- About Project
- Testimonials

Business Management Ideas

Essay on Drug Addiction in Youth

Essay on the Signs of Drug Addiction
Essay on the causes of drug addiction, essay on the effects of drug addiction.
- Essay on the Prevention of Drug Addiction
- Essay on the Treatment of Drug Addiction
The most disturbing thing about drug addiction is that people in different countries of the world are becoming addicted to all kinds of drugs. There are different types of street drugs such as – cocaine, meth, marijuana, crack, heroin etc. Heroin is one of the dangerous drugs that suppress your heart’s work and is appropriate to achieve narcotic effect.
The alarming rate of drug consumption has always been a problem and has detrimental effects on the society. Personal and family problems also lead to drug abuse among youngsters who fail to deal with personal problems. The physiological effects of drug addiction can be difficult to endure and this is why the addict must be treated for their condition. The worst thing is that drugs are that they affect youth in every country of the world.
The term drug not only means medicine, but fatal narcotics with different specifications. These drugs have their evil effects on mind and body cells of the addicts. The addict becomes dependent on the drug to a great extent that he/she cannot stop using it. Despite of having full knowledge of its effects on health, addicts use it on a regular basis.
Drug addiction is basically a brain disease that changes the functioning of brain. There is an uncontrollable desire to consume drugs, as a result of which addicted people engage in compulsive behavior to take drugs. The addicts find it impossible to control the intake of drugs, as a result of which they fail to fulfill day-to-day responsibilities in efficient manner. Drug addiction is also referred as drug dependency, as the addict develops dependency for particular substance.
Drug addiction is a compulsive disorder that leads an individual to use substance habitually to achieve desired outcome. Millions of people in the world are suffering with drug addiction and the number is expected to increase in the coming years. If the person is using drugs for a longer period, the outcome may change. For example – early experimentation with drugs is rooted in curiosity. However, as the frequency of substance becomes frequent – the body starts to depend in it to function properly.
The most common signs and symptoms of drug addiction are – obsession with a particular substance, loss of control over the usage of drugs, abandoning the activities which you used to enjoy, etc. Drug addiction may have long term impact on life and one may develop severe symptoms such as – fatigue, trembling, depression, anxiety, headache, insomnia, chills and sweating, paranoia, behavior changes, dilated pupils, poor coordination problems, nausea etc.
There are a number of reasons why youth and teenagers are addicted to drugs or related substances. Lack of self-confidence is considered as one of the primary causes of drug addiction. It can also be due to excessive stress, peer pressure, lack of parental involvement in child’s activities etc. some people consider drug addiction can be the cause of drug use and ignorance. The ignorance of drug addiction along with physical pain of condition becomes a primary cause of drug addiction. Here are some of the causes of drug addiction.
High Level Stress
Young people who have just started their college life or moved to a new city in search of job often face problems with life change. They are more likely to alleviate stress through the use of drugs and similar substances. Finding an easy fix often seems easier than facing the real problem and dealing with it. Trying illegal drugs can lead to addiction and becomes a long term habit.
Social Pressure
Today, we are living in a highly competitive world and it is difficult to grow in such world. There is always a peer pressure in young and old people. However, it is never visible. A lot of young people expect to experience the pressure to use drugs, smoke and drink alcohol. Young people find it difficult to be the person who doesn’t drink or smoke. As they feel isolated and like a social outcast, they make a habit of taking drugs.
Mental Health Conditions
Another primary reason for trying drugs is mental health condition. People who are emotionally weaker tend to feel depressed about the facts of the world. They look for ways to feel free and live life in a normal way as they go through the period of growing up. In such situation, they make a habit of taking drugs and can lead to addiction.
Psychological Trauma
A history of psychological trauma appears to increase the risk of substance abuse. More than 75% of people who suffered from psychological trauma use drugs as a part of self-medicating strategy or provide an avenue towards self-destructive behaviors. Women are more sensitive to drugs than men, and hence need less exposure to similar effects. The availability of these drugs plays an integral role in perpetuation of addictive behaviors within families.
Exposure to Drug Abuse
Exposure to drug abuse in which the young people are raised is another cause why young people get addicted to drugs. If the individuals grow up in an area where adults use drugs, then the person is likely to try the substance themselves. Setting a good example is extremely important to keep them off drugs and related substances. Providing genuine information about drugs is the best way to prevent drug addiction.
There are many negative effects of drug addiction on physical and mental health. As said, drug addiction refers to compulsive and repeated use of dangerous substances. The effects of drug addiction are wide and profound. The psychological effects of drug addiction comes form the reason that the user is addicted to drugs as well as the changes that take place in brain. Many people start using drugs to handle stress. However, the psychological effects of drug addiction involves craving of the substance and using it to the exclusion of all else.
Emotional Effects
The emotional effects of drug addiction include – mood swings, depression, violence, anxiety, decrease in everyday activities, hallucinations, confusion, psychological tolerance to drug effects etc. Besides these, there are many physical effects of drug addiction that are seen in the systems of the body. The primary effects of drug addiction take place in brain, which changes the brain functions and impacts how the body perceives pleasure.
Physical Effects
Other effects of drug addiction include – heart attack, irregular heartbeat, and contraction of HIV, respiratory problems, lung cancer, abdominal pain, kidney damage, liver problem, brain damage, stroke, seizures, and changes in appetite. The impact of drug addiction can be far-reaching and affects every organ of the body. Excessive usage of drugs can weaken immune system and increase susceptibility to infection.
Brain & Liver Damage
The effects of drug addiction are seen in people because the drug floods the brain repeatedly with chemicals such as – serotonin and dopamine. The brain becomes highly dependent on these drugs and cannot function without them. The effects of drug addiction are also seen in babies of drug abusers and can be affected throughout their life.
Drug addiction can cause the liver to work harder, causing significant liver failure or damage. Regarding brain function, drugs can impact daily activities by causing problems with memory, decision making, mental confusion and even permanent brain damage.
Short Term Effects
Different drugs affect body in different ways. There are some short term effects that occur in drug users depending on the amount of substance used, its purity and potency. Drugs can affect the person’s thinking, mood and perception to a great extent. Drugs can temporarily impair motor functioning and interfere with decision making and even reduce inhibition. The most common substances of drug addiction include – opiates, alcohol, barbiturates, inhalants etc.
A lot of people do not realize the damage caused by drug addiction because the short term effects are not apparent at first. The individual may feel quite invincible and unaware that drugs can actually affect almost every system in the body. The long lasting effects of drug addiction may not be known to addict. If treatment is not sought in time, the physical and emotional health will deteriorate.
Long Term Effects
The long term effects of drug addiction can have disastrous consequences on physical and mental health. As the body adapts to the substance, it needs increasing amount of it to experience the desired outcome. As the individual continues to increase the dosage, he/she may develop physical dependence. The individual may face deadly withdrawal symptoms, once he/she stops using the substance.
Legal Consequences
Drug abuse not only causes negative effects on your physical and mental health, but can have legal consequences. Individuals may have to deal with the legal consequences for the rest of their life. A lot of companies require the employees to take drug test before offering job. Driving under the influence of drugs can lead to serious legal action and even heavy fines.
By understanding the physical impact of the substance, individuals can make informed decision regarding their health. Remember that it is never late to seek help, when it comes to treat drug addiction. There are many rehabilitation centers that help you combat drug addiction in a supportive environment.
Essay on the P revention of Drug Addiction
As said, prevention is always better than cure. It is always best option to deter people from drug abuse. Though it is practically impossible to prevent everyone from using drugs, there are things we can do to avoid drug addiction. Here are some effective tips to prevent drug addiction.
Deal with Peer Pressure
The biggest reason why people start using drugs is because of their friends or colleagues who utilize per pressure. No one in this world likes to be left out, especially teens and youngsters. If you are in such situation, you should find a better group of friends who won’t pressure you into harmful things. You should plan ahead of time or prepare a good excuse to stay away from tempting situations.
Treat Emotional Illness
Individuals suffering with any mental condition such as – anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress etc. should seek help from a physiatrist. There is a strong connection between mental illness and drug addiction. Those with weak emotional status may easily turn to drugs.
Learn to Deal with Pressure
People of today’s generation are overworked and often feel like taking a good break. However, they make the mistake of turning to drugs and end up making life more stressful. Many of us fail to recognize this. The best way is to find other ways to handle stress. Whether it is taking up exercising or reading a good book, you should try positive things that help in relieving stress.
Understand the Risk Factors
If you are not aware of the risk factors of drug addiction, you should first know about drug abuse. Individuals who are aware of the physical and emotional effects of drug addiction are likely to overcome them. People take up drugs when something in their life is not going well and they are unhappy about their life. One should always look at the big picture and focus on priorities, instead of worrying about short term goals.
Develop Healthy Habits
Eating a well-balanced diet and doing regular exercise is the best way to prevent drug addiction. A healthy body makes it easier for people to deal with stress and handle life effectively, which eventually reduces the temptation to use drugs.
The above tips are a just a few ideas that can help prevent drug addiction. However, if the person has already developed drug addiction, he/she should seek drug detox treatment at the earliest.
Essay on the T reatment of Drug Addiction
Drug addiction can be managed effectively like other chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, asthma etc. Treatment of drug addiction is becoming personalized. The comprehensive treatment options not only address addiction, but treat the underlying issues resulting in addiction.
Though there are many options to treat drug addiction, it is not easy. Drug addiction is a chronic disease and one can’t stop using drugs within a few days. A lot of patients need long term or repeated care to stop using drugs completely. Drug addiction treatment depends on the severity of drug abuse. The treatment must stop the person from using drugs as well as keep him away from drugs.
Different treatment methodologies are employed in treating drug abuse. The treatment plan will be devised as per the condition of the addict. It is essential that the treatment is tailored to the unique individual as there is no single treatment that works for all.
Inpatient drug abuse treatment is one of the options that allow the addict to focus on his/her recovery. Attending this treatment facility can increase the chances of completing the drug addiction rehabilitation program, especially if the addict does not have good support system at home.
Outpatient drug abuse treatment is ideal for those addicts who have a supportive environment at home. It is usually recommended for those who want to attend short-term inpatient treatment program.
Cognitive behavioral therapy is another treatment option that is highly effective in treating drug addiction issues. CBT helps in controlling negative thought patterns that lead to drug abuse. Patients can identify the triggers that cause them to use drugs and learn to respond without the need to turn to the substance.
Drug addiction is a complex disease that results from a number of factors such as genetic predisposition, history of violence at home and stress. Researchers have been able to identify the factors that lead to drug abuse. Understanding the root cause of drug addiction is one of the best ways to improve treatment options and outcomes of drug addiction in future.
A lot of people do not understand why people get addicted to drugs and related substances. They mistakenly view drug abuse as a social problem and characterize the addict as a weak person. Though there is no scientific evidence on how exactly drugs work in brain, it can be successfully treated to help people stop abusing drugs. There are many treatments that help people counteract the disruptive effects of drug addiction and regain complete control over life.
Behavioral therapy is the best way to ensure success in most of the drug addicts. The treatment approaches are tailored to meet the drug abuse pattern of patients. It is not uncommon for an individual to relapse and start drug abuse again. In such case, an alternate treatment is required to regain control and recover completely.
Get FREE Work-at-Home Job Leads Delivered Weekly!

