Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write a Conclusion for Research Papers (with Examples)

The conclusion of a research paper is a crucial section that plays a significant role in the overall impact and effectiveness of your research paper. However, this is also the section that typically receives less attention compared to the introduction and the body of the paper. The conclusion serves to provide a concise summary of the key findings, their significance, their implications, and a sense of closure to the study. Discussing how can the findings be applied in real-world scenarios or inform policy, practice, or decision-making is especially valuable to practitioners and policymakers. The research paper conclusion also provides researchers with clear insights and valuable information for their own work, which they can then build on and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
The research paper conclusion should explain the significance of your findings within the broader context of your field. It restates how your results contribute to the existing body of knowledge and whether they confirm or challenge existing theories or hypotheses. Also, by identifying unanswered questions or areas requiring further investigation, your awareness of the broader research landscape can be demonstrated.
Remember to tailor the research paper conclusion to the specific needs and interests of your intended audience, which may include researchers, practitioners, policymakers, or a combination of these.
Table of Contents
What is a conclusion in a research paper, summarizing conclusion, editorial conclusion, externalizing conclusion, importance of a good research paper conclusion, how to write a conclusion for your research paper, research paper conclusion examples.
- How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
Frequently Asked Questions
A conclusion in a research paper is the final section where you summarize and wrap up your research, presenting the key findings and insights derived from your study. The research paper conclusion is not the place to introduce new information or data that was not discussed in the main body of the paper. When working on how to conclude a research paper, remember to stick to summarizing and interpreting existing content. The research paper conclusion serves the following purposes: 1
- Warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem.
- Recommend specific course(s) of action.
- Restate key ideas to drive home the ultimate point of your research paper.
- Provide a “take-home” message that you want the readers to remember about your study.

Types of conclusions for research papers
In research papers, the conclusion provides closure to the reader. The type of research paper conclusion you choose depends on the nature of your study, your goals, and your target audience. I provide you with three common types of conclusions:
A summarizing conclusion is the most common type of conclusion in research papers. It involves summarizing the main points, reiterating the research question, and restating the significance of the findings. This common type of research paper conclusion is used across different disciplines.
An editorial conclusion is less common but can be used in research papers that are focused on proposing or advocating for a particular viewpoint or policy. It involves presenting a strong editorial or opinion based on the research findings and offering recommendations or calls to action.
An externalizing conclusion is a type of conclusion that extends the research beyond the scope of the paper by suggesting potential future research directions or discussing the broader implications of the findings. This type of conclusion is often used in more theoretical or exploratory research papers.
Align your conclusion’s tone with the rest of your research paper. Start Writing with Paperpal Now!
The conclusion in a research paper serves several important purposes:
- Offers Implications and Recommendations : Your research paper conclusion is an excellent place to discuss the broader implications of your research and suggest potential areas for further study. It’s also an opportunity to offer practical recommendations based on your findings.
- Provides Closure : A good research paper conclusion provides a sense of closure to your paper. It should leave the reader with a feeling that they have reached the end of a well-structured and thought-provoking research project.
- Leaves a Lasting Impression : Writing a well-crafted research paper conclusion leaves a lasting impression on your readers. It’s your final opportunity to leave them with a new idea, a call to action, or a memorable quote.

Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper is essential to leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here’s a step-by-step process to help you create and know what to put in the conclusion of a research paper: 2
- Research Statement : Begin your research paper conclusion by restating your research statement. This reminds the reader of the main point you’ve been trying to prove throughout your paper. Keep it concise and clear.
- Key Points : Summarize the main arguments and key points you’ve made in your paper. Avoid introducing new information in the research paper conclusion. Instead, provide a concise overview of what you’ve discussed in the body of your paper.
- Address the Research Questions : If your research paper is based on specific research questions or hypotheses, briefly address whether you’ve answered them or achieved your research goals. Discuss the significance of your findings in this context.
- Significance : Highlight the importance of your research and its relevance in the broader context. Explain why your findings matter and how they contribute to the existing knowledge in your field.
- Implications : Explore the practical or theoretical implications of your research. How might your findings impact future research, policy, or real-world applications? Consider the “so what?” question.
- Future Research : Offer suggestions for future research in your area. What questions or aspects remain unanswered or warrant further investigation? This shows that your work opens the door for future exploration.
- Closing Thought : Conclude your research paper conclusion with a thought-provoking or memorable statement. This can leave a lasting impression on your readers and wrap up your paper effectively. Avoid introducing new information or arguments here.
- Proofread and Revise : Carefully proofread your conclusion for grammar, spelling, and clarity. Ensure that your ideas flow smoothly and that your conclusion is coherent and well-structured.
Write your research paper conclusion 2x faster with Paperpal. Try it now!
Remember that a well-crafted research paper conclusion is a reflection of the strength of your research and your ability to communicate its significance effectively. It should leave a lasting impression on your readers and tie together all the threads of your paper. Now you know how to start the conclusion of a research paper and what elements to include to make it impactful, let’s look at a research paper conclusion sample.

How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
A research paper conclusion is not just a summary of your study, but a synthesis of the key findings that ties the research together and places it in a broader context. A research paper conclusion should be concise, typically around one paragraph in length. However, some complex topics may require a longer conclusion to ensure the reader is left with a clear understanding of the study’s significance. Paperpal, an AI writing assistant trusted by over 800,000 academics globally, can help you write a well-structured conclusion for your research paper.
- Sign Up or Log In: Create a new Paperpal account or login with your details.
- Navigate to Features : Once logged in, head over to the features’ side navigation pane. Click on Templates and you’ll find a suite of generative AI features to help you write better, faster.
- Generate an outline: Under Templates, select ‘Outlines’. Choose ‘Research article’ as your document type.
- Select your section: Since you’re focusing on the conclusion, select this section when prompted.
- Choose your field of study: Identifying your field of study allows Paperpal to provide more targeted suggestions, ensuring the relevance of your conclusion to your specific area of research.
- Provide a brief description of your study: Enter details about your research topic and findings. This information helps Paperpal generate a tailored outline that aligns with your paper’s content.
- Generate the conclusion outline: After entering all necessary details, click on ‘generate’. Paperpal will then create a structured outline for your conclusion, to help you start writing and build upon the outline.
- Write your conclusion: Use the generated outline to build your conclusion. The outline serves as a guide, ensuring you cover all critical aspects of a strong conclusion, from summarizing key findings to highlighting the research’s implications.
- Refine and enhance: Paperpal’s ‘Make Academic’ feature can be particularly useful in the final stages. Select any paragraph of your conclusion and use this feature to elevate the academic tone, ensuring your writing is aligned to the academic journal standards.
By following these steps, Paperpal not only simplifies the process of writing a research paper conclusion but also ensures it is impactful, concise, and aligned with academic standards. Sign up with Paperpal today and write your research paper conclusion 2x faster .
The research paper conclusion is a crucial part of your paper as it provides the final opportunity to leave a strong impression on your readers. In the research paper conclusion, summarize the main points of your research paper by restating your research statement, highlighting the most important findings, addressing the research questions or objectives, explaining the broader context of the study, discussing the significance of your findings, providing recommendations if applicable, and emphasizing the takeaway message. The main purpose of the conclusion is to remind the reader of the main point or argument of your paper and to provide a clear and concise summary of the key findings and their implications. All these elements should feature on your list of what to put in the conclusion of a research paper to create a strong final statement for your work.
A strong conclusion is a critical component of a research paper, as it provides an opportunity to wrap up your arguments, reiterate your main points, and leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here are the key elements of a strong research paper conclusion: 1. Conciseness : A research paper conclusion should be concise and to the point. It should not introduce new information or ideas that were not discussed in the body of the paper. 2. Summarization : The research paper conclusion should be comprehensive enough to give the reader a clear understanding of the research’s main contributions. 3 . Relevance : Ensure that the information included in the research paper conclusion is directly relevant to the research paper’s main topic and objectives; avoid unnecessary details. 4 . Connection to the Introduction : A well-structured research paper conclusion often revisits the key points made in the introduction and shows how the research has addressed the initial questions or objectives. 5. Emphasis : Highlight the significance and implications of your research. Why is your study important? What are the broader implications or applications of your findings? 6 . Call to Action : Include a call to action or a recommendation for future research or action based on your findings.
The length of a research paper conclusion can vary depending on several factors, including the overall length of the paper, the complexity of the research, and the specific journal requirements. While there is no strict rule for the length of a conclusion, but it’s generally advisable to keep it relatively short. A typical research paper conclusion might be around 5-10% of the paper’s total length. For example, if your paper is 10 pages long, the conclusion might be roughly half a page to one page in length.
In general, you do not need to include citations in the research paper conclusion. Citations are typically reserved for the body of the paper to support your arguments and provide evidence for your claims. However, there may be some exceptions to this rule: 1. If you are drawing a direct quote or paraphrasing a specific source in your research paper conclusion, you should include a citation to give proper credit to the original author. 2. If your conclusion refers to or discusses specific research, data, or sources that are crucial to the overall argument, citations can be included to reinforce your conclusion’s validity.
The conclusion of a research paper serves several important purposes: 1. Summarize the Key Points 2. Reinforce the Main Argument 3. Provide Closure 4. Offer Insights or Implications 5. Engage the Reader. 6. Reflect on Limitations
Remember that the primary purpose of the research paper conclusion is to leave a lasting impression on the reader, reinforcing the key points and providing closure to your research. It’s often the last part of the paper that the reader will see, so it should be strong and well-crafted.
- Makar, G., Foltz, C., Lendner, M., & Vaccaro, A. R. (2018). How to write effective discussion and conclusion sections. Clinical spine surgery, 31(8), 345-346.
- Bunton, D. (2005). The structure of PhD conclusion chapters. Journal of English for academic purposes , 4 (3), 207-224.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
- Paraphrasing in Academic Writing: Answering Top Author Queries
Preflight For Editorial Desk: The Perfect Hybrid (AI + Human) Assistance Against Compromised Manuscripts
You may also like, how to write a high-quality conference paper, academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , should you use ai tools like chatgpt for....
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 9. The Conclusion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research. For most college-level research papers, two or three well-developed paragraphs is sufficient for a conclusion, although in some cases, more paragraphs may be required in describing the key findings and their significance.
Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Importance of a Good Conclusion
A well-written conclusion provides you with important opportunities to demonstrate to the reader your understanding of the research problem. These include:
- Presenting the last word on the issues you raised in your paper . Just as the introduction gives a first impression to your reader, the conclusion offers a chance to leave a lasting impression. Do this, for example, by highlighting key findings in your analysis that advance new understanding about the research problem, that are unusual or unexpected, or that have important implications applied to practice.
- Summarizing your thoughts and conveying the larger significance of your study . The conclusion is an opportunity to succinctly re-emphasize your answer to the "So What?" question by placing the study within the context of how your research advances past research about the topic.
- Identifying how a gap in the literature has been addressed . The conclusion can be where you describe how a previously identified gap in the literature [first identified in your literature review section] has been addressed by your research and why this contribution is significant.
- Demonstrating the importance of your ideas . Don't be shy. The conclusion offers an opportunity to elaborate on the impact and significance of your findings. This is particularly important if your study approached examining the research problem from an unusual or innovative perspective.
- Introducing possible new or expanded ways of thinking about the research problem . This does not refer to introducing new information [which should be avoided], but to offer new insight and creative approaches for framing or contextualizing the research problem based on the results of your study.
Bunton, David. “The Structure of PhD Conclusion Chapters.” Journal of English for Academic Purposes 4 (July 2005): 207–224; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Rules
The general function of your paper's conclusion is to restate the main argument . It reminds the reader of the strengths of your main argument(s) and reiterates the most important evidence supporting those argument(s). Do this by clearly summarizing the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem you investigated in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found in the literature. However, make sure that your conclusion is not simply a repetitive summary of the findings. This reduces the impact of the argument(s) you have developed in your paper.
When writing the conclusion to your paper, follow these general rules:
- Present your conclusions in clear, concise language. Re-state the purpose of your study, then describe how your findings differ or support those of other studies and why [i.e., what were the unique, new, or crucial contributions your study made to the overall research about your topic?].
- Do not simply reiterate your findings or the discussion of your results. Provide a synthesis of arguments presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem and the overall objectives of your study.
- Indicate opportunities for future research if you haven't already done so in the discussion section of your paper. Highlighting the need for further research provides the reader with evidence that you have an in-depth awareness of the research problem but that further investigations should take place beyond the scope of your investigation.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is presented well:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If, prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from the data [this is opposite of the introduction, which begins with general discussion of the context and ends with a detailed description of the research problem].
The conclusion also provides a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate the research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with all the information about the topic . Depending on the discipline you are writing in, the concluding paragraph may contain your reflections on the evidence presented. However, the nature of being introspective about the research you have conducted will depend on the topic and whether your professor wants you to express your observations in this way. If asked to think introspectively about the topics, do not delve into idle speculation. Being introspective means looking within yourself as an author to try and understand an issue more deeply, not to guess at possible outcomes or make up scenarios not supported by the evidence.
II. Developing a Compelling Conclusion
Although an effective conclusion needs to be clear and succinct, it does not need to be written passively or lack a compelling narrative. Strategies to help you move beyond merely summarizing the key points of your research paper may include any of the following:
- If your essay deals with a critical, contemporary problem, warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem proactively.
- Recommend a specific course or courses of action that, if adopted, could address a specific problem in practice or in the development of new knowledge leading to positive change.
- Cite a relevant quotation or expert opinion already noted in your paper in order to lend authority and support to the conclusion(s) you have reached [a good source would be from your literature review].
- Explain the consequences of your research in a way that elicits action or demonstrates urgency in seeking change.
- Restate a key statistic, fact, or visual image to emphasize the most important finding of your paper.
- If your discipline encourages personal reflection, illustrate your concluding point by drawing from your own life experiences.
- Return to an anecdote, an example, or a quotation that you presented in your introduction, but add further insight derived from the findings of your study; use your interpretation of results from your study to recast it in new or important ways.
- Provide a "take-home" message in the form of a succinct, declarative statement that you want the reader to remember about your study.
III. Problems to Avoid
Failure to be concise Your conclusion section should be concise and to the point. Conclusions that are too lengthy often have unnecessary information in them. The conclusion is not the place for details about your methodology or results. Although you should give a summary of what was learned from your research, this summary should be relatively brief, since the emphasis in the conclusion is on the implications, evaluations, insights, and other forms of analysis that you make. Strategies for writing concisely can be found here .
Failure to comment on larger, more significant issues In the introduction, your task was to move from the general [the field of study] to the specific [the research problem]. However, in the conclusion, your task is to move from a specific discussion [your research problem] back to a general discussion framed around the implications and significance of your findings [i.e., how your research contributes new understanding or fills an important gap in the literature]. In short, the conclusion is where you should place your research within a larger context [visualize your paper as an hourglass--start with a broad introduction and review of the literature, move to the specific analysis and discussion, conclude with a broad summary of the study's implications and significance].
Failure to reveal problems and negative results Negative aspects of the research process should never be ignored. These are problems, deficiencies, or challenges encountered during your study. They should be summarized as a way of qualifying your overall conclusions. If you encountered negative or unintended results [i.e., findings that are validated outside the research context in which they were generated], you must report them in the results section and discuss their implications in the discussion section of your paper. In the conclusion, use negative results as an opportunity to explain their possible significance and/or how they may form the basis for future research.
Failure to provide a clear summary of what was learned In order to be able to discuss how your research fits within your field of study [and possibly the world at large], you need to summarize briefly and succinctly how it contributes to new knowledge or a new understanding about the research problem. This element of your conclusion may be only a few sentences long.
Failure to match the objectives of your research Often research objectives in the social and behavioral sciences change while the research is being carried out. This is not a problem unless you forget to go back and refine the original objectives in your introduction. As these changes emerge they must be documented so that they accurately reflect what you were trying to accomplish in your research [not what you thought you might accomplish when you began].
Resist the urge to apologize If you've immersed yourself in studying the research problem, you presumably should know a good deal about it [perhaps even more than your professor!]. Nevertheless, by the time you have finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you have produced. Repress those doubts! Don't undermine your authority as a researcher by saying something like, "This is just one approach to examining this problem; there may be other, much better approaches that...." The overall tone of your conclusion should convey confidence to the reader about the study's validity and realiability.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Concluding Paragraphs. College Writing Center at Meramec. St. Louis Community College; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Leibensperger, Summer. Draft Your Conclusion. Academic Center, the University of Houston-Victoria, 2003; Make Your Last Words Count. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin Madison; Miquel, Fuster-Marquez and Carmen Gregori-Signes. “Chapter Six: ‘Last but Not Least:’ Writing the Conclusion of Your Paper.” In Writing an Applied Linguistics Thesis or Dissertation: A Guide to Presenting Empirical Research . John Bitchener, editor. (Basingstoke,UK: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010), pp. 93-105; Tips for Writing a Good Conclusion. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Writing Conclusions. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Writing: Considering Structure and Organization. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Don't Belabor the Obvious!
Avoid phrases like "in conclusion...," "in summary...," or "in closing...." These phrases can be useful, even welcome, in oral presentations. But readers can see by the tell-tale section heading and number of pages remaining that they are reaching the end of your paper. You'll irritate your readers if you belabor the obvious.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Another Writing Tip
New Insight, Not New Information!
Don't surprise the reader with new information in your conclusion that was never referenced anywhere else in the paper. This why the conclusion rarely has citations to sources. If you have new information to present, add it to the discussion or other appropriate section of the paper. Note that, although no new information is introduced, the conclusion, along with the discussion section, is where you offer your most "original" contributions in the paper; the conclusion is where you describe the value of your research, demonstrate that you understand the material that you’ve presented, and position your findings within the larger context of scholarship on the topic, including describing how your research contributes new insights to that scholarship.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
- << Previous: Limitations of the Study
- Next: Appendices >>
- Last Updated: May 18, 2024 11:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
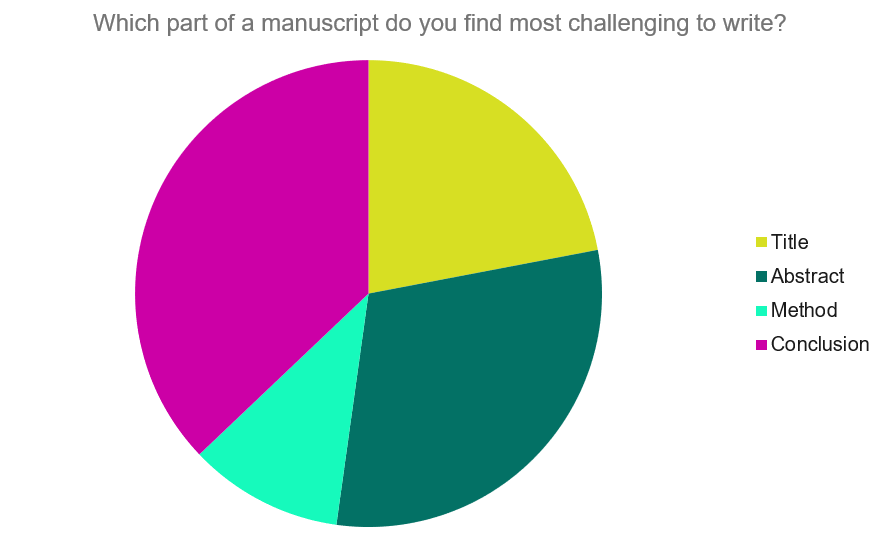
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
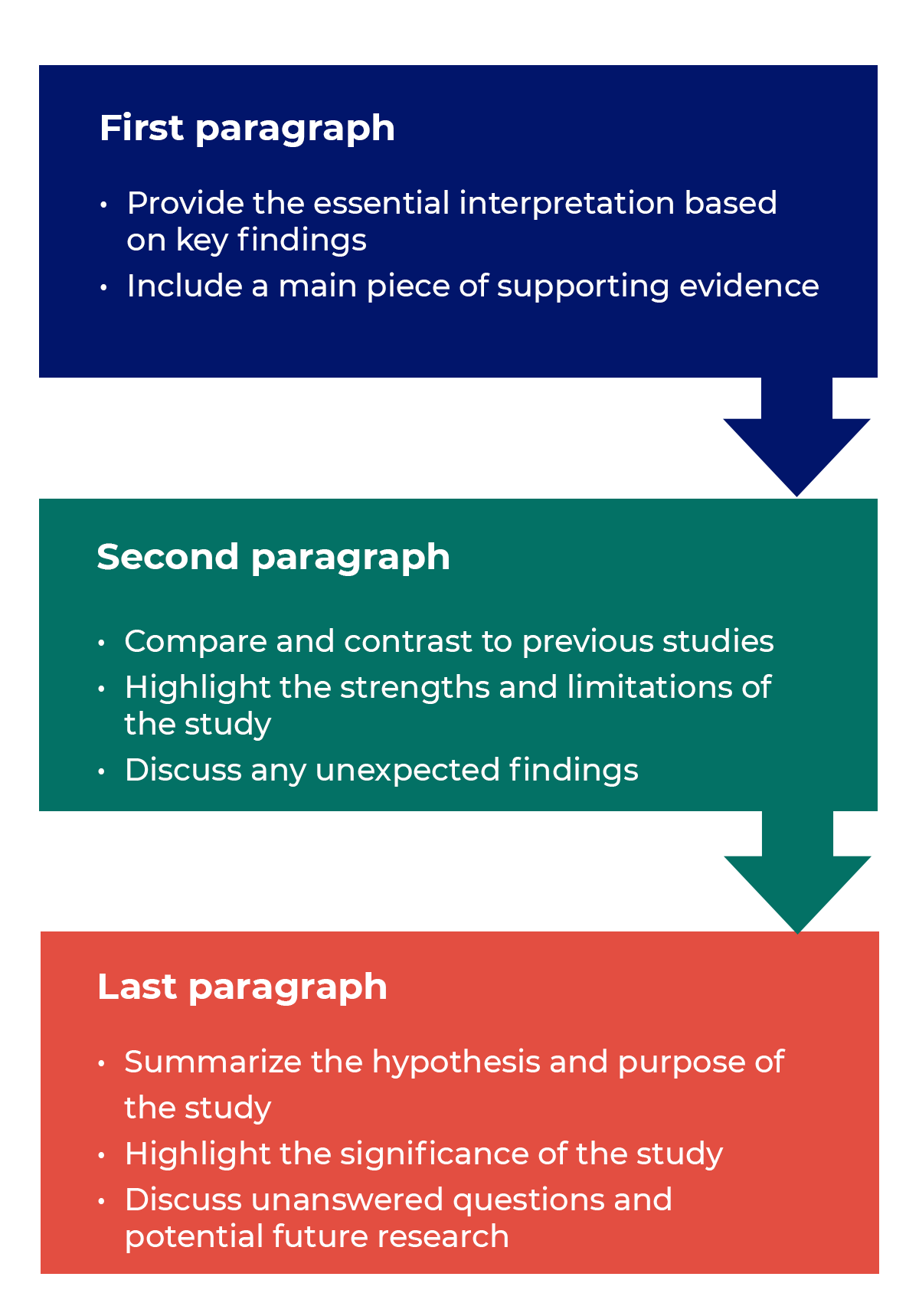
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
Published on 25 February 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research.
