The best ways to reduce air pollution and tackle climate change together

Electrifying public transport is one way to lower both air pollution and carbon emissions Image: REUTERS/Rodrigo Garrido

.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Richard Fuller

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Air Pollution is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, air pollution.
- Prevailing wisdom holds that measures to reduce air pollution will also tackle climate change, and vice versa - but this is not always the case.
- A new report has identified the most effective interventions for addressing both issues at once.
When we look at air pollution and climate change, we see two dire situations:
1. People, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC), are becoming ill and dying prematurely because of the poor quality of the air they breathe. Air pollution is linked to an estimated 4.2 million premature deaths a year , according to the World Health Organization. When indoor air quality is considered, that number rises by an estimated 2.9 to 4.3 million deaths a year, according to The Lancet Commission .
2. Glacial ice is melting, droughts are becoming more prolonged, extreme weather events are more common, and cities around the world are reporting record-breaking heat, all against a backdrop of predictions from the International Panel on Climate Change of temperature increases between 2.5˚C and 10˚C over the next century.
Have you read?
Air pollution in europe is decreasing but it still has some hotspots, youth can help fight air pollution in africa. here's how, here's a cost-effective way to improve air quality, indoor air pollution: what causes it and how to tackle it.
For years, the prevailing wisdom has argued that the same adverse conditions that propel climate change also are responsible for air pollution, and that by correcting one problem we can also solve the other.
Unfortunately, it's not as simple as that. Some interventions that can massively improve air quality and the health of people in affected communities, such as using lower-sulphur diesel fuel, have little or no impact on climate change. Others produce benefits for the climate but do not significantly impact health. And still other popular and often costly interventions do little to improve air quality or slow the pace of climate change.
With our partners – AirQualityAsia, The Schiller Institute for Integrated Science and Society at Boston College, and with support from the Clean Air Fund – we set out to identify the most successful and practical actions that can improve health by reducing air pollution and impact climate change . Because very little analytical data is available about outcomes for specific interventions, our researchers and consultants went directly to those deeply involved in air pollution projects around the world to learn what had worked, what had not, and why.
The result of these efforts – a new report entitled Air Pollution Interventions: Seeking the Intersection between Climate and Health – is intended to help governments and policy-makers identify and implement the most effective interventions for their communities and particular situations.

When we talk about adverse health effects from air pollution, our report focuses primarily on particulate matter 2.5 microns and smaller in size (PM2.5), which are largely produced by carbon burning. These microscopic particles, less than one-thirtieth the width of a human air, pass through the lungs and into the bloodstream where they are carried throughout the body to cause damage to respiratory, cardiovascular, and other systems, and according to the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation account for more than 85% of air pollution-related mortality .
With regard to climate change, the report mainly looks at activities that increase atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide and black carbon.
PM2.5, black carbon and CO2 are largely the byproducts of carbon burning. The three primary sources are:
1. Energy generation from coal and natural gas
2. Public and private transportation of people and goods using diesel or gasoline
3. Open fires, mostly crop burning and forest fires, but also uncontrolled waste incineration
Coal-fired power plants are the granddaddies of air pollution and climate change – and we've known this for some time. Likewise, the single most effective action governments can take to improve air quality and to impact climate change is to phase out the use of coal and other fossil fuels, such as tar and lignite, for power generation.
If you take a big coal-fired power plant in the middle of a city and replace it with renewable energy, that's a huge step to reduce air pollution. Converting coal-fired power plants to natural gas or installing scrubbers reduces PM2.5 emissions – and so benefits health – but the carbon-burning power plants are still producing CO2 and climate-changing emissions. While moving that coal-fired power plant outside the city may be politically popular with millions of city dwellers (less so, perhaps, with people near the new plant), the action is costly and does nothing to benefit health or climate change.

Best ways to reduce air pollution
Other significant interventions that improve both health by reducing PM2.5 and impact climate change by reducing CO2 emissions include:
• Replacing diesel and gasoline-powered vehicles with electric vehicles. Shenzhen, China, for instance, has switched from diesel-powered public transportation to an electric bus fleet with an expected 48% reduction in CO2 emissions and significant reductions in particulate matter.
• Eliminating uncontrolled diesel emissions. Studies have found that reducing vehicle fleet levels from the equivalent of Euro I to Euro IV can reduce fleet emissions by about 80% and moving up to Euro V standards further reduces the remaining emissions by 80%. This is a great step to remove air pollution and CO2 levels.
• Preventing crop burning. Specific technologies and education can improve outcomes for farmers without burning – creating win-win situations. Education and support for agricultural extension programmes in developing countries are key to their success. Poland, for example, has largely phased out the practice of burning the stubble left after the wheat harvest. Government initiatives in Delhi to combat crop burning, a significant source of air pollution, include awareness and capacity building, technological interventions, and subsidies for farmers to purchase straw management machines. Still, the twice-annual traditional crop burning contributes significantly to Delhi's notorious haze.
Our team considered 22 interventions with dozens of supporting case studies with the goal of helping governments and policy-makers determine which interventions may be most practical and beneficial for their particular problems.
Climate change poses an urgent threat demanding decisive action. Communities around the world are already experiencing increased climate impacts, from droughts to floods to rising seas. The World Economic Forum's Global Risks Report continues to rank these environmental threats at the top of the list.
To limit global temperature rise to well below 2°C and as close as possible to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, it is essential that businesses, policy-makers, and civil society advance comprehensive near- and long-term climate actions in line with the goals of the Paris Agreement on climate change.
The World Economic Forum's Climate Initiative supports the scaling and acceleration of global climate action through public and private-sector collaboration. The Initiative works across several workstreams to develop and implement inclusive and ambitious solutions.
This includes the Alliance of CEO Climate Leaders, a global network of business leaders from various industries developing cost-effective solutions to transitioning to a low-carbon, climate-resilient economy. CEOs use their position and influence with policy-makers and corporate partners to accelerate the transition and realize the economic benefits of delivering a safer climate.
Contact us to get involved.
We know that exposure to PM2.5 makes people more susceptible to respiratory illnesses; preliminary studies and anecdotal reporting early in the COVID-19 pandemic suggest that infection rates initially were higher and illnesses more severe in cities with poorer air quality. We also know that increasingly the citizenry is demanding that its leaders take swift and sure action to combat air pollution, as underscored by a recent survey by the Clean Air Fund of people in the UK, Bulgaria, India, Nigeria and Poland. As The New York Times reports , the survey, which was conducted during the pandemic between 22 May 22 and 2 June, found overwhelming support for stricter air quality regulations and better enforcement of existing rules. In Nigeria and India, for instance, 90% of those surveyed said they wanted improved air quality.
The most important step for municipal and national agencies to reduce air pollution is to raise their level of ambition in achieving their air quality and climate objectives. The overall aim must be an economy where development is uncoupled from resource use and energy provision is de-carbonized. Short-term actions can then be selected and implemented within that framework.
The solutions exist – and with technical support, strategic funding, and public and private initiatives, we can successfully improve public health and combat climate change.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Nature and Biodiversity .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Tourism is bouncing back - but can we make travel sustainable?
Robin Pomeroy and Sophia Akram
May 23, 2024

Businesses must do more to protect biodiversity: Here are key steps to a nature-positive future
Anna-Maria Fyfe Hug
May 22, 2024

250 million more older people could be exposed to dangerous heat levels, and other nature and climate stories you need to read this week
Michael Purton

Critical minerals demand has doubled in the past five years – here are some solutions to the supply crunch
Emma Charlton
May 16, 2024

The fascinating link between biodiversity and mental wellbeing
Andrea Mechelli
May 15, 2024

These Japanese volunteers are planting seagrass to fight climate change
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Air Pollution Essay

Essay on Air Pollution
Environmental changes are caused by the natural or artificial content of harmful pollutants and can cause instability, disturbance, or adverse effects on the ecosystem. Earth and its environment pose a more serious threat due to the increasing pollution of air, water, and soil. Environmental damage is caused by improper resource management or careless human activities. Therefore, any activity that violates the original nature of the environment and leads to degradation is called pollution. We need to understand the origin of these pollutants and find ways to control pollution. This can also be done by raising awareness of the effects of pollutants.
Air pollution is any physical, chemical, or biological change in the air. A certain percentage of the gas is present in the atmosphere. Increasing or decreasing the composition of these gasses is detrimental to survival. This imbalance in gas composition causes an increase in global temperature which is called global warming.
Introduction to air pollution
The Earth and its environment are facing a serious threat by the increasing pollution of the air, water, and soil—the vital life support systems of the Earth. The damage to the environment is caused by improper management of resources or by careless human activity. Hence any activity that violates the original character of nature and leads to its degradation is called pollution. We need to understand the sources of these pollutants and find ways to control pollution. This can be also done by making people aware of the effects of pollutants.
Air with 78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, and 1% of all other gasses support life on Earth. Various processes take place to sustain the regular percentage of gasses and their composition in general.
Atmospheric pollution can have natural sources, for example, volcanic eruptions. The gaseous by-products of man-made processes such as energy production, waste incineration, transport, deforestation and agriculture, are the major air pollutants.
Although air is made up of mostly Oxygen and Nitrogen, mankind, through pollution, has increased the levels of many trace gasses, and in some cases, released completely new gasses to the atmosphere.
Air pollution can result in poor air quality, both in cities and in the countryside. Some air pollutants make people sick, causing breathing problems and increasing the likelihood of cancer.
Some air pollutants are harmful to plants, animals, and the ecosystems in which they live. Statues, monuments, and buildings are being corroded by the air pollutants in the form of acid rain. It also damages crops and forests, and makes lakes and streams unsuitable for fish and other plant and animal life.
Air pollution created by man-made resources is also changing the Earth’s atmosphere. It is causing the depletion of the ozone layer and letting in more harmful radiation from the Sun. The greenhouse gasses released into the atmosphere prevents heat from escaping back into space and leads to a rise in global average temperatures. Global warming affects the average sea-level and increases the spread of tropical diseases.
Air pollution occurs when large amounts of gas and tiny particles are released into the air and the ecological balance is disturbed. Each year millions of tons of gasses and particulate matter are emitted into the air.
Primary air pollutants are pollutants, which are directly released into the air. They are called SPM, i.e., Suspended Particulate Matter. For example, smoke, dust, ash, sulfur oxide, nitrogen oxide, and radioactive compounds, etc.
Secondary Pollutants are pollutants, which are formed due to chemical interactions between the atmospheric components and primary pollutants. For example, Smog (i.e. Smoke and fog), ozone, etc.
Major gaseous air pollutants include Carbon Dioxide, Hydrogen Sulfide, Sulfur Dioxide and Nitrogen Oxide, etc.
Natural sources are volcanic eruptions, forest fires, dust storms, etc.
Man-made sources include gasses released from the automobiles, industries, burning of garbage and bricks kilns, etc.
Effects of Air Pollution on Human Health
Air pollution has adverse effects on human health.
Breathing polluted air puts you at higher risk of asthma.
When exposed to ground ozone for 6 to 7 hours, people suffer from respiratory inflammation.
Damages the immune system, endocrine, and reproductive systems.
A high level of air pollution has been associated with higher incidents of heart problems.
The toxic chemicals released into the air are affecting the flora and fauna immensely.
Preventive Measures to Reduce Air Pollution
We can prevent pollution by utilizing raw materials, water energy, and other resources more efficiently. When less harmful substances are substituted for hazardous ones, and when toxic substances are eliminated from the production process, human health can be protected and economic wellbeing can be strengthened.
There are several measures that can be adopted by people to reduce pollution and to save the environment.
Carpooling.
Promotion of public transport.
No smoking zone.
Restricted use of fossil fuels.
Saving energy.
Encouraging organic farming.
The government has put restrictions on the amount of fossil fuels that can be used as well as restrictions on how much carbon dioxide and other pollutants can be emitted. Although the government is attempting to save our environment from these harmful gasses, it is not sufficient. We as a society need to keep the environment clean by controlling the pollution of air.

FAQs on Air Pollution Essay
1. State the Causes of Air Pollution ?
The following are the causes of air pollution.
Vehicular pollution consisting of Carbon Monoxide causes pollution.
Emission of Nitrogen oxide by a large number of supersonic transport airplanes causes deterioration of the Ozone layer and also causes serious damage to the flora and fauna.
The release of Chlorofluorocarbons into the Stratosphere causes depletion of Ozone, which is a serious concern to animals, microscopic, and aquatic organisms.
Burning garbage causes smoke, which pollutes the atmosphere. This smoke contains harmful gases such as Carbon dioxide and Nitrogen oxides.
In India, brick kilns are used for many purposes and coal is used to burn the bricks. They give out huge quantities of Carbon dioxide and particulate matter such as smoke, dust that are very harmful to people working there and the areas surrounding it.
Many cleansing agents release poisonous gases such as Ammonia and Chlorine into the atmosphere.
Radioactive elements emit harmful rays into the air.
Decomposed animals and plants emit Methane and Ammonia gas into the air.
2. What Does Global Warming Mean?
Global warming is the gradual rising average temperature of the Earth's atmosphere due to the concentration of methane in certain toxic gasses such as carbon dioxide. This has a major impact on the world climate. The world is warming. The land and the sea are now warmer than they were at the beginning and temperatures are still rising. This rise in temperature is, in short, global warming. This temperature rise is man-made. The burning of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere which capture solar heat and raise surface and air temperatures.
3. Name the Alternative Modes of Transport. In What Way Does it Help to Reduce Air Pollution?
Public transport could be an alternative mode of transport. Public transport like trains, buses and trams, can relieve traffic congestion and reduce air pollution from road transport. The use of public transport must be encouraged in order to develop a sustainable transport policy.
4. Mention other means of transportation! How can I help reduce air pollution?
Public transportation can be another mode of transportation. Public transport such as trains, buses and trams can reduce traffic congestion and reduce air pollution from road transport. The use of public transport and to develop sustainable transport policies should be encouraged. While one passenger vehicle has the convenience factor, other modes of transportation reduce travel costs, spend less time, reduce stress, improve health, and reduce energy consumption and parking. Other trips for work include walking/cycling, public transport, hybrid travel and transport.
5. What are the effects of pollution?
Excessive air pollution can increase the risk of heart attack, wheezing, coughing and difficulty breathing, as well as irritation of the eyes, nose and throat. Air pollution can also cause heart problems, asthma, and other lung problems. Due to the emission of greenhouse gases, the composition of the air in the air is disturbed. This causes an increase in global temperature. The damaging ozone layer due to air pollution does not prevent harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun, which cause skin and eye problems in individuals. Air pollution has caused a number of respiratory and heart diseases among people. The incidence of lung cancer has increased in recent decades. Children living in contaminated areas are more likely to develop pneumonia and asthma. Many people die every year due to the direct or indirect effects of air pollution. When burning fossil fuels, harmful gases such as nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides are released into the air. Water droplets combine with these pollutants and become acidic and fall as acid rain, which harms human, animal and plant life.
6. What is the solution to air pollution?
Production of renewable fuels and clean energy. The basic solution to air pollution is to get away from fossil fuels and replace them with other energies such as solar, wind and geothermal. The government limits the amount of fossil fuel that can be used and how much carbon dioxide and other pollutants it can emit. While the government is trying to save our environment from this harmful gas, it is not enough. We as a society need to keep the environment clean by controlling air pollution. To more in detail about air pollution and its causes. To learn more about air pollution and its impact on the environment, visit the Vedantu website.
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- Climate Change
- Policy & Economics
- Biodiversity
- Conservation
Get focused newsletters especially designed to be concise and easy to digest
- ESSENTIAL BRIEFING 3 times weekly
- TOP STORY ROUNDUP Once a week
- MONTHLY OVERVIEW Once a month
- Enter your email *
5 Effective Air Pollution Prevention Strategies

