Essay on Inflation: Types, Causes and Effects
Essay on Inflation!

Essay on the Meaning of Inflation:
Inflation and unemployment are the two most talked-about words in the contemporary society. These two are the big problems that plague all the economies. Almost everyone is sure that he knows what inflation exactly is, but it remains a source of great deal of confusion because it is difficult to define it unambiguously.
Inflation is often defined in terms of its supposed causes. Inflation exists when money supply exceeds available goods and services. Or inflation is attributed to budget deficit financing. A deficit budget may be financed by additional money creation. But the situation of monetary expansion or budget deficit may not cause price level to rise. Hence the difficulty of defining ‘inflation’ .
Inflation may be defined as ‘a sustained upward trend in the general level of prices’ and not the price of only one or two goods. G. Ackley defined inflation as ‘a persistent and appreciable rise in the general level or average of prices’ . In other words, inflation is a state of rising price level, but not rise in the price level. It is not high prices but rising prices that constitute inflation.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is an increase in the overall price level. A small rise in prices or a sudden rise in prices is not inflation since these may reflect the short term workings of the market. It is to be pointed out here that inflation is a state of disequilibrium when there occurs a sustained rise in price level.
It is inflation if the prices of most goods go up. However, it is difficult to detect whether there is an upward trend in prices and whether this trend is sustained. That is why inflation is difficult to define in an unambiguous sense.
Let’s measure inflation rate. Suppose, in December 2007, the consumer price index was 193.6 and, in December 2008 it was 223.8. Thus the inflation rate during the last one year was 223.8 – 193.6/193.6 × 100 = 15.6%.
As inflation is a state of rising prices, deflation may be defined as a state of falling prices but not fall in prices. Deflation is, thus, the opposite of inflation, i.e., rise in the value or purchasing power of money. Disinflation is a slowing down of the rate of inflation.
Essay on the Types of Inflation :
As the nature of inflation is not uniform in an economy for all the time, it is wise to distinguish between different types of inflation. Such analysis is useful to study the distributional and other effects of inflation as well as to recommend anti-inflationary policies.
Inflation may be caused by a variety of factors. Its intensity or pace may be different at different times. It may also be classified in accordance with the reactions of the government toward inflation.
Thus, one may observe different types of inflation in the contemporary society:
(a) According to Causes:
i. Currency Inflation:
This type of inflation is caused by the printing of currency notes.
ii. Credit Inflation:
Being profit-making institutions, commercial banks sanction more loans and advances to the public than what the economy needs. Such credit expansion leads to a rise in price level.
iii. Deficit-Induced Inflation:
The budget of the government reflects a deficit when expenditure exceeds revenue. To meet this gap, the government may ask the central bank to print additional money. Since pumping of additional money is required to meet the budget deficit, any price rise may be called deficit-induced inflation.
iv. Demand-Pull Inflation:
An increase in aggregate demand over the available output leads to a rise in the price level. Such inflation is called demand-pull inflation (henceforth DPI). But why does aggregate demand rise? Classical economists attribute this rise in aggregate demand to money supply.
If the supply of money in an economy exceeds the available goods and services, DPI appears. It has been described by Coulborn as a situation of “too much money chasing too few goods” .
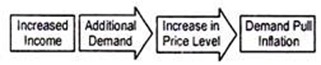
Note that, in this region, price level begins to rise. Ultimately, the economy reaches full employment situation, i.e., Range 3, where output does not rise but price level is pulled upward. This is demand-pull inflation. The essence of this type of inflation is “too much spending chasing too few goods.”
v. Cost-Push Inflation:
Inflation in an economy may arise from the overall increase in the cost of production. This type of inflation is known as cost-push inflation (henceforth CPI). Cost of production may rise due to increase in the price of raw materials, wages, etc. Often trade unions are blamed for wage rise since wage rate is not market-determined. Higher wage means higher cost of production.
Prices of commodities are thereby increased. A wage-price spiral comes into operation. But, at the same time, firms are to be blamed also for the price rise since they simply raise prices to expand their profit margins. Thus we have two important variants of CPI: wage-push inflation and profit-push inflation. Anyway, CPI stems from the leftward shift of the aggregate supply curve.

