Should Kids Get Homework?
Homework gives elementary students a way to practice concepts, but too much can be harmful, experts say.

Getty Images
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful.
How much homework students should get has long been a source of debate among parents and educators. In recent years, some districts have even implemented no-homework policies, as students juggle sports, music and other activities after school.
Parents of elementary school students, in particular, have argued that after-school hours should be spent with family or playing outside rather than completing assignments. And there is little research to show that homework improves academic achievement for elementary students.
But some experts say there's value in homework, even for younger students. When done well, it can help students practice core concepts and develop study habits and time management skills. The key to effective homework, they say, is keeping assignments related to classroom learning, and tailoring the amount by age: Many experts suggest no homework for kindergartners, and little to none in first and second grade.

Value of Homework
Homework provides a chance to solidify what is being taught in the classroom that day, week or unit. Practice matters, says Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University 's Wheelock College of Education & Human Development.
"There really is no other domain of human ability where anybody would say you don't need to practice," she adds. "We have children practicing piano and we have children going to sports practice several days a week after school. You name the domain of ability and practice is in there."
Homework is also the place where schools and families most frequently intersect.
"The children are bringing things from the school into the home," says Paula S. Fass, professor emerita of history at the University of California—Berkeley and the author of "The End of American Childhood." "Before the pandemic, (homework) was the only real sense that parents had to what was going on in schools."
Harris Cooper, professor emeritus of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University and author of "The Battle Over Homework," examined more than 60 research studies on homework between 1987 and 2003 and found that — when designed properly — homework can lead to greater student success. Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary.
"Every child should be doing homework, but the amount and type that they're doing should be appropriate for their developmental level," he says. "For teachers, it's a balancing act. Doing away with homework completely is not in the best interest of children and families. But overburdening families with homework is also not in the child's or a family's best interest."
Negative Homework Assignments
Not all homework for elementary students involves completing a worksheet. Assignments can be fun, says Cooper, like having students visit educational locations, keep statistics on their favorite sports teams, read for pleasure or even help their parents grocery shop. The point is to show students that activities done outside of school can relate to subjects learned in the classroom.
But assignments that are just busy work, that force students to learn new concepts at home, or that are overly time-consuming can be counterproductive, experts say.
Homework that's just busy work.
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful, experts say. Assignments that look more like busy work – projects or worksheets that don't require teacher feedback and aren't related to topics learned in the classroom – can be frustrating for students and create burdens for families.
"The mental health piece has definitely played a role here over the last couple of years during the COVID-19 pandemic, and the last thing we want to do is frustrate students with busy work or homework that makes no sense," says Dave Steckler, principal of Red Trail Elementary School in Mandan, North Dakota.
Homework on material that kids haven't learned yet.
With the pressure to cover all topics on standardized tests and limited time during the school day, some teachers assign homework that has not yet been taught in the classroom.
Not only does this create stress, but it also causes equity challenges. Some parents speak languages other than English or work several jobs, and they aren't able to help teach their children new concepts.
" It just becomes agony for both parents and the kids to get through this worksheet, and the goal becomes getting to the bottom of (the) worksheet with answers filled in without any understanding of what any of it matters for," says professor Susan R. Goldman, co-director of the Learning Sciences Research Institute at the University of Illinois—Chicago .
Homework that's overly time-consuming.
The standard homework guideline recommended by the National Parent Teacher Association and the National Education Association is the "10-minute rule" – 10 minutes of nightly homework per grade level. A fourth grader, for instance, would receive a total of 40 minutes of homework per night.
But this does not always happen, especially since not every student learns the same. A 2015 study published in the American Journal of Family Therapy found that primary school children actually received three times the recommended amount of homework — and that family stress increased along with the homework load.
Young children can only remain attentive for short periods, so large amounts of homework, especially lengthy projects, can negatively affect students' views on school. Some individual long-term projects – like having to build a replica city, for example – typically become an assignment for parents rather than students, Fass says.
"It's one thing to assign a project like that in which several kids are working on it together," she adds. "In (that) case, the kids do normally work on it. It's another to send it home to the families, where it becomes a burden and doesn't really accomplish very much."
Private vs. Public Schools
Do private schools assign more homework than public schools? There's little research on the issue, but experts say private school parents may be more accepting of homework, seeing it as a sign of academic rigor.
Of course, not all private schools are the same – some focus on college preparation and traditional academics, while others stress alternative approaches to education.
"I think in the academically oriented private schools, there's more support for homework from parents," says Gerald K. LeTendre, chair of educational administration at Pennsylvania State University—University Park . "I don't know if there's any research to show there's more homework, but it's less of a contentious issue."
How to Address Homework Overload
First, assess if the workload takes as long as it appears. Sometimes children may start working on a homework assignment, wander away and come back later, Cooper says.
"Parents don't see it, but they know that their child has started doing their homework four hours ago and still not done it," he adds. "They don't see that there are those four hours where their child was doing lots of other things. So the homework assignment itself actually is not four hours long. It's the way the child is approaching it."
But if homework is becoming stressful or workload is excessive, experts suggest parents first approach the teacher, followed by a school administrator.
"Many times, we can solve a lot of issues by having conversations," Steckler says, including by "sitting down, talking about the amount of homework, and what's appropriate and not appropriate."
Study Tips for High School Students

Tags: K-12 education , students , elementary school , children
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.

Is Homework Good for Kids?
Research suggests that homework may be most beneficial when it is minimal..
Updated October 3, 2023 | Reviewed by Devon Frye
- Why Education Is Important
- Find a Child Therapist
- Research finds that homework can academically benefit middle and high schoolers, but not elementary students.
- There are non-academic benefits to homework, but too much work may interfere with other areas of development.
- Research suggests students should be given about 10 minutes of homework per grade level.
- Parents can help with homework by encouraging a growth mindset and supporting their child's autonomy.
In recent years, homework has become a very hot topic. Many parents and educators have raised concerns about homework and questioned how effective it is in enhancing students’ learning. There are also concerns that students may simply be getting too much homework, which ultimately interferes with quality family time and opportunities for physical activity and play.
Research suggests that these concerns may be valid. For example, one study reported that elementary school students, on average, are assigned three times the recommended amount of homework.
What does the research say? What are the potential risks and benefits of homework, and how much is “too much”?
Academic vs. Non-Academic Benefits
First, research finds that homework is associated with higher scores on academic standardized tests for middle and high school students, but not elementary school students . A recent experimental study in Romania found some benefits for a small amount of writing homework in elementary students but not math homework. Yet, interestingly, this positive impact only occurred when students were given a moderate amount of homework (about 20 minutes on average).
Yet the goal of homework is not simply to improve academic skills. Research finds that homework may have some non-academic benefits, such as building responsibility , time management skills, and task persistence . Homework may also increase parents’ involvement in their children’s schooling.
Yet too much homework may also have some negative impacts on non-academic skills by reducing opportunities for free play , which is essential for the development of language, cognitive, self-regulation , and social-emotional skills. Homework may also interfere with physical activity ; indeed, too much homework is associated with an increased risk of being overweight . As with the research on academic benefits, this research also suggests that homework may be beneficial when it is minimal.
What is the “Right” Amount of Homework?
Research suggests that homework should not exceed 1.5 to 2.5 hours per night for high school students and no more than 1 hour per night for middle school students. Homework for elementary school students should be minimal and assigned with the aim of building self-regulation and independent work skills. Any more than this and homework may no longer have a positive impact.
The National Education Association recommends 10 minutes of homework per grade and there is also some experimental evidence that backs this up.
What Can Parents Do?
Research finds that parental help with homework is beneficial but that it matters more how the parent is helping rather than how often the parent is helping.
So how should parents help with homework (according to the research)?
- Focus on providing general monitoring, guidance, and encouragement, but allow children to complete their homework as independently as possible. Research shows that allowing children more autonomy in completing homework may benefit their academic skills.
- Only provide help when your child asks for it and step away whenever possible. Research finds that too much parental involvement or intrusive and controlling involvement with homework is associated with worse academic performance .
- Help your children to create structure and develop some routines that help your child to independently complete their homework. Research finds that providing this type of structure and responsiveness is related to improved academic skills.
- Set specific rules around homework. Research finds an association between parents setting rules around homework and academic performance.
- Help your child to view homework as an opportunity to learn and improve skills. Parents who view homework as a learning opportunity (that is, a “mastery orientation”) rather than something that they must get “right” or complete successfully to obtain a higher grade (that is, a “performance orientation”) are more likely to have children with the same attitudes.
- Encourage your child to persist in challenging assignments and emphasize difficult assignments as opportunities to grow. Research finds that this attitude is associated with student success. Research also indicates that more challenging homework is associated with enhanced academic performance.
- Stay calm and positive during homework. Research shows that mothers’ showing positive emotions while helping with homework may improve children’s motivation in homework.
- Praise your child’s hard work and effort during homework. This type of praise is likely to increase motivation. In addition, research finds that putting more effort into homework may be associated with enhanced development of conscientiousness in children.
- Communicate with your child and the teacher about any problems your child has with homework and the teacher’s learning goals. Research finds that open communication about homework is associated with increased academic performance.

Cara Goodwin, Ph.D., is a licensed clinical psychologist who specializes in translating scientific research into information that is useful, accurate, and relevant for parents.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Our Mission

What’s the Right Amount of Homework?
Decades of research show that homework has some benefits, especially for students in middle and high school—but there are risks to assigning too much.
Many teachers and parents believe that homework helps students build study skills and review concepts learned in class. Others see homework as disruptive and unnecessary, leading to burnout and turning kids off to school. Decades of research show that the issue is more nuanced and complex than most people think: Homework is beneficial, but only to a degree. Students in high school gain the most, while younger kids benefit much less.
The National PTA and the National Education Association support the “ 10-minute homework guideline ”—a nightly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. But many teachers and parents are quick to point out that what matters is the quality of the homework assigned and how well it meets students’ needs, not the amount of time spent on it.
The guideline doesn’t account for students who may need to spend more—or less—time on assignments. In class, teachers can make adjustments to support struggling students, but at home, an assignment that takes one student 30 minutes to complete may take another twice as much time—often for reasons beyond their control. And homework can widen the achievement gap, putting students from low-income households and students with learning disabilities at a disadvantage.
However, the 10-minute guideline is useful in setting a limit: When kids spend too much time on homework, there are real consequences to consider.
Small Benefits for Elementary Students
As young children begin school, the focus should be on cultivating a love of learning, and assigning too much homework can undermine that goal. And young students often don’t have the study skills to benefit fully from homework, so it may be a poor use of time (Cooper, 1989 ; Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). A more effective activity may be nightly reading, especially if parents are involved. The benefits of reading are clear: If students aren’t proficient readers by the end of third grade, they’re less likely to succeed academically and graduate from high school (Fiester, 2013 ).
For second-grade teacher Jacqueline Fiorentino, the minor benefits of homework did not outweigh the potential drawback of turning young children against school at an early age, so she experimented with dropping mandatory homework. “Something surprising happened: They started doing more work at home,” Fiorentino writes . “This inspiring group of 8-year-olds used their newfound free time to explore subjects and topics of interest to them.” She encouraged her students to read at home and offered optional homework to extend classroom lessons and help them review material.
Moderate Benefits for Middle School Students
As students mature and develop the study skills necessary to delve deeply into a topic—and to retain what they learn—they also benefit more from homework. Nightly assignments can help prepare them for scholarly work, and research shows that homework can have moderate benefits for middle school students (Cooper et al., 2006 ). Recent research also shows that online math homework, which can be designed to adapt to students’ levels of understanding, can significantly boost test scores (Roschelle et al., 2016 ).
There are risks to assigning too much, however: A 2015 study found that when middle school students were assigned more than 90 to 100 minutes of daily homework, their math and science test scores began to decline (Fernández-Alonso, Suárez-Álvarez, & Muñiz, 2015 ). Crossing that upper limit can drain student motivation and focus. The researchers recommend that “homework should present a certain level of challenge or difficulty, without being so challenging that it discourages effort.” Teachers should avoid low-effort, repetitive assignments, and assign homework “with the aim of instilling work habits and promoting autonomous, self-directed learning.”
In other words, it’s the quality of homework that matters, not the quantity. Brian Sztabnik, a veteran middle and high school English teacher, suggests that teachers take a step back and ask themselves these five questions :
- How long will it take to complete?
- Have all learners been considered?
- Will an assignment encourage future success?
- Will an assignment place material in a context the classroom cannot?
- Does an assignment offer support when a teacher is not there?
More Benefits for High School Students, but Risks as Well
By the time they reach high school, students should be well on their way to becoming independent learners, so homework does provide a boost to learning at this age, as long as it isn’t overwhelming (Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). When students spend too much time on homework—more than two hours each night—it takes up valuable time to rest and spend time with family and friends. A 2013 study found that high school students can experience serious mental and physical health problems, from higher stress levels to sleep deprivation, when assigned too much homework (Galloway, Conner, & Pope, 2013 ).
Homework in high school should always relate to the lesson and be doable without any assistance, and feedback should be clear and explicit.
Teachers should also keep in mind that not all students have equal opportunities to finish their homework at home, so incomplete homework may not be a true reflection of their learning—it may be more a result of issues they face outside of school. They may be hindered by issues such as lack of a quiet space at home, resources such as a computer or broadband connectivity, or parental support (OECD, 2014 ). In such cases, giving low homework scores may be unfair.
Since the quantities of time discussed here are totals, teachers in middle and high school should be aware of how much homework other teachers are assigning. It may seem reasonable to assign 30 minutes of daily homework, but across six subjects, that’s three hours—far above a reasonable amount even for a high school senior. Psychologist Maurice Elias sees this as a common mistake: Individual teachers create homework policies that in aggregate can overwhelm students. He suggests that teachers work together to develop a school-wide homework policy and make it a key topic of back-to-school night and the first parent-teacher conferences of the school year.
Parents Play a Key Role
Homework can be a powerful tool to help parents become more involved in their child’s learning (Walker et al., 2004 ). It can provide insights into a child’s strengths and interests, and can also encourage conversations about a child’s life at school. If a parent has positive attitudes toward homework, their children are more likely to share those same values, promoting academic success.
But it’s also possible for parents to be overbearing, putting too much emphasis on test scores or grades, which can be disruptive for children (Madjar, Shklar, & Moshe, 2015 ). Parents should avoid being overly intrusive or controlling—students report feeling less motivated to learn when they don’t have enough space and autonomy to do their homework (Orkin, May, & Wolf, 2017 ; Patall, Cooper, & Robinson, 2008 ; Silinskas & Kikas, 2017 ). So while homework can encourage parents to be more involved with their kids, it’s important to not make it a source of conflict.
Is Homework Good for Kids? Here’s What the Research Says
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.
The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in Texas went viral last week , earning praise from parents across the country who lament the heavy workload often assigned to young students. Brandy Young told parents she would not formally assign any homework this year, asking students instead to eat dinner with their families, play outside and go to bed early.
But the question of how much work children should be doing outside of school remains controversial, and plenty of parents take issue with no-homework policies, worried their kids are losing a potential academic advantage. Here’s what you need to know:
For decades, the homework standard has been a “10-minute rule,” which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 minutes of homework each night. High school seniors should complete about two hours of homework each night. The National PTA and the National Education Association both support that guideline.
But some schools have begun to give their youngest students a break. A Massachusetts elementary school has announced a no-homework pilot program for the coming school year, lengthening the school day by two hours to provide more in-class instruction. “We really want kids to go home at 4 o’clock, tired. We want their brain to be tired,” Kelly Elementary School Principal Jackie Glasheen said in an interview with a local TV station . “We want them to enjoy their families. We want them to go to soccer practice or football practice, and we want them to go to bed. And that’s it.”
A New York City public elementary school implemented a similar policy last year, eliminating traditional homework assignments in favor of family time. The change was quickly met with outrage from some parents, though it earned support from other education leaders.
New solutions and approaches to homework differ by community, and these local debates are complicated by the fact that even education experts disagree about what’s best for kids.
The research
The most comprehensive research on homework to date comes from a 2006 meta-analysis by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper, who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was stronger for older students—in seventh through 12th grade—than for those in younger grades, for whom there was a weak relationship between homework and performance.
Cooper’s analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school, self-discipline, inquisitiveness and independent problem solving skills. On the other hand, some studies he examined showed that homework can cause physical and emotional fatigue, fuel negative attitudes about learning and limit leisure time for children. At the end of his analysis, Cooper recommended further study of such potential effects of homework.
Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing two hours of homework each night, he said, but they also shouldn’t be doing no homework.
Not all education experts agree entirely with Cooper’s assessment.
Cathy Vatterott, an education professor at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, supports the “10-minute rule” as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary school.
“Correlation is not causation,” she said. “Does homework cause achievement, or do high achievers do more homework?”
Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs , thinks there should be more emphasis on improving the quality of homework tasks, and she supports efforts to eliminate homework for younger kids.
“I have no concerns about students not starting homework until fourth grade or fifth grade,” she said, noting that while the debate over homework will undoubtedly continue, she has noticed a trend toward limiting, if not eliminating, homework in elementary school.
The issue has been debated for decades. A TIME cover in 1999 read: “Too much homework! How it’s hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.” The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push for better math and science education in the U.S. The ensuing pressure to be competitive on a global scale, plus the increasingly demanding college admissions process, fueled the practice of assigning homework.
“The complaints are cyclical, and we’re in the part of the cycle now where the concern is for too much,” Cooper said. “You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness.”
Cooper acknowledged that some students really are bringing home too much homework, and their parents are right to be concerned.
“A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements,” he said. “If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- The New Face of Doctor Who
- Putin’s Enemies Are Struggling to Unite
- Women Say They Were Pressured Into Long-Term Birth Control
- Scientists Are Finding Out Just How Toxic Your Stuff Is
- Boredom Makes Us Human
- John Mulaney Has What Late Night Needs
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Katie Reilly at [email protected]

