable deprecated web platform features for a limited time (obsolete)
- Re-enable Web Components v0 API until M84 (obsolete)
- Require that the Enterprise Mode Site List is available before tab navigation
- Restrict exposure of local IP address by WebRTC
- Restrict the range of local UDP ports used by WebRTC
- Restrict which accounts can be used as Microsoft Edge primary accounts
- Save cookies when Microsoft Edge closes
- Send all intranet sites to Internet Explorer
- Send required and optional diagnostic data about browser usage
- Send site information to improve Microsoft services (deprecated)
- Set a timeout for delay of tab navigation for the Enterprise Mode Site List
- Set disk cache directory
- Set disk cache size, in bytes
- Set limit on megabytes of memory a single Microsoft Edge instance can use
- Set Microsoft Edge as default browser
- Set the roaming profile directory
- Set the time period for update notifications
- Set the user data directory
- Set WPAD optimization
- Show an "Always open" checkbox in external protocol dialog
- Show context menu to open a link in Internet Explorer mode
- Show Microsoft Office shortcut in favorites bar (deprecated)
- Sites that can access audio capture devices without requesting permission
- Sites that can access video capture devices without requesting permission
- Specify custom help link
- Specify how "in-page" navigations to unconfigured sites behave when started from Internet Explorer mode pages
- Specify if online OCSP/CRL checks are required for local trust anchors
- Specify the TLS cipher suites to disable
- Specify URI template of desired DNS-over-HTTPS resolver
- Suppress the unsupported OS warning
- URLs where AutoOpenFileTypes can apply
- Use a default referrer policy of no-referrer-when-downgrade (deprecated)
- Use built-in DNS client
- Use hardware acceleration when available
- Use Windows proxy resolver (deprecated)
- Websites or domains that don't need permission to use direct Security Key attestation
- Allow installation
- Prevent Desktop Shortcut creation upon install
- Rollback to Target version
- Target version override
- Update policy override
- Allow installation default
- Allow Microsoft Edge Side by Side browser experience
- Prevent Desktop Shortcut creation upon install default
- Update policy override default
- Auto-update check period override
- Time period in each day to suppress auto-update check
- Address or URL of proxy server
- Choose how to specify proxy server settings
- URL to a proxy .pac file
- Configure the location of the browser executable folder
- Set the release channel search order preference
Administrative Templates (Users)
Group Policy Central
News, Tips and Tutorials for all your Group Policy needss
How to use Group Policy to configure Internet Explorer security zone sites
As you know Group Policy Preferences are these fantastic new settings that allow IT administrators perform any configuration they want on a users group using Group Policy… well almost.. In this tutorial I will show you how to configured one of the few settings that are not controlled by preferences but can be configured using a native Group Policy.
The Internet Explore site zone assignment is one of the few settings you specifically can’t configured using preferences, as you can see (image below) the User Interface to this options has been disabled.
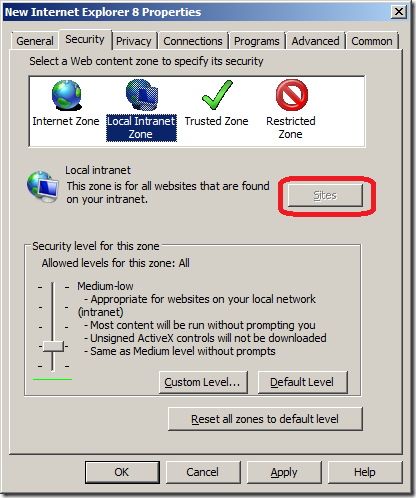
There is a native Group Policy that allows you to control Internet Explorer site zone list is called “Site to Zone Assignment List†which I will go thought below how to use.
Step 1. Edit the Group Policy Object that is targeted to the users you whish this setting to be applied.
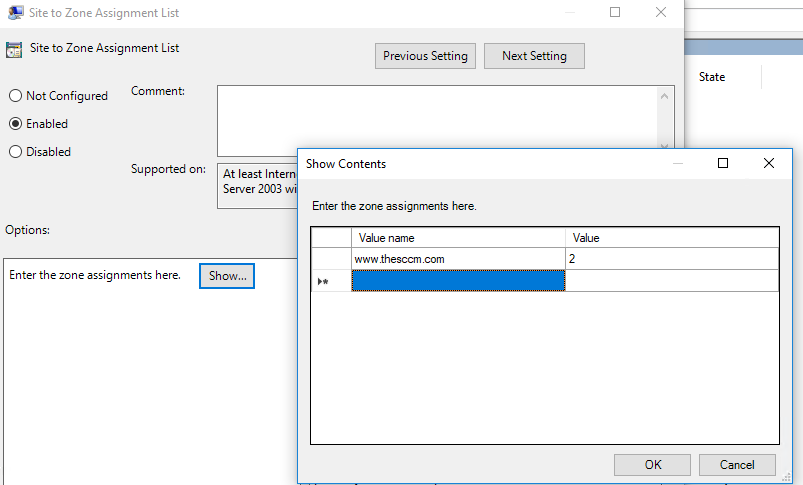
Step 2 . Navigate to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel > Security Page and double click on the “Site to Zone Assignment List†and check the “Enable†option then click on the “Show..†button.
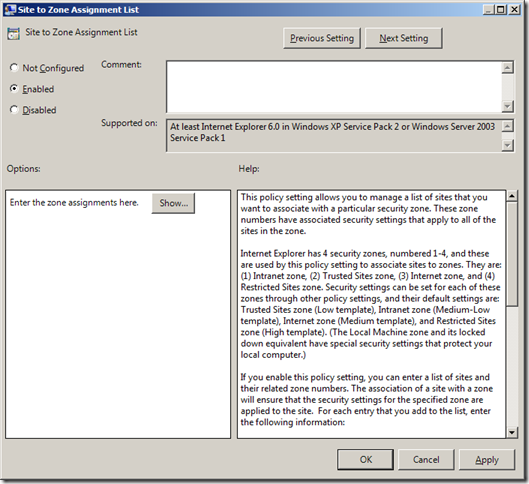
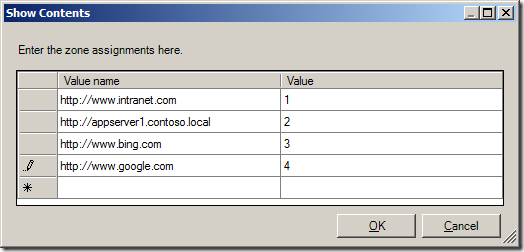
Step 3. Now type the URL in the “Value name†field with the >* on the far left and then type the zone number (see table below) you want to assign to that zone.
Internet Explorer Group Policy Zone Number Mapping
As soon as you start typing the URL a new line will appear for the next URL.
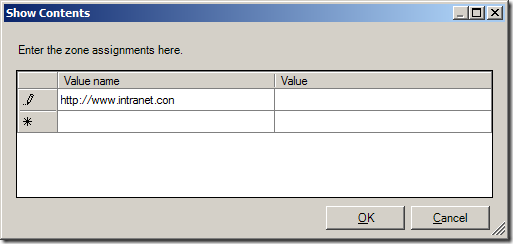
Step 4. One you have finished assigning adding the URL’s and site zone number click OK
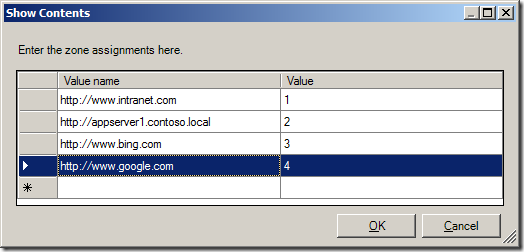
Tip: If you want to delete a row click on the button on the far left to select the row you want to delete (see image below) and then press the “Delete†key.
(sites in above list are example only)
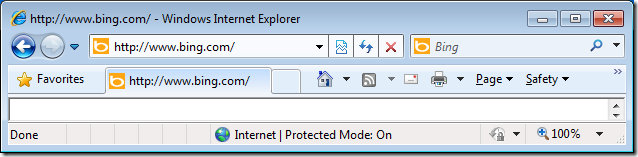
Now the Internet Explorer Site zone list will now be populated with the zone you configured above and as you can see in the images below the Internet Explorer status bar now show the correct zone based on the that the URL’s in the address bar.
Author: Alan Burchill
Related articles.