The price level thus determined is OP 1 . As aggregate demand curve shifts to AD 2 , price level rises to OP 2 . Thus, an increase in aggregate demand at the full employment stage leads to an increase in price level only, rather than the level of output. However, how much price level will rise following an increase in aggregate demand depends on the slope of the AS curve.
Causes of Demand-Pull Inflation :
DPI originates in the monetary sector. Monetarists’ argument that “only money matters” is based on the assumption that at or near full employment, excessive money supply will increase aggregate demand and will thus cause inflation.
An increase in nominal money supply shifts aggregate demand curve rightward. This enables people to hold excess cash balances. Spending of excess cash balances by them causes price level to rise. Price level will continue to rise until aggregate demand equals aggregate supply.
Keynesians argue that inflation originates in the non-monetary sector or the real sector. Aggregate demand may rise if there is an increase in consumption expenditure following a tax cut. There may be an autonomous increase in business investment or government expenditure. Governmental expenditure is inflationary if the needed money is procured by the government by printing additional money.
In brief, an increase in aggregate demand i.e., increase in (C + I + G + X – M) causes price level to rise. However, aggregate demand may rise following an increase in money supply generated by the printing of additional money (classical argument) which drives prices upward. Thus, money plays a vital role. That is why Milton Friedman believes that inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon.
There are other reasons that may push aggregate demand and, hence, price level upwards. For instance, growth of population stimulates aggregate demand. Higher export earnings increase the purchasing power of the exporting countries.
Additional purchasing power means additional aggregate demand. Purchasing power and, hence, aggregate demand, may also go up if government repays public debt. Again, there is a tendency on the part of the holders of black money to spend on conspicuous consumption goods. Such tendency fuels inflationary fire. Thus, DPI is caused by a variety of factors.
Cost-Push Inflation Theory :
In addition to aggregate demand, aggregate supply also generates inflationary process. As inflation is caused by a leftward shift of the aggregate supply, we call it CPI. CPI is usually associated with the non-monetary factors. CPI arises due to the increase in cost of production. Cost of production may rise due to a rise in the cost of raw materials or increase in wages.
Such increases in costs are passed on to consumers by firms by raising the prices of the products. Rising wages lead to rising costs. Rising costs lead to rising prices. And rising prices, again, prompt trade unions to demand higher wages. Thus, an inflationary wage-price spiral starts.
This causes aggregate supply curve to shift leftward. This can be demonstrated graphically (Fig. 11.4) where AS 1 is the initial aggregate supply curve. Below the full employment stage this AS curve is positive sloping and at full employment stage it becomes perfectly inelastic. Intersection point (E 1 ) of AD 1 and AS 1 curves determines the price level.
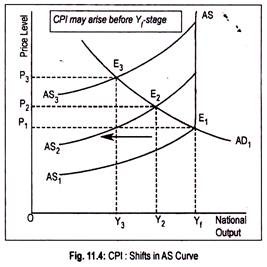
Now, there is a leftward shift of aggregate supply curve to AS 2 . With no change in aggregate demand, this causes price level to rise to OP 2 and output to fall to OY 2 .
With the reduction in output, employment in the economy declines or unemployment rises. Further shift in the AS curve to AS 2 results in higher price level (OP 3 ) and a lower volume of aggregate output (OY 3 ). Thus, CPI may arise even below the full employment (Y f ) stage.
Causes of CPI :
It is the cost factors that pull the prices upward. One of the important causes of price rise is the rise in price of raw materials. For instance, by an administrative order the government may hike the price of petrol or diesel or freight rate. Firms buy these inputs now at a higher price. This leads to an upward pressure on cost of production.
Not only this, CPI is often imported from outside the economy. Increase in the price of petrol by OPEC compels the government to increase the price of petrol and diesel. These two important raw materials are needed by every sector, especially the transport sector. As a result, transport costs go up resulting in higher general price level.
Again, CPI may be induced by wage-push inflation or profit-push inflation. Trade unions demand higher money wages as a compensation against inflationary price rise. If increase in money wages exceeds labour productivity, aggregate supply will shift upward and leftward. Firms often exercise power by pushing up prices independently of consumer demand to expand their profit margins.
Fiscal policy changes, such as an increase in tax rates leads to an upward pressure in cost of production. For instance, an overall increase in excise tax of mass consumption goods is definitely inflationary. That is why government is then accused of causing inflation.
Finally, production setbacks may result in decreases in output. Natural disaster, exhaustion of natural resources, work stoppages, electric power cuts, etc., may cause aggregate output to decline.
In the midst of this output reduction, artificial scarcity of any goods by traders and hoarders just simply ignite the situation.
Inefficiency, corruption, mismanagement of the economy may also be the other reasons. Thus, inflation is caused by the interplay of various factors. A particular factor cannot be held responsible for inflationary price rise.
Essay on the Effects of Inflation :
People’s desires are inconsistent. When they act as buyers they want prices of goods and services to remain stable but as sellers they expect the prices of goods and services should go up. Such a happy outcome may arise for some individuals; “but, when this happens, others will be getting the worst of both worlds.” Since inflation reduces purchasing power it is bad.
The old people are in the habit of recalling the days when the price of say, meat per kilogram cost just 10 rupees. Today it is Rs. 250 per kilogram. This is true for all other commodities. When they enjoyed a better living standard. Imagine today, how worse we are! But meanwhile, wages and salaries of people have risen to a great height, compared to the ‘good old days’. This goes unusually untold.
When price level goes up, there is both a gainer and a loser. To evaluate the consequence of inflation, one must identify the nature of inflation which may be anticipated and unanticipated. If inflation is anticipated, people can adjust with the new situation and costs of inflation to the society will be smaller.
In reality, people cannot predict accurately future events or people often make mistakes in predicting the course of inflation. In other words, inflation may be unanticipated when people fail to adjust completely. This creates various problems.
One can study the effects of unanticipated inflation under two broad headings:
(i) Effect on distribution of income and wealth
(ii) Effect on economic growth.
(a) Effects of Inflation on Income and Wealth Distribution :
During inflation, usually people experience rise in incomes. But some people gain during inflation at the expense of others. Some individuals gain because their money incomes rise more rapidly than the prices and some lose because prices rise more rapidly than their incomes during inflation. Thus, it redistributes income and wealth.
Though no conclusive evidence can be cited, it can be asserted that following categories of people are affected by inflation differently:
i. Creditors and Debtors:
Borrowers gain and lenders lose during inflation because debts are fixed in rupee terms. When debts are repaid their real value declines by the price level increase and, hence, creditors lose. An individual may be interested in buying a house by taking a loan of Rs. 7 lakh from an institution for 7 years.
The borrower now welcomes inflation since he will have to pay less in real terms than when it was borrowed. Lender, in the process, loses since the rate of interest payable remains unaltered as per agreement. Because of inflation, the borrower is given ‘dear’ rupees, but pays back ‘cheap’ rupees.
However, if in an inflation-ridden economy creditors chronically loose, it is wise not to advance loans or to shut down business. Never does it happen. Rather, the loan- giving institution makes adequate safeguard against the erosion of real value.
ii. Bond and Debenture-Holders:
In an economy, there are some people who live on interest income—they suffer most.
Bondholders earn fixed interest income:
These people suffer a reduction in real income when prices rise. In other words, the value of one’s savings decline if the interest rate falls short of inflation rate. Similarly, beneficiaries from life insurance programmes are also hit badly by inflation since real value of savings deteriorate.
iii. Investors:
People who put their money in shares during inflation are expected to gain since the possibility of earning business profit brightens. Higher profit induces owners of firms to distribute profit among investors or shareholders.
iv. Salaried People and Wage-Earners:
Anyone earning a fixed income is damaged by inflation. Sometimes, unionized worker succeeds in raising wage rates of white-collar workers as a compensation against price rise. But wage rate changes with a long time lag. In other words, wage rate increases always lag behind price increases.
Naturally, inflation results in a reduction in real purchasing power of fixed income earners. On the other hand, people earning flexible incomes may gain during inflation. The nominal incomes of such people outstrip the general price rise. As a result, real incomes of this income group increase.
v. Profit-Earners, Speculators and Black Marketeers:
It is argued that profit-earners gain from inflation. Profit tends to rise during inflation. Seeing inflation, businessmen raise the prices of their products. This results in a bigger profit. Profit margin, however, may not be high when the rate of inflation climbs to a high level.
However, speculators dealing in business in essential commodities usually stand to gain by inflation. Black marketeers are also benefited by inflation.
Thus, there occurs a redistribution of income and wealth. It is said that rich becomes richer and poor becomes poorer during inflation. However, no such hard and fast generalizations can be made. It is clear that someone wins and someone loses from inflation.
These effects of inflation may persist if inflation is unanticipated. However, the redistributive burdens of inflation on income and wealth are most likely to be minimal if inflation is anticipated by the people.
With anticipated inflation, people can build up their strategies to cope with inflation. If the annual rate of inflation in an economy is anticipated correctly people will try to protect them against losses resulting from inflation.
Workers will demand 10 p.c. wage increase if inflation is expected to rise by 10 p.c. Similarly, a percentage of inflation premium will be demanded by creditors from debtors. Business firms will also fix prices of their products in accordance with the anticipated price rise. Now if the entire society “learns to live with inflation” , the redistributive effect of inflation will be minimal.
However, it is difficult to anticipate properly every episode of inflation. Further, even if it is anticipated it cannot be perfect. In addition, adjustment with the new expected inflationary conditions may not be possible for all categories of people. Thus, adverse redistributive effects are likely to occur.
Finally, anticipated inflation may also be costly to the society. If people’s expectation regarding future price rise become stronger they will hold less liquid money. Mere holding of cash balances during inflation is unwise since its real value declines. That is why people use their money balances in buying real estate, gold, jewellery, etc.
Such investment is referred to as unproductive investment. Thus, during inflation of anticipated variety, there occurs a diversion of resources from priority to non-priority or unproductive sectors.
b. Effect on Production and Economic Growth :
Inflation may or may not result in higher output. Below the full employment stage, inflation has a favourable effect on production. In general, profit is a rising function of the price level. An inflationary situation gives an incentive to businessmen to raise prices of their products so as to earn higher doses of profit.
Rising price and rising profit encourage firms to make larger investments. As a result, the multiplier effect of investment will come into operation resulting in higher national output. However, such a favourable effect of inflation will be temporary if wages and production costs rise very rapidly.
Further, inflationary situation may be associated with the fall in output, particularly if inflation is of the cost-push variety. Thus, there is no strict relationship between prices and output. An increase in aggregate demand will increase both prices and output, but a supply shock will raise prices and lower output.
Inflation may also lower down further production levels. It is commonly assumed that if inflationary tendencies nurtured by experienced inflation persist in future, people will now save less and consume more. Rising saving propensities will result in lower further outputs.
One may also argue that inflation creates an air of uncertainty in the minds of business community, particularly when the rate of inflation fluctuates. In the midst of rising inflationary trend, firms cannot accurately estimate their costs and revenues. Under the circumstance, business firms may be deterred in investing. This will adversely affect the growth performance of the economy.
However, slight dose of inflation is necessary for economic growth. Mild inflation has an encouraging effect on national output. But it is difficult to make the price rise of a creeping variety. High rate of inflation acts as a disincentive to long run economic growth. The way the hyperinflation affects economic growth is summed up here.
We know that hyperinflation discourages savings. A fall in savings means a lower rate of capital formation. A low rate of capital formation hinders economic growth. Further, during excessive price rise, there occurs an increase in unproductive investment in real estate, gold, jewellery, etc.
Above all, speculative businesses flourish during inflation resulting in artificial scarcities and, hence, further rise in prices. Again, following hyperinflation, export earnings decline resulting in a wide imbalance in the balance of payments account.
Often, galloping inflation results in a ‘flight’ of capital to foreign countries since people lose confidence and faith over the monetary arrangements of the country, thereby resulting in a scarcity of resources. Finally, real value of tax revenue also declines under the impact of hyperinflation. Government then experiences a shortfall in investible resources.
Thus, economists and policy makers are unanimous regarding the dangers of high price rise. But the consequence of hyperinflation is disastrous. In the past, some of the world economies (e.g., Germany after the First World War (1914-1918), Latin American countries in the 1980s) had been greatly ravaged by hyperinflation.
The German Inflation of 1920s was also Catastrophic:
During 1922, the German price level went up 5,470 per cent, in 1923, the situation worsened; the German price level rose 1,300,000,000 times. By October of 1923, the postage of the lightest letter sent from Germany to the United States was 200,000 marks.
Butter cost 1.5 million marks per pound, meat 2 million marks, a loaf of bread 200,000 marks, and an egg 60,000 marks Prices increased so rapidly that waiters changed the prices on the menu several times during the course of a lunch!! Sometimes, customers had to pay double the price listed on the menu when they observed it first!!!
During October 2008, Zimbabwe, under the President-ship of Robert G. Mugabe, experienced 231,000,000 p.c. (2.31 million p.c.) as against 1.2 million p.c. price rise in September 2008—a record after 1923. It is an unbelievable rate. In May 2008, the cost of price of a toilet paper itself and not the costs of the roll of the toilet paper came to 417 Zimbabwean dollars.
Anyway, people are harassed ultimately by the high rate of inflation. That is why it is said that ‘inflation is our public enemy number one’. Rising inflation rate is a sign of failure on the part of the government.
Related Articles:
- Essay on the Causes of Inflation (473 Words)
- Cost-Push Inflation and Demand-Pull or Mixed Inflation
- Demand Pull Inflation and Cost Push Inflation | Money
- Essay on Inflation: Meaning, Measurement and Causes
Home — Essay Samples — Economics — Political Economy — Inflation
Essays on Inflation
Inflation essay topics and outline examples, essay title 1: understanding inflation: causes, effects, and economic policy responses.
Thesis Statement: This essay provides a comprehensive analysis of inflation, exploring its root causes, the economic and societal effects it generates, and the various policy measures employed by governments and central banks to manage and mitigate inflationary pressures.
- Introduction
- Defining Inflation: Concept and Measurement
- Causes of Inflation: Demand-Pull, Cost-Push, and Monetary Factors
- Effects of Inflation on Individuals, Businesses, and the Economy
- Inflationary Policies: Central Bank Actions and Government Interventions
- Case Studies: Historical Inflationary Periods and Their Consequences
- Challenges in Inflation Management: Balancing Growth and Price Stability
Essay Title 2: Inflation and Its Impact on Consumer Purchasing Power: A Closer Look at the Cost of Living
Thesis Statement: This essay focuses on the effects of inflation on consumer purchasing power, analyzing how rising prices affect the cost of living, household budgets, and the strategies individuals employ to cope with inflation-induced challenges.
- Inflation's Impact on Prices: Understanding the Cost of Living Index
- Consumer Behavior and Inflation: Adjustments in Spending Patterns
- Income Inequality and Inflation: Examining Disparities in Financial Resilience
- Financial Planning Strategies: Savings, Investments, and Inflation Hedges
- Government Interventions: Indexation, Wage Controls, and Social Programs
- The Global Perspective: Inflation in Different Economies and Regions
Essay Title 3: Hyperinflation and Economic Crises: Case Studies and Lessons from History
Thesis Statement: This essay explores hyperinflation as an extreme form of inflation, examines historical case studies of hyperinflationary crises, and draws lessons on the devastating economic and social consequences that result from unchecked inflationary pressures.
- Defining Hyperinflation: Thresholds and Characteristics
- Case Study 1: Weimar Republic (Germany) and the Hyperinflation of 1923
- Case Study 2: Zimbabwe's Hyperinflationary Collapse in the Late 2000s
- Impact on Society: Currency Devaluation, Poverty, and Social Unrest
- Responses and Recovery: Stabilizing Currencies and Rebuilding Economies
- Preventative Measures: Policies to Avoid Hyperinflationary Crises
Report on Inflation and Its Causes
The rise of inflation rate in the us, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Iflation and Its Causes
Methods to control inflation, the grade inflation, inflation: a deceitful solution to debt, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
How to Control Inflation in Pakistan
Main factors of inflation in singapore, effects of inflation on commercial banks’ lending: a case of kenya commercial bank limited, food inflation in the republic of india, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
The Issue of Unemployment and Inflation in Colombia
The theory and policy of macroeconomics on inflation rate, socio-economic conditions in 'what is poverty' by jo goodwin parker, non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment (nairu), targeting zero inflation and increase of government spending as a way of curbing recession, howa spiraling inflation has impacted the venezuelan economy, how venezuela has been affected by inflation, effects of inflation on kenya commercial banks lending, exploring theories of inflation in economics, about fuel prices: factors, impacts, and solutions, analyzing the inflation reduction act, the oscillating tides of the american economy, exploring the implications of the inflation reduction act, inflation reduction act in the frame of macroeconomic challenges, the impact of inflation reduction act on the international economic stage, relevant topics.
- Unemployment
- Penny Debate
- Supply and Demand
- American Dream
- Minimum Wage
- Real Estate
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
What is inflation, and why has it been so high?
Subscribe to election ’24, ben harris ben harris vice president and director - economic studies , director - retirement security project @econ_harris.
April 3, 2024
Transcript:
Inflation, the change in price of goods and services over time, is often confused with the cost of things.
Inflation is not about how much things cost, but rather how prices are changing in a given month or year.
There’s no single culprit. Early in the pandemic, there were fewer workers and disruptions in the availability of goods due to snarled shipping routes and shuttered childcare centers, among other factors.
At the same time, demand for some products soared: pandemic-era stimulus programs left shoppers with extra cash to spend, and everyone wanted to buy the same types of things.
More recently, inflation has been driven mostly by the cost of buying or renting a home. This is due to entirely different reasons, mainly that new homebuilding has been slow and older Americans are not moving out of their homes as frequently.
Inflation has slowed since its peak, but that only means prices aren’t rising as quickly as before. The chance that prices actually fall are very slim, although we have seen price declines in products likes eggs and used cars.
Still, the U.S. has made great progress. Reining in inflation has not led to a recession and widespread job loss.
Cooling inflation, while keeping unemployment at historically low levels, has been the ideal scenario, or what economists like to call a “soft landing.”
The Fed has targeted an average inflation rate of 2% and will use the tools necessary to get the economy to that place. It’s less a question of “if” inflation will reach this level, and more a question of “when” and how much economic pain it will take.
Right now it seems like the answer appears to be “soon” and “not too much.”
The Brookings Institution is financed through the support of a diverse array of foundations, corporations, governments, individuals, as well as an endowment. A list of donors can be found in our annual reports published online here . The findings, interpretations, and conclusions in this report are solely those of its author(s) and are not influenced by any donation.
Federal Fiscal Policy
Economic Studies
Election ’24: Issues at Stake
The Brookings Institution, Washington D.C.
10:00 am - 3:00 pm EDT
William G. Gale
May 8, 2024
Stefanie Stantcheva
March 27, 2024

