
- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.


4.3: Types of Essays and Suggested Structures
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 67153
Introduction
The structural organization of an essay will vary, depending on the type of writing task you’ve been assigned. Below are outline templates for specific types of writing projects. Keep in mind these are just a starting point: there is always room for variation and creativity in how a subject is most effectively presented to a reader.
Analytical essay
This is perhaps the most common structure. Examples of this include questions which ask you to discuss , analyze , investigate , explore, or review . In an analytical structure you are required to break the topic into its different components and discuss these in separate paragraphs or sections, demonstrating balance where possible.
- Background information on topic
- Overall point of view of the topic (thesis)
- Overview of components to be discussed (structure)
- Topic sentence outlining first component
- Sentences giving explanations and providing evidence to support topic sentence
- Concluding sentence – link to next paragraph
- Topic sentence outlining second component
- Sentences giving explanations and providing evidence to back topic sentence
- These follow the same structure for as many components as you need to outline
- Summary of the main points of the body
- Restatement of the main point of view
- Justification/evaluation (if required by task)
Argumentative essay
Examples of this type of essay include questions which ask you to take a position on a topic, such as a particular decision or policy, and present arguments which support your position. An effective way to argue a point can be to present the opposing view first then counter this view with stronger evidence.
- Statement of your position on the topic (thesis)
- Overview of arguments to be presented (structure)
- Topic sentence outlining first argument
- Topic sentence outlining second argument
- These follow the same structure for as many arguments as you wish to put forward in support of the topic.
- Restatement of the position
Interpretive essay
Examples of this type of essay include assignments where you are given data such as a case study or scenario, a diagram, graphical information, or a picture and expected to interpret this information to demonstrate your application of knowledge when answering the task. Based on this data, you may be asked to do a range of things such as provide recommendations or solutions, develop a nursing care plan, a teaching plan, suggest legal advice, or plan a marketing strategy.
- Brief background information on topic
- Overview of issues to be addressed in the essay (structure)
- State overall interpretation (thesis)
- Topic sentence outlining first issue identified from the data
- Sentences giving further explanation and providing evidence from both the literature and the data, e.g. the case study to support the topic sentence (it is very important in this types of essays to make reference to the data you have been supplied to give your essay context).
- Topic sentence outlining second issue identified
- These follow the same structure for as many issues as you wish to discuss from the data you have been supplied.
- Statement of overall interpretation
- Summary of the main issues from the data supplied
- Make recommendations or suggest solutions to address the issues arising from the data supplied.
Comparative essay
Examples of this type of essay include compare , compare and contrast , or differentiate questions. In this structure the similarities and/or differences between two or more items (for example, theories or models) are discussed paragraph by paragraph. Your assignment task may require you to make a recommendation about the suitability of the items you are comparing.
- Outline of two (or more) things being compared or contrasted
- Purpose for making the comparison / contrast
- Overview of the specific points to be compared / contrasted
- Topic sentence outlining first similarity or difference
- Topic sentence outlining second similarity or different
- These follow the same structure for as many items or aspects as you need to compare/contrast
- Restatement of the main purpose for the comparison / contrast
- Summary of the main similarities and differences
- Recommendation about suitability of compared items for purpose (if requirement of assessment task)
- Overall conclusion
Problem and solution essay
These essay questions often require you to structure your answer in several parts. An example may be to ask you to investigate a problem and explore a range of solutions. You may also be asked to choose the best solution and justify your selection, so allow space for this in your essay if needed.
- Background information about the problem
- Description of the problem and why it is serious
- Overview of the solutions to be outlined
- Topic sentence outlining first solution
- Explanation of the positive and negative aspects of the solution
- Evidence to support explanations
- Concluding sentence
- Topic sentence outlining second solution
- Evidence to support explanation
- These follow the same structure for as many solutions as you need to discuss
- Summary of the problem and overview of the solutions
- Evaluation of solutions and recommendation of best option
Note : Depending on the topic, body paragraphs in a problem and solution essay could be devoted to discussing the problem in more detail, as well as the solution. It’s up to the writer to assess the needs of the project, in order to decide how much time is spent on each part.
Cause and effect essay
Examples of this type of essay include questions which ask you to state or investigate the effects or outline the causes of the topic. This may be, for example, an historical event, the implementation of a policy, a medical condition, or a natural disaster. These essays may be structured in one of two ways: either the causes(s) of a situation may be discussed first followed by the effect(s), or the effect(s) could come first with the discussion working back to outline the cause(s). Sometimes with cause and effect essays you are required to give an assessment of the overall effects, such as on a community, a workplace, an individual. Space must be allocated for this assessment in your structure if needed.
- Background information on situation under discussion
- Description of the situation
- Overview of the causes or effects to be outlined
- Topic sentence outlining first cause or effect
- Sentences giving explanations and providing evidence to support the topic sentence
- Concluding sentence – linking to next paragraph
- Topic sentence outlining second cause or effect
- These follow the same structure for as many causes or effects as you need to outline
- Conclusion, prediction or recommendation
Finally, consider that some essay assignments may ask you to combine approaches, especially in more advanced classes. At that point, you may have to vary your body paragraph strategy from section to section.
This chart gives an idea of what different roles paragraphs can play in a mixed-structure essay assignment.