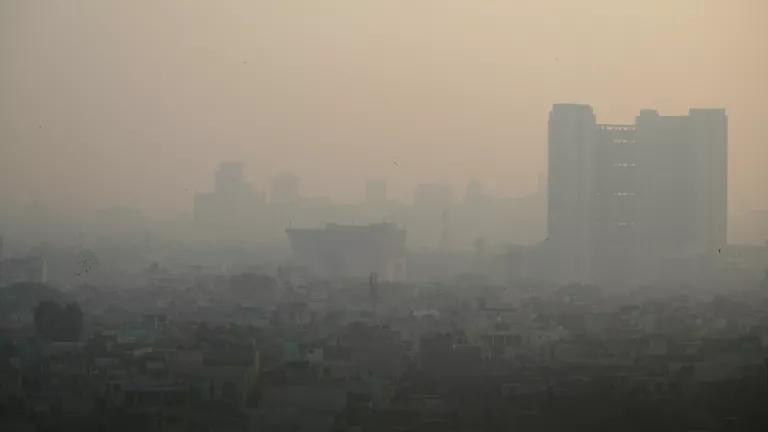
Every year, air pollution prematurely kills about seven million people worldwide. It is also one of the biggest threats to human health, increasing the risk of chronic heart and pulmonary diseases, lung cancer, stroke, and respiratory infections. What’s more, air pollution is contributing to the climate crisis and accelerating global warming. Governments urgently need to commit to air pollution prevention in an effort to solve one of the direst environmental problems in the world right now. As we celebrate the International Day of Clean Air for Blue Skies, which every year falls on September 7, we reflect on some of the most promising solutions to air pollution out there.
Sometime between 1820 and 1840, the world began transitioning to new manufacturing processes that became known as the Industrial Revolution. While this represented a turning point in the history of technological advancement and moulding the world as we know it today, industrialisation came at a huge cost for the environment and affected worldwide air quality, especially in new, developing urban areas. Even today, the highest levels of air pollution are recorded in cities. Six of the world’s 10 most polluted cities in 2021 were in India, with Bhiwadi topping the list, while neighbouring countries like Pakistan and Bangladesh are also some of the worst affected. In China, despite the huge progress made in recent years, where particulate pollution saw a 29% drop globally, 1.25 million people still die prematurely from pollution-related diseases every year.
The world has made remarkable advancements in air pollution reduction technologies and an increasing number of countries around the world have pledged to end all emissions in the coming decades. We explore the main drivers and effects of air pollution on the environment before diving deep into some of the best strategies for air pollution prevention.
Drivers of Air Pollution
Air pollution refers to the release of chemicals and pollutant particles into the air, mainly through human activities. Among the biggest contributors are fossil fuels. Global demand for oil, natural gas, and coal continues to increase despite calls to end our dependence on these energy sources in order to meet net-zero emissions goals. In 2021, global energy-related emissions reached a staggering 36.3 billion tonnes of CO2, their highest-ever level. 40% of which came from coal – soaring to an all-time high of 15.3 billion tonnes – followed by 10.7 billion tonnes from oil, and 7.5 billion tonnes from natural gas.
Another driver is ozone, a toxic gas that turns into smog – an extremely harmful form of air pollution – when it reaches too close to the ground, significantly reducing visibility. Extreme climate events like dust storms as well as changing weather conditions are also responsible for poisoning the atmosphere. For example, high air pressure and heat waves can create stagnant air where pollutants usually concentrate in large quantities. Extreme heat waves also increase the risks of large-scale wildfires, notorious for releasing more carbon emissions, smog, and pollutants into the air.
Effects of Air Pollution on the Environment
Apart from causing millions of premature deaths and illnesses – especially in low-income countries like South and East Asia – there is growing evidence among the scientific community that air pollution can have detrimental impacts on other aspects of human health and wellbeing – such as their cognitive function. Several studies have found that polluted air often impedes or lowers the cognitive ability of those frequently exposed to it.
But air pollution does not only impact humans. Its environmental effects are also vast and worrying. They range from acid rain – which is extremely harmful to the soil and plants – to birth defects, reproductive failure, and diseases among wildlife animals. Highly polluted rain can also compromise agriculture, as it makes crops more vulnerable to diseases from increased UV radiation caused by ozone depletion.
You might also like: History of Air Pollution: Have We Reached A Point of No Return?
Air Pollution Prevention
While we know much about the causes and effects of air pollution, there is still much to be done in terms of prevention. To understand how governments can tackle the problem, it is useful to have a look at the main sectors contributing to global greenhouse gas emissions. Indeed, the only ways to drastically reduce air pollution are to adopt a wide range of policies that regulate all polluting industries – from energy production to transportation and agriculture – as well as to reflect on broader solutions such as carbon tax systems.
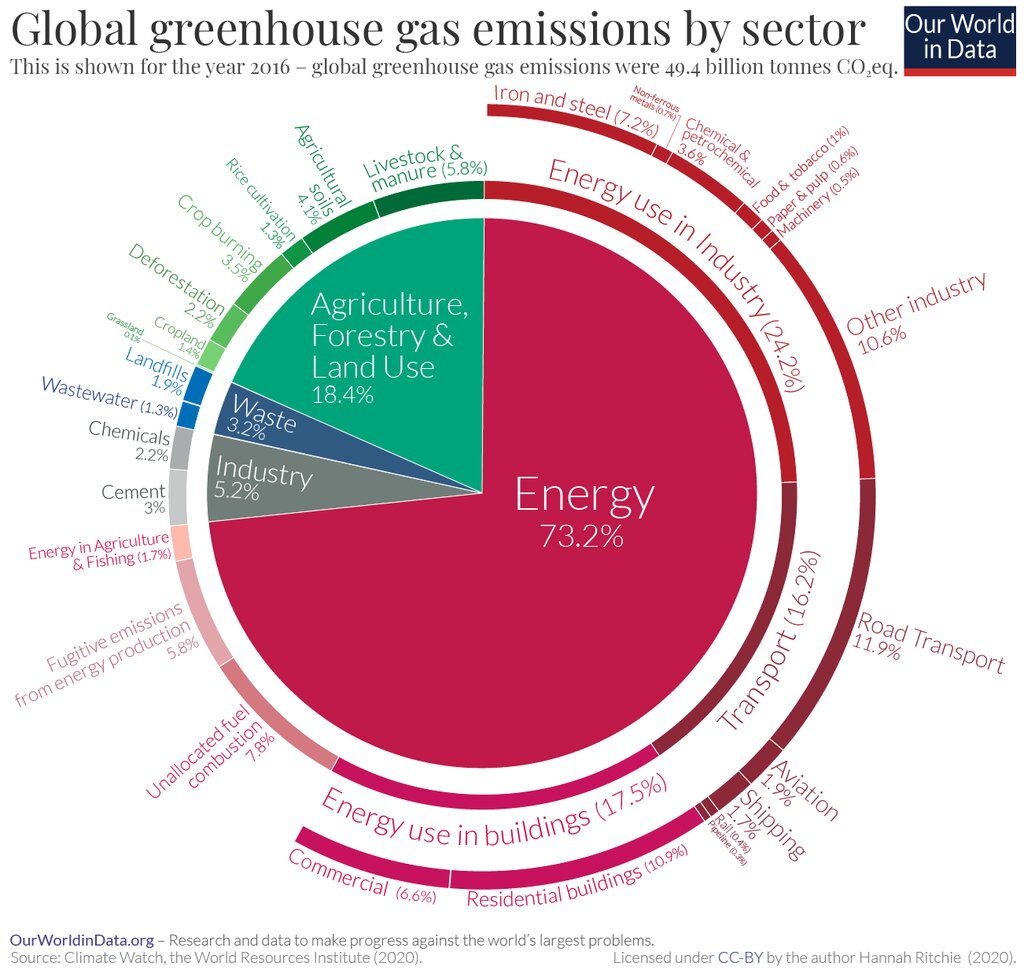
Figure 1: World’s Most Polluting Sectors, 2020
1. Cut Down Emissions from Power Plants
One obvious but effective strategy to cut down emissions is to phase out fossil fuels immediately, yet it has proven to be difficult to implement. As the latest IPCC climate report clearly stated, in the race to reach net-zero emissions, there is no room for any fossil fuel developments . Shifting to other energy sources like nuclear and renewables is a long and complicated process that requires global coordination and collaboration. Yet, not all countries are on board and while some are slowly making the transition, others have no intentions of phasing out fossil fuels.
In the meantime, countries like the US are implementing strategies to hold power plants accountable for their pollution. For example, in March 2022, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) unveiled the “Good Neighbor” plan to cut interstate smog pollution from power stations by requiring them to operate their pollution control equipment and keep their daily emissions under a pre-established limit.
2. Decarbonise the Global Transport Sector
Transport accounts for 8 billion tonnes – or approximately one-fifth – of global carbon dioxide emissions. These are expected to grow significantly over the next 30 years as a result of increasing transport demand.
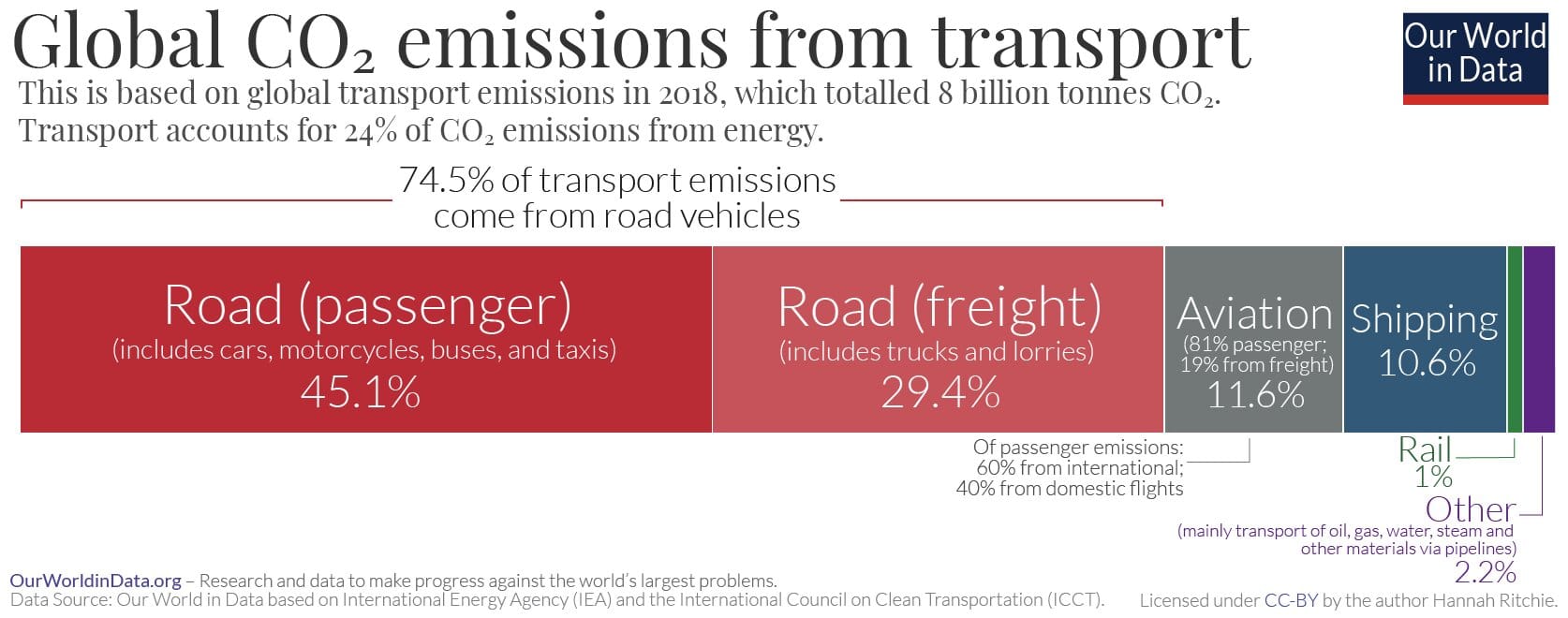
Figure 2: Global CO2 Emissions from Transport, 2018
According to the EPA, there are three methods to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from transportation. The first is to increase the efficiency of vehicle technology. A good start – according to a report by the United Nations – is developing weight reduction and improvements to engines and tires that can make vehicles more fuel-efficient, reduce their reliance on oil, and cut expenses.
One of the most important technologies we have to decarbonise the transport sector is electric vehicles (EV). Significant progress has been made in this industry and costs of batteries have declined by 90% in recent years. Despite EVs being a much better alternative than fossil fuel vehicles, as the latter generate much higher emissions over their lifetime, the electrification of the transportation sector has a dark side. Producing EV batteries requires greater resource extractivism , which has substantial destructive consequences for the environment and local communities, an aspect of this industry that cannot be ignored. Fortunately, EV companies are building a much more sustainable supply chain by improving the efficiency and lifespan of batteries, researching a way to build them using other resources as well as recycling old batteries to reuse raw materials.
But switching to EVs is not the only option we have. We can lower transportation’s carbon footprint by changing how we travel – for example, opting for public transport and car-sharing – as well as how we transport goods around the world. Emissions from the global supply chain have reached historic heights. In 2020, the shipping and return of products within the e-commerce industry alone accounted for 37% of the total GHG emissions , attributing to the unsustainable habits of modern consumers and their appetite for convenience. It is estimated that by 2030, the number of delivery vehicles will increase by 36%, reaching approximately 7.2 million vehicles . This will not only result in an increase of about 6 million tonnes of CO2 emissions, but it will also increase commutes by 21%, as vehicles will take longer to travel due to higher traffic congestion. All things considered, the best way to drastically reduce the impact of the shipping industry is by rethinking the means of transport, for example by prioritising rail and marine vessels over truck drivers.
Emissions can also be reduced by using fuels with a minimal carbon footprint such as biofuels , renewable natural gas, hydrogen as well as sustainable aviation fuel . Lastly, it is the governments’ job to implement tighter fuel and vehicle emission standards. As part of its targets to reduce the net greenhouse gas emissions by 50% in 2030, the US has taken into account many sector-specific reduction pathways . The Biden administration is currently working on incentives for zero-emission personal vehicles, funding for charging infrastructure, and support for research in low carbon, new-generation renewable fuels. Simultaneously, sixteen states including California, New York, and Pennsylvania, are imposing their own pollution limits on cars . Similarly, the European Union is encouraging the production of greener vehicles and it has recently strengthened the CO2 standards for cars and vans as a way to facilitate its phase-out of internal combustion engines.
3. Adopt a More Sustainable Approach to Agriculture
Recent data from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) shows that 31% of human-caused GHG emissions originate from the world’s agri-food systems. From the 16.5 tonnes generated in 2019, the largest share – 7.2 billion tonnes – came from within the farm gate, 5.8 billion tonnes from the supply-chain processes, while 3.5 billion tonnes from land use change.
Thus, efforts to address the exploitation of resources like land and water as well as the promotion of sustainable agriculture are among the most crucial steps in air pollution prevention. A big issue related to soil depletion is the excessive use of fertilisers. Switching to nitrate-based solutions can be one of the easiest fixes in reducing farms’ impact on air pollution. Israel has made incredible technological advances and managed to reduce the overconsumption of water through drip irrigation , a system that delivers water and nutrients directly into the plant’s root through pipes. The technology is now being used in some African countries as well, thanks to funding from the World Bank. Lastly, countries like Australia have found ways to reduce agricultural methane emissions from farming by modifying the diets of livestock .
4. Introduce a Carbon Tax System
A carbon tax is an instrument of environmental cost internalisation, imposed on producers of raw fossil fuels based on the relative carbon content of those fuels. Governments usually set a fixed price that emitting companies must pay for each ton of greenhouse gas emissions they emit.
So far, 27 countries have implemented a carbon tax system as a way to incentivise polluters to lower emissions or switch to more efficient processes and cleaner fuels. At the same time, the carbon tax is a great way to reduce air pollution and greenhouse gases generated from the same human activities and it is thus a good way to hit two birds with one stone .
5. Improving Air Quality While Fighting Climate Change
Last but not least, air pollution can be prevented by tackling climate change. These two phenomena are closely intertwined and neither can be seen exclusively as the cause or the effect. While deteriorating air quality is a consequence of climate change, air pollution also contributes to worsening global warming. That is why the climate crisis cannot be left out of the equation. Effective efforts to tackle climate change would significantly reduce deforestation and wildfires, two of the main sources of air pollution. Air quality and climate change are just one example of causes and effects overlapping. Therefore, the best shot for governments around the world to reduce air pollution is to implement broader policies that aim at tackling all aspects of the looming climate crisis.
You might also like: 15 Most Polluted Cities in the US
About the Author

Martina Igini

15 Biggest Environmental Problems of 2024

Water Shortage: Causes and Effects

International Day of Forests: 10 Deforestation Facts You Should Know About
Hand-picked stories weekly or monthly. We promise, no spam!
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Boost this article By donating us $100, $50 or subscribe to Boosting $10/month – we can get this article and others in front of tens of thousands of specially targeted readers. This targeted Boosting – helps us to reach wider audiences – aiming to convince the unconvinced, to inform the uninformed, to enlighten the dogmatic.

Russell Millner/Alamy
Defend Our Planet and Most Vulnerable Species
Your donation today will be triple-matched to power NRDC’s next great chapter in protecting our ecosystems and saving imperiled wildlife.
Air Pollution: Everything You Need to Know
How smog, soot, greenhouse gases, and other top air pollutants are affecting the planet—and your health.

- Share this page block
What is air pollution?
What causes air pollution, effects of air pollution, air pollution in the united states, air pollution and environmental justice, controlling air pollution, how to help reduce air pollution, how to protect your health.
Air pollution refers to the release of pollutants into the air—pollutants that are detrimental to human health and the planet as a whole. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) , each year, indoor and outdoor air pollution is responsible for nearly seven million deaths around the globe. Ninety-nine percent of human beings currently breathe air that exceeds the WHO’s guideline limits for pollutants, with those living in low- and middle-income countries suffering the most. In the United States, the Clean Air Act , established in 1970, authorizes the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to safeguard public health by regulating the emissions of these harmful air pollutants.
“Most air pollution comes from energy use and production,” says John Walke , director of the Clean Air team at NRDC. Driving a car on gasoline, heating a home with oil, running a power plant on fracked gas : In each case, a fossil fuel is burned and harmful chemicals and gases are released into the air.
“We’ve made progress over the last 50 years in improving air quality in the United States, thanks to the Clean Air Act. But climate change will make it harder in the future to meet pollution standards, which are designed to protect health ,” says Walke.
Air pollution is now the world’s fourth-largest risk factor for early death. According to the 2020 State of Global Air report —which summarizes the latest scientific understanding of air pollution around the world—4.5 million deaths were linked to outdoor air pollution exposures in 2019, and another 2.2 million deaths were caused by indoor air pollution. The world’s most populous countries, China and India, continue to bear the highest burdens of disease.
“Despite improvements in reducing global average mortality rates from air pollution, this report also serves as a sobering reminder that the climate crisis threatens to worsen air pollution problems significantly,” explains Vijay Limaye , senior scientist in NRDC’s Science Office. Smog, for instance, is intensified by increased heat, forming when the weather is warmer and there’s more ultraviolet radiation. In addition, climate change increases the production of allergenic air pollutants, including mold (thanks to damp conditions caused by extreme weather and increased flooding) and pollen (due to a longer pollen season). “Climate change–fueled droughts and dry conditions are also setting the stage for dangerous wildfires,” adds Limaye. “ Wildfire smoke can linger for days and pollute the air with particulate matter hundreds of miles downwind.”
The effects of air pollution on the human body vary, depending on the type of pollutant, the length and level of exposure, and other factors, including a person’s individual health risks and the cumulative impacts of multiple pollutants or stressors.
Smog and soot
These are the two most prevalent types of air pollution. Smog (sometimes referred to as ground-level ozone) occurs when emissions from combusting fossil fuels react with sunlight. Soot—a type of particulate matter —is made up of tiny particles of chemicals, soil, smoke, dust, or allergens that are carried in the air. The sources of smog and soot are similar. “Both come from cars and trucks, factories, power plants, incinerators, engines, generally anything that combusts fossil fuels such as coal, gasoline, or natural gas,” Walke says.
Smog can irritate the eyes and throat and also damage the lungs, especially those of children, senior citizens, and people who work or exercise outdoors. It’s even worse for people who have asthma or allergies; these extra pollutants can intensify their symptoms and trigger asthma attacks. The tiniest airborne particles in soot are especially dangerous because they can penetrate the lungs and bloodstream and worsen bronchitis, lead to heart attacks, and even hasten death. In 2020, a report from Harvard’s T.H. Chan School of Public Health showed that COVID-19 mortality rates were higher in areas with more particulate matter pollution than in areas with even slightly less, showing a correlation between the virus’s deadliness and long-term exposure to air pollution.
These findings also illuminate an important environmental justice issue . Because highways and polluting facilities have historically been sited in or next to low-income neighborhoods and communities of color, the negative effects of this pollution have been disproportionately experienced by the people who live in these communities.
Hazardous air pollutants
A number of air pollutants pose severe health risks and can sometimes be fatal, even in small amounts. Almost 200 of them are regulated by law; some of the most common are mercury, lead , dioxins, and benzene. “These are also most often emitted during gas or coal combustion, incineration, or—in the case of benzene—found in gasoline,” Walke says. Benzene, classified as a carcinogen by the EPA, can cause eye, skin, and lung irritation in the short term and blood disorders in the long term. Dioxins, more typically found in food but also present in small amounts in the air, is another carcinogen that can affect the liver in the short term and harm the immune, nervous, and endocrine systems, as well as reproductive functions. Mercury attacks the central nervous system. In large amounts, lead can damage children’s brains and kidneys, and even minimal exposure can affect children’s IQ and ability to learn.
Another category of toxic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), are by-products of traffic exhaust and wildfire smoke. In large amounts, they have been linked to eye and lung irritation, blood and liver issues, and even cancer. In one study , the children of mothers exposed to PAHs during pregnancy showed slower brain-processing speeds and more pronounced symptoms of ADHD.
Greenhouse gases
While these climate pollutants don’t have the direct or immediate impacts on the human body associated with other air pollutants, like smog or hazardous chemicals, they are still harmful to our health. By trapping the earth’s heat in the atmosphere, greenhouse gases lead to warmer temperatures, which in turn lead to the hallmarks of climate change: rising sea levels, more extreme weather, heat-related deaths, and the increased transmission of infectious diseases. In 2021, carbon dioxide accounted for roughly 79 percent of the country’s total greenhouse gas emissions, and methane made up more than 11 percent. “Carbon dioxide comes from combusting fossil fuels, and methane comes from natural and industrial sources, including large amounts that are released during oil and gas drilling,” Walke says. “We emit far larger amounts of carbon dioxide, but methane is significantly more potent, so it’s also very destructive.”
Another class of greenhouse gases, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) , are thousands of times more powerful than carbon dioxide in their ability to trap heat. In October 2016, more than 140 countries signed the Kigali Agreement to reduce the use of these chemicals—which are found in air conditioners and refrigerators—and develop greener alternatives over time. (The United States officially signed onto the Kigali Agreement in 2022.)
Pollen and mold
Mold and allergens from trees, weeds, and grass are also carried in the air, are exacerbated by climate change, and can be hazardous to health. Though they aren’t regulated, they can be considered a form of air pollution. “When homes, schools, or businesses get water damage, mold can grow and produce allergenic airborne pollutants,” says Kim Knowlton, professor of environmental health sciences at Columbia University and a former NRDC scientist. “ Mold exposure can precipitate asthma attacks or an allergic response, and some molds can even produce toxins that would be dangerous for anyone to inhale.”
Pollen allergies are worsening because of climate change . “Lab and field studies are showing that pollen-producing plants—especially ragweed—grow larger and produce more pollen when you increase the amount of carbon dioxide that they grow in,” Knowlton says. “Climate change also extends the pollen production season, and some studies are beginning to suggest that ragweed pollen itself might be becoming a more potent allergen.” If so, more people will suffer runny noses, fevers, itchy eyes, and other symptoms. “And for people with allergies and asthma, pollen peaks can precipitate asthma attacks, which are far more serious and can be life-threatening.”