It should include:
- The type of research you conducted
- How you collected and analysed your data
- Any tools or materials you used in the research
- Why you chose these methods
- Your methodology section should generally be written in the past tense .
- Academic style guides in your field may provide detailed guidelines on what to include for different types of studies.
- Your citation style might provide guidelines for your methodology section (e.g., an APA Style methods section ).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to write a research methodology, why is a methods section important, step 1: explain your methodological approach, step 2: describe your data collection methods, step 3: describe your analysis method, step 4: evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made, tips for writing a strong methodology chapter, frequently asked questions about methodology.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Your methods section is your opportunity to share how you conducted your research and why you chose the methods you chose. It’s also the place to show that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated .
It gives your research legitimacy and situates it within your field, and also gives your readers a place to refer to if they have any questions or critiques in other sections.
You can start by introducing your overall approach to your research. You have two options here.
Option 1: Start with your “what”
What research problem or question did you investigate?
- Aim to describe the characteristics of something?
- Explore an under-researched topic?
- Establish a causal relationship?
And what type of data did you need to achieve this aim?
- Quantitative data , qualitative data , or a mix of both?
- Primary data collected yourself, or secondary data collected by someone else?
- Experimental data gathered by controlling and manipulating variables, or descriptive data gathered via observations?
Option 2: Start with your “why”
Depending on your discipline, you can also start with a discussion of the rationale and assumptions underpinning your methodology. In other words, why did you choose these methods for your study?
- Why is this the best way to answer your research question?
- Is this a standard methodology in your field, or does it require justification?
- Were there any ethical considerations involved in your choices?
- What are the criteria for validity and reliability in this type of research ?
Once you have introduced your reader to your methodological approach, you should share full details about your data collection methods .
Quantitative methods
In order to be considered generalisable, you should describe quantitative research methods in enough detail for another researcher to replicate your study.
Here, explain how you operationalised your concepts and measured your variables. Discuss your sampling method or inclusion/exclusion criteria, as well as any tools, procedures, and materials you used to gather your data.
Surveys Describe where, when, and how the survey was conducted.
- How did you design the questionnaire?
- What form did your questions take (e.g., multiple choice, Likert scale )?
- Were your surveys conducted in-person or virtually?
- What sampling method did you use to select participants?
- What was your sample size and response rate?
Experiments Share full details of the tools, techniques, and procedures you used to conduct your experiment.
- How did you design the experiment ?
- How did you recruit participants?
- How did you manipulate and measure the variables ?
- What tools did you use?
Existing data Explain how you gathered and selected the material (such as datasets or archival data) that you used in your analysis.
- Where did you source the material?
- How was the data originally produced?
- What criteria did you use to select material (e.g., date range)?
The survey consisted of 5 multiple-choice questions and 10 questions measured on a 7-point Likert scale.
The goal was to collect survey responses from 350 customers visiting the fitness apparel company’s brick-and-mortar location in Boston on 4–8 July 2022, between 11:00 and 15:00.
Here, a customer was defined as a person who had purchased a product from the company on the day they took the survey. Participants were given 5 minutes to fill in the survey anonymously. In total, 408 customers responded, but not all surveys were fully completed. Due to this, 371 survey results were included in the analysis.
Qualitative methods
In qualitative research , methods are often more flexible and subjective. For this reason, it’s crucial to robustly explain the methodology choices you made.
Be sure to discuss the criteria you used to select your data, the context in which your research was conducted, and the role you played in collecting your data (e.g., were you an active participant, or a passive observer?)
Interviews or focus groups Describe where, when, and how the interviews were conducted.
- How did you find and select participants?
- How many participants took part?
- What form did the interviews take ( structured , semi-structured , or unstructured )?
- How long were the interviews?
- How were they recorded?
Participant observation Describe where, when, and how you conducted the observation or ethnography .
- What group or community did you observe? How long did you spend there?
- How did you gain access to this group? What role did you play in the community?
- How long did you spend conducting the research? Where was it located?
- How did you record your data (e.g., audiovisual recordings, note-taking)?
Existing data Explain how you selected case study materials for your analysis.
- What type of materials did you analyse?
- How did you select them?
In order to gain better insight into possibilities for future improvement of the fitness shop’s product range, semi-structured interviews were conducted with 8 returning customers.
Here, a returning customer was defined as someone who usually bought products at least twice a week from the store.
Surveys were used to select participants. Interviews were conducted in a small office next to the cash register and lasted approximately 20 minutes each. Answers were recorded by note-taking, and seven interviews were also filmed with consent. One interviewee preferred not to be filmed.
Mixed methods
Mixed methods research combines quantitative and qualitative approaches. If a standalone quantitative or qualitative study is insufficient to answer your research question, mixed methods may be a good fit for you.
Mixed methods are less common than standalone analyses, largely because they require a great deal of effort to pull off successfully. If you choose to pursue mixed methods, it’s especially important to robustly justify your methods here.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Next, you should indicate how you processed and analysed your data. Avoid going into too much detail: you should not start introducing or discussing any of your results at this stage.
In quantitative research , your analysis will be based on numbers. In your methods section, you can include:
- How you prepared the data before analysing it (e.g., checking for missing data , removing outliers , transforming variables)
- Which software you used (e.g., SPSS, Stata or R)
- Which statistical tests you used (e.g., two-tailed t test , simple linear regression )
In qualitative research, your analysis will be based on language, images, and observations (often involving some form of textual analysis ).
Specific methods might include:
- Content analysis : Categorising and discussing the meaning of words, phrases and sentences
- Thematic analysis : Coding and closely examining the data to identify broad themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying communication and meaning in relation to their social context
Mixed methods combine the above two research methods, integrating both qualitative and quantitative approaches into one coherent analytical process.
Above all, your methodology section should clearly make the case for why you chose the methods you did. This is especially true if you did not take the most standard approach to your topic. In this case, discuss why other methods were not suitable for your objectives, and show how this approach contributes new knowledge or understanding.
In any case, it should be overwhelmingly clear to your reader that you set yourself up for success in terms of your methodology’s design. Show how your methods should lead to results that are valid and reliable, while leaving the analysis of the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results for your discussion section .
- Quantitative: Lab-based experiments cannot always accurately simulate real-life situations and behaviours, but they are effective for testing causal relationships between variables .
- Qualitative: Unstructured interviews usually produce results that cannot be generalised beyond the sample group , but they provide a more in-depth understanding of participants’ perceptions, motivations, and emotions.
- Mixed methods: Despite issues systematically comparing differing types of data, a solely quantitative study would not sufficiently incorporate the lived experience of each participant, while a solely qualitative study would be insufficiently generalisable.
Remember that your aim is not just to describe your methods, but to show how and why you applied them. Again, it’s critical to demonstrate that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated.
1. Focus on your objectives and research questions
The methodology section should clearly show why your methods suit your objectives and convince the reader that you chose the best possible approach to answering your problem statement and research questions .
2. Cite relevant sources
Your methodology can be strengthened by referencing existing research in your field. This can help you to:
- Show that you followed established practice for your type of research
- Discuss how you decided on your approach by evaluating existing research
- Present a novel methodological approach to address a gap in the literature
3. Write for your audience
Consider how much information you need to give, and avoid getting too lengthy. If you are using methods that are standard for your discipline, you probably don’t need to give a lot of background or justification.
Regardless, your methodology should be a clear, well-structured text that makes an argument for your approach, not just a list of technical details and procedures.
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research. Developing your methodology involves studying the research methods used in your field and the theories or principles that underpin them, in order to choose the approach that best matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyse data (e.g. interviews, experiments , surveys , statistical tests ).
In a dissertation or scientific paper, the methodology chapter or methods section comes after the introduction and before the results , discussion and conclusion .
Depending on the length and type of document, you might also include a literature review or theoretical framework before the methodology.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/methodology/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide.
How to write a strong conclusion for your research paper
Last updated
17 February 2024
Reviewed by
Writing a research paper is a chance to share your knowledge and hypothesis. It's an opportunity to demonstrate your many hours of research and prove your ability to write convincingly.
Ideally, by the end of your research paper, you'll have brought your readers on a journey to reach the conclusions you've pre-determined. However, if you don't stick the landing with a good conclusion, you'll risk losing your reader’s trust.
Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper involves a few important steps, including restating the thesis and summing up everything properly.
Find out what to include and what to avoid, so you can effectively demonstrate your understanding of the topic and prove your expertise.
- Why is a good conclusion important?
A good conclusion can cement your paper in the reader’s mind. Making a strong impression in your introduction can draw your readers in, but it's the conclusion that will inspire them.
- What to include in a research paper conclusion
There are a few specifics you should include in your research paper conclusion. Offer your readers some sense of urgency or consequence by pointing out why they should care about the topic you have covered. Discuss any common problems associated with your topic and provide suggestions as to how these problems can be solved or addressed.
The conclusion should include a restatement of your initial thesis. Thesis statements are strengthened after you’ve presented supporting evidence (as you will have done in the paper), so make a point to reintroduce it at the end.
Finally, recap the main points of your research paper, highlighting the key takeaways you want readers to remember. If you've made multiple points throughout the paper, refer to the ones with the strongest supporting evidence.
- Steps for writing a research paper conclusion
Many writers find the conclusion the most challenging part of any research project . By following these three steps, you'll be prepared to write a conclusion that is effective and concise.
- Step 1: Restate the problem
Always begin by restating the research problem in the conclusion of a research paper. This serves to remind the reader of your hypothesis and refresh them on the main point of the paper.
When restating the problem, take care to avoid using exactly the same words you employed earlier in the paper.
- Step 2: Sum up the paper
After you've restated the problem, sum up the paper by revealing your overall findings. The method for this differs slightly, depending on whether you're crafting an argumentative paper or an empirical paper.
Argumentative paper: Restate your thesis and arguments
Argumentative papers involve introducing a thesis statement early on. In crafting the conclusion for an argumentative paper, always restate the thesis, outlining the way you've developed it throughout the entire paper.
It might be appropriate to mention any counterarguments in the conclusion, so you can demonstrate how your thesis is correct or how the data best supports your main points.
Empirical paper: Summarize research findings
Empirical papers break down a series of research questions. In your conclusion, discuss the findings your research revealed, including any information that surprised you.
Be clear about the conclusions you reached, and explain whether or not you expected to arrive at these particular ones.
- Step 3: Discuss the implications of your research
Argumentative papers and empirical papers also differ in this part of a research paper conclusion. Here are some tips on crafting conclusions for argumentative and empirical papers.
Argumentative paper: Powerful closing statement
In an argumentative paper, you'll have spent a great deal of time expressing the opinions you formed after doing a significant amount of research. Make a strong closing statement in your argumentative paper's conclusion to share the significance of your work.
You can outline the next steps through a bold call to action, or restate how powerful your ideas turned out to be.
Empirical paper: Directions for future research
Empirical papers are broader in scope. They usually cover a variety of aspects and can include several points of view.
To write a good conclusion for an empirical paper, suggest the type of research that could be done in the future, including methods for further investigation or outlining ways other researchers might proceed.
If you feel your research had any limitations, even if they were outside your control, you could mention these in your conclusion.
After you finish outlining your conclusion, ask someone to read it and offer feedback. In any research project you're especially close to, it can be hard to identify problem areas. Having a close friend or someone whose opinion you value read the research paper and provide honest feedback can be invaluable. Take note of any suggested edits and consider incorporating them into your paper if they make sense.
- Things to avoid in a research paper conclusion
Keep these aspects to avoid in mind as you're writing your conclusion and refer to them after you've created an outline.
Dry summary
Writing a memorable, succinct conclusion is arguably more important than a strong introduction. Take care to avoid just rephrasing your main points, and don't fall into the trap of repeating dry facts or citations.
You can provide a new perspective for your readers to think about or contextualize your research. Either way, make the conclusion vibrant and interesting, rather than a rote recitation of your research paper’s highlights.
Clichéd or generic phrasing
Your research paper conclusion should feel fresh and inspiring. Avoid generic phrases like "to sum up" or "in conclusion." These phrases tend to be overused, especially in an academic context and might turn your readers off.
The conclusion also isn't the time to introduce colloquial phrases or informal language. Retain a professional, confident tone consistent throughout your paper’s conclusion so it feels exciting and bold.
New data or evidence
While you should present strong data throughout your paper, the conclusion isn't the place to introduce new evidence. This is because readers are engaged in actively learning as they read through the body of your paper.
By the time they reach the conclusion, they will have formed an opinion one way or the other (hopefully in your favor!). Introducing new evidence in the conclusion will only serve to surprise or frustrate your reader.
Ignoring contradictory evidence
If your research reveals contradictory evidence, don't ignore it in the conclusion. This will damage your credibility as an expert and might even serve to highlight the contradictions.
Be as transparent as possible and admit to any shortcomings in your research, but don't dwell on them for too long.
Ambiguous or unclear resolutions
The point of a research paper conclusion is to provide closure and bring all your ideas together. You should wrap up any arguments you introduced in the paper and tie up any loose ends, while demonstrating why your research and data are strong.
Use direct language in your conclusion and avoid ambiguity. Even if some of the data and sources you cite are inconclusive or contradictory, note this in your conclusion to come across as confident and trustworthy.
- Examples of research paper conclusions
Your research paper should provide a compelling close to the paper as a whole, highlighting your research and hard work. While the conclusion should represent your unique style, these examples offer a starting point:
Ultimately, the data we examined all point to the same conclusion: Encouraging a good work-life balance improves employee productivity and benefits the company overall. The research suggests that when employees feel their personal lives are valued and respected by their employers, they are more likely to be productive when at work. In addition, company turnover tends to be reduced when employees have a balance between their personal and professional lives. While additional research is required to establish ways companies can support employees in creating a stronger work-life balance, it's clear the need is there.
Social media is a primary method of communication among young people. As we've seen in the data presented, most young people in high school use a variety of social media applications at least every hour, including Instagram and Facebook. While social media is an avenue for connection with peers, research increasingly suggests that social media use correlates with body image issues. Young girls with lower self-esteem tend to use social media more often than those who don't log onto social media apps every day. As new applications continue to gain popularity, and as more high school students are given smartphones, more research will be required to measure the effects of prolonged social media use.
What are the different kinds of research paper conclusions?
There are no formal types of research paper conclusions. Ultimately, the conclusion depends on the outline of your paper and the type of research you’re presenting. While some experts note that research papers can end with a new perspective or commentary, most papers should conclude with a combination of both. The most important aspect of a good research paper conclusion is that it accurately represents the body of the paper.
Can I present new arguments in my research paper conclusion?
Research paper conclusions are not the place to introduce new data or arguments. The body of your paper is where you should share research and insights, where the reader is actively absorbing the content. By the time a reader reaches the conclusion of the research paper, they should have formed their opinion. Introducing new arguments in the conclusion can take a reader by surprise, and not in a positive way. It might also serve to frustrate readers.
How long should a research paper conclusion be?
There's no set length for a research paper conclusion. However, it's a good idea not to run on too long, since conclusions are supposed to be succinct. A good rule of thumb is to keep your conclusion around 5 to 10 percent of the paper's total length. If your paper is 10 pages, try to keep your conclusion under one page.
What should I include in a research paper conclusion?
A good research paper conclusion should always include a sense of urgency, so the reader can see how and why the topic should matter to them. You can also note some recommended actions to help fix the problem and some obstacles they might encounter. A conclusion should also remind the reader of the thesis statement, along with the main points you covered in the paper. At the end of the conclusion, add a powerful closing statement that helps cement the paper in the mind of the reader.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Methodology
Definition:
Research Methodology refers to the systematic and scientific approach used to conduct research, investigate problems, and gather data and information for a specific purpose. It involves the techniques and procedures used to identify, collect , analyze , and interpret data to answer research questions or solve research problems . Moreover, They are philosophical and theoretical frameworks that guide the research process.
Structure of Research Methodology
Research methodology formats can vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project, but the following is a basic example of a structure for a research methodology section:
I. Introduction
- Provide an overview of the research problem and the need for a research methodology section
- Outline the main research questions and objectives
II. Research Design
- Explain the research design chosen and why it is appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Discuss any alternative research designs considered and why they were not chosen
- Describe the research setting and participants (if applicable)
III. Data Collection Methods
- Describe the methods used to collect data (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations)
- Explain how the data collection methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or instruments used for data collection
IV. Data Analysis Methods
- Describe the methods used to analyze the data (e.g., statistical analysis, content analysis )
- Explain how the data analysis methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or software used for data analysis
V. Ethical Considerations
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise from the research and how they were addressed
- Explain how informed consent was obtained (if applicable)
- Detail any measures taken to ensure confidentiality and anonymity
VI. Limitations
- Identify any potential limitations of the research methodology and how they may impact the results and conclusions
VII. Conclusion
- Summarize the key aspects of the research methodology section
- Explain how the research methodology addresses the research question(s) and objectives
Research Methodology Types
Types of Research Methodology are as follows:
Quantitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of numerical data using statistical methods. This type of research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Qualitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
Mixed-Methods Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that combines elements of both quantitative and qualitative research. This approach can be particularly useful for studies that aim to explore complex phenomena and to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular topic.
Case Study Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves in-depth examination of a single case or a small number of cases. Case studies are often used in psychology, sociology, and anthropology to gain a detailed understanding of a particular individual or group.
Action Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves a collaborative process between researchers and practitioners to identify and solve real-world problems. Action research is often used in education, healthcare, and social work.
Experimental Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the manipulation of one or more independent variables to observe their effects on a dependent variable. Experimental research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Survey Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection of data from a sample of individuals using questionnaires or interviews. Survey research is often used to study attitudes, opinions, and behaviors.
Grounded Theory Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the development of theories based on the data collected during the research process. Grounded theory is often used in sociology and anthropology to generate theories about social phenomena.
Research Methodology Example
An Example of Research Methodology could be the following:
Research Methodology for Investigating the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Reducing Symptoms of Depression in Adults
Introduction:
The aim of this research is to investigate the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. To achieve this objective, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) will be conducted using a mixed-methods approach.
Research Design:
The study will follow a pre-test and post-test design with two groups: an experimental group receiving CBT and a control group receiving no intervention. The study will also include a qualitative component, in which semi-structured interviews will be conducted with a subset of participants to explore their experiences of receiving CBT.
Participants:
Participants will be recruited from community mental health clinics in the local area. The sample will consist of 100 adults aged 18-65 years old who meet the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder. Participants will be randomly assigned to either the experimental group or the control group.
Intervention :
The experimental group will receive 12 weekly sessions of CBT, each lasting 60 minutes. The intervention will be delivered by licensed mental health professionals who have been trained in CBT. The control group will receive no intervention during the study period.
Data Collection:
Quantitative data will be collected through the use of standardized measures such as the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7). Data will be collected at baseline, immediately after the intervention, and at a 3-month follow-up. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a subset of participants from the experimental group. The interviews will be conducted at the end of the intervention period, and will explore participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-tests, and mixed-model analyses of variance (ANOVA) to assess the effectiveness of the intervention. Qualitative data will be analyzed using thematic analysis to identify common themes and patterns in participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Ethical Considerations:
This study will comply with ethical guidelines for research involving human subjects. Participants will provide informed consent before participating in the study, and their privacy and confidentiality will be protected throughout the study. Any adverse events or reactions will be reported and managed appropriately.
Data Management:
All data collected will be kept confidential and stored securely using password-protected databases. Identifying information will be removed from qualitative data transcripts to ensure participants’ anonymity.
Limitations:
One potential limitation of this study is that it only focuses on one type of psychotherapy, CBT, and may not generalize to other types of therapy or interventions. Another limitation is that the study will only include participants from community mental health clinics, which may not be representative of the general population.
Conclusion:
This research aims to investigate the effectiveness of CBT in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. By using a randomized controlled trial and a mixed-methods approach, the study will provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying the relationship between CBT and depression. The results of this study will have important implications for the development of effective treatments for depression in clinical settings.
How to Write Research Methodology
Writing a research methodology involves explaining the methods and techniques you used to conduct research, collect data, and analyze results. It’s an essential section of any research paper or thesis, as it helps readers understand the validity and reliability of your findings. Here are the steps to write a research methodology:
- Start by explaining your research question: Begin the methodology section by restating your research question and explaining why it’s important. This helps readers understand the purpose of your research and the rationale behind your methods.
- Describe your research design: Explain the overall approach you used to conduct research. This could be a qualitative or quantitative research design, experimental or non-experimental, case study or survey, etc. Discuss the advantages and limitations of the chosen design.
- Discuss your sample: Describe the participants or subjects you included in your study. Include details such as their demographics, sampling method, sample size, and any exclusion criteria used.