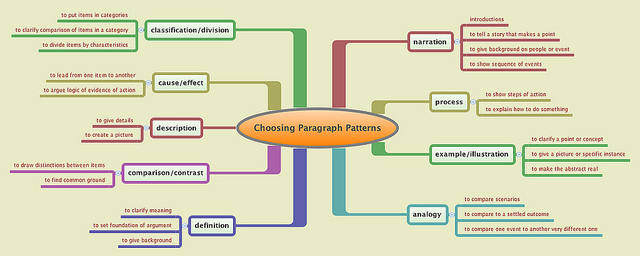
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)
- Clerc Center | PK-12 & Outreach
- KDES | PK-8th Grade School (D.C. Metro Area)
- MSSD | 9th-12th Grade School (Nationwide)
- Gallaudet University Regional Centers
- Parent Advocacy App
- K-12 ASL Content Standards
- National Resources
- Youth Programs
- Academic Bowl
- Battle Of The Books
- National Literary Competition
- Youth Debate Bowl
- Bison Sports Camp
- Discover College and Careers (DC²)
- Financial Wizards
- Immerse Into ASL
- Alumni Relations
- Alumni Association
- Homecoming Weekend
- Class Giving
- Get Tickets / BisonPass
- Sport Calendars
- Cross Country
- Swimming & Diving
- Track & Field
- Indoor Track & Field
- Cheerleading
- Winter Cheerleading
- Human Resources
- Plan a Visit
- Request Info

- Areas of Study
- Accessible Human-Centered Computing
- American Sign Language
- Art and Media Design
- Communication Studies
- Data Science
- Deaf Studies
- Early Intervention Studies Graduate Programs
- Educational Neuroscience
- Hearing, Speech, and Language Sciences
- Information Technology
- International Development
- Interpretation and Translation
- Linguistics
- Mathematics
- Philosophy and Religion
- Physical Education & Recreation
- Public Affairs
- Public Health
- Sexuality and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Theatre and Dance
- World Languages and Cultures
- B.A. in American Sign Language
- B.A. in Art and Media Design
- B.A. in Biology
- B.A. in Communication Studies
- B.A. in Communication Studies for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Deaf Studies
- B.A. in Deaf Studies for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Education with a Specialization in Early Childhood Education
- B.A. in Education with a Specialization in Elementary Education
- B.A. in English
- B.A. in Government
- B.A. in Government with a Specialization in Law
- B.A. in History
- B.A. in Interdisciplinary Spanish
- B.A. in International Studies
- B.A. in Interpretation
- B.A. in Mathematics
- B.A. in Philosophy
- B.A. in Psychology
- B.A. in Psychology for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Social Work (BSW)
- B.A. in Sociology
- B.A. in Sociology with a concentration in Criminology
- B.A. in Theatre Arts: Production/Performance
- B.A. or B.S. in Education with a Specialization in Secondary Education: Science, English, Mathematics or Social Studies
- B.S in Risk Management and Insurance
- B.S. in Accounting
- B.S. in Accounting for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.S. in Biology
- B.S. in Business Administration
- B.S. in Business Administration for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.S. in Information Technology
- B.S. in Mathematics
- B.S. in Physical Education and Recreation
- B.S. In Public Health
- General Education
- Honors Program
- Peace Corps Prep program
- Self-Directed Major
- M.A. in Counseling: Clinical Mental Health Counseling
- M.A. in Counseling: School Counseling
- M.A. in Deaf Education
- M.A. in Deaf Education Studies
- M.A. in Deaf Studies: Cultural Studies
- M.A. in Deaf Studies: Language and Human Rights
- M.A. in Early Childhood Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in Early Intervention Studies
- M.A. in Elementary Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in International Development
- M.A. in Interpretation: Combined Interpreting Practice and Research
- M.A. in Interpretation: Interpreting Research
- M.A. in Linguistics
- M.A. in Secondary Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in Sign Language Education
- M.S. in Accessible Human-Centered Computing
- M.S. in Speech-Language Pathology
- Master of Social Work (MSW)
- Au.D. in Audiology
- Ed.D. in Transformational Leadership and Administration in Deaf Education
- Ph.D. in Clinical Psychology
- Ph.D. in Critical Studies in the Education of Deaf Learners
- Ph.D. in Hearing, Speech, and Language Sciences
- Ph.D. in Linguistics
- Ph.D. in Translation and Interpreting Studies
- Ph.D. Program in Educational Neuroscience (PEN)
- Individual Courses and Training
- Summer On-Campus Courses
- Summer Online Courses
- Certificates
- Certificate in Sexuality and Gender Studies
- Educating Deaf Students with Disabilities (online, post-bachelor’s)
- American Sign Language and English Bilingual Early Childhood Deaf Education: Birth to 5 (online, post-bachelor’s)
- Peer Mentor Training (low-residency/hybrid, post-bachelor’s)
- Early Intervention Studies Graduate Certificate
- Online Degree Programs
- ODCP Minor in Communication Studies
- ODCP Minor in Deaf Studies
- ODCP Minor in Psychology
- ODCP Minor in Writing
- Online Degree Program General Education Curriculum
- University Capstone Honors for Online Degree Completion Program
Quick Links
- PK-12 & Outreach
- NSO Schedule

Guide to Different Kinds of Essays
202.448-7036
An essay is a paper that discusses, describes or analyzes one topic. It can discuss a subject directly or indirectly, seriously or humorously. It can describe personal opinions, or just report information. An essay can be written from any perspective, but essays are most commonly written in the first person ( I ), or third person (subjects that can be substituted with the he, she, it, or they pronouns).
There are many different kinds of essays. The following are a some of the most common ones:
Descriptive Cause/Effect Argumentative Definition Narrative Critical Compare/Contrast Process
Descriptive:
Examples: A descriptive essay could describe . . .
The descriptive essay provides details about how something looks, feels, tastes, smells, makes one feel, or sounds. It can also describe what something is, or how something happened. These essays generally use a lot of sensory details. The essay could be a list-like description that provides point by point details. Or, it could function as a story, keeping the reader interested in the plot and theme of the event described.
Definition:
Examples: A definition essay may try and define . . .
A definition essay attempts to define a specific term. It could try to pin down the meaning of a specific word, or define an abstract concept. The analysis goes deeper than a simple dictionary definition; it should attempt to explain why the term is defined as such. It could define the term directly, giving no information other than the explanation of the term. Or, it could imply the definition of the term, telling a story that requires the reader to infer the meaning.
Compare/Contrast:
Examples:A compare/contrast essay may discuss . . .
The compare/contrast essay discusses the similarities and differences between two things, people, concepts, places, etc. The essay could be an unbiased discussion, or an attempt to convince the reader of the benefits of one thing, person, or concept. It could also be written simply to entertain the reader, or to arrive at an insight into human nature. The essay could discuss both similarities and differences, or it could just focus on one or the other. A comparison essay usually discusses the similarities between two things, while the contrast essay discusses the differences.
Cause/Effect:
Examples:A cause/effect essay may explain . . .
The cause/effect essay explains why or how some event happened, and what resulted from the event.
This essay is a study of the relationship between two or more events or experiences. The essay could discuss both causes and effects, or it could simply address one or the other. A cause essay usually discusses the reasons why something happened. An effect essay discusses what happens after a specific event or circumstance.
The example below shows a cause essay, one that would explain how and why an event happened.
If this cause essay were about a volcanic eruption, it might go something like this: “Pressure and heat built up beneath the earth’s surface; the effect of this was an enormous volcanic eruption.”
The next example shows an effect essay, one that would explain all the effects that happened after a specific event, like a volcanic eruption.
If this effect essay were about a volcanic eruption again, it might go something like this:
“The eruption caused many terrible things to happen; it destroyed homes, forests, and polluted the atmosphere.”
Examples:A narrative essay could tell of . . .
The narrative essay tells a story. It can also be called a “short story.” Generally, the narrative essay is conversational in style and tells of a personal experience. It is most commonly written in the first person (uses I ). This essay could tell of a single, life-shaping event, or simply a mundane daily experience.
Examples: A process essay may explain . . .
A process essay describes how something is done. It generally explains actions that should be performed in a series. It can explain in detail how to accomplish a specific task, or it can show how an individual came to a certain personal awareness. The essay could be in the form of step-by-step instructions, or in story form, with the instructions/explanations subtly given along the way.
Argumentative:
Examples: An argumentative essay may persuade a reader that . . .
An argumentative essay is one that attempts to persuade the reader to the writer’s point of view. The writer can either be serious or funny, but always tries to convince the reader of the validity of his or her opinion. The essay may argue openly, or it may attempt to subtly persuade the reader by using irony or sarcasm.
Examples: A critical essay may analyze . . .
A critical essay analyzes the strengths, weaknesses, and methods of someone else’s work. Generally, these essays begin with a brief overview of the main points of the text, movie, or piece of art, followed by an analysis of the work’s meaning. It should then discuss how well the author/creator accomplishes his/her goals and makes his/her points. A critical essay can be written about another essay, story, book, poem, movie, or work of art.