More than one in three U.S. residents—120 million people—live in counties with unhealthy levels of air pollution, according to the 2023 State of the Air report by the American Lung Association (ALA). Since the annual report was first published, in 2000, its findings have shown how the Clean Air Act has been able to reduce harmful emissions from transportation, power plants, and manufacturing.
Recent findings, however, reflect how climate change–fueled wildfires and extreme heat are adding to the challenges of protecting public health. The latest report—which focuses on ozone, year-round particle pollution, and short-term particle pollution—also finds that people of color are 61 percent more likely than white people to live in a county with a failing grade in at least one of those categories, and three times more likely to live in a county that fails in all three.
In rankings for each of the three pollution categories covered by the ALA report, California cities occupy the top three slots (i.e., were highest in pollution), despite progress that the Golden State has made in reducing air pollution emissions in the past half century. At the other end of the spectrum, these cities consistently rank among the country’s best for air quality: Burlington, Vermont; Honolulu; and Wilmington, North Carolina.
No one wants to live next door to an incinerator, oil refinery, port, toxic waste dump, or other polluting site. Yet millions of people around the world do, and this puts them at a much higher risk for respiratory disease, cardiovascular disease, neurological damage, cancer, and death. In the United States, people of color are 1.5 times more likely than whites to live in areas with poor air quality, according to the ALA.
Historically, racist zoning policies and discriminatory lending practices known as redlining have combined to keep polluting industries and car-choked highways away from white neighborhoods and have turned communities of color—especially low-income and working-class communities of color—into sacrifice zones, where residents are forced to breathe dirty air and suffer the many health problems associated with it. In addition to the increased health risks that come from living in such places, the polluted air can economically harm residents in the form of missed workdays and higher medical costs.
Environmental racism isn't limited to cities and industrial areas. Outdoor laborers, including the estimated three million migrant and seasonal farmworkers in the United States, are among the most vulnerable to air pollution—and they’re also among the least equipped, politically, to pressure employers and lawmakers to affirm their right to breathe clean air.
Recently, cumulative impact mapping , which uses data on environmental conditions and demographics, has been able to show how some communities are overburdened with layers of issues, like high levels of poverty, unemployment, and pollution. Tools like the Environmental Justice Screening Method and the EPA’s EJScreen provide evidence of what many environmental justice communities have been explaining for decades: that we need land use and public health reforms to ensure that vulnerable areas are not overburdened and that the people who need resources the most are receiving them.
In the United States, the Clean Air Act has been a crucial tool for reducing air pollution since its passage in 1970, although fossil fuel interests aided by industry-friendly lawmakers have frequently attempted to weaken its many protections. Ensuring that this bedrock environmental law remains intact and properly enforced will always be key to maintaining and improving our air quality.
But the best, most effective way to control air pollution is to speed up our transition to cleaner fuels and industrial processes. By switching over to renewable energy sources (such as wind and solar power), maximizing fuel efficiency in our vehicles, and replacing more and more of our gasoline-powered cars and trucks with electric versions, we'll be limiting air pollution at its source while also curbing the global warming that heightens so many of its worst health impacts.
And what about the economic costs of controlling air pollution? According to a report on the Clean Air Act commissioned by NRDC, the annual benefits of cleaner air are up to 32 times greater than the cost of clean air regulations. Those benefits include up to 370,000 avoided premature deaths, 189,000 fewer hospital admissions for cardiac and respiratory illnesses, and net economic benefits of up to $3.8 trillion for the U.S. economy every year.
“The less gasoline we burn, the better we’re doing to reduce air pollution and the harmful effects of climate change,” Walke explains. “Make good choices about transportation. When you can, ride a bike, walk, or take public transportation. For driving, choose a car that gets better miles per gallon of gas or buy an electric car .” You can also investigate your power provider options—you may be able to request that your electricity be supplied by wind or solar. Buying your food locally cuts down on the fossil fuels burned in trucking or flying food in from across the world. And most important: “Support leaders who push for clean air and water and responsible steps on climate change,” Walke says.
- “When you see in the news or hear on the weather report that pollution levels are high, it may be useful to limit the time when children go outside or you go for a jog,” Walke says. Generally, ozone levels tend to be lower in the morning.
- If you exercise outside, stay as far as you can from heavily trafficked roads. Then shower and wash your clothes to remove fine particles.
- The air may look clear, but that doesn’t mean it’s pollution free. Utilize tools like the EPA’s air pollution monitor, AirNow , to get the latest conditions. If the air quality is bad, stay inside with the windows closed.
- If you live or work in an area that’s prone to wildfires, stay away from the harmful smoke as much as you’re able. Consider keeping a small stock of masks to wear when conditions are poor. The most ideal masks for smoke particles will be labelled “NIOSH” (which stands for National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) and have either “N95” or “P100” printed on it.
- If you’re using an air conditioner while outdoor pollution conditions are bad, use the recirculating setting to limit the amount of polluted air that gets inside.
This story was originally published on November 1, 2016, and has been updated with new information and links.
This NRDC.org story is available for online republication by news media outlets or nonprofits under these conditions: The writer(s) must be credited with a byline; you must note prominently that the story was originally published by NRDC.org and link to the original; the story cannot be edited (beyond simple things such as grammar); you can’t resell the story in any form or grant republishing rights to other outlets; you can’t republish our material wholesale or automatically—you need to select stories individually; you can’t republish the photos or graphics on our site without specific permission; you should drop us a note to let us know when you’ve used one of our stories.
Related Stories

The Particulars of PM 2.5

What Are the Effects of Climate Change?

Fossil Fuel Air Pollution Kills One in Five People
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 04 October 2021
Clean air for a sustainable world
Nature Communications volume 12 , Article number: 5824 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
20k Accesses
6 Citations
17 Altmetric
Metrics details
Air pollution is a cause of disease for millions around the world and now more than ever urgent action is required to tackle the burden of its impacts. Doing so will not only improve both life expectancy and quality of life, but will also lead to a more just and sustainable world.
Recently, we announced that we will publish a new series of collections focused on issues related to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). We start this series with a multidisciplinary collection on air pollution. As tackling air pollution is not one of the core SDGs, this may seem like an unusual choice. It is, however, a pressing environmental hazard affecting an ever increasing part of the world’s population. Currently, 91% of the world’s population live in locations where pollution levels exceed WHO guidelines, and in a recent announcement the WHO have further cut the recommended limits. Air pollution kills around 6.7 million people per year mainly through respiratory and cardiovascular diseases 1 , and has significant impacts on mental health. The main pollutants are sourced from fossil fuel combustion for transport, industry, agriculture and cooking stoves and, therefore, air pollution is linked directly with fulfilling many of our basic needs. As the SDGs aim to tackle the issue of how humanity can live sustainably, it is thus no surprise that addressing air pollution is related to the SDGs in many different ways. Promoting specific SDGs will lead to improved air quality as a side-effect, while reducing emissions will also progress a number of SDGs directly.
The high air pollution levels that we live with today is another demonstration of how our unsustainable lifestyles are one of the key challenges that needs to be overcome to create a more just and liveable world, which is the ultimate goal of the SDGs.

Although air pollution is a global issue, exposure is often not distributed equally. Industrial processes related to the production, trade and consumption of goods is a key source of air pollution. Much of this pollution is released in low- and middle-income countries while they manufacture goods that are traded abroad, allowing rich countries to outsource the air pollution and health effects of their consumption. Hence, global implementation of responsible consumption and sustainable production practices—the focus of SDG9 (“Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure”) and SDG12 (“Responsible Consumption and Production”)—will be key to reduce this unequal responsibility and exposure to dangerous environmental conditions.
Inequality in exposure does not only occur at an international level, but also within countries. Systematic and historical forms of discrimination often translate into higher exposure levels and, hence, enhanced health burdens to marginalized groups around the world. This is probably best studied in the US, where people of colour are shown to live under poorer air quality, independent of other factors like income 2 . In a commentary for our collection Viniece Jennings highlights that whilst green infrastructure has the potential to reduce air pollution, unequal access can limit improvements for marginalised communities 3 . While we often think of air pollution as an outdoor issue, much of the exposure to harmful particles actually happens inside houses. Household air pollution is mainly related to cooking, heating or lighting, often through the combustion of solid fuels. This exposure affects women and children disproportionately, especially in the developing world 4 . Consequently, targeting SDG10 (“Reduce inequality within and among countries”) and SDG 7 (“Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all.”) will be of vital importance to tackle embedded inequalities within and among countries to reduce air pollution exposure.
Air pollution and climate change are closely intertwined as they share the same root cause of human emissions. Even though ambitious climate mitigation policies do not come for free, they will in many cases also lead to improved air quality and lower health costs. The societal costs of air pollution avoided through reduced exposure levels as a result of climate mitigation measures alone are thought to outweigh the initial costs of these policies 5 . Air pollution also physically interacts with the climate system; particles in the atmosphere affect surface temperatures as well as clouds and precipitation. Climate change thus has the potential to “worsen air pollution, even in areas where it has been improving”, as pointed out by Denise Mauzarell in a Q&A for our Clean Air collection 6 . An example of this are the dangerous pollutants released by wildfires that are expected to become ever more frequent and intense in many parts of the world.
Similarly, to climate mitigation, improving air quality depends on strict and ambitious regulatory policies and controls, which must be implemented equitably. In this regard, there are reasons to be optimistic, as strict air quality policies like the Clean Air Act in the US and similar policies in Europe have resulted in reductions in pollution since the 1970s even though levels are still too high and continued efforts are crucial. These efforts show that ambitious policy supported by technological advances like improved filtering and modernization can be successful. These efforts should not only be done at national levels, but also need international collaboration, technology and knowledge transfer in order to acknowledge the shared responsibilities of air pollution. As part of the Clean Air collection we highlight papers Nature Communications has published that look at how policy and technology can be part of the solution to air pollution.
The high air pollution levels that we live with today is another demonstration of how our unsustainable lifestyles are one of the key challenges that needs to be overcome to create a more just and liveable world, which is the ultimate goal of the SDGs. Of course, reducing air pollution on its own will not meet the aims of all the other SDGs. Still, it is an illustrative example of how an interdisciplinary focus on a measurable and technologically approachable issue can help to also achieve other goals. It is in this spirit that our collection brings together research from different disciplines, such as applied scientists, economists, political scientists, health scientists and climate scientists as it is this interdisciplinary collaboration that Nature Communications wants to support will be vital in informing policy and decision makers. We envision that our collection on Clean Air will continue to grow and we welcome submissions across disciplines in this area.
GBD Global Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet 396 , 1223–1249 (2020).
Tessum, C. W. et al. PM 2.5 polluters disproportionately and systemically affect people of color in the United States. Sci. Adv. 7 , 18 (2021).
Jennings, V., Reid C. E., & Fuller C. H. Green infrastructure can limit but not solve air pollution injustice. Nat. Commun. 12 , 4681 (2021).
Gordon, S. B., et al. Respiratory risks from household air pollution in low and middle income countries. Lancet Respir. Med. 2 , 823–860 (2014).
Vandyck, T. et al. Air quality co-benefits for human health and agriculture counterbalance costs to meet Paris Agreement pledges. Nat. Commun. 9 , 4939 (2018).
Nat. Commun. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25491-w .
Download references
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Clean air for a sustainable world. Nat Commun 12 , 5824 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25885-w
Download citation
Published : 04 October 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25885-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Processing nomex nanofibers by ionic solution blow-spinning for efficient high-temperature exhausts treatment.
- Zekun Cheng
- Haiyang Wang
Advanced Fiber Materials (2023)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Air Pollution Solutions
While air pollution is a serious problem, it is a problem that we can solve! In the United States and around the world, people are taking action to reduce emissions and improve air quality.
The Clean Air Act: How Laws Can Help Clean Up the Air
Creating policies and passing laws to restrict air pollution has been an important step toward improving air quality. In 1970, fueled by persistent visible smog in many U.S. cities and industrial areas and an increase in health problems caused by air pollution, the Clean Air Act paved the way for numerous efforts to improve air quality in the United States. The Clean Air Act requires the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to set air quality standards for several hazardous air pollutants reported in the Air Quality Index (AQI) , requires states to have a plan to address air pollution and emissions reduction, and also addresses problems such as acid rain, ozone holes, and greenhouse gas pollution which is causing the climate to warm.
Since the Clean Air Act was passed:
- The amounts of the six common pollutants in the atmosphere measured by the EPA (particulates, ozone, lead, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide) are declining.
- The risks of premature death, low birth weight, and other health problems due to air pollution have decreased.
- Vehicle emissions have decreased, despite increases in the number of miles driven each year, due to stricter emissions standards and increased efficiency in vehicle engines.
- Emissions and toxic pollutants (such as mercury and benzenes) from factories and power plants have decreased, due to new technologies.
- There is less acid rain, due to decreased power plant emissions.
- The ozone hole continues to shrink as a result of banning the use of CFCs.
- Pollution-caused haze in cities and wilderness areas has decreased.
Source: EPA
Most industrialized countries have laws and regulations about air quality. The United Kingdom first passed its Clean Air Act in 1956 following a deadly smog event that killed many London residents. In China, where rapid industrial and urban growth in recent decades resulted in a sharp decrease in air quality, numerous laws about air pollution have been passed, including a frequently updated five-year national plan to meet target reductions in air pollution.
It is important to note that while laws and regulations are helping, the effects of air pollution are still apparent. The decline of toxic air pollutants and health improvements are welcome changes, yet the growing threat of climate change due to fossil fuel emissions remains a problem that still needs to be solved.
There Are Many Solutions to Air Pollution
In order to improve air quality and slow climate warming, change needs to happen on a national and global scale. However, actions at the individual and community level are also important.
- Burn less coal. Pollution from burning all fossil fuels is harmful to the atmosphere, but burning coal has a larger impact on air pollution than burning oil or gas because it releases more carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and heavy metal pollutants per unit of energy. Also, over one-third of the electricity produced in the world comes from burning coal. As of 2014, the global demand for coal is beginning to decline. In North America, coal plants are being replaced by natural gas. Some countries, such as Japan and South Korea, rely more on nuclear energy, and there is a global increase in electricity supplied by clean, renewable sources like wind, solar, and water.

- Conserve energy — at home, work, and everywhere! The demand for electricity, which is most often produced by burning fossil fuels, has grown exponentially over the past decades. Conserve energy by turning off lights, buy appliances rated for energy efficiency, and keep the thermostat set higher in the summer and lower in the winter. Whenever possible, invest in renewable energy sources to power your home. Several countries are using renewables, nuclear power, or lower-emission sources like natural gas to meet their increasing power demand. And many countries plan to significantly increase their use of renewable energy sources in the future.
- Monitor air quality warnings and take action on poor air quality days. On days when pollution levels are high, taking action can help reduce the risk of harm to those who are most vulnerable. Reducing overall car usage and avoiding idling your car can help on days with high levels of ozone pollution. Save refueling and use of gas-powered yard equipment for the evening when it is cooler and ozone levels are lower. On days when particle pollutants are high, avoid burning yard waste and wood. Choosing to carpool or using a clean transportation method is always helpful, especially on days with high levels of air pollution. Check on the air quality in your area at the AirNow website .
- Take action within your community to find solutions to air pollution. Around the world, many of the current solutions are the result of communities coming together to demand change. Citizens in Shenzhen, China, inspired a switch to electric buses in their city. In Brussels, Belgium, a movement started by parents concerned about poor air quality in schools led to a plan to invest in public transportation and bicycling, along with a ban on fueled cars by 2030. And in many countries, governments are closing coal plants and exploring new sources of energy because of citizens who are concerned about climate warming.
Check out the EPA's website to learn more about actions you can take to reduce air pollution.
- Air Quality Activities
- Air Quality Gallery
- Solving Climate Change
ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Air pollution.
Air pollution consists of chemicals or particles in the air that can harm the health of humans, animals, and plants. It also damages buildings.
Biology, Ecology, Earth Science, Geography
Loading ...