34 thoughts on “ How to use Group Policy to configure Internet Explorer security zone sites ”
Blog Post: How to use Group Policy to configure Internet Explorer security zone sites http://bit.ly/bNHowK
How to use Group Policy to configure Internet Explorer security zone sites http://bit.ly/bNHowK
- Pingback: Group Policy Center » Blog Archive » Group Policy Setting of the Week 18 – Allow file downlaod (Internet Explorer)
- Pingback: Group Policy Center » Blog Archive » How to use Group Policy to mitigate security issue KB981374
Yup, that is right and excately how we do it, however there is one problem that is of slight concern 🙁
Once the Zones are set via this GP the user can not add his own and as banks etc. today rely on Trusted Zones this is a slight problem. Our IT policy allow for users to use their PC for personal business as well as work and thus it is a slight problem that they cant add Zones for eg. their bank etc.
I have been thinking, maybe one could make a script to set Zones and deploy this via SCCM 2007.
I have not tried this for a while but i believe you can still do this if you configure it under the Internet Explorer Maintainence section of Group Policy…
The configuration for regular zones works fine. Bu the real pain starts when trying to cover zones for “Enahanced Security Configuration” which require other hives in the registry (e.g. “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\ESCDomains\MyDomain”). I have not seen a Microsoft solution for that so far. If anybody knows a smart solution and would share it, I’d really appreciate that.
You will not have to resort to a script and SCCM. Contrary to what this blog entry says can’t be done, we do use GPP to set sites into speicfic security zones. But we don’t set it as a GPP Internet Setting. We use GPP to assign the sites to their proper zones in HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains. Doing it this way we configure the sites we need configured for the organization but do not block the users’ ability to add sites they need set for their individual machines.
Ditto. This was my conclusion a few years ago when researching the various IE management methods. Have been scripting the site/zone assignment manually since then. Primarily with GPP which is fairly simple to manage Colin
GPP is server 2008 only and requires client side software correct? Anyway to do achieve the same results (managed IE Zones without disabling user access) in a 2003 AD environment?
Is there somebody who know how to do the same but with Cookies ?
Because of that, I still have to use IEM which sucks…
@AdamFowler_IT this is how you do IE zones http://t.co/uKug8h9h /cc @auteched
@alanburchill @auteched Worth noting that IE zones via this method http://t.co/qiaLSFK7 will wipe out settings from the old method!!!
with this GPO can we block all internet traffic except google and some other sites to users in the domain??
- Pingback: Best Practice: Roaming Profiles and Folder Redirection (a.k.a. User State Virtualization) : The Digital Jedi's Blog
If I understand GPOs properly, configuring this policy setting will centrally manage this setting without allowing the user to add/delete/modify any of the site to zone settings. Wouldn’t it be preferable to configure these directly in the user’s registry by use of “Preference” registry settings? I.e. creating records in “User Configuration\Preferences\Windows Settings\Registry”.
Hi, Quick question. Is it possible to have multiple sites assigned to “Intranet Zone”? If I try and add additional sites with the same zone number it states that this is not allowed. Can the links be broken up with ; , or something similar? Thanks,
you add each url in separate lines and repeat the zone number code on the right as many times in the list as you like for that zone. Each url will appear listed in that zone then.
I have a question, when you apply this group policy, users cannot add trusted website anymore by themselves. Did you know how to manage that ?
For those trying to find the answer for the above this post may be useful: http://blog.thesysadmins.co.uk/group-policy-internet-explorer-security-zones.html
It covers two methods. The first method will remove the option for the end user to edit or change the security zones, the second will allow the user to add or remove sites.
- Pingback: How to configure Roaming Profiles and Folder Redirection
- Pingback: genuine uggs
Is there a trick to copy/pasting in multiple Value names at once? I have like 100+ IP addresses to insert… Do I have to enter them in 1 at a time?!?
I found this extremely helpful and thank you for posting this. However, for some reason, on my PC when I test the GPO, my trusted sites are affected by the GPO but the only thing that happens is that I can no longer add them; the list is empty. I added about 10 sites to the list using the method above but they are not showing up. I checked to make sure the policy was being applied correctly and it is being applied; it is making it impossible to add to my trusted sites, but the list is empty. With IE 9, the GPO would do the opposite, it would add the sites but the end-user could still add more. I used IEAK for IE 9 years ago and never had a problem, but when I installed IEAK 10 or 11, it never worked.
OK, never mind! To answer my own question, in IE 10, it no longer displays the security zone on the status bar, which stinks, but one can right-click + properties (in an empty space in the body of the webpage) and it will tell the zone you are in. Looks like the zones I added are at least showing in trusted sites. That is good enough for me I guess. Thanks for the original post once again!
I too miss the security bar on IE 10. Will be interesting to review the browser user growths next year.
any news on the copying and pasting I have 100 ips to add need help with the distribution T
Computer specialists are often called IT experts/ advisors or business development advisors, and the division of a corporation or institution of higher education that deals with software technology is often called the IT sector. Countless IT service providers such as The Roots International are offering different facilities like real estate, IT solutions and many more.
I think I have a weird question/request. I want to include my whole domain such as http://www.domain.com as a trusted site. Although, I want to exclude a single web page such as http://www.my.domain.com .
I have *www.domain.com, can http://www.my.domain.com be excluded in any way?
Well, it will provide the internet user user better experience to use internet and surfing websites through internet explorer.
Invaluable discussion ! Coincidentally , if your company has been searching for a a form , my business discovered a blank version here http://goo.gl/eJ3ETg
دم شما گرم.
- Pingback: Allow Previously Unused ActiveX Controls To Run Without Prompt - PC Moment
- Pingback: Internet Options to add Trusted Site Greyed Out - SysPreped Windows 10 LTSB - Boot Panic
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Site sponsor, featured post.
Popular Posts

- Best Practice (40)
- Group Policy FAQ (3)
- KB Focus (5)
- Other Site Links (15)
- Podcast (2)
- ScreenCast (4)
- Security (33)
- Setting of the Week (41)
- Site News (19)
- TechEd (35)
- Tutorials (117)
- Uncategorized (6)
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments

Managing Internet Explorer Trusted Sites with Group Policy
Internet Explorer Maintenance is dead. We all have our regrets, missed chances, and memories. But we have to move on. Depending on your love for power, you have two options. You can take the totalitarian route (known as Administrative Templates) or the benevolent method (known as Group Policy Preferences). Here are the two ways that you can configure Internet Explorer Trusted Sites with Group Policy.
Configuring IE Trusted Sites with Administrative Templates
Site to Zone Mapping allows you to configure trusted sites with Group Policy Administrative Templates. This setting can be found at:
- Computer Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/Windows Components/Internet Explorer / Internet Control Panel/Security Page/Site to Zone Assignment List
- User Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/Windows Components/Internet Explorer / Internet Control Panel/Security Page/Site to Zone Assignment List
When possible, use the computer configuration option as it will not impact user logons. When you enable the setting, you will be prompted for a value name (the website) and a value (the zone list). Here are the possible values and the zone that they correspond to:
- 1 = Intranet/Local Zone
- 2 = Trusted Sites
- 3 = Internet/Public Zone
- 4 = Restricted Sites

The screenshot above shows one trusted site and one restricted site. There is a potential downside to managing trusted sites with Administrative Templates. You will not be able to edit the trusted sites list within Internet Explorer. If you have more than four items listed, you won’t be able to see the entire list in the IE Trusted Sites window. If you view the site properties (Alt – File – Properties), you can check a specific site’s zone though. Remember this trick as it will help you when troubleshooting! You can view the entire list in the Registry by navigating to HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains. If you are an administrator, you can edit/add/remote items from this list for testing. Just be sure to run a GPUpdate /force to undo your changes.
Bonus Points : Leave a comment below explaining why a GPUpdate /force is required to undo your changes. Super Bonus Points if you answer in a haiku.
Configuring IE Trusted Sites with Group Policy Preferences Registry
You would think that Group Policy Preferences Internet Settings could set trusted sites. Unfortunately, that setting is greyed out.

You can still configure IE site mappings with Group Policy Registry Preferences though.* The benefit of this is that your users can edit the zone lists and view all of the added sites. To set this up, create a new user side registry preference. This trick will not work under computer configuration. Enter in the following details:
- Keypath: Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains\WEBSITENAME
- Value Name: http
- Value Type: REG_DWORD
- Value Data: 2
Here is an example showing DeployHappiness being set as a trusted site with registry preferences:

If your site isn’t being placed in the Trusted Sites list, add it manually and then navigate to the registry location above. Ensure that the manual addition exactly matches your registry preference. You will also need to ensure that no Administrative Template Site to Zone settings are applied. If they are, they will wipe out your preference settings. Remember that Policies always win!
You can search your domain for site to zone settings by using this Group Policy Search script. Alan Burchill taught me this trick.
To see additional ways to configure site to zone mappings, read this very in depth example guide.
24 thoughts on “ Managing Internet Explorer Trusted Sites with Group Policy ”
I hope to replace our Site to Zone list to allow our users to enter their own in but I am not sure how to enter our entries that don’t specify a specific protocal such as http or https. So can someone tell me how I would create an entry for this:
*://*.sharepoint.com
and what about something like this – how would this be entered?
https://192.192.192.192 .:9443 (example only)
As for your first question, this info should help: https://community.spiceworks.com/topic/326140-add-trusted-sites-via-gpo-but-still-allow-users-to-add-trusted-sites?page=1#entry-2849140
As for the second question, I don’t know of a way to handle ports. In reference to your example, a link like that would be entered like this: *://192.192.192.192
This is excellent – I have used the GP preferences to add trused sites without locking users out of the setting if they need to add a site. But what about this – a program in the startup group – it is a shortcut to a file on a server – a member server of the local domain – domain.local. I want to prevent this program from prompting end-users to run it, and make sure it will run without prompting. Can this be accomplished with a GP preference as well? If so, do I need to add it to trusted sites, or to the local intranet zone or local machine zone? It would seem to be a local intranet or local machine zone I am working with here. I am not sure how to add it – whether I just need to add the local domain, or the computer name FQDN, or the path to the shared folder and the file. thanks!
This sounds like two different problems: 1. How do I get an app to run without prompting? 2. How do I make it run on startup with group policy?
The latter is easy, create it as a scheduled task that runs on startup. The former depends on what type of script it is. If it’s a vbscript then run it with cscript /b “name.vbs”.
With the old approach we had a file under trusted sites to allow the file to run. It has stopped working under 2012. Could I use this with a file? The old setting was:
file:\\Domain.com\netlogon\AsmallExe.exe
See this article on what you can configure with trusted sites: http://evilgpo.blogspot.com/2016/03/internet-explorer-site-to-zone.html
Just the ticket. Thanks a lot.
I have double-checked that the site to zone assignment policy is not configured, both under user and computer settings. We used group policy preferences because we do not want to lock down the trusted sites – only to push out the sites we want to be trusted. But for some absurd reason, the trusted sites are locked down and greyed out half the time – one day I will look and the sites are not dimmed out and will let me add or remove them. Then the next day they will be greyed out again. It is amazingly ridiculous. I am the only admin; no one else knows how to mess with the settings even if they had the admin credentials. So I have no clue why it keeps reverting back to the wrong settings. I thing our active directory needs to have dcdiag run on it a few times. Any ideas will be sincerely appreciated.
If it is locked down, it is a GP policy that is doing it (the site to zone assignment one) or a registry key that is enabling that site to zone assignment.
When you see one that does it, run a GPResult /h report.htm /f and look through that report.htm. You will see any GP settings that would block it then.
A reply to my own post – the problem was corrupted group policy on the Windows 7 computers – some of the computers were working fine. The ones that were not working, we had to delete the corrupt policy (it was preventing the updated policy settings from being applied). It was in the path C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Group Policy\History\{policy GUID}. After deleting the corrupt policy and rebooting, it fixed the problem!
Thanks for the update Sam!
You’re welcome! I am still having some issues with the trusted sites being greyed out in IE, even though I made certain not to use site to zone assignment in the policy, and only used GP preferences to add registry items for the sites in the trusted zone. Do you know what registry key I need to be looking for, that might be causing this issue?
Many thanks! Sam S.
Are you making sure that you’re applying it under HKCU, and not under HKLM? If you configure it under HKCU, users will still have the ability to add their own entries. But if you configure it under HKLM, the option to add entries will be greyed out.
Yes, I definitely deployed the preferences under the Users GP Preferences and not computer policy/preferences. However, there are some policy settings that I set in both computer and user settings in the GPO. None of these are site to zone assignments though. These settings are for all the security settings within the zones, like, download signed activeX controls – enable, download unsigned activeX controls, Prompt… etc.. – these settings are set in the computer policy and the user policy which is probably what is wrong. I should probably just disable the computer policies in the GPO. I will try that and see if it helps. Why are all these settings available in the computer side and the user side both? Is there a reason someone would set these settings in one policy over the other?
A computer side policy is available for every user that logs in already. These are generally faster to apply and are my preferred way to configure something. However, times like this are when a user side policy would be the best route for you. Remove the computer side settings and try John’s suggestions. Let us know what you find out.
Sam, another thing you can try is to access the GPO from a Windows 7 workstation running IE 9 (and make sure that there are no current Internet Explorer policies being applied to the workstation; put it in an OU that is blocking inheritance if you have to), then drill down to “User Config\Policies\Windows Settings\Internet Explorer Maintenance\Security\Security Zones and Content Ratings”. Double-click on “Security Zones and Content Ratings”, then choose “Import…” under “Security Zones and Privacy’, click “Continue” when prompted, then click “Modify Settings, then “Trusted Sites”, then the “Sites” button. You can then make whatever changes you want (add a site, remove a site, remove the check from the https box, etc). This should give you the freedom you’re looking for :).
i`ve add multiple Sites to the Site to Zone assigment list (Trusted Sites). After a new logon, i`ve check my settings, start IE11, visit the site i`ve add to the list, press Alt – File – Properties and check the Zone. Some of the sites are correct, shown in the trusted site zone, some of them not, they are in an unkown zone (mixed). I want to check the registry path Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains but this key is empty, for HKLM and HKCU. What`s wrong?
Thanks and Regards Patrick
Are you deploying the trusted sites with Policies or registry preferences?
> comment below explaining why GPUpdate /force is required to undo your changes.
For Group Policy to apply efficiently changes trigger it.
Exceptions apply. GPUPDate force is one. Security too.
Less obtusely said: “Group Policy will normally only reprocess client side extensions that have at least one policy element that changed. The exceptions to this are Security Option settings which reapply every ~16 hours on most machines and every 5 minutes on Domain Controllers. The other exceptions are when you run a gpupdate /force, and any CSEs you configure to auto-reapply. You can view this decision tree by enabling UserEnv logging as described in http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc775423%28v=ws.10%29.aspx ” … But not as haiku.
Hi, Is it possible to select the users you want that this GPO applies? It is because I need to add a web to trusted sites, but only to two users. Any idea?
You would need to configure these settings under user configuration. Then change the scope of the GPO from authenticated users to a group containing those two users.
With regards to deploying trusted sites via GPO, while allowing users to add their own entries, see if this post helps: http://community.spiceworks.com/topic/post/2849140
I’m finding that when I deploy Trusted Sites using GPP and the registry, users aren’t able to add entries themselves (it allows them to add to the list, but the entries don’t stick and are gone as soon as you reopen the dialog). Any ideas?
You sir, have a good last name! 🙂
Do you have any delete preferences configured to that registry key? If you manually browse to that key, do you see what the user added?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Security Essentials
- Deploying Windows 10 (without touching a client)
- Group Policy – Preferences to Software and Everything In Between
- OneNote Can Centralize Your Documentation
- Lunch and Learn: PowerShell 3
- Lunch and Learn: Software Extraction
- Disclosure Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Rebuild the Administrative Start Menu
- Guest Posting
- What’s This? Q&A on Sponsored Posts
- Blogs that I Follow – 2018 Edition
- Books to Boost Your Career!
- Top Articles to Teach You Now!
- Top Gadgets to be more Productive!
- Software Tools
- Other – eBooks, Virtual labs, etc
- My Articles
- Clients and Desktops
- Group Policy
- Deployment/MDT
- About DeployHappiness
- February 2024
- October 2023
- January 2023
- October 2021
- November 2020
- October 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- November 2019
- October 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- August 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- Group Policy (85)
- Best Practice (90)
- Hardware (9)
- Management (100)
- Networking (3)
- Office 365 (8)
- Performance (23)
- Quick Tip (26)
- PowerShell (87)
- Security (28)
- Server (16)
- Thinking about IT (14)
- Training (6)
- TroubleShooting (36)
- Uncategorized (29)
- Walkthrough (109)
- Entries (RSS)
- Comments (RSS)

an endpoint admin's journal
- Recent Posts
- Popular Posts
- Recent Comments

Deploy Trusted sites zone assignment using Intune
November 6, 2023

Zoom Desktop Client – Download older build versions from Zoom
October 31, 2023

Uninstall Teams chat app using remediation script and a configuration profile in Intune
October 30, 2023

Intune Last Check-in date not updating for Windows device
October 25, 2023

How to use Event Viewer to check cause of Blue screen of Death (BSOD)
October 23, 2023
5 Quick Mac OS Terminal commands to make a Mac user life easier

Powershell : Find disabled users and computers in AD
- Active Directory (1)
- Windows (7)
- November 2023
- October 2023
Deploy a set of trusted sites overriding users’ ability to add trusted sites themselves. To acheive this, an Intune configuration profile Trusted site zone assignment can be deployed to devices/users group as required.
Login to Intune Portal and navigate to: Devices > Windows > Configuration Profiles .
Hit the Create button and Select New policy

From the Create a profile menu, select Windows 10 and later for Platform , Templates for Profile type. Select Administrative templates and click Create .

Give the profile desired name and click Next .

In Configurations settings, select Computer Configuration and search for keyword “ Site to Zone “, Site to Zone Assignment List setting will be listed under search results. Go ahead click on it to Select it.

Once selected, a Site to Zone Assignment List page will appear on right side explaining different zones and values required for these zone for setup. Since this profile is being used for trusted sites, we will use the Value “2” . Go ahead and select Enabled button and start entering the trusted sites as required. please ensure to set each value to “2” . See example below:
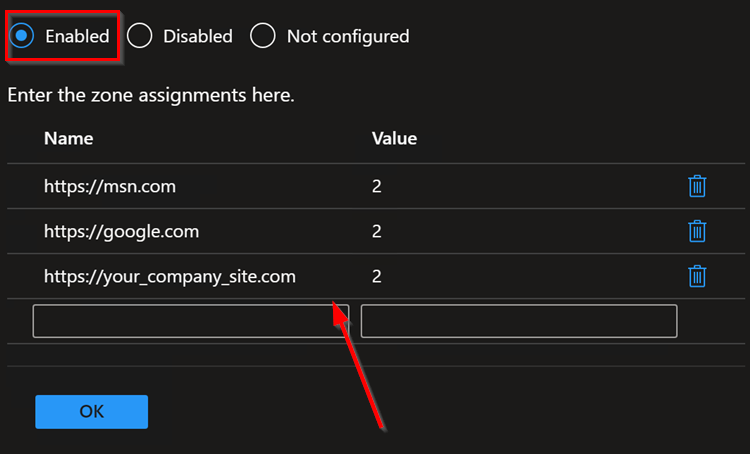
Once done adding the list of sites, click OK to close it and Hit Next on Configuration settings page.
Add Scope tags if needed.
Under Assignments , Click Add groups to target the policy deployment to specific group of devices/users. You can also select Add all users / All all devices .
Hit Next . Then Hit Review + Save button to save.
Tags: Intune Windows
You may also like...

[Windows 10] How to completely uninstall Flash player

- Previous Zoom Desktop Client – Download older build versions from Zoom
thanks! I was just looking for this exact solution!