- Describe your data collection methods : Explain how you collected data from your participants. This could include surveys, interviews, observations, questionnaires, or experiments. Include details on how you obtained informed consent, how you administered the tools, and how you minimized the risk of bias.
- Explain your data analysis techniques: Describe the methods you used to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, content analysis, thematic analysis, or discourse analysis. Explain how you dealt with missing data, outliers, and any other issues that arose during the analysis.
- Discuss the validity and reliability of your research : Explain how you ensured the validity and reliability of your study. This could include measures such as triangulation, member checking, peer review, or inter-coder reliability.
- Acknowledge any limitations of your research: Discuss any limitations of your study, including any potential threats to validity or generalizability. This helps readers understand the scope of your findings and how they might apply to other contexts.
- Provide a summary: End the methodology section by summarizing the methods and techniques you used to conduct your research. This provides a clear overview of your research methodology and helps readers understand the process you followed to arrive at your findings.
When to Write Research Methodology
Research methodology is typically written after the research proposal has been approved and before the actual research is conducted. It should be written prior to data collection and analysis, as it provides a clear roadmap for the research project.
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
The methodology should be written in a clear and concise manner, and it should be based on established research practices and standards. It is important to provide enough detail so that the reader can understand how the research was conducted and evaluate the validity of the results.
Applications of Research Methodology
Here are some of the applications of research methodology:
- To identify the research problem: Research methodology is used to identify the research problem, which is the first step in conducting any research.
- To design the research: Research methodology helps in designing the research by selecting the appropriate research method, research design, and sampling technique.
- To collect data: Research methodology provides a systematic approach to collect data from primary and secondary sources.
- To analyze data: Research methodology helps in analyzing the collected data using various statistical and non-statistical techniques.
- To test hypotheses: Research methodology provides a framework for testing hypotheses and drawing conclusions based on the analysis of data.
- To generalize findings: Research methodology helps in generalizing the findings of the research to the target population.
- To develop theories : Research methodology is used to develop new theories and modify existing theories based on the findings of the research.
- To evaluate programs and policies : Research methodology is used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and policies by collecting data and analyzing it.
- To improve decision-making: Research methodology helps in making informed decisions by providing reliable and valid data.
Purpose of Research Methodology
Research methodology serves several important purposes, including:
- To guide the research process: Research methodology provides a systematic framework for conducting research. It helps researchers to plan their research, define their research questions, and select appropriate methods and techniques for collecting and analyzing data.
- To ensure research quality: Research methodology helps researchers to ensure that their research is rigorous, reliable, and valid. It provides guidelines for minimizing bias and error in data collection and analysis, and for ensuring that research findings are accurate and trustworthy.
- To replicate research: Research methodology provides a clear and detailed account of the research process, making it possible for other researchers to replicate the study and verify its findings.
- To advance knowledge: Research methodology enables researchers to generate new knowledge and to contribute to the body of knowledge in their field. It provides a means for testing hypotheses, exploring new ideas, and discovering new insights.
- To inform decision-making: Research methodology provides evidence-based information that can inform policy and decision-making in a variety of fields, including medicine, public health, education, and business.
Advantages of Research Methodology
Research methodology has several advantages that make it a valuable tool for conducting research in various fields. Here are some of the key advantages of research methodology:
- Systematic and structured approach : Research methodology provides a systematic and structured approach to conducting research, which ensures that the research is conducted in a rigorous and comprehensive manner.
- Objectivity : Research methodology aims to ensure objectivity in the research process, which means that the research findings are based on evidence and not influenced by personal bias or subjective opinions.
- Replicability : Research methodology ensures that research can be replicated by other researchers, which is essential for validating research findings and ensuring their accuracy.
- Reliability : Research methodology aims to ensure that the research findings are reliable, which means that they are consistent and can be depended upon.
- Validity : Research methodology ensures that the research findings are valid, which means that they accurately reflect the research question or hypothesis being tested.
- Efficiency : Research methodology provides a structured and efficient way of conducting research, which helps to save time and resources.
- Flexibility : Research methodology allows researchers to choose the most appropriate research methods and techniques based on the research question, data availability, and other relevant factors.
- Scope for innovation: Research methodology provides scope for innovation and creativity in designing research studies and developing new research techniques.
Research Methodology Vs Research Methods
About the author.
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Organizing Academic Research Papers: 9. The Conclusion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of your points or a re-statement of your research problem but a synthesis of key points. For most essays, one well-developed paragraph is sufficient for a conclusion, although in some cases, a two-or-three paragraph conclusion may be required.
Importance of a Good Conclusion
A well-written conclusion provides you with several important opportunities to demonstrate your overall understanding of the research problem to the reader. These include:
- Presenting the last word on the issues you raised in your paper . Just as the introduction gives a first impression to your reader, the conclusion offers a chance to leave a lasting impression. Do this, for example, by highlighting key points in your analysis or findings.
- Summarizing your thoughts and conveying the larger implications of your study . The conclusion is an opportunity to succinctly answer the "so what?" question by placing the study within the context of past research about the topic you've investigated.
- Demonstrating the importance of your ideas . Don't be shy. The conclusion offers you a chance to elaborate on the significance of your findings.
- Introducing possible new or expanded ways of thinking about the research problem . This does not refer to introducing new information [which should be avoided], but to offer new insight and creative approaches for framing/contextualizing the research problem based on the results of your study.
Conclusions . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion . San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008.
Structure and Writing Style
https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2018/07/conclusions_uwmadison_writingcenter_aug2012.pdf I. General Rules
When writing the conclusion to your paper, follow these general rules:
- State your conclusions in clear, simple language.
- Do not simply reiterate your results or the discussion.
- Indicate opportunities for future research, as long as you haven't already done so in the discussion section of your paper.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to restate the main argument . It reminds the reader of the strengths of your main argument(s) and reiterates the most important evidence supporting those argument(s). Make sure, however, that your conclusion is not simply a repetitive summary of the findings because this reduces the impact of the argument(s) you have developed in your essay.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or point of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If, prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from the data.
The conclusion also provides a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with all the information about the topic . Depending on the discipline you are writing in, the concluding paragraph may contain your reflections on the evidence presented, or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the research you have done will depend on the topic and whether your professor wants you to express your observations in this way.
NOTE : Don't delve into idle speculation. Being introspective means looking within yourself as an author to try and understand an issue more deeply not to guess at possible outcomes.
II. Developing a Compelling Conclusion
Strategies to help you move beyond merely summarizing the key points of your research paper may include any of the following.
- If your essay deals with a contemporary problem, warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem.
- Recommend a specific course or courses of action.
- Cite a relevant quotation or expert opinion to lend authority to the conclusion you have reached [a good place to look is research from your literature review].
- Restate a key statistic, fact, or visual image to drive home the ultimate point of your paper.
- If your discipline encourages personal reflection, illustrate your concluding point with a relevant narrative drawn from your own life experiences.
- Return to an anecdote, an example, or a quotation that you introduced in your introduction, but add further insight that is derived from the findings of your study; use your interpretation of results to reframe it in new ways.
- Provide a "take-home" message in the form of a strong, succient statement that you want the reader to remember about your study.
III. Problems to Avoid Failure to be concise The conclusion section should be concise and to the point. Conclusions that are too long often have unnecessary detail. The conclusion section is not the place for details about your methodology or results. Although you should give a summary of what was learned from your research, this summary should be relatively brief, since the emphasis in the conclusion is on the implications, evaluations, insights, etc. that you make. Failure to comment on larger, more significant issues In the introduction, your task was to move from general [the field of study] to specific [your research problem]. However, in the conclusion, your task is to move from specific [your research problem] back to general [your field, i.e., how your research contributes new understanding or fills an important gap in the literature]. In other words, the conclusion is where you place your research within a larger context. Failure to reveal problems and negative results Negative aspects of the research process should never be ignored. Problems, drawbacks, and challenges encountered during your study should be included as a way of qualifying your overall conclusions. If you encountered negative results [findings that are validated outside the research context in which they were generated], you must report them in the results section of your paper. In the conclusion, use the negative results as an opportunity to explain how they provide information on which future research can be based. Failure to provide a clear summary of what was learned In order to be able to discuss how your research fits back into your field of study [and possibly the world at large], you need to summarize it briefly and directly. Often this element of your conclusion is only a few sentences long. Failure to match the objectives of your research Often research objectives change while the research is being carried out. This is not a problem unless you forget to go back and refine your original objectives in your introduction, as these changes emerge they must be documented so that they accurately reflect what you were trying to accomplish in your research [not what you thought you might accomplish when you began].
Resist the urge to apologize If you've immersed yourself in studying the research problem, you now know a good deal about it, perhaps even more than your professor! Nevertheless, by the time you have finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you have produced. Repress those doubts! Don't undermine your authority by saying something like, "This is just one approach to examining this problem; there may be other, much better approaches...."
Concluding Paragraphs. College Writing Center at Meramec. St. Louis Community College; Conclusions . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions . The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Leibensperger, Summer. Draft Your Conclusion. Academic Center, the University of Houston-Victoria, 2003; Make Your Last Words Count . The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Tips for Writing a Good Conclusion . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion . San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Writing Conclusions . Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Writing: Considering Structure and Organization . Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Don't Belabor the Obvious!
Avoid phrases like "in conclusion...," "in summary...," or "in closing...." These phrases can be useful, even welcome, in oral presentations. But readers can see by the tell-tale section heading and number of pages remaining to read, when an essay is about to end. You'll irritate your readers if you belabor the obvious.
Another Writing Tip
New Insight, Not New Information!
Don't surprise the reader with new information in your Conclusion that was never referenced anywhere else in the paper. If you have new information to present, add it to the Discussion or other appropriate section of the paper. Note that, although no actual new information is introduced, the conclusion is where you offer your most "original" contributions in the paper; it's where you describe the value of your research, demonstrate your understanding of the material that you’ve presented, and locate your findings within the larger context of scholarship on the topic.
- << Previous: Limitations of the Study
- Next: Appendices >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
- Open access
- Published: 07 September 2020
A tutorial on methodological studies: the what, when, how and why
- Lawrence Mbuagbaw ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5855-5461 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Daeria O. Lawson 1 ,
- Livia Puljak 4 ,
- David B. Allison 5 &
- Lehana Thabane 1 , 2 , 6 , 7 , 8
BMC Medical Research Methodology volume 20 , Article number: 226 ( 2020 ) Cite this article
39k Accesses
53 Citations
58 Altmetric
Metrics details
Methodological studies – studies that evaluate the design, analysis or reporting of other research-related reports – play an important role in health research. They help to highlight issues in the conduct of research with the aim of improving health research methodology, and ultimately reducing research waste.
We provide an overview of some of the key aspects of methodological studies such as what they are, and when, how and why they are done. We adopt a “frequently asked questions” format to facilitate reading this paper and provide multiple examples to help guide researchers interested in conducting methodological studies. Some of the topics addressed include: is it necessary to publish a study protocol? How to select relevant research reports and databases for a methodological study? What approaches to data extraction and statistical analysis should be considered when conducting a methodological study? What are potential threats to validity and is there a way to appraise the quality of methodological studies?
Appropriate reflection and application of basic principles of epidemiology and biostatistics are required in the design and analysis of methodological studies. This paper provides an introduction for further discussion about the conduct of methodological studies.
Peer Review reports
The field of meta-research (or research-on-research) has proliferated in recent years in response to issues with research quality and conduct [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. As the name suggests, this field targets issues with research design, conduct, analysis and reporting. Various types of research reports are often examined as the unit of analysis in these studies (e.g. abstracts, full manuscripts, trial registry entries). Like many other novel fields of research, meta-research has seen a proliferation of use before the development of reporting guidance. For example, this was the case with randomized trials for which risk of bias tools and reporting guidelines were only developed much later – after many trials had been published and noted to have limitations [ 4 , 5 ]; and for systematic reviews as well [ 6 , 7 , 8 ]. However, in the absence of formal guidance, studies that report on research differ substantially in how they are named, conducted and reported [ 9 , 10 ]. This creates challenges in identifying, summarizing and comparing them. In this tutorial paper, we will use the term methodological study to refer to any study that reports on the design, conduct, analysis or reporting of primary or secondary research-related reports (such as trial registry entries and conference abstracts).
In the past 10 years, there has been an increase in the use of terms related to methodological studies (based on records retrieved with a keyword search [in the title and abstract] for “methodological review” and “meta-epidemiological study” in PubMed up to December 2019), suggesting that these studies may be appearing more frequently in the literature. See Fig. 1 .
Trends in the number studies that mention “methodological review” or “meta-
epidemiological study” in PubMed.
The methods used in many methodological studies have been borrowed from systematic and scoping reviews. This practice has influenced the direction of the field, with many methodological studies including searches of electronic databases, screening of records, duplicate data extraction and assessments of risk of bias in the included studies. However, the research questions posed in methodological studies do not always require the approaches listed above, and guidance is needed on when and how to apply these methods to a methodological study. Even though methodological studies can be conducted on qualitative or mixed methods research, this paper focuses on and draws examples exclusively from quantitative research.
The objectives of this paper are to provide some insights on how to conduct methodological studies so that there is greater consistency between the research questions posed, and the design, analysis and reporting of findings. We provide multiple examples to illustrate concepts and a proposed framework for categorizing methodological studies in quantitative research.
What is a methodological study?
Any study that describes or analyzes methods (design, conduct, analysis or reporting) in published (or unpublished) literature is a methodological study. Consequently, the scope of methodological studies is quite extensive and includes, but is not limited to, topics as diverse as: research question formulation [ 11 ]; adherence to reporting guidelines [ 12 , 13 , 14 ] and consistency in reporting [ 15 ]; approaches to study analysis [ 16 ]; investigating the credibility of analyses [ 17 ]; and studies that synthesize these methodological studies [ 18 ]. While the nomenclature of methodological studies is not uniform, the intents and purposes of these studies remain fairly consistent – to describe or analyze methods in primary or secondary studies. As such, methodological studies may also be classified as a subtype of observational studies.
Parallel to this are experimental studies that compare different methods. Even though they play an important role in informing optimal research methods, experimental methodological studies are beyond the scope of this paper. Examples of such studies include the randomized trials by Buscemi et al., comparing single data extraction to double data extraction [ 19 ], and Carrasco-Labra et al., comparing approaches to presenting findings in Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) summary of findings tables [ 20 ]. In these studies, the unit of analysis is the person or groups of individuals applying the methods. We also direct readers to the Studies Within a Trial (SWAT) and Studies Within a Review (SWAR) programme operated through the Hub for Trials Methodology Research, for further reading as a potential useful resource for these types of experimental studies [ 21 ]. Lastly, this paper is not meant to inform the conduct of research using computational simulation and mathematical modeling for which some guidance already exists [ 22 ], or studies on the development of methods using consensus-based approaches.
When should we conduct a methodological study?
Methodological studies occupy a unique niche in health research that allows them to inform methodological advances. Methodological studies should also be conducted as pre-cursors to reporting guideline development, as they provide an opportunity to understand current practices, and help to identify the need for guidance and gaps in methodological or reporting quality. For example, the development of the popular Preferred Reporting Items of Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were preceded by methodological studies identifying poor reporting practices [ 23 , 24 ]. In these instances, after the reporting guidelines are published, methodological studies can also be used to monitor uptake of the guidelines.
These studies can also be conducted to inform the state of the art for design, analysis and reporting practices across different types of health research fields, with the aim of improving research practices, and preventing or reducing research waste. For example, Samaan et al. conducted a scoping review of adherence to different reporting guidelines in health care literature [ 18 ]. Methodological studies can also be used to determine the factors associated with reporting practices. For example, Abbade et al. investigated journal characteristics associated with the use of the Participants, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Timeframe (PICOT) format in framing research questions in trials of venous ulcer disease [ 11 ].
How often are methodological studies conducted?
There is no clear answer to this question. Based on a search of PubMed, the use of related terms (“methodological review” and “meta-epidemiological study”) – and therefore, the number of methodological studies – is on the rise. However, many other terms are used to describe methodological studies. There are also many studies that explore design, conduct, analysis or reporting of research reports, but that do not use any specific terms to describe or label their study design in terms of “methodology”. This diversity in nomenclature makes a census of methodological studies elusive. Appropriate terminology and key words for methodological studies are needed to facilitate improved accessibility for end-users.
Why do we conduct methodological studies?
Methodological studies provide information on the design, conduct, analysis or reporting of primary and secondary research and can be used to appraise quality, quantity, completeness, accuracy and consistency of health research. These issues can be explored in specific fields, journals, databases, geographical regions and time periods. For example, Areia et al. explored the quality of reporting of endoscopic diagnostic studies in gastroenterology [ 25 ]; Knol et al. investigated the reporting of p -values in baseline tables in randomized trial published in high impact journals [ 26 ]; Chen et al. describe adherence to the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) statement in Chinese Journals [ 27 ]; and Hopewell et al. describe the effect of editors’ implementation of CONSORT guidelines on reporting of abstracts over time [ 28 ]. Methodological studies provide useful information to researchers, clinicians, editors, publishers and users of health literature. As a result, these studies have been at the cornerstone of important methodological developments in the past two decades and have informed the development of many health research guidelines including the highly cited CONSORT statement [ 5 ].
Where can we find methodological studies?
Methodological studies can be found in most common biomedical bibliographic databases (e.g. Embase, MEDLINE, PubMed, Web of Science). However, the biggest caveat is that methodological studies are hard to identify in the literature due to the wide variety of names used and the lack of comprehensive databases dedicated to them. A handful can be found in the Cochrane Library as “Cochrane Methodology Reviews”, but these studies only cover methodological issues related to systematic reviews. Previous attempts to catalogue all empirical studies of methods used in reviews were abandoned 10 years ago [ 29 ]. In other databases, a variety of search terms may be applied with different levels of sensitivity and specificity.
Some frequently asked questions about methodological studies
In this section, we have outlined responses to questions that might help inform the conduct of methodological studies.
Q: How should I select research reports for my methodological study?
A: Selection of research reports for a methodological study depends on the research question and eligibility criteria. Once a clear research question is set and the nature of literature one desires to review is known, one can then begin the selection process. Selection may begin with a broad search, especially if the eligibility criteria are not apparent. For example, a methodological study of Cochrane Reviews of HIV would not require a complex search as all eligible studies can easily be retrieved from the Cochrane Library after checking a few boxes [ 30 ]. On the other hand, a methodological study of subgroup analyses in trials of gastrointestinal oncology would require a search to find such trials, and further screening to identify trials that conducted a subgroup analysis [ 31 ].
The strategies used for identifying participants in observational studies can apply here. One may use a systematic search to identify all eligible studies. If the number of eligible studies is unmanageable, a random sample of articles can be expected to provide comparable results if it is sufficiently large [ 32 ]. For example, Wilson et al. used a random sample of trials from the Cochrane Stroke Group’s Trial Register to investigate completeness of reporting [ 33 ]. It is possible that a simple random sample would lead to underrepresentation of units (i.e. research reports) that are smaller in number. This is relevant if the investigators wish to compare multiple groups but have too few units in one group. In this case a stratified sample would help to create equal groups. For example, in a methodological study comparing Cochrane and non-Cochrane reviews, Kahale et al. drew random samples from both groups [ 34 ]. Alternatively, systematic or purposeful sampling strategies can be used and we encourage researchers to justify their selected approaches based on the study objective.
Q: How many databases should I search?
A: The number of databases one should search would depend on the approach to sampling, which can include targeting the entire “population” of interest or a sample of that population. If you are interested in including the entire target population for your research question, or drawing a random or systematic sample from it, then a comprehensive and exhaustive search for relevant articles is required. In this case, we recommend using systematic approaches for searching electronic databases (i.e. at least 2 databases with a replicable and time stamped search strategy). The results of your search will constitute a sampling frame from which eligible studies can be drawn.
Alternatively, if your approach to sampling is purposeful, then we recommend targeting the database(s) or data sources (e.g. journals, registries) that include the information you need. For example, if you are conducting a methodological study of high impact journals in plastic surgery and they are all indexed in PubMed, you likely do not need to search any other databases. You may also have a comprehensive list of all journals of interest and can approach your search using the journal names in your database search (or by accessing the journal archives directly from the journal’s website). Even though one could also search journals’ web pages directly, using a database such as PubMed has multiple advantages, such as the use of filters, so the search can be narrowed down to a certain period, or study types of interest. Furthermore, individual journals’ web sites may have different search functionalities, which do not necessarily yield a consistent output.
Q: Should I publish a protocol for my methodological study?
A: A protocol is a description of intended research methods. Currently, only protocols for clinical trials require registration [ 35 ]. Protocols for systematic reviews are encouraged but no formal recommendation exists. The scientific community welcomes the publication of protocols because they help protect against selective outcome reporting, the use of post hoc methodologies to embellish results, and to help avoid duplication of efforts [ 36 ]. While the latter two risks exist in methodological research, the negative consequences may be substantially less than for clinical outcomes. In a sample of 31 methodological studies, 7 (22.6%) referenced a published protocol [ 9 ]. In the Cochrane Library, there are 15 protocols for methodological reviews (21 July 2020). This suggests that publishing protocols for methodological studies is not uncommon.
Authors can consider publishing their study protocol in a scholarly journal as a manuscript. Advantages of such publication include obtaining peer-review feedback about the planned study, and easy retrieval by searching databases such as PubMed. The disadvantages in trying to publish protocols includes delays associated with manuscript handling and peer review, as well as costs, as few journals publish study protocols, and those journals mostly charge article-processing fees [ 37 ]. Authors who would like to make their protocol publicly available without publishing it in scholarly journals, could deposit their study protocols in publicly available repositories, such as the Open Science Framework ( https://osf.io/ ).
Q: How to appraise the quality of a methodological study?