Home » Tools for Your 6-Year-Old » Homework for Your 6-Year-Old
Homework for Your 6-Year-Old
Listen to an audio file of this tool.
Now Is the Right Time!
As a parent or someone in a parenting role, you play an essential role in your 6-year-old child’s success. There are intentional ways to grow a healthy parent-child relationship, and setting up a daily homework routine provides a perfect opportunity.
Children ages 5-10 are in the process of establishing critical learning habits, including how they approach homework, that will extend throughout their school years. For most children, homework is a nightly reality. Children who have a parent or someone in a parenting role involved in supporting learning at home and are engaged in their school community have more consistent attendance, better social skills, and higher grade point averages and test scores than those children without such support. 1 Indeed, the best predictor of students’ academic achievement is parental involvement.
Yet, there are challenges. “I don’t want to do homework. I haven’t had any time to play,” might be a frequent complaint you hear from your seven-year-old. Your child may engage you in power struggles when they have other goals in mind. Their goal – “How can I play longer?” – is typical.
A study by the National Center on Families Learning found that 60% of American families struggle to help children with their homework. 2 More than 25% admit that the reason they struggle is that they are too busy; this is up from just over 20% in 2013. Other reasons parents identified for having trouble with helping with homework were not understanding the subject matter (34%) and pushback from their kids (41%). 3
While getting a regular homework routine going might be a challenge, it can be a joyful experience that promotes valuable skills for school and life success. The steps below include specific, practical strategies along with effective conversation starters to support a homework routine in cooperative ways that avoid a daily struggle.
Why Homework?
Five and six-year-olds will be brand new to the homework experience, and you will have an opportunity to establish positive habits that will stay with them for years to come. Seven, eight, nine, and ten-year-olds will be bringing brand new academic challenges home like reading with competence and learning fractions. Additionally, they may be expected to complete long-term projects. This will take a whole new level of planning and organization. These homework assignments can become a challenge if regular routines are not established. Today, in the short term, establishing effective homework habits will create
- greater cooperation and motivation;
- greater opportunities for connection and enjoyment as you implement your respective roles and feel set up for success;
- trust in each other that you have the competence to complete your responsibilities with practice and care;
- reduced frustrations from a lack of organization, space, or resources; and
- learning about your child’s school curriculum.
Tomorrow, in the long term, homework helps your child
- build skills in collaboration and cooperative goal setting;
- build skills in responsible decision making, hard work, and persistence;
- gains independence, life skills competence, and self-sufficiency; and
- develops positive learning habits that contribute directly to school success.
Five Steps for Creating a Homework Routine
This five-step process helps your family establish a routine for homework. It also builds important skills in your child. The same process can be used to address other parenting issues as well ( learn more about the process ).
These steps are done best when you and your child are not tired or in a rush.
Intentional communication and a healthy parenting relationship support these steps.
Step 1. Get Your Child Thinking by Getting Their Input
You can get your child thinking about establishing a homework routine by asking them open-ended questions. You’ll help prompt your child’s thinking. You’ll also begin to better understand their thoughts, feelings, and challenges related to homework so that you can address them. In gaining input, your child
- has the opportunity to think through the routine and problem solve through any challenges they may encounter ahead of time;
- has a greater stake in anything they’ve designed themselves (and with that sense of ownership, comes a greater responsibility for implementing the routine);
- will have more motivation to work together and cooperate because of their sense of ownership; and
- will be working with you on making informed decisions (understanding the reasons behind those decisions) about a critical aspect of their learning — their homework.
- “How do you want to spend your time after school?”
- “Would you like a snack first?”
- “Do you want to change into play clothes first?”
- “Do you want time to rest or run outside and play?”
- “Considering all of the activities that typically take place after school, when is the best time for you to do homework?”
- Experiment to figure out a plan for homework. Since the homework experience for younger children is new, you’ll want to take a week and try out different times to see what works best with your child’s energy. Your child, for example, may say that they want to get homework done right after school only to find that they’re mentally worn and need a break. So, ask key questions and assign a first trial week. If one way doesn’t work, try out an after-dinner time and ask again: “Does this time work better?” Everyone has different energy cycles and times when they feel better able to focus, so work on discovering that rhythm with your child and you’ll go a long way toward setting them up for success!
- Once you agree upon a time that makes sense for all, your attempts to keep that time sacred and consistent for homework will be important to ensure it becomes a habit and routine. If you are consistent, it can serve as a predictable, non-negotiable process. Your child knows what to expect and when to expect it.
- Take note of the time when your child has said is the best time to do homework. Set a timer to go off at that time. Instead of you calling out, “Time for homework!” which may incite a battle, an inanimate, dispassionate object is alerting them. You can use a kitchen timer outside or inside.
- If your child has decided to do homework right after school, be certain to provide a healthy high protein snack first (peanut butter crackers, cheese stick and apples). You may even consider having this snack ready for the car ride home.
- If you cannot offer a choice in the time of day homework is completed, then find another choice your child can make. For example, you could allow your child to decide what space they use, or what snack they will have to accompany homework completion. Adding some level of choice to the process will prevent power struggles and help your child take ownership.
- a well-lit location (or get a task lamp to light up a preferred spot);
- close proximity to your family’s living space or kitchen (wherever you’ll typically be so that you are never far to offer support); and
- a hard work surface that can get dirty. (Your child may need to color with markers, use glue sticks, cut, and more. Make sure your surface is durable.)
- School supplies: loose leaf paper, crayons, glue sticks, scissors, pencils, pencil sharpener, a children’s dictionary, and any other items you anticipate they might need.
- No clutter. In fact, a disorganized environment can distract from a child’s focus. So eliminate clutter, organize tools, and only have the essentials at hand. Invest in a few supply holders to keep tools neat and ready.
- A binder, bin, or other receptacle designated for school papers that are brought home and stay at home.
- The goal of a homework space is to provide a well-equipped, consistent place for your child to fully focus on the work at hand. In this way, they’ll know what to expect. You won’t have to struggle over frustrations when they can’t find a school tool. And, they’ll learn to take greater responsibility for their learning as they work with you to organize this space.
- Make it fun! Designing a homework spot together can be an enjoyable experience. Allow your child to pick out their own organization bins and school tools. Perhaps they could make a sign with their name on it to designate the space. Or, create a poster with an inspirational saying like, “Good things come from hard work!” Take a little time to label your new supply holders not only with names but also with stickers or drawings to allow your child to personalize them. All this can be motivating to a child.
- Create a family homework rule. Be sure to discuss (at a family dinner, for example) how the family can respect homework time. Consider if you want all siblings to do homework at the same time or not. If you want everyone to do homework at the same time, consider what would need to be in place to make that happen. Either way, agree upon a homework rule that everyone will respect the person who is focused on their work and will be quiet in that area of the house.
Step 2. Teach New Skills by Interactive Modeling
As a parent or someone in a parenting role, learning on which developmental milestones a child is working can help a parent know which tasks might be more difficult. Here are some examples as they relate to homework: 4
- Five-year-olds like to help and follow rules. They typically see only one way of doing things (so if you suggest another, it might be difficult for them to understand and follow). They also may fear making mistakes, so it’s important to send the message that “Everyone makes mistakes, and mistakes are essential to learning.”
- Six-year-olds may be more apt to question your rules and refuse to proceed with the routine. But, they are ambitious and eager to do well, so recognize small steps toward competence.
- Seven-year-olds crave routine and structure, so they may not be able to deal well with a chaotic household distracting from their focus.
- Eight-year-olds are highly social and thrive in cooperative learning groups. This could be a great time to introduce a study partner/friend where buddies complete homework together discussing the issues and supporting one another. (This may not work for every child, so it is important to know your child and their ways of learning and focusing.) Eight-year-olds also may simply enjoy talking about what they are working on with you more than in past years.
- Nine-year-olds are highly competent with fine motor skills but can become easily frustrated. They may need directions that contain one instruction. They require patience and can be hard on themselves.
- Ten-year-olds are growing rapidly so they require more movement. They have a strong sense of right and wrong and awareness of fairness issues. They can feel more competent with homework, though challenging work may trigger anger and/or frustration.
Teaching is different than just telling. Teaching builds basic skills, grows problem-solving abilities, and sets your child up for success. Teaching also involves modeling and practicing the positive behaviors you want to see, promoting skills, and preventing problems.
As a parent or someone in a parenting role, it is easy to be confused about how best to support your child’s homework. Here are some specific ways you can define your role while ensuring your child has full ownership over their learning process.
- “Where in your book did you find this lesson?”
- “Where else could you look to find the answer?”
- “What other ways can you think about your answer?”
- Share your curiosity and interest in the subject, but do not provide an answer.
- Focus on keywords so that they too can learn to spot key words.
- Attempt to read together. Young children who are learning to read may require help reading and understanding directions.
- Use your finger to underscore the text you are reading.
- Ask your child which words are most important when you are talking about a problem.
- Have your child underline or highlight those words in the instructions or in the specific question they are trying to answer so that you have a focusing point. Children need support in figuring out what is most important in making sense out of text of any kind.
- Research together. If you cannot find the source of the problem in your child’s books, then do some online research together. But be certain that you allow your child to drive the process. You might ask, “What should we look up or search for together?” These are the first seeds of strong research skills.
- Teach the essential “brain break.” Breaks do not represent weakness or a lack of persistence. In fact, people’s brains work better if they take frequent breaks.
- Show proactively what a brain break might look like. Pretend play through it. Parent: sit with your pencil and paper and say aloud, “I am really starting to feel frustrated.” Then, move away from your seat and breathe deeply and loudly. Get a drink of water. Walk outside and breathe in the fresh air. Take your child with you to do this alongside you.
- You might ask, “What else makes you feel better and comforted when you are frustrated?” Brainstorm a brief list of spaces, places, things, and actions that offer comfort when frustrated. Leave that list in your school tool homework space. It will serve as an ongoing resource when brain breaks are required.
- It’s a common challenge of homework time for a child to fear making mistakes. Homework is practice, it is intended as a time to try out an answer, get it wrong, and try again. Hang up a sign near your homework spot to remind your child, “Mistakes are part of learning.”
- You do not need to be a subject matter expert EVER! If you find that you are struggling to get the right answer for yourself, take a step back. Realize that you are stealing a learning opportunity away from your child. Ask yourself how you can provide the guidance and support for them to answer the question or solve the problem (even if they get it wrong).
Step 3. Practice to Grow Skills and Develop Habits
Homework practice can take the form of cooperatively completing the task together or trying out a task with you as a coach and ready support. Practice grows vital new brain connections that strengthen (and eventually form habits) each time your child practices.
- Use “Show me…” statements. When a child learns a new ability, they are eager to show it off! Give them that chance. Say: “Show me you know what’s next when our timer goes off.” This can be used when you are in the after school routine and need an alert to move on to homework.
- Do a “brain break” dry run. In the midst of homework one night, maybe at a natural breaking point, play “brain break.” Practice moving away from homework. Get a drink of water. Walk outside and sniff the fresh air. Then, go back and ask, “Do you feel refreshed and ready or do you need a little more time?” If your child responds they need more time, then what would make them feel better? Perhaps a hug on a teddy bear or a couple of runs around the house might do the trick. This practice is super important if you plan to use it as a tool when your child is really upset.
- Recognize effort by using “I notice…” statements. For example, “I noticed how you got to work this afternoon when the timer sounded without me asking. That’s taking responsibility!”
- Proactively remind your child to help them be successful. Often the challenges in a homework routine seem to recur day after day and may be predictable. You might know exactly what they are and when they are going to happen. So, just before they do, remind in a gentle, non-public way. You may whisper in your child’s ear, “Remember what we can do next to figure out the problem? What is it?”
Resist the temptation to nag. Children often need more time to perform tasks that challenge them even if you believe they are simple and don’t require much time. Be sure to wait long enough for your child to show you they are competent. Your waiting could make all the difference in whether they are able to do what you need them to do.
Step 4. Support Your Child’s Development and Success
At this point, you’ve taught your child several new positive learning habits so that they understand how to perform them. You’ve practiced together. Now, you can offer support when it’s needed. Parents naturally offer support as they see their child fumble with a situation in which they need help. This is no different.
- Promote a learning attitude. Show confidence that your child can learn anything with time and practice (because they truly can!). Your comments and reflections will matter greatly in how competent they feel to meet any learning challenge.
- Ask key questions when your child struggles. You could say, “It looks like you feel stuck. Is there another way you could approach the problem?” or “How are you feeling about homework tonight?”
- Coach on communications. You might notice your child struggling and getting stuck even with your support. You might then say, “Seems like you are having trouble figuring this problem out and cannot find the answer in your resources. This would be a good time to ask your teacher about this problem. You might say, ‘Mrs. Johnson, I struggled with this one. Can you help me?’”
- Stay engaged. It can be motivating for a child when a parent does their own paperwork alongside them keeping them company. Working together, after all, is much more enjoyable than working alone.
- Allow for and reflect on real world consequences. If you see a mistake on your child’s worksheet, don’t correct it. You’ll be taking away a valuable learning opportunity. You could leave it alone altogether or ask once, “Do you feel like this is right or are you struggling with it?” If your child confirms it’s the answer they want to give, then allow them the experience of their teacher correcting it. It’s an important learning opportunity. It may open a door to extra support from their teacher.
- Apply logical consequences when needed. Logical consequences should come soon after the negative behavior and need to be provided in a way that maintains a healthy relationship. Rather than punishment, a consequence is about supporting the learning process. First, get your own feelings in check. Not only is this good modeling, when your feelings are in check you are able to provide logical consequences that fit the behavior. Second, invite your child into a discussion about the expectations established in Step 2. Third, if you feel that your child is not holding up their end of the bargain (unless it is a matter of them not knowing how), then apply a logical consequence as a teachable moment.
If you groan that it’s homework time, surely your child will groan too. Become aware of your own reactions to homework. Be sure that the tone and attitude you bring to homework is one of digging in, being curious, and learning.
A research study noted whether mothers’ comments during homework completion were controlling or supporting autonomy and competence. 5 The researchers concluded that those children who brought worries about their ability to perform had a heightened sensitivity to their mothers’ comments. Moms who supported their autonomy – “I know you can do it!” – and demonstrated that they believed in their child’s ability to do the work predicted increased achievement over time. However, those mothers who were more controlling in their comments – “I need to check your work. That’s not right.” – predicted less engagement and lower achievement in their children.
Step 5. Recognize Effort and Quality to Foster Motivation
No matter how old your child is, your praise and encouragement are their sweetest reward.
If your child is working to grow their skills – even in small ways – it will be worth your while to recognize it. Your recognition can go a long way to promoting positive behaviors and helping your child manage their feelings. Your recognition also promotes safe, secure, and nurturing relationships — a foundation for strong communication and a healthy relationship with you as they grow.
You can recognize your child’s efforts with praise, high fives, and hugs. Praise is most effective when you name the specific behavior of which you want to see more. For example, “You put your game away when the timer went off and got out your work. Love seeing that!”
Avoid bribes. A bribe is a promise for a behavior, while praise is special attention after the behavior. While bribes may work in the short term, praise grows lasting motivation for good behavior and effort. For example, instead of saying, “If you get your homework done right after school, I will let you choose the game we play after dinner” (which is a bribe), try recognizing the behavior after. “You got to work on your homework like we practiced. Love seeing that!”
- Recognize and call out when it is going well. It may seem obvious, but it’s easy not to notice when all is moving along smoothly. When children are completing their homework tasks on time, for example, a short, specific call out is all that’s needed. “I noticed you completed your homework today on your own in the time we agreed upon. Yes! Excellent.”
- Recognize small steps along the way. Don’t wait for the big accomplishments – like the entire homework routine to go smoothly – in order to recognize. Remember that your recognition can work as a tool to promote more positive behaviors. Find small ways your child is making an effort and let them know you see them.
- Build celebrations into your routine. For example, “We’ll get our business taken care of first with our homework, and then we’ll run around outside or take a bike ride.” Include hugs as a way to appreciate one another.
Engaging in these five steps is an investment that builds your skills as an effective parent to use on many other issues and builds important skills that will last a lifetime for your child. Throughout this tool, there are opportunities for children to become more self-aware, to deepen their social awareness, to exercise their self-management skills, to work on their relationship skills, and to demonstrate and practice responsible decision making.
[ 1 ] Henderson, A.T., Mapp, K.L., Johnson, V.R., & Davies, D. (2007). Beyond the bake sale: The essential guide to family-school partnerships. NY: The New York Press.
[ 2 ] reid, k. s. (2014). survey finds more parents troubled by their children’s homework . education week, september 19. retrieved on september 25, 2104., [ 3 ] national center for families learning. (2014). annual survey on parents and homework . google consumer surveys, august 12, 2014, to august 22, 2014, based on 1,039 online responses., [ 4 ] wood, c. (2017). yardsticks; child and adolescent development ages 4-14. turners falls, ma: center for responsive schools., [ 5 ] fei-yin ng, f., kenney-benson, g.a., & pomerantz, e.m. (2004). children’s achievement moderates the effects of mothers’ use of control and autonomy support. child development. vol. 75, 3, 764-780., recommended citation: center for health and safety culture. (2020). homework. ages 5-10. retrieved from https://parentingmontana.org..
ParentingMontana.org was supported [in part] by CFDA 93.959 and 93.243 from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), and by the Preschool Development Grant Birth through Five Initiative (PDG B-5), Grant Number 90TP0026-01-00, from the Office of Child Care, Administration for Children and Families, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, and by the Montana State General Fund. The views and opinions contained do not necessarily reflect those of SAMHSA, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, or the Montana Department of Health and Human Services, and should not be construed as such.