Join more than 50,000 subscribers receiving regular updates! Plus, get a FREE copy of How to Make Money Blogging!
Message from Sophia!
No related posts.
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Billionaires
- Donald Trump
- Warren Buffett
- Email Address
- Free Stock Photos
- Keyword Research Tools
- URL Shortener Tools
- WordPress Theme
Book Summaries
- How To Win Friends
- Rich Dad Poor Dad
- The Code of the Extraordinary Mind
- The Luck Factor
- The Millionaire Fastlane
- The ONE Thing
- Think and Grow Rich
- 100 Million Dollar Business
- Business Ideas
Digital Marketing
- Mobile Addiction
- Social Media Addiction
- Computer Addiction
- Drug Addiction
- Internet Addiction
- TV Addiction
- Healthy Habits
- Morning Rituals
- Wake up Early
- Cholesterol
- Reducing Cholesterol
- Fat Loss Diet Plan
- Reducing Hair Fall
- Sleep Apnea
- Weight Loss
Internet Marketing
- Email Marketing
Law of Attraction
- Subconscious Mind
- Vision Board
- Visualization
Law of Vibration
- Professional Life
Motivational Speakers
- Bob Proctor
- Robert Kiyosaki
- Vivek Bindra
- Inner Peace
Productivity
- Not To-do List
- Project Management Software
- Negative Energies
Relationship
- Getting Back Your Ex
Self-help 21 and 14 Days Course
Self-improvement.
- Body Language
- Complainers
- Emotional Intelligence
- Personality
Social Media
- Project Management
- Anik Singal
- Baba Ramdev
- Dwayne Johnson
- Jackie Chan
- Leonardo DiCaprio
- Narendra Modi
- Nikola Tesla
- Sachin Tendulkar
- Sandeep Maheshwari
- Shaqir Hussyin
Website Development
Wisdom post, worlds most.
- Expensive Cars
Our Portals: Gulf Canada USA Italy Gulf UK
Privacy Overview
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Supplements
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
Teenage Drug Addiction: An Overview
- Substance Use Statistics
- Why Teens Use Drugs
- Drug Effects
- Specific Health Risks
- Symptoms and Warning Signs
- Four Stages of Addiction
Many teens experiment with substances but don’t continue to use them. For some adolescents, however, trying a substance like alcohol, marijuana, or illicit drugs leads to regular use. Once withdrawal and cravings set in, a teen dealing with addiction and dependence may not be able to stop using a substance, even if they want to.
Caregivers can prevent teen drug abuse by knowing the signs and talking to their children about the consequences of using substances. This article reviews statistics, risk factors, health effects, signs, and treatment for teenage drug addiction .
Sturti / Getty Images
Teenage Substance Use Statistics
Public health experts track the rates of substance use in people of all ages. One group that they pay particular attention to is teens.
Basic Statistics
Here are some of the key statistics from the Monitoring the Future survey, which has been tracking youth substance use in the United States for over 40 years.
In 2023, here’s how many teens in the U.S. reported any illicit drug use in the last year:
- Eighth graders: 10.9%
- 10th graders: 19.2%
- 12th graders: 31.2%
In addition:
- By the time they reach 12th grade, 21.3% of teens have tried an illicit drug at least once.
- From 2016 to 2020, drug use among eighth graders increased by 61%.
- In a year, around 4,477 15-to-24-year-olds die of illicit drug overdoses (about 11.2% of all overdose deaths are in this age group).
Substances Used
Here is how many teens reported using a specific substance in the last year:
- Eighth graders: 15.1%
- 10th graders: 30.6%
- 12th graders: 45.7%
- Eighth graders: 8.3%
- 10th graders: 17.8%
- 12th graders: 29%
- Any illicit drugs:
- 10th graders: 19.8%
- 12th graders: 31.2 %
- Cigarettes:
- Eighth graders: 5.8%
- 10th graders: 9.4%
- 12 t thgraders: 15%
- Vaping nicotine (e-cigarettes):
- Eighth graders: 11.4%
- 10th graders: 17.6%
- 12th graders: 23.2%
Prescription Medications
Alcohol is the most commonly abused substance among teens, but rates of nicotine and prescription medication abuse are increasing. Examples of prescription drugs teens may misuse include stimulants like Adderall and benzodiazepines like Xanax .
What Causes Teens to Use Drugs?
The reasons why any person uses drugs are complex, and the same is true for teens. Wanting to fit in with peers, feeling overwhelmed by their changing brains and bodies, and pressure to perform in school or sports are just a few reasons why teens may start experimenting with drugs. Teens may not seek drugs out but are instead introduced to substances by someone they know, such as a friend, teammate, or even a family member.
In addition, teens often don’t know or understand the dangers of substance abuse. They may see occasional use as being safe and don’t believe they could become addicted to drugs or face consequences. They may also assume that they can stop using if they want to.
Other risk factors for drug use in teens include:
- Family history of substance use
- Academic pressure
- Adverse childhood events ( ACES )
- Lack of supervision
- Mental health disorders
- Peer pressure
- Desire to escape (e.g., external situation like home life or internal situation like complex feelings)
- Social acceptance (e.g., fitting in with peers)
- Low self-esteem
- Increased access to substances
- Transitional periods (e.g., starting puberty or attending a new school)
While drug use can lead to mental health disorders, sometimes it’s the other way around. Teens may use substances to self-medicate or numb emotional pain.
What Are the Effects of Using Drugs During Adolescence?
The body sends out a “feel good” chemical called dopamine when using a substance. This response tells the brain that it is worth using the substance again to get that feeling. As a result, a person starts having cravings for the substance. Addiction happens when cravings don’t stop, withdrawal occurs without the substance, and use continues even when there are negative consequences. Since the physical and mental urge to use is so strong, it becomes very hard to stop using a substance.
Teenagers who misuse substances can experience drug dependence ( substance use disorder ). Developmentally, adolescents are at the highest risk for drug dependence and severe addiction.
Effects on Brain Development and Growth
The human brain continues to develop until about the age of 25. Using substances during adolescence can change brain structure and negatively affect brain functions like learning, processing emotions, and decision-making. It can also lead to the following:
- More risky behaviors : Substance abuse makes teens more likely to engage in risky behaviors like unprotected sex (or "condomless sex") or dangerous driving.
- Higher risk for adult health problems : Teenagers who abuse substances have a higher risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and sleep disorders.
- Mental health disorders : It is common for teens with substance abuse disorders to have mental health conditions (and vice versa).
- Impaired academic performance : Substance use affects a teen’s concentration and memory, which may negatively affect their schoolwork.
Substance Misuse and Mental Health
A study showed that 60% of teens in a community-based substance use treatment program were also diagnosed with a mental health disorder.
What Are the Health Risks of Drug Abuse?
Drug and alcohol use can lead to substance use disorder as well as the specific health risks of the substance being abused.
Alcohol use can lead to an increased risk of:
- Liver disease, cirrhosis, and cancer
- Heart disease and stroke
- Depression
- Lack of focus
- Alcohol poisoning
- Increased risky behavior
Alcohol Statistics
In the United States, 29.5 million people ages 12 and older have an alcohol use disorder.
Marijuana can impair concentration, worsen mental health, interfere with prescription medications, lead to risky sexual behaviors, or contribute to dangerous driving. Smoking marijuana can also negatively affect lung health.
Marijuana is often thought of as not being "as bad" as other drugs and, in some cases, even good for you. However, marijuana can be harmful to teens because their brains are still developing. Marijuana use in teens is linked to difficulty with problem-solving, memory and learning issues, impaired coordination, and problems with maintaining attention.
Vaping and Edible Marijuana Use Is on the Rise
Recent data shows a shift from teens smoking marijuana to using vaping devices and edibles instead.
Opioids include legal prescription medications such as hydrocodone, oxycontin, and fentanyl, as well as illegal drugs such as heroin. These drugs carry a high risk of overdose and death. The annual rate of opioid overdose deaths for those aged 15 to 24 years is 12.6 per 100,000 people.
Over-the-Counter and Prescription Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications can be misused more easily than others because they’re often easy for teens to obtain. Diet pills, caffeine pills, and cold and flu products with dextromethorphan are just a few examples of OTC substances teens may use. They may also have access to family member’s prescriptions for drugs like opiate painkillers and stimulants or get them from friends who do.
There are serious health risks to misusing OTC cold and cough products, including increased blood pressure, loss of consciousness, and overdose. There can also be legal issues if a teen is using someone else’s prescriptions.
Tobacco can lead to multiple chronic illnesses, including:
- Lung disease
- Heart disease
- Vision loss
- Decreased fertility
E-Cigarettes (Vaping)
Vaping is attractive to teens because e-cigarettes are often flavored like fruit, candy, or mint. These products may contain nicotine or other synthetic substances that damage the brain and lungs. The teenage brain is vulnerable to the harmful effects of nicotine, including anxiety and addiction.
E-cigarettes come in a variety of shapes and sizes and might be disguised as everyday items, such as:
- USB Flash Drives
- Hoodie (sweatshirt) strings
- Smartwatches
- Toys (e.g., fidget spinners)
- Phone cases
Cocaine carries a risk of overdose and withdrawal. It causes decreased impulse control and poor decision-making. Withdrawal symptoms from cocaine include restlessness, paranoia, and irritability. Snorting cocaine can cause nosebleeds and a loss of smell. Using cocaine can lead to heart attacks, lung problems, strokes, seizures, and coma.
Cocaine Can Be Fatal With First Use
There have been reports of people dying the first time they use cocaine, often from sudden cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, or seizures.
Ecstasy (MDMA)
Ecstasy is a stimulant that causes an increased heart rate, blurred vision, and nausea. It can also lead to brain swelling, seizures, and organ damage.
Ecstasy is also known as:
Inhalants are fumes from gases, glue, aerosols, or solvents that can damage the brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, and liver. Using inhalants even once can lead to overdose, suffocation, seizures, and death.
Methamphetamine
Methamphetamine (crystal meth) is a highly addictive stimulant that has multiple health consequences, including:
- Severe weight loss
- Lack of sleep
- Dental problems
- Change in brain structure
- Paranoia and hallucinations
Disease Transmission Risk
Injecting drugs with shared needles increases the risk of contracting HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
What Are the Signs a Teen Is Using Drugs?
Being on the lookout for drug paraphernalia and signs and symptoms of drug abuse can help adults recognize at-risk teens.
Behavioral warning signs of drug use in teens include:
- Personality changes
- Irritability
- Difficulty sleeping
- Inappropriate or odd behavior (e.g., laughing randomly)
- Loss of interest in hobbies or extracurricular activities
- Avoiding eye contact
- Acting secretive or like they’re hiding something
- Staying out late
- Social withdrawal (e.g., from family, friends)
- Poor academic performance
- Hanging out with new friends or no longer hanging out with their usual friend group
- Poor hygiene
- Skipping school
- Isolation (e.g., staying in their room, refusing family meals)
Not All Warning Signs Indicate Drug Use
These warning signs do not necessarily mean a teen is using drugs. Other health problems like allergies, sinus infections, hormone imbalances, or mental disorders can also cause these symptoms in teens.
Physical signs of drug use in teens may include:
- Persistent cough
- Dilated pupils
- Increased or decreased energy
- Sleeping all the time or not at all
- Mood swings
- Memory problems
- Talking very fast or slowly
- Runny nose or nosebleeds
- Increased/decreased appetite
- Weight loss
- Smells like smoke or alcohol (e.g., on clothes, skin, or breath)
Other than behavior and physical signs in a teen, you should also be aware of objects that can be used to do drugs. Examples of drug paraphernalia include:
- Mirrors with white powder
- Razorblades
- Rolled dollar bills
- Crack pipes and spoons
- Needles and syringes
- Rolling paper
Substance Abuse Screening
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that teens be screened at each annual medical exam appointment with questionnaires that ask them about substance use and their knowledge of the risks.
What Are the Four Stages of Drug Addiction?
You should also be aware of the four stages of addiction. The earlier teen drug use is recognized, the sooner they can get help.
- Experimentation: A teen tries one or more substances. Some teens will only try a substance once. Others will continue to experiment and increase their use.
- Regular or “social” use: A teen begins to use one or more substances regularly. At this stage, they may limit their use to just when they’re with friends or only in situations where they feel it’s needed—e.g., before a test.
- Risky use: A teen continues to use a substance that they have regularly been using, even if it’s caused problems for them at school, at home, and in their relationships. They crave the substance, both physically and mentally. At this stage, the substance has become central to a teen’s life, and they’ll take risks to get and use it.
- Dependence and Addiction: A teen is addicted to a substance, and most of their time and energy is devoted to getting and using it. At this stage, they would need intervention and treatment to quit, as they may not be able to stop on their own, even if they wanted to.
How Can Parents Prevent Teenage Drug Use?
While they may not express it, teens do value bonds with the adults in their lives. Nurturing that connection with them includes being involved in their lives and having open, honest communication.
How to Talk to Your Teen About Drug Use
Open communication starts by showing an interest in and talking to your teen about everything. This dialogue builds trust and respect, making it easier for you to talk about difficult topics.
Giving teens your undivided attention, without distractions, helps them feel special and heard. This quality time could be during chores, dinner, walks, car rides, or a fun family game night.
Here are some general tips to keep in mind when you’re talking about drugs with your teen:
- Stay curious and show interest.
- Ask open-ended questions.
- Actively listen.
- Don’t interrupt.
- Give compliments.
- Stay up late to talk.
- Chat over their favorite food.
If you’re trying to start a conversation with your teen because you think they may be using drugs, their response to being confronted will determine how you’ll need to approach the conversation.
If your teen admits to using drugs, stay calm. Be supportive and willing to listen. Find out as much as you can about their drug use—what substances they’re using, how often they’re using them, and how they’re getting them. Be clear that the risks of drugs are serious and that drug use will not be tolerated. At the same time, make sure that you reassure your teen that you love them and that you want to help.
If your teen denies using drugs and you think they are lying , communicate the negative consequences of drug and alcohol use. Be clear that you want them to be safe and that experimenting with substances is dangerous—even if it’s just one time. If you are not able to keep the line of communication open with your teen, talk to their healthcare provider. They can help connect you to resources and support you in taking more decisive action, like drug testing.
Other Strategies
Talking to your teen openly and often is key, but there are also other steps you can take:
- Model responsible behavior for them.
- Stay involved with their activities but let them express their boundaries.
- Meet their friends and their parents.
- Teach them how to make good decisions when under pressure.
Protect Teens From Prescription Medications
Prescription drugs are generally safe when they're taken as prescribed. However, any time a person takes medication for reasons other than what they were prescribed for, it is considered medication abuse. Strategies to protect teens from prescription medication misuse include:
- Storing prescription medications in a safe place
- Locking up controlled substances
- Getting rid of old medications
Safe Medication Disposal
Do not dispose of medications by flushing them down the toilet or pouring them down the sink. Medications can be crushed and mixed into the trash (to keep them away from children and pets) or returned to your local pharmacy or community drug take-back program.
Drug Addiction Treatment for Teens
Even if the adults in their lives try to prevent it, some teens will develop substance use disorders. Support for teens with drug addiction includes treating withdrawal or underlying mental health conditions, and addressing emotional needs, usually with a qualified mental health professional such as a psychiatrist or psychologist.
Treatment for teens experiencing substance use disorder includes a combination of the following:
- Outpatient clinics
- 12-step programs
- Inpatient mental health or substance use units
- Medications
- Therapy (individual, group, or family)
Substance Use Helpline
If your teen is struggling with substance use or addiction, contact the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) National Helpline at 1-800-662-4357 for information on support and treatment facilities in your area.
If you are having suicidal thoughts, dial 988 to contact the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline and connect with a trained counselor. If you or a loved one are in immediate danger, call 911 .
For more mental health resources, see our National Helpline Database .
Talk to your teen’s healthcare provider about what treatment would be best for them. Here are a few topics to discuss:
- Underlying health problems
- Benefits of treatment
- Credentials of team members
- Side effects
- Family involvement
- Schoolwork during treatment
- Length of treatment
- Follow-up care
Experimenting with drugs or alcohol is tempting for teenagers because they may not know or understand the dangers of using substances—even just once. Academic pressure, low self-esteem, and peer pressure are just a few factors that increase their risk of substance use.
Caregivers need to have an open line of communication with their teens and teach them about the risks of using drugs. It’s also important to know the signs of drug use and intervene early to help teens who are at risk for or have already developed substance use disorders.
While drug use may increase the risk of mental health disorders, it’s also important to note that these disorders can lead to substance abuse to self-medicate or numb the emotional pain. If you suspect that a teenager is experiencing either, consult a pediatrician or mental health professional as soon as possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Depending on the substance and severity, a tube may be placed through the nose to suction drugs from the stomach. Activated charcoal is given through the tube to bind with the drug to release it from the body, decreasing the amount released into the bloodstream. If an antidote (reversal agent) such as Narcan is available for that substance, it may be given.
National surveys from the National Institute on Drug Abuse show adolescent drug use rates have remained steady. However, the survey’s detected a shift in the types of drugs used by teens. Alcohol is still the most often abused substance, but the rates are decreasing. Instead, nicotine use and misuse of prescription medications are on the rise.
University of Michigan. Teen drug use remains below pre-pandemic levels .
National Center for Drug Abuse Statistics. Drug use among youth: facts & statistics .
Monitoring the Future. National Survey Results on Drug Use, 1975-2023: Secondary School Students.
NCDAS. Drug use among youth: facts & statistics .
Monitoring the Future. Alcohol: Trends in last 12 months prevalence of use in 8 th , 10 th , and 12 th grade .
Monitoring the Future. Marijuana: Trends in last 12 months prevalence of use in 8 th , 10 th , and 12 th grade .
Monitoring the Future. Any illicit drug: Trends in last 12 months prevalence of use in 8 th , 10 th , and 12 th grade .
Monitoring the Future. Cigarettes: Trends in last 12 months prevalence of use in 8 th , 10 th , and 12 th grade.
Monitoring the Future. Vape nicotine (e-cigarettes): Trends in last 12 months prevalence of use in 8 th , 10 th , and 12 th grade.
DEA. Prescription for disaster: How teens abuse medicines .
National Institute of Health: National Institute on Drug Abuse, Advancing Addiction Science. NIH-funded study finds overall rate of drug use among 10-14 year-olds remained stable during the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic .
Scholastic and the National Institute of Drug Abuse (NIDA). How nicotine affects the teen brain .
Steinfeld M, Torregrossa MM. Consequences of adolescent drug use . Translational Psychiatry . 2023;13(1). doi:10.1038/s41398-023-02590-4
University of Rochester Medical Center. Understanding the teen brain .
National Institute of Health: National Institute on Drug Abuse, Advancing Addiction Science. Common comorbidities with substance use disorders research report: part 1: the connection between substance use disorders and mental illness .
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Alcohol use in the United States .
NIH. Alcohol use disorder (AUD) in the United States: Age groups and demographic characteristics.
American Lung Association. Marijuana and lung health .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. What you need to know about marijuana use in teens .
Sharma P, Mathews DB, Nguyen QA, Rossmann GL, A Patten C, Hammond CJ. Old dog, new tricks: A review of identifying and addressing youth cannabis vaping in the pediatric clinical setting . Clin Med Insights Pediatr . 2023;17:11795565231162297. Published 2023 Mar 25. doi:10.1177/11795565231162297
NCDAS. Drug overdose death rates .
NIDA. Over-the-counter medicines .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Smoking & tobacco use: health effects .
Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Smoking and tobacco use: Quick facts on the risks of e-cigarettes for kids, teens, and young adults .
NYC Health. Cocaine abuse and addiction .
Nemours Teens Health. MDMA (ecstasy) .
Medline Plus. Inhalants .
National Institute of Health: National Institute on Drug Abuse, Advancing Addiction Science. Methamphetamine drug facts .
CDC. Injection drug use .
Levy S, Williams JF, Ryan S, et al. Substance Use Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment . Pediatrics . 2016;138(1). doi:10.1542/peds.2016-1211
- AAP. Bright Futures Toolkit: Links to Commonly Used Screening Instruments and Tools .
Orlando Recovery Center. The four stages of addiction – what are they?.
Casa Palmera. The four stages of drug addiction.
Partnership to End Addiction. Preventing drug use: connecting and talking with your teen .
SAMHSA. Talking with teens about alcohol and other drugs .
American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP). Substance abuse treatment for children and adolescents: questions to ask .
National Council Against Prescription Drug Abuse (NCAPDA). Drug overdose response: know the signs .
American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP). Teens: alcohol and other drugs .
Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs). Teen substance use & risks .
National Center for Drub Abuse Statistics. Drug use among youth: facts & statistics .
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). Tips for teens: cocaine .
By Brandi Jones, MSN-ED RN-BC Jones is a registered nurse and freelance health writer with more than two decades of healthcare experience.
Appointments at Mayo Clinic
- Tween and teen health
Teen drug abuse: Help your teen avoid drugs
Teen drug abuse can have a major impact on your child's life. Find out how to help your teen make healthy choices and avoid using drugs.
The teen brain is in the process of maturing. In general, it's more focused on rewards and taking risks than the adult brain. At the same time, teenagers push parents for greater freedom as teens begin to explore their personality.
That can be a challenging tightrope for parents.
Teens who experiment with drugs and other substances put their health and safety at risk. The teen brain is particularly vulnerable to being rewired by substances that overload the reward circuits in the brain.
Help prevent teen drug abuse by talking to your teen about the consequences of using drugs and the importance of making healthy choices.
Why teens use or misuse drugs
Many factors can feed into teen drug use and misuse. Your teen's personality, your family's interactions and your teen's comfort with peers are some factors linked to teen drug use.
Common risk factors for teen drug abuse include:
- A family history of substance abuse.
- A mental or behavioral health condition, such as depression, anxiety or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- Impulsive or risk-taking behavior.
- A history of traumatic events, such as seeing or being in a car accident or experiencing abuse.
- Low self-esteem or feelings of social rejection.
Teens may be more likely to try substances for the first time when hanging out in a social setting.
Alcohol and nicotine or tobacco may be some of the first, easier-to-get substances for teens. Because alcohol and nicotine or tobacco are legal for adults, these can seem safer to try even though they aren't safe for teens.
Teens generally want to fit in with peers. So if their friends use substances, your teen might feel like they need to as well. Teens also may also use substances to feel more confident with peers.
If those friends are older, teens can find themselves in situations that are riskier than they're used to. For example, they may not have adults present or younger teens may be relying on peers for transportation.
And if they are lonely or dealing with stress, teens may use substances to distract from these feelings.
Also, teens may try substances because they are curious. They may try a substance as a way to rebel or challenge family rules.
Some teens may feel like nothing bad could happen to them, and may not be able to understand the consequences of their actions.
Consequences of teen drug abuse
Negative consequences of teen drug abuse might include:
- Drug dependence. Some teens who misuse drugs are at increased risk of substance use disorder.
- Poor judgment. Teenage drug use is associated with poor judgment in social and personal interactions.
- Sexual activity. Drug use is associated with high-risk sexual activity, unsafe sex and unplanned pregnancy.
- Mental health disorders. Drug use can complicate or increase the risk of mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety.
- Impaired driving. Driving under the influence of any drug affects driving skills. It puts the driver, passengers and others on the road at risk.
- Changes in school performance. Substance use can result in worse grades, attendance or experience in school.
Health effects of drugs
Substances that teens may use include those that are legal for adults, such as alcohol or tobacco. They may also use medicines prescribed to other people, such as opioids.
Or teens may order substances online that promise to help in sports competition, or promote weight loss.
In some cases products common in homes and that have certain chemicals are inhaled for intoxication. And teens may also use illicit drugs such as cocaine or methamphetamine.
Drug use can result in drug addiction, serious impairment, illness and death. Health risks of commonly used drugs include the following:
- Cocaine. Risk of heart attack, stroke and seizures.
- Ecstasy. Risk of liver failure and heart failure.
- Inhalants. Risk of damage to the heart, lungs, liver and kidneys from long-term use.
- Marijuana. Risk of impairment in memory, learning, problem-solving and concentration; risk of psychosis, such as schizophrenia, hallucination or paranoia, later in life associated with early and frequent use. For teens who use marijuana and have a psychiatric disorder, there is a risk of depression and a higher risk of suicide.
- Methamphetamine. Risk of psychotic behaviors from long-term use or high doses.
- Opioids. Risk of respiratory distress or death from overdose.
- Electronic cigarettes (vaping). Higher risk of smoking or marijuana use. Exposure to harmful substances similar to cigarette smoking; risk of nicotine dependence. Vaping may allow particles deep into the lungs, or flavorings may include damaging chemicals or heavy metals.
Talking about teen drug use
You'll likely have many talks with your teen about drug and alcohol use. If you are starting a conversation about substance use, choose a place where you and your teen are both comfortable. And choose a time when you're unlikely to be interrupted. That means you both will need to set aside phones.
It's also important to know when not to have a conversation.
When parents are angry or when teens are frustrated, it's best to delay the talk. If you aren't prepared to answer questions, parents might let teens know that you'll talk about the topic at a later time.
And if a teen is intoxicated, wait until the teen is sober.
To talk to your teen about drugs:
- Ask your teen's views. Avoid lectures. Instead, listen to your teen's opinions and questions about drugs. Parents can assure teens that they can be honest and have a discussion without getting in trouble.
- Discuss reasons not to use drugs. Avoid scare tactics. Emphasize how drug use can affect the things that are important to your teen. Some examples might be sports performance, driving, health or appearance.
- Consider media messages. Social media, television programs, movies and songs can make drug use seem normal or glamorous. Talk about what your teen sees and hears.
- Discuss ways to resist peer pressure. Brainstorm with your teen about how to turn down offers of drugs.
- Be ready to discuss your own drug use. Think about how you'll respond if your teen asks about your own drug use, including alcohol. If you chose not to use drugs, explain why. If you did use drugs, share what the experience taught you.
Other preventive strategies
Consider other strategies to prevent teen drug abuse:
- Know your teen's activities. Pay attention to your teen's whereabouts. Find out what adult-supervised activities your teen is interested in and encourage your teen to get involved.
- Establish rules and consequences. Explain your family rules, such as leaving a party where drug use occurs and not riding in a car with a driver who's been using drugs. Work with your teen to figure out a plan to get home safely if the person who drove is using substances. If your teen breaks the rules, consistently enforce consequences.
- Know your teen's friends. If your teen's friends use drugs, your teen might feel pressure to experiment, too.
- Keep track of prescription drugs. Take an inventory of all prescription and over-the-counter medications in your home.
- Provide support. Offer praise and encouragement when your teen succeeds. A strong bond between you and your teen might help prevent your teen from using drugs.
- Set a good example. If you drink, do so in moderation. Use prescription drugs as directed. Don't use illicit drugs.
Recognizing the warning signs of teen drug abuse
Be aware of possible red flags, such as:
- Sudden or extreme change in friends, eating habits, sleeping patterns, physical appearance, requests for money, coordination or school performance.
- Irresponsible behavior, poor judgment and general lack of interest.
- Breaking rules or withdrawing from the family.
- The presence of medicine containers, despite a lack of illness, or drug paraphernalia in your teen's room.
Seeking help for teen drug abuse
If you suspect or know that your teen is experimenting with or misusing drugs:
- Plan your action. Finding out your teen is using drugs or suspecting it can bring up strong emotions. Before talking to your teen, make sure you and anyone who shares caregiving responsibility for the teen is ready. It can help to have a goal for the conversation. It can also help to figure out how you'll respond to the different ways your teen might react.
- Talk to your teen. You can never step in too early. Casual drug use can turn into too much use or addiction. This can lead to accidents, legal trouble and health problems.
- Encourage honesty. Speak calmly and express that you are coming from a place of concern. Share specific details to back up your suspicion. Verify any claims your child makes.
- Focus on the behavior, not the person. Emphasize that drug use is dangerous but that doesn't mean your teen is a bad person.
- Check in regularly. Spend more time with your teen. Know your teen's whereabouts and ask questions about the outing when your teen returns home.
- Get professional help. If you think your teen is involved in drug use, contact a health care provider or counselor for help.
It's never too soon to start talking to your teen about drug abuse. The conversations you have today can help your teen make healthy choices in the future.
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
Children’s health information and parenting tips to your inbox.
Sign-up to get Mayo Clinic’s trusted health content sent to your email. Receive a bonus guide on ways to manage your child’s health just for subscribing. Click here for an email preview.
Error Email field is required
Error Include a valid email address
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Thank you for subscribing
Our e-newsletter will keep you up-to-date on the latest health information.
Something went wrong with your subscription.
Please try again in a couple of minutes
- Dulcan MK, ed. Substance use disorders and addictions. In: Dulcan's Textbook of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2021. https://psychiatryonline.org. Accessed Jan. 24, 2023.
- 6 parenting practices: Help reduce the chances your child will develop a drug or alcohol problem. Partnership to End Addiction. https://drugfree.org/addiction-education/. Accessed Jan. 24, 2023.
- Why do teens drink and use substances and is it normal? Partnership to End Addiction. https://drugfree.org/article/why-do-teens-drink-and-use-substances/. Accessed Jan. 24, 2023.
- Teens: Alcohol and other drugs. American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. https://www.aacap.org/aacap/families_and_youth/facts_for_families/fff-guide/Teens-Alcohol-And-Other-Drugs-003.aspx. Accessed Dec. 27, 2018.
- Drugged driving. National Institute on Drug Abuse. https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugfacts/drugged-driving. Accessed Jan. 24, 2023.
- Marijuana talk kit. Partnership for Drug-Free Kids. https://drugfree.org/drugs/marijuana-what-you-need-to-know/. Accessed Jan. 24, 2023.
- Drug guide for parents: Learn the facts to keep your teen safe. Partnership for Drug-Free Kids. https://www.drugfree.org/resources/. Accessed Dec. 12, 2018.
- Vaping: What you need to know and how to talk with your kids about vaping. Partnership to End Addiction. https://drugfree.org/addiction-education/. Accessed Jan. 24, 2023.
- How to listen. Partnership for Drug-Free Kids. https://www.drugfree.org/resources/. Accessed Dec. 12, 2018.
- Drug abuse prevention starts with parents. American Academy of Pediatrics. https://publications.aap.org/patiented/article/doi/10.1542/peo_document352/81984/Drug-Abuse-Prevention-Starts-With-Parents. Accessed Jan. 24, 2023.
- How to talk to your kids about drugs if you did drugs. Partnership for Drug-Free Kids. https://www.drugfree.org/resources/. Accessed Dec. 12, 2018.
- My child tried drugs, what should I do? Partnership to End Addiction. https://drugfree.org/article/my-child-tried-drugs-what-should-i-do/. Accessed Jan. 24, 2023.
- Gage SH, et al. Association between cannabis and psychosis: Epidemiologic evidence. Biological Psychiatry. 2016;79:549.
- Quick facts on the risks of e-cigarettes for kids, teens and young adults. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/basic_information/e-cigarettes/Quick-Facts-on-the-Risks-of-E-cigarettes-for-Kids-Teens-and-Young-Adults.html. Accessed Jan. 30, 2023.
- Distracted Driving
- Piercings: How to prevent complications
- Talking to your teen about sex
- Teen suicide
- Teens and social media use
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Weight loss surgery for kids
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
- Healthy Lifestyle
- Teen drug abuse Help your teen avoid drugs
Your gift holds great power – donate today!
Make your tax-deductible gift and be a part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine.
- Open access
- Published: 28 May 2022
A qualitative study exploring how young people perceive and experience substance use services in British Columbia, Canada
- Roxanne Turuba 1 , 2 ,
- Anurada Amarasekera 1 , 2 ,
- Amanda Madeleine Howard 1 , 2 ,
- Violet Brockmann 1 , 2 ,
- Corinne Tallon 1 , 2 ,
- Sarah Irving 1 , 2 ,
- Steve Mathias 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ,
- Joanna Henderson 6 , 7 ,
- Kirsten Marchand 1 , 4 , 5 , 8 &
- Skye Barbic 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 8
Substance Abuse Treatment, Prevention, and Policy volume 17 , Article number: 43 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
14k Accesses
8 Citations
11 Altmetric
Metrics details
Substance use among youth (ages 12–24) is troublesome given the increasing risk of harms associated. Even more so, substance use services are largely underutilized among youth, most only accessing support when in crisis. Few studies have explored young people’s help-seeking behaviours to address substance use concerns. To address this gap, this study explored how youth perceive and experience substance use services in British Columbia (BC), Canada.
Participatory action research methods were used by partnering with BC youth (under the age of 30) from across the province who have lived and/or living experience of substance use to co-design the research protocol and materials. An initial focus group and interviews were held with 30 youth (ages 12–24) with lived and/or living experience of substance use, including alcohol, cannabis, and illicit substances. The discussions were audio-recorded, transcribed verbatim, and analyzed thematically using a data-driven approach.
Three main themes were identified and separated by phase of service interaction, starting with: Prevention/Early intervention , where youth described feeling unworthy of support; Service accessibility , where youth encountered many barriers finding relevant substance use services and information; and Service delivery , where youth highlighted the importance of meeting them where they are at, including supporting those who have milder treatment needs and/or do not meet the diagnosis criteria of a substance use disorder.
Conclusions
Our results suggest a clear need to prioritize substance use prevention and early interventions specifically targeting youth and young adults. Youth and peers with lived and/or living experience should be involved in co-designing and co-delivering such programs to ensure their relevance and credibility among youth. The current disease model of care leaves many of the needs of this population unmet, calling for a more integrated youth-centred approach to address the multifarious concerns linked to young people’s substance use and service outcomes and experiences.
Substance use initiation is common during adolescence and young adulthood [ 1 ]. In North America, youth (defined here as aged 12–24) report the highest prevalence of substance use compared to older age groups [ 2 , 3 ], alcohol being the most common (youth 15–19: 57%; youth 20–24: 83%), followed by cannabis (youth 15–19: 19%; youth 20–24: 33%), and illicit substances (youth 15–19: 4%; youth 20–24: 10%) [ 2 ]. High rates of substance use among youth are worrisome given the ample evidence linking early onset to an increased risk of developing a substance use disorder (SUD) and further mental health and psychosocial problems [ 4 , 5 , 6 ]. Youth are also more likely to use more heavily and in riskier ways than adults, making them especially vulnerable to substance use related harms [ 2 , 7 ]. For example, polysubstance use is more common and increasing among youth [ 8 , 9 , 10 ], which has been associated with an increase in youth overdose hospitalizations [ 11 ]. Substance use is also associated with several leading causes of death among youth (e.g., suicide, unintentional injury, violence) [ 12 , 13 ], demonstrating an urgent need to provide effective substance use services to this population.
Current evidence-based recommendations to address substance use issues among youth include a range of comprehensive services, including family-oriented treatments, behavioural therapy, harm reduction services, pharmacological treatments, and long-term recovery services [ 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ]. Like with adults, these services should be tailored based on young people’s individual needs and circumstances and should consider concurrent mental health disorders which are common among youth who use substances [ 3 , 15 , 18 ]. Merikangas et al. [ 18 ] reported rates of co-occurring mental health disorders as high as 77% among a community sample of youth with a SUD diagnosis. Regardless of precedence, both mental health and SUD can have exacerbating effects on each other if not treated, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and early access to care [ 19 ]. However, current practices utilizing an integrative approach to diagnose and treat SUD and concurrent mental health disorders have yet to be widely implemented [ 20 , 21 , 22 ]. Further, the current substance use service landscape has been largely designed to treat SUD in adult populations [ 17 ], who often require more intensive treatment compared to youth [ 15 ].
Literature suggests that there are differences between how youth and adults perceive and present substance use issues, suggesting different approaches may be needed to address substance use concerns [ 15 ]. For example, youth have shorter substance use histories and therefore often express fewer negative consequences related to their substance use, which may reduce their perceived need for services [ 15 ]. Further, the normalization of substance use among younger populations and the influence of peers and family members may also play a factor in reducing young people’s ability to recognize problems that arise due to their substance use [ 9 , 23 ]. Confidentiality concerns may also prevent youth from accessing services when needed [ 23 ]. Youth are therefore unlikely to access substance use services before they are in crisis. The 2019 National Survey on Drug Use and Health [ 24 ] reported that only 7.2% of youth ages 12–25 who were identified as needing specialized substance use treatment (defined as substance use treatment received at a hospital (inpatient), rehabilitation facility (inpatient or outpatient), or a mental health centre) accessed appropriate services and that 92% of youth did not feel they needed to access specialized services for substance use. In 2020, the percentage of youth who received specialized treatment dropped to 3.6 and 98% of youth did not perceive the need for it [ 3 ], demonstrating the exacerbating effects the pandemic has had on young people’s service trajectory and experiences.
Although help-seeking behaviours to address mental health concerns among youth have been explored [ 25 , 26 ], few studies have been specifically designed to explore young people’s experiences with substance use services. Existing evidence has largely focused on the experiences of street entrenched youth and youth who specifically use illicit substances (e.g., opioids, heroin, fentanyl) ([ 1 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 ], (Marchand K, Fogarty O, Pellat KM, Vig K, Melnychuk J, Katan C, et al: “We need to build a better bridge”: findings from a multi-site qualitative analysis of opportunities for improving opioid treatment services for youth, Under review)), which remains an important research focus, but may not be representative of those who have milder treatment needs. As such, this qualitative study aims to understand how youth perceive and experience substance use services in British Columbia (BC) more broadly. This study also explored young people’s recommendations to improving current models of care to address substance use concerns.
Study design & setting
This study is part of the Building capacity for early intervention: Increasing access to youth-centered, evidence-based substance use and addictions services in BC and Ontario project, which aims to create youth-informed substance use training for peer support workers and other service providers working within an integrated care model. The project is being led by Foundry Central Office and the Youth Wellness Hubs Ontario (YWHO), two youth integrated health service hubs in BC and Ontario respectively. As part of this project, the BC project team conducted a qualitative research study, entitled The Experience Project , to support the development of substance use training. This paper focuses on this BC study, which follows standards for reporting qualitative research (SRQR) [ 31 ].
In May 2020, we applied participatory action research (PAR) methods [ 32 , 33 ], by partnering with 14 youth (under the age of 30) throughout the course of the project, who had lived and/or living experience of substance use and lived in BC. Youth advisors were recruited through social media and targeted outreach (i.e., advisory councils from Indigenous-led organizations and rural and remote communities) in order to engage a diverse group of young people. A full description of our youth engagement methods has been described elsewhere (Turuba R, Irving S, Turnbull H, Howard AM, Amarasekera A, Brockmann V, et al: Practical considerations for engaging youth with lived and/or living experience of substance use as youth advisors and co-researchers, Under review). British Columbia has a population of approximately 4.6 million people, 88% of which reside within a metropolitan area; only 12% live in rural and remote communities across a vast region of land. Nationally, BC has been disproportionately impacted by the opioid crisis, counting 1782 illicit drug overdose deaths in 2021 alone, 84% of which were due to fentanyl poisoning [ 34 ]. Although more than half of BC’s population reside in the Metro Vancouver area, rates of illicit drug overdose deaths are similar across all health regions [ 34 ].
The youth partners formed a project advisory which co-created and revised the research protocol and materials. The initial focus group questions were informed by Foundry’s Clinician Working Group, based on what Foundry clinicians wanted to know about youth who use substances and how best to support them. The subsequent interview guide was developed based on the focus group learnings and debriefing sessions with the project youth advisory (see Data Collection section below). Three advisory members were also hired as youth research assistants to support further research activities including data collection, transcription, and analysis.
Participants
Participants were defined as youth between the ages of 12–24 who had lived and/or living experience of substance use (including alcohol, cannabis, and/or illicit substance use) in their lifetime and lived in BC. Substance use service experience was not a requirement as we wanted to understand young people’s perception of services and barriers to accessing them. Youth were recruited through Foundry’s social media pages and targeted advertisements. Organizations serving youth across the province were contacted about the study and asked to share recruitment adverts with youth clients. Organizations were identified by our youth advisors and Foundry service teams from across the province in order to recruit a geographically diverse sample of youth. This included mental health services, child and family services, social services, crisis centres, youth shelters, harm reduction services, treatment centres, substance use research partners, community centres, friendship centres, schools, and youth advisories. Interested youth contacted the research coordinator (author RT) to confirm their eligibility. Youth under the age of 16 required consent from a parent or legal guardian and gave their assent in order to participate, while youth ages 16–24 consented on their own behalf. Verbal consent was obtained from participants/legal guardians over the phone or Zoom after being read the consent form, prior to the focus group/interview. A hard copy of their consent form was signed by the research coordinator and sent to the participant/legal guardian for their records.
Data collection
Data collection began in November 2020 until April 2021. An initial semi-structured 2-h focus group with 3 youth (ages 16–24) was facilitated by 2 trained research team members, including a youth research assistant with lived/living experience. A peer support worker was also available for further support. The focus group discussion highlighted youth participants’ multifarious experiences with substance use services and the variety of substances used, which led us to change our data collection methods to individual in-depth interviews. Two interview guides were developed based on the focus group learnings to reflect the different range of service experiences. Interviews questions were reviewed and modified with the project youth advisory. Semi-structured interviews were held with 27 youth participants, which were facilitated by 1–2 members of the research team and lasted 30-min to an hour. In an effort to promote a safe and inclusive space for youth to share their experiences, participants were given the option to request a focus group/interview facilitator who identified as a person of color if preferred. The focus group/interviews began with introductions and the development of a community agreement to ensure youth felt safe to share their experiences. Participants were also sent a demographic survey to fill out prior to the focus group/interview, which was voluntary and not a requirement for participating in the qualitative focus group/interview. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the discussions were conducted virtually over Zoom. Participants were provided with a $30 or $50 honoraria for taking part in an interview or focus group, respectively.
Data analysis
The focus group and interviews were audio-recorded, transcribed verbatim, and analyzed thematically using NVivo (version 12) following an inductive approach using Braun and Clarke’s six step method [ 35 ]. The research coordinator led the analysis and debriefed regularly with author KM, who has extensive experience with qualitative health research in substance use [ 36 , 37 ]. The transcripts were read multiple times and initial memos were taken. A data driven approach was used to generate verbatim codes and identify themes. Meetings were also held with the youth research assistants to discuss the data and review and refine the themes to strengthen the credibility and validity of the findings, given their role as facilitators and their lived/living experience with substance use. This included selecting supporting quotes to highlight in the manuscript and conference presentations.
We interviewed a total of 30 youth participants. Socio-demographics, substance use patterns and service experiences are listed in Table 1 . Participants’ median age was 21 and primarily identified as women (55.6%) and white/Caucasian (66.7%). Most youth had used multiple substances in their lifetime and over the past 12-months, with alcohol being the most common, followed by marijuana/cannabis, psychedelics, amphetamines (e.g., MDMA, ecstasy) and other stimulants, non-prescription or illicit opioids, depressants, and inhalants. More than half (55.6%) had some post-secondary education and almost all participants were either in school and/or employed (94.4%). Seventy-five percent of participants had experience accessing substance use services.
Three overarching themes of youths’ substance use service perceptions and experiences were identified (see Fig. 1 ). These themes were specific to the phase of service interaction youth described, given that they were all at different phases of their substance use journeys and had different levels of interaction with substance use services. For example, some youth had never accessed substance use services but described their perceptions of services based on the information available to them, while others described specific service interactions they had. The themes were therefore separated by phase of service interaction, starting with 1. Prevention/Early intervention, where youth describe feeling unworthy of support; 2. Service accessibility, where youth encounter many barriers finding relevant services and information; and 3. Service delivery, where youth highlight the importance of meeting them where they are at.
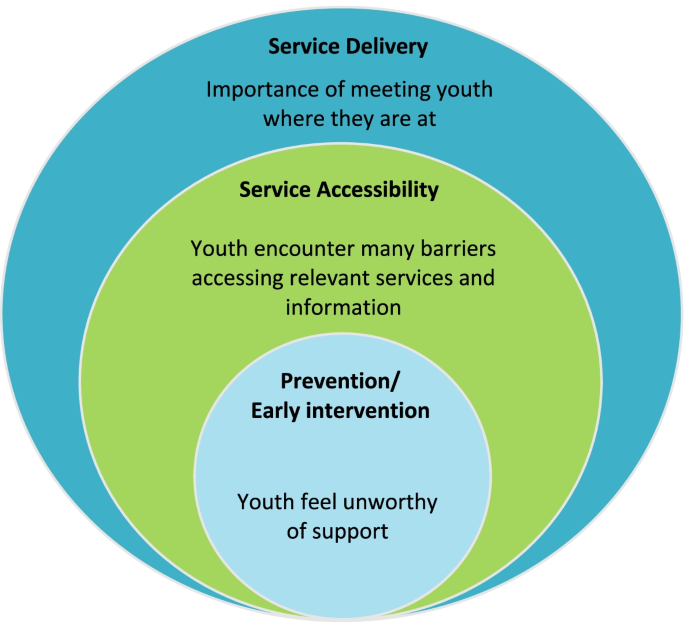
Overarching themes describing young people’s experiences with substance use services
Prevention/early intervention: youth feel unworthy of support
Many youth described feeling unworthy of health and social services, especially when they did not identify as having a SUD. Young people’s perception of SUD typically revolved around the use of “ harder substances”, which participants defined as heroin, crack cocaine, intravenous drugs, and being in crisis situations, such as being homeless or at risk of an overdose. Youth perceived that most services were geared towards this population and therefore not for them. Many described suffering from “ imposter syndrome ” fearing that they would be taking space away from others who needed it more or judged by services providers for accessing services they did not ‘need’:
“...that idea that you could go get help for your drug use without it – without you being some stereotype of an addict, right?... like there’s different severities of addiction, or you could not have an addiction but also still have some sort of issue related to substance use that should be dealt with. I think my biggest fear as a person with anxiety, through all aspects of accessing health care, is that...I am gonna go to the doctor and they’re going to say ‘Oh my god what an idiot, she doesn’t need to be here, I’m just going to give her something to shut her up’.”
Youth described feeling embarrassed or afraid of how people in the community (including friends, family, and service providers), would react to their substance use, not wanting to disappoint anyone or be stereotyped as an “ addict ”, a “ bad person ” or a “ criminal ”. Alternately, some youth were simply not ready to change their substance use behaviours and assumed this would be expected of them if they reached out for support. As one participant described: “A lot of people are under the idea that if they tell people about their problems, they’re just going to ship them off somewhere, and the only form of recovery is abstinence based, which is not at all helpful and way too intimidating.”
Youth also felt that substance use adverts were often irrelevant to their experiences, and that public health messaging was polarizing and unconvincing:
“I feel like maybe there could be a larger conversation about how drugs are fun, and we should stop – like that’s the thing, if everyone pretends that they’re not and that it’s all bad – that’s why people don’t believe you, they don’t believe what you’re saying, right? Drugs are really fun, that’s why they’re dangerous. That’s why people have addiction problems. They’re really fun until they’re not.”
“I think if they had signs that spoke more to the average college student who is maybe getting black out every weekend or popping zanies...instead I’m hearing about a 40-year old who’s been using hard drugs for like 20 years”.
Further, youth described how marijuana/cannabis and stimulant use were often disregarded, which are commonly used among youth and young adults [ 24 ]. For example, participants described the lack of recognition marijuana/cannabis has as being an addictive substance for some people, which invalidated their experiences. Hence, youth struggled to understand when their substance use “hit a threshold of bad enough to bother public health services” and therefore often only reached out for support when in crisis: “What stopped me from accessing services after this initial attempt was me just second-guessing that I actually had an issue ”.
Youth expressed wanting more information about the neuroscience of addiction, and how to differentiate between substance use, abuse, and disorder to reduce feelings of shame and increase their ability to identify when they should reach out for support. Youth also appreciated learning that substances affect people differently, which validated their experiences : “I learned that it’s very different for everyone....and I was like ‘Oh, I didn’t think there was anybody like me’. So it was this amazing thing, learning that I’m not the only high schooler struggling with this.”
Youth were more likely to reach out to friends for support; however, participants reported that the normalization of substance use among youth meant peers often did not take issues seriously and therefore could not be an effective source of support long-term. This also strengthened participants’ self-doubt about whether their issues warranted support from health and social services, often delaying accessing to care.
Service accessibility: youth encounter many barriers finding substance use services and information “zero to 100”
When youth were ready to access services and information for their substance use, they encountered many barriers. Youth expressed not knowing what services and supports were available, or which services they would benefit from: “It seems like through my searching, it’s either you can get counselling, or you can reach out for people – to health professionals to chat with on a hotline. Or it goes from zero to 100 where you have to get admitted to a rehab treatment program.”
Youth expressed a lack of available information about substance use and services and identified a need to reach those who were not already actively accessing services. This included advertising about different service options in schools, coffee shops, bars, and social media. “I would’ve never went up and asked somebody about it [information about substance use services] or looked it up on the internet. That just wasn’t an interest at all.... I feel like it’s got to be in schools where you can just plain and broad see it in the office or have school counsellors talk about it.” Youth also wanted more information provided in schools about the long-term effects of different substances, harm reduction, and how lifestyle choices and emotional regulation can play a role in substance use behaviours.
Having information more widely available was also identified to “ help break the stigma” by increasing people’s awareness about substance use and available supports. Youth often had to research information independently, which had its own barriers. This included not knowing what to look for or where to start, a lack of information about services listed on service websites, requiring further research through phone calls and emails, and a lack of service options available. As one youth described:
“When I saw people talking about their problems on social media...it just made me realize there’s so much other treatments out there that are just very simple. Like, you can honestly learn breathing techniques...or like cognitive behavioural therapy or all these other things...I guess for people to be able to talk about it – people don’t really see what is cognitive behavioural therapy online, you have to search it up yourself. But for some companies being able to express what it is, express what their services are, it would be able to give an idea to some people.”
When trying to access services, youth described encountering other challenges, including long wait times, challenges getting to appointments (e.g., lack of transportation), limited hours of operation, and a lack of services available, including a lack of affordable services, especially for specialized care (e.g., service providers specializing in substance use, LGBTQ2S+, etc.). A lack of referrals between services was also a barrier to receiving care, placing the responsibility on the youth to reconnect with care, which required them to continuously retell their story. Youth also felt like service providers tended to withhold information about service options based on their level of perceived need, which was often inaccurate, and thus, felt they needed to appear more in crisis to receive more options:
“They [service providers] will withhold certain information from you based on what your need is, because I feel like they try to assess people, and they place them on a sliding scale of like, “Who needs one more?” Which is why I didn’t really like that because … a lot of… supports only became available to me after I had been in the hospital, when I feel like I would’ve benefitted from the support even more, like beforehand.”
Service delivery: importance of meeting youth where they are at
For youth who accessed substance use services, their care experiences varied widely depending on their interactions with their service providers, with some who “ genuinely listened ” and “ took their time to make a connection ”, while others were described as “ uncompassionate ” and ‘ don’t really understand what I’m going through’ . Youth wanted to be “ treated with the same respect and dignity like anyone ” but described being treated like children, as though they were being “ lectured by a parent ” or treated as though incapable of making good decisions for themselves. Youth described “ not being taken seriously” and their issues often “ pushed aside” for not fitting a certain “ stereotype ”. For example, one participant expressed: “I was a really good student, I had a really good home life, and everything was, on the outside, literally perfect. And there was kind of that stigma around “You don’t have any problems, why would you have problems?”.” This strengthened youths’ perceptions that substance use services were not for them and prevented them from accessing further support. As one youth described their experience after an overdose:
“When they had asked me my age and I had told them my age, they were like, ‘Oh my goodness. What are you doing?’ And it was just a random nurse. It wasn’t actually anyone trained, but I just felt like, ‘Wow. Maybe I should go home’. Even though I really needed to be there, it was just hard to not get up and run.”
Youth recognized the importance of crisis-oriented services; however they expressed that “the goal should be preventing crisis rather than just helping people when they get there.” This implied taking youth’s concerns at face value, regardless of how service providers perceived their situation:
“Yeah, I guess assuming that people are asking for help because they really need it, and because... people that are good at holding it together, that have extreme privilege, that look like they’re healthy and making it work, they’re still accessing services for a reason and maybe to include more of a preventative mind frame in their model of care in the sense that, this person may be not be at their worst right now, and that’s actually wonderful that they’re here before that happens, so let’s take this seriously and try to work with them before, you know, they look like they need help.”
Having a service provider who took additional steps to support them, such as providing rides, meeting them in more casual settings, and checking in with them regularly, made youth feel genuinely cared for and increased their likelihood of returning. As one youth described:
“I found that they checked in a lot and it made me feel like they actually cared. You know what I mean? It’s not like just because I’m not there in that moment seeing them... Sometimes, I’d get a text or a phone call being like, “Hey, what are you doing? I haven’t you seen in a while.” You know what I mean? And I had a period of time with the counsellor that I was seeing that I literally ignored her calls for 2 months and [she] was still calling me and leaving voice mails. Even though I wasn’t answering and speaking to her, I still felt like, "Wow, she actually gives a shit. She's still trying to communicate and be there even though I’m not putting the same effort back.”
Being able to connect with someone of similar age, gender, and race/ethnicity generally made it easier for youth to relate to their service provider, however this varied and highlighted the importance of providing youth with options to choose from. Youth described being more comfortable talking to someone who could relate to them and had their own lived experiences. Hearing about similar experiences helped youth feel “ normal ” and validated. This came in the form of peer support, friends, support groups, and online forums such as Reddit and Facebook groups. However, some youth described hesitancy accessing peer support services given that peers may not have received any formal substance use training. Meanwhile, some youth assumed their problems would not compare to the lived experiences of peer support workers, and therefore did not see its value. As one youth described “Hearing [about] other people’s problems...[it] reminds me that other people have gone through wars and made it out of wars, which is like, would be comforting for some people, but for me, makes me feel like [I should] “get over it”.”
Youth desired a holistic approach to care, where all aspects of their life were considered rather than solely focusing on their substance use. As one participant describes: “It wasn’t just substance abuse going on for me, so programs kind of like CBT again, it kind of helps you deal with emotions no matter what way you choose to cope...I think just more effort to get to the root of the problem instead of just trying to stop the symptom.” Focusing on accomplishments rather than abstinence was important, as abstinence was not always young people’s objective for accessing services. Setting more attainable and flexible goals also reduced pressures associated with potential relapses, which were often a source of shame. Having providers who rejected the “ all or nothing approach ” made youth feel more confident and comfortable admitting setbacks.
Addressing mental health concerns was also a priority for most youth, many for whom it had been the primary reason for their service visit. “When I started talking about my mental health as a factor in substance abuse rather than two different things...once I figured out what works for me...and that [mental health] was more stable, everything fell into place after that.” Other factors youth wanted service providers to consider included traumatic experiences, parental substance use, school and work stress, social pressures, and relationship issues. Youth also found it helpful when service providers helped them build recovery capital, including helping them meet their basic needs, recommending school and employment programs, and finding activities and healthy habits. As one youth described “We talked about lots of different ways to cope and things that do not necessarily have anything to do with my substance use, such as eating habits and exercising and study habits when I’m in school. Those really impact me. When those are going well, then it is easier for me to heal from my substance use.”
Youth experience many challenges engaging with existing substance use services in BC as they are currently delivered. Participants in our study described their perceptions towards substance use and their experiences trying to navigate services, and they reflected on multi-level barriers associated with accessing information and support. Throughout these discussions, youth described how the crisis-oriented state of the current health care system leaves many of their needs unmet, calling for a more youth-centred and driven preventative and early intervention approach for diverse youth across BC.
In accordance with the Canadian Drugs and Substances Strategy [ 38 ], all three themes demonstrate a clear need to prioritize substance use prevention and early intervention specifically targeting youth. Youth are in the early phase of substance use, which presents a critical opportunity to reduce potential related harms, including SUDs. However, many existing prevention programs and early interventions have shown limited effectiveness in reducing substance use and associated harms among youth [ 39 ], and very few youths receive evidence-based substance use prevention and education [ 40 , 41 ]. Hanley et al. [ 41 ] reported only 35% of schools in the United States used evidence-based programing, and that only 14% used evidence-based strategies as their primary source of programming. Programs like D.A.R.E. are still being used [ 42 ], which focus on the potential negative consequences associated with substance use to deter young people from using, rather than acknowledging their place in society [ 43 , 44 ]. This approach fails to acknowledge that youth often use substances for enjoyment and social benefits, rather than solely responding to distress [ 44 , 45 ], leading to unconvincing public health messages that fail to resonate with youth.
Following the principles of the Canadian Standards for Community-Based Youth Substance Abuse Prevention [ 46 ], substance use prevention and education should be informed by youth to ensure messaging is relevant to their experiences and is effective in providing youth with the tools needed to make informed decisions about substance use. Moffat et al. [ 47 ] reported that involving youth in prevention efforts helped develop public health recommendations about cannabis that were less ambiguous and stimulated productive conversations among youth about the associated risks. A systematic review on the involvement of youth in substance use prevention efforts also reported that these practices increased youths’ knowledge about substance use and supported the development of prevention interventions that were specifically tailored to the needs of the community [ 48 ].
Youth participants also highlighted the benefits of hearing from peer experiences and advocated for more opportunities for peers to talk in schools. Although there has been increasing evidence supporting the effectiveness of peer-led programs in reducing substance use and associated harms, peers remain largely underutilized in substance use prevention efforts [ 49 , 50 ]. These findings underline the importance of reducing stigma and discrimination against people who use substances, so that peers can be actively engaged in programs design and delivery. However, the findings from this study also indicates that youth may worry about peers invalidating their own experiences through self-disclosure, highlighting the different preferences among youth. This also suggests that the purpose of self-disclosure may need to be better conveyed to youth as a tool to help build common humanity and trust rather than the focus of peer roles.
The study also highlighted that preventative efforts are not only important in school settings but should also be applied in other healthcare settings. As youth from this study explained, services should address the motivations for using substances from a holistic perspective rather than trying to treat substance use alone, requiring an individualized approach. Concurrent mental health disorders, including internalizing (e.g., anxiety, depression) and externalizing disorders (e.g., attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, conduct disorder) are common among youth and are often linked to substance use issues, highlighting the importance of diagnosing and treating substance use and mental health concerns simultaneously [ 22 , 51 ]. However, our results emphasized that the current fragmented state of the healthcare system makes this approach challenging for young people and their families. As many youths access the healthcare system for reasons other than substance use concerns, substance use screening and brief interventions need to occur in a variety of health care settings, accompanied with proper staff training. This approach has been proven to be effective in reducing substance use and violence among youth by screening for substance use in schools, emergency departments, and primary care settings among high-risk youth [ 52 ]. However, this study suggests that substance use screening should be applied more broadly and intentionally integrated as youth may not present external signs of problematic substance use and may not feel comfortable bringing it up unless explicitly asked or in crisis. Providing service providers with training on how to provide culturally safe care to youth who use substances is imperative for this approach to be effective and maintain trusting relationships with youth, given young people’s fears of being stigmatized and judged when accessing services [ 53 , 54 ].
There has been increasing evidence supporting the benefits of an integrated approach to address substance use and mental health concerns among youth, which would facilitate the early identification of possible substance use issues [ 21 ]. Although several barriers can impede the implementation of such services (e.g., organizational-level barriers, distinct health financing systems, and having to train providers in multiple disciplines) [ 54 ], this model of care has been successfully implemented in Australia (Headspace) [ 55 ], Ireland (Jigsaw) [ 56 ], and Canada (Foundry, Youth Wellness Hubs Ontario, ACCESS Open Minds, and YouthCAN Impact) [ 21 , 57 ]. This framework has the potential to increase service provider awareness about the complexities associated with substance use and facilitate the delivery of a wide range of services to support recovery, such as primary care, financial assistance, supportive housing, employment, education, and family support. Given youths’ hesitancy to discuss substance use issues with health care providers, this framework should also integrate peer support services to provide youth with a relatable point of contact to discuss issues without fear of judgment or negative consequences [ 21 ]. Although peer support has been associated with positive treatment outcomes [ 58 ], this study suggests that these services need to be better integrated and conveyed to youth who may benefit.
The service accessibility barriers described by youth in this study reflect the undeniable need to increase the service system’s capacity to provide substance use services. These barriers are consistent with other Canadian studies [ 26 , 59 , 60 ], including a study conducted with youth in urban, rural, and remote Ontario [ 59 ] who described a general lack of substance use services available, low service awareness by youth, and a lack of coordination and collaboration between services. Family members in this study validated these challenges as they described trying to navigate the system for and/or with their young person, which was further substantiated by caregivers trying to navigate youth opioid treatment services in BC (Marchand KM, Turuba R, Katan C, Brasset C, Fogarty O, Tallon C, et al: Becoming our young people’s case managers:Caregivers’ experiences, needs, and ideas for improving opioid use treatments for young people using opioids, Under review). Given the increasing harms associated with the opioid crisis [ 7 ], coordinated efforts across all levels of government and multiple sectors are imperative to improving young people’s access to substance use services and create space, not only for youth in dire need of these services, but for those trying to address substance use concerns proactively.
This study had several limitations. Participants were recruited through Foundry social media channels and targeted advertisements, therefore youth who had access to a phone or a computer and followed mental health and/or substance use organizations were more likely to hear about the study. Consequently, our sample mainly included youth who were actively employed and in school and living in stable living environments. Yet, similar accessibility barriers are described by street-entrenched youth in Ontario [ 27 ] and British Columbia [ 30 ], including long wait times and difficulties seeking support due to stigma, as well as negative experiences with abstinent-based approaches, highlighting young people’s desire for holistic care regardless of substance use patterns. Although we tried to recruit through several health and social services across the province, the COVID-19 pandemic likely limited organizations’ capacity to support with local promotion. Further, we were only able to recruit 1 youth between the ages of 12–15, likely due to our inability to recruit through schools and need for parental consent, which hindered our ability to identify potential differences in substance use service perceptions and experiences between adolescents and young adults. Given the important life transitions that occur between adolescence and young adulthood, future studies exploring these differences are important as different prevention and early intervention approaches may be warranted. Exploring how perceptions and experiences differ across communities could also be an important consideration for future research to better understand how geographic location, including urban and rural differences, impacts young peoples’ access to services. Despite these limitations, the findings of this study have important implications in the way we co-design and deliver substance use services to youth. They also have important considerations for policy makers who are considering how to shape substance use services for diverse youth in their jurisdictions.
This study highlights the many challenges youth experience when engaging with substance use services and emphasizes a need for a more preventative approach. The lack of integration and capacity among service providers to provide substance use services implies that youth who have milder treatment needs and/or do not meet the diagnosis criteria of SUD often do not have access to adequate substance use service interventions. Research, health service, and policy efforts should focus on substance use prevention and early interventions to address young people’s concerns before they are in crisis and increase their ability to perceive the need to reach out for support. Moving forward, it is critical that diverse youth and peers with lived and/or living experience be involved in these efforts, including the co-design of new services and evaluation of impact of prevention and early intervention services, including quality improvement efforts. Intentional, sustained investment in youth substance use services will optimize the health outcomes and experiences of young people across BC, transformation that young people can no longer patiently wait for.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to the potential for identifying participants but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable requests.
Abbreviations
British Columbia
Drug Abuse Resistance Education
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine
- Participatory action research
Substance use disorder
Barbic SP, Jones AA, Woodward M, Piercy M, Mathias S, Vila-Rodriguez F, et al. Clinical and functional characteristics of young adults living in single room occupancy housing: preliminary findings from a 10-year longitudinal study. Can J Public Health. 2018;109(2):204–14. https://doi.org/10.17269/s41997-018-0087-9 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Health Canada. Canadian tobacco, alcohol and drugs survey (CTADS): summary of results for 2017. Ottawa: Health Canada; 2019. Available from: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/canadian-alcohol-drugs-survey/2017-summary.html . [updated 2021 Aug 12; cited 2021 Nov 16]
Google Scholar
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration [SAMHSA]. Key substance use and mental health indicators in the United States: Results from the 2020 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (HHS Publication No. PEP21–07–01-003, NSDUH Series H-56). Rockville: Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 2021 Available from: https://www.samhsa.gov/data/ . [updated 2021 Oct;e cited 18 Nov 2021]
Poudel A, Gautam S. Age of onset of substance use and psychosocial problems among individuals with substance use disorders. BMC Psychiatry. 2017;17(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-016-1191-0 .
McCabe SE, West BT, Morales M, Cranford JA, Boyd CJ. Does early onset of non-medical use of prescription drugs predict subsequent prescription drug abuse and dependence? Results from a national study. Addiction. 2007;102(12):1920–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2007.02015.x .
Chen CY, Storr CL, Anthony JC. Early-onset drug use and risk for drug dependence programs. Addict Behav. 2009;34(3):319–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2008.10.021 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Canadian Institute for Health Information. Opioid-related harms in Canada, December 2018. Ottawa: CIHI; 2018. p. 79. Report No.: ISBN 978–1–77109-767-3.
Choi HJ, Lu Y, Schulte M, Temple JR. Adolescent substance use: latent class and transition analysis. Addict Behav. 2018;77:160–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2017.09.022 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Breda C, Heflinger CA. Predicting incentives to change among adolescents with substance abuse disorder. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2004;30(2):251–67. https://doi.org/10.1081/ADA-120037377 .
Zuckermann AME, Williams G, Battista K, de Groh M, Jiang Y, Leatherdale ST. Trends of poly-substance use among Canadian youth. Addict Behav Rep. 2019;10:100189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abrep.2019.100189 .
White AM, Hingson RW, Pan IJ, Yi HY. Hospitalizations for alcohol and drug overdoses in young adults ages 18-24 in the United States, 1999-2008: results from the nationwide inpatient sample. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2011;72(5):774–86. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsad.2011.72.774 .
Wong SS, Zhou B, Goebert D, et al. The risk of adolescent suicide across patterns of drug use: a nationally representative study of high school students in the United States from 1999 to 2009. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2013;48(10):1611–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-013-0721-z PMID: 23744443.
Keyes KM, Brady JE, Li G. Effects of minimum legal drinking age on alcohol and marijuana use: evidence from toxicological testing data for fatally injured drivers aged 16 to 25 years. Inj Epidemiol. 2015;2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40621-014-0032-1 .
Hadland SE, Yule AM, Levy SJ, Hallett E, Silverstein M, Bagley SM. Evidence-based treatment of young adults with substance use disorders. Pediatrics. 2021;147(S2):204–14. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-023523D .
Article Google Scholar
Winters KC, Tanner-Smith EE, Bresani E, Meyers K. Current advances in the treatment of adolescent drug use. Adolesc Health Med Ther. 2014;5:199–210. https://doi.org/10.2147/AHMT.S48053 .
British Columbia Centre on Substance Use. A Guideline for the Clinical Management of Opioid Use Disorder—Youth Supplement. B.C. Ministry of Health, & B.C. Ministry of Mental Health and Addictions; 2018. Available from: http://www.bccsu.ca/care-guidance-publications/ [updated 2018 June 13, cited 2021 Nov 18]
Christie GIG, Cheetham A, Lubman DI. Interventions for alcohol and drug use disorders in young people: 10 key evidence-based approaches to inform service delivery. Curr Addict Rep. 2020;7:464–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40429-020-00336-6 .
Merikangas KR, He J, Burstein M, Swanson SA, Avenevoli S, Cui L, et al. Lifetime prevalence of mental disorders in US adolescents: results from the National Comorbidity Study-Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A). J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2010;49(1):980–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2010.05.017 .
Otasowie J. Co-occurring mental health disorder and substance use disorder in young people: aetiology, assessment and treatment. BJPsych Adv. 2021;27(4):272–81. https://doi.org/10.1192/bja.2020.64 .
Sterling S, Weisner C, Hinman A, Parthasarathy S. Access to treatment for adolescents with substance use and co-occurring disorders: challenges and opportunities. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2010;49:637–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2010.03.019 .
Halsall T, Manion I, Iyer SN, Mathias S, Purcell R, Henderson J. Trends in mental health system transformation: integrating youth services within the Canadian context. Healthc Manage Forum. 2019;32(2):51–5. https://doi.org/10.1177/0840470418808815 .
Brownlie E, Beitchman JH, Chaim G, Wolfe DA, Rush B, Henderson J. Early adolescent substance use and mental health problems and service utilization in a school-based sample. C J Psychiatry. 2019;64(2):116–25. https://doi.org/10.1177/0706743718784935 .
Winters KC, Botzet AM, Fahnhorst T, Stinchfield R, Koskey R. Adolescent substance abuse treatment: a review of evidence-based research. In: Leukefeld C, Gullota T, Tindall MS, editors. Adolescent substance abuse: evidence-based approaches to prevention and treatment. New York: Springer Science + Buisness Media; 2009.
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration [SAMHSA]. Key substance use and mental health indicators in the United States: results from the 2019 National Survey on drug use and health (HHS publication no. PEP20-07-01-001, NSDUH series H-55). Rockville: Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 2020 Available from: https://www.samhsa.gov/data/ . [updated 2020 Sept; cited 18 Nov 2021]
Tylee A, Haller DM, Graham T, Churchill R, Sanci LA. Youth-friendly primary-care services: how are we doing and what more needs to be done? Lancet. 2007;369:1565–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60371-7 .
Gulliver A, Griffiths KM, Christensen H. Perceived barriers and facilitators to mental health help-seeking in young people: a systematic review. BMC Psychiatry. 2010;10:113. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-244X-10-113 .
Kozloff N, Cheung AH, Ross LE, Winer H, Ierfino D, Bullock H, et al. Factors influencing service use among homeless youths with co-occurring disorders. Psychiatr Serv. 2013;64(9):925–8. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.201200257 .
Bozinoff N, Small W, Long C, DeBeck K, Fast D. Still “at risk”: an examination of how street-involved young people understand, experience, and engage with “harm reduction” in Vancouver’s inner city. Int J Drug Policy. 2017;45:33–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugpo.2017.05.006 .
Giang V, Thulien M, McNeil R, Sedgemore K, Anderson H, Fast D. Opioid agonist therapy trajectories among street entrenched youth in the context of a public health crisis. SSM Popu Health. 2020;11:1006009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssmph.2020.100609 .
Boyd J, Fast D, Hobbins M, McNeil R, Small W. Social-structural factors influencing periods of injection cessation among marginalized youth who inject drugs in Vancouver, Canada: an ethno-epidemiological study. Harm Reduct J. 2017;14:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12954-017-0159-9 .
O’Brien BC, Harris IB, Beckman TJ, Reed DA, Cook DA. Standards for reporting qualitative research: a synthesis of recommendations. Acad Med. 2014;89(9):1245–51. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACM.0000000000000388 .
Kindon S, Pain R, Kesby M. Participatory action research approaches and methods: connecting people, participation and place. Oxfordshire: Routledge; 2010.
Hawke LD, Relihan J, Miller J, McCann E, Rong J, Darnay K, et al. Engaging youth in research planning, design and exercise: practical recommendations for researchers. Health Expect. 2018;21(6):944–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/hex.12795 .
BC Coroner’s Service. Illicit Drug Toxicity Deaths in BC. January 1, 2011 – October 31, 2021. 2021. Available from: https://www2.gov.bc.ca/assets/gov/birth-adoption-death-marriage-and-divorce/deaths/coroners-service/statistical/illicit-drug.pdf
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77–101. https://doi.org/10.1191/1478088706qp063oa .
Marchand K, Foreman J, MacDonald S, Harrison S, Schechter MT, Oviedo-Joekes E. Building healthcare provider relationships for patient-centered care: a qualitative study of the experiences of people receiving injectable opioid agonist treatment. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2020;15(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13011-020-0253-y .
Palis H, Marchand K, Spike G, Westfall PJ, Lock K, MacDonald S. Exploring the effectiveness of dextroamphetamine for treatment of stimulant use disorder: a qualitative study with patients receiving injectable opioid agonist treatment. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2021;16(68). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13011-021-00399-2 .
Health Canada. Canadian drugs and substances strategy. Ottawa: Health Canada; 2019. Available from: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/substance-use/canadian-drugs-substances-strategy.html#shr-pg0 [updated 2019 July; cited 18 Nov 2021]
Stockings E, Hall WD, Lynskey M, Morley K, Reavley N, Strang J, et al. Prevention, early intervention, harm reduction, and treatment of substance use in young people. Lancet Psychiatry. 2016;3(3):280–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(16)00002-X .
Cho H, Dion Hallfors D, Iritani BJ, Hartman S. The influence of “no child left behind” legislation on drug prevention in US schools. Eval Rev. 2009;33(5):446–63. https://doi.org/10.1177/0193841X09335050 .
Hanley SM, Ringwalt C, Ennett ST, Vincus AA, Bowling JM, Haws SW, et al. The prevalence of evidence-based substance use prevention curricula in the nation’s elementary schools. J Drug Educ. 2010;40(1):51–60. https://doi.org/10.2190/DE.40.1.d .
Tremblay M, Baydala L, Khan M, Currie C, Morley K, Burkholder C, et al. Primary substance use prevention programs for children and youth: a systematic review. Pediatrics. 2020;146(3):e20192747. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2019-2747 .
Moreland AD, Lopez CM, Gilmore AK, Borkman AL, McCauley JL, Rheingold AA, et al. Substance use prevention programming for adolescents and young adults: a mixed-method examination of substance use perceptions and use of prevention services. Subst Use Misuse. 2020;55(14):2341–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826084.2020.1817079 .
Farrugia A. Assembling the dominant accounts of youth drug use in Australian harm reduction drug education. Int J Drug Policy. 2014;25(4):663–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugpo.2014.04.019 .
Fry ML. Seeking the pleasure zone: understanding young adult’s intoxication culture. AMJ. 2011;19:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ausmj.2010.11.009 .
Canadian Centre on Substance Abuse. Stronger together: Canadian standards for community-based youth substance abuse prevention. Ottawa: Canadian Centre on Substance Abuse; 2010. Available from: https://www.drugsandalcohol.ie/19993/1/Canada_Stronger_together.pdf [cited 18 Nov 2021]
Moffat BM, Jenkins EK, Johnson JL. Weeding out the information: an ethnographic approach to exploring how young people make sense of the evidence on cannabis. Harm Reduct J. 2013;10(34):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7517-10.34 .
Valdez EA, Skobic I, Valdez L, Garcia DO, Korchmaros J, Stevens S, et al. Youth participatory action research for youth substance use prevention: a systematic review. Subst Use Misuse. 2020;55(2):314–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826084.2019.1668014 .
Ti L, Tzemis D, Buxton JA. Engaging people who use drugs in policy and program development: a review of the literature. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2012;7(47):1–9.
Greer AM, Luchenski SA, Amlani AA, Lacroix K, Burmeister C, Buxton JA. Peer engagement in harm reduction strategies and services: a critical case study and evaluation framework from British Columbia, Canada. BMC Public Health. 2016;16(450):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-016-3136-4 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Henderson JL, Wilkins LK, Hawe LD, Wang W, Sanches M, Brownlie EB, et al. Longitudinal emergence of concurrent mental health and substance use concerns in an Ontario school-based sample: the research and action for teens study. J Can Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2021;30(4):249–63.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sterling S, Valkanoff T, Hinman A, Weisner C. Integrating substance use treatment into adolescent health care. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2012;14:453–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-012-0304-9 .
Urbanoski K, Pauly B, Inglis D, Cameron F, Haddad T, Phillips J, et al. Defining culturally safe primary care for people who use substances: a participatory concept mapping study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20:1060. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-030-05915-x .
Sterling S, Chi F, Hinman A. Integrating care for people with co-occurring alcohol and other drug, medical, and mental health conditions. Alcohol Res Health. 2011;33(4):338–49.
Hilferty F, Cassells R, Muir K, Duncan A, Christensen D, Mitrou F, et al. Is headspace making a difference to young people’s lives? Final report of the independent evaluation of the headspace program. Sydney: Social Policy Research Centre, University of New South Whales; 2015.
O’Keeffe L, O’Reilly A, O’Brien G, Buckley R, Illback R. Description and outcome evaluation of jigsaw: an emergent Irish mental health early intervention programme for young people. Ir J Psychol Med. 2015;32(1):72–7. https://doi.org/10.1017/ipm.2014.86 .
Mathias S, Tee K, Helfrich W, Gerty K, Chan G, Barbic SP. Foundry: early learnings from the implementation of an integrated youth service network. Early Interv. 2021:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/eip.13181 .
Barton J, Henderson J. Peer support and youth recovery: a brief review of the theoretical underpinnings and evidence. CJFY. 2016;8(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.29173/cjfy27140 .
Brownlie EB, Chaim G, Heffernan O, Herzog T, Henderson J. Youth services system review: moving from knowledge gathering to implementation through collaboration, youth engagement, and exploring local community needs. Can J Community Ment Health. 2017;36(2):1–17. https://doi.org/10.7870/cjcmh-2017-018 .
Russell C, Neufeld M, Sabioni P, Varatharajan T, Ali F, Miles S, et al. Assessing service and treatment needs and barriers of youth who use illicit and non-medical prescription drugs in northern Ontario, Canada. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0225548. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0225548 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Download references
Acknowledgements
The Experience Project is grateful to have taken place on the ancestral lands of many different Indigenous Nations and Peoples across what we now call British Columbia. We are also very grateful to the Youth4Youth Advisory Committee who supported the research and the participants who shared their experiences and insights with us.
The Experience Project has been made possible through the financial contributions of Health Canada under their Substance Use and Addiction Program. The views herein do not necessarily represent the views of Health Canada. Author Kirsten Marchand is supported by a Michael Smith Foundation for Health Research/Centre for Health Evaluation & Outcome Sciences Research Trainee award and author Skye Barbic by a Scholar grant funded by the Michael Smith Foundation for Health Research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Foundry, 915-1045 Howe Street, Vancouver, BC, V6Z 2A9, Canada
Roxanne Turuba, Anurada Amarasekera, Amanda Madeleine Howard, Violet Brockmann, Corinne Tallon, Sarah Irving, Steve Mathias, Kirsten Marchand & Skye Barbic
Providence Health Care, 1081 Burrard Street, Vancouver, BC, V6Z 1Y6, Canada
Roxanne Turuba, Anurada Amarasekera, Amanda Madeleine Howard, Violet Brockmann, Corinne Tallon, Sarah Irving, Steve Mathias & Skye Barbic
Providence Research, 1190 Hornby, Vancouver, BC, V6Z 2K5, Canada
Steve Mathias & Skye Barbic
Faculty of Medicine, University of British Columbia, 317-2194 Health Sciences Mall, Vancouver, BC, V6T 1Z3, Canada
Steve Mathias, Kirsten Marchand & Skye Barbic
Centre for Health Evaluation Outcome Sciences, 588-1081 Burrard Street, Vancouver, BC, V6Z 1Y6, Canada
Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, 80 Workman Way, Toronto, ON, M6J 1H4, Canada
Joanna Henderson
Department of Psychiatry, University of Toronto, 250 College Street, 8th floor, Toronto, ON, M5T 1R8, Canada
Department of Occupational Science and Occupational Therapy, University of British Columbia, 317-2194 Health Sciences Mall, Vancouver, BC, V6T 1Z3, Canada
Kirsten Marchand & Skye Barbic
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception and design of the Experience Project. Authors RT, AA, AH, VB and CT collected the data and RT, AA, AH, VB and KM contributed to the analysis and interpretation of the data. All authors contributed to the manuscript and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Roxanne Turuba .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was approved by the University of British Columbia/Providence Health Care Behavioural Research Ethics Board (Study ID: H20–01815-A005). All participants gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Turuba, R., Amarasekera, A., Howard, A.M. et al. A qualitative study exploring how young people perceive and experience substance use services in British Columbia, Canada. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy 17 , 43 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13011-022-00456-4
Download citation
Accepted : 31 March 2022
Published : 28 May 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13011-022-00456-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Substance use
- Adolescents
- Young adults
- Service experiences
- Qualitative research
Substance Abuse Treatment, Prevention, and Policy
ISSN: 1747-597X
- General enquiries: [email protected]