Windows security encyclopedia
#microsoft #windows #security
Search form
Site to zone assignment list.
This policy setting allows you to manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. These zone numbers have associated security settings that apply to all of the sites in the zone.Internet Explorer has 4 security zones numbered 1-4 and these are used by this policy setting to associate sites to zones. They are: (1) Intranet zone (2) Trusted Sites zone (3) Internet zone and (4) Restricted Sites zone. Security settings can be set for each of these zones through other policy settings and their default settings are: Trusted Sites zone (Low template) Intranet zone (Medium-Low template) Internet zone (Medium template) and Restricted Sites zone (High template). (The Local Machine zone and its locked down equivalent have special security settings that protect your local computer.)If you enable this policy setting you can enter a list of sites and their related zone numbers. The association of a site with a zone will ensure that the security settings for the specified zone are applied to the site. For each entry that you add to the list enter the following information:Valuename – A host for an intranet site or a fully qualified domain name for other sites. The valuename may also include a specific protocol. For example if you enter http://www.contoso.com as the valuename other protocols are not affected. If you enter just www.contoso.com then all protocols are affected for that site including http https ftp and so on. The site may also be expressed as an IP address (e.g. 127.0.0.1) or range (e.g. 127.0.0.1-10). To avoid creating conflicting policies do not include additional characters after the domain such as trailing slashes or URL path. For example policy settings for www.contoso.com and www.contoso.com/mail would be treated as the same policy setting by Internet Explorer and would therefore be in conflict.Value - A number indicating the zone with which this site should be associated for security settings. The Internet Explorer zones described above are 1-4.If you disable or do not configure this policy users may choose their own site-to-zone assignments.
Policy path:
Scope: , supported on: , registry settings: , filename: , related content.
Use Intune Policy CSP manage Windows 10 settings – Internet Explorer Site to Zone Assignment List
- October 23, 2017 July 5, 2020
- 12 Comments
For start, I was actually testing ConfigMgr cloud gateway management and Client Installation over Internet, see this post https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/arnabm/2017/08/27/client-installation-over-internet/
I did managed install ConfigMgr client on AAD joined Windows 10 (version 1709), but I also want configure some Internet Explorer settings to my AAD joined device.
Since Windows 10 (version 1703), we can use Intune Policy CSP to configure more settings, it call admx-backed policies .
Here is how I make Site to Zone Assignment list setting using Intune OMA-URI
Test result: Works only on Windows 10 version 1709
./User/Vendor/MSFT/Policy/Config/ InternetExplorer/AllowSiteToZoneAssignmentList
Works both Windows 10 version 1703 and 1709
./Vendor/MSFT/Policy/Config/ InternetExplorer/AllowSiteToZoneAssignmentList
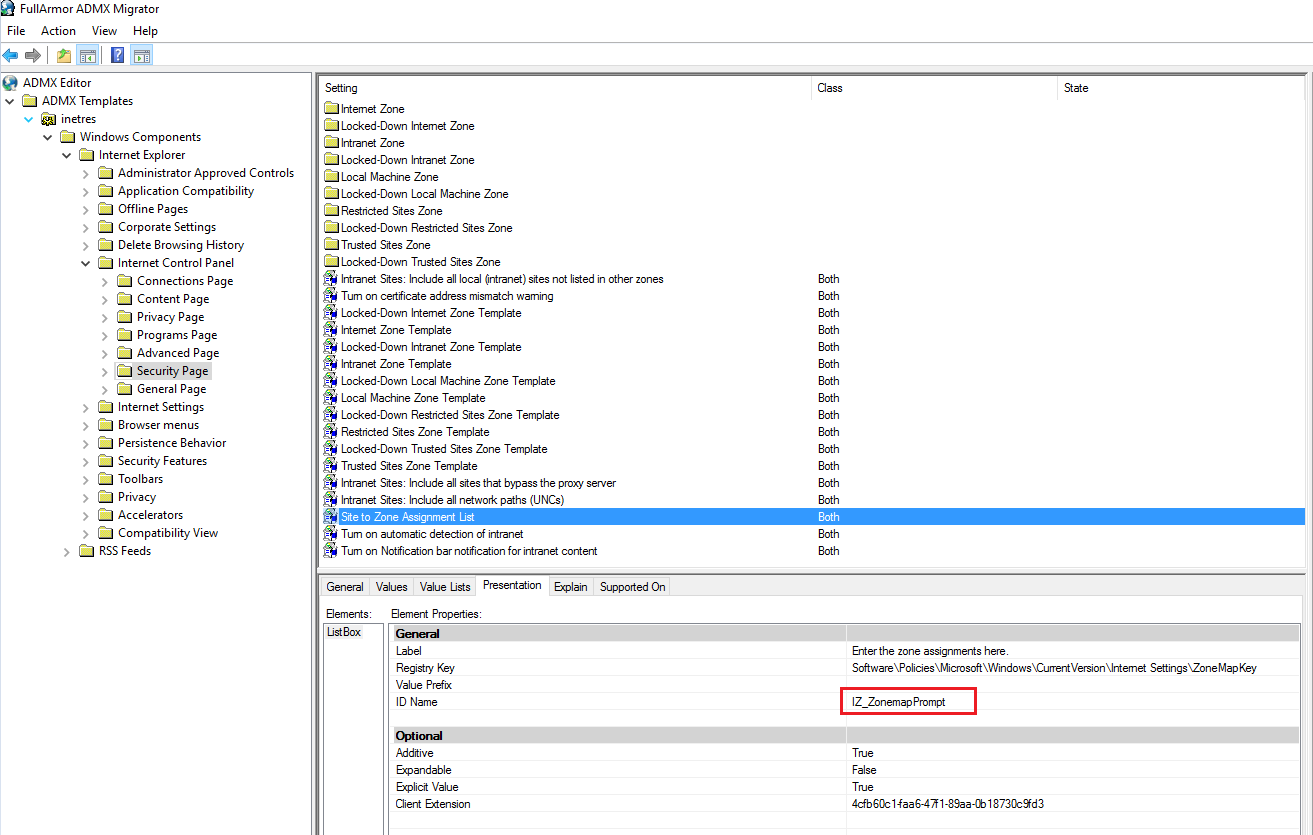
Let’s check first Policy CPS list, InternetExplorer/AllowSiteToZoneAssignmentList is the one we are looking for, it tells admx file name is inetres.admx
Open gpedit.msc in Windows 10 (version 1709). Open Windows Components/Internet Explorer/Internet Control Panel/Security Page/Site to Zone Assignment List, there are two settings that you will need. Enabled , and Zone assignment list .
I use ADMX Migrator open inetres.admx , zone list Elements is ListBox , ID name is IZ_ZonemapPrompt, this is the ID I will need to use for assigning those zone list in Intune. You can also just use notepad open inetres.admx, then search what is the ID you will need.
Go to Intune portal – Device configuration – Profiles – Create Profile
Click Add. Input the following information:
Name: AllowSiteToZoneAssignmentList (you can use anything you want) OMA-URI: ./Vendor/MSFT/Policy/Config/InternetExplorer/AllowSiteToZoneAssignmentList Data type: String Value: <enabled/> <Data id=”IZ_ZonemapPrompt” Value=”https://login.microsoftonline.com2https://sandyzeng.com1”/>
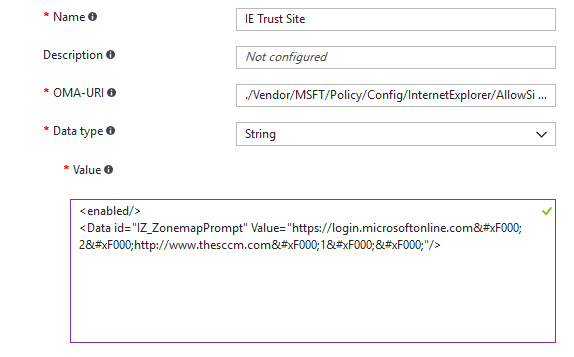
So if want to choose “Enabled”, value will be <enabled/>, if want to choose disabled, value will be <disabled/>
Because we need to input those sites to zone list, ID name is IZ_ZonemapPrompt, so we use <Data id=”IZ_ZonemapPrompt”
In this article https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/client-management/mdm/registry-csp Supported date type, it tells:
Multiple strings are separated by  and ended with two  – A query of this parameter returns a multistring type.
You can find more information from internet about  ( use search key word MDM )
In this case, I want to have https://login.microsoftonline.com in zone list 2 (trusted zone) and https://sandyzeng.com in zone list 1 (local intra), so I need to put  between those strings, and also in the end  
After create this profile, assign it to a user group.
In my Windows 10 machine, open Settings – Accounts – Access work or schoo l, click on Sync, because I was using ./Vendor/MSFT/Policy/Config/ InternetExplorer/AllowSiteToZoneAssignmentList, so those are device settings, you can find it under registry Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PolicyManager\current\device
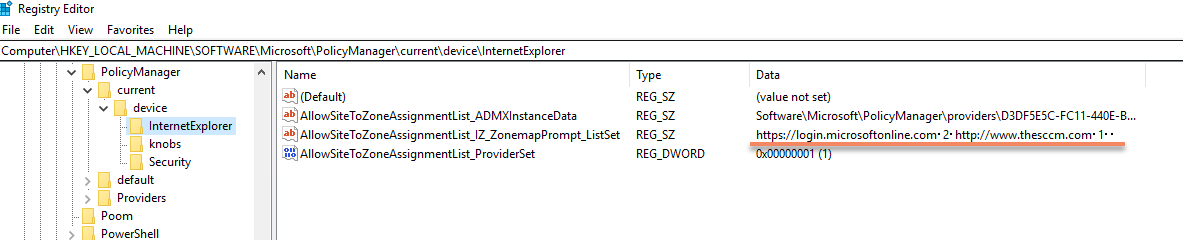
Generate Advanced Diagnostic Report

You should able to see this in your report.