A: To date, there is no published tool for appraising the risk of bias in a methodological study, but in principle, a methodological study could be considered as a type of observational study. Therefore, during conduct or appraisal, care should be taken to avoid the biases common in observational studies [ 38 ]. These biases include selection bias, comparability of groups, and ascertainment of exposure or outcome. In other words, to generate a representative sample, a comprehensive reproducible search may be necessary to build a sampling frame. Additionally, random sampling may be necessary to ensure that all the included research reports have the same probability of being selected, and the screening and selection processes should be transparent and reproducible. To ensure that the groups compared are similar in all characteristics, matching, random sampling or stratified sampling can be used. Statistical adjustments for between-group differences can also be applied at the analysis stage. Finally, duplicate data extraction can reduce errors in assessment of exposures or outcomes.
Q: Should I justify a sample size?
A: In all instances where one is not using the target population (i.e. the group to which inferences from the research report are directed) [ 39 ], a sample size justification is good practice. The sample size justification may take the form of a description of what is expected to be achieved with the number of articles selected, or a formal sample size estimation that outlines the number of articles required to answer the research question with a certain precision and power. Sample size justifications in methodological studies are reasonable in the following instances:
Comparing two groups
Determining a proportion, mean or another quantifier
Determining factors associated with an outcome using regression-based analyses
For example, El Dib et al. computed a sample size requirement for a methodological study of diagnostic strategies in randomized trials, based on a confidence interval approach [ 40 ].
Q: What should I call my study?
A: Other terms which have been used to describe/label methodological studies include “ methodological review ”, “methodological survey” , “meta-epidemiological study” , “systematic review” , “systematic survey”, “meta-research”, “research-on-research” and many others. We recommend that the study nomenclature be clear, unambiguous, informative and allow for appropriate indexing. Methodological study nomenclature that should be avoided includes “ systematic review” – as this will likely be confused with a systematic review of a clinical question. “ Systematic survey” may also lead to confusion about whether the survey was systematic (i.e. using a preplanned methodology) or a survey using “ systematic” sampling (i.e. a sampling approach using specific intervals to determine who is selected) [ 32 ]. Any of the above meanings of the words “ systematic” may be true for methodological studies and could be potentially misleading. “ Meta-epidemiological study” is ideal for indexing, but not very informative as it describes an entire field. The term “ review ” may point towards an appraisal or “review” of the design, conduct, analysis or reporting (or methodological components) of the targeted research reports, yet it has also been used to describe narrative reviews [ 41 , 42 ]. The term “ survey ” is also in line with the approaches used in many methodological studies [ 9 ], and would be indicative of the sampling procedures of this study design. However, in the absence of guidelines on nomenclature, the term “ methodological study ” is broad enough to capture most of the scenarios of such studies.
Q: Should I account for clustering in my methodological study?
A: Data from methodological studies are often clustered. For example, articles coming from a specific source may have different reporting standards (e.g. the Cochrane Library). Articles within the same journal may be similar due to editorial practices and policies, reporting requirements and endorsement of guidelines. There is emerging evidence that these are real concerns that should be accounted for in analyses [ 43 ]. Some cluster variables are described in the section: “ What variables are relevant to methodological studies?”
A variety of modelling approaches can be used to account for correlated data, including the use of marginal, fixed or mixed effects regression models with appropriate computation of standard errors [ 44 ]. For example, Kosa et al. used generalized estimation equations to account for correlation of articles within journals [ 15 ]. Not accounting for clustering could lead to incorrect p -values, unduly narrow confidence intervals, and biased estimates [ 45 ].
Q: Should I extract data in duplicate?
A: Yes. Duplicate data extraction takes more time but results in less errors [ 19 ]. Data extraction errors in turn affect the effect estimate [ 46 ], and therefore should be mitigated. Duplicate data extraction should be considered in the absence of other approaches to minimize extraction errors. However, much like systematic reviews, this area will likely see rapid new advances with machine learning and natural language processing technologies to support researchers with screening and data extraction [ 47 , 48 ]. However, experience plays an important role in the quality of extracted data and inexperienced extractors should be paired with experienced extractors [ 46 , 49 ].
Q: Should I assess the risk of bias of research reports included in my methodological study?
A : Risk of bias is most useful in determining the certainty that can be placed in the effect measure from a study. In methodological studies, risk of bias may not serve the purpose of determining the trustworthiness of results, as effect measures are often not the primary goal of methodological studies. Determining risk of bias in methodological studies is likely a practice borrowed from systematic review methodology, but whose intrinsic value is not obvious in methodological studies. When it is part of the research question, investigators often focus on one aspect of risk of bias. For example, Speich investigated how blinding was reported in surgical trials [ 50 ], and Abraha et al., investigated the application of intention-to-treat analyses in systematic reviews and trials [ 51 ].
Q: What variables are relevant to methodological studies?
A: There is empirical evidence that certain variables may inform the findings in a methodological study. We outline some of these and provide a brief overview below:
Country: Countries and regions differ in their research cultures, and the resources available to conduct research. Therefore, it is reasonable to believe that there may be differences in methodological features across countries. Methodological studies have reported loco-regional differences in reporting quality [ 52 , 53 ]. This may also be related to challenges non-English speakers face in publishing papers in English.
Authors’ expertise: The inclusion of authors with expertise in research methodology, biostatistics, and scientific writing is likely to influence the end-product. Oltean et al. found that among randomized trials in orthopaedic surgery, the use of analyses that accounted for clustering was more likely when specialists (e.g. statistician, epidemiologist or clinical trials methodologist) were included on the study team [ 54 ]. Fleming et al. found that including methodologists in the review team was associated with appropriate use of reporting guidelines [ 55 ].
Source of funding and conflicts of interest: Some studies have found that funded studies report better [ 56 , 57 ], while others do not [ 53 , 58 ]. The presence of funding would indicate the availability of resources deployed to ensure optimal design, conduct, analysis and reporting. However, the source of funding may introduce conflicts of interest and warrant assessment. For example, Kaiser et al. investigated the effect of industry funding on obesity or nutrition randomized trials and found that reporting quality was similar [ 59 ]. Thomas et al. looked at reporting quality of long-term weight loss trials and found that industry funded studies were better [ 60 ]. Kan et al. examined the association between industry funding and “positive trials” (trials reporting a significant intervention effect) and found that industry funding was highly predictive of a positive trial [ 61 ]. This finding is similar to that of a recent Cochrane Methodology Review by Hansen et al. [ 62 ]
Journal characteristics: Certain journals’ characteristics may influence the study design, analysis or reporting. Characteristics such as journal endorsement of guidelines [ 63 , 64 ], and Journal Impact Factor (JIF) have been shown to be associated with reporting [ 63 , 65 , 66 , 67 ].
Study size (sample size/number of sites): Some studies have shown that reporting is better in larger studies [ 53 , 56 , 58 ].
Year of publication: It is reasonable to assume that design, conduct, analysis and reporting of research will change over time. Many studies have demonstrated improvements in reporting over time or after the publication of reporting guidelines [ 68 , 69 ].
Type of intervention: In a methodological study of reporting quality of weight loss intervention studies, Thabane et al. found that trials of pharmacologic interventions were reported better than trials of non-pharmacologic interventions [ 70 ].
Interactions between variables: Complex interactions between the previously listed variables are possible. High income countries with more resources may be more likely to conduct larger studies and incorporate a variety of experts. Authors in certain countries may prefer certain journals, and journal endorsement of guidelines and editorial policies may change over time.
Q: Should I focus only on high impact journals?
A: Investigators may choose to investigate only high impact journals because they are more likely to influence practice and policy, or because they assume that methodological standards would be higher. However, the JIF may severely limit the scope of articles included and may skew the sample towards articles with positive findings. The generalizability and applicability of findings from a handful of journals must be examined carefully, especially since the JIF varies over time. Even among journals that are all “high impact”, variations exist in methodological standards.
Q: Can I conduct a methodological study of qualitative research?
A: Yes. Even though a lot of methodological research has been conducted in the quantitative research field, methodological studies of qualitative studies are feasible. Certain databases that catalogue qualitative research including the Cumulative Index to Nursing & Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) have defined subject headings that are specific to methodological research (e.g. “research methodology”). Alternatively, one could also conduct a qualitative methodological review; that is, use qualitative approaches to synthesize methodological issues in qualitative studies.
Q: What reporting guidelines should I use for my methodological study?
A: There is no guideline that covers the entire scope of methodological studies. One adaptation of the PRISMA guidelines has been published, which works well for studies that aim to use the entire target population of research reports [ 71 ]. However, it is not widely used (40 citations in 2 years as of 09 December 2019), and methodological studies that are designed as cross-sectional or before-after studies require a more fit-for purpose guideline. A more encompassing reporting guideline for a broad range of methodological studies is currently under development [ 72 ]. However, in the absence of formal guidance, the requirements for scientific reporting should be respected, and authors of methodological studies should focus on transparency and reproducibility.
Q: What are the potential threats to validity and how can I avoid them?
A: Methodological studies may be compromised by a lack of internal or external validity. The main threats to internal validity in methodological studies are selection and confounding bias. Investigators must ensure that the methods used to select articles does not make them differ systematically from the set of articles to which they would like to make inferences. For example, attempting to make extrapolations to all journals after analyzing high-impact journals would be misleading.
Many factors (confounders) may distort the association between the exposure and outcome if the included research reports differ with respect to these factors [ 73 ]. For example, when examining the association between source of funding and completeness of reporting, it may be necessary to account for journals that endorse the guidelines. Confounding bias can be addressed by restriction, matching and statistical adjustment [ 73 ]. Restriction appears to be the method of choice for many investigators who choose to include only high impact journals or articles in a specific field. For example, Knol et al. examined the reporting of p -values in baseline tables of high impact journals [ 26 ]. Matching is also sometimes used. In the methodological study of non-randomized interventional studies of elective ventral hernia repair, Parker et al. matched prospective studies with retrospective studies and compared reporting standards [ 74 ]. Some other methodological studies use statistical adjustments. For example, Zhang et al. used regression techniques to determine the factors associated with missing participant data in trials [ 16 ].
With regard to external validity, researchers interested in conducting methodological studies must consider how generalizable or applicable their findings are. This should tie in closely with the research question and should be explicit. For example. Findings from methodological studies on trials published in high impact cardiology journals cannot be assumed to be applicable to trials in other fields. However, investigators must ensure that their sample truly represents the target sample either by a) conducting a comprehensive and exhaustive search, or b) using an appropriate and justified, randomly selected sample of research reports.
Even applicability to high impact journals may vary based on the investigators’ definition, and over time. For example, for high impact journals in the field of general medicine, Bouwmeester et al. included the Annals of Internal Medicine (AIM), BMJ, the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), Lancet, the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), and PLoS Medicine ( n = 6) [ 75 ]. In contrast, the high impact journals selected in the methodological study by Schiller et al. were BMJ, JAMA, Lancet, and NEJM ( n = 4) [ 76 ]. Another methodological study by Kosa et al. included AIM, BMJ, JAMA, Lancet and NEJM ( n = 5). In the methodological study by Thabut et al., journals with a JIF greater than 5 were considered to be high impact. Riado Minguez et al. used first quartile journals in the Journal Citation Reports (JCR) for a specific year to determine “high impact” [ 77 ]. Ultimately, the definition of high impact will be based on the number of journals the investigators are willing to include, the year of impact and the JIF cut-off [ 78 ]. We acknowledge that the term “generalizability” may apply differently for methodological studies, especially when in many instances it is possible to include the entire target population in the sample studied.
Finally, methodological studies are not exempt from information bias which may stem from discrepancies in the included research reports [ 79 ], errors in data extraction, or inappropriate interpretation of the information extracted. Likewise, publication bias may also be a concern in methodological studies, but such concepts have not yet been explored.
A proposed framework
In order to inform discussions about methodological studies, the development of guidance for what should be reported, we have outlined some key features of methodological studies that can be used to classify them. For each of the categories outlined below, we provide an example. In our experience, the choice of approach to completing a methodological study can be informed by asking the following four questions:
What is the aim?
Methodological studies that investigate bias
A methodological study may be focused on exploring sources of bias in primary or secondary studies (meta-bias), or how bias is analyzed. We have taken care to distinguish bias (i.e. systematic deviations from the truth irrespective of the source) from reporting quality or completeness (i.e. not adhering to a specific reporting guideline or norm). An example of where this distinction would be important is in the case of a randomized trial with no blinding. This study (depending on the nature of the intervention) would be at risk of performance bias. However, if the authors report that their study was not blinded, they would have reported adequately. In fact, some methodological studies attempt to capture both “quality of conduct” and “quality of reporting”, such as Richie et al., who reported on the risk of bias in randomized trials of pharmacy practice interventions [ 80 ]. Babic et al. investigated how risk of bias was used to inform sensitivity analyses in Cochrane reviews [ 81 ]. Further, biases related to choice of outcomes can also be explored. For example, Tan et al investigated differences in treatment effect size based on the outcome reported [ 82 ].
Methodological studies that investigate quality (or completeness) of reporting
Methodological studies may report quality of reporting against a reporting checklist (i.e. adherence to guidelines) or against expected norms. For example, Croituro et al. report on the quality of reporting in systematic reviews published in dermatology journals based on their adherence to the PRISMA statement [ 83 ], and Khan et al. described the quality of reporting of harms in randomized controlled trials published in high impact cardiovascular journals based on the CONSORT extension for harms [ 84 ]. Other methodological studies investigate reporting of certain features of interest that may not be part of formally published checklists or guidelines. For example, Mbuagbaw et al. described how often the implications for research are elaborated using the Evidence, Participants, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Timeframe (EPICOT) format [ 30 ].
Methodological studies that investigate the consistency of reporting
Sometimes investigators may be interested in how consistent reports of the same research are, as it is expected that there should be consistency between: conference abstracts and published manuscripts; manuscript abstracts and manuscript main text; and trial registration and published manuscript. For example, Rosmarakis et al. investigated consistency between conference abstracts and full text manuscripts [ 85 ].
Methodological studies that investigate factors associated with reporting
In addition to identifying issues with reporting in primary and secondary studies, authors of methodological studies may be interested in determining the factors that are associated with certain reporting practices. Many methodological studies incorporate this, albeit as a secondary outcome. For example, Farrokhyar et al. investigated the factors associated with reporting quality in randomized trials of coronary artery bypass grafting surgery [ 53 ].
Methodological studies that investigate methods
Methodological studies may also be used to describe methods or compare methods, and the factors associated with methods. Muller et al. described the methods used for systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies [ 86 ].
Methodological studies that summarize other methodological studies
Some methodological studies synthesize results from other methodological studies. For example, Li et al. conducted a scoping review of methodological reviews that investigated consistency between full text and abstracts in primary biomedical research [ 87 ].
Methodological studies that investigate nomenclature and terminology
Some methodological studies may investigate the use of names and terms in health research. For example, Martinic et al. investigated the definitions of systematic reviews used in overviews of systematic reviews (OSRs), meta-epidemiological studies and epidemiology textbooks [ 88 ].
Other types of methodological studies
In addition to the previously mentioned experimental methodological studies, there may exist other types of methodological studies not captured here.
What is the design?
Methodological studies that are descriptive
Most methodological studies are purely descriptive and report their findings as counts (percent) and means (standard deviation) or medians (interquartile range). For example, Mbuagbaw et al. described the reporting of research recommendations in Cochrane HIV systematic reviews [ 30 ]. Gohari et al. described the quality of reporting of randomized trials in diabetes in Iran [ 12 ].
Methodological studies that are analytical
Some methodological studies are analytical wherein “analytical studies identify and quantify associations, test hypotheses, identify causes and determine whether an association exists between variables, such as between an exposure and a disease.” [ 89 ] In the case of methodological studies all these investigations are possible. For example, Kosa et al. investigated the association between agreement in primary outcome from trial registry to published manuscript and study covariates. They found that larger and more recent studies were more likely to have agreement [ 15 ]. Tricco et al. compared the conclusion statements from Cochrane and non-Cochrane systematic reviews with a meta-analysis of the primary outcome and found that non-Cochrane reviews were more likely to report positive findings. These results are a test of the null hypothesis that the proportions of Cochrane and non-Cochrane reviews that report positive results are equal [ 90 ].
What is the sampling strategy?
Methodological studies that include the target population
Methodological reviews with narrow research questions may be able to include the entire target population. For example, in the methodological study of Cochrane HIV systematic reviews, Mbuagbaw et al. included all of the available studies ( n = 103) [ 30 ].
Methodological studies that include a sample of the target population
Many methodological studies use random samples of the target population [ 33 , 91 , 92 ]. Alternatively, purposeful sampling may be used, limiting the sample to a subset of research-related reports published within a certain time period, or in journals with a certain ranking or on a topic. Systematic sampling can also be used when random sampling may be challenging to implement.
What is the unit of analysis?
Methodological studies with a research report as the unit of analysis
Many methodological studies use a research report (e.g. full manuscript of study, abstract portion of the study) as the unit of analysis, and inferences can be made at the study-level. However, both published and unpublished research-related reports can be studied. These may include articles, conference abstracts, registry entries etc.
Methodological studies with a design, analysis or reporting item as the unit of analysis
Some methodological studies report on items which may occur more than once per article. For example, Paquette et al. report on subgroup analyses in Cochrane reviews of atrial fibrillation in which 17 systematic reviews planned 56 subgroup analyses [ 93 ].
This framework is outlined in Fig. 2 .

A proposed framework for methodological studies
Conclusions
Methodological studies have examined different aspects of reporting such as quality, completeness, consistency and adherence to reporting guidelines. As such, many of the methodological study examples cited in this tutorial are related to reporting. However, as an evolving field, the scope of research questions that can be addressed by methodological studies is expected to increase.
In this paper we have outlined the scope and purpose of methodological studies, along with examples of instances in which various approaches have been used. In the absence of formal guidance on the design, conduct, analysis and reporting of methodological studies, we have provided some advice to help make methodological studies consistent. This advice is grounded in good contemporary scientific practice. Generally, the research question should tie in with the sampling approach and planned analysis. We have also highlighted the variables that may inform findings from methodological studies. Lastly, we have provided suggestions for ways in which authors can categorize their methodological studies to inform their design and analysis.

Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Abbreviations
Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials
Evidence, Participants, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Timeframe
Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations
Participants, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Timeframe
Preferred Reporting Items of Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses
Studies Within a Review
Studies Within a Trial
Chalmers I, Glasziou P. Avoidable waste in the production and reporting of research evidence. Lancet. 2009;374(9683):86–9.
PubMed Google Scholar
Chan AW, Song F, Vickers A, Jefferson T, Dickersin K, Gotzsche PC, Krumholz HM, Ghersi D, van der Worp HB. Increasing value and reducing waste: addressing inaccessible research. Lancet. 2014;383(9913):257–66.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ioannidis JP, Greenland S, Hlatky MA, Khoury MJ, Macleod MR, Moher D, Schulz KF, Tibshirani R. Increasing value and reducing waste in research design, conduct, and analysis. Lancet. 2014;383(9912):166–75.
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC, Juni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928.
Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman DG. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel-group randomised trials. Lancet. 2001;357.
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000100.
Shea BJ, Hamel C, Wells GA, Bouter LM, Kristjansson E, Grimshaw J, Henry DA, Boers M. AMSTAR is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62(10):1013–20.
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, Moher D, Tugwell P, Welch V, Kristjansson E, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. Bmj. 2017;358:j4008.
Lawson DO, Leenus A, Mbuagbaw L. Mapping the nomenclature, methodology, and reporting of studies that review methods: a pilot methodological review. Pilot Feasibility Studies. 2020;6(1):13.
Puljak L, Makaric ZL, Buljan I, Pieper D. What is a meta-epidemiological study? Analysis of published literature indicated heterogeneous study designs and definitions. J Comp Eff Res. 2020.
Abbade LPF, Wang M, Sriganesh K, Jin Y, Mbuagbaw L, Thabane L. The framing of research questions using the PICOT format in randomized controlled trials of venous ulcer disease is suboptimal: a systematic survey. Wound Repair Regen. 2017;25(5):892–900.
Gohari F, Baradaran HR, Tabatabaee M, Anijidani S, Mohammadpour Touserkani F, Atlasi R, Razmgir M. Quality of reporting randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in diabetes in Iran; a systematic review. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2015;15(1):36.
Wang M, Jin Y, Hu ZJ, Thabane A, Dennis B, Gajic-Veljanoski O, Paul J, Thabane L. The reporting quality of abstracts of stepped wedge randomized trials is suboptimal: a systematic survey of the literature. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2017;8:1–10.
Shanthanna H, Kaushal A, Mbuagbaw L, Couban R, Busse J, Thabane L: A cross-sectional study of the reporting quality of pilot or feasibility trials in high-impact anesthesia journals Can J Anaesthesia 2018, 65(11):1180–1195.
Kosa SD, Mbuagbaw L, Borg Debono V, Bhandari M, Dennis BB, Ene G, Leenus A, Shi D, Thabane M, Valvasori S, et al. Agreement in reporting between trial publications and current clinical trial registry in high impact journals: a methodological review. Contemporary Clinical Trials. 2018;65:144–50.
Zhang Y, Florez ID, Colunga Lozano LE, Aloweni FAB, Kennedy SA, Li A, Craigie S, Zhang S, Agarwal A, Lopes LC, et al. A systematic survey on reporting and methods for handling missing participant data for continuous outcomes in randomized controlled trials. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017;88:57–66.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Hernández AV, Boersma E, Murray GD, Habbema JD, Steyerberg EW. Subgroup analyses in therapeutic cardiovascular clinical trials: are most of them misleading? Am Heart J. 2006;151(2):257–64.
Samaan Z, Mbuagbaw L, Kosa D, Borg Debono V, Dillenburg R, Zhang S, Fruci V, Dennis B, Bawor M, Thabane L. A systematic scoping review of adherence to reporting guidelines in health care literature. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2013;6:169–88.
Buscemi N, Hartling L, Vandermeer B, Tjosvold L, Klassen TP. Single data extraction generated more errors than double data extraction in systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2006;59(7):697–703.
Carrasco-Labra A, Brignardello-Petersen R, Santesso N, Neumann I, Mustafa RA, Mbuagbaw L, Etxeandia Ikobaltzeta I, De Stio C, McCullagh LJ, Alonso-Coello P. Improving GRADE evidence tables part 1: a randomized trial shows improved understanding of content in summary-of-findings tables with a new format. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;74:7–18.