Economic essays on inflation
- Definition – Inflation – Inflation is a sustained rise in the cost of living and average price level.
- Causes Inflation – Inflation is caused by excess demand in the economy, a rise in costs of production, rapid growth in the money supply.
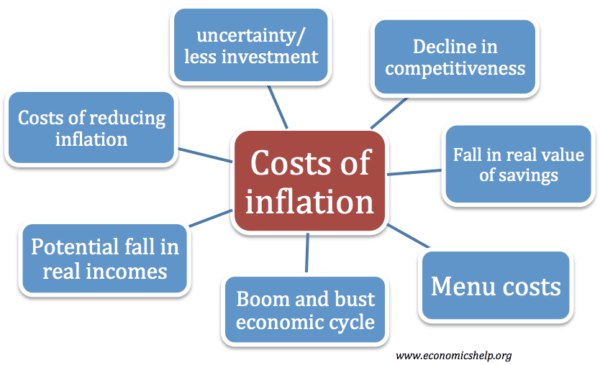
- Costs of Inflation – Inflation causes decline in value of savings, uncertainty, confusion and can lead to lower investment.
- Problems measuring inflation – why it can be hard to measure inflation with changing goods.
- Different types of inflation – cost-push inflation, demand-pull inflation, wage-price spiral,
- How to solve inflation . Policies to reduce inflation, including monetary policy, fiscal policy and supply-side policies.
- Trade off between inflation and unemployment . Is there a trade-off between the two, as Phillips Curve suggests?
- The relationship between inflation and the exchange rate – Why high inflation can lead to a depreciation in the exchange rate.
- What should the inflation target be? – Why do government typically target inflation of 2%
- Deflation – why falling prices can lead to negative economic growth.
- Monetarist Theory – Monetarist theory of inflation emphasises the role of the money supply.
- Criticisms of Monetarism – A look at whether the monetarist theory holds up to real-world scenarios.
- Money Supply – What the money supply is.
- Can we have economic growth without inflation?
- Predicting inflation
- Link between inflation and interest rates
- Should low inflation be the primary macroeconomic objective?
See also notes on Unemployment

Essay on Inflation
Essay generator.
Inflation is a term that resonates through the corridors of our daily lives, affecting decisions made by individuals, businesses, and governments alike. It refers to the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, and subsequently, purchasing power is falling. Central banks attempt to limit inflation, and avoid deflation, to keep the economy running smoothly. This essay delves into the causes of inflation, its various effects on the economy and individuals, and the strategies employed to manage it, aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding suitable for a student participating in an essay writing competition.
The Causes of Inflation
Inflation is primarily caused by two factors: demand-pull and cost-push inflation. Demand-pull inflation occurs when demand for goods and services exceeds supply, causing prices to rise. This can happen due to increased consumer spending, government expenditure, or investment. Cost-push inflation, on the other hand, happens when the cost of production increases, leading producers to raise prices to maintain their profit margins. This increase in production costs can be due to rising wages, increased taxes, or higher prices for raw materials.
- Demand-pull inflation occurs when the overall demand for goods and services in an economy exceeds its supply. This excess demand leads to rising prices as businesses raise prices to capitalize on increased consumer demand.
- Factors contributing to demand-pull inflation include robust consumer spending, increased government spending, low-interest rates, and high levels of investment.
- Cost-push inflation is driven by rising production costs, which are then passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices. These rising costs can result from various factors, such as increased wages, higher energy prices, or supply chain disruptions.
- For example, if oil prices spike, it can lead to increased transportation costs, which may cause businesses to raise prices on their products.
- Built-in inflation, also known as the wage-price spiral, occurs when workers demand higher wages to keep up with rising prices. When businesses pay higher wages, they often pass those costs on to consumers, causing prices to rise further. This cycle can continue, perpetuating inflation.
- Expectations of future inflation can also contribute to built-in inflation, as people adjust their behavior and spending patterns in anticipation of rising prices.
- The policies of central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, can influence inflation. When central banks implement loose monetary policies, such as low-interest rates and quantitative easing, it can increase the money supply and potentially lead to demand-pull inflation.
- Central banks can also use tight monetary policies, such as raising interest rates, to combat inflation and reduce spending.
- Government fiscal policies, including changes in taxation and government spending, can affect inflation. An increase in government spending without corresponding revenue sources can stimulate demand and contribute to inflation.
- Tax cuts can also increase disposable income, leading to higher consumer spending and potential demand-pull inflation.
- Exchange rate fluctuations can impact inflation by influencing the prices of imported goods. A depreciating domestic currency can make imports more expensive, contributing to cost-push inflation.
- Conversely, a strengthening currency can lower import prices and help reduce inflation.
- Unforeseen events, such as natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, or disruptions in the supply chain, can cause sudden supply shortages or surpluses. These shocks can result in sharp price movements and contribute to inflation.
- For instance, a severe drought can reduce agricultural output, leading to higher food prices.
- Global economic conditions and trends, such as changes in international commodity prices or global economic growth, can influence inflation in individual countries.
- Economic policies in major trading partners can also have spill-over effects on domestic inflation.
The Effects of Inflation
Inflation impacts various facets of the economy and society. Moderate inflation is a sign of a growing economy, but high inflation can have detrimental effects.
Economic Effects
1. Reduced Purchasing Power: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, meaning consumers can buy less with the same amount of money. This reduction can impact living standards and consumer spending.
2. Income Redistribution: Inflation can act as a regressive tax, hitting harder on low-income families. Fixed-income recipients, such as pensioners, find their incomes do not stretch as far, while borrowers may benefit from repaying loans with money that is worth less.
3. Investment Uncertainty: High inflation can lead to uncertainty in the investment market. Investors become wary of long-term investments due to the unpredictability of future costs and returns.
Social Effects
1. Cost of Living: As the cost of goods and services increases, individuals may struggle to afford basic necessities, leading to a lower quality of life.
2. Wage-Price Spiral: Continuous inflation can lead to a wage-price spiral, where workers demand higher wages to keep up with rising prices, which in turn causes prices to rise further.
3. Access to Education and Healthcare: Rising costs can make education and healthcare less accessible to the general population, affecting long-term social and economic development.
Managing Inflation
Governments and central banks use various tools to manage inflation, aiming to maintain it at a level that promotes economic stability and growth.
Monetary Policy
The most common tool for managing inflation is monetary policy, which involves regulating the money supply and interest rates. Central banks can increase interest rates to reduce spending and borrowing, thereby slowing down the economy and reducing inflation. Conversely, lowering interest rates can stimulate spending and investment, increasing demand and potentially causing inflation.
Fiscal Policy
Governments can also use fiscal policy to control inflation by adjusting spending and taxation. Reducing government spending or increasing taxes can decrease the overall demand in the economy, lowering inflation. However, these measures can be unpopular politically as they may lead to reduced public services and higher taxes.
Supply-Side Policies
Improving efficiency and increasing supply can also combat inflation. This can be achieved through investment in technology, deregulation, and policies aimed at increasing productivity. By increasing the supply of goods and services, prices can stabilize or even decrease.
In conclusion, Inflation is a complex phenomenon with wide-ranging effects on the economy and society. Understanding its causes and impacts is crucial for effective management and policy-making. While moderate inflation is a sign of a healthy economy, unchecked inflation can lead to significant economic and social challenges. Through a combination of monetary, fiscal, and supply-side policies, governments and central banks strive to balance inflation to ensure economic stability and growth. As students delve into the intricacies of inflation, they gain insight into the delicate balance required to manage an economy, preparing them for informed citizenship and, possibly, roles in shaping economic policy in the future.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate an essay on the importance of extracurricular activities for student development
Write an essay discussing the role of technology in modern education.
What is inflation?

Inflation has been top of mind for many over the past few years. But how long will it persist? In June 2022, inflation in the United States jumped to 9.1 percent, reaching the highest level since February 1982. The inflation rate has since slowed in the United States , as well as in Europe , Japan , and the United Kingdom , particularly in the final months of 2023. But even though global inflation is higher than it was before the COVID-19 pandemic, when it hovered around 2 percent, it’s receding to historical levels . In fact, by late 2022, investors were predicting that long-term inflation would settle around a modest 2.5 percent. That’s a far cry from fears that long-term inflation would mimic trends of the 1970s and early 1980s—when inflation exceeded 10 percent.
Get to know and directly engage with senior McKinsey experts on inflation.
Ondrej Burkacky is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Munich office, Axel Karlsson is a senior partner in the Stockholm office, Fernando Perez is a senior partner in the Miami office, Emily Reasor is a senior partner in the Denver office, and Daniel Swan is a senior partner in the Stamford, Connecticut, office.
Inflation refers to a broad rise in the prices of goods and services across the economy over time, eroding purchasing power for both consumers and businesses. Economic theory and practice, observed for many years and across many countries, shows that long-lasting periods of inflation are caused in large part by what’s known as an easy monetary policy . In other words, when a country’s central bank sets the interest rate too low or increases money growth too rapidly, inflation goes up. As a result, your dollar (or whatever currency you use) will not go as far today as it did yesterday. For example: in 1970, the average cup of coffee in the United States cost 25 cents; by 2019, it had climbed to $1.59. So for $5, you would have been able to buy about three cups of coffee in 2019, versus 20 cups in 1970. That’s inflation, and it isn’t limited to price spikes for any single item or service; it refers to increases in prices across a sector, such as retail or automotive—and, ultimately, a country’s economy.
How does inflation affect your daily life? You’ve probably seen high rates of inflation reflected in your bills—from groceries to utilities to even higher mortgage payments. Executives and corporate leaders have had to reckon with the effects of inflation too, figuring out how to protect margins while paying more for raw materials.
But inflation isn’t all bad. In a healthy economy, annual inflation is typically in the range of two percentage points, which is what economists consider a sign of pricing stability. When inflation is in this range, it can have positive effects: it can stimulate spending and thus spur demand and productivity when the economy is slowing down and needs a boost. But when inflation begins to surpass wage growth, it can be a warning sign of a struggling economy.