Open Internet Explorer
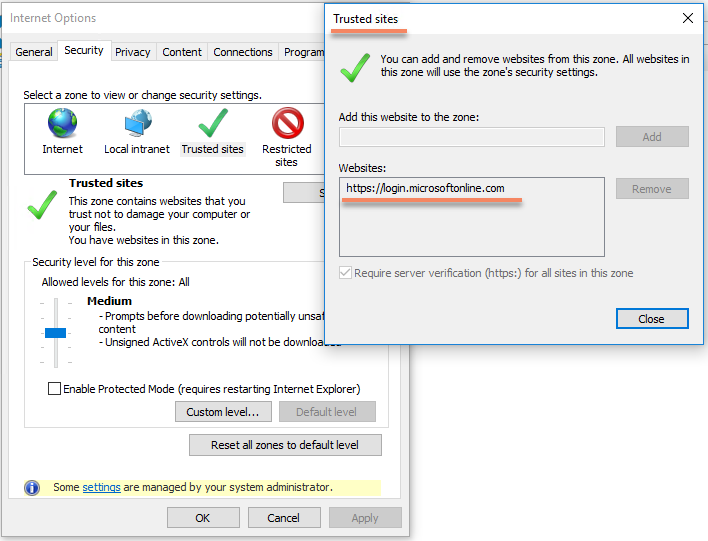
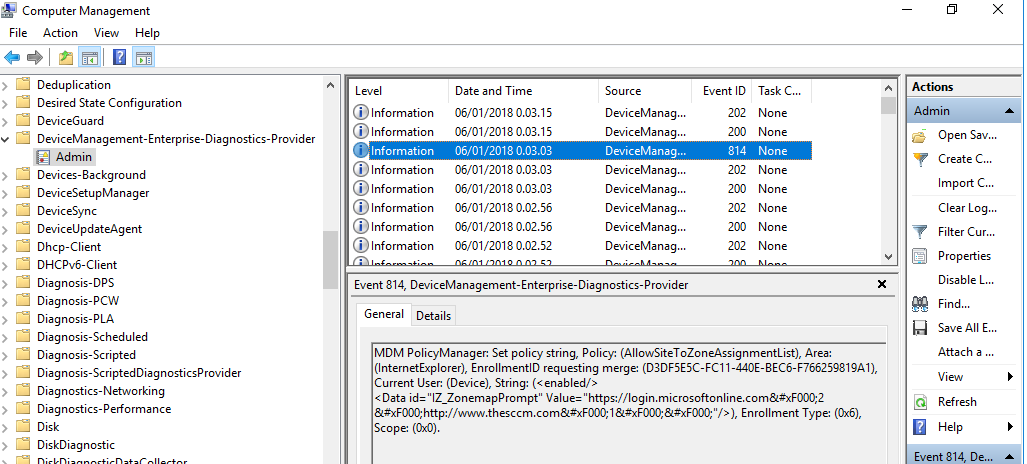
If you can’t see your policy, check Event Viewer – Applications and services log – Microsoft – Windows – DeviceManagement-Enterprise-Diagnostics-Provider , see if there is any errors about the policy you created, then start trouble shooting.
Share this:
12 thoughts on “use intune policy csp manage windows 10 settings – internet explorer site to zone assignment list”.
Thanks for this article. I notice that old (test) URL’s remain in the registry, even if I change the string . Is this by design ?
Hi, is the old (test) URL’s and new URLs are assigned with same policy or created a new policy for new URLs? I will test this and get back to you. Thanks.
Hi Sandy, I used the same policy. Thanks!
Hi Jan. I just tested it again. Using Windows 10 version 1709 Enterprise. URLs updated without issues. Tested remove old URLs, add new URLs, all worked. But it did take some time to update. I updated my post, because there are some typo and wrong print screen pictures. Event logs should show if the policy apply succeeded or failed.
Ok, thank you for testing. I did a check on my settings, and fixed a typo. Works as expected now.
Hi Sandy, thanks for this article. Unfortunally I’m not able to let it work. I just configured it like your example. In the eventlog it says: EnrollmentID requesting set. At your screenshot is says merge. Do you have any idea? Thanks. Edward
Hello Edward, can you try do it again? When you copy and paste those settings from my post, please check again if those double quotes are correct. Would be better copy those to first to notepad++, and make sure those single or double quotes are correct, also no extra space, then copy them again back to Intune. Those setting are still working, I just tested it few days ago. Sandy.
The quotes was indeed the issue. Thank you very much!
I modified my blog function, hope this quotes problem won’t happen again. 🙂
Hi, Gone through the post ,could you please confirm whether this policy works for Windows 10 1803
Regards, Arjun
Best way to find out is testing by yourself. 🙂 However, it still works in my Windows 10 1803 Enterprise version, not sure about Pro or others.
Pingback: ADMX Backed Policies – Quick(ish) Reference Guide – Modern Workplace Configuration with Intune
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Configure same Internet Explorer zone mappings with and without ESC via GPO
Our Active Directory domain consisting of Windows Server 2012 R2 servers and Windows 7 workstations configures Internet Explorer security zones using this Group Policy setting:
Computer Configuration/Policies/Administrative Template/Windows Components/Internet Explorer/Internet Control Panel/Security Page/Site to Zone Assignment List
However, this has no effect on the servers, which have IE Enhanced Security Configuration enabled. How do I configure them using Group Policy? Ideally, I'd want the same settings to apply both with and without ESC without listing them twice.
- active-directory
- group-policy
- internet-explorer
- Did you tried the same setting from User Configuration, not Computer. I guess your server act as terminal server ? – yagmoth555 ♦ Apr 15, 2016 at 12:50
- I haven't tried that, but we have "Security Zones: Use only machine settings" enabled and I don't want to change that. Users connect to that server via RDP, yes. – EM0 Apr 15, 2016 at 13:13
2 Answers 2
There are separate settings under each ZoneMap key for “ESC on” and “ESC off”. If ESC is on, only those settings under the EscDomains and EscRanges subkeys are used; if ESC is off, only the settings under the Domains and Ranges subkeys are used.
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms537181%28v=vs.85%29.aspx
As you want a machine setting, those would be configured like that;
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\EscDomains\mytest.org ... ]
As the settings is not there via the normal ZoneMap GPO setting, I recommand a GPP to set the registry item within your GPO
- I tried this, but it had no effect. That is, the registry value was added, but my Trusted Sites zone is still empty when I view it in Internet Settings. (There were already other domains listed under the EscDomains registry key, such as runonce.msn.com, and they don't appear under Trusted Sites, either.) – EM0 Apr 18, 2016 at 15:00
- @EM I seen report that if the two branches are set, Domain & EscDomain a bug can happen, thus leading to your bug (empty list). Is it something you can test out on your TS ? – yagmoth555 ♦ Apr 18, 2016 at 17:33
- Turns out it was something quite similar to that - see my answer. Thanks for your help! – EM0 Apr 19, 2016 at 9:48
In addition to adding EscDomains registry keys per yagmoth555 's answer, I had to set HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main\FeatureControl\FEATURE_IGNORE_POLICIES_ZONEMAP_IF_ESC_ENABLED_KB918915\* to 1 (DWORD) for the registry settings to be applied.
https://support.microsoft.com/en-gb/kb/918915 describes the problem. I initially ignored it, because it's for Windows Server 2003 and we're running 2012 R2. It turns out that, while the hotfix doesn't need to be applied to later Windows Server versions, it still needs to be enabled using this registry key.
- I tried quite a lot of permutations of this, and I don't think you do need the FEATURE_IGNORE_POLICIES_ZONEMAP_IF_ESC_ENABLED_KB918915 key workaround beyond Windows Server 2003. I think you've just got to be careful about which key path you use to get to the EscDomains key. For me, when I put my intranet sites under the HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\EscDomains key, everything worked fine. Note that there is a Policies key in the path, which is presumably where group policy configuration of the site/zone assignments goes. – Adam Goodwin Jun 20, 2016 at 0:56
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged active-directory security group-policy internet-explorer ..
- The Overflow Blog
- You should keep a developer’s journal
- Would you board a plane safety-tested by GenAI?
- Featured on Meta
- Testing a new version of Stack Overflow Jobs
- What deliverables would you like to see out of a working group?
Hot Network Questions
- Can Maglev trains ever reach escape velocity?
- Is it correct to put a section separator (double thin lines) in the middle of a measure?
- What do people call a chart with a strip of peak values in time intervals?
- Readied action with more than one trigger
- Accidently Glued PVC to threaded PVC and it Leaks
- Story read almost 50 years ago about invisible spiders
- Evidence of lightning-caused mass extinction
- What is the difference between Clear and Remove?
- Can someone explain the logic behind Pause and Print Screen modifiers?
- Under what circumstances could this dragon-like creature carry a human?
- Understanding a 7th century hymn
- Why have Norway, Ireland and Spain only now recognised the Palestinian state?
- Identify a set from bags
- Manipulating Algebraic Equations
- How can I find the area situated under an airport traffic pattern?
- Are transponders sometimes referred to as ‘parrots’?
- Will chaos (or other problems) result from letting my players use Open5e.com instead of the WOTC collection of books?
- Factor from numeric vector drops every 100.000th element from its levels
- Diagonal box in a table
- Should I use stainless or galvanized structural screws for a deck?
- Java - Converting a skip list to the ASCII art
- DIY Sudoku Solver (Windows Console App)
- Rotating a Pot of Boiling Water on a Stove
- THD of two passive circuits
Knowledge Home : PingFederate >> Integrations
Related articles.
- Number of Views 4.51K
- Number of Views 379
- Number of Views 5.85K
- Number of Views 7.46K
- Number of Views 6.83K
Using Group Policy to Configure Supported Browsers for Integrated Windows Authentication
How to use windows group policy to manage browser settings for iwa. may 10, 2023 • knowledge, information.
• Internet Explorer • Google Chrome • Mozilla Firefox Within Group Policy (GP) there are two subsets of configurations available: policies and preferences. GP Policies are typically used for configuring system-specific policies including Windows, security, and software settings. GP Preferences are contrasted from Policies by that when the GPO falls out of scope, the settings defined in the GP Preference remain the same (i.e. "tattoo" the setting). In GP Policies, the settings defined supersede that of the local system or user setting, but when they fall out of scope, the local settings will revert to either the previous setting. These settings in Group Policy are typically applied by Administrative Templates -- preconfigured collections of settings specific to Windows. The scope of this document is for applying browser settings via GP Policy.
While Internet Explorer can be configured directly within a native GPO policy, additional browser settings for Firefox and Chrome must make use of ADM or ADMX templates specific to each browser.
Configuring Group Policy for Internet Explorer
Follow these steps to assign the PingFederate server base URL in the Trusted Sites zone, and set the Trusted Sites zone logon options for the setting Automatic logon with current username and password. 1. Create a new GPO, or use an existing GPO.
Configuring Group Policy for Chrome
Configuring startup script via group policy for firefox, system information, was this article helpful.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Intranet zone settings apply to Edge and Chrome, but not to Firefox
We have GPO settings active that place a certain website https://www.example.com into the trustworthy intranet zone. The setting (User Settings -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Internet Explorer -> Internet Control Panel -> Security Page -> Site to Zone Assignment List) still has good old IE in its name, but apparently should apply generally. At least this used to work across all browsers in the past.
Accordingly, files that are downloaded from https://www.example.com are considered "harmless" (as in: right click-properties does not show a "This file came from another computer and might be blocked ..." warning, or in case of e.g. Word documents: a yellow warning bar is not shown when opening the file).
At least, this works as desired in Edge and Chrome. I also verified that it is not the case that Edge and Chrome never block files from the "wild"; e.g., sample documents from https://file-examples.com/index.php/sample-documents-download/sample-doc-download/ are correctly marked as "dangerous". This shows that the setting is indeed used to distinguish "good" from "evil" downloads, as desired.
However, it seems that the setting does not apply to Firefox. That is, downloading the very same file from https://www.example.com using Firefox produces a file that is considered "dangerous". I am very sure that this is a fairly recent problem and used to work as desired for Firefox as well until a few weeks ago. Unfortunately, I cannot pin down the moment of failure with enough certainty do decide whether the change happened in connection with (a) a Firefox version upgrade, (b) some Windows update, (c) changes to company GPO, or (d) perhaps anything else.
Q: How can I ensure that the desired zone settings also apply to Firefox downloads? That is, files from the configured site shall be considered harmless while general downloads from the wild are still considered dangerous by the operating system? Is there perhaps a FF-specific setting with the same semantics?
- google-chrome
- internet-explorer
- group-policy
- internet-security
You must log in to answer this question.
Browse other questions tagged google-chrome firefox internet-explorer group-policy internet-security ..
- The Overflow Blog
- You should keep a developer’s journal
- Would you board a plane safety-tested by GenAI?
- Featured on Meta
- Testing a new version of Stack Overflow Jobs
- What deliverables would you like to see out of a working group?
Hot Network Questions
- Is this a solvable Numberlink?
- Evidence of lightning-caused mass extinction
- What is the name of the grammatical function of "there" in "there is"?
- Why have Norway, Ireland and Spain only now recognised the Palestinian state?
- What do people call a chart with a strip of peak values in time intervals?
- Regarding a Coin Toss Experiment by Neil DeGrasse Tyson, and its validity
- Kali linux does not update and does not upgrade
- How do I make cracks in this picture?
- Accidently Glued PVC to threaded PVC and it Leaks
- Manipulating Algebraic Equations
- Using QgsProcessingParameterEnum in a QGIS Python processing script
- Can a salary be reduced?
- Reg.exe Query Only Works In Interactive Mode
- Can the topologist's sine curve be realized as a Julia set?
- Authorship issue between two PhD students
- Newcommand with adaptive number of arguments
- Polygon and trace arrows
- Meaning of "A Babe in Arms Will be Their Tyrant"?
- Can we save thermal noise?
- Is this Nintendo Pro Controller real or fake?
- Why can’t God just be replaced by a naturalistic alternative and end the god debate?
- DFT of a pure sine wave not showing ideal sine wave
- Does relativity of simultaneity affect the outcome of an experiment?
- 3-clue 5x5 Hidato

- Support & Services
VMware Explore Registration Is Open
Map your next move at the industry’s essential cloud event in Las Vegas August 26 – 29.