Air pollution consists of chemicals or particles in the air that can harm the health of humans, animals, and plants. It also damages buildings. Pollutants in the air take many forms. They can be gases , solid particles, or liquid droplets. Sources of Air Pollution Pollution enters the Earth's atmosphere in many different ways. Most air pollution is created by people, taking the form of emissions from factories, cars, planes, or aerosol cans . Second-hand cigarette smoke is also considered air pollution. These man-made sources of pollution are called anthropogenic sources . Some types of air pollution, such as smoke from wildfires or ash from volcanoes , occur naturally. These are called natural sources . Air pollution is most common in large cities where emissions from many different sources are concentrated . Sometimes, mountains or tall buildings prevent air pollution from spreading out. This air pollution often appears as a cloud making the air murky. It is called smog . The word "smog" comes from combining the words "smoke" and " fog ." Large cities in poor and developing nations tend to have more air pollution than cities in developed nations. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) , some of the worlds most polluted cities are Karachi, Pakistan; New Delhi, India; Beijing, China; Lima, Peru; and Cairo, Egypt. However, many developed nations also have air pollution problems. Los Angeles, California, is nicknamed Smog City. Indoor Air Pollution Air pollution is usually thought of as smoke from large factories or exhaust from vehicles. But there are many types of indoor air pollution as well. Heating a house by burning substances such as kerosene , wood, and coal can contaminate the air inside the house. Ash and smoke make breathing difficult, and they can stick to walls, food, and clothing. Naturally-occurring radon gas, a cancer -causing material, can also build up in homes. Radon is released through the surface of the Earth. Inexpensive systems installed by professionals can reduce radon levels. Some construction materials, including insulation , are also dangerous to people's health. In addition, ventilation , or air movement, in homes and rooms can lead to the spread of toxic mold . A single colony of mold may exist in a damp, cool place in a house, such as between walls. The mold's spores enter the air and spread throughout the house. People can become sick from breathing in the spores. Effects On Humans People experience a wide range of health effects from being exposed to air pollution. Effects can be broken down into short-term effects and long-term effects . Short-term effects, which are temporary , include illnesses such as pneumonia or bronchitis . They also include discomfort such as irritation to the nose, throat, eyes, or skin. Air pollution can also cause headaches, dizziness, and nausea . Bad smells made by factories, garbage , or sewer systems are considered air pollution, too. These odors are less serious but still unpleasant . Long-term effects of air pollution can last for years or for an entire lifetime. They can even lead to a person's death. Long-term health effects from air pollution include heart disease , lung cancer, and respiratory diseases such as emphysema . Air pollution can also cause long-term damage to people's nerves , brain, kidneys , liver , and other organs. Some scientists suspect air pollutants cause birth defects . Nearly 2.5 million people die worldwide each year from the effects of outdoor or indoor air pollution. People react differently to different types of air pollution. Young children and older adults, whose immune systems tend to be weaker, are often more sensitive to pollution. Conditions such as asthma , heart disease, and lung disease can be made worse by exposure to air pollution. The length of exposure and amount and type of pollutants are also factors. Effects On The Environment Like people, animals, and plants, entire ecosystems can suffer effects from air pollution. Haze , like smog, is a visible type of air pollution that obscures shapes and colors. Hazy air pollution can even muffle sounds. Air pollution particles eventually fall back to Earth. Air pollution can directly contaminate the surface of bodies of water and soil . This can kill crops or reduce their yield . It can kill young trees and other plants. Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide particles in the air, can create acid rain when they mix with water and oxygen in the atmosphere. These air pollutants come mostly from coal-fired power plants and motor vehicles . When acid rain falls to Earth, it damages plants by changing soil composition ; degrades water quality in rivers, lakes and streams; damages crops; and can cause buildings and monuments to decay . Like humans, animals can suffer health effects from exposure to air pollution. Birth defects, diseases, and lower reproductive rates have all been attributed to air pollution. Global Warming Global warming is an environmental phenomenon caused by natural and anthropogenic air pollution. It refers to rising air and ocean temperatures around the world. This temperature rise is at least partially caused by an increase in the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases trap heat energy in the Earths atmosphere. (Usually, more of Earths heat escapes into space.) Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that has had the biggest effect on global warming. Carbon dioxide is emitted into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels (coal, gasoline , and natural gas ). Humans have come to rely on fossil fuels to power cars and planes, heat homes, and run factories. Doing these things pollutes the air with carbon dioxide. Other greenhouse gases emitted by natural and artificial sources also include methane , nitrous oxide , and fluorinated gases. Methane is a major emission from coal plants and agricultural processes. Nitrous oxide is a common emission from industrial factories, agriculture, and the burning of fossil fuels in cars. Fluorinated gases, such as hydrofluorocarbons , are emitted by industry. Fluorinated gases are often used instead of gases such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). CFCs have been outlawed in many places because they deplete the ozone layer . Worldwide, many countries have taken steps to reduce or limit greenhouse gas emissions to combat global warming. The Kyoto Protocol , first adopted in Kyoto, Japan, in 1997, is an agreement between 183 countries that they will work to reduce their carbon dioxide emissions. The United States has not signed that treaty . Regulation In addition to the international Kyoto Protocol, most developed nations have adopted laws to regulate emissions and reduce air pollution. In the United States, debate is under way about a system called cap and trade to limit emissions. This system would cap, or place a limit, on the amount of pollution a company is allowed. Companies that exceeded their cap would have to pay. Companies that polluted less than their cap could trade or sell their remaining pollution allowance to other companies. Cap and trade would essentially pay companies to limit pollution. In 2006 the World Health Organization issued new Air Quality Guidelines. The WHOs guidelines are tougher than most individual countries existing guidelines. The WHO guidelines aim to reduce air pollution-related deaths by 15 percent a year. Reduction Anybody can take steps to reduce air pollution. Millions of people every day make simple changes in their lives to do this. Taking public transportation instead of driving a car, or riding a bike instead of traveling in carbon dioxide-emitting vehicles are a couple of ways to reduce air pollution. Avoiding aerosol cans, recycling yard trimmings instead of burning them, and not smoking cigarettes are others.
Downwinders The United States conducted tests of nuclear weapons at the Nevada Test Site in southern Nevada in the 1950s. These tests sent invisible radioactive particles into the atmosphere. These air pollution particles traveled with wind currents, eventually falling to Earth, sometimes hundreds of miles away in states including Idaho, Utah, Arizona, and Washington. These areas were considered to be "downwind" from the Nevada Test Site. Decades later, people living in those downwind areascalled "downwinders"began developing cancer at above-normal rates. In 1990, the U.S. government passed the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act. This law entitles some downwinders to payments of $50,000.
Greenhouse Gases There are five major greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere.
- water vapor
- carbon dioxide
- nitrous oxide
London Smog What has come to be known as the London Smog of 1952, or the Great Smog of 1952, was a four-day incident that sickened 100,000 people and caused as many as 12,000 deaths. Very cold weather in December 1952 led residents of London, England, to burn more coal to keep warm. Smoke and other pollutants became trapped by a thick fog that settled over the city. The polluted fog became so thick that people could only see a few meters in front of them.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Illustrators
Educator reviewer, last updated.
March 6, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
Home — Essay Samples — Environment — Human Impact — Air Pollution
Essays on Air Pollution
As you embark on writing an air pollution essay, it's essential to structure your content effectively. Begin with the introductory paragraph, where you provide basic facts, statistics, and definitions to establish context. Depending on the scope of your essay, you may choose to focus on indoor or outdoor pollution. Tailor your introduction to set the tone and direction of your essay.
Delve into the heart of your essay by discussing the problem of air pollution and its sources. Explain why these sources exist and highlight the pollutants involved. Consider various air pollution essay topics, including respiratory issues, child health concerns, ozone layer depletion, and impacts on wildlife and cardiovascular health. From municipal waste management to green energy initiatives, explore potential solutions and effective strategies for mitigating pollution.
In crafting your essay, ensure you present a methodical approach and propose at least one viable solution to address the problem. Draw inspiration from examples of proposal essays, where statistical data and compelling facts enhance the narrative. Your main thesis statement should encapsulate the causes and effects of air pollution.
To add depth to your essay, consider discussing environmental issues in your local area and drawing comparisons to broader ecological challenges. Providing concrete examples and leveraging factual evidence will enrich your argument and make your essay more compelling.
Consider exploring examples of proposal essays on air pollution to gain valuable insights into structuring and presenting your ideas effectively. By incorporating relevant examples, factual information, and a persuasive argument, your essay will resonate with readers and contribute to greater awareness and action on this critical issue.
Hook Examples for Air Pollution Essays
Statistical hook.
Did you know that each year, air pollution causes over 4.2 million premature deaths worldwide? These startling statistics underscore the urgent need to address this global crisis.
Anecdotal Hook
Picture this: A bustling cityscape obscured by a thick haze of smog, where children play wearing masks. This is the stark reality faced by many urban areas grappling with air pollution.
Question Hook
How can we breathe easy when the air we inhale is increasingly toxic? Explore the consequences of air pollution and discover potential solutions to this pressing environmental issue.
Rhetorical Question Hook
Can we afford to ignore the invisible threat that hangs in the air we breathe? Delve into the hidden dangers of air pollution and its far-reaching impact on public health.
Quotation Hook
"The earth does not belong to us: we belong to the earth." — Marlee Matlin. Reflect on this thought-provoking quote as we delve into the environmental implications of air pollution.
Historical Hook
Travel back to the mid-20th century when air quality in major cities like London and Los Angeles was notoriously poor. Explore the historical context of air pollution regulation and its impact.
Definition Hook
What exactly is air pollution, and how does it differ from other environmental issues? Gain a clear understanding of this concept and its multifaceted nature.
Contrast Hook
Contrast the serene beauty of pristine landscapes with images of smog-choked cities. This stark juxtaposition highlights the importance of combating air pollution.
Narrative Hook
Step into the shoes of individuals living in heavily polluted areas and experience their daily struggles. Their stories shed light on the human side of the air pollution crisis.
Shocking Statement Hook
Prepare to be shocked by the surprising sources of indoor air pollution lurking within our homes. The danger may be closer than you think.
Multidimensional Perspectives on Air Pollution
Ecological impacts of tear gas, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Analysis of The Correlation Between Smog and Allergies
Air pollution: causes and effects, how does air pollution effect on our health, problem of the air pollution, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
The Move to Reduce Air Pollution to Preserve The Human Population
Air pollution: causes, effects, and solutions, air pollution its causes and damaging effects, air pollution in china, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Human Impacts on The Environment
Cases of air pollution in malaysia, the urgent problem of pollution in modern world, negative impacts of air pollution and steps that the usa is taking to curb this problem, environmental pollution in the transport sector and the benefits of electric cars to our environment, ways you can reduce air pollution from your business , environmental factors and climate influences in california, environmental probelms in pakistan: issues in the big cities, evaluation of the health impact of air pollution in america and china, assessment of the ecological problem arising from air pollutants, analysis of the bronx air pollutants problem and the responsibility of the government, trees against world pollution, informative pollutions, their types, causes, impacts, and solutions, understanding the problem of air pollutants and its impact on temperature, the difficulties in mitigating the effects of climate change in the current world, analysis of the approach to better air quality and reduction of air pollution in the us, review of the documentary "under the dome" and the risks associated with air pollution in china, air filter in thailand, a study on the correlation between changes in air pollution and water sources, the serious problem of air pollution in saudi arabia and the solutions to the environmental issue.
Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere.
Household combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities and forest fires are common sources of air pollution. Pollutants of major public health concern include particulate matter, carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide.
Respiratory and heart problems, child health problems, mortality, global warming, acid rain, eutrophication, depletion of the ozone layer, negative effect on wildlife.
Policies and investments that support sustainable land use, cleaner household energy and transport, energy-efficient housing, power generation, industry, and better municipal waste management can effectively reduce key sources of ambient air pollution.
A child born today might not breathe clean air until they are 8. Inhaling air pollution takes away at least 1-2 years of a typical human life. Pollutants that are released into the air, as opposed to land and water pollutants, are the most harmful. Rising levels of air pollution in Beijing has brought a new disease – Beijing cough.
Relevant topics
- Ocean Pollution
- Fast Fashion
- Water Pollution
- Deforestation
- Global Warming
- Climate Change
- Natural Disasters
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Essay on How to Reduce Air Pollution
Students are often asked to write an essay on How to Reduce Air Pollution in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on How to Reduce Air Pollution
Understanding air pollution.
Air pollution is harmful substances in the air. It harms our health and the environment. It’s mainly caused by human activities like burning fossil fuels.
Ways to Reduce Air Pollution
1. Use Public Transport: Using buses, trains, or carpooling reduces the number of vehicles on the road, reducing air pollution. 2. Save Energy: By turning off lights and electronics when not in use, we save energy and reduce pollution. 3. Plant Trees: Trees absorb harmful pollutants and release clean oxygen. 4. Recycle: Recycling reduces the need to burn waste, reducing air pollution.
Remember, every small action counts in fighting air pollution.
Also check:
- Paragraph on How to Reduce Air Pollution
250 Words Essay on How to Reduce Air Pollution
Understanding the gravity of air pollution.
Air pollution, a global environmental menace, poses severe risks to human health and ecosystems. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that approximately 7 million people die annually due to exposure to polluted air. Consequently, it is imperative to devise strategies to mitigate this issue.
Adopting Sustainable Transportation
A significant contributor to air pollution is vehicular emissions. To address this, we must shift towards sustainable modes of transportation. Encouraging public transit, carpooling, biking, or walking can significantly reduce the number of vehicles on the road, thus curbing pollution. Additionally, promoting electric vehicles can help eliminate exhaust emissions.
Embracing Renewable Energy
The energy sector, particularly coal-based power plants, significantly contributes to air pollution. Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power can significantly reduce air pollution. These energy sources are not only sustainable but also emit no pollutants, making them an ideal replacement for fossil fuels.
Improving Waste Management
Improper waste disposal, especially burning, releases harmful pollutants into the air. Implementing effective waste management strategies, such as recycling and composting, can minimize waste burning. Additionally, promoting waste-to-energy technologies can help transform waste into useful energy while reducing pollution.
Enforcing Strict Regulations
Governmental bodies must enforce stringent air quality standards and regulations. Strict penalties for non-compliance can deter potential polluters, ensuring cleaner air.
In conclusion, reducing air pollution requires a collective, concerted effort. Through sustainable transportation, renewable energy, effective waste management, and strict regulations, we can significantly mitigate this global issue.
500 Words Essay on How to Reduce Air Pollution
Introduction.
Air pollution is a pressing issue that threatens the health of our planet and its inhabitants. It is primarily caused by harmful gases and particles released into the atmosphere, mostly from human activities. Addressing this problem requires a multi-faceted approach, involving both individual and collective actions.
One of the primary sources of air pollution is vehicular emissions. As such, it is crucial to promote sustainable transportation methods. Individuals can contribute to reducing air pollution by utilizing public transport, cycling, walking, or carpooling. On a larger scale, governments and corporations can invest in infrastructure for electric vehicles and renewable fuels, which produce fewer emissions than traditional fossil fuels.
Energy Conservation and Efficiency
Energy production, particularly through burning fossil fuels, significantly contributes to air pollution. Therefore, energy conservation is an effective strategy to combat this issue. This can be achieved by using energy-efficient appliances, reducing energy usage, and promoting renewable energy sources. On an institutional level, energy producers can transition to cleaner technologies, such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power.
Waste Management
Improper waste disposal, including open burning of waste, contributes to air pollution. Therefore, effective waste management strategies are essential. This includes recycling, composting, and reducing waste production. On a larger scale, governments can implement policies to regulate waste disposal and encourage recycling.
Legislative Actions
Governments play a crucial role in air pollution reduction by enforcing regulations that limit emissions from various sources. This includes setting stringent standards for industries and vehicles, promoting clean energy, and implementing pollution-control laws. Governments can also incentivize businesses to adopt environmentally friendly practices through tax benefits and subsidies.
Public Awareness and Education
Public awareness and education about air pollution and its impacts are vital for promoting environmentally friendly behavior. This can be achieved through campaigns, workshops, and incorporating environmental education in school curriculums. An informed public is more likely to make sustainable choices and support environmental policies.
Air pollution is a complex issue that requires a comprehensive, multi-pronged approach to address effectively. While individual actions are important, large-scale changes driven by governments and corporations are crucial. Through the combined efforts of individuals, governments, and businesses, we can work towards a future with cleaner air and a healthier planet. It is not just a matter of environmental concern but a significant health and economic issue that, if unchecked, will have far-reaching consequences for future generations. Hence, it is our collective responsibility to reduce air pollution and safeguard our planet.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Causes of Water Pollution
- Essay on Problem of Pollution
- Essay on Wisdom
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Wiley Open Access Collection

Air pollution: Impact and prevention
Martha patricia sierra-vargas.
1 National Institute for Respiratory Diseases ‘Ismael Cosío Villegas’, México
LUIS M TERAN
2 Biomedicine in the Post-Genomic Era, Huitzilac, Morelos, Mexico
Air pollution is becoming a major health problem that affects millions of people worldwide. In support of this observation, the World Health Organization estimates that every year, 2.4 million people die because of the effects of air pollution on health. Mitigation strategies such as changes in diesel engine technology could result in fewer premature mortalities, as suggested by the US Environmental Protection Agency. This review: (i) discusses the impact of air pollution on respiratory disease; (ii) provides evidence that reducing air pollution may have a positive impact on the prevention of disease; and (iii) demonstrates the impact concerted polices may have on population health when governments take actions to reduce air pollution.
INTRODUCTION
Environmental pollution has been a matter of concern for many years. The Mellon Institute of Pittsburgh, PA, USA, sponsored the first broad scientific study of smoke abatement, which resulted in legislation designed to decrease the effects of smoke. 1 It is now well known that environmental contamination impacts on health; the World Health Organization estimates that every year, 2.4 million people die from causes associated with air pollution. It is increasingly recognized that implementation of strategies to reduce pollution can have substantial health benefits. For example, the Environmental Protection Agency proposed that the implementation of measures to reduce emissions from diesel e ngines could result in 12 000 fewer mortalities and prevent 15 000 heart attacks and 8900 hospital admissions in the United States each year. 2 The aim of this review is to provide information on the impact of pollution on respiratory health, as well as to discuss strategies for reducing air pollution, as proposed in a number of clinical reports. Particulate matter (PM) and ozone (O 3 ) pollution are major causes of concern in the community.
PARTICULATE MATTER (PM)
PM is a complex mixture of solid and liquid particles suspended in air that is released into the atmosphere when coal, gasoline, diesel fuels and wood are burned. It is also produced by chemical reactions of nitrogen oxides and organic compounds that occur in the environment. Vegetation and livestock are also sources of PM. In big cities, production of PM is attributed to cars, trucks and coal-fired power plants.
The health effects of PM depend on several factors, including the size and composition of the particles, the level and duration of exposure, and the gender, age and sensitivity of the exposed individual. Symptoms of exposure may include persistent cough, sore throat, burning eyes and chest tightness. PM may also trigger asthma or lead to premature death, particularly in elderly individuals with pre-existing disease. 3,4 In addition, people who are active outdoors are at higher risk, as physical activity increases the amounts of PM penetrating into the airways. People with disease (e.g. diabetes mellitus, malnutrition) are also at increased risk. 5–7 A comprehensive review on diesel PM by Ristovski et al . was published in an earlier issue of this review series on air pollution and lung disease. 8
OZONE (O 3 )
O 3 is mainly formed by the interaction of ultraviolet light with both nitrogen oxides and organic compounds. O 3 exhibits potent anti-oxidant properties and induces alterations in the airways that depend on concentration and the duration of exposure.
EFFECTS ON RESPIRATORY HEALTH
The airways are a point of entry for pollutants, which in turn may cause lung disease. For example, PM may be deposited into any of the three respiratory compartments: the extrathoracic, tracheobronchial and alveolar regions. 9 PM > 10 µm in diameter (coarse particles) is deposited in the extrathoracic region, PM with a diameter between 5 and 10 µm is deposited in the tracheobronchial region and particles <2.5 µm in diameter (fine particles) are deposited in the alveolar region ( Fig. 1 , Table 1 ). 10 For particles between 3 and 5 µm in diameter, the total deposition fraction is greater for women than for men. 11 The potential health effects of greatest concern are associated with particles that penetrate to the tracheobronchial and alveolar regions. 12 The deposition rate may also be increased in individuals with pre-existing respiratory disease, as compared with healthy individuals. 13 It has been suggested that particles ≤0.1 µm in diameter (ultrafine particles) are more toxic than larger particles as they may cover a greater area of the alveolus. One host defence mechanism is phagocytosis of ultrafine particles by alveolar macrophages ( Fig. 2 ). However, due to their small size, ultrafine particles overwhelm macrophage phagocytosis, resulting in increased penetration, which causes deleterious effects in other organs (e.g. brain, heart, bone marrow, etc.). 14,15

Regional deposition of particles in the human respiratory tract.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) terminology for particle sizes
d pa , aerodynamic particle diameter.
Data taken from http://www.epa.gov/apti/bces/module3/category/category.htm

Alveolar deposition of particles and cell activation. Particles deposited in the bronchoalveolar region may be trapped and are cleared by the mucus layer (1); particles phagocytosed by alveolar macrophages follow the lymphatic clearance pathway, can impair phagocytosis and trigger the release of inflammatory mediators (2, 3) and neutrophil chemotactic factors, which in turn results in the release of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (4). Furthermore, soluble particle components (e.g. metals) can cross the epithelial barrier and be distributed to other organs where they can cause adverse effects (5). ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule; IL, interleukin; MPO, myeloperoxidase; VCAM, vascular cell adhesion molecule (6).
Toxicological studies have demonstrated the translocation of particles from the olfactory mucosa via axons to the olfactory bulb of the brain. 16,17 Indoor activities in the home that result in the generation of particles include cooking (in ovens, toasting, frying, barbecuing), cleaning (dusting, sweeping, vacuuming) and the movement of people. Ozkaynak et al . reported that cooking resulted in the generation of 4.1 ± 1.6 mg/min of PM 10 , with the fine fraction contributing 40% of the total PM. 18 Once PM enters the body, it affects different organ systems.
The source and composition of particles determine their toxicity, 19,20 but size is a major factor determining toxicity in the lungs due to the generation of reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species. Particle size may also physically hinder macrophage clearance, 21 thereby increasing toxicity. In general, particles exacerbate acute and pre-existing respiratory diseases, including viral infections, asthma, bronchitis and chronic respiratory disease. 22–24 Many transition metals present on particles serve as catalysts for a Fenton-like reaction that initiates the production of reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species, resulting in an inflammatory response. Using electron microscopy, Brauer et al . 25 showed significantly higher particle concentrations in the lungs, at autopsy of Mexican females who had never smoked, as compared with control Vancouver residents. Interestingly, Budinger et al . 26 reported that inhalation of PM 2.5 was sufficient to activate coagulation and inhibit fibrinolysis. Traffic particles appear to be more strongly associated with these effects, 27 as they are rich in elemental carbon, which can cause an increase in respiratory symptoms in children 28,29 and women living in urban areas. 30
It is now well established that exposure to O 3 impairs lung function. In healthy individuals, O 3 causes reductions in vital capacity, forced expiratory volume in 1 s and lung resistance. The effects of O 3 exposure increase with physical exercise. Patients with respiratory diseases are more susceptible to the effects of O 3 . Under conditions of oxidizing air pollution, as in summer, O 3 exposure may lead to asthma exacerbations.
ALLERGIC DISEASES
Allergic diseases such as asthma and allergic rhinitis are very common in children and young adults. In most cases, asthma in these groups of patients is characterized by increased synthesis of immunoglobulin E against common allergens. 31 Exposure of these patients to specific aeroallergens such as pollens leads to a series of immunological changes culminating in the symptoms of asthma. It is now well established that increased air pollution affects pollen production, which in turn impacts negatively on the prevalence and severity of allergic asthma.
Diesel exhaust contains numerous pollutants and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which enhance allergenicity and asthma symptoms by acting in synergy with allergens. Experimental studies conducted by Muranaka et al . 32 showed that diesel-exhaust particles act as an adjuvant for immunoglobulin E production in response to specific allergens (ovalbumin or Japanese Cedar pollen). Moreover, inhalation of diesel-exhaust particle leads to a typical asthma phenotype, characterized by pulmonary inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness. 33,34 It has been proposed that when diesel-exhaust particles are engulfed by macrophages, a Th2-type inflammatory response is induced, whereas diesel-exhaust particles that are not engulfed produce a Th1-type inflammatory response. 35–37
High carbon dioxide concentrations in the environment increase both pollen production and the allergenicity of pollen. Indeed, Singer et al . 38 showed that high concentrations of carbon dioxide enhanced the production of Amb a 1, an allergenic protein in ragweed pollen, while Ziska et al . 39 reported that in urban locations where carbon dioxide concentrations are higher, ragweed produces greater amounts of pollen (which contains the Amb allergen) than it does in rural locations. The enhanced allergenicity of pollen may be explained by the synergistic association between allergen-loaded pollen debris and aromatic hydrocarbons contained in fine particles. 40
On the other hand, traffic-related pollutants (nitrogen dioxide, O 3 ) can trigger the release of allergens from pollen granules, leading to an increase in the concentration of airborne pollen allergens. 41 For example, Dutch children attending schools that were within 400 m of a major roadway showed increased sensitization to outdoor allergens; the relationship between symptoms and traffic-related pollution was observed mainly in children who were sensitive to allergens. 42 Similarly, increased levels of O 3 and PM 2.5 in summer were found to be associated with a higher prevalence of respiratory allergy symptoms in US children living in urban areas. 43 D'Amato et al . 44 hypothesize that air pollutants: (i) allow easier penetration of pollen allergens into the airways; (ii) increase the release of antigens from pollen grains, thereby leading to allergic responses; and (iii) absorb pollen grains, leading to prolonged retention of pollen grains in the body. A recent prospective birth cohort study involving over 2000 children showed that exposure to ambient PM increased the risk of atopic diseases. 45
MECHANISMS OF LUNG DAMAGE
Oxidative stress.
Oxidative stress plays a central role in the mechanisms by which air pollutants damage human health. In addition, reactive nitrogen species are generated in the lungs following exposure to particles. Nitric oxide released by inflammatory cells reacts with superoxide anion radicals to form peroxynitrite, which then initiates the nitration of tyrosine residues on proteins. These changes contribute to the progression of disease. 46,47 On the other hand, the endogenous pool of H 2 O 2 reacts with some enzymes such as myeloperoxidase to produce highly reactive metabolites (hypochlorous acid). 47,48 Vujovic et al . reported an increase in malondialdehyde concentrations, whereas there was a reduction in superoxide dismutase activity (anti-oxidant defence) in children exposed to air pollution. 49 Similarly, increased plasma levels of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances have been associated with exposure to black carbon and PM 2.5 . 50 Individuals living in a polluted environment also showed increased plasma levels of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances. 52
In animals, intratracheal instillation of PM causes a significant increase in serum levels of cytokines such as interleukin-6. 53 Human macrophages exposed to particles, release a range of cytokines, including tumour necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, interleukin-1β, macrophage inflammatory protein-1-α and granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor. 54 These cytokines activate nuclear factor kappa B and/or activator protein 1. 55,56 Ultrafine black carbon is also involved in the activation of nuclear factor kappa B via protein kinase C. 57,58 Metals contained in PM can induce a series of redox reactions causing oxidative DNA damage.
We have shown that exposure to O 3 results in the release of increased levels of growth-related oncogene-α into the airway lining fluid in normal subjects. 59 Interestingly, in a separate study, we demonstrated that neutrophils from asthmatic patients exposed to fine particles (PM 2.5 ) generated reactive oxygen species. 60 There is also a relationship between air pollution and cancer; pollutants may increase the risk of cancer through the formation of reactive oxygen species, especially hydroxyl and superoxide anion radicals, which may induce oxidative damage to cellular membrane lipids, protein enzymes and DNA. 61
PREVENTION OF AIR POLLUTION
Clinical studies.
It is well understood that pollution has a profound effect on health; therefore, reduction of pollution has a positive effect on health, particularly the health of susceptible individuals. The first population-based study that showed significant improvements in life expectancy in relation to reductions in PM 2.5 concentrations was conducted in the United States, 62 and showed a clear relationship between reduction in fine-particle concentrations and life expectancy. This observation was confirmed in a cohort study of Swiss adults, which demonstrated that decreases in ambient PM 10 levels were associated with reductions in respiratory symptoms. 63
Reductions in the levels of air pollution can be achieved in many ways, and governments can play a key role. Figure 3 shows PM 10 levels in some of the most polluted countries. For example, during the 2008 Olympic Games, the Chinese government was able to control air pollution. 64 This resulted in a 41.6% decrease in the average number of outpatient visits for asthma during the Olympics, as compared with before the games started. A separate study of 36 fourth-grade Beijing children, before, during and after the Beijing Olympics, showed that fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) levels were significantly lower during the period of the Olympics and increased by 16.6% in the first hours after exposure, suggesting that rapid inflammatory changes took place. 65