Introducing McKinsey Explainers : Direct answers to complex questions
Inflation may be declining in many markets, but there’s still uncertainty ahead: without a significant surge in productivity, Western economies may be headed for a period of sustained inflation or major economic reset , as Japan has experienced in the first decades of the 21st century.
What does seem to be changing are leaders’ attitudes. According to the 2023 year-end McKinsey Global Survey on economic conditions , respondents reported less fear about inflation as a risk to global and domestic economic growth . But this sentiment varies significantly by region: European respondents were most concerned about the effects of inflation, whereas respondents in North America offered brighter views.
What causes inflation?
Monetary policy is a critical driver of inflation over the long term. The current high rate of inflation is a result of increased money supply , high raw materials costs , labor mismatches , and supply disruptions —exacerbated by geopolitical conflict .
In general, there are two primary types, or causes, of short-term inflation:
- Demand-pull inflation occurs when the demand for goods and services in the economy exceeds the economy’s ability to produce them. For example, when demand for new cars recovered more quickly than anticipated from its sharp dip at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, an intervening shortage in the supply of semiconductors made it hard for the automotive industry to keep up with this renewed demand. The subsequent shortage of new vehicles resulted in a spike in prices for new and used cars.
- Cost-push inflation occurs when the rising price of input goods and services increases the price of final goods and services. For example, commodity prices spiked sharply during the pandemic as a result of radical shifts in demand, buying patterns, cost to serve, and perceived value across sectors and value chains. To offset inflation and minimize impact on financial performance, industrial companies were forced to increase prices for end consumers.
Learn more about McKinsey’s Growth, Marketing & Sales Practice.
What are some periods in history with high inflation?
Economists frequently compare the current inflationary period with the post–World War II era , when price controls, supply problems, and extraordinary demand in the United States fueled double-digit inflation gains—peaking at 20 percent in 1947—before subsiding at the end of the decade. Consumption patterns today have been similarly distorted, and supply chains have been disrupted by the pandemic.
The period from the mid-1960s through the early 1980s in the United States, sometimes called the “Great Inflation,” saw some of the country’s highest rates of inflation, with a peak of 14.8 percent in 1980. To combat this inflation, the Federal Reserve raised interest rates to nearly 20 percent. Some economists attribute this episode partially to monetary policy mistakes rather than to other causes, such as high oil prices. The Great Inflation signaled the need for public trust in the Federal Reserve’s ability to lessen inflationary pressures.
Inflation isn’t solely a modern-day phenomenon, of course. One very early example of inflation comes from Roman times, from around 200 to 300 CE. Roman leaders were struggling to fund an army big enough to deal with attackers from multiple fronts. To help, they watered down the silver in their coinage, causing the value of money to slowly fall—and inflation to pick up. This led merchants to raise their prices, causing widespread panic. In response, the emperor Diocletian issued what’s now known as the Edict on Maximum Prices, a series of price and wage controls designed to stop the rise of prices and wages (one helpful control was a maximum price for a male lion). But because the edict didn’t address the root cause of inflation—the impure silver coin—it didn’t fix the problem.
How is inflation measured?
Statistical agencies measure inflation first by determining the current value of a “basket” of various goods and services consumed by households, referred to as a price index. To calculate the rate of inflation over time, statisticians compare the value of the index over one period with that of another. Comparing one month with another gives a monthly rate of inflation, and comparing from year to year gives an annual rate of inflation.
In the United States, the Bureau of Labor Statistics publishes its Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures the cost of items that urban consumers buy out of pocket. The CPI is broken down by region and is reported for the country as a whole. The Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) price index —published by the US Bureau of Economic Analysis—takes into account a broader range of consumer spending, including on healthcare. It is also weighted by data acquired through business surveys.
How does inflation affect consumers and companies differently?
Inflation affects consumers most directly, but businesses can also feel the impact:
- Consumers lose purchasing power when the prices of items they buy, such as food, utilities, and gasoline, increase. This can lead to household belt-tightening and growing pessimism about the economy .
- Companies lose purchasing power and risk seeing their margins decline , when prices increase for inputs used in production. These can include raw materials like coal and crude oil , intermediate products such as flour and steel, and finished machinery. In response, companies typically raise the prices of their products or services to offset inflation, meaning consumers absorb these price increases. The challenge for many companies is to strike the right balance between raising prices to cover input cost increases while simultaneously ensuring that they don’t raise prices so much that they suppress demand.
How can organizations respond to high inflation?
During periods of high inflation, companies typically pay more for materials , which decreases their margins. One way for companies to offset losses and maintain margins is by raising prices for consumers. However, if price increases are not executed thoughtfully, companies can damage customer relationships and depress sales —ultimately eroding the profits they were trying to protect.
When done successfully, recovering the cost of inflation for a given product can strengthen relationships and overall margins. There are five steps companies can take to ADAPT (adjust, develop, accelerate, plan, and track) to inflation:
- Adjust discounting and promotions and maximize nonprice levers. This can include lengthening production schedules or adding surcharges and delivery fees for rush or low-volume orders.
- Develop the art and science of price change. Instead of making across-the-board price changes, tailor pricing actions to account for inflation exposure, customer willingness to pay, and product attributes.
- Accelerate decision making tenfold. Establish an “inflation council” that includes dedicated cross-functional, inflation-focused decision makers who can act quickly and nimbly on customer feedback.
- Plan options beyond pricing to reduce costs. Use “value engineering” to reimagine a portfolio and provide cost-reducing alternatives to price increases.
- Track execution relentlessly. Create a central supporting team to address revenue leakage and to manage performance rigorously. Traditional performance metrics can be less reliable when inflation is high .
Beyond pricing, a variety of commercial and technical levers can help companies deal with price increases in an inflationary market , but other sectors may require a more tailored response to pricing.
Learn more about our Financial Services , Industrials & Electronics , Operations , Strategy & Corporate Finance , and Growth, Marketing & Sales Practices.
How can CEOs help protect their organizations against uncertainty during periods of high inflation?
In today’s uncertain environment, in which organizations have a much wider range of stakeholders, leaders must think about performance beyond short-term profitability. CEOs should lead with the complete business cycle and their complete slate of stakeholders in mind.
CEOs need an inflation management playbook , just as central bankers do. Here are some important areas to keep in mind while scripting it:
- Design. Leaders should motivate their organizations to raise the profile of design to a C-suite topic. Design choices for products and services are critical for responding to price volatility, scarcity of components, and higher production and servicing costs.
- Supply chain. The most difficult task for CEOs may be convincing investors to accept supply chain resiliency as the new table stakes. Given geopolitical and economic realities, supply chain resiliency has become a crucial goal for supply chain leaders, alongside cost optimization.
- Procurement. CEOs who empower their procurement organizations can raise the bar on value-creating contributions. Procurement leaders have told us time and again that the current market environment is the toughest they’ve experienced in decades. CEOs are beginning to recognize that purchasing leaders can be strategic partners by expanding their focus beyond cost cutting to value creation.
- Feedback. A CEO can take a lead role in playing back the feedback the organization is hearing. In today’s tight labor market, CEOs should guide their companies to take a new approach to talent, focusing on compensation, cultural factors, and psychological safety .
- Pricing. Forging new pricing relationships with customers will test CEOs in their role as the “ultimate integrator.” Repricing during inflationary times is typically unpleasant for companies and customers alike. With setting new prices, CEOs have the opportunity to forge deeper relationships with customers, by turning to promotions, personalization , and refreshed communications around value.
- Agility. CEOs can strive to achieve a focus based more on strategic action and less on firefighting. Managing the implications of inflation calls for a cross-functional, disciplined, and agile response.
A practical example: How is inflation affecting the US healthcare industry?
Consumer prices for healthcare have rarely risen faster than the rate of inflation—but that’s what’s happening today. The impact of inflation on the broader economy has caused healthcare costs to rise faster than the rate of inflation. Experts also expect continued labor shortages in healthcare—gaps of up to 450,000 registered nurses and 80,000 doctors —even as demand for services continues to rise. This drives up consumer prices and means that higher inflation could persist. McKinsey analysis as of 2022 predicted that the annual US health expenditure is likely to be $370 billion higher by 2027 because of inflation.
This climate of risk could spur healthcare leaders to address productivity, using tech levers to boost productivity while also reducing costs. In order to weather the storm, leaders will need to quickly set high aspirations, align their organizations around them, and execute with speed .
What is deflation?
If inflation is one extreme of the pricing spectrum, deflation is the other. Deflation occurs when the overall level of prices in an economy declines and the purchasing power of currency increases. It can be driven by growth in productivity and the abundance of goods and services, by a decrease in demand, or by a decline in the supply of money and credit.
Generally, moderate deflation positively affects consumers’ pocketbooks, as they can purchase more with less money. However, deflation can be a sign of a weakening economy, leading to recessions and depressions. While inflation reduces purchasing power, it also reduces the value of debt. During a period of deflation, on the other hand, debt becomes more expensive. And for consumers, investments such as stocks, corporate bonds, and real estate become riskier.
A recent period of deflation in the United States was the Great Recession, between 2007 and 2008. In December 2008, more than half of executives surveyed by McKinsey expected deflation in their countries, and 44 percent expected to decrease the size of their workforces.
When taken to their extremes, both inflation and deflation can have significant negative effects on consumers, businesses, and investors.
For more in-depth exploration of these topics, see McKinsey’s Operations Insights collection. Learn more about Operations consulting , and check out operations-related job opportunities if you’re interested in working at McKinsey.
Articles referenced:
- “ Investing in productivity growth ,” March 27, 2024, Jan Mischke , Chris Bradley , Marc Canal, Olivia White , Sven Smit , and Denitsa Georgieva
- “ Economic conditions outlook during turbulent times, December 2023 ,” December 20, 2023
- “ Forward Thinking on why we ignore inflation—from ancient times to the present—at our peril with Stephen King ,” November 1, 2023
- “ Procurement 2023: Ten CPO actions to defy the toughest challenges ,” March 6, 2023, Roman Belotserkovskiy , Carolina Mazuera, Marta Mussacaleca , Marc Sommerer, and Jan Vandaele
- “ Why you can’t tread water when inflation is persistently high ,” February 2, 2023, Marc Goedhart and Rosen Kotsev
- “ Markets versus textbooks: Calculating today’s cost of equity ,” January 24, 2023, Vartika Gupta, David Kohn, Tim Koller , and Werner Rehm
- “ Inflation-weary Americans are increasingly pessimistic about the economy ,” December 13, 2022, Gonzalo Charro, Andre Dua , Kweilin Ellingrud , Ryan Luby, and Sarah Pemberton
- “ Inflation fighter and value creator: Procurement’s best-kept secret ,” October 31, 2022, Roman Belotserkovskiy , Ezra Greenberg , Daphne Luchtenberg, and Marta Mussacaleca
- “ Prime Numbers: Rethink performance metrics when inflation is high ,” October 28, 2022, Vartika Gupta, David Kohn, Tim Koller , and Werner Rehm
- “ The gathering storm: The threat to employee healthcare benefits ,” October 20, 2022, Aditya Gupta , Akshay Kapur , Monisha Machado-Pereira , and Shubham Singhal
- “ Utility procurement: Ready to meet new market challenges ,” October 7, 2022, Roman Belotserkovskiy , Abhay Prasanna, and Anton Stetsenko
- “ The gathering storm: The transformative impact of inflation on the healthcare sector ,” September 19, 2022, Addie Fleron, Aneesh Krishna , and Shubham Singhal
- “ Pricing during inflation: Active management can preserve sustainable value ,” August 19, 2022, Niels Adler and Nicolas Magnette
- “ Navigating inflation: A new playbook for CEOs ,” April 14, 2022, Asutosh Padhi , Sven Smit , Ezra Greenberg , and Roman Belotserkovskiy
- “ How business operations can respond to price increases: A CEO guide ,” March 11, 2022, Andreas Behrendt , Axel Karlsson , Tarek Kasah, and Daniel Swan
- “ Five ways to ADAPT pricing to inflation ,” February 25, 2022, Alex Abdelnour , Eric Bykowsky, Jesse Nading, Emily Reasor , and Ankit Sood
- “ How COVID-19 is reshaping supply chains ,” November 23, 2021, Knut Alicke , Ed Barriball , and Vera Trautwein
- “ Navigating the labor mismatch in US logistics and supply chains ,” December 10, 2021, Dilip Bhattacharjee , Felipe Bustamante, Andrew Curley, and Fernando Perez
- “ Coping with the auto-semiconductor shortage: Strategies for success ,” May 27, 2021, Ondrej Burkacky , Stephanie Lingemann, and Klaus Pototzky
This article was updated in April 2024; it was originally published in August 2022.

Want to know more about inflation?
Related articles.

What is supply chain?