Welcome VMware Members
We are pleased to announce that VMware Communities, Carbon Black Community, Pivotal Community, and the Developer Sample Exchange will go live on Monday, 5/6. Stay tuned for updates.
VMware Communities, Carbon Black Community, Pivotal Community, and VMware Sample Exchange have merged with Broadcom Communities.
Fusion and Workstation Communities are available.
Community Search
Find Your Communities
Our communities are designed by division, as you can see below. Visit each division's homepage for a list of product communities under each division. From there, click on the communities you're interested in, choose "Join Community," and select your notification settings. It's that simple. Join as many as you'd like. Register Here Please note: Your first post to any of our communities will be placed in a moderation queue for review to help us prevent spammers from posting unwanted content. Our community managers closely monitor this moderation queue, and once your first post is approved, your posts will no longer go through moderation. Please do not submit the same post multiple times. Check Out Our Events
Looking for product roadmap webcasts, technical sessions, user group meetings, conferences, and workshops? Check out our events calendars:
Application Networking and Security
- Carbon Black - Symantec
- Software Defined Edge
VMware Cloud Foundation
- Enterprise Software Events
- Mainframe Software Events
- Symantec Enterprise Events
- VMware Events
Tanzu Application Catalog allows you to build a private catalog of custom-configured, pre-packaged open source application components that are continuously maintained and verifiably tested for use in production environments..
Mainframe Solutions
Every business is in pursuit of growth. At Broadcom, we are helping customers embrace open tools and technologies, integrate their Mainframe as part of their cloud, and create new innovation opportunities that drive their businesses forward.
Symantec Enterprise
Bringing cyber security to the world of infrastructure software that is dedicated to building best-in-class enterprise security solutions that strengthen protection, detection, and response for our customers against today’s increasingly powerful adversaries.
Deploy a cloud operating model that combines the scale and agility of public cloud with the security and performance of private cloud.
Software Defined Networking
Get complete network traffic inspection with the industry’s highest fidelity insights into advanced threats.
Deliver high performance, reliable branch access across clouds and apps. Optimize traffic over multiple connections for a better user experience anywhere.
Latest Discussions

RE: IP Spaces menu missing using OrgAdmin User
Posted in: vcloud.
You need to add the rights to the Default Rights Bundle also in order for a Tenant to have them.

Unable to view scores sent by pearson vue through email ...
Posted in: symantec access management.
I passed the VCP DCV 2023 exam and score results email sent by pearson is redirecting from vmware site to broadcom site. Where there used to be exam and other details. Now there is no record of either written exam or the certificate. Help me sort out ...
Recent Blogs