Pollution in 37 cities selected from 91 countries, as reported by the World Health Organization (WHO). Particulate matter (PM) 10 levels >20 µg/m 3 may pose health risks (data taken from http://apps.who.int/ghodata/?vid=4201 ).
In rural Mexico, a randomized trial of properly vented wood-burning cooking stoves versus open fires showed reductions in the longitudinal decline in forced expiratory volume in 1 s and improvements in respiratory symptoms, when proper cooking stoves were used. 66 The use of improved cooking stoves has also been found to halve the exposure to carbon monoxide and resulted in a lower rate of diagnosis of pneumonia. 67
Evidence is accumulating that polymorphisms in several genes involved in oxidative stress play an important role in susceptibility to O 3 . 68–70 These genes include those coding for phase II enzymes, including glucuronosyl transferases, glutathione S -transferases (GST), NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductases and N -acetyltransferases, all of which mediate the detoxification and elimination of toxic products.
GSTM1 and GSTP1 have been the most frequently studied enzymes. A study of Mexican children exposed to high concentrations of O 3 showed an association between polymorphisms in the oxidative stress-related GSTM1 gene and the development of asthma. 68 Interestingly, children with the GSTM1-null genotype were more susceptible to the effects of O 3 . However, taking supplements containing the anti-oxidant vitamins C and E conferred protection against O 3 exposure. 68 Similarly, sulforaphane, a potent inducer of phase II enzymes, was also shown to enhance enzyme expression and downregulate inflammatory responses in human bronchial epithelial cells; 69 sulforaphane increased GSTM1 and NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 expression, as well as GST activity while decreasing cytokine production. More recently, long-term supplementation with D-α-tocopheryl acetate, a natural vitamin E anti-oxidant, was shown to inhibit oxidant stress in the airways of mild atopic asthmatics exposed to segmental allergen challenge; improvements in allergic inflammation and bronchial hyperreactivity were observed. 70 Studies of additional genes involved in the oxidative stress response have been reviewed previously. 71
AIR POLLUTION AND CLIMATE-CHANGE MITIGATION
Climate change can enhance the levels of some environmental pollutants, including O 3 and PM 2.5 . For example, the formation of photochemical smog and O 3 increases with higher temperatures. Doherty et al . quantified the burden of heat and O 3 on mortality in 15 UK conurbations during the 2003, 2005 and 2006 heatwave periods. 72 The results indicated that the number of deaths attributable to O 3 was higher than the number attributable to heat. Furthermore, O 3 concentrations rose significantly during the summer of 2003, reaching a maximum of 100 ppb. 72 Ambient concentrations of particles may increase due to forest fires that are a consequence of a dry environment and other climatological effects such as El Niño. During 1998 in Indonesia, forest fires linked with El Niño resulted in the exposure of some 20 million people across South-East Asia to harmful smoke-borne pollutants. Monthly PM 10 values, which usually fluctuate between 30 and 50 µg/m 3 , increased to between 60 and 110 µg/m 3 during September–October 1997. The incidence of medical complaints rose by about 30% during this period.
Some of the planned climate-change mitigation strategies include more efficient use of fossil fuels for industrial processes and electricity generation, switching to renewable energy (solar/wind/wave power), increasing the fuel efficiency of vehicles, improving the insulation of buildings, growing new forests, nuclear power and carbon sequestration. It is generally accepted that efforts in all these areas will, at best, prevent further warming but not reverse existing warming.
The Mexican Government recently introduced significant measures aimed at reducing climate change, including a law to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 30% by 2020 and by 50% below 2000 levels by 2050. 73 Furthermore, it aims to generate 35% of the country's energy from renewable sources by 2024. At the beginning of 2001, the authorities in Monterrey, Mexico, built a 7-megawatt plant that converts 214 million m 3 of landfill gas into electricity and powers the light rail transit system and city street lighting at night. Despite these changes, Mexico still faces some hurdles, including enforcement of the new laws; current problems include urban planning, excessive industrialization and traffic jams in large cities. In this regard, the United Kingdom has implemented some measures in London, to take taxis older than 15 years and private hire vehicles older than 10 years off the road, build bicycle superhighways (cycle revolution) and introduce 300 hybrid buses by the end of 2012.
Urban forests and green roofs have also been proposed as strategies for reducing pollution in urban areas. 74 Vegetation removes pollutants in several ways; by absorbing gaseous pollutants, through interception of PM by leaves, and by breaking down organic compounds such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. 75 Transpirational cooling also reduces temperatures indirectly, which results in a reduction in photochemical reactions that form O 3 and other air pollutants in the atmosphere. It has been estimated that in the United States, trees remove 711 000 metric tonnes of carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, O 3 , PM and sulphur dioxide per year. 76 However, in many urban areas, there is little space for planting trees or cultivating urban forests. For example, in the mid-Manhattan, west section of New York, 94% of the land is covered with concrete, leaving little space for planting trees at ground level. 77 However, rooftops, which often comprise nearly half the impermeable area in a city, provide an opportunity for growing vegetation. 78 Two thousand square metres of uncut grass on a green roof can remove upto 4000 kg of PM. 79
Public policy and individual action are both required to reduce the effects of pollutants on respiratory health. Interventions at the individual level may include the avoidance of exercise or cycling near busy roadways to reduce exposure, and improvements in the ventilation of homes in which biomass fuels are used. Moreover, public policies can encourage or mandate engineering solutions that drastically reduce emissions from cooking stoves and vehicles. Trials such as those performed during the Beijing Olympics have demonstrated how such changes may have implications for human health. Taken together, these observations suggest that reducing the levels of air pollutants will have a substantial impact on health, particularly the health of patients with respiratory diseases.
The main public health responses to the projected health impacts of climate change are mitigation and adaptation. Adaptation is not an effective risk management strategy for poor air quality, because physiological mechanisms for decreasing susceptibility to O 3 and other air pollutants are limited. Therefore, if improved modelling experiments continue to predict higher O 3 concentrations with changing climate, rapid reductions in emissions from the burning of fossil fuels are needed, in order to protect the health of current and future generations. Evidence suggests that reducing current tropospheric O 3 concentrations reduces morbidity and mortality, with significant savings in the costs of medical care. 80
CONCLUSIONS
Air pollution currently affects the health of millions of people. We have presented evidence on the effects of pollutants on patients with limitations in their respiratory capacities. For example, O 3 and PM may trigger asthma symptoms or lead to premature death, particularly in elderly individuals with pre-existing respiratory or cardiovascular disease. In addition, pollutants enhance the release of allergenic pollen grains, which results in an increased prevalence of pollen-induced asthma. Thus, the case for action to reduce air pollution is overwhelming and this action can take many forms. Some of these include urban planning, technological developments (e.g. the design of new vehicles that produce less pollution), and at the government level, the introduction of new laws. It has been estimated that reducing both black carbon and O 3 levels would prevent over 3 million premature deaths and increase crop yields by around 50 million tonnes annually. Improvements to cooking stoves would also decrease demand for firewood and reduce deforestation in the developing world. Similarly, improved brick kilns that are used in parts of Latin America and Asia use 50% of the fuel used by traditional kilns. 81
If air pollution levels in heavy traffic areas were reduced, the incidence of asthma and other respiratory diseases would be significantly reduced. 28 While it is generally accepted that efforts to reduce air pollution will prevent further environmental changes, they will not reverse existing warming. Interestingly, an increasing number of studies show that in individuals with low anti-oxidant levels, dietary supplements could be used as a promising approach to reducing susceptibility to air pollution, and providing an alternative strategy for neutralizing the effects of pollutants on health.
- About Us 👨👩👧
20 Ways to Prevent Indoor and Outdoor Air Pollution
Since the Industrial Revolution, people have been polluting the Earth like never before. There is rarely a place today that has not been subjected to pollutants in one form or another.
Some pollution comes in a visible form, like pieces of plastic washed up on our beaches or illegal dumpsites in groves nearby large cities, other pollution comes in a hidden and perhaps even more dangerous form, in the air we breathe daily.
Our continuous existence depends on the clean air and yet our activities are constantly releasing extremely toxic particles that contaminate our atmosphere.
Polluted air is costing us lives
The issue has become so serious that scientists attribute a large number of deaths to ever increasing effects of air pollution. In fact, polluted air kills each year more people than malaria or tuberculosis [1] . Some cities are even shut down during certain parts of the year because the air is so toxic that it is impossible to function.
Another alarming record comes from New Delhi in India, infamous for its pollution exceeding safe air quality levels by 20 times on days when thick smog wraps around the city. According to a study by the Chittaranjan National Cancer Institute, almost half of Delhi’s children develop irreversible lung damage during their childhood years [2] .
To imagine the severity of the global pollution even better, there is an animal in the remote Arctic whose body contains one of the highest level of pollutants of any organism on this planet. The word is about a polar bear who is due to the global distillation effect exposed to anthropologically created pollution even in the most remote corner of the planet.
Although increasing number of countries enforce stricter regulations to prevent further emissions of air pollutants, there is still a lot to do on an individual level.
The key to have a healthier life is to adopt measures that do not pollute air so much because we all have a role to play when it comes to creating healthy environment for living.
Simple ways to reduce outdoor air pollution
Being aware and changing our habits is the only way to reversing negative actions we have adopted in our modern lifestyles. Even though some initiative needs to be taken by authorities, individual habits still can make a big impact. If not globally, they will make impact locally – directly in the environment where you live.
The following list will help you get started with the transition to improving the quality of your life by addressing the problem of air pollution and learning about ways of reducing it.
#1 Minimize air pollution from cars
Road transportation is one of the biggest emitters of nitrogen oxides. Oxides of nitrogen are closely monitored air pollutants with an adverse effect on the healthy lung development and the overall lifetime expectancy.
The problem of harmful emissions from cars can be felt especially in cities with heavy traffic. Personal diesel cars and smaller vans top the list of the dirtiest polluters in such instances.
As a driver you can help reduce the pollution from your car by sticking to a few of simple rules.
- When you are out for a drive, do not idle your vehicle.
- Drive less by combining trips, telecommuting, carpooling, or carsharing. A great idea is to bring your lunch to work, so you do not have to drive out during the lunch break, or agree with your co-workers on going to get lunch together.
- Do not speed up or drive aggressively because that only produces more emissions.
- If possible avoid driving out during rush hours.
- When you are in the market to buy a new vehicle, consider buying a car that has done well on emission tests. In general, newer models have better fuel economy than older models because they are developed with the latest technologies.
- Go away from diesel cars. Diesel cars emit more nitrogen oxides than petrol cars. That’s why some of the largest European cities have banned or are preparing to ban older diesel cars from their downtown .
- If you want to choose the cleanest option, look into hybrid or all-electric cars. These cars should have a smaller ecological footprint than conventional cars do. Although it is important to realize that there are still some emissions involved. These are emissions from power plants that supply the electricity to power your e-drive.
- Be sure to keep your car tuned and regularly replace air filters at recommended intervals.
- Even something so easily overlooked as keeping your tires properly inflated plays a role in the amount of gases your car will emit. When the tires are not properly inflated, your car needs to burn more fuel and therefore pollutes the environment on a larger scale.
By following this advice you will definitely help reducing air pollution caused by cars, but you should still be aware that any car with an exhaust pipe will emit some amounts of nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide into the air. Therefore, the most effective strategy to keep the air clean is to avoid driving your car when possible .
#2 Walk, bike or use public transportation to reduce air pollution
When you have the option, take public transportation to get to work. Many cities have already invested in a good public transportation network and by choosing public transportation (even just one or two days a week) you are helping to reduce the number of cars on the road.
Many municipalities also offer great benefits to encourage people to use their public transportation. Some commonly applied advantages are cheap long-term fares, shorter times to reach your destination, short waiting times, punctuality, and fares for free at certain hours, weekends or for seniors and students.
For example, the city of Vienna, Austrian capital, offers a yearly ticket to their extensive public transportation network for only 1 Euro a day (that is USD 1.14). This means that as a holder of the yearly card you can travel as much as you want in one day for just 1 Euro. Isn’t that wonderful?
*And a little insider tip: Your pup can travel with you for free when you have this card… 😉
Or German city Stuttgart lets students travel for free on weekends and after 6 pm every day.
Additional benefit to consider is that many cities place emphasis on lowering carbon emissions of their public transportation means. They invest in electric buses and other modern vehicles that enable them to do so. The website of the abundantly used public transportation in Vienna mentions that every person who switches to public transportation prevents 1,500 kg of carbon dioxide from being released into the air each year [3] .
Walking or riding a bike to get to work comes with numerous benefits for your wellbeing. You can take less frequent roads and backstreets to arrive to work sooner and less stressed than you would be if stuck in traffic. Both of these activities also contribute to maintaining active lifestyle and improving your self-confidence and health.
However, when biking or walking you should take into consideration the level of already existent air pollution along your route. If you cannot avoid too busy roads, it’s better to stick with public transportation because on bike you would directly breathe all the emissions produced by the heavy traffic.
#3 Save energy and make sure you use energy efficiently
In 2016, the International Energy Agency released a report with the key statement that “air pollution is an energy problem.”
Similar concept repeats in other scientific papers. For example, the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health published a study that lists a myriad of health problems arising from the air contamination due to the combustion of fossil fuels.
Burning of fossil fuels for energy production releases potent pollutants such as:
- Sulphur dioxide
- Nitrogen oxide
- Black carbon
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- Carbon dioxide
- Particulate matter [4]
All of these substances are known to have negative impacts on human health and the environment.
That is why being mindful about your energy consumption matters . Decreasing your energy need will not only save you money on utility bills but more importantly will benefit your health in the long-term.
When you save energy, whether it is at home, at work, or while you are traveling, you are reducing production of many polluting substances as well as carbon emissions that make the air dirty and cause global warming.
Some effective strategies to lower your energy consumption to set you on the right track are:
- Increase energy efficiency of your home Make sure you use energy efficiently. For a detailed information on energy efficiency, check our article on 10 Tips on How to Improve Energy Efficiency at Home .
- M inimize the use of air conditioners Use air conditioners in the summer only when absolutely necessary. Air conditioners need much more power than fans do. Give a try to strategically placed fans and open windows at night to cool down your room.
- Use appliances smartly Run your dishwasher and washing machine only when full and if possible at night. When running these appliances outside the peak hours, it is more likely that the biggest (and the most polluting) power plants won’t work because the demand for power is lower and can be covered from smaller power plants that often use newer technologies.
- Switch to renewable energy Renewables are much cleaner version of power generation. The technology has made such a great progress that there are many affordable options and programs available for the residential use of renewable energy nowadays. For example, photovoltaic solar panels produce energy without emitting gases. So, if you switched to solar energy, you would lower your personal amount of emissions significantly – the exact number depends on how much of your total energy demand would be covered entirely from solar power.
#4 Take a good care of your wood stove or fireplace
If you own a wood burning stove or a fireplace, be sure to keep it well-maintained. When burning fire-wood in wood stoves, incomplete combustion often releases particulate matter of a very small size (less than 2.5 micrometer). These tiny particles are the most harmful to our respiratory tracts because they can easily get deep into our lungs, and for their small size may even enter our bloodstream.
Other noxious gases released from fireplaces and wood stoves are:
- Carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen oxides [5]
What amount of emissions your stove produces depends on:
- The efficiency of the wood stove
Newer models are usually more efficient than older, improperly maintained models. Old wood stoves from 80s release three to six times more particulate air pollutants than newer stoves [5] . This is due to lower burning temperature and insufficient aeration.
You should also preferably have the stove (fireplace) installed by a professional with a necessary certification. This ensures that your stove will perform with the best efficiency and at the lowest risk of unwanted accidents.
- The type and the condition of fuel you are burning
Dry firewood burns better than humid wood. It will thus emit less air pollutants. Also make sure you don’t burn wood with paint, glue or other coating because it could release additional toxins into the air.
Pellets made of compacted sawdust and wood waste are a less polluting and more heat-producing alternative to wood.
#5 Recycle and buy recycled products
Imagine all complex processes needed to create new items from scratch. You need to begin with mining for raw materials. Mined materials then need to be transported, cleaned from impurities, processed and treated until they can finally be transformed into desired products.
Each stage of the manufacture from raw materials is accompanied by emissions of polluting particles, heavy metals, chemicals and greenhouse gases.
It also takes more energy to make new items from raw materials, increasing the environmental footprint (including the air pollution that is produced) of those products, compared with those products that are made from recycled materials.
Since recycled products have already been extracted and processed once, manufacturing the same products the second time is much less-energy intensive and polluting.
#6 Consume less and choose sustainable products
A 2017 study published in the International Journal of Science highlighted that 22 percent of premature deaths caused by air pollution happened in countries that produce (cheap) goods for export to developed countries [6] .
European and North American love of cheaper gadgets from China actually killed more than 100,000 people in Chinese towns where factories manufacturing many of our favorite products are located [6] .
Higher levels of environmental pollution in these regions are often due to weak or lacking emission restrictions in place (which is also why these goods can be produced at a lower cost), but the air they are polluting is still part of the same air you are and will be breathing for as long as you are on this planet.
So, our consumption patterns affect pollution levels globally. Even if you haven’t ever traveled to China, your choice of products in your local supermarket will decide whether you encourage polluting businesses abroad.
Consuming less and thinking twice before buying new item is the best you can do for the environment and the air quality. If you need to buy new products, whatever they are, support local companies that are committed to sustainable manufacturing practices and reducing pollution in the air.
#7 Eat local and organic produce & eat less meat
In countries with intensively farmed lands, agriculture is the main emitter of ammonia and other nitrogen-containing compounds like nitrous oxide or nitric oxide. Livestock farming also emits high concentrations of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, and non-methane volatile organic compounds.
Agricultural pesticides and fertilizers release Persistent Organic Pollutants, such as hexachlorobenzene, hexachlorocyclohexane and pentachlorophenol in the air [7] . Those names don’t sound that good, do they? Now, consider that the air you breathe may contains also these compounds with their complex names. There is nothing natural about that…
A study by the Earth Institute of Columbia University warns over health-damaging effects of gases emitted from conventional agriculture in combination with industrial emissions. The research says that when these pollutants combine together, they form fine particles that easily damage our respiratory system, leading to chronic health problems [8] .
Organic agriculture is not entirely emission-free as well, but the amounts of many pollutants are lower.
This is due to a number of reasons:
- Nitrogen input to organic soils is lower, so even nitrogen compounds escaping into the air decrease.
- Sustainable soil conservation practices such as no-tilling, green manuring and crop rotation help preserve nutrients in soils where they are utilized by plants instead of being lost into the environment as often happens in heavily tilled crops.
- Healthy, well-aerated soils with good microbial activity have improved methane uptake.
If possible, consider buying organically-grown produce over the conventional one, and look for local products because this way you cut down emissions from transportation and energy needed to get the food on your plate.
A very important step to take in regard to your consumption pattern is to eat less meat . You may have heard already about the significant greenhouse gas footprint of the modern livestock industry. By going meatless some days a week or eating maximum 90 grams of meat a day, you will lower air pollution and will even benefit your health (and wallet – since plant-based diet is cheaper).