How business operations can respond to price increases: A CEO guide

Five ways to ADAPT pricing to inflation

Essay on Inflation – Causes, Effects, and Mitigation

Essay on Inflation
Introduction:.
Inflation, the gradual increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy, is a phenomenon that affects individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. While moderate inflation is considered a normal part of a healthy economy, excessive inflation can lead to various economic challenges. This essay explores the causes, effects, and possible measures to mitigate inflation.
Causes of Inflation:
- Demand-Pull Inflation: One common cause of inflation is demand-pull inflation, where the overall demand for goods and services surpasses the available supply. This can result from increased consumer spending, investment, or government expenditures, leading to higher prices.
- Cost-Push Inflation: Cost-push inflation occurs when the costs of production rise, causing businesses to pass on these increased costs to consumers in the form of higher prices for goods and services. Factors such as rising wages, increased raw material costs, or external shocks can contribute to cost-push inflation.
- Built-in Inflation: Built-in inflation, also known as wage-price inflation, occurs when workers demand higher wages, and businesses, in turn, increase prices to maintain profit margins. This creates a cycle where higher wages lead to higher prices, and vice versa.
Effects of Inflation:
- Reduced Purchasing Power: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, as the same amount of currency can buy fewer goods and services over time. This reduction in purchasing power can adversely affect individuals on fixed incomes, such as retirees.
- Uncertainty and Planning Challenges: High or unpredictable inflation can create uncertainty in the economy, making it challenging for businesses and individuals to plan for the future. Long-term investments and financial planning become more difficult in an inflationary environment.
- Redistribution of Income and Wealth: Inflation can lead to a redistribution of income and wealth. Debtors may benefit from inflation as the real value of their debts decreases, while creditors may suffer losses. Similarly, those with assets like real estate may experience increased wealth, while renters face higher housing costs.
- Interest Rate Adjustments: Central banks often respond to inflation by adjusting interest rates. Higher inflation may prompt central banks to raise interest rates to cool down the economy. This, in turn, affects borrowing costs, investment, and overall economic activity.
Mitigating Inflation:
- Monetary Policy: Central banks play a crucial role in controlling inflation through monetary policy. By adjusting interest rates, open market operations, and reserve requirements, central banks aim to influence the money supply and, consequently, inflation.
- Fiscal Policy: Governments can use fiscal policy tools, such as taxation and government spending, to manage inflation. Reducing government expenditures or increasing taxes can help cool down an overheated economy, while increased spending can stimulate economic activity during periods of low inflation.
- Supply-Side Policies: Addressing the root causes of inflation, such as supply-side constraints, is essential. Policies that focus on improving productivity, reducing production costs, and enhancing the efficiency of markets can help alleviate inflationary pressures.
- Wage and Price Controls: In extreme cases, governments may resort to implementing wage and price controls to directly manage inflation. However, these measures are often considered temporary and can have unintended consequences, such as creating shortages or distortions in the market.
Conclusion:
Inflation is a complex economic phenomenon with multifaceted causes and effects. While moderate inflation is a normal part of economic growth, policymakers must carefully manage it to avoid detrimental consequences. By implementing effective monetary and fiscal policies, addressing supply-side issues, and promoting stability, governments can strike a balance that fosters sustainable economic development while keeping inflation in check. A proactive and balanced approach is crucial to ensuring the well-being of individuals and the stability of economies in the face of inflationary pressures.
Related Posts
Essay on pollution in 500+ words for students, essay on covid-19 in english 500 words, the emerging threat of congo virus in pakistan (2023) essay in 500 words, essay on quaid-e-azam in english 500 words.
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

- IMF at a Glance
- Surveillance
- Capacity Development
- IMF Factsheets List
- IMF Members
- IMF Financial Statements
- IMF Senior Officials
- IMF in History
- Archives of the IMF
- Job Opportunities
- Climate Change
- Fiscal Policies
- Income Inequality
Flagship Publications
Other publications.
- World Economic Outlook
- Global Financial Stability Report
- Fiscal Monitor
- External Sector Report
- Staff Discussion Notes
- Working Papers
- IMF Research Perspectives
- Economic Review
- Global Housing Watch
- Commodity Prices
- Commodities Data Portal
- IMF Researchers
- Annual Research Conference
- Other IMF Events
IMF reports and publications by country
Regional offices.
- IMF Resident Representative Offices
- IMF Regional Reports
- IMF and Europe
- IMF Members' Quotas and Voting Power, and Board of Governors
- IMF Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific
- IMF Capacity Development Office in Thailand (CDOT)
- IMF Regional Office in Central America, Panama, and the Dominican Republic
- Eastern Caribbean Currency Union (ECCU)
- IMF Europe Office in Paris and Brussels
- IMF Office in the Pacific Islands
- How We Work
- IMF Training
- Digital Training Catalog
- Online Learning
- Our Partners
- Country Stories
- Technical Assistance Reports
- High-Level Summary Technical Assistance Reports
- Strategy and Policies
For Journalists
- Country Focus
- Chart of the Week
- Communiqués
- Mission Concluding Statements
- Press Releases
- Statements at Donor Meetings
- Transcripts
- Views & Commentaries
- Article IV Consultations
- Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP)
- Seminars, Conferences, & Other Events
- E-mail Notification

Press Center
The IMF Press Center is a password-protected site for working journalists.
- Login or Register
- Information of interest
- About the IMF
- Conferences
- Press briefings
- Special Features
- Middle East and Central Asia
- Economic Outlook
- Annual and spring meetings
- Most Recent
- Most Popular
- IMF Finances
- Additional Data Sources
- World Economic Outlook Databases
- Climate Change Indicators Dashboard
- IMF eLibrary-Data
- International Financial Statistics
- G20 Data Gaps Initiative
- Public Sector Debt Statistics Online Centralized Database
- Currency Composition of Official Foreign Exchange Reserves
- Financial Access Survey
- Government Finance Statistics
- Publications Advanced Search
- IMF eLibrary
- IMF Bookstore
- Publications Newsletter
- Essential Reading Guides
- Regional Economic Reports
- Country Reports
- Departmental Papers
- Policy Papers
- Selected Issues Papers
- All Staff Notes Series
- Analytical Notes
- Fintech Notes
- How-To Notes
- Staff Climate Notes

Finance & Development

Inflation: Prices on the Rise
Back to Basics
Credit: ISTOCK / RASTUDIO
Download PDF
BACK TO BASICS COMPILATION
Inflation measures how much more expensive a set of goods and services has become over a certain period, usually a year
It may be one of the most familiar words in economics. Inflation has plunged countries into long periods of instability. Central bankers often aspire to be known as “inflation hawks.” Politicians have won elections with promises to combat inflation, only to lose power after failing to do so. Inflation was even declared Public Enemy No. 1 in the United States—by President Gerald Ford in 1974. What, then, is inflation, and why is it so important?
Inflation is the rate of increase in prices over a given period of time. Inflation is typically a broad measure, such as the overall increase in prices or the increase in the cost of living in a country. But it can also be more narrowly calculated—for certain goods, such as food, or for services, such as a haircut, for example. Whatever the context, inflation represents how much more expensive the relevant set of goods and/or services has become over a certain period, most commonly a year.

Measuring inflation
Consumers’ cost of living depends on the prices of many goods and services and the share of each in the household budget. To measure the average consumer’s cost of living, government agencies conduct household surveys to identify a basket of commonly purchased items and track over time the cost of purchasing this basket. (Housing expenses, including rent and mortgages, constitute the largest component of the consumer basket in the United States.) The cost of this basket at a given time expressed relative to a base year is the consumer price index (CPI), and the percentage change in the CPI over a certain period is consumer price inflation , the most widely used measure of inflation. (For example, if the base year CPI is 100 and the current CPI is 110, inflation is 10 percent over the period.)
Core consumer inflation focuses on the underlying and persistent trends in inflation by excluding prices set by the government and the more volatile prices of products, such as food and energy, most affected by seasonal factors or temporary supply conditions. Core inflation is also watched closely by policymakers. Calculation of an overall inflation rate—for a country, say, and not just for consumers—requires an index with broader coverage, such as the GDP deflator .
The CPI basket is mostly kept constant over time for consistency, but is tweaked occasionally to reflect changing consumption patterns—for example, to include new hi-tech goods and to replace items no longer widely purchased. Because it shows how, on average, prices change over time for everything produced in an economy, the contents of the GDP deflator vary each year and are more current than the mostly fixed CPI basket. On the other hand, the deflator includes nonconsumer items (such as military spending) and is therefore not a good measure of the cost of living.
The good and the bad
To the extent that households’ nominal income, which they receive in current money, does not increase as much as prices, they are worse off, because they can afford to purchase less. In other words, their purchasing power or real —inflation-adjusted—income falls. Real income is a proxy for the standard of living. When real incomes are rising, so is the standard of living, and vice versa.
In reality, prices change at different paces. Some, such as the prices of traded commodities, change every day; others, such as wages established by contracts, take longer to adjust (or are “sticky,” in economic parlance). In an inflationary environment, unevenly rising prices inevitably reduce the purchasing power of some consumers, and this erosion of real income is the single biggest cost of inflation.
Inflation can also distort purchasing power over time for recipients and payers of fixed interest rates. Take pensioners who receive a fixed 5 percent yearly increase to their pension. If inflation is higher than 5 percent, a pensioner’s purchasing power falls. On the other hand, a borrower who pays a fixed-rate mortgage of 5 percent would benefit from 5 percent inflation, because the real interest rate (the nominal rate minus the inflation rate) would be zero; servicing this debt would be even easier if inflation were higher, as long as the borrower’s income keeps up with inflation. The lender’s real income, of course, suffers. To the extent that inflation is not factored into nominal interest rates , some gain and some lose purchasing power.
Indeed, many countries have grappled with high inflation—and in some cases hyperinflation , 1,000 percent or more a year. In 2008, Zimbabwe experienced one of the worst cases of hyperinflation ever, with estimated annual inflation at one point of 500 billion percent. Such high levels of inflation have been disastrous, and countries have had to take difficult and painful policy measures to bring inflation back to reasonable levels, sometimes by giving up their national currency, as Zimbabwe has.
Although high inflation hurts an economy, deflation , or falling prices, is not desirable either. When prices are falling, consumers delay making purchases if they can, anticipating lower prices in the future. For the economy this means less economic activity, less income generated by producers, and lower economic growth. Japan is one country with a long period of nearly no economic growth, largely because of deflation. Preventing deflation during the global financial crisis that began in 2007 was one of the reasons the US Federal Reserve and other central banks around the world kept interest rates low for a prolonged period and have instituted other monetary policies to ensure financial systems have plenty of liquidity.
Most economists now believe that low, stable, and—most important—predictable inflation is good for an economy. If inflation is low and predictable, it is easier to capture it in price-adjustment contracts and interest rates, reducing its distortionary impact. Moreover, knowing that prices will be slightly higher in the future gives consumers an incentive to make purchases sooner, which boosts economic activity. Many central bankers have made their primary policy objective maintaining low and stable inflation, a policy called inflation targeting .
What creates inflation?
Long-lasting episodes of high inflation are often the result of lax monetary policy. If the money supply grows too big relative to the size of an economy, the unit value of the currency diminishes; in other words, its purchasing power falls and prices rise. This relationship between the money supply and the size of the economy is called the quantity theory of money and is one of the oldest hypotheses in economics.
Pressures on the supply or demand side of the economy can also be inflationary. Supply shocks that disrupt production, such as natural disasters, or raise production costs, such as high oil prices, can reduce overall supply and lead to “cost-push” inflation, in which the impetus for price increases comes from a disruption to supply. The food and fuel inflation of 2008 was such a case for the global economy—sharply rising food and fuel prices were transmitted from country to country by trade. Conversely, demand shocks , such as a stock market rally, or expansionary policies , such as when a central bank lowers interest rates or a government raises spending, can temporarily boost overall demand and economic growth. If, however, this increase in demand exceeds an economy’s production capacity, the resulting strain on resources is reflected in “demand-pull” inflation. Policymakers must find the right balance between boosting demand and growth when needed without overstimulating the economy and causing inflation.
Expectations also play a key role in determining inflation. If people or firms anticipate higher prices, they build these expectations into wage negotiations and contractual price adjustments (such as automatic rent increases). This behavior partly determines the next period’s inflation; once the contracts are exercised and wages or prices rise as agreed, expectations become self-fulfilling. And to the extent that people base their expectations on the recent past, inflation would follow similar patterns over time, resulting in inflation inertia .
How policymakers deal with inflation
The right set of disinflationary policies , those aimed at reducing inflation, depends on the causes of inflation. If the economy has overheated, central banks—if they are committed to ensuring price stability—can implement contractionary policies that rein in aggregate demand, usually by raising interest rates. Some central bankers have chosen, with varying degrees of success, to impose monetary discipline by fixing the exchange rate —tying the value of its currency to that of another currency, and thereby its monetary policy to that of another country. However, when inflation is driven by global rather than domestic developments, such policies may not help. In 2008, when inflation rose across the globe on the back of high food and fuel prices, many countries allowed the high global prices to pass through to the domestic economy. In some cases the government may directly set prices (as some did in 2008 to prevent high food and fuel prices from passing through). Such administrative price-setting measures usually result in the government’s accrual of large subsidy bills to compensate producers for lost income.
Central bankers are increasingly relying on their ability to influence inflation expectations as an inflation-reduction tool. Policymakers announce their intention to keep economic activity low temporarily to bring down inflation, hoping to influence expectations and contracts’ built-in inflation component. The more credibility central banks have, the greater the influence of their pronouncements on inflation expectations.