Essay on Drugs On Youth
Students are often asked to write an essay on Drugs On Youth in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Drugs On Youth
Introduction.
Drugs are harmful substances that can hurt our bodies. When young people use drugs, it can cause big problems. This essay will talk about how drugs affect youth.
Why Youth Use Drugs
Many young people start using drugs because of peer pressure or stress. They might think it’s cool or a way to escape problems. But, it’s not a good solution and can lead to serious issues.
Effects of Drugs on Youth
Drugs can harm a person’s mind and body. They can make a young person feel sick, act differently, and have trouble in school. Over time, it can even lead to addiction.
Prevention and Help
It’s important to teach young people about the dangers of drugs. If someone is using drugs, they should seek help from a trusted adult or a professional. There are many resources available to help.
In conclusion, drugs can have a negative impact on youth. It’s important to understand the risks and seek help if needed. We must work together to prevent drug use and help those in need.
250 Words Essay on Drugs On Youth
Drugs can harm young people in many ways. They can change how the brain works, making it hard for youth to think, learn, and make good choices.
Drugs and Health Risks
Drugs are risky for everyone, but they’re especially dangerous for young people. This is because their bodies and brains are still growing. Drugs can harm this growth, leading to long-term health problems. For example, drugs can harm the heart, lungs, and other important parts of the body.
Drugs and Behavior
Drugs can also change how young people behave. They can make youth act in ways they normally wouldn’t, like being violent or taking risks. This can lead to problems at school, with friends, or with the law.
Drugs and Addiction
Drugs can be very addictive. This means that once a young person starts using drugs, it can be hard for them to stop. This can lead to a life-long struggle with drug use.
It’s important for young people to understand the risks of drug use. This can help them make good choices and stay healthy. Remember, saying no to drugs is always the best choice.
500 Words Essay on Drugs On Youth
Drugs are harmful substances that can change the way our body works. When we talk about ‘Drugs On Youth’, we mean the impact of these substances on young people. This is a serious issue because drugs can harm young people’s health, their school work, and their relationships.
The Attraction of Drugs
Many young people start using drugs out of curiosity or because friends are doing it. They might think that drugs can help them forget their problems or feel more relaxed and happy. But this is not true. Drugs can make problems worse and can lead to new problems.
Health Problems
One of the main impacts of drugs on youth is health problems. Drugs can damage important parts of the body like the brain, heart, and lungs. They can also make young people feel tired, confused, or scared. Some drugs can even lead to death.
Impact on School Work
Another impact of drugs on youth is on their school work. Drugs can make it hard for young people to concentrate, learn, and remember things. This can lead to poor grades, trouble with teachers, and even dropping out of school.
Relationship Problems
Drugs can also harm young people’s relationships. They can lead to fights with family and friends, and can make it hard to trust others. Young people who use drugs might also start hanging out with other drug users, which can lead to more problems.
Prevention is Key
To stop the impact of drugs on youth, we need to prevent young people from starting to use drugs in the first place. This can be done by teaching them about the dangers of drugs, and by giving them healthy ways to deal with stress and problems. Parents, teachers, and friends can all help in this.
In conclusion, drugs can have a big impact on young people’s health, school work, and relationships. It’s important to prevent young people from starting to use drugs, and to help those who are already using drugs to stop. By doing this, we can protect our youth and help them to have a bright and healthy future.
(Word Count: 325)
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Drugs Education
- Essay on Drugs And Alcohol
- Essay on Drug Prevention
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Student Essays
Essays on Drug Addiction | Causes & Impacts of Drug Addiction in Youth
Drug addiction is the curse. It eats out the very fabric of our society. The following essay discusses the drug addiction with its underlying causes, its impacts and possible solutions for our youth. The essay is in simple language with easy to understand way. It would surely help primary, high school and college level students.
Drug addiction Essay; Major Causes, Impacts & Possible Solution