#8 Grow your own food and eat seasonal products
It is easy to get produce from all over the world these days. Just a quick trip to supermarket opens up a world of a great variety of exotic fruits, vegetables and spices. Although, having such a great diversity is wonderful, it always comes with a cost – in this case the cost of polluting the air we breathe by long-distance transportation.
Just think about it. Bananas imported from Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras or other exotic destinations. Kiwis from Italy, Chile, New Zealand… Mangoes brought from Thailand, Philippines, India or Pakistan. These favorite fruits have to travel really long distances to make it to your supermarket.
One easy and fun way to make sure you have a nutrient-rich diet, which even helps offset some of the harmful emissions of the food industry, is to grow your own food. This way you will have direct access to fresh produce of your preference, and you will even be sure that what you eat is chemical-free.
If you are unable to grow fruits and vegetables due to time and/or space limitations, stick to the rule of eating mostly seasonal products that are native to your area. The reason for this is very simple – when in season, products will be more likely sourced from regional farmers.
#9 Plant trees
Trees around your house and in your neighborhood help reduce air pollutants significantly. Researchers from the University of Southampton measured the ability of trees in London to remove particulate pollutants from the air. Their findings were truly astonishing. Trees remove between 850 to 2,000 tons of harmful particles from the urban air each year [9] .
Except of removing the particulate matter, trees also decrease levels of nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide, carbon dioxide and monoxide, ozone, benzene and dioxin.
Some of the most efficient tree “air cleaners” are large-growing species with leaves. For example, common ash, ginkgo biloba, oak, various linden trees and elms [10] .
Trees planted alongside roads or on the boundaries of your property also slow down polluted air from being carried far by wind. You can think of it as a protective shield formed by tree canopy. This way trees prevent spreading of air pollution over large distances. Then, they gradually filter the pollution at the spot without giving it much chances of contaminating neighboring areas.
But trees are not only natural air filters, they also cool down summer temperatures by a few degrees. Even the slightest temperature reduction can make a real difference in keeping the air clean, because many compounds and ground-level-ozone-forming chemicals are temperature dependent [11] . This means that they transform into pollutants only when outdoor temperature reaches certain level.
Additionally, cooler temperatures are more comfortable for our wellbeing, which makes trees a great substitute for energy demanding air conditioners.
#10 Raise awareness and become interested in local matters
Awareness-raising can be the first step to increase the knowledge of people around you and start the change in their attitudes towards mitigating the problem of poor air quality in affected areas.
As you can see most of these ways on dealing with air pollution are rooted in the consumer behavior. Often, all it takes is just being a little bit more aware of the impact of your personal decisions as a consumer on the air quality–even so far from you as on a different continent.
By making conscious consumer choices, your initiative can serve as a good example to your friends, family and community. This way you can become one of the initiators of a bigger change in your area.
Equally important is to express your support to public policies and representative politicians who work to protect the air and the environment. If you care about the quality of life in the place you call home, it is necessary to stay informed and take supportive actions for good causes.
Preventive measures of indoor air pollution: How to clean the air in your home?
When we think of air pollution, most of us think of poor outdoor air quality. However, did you know that indoor air is on average two to five times more polluted than outdoor air? This happens because the air circulation indoors is much lower than outdoors, which allows toxins from dust particles, vapors from cooking, painting or furniture dyes to accumulate inside our houses.
And since most of us spend so much time indoors, we are at a higher risk of developing health issues from the toxic indoor air . In fact, the World Health Organization estimates that 30 percent of global diseases are a result of indoor air pollution [12] .
For example, one of the most common indoor pollutants is formaldehyde. Sources of formaldehyde are everywhere around us. It can be found in furniture, insulation, textiles, wallpapers, glues, detergents, softeners, disinfectants, cosmetic products and even in electronics [13] . But did you also know that increased concentrations of formaldehyde cause irritations, asthma and eczema?!
It’s time to become more cautious about what pollutants you introduce to your life. And since you have already learned how to help reduce outdoor air pollution, it is time to have a look at some preventative measures that will teach you how to improve air quality in your home and office.
#1 Keep air purifying indoor plants
Very elegant solution to improving air indoors, that would also have a beneficial effect on our health, is keeping houseplants.
Many houseplants have the same ability as trees to metabolize air pollutants from indoor spaces as well as refresh air by removing carbon dioxide and replenishing oxygen levels. Plants with large leaves that originate from tropics and rainforests are especially effective in doing so.
Some examples of the best houseplants for cleaning indoor air are:
- Spider Plants
- Peace Lilies
- Snake Plants (“Mother-in-Law’s Tongue”)
- Elephant Ears
- Weeping Figs
- Rubber Plants
- Bamboo Palms
- Heartleaf Philodendron
Common indoor toxins these plants can absorb include compounds such as formaldehyde, xylene, benzene, trichloroethylene, toluene, octane and carbon monoxide [14] .
Can there be any easier solution how to get better air quality in your home than surrounding yourself by pretty flowers?
#2 Open your windows
Opening your windows fully at least once a day for three to five minutes can replace stagnant and polluted indoor air with fresh air from outside.
It is important to let the air in your house circulate even for short periods of time because this way you let accumulated toxins out and decrease humidity that gathers from many indoor activities like cooking, doing laundry or taking a steamy shower.
One of the common issues of well-insulated houses is that indoor-outdoor air exchange is entirely disabled. While this is a desired effect when it comes to preserving heat and energy, it is not the best for maintaining healthy air quality inside. If that’s the case, the stagnant air in your house needs to be refreshed once a while by opening windows to create a little draft.
Do not forget to open your windows to ventilate a room if you must use any volatile chemicals, such as those found in paint strippers and paints. Better yet, look for low- or no-VOC products to avoid being exposed to the toxic fumes from these products in the first place.
#3 Use natural products and non-toxic cleaners
When purchasing household products for your home and your yard, opt for the cleanest and greenest products that don’t contain any harmful polluting chemicals.
The majority of the air fresheners, detergents, paints, and cleaners on the market contain toxic substances, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), that easily vaporize into indoor air.
VOCs represent a variety of chemicals derived from petroleum, for example, formaldehyde, benzene, perchloroethylene and chlorofluorocarbons.
These chemicals not only pollute indoor air, they can be detrimental to your and your pets’ health. Some symptoms include irritations, nausea, dizziness, asthma, liver and kidney failures, central nervous system damage and cancer [15] .
To minimize your exposure to these chemicals, choose products that have been made with natural substances, and do not produce harmful fumes.
When seeking out natural products, resources such as the Environmental Working Group’s Guide to Healthy Cleaning and the United States Environmental Protection Agency Safer Choice page are great places to learn about the product safety. A few great tips to stick to:
- Opt for no-VOC or low-VOC paints, stains, finishes, paint strippers, and glues. Paint with a brush rather than spray.
- Instead of using chemical-filled air fresheners, use essential oils, herbs and flowers to make your home smell nice.
- Use green cleaning products instead of conventional chemical-filled products.
- Use perfumes moderately or not at all. Perfumes consist of a number of synthetic chemicals that when being sprayed in the air break down into harmful compounds. You can learn more here .
#4 Use essential oils
Essential oils are potent plant extracts that can be used for many purposes, including cleaning, purifying and freshening indoor air. They also offer an eco-friendly, healthy, and often more effective alternative to many chemical and synthetic products.
Using high quality essential oils in a diffuser will not only produce a nice scent throughout a room, you will also gain many health benefits from the complex natural compounds that the essential oils contain. For example, lavender oil with eucalyptus oil have calming properties; peppermint and chamomile oils are good for digestion and relieving symptoms of cold; rosemary oil improves concentration and memory.
You can also use essential oils to make your own homemade cleaning products and personal care products. Some favorite oils that have been used for skin and hair are rose, cedarwood, thyme or clary sage oils.
For purposes of purity, safety, and to experience the most benefits, be sure to use only therapeutic grade essential oils from a reputable company.
#5 Test your home for radon
Radon is an invisible, odorless and radioactive gas that naturally seeps up from the soil and bedrock of the Earth. It is one of the products of the radioactive decay of uranium, which can be found naturally in all rocks on this planet.
Most houses draw less than one percent of their indoor air from subjacent soils, but when your house is built on a highly permeable soil and foundations are not properly sealed, more than 10 percent of indoor air can come from the ground. This can lead to increased radon accumulation in the indoor air, even though its concentration in the soil is within safe limits.
It is good to know that radon can also seep from some building materials, such as granite countertops, alum shale concrete or volcanic tuff [13] .
Radon is after smoking the second most frequent cause of lung cancer [13] , so it is important to have your home tested for it. The testing procedure is very simple and inexpensive.
When radon levels in your house are above limits, some mitigation strategies for reducing its concentration need to be applied. One reliable technique is ‘ Active soil depressurization , ‘which draws radon from beneath the foundation and emits it outside.
#6 Do not smoke indoors
Do not smoke inside your home. Cigarette smoke contains up to 70 carcinogenic substances and toxins that remain in the indoor air for a long time.
Passive exposure to the cigarette smoke can also cause serious health problems to other family members and pets.
Some of the health deteriorating compounds found in smoke include lead, arsenic, ammonia, carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide. By smoking in a confined space, the level of these compounds quickly exceeds safe limits without you even realizing the danger associated with inhaling them.
For example, nitrogen dioxide contributes to seemingly unrelated health problems such as ear infections and development of food allergies in children.
#7 Keep indoor humidity low
We do many activities at home that make rooms damp. But did you know that in humid environments hundreds of different bacteria species, fungi and molds thrive? And that breathing their spores affects the health of your skin and respiratory tract?
Keep your home dry to prevent mold and mildew from proliferating. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency recommends keeping an indoor humidity level of 30 to 60 percent.
You can do this by opening windows to exchange air inside your house. Remember that stagnant air retains all the moisture from your activities, so you should allow proper air movement by creating a draft inside at least once a day.
Use exhaust hoods or fans to reduce the level of moisture that can travel throughout the air when you cook or take shower. When showering, keep the bathroom door closed to not let excess humidity out. Rather leave the fan remove the moisture after you finish the shower.
Also, when possible dry your clothes outside.
If necessary, use a dehumidifier to reduce the humidity level of your home. If anything else have failed, this could be the solution to your problem with high humidity.
#8 Vacuum clean with a HEPA filter
It may sound surprising, but some vacuum cleaners actually contribute to indoor air pollution.
Yes, that’s right.
Vacuum cleaners without a proper filter, that would allow small particles escape back into the air, only worsen home air quality by stirring and redistributing pollutants.
To be sure you are not causing more harm when cleaning your house, use a vacuum cleaner that has a HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) or ULPA (Ultra Low Penetration Air) filter.
HEPA filters should be able to capture 99.7 percent of particles as small as 0.3 micrometers. ULPA filters perform even better by retaining 99.9 percent of particles of 0.12 micrometers in size [16] .
The design and cleaning efficiency are also important criteria. No HEPA filter will perform as promised if the vacuum cleaner is not properly sealed. Only well-sealed vacuum cleaners direct all collected particles to pass through the filter.
When looking for a new vacuum cleaner, make sure that it contains the real HEPA filter and not something labelled misleadingly as “HEPA-like” or “HEPA-type” filters. Beware of this marketing trick to confuse customers, as these types of filters might not comply with the standards of removing the most harmful particles.
#9 Keep your home dust free
Do you know where dust comes from and how come it always reappears in your home?
According to researchers, most household dust is a mixture of organic matter and particulate matter from outdoor air, which is brought inside every time you, other family members or your pets come from the outside [17] .
What should you imagine under this label?
Well, let’s see… It includes tiny particles like dead skin cells, pet dander, microscopic soil particles from your shoes, decomposing organic materials, microfibers from clothing, bacteria, molds, and dust mites.
Scientists have also found traces of many chemicals in common household dust. These chemicals usually originate from cleaning products, plastic items, paints, oil, cosmetics, pesticides or other products commonly used at home.
No one can write down a precise list of compounds contained in dust since they differ based on the area where you live, your lifestyle and your household, but every time you walk across a room, your kids play, pets run around, dust gets suspended into the air, from where it can be easily inhaled by you and your children.
You cannot prevent dust from entering your house, but you can minimize chances of your exposure to it by regular cleaning. Vacuum cleaners with HEPA filter should help in retaining most of the harmful particles (read the previous section to learn more about them).
Do not forget to clean your heating and air conditioning filters, ducts, and vents regularly as well. It will reduce particles accumulated over the time from re-circulating throughout the air in your home.
#10 Use air purifiers with HEPA filter
If you live in an area with poor outdoor air quality, it’s worth considering the use of air purifier at home. On critical days when authorities issue health warning, you should keep your windows closed and use air purifier to minimize the risk of breathing polluted air.
For example , a two-year study in Salt Lake City , which chokes under a thick blanket of smog on cold winter days when inversion hits in, has found out that air purifiers with HEPA filters reduced fine-particulate matter (PM2.5) in observed households by 55 percent.
Similar results were confirmed by other studies, coming to a conclusion that at least 50 percent of particulate matter can be removed by a high-efficiency air filtration system [19] .
Most modern air purifiers work with a multilayer filter system, consisting of a prefilter, a carbon filter, an antibacterial filter and a HEPA filter [19] . You can even find some ENERGY STAR purifiers on the market that offer better energy efficiency.
So, there are plenty of options to choose from.
Final words
Do not take the quality of the air you breathe every day lightly. It is easy to overlook your own health when other daily chores demand your immediate attention. But do not forget that throughout one day around 10,000 liters of air enter your lungs and take part of the most important metabolic processes in your body [18] .
Was this article helpful?
About greentumble.
Greentumble was founded in the summer of 2015 by us, Sara and Ovi . We are a couple of environmentalists who seek inspiration for life in simple values based on our love for nature. Our goal is to inspire people to change their attitudes and behaviors toward a more sustainable life. Read more about us .
- Agriculture
- Biodiversity
- Deforestation
- Endangered Species
- Green Living
- Solar Energy
Sliding Sidebar
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Advanced Admit Card
- JEE Advanced Admit Card 2024
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Admit Card
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Admit Card 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET Result 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET 2024 Exam Live
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Air Pollution Essay for Students in English: 100, 200 and 500 Words
Air pollution is becoming a serious issue that’s affecting human health, flora and fauna and overall well-being of Earth. As responsible citizens of the world, it’s our duty to take care of anything that’s harming the planet and leave it in better condition for future generations. Here are a few sample essays children can use to write about air pollution and learn about different ways to mitigate this crisis.
100 Words Essay on Air Pollution
200 words essay on air pollution, 500 words essay on air pollution.

Any physical, chemical, or biological alteration in the air is referred to as air pollution. The atmosphere contains a specific portion of the gas. It is harmful to survival to change the makeup of these gases. “Global warming” is the term used to describe the rise in global temperature caused by this imbalance in gas composition. Hazardous pollutants, whether present naturally or artificially, can modify the environment and have a negative impact on the ecosystem. Ineffective resource management and reckless human activity are harming the environment and therefore it is our responsibility as inhabitants of Earth to take care of it.
Pollution is any activity that tampers with the environment's fundamental characteristics and causes damage. The air we breathe is no longer clean and fresh, it has been contaminated by pollutants. The threat to Earth and its ecosystem is getting worse as a result of the contamination of the air, water, and soil. These pollutants are causing a number of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases—our immune system is getting affected negatively, and children are at a high risk of developing asthma and other breathing problems. There are numerous factors that frequently increase this air pollution. Automobiles, transportation methods, industrialization, expanding cities, etc. are the main causes of air pollution. The contamination of the entire atmosphere is brought on by the release of various toxic gases or dangerous components from such sources.
Air pollution, which has a negative impact on the environment, also has a significant impact on the ozone layer. The primary contributor to pollution is the ever-increasing demands of the human population. Daily human activities pump harmful chemicals into the atmosphere, making it more polluted than ever and accelerating climate change. The flora and fauna are also being severely impacted by the airborne harmful chemical releases. The rising contamination of the Earth's air, water, and soil—the essential life support systems of the planet—poses a major threat to the planet and its environment.
One of today's top environmental concerns is air pollution. There are numerous factors that frequently increase this air pollution. Toxic gases, particulates, paint, and batteries containing lead are released throughout the industrialization process. The ozone layer is also being destroyed and the world is being exposed to dangerous solar rays as a result of all the contaminants in touch with the atmosphere.
Ozone is a contaminant that exists at the ground level and can be harmful to human health. But the same ozone creates a layer of defence in the stratosphere. The "good" ozone, however, is being destroyed by ozone-depleting substances—such as hydrochlorofluorocarbons, and chlorofluorocarbons. These chemicals were once used in coolants, foaming agents, insecticides, solvents, and fire extinguishers and occasionally still are.
Primary and secondary pollutants are the two categories that have emerged as a result of the growing number of air pollutants. Primary pollutants, which include smoke, ash, dust, fumes, mist, spray, inorganic gases, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and radioactive substances, have a direct negative impact on fresh air. Secondary pollutants are those that interact chemically with primary pollutants, as well as other elements in the atmosphere, such as sulphate trioxide, ozone, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen dioxide.
Causes of Air Pollution
The disposal of solid wastes that release methane gas and the breakdown of trash landfills are major sources of air pollution. This problem has become a severe environmental and health issue as a result of the population's rapid development, industrialisation, and greater use of cars, planes, and other transportation.
Common Effects of Air Pollution
Pollutants in the air we breathe every minute enter our bloodstream and travel to our lungs and entire body, producing a plethora of health issues. Animals can have health issues similar to people if they are exposed to air toxics in high enough quantities over an extended period of time. Air toxics also play a role in animal sickness, infertility, and birth abnormalities. Therefore, both directly and indirectly, pollution of the environment harms both plants, animals, and people.
What Can We Do
Using public transportation is a surefire short method to reduce air pollution because it uses less gas and electricity, even carpools help with the situation. A permanent, non-polluting, and extremely secure source of energy is the sun or solar power. Solar panels, which are special in design and simple to install, are also a technical benefit to society and the planet. They take in solar energy and store it to power various equipment and electronics. Another step you can take on this path is to plant more trees and live a simplistic life. Minimalist living is not only a trendy millennial lifestyle, but it also has significant societal and environmental benefits.
Air pollution may reach one million tonnes annually in the next decades if environmental protection measures are not taken seriously and effectively enforced. We need to drastically alter our everyday routines if we want to lower the level of air pollution. By making better use of raw materials, water energy, and other resources, we can reduce pollution. Human health can be safeguarded and economic wellbeing can be increased when less harmful compounds are exchanged for hazardous ones.
You may also like:
- Types of Pollution Essay
- Environmental Pollution Essay
- Noise Pollution Essay
- Plastic Pollution Essay
- Air Pollution Essay
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Actions You Can Take to Reduce Air Pollution
Follow these tips every day to reduce pollution:.
- Conserve energy - at home, at work, everywhere.
- Look for the ENERGY STAR label when buying home or office equipment.
- Carpool, use public transportation, bike, or walk whenever possible.
- Follow gasoline refueling instructions for efficient vapor recovery, being careful not to spill fuel and always tightening your gas cap securely.
- Consider purchasing portable gasoline containers labeled “spill-proof,” where available.
- Keep car, boat, and other engines properly tuned.
- Be sure your tires are properly inflated.
- Use environmentally safe paints and cleaning products whenever possible.
- Mulch or compost leaves and yard waste.
- Consider using gas logs instead of wood.
On Days when High Ozone Levels are Expected, Take these Extra Steps to Reduce Pollution:
- Choose a cleaner commute - share a ride to work or use public transportation.
- Combine errands and reduce trips. Walk to errands when possible.
- Avoid excessive idling of your automobile.
- Refuel your car in the evening when its cooler.
- Conserve electricity and set air conditioners no lower than 78 degrees.
- Defer lawn and gardening chores that use gasoline-powered equipment, or wait until evening.
On Days when High Particle Levels are Expected, Take these Extra Steps to Reduce Pollution:
- Reduce the number of trips you take in your car.
- Reduce or eliminate fireplace and wood stove use.
- Avoid burning leaves, trash, and other materials.
- Avoid using gas-powered lawn and garden equipment.
You can also take steps to minimize your exposure to air pollution and protection your health.
- Information on the health effects of ozone
- Information on the health effects of particles
- More Air Quality Index Publications
Contact Us to ask a question, provide feedback, or report a problem.
Air Pollution Essay
Air pollution is a significant concern across the world. Air pollution occurs when dangerous particles, gases, and chemicals are released into the air. The pollutants of air can be found in vehicles, factories, power plants, and construction sites. Air pollution also causes smog, making it difficult to breathe or even see things as near as 100 feet. To combat this, many governments have created and enforced policies to reduce air pollution, such as shutting down coal power plants or requiring car owners to switch over to electric cars. It is high time we realise the severity of this issue and act towards avoiding air pollution. To learn more about air pollution, let us go through the air pollution essay available at BYJU’S.

Table of Contents
Air pollution essay 100 words, causes of air pollution.
Effects of Air Pollution
How to Reduce Air Pollution?
Air pollution is a concern for people all over the world. Air pollution is most often caused by burning fossil fuels like petroleum, coal, and natural gas. The exhaust fumes released by vehicles fill the air with toxic particles. Pollution can cause health problems, such as asthma, headaches and other symptoms of allergies.
The World Health Organisation has classified air pollution as an environmental risk to human health. Many countries have taken action concerning air pollution. After reading the air pollution essay 100 words and learning about air pollution, let us now move on to understand the causes.
Air pollution is caused by vehicles, factories, power plants, and trash burning. Vehicles cause air pollution by burning gasoline or diesel. The most significant cause of air pollution is burning fossil fuels to create energy like coal and oil. Air pollution can be considered a contributor to global warming , a major challenge we face today.
You can keep your little ones engaged in learning by asking them to write an essay on air pollution and create a pictorial representation of the same.
Effects of Air Pollution on Human Health
There are many harmful effects of air pollution. It causes respiratory problems and other health issues in people. It also causes lung diseases and cancer. Like any other type of pollution, the health risks of air pollution are high for any living being.
People are more likely to die from respiratory disease and lung cancer in heavily polluted areas. Air pollution causes conditions that make people more susceptible to respiratory infection and inflammation. The body can also absorb harmful substances in polluted air easily.
These are the adverse effects of air pollution that we come across in the air pollution essay pdf. There are a few preventive measures and remedies to reduce air pollution for these harmful effects. Let us understand how to reduce air pollution by referring to the air pollution essay.
Air pollution has been a critical issue for many countries. It is the second-largest contributor to drastic climate change after carbon dioxide. BYJU’S air pollution essay in English helps us learn some new ways to control air pollution.
Planting more trees is one of the significant ways to reduce air pollution. Afforestation is a much-needed action to protect our planet from further damage.
Increasing the usage of eco-friendly materials and renewable energy play a vital role in combating air pollution. In addition, eco-friendly fuels, such as compressed natural gas (CNG), biogas, liquid petroleum gas (LPG), etc. play an essential role in reducing air pollution.
To conclude, air pollution is a serious issue, and we must fight to overcome this and save the Earth . For more kids learning activities, ensure to visit BYJU’S website.
Frequently Asked Questions on Air Pollution Essay
Does afforestation help reduce air pollution.
Yes. Afforestation helps in reducing air pollution as it increases the supply of oxygen and decreases the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
How does air pollution harm human beings?
Air pollution is hazardous for humans, and it can lead to respiratory problems and a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. It also causes heart attacks and strokes.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Essay on Pollution for Students and Children
500+ words essay on pollution.
Pollution is a term which even kids are aware of these days. It has become so common that almost everyone acknowledges the fact that pollution is rising continuously. The term ‘pollution’ means the manifestation of any unsolicited foreign substance in something. When we talk about pollution on earth, we refer to the contamination that is happening of the natural resources by various pollutants . All this is mainly caused by human activities which harm the environment in ways more than one. Therefore, an urgent need has arisen to tackle this issue straightaway. That is to say, pollution is damaging our earth severely and we need to realize its effects and prevent this damage. In this essay on pollution, we will see what are the effects of pollution and how to reduce it.