Ceyda Oner is a deputy division chief in the IMF’s Finance Department.
Opinions expressed in articles and other materials are those of the authors; they do not necessarily reflect IMF policy.
You might also like
- How Inflation Radically Changes Economic Ideas
- History’s Inflation Lessons
- Euro Area Inflation and how Import Prices, Profits, and Wages fit in
- Unwelcome Return
- Time for Change
- How We Missed the Recent Inflation Surge
- F&D HOMEPAGE
Latest Issues

December 2023

September 2023

- About F&D Magazine
Social Media
- F&D on Facebook
- F&D on LinkedIn
F&D STAFF
- Gita Bhatt, Editor-In-Chief
- Maureen Burke, Managing Editor
- Peter J. Walker, Senior Editor
- Jeff Kearns, Senior Editor
- Nicholas Owen, Senior Editor
- Smita Aggarwal, Assistant Editor
- Andrew Stanley, Assistant Editor
- Bruce Edwards, Multimedia Content
- Noha Elbadawy, Multimedia content
- Melinda Weir, Production Manager
- Rekia Ennaboulssi, Web Manager
- Marta Doroszczyk, Digital Marketing
- Kwabena Akuamoah-Boateng, Social Media Editor
The Relationship Between Money Supply and Inflation Essay
Introduction, money supply, the relationship between money supply and inflation, reference list.
The current globalisation rate has led to many changes and effects on the value of most resources and especially the financial resources. The world’s population is increasing at a fast rate while on the other hand resources are being depleted without being replenished thus causing scarcity.
As a result, economic crisis have occurred which have as well affected the living standards of a better part of the world’s population (Hardwick, 2002, p.176). Among the common effects are the high inflation and the amount of money supplied.
Economists have however established the rate of Inflation and the money supply of a nation are correlated with one leading to another. This paper is therefore an analysis of the relationship between the inflation rate and money supply.
Inflation is said to be the increase in the prices of commodities and services in a given economy. This makes the people buy less since their purchasing power goes down as a result of the lower value of the currency. Inflation rates of most countries keep fluctuating but their central banks try to keep the rates at a range of about two to three percent.
The consumer price index is what is used to measure the inflation rates of an economy. It has been theoretically argued that inflation is caused by an increase in money supply in the economy (Hall and Taylor, 1997, p.637).
Money supply is an economic term which refers to the amount of money circulating in an economy. The central bank is bestowed with controlling the money supply of a country through regulation of the circulation (Williams, 2008, p.1). Money supply can be measured by looking at the value of currency, bills, credit, loans as well as other liquid instruments in an economy.
Economists have suggested that there is a high degree of correlation between the inflation rate and money supply in an economy. To begin with is the fact that when the money supply is high the demand for money goes down.
This is because people are able to afford even the high priced commodities and services that they could not have initially afforded (Mishkin, 1995, p.89). It can thus be depicted that an upward supply of money in the economy results to inflation according to the graph shown below.
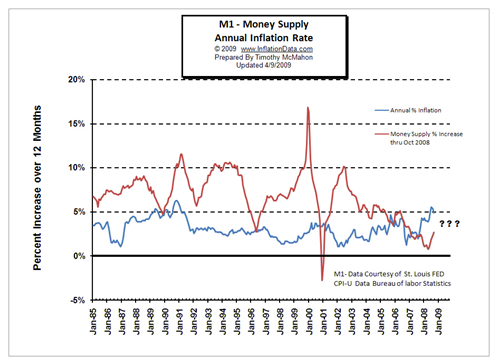
A look at the graph at first glance does not show any instances of correlation however after the introduction of a time lag in which the two occur a situation of relationship is then established. This time lag is the difference in time between changes in the money supply and the changes in the inflation rates. Thus, the relationship occurs after a period of time as it can be depicted on the graph in the years 1990, 1996, 2000 and 2001 among others.
This can be practically explained in a situation whereby the people of a given small town are given the opportunity to raise a higher income than they would have before in a month. They would thus shift from using gasoline to gas as their source of fuel which costs higher.
This is because in real sense, the gas will cost proportionally lower than the price they were paying for gasoline before the increase in income. As a result, the market will bear high prices for commodities and services leading to inflation which has come about due to increased money supply (Williams, 2008, p.1).
The relationship between inflation rates and money supply can be differently explained using different economic theories. The Monetary theory explains that money supply is the most significant factor that leads to incidences of inflation in an economy.
Quoting the words of a renowned monetarist by the name Milton Friedman, he said, “Inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon” (Williams, 2008, p.1). Thus according to empirical studies conducted by most historical monetarists, it can be asserted that inflation is a monetary phenomenon. This is in accordance to the equation;
- M is the nominal value of money (money supply)
- V is the money velocity
- P is the price level
- Q is the real value index (Transactions)
From the above equation, monetarists argue that the money velocity is not affected by changes in the money supply in the long-run (Mankiw, 2002, p.153). Therefore the output is highly dependent on the productivity of the economy.
Working with these assumptions it can be said that changes in price are dependent on the changes in the quantity of money in the economy thus the money supply. The chart below derived from the above equation shows the differences in inflation reflected by CPI and the money supply reflected as M2.
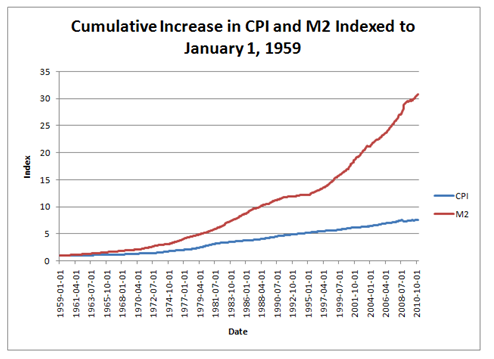
Fig. A chart showing the relationship between inflation and money supply (Burda and Wyplosz, 1997, p. 267)
According to the Keynesian theory, there still exists a relationship between money supply and inflation. However, they argue that money supply is not the only big factor that causes inflation as there are also other contributing factors.
The Keynesians emphasize that aggregate demand is the main reason behind inflation and thus regulating the aggregate demands in periods of recessions and economic expansions helps stabilize the inflation rates as well. Nevertheless, the relationship comes about as aggregate demand is effectively controlled using economic instruments such as monetary policy and fiscal policy (Burda and Wyplosz, 1997, p. 275)
From the above discussion, it can be concluded that there is indeed a great correlation between money supply and inflation rates of an economy. It is evidenced that changing the money supply through the central banks leads to a control of the inflationary situations in the same economy.
For instance, a country with high inflation rates and willing to lower them, they will do this through the operations of the central bank whereby the lending rates and the interest rates will be increased to reduce the amount f money leaving the bank (Baumol and Blinder, 2006, p.109).
As a matter of fact, people will rush to deposit the cash they have so that it can earn as much interest as possible. This will in turn reduce the amount of money circulating in the region hence reducing the inflation rates as well.
In a situation of deflation the vice versa will be applied where the central bank will reduce the lending rates and interest rates so as to enable flow of money into the economy (Baumol and Blinder, 2006, p.109). The control between money supply and inflation rates is thus operated using the federal banking system of the central bank of the region.
Baumol, W. and Blinder, A. (2006). Macroeconomics: Principles and Policy , Tenth edition. Thomson South-Western.
Burda, M. and Wyplosz, C. (1997). Macroeconomics: a European text . Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Oxford University Press.
Hall, R. and Taylor, J. (1993). Macroeconomics . New York: W.W. Norton.
Hardwick, P. (2002). Introduction to modern economics, prentice hall publishers, New York.
Mankiw, N. (2002). Macroeconomics (5th Ed.). Worth.
McMahon, T. (2009). Money Supply and Inflation. Web.
Mishkin, F. (1995). The Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets , New York, Harper Collins.
Williams, J. (2008). Money Supply Special Report. Web.
- Price of Oil and Particularly Gasoline
- Causes of Gasoline Price Fluctuations
- Income Equality and Social Policy Advocacy Lag
- National Economic Policy in Australia
- The Business Role in the Economy
- International Monetary System
- Money Mechanics in the U.S.
- Monetary Policy: Easier does it
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, May 4). The Relationship Between Money Supply and Inflation. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-relationship-between-money-supply-and-inflation-essay/
"The Relationship Between Money Supply and Inflation." IvyPanda , 4 May 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/the-relationship-between-money-supply-and-inflation-essay/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'The Relationship Between Money Supply and Inflation'. 4 May.
IvyPanda . 2019. "The Relationship Between Money Supply and Inflation." May 4, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-relationship-between-money-supply-and-inflation-essay/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Relationship Between Money Supply and Inflation." May 4, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-relationship-between-money-supply-and-inflation-essay/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Relationship Between Money Supply and Inflation." May 4, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-relationship-between-money-supply-and-inflation-essay/.