Sign up here for updates to ParentingMontana.org.
Connect with a Child Care Resource & Referral Agency in your region
Connect with a montana prevention specialist in your region.
Internet Explorer is no longer supported
Please upgrade to Microsoft Edge , Google Chrome , or Firefox .
Lo sentimos, la página que usted busca no se ha podido encontrar. Puede intentar su búsqueda de nuevo o visitar la lista de temas populares.
Get this as a PDF
Enter email to download and get news and resources in your inbox.
Share this on social
Strategies to make homework go more smoothly.
Routines and incentive systems to help kids succeed
Writer: Peg Dawson, EdD, NCSP
Clinical Expert: Peg Dawson, EdD, NCSP
Here is the best guide to helping kids do homework successfully that we’ve seen, published by the National Association of School Psychologists on their website, NASPonline.org . Our thanks to NASP for sharing it with us.
There are two key strategies parents can draw on to reduce homework hassles. The first is to establish clear routines around homework, including when and where homework gets done and setting up daily schedules for homework. The second is to build in rewards or incentives to use with children for whom “good grades” is not a sufficient reward for doing homework.
Homework Routines
Tasks are easiest to accomplish when tied to specific routines. By establishing daily routines for homework completion, you will not only make homework go more smoothly, but you will also be fostering a sense of order your child can apply to later life, including college and work.
Step 1. Find a location in the house where homework will be done. The right location will depend on your child and the culture of your family. Some children do best at a desk in their bedroom. It is a quiet location, away from the hubbub of family noise. Other children become too distracted by the things they keep in their bedroom and do better at a place removed from those distractions, like the dining room table. Some children need to work by themselves. Others need to have parents nearby to help keep them on task and to answer questions when problems arise. Ask your child where the best place is to work. Both you and your child need to discuss pros and cons of different settings to arrive at a mutually agreed upon location.
Step 2. Set up a homework center. Once you and your child have identified a location, fix it up as a home office/homework center. Make sure there is a clear workspace large enough to set out all the materials necessary for completing assignments. Outfit the homework center with the kinds of supplies your child is most likely to need, such as pencils, pens, colored markers, rulers, scissors, a dictionary and thesaurus, graph paper, construction paper, glue and cellophane tape, lined paper, a calculator, spell checker, and, depending on the age and needs of your child, a computer or laptop. If the homework center is a place that will be used for other things (such as the dining room table), then your child can keep the supplies in a portable crate or bin. If possible, the homework center should include a bulletin board that can hold a monthly calendar on which your child can keep track of longterm assignments. Allowing children some leeway in decorating the homework center can help them feel at home there, but you should be careful that it does not become too cluttered with distracting materials.
Step 3. Establish a homework time. Your child should get in the habit of doing homework at the same time every day. The time may vary depending on the individual child. Some children need a break right after school to get some exercise and have a snack. Others need to start homework while they are still in a school mode (i.e., right after school when there is still some momentum left from getting through the day). In general, it may be best to get homework done either before dinner or as early in the evening as the child can tolerate. The later it gets, the more tired the child becomes and the more slowly the homework gets done.
Step 4. Establish a daily homework schedule. In general, at least into middle school, the homework session should begin with your sitting down with your child and drawing up a homework schedule. You should review all the assignments and make sure your child understands them and has all the necessary materials. Ask your child to estimate how long it will take to complete each assignment. Then ask when each assignment will get started. If your child needs help with any assignment , then this should be determined at the beginning so that the start times can take into account parent availability. A Daily Homework Planner is included at the end of this handout and contains a place for identifying when breaks may be taken and what rewards may be earned.
Incentive Systems
Many children who are not motivated by the enjoyment of doing homework are motivated by the high grade they hope to earn as a result of doing a quality job. Thus, the grade is an incentive, motivating the child to do homework with care and in a timely manner. For children who are not motivated by grades, parents will need to look for other rewards to help them get through their nightly chores. Incentive systems fall into two categories: simple and elaborate.
Simple incentive systems. The simplest incentive system is reminding the child of a fun activity to do when homework is done. It may be a favorite television show, a chance to spend some time with a video or computer game, talking on the telephone or instant messaging, or playing a game with a parent. This system of withholding fun things until the drudgery is over is sometimes called Grandma’s Law because grandmothers often use it quite effectively (“First take out the trash, then you can have chocolate chip cookies.”). Having something to look forward to can be a powerful incentive to get the hard work done. When parents remind children of this as they sit down at their desks they may be able to spark the engine that drives the child to stick with the work until it is done.
Elaborate incentive systems. These involve more planning and more work on the part of parents but in some cases are necessary to address more significant homework problems. More complex incentives systems might include a structure for earning points that could be used to “purchase” privileges or rewards or a system that provides greater reward for accomplishing more difficult homework tasks. These systems work best when parents and children together develop them. Giving children input gives them a sense of control and ownership, making the system more likely to succeed. We have found that children are generally realistic in setting goals and deciding on rewards and penalties when they are involved in the decision-making process.
Building in breaks. These are good for the child who cannot quite make it to the end without a small reward en route. When creating the daily homework schedule, it may be useful with these children to identify when they will take their breaks. Some children prefer to take breaks at specific time intervals (every 15 minutes), while others do better when the breaks occur after they finish an activity. If you use this approach, you should discuss with your child how long the breaks will last and what will be done during the breaks (get a snack, call a friend, play one level on a video game). The Daily Homework Planner includes sections where breaks and end-of-homework rewards can be identified.
Building in choice. This can be an effective strategy for parents to use with children who resist homework. Choice can be incorporated into both the order in which the child agrees to complete assignments and the schedule they will follow to get the work done. Building in choice not only helps motivate children but can also reduce power struggles between parents and children.
Developing Incentive Systems
Step 1. Describe the problem behaviors. Parents and children decide which behaviors are causing problems at homework time. For some children putting homework off to the last minute is the problem; for others, it is forgetting materials or neglecting to write down assignments. Still others rush through their work and make careless mistakes, while others dawdle over assignments, taking hours to complete what should take only a few minutes. It is important to be as specific as possible when describing the problem behaviors. The problem behavior should be described as behaviors that can be seen or heard; for instance, complains about h omework or rushes through homework, making many mistakes are better descriptors than has a bad attitude or is lazy.
Step 2. Set a goal. Usually the goal relates directly to the problem behavior. For instance, if not writing down assignments is the problem, the goal might be: “Joe will write down his assignments in his assignment book for every class.”
Step 3. Decide on possible rewards and penalties. Homework incentive systems work best when children have a menu of rewards to choose from, since no single reward will be attractive for long. We recommend a point system in which points can be earned for the goal behaviors and traded in for the reward the child wants to earn. The bigger the reward, the more points the child will need to earn it. The menu should include both larger, more expensive rewards that may take a week or a month to earn and smaller, inexpensive rewards that can be earned daily. It may also be necessary to build penalties into the system. This is usually the loss of a privilege (such as the chance to watch a favorite TV show or the chance to talk on the telephone to a friend).
Once the system is up and running, and if you find your child is earning more penalties than rewards, then the program needs to be revised so that your child can be more successful. Usually when this kind of system fails, we think of it as a design failure rather than the failure of the child to respond to rewards. It may be a good idea if you are having difficulty designing a system that works to consult a specialist, such as a school psychologist or counselor, for assistance.
Step 4. Write a homework contract. The contract should say exactly what the child agrees to do and exactly what the parents’ roles and responsibilities will be. When the contract is in place, it should reduce some of the tension parents and kids often experience around homework. For instance, if part of the contract is that the child will earn a point for not complaining about homework, then if the child does complain, this should not be cause for a battle between parent and child: the child simply does not earn that point. Parents should also be sure to praise their children for following the contract. It will be important for parents to agree to a contract they can live with; that is, avoiding penalties they are either unable or unwilling to impose (e.g., if both parents work and are not at home, they cannot monitor whether a child is beginning homework right after school, so an alternative contract may need to be written).
We have found that it is a rare incentive system that works the first time. Parents should expect to try it out and redesign it to work the kinks out. Eventually, once the child is used to doing the behaviors specified in the contract, the contract can be rewritten to work on another problem behavior. Your child over time may be willing to drop the use of an incentive system altogether. This is often a long-term goal, however, and you should be ready to write a new contract if your child slips back to bad habits once a system is dropped.
Click here to download the homework planner and incentive sheet .
Was this article helpful?
Explore popular topics, subscribe to our newsletters.
" * " indicates required fields

Don’t Miss Out
Sign up for more articles and parenting tips direct to your inbox.
Welcome, Login to your account.
Recover your password.
A password will be e-mailed to you.
- 6 Tips For Raising a Child Alone as a Single Parent
- Sex, Love & Feelings: How Do Guys Get Emotionally Attached?
- How Do You Define Family? The True Meaning (& Some Definitions) of Family
- Step-Parents: 17 Tips to Balance Your Family and Your Relationship
- Having a Fun Time with Early-Teen Grandchildren (Ages 12-15)
- What’s Wrong With “Mommy Juice” & “Wine-O-Clock” Culture?
- What Are The Positive Effects of Helicopter Parenting?
- Soap for Swearing: Is it Acceptable Today?
- Here’s What You Can Do When Your Partner Doesn’t Want To Have Children
- Step Parent Problems: Advice on Boundaries

Your Age-by-Age Guide to Homework
Are you scared to look in your child’s book bag at the end of the day?
And I’m not talking about the forgotten sandwiches that migrate to the bottom of a full backpack.
I mean the dreaded homework assignments that loom within folders and binders, just waiting to be ignored and fought over for the rest of the evening.
Typically when parents think of the word “homework”, they quickly associate it with the term “fight”.
But homework doesn’t have to be a fight – a struggle at times, yes, but now a full out war.
Understanding what homework looks like at each grade level is a great start to helping support your child in completing their school work.
Also, the earlier you focus on creating an environment of learning and studying, the easier time your child will have as they progress through school.
Here’s your guide on setting up your child for academic success as well as what kind of homework to expect for each grade:
Setting Up For Success
From day one, homework is important in developing good study skills.
In order to encourage your child to complete their homework and take it seriously, you need to establish a proper homework environment .
Here are some tips for setting your child up for homework success:
- Set a regular homework time. Homework should be done at the same time each evening to establish a routine. Just make sure you’re allowing your little one some time to decompress when they get home before jumping into more schoolwork.
- Create a study area. Give your child a place to with proper lighting, materials and few to now distractions.
- Keep an eye on their work. Involve yourself in the process not only by helping them with homework, but monitoring their progress as well.
- Be a role model. While you may not have homework at this stage in your life, you can model good study habits by reading and pursuing your own learning opportunities.
You may think your child is a little Einstein when they start school, but the learning material will progressively get more difficult as they age.
Encouraging good study habits will give them the skills they need to continue their success through school.
Grade-by-Grade Homework Guide
Kindergarten.

When your little one is in kindergarten, it’s likely they won’t have much for homework.
However, you may find the teacher sending home easy tasks such as practicing sight words, letters, numbers and working on patterns.
Since there shouldn’t be a lot of academic expectation from children this young, it’s easy to navigate the homework by making it fun and play-based.
Children learn best through tactile activities, so materials such as PlayDoh can be used to create numbers and letters as well as designing patterns using different colors.
A whiteboard is a great tool to practice what they are learning, especially sight words. Write out the word, have your child read it and let them erase it before moving on to the next one.
Kindergarten homework tends to be pretty repetitive, meaning that your child is likely going to practice the same material each night on a week-to-week basis.
Even if your little one is catching on quick to the material, it’s important to keep up with the homework habit. This is going to help them develop healthy studying habits as they move from grade to grade.
Elementary School: Grades 1 to 2

Once your child moves from kindergarten into grade 1, the learning environment becomes less play-based and more academic.
This doesn’t mean you can’t continue making homework fun! At this age, their focus is still on playing, so you can keep using novel materials when doing homework.
The workload is likely not going to increase during these grades, but the material may become more challenging.
In order to keep homework from becoming too time consuming, you may have to mix straight-up review with play.
Use unique activities when it comes to concepts your child is struggling with and quick reviews for the learning objectives they have easily grasped.
By these grades, teachers typically encourage your child to be reading. This aspect of homework can be delayed until bedtime – which makes reading seem less like “work” and more like a leisurely activity.
Elementary School: Grades 3 to 5

By the time your little one enters grade 3, and until they finish elementary school, they should begin to complete their homework independently.
While it’s important that you remain on standby to help them with difficult concepts, you should be able to set up each homework activity and allow them to complete them on their own.
During this time, students begin to progress from simply practicing basic skills and mastering them onto more complex skills.
This means that homework is going to become more challenging, which is why focusing on a good homework routine during these grades is very important.
If you find your child resisting their homework at this age, there’s nothing wrong with offering an incentive for completing it. Try to stay away from monetary rewards and focus more on fun activities they can engage in once homework is completed.
Remember to not make homework seem like a cumbersome chore – instead, cheer your child on as they work through it. Praise them for doing a good job.
Middle School: Grades 6 to 8

Once your child hits middle school, they should be able to complete their homework assignments on their own.
Homework at this grade level is going to shift more heavily from practicing concepts to completing assignments such as essays and projects.
This is the beginning stages of the foundation of study skills they will need to succeed in high school as well as college or university.
During this time, students are beginning to rely more on technology to complete their assignments. Make sure your child has access to a tablet or computer they can use to conduct research as well as seek help for their homework.
However, it’s important for you to stay involved in their progress. Regular check-ins with their homework will not only help your child stay on track but it will also show them that you want to be involved in their education.
High School: Grades 9 to 12

It’s in high school where a student’s homework load balloons and becomes more time consuming than it was before.
Luckily, kids at these grade levels are able to choose a portion of their courses, so they have a vested interest in what they are learning.
However, with all the changes they are experiencing emotionally and physically, this period of their lives can be extremely stressful.
Maintaining that homework routine is more important now than ever. Stressed-out teens may become overwhelmed with the workload and feel compelled on throwing in the towel on completing homework assignments.
Continue to be supportive by helping them plan and prepare for homework assignments as well as tests and exams .
While you may not be able to help them with the homework material (what is “new” math, anyway?), you can certainly lend a hand when it comes to time management and getting the homework done.
You Can Make the Difference
When left to their own devices, children can’t be expected to take their schoolwork 100% seriously.
It’s your job as the parent to support and guide them through their homework and assignments.
Building good habits now is going to make all the differences as your child progresses through school.
How do you deal with homework hurdles? Share your tips in the comments!
My name is Chelsy and I am a single mother, blogger, and freelance writer. I blog about parenting at Motherhood+Mayhem (motherhoodandmayhem.online) and about working from home at Mama Needs Coffee (mamaneedscoffee.online). When I'm not writing or blogging, you can find me building blanket forts in my living room.
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
7 Easy Ways to Help Your Kids To Finish Their Homework…
404 Not Found
- Subscribers
Top Stories
- Ask the Professor
What is the appropriate age for children to start getting homework?
Debbie leekeenan, director of the eliot-pearson children’s school and a lecturer in the department of child development, fills us in.
“In recent times, there seems to be more homework, especially for our youngest students,” says Debbie LeeKeenan. Photo: iStock
Homework is such an established part of education, it’s hard to believe it’s not all beneficial. But recent studies have found almost no correlation between homework and long-term achievement in elementary school, and only a moderate correlation in middle school.
Yet in recent times, there seems to be more homework, especially for our youngest students. That seems to have led to a backlash. Often-cited negative effects include children’s frustration and exhaustion, lack of time for other activities and downtime and a loss of interest in learning. Many parents lament that homework is a constant source of tension at home.
What is the purpose of homework? The best homework assignments are meaningful and authentic and are connected to classroom learning. Homework can be used to teach time management and organization, to broaden experiences and to reinforce classroom skills. Parents are not expected to play the role of the teacher or introduce new skills.
Homework can certainly benefit students. It may encourage:
Practice and review —such as reading 15 minutes each night, studying spelling words or number facts
Pre-learning —a way to introduce a new topic; for example, if the class will be studying ants, having students write questions they have about ants
Processing —if learning about moon phases in class, students would observe the moon for several nights and draw what they see and identify the phases
Checking for understanding —keeping a journal about science experiments done in class, for instance
How much homework is too much? The idea that “less is more” rules here. According to the National Education Association, guidelines are no more than 10 minutes per grade level per night (that’s 10 minutes total for a first-grader, 30 minutes for a third-grader). Some students do their homework on their own, and some parents help their children. Many teachers now give homework once a week that is due the following week to allow more flexibility and accommodate a range of student and family schedules.
Successful homework experiences have strong home-school partnerships, where the purpose of homework is clearly defined by the teacher and communicated with the student and family. When in doubt, ask!
Do you have a question for Ask the Professor? Send it to Tufts Journal editor Taylor McNeil .
Posted September 01, 2010
Another fine mess.
Fletcher professor exposes the limits of financial models and calls for a return to old-fashioned banking values
The Right Whey
Molly Pindell, N05, took her own path to making scrumptious, sustainable goat cheese
New Accolade for the Dental School
William J. Gies Award recognizes leadership in teaching, research, community service and diversity
Combating a Brand-New Superbug
Biomedical researchers launch a three-front assault on a potentially lethal bacterium
Pow! Women Pop Artists Get Their Day
SLIDESHOW: New Tufts Art Gallery exhibition highlights works hidden in the shadows for decades
From The Archives
The spark of revolt, february 16, 2011, when health care is lost in translation, record applications for fall, january 31, 2011, dental force, january 18, 2011, rough and ready vaccine, people notes, accomplishments from the tufts community.
Catch up with events at Tufts
Send us your comments and story ideas
Keep up with our news via RSS
© Copyright 2011 Tufts University
Home / Expert Articles / Child Behavior Problems / School & Homework
The Homework Battle: How to Get Children to Do Homework
By debbie pincus, ms lmhc.