Effects of Pollution
Pollution affects the quality of life more than one can imagine. It works in mysterious ways, sometimes which cannot be seen by the naked eye. However, it is very much present in the environment. For instance, you might not be able to see the natural gases present in the air, but they are still there. Similarly, the pollutants which are messing up the air and increasing the levels of carbon dioxide is very dangerous for humans. Increased level of carbon dioxide will lead to global warming .
Further, the water is polluted in the name of industrial development, religious practices and more will cause a shortage of drinking water. Without water, human life is not possible. Moreover, the way waste is dumped on the land eventually ends up in the soil and turns toxic. If land pollution keeps on happening at this rate, we won’t have fertile soil to grow our crops on. Therefore, serious measures must be taken to reduce pollution to the core.
Get English Important Questions here
Types of Pollution
- Air Pollution
- Water Pollution
- Soil Pollution
How to Reduce Pollution?
After learning the harmful effects of pollution, one must get on the task of preventing or reducing pollution as soon as possible. To reduce air pollution, people should take public transport or carpool to reduce vehicular smoke. While it may be hard, avoiding firecrackers at festivals and celebrations can also cut down on air and noise pollution. Above all, we must adopt the habit of recycling. All the used plastic ends up in the oceans and land, which pollutes them.

So, remember to not dispose of them off after use, rather reuse them as long as you can. We must also encourage everyone to plant more trees which will absorb the harmful gases and make the air cleaner. When talking on a bigger level, the government must limit the usage of fertilizers to maintain the soil’s fertility. In addition, industries must be banned from dumping their waste into oceans and rivers, causing water pollution.
To sum it up, all types of pollution is hazardous and comes with grave consequences. Everyone must take a step towards change ranging from individuals to the industries. As tackling this problem calls for a joint effort, so we must join hands now. Moreover, the innocent lives of animals are being lost because of such human activities. So, all of us must take a stand and become a voice for the unheard in order to make this earth pollution-free.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
FAQs on Pollution
Q.1 What are the effects of pollution?
A.1 Pollution essentially affects the quality of human life. It degrades almost everything from the water we drink to the air we breathe. It damages the natural resources needed for a healthy life.
Q.2 How can one reduce pollution?
A.2 We must take individual steps to reduce pollution. People should decompose their waster mindfully, they should plant more trees. Further, one must always recycle what they can and make the earth greener.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Latest Education News
- Engineering
- Law Admission
- Design Admission
- PG Admission
- Preparation Guide
- Entrance Exam Results
- Board Exam Results
- UPSC Civil Services 2025
- NDA 2024 (I & II)
- SSC Recruitment
- Railway Recruitment
- Board Time Table
- Bihar Board (BSEB)
- Chhattisgarh Board
- Gujarat Board
- Haryana Board
- Course Guides

Essay on Pollution in 150, 250, 500 Words – Students of almost each class get an assignment or homework to write an essay on pollution. The word limit can be 150, 250 or 500 depending upon the class they study. Students from class 1 to 12 can take help of this short essay about pollution taking important points. Take help from this short essay on pollution in English to complete their homework on time. To help students, we have provided a pollution essay in 150, 250, 500 Words. Instead of using the exact words, students are suggested to modify the word and include more thoughts to make the essay on pollution more enticing. With the help of a well-phrased pollution essay, students will be able to get good marks in their final exams. Also read- Essay on Mahatma Gandhi
Essay on Pollution in 500 Words
Pollution is the presence of harmful substances in the environment. These harmful substances are called pollutants. There are various types of pollution that are Air Pollution, Water Pollution, Noise pollution and more. Because of the increase in population, pollution is also increasing on a daily basis. People are getting hazardous diseases with the increased level of pollution. Hence, everyone should be aware of the pollution, its effects and how to reduce it effectively. Also read- Essay on My School
What is Pollution?
Like a balanced diet for a healthy body, our environment also needs every substance in a balanced proportion. If any substance increases more than its threshold amount then it pollutes the environment such as increased carbon dioxide, Nitrogen oxides in the atmosphere pollutes the air and adversely affects the health of humans. Also Read- Essay on Diwali
Types of Pollution
There are different types of pollution that affect different sections of the environment.
- Air Pollution
- Water Pollution
- Noise Pollution
- Soil Pollution
- Environment Pollution
Effects of Pollution
Due to the pollution, people and the environment are getting affected in different ways. Here are some of the most recognised bad impacts of pollution.
- People exposed to high levels of noise pollution face hearing problems, high blood pressure, sleep disturbance and other issues.
- Because of the high level of air pollution, Global warming is increasing which will further depleting the ozone layer. Besides, breathing problems are increasing in humans.
- Many species of animals and birds are at the verge of extinction such as sparrow which are almost extinct.
- Increased water pollution is destroying life underwater.
- Pesticides used in crops are increasing the risk of cancer and other dangerous diseases. Continuous increase of soil pollution is making the soil infertile.
How to Reduce Pollution?
People should join hands to reduce pollution. So that our coming generations can experience the healthy environment. To preserve the healthy living environment, people should take some precautions and measures. Check the below steps that can help in reducing the pollutants-
- Reduce the use of non-biodegradable things – Environment has a property of reviving itself by degrading the naturally produced substances. However, the non- biodegradable things like plastic bags and bottles pollute the environment.
- Plant more trees – To decrease the air pollution and save the species, it is very important to plant more number of trees. Trees help in purifying the air by adding more oxygen in the environment.
- Less Use of Chemicals – With advancement in technology, many chemical-made substances are used to improve the yield of food products. People should produce food without using pesticides and
- Reduce Population – Continuously increasing population is the major reason for increased pollution. People should follow the policy We two, our two (hum do hamare do) to keep the population under control.
- Recycling is also a very effective and efficient way to reduce the pollution. It helps in limiting the use of non- biodegradable products.
Essay on Pollution in 250 words for Class 5 Students
Pollution is referred as the presence of harmful substance in the environment. It impact on every person, animal or lining creature on this earth. These unwanted substances added in the environment also known as pollutant. These pollutant creates various diseases and often lead to death of the living creature. There are different types of pollution, and each one has its own problems.
- Air Pollution: When pollutant or harmful elements are present in air is called Air Pollution. Air pollution is formed from smoke and gases from cars and factories get into the air we breathe. It can make our air dirty and cause us to get sick with coughs and other bad things.
- Water Pollution: When factories dump dirty water into rivers or lakes, it makes the water dirty and not safe to drink. This hurts the fish and other animals living in the water too.
- Soil Pollution: Sometimes, chemicals from things like trash and pesticides get into the soil. This makes it hard for plants to grow and can even make our food unsafe to eat.
- Noise Pollution: Have you ever heard loud sounds that bother you? That’s noise pollution! It comes from things like cars honking, machines at work, and even loud music. It can make it hard for animals to hear and cause people to feel stressed.
- Light Pollution : At night, when there are too many lights on, it can confuse animals that need darkness. Even we humans need dark nights to sleep well!
Pollution is a big problem, but we can help stop it! We can do things like using less energy, recycling our trash, and not wasting water. Governments and scientists are also working on ways to make cleaner technologies and laws to protect our environment.
Remember, we all share this beautiful planet, so let’s work together to keep it clean and safe for everyone! By learning about pollution and taking small steps to help, we can make a big difference and have a happy, healthy world for us and future generations.
Short Essay on Pollution
Pollution is a pressing global issue that threatens the health of our planet and its inhabitants. It refers to the introduction of harmful substances or contaminants into the environment, leading to adverse effects on air, water, soil, and living organisms.
Air pollution is one of the most significant forms of pollution, caused by emissions from vehicles, industries, and burning of fossil fuels. These pollutants, such as carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter, contribute to respiratory diseases, smog, and climate change.
Water pollution occurs when harmful substances are discharged into rivers, lakes, and oceans, contaminating drinking water sources and harming aquatic life. Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and improper disposal of sewage are major contributors to water pollution.
Soil pollution, often caused by industrial activities, mining, and improper waste disposal, degrades soil quality and affects agricultural productivity. Contaminants like heavy metals, pesticides, and chemicals can accumulate in the soil, posing risks to human health and the environment.
Pollution not only harms the environment but also impacts human health, leading to respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. It also disrupts ecosystems, causing biodiversity loss and ecological imbalance.
Addressing pollution requires collective action at local, national, and global levels. Implementing stricter regulations, adopting cleaner technologies, promoting renewable energy sources, and raising public awareness are crucial steps in mitigating pollution and safeguarding the planet for future generations. It’s imperative that we take urgent and concerted efforts to combat pollution and protect the health and well-being of all living beings on Earth.
Essay on Pollution in 150 words
Pollution is a significant environmental issue that affects our planet and its inhabitants. It occurs when harmful substances or contaminants are introduced into the environment, leading to adverse effects on air, water, soil, and living organisms.
One of the most prevalent forms of pollution is air pollution, caused by emissions from vehicles, industries, and burning of fossil fuels. These pollutants include carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter, which can cause respiratory illnesses, smog, and climate change.
Water pollution is another pressing concern, resulting from the discharge of pollutants into rivers, lakes, and oceans. Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and improper sewage disposal contaminate water sources, endangering aquatic life and compromising human health.
Soil pollution, caused by industrial activities and improper waste disposal, degrades soil quality and affects agricultural productivity.
Pollution poses serious health risks to humans and wildlife, disrupts ecosystems, and threatens biodiversity. To combat pollution, it’s essential to adopt sustainable practices, reduce emissions, and promote environmental conservation efforts. Only by working together can we mitigate pollution and safeguard the health of our planet for future generations.
10 Lines of Pollution
- Pollution is the introduction of harmful substances or contaminants into the environment.
- It can take various forms, including air pollution, water pollution, and soil pollution.
- Air pollution is caused by emissions from vehicles, industries, and burning of fossil fuels.
- Water pollution occurs due to the discharge of pollutants into rivers, lakes, and oceans.
- Soil pollution results from industrial activities, mining, and improper waste disposal.
- Pollution poses serious health risks to humans, including respiratory diseases and cancer.
- It also harms wildlife and ecosystems, leading to biodiversity loss and habitat destruction.
- Plastic pollution, caused by the accumulation of plastic waste, is a major concern in oceans and water bodies.
- Pollution is exacerbated by unsustainable practices and overconsumption of natural resources.
- Addressing pollution requires collective action and sustainable solutions to protect the environment and human health.
Essay on Pollution- How to Write Effectively?
While writing an essay on Pollution, students should keep a few tips in mind to get good marks.
- Always highlight the important facts or information so that the teacher can get the highlights at one glance. This will improve the readability of the essay on pollution.
- Make sure you write essays in pointers to make it easier to read. If the essay is of 10 marks then do not forget to add 10 unique lines in points. This will help in getting good scores in the essay writing section.
- Students can use some facts and quotes to support their statement that will give some extra points in board exams.
Also Read- Essay on Internet
Stay Connected With StudyGrades for Essays for Different Classes!
Related Articles
Ap pgecet hall ticket 2024 (out)- download link here, maharashtra hsc result 2024 out- maha 12th results link, mbse hsslc result 2024 (out)- check mizoram class 12 reults, latest articles, hotel management- course eligibility, college, fee, future scope, rbse 12th result 2024 (out) | rajasthan class 12 results.

StudyGrades - A one stop-destination to know latest updates in exam, admission, career, courses, recruitment and more.
Rashtriya Military School Admission 2023-24 (Started)-Date, Notifcation
Imo results 2023-24 | sof imo result date, link, ieo result 2023-24 declared (level 1) | sof ieo results 2023.
- Admission 487
- Latest Education News 309
- UG Admission News 270
- Board Exams 169
- PG Admission 167
- Entrance Exam Results 142
Evaluation of hybrid deep learning approaches for air pollution forecasting
- Original Paper
- Published: 23 May 2024
Cite this article

- T. Omri ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9428-868X 1 ,
- A. Karoui 2 ,
- D. Georges 3 &
- M. Ayadi 1
This paper aims at applying different architectures of hybrid deep learning methods and an RBF (Radial Basis Functions)-based approach, with a comparison to traditional deep learning models, for air pollution forecasting which is the key of the air quality control management. The hybrid deep learning models are based on the combination between 1D convolutional neural network which prove during the research literature its excellent ability for features extraction, with recurrent neural network (RNN) which is appropriated for prediction tasks. The RBF-based approach is another way of approximating a nonlinear autoregressive model, using that RBF are powerful interpolation tool. The traditional deep learning methods used for comparison in this work are the simple RNN and the NARMAX model (Non-Linear AutoRegressive Moving Average with eXogenous inputs). The prediction methods are based on a real data base of pollutant concentrations and other influencing environmental air quality parameters (temperature, humidity, pressure, wind speed and wind direction) tested for different locations. All available data values are hourly recorded. As a result of this research work, it was proven that the hybrid deep learning architectures succeeded to provide the best forecasting results based on different errors measurements used as comparison criteria between all the proposed methods.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Data availablity
The data used in this paper are well presented in the concerned sections and can be provided in case of need.
Agana NA, Homaifar A (2017) A deep learning based approach for long-term drought prediction. In: SoutheastCon IEEE, pp. 1–8
Bakar MAA, Ariff NM, Nadzir MSM et al (2022) Prediction of multivariate air quality time series data using long short-term memory network. Malays J Fundam Appl Sci 18(1):52–59
Article Google Scholar
Broomhead D, Lowe D (1988) Multivariable functional interpolation and adaptive networks. Complex Systems, vol. 2
Cirstea RG, Micu DV, Muresan GM, Guo C, Yang B (2018) Correlated time series forecasting using deep neural networks: a summary of results. http://arxiv.org/abs/1808.09794
Díaz-Robles LA, Ortega JC, Fu JS et al (2008) A hybrid ARIMA and artificial neural networks model to forecast particulate matter in urban areas: the case of Temuco Chile. Atmos Environ 42(35):8331–8340
Dong M, Yang D, Kuang Y et al (2009) PM2.5 concentration prediction using hidden semi-markovmodel-based times series data mining. Expert Syst Appl 36(5):9046–9055
Du S, Li T, Yang Y et al (2021) Deep air quality forecasting using hybrid deep learning framework. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 33(6):2412–2424
Eravci B, Ferhatosmanoglu H (2018) Diverse relevance feedback for time series with autoencoder based summarizations. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 30(12):2298–2311
Gamboa JCB (2017) Deep learning for time-series analysis. arXiv preprint. arXiv:1701.01887
Hardini M, Sunarjo RA, Asfi M et al (2023) Predicting air quality index using ensemble machine learning. ADI J Recent Innov 5(1Sp):78–86
https://les.data.gouv.fr/lcsqa/concentrations-de-polluants-atmospheriques-reglementes/temps-reel/2021/
https://prevision-meteo.ch/climat/horaire/metz-nancy-lorraine/2021-01-21
Janarthanan R, Partheeban P, Somasundaram K, Elamparithi PN (2021) A deep learning approach for prediction of air quality index in a metropolitan city. Sustain Cities Soc 67:102720
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2017) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun ACM 60(6):84–90
Lv Y, Duan Y, Kang W, Li Z, Wang FY (2015) Traffic flow prediction with big data: a deep learning approach. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 16(2):865–873
Google Scholar
Omri T, Karoui A, Georges D, Ayadi M (2020) Prediction of water ow depth with kinematic wave equations and NARMAX approach based on neural networks in overland ow model. Presented at ICASET’2020 conference, pp. 193–198
Philippe C (2004) Analyse de la pollution atmosphérique aux échelles locale et régionale. Modélisation spatiale et temporelle à l’aide d’une méthode de scénarii épisodiques, Thèse de doctorat, INSA de Rouen
Qi Z, Wang T, Song G et al (2018) Deep air learning: interpolation, prediction, and feature analysis of fine-grained air quality. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 30(12):2285–2297
Sanchez H (2022) Time Series Forecasting Using Hybrid CNN–RNN. MATLAB Central File Exchange. https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/_leex-change/91360-time-series-forecasting-using-hybrid-cnn-rnn
Sarkar N, Gupta R, Keserwanti PK et al (2022) Air quality index prediction using an effective hybrid deep learning model. Environ Pollut 315:120404
Article CAS Google Scholar
Schoukens J, Ljung L (2019) Nonlinear system identification: a user-oriented road map. IEEE Control Syst Mag 39(6):28–99
Sousa Junior E, Freitas A, Rabelo R et al (2022) Estimation of radial basis function network centers via information forces. Entropy 24(10):1347
Sun Y, Wang X, Tang X (2013) Hybrid deep learning for face verification. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1489–1496
Vardoulakis S, Fisher BEA, Pericleous K et al (2003) Modelling air quality in street canyons: a review. Atmos Environ 37(2):155–182
Wang J, Song G (2018) A deep spatial-temporal ensemble model for air quality prediction. Neurocomputing 314:198–206
Wu Z, Wang X, Jiang YG et al. (2015) Modelling spatial-temporal clues in a hybrid deep learning framework for video classification. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 461–470
Xie T, Yu H, Wilamowski B (2011) Comparison between traditional neural networks and radial basis function networks. Presented at IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, pp. 1194–1199
Yi X, Zhang J, Wang Z et al . (2018) Deep distributed fusion network for air quality prediction. In: Proceedings. 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference of Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 965–973
Zhang GP (2003) Time series forecasting using a hybrid ARIMA and neural network model. Neurocomputing 50:159–157
Zhang Y, Bocquet M, Mallet V, Seigneur C et al (2012a) Real-time air quality forecasting, Part I: history, techniques, and current status. Atmos Environ 60:632–655
Zhang Y, Bocquet M, Vi M, Seigneur C et al (2012b) Real-time air quality forecasting, part II: state of the science, current research needs, and future prospects. Atmos Environ 60:656–676
Zheng Y, Carpa L, Wolfson O, Yang H (2014) Urban computing: concepts, methodologies, and applications. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol 5(3):1–55
Zhou Q, Jiang H, Wang J, Zhou J (2014) A hybrid model for PM2.5 forecasting based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition and a general regression neural network. Sci Total Environ 496:264–274
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Ma F, Ding F, Hayat T (2021) Parameter estimation for a class of radial basis function-based nonlinear time-series models with moving average noises. J Frankl Inst 358(4):2576–2595
Download references
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Research Laboratory On Automatic Control (LARA), National Engineering School of Tunis (ENIT), University of Tunis El Manar (UTM), LE BELVEDERE, 1002, Tunis, Tunisia
T. Omri & M. Ayadi
Private Higher School of Engineering and Technology (ESPRIT), 2083, Tunis, Tunisia
GIPSA-Lab, CNRS, Grenoble INP, Univ. Grenoble Alpes, 38000, Grenoble, France
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and analysis. All authors contributed to the data collection and analysis. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to T. Omri .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
Consent to participate, consent to publish, additional information.
Editorial responsibility: S. Mirkia.
See Figs. 13 , 14 and 15 .

Influence of parameter delay with the CNN-RNN method
Influence of parameter delay with the RNN method

Influence of parameter delay with the NARMAX method
See Figs. 16 , 17 and 18 .