The Northern Ireland Hub for Trials Methodology Research: SWAT/SWAR Information [ https://www.qub.ac.uk/sites/TheNorthernIrelandNetworkforTrialsMethodologyResearch/SWATSWARInformation/ ]. Accessed 31 Aug 2020.
Chick S, Sánchez P, Ferrin D, Morrice D. How to conduct a successful simulation study. In: Proceedings of the 2003 winter simulation conference: 2003; 2003. p. 66–70.
Google Scholar
Mulrow CD. The medical review article: state of the science. Ann Intern Med. 1987;106(3):485–8.
Sacks HS, Reitman D, Pagano D, Kupelnick B. Meta-analysis: an update. Mount Sinai J Med New York. 1996;63(3–4):216–24.
CAS Google Scholar
Areia M, Soares M, Dinis-Ribeiro M. Quality reporting of endoscopic diagnostic studies in gastrointestinal journals: where do we stand on the use of the STARD and CONSORT statements? Endoscopy. 2010;42(2):138–47.
Knol M, Groenwold R, Grobbee D. P-values in baseline tables of randomised controlled trials are inappropriate but still common in high impact journals. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2012;19(2):231–2.
Chen M, Cui J, Zhang AL, Sze DM, Xue CC, May BH. Adherence to CONSORT items in randomized controlled trials of integrative medicine for colorectal Cancer published in Chinese journals. J Altern Complement Med. 2018;24(2):115–24.
Hopewell S, Ravaud P, Baron G, Boutron I. Effect of editors' implementation of CONSORT guidelines on the reporting of abstracts in high impact medical journals: interrupted time series analysis. BMJ. 2012;344:e4178.
The Cochrane Methodology Register Issue 2 2009 [ https://cmr.cochrane.org/help.htm ]. Accessed 31 Aug 2020.
Mbuagbaw L, Kredo T, Welch V, Mursleen S, Ross S, Zani B, Motaze NV, Quinlan L. Critical EPICOT items were absent in Cochrane human immunodeficiency virus systematic reviews: a bibliometric analysis. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;74:66–72.
Barton S, Peckitt C, Sclafani F, Cunningham D, Chau I. The influence of industry sponsorship on the reporting of subgroup analyses within phase III randomised controlled trials in gastrointestinal oncology. Eur J Cancer. 2015;51(18):2732–9.
Setia MS. Methodology series module 5: sampling strategies. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61(5):505–9.
Wilson B, Burnett P, Moher D, Altman DG, Al-Shahi Salman R. Completeness of reporting of randomised controlled trials including people with transient ischaemic attack or stroke: a systematic review. Eur Stroke J. 2018;3(4):337–46.
Kahale LA, Diab B, Brignardello-Petersen R, Agarwal A, Mustafa RA, Kwong J, Neumann I, Li L, Lopes LC, Briel M, et al. Systematic reviews do not adequately report or address missing outcome data in their analyses: a methodological survey. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;99:14–23.
De Angelis CD, Drazen JM, Frizelle FA, Haug C, Hoey J, Horton R, Kotzin S, Laine C, Marusic A, Overbeke AJPM, et al. Is this clinical trial fully registered?: a statement from the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors*. Ann Intern Med. 2005;143(2):146–8.
Ohtake PJ, Childs JD. Why publish study protocols? Phys Ther. 2014;94(9):1208–9.
Rombey T, Allers K, Mathes T, Hoffmann F, Pieper D. A descriptive analysis of the characteristics and the peer review process of systematic review protocols published in an open peer review journal from 2012 to 2017. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019;19(1):57.
Grimes DA, Schulz KF. Bias and causal associations in observational research. Lancet. 2002;359(9302):248–52.
Porta M (ed.): A dictionary of epidemiology, 5th edn. Oxford: Oxford University Press, Inc.; 2008.
El Dib R, Tikkinen KAO, Akl EA, Gomaa HA, Mustafa RA, Agarwal A, Carpenter CR, Zhang Y, Jorge EC, Almeida R, et al. Systematic survey of randomized trials evaluating the impact of alternative diagnostic strategies on patient-important outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017;84:61–9.
Helzer JE, Robins LN, Taibleson M, Woodruff RA Jr, Reich T, Wish ED. Reliability of psychiatric diagnosis. I. a methodological review. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1977;34(2):129–33.
Chung ST, Chacko SK, Sunehag AL, Haymond MW. Measurements of gluconeogenesis and Glycogenolysis: a methodological review. Diabetes. 2015;64(12):3996–4010.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sterne JA, Juni P, Schulz KF, Altman DG, Bartlett C, Egger M. Statistical methods for assessing the influence of study characteristics on treatment effects in 'meta-epidemiological' research. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1513–24.
Moen EL, Fricano-Kugler CJ, Luikart BW, O’Malley AJ. Analyzing clustered data: why and how to account for multiple observations nested within a study participant? PLoS One. 2016;11(1):e0146721.
Zyzanski SJ, Flocke SA, Dickinson LM. On the nature and analysis of clustered data. Ann Fam Med. 2004;2(3):199–200.
Mathes T, Klassen P, Pieper D. Frequency of data extraction errors and methods to increase data extraction quality: a methodological review. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2017;17(1):152.
Bui DDA, Del Fiol G, Hurdle JF, Jonnalagadda S. Extractive text summarization system to aid data extraction from full text in systematic review development. J Biomed Inform. 2016;64:265–72.
Bui DD, Del Fiol G, Jonnalagadda S. PDF text classification to leverage information extraction from publication reports. J Biomed Inform. 2016;61:141–8.
Maticic K, Krnic Martinic M, Puljak L. Assessment of reporting quality of abstracts of systematic reviews with meta-analysis using PRISMA-A and discordance in assessments between raters without prior experience. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019;19(1):32.
Speich B. Blinding in surgical randomized clinical trials in 2015. Ann Surg. 2017;266(1):21–2.
Abraha I, Cozzolino F, Orso M, Marchesi M, Germani A, Lombardo G, Eusebi P, De Florio R, Luchetta ML, Iorio A, et al. A systematic review found that deviations from intention-to-treat are common in randomized trials and systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017;84:37–46.
Zhong Y, Zhou W, Jiang H, Fan T, Diao X, Yang H, Min J, Wang G, Fu J, Mao B. Quality of reporting of two-group parallel randomized controlled clinical trials of multi-herb formulae: A survey of reports indexed in the Science Citation Index Expanded. Eur J Integrative Med. 2011;3(4):e309–16.
Farrokhyar F, Chu R, Whitlock R, Thabane L. A systematic review of the quality of publications reporting coronary artery bypass grafting trials. Can J Surg. 2007;50(4):266–77.
Oltean H, Gagnier JJ. Use of clustering analysis in randomized controlled trials in orthopaedic surgery. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2015;15:17.
Fleming PS, Koletsi D, Pandis N. Blinded by PRISMA: are systematic reviewers focusing on PRISMA and ignoring other guidelines? PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96407.
Balasubramanian SP, Wiener M, Alshameeri Z, Tiruvoipati R, Elbourne D, Reed MW. Standards of reporting of randomized controlled trials in general surgery: can we do better? Ann Surg. 2006;244(5):663–7.
de Vries TW, van Roon EN. Low quality of reporting adverse drug reactions in paediatric randomised controlled trials. Arch Dis Child. 2010;95(12):1023–6.
Borg Debono V, Zhang S, Ye C, Paul J, Arya A, Hurlburt L, Murthy Y, Thabane L. The quality of reporting of RCTs used within a postoperative pain management meta-analysis, using the CONSORT statement. BMC Anesthesiol. 2012;12:13.
Kaiser KA, Cofield SS, Fontaine KR, Glasser SP, Thabane L, Chu R, Ambrale S, Dwary AD, Kumar A, Nayyar G, et al. Is funding source related to study reporting quality in obesity or nutrition randomized control trials in top-tier medical journals? Int J Obes. 2012;36(7):977–81.
Thomas O, Thabane L, Douketis J, Chu R, Westfall AO, Allison DB. Industry funding and the reporting quality of large long-term weight loss trials. Int J Obes. 2008;32(10):1531–6.
Khan NR, Saad H, Oravec CS, Rossi N, Nguyen V, Venable GT, Lillard JC, Patel P, Taylor DR, Vaughn BN, et al. A review of industry funding in randomized controlled trials published in the neurosurgical literature-the elephant in the room. Neurosurgery. 2018;83(5):890–7.
Hansen C, Lundh A, Rasmussen K, Hrobjartsson A. Financial conflicts of interest in systematic reviews: associations with results, conclusions, and methodological quality. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;8:Mr000047.
Kiehna EN, Starke RM, Pouratian N, Dumont AS. Standards for reporting randomized controlled trials in neurosurgery. J Neurosurg. 2011;114(2):280–5.
Liu LQ, Morris PJ, Pengel LH. Compliance to the CONSORT statement of randomized controlled trials in solid organ transplantation: a 3-year overview. Transpl Int. 2013;26(3):300–6.
Bala MM, Akl EA, Sun X, Bassler D, Mertz D, Mejza F, Vandvik PO, Malaga G, Johnston BC, Dahm P, et al. Randomized trials published in higher vs. lower impact journals differ in design, conduct, and analysis. J Clin Epidemiol. 2013;66(3):286–95.
Lee SY, Teoh PJ, Camm CF, Agha RA. Compliance of randomized controlled trials in trauma surgery with the CONSORT statement. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013;75(4):562–72.
Ziogas DC, Zintzaras E. Analysis of the quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials in acute and chronic myeloid leukemia, and myelodysplastic syndromes as governed by the CONSORT statement. Ann Epidemiol. 2009;19(7):494–500.
Alvarez F, Meyer N, Gourraud PA, Paul C. CONSORT adoption and quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials: a systematic analysis in two dermatology journals. Br J Dermatol. 2009;161(5):1159–65.
Mbuagbaw L, Thabane M, Vanniyasingam T, Borg Debono V, Kosa S, Zhang S, Ye C, Parpia S, Dennis BB, Thabane L. Improvement in the quality of abstracts in major clinical journals since CONSORT extension for abstracts: a systematic review. Contemporary Clin trials. 2014;38(2):245–50.
Thabane L, Chu R, Cuddy K, Douketis J. What is the quality of reporting in weight loss intervention studies? A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Int J Obes. 2007;31(10):1554–9.
Murad MH, Wang Z. Guidelines for reporting meta-epidemiological methodology research. Evidence Based Med. 2017;22(4):139.
METRIC - MEthodological sTudy ReportIng Checklist: guidelines for reporting methodological studies in health research [ http://www.equator-network.org/library/reporting-guidelines-under-development/reporting-guidelines-under-development-for-other-study-designs/#METRIC ]. Accessed 31 Aug 2020.
Jager KJ, Zoccali C, MacLeod A, Dekker FW. Confounding: what it is and how to deal with it. Kidney Int. 2008;73(3):256–60.
Parker SG, Halligan S, Erotocritou M, Wood CPJ, Boulton RW, Plumb AAO, Windsor ACJ, Mallett S. A systematic methodological review of non-randomised interventional studies of elective ventral hernia repair: clear definitions and a standardised minimum dataset are needed. Hernia. 2019.
Bouwmeester W, Zuithoff NPA, Mallett S, Geerlings MI, Vergouwe Y, Steyerberg EW, Altman DG, Moons KGM. Reporting and methods in clinical prediction research: a systematic review. PLoS Med. 2012;9(5):1–12.
Schiller P, Burchardi N, Niestroj M, Kieser M. Quality of reporting of clinical non-inferiority and equivalence randomised trials--update and extension. Trials. 2012;13:214.
Riado Minguez D, Kowalski M, Vallve Odena M, Longin Pontzen D, Jelicic Kadic A, Jeric M, Dosenovic S, Jakus D, Vrdoljak M, Poklepovic Pericic T, et al. Methodological and reporting quality of systematic reviews published in the highest ranking journals in the field of pain. Anesth Analg. 2017;125(4):1348–54.
Thabut G, Estellat C, Boutron I, Samama CM, Ravaud P. Methodological issues in trials assessing primary prophylaxis of venous thrombo-embolism. Eur Heart J. 2005;27(2):227–36.
Puljak L, Riva N, Parmelli E, González-Lorenzo M, Moja L, Pieper D. Data extraction methods: an analysis of internal reporting discrepancies in single manuscripts and practical advice. J Clin Epidemiol. 2020;117:158–64.
Ritchie A, Seubert L, Clifford R, Perry D, Bond C. Do randomised controlled trials relevant to pharmacy meet best practice standards for quality conduct and reporting? A systematic review. Int J Pharm Pract. 2019.
Babic A, Vuka I, Saric F, Proloscic I, Slapnicar E, Cavar J, Pericic TP, Pieper D, Puljak L. Overall bias methods and their use in sensitivity analysis of Cochrane reviews were not consistent. J Clin Epidemiol. 2019.
Tan A, Porcher R, Crequit P, Ravaud P, Dechartres A. Differences in treatment effect size between overall survival and progression-free survival in immunotherapy trials: a Meta-epidemiologic study of trials with results posted at ClinicalTrials.gov. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(15):1686–94.
Croitoru D, Huang Y, Kurdina A, Chan AW, Drucker AM. Quality of reporting in systematic reviews published in dermatology journals. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182(6):1469–76.
Khan MS, Ochani RK, Shaikh A, Vaduganathan M, Khan SU, Fatima K, Yamani N, Mandrola J, Doukky R, Krasuski RA: Assessing the Quality of Reporting of Harms in Randomized Controlled Trials Published in High Impact Cardiovascular Journals. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes 2019.
Rosmarakis ES, Soteriades ES, Vergidis PI, Kasiakou SK, Falagas ME. From conference abstract to full paper: differences between data presented in conferences and journals. FASEB J. 2005;19(7):673–80.
Mueller M, D’Addario M, Egger M, Cevallos M, Dekkers O, Mugglin C, Scott P. Methods to systematically review and meta-analyse observational studies: a systematic scoping review of recommendations. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18(1):44.
Li G, Abbade LPF, Nwosu I, Jin Y, Leenus A, Maaz M, Wang M, Bhatt M, Zielinski L, Sanger N, et al. A scoping review of comparisons between abstracts and full reports in primary biomedical research. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2017;17(1):181.
Krnic Martinic M, Pieper D, Glatt A, Puljak L. Definition of a systematic review used in overviews of systematic reviews, meta-epidemiological studies and textbooks. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019;19(1):203.
Analytical study [ https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/analytical+study ]. Accessed 31 Aug 2020.
Tricco AC, Tetzlaff J, Pham B, Brehaut J, Moher D. Non-Cochrane vs. Cochrane reviews were twice as likely to have positive conclusion statements: cross-sectional study. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62(4):380–6 e381.
Schalken N, Rietbergen C. The reporting quality of systematic reviews and Meta-analyses in industrial and organizational psychology: a systematic review. Front Psychol. 2017;8:1395.
Ranker LR, Petersen JM, Fox MP. Awareness of and potential for dependent error in the observational epidemiologic literature: A review. Ann Epidemiol. 2019;36:15–9 e12.
Paquette M, Alotaibi AM, Nieuwlaat R, Santesso N, Mbuagbaw L. A meta-epidemiological study of subgroup analyses in cochrane systematic reviews of atrial fibrillation. Syst Rev. 2019;8(1):241.
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work did not receive any dedicated funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Health Research Methods, Evidence and Impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Lawrence Mbuagbaw, Daeria O. Lawson & Lehana Thabane
Biostatistics Unit/FSORC, 50 Charlton Avenue East, St Joseph’s Healthcare—Hamilton, 3rd Floor Martha Wing, Room H321, Hamilton, Ontario, L8N 4A6, Canada
Lawrence Mbuagbaw & Lehana Thabane
Centre for the Development of Best Practices in Health, Yaoundé, Cameroon
Lawrence Mbuagbaw
Center for Evidence-Based Medicine and Health Care, Catholic University of Croatia, Ilica 242, 10000, Zagreb, Croatia
Livia Puljak
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health – Bloomington, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN, 47405, USA
David B. Allison
Departments of Paediatrics and Anaesthesia, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Lehana Thabane
Centre for Evaluation of Medicine, St. Joseph’s Healthcare-Hamilton, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Population Health Research Institute, Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton, ON, Canada
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
LM conceived the idea and drafted the outline and paper. DOL and LT commented on the idea and draft outline. LM, LP and DOL performed literature searches and data extraction. All authors (LM, DOL, LT, LP, DBA) reviewed several draft versions of the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lawrence Mbuagbaw .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
DOL, DBA, LM, LP and LT are involved in the development of a reporting guideline for methodological studies.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Mbuagbaw, L., Lawson, D.O., Puljak, L. et al. A tutorial on methodological studies: the what, when, how and why. BMC Med Res Methodol 20 , 226 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-020-01107-7
Download citation
Received : 27 May 2020
Accepted : 27 August 2020
Published : 07 September 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-020-01107-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Methodological study
- Meta-epidemiology
- Research methods
- Research-on-research
BMC Medical Research Methodology
ISSN: 1471-2288
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
2.7 Conclusion
In this chapter, you have learned about the processes involved in planning a research project. The process of research involves identifying a research problem or question, conducting a literature review to understand what is already known about the topic, formulating a hypothesis or research question, designing a study to test the hypothesis or answer the research question, collecting and analysing data, and finally drawing conclusions and sharing the findings with the wider community.
As indicated in the opening scenario, just like a GPS, a research plan is essential for a successful research project. Planning helps to steer the project in the right direction, keep it on track, and ultimately achieve the desired outcome. Here are some of the reasons presented in this chapter about why planning is important in research:
- Clarifies the research question: A clear research question is critical for the success of a research project. Planning helps to define the research question and identify the variables that need to be measured. This ensures that the research is focused and specific.
- Establishes a research design: A research design outlines the methods that will be used to collect and analyse data. Planning helps to establish a research design that is appropriate for the research question and ensures that data will be collected and analysed in a way that is valid and reliable.
- Identifies potential challenges: Planning helps to identify potential challenges and obstacles that may arise during the research project. This allows researchers to anticipate these challenges and take steps to address them.
- Maximizes resources: Planning helps to maximize resources, including time, funding, and personnel. By having a clear plan, researchers can allocate resources more effectively and efficiently.
- Provides a framework for evaluation: Planning provides a framework for evaluating the success of the research project. By having clear objectives and a plan for achieving them, researchers can assess the success of the project and identify areas for improvement.
In conclusion, just like a GPS is crucial for finding our way during a road trip, planning is essential for the success of a research project. It helps to define the research question, establish a research design, identify potential challenges, maximize resources, and provide a framework for evaluation. By taking the time to plan, researchers can increase the likelihood of a successful outcome and avoid feelings of dissatisfaction.
An Introduction to Research Methods for Undergraduate Health Profession Students Copyright © 2023 by Faith Alele and Bunmi Malau-Aduli is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Research Methodology-5: Writing The Conclusion

Related Papers
Dr. Khalil A. Agha
Denis Robinson
Writing a succesful a cademic thesis
Raphael Akeyo
This article is a brief guidance on effective writing of academic research thesis with a focus on the results/ findings section/ chapters. It provides step by step highlights on how to present data from the field, interpretation of the findings, corroborating the findings with existing studies as well as the use of theoretical tenets to discuss the findings. The conclusions and recommendations sections are also highlighted.
Scientific Research Publishing: Creative Education
Dr. Qais Faryadi
I have already discussed the PhD introduction and literature review in detail. In this paper, I discuss the PhD methodology, results and how to write a stunning conclusion for your thesis. The main objective of this paper is to help PhD candidates to understand what is a PhD methodology and guide them in writing a systematic and meaningful PhD methodology, results and conclusion. The methodology used in this research is a descriptive method as it deliberates and defines the various parts of PhD methodology, results and conclusion writing process and elucidates the "how to do" in a very unpretentious and understanding manner. As thus, this paper summarises the various steps of thesis methodology, results and conclusion writing to pilot the PhD students. This road map is a useful guidance especially for students of social science studies. Additionally, in this paper, methodology writing techniques , procedures and important strategies are enlightened in a simple manner. This paper adopts a "how-to approach" when discussing a variety of relevant topics such as introduction, formulation of the methodology, variables , research design process, types of sampling, data collection process, interviews, questionnaires, data analysis techniques and so on. Results and conclusions are also discussed in detail, so that PhD candidates can follow the guide clearly. This paper has 5 parts such as Introduction, Literature reviews, Methodology, Results and Conclusion. As such, I discuss Methodology, Results and Conclusion as the final assessment of the PhD thesis writing process.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting an Integrative Review
Coleen Toronto
Jacinta Browne
Basics of Summarizing Research Findings
Dr Saad M Butt
Abdilahi Adam Mohamoud
Pamela Olmos
"The conclusions section of a thesis is the last chapter people read and usually the section that leaves the lasting impression. This study presents a framework for the analysis of thesis conclusions at an undergraduate level in the field of humanities, which –as the literature reveals–, lacks an agenda for its analysis at the undergraduate level. A sevenmove generic organization is proposed as a Framework for Undergraduate Thesis Conclusions (FUTC). This framework sheds a light on the complex construction of the thesis conclusions chapter towards its analysis. Moreover, the FUTC shows potentiality for further research, pedagogic implications and applications for genre and writing studies. Moreover, the FUTC shows potentiality for further research, pedagogic implications and applications for genre and writing studies."