202-448-7036
At a Glance
- Quick Facts
- University Leadership
- History & Traditions
- Accreditation
- Consumer Information
- Our 10-Year Vision: The Gallaudet Promise
- Annual Report of Achievements (ARA)
- The Signing Ecosystem
- Not Your Average University
Our Community
- Library & Archives
- Technology Support
- Interpreting Requests
- Ombuds Support
- Health and Wellness Programs
- Profile & Web Edits
Visit Gallaudet
- Explore Our Campus
- Virtual Tour
- Maps & Directions
- Shuttle Bus Schedule
- Kellogg Conference Hotel
- Welcome Center
- National Deaf Life Museum
- Apple Guide Maps
Engage Today
- Work at Gallaudet / Clerc Center
- Social Media Channels
- University Wide Events
- Sponsorship Requests
- Data Requests
- Media Inquiries
- Gallaudet Today Magazine
- Giving at Gallaudet
- Financial Aid
- Registrar’s Office
- Residence Life & Housing
- Safety & Security
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- University Communications
- Clerc Center

Gallaudet University, chartered in 1864, is a private university for deaf and hard of hearing students.
Copyright © 2024 Gallaudet University. All rights reserved.
- Accessibility
- Cookie Consent Notice
- Privacy Policy
- File a Report
800 Florida Avenue NE, Washington, D.C. 20002
Types of Essay
Definition of types of essay.
An essay is a short academic composition. The word “essay” is derived from a French word “essai” or “essayer,” which mean “trail.” In composition, however, an essay is a piece of non- fiction writing that talks or discusses a specific topic. Presently, essay is part of every degree program.
Each subject has specific requirements for the essays to be written. Some subjects need longer essays, while others need shorter ones, such as a five-paragraph essay. In composition, the start is made from a five-paragraph essay. Based on the requirements, there are seventeen types of essays.
- Definition Essay As the name suggests, a definition type of essay defines different things, ideas, and perceptions.
- Narrative Essay A narrative essay is a narration like a short story . It is, however, different from a short story in that it is written in an essay format.
- Descriptive Essay A descriptive essay describes something to make readers feel, smell, see, taste, or hear what is described.
- Expository Essay An expository essay exposes things in detail to make readers understand without any complications.
- Persuasive Essay A persuasive essay is meant to convince the target audience to do something or not do something.
- Argumentative Essay An argumentative essay is meant to present arguments in the favor of something. It has an additional fourth body paragraph that is meant to present opposite arguments.
- Analytical Essay An analytical essay analyzes something, such as in literature an analytical essay analyzes a piece of literature from different angles.
- Comparison and Contrast Essay A comparison and contrast essay makes either a comparison, a contrast, or both between two different or similar things.
- Cause and Effect Essay A cause and effect essay makes readers understand the cause of things, and their effects on other things.
- Critical Essay A critical essay is written on literary pieces to evaluate them on the basis of their merits or demerits.
- Process Essay A process essay outlines a process of making or breaking or doing something that readers understand fully and are able to do it after reading it.
- Synthesis Essay A synthesis essay means to synthesize different ideas to make a judgement about their merit and demerits.
- Explicatory Essay An explicatory essay is meant to explain a piece of literature. It is often written about poems , short stories, and novels .
- Rhetorical Analysis Essay A rhetorical analysis essay evaluates a speech or a piece of rhetoric on the basis of rhetorical strategies and devices used in it.
- Review Essay A review essay discusses the merits and demerits of a book and evaluates it through a review.
- Simple Essay A simple essay is just a five-paragraph essay that is written on any topic after it is specified.
- Research Essay A research essay revolves around a research question that is meant to answer some specific question through a research of the relevant literature.
Format of an Essay
Generally, a simple a five-paragraph has five paragraphs including an introduction , three body paragraphs, and a conclusion . An argumentative essay, however, has an additional paragraph which presents counter argument or opposing arguments in the same sequence. However, at the end of this paragraph, both the arguments are weighed in the favor of stronger arguments presented earlier in three body paragraphs.
The format of an argumentative essay is given below:
Function of types of essay.
An essay is a specific discussion or debate on a topic from a specific point of view . A student discusses the topic from his own specific angle. Readers not only get a glimpse of what the other aspect of the topic is, they also come to know about the tone and voice of the student writers to decide whether he has achieved a certain level of capability in writing. In literary essays, a writer becomes discusses the influence that literary piece has upon the readers about a certain point of view. Essays are also useful in winning public approval about certain political ideas.
Related posts:
- Seven Types of Ambiguity
- 6 Types of Conflicts in Literature With Examples
- 20 Major Types of Archetypes with Examples
- Four Main Types of Sonnets with Examples
- Elements of an Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Definition Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Analytical Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Cause and Effect Essay
- Critical Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Process Essay
- Explicatory Essay
- An Essay on Man: Epistle I
- Comparison and Contrast Essay
Post navigation


Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 3 strong argumentative essay examples, analyzed.
General Education

Need to defend your opinion on an issue? Argumentative essays are one of the most popular types of essays you’ll write in school. They combine persuasive arguments with fact-based research, and, when done well, can be powerful tools for making someone agree with your point of view. If you’re struggling to write an argumentative essay or just want to learn more about them, seeing examples can be a big help.
After giving an overview of this type of essay, we provide three argumentative essay examples. After each essay, we explain in-depth how the essay was structured, what worked, and where the essay could be improved. We end with tips for making your own argumentative essay as strong as possible.
What Is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is an essay that uses evidence and facts to support the claim it’s making. Its purpose is to persuade the reader to agree with the argument being made.
A good argumentative essay will use facts and evidence to support the argument, rather than just the author’s thoughts and opinions. For example, say you wanted to write an argumentative essay stating that Charleston, SC is a great destination for families. You couldn’t just say that it’s a great place because you took your family there and enjoyed it. For it to be an argumentative essay, you need to have facts and data to support your argument, such as the number of child-friendly attractions in Charleston, special deals you can get with kids, and surveys of people who visited Charleston as a family and enjoyed it. The first argument is based entirely on feelings, whereas the second is based on evidence that can be proven.
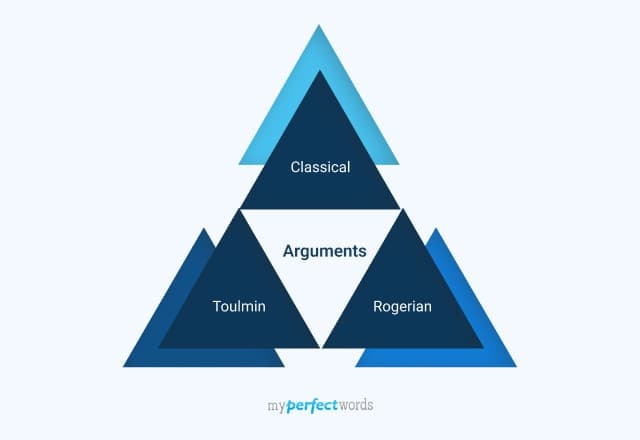
The standard five paragraph format is common, but not required, for argumentative essays. These essays typically follow one of two formats: the Toulmin model or the Rogerian model.