Parents often feel it’s their job to get their kids to do well in school. Naturally, you might get anxious about this responsibility as a parent. You might also get nervous about your kids succeeding in life—and homework often becomes the focus of that concern.
But when parents feel it’s their responsibility to get their kids to achieve, they now need something from their children—they need them to do their homework and be a success. I believe this need puts you in a powerless position as a parent because your child doesn’t have to give you what you want.
The battle about homework becomes a battle over control. Your child starts fighting to have more control over the choices in their life, while you feel that your job as a parent is to be in control of things. So you both fight harder, and it turns into a war in your home.
Over the years, I’ve talked to many parents who are in the trenches with their kids, and I’ve seen firsthand that there are many creative ways kids rebel when it comes to schoolwork. Your child might forget to do their homework, do their homework but not hand it in, do it sloppily or carelessly, or not study properly for their test. These are just a few ways that kids try to hold onto the little control they have.
When this starts happening, parents feel more and more out of control, so they punish, nag, threaten, and argue. Some parents stop trying altogether to get their children to do homework. Or, and this is common, parents will over-function for their kids by doing the work for them.
Now the battle is in full swing: reactivity is heightened as anxiety is elevated—and homework gets lost in the shuffle. The hard truth for parents is that you cannot make your children do anything, let alone homework. But what you can do is to set limits, respect their individual choices, and help motivate them to motivate themselves.
You might be thinking to yourself, “You don’t know my child. I can’t motivate him to do anything.” Many parents tell me that their children are not motivated to do their work. I believe that children are motivated—they just may not be motivated the way you’d like them to be. Keep reading for some concrete tips to help you guide them in their work without having to nag, threaten, or fight with them.

Also, keep in mind that if you carry more of the worry, fear, disappointments, and concern than your child does about their work, ask yourself, “What’s wrong with this picture, and how did this happen?” Remember, as long as you carry their concerns, they don’t have to.
Stop the Nightly Fights
The way you can stop fighting with your kids over homework every night is to stop fighting with them tonight. Disengage from the dance. Choose some different steps or decide not to dance at all. Let homework stay where it belongs—between the teacher and the student. Stay focused on your job, which is to help your child do their job. Don’t do it for them.
If you feel frustrated, take a break from helping your child with homework. Your blood pressure on the rise is a no-win for everyone. Take five or ten minutes to calm down, and let your child do the same if you feel a storm brewing.
Create Structure Around Homework Time
Set limits around homework time. Here are a few possibilities that I’ve found to be effective with families:
- Homework is done at the same time each night.
- Homework is done in a public area of your house.
- If grades are failing or falling, take away screen time so your child can focus and have more time to concentrate on their work.
- Make it the rule that weekend activities don’t happen until work is completed. Homework comes first. As James Lehman says, “The weekend doesn’t begin until homework is done.”
Let Your Child Make Their Own Choices
I recommend that your child be free to make their own choices within the parameters you set around schoolwork. You need to back off a bit as a parent. Otherwise, you won’t be helping them with their responsibilities.
If you take too much control over the situation, it will backfire on you by turning into a power struggle. And believe me, you don’t want a power struggle over homework. I’ve seen many kids purposely do poorly just to show their parents who’s in charge. I’ve also seen children who complied to ease their parents’ anxiety, but these same kids never learned to think and make choices for themselves.
Let Your Child Own the Consequences of Their Choices
I’m a big believer in natural consequences when it comes to schoolwork. Within the structure you set up, your child has some choices. They can choose to do their homework or not. And they can choose to do it well and with effort or not. The natural consequences will come from their choices—if they don’t choose to do their work, their grades will drop.
When that happens, you can ask them some honest questions:
“Are you satisfied with how things are going?”
“What do you want to do about your grade situation?”
“How can I be helpful to you?”
Be careful not to be snarky or judgmental. Just ask the question honestly. Show honest concern and try not to show disappointment.
Intervene Without Taking Control
The expectation is that homework is done to the best of your child’s ability. When they stop making an effort, and you see their grades drop, that’s when you invite yourself in. You can say:
“It’s my job to help you do your job better. I’m going to help you set up a plan to help yourself, and I will check in to make sure you’re following it.”
Set up a plan with your child’s input to get them back on their feet. For example, the new rules might be that homework must be done in a public place in your home until they get their grades back up. You and your child might meet with the teacher to discuss disciplinary actions should their grades continue to drop.
In other words, you will help your child get back on track by putting a concrete plan in place. And when you see this change, you can step back out of it. But before that, your child is going to sit in a public space and you’re going to monitor their work.
You’re also checking in more. Depending on your child’s age, you’re making sure that things are checked off before they go out. You’re adding a half-hour of review time for their subjects every day. And then, each day after school, they’re checking with their teacher or going for some extra help.
Remember, this plan is not a punishment—it’s a practical way of helping your child to do their best.
“I Don’t Care about Bad Grades!”
Many parents will say that their kids just don’t care about their grades. My guess is that somewhere inside, they do care. “I don’t care” also becomes part of a power struggle.
In other words, your child is saying, “I’m not going to care because you can’t make me. You don’t own my life.” And they’re right. The truth is, you can’t make them care. Instead, focus on what helps their behavior improve. And focus more on their actions and less on their attitude because it’s the actions that matter the most.
Motivation Comes From Ownership
It’s important to understand that caring and motivation come from ownership. You can help your child be motivated by allowing them to own their life more.
So let them own their disappointment over their grades. Don’t feel it more than they do. Let them choose what they will do or not do about their homework and face the consequences of those choices. Now they will begin to feel ownership, which may lead to caring.
Let them figure out what motivates them, not have them motivated by fear of you. Help guide them, but don’t prevent them from feeling the real-life consequences of bad choices. Think of it this way: it’s better for your child to learn from those consequences at age ten by failing their grade and having to go to summer school than for them to learn at age 25 by losing their job.
When Your Child Has a Learning Disability
I want to note that it’s very important that you check to see that there are no other learning issues around your child’s refusal to do homework. If they’re having difficulty doing the work or are performing below grade-level expectations, they should be tested to rule out any learning disabilities or other concerns.
If there is a learning disability, your child may need more help. For example, some kids need a little more guidance; you may need to sit near your child and help a little more. You can still put structures into place depending on who your child is.

But be careful. Many times, kids with learning disabilities get way too much help and develop what psychologists call learned helplessness . Be sure you’re not over-functioning for your learning disabled child by doing their work for them or filling in answers when they’re capable of thinking through them themselves.
The Difference Between Guidance and Over-Functioning
Your child needs guidance from you, but understand that guidance does not mean doing their spelling homework for them. Rather, it’s helping them review their words. When you cross the line into over-functioning, you take on your child’s work and put their responsibilities on your shoulders. So you want to guide them by helping them edit their book report themselves or helping them take the time to review before a test. Those can be good ways of guiding your child, but anything more than that is taking too much ownership of their work.
If your child asks for help, you can coach them. Suggest that they speak with their teacher on how to be a good student and teach them those communication skills. In other words, show them how to help themselves. So you should not back off altogether—it’s that middle ground that you’re looking for. That’s why I think it’s essential to set up a structure. And within that structure, you expect your child to do what they have to do to be a good student.
Focus on Your Own Goals
When you start over-focusing on your child’s work, pause and think about your own goals and what do you need to get done to achieve those goals. Model your own persistence and perseverance to your child.
Believe In Your Child
I also tell parents to start believing in their children. Don’t keep looking at your child as a fragile creature who can’t do the work. I think we often come to the table with fear and doubt—we think if we don’t help our kids, they’re just not going to do it.
But as much as you say, “I’m just trying to help you,” what your child hears is, “You’re a failure; I don’t believe you can do it on your own.”
Instead, your message should be, “I know you can do it. And I believe in you enough to let you make your own choices and deal with the consequences.”
Related content: What Can I Do When My Child Refuses to Go to School? “My Child Refuses to Do Homework” — How to Stop the Nightly Struggle Over Schoolwork
For more information on the concept of learned helplessness in psychology and behavior, we recommend the following articles:
Psychology Today: Learned Helplessness
VeryWell Mind: What Is Learned Helplessness and Why Does it Happen?
About Debbie Pincus, MS LMHC
For more than 25 years, Debbie has offered compassionate and effective therapy and coaching, helping individuals, couples and parents to heal themselves and their relationships. Debbie is the creator of the Calm Parent AM & PM™ program and is also the author of numerous books for young people on interpersonal relations.
You must log in to leave a comment. Don't have an account? Create one for free!
Frank My daughter Nina just turned 8 (Feb 11). She does not like to do homework one bit. Her teacher gives her homework every day except Friday. She loves Fridays because she doesn't like homework. She always hides her homework under her bed, refuses to do her homework, and in the More morning she tells her teacher "I lost it last night and can't find it!". She feels homework is a waste of time, yes, we all feel that way, but poor Nina needs to learn that homework is important to help you stay smart. She needs to start doing homework. How can I make her 2nd-grade brain know that homework is actually good? Is there a way to make her love, love, LOVE homework? Let me know.
Rebecca Wolfenden, Parent Coach We appreciate you writing in to Empowering Parents and sharing your story. Because we are a website aimed at helping people become more effective parents, we are limited in the advice and suggestions we can give to those outside of a direct parenting role. In addition to the tips in More the article above, it may be helpful to look into local resources to help you develop a plan for addressing these particular issues with your cousins, such as their doctor or their teachers. We wish you the best going forward. Take care.
Rebecca Wolfenden, Parent Coach I hear you. Homework can be a challenging, frustrating time in many families even under the best of circumstances, so you are not alone. When kids struggle with a subject, it can be even more difficult to get assignments completed. Although you didn’t indicate that your daughter More has ADHD, you might find some helpful tips in Why School is Hard for Kids with ADHD—and How You Can Help . Author Anna Stewart outlines techniques that can be useful to help make homework more interesting for kids with a variety of learning challenges in this article. You might also consider checking in with your daughter’s teacher, as s/he might have some additional ideas for engaging your daughter in her homework. Please be sure to write back and let us know how things are going for you and your family. Take care.
So, after reading this I get to say…GREAT…You really do not know my child. We have done 100% of everything listed in this article. In the end, my son has utterly declared “I DON’T CARE, AND I DON’T NEED SCHOOL”. We have attempted a “reward” system as well, and that doesn’t work. He cares about 3 or 4 things. Nintendo DS, Lego, K’Nex, TV…all of those he has lost over the past year. Now he reads, ALL the time. Fine, but that doesn’t get his homework done. It also doesn’t get anything else he needs to do done. We’ve done “task boards”, we’ve done “Reward Systems”, we’ve done the “What is on your list to complete”. EVERYTHING is met with either a full fledged meltdown (think 2 year old…on the floor, kicking and screaming and crying). His IMMEDIATE response to ANYTHING that may interrupt him is “NO” or worse. If something doesn’t go his way directly he throws a fit INSTANTLY, even if the response is “Give me a second” it’s NOW OR I’M DESTROYING SOMETHING. He’s been suspended multiple times for his anger issues, and he’s only 10. Unfortuantely we have no family history as he was adopted from Russia. His “formal” diagnosis are ADHD and Anxiety. I’m thinking there is something much more going on. BTW: He did have an IQ test and that put him at 145 for Spacial and Geometric items, with a 136 for written and language. His composite was 139, which puts him in the genius category, but he’s failing across the board…because he refuses to do the work.
Interesting article and comments. Our son (6th grade) was early diagnosed as ADHD and for the first 3 years of elementary school several of his teachers suggested he might require special education. But then the school counseling staff did a workup and determined that his IQ is 161 and from that point forward his classroom antics were largely tolerated as “eccentric”. He has now moved to middle school (6th grade) and while his classroom participation seems to be satisfactory to all teachers, he has refused to do approximately 65% of his homework so far this school year. We have tried talking with him, reasoning with him, removing screen time, offering cash payments (which he lectures us as being unethical “bribes”), offering trips, offering hobbies and sporting events, and just about anything we can think of. Our other children have all been through the “talented and gifted” programs, but he simply refuses to participate in day-to-day school work. His fall report card was pretty much solid “F” or “O” grades. He may be bored out of his mind, or he may have some other issues. Unfortunately, home schooling is not an option, and neither is one of the $40,000 per year local private schools which may or may not be in a better position to deal with his approach to school. Do “learning centers” work for kids like this? Paying somebody else to force him to do his homework seems like a coward’s solution but I am nearly at the end of my rope! Thanks..
RebeccaW_ParentalSupport 12yokosuka Many parents struggle with staying calm when their child is acting out and screaming, so you are not alone. It tends to be effective to set up a structured time for kids to do their homework and study, and they can earn a privilege if they comply and meet More their responsibilities. What this might look like for your daughter is that if she studies, she can earn her phone that day. If she refuses, and chooses to argue or scream at you instead, then she doesn’t earn her phone that day and has another chance the next day. You can read more about this in https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/end-the-nightly-homework-struggle-5-homework-strategies-that-work-for-kids/. If you are also looking for resources to help you stay calm, I encourage you to check out our articles, blogs, and other resources on https://www.empoweringparents.com/article-categories/parenting-strategies-techniques/calm-parenting/. Please let us know if you have any additional questions. Take care.
Scott carcione
I’m sorry to hear about the challenges you are experiencing with your
son.I also hear the different
approaches you and your ex are taking toward parenting your son.While it would be ideal if you were able to
find common ground, and present a consistent, united response to your son’s
choices, in the end, you can only https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/parenting-after-divorce-9-ways-to-parent-on-your-own-terms/.At
this point, it might be useful to meet with the school to discuss how you can
work together to hold your son accountable for his actions, such as receiving a
poor grade if he refuses to do his work.Janet Lehman discusses this more in https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/when-your-child-has-problems-at-school-6-tips-for-parents/.Take care.
It can be so challenging when your child is acting out at school, yet does
not act that way at home.One strategy I
recommend is talking with your son at home about his behavior at school.During this conversation, I encourage you to
address his choices, and come up with a specific plan for what he can do differently
to follow the rules.I also recommend
working with his teachers, and discussing how you can assist them in helping
your son to follow the rules.You might
find additional useful tips in our article, https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/acting-out-in-school-when-your-child-is-the-class-troublemaker/.Please be sure to write back and let us know
how things are going for you and your son.Take care.
I hear you.It can be so challenging
when your young child is having outbursts like this.A lot of young children tend to act out and
have tantrums when they are experiencing a big transition, such as starting a
new school or adjusting to having a younger sibling, so you are not alone.Something that can be helpful is to set up
clear structure and expectations around homework, as Janet Lehman points out in
https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/my-child-refuses-to-do-homework-heres-how-to-stop-the-struggle/.I also encourage you to set aside some time
for you to have https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/attention-seeking-behavior-in-young-children-dos-and-donts-for-parents/ with your daughter as well.Please be sure to write back and let us know
how things are going for you and your family.Take care.
JoJoSuma I am having the exact same problem with my 9 year old son. His grades are quickly falling and I have no idea why or where to begin with helping him turn things around. When he applies himself he receives score of 80% or higher, and when he doesn't it clearly shows and he receives failing scores. He, too, says that he doesn't do or want to do the work because it is boring, or that he "Forgot" or "lost it". He has started to become a disruption to the class and at this rate I am afraid that he will have to repeat 5th grade. I am also a single parent so my frustration is at an all time high. You are not alone and I wish you and your family the best.
Thank you so much for these tips RebeccaW_ParentalSupport because I SERIOUSLY had nowhere to turn and no clue where to begin. I have cried many nights feeling like I was losing control. I will try your tips and see where things go from here.
It’s not uncommon
for kids to avoid doing homework, chores or other similar tasks. After
all, homework can be boring or difficult, and most people (both kids and adults
alike) tend to prefer activities which are enjoyable or fun. This does
not mean that you cannot address this with your daughter, though.
Something which can be helpful for many families is to set up a structured
homework time, and to require that your daughter complete her homework in order
to earn a privilege later on that evening. You can read about this, and
other tips, in https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/end-the-nightly-homework-struggle-5-homework-strategies-that-work-for-kids/.
Please be sure to write back and let us know how things are going for you and
your daughter. Take care.
Thestruggleisreal I'm just now signing up for these articles, I'm struggling with my 12 year and school work, she just doesn't want to do it, she has no care I'm world to do, she is driving me crazy over not doing, I hate to see her More fail, but I don't know what to do
FamilyMan888
I can hear how much your
daughter’s education means to you, and the additional difficulties you are
facing as a result of her learning disabilities. You make a great point
that you cannot force her to do her work, or get additional help, and I also
understand your concern that getting her teachers to “make” her do these things
at school might create more conflict there as well. As James Lehman
points out in his article, https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/stop-the-blame-game-how-to-teach-your-child-to-stop-making-excuses-and-start-taking-responsibility/, lowering your expectations for your daughter due to her
diagnosis is probably not going to be effective either. Instead, what you
might try is involving her in the https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/the-surprising-reason-for-bad-child-behavior-i-cant-solve-problems/, and asking her what she thinks she needs, and what she will do
differently, to meet classroom expectations. Please be sure to write back
and let us know how things are going for you and your family. Take care.
tvllpit Very effective to kids age of 5, 7, and 11 years old. Thank you for sharing your idea.
Thank you for
your question. You are correct that we recommend setting up a structured
time for kids to do homework, yet not getting into a power struggle with them
if they refuse to do their work during that time. It could be useful to
talk with your 11 year old about what makes it difficult to follow through with
doing homework at that time, and perhaps experimenting with doing homework at
another time to see if that works more effectively. In the end, though,
if your child is simply refusing to do the work, then we recommend giving a
consequence and avoiding a power struggle. Megan Devine details this
process more in her article, https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/end-the-nightly-homework-struggle-5-homework-strategies-that-work-for-kids/.
Please let us know if you have any additional questions. Take care.
jovi916 I'm a mother to a 10 year old 5th grader. Since 3rd grade I've been struggling with homework. That first year, I thought it was just lack of consistency since my children go between mine and dad's house. I tried setting some sort of system up with More the teacher to get back on track, but the teacher said it was the child's responsibility to get the hw done. This year has been esp. Difficult. He stopped doing hw, got an F, so I got on him. He stared turning half done work, but same grades so I still got on him. Grades went up, I loosened up, then he stopped with in school work. Now it's back to not turning anything in, even big projects and presentations. He had never really been allowed to watch tv, but now it's a definite no, I took his Legos away, took him out of sports. Nothing is working. He's basically sitting at the table every night, and all weekend long in order to get caught up with missing assignments. I'm worried, and next year he'll be in middle school. I try setting an example by studying in front of him. My daughter just does her homework and gets good grades. Idk what to do.
I can hear your concern. Academic achievement is important
to most parents and when your children seem to be struggling to complete their
work and get good grades, it can be distressing. Ultimately, your childrens’
school work and grades are their responsibility. You shouldn’t have to quit
your own studies in order to help them improve theirs. The above article gives
some great tips for helping motivate your children to complete their homework.
We do have a couple other articles you may also find useful: https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/10-ways-to-motivate-your-child-to-do-better-in-school/ & https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/sinking-fast-at-school-how-to-help-your-child-stay-afloat/. We appreciate you
writing in and hope you find the information useful. Take care.
RNM I have the exact same issues with my 8 year old. It makes me feel like I'm doing something wrong. He's a smart kid, he just doesn't seem to care to do his homework let alone if he gets a bad grade as a result. He hates reading, but does More very well in spelling and science. Homework is an issue nightly and the teacher pulled me aside today to tell me again how much he talks in class and that now he isn't writing down his assignments and is missing 3 assignments this week. SMH, I don't know what to do anymore other than to coach him (some more) and take away basketball if he doesn't do his homework.
What? "Let homework stay where it belongs—between the teacher and the student. Refuse to get pulled in by the school.." I do not see the logic or benefit of this advice. Homework, by definition, is the responsibility of the student and parent (NOT the teacher). The teacher does not live at the student's home or run the house.
In my opinion, the lack of parental involvement with academics often causes the low student performance evident across the U.S. I do not agree with advocating for even LESS parental involvement.
I completely agree with you. Parental, or adult, engagement at home can be a deal-maker/breaker when it comes to student performance. I subscribe to theories that differ from the author's.
First, if an adult is involved with the child and his activities, then the child will commonly react with "hey, somebody cares about me" leading to an increased sense of self-worth. A sense of caring about one's-self leads to caring about grades and other socially acceptable behaviors (Maslow).
Secondly, I am a FIRM believer in the techniques of behavior modification through positive reinforcement (Karen Pryor). It's up to an invested adult to determine what motivates the student and use those motivators to shape and reinforce desirable behavior such as daily homework completion. A classroom teacher has too many students and too little time to apply this theory.
Letting a child sink or swim by himself is a bad idea. Children have only one childhood; there are no do-overs.
And yes, children are work.
Many experience similar feelings of being at fault when
their child fails, so, you’re not alone. Truth of the matter is, allowing your
child to experience natural consequences of their actions by allowing them to
fail gives them the opportunity to look at themselves and change their
behavior. We have a couple articles I think you may find helpful: When You Should Let Your Child Fail: The Benefits of Natural Consequences & 5 Natural Consequences You Should Let Your Child Face . Good luck to you and
your family moving forward. Take care.
hao hao It is so true, we can't control our children's home. It is their responsibility. But they don't care it. What can we do it?
indusreepradeep
How great it is that you want to help your brother be more
productive with his homework. He’s lucky to have a sibling who cares about him
and wants him to be successful. Because we are a website aimed at helping
parents develop better ways of managing acting out behavior, we are limited in
the advice we can offer you as his sibling. There is a website that may be able
to offer you some suggestions. http://www.yourlifeyourvoice.org/
is a website aimed at helping teens and young adults figure out ways of dealing
with challenges they may be facing in their lives. They offer several ways of
getting support, such as by e-mail or text, through an online forum and chat,
and also a call in helpline. You can check out what they have to offer at http://www.yourlifeyourvoice.org/. Good luck
to you and your family moving forward. Take care.
Kathleenann indusreepradeep
Thank you so much for your humble support....
It sounds like you have done a lot
of work to try to help your daughter achieve her educational goals, and it’s
normal to feel frustrated when she does not seem to be putting in the same
amount of effort. It can be useful to keep your focus on whether your
daughter is doing her work, and to keep that separate from whether she “cares”
about doing her work. Ultimately, it is up to your daughter to do her
work, regardless of how she appears to feel about it. To that end, we
recommend working with the various local supports you have in place, such as
her therapists and others on her IEP team, to talk about what could be useful
to motivate your daughter to do her school work. Because individuals with
autism can vary greatly with their abilities, it’s going to be more effective
to work closely with the professionals who are familiar with your daughter’s
strengths and level of functioning in order to develop a plan to address this
issue. Thank you so much for writing in; we wish you and your daughter
all the best as you continue to address her difficulties with school.
is there a blog for parents that went to Therapeutic boarding schooling for their adolescent?
Responses to questions posted on EmpoweringParents.com are not intended to replace qualified medical or mental health assessments. We cannot diagnose disorders or offer recommendations on which treatment plan is best for your family. Please seek the support of local resources as needed. If you need immediate assistance, or if you and your family are in crisis, please contact a qualified mental health provider in your area, or contact your statewide crisis hotline.
We value your opinions and encourage you to add your comments to this discussion. We ask that you refrain from discussing topics of a political or religious nature. Unfortunately, it's not possible for us to respond to every question posted on our website.
- 1. What to Do When Your Child or Teen is Suspended or Expelled From School
- 2. "My Child Refuses to Do Homework" — How to Stop the Nightly Struggle Over Schoolwork
- 3. Acting Out in School: When Your Child is the Class Troublemaker
- 4. Young Kids in School: Help for the Top 4 Behavior Problems
- 5. When Your Child Has Problems at School: 6 Tips for Parents
- 140,000+ Subscribers Subscribe
- 50,000+ Fans Follow
- 10,000+ Followers Follow
- 6,000+ Followers Follow
Disrespect... defiance... backtalk... lack of motivation...
Frustrated and exhausted by your child's behavior?
Get your FREE Personal Parenting Plan today.
Does your child exhibit angry outbursts , such as tantrums, lashing out, punching walls, and throwing things?
Would you like to learn about how to use consequences more effectively?
Backtalk... complaints... arguments... attitude... just plain ignoring you
Do you struggle with disrespect or verbal abuse from your child?
Has your child been diagnosed with oppositional defiant disorder (ODD)?
Or does your child exhibit a consistent and severe pattern of anger, irritability, arguing, defiance, and vindictiveness toward you or other authority figures?
Intimidation... aggression... physical abuse and violence ...
Are you concerned that your child may physically hurt you or others?
You must select at least one category to create your Personal Parenting Plan:
We're just about finished! Create a secure account with Empowering Parents to access your Personal Parenting Plan.
How to Help a 6-Year-Old With Homework