Althea Amor Galdo
RELATED PAPERS
Horst Enzensberger
Série-Estudos - Periódico do Programa de Pós-Graduação em Educação da UCDB
Léia Hegeto
lena Aarekol
Salete Valer
Revue du Nord
Xavier Deru
British Journal of Cancer
Helle Johannesen
Proceedings of the …
Paulo Bandiera-Paiva
Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine
Edward Sivak
Science Journal of Education
Maria Clara Bonaglia
Tribology Transactions
xueyuan zhao
Jurnal Kedokteran Gigi Universitas Padjadjaran
hubban nasution
Dermatología …
Pedro Arzola
SAÜ Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü Dergisi
Beytullah Eren
Hakeem Ajeigbe
Journal of Physics: Conference Series
Manolis Plionis
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing
Lorenzo Famiglini
Dermatology Online Journal
Marta Sales
Brain Sciences
Selma Kanazir
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

- Research Process
Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers
- 3 minute read
- 38.8K views
Table of Contents
Choosing an optimal research methodology is crucial for the success of any research project. The methodology you select will determine the type of data you collect, how you collect it, and how you analyse it. Understanding the different types of research methods available along with their strengths and weaknesses, is thus imperative to make an informed decision.
Understanding different research methods:
There are several research methods available depending on the type of study you are conducting, i.e., whether it is laboratory-based, clinical, epidemiological, or survey based . Some common methodologies include qualitative research, quantitative research, experimental research, survey-based research, and action research. Each method can be opted for and modified, depending on the type of research hypotheses and objectives.
Qualitative vs quantitative research:
When deciding on a research methodology, one of the key factors to consider is whether your research will be qualitative or quantitative. Qualitative research is used to understand people’s experiences, concepts, thoughts, or behaviours . Quantitative research, on the contrary, deals with numbers, graphs, and charts, and is used to test or confirm hypotheses, assumptions, and theories.
Qualitative research methodology:
Qualitative research is often used to examine issues that are not well understood, and to gather additional insights on these topics. Qualitative research methods include open-ended survey questions, observations of behaviours described through words, and reviews of literature that has explored similar theories and ideas. These methods are used to understand how language is used in real-world situations, identify common themes or overarching ideas, and describe and interpret various texts. Data analysis for qualitative research typically includes discourse analysis, thematic analysis, and textual analysis.
Quantitative research methodology:
The goal of quantitative research is to test hypotheses, confirm assumptions and theories, and determine cause-and-effect relationships. Quantitative research methods include experiments, close-ended survey questions, and countable and numbered observations. Data analysis for quantitative research relies heavily on statistical methods.
Analysing qualitative vs quantitative data:
The methods used for data analysis also differ for qualitative and quantitative research. As mentioned earlier, quantitative data is generally analysed using statistical methods and does not leave much room for speculation. It is more structured and follows a predetermined plan. In quantitative research, the researcher starts with a hypothesis and uses statistical methods to test it. Contrarily, methods used for qualitative data analysis can identify patterns and themes within the data, rather than provide statistical measures of the data. It is an iterative process, where the researcher goes back and forth trying to gauge the larger implications of the data through different perspectives and revising the analysis if required.
When to use qualitative vs quantitative research:
The choice between qualitative and quantitative research will depend on the gap that the research project aims to address, and specific objectives of the study. If the goal is to establish facts about a subject or topic, quantitative research is an appropriate choice. However, if the goal is to understand people’s experiences or perspectives, qualitative research may be more suitable.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, an understanding of the different research methods available, their applicability, advantages, and disadvantages is essential for making an informed decision on the best methodology for your project. If you need any additional guidance on which research methodology to opt for, you can head over to Elsevier Author Services (EAS). EAS experts will guide you throughout the process and help you choose the perfect methodology for your research goals.

Why is data validation important in research?

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

Writing a good review article

Scholarly Sources: What are They and Where can You Find Them?
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.

Conclusive Research
Conclusive research design, as the name implies, is applied to generate findings that are practically useful in reaching conclusions or decision-making. In this type of studies research objectives and data requirements need to be clearly defined. Findings of conclusive studies usually have specific uses. Conclusive research design provides a way to verify and quantify findings of exploratory studies .
Conclusive research design usually involves the application of quantitative methods of data collection and data analysis. Moreover, conclusive studies tend to be deductive in nature and research objectives in these types of studies are achieved via testing hypotheses.
The table below illustrates the main differences between conclusive and exploratory research design:
Main differences between conclusive and exploratory research design
It has to be noted that “conclusive research is more likely to use statistical tests, advanced analytical techniques, and larger sample sizes, compared with exploratory studies. Conclusive research is more likely to use quantitative, rather than qualitative techniques” [1] . Conclusive research is helpful in providing a reliable or representative picture of the population through the application of valid research instrument.
Conclusive research design can be divided into two categories: descriptive research and causal research .
Descriptive research is used to describe some functions or characteristics of phenomenon and can be further divided into the following groups:
- Case study ;
- Case series study;
- Cross-sectional study;
- Longitudinal study;
- Retrospective study.
Causal research, on the other hand, is used to research cause and affect relationships. Two popular research methods for causal studies are experimental and quasi-experimental studies.
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance contains discussions of theory and application of research designs. The e-book also explains all stages of the research process starting from the selection of the research area to writing personal reflection. Important elements of dissertations such as research philosophy , research approach , methods of data collection , data analysis and sampling are explained in this e-book in simple words.
John Dudovskiy

[1] Nargundkar, R. (2008) “Marketing Research: Text and Cases”, Tata McGraw-Hill Educational, p.39
- Search Menu
- Advance articles
- Editor's Choice
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- About The British Journal of Social Work
- About the British Association of Social Workers
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Article Contents
- Introduction
- Limitations
- Supplementary material
Social Workers’ Perceived Barriers and Facilitators to Social Work Practice in Schools: A Scoping Review
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Sarah Binks, Lyndal Hickey, Airin Heath, Anna Bornemisza, Lauren Goulding, Arno Parolini, Social Workers’ Perceived Barriers and Facilitators to Social Work Practice in Schools: A Scoping Review, The British Journal of Social Work , 2024;, bcae046, https://doi.org/10.1093/bjsw/bcae046
- Permissions Icon Permissions
The aim of this scoping review was to establish the breadth of the academic literature regarding the barriers and facilitators to social work practice in schools as perceived by School Social Workers (SSWs). Following the PRISMA-ScR Scoping Review Framework, 42 articles were identified as meeting the inclusion criteria. Five interrelated themes related to the barriers and facilitators to SSW practice were identified: (1) Inadequacy of service delivery infrastructure; (2) SSWs’ role ambiguities and expectations; (3) SSWs’ competency, knowledge and support; (4) School climate and context; and (5) Cultivating relationships and engagement. This scoping review found that social workers perceive far greater barriers than facilitators when delivering services in school settings, with limited evidence related to the facilitators that enhance School Social Work (SSW) practice. Further research regarding the facilitators of SSW practice is needed, specifically in countries where research on this topic is emergent.
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1468-263X
- Print ISSN 0045-3102
- Copyright © 2024 British Association of Social Workers
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Open access
- Published: 14 May 2024
Rain, rain, go away, come again another day: do climate variations enhance the spread of COVID-19?
- Masha Menhat 1 ,
- Effi Helmy Ariffin ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8534-0113 2 ,
- Wan Shiao Dong 3 ,
- Junainah Zakaria 2 ,
- Aminah Ismailluddin 3 ,
- Hayrol Azril Mohamed Shafril 4 ,
- Mahazan Muhammad 5 ,
- Ahmad Rosli Othman 6 ,
- Thavamaran Kanesan 7 ,
- Suzana Pil Ramli 8 ,
- Mohd Fadzil Akhir 2 &
- Amila Sandaruwan Ratnayake 9
Globalization and Health volume 20 , Article number: 43 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
315 Accesses
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
The spread of infectious diseases was further promoted due to busy cities, increased travel, and climate change, which led to outbreaks, epidemics, and even pandemics. The world experienced the severity of the 125 nm virus called the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a pandemic declared by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2019. Many investigations revealed a strong correlation between humidity and temperature relative to the kinetics of the virus’s spread into the hosts. This study aimed to solve the riddle of the correlation between environmental factors and COVID-19 by applying RepOrting standards for Systematic Evidence Syntheses (ROSES) with the designed research question. Five temperature and humidity-related themes were deduced via the review processes, namely 1) The link between solar activity and pandemic outbreaks, 2) Regional area, 3) Climate and weather, 4) Relationship between temperature and humidity, and 5) the Governmental disinfection actions and guidelines. A significant relationship between solar activities and pandemic outbreaks was reported throughout the review of past studies. The grand solar minima (1450-1830) and solar minima (1975-2020) coincided with the global pandemic. Meanwhile, the cooler, lower humidity, and low wind movement environment reported higher severity of cases. Moreover, COVID-19 confirmed cases and death cases were higher in countries located within the Northern Hemisphere. The Blackbox of COVID-19 was revealed through the work conducted in this paper that the virus thrives in cooler and low-humidity environments, with emphasis on potential treatments and government measures relative to temperature and humidity.
• The coronavirus disease 2019 (COIVD-19) is spreading faster in low temperatures and humid area.
• Weather and climate serve as environmental drivers in propagating COVID-19.
• Solar radiation influences the spreading of COVID-19.
• The correlation between weather and population as the factor in spreading of COVID-19.
Graphical abstract
Introduction
The revolution and rotation of the Earth and the Sun supply heat and create differential heating on earth. The movements and the 23.5° inclination of the Earth [ 1 ] separate the oblate-ellipsoid-shaped earth into northern and southern hemispheres. Consequently, the division results in various climatic zones at different latitudes and dissimilar local temperatures (see Fig. 1 ) and affects the seasons and length of a day and night in a particular region [ 2 ]. Global differential heating and climate variability occur due to varying solar radiation received by each region [ 3 ]. According to Trenberth and Fasullo [ 4 ] and Hauschild et al. [ 5 ] the new perspective on the issue of climate change can be affected relative to the changes in solar radiation patterns. Since the study by Trenberth and Fasullo [ 4 ] focused on climate model changes from 1950 to 2100, it was found that the role of changing clouds and trapped sunlight can lead to an opening of the aperture for solar radiation.
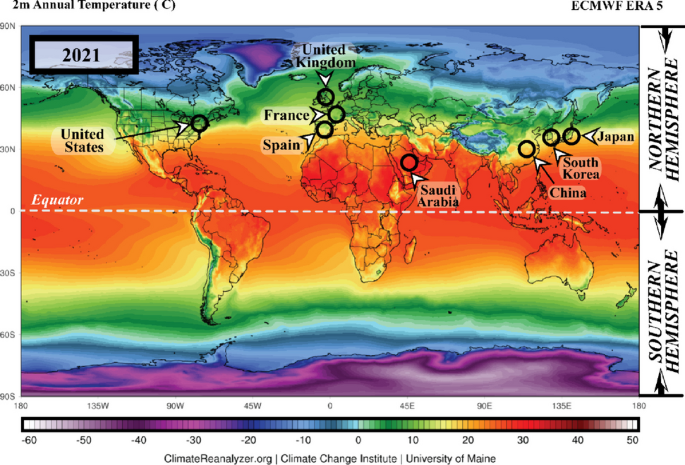
The annual average temperature data for 2021 in the northern and southern hemispheres ( Source: meteoblue.com ). Note: The black circles mark countries with high Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections
Furthermore, the heat from sunlight is essential to humans; several organisms could not survive without it. Conversely, the spread of any disease-carrying virus tends to increase with less sunlight exposure [ 6 ]. Historically, disease outbreaks that led to epidemic and pandemic eruptions were correlated to atmospheric changes. Pandemic diseases, such as the flu (1918), Asian flu (1956–1958), Hong Kong flu (1968), and recently, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) (2019), recorded over a million death toll each during the winter season or minimum temperature conditions [ 7 ]. The total number of COVID-19 cases is illustrated in Fig. 2 .
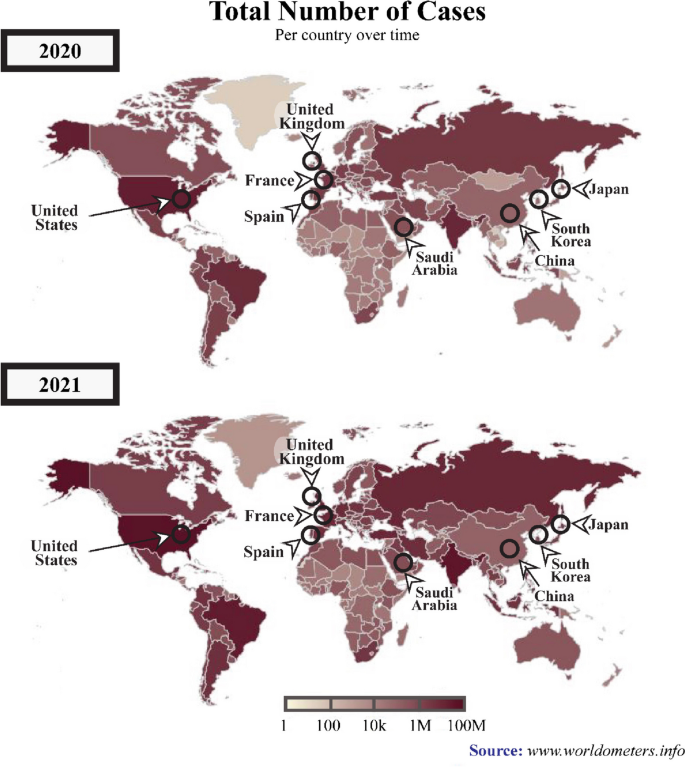
A graphical representation of the total number of COVID-19 cases across various periods between 2020 and 2021. ( Source : www.worldometers.info ). Note: The black circles indicate countries with high numbers COVID-19-infections
In several previous outbreaks, investigations revealed a significant association between temperature and humidity with a particular focus on the transmission dynamics of the infection from the virus into the hosts [ 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Moreover, disease outbreaks tended to heighten in cold temperatures and low humidity [ 11 ]. Optimal temperature and sufficient relative humidity during evaporation are necessary for cloud formation, resulting in the precipitated liquid falling to the ground as rain, snow, or hail due to the activity of solar radiation balancing [ 4 ].
Consequently, the radiation balancing processes in the atmosphere are directly linked to the living beings on the earth, including plants and animals, and as well as viruses and bacterias. According to Carvalho et al. [ 12 ]‘s study, the survival rate of the Coronaviridae Family can decrease during summer seasons. Nevertheless, numerous diseases were also developed from specific viruses, such as influenza, malaria, and rubella, and in November 2019, a severe health threat originated from a 125 nm size of coronavirus, had resulted in numerous deaths worldwide.
Transmission and symptoms of COVID-19
The COVID-19, or severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is an infectious disease caused by a newly discovered pathogenic virus from the coronavirus family, the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) [ 13 ]. The first case was recorded in Wuhan, China, in December 2019 [ 14 ]. The pathogenic virus is transmitted among humans when they breathe in air contaminated with droplets and tiny airborne particles containing the virus [ 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 ].
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the most common symptoms of COVID-19 infection include fever, dry cough, and tiredness. Nevertheless, older people and individuals with underlying health problems (lung and heart problems, high blood pressure, diabetes, or cancer) are at higher risk of becoming seriously ill and developing difficulty breathing [ 19 ]. The COVID-19 was initially only predominant in China but rapidly spread to other countries globally. The remarkably swift acceleration of the number of infections and mortality forced WHO to declare COVID-19 a global public health emergency on the 30th of January 2020, which was later declared as a pandemic on the 11th of March 2020 [ 20 ].
Since no vaccine was available then, WHO introduced the COVID-19 preventative measures to reduce the chances of virus transmission. The guideline for individual preventative included practising hand and respiratory hygiene by regularly cleaning hands with soap and water or alcohol-based sanitisers, wear a facemask and always maintaining at least a one-meter physical distance [ 21 ]. Nevertheless, the worldwide transmission of COVID-19 has resulted in fear and forced numerous countries to impose restrictions rules, such as lockdown, travel bans, closed country borders, restrictions on shipping activities, and movement limitations, to diminish the spread of COVID-19 [ 22 ].
According to WHO, by the 2nd of December 2020, 63,379,338 confirmed cases and 1,476,676 mortalities were recorded globally. On the 3rd of December 2021, 263,655,612 confirmed cases and deaths were recorded, reflecting increased COVID-19 infections compared to the previous year. The American and European regions documented the highest COVID-19 patients with 97,341,769 and 88,248,591 cases, respectively (see Fig. 2 ), followed by Southeast Asia with 44,607,287, Eastern Mediterranean accounted 16,822,791, Western Pacific recorded 6,322,034, and Africa reported the lowest number of cases at 6,322,034 [ 19 ].
Recently, an increasing number of studies are investigating the association between environmental factors (temperature and humidity) and the viability, transmission, and survival of the coronavirus [ 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ]. The results primarily demonstrated that temperature was more significantly associated with the transmission of COVID-19 [ 27 , 28 , 29 ] and its survival period on the surfaces of objects [ 30 ]. Consequently, the disease was predominant in countries with low temperature and humidity [ 31 ], which was also proven by Diao et al. [ 32 ]‘s study demonstrating higher rates of COVID-19 transmission in China, England, Germany, and Japan.
A comprehensive systematic literature review (SLR) is still lacking despite numerous research on environmental factors linked to coronavirus. Accordingly, this article aimed to fill the gap in understanding and identifying the correlation between environmental factors and COVID-19 by analysing existing reports. Systematically reviewing existing literature is essential to contribute to the body of knowledge and provide beneficial information for public health policymakers.
Methodology
The present study reviewed the protocols, formulation of research questions, selection of studies, appraisal of quality, and data abstraction and analysis.
The protocol review
The present SLR was performed according to the reporting standards for systematic evidence syntheses (ROSES) and followed or adapted the guidelines as closely as possible. Thus, in this study, a systematic literature review was guided by the ROSES review protocol (Fig. 3 ). Compared to preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis (PRISMA), ROSES is a review protocol specifically designed for a systematic review in the conservation or environment management fields [ 33 ]. Compared to PRISMA, ROSES offers several advantages, as it is tailored to environmental systematic review, which reduces emphasis on quantitative synthesis (e.g. meta-analysis etc.) that is only reliable when used with appropriate data [ 34 ].
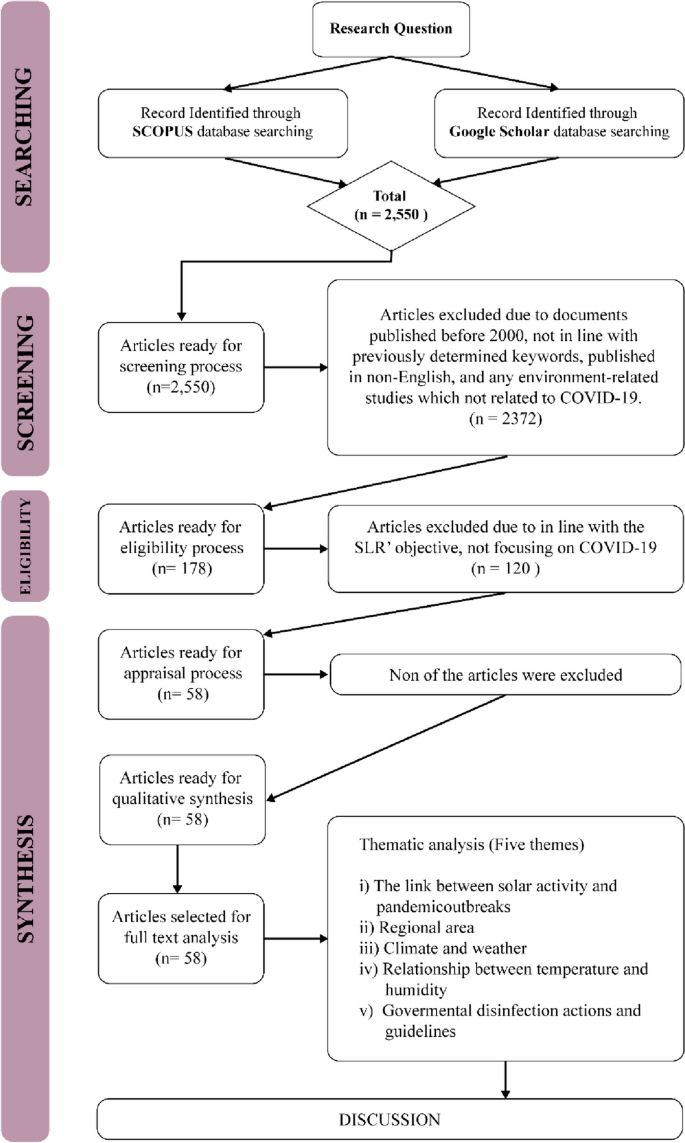
The flow diagram guide by ROSES protocol and Thematical Analysis
The current SLR started by determining the appropriate research questions, followed by the selection criteria, including the review, specifically on the keywords employed and the selection of journals database. Subsequently, the appraisal quality process and data abstraction and analysis were conducted.
Formulation of research questions
The entire process of this SLR was guided by the specific research questions, while sources to be reviewed and data abstraction and analysis were in line with the determined research question [ 35 , 36 ]. In the present article, a total of five research questions were formed, namely:
What the link between solar activity and COVID-19 pandemic outbreaks?
Which regions were more prone to COVID-19?
What were the temporal and spatial variabilities of high temperature and humidity during the spread of COVID-19?
What is the relationship between temperature and humidity in propagating COVID-19?
How did the government’s disinfection actions and guidelines can be reducing the spread of COVID-19?
Systematic searching strategies
Selection of studies.
In this stage of the study, the appropriate keywords to be employed in the searching process were determined. After referring to existing literature, six main keywords were chosen for the searching process, namely COVID-19, coronavirus, temperature, humidity, solar radiation and population density. The current study also utilised the boolean operators (OR, AND, AND NOT) and phrase searching.
Scopus was employed as the main database during the searching process, in line with the suggestion by Gusenbauer and Haddaway [ 37 ], who noted the strength of the database in terms of quality control and search and filtering functions. Furthermore, Google Scholar was selected as the supporting database. Although Halevi et al. [ 38 ] expressed concerns about its quality, Haddaway et al. [ 39 ] reported that due to its quantity, Google Scholar was suitable as a supporting database in SLR studies.