- The Toulmin model is the most common. It begins with an introduction, follows with a thesis/claim, and gives data and evidence to support that claim. This style of essay also includes rebuttals of counterarguments.
- The Rogerian model analyzes two sides of an argument and reaches a conclusion after weighing the strengths and weaknesses of each.
3 Good Argumentative Essay Examples + Analysis
Below are three examples of argumentative essays, written by yours truly in my school days, as well as analysis of what each did well and where it could be improved.
Argumentative Essay Example 1
Proponents of this idea state that it will save local cities and towns money because libraries are expensive to maintain. They also believe it will encourage more people to read because they won’t have to travel to a library to get a book; they can simply click on what they want to read and read it from wherever they are. They could also access more materials because libraries won’t have to buy physical copies of books; they can simply rent out as many digital copies as they need.
However, it would be a serious mistake to replace libraries with tablets. First, digital books and resources are associated with less learning and more problems than print resources. A study done on tablet vs book reading found that people read 20-30% slower on tablets, retain 20% less information, and understand 10% less of what they read compared to people who read the same information in print. Additionally, staring too long at a screen has been shown to cause numerous health problems, including blurred vision, dizziness, dry eyes, headaches, and eye strain, at much higher instances than reading print does. People who use tablets and mobile devices excessively also have a higher incidence of more serious health issues such as fibromyalgia, shoulder and back pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, and muscle strain. I know that whenever I read from my e-reader for too long, my eyes begin to feel tired and my neck hurts. We should not add to these problems by giving people, especially young people, more reasons to look at screens.
Second, it is incredibly narrow-minded to assume that the only service libraries offer is book lending. Libraries have a multitude of benefits, and many are only available if the library has a physical location. Some of these benefits include acting as a quiet study space, giving people a way to converse with their neighbors, holding classes on a variety of topics, providing jobs, answering patron questions, and keeping the community connected. One neighborhood found that, after a local library instituted community events such as play times for toddlers and parents, job fairs for teenagers, and meeting spaces for senior citizens, over a third of residents reported feeling more connected to their community. Similarly, a Pew survey conducted in 2015 found that nearly two-thirds of American adults feel that closing their local library would have a major impact on their community. People see libraries as a way to connect with others and get their questions answered, benefits tablets can’t offer nearly as well or as easily.
While replacing libraries with tablets may seem like a simple solution, it would encourage people to spend even more time looking at digital screens, despite the myriad issues surrounding them. It would also end access to many of the benefits of libraries that people have come to rely on. In many areas, libraries are such an important part of the community network that they could never be replaced by a simple object.
The author begins by giving an overview of the counter-argument, then the thesis appears as the first sentence in the third paragraph. The essay then spends the rest of the paper dismantling the counter argument and showing why readers should believe the other side.
What this essay does well:
- Although it’s a bit unusual to have the thesis appear fairly far into the essay, it works because, once the thesis is stated, the rest of the essay focuses on supporting it since the counter-argument has already been discussed earlier in the paper.
- This essay includes numerous facts and cites studies to support its case. By having specific data to rely on, the author’s argument is stronger and readers will be more inclined to agree with it.
- For every argument the other side makes, the author makes sure to refute it and follow up with why her opinion is the stronger one. In order to make a strong argument, it’s important to dismantle the other side, which this essay does this by making the author's view appear stronger.
- This is a shorter paper, and if it needed to be expanded to meet length requirements, it could include more examples and go more into depth with them, such as by explaining specific cases where people benefited from local libraries.
- Additionally, while the paper uses lots of data, the author also mentions their own experience with using tablets. This should be removed since argumentative essays focus on facts and data to support an argument, not the author’s own opinion or experiences. Replacing that with more data on health issues associated with screen time would strengthen the essay.
- Some of the points made aren't completely accurate , particularly the one about digital books being cheaper. It actually often costs a library more money to rent out numerous digital copies of a book compared to buying a single physical copy. Make sure in your own essay you thoroughly research each of the points and rebuttals you make, otherwise you'll look like you don't know the issue that well.

Argumentative Essay Example 2
There are multiple drugs available to treat malaria, and many of them work well and save lives, but malaria eradication programs that focus too much on them and not enough on prevention haven’t seen long-term success in Sub-Saharan Africa. A major program to combat malaria was WHO’s Global Malaria Eradication Programme. Started in 1955, it had a goal of eliminating malaria in Africa within the next ten years. Based upon previously successful programs in Brazil and the United States, the program focused mainly on vector control. This included widely distributing chloroquine and spraying large amounts of DDT. More than one billion dollars was spent trying to abolish malaria. However, the program suffered from many problems and in 1969, WHO was forced to admit that the program had not succeeded in eradicating malaria. The number of people in Sub-Saharan Africa who contracted malaria as well as the number of malaria deaths had actually increased over 10% during the time the program was active.
One of the major reasons for the failure of the project was that it set uniform strategies and policies. By failing to consider variations between governments, geography, and infrastructure, the program was not nearly as successful as it could have been. Sub-Saharan Africa has neither the money nor the infrastructure to support such an elaborate program, and it couldn’t be run the way it was meant to. Most African countries don't have the resources to send all their people to doctors and get shots, nor can they afford to clear wetlands or other malaria prone areas. The continent’s spending per person for eradicating malaria was just a quarter of what Brazil spent. Sub-Saharan Africa simply can’t rely on a plan that requires more money, infrastructure, and expertise than they have to spare.
Additionally, the widespread use of chloroquine has created drug resistant parasites which are now plaguing Sub-Saharan Africa. Because chloroquine was used widely but inconsistently, mosquitoes developed resistance, and chloroquine is now nearly completely ineffective in Sub-Saharan Africa, with over 95% of mosquitoes resistant to it. As a result, newer, more expensive drugs need to be used to prevent and treat malaria, which further drives up the cost of malaria treatment for a region that can ill afford it.
Instead of developing plans to treat malaria after the infection has incurred, programs should focus on preventing infection from occurring in the first place. Not only is this plan cheaper and more effective, reducing the number of people who contract malaria also reduces loss of work/school days which can further bring down the productivity of the region.
One of the cheapest and most effective ways of preventing malaria is to implement insecticide-treated bed nets (ITNs). These nets provide a protective barrier around the person or people using them. While untreated bed nets are still helpful, those treated with insecticides are much more useful because they stop mosquitoes from biting people through the nets, and they help reduce mosquito populations in a community, thus helping people who don’t even own bed nets. Bed nets are also very effective because most mosquito bites occur while the person is sleeping, so bed nets would be able to drastically reduce the number of transmissions during the night. In fact, transmission of malaria can be reduced by as much as 90% in areas where the use of ITNs is widespread. Because money is so scarce in Sub-Saharan Africa, the low cost is a great benefit and a major reason why the program is so successful. Bed nets cost roughly 2 USD to make, last several years, and can protect two adults. Studies have shown that, for every 100-1000 more nets are being used, one less child dies of malaria. With an estimated 300 million people in Africa not being protected by mosquito nets, there’s the potential to save three million lives by spending just a few dollars per person.