Drugs are very dangerous for health, addiction of drugs destroys the health.
Habitual drug users spend lot of money on buying drugs and they spend their accumulated wealth on drugs and when they become bankrupt they adopt illegal means of earning money.
The drugs which cause addiction are cocaine, meth, Marijuana, crack and heroin. All types of narcotics are fatal.
Causes of drug Addiction
The consumption of drugs often is observed when an individual specially youngster fail to cope up with personal problems.
Sometimes family issues are give birth to addiction of drugs. The youth throughout the world is vulnerable to drugs, mostly youngsters chose drugs to satiate their desires. Lack of self confidence is the root cause of addiction of drugs.
Due to pressure and excessive stress man often chose drugs and tries to lessen his or her stress by sing drugs. The high level stress compels an individual to use drugs. The social and personal pressure often result in smoking and drinking. It means when an individual start feeling isolated or is ignored in society he or she develop habit of using drugs.
The lack of parental involvement in child’s activities is also a cause of drug addiction in youngsters. Those who are emotionally weak they become drug addict. The availability and exposure of drugs is also a cause of addiction. An individual living in an area where drugs are available and people consume drugs there that individual will also develop habit of consuming drugs.
Effects of drug Addiction on Youth
The addiction of drugs leave adverse effects on the mind and body of an addict. It is a type of brain disease, regular consumption of drugs disrupts the proper functioning of brain.
The uncontrollable desire to consume drugs become worse day by day ultimately an addict find it impossible to control the intake of drugs.
A regular user of drug loses the efficiency of working. One who is drug addict can’t fulfill his or her responsibilities in good manner. The personal health of an individual is entirely lost when he or she become a drug addict. One who consumes more drugs often experiences anxiety, depression, fatigue, headache, sweating, insomnia etc.
The repeated and regular use of drugs leave psychological effects on an individual too. Many physical and mental disorders appear in an individual who uses drugs on regular basis.
Many respiratory diseases, heart attack, lung cancer, kidney failure, liver problems and brain damage are often caused of intake of drugs in excess. The immune system of man is badly affected because of drugs.
Solutions; How to Control Drug Addiction
Drug addiction is very hard to quit, those who are addicted they must be treated tenderly to quit bad habit. One who consumes more drugs he or she must be informed of ill effects of drugs. It is necessary to keep drugs off so that one who is not indulged in it remain far from it.
Though addiction of drugs is very difficult to prevent but there are some steps that can be taken to help stop consumption of drugs.
All individuals who are suffering from mental disorders or are victim of depression and stress must be taken to psychiatrist so that their mental illness is cured and they become able to quit drugs.
People must learn to deal with pressure and stress, the best way to get rid of stress is to handle it properly not to take drugs. There is ignorance among people, they are not known of the risk factors of addiction of drugs, they don’t know the abuse of drugs.
Drug addiction is one the gravest issues that our youths are facing these days. It brings a lot of problems in our lives. Therefore, every possible effort must be made in order to contain this issue forever.
Paragraph On Drug Addiction | Short & Long Paragraphs On Drug Addiction, Causes & Impacts
Any substance consumed by a person which is harmful to his health is called a drug. When one consume these dangerous substances regularly is called an addiction.
Users are mostly addicted in alcohol, cocaine, heroin, nicotine, opioid, painkillers etc. All these drugs are very harmful for physical and mental health. Drugs affect the mental cognition of a user, an addict can’t take good decisions nor he can retain information.
Signs of a drug Addict
The most vivid signs of a drug addict are red eyes, increased heart rate, anxiety, depression, paranoia and inactivity. Their memory power reduces, they feel difficulty in remembering something.
A drug addict can’t work properly without injecting it, he lack to properly coordinate with others. Due to drug addiction, the user become victim of erratic sleep patterns.
Apart from it a drug addict become happy and sad quickly. Sometimes they lose their consciousness, they are not aware of their surroundings and they forget their very existence.
Why Addiction of Drugs is Caused?
Drug addiction is mainly caused to feel happier, when an individual faces loss in life or fails to get something. He feel dejected, sad and unhappy.
In order to overcome this condition the individual start using drugs to feel happy because drugs contain a chemical called dopamine which induces happiness in the consumer and he feel happy. Slowly and gradually he become addicted and doesn’t feel happy until and unless he doesn’t consume the drug.
Effects of Drug Addiction
Drug addiction is very harmful, it not only destroy health but also leave many negatively influences on the psyche of the user.
Mostly drug addicts engage in reckless activities like gambling, stealing, adultery etc. Because of these activities they lose their respect and lose many relationships. Due to addiction of drugs many problems in personal and public relationships are created.
Their personality is badly affected by the excessive consumption of drugs, they stop caring of their hygiene. In both conditions while injecting any drug or without injecting it, a drug addict can’t communicate properly nor can Converse with anyone soundly.
It is observed that as the addiction increases the user lose interest in doing all activities which he loved to do. The addiction of drugs is fatal, it is a life-threatening act because it can kill a person.
All fatal and deadly diseases like kidney failure, lung diseases, heart diseases, brain damage, respiratory problems etc are caused by addiction of drugs.
A drug consumer feel difficulty in breathing, he feel lazy and inactive all the time and can’t perform any work in good way. Memory loss and speech problems affect the user’s personality.
Above all, the users of drugs become moody, hyperactive and victim of hallucinations.
Drug addiction is fatal, we must take steps to control addiction of drugs. Behavioral counseling is the most effective way to treat this disease, it is very important to have counseling with the user and motivate him to quit it before it takes his or her life.
Only the family members and friends can do this, if you find your loved ones addicted make a behavioral counseling with them and motivate them to quit it. Family members and friends can encourage them and can help them to get rid of bad addiction.
1 thought on “Essays on Drug Addiction | Causes & Impacts of Drug Addiction in Youth”
very usiful
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Teen Drug Use, by the Numbers
Annual survey data points to which drugs and other substances are most commonly used among teenagers today.