NSX Multisite demos
Posted in: vmware nsx.
Here is one NSX Multisite demo focused on Disaster ...
NSX-T LB Encyclopedia
This NSX-T LB Encyclopedia document goes over all ...
Upcoming Events
Devops office hours, how to monitor user experience with apdex, code4z roadmap webcast, engagement leaderboard.
- Terms of Use
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Policy CSP - ADMX_DnsClient
- 7 contributors
This CSP contains ADMX-backed policies which require a special SyncML format to enable or disable. You must specify the data type in the SyncML as <Format>chr</Format> . For details, see Understanding ADMX-backed policies .
The payload of the SyncML must be XML-encoded; for this XML encoding, there are a variety of online encoders that you can use. To avoid encoding the payload, you can use CDATA if your MDM supports it. For more information, see CDATA Sections .
DNS_AllowFQDNNetBiosQueries
Specifies that NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) queries are issued for fully qualified domain names.
If you enable this policy setting, NetBT queries will be issued for multi-label and fully qualified domain names such as "www.example.com" in addition to single-label names.
If you disable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, NetBT queries will only be issued for single-label names such as "example" and not for multi-label and fully qualified domain names.
Description framework properties :
This is an ADMX-backed policy and requires SyncML format for configuration. For an example of SyncML format, refer to Enabling a policy .
ADMX mapping :
DNS_AppendToMultiLabelName
Specifies that computers may attach suffixes to an unqualified multi-label name before sending subsequent DNS queries if the original name query fails.
A name containing dots, but not dot-terminated, is called an unqualified multi-label name, for example "server.corp" is an unqualified multi-label name. The name "server.corp.contoso.com" is an example of a fully qualified name because it contains a terminating dot.
For example, if attaching suffixes is allowed, an unqualified multi-label name query for "server.corp" will be queried by the DNS client first. If the query succeeds, the response is returned to the client. If the query fails, the unqualified multi-label name is appended with DNS suffixes. These suffixes can be derived from a combination of the local DNS client's primary domain suffix, a connection-specific domain suffix, and a DNS suffix search list.
If attaching suffixes is allowed, and a DNS client with a primary domain suffix of "contoso.com" performs a query for "server.corp" the DNS client will send a query for "server.corp" first, and then a query for "server.corp.contoso.com" second if the first query fails.
If you enable this policy setting, suffixes are allowed to be appended to an unqualified multi-label name if the original name query fails.
If you disable this policy setting, no suffixes are appended to unqualified multi-label name queries if the original name query fails.
If you don't configure this policy setting, computers will use their local DNS client settings to determine the query behavior for unqualified multi-label names.
Specifies a connection-specific DNS suffix. This policy setting supersedes local connection-specific DNS suffixes, and those configured using DHCP.
To use this policy setting, click Enabled, and then enter a string value representing the DNS suffix.
If you enable this policy setting, the DNS suffix that you enter will be applied to all network connections used by computers that receive this policy setting.
If you disable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, computers will use the local or DHCP supplied connection specific DNS suffix, if configured.
DNS_DomainNameDevolutionLevel
Specifies if the devolution level that DNS clients will use if they perform primary DNS suffix devolution during the name resolution process.
With devolution, a DNS client creates queries by appending a single-label, unqualified domain name with the parent suffix of the primary DNS suffix name, and the parent of that suffix, and so on, stopping if the name is successfully resolved or at a level determined by devolution settings. Devolution can be used when a user or application submits a query for a single-label domain name.
The DNS client appends DNS suffixes to the single-label, unqualified domain name based on the state of the Append primary and connection specific DNS suffixes radio button and Append parent suffixes of the primary DNS suffix check box on the DNS tab in Advanced TCP/IP Settings for the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box.
Devolution isn't enabled if a global suffix search list is configured using Group Policy.
If a global suffix search list isn't configured, and the Append primary and connection specific DNS suffixes radio button is selected, the DNS client appends the following names to a single-label name when it sends DNS queries:
The primary DNS suffix, as specified on the Computer Name tab of the System control panel.
Each connection-specific DNS suffix, assigned either through DHCP or specified in the DNS suffix for this connection box on the DNS tab in the Advanced TCP/IP Settings dialog box for each connection.
For example, when a user submits a query for a single-label name such as "example," the DNS client attaches a suffix such as "microsoft.com" resulting in the query "example.microsoft.com," before sending the query to a DNS server.
If a DNS suffix search list isn't specified, the DNS client attaches the primary DNS suffix to a single-label name. If this query fails, the connection-specific DNS suffix is attached for a new query. If none of these queries are resolved, the client devolves the primary DNS suffix of the computer (drops the leftmost label of the primary DNS suffix), attaches this devolved primary DNS suffix to the single-label name, and submits this new query to a DNS server.
For example, if the primary DNS suffix ooo.aaa.microsoft.com is attached to the non-dot-terminated single-label name "example," and the DNS query for example.ooo.aaa.microsoft.com fails, the DNS client devolves the primary DNS suffix (drops the leftmost label) till the specified devolution level, and submits a query for example.aaa.microsoft.com. If this query fails, the primary DNS suffix is devolved further if it's under specified devolution level and the query example.microsoft.com is submitted. If this query fails, devolution continues if it's under specified devolution level and the query example.microsoft.com is submitted, corresponding to a devolution level of two. The primary DNS suffix can't be devolved beyond a devolution level of two. The devolution level can be configured using this policy setting. The default devolution level is two.
If you enable this policy setting and DNS devolution is also enabled, DNS clients use the DNS devolution level that you specify.
If this policy setting is disabled, or if this policy setting isn't configured, DNS clients use the default devolution level of two provided that DNS devolution is enabled.
DNS_IdnEncoding
Specifies whether the DNS client should convert internationalized domain names (IDNs) to Punycode when the computer is on non-domain networks with no WINS servers configured.
If this policy setting is enabled, IDNs aren't converted to Punycode.
If this policy setting is disabled, or if this policy setting isn't configured, IDNs are converted to Punycode when the computer is on non-domain networks with no WINS servers configured.
DNS_IdnMapping
Specifies whether the DNS client should convert internationalized domain names (IDNs) to the Nameprep form, a canonical Unicode representation of the string.
If this policy setting is enabled, IDNs are converted to the Nameprep form.
If this policy setting is disabled, or if this policy setting isn't configured, IDNs aren't converted to the Nameprep form.
DNS_NameServer
Defines the DNS servers to which a computer sends queries when it attempts to resolve names. This policy setting supersedes the list of DNS servers configured locally and those configured using DHCP.
To use this policy setting, click Enabled, and then enter a space-delimited list of IP addresses in the available field. To use this policy setting, you must enter at least one IP address.
If you enable this policy setting, the list of DNS servers is applied to all network connections used by computers that receive this policy setting.
If you disable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, computers will use the local or DHCP supplied list of DNS servers, if configured.
DNS_PreferLocalResponsesOverLowerOrderDns
Specifies that responses from link local name resolution protocols received over a network interface that's higher in the binding order are preferred over DNS responses from network interfaces lower in the binding order. Examples of link local name resolution protocols include link local multicast name resolution (LLMNR) and NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT).
If you enable this policy setting, responses from link local protocols will be preferred over DNS responses if the local responses are from a network with a higher binding order.
If you disable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, then DNS responses from networks lower in the binding order will be preferred over responses from link local protocols received from networks higher in the binding order.
This policy setting is applicable only if the turn off smart multi-homed name resolution policy setting is disabled or not configured.
DNS_PrimaryDnsSuffix
Specifies the primary DNS suffix used by computers in DNS name registration and DNS name resolution.
To use this policy setting, click Enabled and enter the entire primary DNS suffix you want to assign. For example: microsoft.com.
In order for changes to this policy setting to be applied on computers that receive it, you must restart Windows.
- If you enable this policy setting, it supersedes the primary DNS suffix configured in the DNS Suffix and NetBIOS Computer Name dialog box using the System control panel.
You can use this policy setting to prevent users, including local administrators, from changing the primary DNS suffix.
- If you disable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, each computer uses its local primary DNS suffix, which is usually the DNS name of Active Directory domain to which it's joined.
DNS_RegisterAdapterName
Specifies if a computer performing dynamic DNS registration will register A and PTR resource records with a concatenation of its computer name and a connection-specific DNS suffix, in addition to registering these records with a concatenation of its computer name and the primary DNS suffix.
By default, a DNS client performing dynamic DNS registration registers A and PTR resource records with a concatenation of its computer name and the primary DNS suffix. For example, a computer name of mycomputer and a primary DNS suffix of microsoft.com will be registered as: mycomputer.microsoft.com.
- If you enable this policy setting, a computer will register A and PTR resource records with its connection-specific DNS suffix, in addition to the primary DNS suffix. This applies to all network connections used by computers that receive this policy setting.
For example, with a computer name of mycomputer, a primary DNS suffix of microsoft.com, and a connection specific DNS suffix of VPNconnection, a computer will register A and PTR resource records for mycomputer. VPNconnection and mycomputer.microsoft.com when this policy setting is enabled.
This policy setting is ignored on a DNS client computer if dynamic DNS registration is disabled.
- If you disable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, a DNS client computer won't register any A and PTR resource records using a connection-specific DNS suffix.
DNS_RegisterReverseLookup
Specifies if DNS client computers will register PTR resource records.
By default, DNS clients configured to perform dynamic DNS registration will attempt to register PTR resource record only if they successfully registered the corresponding A resource record.
- If you enable this policy setting, registration of PTR records will be determined by the option that you choose under Register PTR records.
To use this policy setting, click Enabled, and then select one of the following options from the drop-down list:
Don't register: Computers won't attempt to register PTR resource records.
Register: Computers will attempt to register PTR resource records even if registration of the corresponding A records wasn't successful.
Register only if A record registration succeeds: Computers will attempt to register PTR resource records only if registration of the corresponding A records was successful.
- If you disable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, computers will use locally configured settings.
DNS_RegistrationEnabled
Specifies if DNS dynamic update is enabled. Computers configured for DNS dynamic update automatically register and update their DNS resource records with a DNS server.
If you enable this policy setting, or you don't configure this policy setting, computers will attempt to use dynamic DNS registration on all network connections that have connection-specific dynamic DNS registration enabled. For a dynamic DNS registration to be enabled on a network connection, the connection-specific configuration must allow dynamic DNS registration, and this policy setting mustn't be disabled.
If you disable this policy setting, computers may not use dynamic DNS registration for any of their network connections, regardless of the configuration for individual network connections.
DNS_RegistrationOverwritesInConflict
Specifies whether dynamic updates should overwrite existing resource records that contain conflicting IP addresses.
This policy setting is designed for computers that register address (A) resource records in DNS zones that don't use Secure Dynamic Updates. Secure Dynamic Update preserves ownership of resource records and doesn't allow a DNS client to overwrite records that are registered by other computers.
During dynamic update of resource records in a zone that doesn't use Secure Dynamic Updates, an A resource record might exist that associates the client's host name with an IP address different than the one currently in use by the client. By default, the DNS client attempts to replace the existing A resource record with an A resource record that has the client's current IP address.
If you enable this policy setting or if you don't configure this policy setting, DNS clients maintain their default behavior and will attempt to replace conflicting A resource records during dynamic update.
If you disable this policy setting, existing A resource records that contain conflicting IP addresses won't be replaced during a dynamic update, and an error will be recorded in Event Viewer.
DNS_RegistrationRefreshInterval
Specifies the interval used by DNS clients to refresh registration of A and PTR resource. This policy setting only applies to computers performing dynamic DNS updates.
Computers configured to perform dynamic DNS registration of A and PTR resource records periodically reregister their records with DNS servers, even if the record hasn't changed. This reregistration is required to indicate to DNS servers that records are current and shouldn't be automatically removed (scavenged) when a DNS server is configured to delete stale records.
If record scavenging is enabled on the zone, the value of this policy setting should never be longer than the value of the DNS zone refresh interval. Configuring the registration refresh interval to be longer than the refresh interval of the DNS zone might result in the undesired deletion of A and PTR resource records.
To specify the registration refresh interval, click Enabled and then enter a value of 1800 or greater. The value that you specify is the number of seconds to use for the registration refresh interval. For example, 1800 seconds is 30 minutes.
If you enable this policy setting, registration refresh interval that you specify will be applied to all network connections used by computers that receive this policy setting.
If you disable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, computers will use the local or DHCP supplied setting. By default, client computers configured with a static IP address attempt to update their DNS resource records once every 24 hours and DHCP clients will attempt to update their DNS resource records when a DHCP lease is granted or renewed.
DNS_RegistrationTtl
Specifies the value of the time to live (TTL) field in A and PTR resource records that are registered by computers to which this policy setting is applied.
To specify the TTL, click Enabled and then enter a value in seconds (for example, 900 is 15 minutes).
If you enable this policy setting, the TTL value that you specify will be applied to DNS resource records registered for all network connections used by computers that receive this policy setting.
If you disable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, computers will use the TTL settings specified in DNS. By default, the TTL is 1200 seconds (20 minutes).
DNS_SearchList
Specifies the DNS suffixes to attach to an unqualified single-label name before submission of a DNS query for that name.
An unqualified single-label name contains no dots. The name "example" is a single-label name. This is different from a fully qualified domain name such as "example.microsoft.com".
Client computers that receive this policy setting will attach one or more suffixes to DNS queries for a single-label name. For example, a DNS query for the single-label name "example" will be modified to "example.microsoft.com" before sending the query to a DNS server if this policy setting is enabled with a suffix of "microsoft.com".
To use this policy setting, click Enabled, and then enter a string value representing the DNS suffixes that should be appended to single-label names. You must specify at least one suffix. Use a comma-delimited string, such as "microsoft.com,serverua.microsoft.com,office.microsoft.com" to specify multiple suffixes.
If you enable this policy setting, one DNS suffix is attached at a time for each query. If a query is unsuccessful, a new DNS suffix is added in place of the failed suffix, and this new query is submitted. The values are used in the order they appear in the string, starting with the leftmost value and proceeding to the right until a query is successful or all suffixes are tried.
If you disable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, the primary DNS suffix and network connection-specific DNS suffixes are appended to the unqualified queries.
DNS_SmartMultiHomedNameResolution
Specifies that a multi-homed DNS client should optimize name resolution across networks. The setting improves performance by issuing parallel DNS, link local multicast name resolution (LLMNR) and NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) queries across all networks. In the event that multiple positive responses are received, the network binding order is used to determine which response to accept.
If you enable this policy setting, the DNS client won't perform any optimizations. DNS queries will be issued across all networks first. LLMNR queries will be issued if the DNS queries fail, followed by NetBT queries if LLMNR queries fail.
If you disable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, name resolution will be optimized when issuing DNS, LLMNR and NetBT queries.
DNS_SmartProtocolReorder
Specifies that the DNS client should prefer responses from link local name resolution protocols on non-domain networks over DNS responses when issuing queries for flat names. Examples of link local name resolution protocols include link local multicast name resolution (LLMNR) and NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT).
If you enable this policy setting, the DNS client will prefer DNS responses, followed by LLMNR, followed by NetBT for all networks.
If you disable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, the DNS client will prefer link local responses for flat name queries on non-domain networks.
DNS_UpdateSecurityLevel
Specifies the security level for dynamic DNS updates.
To use this policy setting, click Enabled and then select one of the following values:
Unsecure followed by secure - computers send secure dynamic updates only when nonsecure dynamic updates are refused.
Only unsecure - computers send only nonsecure dynamic updates.
Only secure - computers send only secure dynamic updates.
If you enable this policy setting, computers that attempt to send dynamic DNS updates will use the security level that you specify in this policy setting.
If you disable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, computers will use local settings. By default, DNS clients attempt to use unsecured dynamic update first. If an unsecured update is refused, clients try to use secure update.
DNS_UpdateTopLevelDomainZones
Specifies if computers may send dynamic updates to zones with a single label name. These zones are also known as top-level domain zones, for example: "com".
By default, a DNS client that's configured to perform dynamic DNS update will update the DNS zone that's authoritative for its DNS resource records unless the authoritative zone is a top-level domain or root zone.
If you enable this policy setting, computers send dynamic updates to any zone that's authoritative for the resource records that the computer needs to update, except the root zone.
If you disable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, computers don't send dynamic updates to the root zone or top-level domain zones that are authoritative for the resource records that the computer needs to update.
DNS_UseDomainNameDevolution
Specifies if the DNS client performs primary DNS suffix devolution during the name resolution process.
For example, if the primary DNS suffix ooo.aaa.microsoft.com is attached to the non-dot-terminated single-label name "example," and the DNS query for example.ooo.aaa.microsoft.com fails, the DNS client devolves the primary DNS suffix (drops the leftmost label) till the specified devolution level, and submits a query for example.aaa.microsoft.com. If this query fails, the primary DNS suffix is devolved further if it's under specified devolution level and the query example.microsoft.com is submitted. If this query fails, devolution continues if it's under specified devolution level and the query example.microsoft.com is submitted, corresponding to a devolution level of two. The primary DNS suffix can't be devolved beyond a devolution level of two. The devolution level can be configured using the primary DNS suffix devolution level policy setting. The default devolution level is two.
If you enable this policy setting, or if you don't configure this policy setting, DNS clients attempt to resolve single-label names using concatenations of the single-label name to be resolved and the devolved primary DNS suffix.
If you disable this policy setting, DNS clients don't attempt to resolve names that are concatenations of the single-label name to be resolved and the devolved primary DNS suffix.
Turn_Off_Multicast
Specifies that link local multicast name resolution (LLMNR) is disabled on client computers.
LLMNR is a secondary name resolution protocol. With LLMNR, queries are sent using multicast over a local network link on a single subnet from a client computer to another client computer on the same subnet that also has LLMNR enabled. LLMNR doesn't require a DNS server or DNS client configuration, and provides name resolution in scenarios in which conventional DNS name resolution isn't possible.
If you enable this policy setting, LLMNR will be disabled on all available network adapters on the client computer.
If you disable this policy setting, or you don't configure this policy setting, LLMNR will be enabled on all available network adapters.
Related articles
Policy configuration service provider
Was this page helpful?
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback .
Submit and view feedback for
Additional resources