Reducing the number of people who contract malaria would also reduce poverty levels in Africa significantly, thus improving other aspects of society like education levels and the economy. Vector control is more effective than treatment strategies because it means fewer people are getting sick. When fewer people get sick, the working population is stronger as a whole because people are not put out of work from malaria, nor are they caring for sick relatives. Malaria-afflicted families can typically only harvest 40% of the crops that healthy families can harvest. Additionally, a family with members who have malaria spends roughly a quarter of its income treatment, not including the loss of work they also must deal with due to the illness. It’s estimated that malaria costs Africa 12 billion USD in lost income every year. A strong working population creates a stronger economy, which Sub-Saharan Africa is in desperate need of.
This essay begins with an introduction, which ends with the thesis (that malaria eradication plans in Sub-Saharan Africa should focus on prevention rather than treatment). The first part of the essay lays out why the counter argument (treatment rather than prevention) is not as effective, and the second part of the essay focuses on why prevention of malaria is the better path to take.
- The thesis appears early, is stated clearly, and is supported throughout the rest of the essay. This makes the argument clear for readers to understand and follow throughout the essay.
- There’s lots of solid research in this essay, including specific programs that were conducted and how successful they were, as well as specific data mentioned throughout. This evidence helps strengthen the author’s argument.
- The author makes a case for using expanding bed net use over waiting until malaria occurs and beginning treatment, but not much of a plan is given for how the bed nets would be distributed or how to ensure they’re being used properly. By going more into detail of what she believes should be done, the author would be making a stronger argument.
- The introduction of the essay does a good job of laying out the seriousness of the problem, but the conclusion is short and abrupt. Expanding it into its own paragraph would give the author a final way to convince readers of her side of the argument.

Argumentative Essay Example 3
There are many ways payments could work. They could be in the form of a free-market approach, where athletes are able to earn whatever the market is willing to pay them, it could be a set amount of money per athlete, or student athletes could earn income from endorsements, autographs, and control of their likeness, similar to the way top Olympians earn money.
Proponents of the idea believe that, because college athletes are the ones who are training, participating in games, and bringing in audiences, they should receive some sort of compensation for their work. If there were no college athletes, the NCAA wouldn’t exist, college coaches wouldn’t receive there (sometimes very high) salaries, and brands like Nike couldn’t profit from college sports. In fact, the NCAA brings in roughly $1 billion in revenue a year, but college athletes don’t receive any of that money in the form of a paycheck. Additionally, people who believe college athletes should be paid state that paying college athletes will actually encourage them to remain in college longer and not turn pro as quickly, either by giving them a way to begin earning money in college or requiring them to sign a contract stating they’ll stay at the university for a certain number of years while making an agreed-upon salary.
Supporters of this idea point to Zion Williamson, the Duke basketball superstar, who, during his freshman year, sustained a serious knee injury. Many argued that, even if he enjoyed playing for Duke, it wasn’t worth risking another injury and ending his professional career before it even began for a program that wasn’t paying him. Williamson seems to have agreed with them and declared his eligibility for the NCAA draft later that year. If he was being paid, he may have stayed at Duke longer. In fact, roughly a third of student athletes surveyed stated that receiving a salary while in college would make them “strongly consider” remaining collegiate athletes longer before turning pro.
Paying athletes could also stop the recruitment scandals that have plagued the NCAA. In 2018, the NCAA stripped the University of Louisville's men's basketball team of its 2013 national championship title because it was discovered coaches were using sex workers to entice recruits to join the team. There have been dozens of other recruitment scandals where college athletes and recruits have been bribed with anything from having their grades changed, to getting free cars, to being straight out bribed. By paying college athletes and putting their salaries out in the open, the NCAA could end the illegal and underhanded ways some schools and coaches try to entice athletes to join.
People who argue against the idea of paying college athletes believe the practice could be disastrous for college sports. By paying athletes, they argue, they’d turn college sports into a bidding war, where only the richest schools could afford top athletes, and the majority of schools would be shut out from developing a talented team (though some argue this already happens because the best players often go to the most established college sports programs, who typically pay their coaches millions of dollars per year). It could also ruin the tight camaraderie of many college teams if players become jealous that certain teammates are making more money than they are.
They also argue that paying college athletes actually means only a small fraction would make significant money. Out of the 350 Division I athletic departments, fewer than a dozen earn any money. Nearly all the money the NCAA makes comes from men’s football and basketball, so paying college athletes would make a small group of men--who likely will be signed to pro teams and begin making millions immediately out of college--rich at the expense of other players.
Those against paying college athletes also believe that the athletes are receiving enough benefits already. The top athletes already receive scholarships that are worth tens of thousands per year, they receive free food/housing/textbooks, have access to top medical care if they are injured, receive top coaching, get travel perks and free gear, and can use their time in college as a way to capture the attention of professional recruiters. No other college students receive anywhere near as much from their schools.
People on this side also point out that, while the NCAA brings in a massive amount of money each year, it is still a non-profit organization. How? Because over 95% of those profits are redistributed to its members’ institutions in the form of scholarships, grants, conferences, support for Division II and Division III teams, and educational programs. Taking away a significant part of that revenue would hurt smaller programs that rely on that money to keep running.
While both sides have good points, it’s clear that the negatives of paying college athletes far outweigh the positives. College athletes spend a significant amount of time and energy playing for their school, but they are compensated for it by the scholarships and perks they receive. Adding a salary to that would result in a college athletic system where only a small handful of athletes (those likely to become millionaires in the professional leagues) are paid by a handful of schools who enter bidding wars to recruit them, while the majority of student athletics and college athletic programs suffer or even shut down for lack of money. Continuing to offer the current level of benefits to student athletes makes it possible for as many people to benefit from and enjoy college sports as possible.
This argumentative essay follows the Rogerian model. It discusses each side, first laying out multiple reasons people believe student athletes should be paid, then discussing reasons why the athletes shouldn’t be paid. It ends by stating that college athletes shouldn’t be paid by arguing that paying them would destroy college athletics programs and cause them to have many of the issues professional sports leagues have.
- Both sides of the argument are well developed, with multiple reasons why people agree with each side. It allows readers to get a full view of the argument and its nuances.
- Certain statements on both sides are directly rebuffed in order to show where the strengths and weaknesses of each side lie and give a more complete and sophisticated look at the argument.
- Using the Rogerian model can be tricky because oftentimes you don’t explicitly state your argument until the end of the paper. Here, the thesis doesn’t appear until the first sentence of the final paragraph. That doesn’t give readers a lot of time to be convinced that your argument is the right one, compared to a paper where the thesis is stated in the beginning and then supported throughout the paper. This paper could be strengthened if the final paragraph was expanded to more fully explain why the author supports the view, or if the paper had made it clearer that paying athletes was the weaker argument throughout.

3 Tips for Writing a Good Argumentative Essay
Now that you’ve seen examples of what good argumentative essay samples look like, follow these three tips when crafting your own essay.
#1: Make Your Thesis Crystal Clear
The thesis is the key to your argumentative essay; if it isn’t clear or readers can’t find it easily, your entire essay will be weak as a result. Always make sure that your thesis statement is easy to find. The typical spot for it is the final sentence of the introduction paragraph, but if it doesn’t fit in that spot for your essay, try to at least put it as the first or last sentence of a different paragraph so it stands out more.