Getty Stock Images
Alcohol, marijuana and nicotine through vaping remained the most commonly used substances among teens in 2023, according to a survey by Monitoring the Future.
It's an age-old worry among many parents: Is my kid using drugs?
Data shows why such concerns these days go beyond fretting over a teen potentially puffing on pot, with the rise of fentanyl fueling record-high fatal overdose totals in the U.S. and research pointing to the synthetic opioid’s deadly impact on youth .
But there’s also more positive news: Illicit drug use among American teens has held fairly steady around the lower levels reached in 2021, amid the school and societal disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. Estimates from the most recent iteration of the annual Monitoring the Future survey also show significant increases in the shares of 10th- and 12th-graders who have never used alcohol, marijuana or nicotine, to approximately 54% and 38%, respectively.
The Monitoring the Future survey since 1975 has provided a national snapshot on the state of substance use among America’s adolescents and teens. The most recent drug use estimates were drawn from surveys of more than 22,000 students in eighth, 10th and 12th grade across 235 public and private schools.
The Top 10 Causes of Death in the U.S.

Here’s a look at some of the notable teen drug use data identified by the project.
Which Drugs and Substances Are Teens Using the Most?
Alcohol, marijuana and nicotine through vaping remained the most commonly used substances among teens in 2023, though at levels notably below what they were prior to the pandemic.
Approximately 29% of 12th-graders, 18% of 10th-graders and 8% of 8th-graders had used marijuana sometime over the previous 12 months in 2023 – rates that remained relatively unchanged since 2021 . Among all three grades combined, lifetime use of marijuana/hashish stood at 23%. The drops in marijuana use since the onset of the pandemic have marked the first substantial change in prevalence in over a decade, researchers said.
Meanwhile, the share of 12th-graders estimated to have used alcohol over the past 12 months decreased from 52% in 2022 to 46% in 2023. Past-year prevalence stood at 31% among 10th-graders and 15% among eighth-graders, while lifetime use among all students was 36%.
Nicotine vaping within the past year fell significantly among both 10th- and 12th-graders from 2022 to 2023, landing at 18% and 23%, respectively. It held fairly steady at 11% among students in eighth grade. Lifetime use among all three grades was 25%.
Other Drug and Substance Use Among Teens
Relatedly, lifetime cigarette use “trended slightly downward in all three grades” in 2023, according to a Monitoring the Future report on the latest survey results. Lifetime use among all grade levels was approximately 10%.
“Overall, cigarette prevalence in 2023 (was) at or near the lowest ever recorded by the survey since the start of the survey in 1975,” the report states.
Lifetime prevalence rates for other drugs across all three grade levels include:
- Cocaine - 1.1%
- Methamphetamine - 0.5%
- Heroin - 0.5%
- Hallucinogens (including LSD and psilocybin ) - 4%
Among 12th-graders, past-year prevalence rates for select drugs include:
- OxyContin - 0.6%
- Vicodin - 0.6%
- Ecstasy (MDMA) - 0.7%
- Ketamine - 1%
- Any prescription drug (without doctor’s orders) - 4.1%
Digging Into Delta-8, aka ‘Diet Weed’
New to the survey in 2023 was asking 12th-graders about their use of delta-8 THC, which is a variant of the main psychoactive compound in cannabis and has been referred to as “diet weed.” Legal at the federal level due to a legislative loophole but not in all states, delta-8 has become accessible in places like gas stations, smoke shops and convenience stores. It comes in various forms, including gummy candies and flavored vaping devices.
More than 11% of 12th-grade students used delta-8 over the past 12 months in 2023, according to MTF estimates. Prevalence of delta-8 use was found to be higher among teens who lived in states that had not legalized recreational marijuana for adults.
“Potential health effects of delta-8, including dependence, are currently unknown,” the report states.
Spike in Legal Use of ADHD Medications
The share of 12th-grade students who had ever legally used drugs to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder declined slightly in 2023 to 14.3% after jumping from 11% in 2021 to a high of 14.6% in 2022 – its largest single-year increase on record.
Lifetime prevalence among 8th-grade students declined from 12% in 2022 to 10% in 2023, while the percentage remained unchanged at close to 11% among 10th grade students in both 2022 and 2023.
“It is possible that the need for treatment of ADHD increased during the pandemic due to adolescents experiencing more stress during the pandemic,” the MTF report states. “Another possibility is that sheltering at home during the pandemic may have made any attention issues of adolescents more salient to their parents.”
Illicit Prescription Drug Use Down
Use of any prescription drug without a doctor’s orders among 12th-graders continued to hover around the lower level reached in 2021, after the pandemic took hold.
In 2023, the past-year prevalence of prescription medication use was 4% among 12th-grade students, compared with 5% in 2022 and 7.5% in 2020. Lifetime prevalence in 2023 was 8.5%, down from 14% in 2020.
Join the Conversation
Tags: teens , drug abuse , drugs , surveys , opioids , alcohol , marijuana , cocaine , prescription drugs
Recommended Articles
National News

Healthiest Communities Health News

America 2024

Healthiest Communities
- # 1 Los Alamos County, NM
- # 2 Falls Church city, VA
- # 3 Douglas County, CO
- # 4 Morgan County, UT
- # 5 Carver County, MN
Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
The 10 worst presidents.
U.S. News Staff Feb. 23, 2024

Cartoons on President Donald Trump
Feb. 1, 2017, at 1:24 p.m.