Essay on Inflation In Philippines
Students are often asked to write an essay on Inflation In Philippines in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Inflation In Philippines
What is inflation.
Inflation means the prices of things we buy are going up. In the Philippines, when prices rise, it becomes harder for people to afford food, clothes, and other items. This can happen when there’s too much money to spend but not enough goods, or when the cost to make products goes higher.
Inflation in the Philippines
The Philippines often experiences inflation. This can be due to natural disasters affecting crops, changes in global oil prices, or government actions. When inflation occurs, Filipino families might struggle to buy what they need, which can be tough for everyone.
Effects on Daily Life
Because of inflation, families in the Philippines might have to change how they spend money. They may buy less food or cheaper items to save money. Sometimes, even going to school or getting healthcare can become more expensive, making life challenging for many people.
250 Words Essay on Inflation In Philippines
Understanding inflation in the philippines.
Inflation means the increase in prices of things we buy, like food, clothes, and toys. In the Philippines, just like in other countries, prices can go up over time. This can make life hard for families, especially if they don’t have a lot of money.
Causes of Inflation
In the Philippines, inflation can happen for many reasons. Sometimes, if there’s a problem with growing food or if there’s a big storm, there might not be enough of it, and this can make prices go up. Also, if the money in the Philippines becomes less valuable compared to other countries’ money, things that come from other countries can become more expensive.
Effects of Inflation
When prices go up, it’s tough for people. They might not be able to buy as much with their money, and this can be stressful. Parents might have to work more to earn more money, and sometimes, kids might not get new toys or clothes as often.
What the Government Does
The government in the Philippines tries to control inflation. They can change how much money is in the economy or make rules about prices to help keep them from going up too fast. They do this because they want to make sure that people can afford what they need.
Inflation in the Philippines is a challenge that affects everyone. It’s important to understand why it happens and how it changes the way people live. While it can be tough when prices go up, the government works to manage inflation for the good of the country.
500 Words Essay on Inflation In Philippines
Inflation is when the prices of things we buy go up. Imagine you could buy a toy car for one peso last year, but this year the same car costs two pesos. That’s inflation: the money you have buys less than before. This can happen with toys, food, clothes, and almost everything. In the Philippines, like in many countries, inflation affects how people live because they need more money to buy the same things.
Causes of Inflation in the Philippines
In the Philippines, inflation happens for a few reasons. Sometimes, when there are not enough goods like rice or vegetables, prices go up because many people want these items but there aren’t enough for everyone. This is called “demand-pull inflation.” Another reason is “cost-push inflation,” which is when the cost to make products goes up. For example, if the price of gas increases, it costs more to deliver goods to stores, so the prices of these goods go up.
Also, when the money value in the Philippines goes down compared to other countries’ money, things we buy from other countries become more expensive. This is known as “imported inflation.”
Effects of Inflation on People
Inflation can make life hard for families. Parents have to spend more money on the same things, so they might have less money left for saving or for fun activities. Kids might notice that their allowance doesn’t buy as much candy or toys as it used to. If inflation is high, people might worry about prices going up even more and rush to buy things, which can make inflation worse.
How the Government Handles Inflation
The government of the Philippines tries to control inflation to make sure prices don’t rise too fast. The Central Bank of the Philippines can change interest rates, which is like changing the cost of borrowing money. If it’s more expensive to borrow money, people and businesses might spend less, and this can help slow down inflation.
The government can also use policies to help make sure there is enough supply of goods. For example, they can encourage farmers to grow more rice or make it easier for stores to get products from other countries when there’s not enough supply in the Philippines.
What Can People Do?
People can also do things to handle inflation. Families can plan their spending and look for better prices before buying something. It’s important to learn about money and how to use it wisely, especially when prices are going up.
Inflation in the Philippines is when prices rise and money buys less. It can be caused by not enough goods, higher costs to make products, or the country’s money value changing. Inflation affects how people live, but the government and people can take steps to manage it. By understanding what inflation is and how it works, even school students can be better prepared to deal with it in their daily lives.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Cold War
- Essay on Cold Weather
- Essay on Inequality In Society
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Essay on Inflation in Pakistan for Students
by Pakiology | May 21, 2024 | Essay | 0 comments
In this essay on inflation in Pakistan, we will look at the causes, effects, and solutions to this issue that has been affecting the country for decades. The term ‘inflation’ refers to a sustained rise in the prices of goods and services in an economy. In Pakistan, inflation has been a major concern since the late 1990s, with the Consumer Price Index (CPI) reaching a peak in 2023. We will explore the various factors that have contributed to inflation in Pakistan, its economic effects, and what can be done to address the issue.
Page Contents
Essay on Inflation Outlines
Causes of inflation in pakistan, effects of inflation, solution to control inflation.
- Introduction
Inflation in Pakistan is caused by several factors, which can be divided into two main categories: domestic and external. The main domestic causes of inflation are an increase in money supply, an increase in government spending, an increase in indirect taxes, and a decrease in economic growth.
The most significant contributor to inflation in Pakistan is an increase in the money supply. When there is too much money chasing after too few goods, prices rise, creating a situation known as demand-pull inflation. An increase in the money supply can be caused by the central bank printing more money or by the government borrowing more money from the public.
In addition, higher government spending can lead to inflation. This occurs when the government prints more money to finance its expenditure or borrows from the public and transfers the cost of this additional spending to businesses and consumers. This leads to higher prices for goods and services. Indirect taxes are another major factor that contributes to inflation in Pakistan. When indirect taxes are increased, prices of goods and services also increase, leading to an overall rise in prices.
Finally, low economic growth can also cause inflation in Pakistan. A weak economy reduces people’s purchasing power, forcing them to buy less, which reduces demand and leads to lower prices. However, when economic growth stalls, businesses are unable to sell their products at the same price as before, leading to a rise in prices.
Overall, inflation in Pakistan is caused by a combination of domestic and external factors. These include an increase in money supply, higher government spending, increases in indirect taxes, and a decrease in economic growth.
The effects of inflation on the economy can be both positive and negative. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, meaning that each unit of currency is worth less than it was before. This means that, as the cost of living increases, people can purchase fewer goods and services for the same amount of money. As a result, their standard of living decreases.
Inflation also reduces the real return on investments and savings, which can have a detrimental effect on economic growth. When inflation is high, people prefer to save their money rather than invest in a business or other activities. This reduces the availability of capital and results in slower economic growth.
In addition to decreasing standards of living, inflation can lead to unemployment if companies are not able to increase wages at the same rate as prices rise. This can lead to an increase in poverty, as people struggle to afford necessities. Furthermore, when prices rise faster than wages, it puts pressure on government budgets and can increase public debt.
Inflation can also cause the value of the local currency to depreciate against foreign currencies. This has a direct impact on the cost of imports and makes domestic goods less competitive in international markets. It can also have an indirect impact on exports, as it reduces the competitiveness of local producers in foreign markets.
Inflation is a serious issue in Pakistan, and it needs to be addressed to improve the country’s economic conditions. The following are some of the measures that can be taken to control inflation in Pakistan:
1. Fiscal policy: A strong fiscal policy is necessary for controlling inflation. The government should increase its revenue by implementing taxes on the wealthy and reducing public spending. This will help reduce budget deficits, which will result in lower inflation.
2. Monetary policy: The State Bank of Pakistan should adopt a tighter monetary policy to control inflation. It should raise interest rates so that investors have an incentive to save rather than spend, thus curbing demand-pull inflation.
3. Supply-side measures: There should be an increase in the production of essential commodities and products to meet the demand of consumers. This will help reduce prices and inflation in the long run.
4. Subsidies: The government should provide subsidies to those who are suffering due to the high prices of essential items. This will help them cope with the rising cost of living and ensure that they have access to essential goods and services.
5. Stabilizing exchange rate: A stable exchange rate between foreign currencies and the rupee is necessary for controlling inflation. The State Bank of Pakistan should strive to keep the rupee’s value stable by using currency swaps and other methods.
These measures can go a long way in controlling inflation in Pakistan. By taking these measures, the government can help improve the country’s economic condition and create an environment conducive to investment and growth.
What is inflation in simple words?
Inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.
What are the 4 main causes of inflation?
The 4 main causes of inflation are: Demand-pull inflation: when there is an increase in demand for goods and services that outstrip the economy’s ability to produce them. Cost-push inflation: when the cost of production increases, causing companies to raise prices to maintain their profit margins. Built-in inflation: when businesses expect prices to rise and build that expectation into their prices, causing a self-fulfilling cycle of inflation. Imported inflation: when the cost of imported goods increases, leading to higher prices for consumers.
What are the 5 main causes of inflation?
The 4 main causes of inflation are: 1. Demand-pull inflation 2. Cost-push inflation 3. Built-in inflation 4. Imported inflation 5. Monetary inflation
What is inflation introduction?
Inflation is a phenomenon that has been observed throughout history. It refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.
Find more Essays on the following Topics
Ask Your Questions
You might like, democracy in pakistan essay with quotations.
Explore the evolution, challenges, and progress of democracy in Pakistan in this in-depth essay. Gain insights into...
Problems of Karachi Essay | 200 & 500 Words
Explore the multifaceted challenges faced by Karachi in this comprehensive essay. From overpopulation to traffic...
A True Muslim Essay With Quotations 2023
A true Muslim essay is about the qualities of a true Muslim and how they embody the teachings of Islam in their daily...
Health is Wealth Essay For Students
In this essay, we explore why health is wealth and why it is crucial to prioritize our physical and mental well-being...
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- class-9-notes
- Friendship quotes
- Scholarships
- Science News
- Study Abroad
- Study in Australia
- SZABMU MDCAT
- UHS Past MCQs
- Universities
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Biden Wants to Send Billions to Rural America, but This Must Happen First

By Tony Pipa
Mr. Pipa is a senior fellow at the Center for Sustainable Development at the Brookings Institution.
President Biden regularly emphasizes how the major pieces of legislation he has signed — the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, the CHIPS and Science Act and the Inflation Reduction Act — expand opportunities for Americans.
This is especially true for rural Americans. Those three laws appropriated billions of dollars — about $464 billion — for many projects that could be particularly relevant to rural communities, allowing them to dream of a different economic future.
I am often asked if rural voters will give Mr. Biden credit for all that money and the changes it could bring and will show their appreciation at the ballot box. My answer is that it is unrealistic to expect place-specific investments to have an immediate impact on elections.
Rural places remain skeptical that federal policymakers have their best interests at heart. Proving otherwise will take intention and time.
Above all, implementation matters. These investment opportunities will be meaningless unless they reach rural America. For that to happen, federal and local officials and many people in between will need to focus on intentional targeting and sensitivity to the challenges that rural places face.
It is important to keep in mind that many rural governments are led by unpaid elected officials, and few rural city halls have staffs to work on planning, project development and grant writing.
Only 15 percent of Michigan’s smallest jurisdictions , for example, express confidence in their ability to get access to federal grants, whereas the rate for jurisdictions over 30,000 people is close to 40 percent. A national survey published in 2019 found more than half of rural counties experienced moderate or significant fiscal stress, so for programs where local governments must match the federal funding, those counties face an additional challenge.
This does not bode well for equitable distribution of those federal investments. According to analysis I did with a fellow researcher, just 2 percent of the appropriations in the bills are reserved exclusively for rural places. Getting any of the remainder means vying successfully with larger jurisdictions.
The demand among rural and small towns clearly exists. For two new programs geared toward energy improvements in remote and rural communities under 10,000 people, the Department of Energy received more than 1,000 submissions combined. The new Recompete pilot program , intended to enable economic renewal in distressed places and overseen by the Economic Development Administration at the Department of Commerce, received a deluge of 565 applications — the most applications the development agency has received for a national program in its history. About half of the areas that were eligible are rural.
The scale of interest compounds the challenge. These and other programs’ popularity, combined with rural communities’ limited resources, means that success rates will be exceptionally low. It highlights the importance of leveling the playing field so the most vulnerable communities are not left out.
A critical first step will be to make sure that local communities have the staff and access to the expertise and administrative capacity necessary to secure and manage these investments.
As the Biden administration makes major investments in creating technical assistance centers in communities across the country, rural places must get to participate and benefit.
Congress also has a vital and continuing role to play. The Rural Partnership and Prosperity Act is bipartisan legislation that has been proposed in the Senate and the House of Representatives , and it is now included in the negotiations for the 2024 Farm Bill . Such a measure could be a game changer in getting flexible support directly to rural partnerships so they can unlock these opportunities.
The processes and requirements to gain access to those investments could also be simplified; no one should be required to fill out a 400-page application. We’ve already seen some improvements. The administration has put so-called navigators in selected communities to help them identify funding opportunities, and some agencies like the U.S. Forest Service have modified their processes to help communities apply for grants. These advances ought to be more widely adopted across the federal government.
States or financial and nonprofit intermediaries will also have the final say on the fate of much of the investment that is important for rural places, like broadband and water .
It’s not just about access to these opportunities. The extent to which local communities are in the driver’s seat and how widely the benefits accrue beyond local elites will be instrumental in avoiding the extractive practices that have often haunted rural economies. This means taking the time and providing the chance for people to influence the decisions that will affect them.
Take rural Humboldt County, Calif., where plans are underway to put immense wind turbines off its coast, a clean energy installation large enough to provide 6 percent of the state’s supply of electricity. A decision is pending by a state agency as to whether any of that electricity will land in Humboldt itself, where some federally recognized Native tribes do not have dependable power to this day.
The biggest risk is that politics stop the momentum created by these laws, because the investments are just getting started. For example, the money has not even begun to flow to local projects from the infrastructure act’s signature $42.5 billion investment to close the broadband gap .
Leading policy voices on the right have proposed dissolving or consolidating agencies like the Economic Development Administration and pulling these resources without offering an alternative vision for supporting rural development. That will simply once again starve rural places of investment. It does not seem like a long-term winning strategy.
Nor does vilifying an entire segment of the rural population based on specious analysis , as parts of the liberal elite seem wont to do.
The struggles that portions of rural America are experiencing were decades in the making. Common sense dictates that the solutions will not transpire overnight. Congress and the Biden administration have put the initial pieces in place to help many rural places transition to a brighter economic future. The president’s campaign pitch to rural voters ought to be the opportunity to stay the course. The political rewards may be far in the future, but it’s the right thing for rural communities — and for the country.
Tony Pipa is a senior fellow at the Center for Sustainable Development at the Brookings Institution, where he leads the Reimagining Rural Policy Initiative and hosts the “ Reimagine Rural ” podcast.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Sanofi’s CEO is giving OpenAI access to its data in the hope of developing drugs more quickly