Also make sure that your thesis makes clear what side of the argument you’re on. After you’ve written it, it’s a great idea to show your thesis to a couple different people--classmates are great for this. Just by reading your thesis they should be able to understand what point you’ll be trying to make with the rest of your essay.
#2: Show Why the Other Side Is Weak
When writing your essay, you may be tempted to ignore the other side of the argument and just focus on your side, but don’t do this. The best argumentative essays really tear apart the other side to show why readers shouldn’t believe it. Before you begin writing your essay, research what the other side believes, and what their strongest points are. Then, in your essay, be sure to mention each of these and use evidence to explain why they’re incorrect/weak arguments. That’ll make your essay much more effective than if you only focused on your side of the argument.
#3: Use Evidence to Support Your Side
Remember, an essay can’t be an argumentative essay if it doesn’t support its argument with evidence. For every point you make, make sure you have facts to back it up. Some examples are previous studies done on the topic, surveys of large groups of people, data points, etc. There should be lots of numbers in your argumentative essay that support your side of the argument. This will make your essay much stronger compared to only relying on your own opinions to support your argument.

Summary: Argumentative Essay Sample
Argumentative essays are persuasive essays that use facts and evidence to support their side of the argument. Most argumentative essays follow either the Toulmin model or the Rogerian model. By reading good argumentative essay examples, you can learn how to develop your essay and provide enough support to make readers agree with your opinion. When writing your essay, remember to always make your thesis clear, show where the other side is weak, and back up your opinion with data and evidence.
What's Next?
Do you need to write an argumentative essay as well? Check out our guide on the best argumentative essay topics for ideas!
You'll probably also need to write research papers for school. We've got you covered with 113 potential topics for research papers.
Your college admissions essay may end up being one of the most important essays you write. Follow our step-by-step guide on writing a personal statement to have an essay that'll impress colleges.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Argumentative Essay Guide
Types Of Argument
Learn the 3 Different Types of Argument and Multiple Argument Claims
People also read
The Ultimate Guide to Argumentative Essay Writing
250+ Argumentative Essay Topic Ideas To Help You Out
Argumentative Essay Outline: How to Structure Your Argumentative Essay
Argumentative Essay Examples: Samples & Tips
An argument is a series of statements or facts intended to develop or support a point of view. It is usually known as a claim backed up with evidence, facts, and examples.
The way you structure the argument in your essay makes a huge difference. It will either set your paper apart or mix up with the other average papers without leaving an impact.
Recently, we created a complete guide to crafting an impressive argumentative essay from scratch. In this article, we will be focusing entirely on three core strategies and types of arguments.
Let’s learn how you can structure your essay with these 3 types of argument.
- 1. 3 Main Types of Argument
- 2. Types of Argument Claims
- 3. Steps to Structure an Argumentative Essay
3 Main Types of Argument
There are 3 types of arguments that you'll most likely encounter while writing an argumentative essay . These are:
Classical Argument
The Classical or Aristotelian model of argument is the most common type of argument. It was developed by the Greek philosopher and Rhetorician Aristotle.
In the classical model, both sides of an argument are analyzed , and one side is proven right using clear evidence .
This model efficiently utilizes Ethos (authenticity) + Pathos (emotion) + Logos (logic) to persuade an audience to a side of an argument.
The classical model argumentative essay takes into account the following things:
- Introduces the main claim or the argument of the essay.
- Present the writer's perspective on the argument. The reasons something is not working and why something should be done.
- Take into account the other side of the argument . Explain them in detail and refute them with the help of evidence.
- Provide clear evidence that proves that your side of the claim is true.
- Provide the conclusion which states the benefits of accepting your claim.
The structure of the classical model is as follows:
- Introduction - hook statement, brief background, thesis statement
- Body - topic sentence, facts & evidence to prove the argument
- Counter argument - opposing arguments, evidence and reasons to refute the counter-arguments
- Conclusion - restating the thesis statement, call to action and concluding remarks
Here is an example that follows this model:
Toulmin Argument
The Toulmin model for argumentative essays was developed by Stephen Toulmin. Unlike the classical model of argument, it presents only one side of the argument . This model works well when there is no clear truth or an absolute solution to a problem.
It breaks the argument into 6 basic components:
The structure of the Toulmin model is as follow:
- Introduction - thesis statement or the main claim
- Body - facts & evidence to support the argument
- Conclusion - rebuttal of counter-arguments
Here is an example outline of an argumentative essay about abortion in the Toulmin Model:
Rogerian Argument
The Rogerian model of argument was developed by Carl R. Rogers to provide a middle ground between opposing parties. This model works on collaboration and cooperation. It acknowledges that an argument can be looked at from different standpoints .
The objectives of the Rogerian model are:
- To show the reader that you have listened to their viewpoints and understood the complexities of the argument.
- To define the area where the writer acknowledges the reader's claim to be valid.
- Show the reader that you both share similar moral qualities and want to discover a solution that is mutually acceptable.
Each Rogerian model argumentative essay should define all of these aims.
The structure of the Rogerian model is as follow:
- Introduction - Introduction to the argument and thesis statement.
- Opposing position: An acknowledgment that there is another side of the argument.
- State your claim: Your own perspective about the argument.
- Provide a middle ground: Carefully bring both sides of the argument together and provide a compromised solution.
- Conclusion - Concluding remarks that state the benefits of a compromised solution.
Here’s a short example:
You can follow any of these 3 types of argument essay models in your argumentative essay. These models will help you to write an argumentative essay in a well-structured and persuasive way.
Types of Argument Claims
An argument claim, often simply referred to as a "claim," is a
“declarative statement or proposition put forward in an argument or discussion.”
It is the central point or thesis that the person making the argument is trying to prove or persuade others to accept.
Factual Claims
Factual claims are statements that assert something as a fact or reality. They are based on observable evidence and can be proven or disproven.
For example,
Value Claims
Value claims express personal opinions, preferences, or judgments about something. They are not about facts but about what someone believes is right, good, or important.
For instance,
Policy Claims
Policy claims propose a specific course of action or advocate for a change in the way things are done. They are often found in discussions about laws, regulations, or actions that should be taken.
An example would be,
Causal Claims
Causal claims assert a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more phenomena. They suggest that one thing is responsible for another.
For instance,
Definitional Claims
Definitional claims seek to clarify or establish the meaning of a term or concept. They aim to set a specific definition or understanding for a particular word or idea.
For example ,
Understanding these different types of argument claims can help you identify the nature of statements in discussions and debates. This makes it easier to analyze and respond to various arguments.
Steps to Structure an Argumentative Essay
You may have a very good and controversial argument in mind with strong evidence to prove it. However, if you haven't structured your argument properly, your argument is wasted.
Here are the easy steps that can help you structure your argument effectively:
- Choose a controversial and debatable topic from a comprehensive list of argumentative essay topics .
- Decide the type of claim that you want to make with your essay.
- Decide the type of argument structure you want to follow in your essay.
- Collect facts and evidence from credible sources and use them to support your claim.
- Develop a strong argumentative essay outline .