by Mike Gruner
Dynamic Environment Manager (DEM) – IE trusted sites
You ever wants to set websites in Microsoft Internet Explorer as default through your whole environment? Sure, that is one of the use cases of VMware´s Dynamic Environment Manager (DEM). But what if you use the Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration? In that case you have to define which sites are associated with which security zone. There are 4 types of zones in that case:
1 = Intranet zone
2 = Trusted Sites zone
3 = Internet zone
4 = Restricted Sites zone.
This led to the conclusion to do the definition with DEM as well, it´s a website, right? You go to your DEM Management console, use the tab “User environment”. On the left side you choose “ADMX-based Settings”. Click create. Choose “Select Categories” and then User Configuration – Policies – Administrative Templates – Windows Components – Internet Explorer – Internet Control Panel – Security Page, click ok.
Now go to Edit
Select on the left side “Windows Components – Internet Explorer – Internet Control Panel – Security Page. On the right side you will find the policy “Site to Zone Assignment List.
And then you see that:
Now unfortunately, the bad news. In that case I have to tell you, that this is not possible with DEM ADMX-based settings. I explain you why, with that policy will not only be set some registry keys or something like that. This policy is a little bit more complex from the policy perspective. It will run the so called Group Policy extensions. DEM is not able to do the same or in better words can´t simulate that behavior. For that reason, VMware marks that as unsupported settings.
If you want to configure things like that in your environment, please use the usual Active Directory GPOs.
Dynamic Environment Manager (DEM) supports a lot of policies (GPOs) but unfortunately, not that.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Environment Manager (EM) — mer (Community Member) asked a question.
I'm currently in the process of transforming our GPO into EM. It seems to work well but I have one problem.
The "apply ADMX policy" actions seems not not be working properly when using it for the "Site to Zone Assignment list" for IE. For example I added 6 entries to the list and when I check the registry there are only 1 or 2 entries from my list configured in EM policy.
I also checked with the client logging tool and this step is marked as "passed". I am also sure that no conflicting GPO is applied during logon.
Anyone else with this issue?
- All forum questions

steven.woods.ivanti (Ivanti Employee)
I have had a case previously similar however we seen in Procmon that this was due to another GPO/Script overwriting the keys the ADMX policy had set. I would advise to have an endpoint completely blank with no GPO/scripts being ran on the endpoint and running a blank configuration that just runs this ADMX policy. If you still see the issue I would raise a case for further troubleshooting to be carried out.
mer (Community Member)
Ok, I have to admit that it was my fault. I made a failure while adding the list and switched the value and value name. :/
But thank you very much for giving a hint.
joeh (Ivanti Employee)
Are you adding a large number of entries? I think I've seen issues with very large numbers where it just fails to complete them all.
Hi Joeh, what do you define as a large number? I think it was around 40 entries per node. One node during computer "network available" trigger and one node under "Pre-Desktop" Trigger.
Hi. I may have been mistaken, I think I was remembering the issue described here: https://forums.ivanti.com/s/article/Slow-application-launch-when-Zone-Map-keys-contains-many-entries
Related Questions
Trending articles.
- Release Notes for DSM 2019.1
- MobileIron Cloud: Azure Active Directory User and Group Import and Authentication
- New CVE-2024-21894 (Heap Overflow), CVE-2024-22052 (Null Pointer Dereference), CVE-2024-22053 (Heap Overflow), CVE-2024-22…
- Cloud Getting Started - STEP 1 of 4 - Register with Ivanti Community and Support Portal
Have a question about this article?
Open up a discussion in our discussion groups HERE
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Trusted Sites Zone Template. This template policy setting allows you to configure policy settings in this zone consistent with a selected security level, for example, Low, Medium Low, Medium, or High. If you enable this template policy setting and select a security level, all values for individual settings in the zone will be overwritten by the ...
This policy setting allows you to manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. These zone numbers have associated security settings that apply to all of the sites in the zone. Internet Explorer has 4 security zones, numbered 1-4, and these are used by this policy setting to associate sites to zones.
Open Group Policy Management Console. Navigate to the desired GPO or create a new one. Expand User Configuration or Computer Configuration and go to Preferences -> Windows Settings -> Registry. Right-click and select New -> Registry Item. Configure the Registry Item to delete the specified entries under the ZoneMap registry key.
Re: Site to Zone Assignment List - Powershell. # Step 2: Navigate to the Site to Zone Assignment List # This step is manual and requires navigating through the Group Policy Management Editor interface. # Step 3: Enable the Policy and Specify Zone Assignments # Define the list of URLs and their corresponding zone assignments.
Configure the Enterprise Mode Site List; Configure the list of names that will bypass the HSTS policy check; Configure the list of sites for which Microsoft Edge will attempt to establish a Token Binding with; Configure the list of types that are excluded from synchronization; Configure the Share experience
Adding Site to Zone assignment list using IE ADMX/L in ProfileUnity. Product: ProfileUnity-FlexApp. Product Version: 6.8.3. Updated: Feb 17, 2020. Expires on: 365 days from publish date. Problem: What's the correct syntax when adding Site to Zone assignment lists in ProfileUnity when using imported ADMX/L for Internet Explorer. Resolution: Make ...
Step 2. Navigate to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel > Security Page and double click on the “Site to Zone Assignment List†and check the “Enable†option then click on the “Show..†button. Step 3.
When possible, use the computer configuration option as it will not impact user logons. When you enable the setting, you will be prompted for a value name (the website) and a value (the zone list). Here are the possible values and the zone that they correspond to: 1 = Intranet/Local Zone. 2 = Trusted Sites. 3 = Internet/Public Zone.
In managed environments, administrators can use Group Policy to assign specific sites to Zones (via "Site to Zone Assignment List" policy) and specify the settings for URLActions on a per-zone basis. Beyond manual administrative or user assignment of sites to Zones, other heuristics could assign sites to the Local Intranet Zone .
Deploy a set of trusted sites overriding users' ability to add trusted sites themselves. To acheive this, an Intune configuration profile Trusted site zone assignment can be deployed to devices/users group as required. Login to Intune Portal and navigate to: Devices > Windows > Configuration Profiles. Hit the Create button and Select New ...
Site to Zone Assignment List. This policy setting allows you to manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. These zone numbers have associated security settings that apply to all of the sites in the zone.Internet Explorer has 4 security zones numbered 1-4 and these are used by this policy setting to ...
aaron9615 (Aaron9615) December 3, 2015, 6:22pm 2. I believe GPO will only allow you to assign the zone assignment to the root domain. Example Spiceworks.com = Value of 2. Then you add spicerex.spiceworks.com = Value of 1. The root domain is going to be assigned the value of 2, so no other sub domains can be added.
Open Windows Components/Internet Explorer/Internet Control Panel/Security Page/Site to Zone Assignment List, there are two settings that you will need. Enabled , and Zone assignment list . I use ADMX Migrator open inetres.admx , zone list Elements is ListBox , ID name is IZ_ZonemapPrompt, this is the ID I will need to use for assigning those ...
For me, when I put my intranet sites under the HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\EscDomains key, everything worked fine. Note that there is a Policies key in the path, which is presumably where group policy configuration of the site/zone assignments goes. -
I'm just adding a few sites to different zones using the admx-backed policy "\Windows Components\Internet Explorer\Internet Control Panel\Security Page" (Administrative Template) in Intune. Until now, I have set these in the following format if a wildcard was necessary.
1. Create a new GPO, or use an existing GPO. 2. Edit the GPO for the following settings: a. Under User Configuration\Policies\Windows Components\Internet Explorer\Internet Control Panel\Security Page\Site to Zone Assignment List: Define this policy setting as Enabled, then click the Show ... button to define the URLs and zone assignment.
These registry entries are located in the following registry subkey: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\<ZoneNumber>. In this registry subkey, <ZoneNumber> is a zone such as 0 (zero). The 1200 registry entry and the 2000 registry entry each contain a setting that is named Administrator approved.
Microsoft. DirectAccess Connectivity Assistant Disable SMB Compression Network Drive Mappings Microsoft Edge for Business Edge Chromium Blocker Toolkit Enhanced Mitigation Experience Toolkit Forefront Endpoint Protection 2010 Forefront Identity Manager 2010 R2 Group Policy Preference Client Side Extensions Azure Hybrid Connection Manager Hide ...
The setting (User Settings -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Internet Explorer -> Internet Control Panel -> Security Page -> Site to Zone Assignment List) still has good old IE in its name, but apparently should apply generally. At least this used to work across all browsers in the past. Accordingly, files that are downloaded ...
Good Afternoon all, Coming across an issue trying to set the Site-to-Zone Assignment Lists within Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel > Security Page The following settings are set: Internet Zone Template - Disabled Locked-Down Trusted Sites Zone Template - Disabled R...
These zones are also known as top-level domain zones, for example: "com". By default, a DNS client that's configured to perform dynamic DNS update will update the DNS zone that's authoritative for its DNS resource records unless the authoritative zone is a top-level domain or root zone.
You go to your DEM Management console, use the tab "User environment". On the left side you choose "ADMX-based Settings". Click create. Choose "Select Categories" and then User Configuration - Policies - Administrative Templates - Windows Components - Internet Explorer - Internet Control Panel - Security Page, click ok.
The "apply ADMX policy" actions seems not not be working properly when using it for the "Site to Zone Assignment list" for IE. For example I added 6 entries to the list and when I check the registry there are only 1 or 2 entries from my list configured in EM policy. I also checked with the client logging tool and this step is marked as ...