Photos: Obama Behind the Scenes
April 8, 2022

Photos: Who Supports Joe Biden?
March 11, 2020

Takeaways From the NCAA’s Settlement
Laura Mannweiler May 24, 2024

Noncitizen Voting: the Fiction and Facts
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton May 24, 2024

Quiz: Who Said What in Trump’s Trial?
U.S. News Staff May 24, 2024

CDC: COVID-19 Strains Are on the Rise
Cecelia Smith-Schoenwalder May 24, 2024

Consumers See Worsening Job Market
Tim Smart May 24, 2024

Biden vs. the Border
Elliott Davis Jr. May 23, 2024

Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Drug Addiction — The Causes, Effects and Prevention of Drug Addiction
The Problem of Drug Addiction: Causes, Effects and Solutions
- Categories: Drug Addiction
About this sample

Words: 1196 |
Published: Jan 15, 2019
Words: 1196 | Pages: 3 | 6 min read
Table of contents
Causes of drug addiction, effects of drug addiction, how to prevent drug addiction (essay), works cited.
- Doan, H. (2007). Police dogs will sniff out drugs at city schools. The Roanoke Times.
- Mayo Clinic. (2019). Drug addiction (substance use disorder).
- National Institute on Drug Abuse. (2022). Principles of drug addiction treatment: A research-based guide (third edition).
- New York Times. (2009). Drug-sniffing dogs are in demand.
- Psychological Studies and Support to Drug Users. (2014). Teenagers and drug use: Facts and figures.
- Smith, M. J., & Stevens, A. (Eds.). (2013). Drug Policy and the Public Good.
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (2018). Key substance use and mental health indicators in the United States: Results from the 2017 National Survey on Drug Use and Health.
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (2021). Treatment for substance use disorders.
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. (2021). World drug report 2021.
- Volkow, N. D., Koob, G. F., & McLellan, A. T. (2016). Neurobiologic advances from the brain disease model of addiction. New England Journal of Medicine, 374(4), 363-371.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Nursing & Health

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 866 words
4 pages / 2018 words
3 pages / 1486 words
2 pages / 910 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Drug Addiction
Drug addiction is a widely misunderstood condition. The timeless nature versus nurture debate is often brought up when discussing drug dependence. Is addiction a mental illness or a consequence of poor lifestyle choices? Are [...]
With the recent country-wide legalization of marijuana in Canada, the recreational and medical use of marijuana is becoming more frequent. Marijuana is known to have many different effects ranging from pain relief to temporarily [...]
Among many other problems, modern society today is faced with the problem of ‘Drug Abuse’. Drug abuse is a misuse of, or over indulgence in drugs resulting in physical or psychological harm to the individual involved in it. The [...]
The United States is one of the highest birth rate for teens. If more teens were to take Birth control we would have less abortion rates and less teen pregnancies in the United States. There are many types and the [...]
Since 2009, MTV has aired shows that revolve around teen pregnancy, something that most conservative parents would shame, is now just another publicity stunt to make a new reality show. The same thing parents warn their [...]
In 2013, Venka Child aged 16 from Bristol worked with Fixers to create a short video about challenges teen mothers go through. In some part of the video, a teen mother is shown opening a fridge which is almost empty. The teen [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Substance Use Among Youth During the COVID-19 Pandemic: a Systematic Review
Hannah m. layman.
1 Department of Social and Behavioral Sciences, School of Public Health, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV USA
Ingibjorg Eva Thorisdottir
2 Department of Psychology, Reykjavik University, Reykjavik, Iceland
3 Icelandic Centre for Social Research and Analysis, Reykjavik University, Reykjavik, Iceland
Thorhildur Halldorsdottir
Inga dora sigfusdottir.
4 Department of Health and Behavior Studies, Teachers College, Columbia University, New York, NY USA
John P. Allegrante
5 Department of Sociomedical Sciences, Mailman School of Public Health, Columbia University, New York, NY USA
Alfgeir Logi Kristjansson
Associated data, purpose of review.
To review the literature on the trends in substance use among youth during the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Recent Findings
The pandemic has given rise to concerns about the mental health and social well-being of youth, including its potential to increase or exacerbate substance use behaviors. This systematic review identified and included 49 studies of use across alcohol, cannabis, tobacco, e-cigarettes/vaping, and other drugs, and unspecified substances. The majority of studies across all categories of youth substance use reported reductions in prevalence, except in the case of other drugs and unspecified drug and substance use, which included three studies that reported an increase in use and three studies that reported decrease in use.
Overall, the results of this review suggest that the prevalence of youth substance use has largely declined during the pandemic. Youth substance use in the post-pandemic years will require monitoring and continued surveillance.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s11920-022-01338-z.
Introduction
The adolescent years represent an important developmental stage during which the foundation for future patterns in substance use is often established [ 1 ]. Both the quantity and frequency of use during this period are strongly associated with risks for heavy use and misuse of substances in adulthood [ 2 , 3 ]. As an example of the staggering economic and societal costs, substance use in the USA alone has been estimated at over $400 billion annually by the US Surgeon General [ 4 ]. In addition to the direct economic impact, the societal harm caused by substance use in the USA has been estimated at over $800 billion annually due to premature death or quality-of-life adjustments [ 5 ]. Youth alcohol, tobacco, and other drug use impairs psychological and neurocognitive development and increases risk for academic failure, chronic disease, and mental illness [ 6 , 7 ]. Thus, the prevention of youth substance use remains an important priority for public health globally.
Various domains of established risk and protective factors play an important role in preventing the development of youth substance use. These include access to care and support provided by parents, family, and friends; structure, supervision, and support from school faculty and staff; and access to and participation in pro-social leisure time activities [ 8 , 9 ]. Studies that take an ecologic view of substance use have further assessed the impact of environmental factors known as “context effects,” which independently contribute to the odds of alcohol, tobacco, and other drug use among youth. Generally, such studies have found that youth who live under challenging home situations or in resource-limited areas, or both, are more likely than other youth to be negatively affected by sudden environmental changes and thus may turn to substance use as a coping mechanism [ 10 – 12 ].
The COVID-19 Pandemic
The novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) was officially declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) on March 11, 2020 [ 13 ]. Over 400 million confirmed cases and close to 6 million deaths worldwide have been attributed to the virus [ 14 ]. Thus, virtually no human on earth has been unaffected by the virus. During this time, entire countries, regions, states, cities, and towns have enacted various laws, rules, and guidelines in their efforts to curb the spread of the virus and its impact on human health. Some of the more drastic mitigation measures have included closing of borders, lockdowns and curfews, or both, in cities and towns; severe limits on social gatherings and assembly (e.g., religious services); restricted access to worksites and entertainment venues and services (e.g., restaurants, theaters, and sports events); and mandates for physical (or social) distancing and wearing face masks. In most places, these efforts have included closing of schools and restriction of services for youth, such as sport clubs and extracurricular programs, and the prohibition of social gatherings [ 15 , 16 ]. Such extreme measures at the societal level are unprecedented in modern times and have not been seen since the influenza pandemic of 1918 [ 17 ].
In addition to the social restrictions, the mitigation efforts to curb the spread of the virus have resulted in unintended consequences that have been harmful in the lives of youth [ 18 ]. These include disruption of parental (or caregiver) income and associated financial consequences and stunted academic progress due to school closings, remote instruction, and recurring changes in instructional formats. The pandemic has also increased feelings of loneliness among young people because of long-term social isolation and limited opportunities to interact with peers [ 12 ]. During this period, inconsistent and poorly planned institutional responses have been reported [ 19 ], including a decline in access to harm-reduction services and treatment of substance use [ 20 ]. In a recent review, Pfefferbaum highlighted the negative psychological effects of the pandemic on children and youth, including the significant increase in the prevalence of clinical depression, suicidal ideation, and anxiety, all of which have the potential to contribute to an increase in substance use behaviors [ 21 ].
The Current Study
Given the human and societal costs associated with youth substance use, we sought to critically assess the impact that the COVID-19 pandemic has had on youth substance use. Some recent studies have shown an increase of substance use among youth, particularly vulnerable youth, such as those living in resource-poor areas or under challenging family circumstances [ 22 ], while others have found a reduction in substance use despite an overall worsening of mental health status [ 23 ••]. However, despite the significance of the pandemic, a wholistic review of research on youth substance use during the era of the COVID-19 pandemic has not been conducted to date. Consequently, the objective of this systematic review was to provide an overview of the most recent research into youth substance use during the period of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This systematic review sought to examine the prevalence of substance use among adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic. Following the identification and selection of peer-reviewed papers, we examined each relevant paper by country, sample characteristics (type, age, sample size, period of study enrollment), study design, substance use behavior or outcome (type, measurement), and covariates included in the analyses. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis (PRISMA) was used to guide the design, execution, and reporting of findings for this systematic review. The research question, inclusion criteria, and search terms were defined using the PICO approach (Population, Intervention [or Exposure], Comparator, and Outcome). We identified and used previously published research articles and reviews on substance use during the COVID-19 pandemic to guide the creation of the search terms. The protocol for this systematic review was registered at PROSPERO (CRD42022311679).
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Studies were selected based on the following criteria: (1) examined the substance use among youth during the COVID-19 pandemic; (2) study participants were 24 years old or younger; and (3) the study was published in the English language. Cross-sectional and longitudinal studies were included. When two manuscripts presented findings from non-independent datasets, the manuscript with the larger number of study participants was included. Articles were excluded if either COVID-19 (or a related term: COVID pandemic, Coronavirus, etc.) or substance use (or related terms: substance abuse, addiction, alcohol, nicotine, smoking, vaping, tobacco, licit drug/s, illicit drug/s, drug/s, etc.) was not identified in the paper’s title or abstract.
Identification of Studies
All databases within Web of Science were used in conducting the search. The search was limited to studies published on, or subsequent to, the date the COVID-19 pandemic began (December 1, 2019) to studies published up to February 15, 2022. Thus, the last search for this review was conducted on February 15, 2022. Titles, abstracts, and articles were reviewed to identify potentially relevant manuscripts. The search terms included combinations of COVID, adolescent*, child*, youth, substance use, substance abuse, drug, substance drug, smoking, tobacco use (Table (Table1). 1 ). Reference lists of included research studies and published reviews of substance use among youth during the COVID-19 pandemic were also searched.
Search terms and linkage (Web of Science)
Data Extraction
The initial search based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria was performed by one investigator (HL) and then repeated by a second investigator (IET) to ensure that all relevant articles were included. The investigators conducting the search were located across two different countries (the USA and Iceland) with access to different research databases. As such, the second investigator’s search yielded an additional 17 studies that were not included in the first search. These discrepancies in the search findings from the two investigators who performed the search were discussed and a consensus was reached by the two investigators. Key elements of relevance for this review were extracted from each paper, summarized, and entered into an Excel spreadsheet, which was used to inform the broader discussion of the current state of the literature among the collaborating authors.
The initial search yielded 423 articles of potential interest. Of those, 49 articles met full eligibility criteria (see Fig. 1 for PRISMA flow chart). Five articles were published in 2020, 38 in 2021, and 6 in 2022. Forty-six articles from 23 countries reported on studies conducted with single-country samples and three articles reported on studies from multiple countries. Most of the studies were conducted in North America ( n = 22) or Europe ( n = 19). Twenty-nine articles reported studies that were based on cross-sectional designs and 20 on longitudinal designs. Forty-four articles reported on participant samples of between 10 and 25 years of age, and five articles also included older individuals. Regarding outcomes, 14 articles reported studies with a single substance use outcome, 29 articles included multiple substance use outcomes, five articles reported on general substance use without specifying type of substance, and one article focused solely on substance abuse disorder. Below, we have organized the summaries of our findings from the review of the 49 articles by substance use outcome (Table (Table2). 2 ). Articles reporting on multiple substance use outcomes are included in multiple summaries based on the respective outcome.