- Study some argumentative essay examples to get a deeper understanding of how to develop an argument in the essay.
- Begin your essay with an arguable claim or premises.
- Make sure your claim is logical and is developed coherently throughout the essay.
- Provide a conclusion that clearly matches the type of argument model you have followed.
Now that you've got the basics of different argument types, you're all set to start writing your argumentative essays.
However, if you still need expert help, you can hire a qualified writer from our custom essay writing online .
We know how to create strong and convincing arguments that will make your essays shine. Our argumentative essay writing service is available 24/7 to assist you with all of your argumentative writing needs.
Place your order today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
The Three Types of Mass Communication
This essay about the various forms of mass communication examines three primary types: broadcast media, online media, and print media. It sheds light on how these mediums play pivotal roles in disseminating information, shaping public discourse, and fostering connections among individuals and communities. By exploring the unique characteristics and impacts of each type, the essay offers valuable insights into the dynamic landscape of modern communication.
How it works
In the kaleidoscope of human interaction and information exchange, the realm of mass communication stands as a vibrant mosaic, weaving together diverse threads of media and messaging. Delving into this tapestry reveals not just the broad strokes of television screens and newspaper headlines, but also the intricate patterns of connection and influence that define our modern world. Within this dynamic landscape, three distinct types of mass communication emerge, each possessing its own character and impact.
First, let’s cast our gaze upon the towering edifice of broadcast media.
Picture the glow of a television screen illuminating a living room, or the crackle of a radio filling the airwaves with voices and music. Broadcast media embodies the essence of shared experience, captivating audiences with its ability to simultaneously reach millions of viewers or listeners. From gripping news reports to gripping dramas, from live sports events to cultural phenomena, broadcast media serves as a communal hearth around which society gathers to witness, react, and engage.
Venturing into the digital realm, we encounter the sprawling landscape of online media. Here, the internet serves as both stage and megaphone, amplifying voices and ideas across vast virtual spaces. Social media platforms buzz with conversation, news websites pulse with real-time updates, and blogs offer intimate glimpses into diverse perspectives. Online media democratizes the dissemination of information, granting individuals the power to share their stories, opinions, and creations with a global audience. Yet, amidst the cacophony of digital chatter, discerning truth from falsehood becomes a critical challenge, as echo chambers and misinformation abound.
And let us not forget the enduring presence of print media, standing as a steadfast sentinel in the midst of digital upheaval. Newspapers, magazines, and books hold a timeless allure, offering tangible artifacts of knowledge and culture in an increasingly ephemeral world. The rustle of turning pages, the scent of ink on paper—these sensory experiences evoke a sense of intimacy and authority that digital mediums often struggle to replicate. Through investigative journalism, thoughtful analysis, and literary exploration, print media continues to shape our understanding of the world with depth and nuance.
In this ever-evolving landscape of mass communication, the interplay of broadcast, online, and print media shapes the contours of our collective consciousness. Each medium carries its own strengths and weaknesses, its own opportunities and challenges. Yet, beneath the surface diversity lies a common thread—the human impulse to connect, to inform, to entertain, and to inspire. As technology advances and societal norms shift, the ways in which we communicate and consume media will undoubtedly continue to evolve. But amidst the flux and uncertainty, one thing remains certain: the enduring power of mass communication to shape our perceptions, our beliefs, and our shared reality.
Cite this page
The Three Types Of Mass Communication. (2024, Apr 29). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-three-types-of-mass-communication/
"The Three Types Of Mass Communication." PapersOwl.com , 29 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-three-types-of-mass-communication/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Three Types Of Mass Communication . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-three-types-of-mass-communication/ [Accessed: 30 Apr. 2024]
"The Three Types Of Mass Communication." PapersOwl.com, Apr 29, 2024. Accessed April 30, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-three-types-of-mass-communication/
"The Three Types Of Mass Communication," PapersOwl.com , 29-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-three-types-of-mass-communication/. [Accessed: 30-Apr-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Three Types Of Mass Communication . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-three-types-of-mass-communication/ [Accessed: 30-Apr-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Advertisement
35 Soal Ujian Sekolah Bahasa Inggris Kelas 6 SD dan Jawabannya Lengkap
45 Soal Ujian IPA Kelas 6 SD 2024 dan Jawabannya Lengkap
Contoh Soal Luas Permukaan Bola beserta Rumus dan Penyelesaiannya Lengkap
11 Contoh Soal Volume Balok beserta Jawabannya Lengkap
30 Contoh Soal Kubus Matematika beserta Rumus dan Jawabannya Lengkap
40 Contoh Soal tentang Tata Surya Pilihan Ganda dan Essay beserta Jawabannya
Apabila kamu sedang mencari contoh latihan soal tentang tata surya untuk belajar, temukan saja di artikel ini.
40 Contoh Soal tentang Tata Surya Pilihan Ganda dan Essay beserta Jawabannya – Tata surya merupakan bagian dari pelajaran IPA (Ilmu Pengetahuan Alam), sehingga perlu dipelajari karena bisa jadi muncul dalam soal ujian.
Bagi kamu yang sedang belajar dan berlatih materi tata surya, berikut adalah contoh soal tentang tata surya pilihan ganda dan essay beserta jawabannya.
Jangan lupa untuk dikerjakan dan dipelajari juga, ya!
- Mengenal Apa itu Tata Surya
Daftar Isi [ hide ]
40 Contoh Soal tentang Tata Surya Pilihan Ganda dan Essay
- Contoh Soal tentang Tata Surya Pilihan Ganda
- Contoh Soal tentang Tata Surya Essay
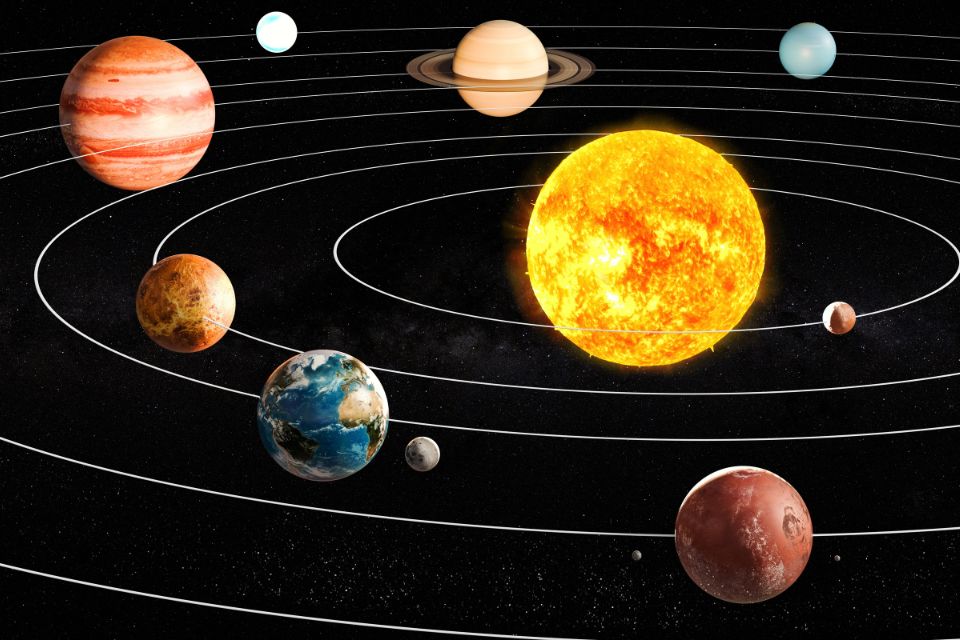
Tata surya adalah sistem planet, bulan, asteroid, komet, dan objek langit lainnya yang terikat oleh gravitasi Matahari di pusatnya.