In the first stage of the search, 2550 articles were retrieved, which were then screened. The suitable criteria were also determined to control the quality of the articles reviewed [ 40 ]. The criteria are: any documents published between 2000 to 2022, documents that consist previously determined keywords, published in English, and any environment-related studies that focused on COVID-19. Based on these criteria, 2372 articles were excluded and 178 articles were proceeded to the next step namely eligibility. In the eligibility process, the title and the abstract of the articles were examined to ensure its relevancy to the SLR and in this process a total of 120 articles were excluded and only 58 articles were processed in the next stage.
Appraisal of the quality
The study ensured the rigor of the chosen articles based on best evidence synthesis. In the process, predefined inclusion criteria for the review were appraised by the systematic review team based on previously established guidelines and the studies were then judged as being scientifically admissible or not [ 40 ]. Hence, by controlling the quality based on the best evidence synthesis, the present SLR controls its quality by including articles that are in line with the inclusion criteria. It means that any article published within the timeline (in the year 2000 and above), composed of predetermined keywords, in English medium, and environment-related investigations focusing on COVID-19 are included in the review. Based on this process, all 58 articles fulfilled all the inclusion criteria and are considered of good quality and included in the review.
Data abstraction and analysis
The data abstraction process in this study was performed based on five research questions (please refer to 2.2, formulation of research questions). The data that was able to answer the questions were abstracted and placed in a table to ease the data analysis process. The primary data analysis technique employed in the current study was qualitative and relied on thematic analysis.
The thematic technique is a descriptive method that combines data flexibly with other information evaluation methods [ 41 ], aiming to identify the patterns in studies. Any similarities and relationships within the abstracted data emerge as patterns. Subsequently, suitable themes and sub-themes would be developed based on obtained patterns [ 42 ]. Following the thematic process, five themes were selected in this study.
Background of the selected articles
The current study selected 58 articles for the SLR. Five themes were developed based on the thematic analysis from the predetermined research questions: the link between solar activity and pandemic outbreaks, regional area, climate and weather, the relationship between temperature and humidity, and government disinfection action guidelines. Among the articles retrieved between 2000 and 2022; two were published in 2010, one in 2011, four in 2013, three in 2014, two in 2015, six in 2016 and 2017, respectively, one in 2018, six in 2019, twelve in 2020, eight in 2021, and seven in 2022.
Temperature- and humidity-related themes
The link between solar activity and pandemic outbreaks.
Numerous scientists have investigated the relationship between solar activities and pandemic outbreaks over the years ([ 43 ]; A [ 27 , 44 , 45 ].). Nuclear fusions from solar activities have resulted in minimum and maximum solar sunspots. Maximum solar activities are characterised by a high number of sunspots and elevated solar flare frequency and coronal mass injections. Minimum solar sunspot occurrences are identified by low interplanetary magnetic field values entering the earth [ 1 ].
A diminished magnetic field was suggested to be conducive for viruses and bacteria to mutate, hence the onset of pandemics. Nonetheless, Hoyle and Wickramasinghe [ 46 ] reported that the link between solar activity and pandemic outbreaks is only speculative. The literature noted that the data recorded between 1930 and 1970 demonstrated that virus transmissions and pandemic occurrences were coincidental. Moreover, no pandemic cases were reported in 1979, when minimum solar activity was recorded [ 47 ].
Chandra Wickramasinghe et al. [ 48 ] suggested a significant relationship between pandemic outbreaks and solar activities as several grand solar minima, including Sporer (1450–1550 AD), Mounder (1650–1700 AD), and Dalton (1800–1830) minimums, were recorded coinciding with global pandemics of diseases, such as smallpox, the English sweat, plague, and cholera pandemics. Furthermore, since the Dalton minimum, which recorded minimum sunspots, studies from 2002 to 2015 have documented the reappearance of previous pandemics. For example, influenza subtype H1N1 1918/1919 episodically returned in 2009, especially in India, China, and other Asian countries. Zika virus, which first appeared in 1950, flared and became endemic in 2015, transmitted sporadically, specifically in African countries. Similarly, SARS-CoV was first recorded in China in 2002 and emerged as an outbreak, MERS-CoV, in middle east countries a decade later, in 2012.
In 2020, the World Data Centre Sunspot Index and Long-term Solar Observations ( http://sidc.be ) confirmed that a new solar activity was initiated in December 2019, during which a novel coronavirus pandemic also occurred, and present a same as the previous hypothesis. Nevertheless, a higher number of pandemic outbreaks were documented during low minimum solar activities, including Ebola (1976), H5N1 (Nipah) (1967–1968), H1N1 (2009), and COVID-19 (2019–current). Furthermore, Wickramasinghe and Qu [ 49 ] reported that since 1918 or 1919, more devastating and recurrent pandemics tend to occur, particularly after a century. Consequently, within 100 years, a sudden surge of influenza was recorded, and novel influenza was hypothesised to emerge.
Figure 4 demonstrates that low minimum solar activity significantly reduced before 2020, hence substantiating the claim that pandemic events are closely related to solar activities. Moreover, numerous studies (i.e. [ 43 ], Chandra [ 46 , 47 , 48 ]) reported that during solar minimums, new viruses could penetrate the surfaces of the earth and high solar radiation would result in lower infection rates, supporting the hypothesis mentioned above.
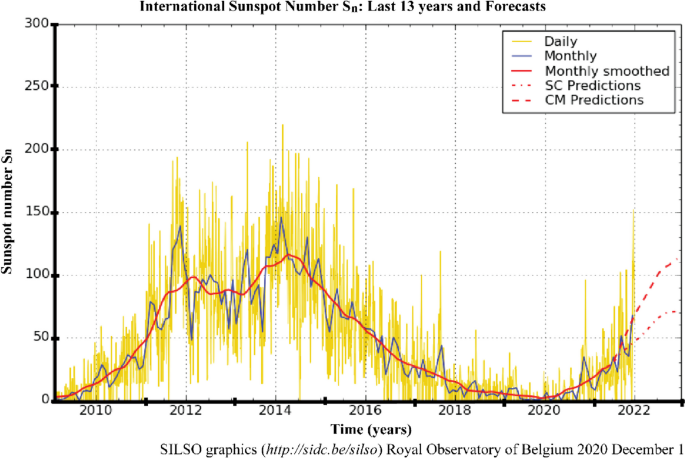
The number of sunspots in the last 13 years. Note : The yellow curve indicates the daily sunspot number and the 2010–2021 delineated curve illustrates the minimum solar activity recorded (source: http://sidc.be/silso )
Regional area
In early December 2019, Wuhan, China, was reported as the centre of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) outbreak [ 50 ]. Chinese health authorities immediately investigated and controlled the spread of the disease. Nevertheless, by late January 2020, the WHO announced that COVID-19 was a global public health emergency. The upgrade was due to the rapid rise in confirmed cases, which were no longer limited to Wuhan [ 28 ]. The disease had spread to 24 other countries, which were mainly in the northern hemisphere, particularly the European and Western Pacific regions, such as France, United Kingdom, Spain, South Korea, Japan, Malaysia, and Indonesia [ 51 , 52 ]. The migration or movement of humans was the leading agent in the spread of COVID-19, resulting in an almost worldwide COVID-19 pandemic [ 53 ].
The first hotspots of the epidemic outspread introduced by the Asian and Western Pacific regions possessed similar winter climates with an average temperature and humidity rate of 5–11 °C and 47–79%. Consequently, several publications reviewed in the current study associated the COVID-19 outbreak with regional climates (i.e. [ 1 , 29 , 54 , 55 ]) instead of its close connection to China. This review also discussed the effects of a range of specific climatological variables on the transmission and epidemiology of COVID-19 in regional climatic conditions.
America and Europe documented the highest COVID-19 cases, outnumbering the number reported in Asia [ 19 ] and on the 2nd of December 2020, the United States of America (USA) reported the highest number of confirmed COVID-19 infections, with over 13,234,551 cases and 264,808 mortalities (Da S [ 56 ].). The cases in the USA began emerging in March 2020 and peaked in late November 2020, during the wintertime in the northern hemisphere (December to March) [ 53 ]. Figure 5 demonstrates the evolution of the COVID-19 pandemic in several country which represent comparison two phase of summer and one phase of winter. Most of these countries tend to increase of COVID cases close to winter season. Then, it can be worsening on phase two of summer due to do not under control of human movement although the normal trend it is presenting during winter phase.
The evolution of the COVID-19 pandemic from the 15th of February 2020 to the 2nd of December 2020 ( Source: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus )
The coronavirus spread aggressively across the European region, which recorded the second highest COVID-19 confirmed cases after America. At the end of 2020, WHO reported 19,071,275 Covid-19 cases in the area, where France documented 2,183,275 cases, the European country with the highest number of confirmed cases, followed by the United Kingdom (1,629,661 cases) and Spain (1,652,801 cases) [ 19 ]. Europe is also located in the northern hemisphere and possesses a temperate climate.
The spatial and temporal transmission patterns of coronavirus infection in the European region were similar to America and the Eastern Mediterranean, where the winter season increased COVID-19 cases. Typically, winter in Europe occurs at the beginning of October and ends in March. Hardy et al. [ 57 ] also stated that temperature commonly drops below freezing (approximately − 1 °C) when snow accumulates between December to mid-March, resulting in an extreme environment. Figure 5 indicates that COVID-19 cases peaked in October when the temperature became colder [ 21 ]. Similarly, the cases were the highest in the middle of the year in Australia and South Asian countries, such as India, that experience winter and monsoon, respectively, during the period.
In African regions, the outbreak of COVID-19 escalated rapidly from June to October before falling from October to March, as summer in South Africa generally occurs from November to March, while winter from June to August. Nevertheless, heavy rainfall generally transpires during summer, hence the warm and humid conditions in South Africa and Namibia during summer, while the opposite happens during winter (cold and dry). Consequently, the outbreak in the region recorded an increasing trend during winter and subsided during the summer, supporting the report by Gunthe et al. [ 58 ]. Novel coronavirus disease presents unique and grave challenges in Africa, as it has for the rest of the world. However, the infrastructure and resources have limitations for Africa countries facing COVID-19 pandemic and the threat of other diseases [ 59 ].
Conclusively, seasonal and regional climate patterns were associated with COVID-19 outbreaks globally. According to Kraemer et al. [ 60 ], they used real-time mobility data in Wuhan and early measurement presented a positive correlation between human mobility and spread of COVID-19 cases. However, after the implementation of control measures, this correlation dropped and growth rates became negative in most locations, although shifts in the demographics of reported cases were still indicative of local chains of transmission outside of Wuhan.
Climate and weather
The term “weather” represents the changes in the environment that occur daily and in a short period, while “climate” is defined as atmospheric changes happening over a long time (over 3 months) in specific regions. Consequently, different locations would experience varying climates. Numerous reports suggested climate and weather variabilities as the main drivers that sped or slowed the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 worldwide [ 44 , 61 , 62 , 63 ].
From a meteorological perspective, a favourable environment has led to the continued existence of the COVID-19 virus in the atmosphere [ 64 ]. Studies demonstrated that various meteorological conditions, such as the rate of relative humidity (i.e. [ 28 ]), precipitation (i.e. [ 65 ]), temperature (i.e. [ 66 ]), and wind speed factors (i.e. [ 54 ]), were the crucial components that contributed to the dynamic response of the pandemic, influencing either the mitigation or exacerbation of novel coronavirus transmission. In other words, the environment was considered the medium for spreading the disease when other health considerations were put aside. Consequently, new opinions, knowledge, and findings are published and shared to increase awareness, thus encouraging preventive measures within the public.
The coronavirus could survive in temperatures under 30 °C with a relative humidity of less than 80% [ 67 ], suggesting that high temperatures and lower relative humidity contributed to the elicitation of COVID-19 cases [ 18 , 51 , 58 , 68 ]. Lagtayi et al. [ 7 ] highlighted temperature as a critical factor, evidently from the increased transmission rate of MERS-Cov in African states with a warm and dry climate. Similarly, the highest COVID-19 cases were recorded in dry temperate regions, especially in western Europe (France and Spain), China, and the USA, while the countries nearer to the equator were less affected. Nevertheless, the temperature factor relative to viral infections depends on the protein available in the viruses. According to Chen and Shakhnovich [ 69 ], there is a good correlation between decreasing temperature and the growth of proteins in virus. Consequently, preventive measures that take advantage of conducive environments for specific viruses are challenging.
Precipitation also correlates with influenza [ 43 ]. A report demonstrated that regions with at least 150 mm of monthly precipitation threshold level experienced fewer cases than regions with lower precipitation rates. According to Martins et al. [ 70 ], influenza and COVID-19 can be affected by climate, where virus can be spread through the respiratory especially during rainfall season. The daily spread of Covid-19 cases in tropical countries, which receive high precipitation levels, are far less than in temperate countries [ 27 ]. Likewise, high cases of COVID-19 were reported during the monsoon season (mid-year) in India during which high rainfall is recorded [ 71 ]. Moreover, the majority of the population in these regions has lower vitamin D levels, which may contribute to weakened immune responses during certain seasons [ 27 ].
Rainfall increases the relative atmospheric humidity, which is unfavourable to the coronaviruses as its transmission requires dry and cold weather. Moreover, several reports hypothesised that rain could wash away viruses on object surfaces, which is still questioned. Most people prefer staying home on rainy days, allowing less transmission or close contact. Conversely, [ 72 ] exhibited that precipitation did not significantly impact COVID-19 infectiousness in Oslo, Norway due the location in northern hemisphere which are during winter season presenting so cold.
Coşkun et al. [ 54 ] and Wu et al. [ 29 ] claimed that wind could strongly correlate with the rate of COVID-19 transmission. Atmospheric instability (turbulent occurrences) leads to increased wind speed and reduces the dispersion of particulate matter (PM 2.5 and PM 10 ) in the environment and among humans. An investigation performed in 55 cities in Italy during the COVID-19 outbreak proved that the areas with low wind movement (stable atmospheric conditions) possessed a higher correlation coefficient and exceeded the threshold value of the safe level of PM 2.5 and PM 10 . Resultantly, more individuals were recorded infected with the disease in the regions. As mentioned in Martins et al. [ 70 ] the COVID-19 can be affected by climate and the virus can be spread through respiratory which is the virus moving in the wind movement.
The relationship between temperature and humidity
Climatic parameters, such as temperature and humidity, were investigated as the crucial factors in the epidemiology of the respiratory virus survival and transmission of COVID-19 ([ 61 ]; S [ 73 , 74 ].). The rising number of confirmed cases indicated the strong transmission ability of COVID-19 and was related to meteorological parameters. Furthermore, several studies found that the disease transmission was associated with the temperature and humidity of the environment [ 55 , 64 , 68 , 75 ], while other investigations have examined and reviewed environmental factors that could influence the epidemiological aspects of Covid-19.
Generally, increased COVID-19 cases and deaths corresponded with temperature, humidity, and viral transmission and mortality. Various studies reported that colder and dryer environments favoured COVID-19 epidemiologically [ 45 , 76 , 77 ]. As example tropical region, the observations indicated that the summer (middle of year) and rainy seasons (end of the year) could effectively diminish the transmission and mortality from COVID-19. High precipitation statistically increases relative air humidity, which is unfavourable for the survival of coronavirus, which prefers dry and cold conditions [ 32 , 34 , 78 , 79 ]. Consequently, warmer conditions could reduce COVID-19 transmission. A 1 °C increase in the temperature recorded a decrease in confirmed cases by 8% increase [ 45 ].
Several reports established that the minimum, maximum, and average temperature and humidity correlated with COVID-19 occurrence and mortality [ 55 , 80 , 81 ]. The lowest and highest temperatures of 24 and 27.3 °C and a humidity between 76 and 91% were conducive to spreading the virulence agents. The propagation of the disease peaked at the average temperature of 26 °C and humidity of 55% before gradually decreasing with elevated temperature and humidity [ 78 ].
Researchers are still divided on the effects of temperature and humidity on coronavirus transmission. Xu et al. [ 26 ] confirmed that COVID-19 cases gradually increased with higher temperature and lower humidity, indicating that the virus was actively transmitted in warm and dry conditions. Nevertheless, several reports stated that the spread of COVID-19 was negatively correlated with temperature and humidity [ 10 , 29 , 63 ]. The conflicting findings require further investigation. Moreover, other factors, such as population density, elderly population, cultural aspects, and health interventions, might potentially influence the epidemiology of the disease and necessitate research.
Governmental disinfection actions and guidelines
The COVID-19 is a severe health threat that is still spreading worldwide. The epidemiology of the SAR-CoV-2 virus might be affected by several factors, including meteorological conditions (temperature and humidity), population density, and healthcare quality, that permit it to spread rapidly [ 16 , 17 ]. Nevertheless, in 2020, no effective pharmaceutical interventions or vaccines were available for the diagnosis, treatment, and epidemic prevention against COVID-19 [ 73 , 82 ]. Consequently, after 2020 the governments globally have designed and executed non-pharmacological public health measures, such as lockdown, travel bans, social distancing, quarantine, public place closure, and public health actions, to curb the spread of COVID-19 infections and several studies have reported on the effects of these plans [ 13 , 83 ].
The COVID-19 is mainly spread via respiratory droplets from an infected person’s mouth or nose to another in close contact [ 84 ]. Accordingly, WHO and most governments worldwide have recommended wearing facemasks in public areas to curb the transmission of COVID-19. The facemasks would prevent individuals from breathing COVID-19-contaminated air [ 85 ]. Furthermore, the masks could hinder the transmission of the virus from an infected person as the exhaled air is trapped in droplets collected on the masks, suspending it in the atmosphere for longer. The WHO also recommended adopting a proper hand hygiene routine to prevent transmission and employing protective equipment, such as gloves and body covers, especially for health workers [ 86 ].
Besides wearing protective equipment, social distancing was also employed to control the Covid-19 outbreak [ 74 , 87 ]. Social distancing hinders the human-to-human transmission of the coronavirus in the form of droplets from the mouth and nose, as evidenced by the report from Sun and Zhai [ 88 ]. Conversely, Nair & Selvaraj [ 89 ] demonstrated that social distancing was less effective in communities and cultures where gatherings are the norm. Nonetheless, the issue could be addressed by educating the public and implementing social distancing policies, such as working from home and any form of plague treatment.
Infected persons, individuals who had contact with confirmed or suspected COVID-19 patients, and persons living in areas with high transmission rates were recommended to undergo quarantine by WHO. The quarantine could be implemented voluntarily or legally enforced by authorities and applicable to individuals, groups, or communities (community containment) [ 90 ]. A person under mandatory quarantine must stay in a place for a recommended 14-day period, based on the estimated incubation period of the SARS-CoV-2 [ 19 , 91 ]. According to Stasi et al. [ 92 ], 14-days period for mandatory quarantine it is presenting a clinical improvement after they found 5-day group and 10-day group can be decrease number of patient whose getting effect of COVID-19 from 64 to 54% respectively. This also proven by Ahmadi et al. [ 43 ] and Foad et al. [ 93 ], quarantining could reduce the transmission of COVID-19.
Lockdown and travel bans, especially in China, the centre of the coronavirus outbreak, reduced the infection rate and the correlation of domestic air traffic with COVID-19 cases [ 17 ]. The observations were supported by Sun & Zhai [ 88 ] and Sun et al. [ 94 ], who noted that travel restrictions diminished the number of COVID-19 reports by 75.70% compared to baseline scenarios without restrictions. Furthermore, example in Malaysia, lockdowns improved the air quality of polluted areas especially in primarily at main cities [ 95 ]. As additional, Martins et al. [ 70 ] measure the Human Development Index (HDI) with the specific of socio-economic variables as income, education and health. In their study, the income and education levels are the main relevant factors that affect the socio-economic.
A mandatory lockdown is an area under movement control as a preventive measure to stop the coronavirus from spreading to other areas. Numerous governments worldwide enforced the policy to restrict public movements outside their homes during the pandemic. Resultantly, human-to-human transmission of the virus was effectively reduced. The lockdown and movement control order were also suggested for individuals aged 80 and above or with low or compromised immunities, as these groups possess a higher risk of contracting the disease [ 44 ].
Governments still enforced movement orders even after the introduction of vaccines by Pfizer, Moderna, and Sinovac, as the vaccines only protect high-risk individuals from the worst effects of COVID-19. Consequently, in most countries, after receiving the first vaccine dose, individuals were allowed to resume life as normal but were still required to follow the standard operating procedures (SOP) outlined by the government.
The government attempted to balance preventing COVID-19 spread and recovering economic activities, for example, local businesses, maritime traders, shipping activities, oil and gas production and economic trades [ 22 , 96 ]. Nonetheless, the COVID-19 cases demonstrated an increasing trend during the summer due to the higher number of people travelling and on vacation, primarily to alleviate stress from lockdowns. Several new variants were discovered, including the Delta and Omicron strains, which spread in countries such as the USA and the United Kingdom. The high number of COVID-19 cases prompted the WHO to suggest booster doses to ensure full protection.
As mentioned in this manuscript, the COVID-19 still uncertain for any kind factors that can be affected on spreading of this virus. However, regarding many sources of COVID-19 study, the further assessment on this factor need to be continue to be sure, that we ready to facing probably in 10 years projection of solar minimum phase can be held in same situation for another pandemic.
The sun has an eleven-year cycle known as the solar cycle, related to its magnetic field, which controls the activities on its surface through sunspots. When the magnetic fields are active, numerous sunspots are formed on its surface, hence the sun produces more radiation energy emitted to the earth. The condition is termed solar maximum (see Fig. 6 , denoted by the yellow boxes). Alternatively, as the magnetic field of the sun weakens, the number of sunspots decreases, resulting in less radiation energy being emitted to the earth. The phenomenon is known as the solar minimum (see Fig. 6 , represented by the blue boxes).