PRISMA flow diagram of the bibliographic search. The 15 Web of Science databases included: Arts & Humanities Citation Index, Book Citation Index, Emerging Sources Citation Index, BIOSIS Citation Index, BIOSIS Previews, Conference Proceedings Citation Index, Data Citation Index, Derwent Innovations Index, KCI-Korean Journal Database, MEDLINE®, Russian Science Citation Index, Science Citation Index Expanded, Social Sciences Citation Index, SciELO Citation Index, Zoological Record, Zoological Record (1864-present). Reasons for excluding reports included the following: reason 1, accidentally included/wrong topic; reason 2, not a research article; and reason 3, date of publications prior to the COVID-19 outbreak
Description of studies included in the review and summary of findings
* Month of administration reported when available. If not, the time of year or solely the year in some cases, as reported by the authors
Alcohol Use
A total of 32 studies included measures on alcohol use; 27 of those also included measures on one or more other types of substance use [ 22 , 23 ••, 24 – 31 , 32 •, 33 , 34 ••, 35 – 48 ], with five focusing exclusively on alcohol use as the outcome [ 49 – 53 ]. Fourteen studies employed a cross-sectional design [ 22 , 25 , 26 , 33 , 37 – 41 , 44 – 46 , 48 , 49 ] and 18 used longitudinal designs [ 23 ••, 24 , 27 – 31 , 32 •, 34 ••, 35 , 36 , 42 , 43 , 47 , 50 – 53 ]. Twenty-four studies used a non-random selection of participants, including convenience, purposive, or volunteer samples [ 22 , 24 – 26 , 28 , 29 , 31 , 35 – 46 , 49 – 53 ].
Five studies reported increase in alcohol use [ 22 , 26 , 30 , 36 , 45 ], 12 studies reported decrease in alcohol use [ 23 ••, 32 •, 34 ••, 35 , 38 , 39 , 47 , 48 , 50 – 53 ], and four studies reported no change [ 24 , 28 , 31 , 43 ], as noted above, mainly because of cross-sectional design where alcohol was employed as a covariate or group divider. Eleven studies reported neither an increase nor a decrease in alcohol use [ 25 , 27 , 29 , 33 , 37 , 40 – 42 , 44 , 46 , 49 ]. Ten studies included a mention of gender [ 23 ••, 25 , 28 , 33 , 41 – 43 , 45 , 46 , 51 ], and five in relation to alcohol use [ 23 ••, 28 , 33 , 45 , 51 ]. One concluded that boys [ 33 ] used more alcohol than girls during the pandemic, while two studies reported on greater increase in use among girls [ 28 , 45 ]. No gender difference was reported in two of the studies [ 23 ••, 51 ].
Cannabis Use
A total of 20 studies included measures on use of cannabis, including marijuana, hashish, and edibles. Seventeen of these also included measures into one or more other type of substance use [ 24 – 28 , 31 , 32 •, 33 , 34 ••, 35 , 36 , 39 , 42 , 44 , 46 , 47 , 54 ], three of which focused exclusively on cannabis use as the outcome [ 55 •, 56 , 57 ]. Nine studies employed a cross-sectional design [ 25 , 26 , 33 , 39 , 44 , 46 , 54 , 56 , 57 ] and 11 used a longitudinal design [ 24 , 27 , 28 , 31 , 32 •, 34 ••, 35 , 36 , 42 , 47 , 55 •]. Fifteen studies used a non-random selection of participants, including convenience, purposive, or volunteer samples [ 24 – 26 , 28 , 31 , 35 , 36 , 39 , 42 , 44 , 46 , 54 , 55 •, 56 , 57 ].
Four studies reported an increase in the prevalence or frequency of cannabis use during the pandemic [ 26 , 36 , 55 •, 57 ], five studies reported a decrease in cannabis use [ 28 , 32 •, 35 , 39 , 47 ], and three studies reported no change [ 24 , 31 , 34 ••]. Eight studies did not report an increase or decrease in cannabis use for similar reasons as mentioned above [ 25 , 27 , 33 , 42 , 44 , 46 , 54 , 56 ]. Three studies included a mention of gender and two in relation to cannabis use [ 25 , 28 , 33 ]. One concluded that cannabis use among boys had increased more than use among girls during the pandemic [ 33 ], and one study reported that use among girls had increased more than for boys [ 28 ]. One study included an assessment of gender without relevance to cannabis use outcome [ 25 ].
Tobacco Use
A total of 27 studies included measures on tobacco use, with all but two including measures on one or more other types of substance use [ 22 , 23 ••, 25 – 27 , 29 , 30 , 33 , 34 ••, 35 – 48 , 54 , 58 ]. One study exclusively assessed nicotine dependence [ 59 ], and one study solely employed a general measure of smoking [ 9 ]. Seventeen studies employed a cross-sectional design [ 22 , 25 , 26 , 33 , 37 – 41 , 44 – 46 , 48 , 54 , 58 – 60 ] and 10 studies used longitudinal designs [ 23 ••, 27 , 29 , 30 , 34 ••, 35 , 36 , 42 , 43 , 47 ]. Twenty studies used a non-random selection of participants, again including convenience, purposive, or volunteer samples [ 22 , 25 , 26 , 29 , 35 – 46 , 54 , 58 – 60 ].
Of all studies included for tobacco use, only two studies reported an increase in smoking behavior during the pandemic [ 26 , 34 ••], six studies reported a decrease in smoking behavior [ 22 , 23 ••, 35 , 36 , 39 , 61 ], and one study reported no change in smoking behavior [ 47 ]. Eighteen studies did not report an increase or decrease in smoking behavior, again, mainly because of cross-sectional design and where smoking was employed as a covariate or group divider, or both [ 25 , 27 , 29 , 30 , 33 , 37 , 38 , 40 – 46 , 48 , 54 , 58 , 59 ]; most of these studies focused on mental health. Nine studies reported on some form of gender difference [ 23 ••, 24 , 33 , 40 , 41 , 43 , 47 , 48 , 59 ] but only two of them reported such difference in smoking, with one reporting increased use among boys [ 33 ] and one increased use for girls [ 48 ].
E-cigarette Use/Vaping
A total of 16 studies included measures on e-cigarettes or vaping. Twelve of those also included measures into one or more other type of substance use [ 23 ••, 24 – 29 , 32 •, 34 ••, 36 , 54 , 58 ] but four were exclusively about e-cigarette use/vaping [ 62 – 65 ]. Nine of the studies employed a cross-sectional design [ 25 , 26 , 58 , 59 , 62 – 65 ] and eight used longitudinal designs [ 23 ••, 24 , 27 – 29 , 32 •, 34 ••, 36 ]. Thirteen of the studies used a non-random selection of participants such as convenience, purposive, or volunteer samples [ 24 – 26 , 28 , 29 , 36 , 54 , 58 , 62 – 65 ].
One study reported an increase in e-cigarette use/vaping [ 26 ], eights studies reported a decrease in e-cigarette use/vaping [ 23 ••, 28 , 36 , 62 – 65 ], and two studies reported no change [ 24 , 34 ••]. Six studies reported neither an increase nor a decrease in e-cigarette use/vaping [ 25 , 27 , 29 , 32 •, 54 , 58 ]. Three studies included a mention of gender [ 23 ••, 25 , 28 ] but only one in relation to e-cigarette use/vaping which reported non-significant gender differences in such use [ 23 ••].
Use of Other Drugs and Unspecified Substance Use
A total of 19 studies included measures on other drugs or substance use without specification. Twelve of these studies employed a general measure of substance use or drug use [ 22 , 25 , 30 , 40 , 43 , 45 , 46 , 66 – 70 ] without specification of substance but the remaining seven studies included measures on substances such as opioids/prescription drugs, heroin, cocaine, methamphetamine, and inhalants [ 27 , 31 , 33 , 34 ••, 39 , 42 , 44 ]. Twelve studies employed a cross-sectional design [ 22 , 25 , 33 , 39 , 40 , 44 – 46 , 67 – 70 ] and seven used longitudinal designs [ 27 , 30 , 31 , 34 ••, 42 , 43 , 67 ]. Fifteen studies used a non-random selection of participants such as via convenience, purposive, or volunteer samples [ 22 , 25 , 31 , 39 , 40 , 42 – 46 , 66 – 70 ].
Three studies reported increase in substance use [ 22 , 27 , 34 ••], three studies reported a decrease in use [ 39 , 67 , 67 ], and one study reported no change during the pandemic [ 31 ]. Twelve studies did not report an increase or decrease in substance use where such measures were primarily employed as covariates or group dividers [ 25 , 30 , 33 , 40 , 42 – 46 , 68 – 70 ]. Four studies included a mention of gender [ 25 , 33 , 43 , 70 ] but none of them in relation to differences in substance use.
The COVID-19 pandemic and associated social restrictions implemented to contain the spread of the virus have led to concerns from parents, educators, and healthcare professionals and researchers about what effects the pandemic may have had on the mental health and social well-being of youth. To partially address this concern, the objective of this systematic review was to examine the prevalence of youth substance use during the COVID-19 pandemic. Based on 49 studies published to date and captured in our search, the overall results of our review suggest that the prevalence of youth alcohol, cannabis, tobacco, and e-cigarette/vaping use has declined during the pandemic.
This finding of an overall decline in the prevalence of substance use during the pandemic is certainly positive, but it begs the question: To what can the decrease be attributed? Youth substance use most often takes place outside the home environment and usually within the context of the peer group. Moreover, youth substance use is highly dependent on availability and access to drugs and other substances. The public health restrictions that were necessary during the COVID-19 pandemic limited the time most adolescents spent in-person with their peers, and it follows that availability and access to alcohol, tobacco, and other substances was effectively limited during community lockdowns. In short, young people confined to their homes with parents had fewer opportunities for accessing and using substances. Thus, limited peer-group gatherings, decreased availability and access to substances, and increased time spent in the home with parents—all well-established factors shown to be effective in prevention efforts aimed at decreasing substance use [ 71 ]—are likely to have conferred important protection against substance use during COVID-19 as observed in the decline in prevalence reported across the bulk of studies we reviewed.
These promising and positive findings of an overall decrease in substance use, however, need to be viewed with some caution. First, some groups of youth may have had more pre-pandemic vulnerability to substance use during the pandemic for several reasons. For instance, there is evidence that mental health problems have been on the rise among many adolescents prior to and during the pandemic. In addition, for older adolescents and young adults experiencing increased stress and mental health problems, there is evidence that alcohol, drugs, and other substances may have offered a coping mechanism during the pandemic [ 12 ]. Youth that used substances by themselves, moreover, had increased symptoms of depression [ 28 ].
Spending more time in the household is not always a consistent protective factor. One study found that youth were drinking and using other substances with their parents shortly after social distancing measures were imposed, suggesting that permissive parental attitudes and behaviors could encourage and facilitate youth alcohol consumption and other substance use [ 72 ]. These permissive attitudes and modelling of health compromising behavior can influence the perceived norms towards substance use, resulting in increased use after the pandemic. Moreover, adolescents living with family conflict or dysfunction are more likely to engage in substance use [ 73 ]. One systematic review of 32 reports [ 74 ] found evidence that domestic violence has increased during the pandemic, indicating that the at-risk group of youth living with family conflict and dysfunction increased during this time. Finally, in addition, youth living under the stress of parental substance use, family dysfunction, and domestic violence could predispose the later onset of substance use and violent behavior. Youth who missed out on “normal teenage years” or important rites of passage that were interrupted by the pandemic may also have difficulties with substance use later in life when restrictions are removed, and social gatherings allowed. What this means for the prevalence of substance use in the post-pandemic years will require monitoring and further surveillance. Thus, the long-term effects of the pandemic and its potential dormant or latent effects on responsible adult substance use are unknown at this time and not likely to be fully understood until years later.
Implications for Prevention and Treatment
Although the findings of our review suggest that the various mitigation strategies to contain the spread of COVID-19—masking, physical distancing, and community lockdowns that imposed restrictions on social gatherings—may have had detrimental impact on the mental health and social well-being of youth [ 21 ], such measures did not necessarily lead or contribute to an increase in youth substance use. Notwithstanding, there are several implications for prevention and treatment that should be considered in the aftermath of this pandemic. First, focusing on improving adolescent mental health should be a priority. Poor mental health is a well-known risk factor for substance use and misuse and the majority of young people with substance use problems suffer from co-occurring mental health issues that are often difficult to treat [ 75 , 76 ]. Second, although remote learning enabled young people to maintain some connection to schooling, studies have pointed to the negative impact of virtual learning on the academic and social development of many young people and thus may have set the stage for a “lost generation” of youth who could be at even greater risk for substance use in the future [ 19 ]. Post-pandemic efforts undoubtedly will need to address the gaps in academic and social development of this cohort of young people—especially those for whom there have been significant disparities in access to educational opportunities. This suggests that community-wide surveillance and prevention of substance use needs to become a greater community priority than prior to the pandemic. Third, COVID-19 has demonstrated both the value of e-health and telemedicine to address the health needs of people during the pandemic [ 77 ]. However, the limited availability and access to mental health counseling and other forms of virtual treatment during the early phases of the COVID-19 pandemic may have contributed to placing young people at greater risk for substance use. As such, greater investment in e-health treatment for mental health problems and referral should be a greater priority in the future.
Limitations
The findings of this review should be viewed with some caution because of design and other methodological limitations of the studies we reviewed. First, most of the published studies we reviewed utilized cross-sectional designs and focused largely on prevalence of use; few studies utilized longitudinal designs, outcome measures varied, and any follow-up was of limited time duration. Second, many studies used non-probability sampling methods to identify and obtain participants, including convenience, purposive, or volunteer samples, all of which limit the external validity of their findings. Third, few studies reported analyses that examined differences by gender. This remains an important question for future research because of the gender differences that have been observed in substance use and mental health outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic [ 23 ••]. Finally, most of the studies reviewed included investigations of substance use of a single category, rather than across multiple categories of substance use, thus precluding analysis of any synergistic or gateway effects of multiple drug use for which the pandemic may have been responsible.
Recommendations for Future Research
Our review suggests several directions for future investigation. First, numerous studies have now documented the impact of COVID-19 on the lives and well-being of adolescents in the immediate aftermath of the pandemic; however, more longitudinal studies are needed to assess the latent and long-term effect of the pandemic on substance use behaviors among youth. Although the pandemic may not have fostered increased substance use among most young people, further investigation is needed to understand differential risk across high-risk adolescents and differences by gender during the pandemic. In addition, more attention should be given to the role of key covariates in understanding youth substance use. For example, covariates such as socioeconomic status and social determinants of mental health should be addressed in research that seeks to understand the relationship of substance use to youth mental health and social well-being. Finally, as more studies are published, meta-analyses of youth substance use during and following the pandemic will be possible and are needed to better understand how and to what extent the pandemic influenced substance use and any underlying causal mechanisms.
Conclusions
This systematic review of youth substance use during the COVID-19 pandemic assessed studies across several categories of substances, including alcohol, cannabis, tobacco, e-cigarette/vaping, and use of other drugs and unspecified substances. Regardless of the type of substance use, we found little evidence across the 49 studies we reviewed that the prevalence of use increased in response to the potential social and emotional deprivations associated with the pandemic. In fact, apart from some increase in the use of unspecified drugs or other substances, the majority of studies reported reductions in use across alcohol, cannabis, and tobacco and related products. Thus, we conclude that the bulk of the available evidence suggests that the prevalence of youth substance use largely declined during the first 2 years of the pandemic.
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Author Contribution
ALK, TH, JPA, IDS, and IET conceived the study. HML and IET conducted the initial search and review of included studies. HML created the PRISMA diagram and tables. ALK drafted the Introduction and Results sections. TH drafted the Methods section and registered the study on PROSPERO. JPA drafted the Abstract and contributed to writing and editing multiple versions of the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
This research was funded in part by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (#U48DP006391), and the Icelandic Research Fund (#217612).
Compliance with Ethical Standards
Alfgeir Kristjansson, Inga Dora Sigfusdottir, and Inga Eva Thorisdottir disclose that they are affiliated with Planet Youth, a youth substance use prevention service organization that is distributed globally through sale of the Planet Youth Guidance Program, which is based on the Icelandic Prevention Model, from which they receive salary or consulting fees; all other authors disclose no financial or non-financial interests that are directly or indirectly related to the work submitted for publication.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Child and Family Disaster Psychiatry
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as:• Of importance •• Of major importance
Fentanyl is fueling a record number of youth drug deaths
The new trend has shocked many pediatricians, who say they feel unprepared to provide counseling on opioid addiction.
Fentanyl, a pervasive killer in America’s illicit drug supply, is increasingly landing in the hands of teens across the region and nation, worrying providers who say treatment options for youths are limited.
Across the country, fentanyl has largely fueled a more than doubling of overdose deaths among children ages 12 to 17 since the start of the pandemic, according to a Washington Post analysis of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data released this month.
Fatal overdoses in D.C., Maryland and Virginia are in keeping with the national increase in opioid fatalities, which until recently primarily claimed the lives of adults. In 2022, 45 teens succumbed to opioids locally, a number roughly equal to the previous three years combined, data show. And incomplete data for 2023 show no sign of the crisis abating in young people.
Physicians at area hospitals report a rise in young people who took opioids arriving to emergency rooms and local addiction specialists say the number of teens seeking help for opioid use is spiking — especially among Latinos.
The surge, experts said, reflects a collision between adolescents’ natural drive to experiment, a decline in teen mental health and an increase in the availability and potency of counterfeit pills that mimic the appearance of prescription medications, making the experimentation that is a hallmark of adolescence more dangerous. A single pill containing fentanyl can be lethal, and those who survive often need comprehensive addiction care that clinicians say isn’t widely available.
“You had this really, really disastrous combination of a dangerous drug supply with teens who were increasingly struggling,” said Scott Hadland, chief of adolescent and young adult medicine at Mass General for Children and Harvard Medical School.
Many pediatricians surveyed nationwide report feeling underprepared to counsel patients on opioid use, Hadland and his co-authors found in an analysis of survey results . As providers try to catch up and government agencies weigh how best to respond, many schools are stocking overdose reversal medication as recently recommended by the Biden administration and are working to teach students and families about the dangers.
Easy to get from friends or through social media, potent pills masquerading as prescription Percocet or oxycodone cost a few dollars each and seemed to flood the market as students reeling from the isolation and the trauma of the pandemic returned to school, treatment providers said in interviews.
Frequently sold online at $2 to $10 a piece, addiction specialists say, pills laced with fentanyl are hard to spot, easy to hide and can quickly lead to powerful dependencies — or worse.
“It’s not easy to stay away from drugs once your body has a substance abuse disorder. The pump is primed. The brain wiring has been rewired,” said Daniel Smith, director of addiction services at Mary’s Center, a community health center that predominantly serves Spanish-speaking patients in D.C. and Maryland.
Smith and Sivabalaji Kaliamurthy, a pediatric addictions specialist who runs the Children’s National Hospital addictions clinic, have spent years treating young people addicted to marijuana or alcohol. In the summer of 2022, they saw a change that shocked them both: teens were seeking treatment for opioid dependency. Now they almost exclusively treat opioid use disorder.
“We did not anticipate this happening with teens. It kind of fell in our lap,” Smith said, adding: “Before 2022, we had no kids ever [for that].”
“All of this has come together when kids were coming back to school post covid,” Kaliamurthy said.
Opioid-related visits to the emergency department at Children’s National in Northwest D.C. from 12-to-21-year-olds doubled from 2022 to 2023, while visits for other drugs remained flat, said Anisha Abraham, the hospital’s chief of the Division of Adolescent and Young Adult Medicine.
A dozen young people ages 16 to 19 died in the District last year, surpassing the previous high of six in 2021 and echoing the precipitous rise in adult overdose deaths which hit a record 522 last year, according to a recent medical examiner’s report.
Montgomery County emergency rooms tracked a spike in opioid-related visits last year among young people ages 10 to 21, according to state surveillance data . Hispanic youths made up 4 in 10 visits; Black youths a quarter and White youths about 20 percent, data show.
While White teens make up the largest share of adolescent opioid deaths nationally and locally, Black and Hispanic adolescents are now dying at a faster rate, CDC data show.
Liseth’s mother knew something was wrong in summer of 2022 when her teenage daughter stopped cleaning her room and started smoking marijuana. Within months, Liseth lost weight, ate less, came home late and vomited often. Even while raising two other children and working, her mother could tell Liseth wasn’t herself. The first doctor the Maryland family saw dismissed her concerns but when they ended up at the Children’s National Hospital emergency department in Northwest Washington last year, Liseth admitted she was using fentanyl.
The mother shared her daughter’s story with her permission, speaking Spanish through an interpreter on the condition of anonymity to protect the family’s privacy and identifying Liseth, now 17, by her middle name.
While data shows the profile of a fatal overdose victim in D.C. is a middle-aged Black man who snorts or injects heroin, treatment providers say adolescents like Liseth almost exclusively use pills, known as M30s, perks or blues, by inhaling the fumes off a foil. Teens tell providers they have easy access to the pills at school and once their friend group begins using, it’s hard to say no.
Experimentation and pushing boundaries is part of being an adolescent, Smith said, “but you can die from using a perk one time and that is terrifying.” As of 2020, drug overdoses and poisonings rank as the third-leading cause of pediatric deaths in America, after firearm-related injuries and motor vehicle crashes. Fentanyl is present in at least three-quarters of teen overdose deaths, CDC data show.
Treatment has been tough on Liseth, who was born in Virginia to Guatemalan parents and lives in a tidy suburban home in Maryland filled with flowers and symbols of her family’s Catholic faith. There were relapses, disappearances, a 911 call and a stay at the Psychiatric Institute of Washington. Her mom considered moving the family back to Guatemala.
Kaliamurthy, Liseth’s doctor, advised them to stay in the U.S. and started the girl on monthly injections of extended-release buprenorphine , a medication commonly used to treat opioid use disorder that blunts withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Finally, things are turning around. She is eating again, looking healthy and — unable to go to school where drugs are ubiquitous — ready to start a GED program.
How families can approach youth opioid use
- Talk to your teen about your concerns. Ask about use by friends and classmates as well
- Remind your child that you love them and will be there to support them
- Consider involving a health professional or counselor soon as possible
- Remind your teen to have Narcan available and to never use alone
- Look out for small, constricted “pinpoint pupils”
- Choking or gurgling sounds
- Slow, shallow breathing
- Limp body; loss of consciousness
- Having pale, blue or cold skin
- Call 911 for emergency medical help.
- Give naloxone (if available) which can reverse the effects of an opioid overdose
- Keep your child or teen awake and breathing by rubbing their chest with your knuckles
- Lay them on their side to prevent choking if they vomit
- Stay with your child or teen until professional help arrives
- Pick it up free at participating pharmacies in each ward
- Text LiveLongDC to 888-811 and an outreach worker will deliver it within two business days
- Fill out a form online to have it mailed to your home in discrete packaging
- Contact a Public Overdose Response Program to pick up free naloxone or have it delivered to your home
- Naloxone may also be found in your local pharmacy and billed to insurance and Medicaid.
- For more information or if you need help finding naloxone, contact [email protected]
- Ask about free naloxone at your local Community Service Board or health department
- Most pharmacies sell a two-pack of naloxone nasal sprays over the counter for about $45
Provisional data released in May by the CDC showed a slight decrease in overdose deaths among all ages across the country last year — heralded by some public health leaders as a glimmer of progress.
The contrasting increase among youths is especially troubling, experts say, because when and where counterfeit pills can trigger a spate of overdoses is unpredictable. Teens are especially vulnerable to the consequences of hidden fentanyl as many are experimenting and have no tolerance to opioids, Hadland said.
A spate of nonfatal overdoses in Loudoun and a suspected overdose in Arlington last year prompted schools to institute drug-sniffing dogs and embrace the overdose antidote naloxone, adding it to first aid kits and allowing students to carry it.
As prevention techniques ramp up, officials are seeking more ways to expand intensive treatment options for adolescents who need inpatient and outpatient care, using medication and individual, group and family therapy. The District this year sought a teen residential treatment provider and awarded the Children’s National clinic an $830,000 contract to expand outpatient substance use services.
For adolescents on public insurance, there are no residential treatment options in D.C. and only a few spots in Maryland, leaving youths to navigate the challenges of outpatient care while surrounded by triggers.
“If you live with people who are using drugs, if you go to school with people who are using drugs, if you encounter people between home and school using drugs … It’s very hard to stay sober,” Smith said.
The mother of a 16-year-old from Silver Spring, who spoke on the condition of anonymity to protect her daughter’s privacy with the teen’s permission, said it never occurred to her that any of her daughter’s friends would be using fentanyl or that her child could become addicted.
Then her daughter’s girlfriend died, and she noticed the teen was spending more time alone. The family smelled the telltale odor of fentanyl fumes, like burnt tires, emanating from the basement.
They turned to Children’s National, where she was already receiving mental health care, and entered an intensive outpatient treatment program. After bristling at the daily reminder of her struggle when taking daily buprenorphine as a tablet, she switched to a longer-acting injection form of the drug and started to feel better.
There are hard days, but the family feels lucky to be able to navigate insurance hurdles and afford the out-of-pocket costs associated with her treatment.
The spike is driving public health experts to rethink preventive drug education for young people. Guidance should present not using drugs as the safest choice but also include information about reducing risk for those who choose to experiment, Mass General’s Hadland and a co-author said in a New England Journal of Medicine article earlier this year.
“We always say to teenagers, ‘Don’t use drugs,’” said Abraham, the Children’s National adolescent medicine specialist. “But I will also say that the nature of being a young person, is that they’re going to try things — especially when you tell them not to.”
David Ovalle contributed to this report.