Helping your 6-year-old child with homework should be pretty elementary, right? Well, it can be, and you won't need a lengthy study guide to pass the quiz. If resisting the temptation to supply more than paper and pencils to your little scholar proves challenging, consider some of the reasons her teacher assigns the homework in the first place. Sure, your child gains practice with new skills taught in the classroom, and her teacher gains perspective about who struggles with the skills, but there's more to think about than a review of daily classroom curriculum. Here's how to help without doing.
Weigh the Rewards
Yes, the immediate goal of turning in a homework assignment is to receive a good grade -- no argument there. But did you know that homework teaches your 6-year-old skills she can use beyond the present moment and environment? Homework helps your child to understand a relationship between her choices and consequences. Children learn about managing time, prioritizing tasks and doing their best. Self-confidence grows from doing a good job, and doing it independently. Children receive more than good grades when loving moms provide positive support for homework tasks instead of the correct answers.
RELATED: Making Teen Boys Do Their Homework
Establish a Routine
You've set up routines for meals, snacks, bathing and bedtime. Don't stop now. You know that routines provide children with a predictable set of events and expectations associated with daily life. Your child does not have to guess or connect imaginary dots to know what happens now and what will follow. Establishing a routine for homework establishes when, where and how the homework will be completed and defines your role in supporting your child's efforts.
Set the Scene
Unlike an older sibling who may prefer completing homework in her room, your 6-year-old will work best when you are in close proximity. Designate a quiet work area that provides adequate lighting. Let your child decorate a box that will hold homework supplies such as paper, pencils, glue and crayons. Keeping in mind that your child will need a snack and "reconnect to mom" time before beginning her homework, schedule a time for homework and stick to it. Give yourself a gold star for providing a place, a time to work and lots of supplies.
RELATED: The Most Expensive Schools in America
Keep It Positive
Ensure that your child understands the instructions associated with the homework assignment, and then be available to field questions, provide suggestions or reframe a problem to offer an additional perspective. Praise her efforts, even when the going gets a bit bumpy. Encourage your child to work independently, but be accessible when she has problems. Intervene if you observe that your child appears overwhelmed or agitated by suggesting a break. Your child will learn to shine in a starring role when you choose to assume a supporting part in her homework routine.
Model Lifelong Learning
You are an influential role model, so do your homework. Model and share your love for learning with your child. Demonstrate the application of learning to real-life events by reading a book, computing the cost of a grocery list or reviewing your email. Discuss with enthusiasm how you have continued to learn new things as an adult, and how learning continues to enrich your life.
Becky Swain's first publication appeared in the "Journal of Personality Assessment" in 1984. Her articles have also appeared on various websites. She is an adjunct college instructor, licensed school psychologist and educational consultant. She holds a Master of Science in clinical psychology and a Doctor of Philosophy in educational psychology, both from Mississippi State University.
Around the Web
Ein Einfacher Trick Gegen Gelenkschmerzen

23 Chilling Childhood Photos of the Worlds Most Evil People

This Video Will Soon Be Banned. Watch Before It's Deleted

Want your content to appear on sites like this?
Want to report this publisher's content as misinformation.
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- Knowledge Base
- Math for kids
Common Topics in Math for 6-Year-Olds to Learn
Created on Apr 18, 2022
Updated on January 5, 2024

Math isn’t new for six-year-olds since they will likely have learned basic counting and number identification before that. As kids develop confidence in playing with numbers, parents, and tutors can introduce them to more complicated concepts. The article will throw light on some topics that will make children more proficient in math.
Math Topics to Boost 6-Year-Olds’ Math Skills
The ability to tell the time is necessary in our daily lives, yet it may be difficult for kids to master. You should first help your kids understand how time relates to their lives before teaching them to interpret it. With simple activities and games, children will develop an awareness of the passage of time from a young age.
Kids learn about time and seasonal changes throughout their school years. Six-year-olds memorize the hour and half-hour markings of a clock and are able to tell how many minutes comprise an hour and how many hours are in a day. Also, they get to differentiate between the “quarter to” and “half past” concepts. With the help of top math learning sites like Brighterly and math games for 6-year-olds, your child’s time-telling skills will improve.
Educating your kids about money is essential in preparing them for life in the real world. You can introduce physical money, worksheets, or money math games for 6-year-olds to practice skills and enhance their understanding of the concept. Brighterly’s money games, virtual coins, and other activities involving the concept can help your kids learn about money in a fun way.
At six years, pupils should be able to recognize monetary denominations and sum currencies in coin and bill form. Combining whole dollars and cents may be difficult for six-year-olds; however, with constant practice, your kids will appreciate the financial applications of math.
Addition and Subtraction
When teaching addition and subtraction concepts to kids, you should start with addition first. Most children understand the idea of gaining better than losing, thanks to the interactions with their parents and toys in their toddler years. When they get comfortable with addition, introduce them to subtraction.
But don’t take away toys as a way to teach kids subtraction since the approach can fuel resentment toward learning in children. Instead, use math worksheets for 6-year-olds or play games that subtly teach subtraction and addition. Also, don’t forget about the importance of repetition as a system for reinforcing ideas you’ve introduced to children.
Counting is among the basic math skills 6-year-olds should master, as it paves the way for other math topics on this list. Six-year-olds can count to a great extent, often up to 200, which reveals the vastness of numbers to kids. Counting as a math concept forms the foundation for a more complex mathematics for 6 year old that the your may face in the future. When the kids practice more, they improve their 6 year old math skills.
You can use counting along with your day-to-day activities or just use simple math games. To help your 6 year old struggling with maths, and make them enjoy counting, use math toys or other attractive colorful items. They can arrange items in a line and stand facing the items, counting them aloud from 1 to 10 first before they move to double-digit numbers.
Add fascinating and complex exercises like backward counting to your math for 6-year-olds curriculum. You can use a simple range, like having them count from 10 down to 1 or from 20 to 1. Don’t go above 50 so that the activity won’t get too complex and tedious for the students
Fractions should be more of a visual concept for children than a written one. For example, children may be unable to comprehend what ⅚ means on paper. But they will have no trouble understanding it when you explain that if they eat five slices of pizza out of a six-sliced pizza, they have consumed ⅚th of the whole pizza.
Before moving to more complex fractions, make sure your youngster understands basic fractions such as a half, a whole, and smaller fractions like ⅓, ⅔, etc. Halves (½) and wholes (1) are concepts children quickly grasp with the help of everyday activities. You can help your kids learn the concept of fractions by describing relatable scenarios, like how two half-glasses of Coke produce a full glass.
Geometry is one of the central themes that six-year-old kids should understand because of its prevalence in daily life. Shapes around us are often in 2D or 3D forms, but six-year-olds won’t know the difference without your help. Make it easy for your kids to recognize basic shapes like cylinders, rectangles, squares, circles, and triangles.
If you want to make your 6-year-old understand geometry better, you can try games where kids try to identify different shapes. A better way to do this is to get involved by showing them shapes you see on everyday objects and asking them to call the shape the image reminded them of. You can then teach them to draw the shapes and show them how different they are.
Another way you can make this happen is by teaching your kids craft-making. You can ask your child to cut a triangular object from a magazine, and then you will draw the real shapes on a cardboard and tell your 6 year old math learner to point to which shape their cut-out is. This is a very creative way for your kids to learn shapes and geometry as part of the 6th grade math curriculum.
Conclusion
Maths for a 6 year old can be very challenging because, let’s face it, a lot of numbers and symbols don’t make any sense at the beginning. So it is not out of place that your 6 year old mathematics learner will look to you for help. It is your job to help them figure out this new terrain.
These steps above are geared towards teaching you how to teach 6 year old maths. You can use math manipulatives for a more hands-on approach, but the knowledge of fundamental math topics you need to focus your efforts on is the first step to building your child’s interest in math.

Jessica is a a seasoned math tutor with over a decade of experience in the field. With a BSc and Master’s degree in Mathematics, she enjoys nurturing math geniuses, regardless of their age, grade, and skills. Apart from tutoring, Jessica blogs at Brighterly. She also has experience in child psychology, homeschooling and curriculum consultation for schools and EdTech websites.

Learning fractions can be hard for many children because it goes beyond basic simple arithmetic calculations. To understand the concept, kids need to practice with examples every day before mastering fractions. This article provides tips on how to learn fractions in a fun and engaging way. What is a Fraction? A fraction is a number […]
Apr 18, 2022

Many adults still face difficulties understanding math concepts like geometry, fractions, and even basic operations as they do not have a solid math foundation. So, imagine how draining it would be for them to help a youngster learn mathematics. One way to scale through this problem is to provide kids with educational resources even if […]
Book 1 to 1 Math Lesson
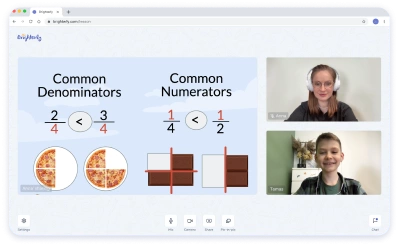
Kid’s grade
After-School Math Program Boost Your Child's Math Abilities! Ideal for 1st-12th Graders, Perfectly Synced with School Curriculum!

After-School Math Program
Related posts.