Good morning from Geneva.
If generative AI is going to be more than hype and hallucinations , the trillion-dollar pharma industry is where the magic may happen. And no one is more ready to make it happen than Sanofi CEO Paul Hudson.
Last week, Hudson proudly announced his company’s new partnership with OpenAI and Formation Bio , a biotech. In the first-of-its-kind partnership, Sanofi will give OpenAI access to its databases, hoping that generative AI can be the key to quicker and more effective drug development.
“Large-language models give us this insane opportunity to suppress, summarize, and create,” Hudson told me on the phone from Paris. “It can help us get to a level in R&D where you can design a [drug candidate’s] molecular structure or identify appropriate patients that a drug will benefit.”
Is this then the generative AI application the world has been waiting for?
“It costs us 3-4 billion [dollars] to develop a drug, and 80% fail in phase 1 clinical trials,” Hudson said. “I’d like to know in advance what will fail. [Our collaboration with OpenAI] is putting that money to work in other projects with a higher probability of success.”
Neither is the promise of AI in health care years or decades away, Hudson believes.
The first results of Sanofi’s OpenAI collaboration should be in by the end of 2024 and will most likely take the form of AI-generated first drafts of FDA documents. The results of the more profound work on research and development and drug discovery should follow soon after. “I want to see early signs next year,” he said.
Still, whether this new partnership will indeed one day unlock billions of dollars in savings or new blockbuster revenues remains to be seen. But Hudson did stress that it is this kind of tie-up between industry and AI innovators on cutting-edge and high-value projects is the real deal.
“We knew we needed to not just buy a license [for the internal use of OpenAI],” he said. There’s a certain vanity to such licensing deals, which essentially create a “powerful Google.” “You can feel good about [OpenAI licensing]. You can write a press release.” This partnership, however, “is less about that, and more about operationalizing LLMs.”
More news below
Peter Vanham [email protected] Follow on LinkedIn
Shareholders get a say in AI
Meta shareholders will vote Wednesday on whether the social media company should release an annual report detailing the risk of “facilitating misinformation and disinformation disseminated or generated” via AI. While the vote is unlikely to succeed (due to Meta’s dual-class stock that gives founders outsized voting power), it could send a message to management about key AI concerns if the proposal wins over shareholders. Fortune
Thinx loses its way
The fall of Thinx, the once-buzzy women’s underwear startup, is now a lesson for other brands hoping to avoid the pitfalls of selling out to a larger company. Former employees complain that Thinx’s new owner, the conglomerate Kimberly-Clark, which bought the brand for around $230 million, of failing to capitalize on its irreverent and transparent voice. Another gripe: a hands-off approach when Thinx battled a forever-chemicals lawsuit that jilted loyal customers. Fortune
Evergrande fallout
The collapse of Chinese real estate developer Evergrande is now hurting the reputation of its former auditor PricewaterhouseCoopers. PwC clients are reportedly changing to other firms as regulators scrutinize the Big Four auditing company. Authorities have accused Evergrande of inflating its revenue by almost $80 billion, in spite of the developer’s results getting PwC’s stamp of approval. Financial Times
AROUND THE WATERCOOLER
Gen Z really are the hardest to work with—even managers of their own generation say they’re difficult. Instead, bosses plan to hire more of their millennial counterparts by Orianna Rosa Royle
Amazon, Walmart, and Target finally realize their colossal pricing mistake—now they’re slashing costs to win back customers by Sasha Rogelberg
Book excerpt: ‘I’m 100% sure that bringing children into this world is still the right thing to do’ by Tom Steyer
Elon Musk is recruiting xAI staffers who are ‘without regard to popularity or political correctness’ a day after raising $6 billion from investors by Christiaan Hetzner
Toyota’s bet on hybrids was mocked, then vindicated. Now it’s trying to repeat the trick with an unlikely bet on the combustion engine by Marco Quiroz-Gutierrez
China is ‘doubling down’ on local chip development with a new $47.5 billion fund: ‘The size of the fundraising speaks for itself’ by Lionel Lim
T his edition of CEO Daily was curated by Nicholas Gordon.
Latest in Newsletters

Why Pinterest, MTV, and Showtime are teaming up to fund cultural approaches to mental health care

Cava’s CFO on how the fast-casual chain’s latest menu item helps with optimizing price points

When is the time right for a CEO to step aside?

Why SAP’s CTO made scale a strategy for generative AI

Sam Altman’s reputation gets dragged further into the mud

How the 100 biggest U.S. companies have changed their DEI messaging
Most popular.

Amazon, Walmart, and Target finally realize their colossal pricing mistake—now they’re slashing costs to win back customers

Toyota’s bet on hybrids was mocked, then vindicated. Now it’s trying to repeat the trick with an unlikely bet on the combustion engine

Gen Z really are the hardest to work with—even managers of their own generation say they’re difficult. Instead bosses plan to hire more of their millennial counterparts

‘How can you tell me it won’t lead to stagflation?’ Jamie Dimon says ‘extraordinary’ government spending has him bracing for high inflation and unemployment

A 35-year-old Chinese man has been tagged as the alleged mastermind behind a gargantuan botnet used to steal billions from zombie computers

The average age of Ukrainian soldiers fighting Russia is 43-45, while the youngest troops remain exempt from front-line combat

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn about the meaning, measurement and types of inflation, such as currency, credit, deficit-induced, demand-pull and cost-push inflation. Also, explore the causes and effects of inflation on the economy and society.
Inflation Essay Topics and Outline Examples Essay Title 1: Understanding Inflation: Causes, Effects, and Economic Policy Responses. Thesis Statement: This essay provides a comprehensive analysis of inflation, exploring its root causes, the economic and societal effects it generates, and the various policy measures employed by governments and central banks to manage and mitigate inflationary ...
Students are often asked to write an essay on Inflation in their schools and colleges. And if you're also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic. ... 500 Words Essay on Inflation Introduction to Inflation. Inflation is a complex economic phenomenon that affects every aspect of our lives ...
The Fed has targeted an average inflation rate of 2% and will use the tools necessary to get the economy to that place. It's less a question of "if" inflation will reach this level, and more ...
UK inflation since 1989. Definition - Inflation - Inflation is a sustained rise in the cost of living and average price level.; Causes Inflation - Inflation is caused by excess demand in the economy, a rise in costs of production, rapid growth in the money supply.; Costs of Inflation - Inflation causes decline in value of savings, uncertainty, confusion and can lead to lower investment.
Essay on Inflation. Inflation is a term that resonates through the corridors of our daily lives, affecting decisions made by individuals, businesses, and governments alike. It refers to the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, and subsequently, purchasing power is falling.
Get to know and directly engage with senior McKinsey experts on inflation. Ondrej Burkacky is a senior partner in McKinsey's Munich office, Axel Karlsson is a senior partner in the Stockholm office, Fernando Perez is a senior partner in the Miami office, Emily Reasor is a senior partner in the Denver office, and Daniel Swan is a senior partner in the Stamford, Connecticut, office.
Economics. This essay provides a detailed and concise analysis of the causes and effects of inflation. It covers the various factors that can lead to inflation, including an increase in demand, production costs, money supply, and taxes. Additionally, it explores the potential negative impacts of inflation, such as a decrease in purchasing power ...
Check our 100% free inflation essay, research paper examples. Find inspiration and ideas Best topics Daily updates. Stuck with your inflation paper? Check our 100% free inflation essay, research paper examples. ... We will write a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts. 808 writers online Learn More
Inflation measures the rate of change of a price index over time. This change is often expressed as a year-over-year percent change (e.g., the percent prices increased in April 2022 relative to April 2021). While price indexes measure price levels, inflation measures price changes. This distinction is important.
Essay on Inflation Introduction: Inflation, the gradual increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy, is a phenomenon that affects individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. While moderate inflation is considered a normal part of a healthy economy, excessive inflation can lead to various economic challenges. This essay explores the causes, […]
Inflation is the rate of increase in prices over a given period of time. Inflation is typically a broad measure, such as the overall increase in prices or the increase in the cost of living in a country. But it can also be more narrowly calculated—for certain goods, such as food, or for services, such as a haircut, for example.
As inflation sets in, both individuals, corporations, and the government usually feels its impacts. However, a significant increase in the level of inflation will cause numerous impacts on me as an individual. We will write a custom essay on your topic. Since inflation means a rise in prices of common and basic goods, my purchasing power will ...
Inflation happens in an economy when there is a rise of level of goods and services, due to an increase in the volume of money in an economy over a period of time. It is also referred to as an (erosion) in the value of an economy's currency. When inflation is high, it affects the entire economy.
The main effects of unanticipated inflation are redistributive. Surprises in inflation rates lead to shifts in income and wealth between different groups of the population. During an inflationary process, borrowers will benefit at the expense of creditors, as inflation erodes real interest rates.
The first essay is a long essay on Inflation of 400-500 words. This long essay about Inflation is suitable for students of class 7, 8, 9 and 10, and also for competitive exam aspirants. The second essay is a short essay on Inflation of 150-200 words. These are suitable for students and children in class 6 and below.
Economists have however established the rate of Inflation and the money supply of a nation are correlated with one leading to another. This paper is therefore an analysis of the relationship between the inflation rate and money supply. Inflation. Inflation is said to be the increase in the prices of commodities and services in a given economy.
Words: 607. Page: 1. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Cite this essay. Download. While increasing demand is generally great news for an economy, a lagged supply chain can cause Inflation.
Inflation is the rate at which prices rise over time. Inflation is usually defined as an increase in the total price level or the cost of living in a country. It can, however, be computed more precisely for some items, such as food, or services, such as a haircut. Inflation, in any context, refers to how much more costly a particular set of ...
Students are often asked to write an essay on Inflation in India in their schools and colleges. And if you're also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic. ... 500 Words Essay on Inflation in India Introduction. Inflation, a sustained rise in the general level of prices for goods and services ...
Conclusion. Inflation in the Philippines is when prices rise and money buys less. It can be caused by not enough goods, higher costs to make products, or the country's money value changing. Inflation affects how people live, but the government and people can take steps to manage it. By understanding what inflation is and how it works, even ...
Writing for the humanities and arts. Essay #3. The crises of our prices. 22.82 dollars, the worth of a dollar from the 1800s today. If you don't think that is crazy try this, 100 dollars in the 1800s is over 2000 dollars. The primary cause of this catastrophe is inflation, an enduring issue that grows over time in size and severity.
In this essay on inflation in Pakistan, we will look at the causes, effects, and solutions to this issue that has been affecting the country for decades. The term 'inflation' refers to a sustained rise in the prices of goods and services in an economy. In Pakistan, inflation has been a major concern since the late 1990s, with the Consumer ...
Guest Essay. Biden Wants to Send Billions to Rural America, but This Must Happen First ... the CHIPS and Science Act and the Inflation Reduction Act — expand opportunities for Americans ...
Sanofi's CEO is giving OpenAI access to its data in the hope of developing drugs more quickly. BY Peter Vanham and Nicholas Gordon. May 29, 2024, 2:57 AM PDT. Paul Hudson, Sanofi CEO, thinks the ...