Dengan Matahari sebagai bintang pusatnya, tata surya ini merupakan bagian dari Galaksi Bima Sakti yang terletak sekitar 27.000 tahun cahaya dari pusat galaksi.
Tata surya terdiri dari delapan planet yang mengelilingi Matahari dalam lintasan yang elips, dimulai dari Merkurius yang terdekat dengan Matahari hingga Neptunus yang terjauh.
Kedelapan planet tersebut adalah Merkurius , Venus, Bumi, Mars, Jupiter, Saturnus, Uranus, dan Neptunus.
Selain planet-planet tersebut, tata surya juga memiliki ribuan asteroid, jutaan komet, dan berbagai objek langit lainnya.
Selain objek-objek yang mengelilingi Matahari, tata surya juga memiliki sabuk asteroid dan sabuk Kuiper yang terdiri dari berbagai objek kecil yang mengorbit di luar planet terjauh, Neptunus.
Di luar sabuk Kuiper, terdapat awan Oort yang menjadi tempat asal komet jangka panjang.
Tata surya adalah tempat kelahiran dan rumah bagi Bumi serta berbagai bentuk kehidupan yang ada di planet ini.
Baca Juga :
18 Fakta Menarik tentang Bulan, Ukurannya yang Lebih Kecil daripada Bumi
Keteraturan gerakan planet-planet dalam tata surya mengikuti hukum-hukum fisika, terutama hukum gravitasi Newton, yang menjelaskan bagaimana benda-benda langit saling mempengaruhi dan bergerak dalam lintasan yang teratur.
Penelitian tentang tata surya terus berkembang, membantu manusia untuk memahami asal-usul, evolusi, dan masa depannya.
Penjelajahan luar angkasa dan misi ke berbagai objek dalam tata surya telah memberikan wawasan yang berharga tentang alam semesta dan tempat kita di dalamnya.
Setelah memahami tentang apa itu tata surya, berikut ini adalah contoh soal tentang tata surya pilihan ganda dan essay yang bisa kamu kerjakan.
Klik dan dapatkan info kost di dekat kampus idamanmu:
Kost Dekat UGM Jogja Kost Dekat UNPAD Jatinangor Kost Dekat UNDIP Semarang Kost Dekat UI Depok Kost Dekat UB Malang Kost Dekat Unnes Semarang Kost Dekat UMY Jogja Kost Dekat UNY Jogja Kost Dekat UNS Solo Kost Dekat ITB Bandung Kost Dekat UMS Solo Kost Dekat ITS Surabaya
Kost Dekat Unesa Surabaya
Kost Dekat UNAIR Surabaya
Kost Dekat UIN Jakarta


COMMENTS
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
Writing. Writing 101: The 8 Common Types of Essays. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 3 min read. Whether you're a first-time high school essay writer or a professional writer about to tackle another research paper, you'll need to understand the fundamentals of essay writing before you put pen to paper and write your ...
3. Argumentative essays. An argumentative essay is a type of essay that aims to persuade the reader to adopt a particular stance based on factual evidence and is one of the most common forms of college essays. 4. Expository essays. An expository essay is a common format used in school and college exams to assess your understanding of a specific ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
This chart gives an idea of what different roles paragraphs can play in a mixed-structure essay assignment. Figure 4.3.1 4.3. 1. 4.3: Types of Essays and Suggested Structures is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.
3 Similarly, if you're asked to compare sources or consider sources in relation to each other, it is not enough to offer a list of similarities and differences. Again, this type of assignment is generally asking you to make some claim about the sources in relation to each other. • Consider the broader goals of the assignment.
An essay is a paper that discusses, describes or analyzes one topic. It can discuss a subject directly or indirectly, seriously or humorously. It can describe personal opinions, or just report information. An essay can be written from any perspective, but essays are most commonly written in the first person (I), or third person (subjects that can be substituted with the he, she, it, or they ...
In this article, we'll explain essay formatting rules for three of the most popular essay styles: MLA, APA, and Chicago. ... Unlike MLA style, in APA essay format, every source type is referenced differently. So the rules for referencing a book are different from those for referencing a journal article are different from those referencing an ...
Definition of Types of Essay. An essay is a short academic composition. The word "essay" is derived from a French word "essai" or "essayer," which mean "trail." In composition, however, an essay is a piece of non-fiction writing that talks or discusses a specific topic.Presently, essay is part of every degree program.
This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people's social and cultural lives.
Though every essay is founded on these two ideas, there are several different types of essays, differentiated by the style of the writing, how the writer presents the thesis, and the types of evidence used to support the thesis statement. Essays can be roughly divided into four different types: #1: Argumentative #2: Persuasive #3: Expository
Expository Essay. Informative Writing, Research, Clarity. Explain the causes and effects of climate change, and discuss its impact on the environment and society. Narrative Essay. Storytelling, Narrative Structure, Engagement. Describe a memorable childhood event that had a significant impact on your life.
The three types of essay most commonly assigned in school — the narrative essay, the persuasive essay, and the expository essay — conveniently correspond to those writing forms most frequently published online and in print. Your experience with these prose forms is ideal preparation for writing for publication. 1. The Narrative Essay.
Here are 10 types of essays you may use in your writing: 1. Narrative essays Narrative essays tell a story and often are the most personal type of essay you may write. They allow you to exercise creativity and imagination, and you can base them on a particular prompt, such as the first time you drove a car by yourself, or a more open-ended ...
Argumentative Essay Example 2. Malaria is an infectious disease caused by parasites that are transmitted to people through female Anopheles mosquitoes. Each year, over half a billion people will become infected with malaria, with roughly 80% of them living in Sub-Saharan Africa.
3 Main Types of Argument. There are 3 types of arguments that you'll most likely encounter while writing an argumentative essay.These are: Classical Argument . The Classical or Aristotelian model of argument is the most common type of argument. It was developed by the Greek philosopher and Rhetorician Aristotle.
This essay about the various forms of mass communication examines three primary types: broadcast media, online media, and print media. It sheds light on how these mediums play pivotal roles in disseminating information, shaping public discourse, and fostering connections among individuals and communities.
Contoh Soal Conditional Sentence Type 1, 2, dan 3 beserta Jawabannya Lengkap. 22 April 2024 | Latihan Soal. Contoh Soal Simple Past Tense Pilihan Ganda dan Essay beserta Jawabannya. 23 April 2024 ... 40 Contoh Soal tentang Tata Surya Pilihan Ganda dan Essay beserta Jawabannya - Tata surya merupakan bagian dari pelajaran IPA (Ilmu Pengetahuan ...