Geometry Games for 3rd Grade: Play and Learn with Brighterly
You know, education doesn’t have to be too serious and boring. Mixed in with a bit of fun can make a big difference, which is what math games are about. Since this article is about geometry and third-grade math, let’s dive deep into the exciting world of geometry games for third-graders. Geometry is all about […]
Aug 25, 2023

How to prevent summer slide of your child
Small breaks may be good for studying process, but summer holidays may cause big learning problems. This phenomenon is named summer slide and leads to learning loss. If you want to prevent summer slide, check out this article. You will see all the factors and methods that will help kids come back to school with […]
May 15, 2024


Parent-Teacher Relationship
Involvement by parents in their child’s academic process is of great importance to the school. Why? For one, the relationship between teacher and parents can influence student achievement, emotional well-being, and personal development. But the advantages run deeper than that. This article aims to explore the significance of the relationship between teacher and parent for […]
May 31, 2022
We use cookies to help give you the best service possible. If you continue to use the website we will understand that you consent to the Terms and Conditions. These cookies are safe and secure. We will not share your history logs with third parties. Learn More
- Main Number: 714-997-3000
- Customer Service: 714-509-3200
- 24/7 Nurse Advice: 844-GET-CHOC
- Contact Us / Directions
- News Media Resources
- Quality and Patient Safety
- Patient and Family Centered Care
- CHOC Docs / Providers
- Residency / Training Programs
- CHOC Foundation
- Main Campus in Orange
- CHOC at Mission Hospital
- Specialty Centers
- Human Resources
- List ALL CHOC Locations
- PRIMARY SERVICES
- Wellness and Primary Care
- Specialty Services
- Mental Health
- OUR INSTITUTES
- Neuroscience
- Orthopaedics
- FEATURED SERVICES
- Emergency Department
- Surgical Services
- Neonatal Services (NICU)
- List of ALL CHOC Services
- Find a Provider
- Make an Appointment
- Access CHOC Portal
- Explore Career Opportunities
- Estimate My Charges
- Pay My Bill
- Request Medical Records
- Download Vaccine Records
- Refer a Patient
- Visit a Patient
- Sign up for eNewsletter
- Read the CHOC Blog
- Attend an Event
- Donate Online
- Donate Blood
- Donate Toys
- Find More Ways to Help
Home » Wellness and Primary Care » Child Development: Milestones, Ages and Stages » Growth & Development: 6 to 12 Years (School Age)
- Find a Pediatrician
- Find a Location
- Our Services
- Why CHOC Primary Care?
Growth & Development: 6 to 12 Years (School Age)
As kids grow from grade-schoolers to preteens, you can expect many changes from their physical appearances to their favorite activities. Children between 6 and 12 years old will begin valuing friendships and become more involved in activities like sports and/or painting.
Doctors use certain milestones to tell if a child is developing as expected. There’s a wide range of what’s considered normal, so some children gain skills earlier or later than others. Children who were born prematurely reach milestones later. Always talk with your doctor about your child’s progress.
What can my 6- to 12-year-old child do at this age?
As your child continues to grow, you will notice new and exciting abilities that your child develops. While children may progress at different rates and have diverse interests, the following are some of the common milestones children may reach in this age group:
6- to 7-year-olds:
- Enjoy many activities and stays busy
- Like to paint and draw
- Practice skills in order to become better
- Can tie shoelaces
- Can do simple math like adding and subtracting
8- to 9-year-olds can:
- Jump, skip and chase
- Dress and groom self completely
- Use tools (i.e., hammer, screwdriver)
10- to 12-year-olds may:
- Like to write, draw and paint
What does my 6- to 12-year-old child understand?
As children enter school-age, their abilities and understanding of concepts and the world around them continue to grow. While children may progress at different rates, the following are some of the common milestones children may reach in this age group:
- Understand concept of numbers
- Know daytime and nighttime
- Can differentiate right and left hands
- Can copy complex shapes, such as a diamond
- Can tell time
- Can understand commands with three separate instructions
- Can explain objects and their use
- Can repeat three numbers backwards
- Can read age-appropriate books and/or materials
8- to 9-year-olds:
- Can count backwards
- Know the date
- Read more and enjoy reading
- Understand fractions
- Understand concept of space
- Draw and paint
- Can name months and days of week, in order
- Enjoys collecting objects
10- to 12-year-olds:
- Write stories
- Like to write letters
- Enjoy talking on the phone or texting

Wellness and Fitness Milestones
Kids at this age need physical activity to build strength, coordination, and confidence — and to lay the groundwork for a healthy lifestyle. They’re also gaining more control over how active they are. Kids who enjoy sports and exercise tend to stay active throughout their lives. Staying fit can improve how kids develop in school, build self-esteem, as well as prevent obesity, and decrease the risk of serious illnesses such as high blood pressure, diabetes and heart disease later in life.
What is “normal” physical growth for a 6- to 12-year-old child?
For 6- to 12-year-olds, there continues to be a wide range of “normal” regarding height, weight and shape. Kids tend to get taller at a steady pace, growing about 2-2.5 inches (6 to 7 centimeters) each year. When it comes to weight, kids gain about 4–7 lbs. (2–3 kg) per year until puberty starts.
This is also a time when kids start to have feelings about how they look and how they’re growing. Some girls may worry about being “too big,” especially those who are developing early. Boys tend to be sensitive about being too short.
Try to help your child understand that the important thing is not to “look” a certain way, but rather to be healthy. Kids can’t change the genes that will determine how tall they will be or when puberty starts. But they can make the most of their potential by developing healthy eating habits and being physically active.
Your doctor will take measurements at regular checkups, then plot your child’s results on a standard growth chart to follow over time and compare with other kids the same age and gender.
How can I help my child grow?
Normal growth — supported by good nutrition, enough sleep, and regular exercise — is one of the best overall indicators of a child’s good health. Your child’s growth pattern is largely determined by genetics.
Pushing kids to eat extra food or get higher amounts of vitamins, minerals, or other nutrients will not increase their height and may lead to weight problems. Accepting kids as they are helps them build self-acceptance. Good mental health is important for healthy development, strong relationships and resilience.

How active should my 6- to 12-year-old be?
School-age kids should have many chances to do a variety of activities, sports, and games that fit their personality, ability, age, and interests. Through physical activities, kids learn about sportsmanship, setting goals, meeting challenges, teamwork, and the value of practice.
Physical activity guidelines for school-age kids recommend that they get at least 1 hour of moderate to strong physical activity daily. In addition:
- Most of the physical activity should be aerobic, where kids use large muscles and continue for a period of time.
- Examples of aerobic activity are running, swimming, and dancing.
- School-age kids usually have brief bouts of moderate to strong physical activity alternating with light activity or rest throughout the day. Any moderate to strong activity counts toward the 60-minute goal.
- Muscle-strengthening and bone-strengthening physical activity should be included at least 3 days a week.
- Children naturally build strong muscles and bones when they run, jump and play. Formal weight programs aren’t needed. However, they are safe when properly designed and supervised.
Should my child participate in sports?
Keep in mind your child’s age and developmental level, natural abilities, and interests. Kids 6 to 8 years old are sharpening basic physical skills like jumping, throwing, kicking, and catching. Some enjoy doing this in organized sports teams, but non-competitive leagues are best for younger kids. Kids 9 to 12 years old are refining, improving and coordinating skills. Some become even more committed to a sport while others drop out as competition heats up and level of play improves. Regardless of the age or activity, it is important that you show your support by coaching your child’s team or cheering from the stands on game days.
It’s okay if a child isn’t interested in traditional sports, but it’s important to find alternative ways to be active. Brainstorm with your kids on activities that feel right for them. Encourage a child who doesn’t like soccer, basketball, or other team sports to explore other active options, like karate, fencing, golf, bicycling, skateboarding, and tennis. Most kids won’t mind the physical activity as long as they are having fun.
Fitness at Home
Many parents and kids think of organized sports when they think of fitness. Though there are many advantages to signing a child up for a sports team, practice and games once or twice a week will not be enough to reach activity goals. Also, parents shouldn’t rely on physical education in schools alone to provide children with enough physical activity.
Here are some ways to keep your child moving at home:
- Make physical activity part of the daily routine. From household chores to an after-dinner walk, keep your family active every day.
- Allow enough time for free play. Kids can burn more calories and have more fun when left to their own devices. Playing tag, riding bikes around the neighborhood, and building snowmen are fun and healthy.
- Keep a variety of games and sports equipment on hand. It doesn’t have to be expensive — an assortment of balls, hula-hoops, and jump ropes can keep kids busy for hours.
- Be active together. It’ll get you moving, and kids love to play with their parents.
- Limit time spent in sedentary activities such as watching TV, using electronic devices, being online and playing video games.
If you run out of possibilities at home, take advantage of local playgrounds and athletic fields. Make family fitness outings part of your regular routine. Let family members choose an activity — go hiking, ice skating, or try out the rock-climbing gym. Anything goes, as long as everyone can participate. And remember: You’ll help show your kids that exercise is important by regularly exercising yourself.
Preventing Sports-Related Injury
Kids who participate in sports are at risk for injuries, so be sure your child wears the proper protective equipment, such as shin-guards and cleats in soccer, or a helmet and protective pads when rollerblading or skateboarding. Kids who specialize in one sport are also at risk of overuse injuries, including stress fractures and joint injuries. If a child is in pain, it is best to rest and let the injury heal before returning to play.
A child with a chronic health condition or disability should not be excluded from these fitness activities in fear of getting a sports-related injury. Some activities may need to be changed or adapted, and some may be too risky depending on the condition. The best thing to do is to talk to your doctor about which activities are safe for your child.
If your child complains of pain during or after physical activity, talk with your doctor.
How long should my 6- to 12-year-old sleep?
School-age kids need 9-12 hours of sleep at night. Bedtime problems can start at this age for a variety of reasons. Homework, sports, after-school activities, screen time, and hectic family schedules all can contribute to kids not getting the sleep they need. Sleep-deprived kids can become hyper or irritable and may have a hard time paying attention in school.
It’s still important to have a consistent bedtime, especially on school nights. Leave enough technology-free time before bed to allow your child to unwind before lights-out. Consider switching off the electronics at least an hour before bed. Avoiding keeping a TV in their bedroom.
Check out our Healthy Sleep Guide for Children for more info.
Puberty — or sexual development — is a time of dramatic change for both boys and girls. The age at which the physical changes of puberty normally begin varies widely.
For both sexes, these hormone-driven changes are accompanied by growth spurts that transform children into physically mature teens as their bodies develop. They may also experience side effects from these hormones like acne and mood changes.
Puberty in Girls
Breast development, usually the first noticeable sign of puberty in girls, may begin anytime between ages 8 and 13. Events in girls as they go through puberty:
- Breasts begin to develop, and hips become rounded.
- The increase in the rate of growth in height begins.
- Pubic hair begins to appear, usually 6–12 months after the start of breast development. About 15% of girls will develop pubic hair before breast development starts.
- The uterus and vagina, as well as labia and clitoris, increase in size.
- Pubic hair is well established, and breasts grow further. Each breast can grow at different rates, may not be the same sizes.
- The rate of growth in height reaches its peak by about 2 years after puberty began. The average age is 12 years.
- Menstruation begins about 2 years after breast start to develop and almost always after the peak growth rate in height has been reached. The average age is 12.5 years.
- Once girls get their periods, they usually grow about 1 or 2 more inches (2.5 to 5 centimeters), reaching their final adult height by about age 14 or 15 years. Girls can experience this at a younger or older age depending on when puberty began.
Puberty in Boys
Most boys show the first physical changes of puberty between ages 10 and 16 and tend to grow most quickly between ages 12 and 15. The growth spurt of boys is, on average, about 2 years later than that of girls. By age 16, most boys have stopped growing, but their muscles will continue to develop.
Other features of puberty in boys include:
- The penis and testicles increase in size. Testicles can grow at different rates, may not be the same sizes.
- Pubic hair appears, followed by underarm and facial hair.
- The voice deepens and may sometimes crack or break.
- The Adam’s apple, or larynx cartilage, gets bigger.
- Testicles begin to produce sperm.
Communication Milestones
How does my 6- to 12-year-old child interact with others.
A very important part of growing up is the ability to interact and socialize with others. During the school-age years, parents will see a transition in their child as he or she moves from playing alone to having multiple friends and social groups. While friendships become more important, the child is still fond of his or her parents and likes being part of a family. While every child is unique and will develop different personalities, the following are some of the common behavioral traits that may be present in your child:
- Cooperate and share
- Can get jealous of others and siblings
- Like to copy adults
- Like to play alone, but friends are becoming important
- Play with friends of the same gender
- May have occasional temper tantrums
- May be modest about body
- Like to play board games
- Like competition and games
- Start to mix friends and play with children of different gender
- Enjoy clubs and groups, such as Boy Scouts or Girl Scouts
- May become curious about relationships, but does not admit it
- Will value friendship; may have a best friend
- May develop romantic interests
- Like and respect parents
- Enjoy talking to others
How can I help increase my 6- to 12-year-old child’s social ability?
Consider the following as ways to foster your school-aged child’s social abilities:
- Set and provide appropriate limits, guidelines and expectations and consistently enforce using appropriate consequences.
- Model appropriate behavior.
- Offer compliments for your child being cooperative and for any personal achievements.
- Help your child choose activities that are appropriate for your child’s abilities.
- Encourage your child to talk with you and be open with his or her feelings.
- Encourage your child to read and read with your child.
- Encourage your child to get involved with hobbies and other activities.
- Encourage physical activity.
- Encourage self-discipline; expect your child to follow rules that are set.
- Teach your child to respect and listen to authority figures.
- Teach your child to be aware of consequences of their behavior and empathy for others.
- Encourage your child to talk about peer pressure and help set guidelines to deal with peer pressure.
- Spend uninterrupted time together – giving full attention to your child. A strong, loving relationship can have a direct positive influence on your child’s mental health.
- Encourage time outside.
- Limit television, video game and computer time.
Reviewed by Dr. Lydia Villa , Clinica CHOC Para Niños, CHOC Primary Care – May 2021
Your child’s health is important at every stage. Visit CHOC Primary Care for pediatric services near you.
What's coming up for your child
Teenager Growth & Development: 13 to 18 Years (Adolescent)
Related articles for this age group

A CHOC expert discusses why Asperger syndrome is not diagnosed anymore, and talks about signs of autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
A CHOC mental health expert offers tips for parents to help their teens with college rejection disappointment.

Get tips and advice about your child’s urine color, hydration and common urinary conditions from a CHOC pediatrician.

CHOC nutrition experts offer a helpful guide to parents for how to read and understand a nutrition facts label.

A CHOC pediatrician explains the causes of colic in babies, and offers tips to parents for helping their colicky baby.

When siblings Julissa and Joseph were diagnosed with the same rare congenital heart disease, CHOC stepped in to treat them both.