CNN-RNN Time step influence

RNN Time step influence

NARMAX Time step influence
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Omri, T., Karoui, A., Georges, D. et al. Evaluation of hybrid deep learning approaches for air pollution forecasting. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05644-2
Download citation
Received : 21 June 2023
Revised : 17 February 2024
Accepted : 10 April 2024
Published : 23 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05644-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Hybrid deep learning
- Air pollution forecasting
- Convolutional neural network
- Recurrent neural network
- RBF interpolation
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Climate Change
- Coronavirus
- Environmental Justice
- Food and Agriculture
- Transportation
- Your Environment Update
- Full Episodes
- Wild Pennsylvania
- Follow the Pipeline
- Hazardous to Your Health
- The Coming Chemical Boom
- Contact Page
Prove your humanity

Allegheny County’s Clean Air Fund could do more to fight pollution, controller says
An audit of Allegheny County’s Clean Air Fund urges health department officials to put more money towards projects aimed at improving local air quality, and simplify the process by which money is distributed.
County Controller Corey O’Connor’s office released the audit’s findings on Tuesday.
“These funds are derived from fines for air quality violations that directly impact the communities where these industries are located,” O’Connor said in a statement accompanying the report. “That’s why it is critical — and the intention of the law that created the Clean Air Fund — that these communities are to benefit from additional projects to mitigate these harms. Our audit shows that the County has fallen far short of meeting this intent.”
Mon Valley leaders have $5M in U.S. Steel fines to spend, but little has gone to public health
The audit looked at spending from the fund in 2021, 2022 and the first nine months of 2023. Throughout that period, the fund maintained a balance of roughly $10 million, money provided by penalties and fees paid for by area polluters.
The fund is intended “solely to support activities related to the improvement of air quality within Allegheny County and to support activities which will increase or improve knowledge concerning air pollution, its causes, its effects, and the control thereof,” according to the rule that established it.
But only a small portion of the fund balance – between $157,565 to $704,586 – was spent during the years the audit reviewed. More money was spent on operating costs for county staff and “professional and technical expenditures,” which are permitted under the guidelines but, auditors wrote, “could have been paid with other money.”
Those costs were offset to some extent by new fines being deposited into the fund. But O’Connor argued the need for investment was urgent.
The money is “not being spent quick enough and it’s not being spent in communities that need it the most,” O’Connor said. “Why are we holding on to this money? Let’s get this money out as quick as we can to help these residents.”
Auditors said one hurdle is a complicated and opaque application process that the county health department, which administers the fund, has not communicated effectively, the authors said.
For example, those who wish to apply for project support from the Clean Air Fund must request information from the county’s Air Pollution Control Advisory Committee through an online form . Auditors reported that staff uses that process to pre-screen potential applicants, and ensure the proposed project meets fund requirements. But critics say it creates a bottleneck for legitimate projects.
Health department pushes back
In a multi-page response from the health department included in the audit, acting health department director Patrick Dowd pushed back strongly on the report’s conclusions.
“Audit findings aside, the ACHD has never stopped anyone from applying for the use of Clean Air Funds,” Dowd wrote.
He said the audit made no mention of efforts to improve the process undertaken during the period the auditors studied, like an enhanced effort to encourage community proposals for projects. He said those efforts led to an additional $2.29 million in grants approved by the Board of Health last September — money that was allocated outside the timeframe of O’Connor’s review. The audit also didn’t reflect the health department’s spending on pollution reduction through other funds and programs, he said.
The audit “omits important reforms and adoption of innovative practices” implemented while the audit was ongoing, including “at least $7.75 million dollars specifically to communities impacted by pollution.”
Dowd also questioned the audit’s downbeat assessment of the county’s overall air quality. He noted that many air-pollution concerns were caused by polluters upwind of the region, whose emissions were outside the health department’s control.
“Even when Allegheny County is meeting federal standards, which it is, it will remain in nonattainment [of federal goals] because Allegheny County is part of the larger regional area that transports pollutants across our boundaries,” Dowd wrote, referring specifically to ozone pollution emitted by cars, power plants and other industrial sources.
O’Connor’s report will likely be welcomed by some local activists.
“Community members can’t even figure out how to apply for the funds,” said Matthew Mehalik, executive director of the Breathe Project. Though Mehalik had not read the audit, he brought up many of the same issues highlighted in the report. And he said that Clean Air Fund money has mostly funded “small ball” efforts to address air pollution, like tree planting projects.
“Tree planting is a good thing. It’s not a bad thing,” he said. But “if you look at a bang-for-the-buck way of looking at it, tree planting is not one thing that is drastically improving, in the short term, the public health of residents impacted by air pollution.”
The fund came under scrutiny last year after the county health department’s Air Quality Program, which monitors and enforces air pollution regulations, sought to increase the portion of the Clean Air Fund it can use for its operating expenses. Officials sought to boost that level from 5% up to as much as 25% — a move that many advocates and community groups vocally opposed.
The proposal was not approved by the Board of Health. But O’Connor’s audit contends that because the county can tap a percentage of the fund balance for its own operating costs, it has an incentive to keep the fund balance as high as possible, rather than spending it down.
Dowd pushed back on that as well, noting that the county is not currently tapping the fund at all for operating expenses. But the health department did acknowledge some accounting errors, stemming from a failure to collect some penalties, and mistakenly placing others in different accounts.
Calls for more transparancy
O’Connor said the recommendations are meant to ensure that fines paid by pollutants actually fund air quality improvements in local communities. He also noted the importance of sharing information with county leaders, including County Executive Sara Innamorato, who pledged to address the county’s poor air quality and high asthma rates while on the campaign trail last year.
“I do know that the executive is very concerned about air quality and health in this county. And I think that’s why the timing of this is beneficial so that we can all work together to solve these issues,” O’Connor said.
Mihalik called for more transparency in how the funds are allocated, but he also said the Clean Air Fund amounts to a “pay to pollute” model in which polluters pay a fine rather than make lasting changes to their operations.
“By considering more strident penalties for an organization or a business that regularly violates the Clean Air Act,” he said, “we could see some real changes and health improvements for people in the Mon Valley and all of Allegheny County.”
He noted that in places like the Mon Valley, many of those who live closest to polluters are poor, people of color, and the elderly — all groups at higher risk to the health impacts of poor air quality.
“People’s families have been disrupted from many years of living in communities with high levels of air pollution,” Mehalik said. “By not using those funds to mitigate and improve quality of life for residents in the Mon Valley, these injustices have been ongoing for some time and they continue to go on.”
“While the Health Department has taken steps to improve the Fund in the past few years, there is still more to do to ensure expenditures are effective and impactful,” Innamorato said in a statement. “We look forward to reviewing the findings of the audit and working closely with the Allegheny County Health Department, stakeholders, and communities that have suffered the harms of air pollution to ensure the Fund is used for its stated purpose of improving air quality in Allegheny County.”
Share this:
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
Advertisement
Subscriber-only Newsletter
Climate Forward
How india is coping with extreme heat.
India is adapting to a new era of dangerous heat, even as climbing temperatures are making its transition to a cleaner economy more difficult.
- Share full article

By Manuela Andreoni
Since April, heat waves, most likely fueled by climate change , have reached dangerous levels across India and other Asian countries. This week, many Indian cities, including New Delhi, the capital, recorded temperatures above 115 degrees Fahrenheit. Local governments sent out heat alerts warning people to avoid staying outside and schools in several states were ordered to close .
It’s all happening as hundreds of millions of Indians head to the polls and are expected to re-elect Prime Minister Narendra Modi .
The grueling heat crisis, one of several in India over the last few years, made me wonder if the nation’s leaders had made climate change more central in their campaigns.
Not really, my colleague Suhasini Raj, who covers India, told me.
“In their election manifestoes, India’s top political parties, including the governing Bharatiya Janata Party and the main opposition, the Congress party, have made multiple promises to act on climate damage and reduce emissions,” she said. “But climate pledges on paper are absent from speeches and rallies in the campaign trails.”
Still, as Raj pointed out, Indians are suffering the effects of climate change more acutely than most. “Climate change and pollution lead to loss of livelihoods, forced migrations and kill over two million Indians annually,” she said. “It is projected that 148.3 million people in India will be living in severe climate hot spots by 2050.”
Measuring the impact of heat can be difficult: Estimates of how many deaths can be attributed to heat in India vary from a few hundred to tens of thousands a year . Official tolls often fail to capture the full lethality of extreme temperatures .
Today, I want to explain how India is adapting to extreme heat, even as climbing temperatures are making its transition to a cleaner economy even more difficult. The country is not short of good ideas. But scaling them in the world’s most populous nation is still a challenge.
The rush to adapt
India was the first country in South Asia to create a heat action plan. It started in the city of Ahmedabad after an extreme heat wave in May 2010 resulted in a 43 percent increase in mortality compared with the same period in previous years, as Somini Sengupta wrote .
The plan involved establishing a system to warn residents when dangerous temperatures are expected, educating health care workers to recognize heat-related illnesses and opening cooling centers. Research estimates these programs save more than 1,000 lives a year .
Since 2010, India’s national government has worked with over 20 states and more than 130 cities to establish their own heat action plans . The results are mixed. Many plans aren’t public, fail to reach vulnerable populations or lack the resources to implement solutions .
But local governments are trying a variety of strategies. I asked Vishwas Chitale, from the Council on Energy, Environment and Water, a think tank based in Delhi, to list some of the most successful.
He mentioned Telangana’s statewide policy to help paint or tile roofs in white colors that can reflect sunlight and cool buildings, new heatstroke wards in big hospitals and a workshop run by India’s National Disaster Management Authority to help local officials prepare for extreme heat .
A lot of the work is supported by the Natural Resources Defense Council, an advocacy group. Vijay Limaye, a climate and health scientist who follows India’s heat policies for the group, told me that the country’s experience showed that there were “some tested solutions.” “But they need to be deployed rapidly and at scale,” he said.
India’s difficult energy transition
India is also the fastest-growing big economy in the world and its dependence on coal to produce electricity is a major source of concern in the struggle to curb climate change.
India’s in a bind: It needs to replace coal even as its energy needs are growing quickly, along with its economy. More extreme temperatures create an even bigger burden, as the country is often forced to burn more coal to keep cooling devices running across the country.
This problem may only get more difficult in the future. Scientists say global temperatures will continue to rise and, though only 9 percent of Indians have air-conditioning units now, that number is likely to increase ninefold by 2050 .
The good news is that, in recent years, renewable energy capacity has been growing fast, said Kaushik Deb, who runs the India program at Columbia University’s Center on Global Energy Policy.
In the first quarter of this year, for example, 71.5 percent of the new power capacity added in India came from renewable energy, according to an analysis by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis . The report also noted that coal accounted for less than half of India’s total capacity for the first time since the 1960s.
Making sure India’s energy needs don’t grow more than necessary is also part of the answer. That means investing in more efficient buildings and appliances, public transportation and electric vehicles, some of which are already part of India’s development plan .
Until India can come up with a “sensible and reasonable adaptation policy for heat wave-kind events,” Deb said, “the demand for electricity will continue to rise.”
Ask NYT Climate: Is biodegradable plastic really a thing?
On the face of it, biodegradable plastic is a miracle. It looks like plastic and works much like plastic. And it goes back to nature after you throw it away.
But there’s a big catch: Just because your plastic fork, cup or doggy poop bag is marketed as biodegradable, that doesn’t necessarily mean it’ll break down in the environment. The same goes for so-called compostable plastic. — Hiroko Tabuchi
Read more about which kinds of plastic break down and under which conditions and ask your own questions via the form at the bottom of the page.
Ask NYT Climate: Is online shopping bad for the planet?
More climate news
Russia has found huge oil reserves in Antarctica, according to evidence submitted to the British Parliament, Newsweek reports .
It’ll cost world governments an extra $34 trillion to reach net-zero emissions by 2050, BloombergNEF estimates . That’s 19 percent more than previously thought.
Between 2016 and 2023, electric vehicle registrations in the United States grew almost three times faster than the United States’ public charging infrastructure, The Washington Post found .
Thanks for being a subscriber.
Read past editions of the newsletter here .
If you’re enjoying what you’re reading, please consider recommending it to others. They can sign up here . Browse all of our subscriber-only newsletters here . And follow The New York Times on Instagram , Threads , Facebook and TikTok at @nytimes.
Reach us at [email protected] . We read every message, and reply to many!
Because of an editing error, a picture caption with an earlier version of this newsletter gave an incorrect temperature conversion. One hundred degrees Fahrenheit is roughly equivalent to 37 Celsius, not 30 Celsius.
How we handle corrections
Manuela Andreoni is a Times climate and environmental reporter and a writer for the Climate Forward newsletter. More about Manuela Andreoni
Our Coverage of Climate and the Environment
News and Analysis
The world’s highest court dealing with the oceans issued a groundbreaking opinion that said excessive greenhouse gases were pollutants that could cause irreversible harm to the marine environment and must be cut back.
The Great Salt Lake, a predictor of the risks of climate change, had a recent increase in its levels , but still remains below healthy levels. Experts worry that conservation efforts will be reduced as a result.
As the world’s coral reefs suffer a fourth global bleaching event, heat stress in the Caribbean is accumulating even earlier than it did in 2023, the previous record year for the region.
A Cosmic Perspective: Alarmed by the climate crisis and its impact on their work, a growing number of astronomers are using their expertise to fight back.
Struggling N.Y.C. Neighborhoods: New data projects are linking social issues with global warming. Here’s what that means for five communities in New York .
Biden Environmental Rules: The Biden administration has rushed to finalize 10 major environmental regulations to meet its self-imposed spring deadline.
F.A.Q.: Have questions about climate change? We’ve got answers .
The Federal Register
The daily journal of the united states government, request access.
Due to aggressive automated scraping of FederalRegister.gov and eCFR.gov, programmatic access to these sites is limited to access to our extensive developer APIs.
If you are human user receiving this message, we can add your IP address to a set of IPs that can access FederalRegister.gov & eCFR.gov; complete the CAPTCHA (bot test) below and click "Request Access". This process will be necessary for each IP address you wish to access the site from, requests are valid for approximately one quarter (three months) after which the process may need to be repeated.
An official website of the United States government.
If you want to request a wider IP range, first request access for your current IP, and then use the "Site Feedback" button found in the lower left-hand side to make the request.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This is a great step to remove air pollution and CO2 levels. • Preventing crop burning. Specific technologies and education can improve outcomes for farmers without burning - creating win-win situations. Education and support for agricultural extension programmes in developing countries are key to their success.
Effects of Air Pollution on Human Health. Air pollution has adverse effects on human health. Breathing polluted air puts you at higher risk of asthma. When exposed to ground ozone for 6 to 7 hours, people suffer from respiratory inflammation. Damages the immune system, endocrine, and reproductive systems.
Consider using air purifiers. Although they do not remove all pollutants, they can improve indoor air quality. Choose an air purifier that has a high clean air delivery rate (CADR) matched for the size of your room. Replace filters. Changing your air conditioner and air purifier filters regularly will improve your air quality and reduce energy use.
Effects Of Air Pollution On Health. The air pollution has many bad effects on the health of people. It is the cause of many skins and respiratory disorder in human beings. Also, it causes heart disease too. Air pollution causes asthma, bronchitis, and many other diseases. Moreover, it increases the rate of aging of lungs, decreases lungs ...
At the same time, the carbon tax is a great way to reduce air pollution and greenhouse gases generated from the same human activities and it is thus a good way to hit two birds with one stone. 5. Improving Air Quality While Fighting Climate Change. Last but not least, air pollution can be prevented by tackling climate change.
A number of air pollutants pose severe health risks and can sometimes be fatal, even in small amounts. Almost 200 of them are regulated by law; some of the most common are mercury, lead, dioxins ...
Air pollution is a cause of disease for millions around the world and now more than ever urgent action is required to tackle the burden of its impacts. Doing so will not only improve both life ...
There Are Many Solutions to Air Pollution. In order to improve air quality and slow climate warming, change needs to happen on a national and global scale. However, actions at the individual and community level are also important. Burn less coal. Pollution from burning all fossil fuels is harmful to the atmosphere, but burning coal has a larger ...
Air pollution goes to the heart of social justice and global inequality, disproportionately affecting poor people. In homes, air pollution comes mostly from fuels and high-emitting heating and cooking systems. Clean cooking and heating fuels and technologies are out of reach for low-income families, so polluting alternatives are the norm.
We need to invest big. Mobilizing finance and investment in low-carbon opportunities and cleaner production and consumption will drive innovation and help to counter pollution. Increased funding is also needed for research, pollution monitoring, infrastructure, management and control. And we need advocacy for action.
10-Line Essay on Air Pollution. Below mentioned is a 10-lined essay on air pollution: Air pollution is caused by harmful substances known as pollutants. The pollutant come from various sources, like vehicle gasses, forest fires, and other human activities. The two of the biggest sources of air pollution are burning of fossil fuels and ...
Air pollution consists of chemicals or particles in the air that can harm the health of humans, animals, and plants. It also damages buildings. Pollutants in the air take many forms. They can be gases, solid particles, or liquid droplets. Sources of Air Pollution Pollution enters the Earth's atmosphere in many different ways. Most air pollution is created by people, taking the form of ...
Air Pollution in China. 1 page / 300 words. Air pollution refers to a position of the Earth's atmosphere when harmful or excessive quantities of substances including biological molecules, particulates, and gases are released. As the Chinese economy gained pace, it had a parallel growth for energy consumption as well.
To reduce the impact of air pollution, my family takes several measures. We ensure proper ventilation, use air purifiers, maintain our vehicles, and support sustainable practices like carpooling and public transportation. However, collective action and government regulations are necessary for more significant changes.
500 Words Essay on How to Reduce Air Pollution Introduction. Air pollution is a pressing issue that threatens the health of our planet and its inhabitants. It is primarily caused by harmful gases and particles released into the atmosphere, mostly from human activities. Addressing this problem requires a multi-faceted approach, involving both ...
If air pollution levels in heavy traffic areas were reduced, the incidence of asthma and other respiratory diseases would be significantly reduced. 28 While it is generally accepted that efforts to reduce air pollution will prevent further environmental changes, they will not reverse existing warming. Interestingly, an increasing number of ...
Use exhaust hoods or fans to reduce the level of moisture that can travel throughout the air when you cook or take shower. When showering, keep the bathroom door closed to not let excess humidity out. Rather leave the fan remove the moisture after you finish the shower. Also, when possible dry your clothes outside.
500 Words Essay on Air Pollution. One of today's top environmental concerns is air pollution. There are numerous factors that frequently increase this air pollution. Toxic gases, particulates, paint, and batteries containing lead are released throughout the industrialization process. The ozone layer is also being destroyed and the world is ...
Today, it is increasingly recognized that air pollution hurts human health. Consequently, efficient mitigation strategies need to be implemented for substantial environmental and health co-benefits. A valid approach to reducing the air pollution effects on the environment and human health is proposed. Specific guidelines have been elucidated by differentiating them on the base of the final ...
On Days when High Particle Levels are Expected, Take these Extra Steps to Reduce Pollution: Reduce the number of trips you take in your car. Reduce or eliminate fireplace and wood stove use. Avoid burning leaves, trash, and other materials. Avoid using gas-powered lawn and garden equipment. You can also take steps to minimize your exposure to ...
Air Pollution Essay 100 Words. Air pollution is a concern for people all over the world. Air pollution is most often caused by burning fossil fuels like petroleum, coal, and natural gas. The exhaust fumes released by vehicles fill the air with toxic particles. Pollution can cause health problems, such as asthma, headaches and other symptoms of ...
Effects of Pollution. Pollution affects the quality of life more than one can imagine. It works in mysterious ways, sometimes which cannot be seen by the naked eye. However, it is very much present in the environment. For instance, you might not be able to see the natural gases present in the air, but they are still there.
130746. - Advertisement -. Essay on Pollution in 150, 250, 500 Words- Students of almost each class get an assignment or homework to write an essay on pollution. The word limit can be 150, 250 or 500 depending upon the class they study. Students from class 1 to 12 can take help of this short essay about pollution taking important points.
This paper aims at applying different architectures of hybrid deep learning methods and an RBF (Radial Basis Functions)-based approach, with a comparison to traditional deep learning models, for air pollution forecasting which is the key of the air quality control management. The hybrid deep learning models are based on the combination between 1D convolutional neural network which prove during ...
Pollution. This story comes from our partner, 90.5 WESA. An audit of Allegheny County's Clean Air Fund urges health department officials to put more money towards projects aimed at improving local air quality, and simplify the process by which money is distributed. County Controller Corey O'Connor's office released the audit's findings ...
May 21, 2024. Since April, heat waves, most likely fueled by climate change, have reached dangerous levels across India and other Asian countries. This week, many Indian cities, including New ...
DOI: 10.1681/asn.20233411s1593c Corpus ID: 269913309; The Impact of Exposure to Air Pollution on the Progression of Primary Glomerular Disease @article{Trachtman2023TheIO, title={The Impact of Exposure to Air Pollution on the Progression of Primary Glomerular Disease}, author={Howard Trachtman and Jonathan P. Troost and Jennifer D'Souza and Sara Adar and Miatta Buxton and Abhijit V ...
Beyond the Numbers: Visualizing Impact. Data visualizations go beyond numbers, painting a vivid picture of progress. Imagine a graph depicting a company's carbon footprint steadily decreasing as they embrace renewable energy sources. This visual representation resonates deeply, making the positive impact of data-driven sustainability tangible.
PDEQ recommended the following actions to reduce adding to ground-level air pollution: Reduce driving - combine errands into one trip; Ride the bus, walk, bike, or share a ride with friends and family
Start Preamble AGENCY: Environmental Protection Agency. ACTION: Proposed rule. SUMMARY: The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is proposing to approve a revision to the State of New York's State Implementation Plan (SIP) for the ozone National Ambient Air Quality Standard (NAAQS) related to a Source-specific SIP (SSSIP) revision for the Sylvamo Ticonderoga Mill (formerly known as ...