108 Drug Abuse Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best drug abuse topic ideas & essay examples, 👍 good essay topics on drug abuse, 💡 most interesting drug abuse topics to write about, ❓ drug abuse research questions.
Drug abuse essays are an excellent way to learn about the issue and its influence on various groups and populations while demonstrating your understanding.
Various substances, including alcohol, narcotics, and other mind-altering products, are a popular method for recreation in some communities.
However, they are prone to result in addiction, psychological as well as mental, and lead the person to pursue another dose before anything else.
In doing so, he or she can eventually ruin his or her life, which is why most drugs are currently banned around the world. This article will offer you some tips that will help you write an excellent essay and receive the top grade.
Youth is a major demographic that is affected by addiction issues due to drug consumption. Young people are impressionable and prone to search for new sensations. Drugs can offer a sense of novelty and provide an experience they have not had before, leading to considerable appeal.
Considering that young people are generally not wealthy and have to focus on work to succeed in life, essays on drug among youth can use a variety of excellent topics. You can offer your ideas on the reason for the phenomenon’s existence and ways in which it can be prevented.
However, remember that the purpose of the programs should be to help the people who are at risk.
There are many other drug abuse essay topics that you can explore, with poverty being a prominent example. Despite their conditions, many people turn to substance abuse to try and escape the unpleasant aspects of their life.
These population segments are more likely to suffer after acquiring a drug habit than young people because they generally receive less attention.
Furthermore, poor neighborhoods with relatively low amounts of surveillance by law enforcement are likely to house drug dealers who prey on vulnerable people.
You can discuss this topic or discuss a variety of other ones, as the relationship between poverty and poor outcomes has been researched deeply.
Here are some additional tips for your essay:
- Try to use examples to illustrate your points about various aspects of the issue. Drug addiction essay quotations from people who are affected by the condition or have overcome it can offer valuable insights. They also legitimize your findings by providing parallels with the real world.
- Alcohol essays are an excellent choice, as the substance is legal and available to everyone without much difficulty. Nevertheless, its effects can be devastating, especially if a person’s consumption is chronic.
- Try to write a drug abuse essay outline before starting work, as it will help you to organize the essay. Select some prominent ideas that you want to discuss and organize them in a manner that represents a logical progression. You do not have to discard all of the other concepts, as you can make them sub-headings under your main titles.
- Be sure to include a drug abuse essay introduction and conclusion in your work. They will help you provide a structure to the essay and make it easier for the reader to understand your ideas. The introduction should describe the topic and provide the thesis, and the conclusion should restate your main points.
Visit IvyPanda for drug abuse essay titles, and other useful samples on various subjects to help you with your writing work!
- Social Media Impact on Drug Abuse Thus, social media platforms definitely contribute to the misuse of various drugs by romanticizing their consumption and making “social drug use” acceptable among users.
- Drug Trafficking and Drug Abuse Drug trafficking contributes to drug abuse in the society. Drug trafficking also contributes to increased criminal activities that affect the security of citizens.
- Drug and Alcohol Abuse For along time now, drug and alcohol abuse in the society has been a problem that affects the youth and the society at large. This paper highlights the problems of drug abuse and alcohol drinking […]
- Drug Abuse and Current Generation Drug abuse also breeds an array of behavioral problems among young people, which may affect their suitability to fit in the society.
- Consequences of Drug Abuse The endless stream of drugs, obtainable to the individuals with little or no restrictions, poses a serious inquiry. When assessing the advantages of using pharmaceutical drugs, it is essential to consider the severity of health […]
- Drug Abuse & Its Effects on Families Focusing on the family seems to be by far, the most known and effective way of finding a solution with regards to the “war on drugs” since it more promising to end the vicious cycle […]
- Merton’s Argument of Deviance: The Case of Drug Abuse The most prominent example in support of Merton’s argument in relation to drug abuse is that cultural and social circumstances play a crucial role in defining people’s desire to engage in drug use.
- Teenage Drug Abuse in the United States The problem of teenage drug abuse inflicts a threat to the future society and health state of the overall population in the United States.
- Drug and Substance Abuse Many experts consider addiction as a disease as it affects a specific part of the brain; the limbic system commonly referred to as the pleasure center.
- Drug Abuse in Adolescents and Its Causes Scientific research shows that the development factors for adolescent drug abuse are not limited to a set of three to five causes, but are usually linked to the integration of destructive environmental conditions.
- Drug Abuse Among the Youth Essentially, this case study will allow the evaluation of the prevailing cases of drug abuse among the youth. In this regard, the pain and peer pleasure cannot be persevered to allow an explicit cure of […]
- Drug Abuse in High School and College With respect to social work and the problem of substance abuse, research has been carried out in terms of investigating the relationship between drug abuse and poverty, the effects of drug abuse on the society.
- “Cocaine: Abuse and Addiction” by National Institute on Drug Abuse The literature provides us with a report of a research that has been conducted in the US regarding the topic of cocaine and drug abuse.
- Drug Abuse in Lake County, California The topic of drug abuse is essential for discussion due to the need to develop strategies to prevent and minimize the dangerous consequences of drug abuse in different regions.
- Community Intervention Practices Against Drug Abuse The key features that result in successful community-based intervention on drug abuse are integrated for effectiveness and efficiency. On the other hand, drug abuse refers to the consumption of substances that elicit particular feelings and […]
- Drug Abuse and Prevention Strategies When specialists deal with preventative factors, they pay attention to both mental and physical ways to resist the drug. The symbiosis of these procedures is exceptionally efficient in terms of the drug rehabilitation process when […]
- A New Alcohol and Drug-Abuse Rehabilitation Center in Liverpool Hospital, Sydney The hospital, in response to this distress, has decided to bring help closer to the people of Liverpool by the construction of the annex facility.
- Music Analysis: Drug Abuse in Music So in this song the artist is also lamenting the dangers of drugs and the theme of the music is one that advocates against tackling the problem with issues of drug abuse by arguing the […]
- Drug Abuse. “Nine Years Under” Book by Sheri Booker The book is thought provoking and important because it allows representing the difficult social situation and the problems of gang violence and drugs in the United States from the personal point of view.
- Impact of Drug Abuse on Adolescent Development Therefore, it is important for counselors to consider these stages to help them address the issue of substance abuse among adolescents. In the habitual stage, most adolescents take drugs to help them modify their moods.
- Reasons Behind Youth’s Engagement to Drug Abuse in the 21st Century Although youths in the 21st century engage in drug abuse due to several factors, it suffices to declare factors such as the rising unemployment status, peer pressure, and their hiked tendency to copy their parents’ […]
- Drug Abuse as a Social Problem This poses as problem to the society because many of the people who are unemployed will resort to different ways of seeking money and pleasure.
- Drug Abuse and Its Psychological Effects The purpose of this paper is to explore in more depth the psychological effects of addiction on the family and inner circle of the addict.
- Drug Abuse, Aggression and Antisocial Behavior The use of abusive drugs can cause anger in people because of the effect they have on the brain. An example of how alcohol can cause aggression in a person is that it impairs an […]
- Policies for Pregnant Women With Drug Abuse Thus, out of all the offered policies, financial support for therapy is the best one, as it motivates prevention and treatment, which, in turn, causes the improvement of this situation.
- The Formative Evaluation: Program of Addressing Drug Abuse in Schools The proposed program sought to educate students about the challenges of drug abuse, its impacts on academic performance, and the best techniques to avoid the vice.
- Alcohol and Drug Abuse in Canada Therefore, it contributes as a central factor in the essence of the character, and it is crucial to understand the core definition and the elements that foster the ideology.
- Mitigating Drug Abuse in Pine View School The inclusion of professionals in the fields of health care, counseling, and drugs is expected to promote the delivery of desirable results.
- Drug Abuse and Its Negative Effects This paper aims to highlight what the field of psychology says about the negative effects of drugs and why people continue using despite the consequences. The main effect is that it creates a memory of […]
- Prevention Programs: Drug Abuse Resistance Education This program focuses on handling peer pressure among youths, a crucial cause of drug abuse in the country. The program is also grounded on sound research, which offers the critical elements vital to handling the […]
- Drug Abuse Among Homeless Young Adults in New Jersey The reason why young adults in New Jersey get involved in drugs and alcohol after becoming homeless is to manage their situations in an attempt to attain the tentative pleasure of life despite their problems. […]
- Drug Abuse Effects on Health and Nervous System These numerous damages severely affect the quality of the brains work and the health of the nervous system. While discussing the effects of drug addiction, it is essential to notice that it has a devastating […]
- Substance Abuse: Prevention Strategies and National Benchmarks Still, this desire to get away from problems by means of substances instead of making effort to improve an individual’s environment contributed to the evolution of the challenge of substance abuse into a real public […]
- Alcoholism, Domestic Violence and Drug Abuse Kaur and Ajinkya researched to investigate the “psychological impact of adult alcoholism on spouses and children”. The work of Kaur and Ajinkya, reveals a link between chronic alcoholism and emotional problems on the spouse and […]
- Monitoring the Future: National Survey Results on Drug Use National survey results on drug use obtained by Monitoring the Future have a significant value to the development of various approaches with regard to the prevention of drug abuse.
- The Health Issues Associated With Drug Abuse It is therefore imperative to develop strategies for health promotion to reduce the number of teenagers, the most at-risk family member when it comes to drug abuse.
- Fentanyl – Drug Profile and Specific and Drug Abuse The drug has the effect of depressing the respiratory center, constricting the pupils, as well as depressing the cough reflex. The remainder 75% of fentanyl is swallowed and absorbed in G-tract.
- Cases of Drug Abuse Amongst Nursing Professionals It is noteworthy that at the top of the information, the date posted is Monday, February 14, 2011, yet against the information, the date is February 11, 2011.
- The Treatment of Drug Abuse Any medical practitioner treating a drug abuse patient has to be careful in many aspects, like: He has to be careful on the issue that if the addiction has effected the brain of the patient.
- Drug Courts and Detoxification: Approach to Drug Abuse Treatment However, since 1989, the US federal system has been providing the majority of drug abusers with proper treatment or education with the help of a drug court option.
- Drug Abuse in Adolescents Aged 15-19 Years Old: A Public Health Menace In addition, the objectives of the paper are as follows: the first aim is to analyze the collected data and produce a review of the information.
- Drug Abuse and Addiction Holimon has succeeded in reviving some of her family relations, and she is still putting a lot of effort to get ahead in this area to the fullest extent possible.
- Sports as a Solution to Youth Substance Abuse: Dr. Collingwood’s View His comments made me realize that it would be unwise by the end of the day for any parent to leave their children under the mercy of the media where they learned that doing drugs […]
- Intervention Techniques Focusing Drug Abuse and Alcoholism A technique of Family Intervention needs the concern, care and supremacy of love to penetrate the denial and start the treatment.
- Critical Issues in Education: Drug Abuse and Alcoholism For this case, the ministry concerned has a very hard task of ensuring there are no critical issues that are left unsolved that relate to education, failure to which will affect the performance of students […]
- The DARE (Drug Abuse Resistance Education) Program’s Effectiveness While evaluating the effectiveness of the DARE program analysis in accordance with the methodologies and evaluation criteria used, the given assessments refer to various methods of the analysis of participants, as well as various data […]
- Depression and Drug Dependence Treatment and Support She states that her father was the main person who was able to give the right pieces of advice and she was not afraid of making the wrong decision.
- Drug Abuse and Dependence: Insights from Clients and Professionals If either the client or the professional wishes to determine the extent to which an individual is dependent on drugs, the only thing he or she would have to do is read the individual’s behavior.
- Biopsychosocial Experience in Drug Abuse Treatment There has to be a preventive strategy in every intervention procedure to avoid the occurrence of a disease. I find the course of treatment in this intervention beneficial for the creation of the needed preventive […]
- Addictive Behavior Programs and Drug Abuse Trends The involvement of stakeholders is an essential condition for the effectiveness of this model of work and its results, and all the roles should be allocated in accordance with the capabilities of the program’s participants.
- Substance Misuse in American Youth: A Socio-Cultural Analysis The paper analyzes studies regarding some of the most widespread types of substances, as well as discusses the role of the rap culture in the growing number of young addicts in the U.S.
- Social Behaviour as a Science: Drug Abuse in Youth Thus, the application of social psychology to the phenomenon of youth drug abuse helps to explain how social factors impact the prevalence of and risk for drug abuse.
- ACTIQ Prescription Drug Abuse The fast-acting characteristic of ACTIQ is a result of being absorbed in the mucosal lining of the mouth. ACTIQ is a synthetic drug that is available as lozenges/lollipops, which are designed to be sucked in […]
- Prescription Drug Abuse and Lebanon Students The first two authors are the representatives of the Department of Epidemiology and Population Health at the American University of Beirut, and Martins is from the Department of Mental Health, the John Hopkins University.
- Financial Planning for Drug Abuse Prevention in Virginia Estates Therefore, the first preferred sources for the program are the County Commission and the Alabama Department of Corrections. The program can be financed by the Montgomery County Commission in the short term and Alabama Department […]
- Addressing the Drug Abuse in Parolees and Probationers The aim of the program is to address the drug abuse in parolees and probationers during their probations and decrease the use of drugs in them.
- Problem of Drug Abuse in Schools The research worked on the hypothesis that the treatment would reduce or result in the total cessation of drug use, and better relations with family and friends.
- Youth Drug Abuse Among, Education, and Policies Although drug abuse encompasses improper use of drugs disregarding the prescriptions of medical practitioners, the principal challenges of drug abuse occasion from abuse of drugs such as cocaine, heroin, and marijuana.
- Prescription Drug Abuse in the United States The combination of Ibuprofen and acetaminophen are effective for the patients, who want to reduce and control the level of pain.
- Drug Use Among Parolees and Probationers: A Comprehensive Plan To reduce drug use in probationers and the probability of a new crime, the approach to drug testing needs to be changed.
- Drug Abuse and Medicaid Program The emergence of alcohol and drug abuse as a problem and the intensification of people with mental health problems, have exposed the society to the likelihood of involvement of the population in substance abuse.
- Drug Abuse: Age, Gender and Addictive Susceptibility This incorporates the aspects of gender where males and females possess varying biological constitutions that might affect the prescribed treatments in the realms of addiction. It is important to consider the rapidity and susceptibility of […]
- Prevention Research: The Fight Against Drug Abuse It is agreeable that US’s ‘War on Drugs’ has been an effective substance abuse prevention plan despite the hiccups that the program faces and its inability to attain some of its designated mandates within the […]
- Drug Abuse Prevention Programs Additionally, it is possible to prospect the success of the program in case the required readiness from the community can be unveiled prior to the program execution.
- The Cultural Context and Ethics of Prevention of Drug Abuse The first prevention strategy outlined in the document is the involvement of young people in all levels of the prevention program establishment. Concurrently, it is crucial to relate this technique with the subject of culture […]
- Use of Psychotropic Medications in the Treatment of Drug Abuse This is because the mental illness is, literally, the one that sustains the abuse of drugs and thus after it is healed; the patient will have no reason to continue abusing the drugs.
- Drug Abuse: Awareness Amongst the Youths This project is going to carry out a public awareness campaign with the aim of educating the young people on the hazards related to the vice of drug and substance abuse. The awareness campaign is […]
- Spirituality Effect on Drug Abuse Treatment Programs The hypothesis of the study was that spirituality is appropriate in the formal treatment of addiction; the study confirmed this hypothesis.
- Drug Abuse and Religious Spirituality Concept Particularly, this high rate of relapses was determined by Olmstead et al.as a direct result of a degree of failure on the part of drug abuse treatment programs to sufficiently address the primary reason why […]
- Drug Abuse and Harmful Health Effects The principle recognizes the importance of helping drug addicts out of the activity but also sees the importance of protecting their rights to health matters if the country is to realize economic development.
- The Extent of Drug Abuse Among People in America Toronto Mayor Rob Ford Said He Lied about Crack Cocaine Use Because He Was Embarrassed Mayor lied about the use of crack cocaine The article titled “Toronto Mayor Rob Ford said he lied about crack […]
- Drug Use and Abuse in America: Historical Analysis The new law was similar to the Boggs Act of 1951 in that it employed the same formula of using perceived increase in drug use in the country.
- Drug Abuse as an Ethical Issue On the side of duties and obligations, the societal norms stipulate that individuals should be caring to other members of the society especially the children and the old.
- Drug Abuse and Society Regardless of the many intervention measures that can be adopted to solve this problem of drug abuse, the most effective intervention measure is to create awareness to youths to enable them change their behaviors and […]
- Prescription Painkillers, the New Drug Abuse of Choice Studies attribute the recent increase in the misuse of prescription drugs to an increase in the use of the Internet, which facilitates the growth of illegitimate online drug stores and uncontrolled online prescription drug sales.
- Drug Abuse: Comprehensive Review The effects associated with drug abuse tend to vary depending on an individual’s age and the phase of drug abuse that the person is in.
- Adolescent’s Drug Abuse and Therapy Success When one accepts to put up with negative peer pressure, they end up giving up the personal trusts and values thus the pressure becomes a form of a negative force.”Does peer pressure affect the decision […]
- What Are Influences That Cause Drug Abuse on Youth?
- What Are Some Solutions to Drug Abuse?
- What Are the Primary Causes and Effects of Alcoholism and Drug Abuse Among Young People?
- What Causes Teenage Drug Abuse?
- What Does Drug Abuse Truly?
- Why Do Children Need to Be Educated About Drug Abuse?
- Why Has the American Government Not Managed to Stop Drug Abuse All These Years?
- How Does Drug Abuse Affect Personal Development of Hong Kong Teenagers?
- How Does Pericarditis Form Due to Drug Abuse?
- How Drug Abuse Ruins Families and Destroys Relationships?
- How Does Prescription Drug Abuse Affect Teens?
- Does the Drug Abuse Resistance Education Program Work?
- What Is the Drug of Abuse?
- What Are the Four Types of Drugs Abused?
- Which Is an Example of Drug Abuse?
- What Is the Leading Cause of Drug Abuse?
- What Are the Causes and Effects of Drug Abuse?
- What Are the Main Consequences of Drug Abuse?
- How Does Drug Abuse Affect Our Society?
- How Can We Prevent Drug Abuse?
- Why Is It Essential to Prevent Drugs?
- What Are the Ten Most Abused Drugs?
- How Do Drugs Affect Mental Health?
- What Are the Effects of Drug Abuse on Youths?
- What Is the Connection Between Adolescents From Divorced Families and Drug Abuse?
- Are Alcohol and Drug Abuse the Most Common Issues of Today?
- What Is Athletes’ Motivation for Performance-Enhancement Drug Abuse?
- What Is the Correlation Between Parietal and Adolescent Drug Abuse?
- How Is Dealing With Teenage Drug Abuse?
- What Is the Difference Between Drug Use and Drug Abuse?
- Crime Ideas
- Alcohol Abuse Paper Topics
- Mental Health Essay Ideas
- Human Behavior Research Topics
- Mental Illness Research Topics
- AIDS Titles
- Criminal Behavior Essay Topics
- Juvenile Delinquency Essay Titles
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 26). 108 Drug Abuse Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/drug-abuse-essay-examples/
"108 Drug Abuse Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 26 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/drug-abuse-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '108 Drug Abuse Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 26 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "108 Drug Abuse Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/drug-abuse-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "108 Drug Abuse Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/drug-abuse-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "108 Drug Abuse Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/drug-abuse-essay-examples/.
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- About Child Abuse and Neglect
- Risk and Protective Factors
- Public Health Strategy
- Essentials for Childhood Framework
Preventing Child Abuse and Neglect
- Offering children safe, stable, nurturing relationships and environments prevents child abuse and neglect.
- Training and treatment for children and families can reduce short- and long-term effects of child abuse and neglect.
- Everyone has a role to play in preventing child abuse and neglect.

Creating safe, stable, nurturing relationships and environments is essential for helping children and families thrive. These relationships and environments also help protect children against or lessen the negative effects of violence.
Safety, stability, and nurturing are defined as follows:
- Safety: extent to which a child is free from fear and secure from physical or psychological harm within their social and physical environment.
- Stability: degree of predictability and consistency in a child's social, emotional, and physical environment.
- Nurturing: extent to which a child's physical, emotional, and developmental needs are sensitively and consistently met.
Everyone has a role to play in preventing child abuse and neglect and helping all children reach their full potential.
Parents and Caregivers
Young children experience the world through their relationships with parents and other caregivers. The quality of these relationships and the environment in which they develop, play a significant role in a child's development. Parents and caregivers can:
- Set aside time each day to talk or play with your child.
- Establish routines. Children feel secure when the environment is structured for them.
- Validate your child's feelings and offer physical and emotional support.
- Know who is supervising your child when they're outside your home.
- Teach your child how to stay safe when they're online or on digital devices.
- Seek parenting skill training programs to help build stronger relationships with your children.
Raising children can be challenging— ask for help when needed . Reach out to babysitters, family members, or close friends. Discuss your concerns with your child's doctor. Also consider finding out if your community offers support groups or programs for parents and caregivers.
Resource
Ensuring the well-being of children is a shared responsibility. Friends, family, and other trusted adults can help by developing nurturing, supportive relationships with the children in their lives. Volunteering as a mentor at an afterschool program or offering to babysit are other ways to help.
Neighborhood associations can connect families to resources and other neighborhood adults to help with household tasks or with childcare.
Employers can adopt or support workplace policies that help families, such as livable wages, paid leave, and flexible and consistent schedules.
Everyone can recognize the challenges that families face and offer support and encouragement to reduce stress. Help encourage parents and caregivers to ask for help when they need it. Everyone can also support efforts to:
- Adopt policies in support of families (such as family-friendly work policies).
- Increase access to high-quality childcare and education.
- Create safe places or neighborhood activities where children are supervised, and families can gather.
- Provide access to free or low-cost evidence-based parent training.
- Discourage violence and help ensure the safety of all members of a community.
Public health practitioners, partners, and other professionals also play a vital role in preventing child abuse and neglect.
Training and treatment for children and families can reduce the short- and long-term effects of child abuse and neglect exposure. These effects can include physical, emotional, behavioral, and mental health issues. It can also improve parent-child interactions, parenting behaviors, and family functioning. Treatment for children and families can also help prevent later involvement in violence.
These are a few evidence-based resources that promote safe, stable, nurturing relationships and environments.
- Early Head Start : These programs are designed to nurture healthy attachments. Services encompass the full range of a family's needs from pregnancy through a child's third birthday.
- Adults and Children Together Against Violence: Parents Raising Safe Kids (ACT) : The program teaches positive parenting skills to parents and caregivers of children from birth to age 10.
- SafeCare : The program focuses on creating positive relationships between caregivers and their children, ensuring homes are safe to reduce the risk of child unintentional injury, and keeping children as healthy as possible.
Child Abuse and Neglect Prevention
Child abuse and neglect can have long-term impact on health, opportunity, and well-being. CDC works to understand the problems of child abuse and neglect and prevent them.
For Everyone
Public health.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essay on Drug Addiction in Youth. Drug addiction has become a worldwide problem, especially in teenagers. Many young people become dependent on different types substances and stimulating medicines that comes hand-in-hand with narcotic effect. The life of addicts becomes spoiled in all aspects, as they lose contact with their family and live in ...
250 Words Essay on Drug Addiction Among Youth The Escalating Issue of Drug Addiction Among Youth. Drug addiction among youth is an alarming issue that has been escalating globally. The vulnerability of the younger demographic to substance abuse is a result of various factors, including peer pressure, stress, and the quest for self-discovery. ...
In 2022, about 1 in 3 high school seniors, 1 in 5 sophomores, and 1 in 10 eighth graders reported using an illicit substance in the past year, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse's (NIDA) annual survey (Monitoring the Future: National Survey Results on Drug Use, 1975-2022: Secondary School Students, NIDA, 2023 [PDF, 7.78MB]).Those numbers were down significantly from ...
Drug addiction, also called substance use disorder, is a. disease that affects a person's brain and behavior and leads to. an inability to control the use of a legal or illegal drug or. medication ...
Around the world, adolescent drug and alcohol addiction has significantly increased morbidity and mortality. The menace of drugs and alcohol has been woven deep into the fabric of society. As its effects reach our youth, India's current generation is at high stake for the risk associated with the abuse of drugs like cannabis, alcohol, and tobacco.
500 Words Essay on Impact of Drugs on Youth Introduction. The global landscape of drug abuse and addiction is a complex issue that has significant implications on the youth. The impact of drugs on youth is far-reaching, affecting not just their physical health, but also their mental well-being, academic performance, and future prospects.
The four stages of drug addiction. Partnership to End Addiction. Preventing drug use: connecting and talking with your teen. SAMHSA. Talking with teens about alcohol and other drugs. American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP). Substance abuse treatment for children and adolescents: questions to ask.
Teens who experiment with drugs and other substances put their health and safety at risk. The teen brain is particularly vulnerable to being rewired by substances that overload the reward circuits in the brain. Help prevent teen drug abuse by talking to your teen about the consequences of using drugs and the importance of making healthy choices.
Most youth who use substances do not become addicted; however, the prevalence of substance use disorders is still quite high, with 15% of youth meeting diagnostic criteria for alcohol abuse and 16% for drug abuse by age 18 (Swendsen et al. 2012). Tobacco, alcohol, and marijuana are typically the first addictive substances that youth try.
Introduction. Drug addiction is a serious problem, and while it spreads to less marginalized parts of society, this problem affects more people. Mattapan Community faced unprecedentedly increasing risks for youth drug addiction among school students. This paper presents the critical aspects of the initiative implementation and creates a basis ...
Cannabis is a consistently available illicit drug that adolescents abuse. An increase in the prices of illicit substances affects the rates of abuse. The cheaper the illegal drugs are, the easier it is for adolescents to access them. An example is from the survey conducted by Molinaro et al. (2011) on cannabis.
1) No/ Low perceived risk increase the odds of past-month marijuana use by 8.22 times compared to those who perceived moderate/great risk. 2) High perceived availability of drug: consistently associated with higher odds of past-month marijuana use. Protective Factors. 1) Moderate/ High perceived risk of substance use.
Background Substance use among youth (ages 12-24) is troublesome given the increasing risk of harms associated. Even more so, substance use services are largely underutilized among youth, most only accessing support when in crisis. Few studies have explored young people's help-seeking behaviours to address substance use concerns. To address this gap, this study explored how youth perceive ...
250 Words Essay on Drugs On Youth Introduction. Drugs can harm young people in many ways. They can change how the brain works, making it hard for youth to think, learn, and make good choices. ... Drugs and Addiction. Drugs can be very addictive. This means that once a young person starts using drugs, it can be hard for them to stop. ...
The following essay discusses the drug addiction with its underlying causes, its impacts and possible solutions for our youth. The essay is in simple language with easy to understand way. It would surely help primary, high school and college level students. Drug addiction Essay; Major Causes, Impacts & Possible Solution
The most recent drug use estimates were drawn from surveys of more than 22,000 students in eighth, 10th and 12th grade across 235 public and private schools. The Top 10 Causes of Death in the U.S.
Substance abuse during adolescence. The use of substances by youth is described primarily as intermittent or intensive (binge) drinking and characterized by experimentation and expediency (Degenhardt et al., Citation 2016; Morojele & Ramsoomar, Citation 2016; Romo-Avilés et al., Citation 2016).Intermittent or intensive substance use is linked to the adolescent's need for activities that ...
Drug abuse can result to depression and suicide as depicted in Jessica's case where she loses self-control. The use of marijuana can affect the intellectual capacity and working capabilities of an individual. This is evident when the addicted person loses the vigor to work and becomes careless. The victims of drug abuse lose the effective ...
Due to the article named "Youth begging for drugs" on the Mayo Clinic, the most significant factor that contributes to the drug addiction in the youth in the whole country today is lack of knowledge about drugs. ... How to prevent Drug addiction (essay) Illegal drugs tend to be highly addictive compared to those that are legal and cause far ...
Teenage drug abuse is one of the largest problems in society today and the problem grows and larger every year. Drugs are a pervasive force in our culture today. To expect kids not to be influenced by the culture of their time is as unrealistic as believing in the tooth fairy (Bauman 140). Teens may feel pressured by their friends to try drugs ...
Drug addiction, also known as substance-use disorder, refers to the dangerous and excessive intake of legal and illegal drugs. This leads to many behavioral changes in the person as well as affects brain functions. Drug addiction includes abusing alcohol, cocaine, heroin, opioid, painkillers, and nicotine, among others.
The pandemic has given rise to concerns about the mental health and social well-being of youth, including its potential to increase or exacerbate substance use behaviors. This systematic review identified and included 49 studies of use across alcohol, cannabis, tobacco, e-cigarettes/vaping, and other drugs, and unspecified substances.
smoking of cigarettes and gradually drowns the person into the trap of drug abuse. Stress, anxiety, peer pressure, poverty are some of the main causes of drug abuse.As is well said -"it is ...
Fentanyl is fueling a record number of youth drug deaths. The new trend has shocked many pediatricians, who say they feel unprepared to provide counseling on opioid addiction. By Jenna Portnoy ...
To learn more about technical assistance services or if you have a question please email NCSACW at [email protected] or call toll-free at 1-866-493-2758. The National Center on Substance Abuse and Child Welfare (NCSACW) created this four-part tip sheet series for child welfare, SUD treatment, court, and health care professionals to ...
Overview. In the United States, youth use e-cigarettes, or vapes, more than any other tobacco product. 1. No tobacco products, including e-cigarettes, are safe, especially for children, teens, and young adults. 2. Most e-cigarettes contain nicotine, which is highly addictive. Nicotine can harm the parts of an adolescent's brain that control ...
Fentanyl - Drug Profile and Specific and Drug Abuse. The drug has the effect of depressing the respiratory center, constricting the pupils, as well as depressing the cough reflex. The remainder 75% of fentanyl is swallowed and absorbed in G-tract. Cases of Drug Abuse Amongst Nursing Professionals.
Toxic stress, or extended or prolonged stress, from ACEs can negatively affect children's brain development, immune systems, and stress-response systems. These changes can affect children's attention, decision-making, and learning. 18. Children growing up with toxic stress may have difficulty forming healthy and stable relationships.
PRESS RELEASE — The North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services today announced the distribution of $6,250,000 to seven counties to provide youth substance use prevention within their communities. NCDHHS applied for and was awarded the funding through the U. S. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, as part of its National Drug Control Strategy.
Key points. Offering children safe, stable, nurturing relationships and environments prevents child abuse and neglect. Training and treatment for children and families can reduce short- and long-term effects of child abuse and neglect. Everyone has a role to play in preventing child abuse and neglect.