CHOC is affiliated with the UC Irvine School of Medicine
CHOC LINKS Contact Us Directions Locations Pressroom Careers Giving
I WANT TO... Find a Doctor Refer a Patient Pay My Bill Request Medical Records MyCHOC Patient Portal Volunteer
LEGAL Privacy Notice Patient Rights Social Media Guidelines Notice of Nondiscrimination Other Policies
- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
How Do Kids Spend the School Day? Recommended Times and Structure
Verywell / Sahara Borja
Attending Class
Doing homework.
- Socializing
- Being With Parents
Eating Meals
Being physically active.
- Enjoying Nature
Using Electronics
How to fit it all in.
Today's kids are busier than ever, dividing their time between school, activities, tutoring , and family time. When they're not busy with scheduled activities, kids have to make time for homework, sleep, and personal care.
Is there a way to balance it all and still provide some structure? Sure; making room for the priorities just takes a little planning. Of course, when it comes to time management , flexibility is also important. There will be times when you need to make adjustments to meet your child's needs. See how your child's schedule compares to others when it comes to key daily activities.
It may seem like your children spend all of their time at school . According to the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), students may spend anywhere from three to seven hours a day in school depending on their age and the state in which they live.
This figure does not include transportation time as well as before or after school activities. Consequently, the number of hours individual children spend at school can vary dramatically.
As for the number of school days in a school year, there is much less variation. According to the NCES, the number of school days in different states ranges from 160 days in Colorado to 180 days in Hawaii.
This means kids are not in school about 185 days or more a year, which includes weekends and breaks. On those days, kids have the opportunity to enjoy nature, spend time with family and friends, and exercise.
How much time each day should kids spend on homework ? A general rule among teachers is 10 minutes per grade level: 30 minutes per day for a third-grader, 50 minutes for a fifth-grader, and so on.
This rule has been around for decades, but gained legitimacy when a review by Harris Cooper of Duke University suggested that 10 minutes per grade level really is the best practice. This amount can vary dramatically between children, however.
Time needed for homework really depends on the school's homework policy, the teacher's philosophy, and the type of coursework your child is taking. High school students taking AP courses might spend more time on homework than a student in general education courses. Some educators don't assign homework unless they see a strong need for at-home practice.
Expect less homework in schools that have a strong hands-on emphasis. You can expect more homework in schools that focus on regular practice or have "flipped" classrooms, where kids cover new material at home and practice skills at school where they are supervised. Another time you can expect more homework is in advanced level classes, like those that offer dual credit to high school students.
To keep your student on task during the school year, try establishing a schedule or block of time when homework will be completed.
Allow your child to help decide when this will take place. Doing so gives them some sense of control over their day and will more likely lead to positive results when it comes to completing assignments.
Socializing With Others
Experts agree that school-age children need to have friends. Friends help children build social skills such as listening, sharing, and problem-solving . Children also learn how to handle their emotions through relationships with other children.
Research doesn't dictate any specific amount of time that is necessary for children to socialize with friends. The quality of the friendships and whether or not the child is generally happy with their social time are most important. Children or teens may have just a few friends or several friends.
If you feel that your child would benefit from having more or better quality friendships , start by suggesting that your child to get involved in clubs or activities where they can meet new friends. If your child seems a little shy or like they need practice meeting new peers, try coaching them on how to make friends.
Being With Parents or Caregivers
Don't stress about spending quality time with your kids. Research from a large-scale longitudinal study on the effects of time with parents compared to child and teen outcomes had some surprising results.
The biggest takeaway is that time spent with a parent who is stressed out and moody can decrease positive outcomes, while more time does not show a strong benefit. For this reason, it's important to be mindful of your family's moods.
It's also important not to put too much pressure on yourself when it comes to spending time as a family. The study, published in the Journal of Marriage and Family , found no relationship between the time a parent spent with their 3- to 11-year-olds and the child's academic achievement, behavior, and well-being. Teens do get into less trouble when they have six hours a week or more of positive, engaged time with parents.
That means that parents can and should take a big sigh of relief. These results suggest taking care of yourself first and not sacrificing or martyring yourself for the sake of your children is best. If you find yourself stressed out about money, you can return to work or work more hours without feeling guilty .
You also will be in a better position to spend time with your kids in the teen years when the benefits are much more tangible. Just try to enjoy your time together no matter what that looks like. It still stands to reason that your child will benefit from having some positive attention from you every day.
The amount of time a child needs to sleep varies according to their age. But every child, no matter their age, needs adequate sleep. Not getting enough sleep has been linked to falling asleep during school or missing school altogether.
What's more, kids who don't get enough sleep struggle to wake up in the mornings, and have trouble learning or doing school work. If you are concerned that your child is not getting enough sleep, learn what symptoms to watch for as well as what steps you can take to improve their sleep habits .
Sleep Recommendations
According to the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the recommended sleep times for school-age children are:
- 10–13 hours each night for 5-year-olds
- 9–12 hours each night for 6- to 12-year-olds
- At least 8 hours each night for kids 13 years old and older
Verywell / Nusha Ashjaee
Most experts recommend 20 to 30 minutes to eat a meal, and 10 to 15 minutes to eat a small snack. Keep in mind that even children's bodies need 20 minutes after eating before they begin to register feeling full.
To make sure your children have plenty of time to finish their food without feeling rushed and get adequate nutrition, emphasize the importance of family meals . This time not only provides your kids with the nutrition they need, but it also gives you valuable time together as a family.
What's more, regular family meals promote healthy eating and protect against childhood obesity . Make sure you are selecting healthy options for your family and that electronics are turned off and away from the table. Meal time also is a great time to catch up on what's going on in everyone's lives and to laugh together as a family.
Children should engage in 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity per day according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Not only does regular physical activity promote health and fitness, it also leads to lower body fat and stronger bones .
Physical activity—which should consist of aerobic, muscle-strengthening, and bone-strengthening activities—also has a positive impact on a child's brain health. Studies have shown that exercise improves cognition and memory as well as enhances academic performance and reduces symptoms of depression.
When kids exercise daily, this also sets them up for good health in adulthood. It reduces the likelihood that they will experience heart disease, obesity, and Type 2 diabetes. Plus, being physically active is a great stress reducer. It allows kids to take their minds off of stressful things and do something fun.
Enjoying Nature and the Outdoors
Many children spend much more time indoors than they did in previous generations. Various studies have linked this increase in indoor time to obesity and other health issues.
While it is important to note that some of these effects do not have enough research to say with certainty that indoor time is to blame, it makes sense that time spent outdoors and away from screens would be good for children and adults alike.
How much time outdoors should you aim for? The U.S. National Wildlife Federation suggests at least one hour a day. This nature advocacy group even includes this concept in its "Be Out There" campaign, calling it a "Green Hour." Likewise, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) also recommends 60 minutes of unstructured, free play (indoors or out) every day.
You can help your children get in their physical activity time and their time in nature by getting them outdoors. If you're short on ideas, try hiking on a local nature trail or tending a small container garden.
For years, the AAP had fairly strict recommendations limiting the use of any electronic devices to a few hours a day. However, in late 2016, new guidelines were announced that are much less stringent. The guidelines were created in response to how we are using media today.
This change came about because electronics and screen time have become a facet of almost every part of our lives. Children use tablets and computers at school. Cell phones with video messaging are used for daily communication. And internet use for homework is more likely to be required than optional. Then, after a child's required use of electronic media, there is still entertainment and free time to consider.
Overall, the recommendations indicate that electronic media use for entertainment should be limited to one or two hours a day. Parents should ensure that this entertainment is high quality, and create screen-free zones (like the family dinner table), so children and teens learn to function without their devices. Doing so not only allows them to relax and de-stress but it also gives them the space needed to be creative.
Of course, during the 2020-2021 school year, kids may have been online multiple hours a day just to get an education. Now that schools are being encouraged by the CDC to return to in-person learning, finding a balance between using electronics for school and for socializing and entertainment is important. You may even want to consider taking a few days to detox from technology as a family.
It can be a challenge to meet all of these recommendations. One way to manage is to combine one or more activities so you can get more done in less time.
For instance, time outdoors in nature, away from electronic devices, can be combined with exercise and even time with same-age friends. Meanwhile, the time a child or teen needs to be engaged with a parent can be met by eating dinner together. Thirty minutes each night totals more than six engaged hours. The only activity you can't mix with others is sleep.
The key to fitting in everything a child needs is to establish a daily plan or school year routine. Pre-planning or scheduling also can reduce parent stress, keeping the time you spend with your child positive.
A Word From Verywell
As you think about how to structure your child's typical school day, try not to be too rigid with your planning. With the exception of sleep, you can be flexible with how your kids are spending their time and tailor your routines to meet their specific needs.
The key is that they are getting appropriate rest, attending school, and doing their homework. Socializing, time with family, physical activity, electronic use, and family meal times can be adapted as the days unfold.
National Center for Education Statistics. Number of instructional days and hours in the school year, by state: 2018 .
American Psychological Association. Is homework a necessary evil ?
Cooper, H. The Battle Over Homework: Common Ground for Administrators, Teachers, and Parents . New York, Carrel Books, 2015.
Sakyi KS, Surkan PJ, Fombonne E, Chollet A, Melchior M. Childhood friendships and psychological difficulties in young adulthood: an 18-year follow-up study . Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry . 2015;24(7):815-26. doi:10.1007/s00787-014-0626-8
Siennick SE, Osgood DW. Hanging out with which friends? Friendship-level predictors of unstructured and unsupervised socializing in adolescence . J Res Adolesc . 2012;22(4):646-661. doi:10.1111/j.1532-7795.2012.00812.x
Milkie MA, Nomaguchi KM, Denny KE. Does the amount of time mothers spend with children or adolescents matter? . J Marriage Fam. 2015;77:355–372. doi:10.1111/jomf.12170
Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. How much sleep do I need? .
Cohen JF, Jahn JL, Richardson S, Cluggish SA, Parker E, Rimm EB. Amount of time to eat lunch is associated with children's selection and consumption of school meal entrée, fruits, vegetables, and milk . J Acad Nutr Diet . 2016;116(1):123-8. doi:10.1016/j.jand.2015.07.019
Dwyer L, Oh A, Patrick H, Hennessy E. Promoting family meals: a review of existing interventions and opportunities for future research . Adolesc Health Med Ther . 2015;6:115-31. doi:10.2147/AHMT.S37316
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Physical activity guidelines for school-aged children and adolescents .
Kemple KM, Oh J, Kenney E, Smith-Bonahue T. The power of outdoor play and play in natural environments . Childhood Education . 2016;92(6):446-454. doi:10.1080/00094056.2016.1251793
Childhood Pediatrics. Nature play: Prescription for healthier children .
Barnett TA, Kelly AS, Young DR, et al. Sedentary behaviors in today’s youth: approaches to the prevention and management of childhood obesity: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association . Circulation . 2018;138(11). doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000591
The National Wildlife Federation. Connecting kids and nature .
American Academy of Pediatrics. Energy out: daily physical activity recommendations .
Media and young minds . Pediatrics . 2016;138(5). doi:10.1542/peds.2016-2591
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidance for COVID-19 prevention in K-12 schools .
By Lisa Linnell-Olsen Lisa Linnell-Olsen has worked as a support staff educator, and is well-versed in issues of education policy and parenting issues.

What to Include in a Daily Schedule for 6 Year Olds
Need to create a daily schedule for a 6 year old at home? Learn what to include in your morning and after school routine for a smooth day!

For one reason or another, you know that you need some sort of structure for your 6 year old.
Maybe all she wants to do is play video games or watch television, scorning any chores or responsibilities you remind her to do. Perhaps she has trouble getting ready in the morning—she still needs your help putting on a shirt and needs multiple reminders to get her shoes on. And even though she’s in school for most of the day, that still doesn’t make the mornings or evenings any easier.
Table of Contents
What to include in a daily schedule for a 6 year old
I’ve long been a fan of routines and schedules. They help us know what to do on any given day (or time of day). Kids don’t have to ask what they should do because everything feels so automatic. And they can even take the initiative and do those tasks on their own.
Everyone’s daily schedule will look different, of course. Some families have parents who work all day and whose kids are in after school care. Other kids attend extracurricular activities a few (or all the) days of the week.
That’s why I want to suggest different ideas you can include in your daily schedule, not so much break your day down hour-by-hour. These are some of the “building blocks” of your schedule and often take place no matter your circumstances.
Take a look at what to include in a daily schedule for a 6 year old:
1. Morning routine
Mornings can be rough when you know you have to get to school or work (or both) by a certain time. And if school starts early, this can really cut those mornings short and make them extra hectic.
Give yourself plenty of time to get ready, even if it means waking up earlier. To start, wake your child at the same time every morning so that her body starts to adjust to waking up around that time. Then, here are a few things you can do to make your mornings smooth:
- Prepare and eat breakfast. I like to prepare breakfast before the kids are awake so that they can start right when they get up. Have the same breakfast (or at least the same weekly menu) to make buying and preparing meals easier. For instance, oatmeal on Mondays, cereal on Tuesdays, and so forth.
- Brush teeth. Have her to brush her teeth on her own.
- Get dressed. Give her a choice on what to wear, so long as the options are reasonable for the weather. For instance, she can choose from any long sleeves and pants to make sure she’s not cold in the winter.
- Pack school bags. Show her how to pack her lunch and choose the snacks she’ll eat. Make sure she has everything she needs for school in her backpack.
Free ebook: Want simple tweaks to stop feeling overwhelmed and start managing your time? Grab Time Management Strategies for the Overwhelmed Mom below—at no cost to you. You’ll also get my newsletters, which parents say they LOVE:

2. Empty backpack
As part of our after school schedule , the first thing we do when my kids get home is to empty their backpacks. Before they even eat a snack, I have them place their lunch dishes in the sink or dishwasher and hand me any folders or paperwork from their teachers.
Then, they hang their bags on the coat rack so they’re exactly where they’re supposed to be the next morning.
Once your child has emptied her backpack, have her eat an afternoon snack. One option is to have something already prepared, especially if she doesn’t know how to make that particular snack yet. Another is to place a few snacks in a “snack area” that she can choose from.
I have my kids eat snacks before they start on homework. This can often avoid any grumpiness that might come from being hungry. It’s also a great way to chat about their day or for them to decompress from a long day at school.
4. Homework
It’s not unusual for kids to have homework even in kindergarten or first grade. Thankfully, most are review or work that can be done within 10 minutes or so. Doing homework after snack can be a good time since your child has just eaten and had a quick break at home.
See if he can do his homework on his own with you nearby. For instance, you can put dishes away while he sits at the kitchen table to work on a few writing exercises. That way, you’re giving him autonomy to complete his work but still making yourself available should he need help.
5. Playtime
With homework done and out of the way, give your 6 year old a chance to play however she likes. Having downtime during the day allows her to be creative, tinker with toys, and make her own choices. This doesn’t mean you can’t encourage her in some way—you just have to let her lead. For instance:
- Bring out a few art supplies she can use to draw and create, like paper, crayons, and play dough.
- Encourage outside play , like bouncing a ball in the backyard or playing in the garden.
- Work through puzzles or bring out a board game.
- Do something together , like baking cookies.
I rarely go on outings on weekdays after school, but this can be a weekly tradition, especially if your child has a half day every week.
Since he had already been in school for hours, keep your outing simple and low-key. You can go to the library to attend a craft event and check out books to take home. Perhaps you’ll visit a local park so he can ride a scooter or climb on the playground.
And once in a while, you can sneak errands in as well, though I try to do these when the kids are at school or on weekends.
I’m a fan of having family dinners at the same time every night. We have an early dinner at 5pm, but that allows us a chance to still have some time after dinner and put the kids to bed early, too.
You might eat dinner depending on when you or your partner get home from work. Perhaps you have some nights when you have dinner late because of one child’s violin lessons. It won’t always be perfect, but aim to have dinner around the same time so that your child gets used to eating around that time.
Even at 6 years old, your child can do plenty to contribute to household chores. A good place to start is with his own items, like putting dishes in the sink or cleaning up toys he played with. He can help load his laundry in the washing machine or pack his backpack for the next morning.
Once he’s comfortable doing chores for himself, expand his responsibilities so that he’s doing tasks for the whole family. This could be helping you spray the dining table so that you can wipe it down. He could tidy up the living room coffee table, help feed the dog, or wipe the bathroom mirrors.
It’s never easy when kids refuse to do chores . But introducing chores now helps make them a normal part of contributing to the family so that he doesn’t resist them so much down the line. He also learns life skills and can feel proud for doing a good job and helping others.
9. Screen time
Not all families allow screen time, especially during the weekdays. Find a balance that you’re comfortable with, whether that’s zero screen time or a mix that allows for some on weekends.
Maybe that’s watching 30 minutes on school nights but letting your child watch a longer movie on weekends. Perhaps you don’t let her use the tablet during the week but she can play a few games on half days or weekends.
Set a timer so that stopping screen time doesn’t fall on your shoulders. She’s more likely to shut the computer down when she hears the timer than when someone tells her to.
10. Bedtime routine
Does your 6 year old struggle with ending the day? A consistent bedtime routine can definitely help. For many of us, our patience and willpower wear down toward the evening, so bedtime can take a hit, especially with tantrums, stall tactics, and multiple wake-ups.
Prevent many of these issues with a solid bedtime routine. A few activities you can do include:
- Brush teeth
- Use the potty
- Take a bath
- Dress in pajamas
- Read bedtime books
- Kiss good night
- Turn off the light
To help the bedtime routine flow smoothly, start at the same time every night and do the same activities in the same order. Soon, she won’t have to wonder what’s next or why you have to start now. It feels automatic and normal, and she’s more likely to take initiative as well.
Best practices for creating a daily schedule
Now that we’ve gone over a few activities to include in a daily schedule, let’s take a look at a few best practices:
1. List a routine chart or checklist
I like to list all the things my kids should have done in the morning before heading to school. That might be brushing their teeth, packing lunches, and getting dressed.
By having a checklist or a visual chart, your child can double-check that she has done everything she needs to do. You can have a list for mornings, after school, or bedtime, too.
2. Be consistent with rules and responsibilities
Being wishy-washy sends the message that rules can fluctuate and doesn’t give her the predictability she craves. Yes, evaluate rules if you need to adjust, but do so with purposeful intent, not because you’re letting it slide this one time.
3. Give your child something to look forward to
Finding it difficult to motivate your child to do the next step? Remind her of something she can look forward to. The “reward” is a perk or activity she gets to do once this next step is done. For instance, you can say, “Let’s get you bathed so we can put on those new pajamas you picked out today!”
4. Schedule plenty of downtime
Kids need time to be able to do what they want to do instead of being shuffled from scheduled activities and tasks. They’re able to tinker and experiment and come up with interesting ideas and creations.
They’re also cultivating patience and tolerance for being bored and learning how to get through it. We don’t have to plan their every second or save them from boredom.
5. Guide, don’t hover
Autonomy can help your 6 year old feel confident and capable of tasks you ask her to do. First, show her how to do a task step-by-step, then ask her to help you do it together. Later, have her do it on her own with you nearby to guide her. At some point, she can ideally do the task completely on her own.
The bottom line
Whether your 6 year old wants to play video games all day or is always late to get ready in the morning, a daily schedule can help. With consistency, your days can flow smoothly, from the morning routine all the way to bedtime.
Get more tips:
- Fine Motor Skills Activities for 5-6 Year Olds
- 8 Life Skills Kids Need in Adulthood
- How to Raise a Bright Child
- 5 Techniques That Help Kids with Transitions
- How to Be an Organized Mom
Don’t forget: Join my newsletter and grab Time Management Strategies for the Overwhelmed Mom below—at no cost to you:
Nina Garcia is the founder and CEO of Sleeping Should Be Easy, a leading parenting resource and online blog. She has spent the last 14 years creating helpful content for parents through online courses and workshops, ebooks, newsletters, and the Sleeping Should Be Easy website.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Worksheets for 6-Year-Olds
- Printable worksheets
- Educational videos
- Learning games
2147 filtered results
- Extra Challenge
- Kindergarten
- ABC Letters
- Tracing Letters
- Letter Recognition
- Upper & Lowercase Letters
- Missing Letters
- Alphabet Coloring Pages
- Phonics
- Numbers
- Counting
- Addition & Subtraction
- Measurement
- Multiplication
- Geometry
- Money
- Math Coloring Pages
- Word Problems
- Capitalization
- Tracing Words
- Punctuation
- 3 Little Pigs
- Holiday Coloring Pages
- Color by Numbers
- Flora and Fauna
- Back to school
- Vocabulary Coloring Pages
- Phonics Coloring Pages
- Cultures and Holidays Coloring Pages
- Weather and Seasons Coloring Pages
- Feelings and Emotions
- Fairy Tale Coloring Pages
- Nursery Rhymes Coloring Pages
- Reading Comprehension
- Rhyming Words
- Building Vocabulary
- Building Vocabulary Coloring Pages
- Itsy Bitsy Spider
- 5 Little Monkeys
- Twinkle Little Star
- Governance and Civics
- Life Science
- Our Body and Health
- Plants and Animals
- The 5 Senses
- Physical Science
- Our Planet and Environment
- Problem Solving
- Plants and Animals
- Tracing Lines and Curves
- Tracing Numbers
- Tracing Shapes
- Cursive Writing
- Connect the Dots
- Fairy Tales
- Black history
- Dinosaurs Day
- International Chess Day
- 4th of July
- Thanksgiving
- Alphabet
- Math
- Writing
- Science
- Reading
- Social Studies
- Maze Puzzles
- Connecting the Dots
- English Language Arts
Introducing our vibrant collection of worksheets designed specifically for 6-Year-Olds! These engaging activities are tailored to foster creativity, enhance problem-solving skills, and build foundational knowledge in various subjects. Crafted by educational experts, our worksheets are perfect for young learners eager to explore the world of numbers, letters, and beyond. With a mix of fun puzzles, exciting coloring pages, and interactive exercises, our worksheets for 6-Year-Olds promise to make learning an adventure. Ideal for both classroom and home use, they are the perfect tool to ignite your child's love for learning and pave the way for academic success.
Letter A Tracing Page
Geometry Worksheet

Christmas Tree Tracing Winter Words Worksheet

A Fox and Bird Coloring Page

Chess Pieces Quest Worksheet

Counting Cupcakes Worksheet

Snowflake Tracing Winter Words Worksheet
The Constitution Worksheet

Plural Nouns Practice Worksheet
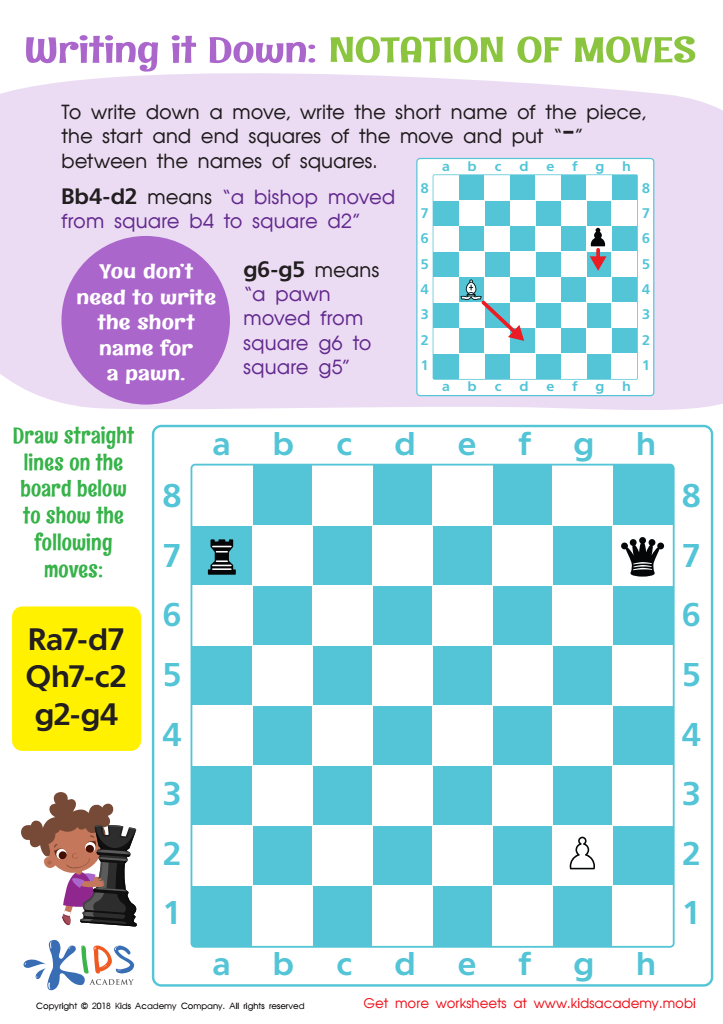
Notation of Moves Writing it Down Worksheet
Shared Food Worksheet

Who Is in a Family? Worksheet

Counting Backwards: Treasure Hunt Worksheet
Trace The Circles Worksheet

Musical Instruments Printable

Lowercase Letters Maze Worksheet

King and Queen Worksheet

Let's Practice Plurals Word Structure Worksheet
Two–Dimensional Shapes: Vertices Printable

Desert Maze Worksheet

Red and Blue Coloring Fun Worksheet

Birthday 3D Shapes Worksheet
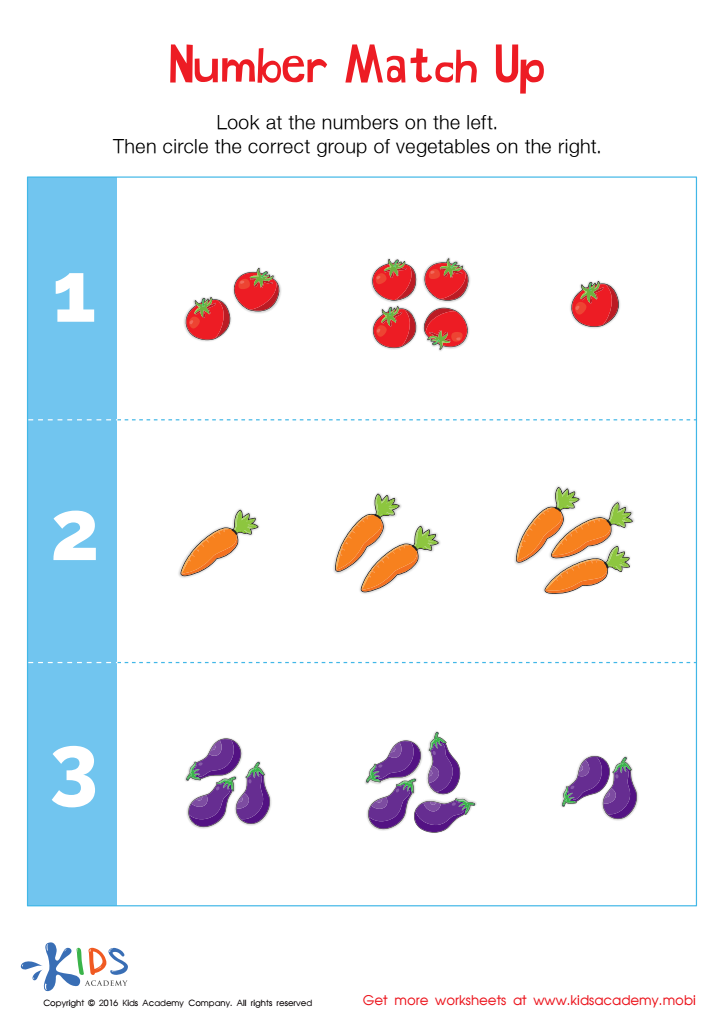
Number Match Up Worksheet
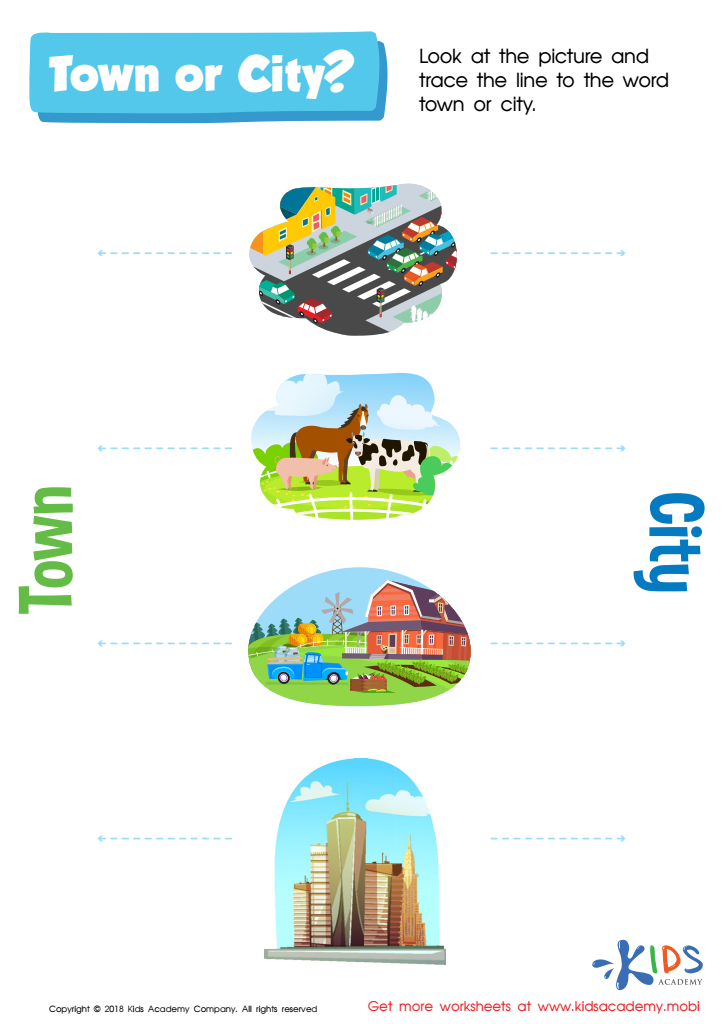
Town or City? Worksheet
Related articles.

Worksheets designed specifically for 6-year-olds play a crucial role in the educational development of children. At this tender age, kids are at a prime stage of learning; they are curious, eager to explore, and ready to absorb knowledge like sponges. Here's why these age-appropriate worksheets are so beneficial:
Tailored Learning Experience : Worksheets for 6-year-olds are meticulously crafted with their cognitive and physical abilities in mind. These resources ensure that the content is neither too challenging nor too simple, striking the perfect balance to engage young minds effectively.
Foundational Skill Development : At the age of six, children are developing essential skills in reading, writing, mathematics, and even critical thinking. Through varied worksheets, they practice these foundational skills in a structured yet fun manner, paving the way for future academic success.
Enhanced Concentration and Discipline : Engaging with worksheets helps 6-year-olds to improve their concentration and learn the importance of completing tasks. This discipline, cultivated early on, benefits their educational journey and beyond.
Interactive Learning : Many worksheets for 6-year-olds include colorful illustrations, puzzles, and activities that make learning interactive and enjoyable. This approach helps to foster a love for learning and encourages children to explore new concepts enthusiastically.
In summary, worksheets for 6-year-olds are invaluable tools that support children's developmental milestones, catering to their learning needs while making education an exciting adventure.
Related Worksheet
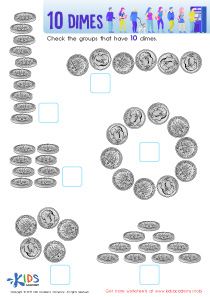
You'll be able to manage the favorite spreadsheets list.
You’ll be able to hide/mark the accomplished tasks.
- School / District Account
- Family Account
- 2 PDF worksheets per day
- Interactive worksheets
- Targeted ads
- KidsAcademy ads
$ 1.99 / month
- Printable and interactive worksheets
- Learning videos
- Ad-free browsing
$9.99 / month
- 7000+ online learning activities
- Curriculum created by education experts!
Cancel anytime
Homeschooling for 6 year olds – A complete Guide

Homeschooling refers to the education of children at home instead of in traditional school. Parents are responsible for their child’s education, regardless of their type of schooling.
The below instructions will guide you through the process of Homeschooling your 6-year-old kids.
Table of Contents
A guide to help parents of 6-year-olds who are homeschooling their children
1. prepare your child to be homeschooled.
It takes a lot of hard work and time to homeschool . It will be difficult for your child if they aren’t ready to learn, so it’s best to begin during the summer when they have more free time.
Please encourage them by letting them watch educational TV shows or go on a field trip once a week.
If you find they are having trouble, you can always look up how to help them on the internet.
2. Be encouraging
Parents are the ones who have the authority when it comes to their children’s education, so they should be encouraging them to feel happy and satisfied with what they are doing.
Even if the 6-year-olds are still young, parents can start this by telling them how wonderful they are and how proud their parents are of them.
Furthermore, the parents should not give up on their children’s education just because it is hard. Parents should keep themselves motivated too.
3. Be patient
Aside from being encouraging, the parents need to be patient, so they will not come up with the thought of giving up.
Parents should understand that 6-year-olds are still young and will not be able to learn everything in the blink of an eye.
Allowing themselves to be patient is one way to help their children without forcing them too much.
Remember your actions will decide your future and should not create hate in their minds for schooling altogether.
4. Be creative
Parents should be open to new ideas and not stick with existing ones, which can make things boring for everyone involved.
They should always think outside the box when it comes to studying to keep themselves and their children interested, no matter how tough it may seem at first.
5. Make it fun
Six-year-olds are still very young, so making school fun for them will not be difficult.
Parents should find ways to make their children want to learn and do well in school, such as involving them in other activities such as sports or games.
Even if they are still very young, parents should be careful about how they handle school . They do not have to completely stop everything fun just because it is time for schooling but finding that fine line will be necessary, so the children are more encouraged than anything else.
6. Be involved with your child’s education
It would be difficult for children to learn if their parents were not there to help them every step of the way.
Parents know their children’s personalities and should make it a point that they are involved with what goes on in their children’s schoolwork.
They should ask them questions at home and participate in making the homework plan, among other things.

Educational activities for Homeschooling for 6-year-olds:
This activity will help your child exercise their vocabulary and logical thinking.
You can either make up riddles yourself, or you can look them up online or on Youtube. But if you do this activity with your child, try using simple riddles that the child could probably guess by themselves; remember, this is their first time Homeschooling!
2. Alphabet learning
This activity requires using upper case and lower case letters; you can make your flashcards with the upper case letter on one side and the lower case letter on the other.
Then all you have to do is go through each card, show them both sides of each card, then have them point out which letter matches that side of the card.
You can do this activity by having your child draw something that’s going on in their life right now, it could be a comic strip about what they did at school, or it could be a drawing with stick figures of them doing an activity they enjoy.
This activity will help exercise the child’s creativity and imagination!
This activity will help the child develop their vocabulary and comprehension skills! You can either read them a story or pick out a book that the child might be interested in. Then, after you’re finished reading, ask them questions about what they just read. This will also help them sharpen their memory.
This is an excellent activity for developing the child’s problem-solving skills. You can either do your puzzles with cardboard, or if you want to encourage the child to be more creative on their terms, buy a mystery they probably wouldn’t do on their own.
Curriculum for Homeschooling for 6-year-olds
According to statistics, below is the most suitable curriculum for 6-year-olds..
- Read and write numbers 1-10
- Learn the alphabet in lower and upper case; remember there are two sides to each card so that you can show them both sides.
- Learn about shapes (circle, square, rectangle, triangle)
- Learn about the five senses (sight, smell, taste, touch, and hearing).
- Identify weather patterns.
- Learn about different types of animals.
- Learn how to care for pets (feeding, grooming, etc.)
- Learn how to spell their name.
- Learn basic sentence structure.
- Learn the parts of speech (nouns, verbs, adjectives).
- Learn the alphabet in upper and lower case.
- Learn how to sound out words (syllables).
- Read and write numbers 1-10.
- Learn how to do puzzles.
- Learn to listen to and follow instructions.
- Learn to problem-solve.
- Learn how to sound out words (phonetic sounds) while reading and writing.
Conclusion – Homeschooling for 6-year-olds
Children learn at different rates; some kids pick things up quickly while others take their time. However, some children may be more interested than others, so if you notice that the child isn’t picking up any of this information after a certain amount of time, then go back to the drawing board and think about how else you could present these concepts to them. Try to have fun with these activities because if the child doesn’t understand what you’re trying to teach them, they probably won’t retain any information.
Share this:


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Third to fifth grades. Many children will be able to do homework independently in grades 3-5. Even then, their ability to focus and follow through may vary from day to day. "Most children are ...
And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary. "Every child should be doing homework, but the amount and type that they're doing ...
What is the "Right" Amount of Homework? Research suggests that homework should not exceed 1.5 to 2.5 hours per night for high school students and no more than 1 hour per night for middle ...
As young children begin school, the focus should be on cultivating a love of learning, and assigning too much homework can undermine that goal. And young students often don't have the study skills to benefit fully from homework, so it may be a poor use of time (Cooper, 1989; Cooper et al., 2006; Marzano & Pickering, 2007). A more effective ...
For decades, the homework standard has been a "10-minute rule," which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 ...
You might not have heard that homework for young children is a thing. But it is a thing. In a survey of more than 2700 kindergarten teachers - all working in the United States circa 2010 - 40% said they believed that "homework should be given to kindergarten children almost every day" (Bassok et al 2016).
Homework becomes more of a "thing" as your child gets a little older, though it tends to be light in early elementary school, increasing in amount as the years pass. Typically by third grade, kids receive up to three assignments per week, and homework can take up to 20 minutes.
Step 3. Practice to Grow Skills and Develop Habits. Homework practice can take the form of cooperatively completing the task together or trying out a task with you as a coach and ready support. Practice grows vital new brain connections that strengthen (and eventually form habits) each time your child practices.
Others need to have parents nearby to help keep them on task and to answer questions when problems arise. Ask your child where the best place is to work. Both you and your child need to discuss pros and cons of different settings to arrive at a mutually agreed upon location. Step 2. Set up a homework center.
A 6-year-old should: Begin to read books that are right for their age; ... Participate in homework assignments. If you think your 6 year old is falling behind, stay calm but be on the lookout for:
Here are some tips for setting your child up for homework success: Set a regular homework time. Homework should be done at the same time each evening to establish a routine. Just make sure you're allowing your little one some time to decompress when they get home before jumping into more schoolwork. Create a study area.
The idea that "less is more" rules here. According to the National Education Association, guidelines are no more than 10 minutes per grade level per night (that's 10 minutes total for a first-grader, 30 minutes for a third-grader). Some students do their homework on their own, and some parents help their children.
Choose some different steps or decide not to dance at all. Let homework stay where it belongs—between the teacher and the student. Stay focused on your job, which is to help your child do their job. Don't do it for them. If you feel frustrated, take a break from helping your child with homework.
Set the Scene. Unlike an older sibling who may prefer completing homework in her room, your 6-year-old will work best when you are in close proximity. Designate a quiet work area that provides adequate lighting. Let your child decorate a box that will hold homework supplies such as paper, pencils, glue and crayons.
Counting. Counting is among the basic math skills 6-year-olds should master, as it paves the way for other math topics on this list. Six-year-olds can count to a great extent, often up to 200, which reveals the vastness of numbers to kids. Counting as a math concept forms the foundation for a more complex mathematics for 6 year old that the ...
For 6- to 12-year-olds, there continues to be a wide range of "normal" regarding height, weight and shape. Kids tend to get taller at a steady pace, growing about 2-2.5 inches (6 to 7 centimeters) each year. When it comes to weight, kids gain about 4-7 lbs. (2-3 kg) per year until puberty starts.
Dave, who co-parents his 14-year-old daughter, thinks there can be a harmonious space between helping and doing their homework for them. "I think that there should be a balance of involvement ...
Sleep Recommendations. According to the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the recommended sleep times for school-age children are: 10-13 hours each night for 5-year-olds. 9-12 hours each night for 6- to 12-year-olds. At least 8 hours each night for kids 13 years old and older.
Kids Need Rest. Others, however, are quick to point out that today's students are already facing high stress levels, and the last thing they need over the holidays is more assignments. Homework over winter break is unnecessary, says Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth. In fact, kids probably don't need to do homework ever.
Take a look at what to include in a daily schedule for a 6 year old: 1. Morning routine. Mornings can be rough when you know you have to get to school or work (or both) by a certain time. And if school starts early, this can really cut those mornings short and make them extra hectic.
Try these steps before you begin, so you can hit the ground running on the first day of homeschooling: Step 1: In some states, compulsory attendance starts at age 6. Make sure to check your state's homeschool laws to ensure you stay compliant. Step 2: Choose your curriculum and format (online or print).
Worksheets for 6-Year-Olds. Introducing our vibrant collection of worksheets designed specifically for 6-Year-Olds! These engaging activities are tailored to foster creativity, enhance problem-solving skills, and build foundational knowledge in various subjects. Crafted by educational experts, our worksheets are perfect for young learners eager ...
A guide to help parents of 6-year-olds who are homeschooling their children. 1. Prepare your child to be homeschooled. It takes a lot of hard work and time to homeschool. It will be difficult for your child if they aren't ready to learn, so it's best to begin during the summer when they have more free time.