The emergence and recurrence of pandemics every 5 years in relation to solar activities ( Source: www.swpc.noaa.gov/ ). Note: The yellow boxes indicate the solar maximum, while the blue boxes represent the solar minimum
The magnetic field of the sun protects the earth from cosmic or galactic cosmic rays emitted by supernova explosions, stars, and gamma-ray bursts [ 97 ]. Nevertheless, galactic cosmic rays could still reach the earth during the solar minimum, the least solar radiation energy period. In the 20th and early 21st centuries, several outbreaks of viral diseases that affected the respiratory system (pneumonia or influenza), namely the Spanish (1918–1919), Asian (1957–1958) and Hong Kong (1968) flu, were documented. Interestingly, the diseases that claimed numerous lives worldwide occurred at the peak of the solar maximum.
Figure 6 illustrates the correlation between the number of sunspots and disease outbreaks from 1975 to 2021, including COVID-19, that began to escalate in December 2019. Under the solar minimum conditions, the spread of Ebola (1976), H5N1 (1997–1998), H1N1 (2009), and COVID-19 (2019-2020) were documented, while the solar maximum phenomenon recorded SARS (2002) and H7N9 (2012–2013) or MERS outbreaks. Nonetheless, solar activity through the production of solar sunspots began to decline since the 22nd solar cycle. Accordingly, further studies are necessary to investigate the influence such solar variations could impart or not on pandemic development.
Despite the findings mentioned above, the sun and cosmic radiations could influence the distribution or outspread of disease-spreading viruses. The rays could kill the viruses via DNA destruction or influence their genetic mutations, which encourage growth and viral evolution. Nevertheless, the connection between radiation and the evolutionary process requires further study by specialists in the field it is become true or not.
The spread of viral diseases transpires naturally in our surroundings and occurs unnoticed by humans. According to records, the spread of pandemic diseases, including the Black Death (fourteenth century) and the Spanish flu (1919), was significantly influenced by the decline and peak of solar activities. Furthermore, in the past 20 years, various diseases related to the influenza virus have been recorded. According to the pattern observed, if all diseases were related to the solar cycle (solar maximum and minimum), the viral diseases would reoccur every 5 to 6 years since they first appeared between 1995 and 2020. Accordingly, the next pandemic might occur around 2024 or 2025 and need to have a proper study for prove these statements. Nonetheless, the activities on the surface of the sun have been weakening since the 23rd solar cycle and it can be proven later after the proper study can be make it.
The beginning of the COVID-19 spread, only several countries with the same winter climate with an average temperature of 5–11 °C and an average humidity rate of 47–79% located at latitudes 30–50 N reported cases. The areas included Wuhan distribution centres in China, the United Kingdom, France, Spain, South Korea, Japan, and the USA (see Fig. 5 ). Other than biological aspects, the higher number of confirmed cases recorded in colder environments was due to the human body secreting less lymphoproliferative hormone, leading to decreased immunogenicity effects and increased risk of infection [ 24 ]. Consequently, the virus could attack and rapidly infect humans during the period [ 1 , 54 ].
The lymphoproliferative response is a protective immune response that plays a vital role in protecting and eradicating infections and diseases. On the other hand, staying in warm conditions or being exposed to more sunlight would lower the risks of infection. According to Asyary and Veruswati [ 98 ], sunlight triggers vitamin D, which increases immunity and increases the recovery rates of infected individuals.
Researchers believe that viruses could survive in the environment for up to 3 to 4 years or even longer. The survival rate of the microorganisms is relatively high, which is related to their biological structures, adaptability on any surfaces, and transmission medium to spread diseases. Viruses possess simple protein structures, namely the spike, membrane, and envelope protein; therefore, when they enter living organisms (such as through the respiratory system), the viruses are easily transmitted.
Once they have entered a host, the viruses duplicate exponentially and swarm the lungs. Subsequently, after the targeted organs, such as the lungs, are invaded, the viruses attack the immune system and create confusion in protective cells to destroy healthy cells. The situation is still considered safe in younger and healthy individuals as their immune systems could differentiate and counter-attack the viruses, curing them. Nonetheless, in elders and individuals with several chronic diseases, most of their protective cells are dead, hence their immune system is forced to work hard to overcome the infection. Pneumonia and death tend to occur when the situation is overwhelming [ 85 ]. Consequently, the viruses are harmful to humans as they could multiply in a short period, enter the blood, and overrun the body.
The coronavirus could attach to surfaces without a host, including door knobs and steel and plastic materials. The microorganisms could survive alone, but virologists have yet to determine how long. If someone touches any surface with the virus, the individual would then be infected. The situation would worsen if the infected person contacted numerous people and became a super spreader. A super spreader does not exhibit any symptoms and continuously transmits the virus without realising it. An infected individual transmits the coronavirus via droplets from coughs or sneezes. Nevertheless, scientists have yet to determine if coronavirus is spread via airborne or droplets, hence requiring thorough evaluation [ 99 ].
The COVID-19 virus mutates over time, and it can be changing any times. Mutations alter the behaviour and genetic structure of the virus, resulting in a new strain. Numerous research have been conducted to procure vaccines and anti-viral medications, but mutations have led to evolutionary disadvantages. The novel strains are more infectious than the original ones. As of November 2020, approximately six new coronavirus strains have been detected, each displaying different transmission behaviours [ 100 ].
Recent studies demonstrated that the mutated viruses exhibit little variability, allowing scientists to produce viable vaccines [ 71 ]. Furthermore, different types of vaccines are manufactured by different countries, which could be advantageous. Currently, most countries also recommend booster doses to attain extra protection after receiving the mandatory two vaccine doses. In same time, the social and physical interactions between humans also necessitate to be aware.
The COVID-19 virus is primarily transmitted through droplets produced by an infected person. Accordingly, physical distancing, a one-metre minimum distance between individuals [ 19 ], and following the SOP might prevent or avoid spreading the disease. Moreover, self-quarantine, school closures, working from home, cancelling large events, limiting gatherings, and avoiding spending long periods in crowded places are essential strategies in enforcing physical distancing at a community level. The policies are essential precautions that could reduce the further spreading of coronavirus and break the chain of transmission.
Government support also need to control the spread of COVID-19 with the strict SOP. The SOP enforcement in public places would enhance adherence to the new practice among the public and the community, aiding in curbing disease transmission. Practising limited meetings and social gatherings, avoiding crowded places, workplace distancing, preventing non-necessary travels of high-risk family members, especially those with chronic disease, and adhering to the recommended SOP could reduce coronavirus outbreaks. Nonetheless, individual awareness is also necessary to achieve COVID-19 spread prevention.
Many researchers are focused on identifying the primary drivers of pandemic outbreaks. Seasonal, temperature, and humidity differences significantly impacted COVID-19 growth rate variations. It is crucial to highlight the potential link between the recurrence of pandemics every 5 years and solar activities, which can influence temperature and humidity variations. Notable variations in COVID-19 mortality rates were observed between northern and southern hemisphere countries, with the former having higher rates. One hypothesis suggests that populations in the northern hemisphere may receive insufficient sunlight to maintain optimal vitamin D levels during winter, possibly leading to higher mortality rates.
The first COVID-19 case was detected in Wuhan, China, which is in the northern hemisphere. The number of cases rapidly propagated in December during the winter season. At the time, the temperature in Wuhan was recorded at 13–18 °C. Accordingly, one theory proposes that the survival and transmission of the coronavirus were due to meteorological conditions, namely temperatures between 13 and 18 °C and 50–80% humidity.
Daily rainfall directly impacts humidity levels. The coronavirus exhibited superior survival rates in cold and dry conditions. Furthermore, transmissible gastroenteritis (TGEV) suspensions and possibly other coronaviruses remain viable longer in their airborne states, which are more reliably collected in low relative humidity than in high humidity. Consequently, summer rains would effectively reduce COVID-19 transmission in southern hemisphere regions.
In southern hemisphere regions, the summer seasons are accompanied by a high average temperature at the end and beginning of the year. Countries with temperatures exceeding 24 °C reported fewer infections. As temperatures rise from winter to summer, virus transmission is expected to decline. Nonetheless, the activities and transmission of the virus were expected to decrease during winter to summer transitions, when the countries would be warmer. The peak intensity of infections strongly depends on the level of seasonal transmissions.
Social distancing plays a critical role in preventing the overload of healthcare systems. Many respiratory pathogens, including those causing mild common cold-like syndromes, show seasonal fluctuations, often peaking in winter. This trend can be attributed to increased indoor crowding, school reopening, and climatic changes during autumn.
The spread of COVID-19 to neighbouring regions can be attributed to population interactions. Migration patterns, such as the movement from northern to southern regions during the warmer months, have significant epidemiological impacts. This trend mirrors the behavior of influenza pandemics where minor outbreaks in spring or summer are often followed by major waves in autumn or winter.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
Novel coronavirus
Coronavirus disease 2019
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Swine influenza
Influenza A virus subtype H5N1
Asian Lineage Avian Influenza A(H7N9) Virus
Middle East respiratory syndrome
Middle East respiratory syndrome Coronavirus
Particulate matter
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
RepOrting standards for Systematic Evidence Syntheses
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus
Syndrome coronavirus 2
Systematic literature review
Standard operating procedure
Transmissible gastroenteritis Virus
United States of America
World Health Organization
Apanovich I. Climate and man. Opposition or natural stage of the earth’s evolution? Norwegian journal of development of the international. Science. 2019;26(25):12–27.
Google Scholar
Borah P, Singh MK, Mahapatra S. Estimation of degree-days for different climatic zones of north-East India. Sustain Cities Soc. 2015;14(1):70–81.
Article Google Scholar
Chen D, Chen HW. Using the Köppen classification to quantify climate variation and change: an example for 1901-2010. Environmental Development. 2013;6(1):69–79.
Trenberth KE, Fasullo JT. Global warming due to increasing absorbed solar radiation. Geophys Res Lett. 2009;36
Hauschild MZ, Huijbregts MAJ, Guinée L, Lane J, Fantke P, Zelm v R, et al. Life Cycle Impact Assessment – The Complete World of Life Cycle Assessment; 2015. p. 345.
Book Google Scholar
Nakada LYK, Urban RC. COVID-19 pandemic: environmental and social factors influencing the spread of SARS-CoV-2 in São Paulo. Brazil Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2021;28(30):40322–8.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Lagtayi, R., Lairgi, L., Daya, A., & Khouya, A. (2021). The impact of the average temperature, humidity, wind speed, altitude and population density on daily COVID-19 infections’ evolution. January, 9094.
Majumder MS, Liu D, Poirier C, Mandl KD, Lipsitch M, The MS. The role of absolute humidity on transmission rates of the COVID-19 outbreak; 2020.
Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, Peacock SJ, Prescott HC. Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A review. JAMA - Journal of the American Medical Association. 2020;324(8):782–93.
Zhang X, Maggioni V, Houser P, Xue Y, Mei Y. The impact of weather condition and social activity on COVID-19 transmission in the United States. J Environ Manag. 2022;302:114085.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Mäkinen TM, Juvonen R, Jokelainen J, Harju TH, Peitso A, Bloigu A, et al. Cold temperature and low humidity are associated with increased occurrence of respiratory tract infections. Respir Med. 2009;103(3):456–62.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Carvalho FRS, Henriques DV, Correia O, Schmalwieser AW. Potential of solar UV radiation for inactivation of Coronaviridae family. Photochem Photobiol. 2021;97:213–20.
Ali I, Alharbi OM. COVID-19: disease, management, treatment, and social impact. Sci Total Environ. 2020;728:138861.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Jin Y, Yang H, Ji W, Wu W, Chen S, Zhang W, et al. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of covid-19. Viruses. 2020;12(4):1–17.
Sohrabi C, Alsafi Z, O’Neill N, Khan M, Kerwan A, Al-Jabir A, et al. World health organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Int J Surg. 2020;76:71–6.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wang J, Tang K, Feng K, Lv W. High temperature and high humidity reduce the transmission of COVID-19; 2020a.
Wang L, Duan Y, Zhang W, Liang J, Xu J, Zhang Y, et al. Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of 26 cases of covid-19 arising from patient-to-patient transmission in Liaocheng, China. Clinical Epidemiology. 2020b;12:387–91.
Xie J, Zhu Y. Science of the Total environment association between ambient temperature and COVID-19 infection in 122 cities from China. Sci Total Environ. 2020;724:138201.
World Health Organization. (2020a). Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19-10April 2020. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19—10- april-2020.
Bostock B. South Korea is testing 200,000 members of a doomsday church linked to more than 60% of its coronavirus cases; 2020.
World Health Organization. (2020b). Health topics/coronavirus. https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_1.
Menhat M, Mohd Zaideen IM, Yusuf Y, Salleh NHM, Zamri MA, Jeevan J. The impact of Covid-19 pandemic: A review on maritime sectors in Malaysia. Ocean Coast Manag. 2021;209:105638.
Byun WS, Heo SW, Jo G, Kim JW, Kim S, Lee S, et al. Is coronavirus disease (COVID-19) seasonal? A critical analysis of empirical and epidemiological studies at global and local scales. Environ Res. 2021;196:110972.
Dhakal P, Pokhrel P, B. Seasonal variation and COVID-19 pandemic in Nepal. Nepal Medical Journal. 2020;3(2):77–80.
Mehmet Ş. Science of the Total environment impact of weather on COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey. 728; 2020.
Xu H, Yan C, Fu Q, Xiao K, Yu Y, Han D, et al. Science of the Total environment possible environmental effects on the spread of COVID-19 in China. Sci Total Environ. 2020;731:139211.
Rosario DKA, Mutz YS, Bernardes PC, Conte-Junior CA. Relationship between COVID-19 and weather: case study in a tropical country. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2020;229:113587.
Wang J, Tang K, Feng K, Lin X, Lv W, Chen K, et al. Impact of temperature and relative humidity on the transmission of COVID-19: A modelling study in China and the United States. BMJ Open. 2021;11(2):1–16.
Wu Y, Jing W, Liu J, Ma Q, Yuan J, Wang Y, et al. Effects of temperature and humidity on the daily new cases and new deaths of COVID-19 in 166 countries. Sci Total Environ. 2020;729:1–7.
Casanova LM, Jeon S, Rutala WA, Weber DJ, Sobsey MD. Effects of air temperature and relative humidity on coronavirus survival on surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76(9):2712–7.
Islam N, Bukhari Q, Jameel Y, Shabnam S, Erzurumluoglu AM, Siddique MA, et al. COVID-19 and climatic factors: A global analysis. Environ Res. 2021;193:110355.
Diao Y, Kodera S, Anzai D, Gomez-Tames J, Rashed EA, Hirata A. Influence of population density, temperature, and absolute humidity on spread and decay durations of COVID-19: A comparative study of scenarios in China, England, Germany, and Japan. One Health. 2021;12:100203.
Haddaway NR, Macura B, Whaley P, Pullin AS. ROSES reporting standards for systematic evidence syntheses: pro forma, flow-diagram and descriptive summary of the plan and conduct of environmental systematic reviews and systematic maps. Environ Evid. 2018;7(1):4–11.
Sharif N, Dey SK. Impact of population density and weather on COVID-19 pandemic and SARS-CoV-2 mutation frequency in Bangladesh. Epidemiol Infect. 2021:1–10.
Kraus S, Breier Dasí-Rodríguez S. El arte de elaborar una revisión bibliográfica sistemática en la investigación sobre el espíritu empresarial. Int Entrep Manag J. 2020;16:1023–42.
Xiao Y, Watson M. Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. J Plan Educ Res. 2019;39(1):93–112.
Gusenbauer M, Haddaway NR. Which academic search systems are suitable for systematic reviews or meta-analyses? Evaluating retrieval qualities of Google scholar, PubMed, and 26 other resources. Res Synth Methods. 2020;11(2):181–217.
Halevi G, Moed H, Bar-Ilan J. Suitability of Google scholar as a source of scientific information and as a source of data for scientific evaluation—review of the literature. Journal of Informetrics. 2017;11(3):823–34.
Haddaway NR, Collins AM, Coughlin D, Kirk S. The role of google scholar in evidence reviews and its applicability to grey literature searching. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):1–17.
Littlewood C, Chance-Larsen K, McLean S. Quality appraisal as a part of the systematic review. International Journal of Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation. 2010;1(1):53–8.
Vaismoradi M, Turunen H, Bondas T. Content analysis and thematic analysis: implications for conducting a qualitative descriptive study. Nurs Health Sci. 2013;15(3):398–405.
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3:77–101.
Ahmadi M, Sharifi A, Dorosti S, Jafarzadeh Ghoushchi S, Ghanbari N. Investigation of effective climatology parameters on COVID-19 outbreak in Iran. Sci Total Environ. 2020;729
Gupta A, Banerjee S, Das S. Significance of geographical factors to the COVID-19 outbreak in India. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment. 2020;6(4):2645–53.
Pequeno P, Mendel B, Rosa C, Bosholn M, Souza JL, Baccaro F, et al. Air transportation, population density and temperature predict the spread of COVID-19 in Brazil. PeerJ. 2020;2020(6):1–15.
Hoyle F, Wickramasinghe NC. Sunspots and influenza [6]. Nature. 1990;343(6256):304.
Wickramasinghe NC, Rocca MC, Tokoro G, Temple R. Journal of infectious diseases. Scienctific Research and Community. 2020;1(4):1–10.
Wickramasinghe NC, Steele EJ, Wainwright M, Tokoro G, Fernando M, Qu J. Sunspot cycle minima and pandemics : A case for vigilance at the present time. Journal of Astrobiology & Outreach. 2017;5:2332–519.
Wickramasinghe NC, Qu J. Are we approaching a new influenza pandemic. Virol Curr Res. 2018;2(107):2.
Guan W, Ni Z, Hu Y, Liang W, Ou C, He J, et al. Disease 2019 in China; 2020.
Bashir MF, Ma B, Bilal K, Bashir MA, Tan D, Bashir M. Correlation between climate indicators and COVID-19 pandemic in New York, USA. Sci Total Environ. 2020;728:138835.
Cucinotta D, Vanelli M. WHO declares COVID-19 a pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020;91:157–60.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lin C, Lau AKH, Fung JCH, Guo C, Chan JWM, Yeung DW, et al. A mechanism-based parameterisation scheme to investigate the association between transmission rate of COVID-19 and meteorological factors on plains in China. Sci Total Environ. 2020;737:140348.
Coşkun H, Yıldırım N, Gündüz S. The spread of COVID-19 virus through population density and wind in Turkey cities. Sci Total Environ. 2021;751
Yang HY, Lee JKW. The impact of temperature on the risk of covid-19: A multinational study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(8)
Candido DD, Watts A, Abade L, Kraemer MUG, Pybus OG, Croda J, et al. Routes for COVID-19 importation in Brazil. Journal of Travel Medicine. 2020;27(3):1–3.
Hardy JP, Groffman PM, Fitzhugh RD, Henry KS, Welman AT, Demers JD, et al. Snow depth manipulation and its influence on soil frost and water dynamics in a northern hardwood forest. Biogeochemistry. 2001;56(2):151–74.
Gunthe SS, Swain B, Patra SS, Amte A. On the global trends and spread of the COVID-19 outbreak: preliminary assessment of the potential relation between location-specific temperature and UV index. Journal of Public Health (Germany). 2020:1–10.
Rosenthal PJ, et al. COVID-19: shining the light on Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020;102(6):1145–8.
Kraemer MUG, et al. The effect of human mobility and control measures on the COVID-19 epidemic in China. Science. 2020;368:493–7.
Dalziel BD, Kissler S, Gog JR, Viboud C, Bjørnstad ON, Metcalf CJE, et al. Urbanization and humidity shape the intensity of influenza epidemics in U.S. cities. Science. 2018;362:75–9.
Sahoo PK, Powell MA, Mittal S, Garg VK. Is the transmission of novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) weather dependent? J Air Waste Manage Assoc. 2020;70(11):1061–4.
Selcuk M, Gormus S, Guven M. Impact of weather parameters and population density on the COVID-19 transmission: evidence from 81 provinces of Turkey. Earth Syst Environ. 2021;5(1):87–100.
Abraham J, Turville C, Dowling K, Florentine S. Does climate play any role in covid-19 spreading?—an Australian perspective. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(17)
Sehra ST, Salciccioli JD, Wiebe DJ, Fundin S, Baker JF. Maximum daily temperature, precipitation, ultraviolet light, and rates of transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in the United States. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(9):2482–7.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Rubin D, Huang J, Fisher BT, Gasparrini A, Tam V, Song L, et al. Association of Social Distancing, population density, and temperature with the instantaneous reproduction number of SARS-CoV-2 in counties across the United States. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(7):1–12.
Comunian S, Dongo D, Milani C, Palestini P. Air pollution and covid-19: The role of particulate matter in the spread and increase of covid-19’s morbidity and mortality. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(12):1–22.
Tosepu R, Gunawan J, Effendy DS, Ahmad LOAI, Lestari H, Bahar H, et al. Correlation between weather and Covid-19 pandemic in Jakarta, Indonesia. Sci Total Environ. 2020;725
Chen and Shakhnovich. Thermal adaptation of viruses and Bacteria. Biophys J. 2010;98:1109–18.
Martins LD, da Silva I, Batista WV, Andrade MF, Freitas ED, Jorge Alberto Martins JA. How socio-economic and atmospheric variables impact COVID-19 and influenza outbreaks in tropical and subtropical regions of Brazil. Environ Res. 2020;191:110184.
Kulkarni H, Khandait H, Narlawar UW, Rathod P, Mamtani M. Independent association of meteorological characteristics with initial spread of Covid-19 in India. Sci Total Environ. 2021;764:142801.
Menebo MM. Science of the Total environment temperature and precipitation associate with Covid-19 new daily cases : A correlation study between weather and Covid-19 pandemic in. Sci Total Environ. 2020;737:139659.
Gupta S, Patel KK. Global Epidemiology of First 90 Days into COVID-19 Pandemic :Disease Incidence , Prevalence , Case Fatality Population Density, Urbanisation. J Health Manag. 2020;22(2):117–28.
Haque SE, Rahman M. Association between temperature, humidity, and COVID-19 outbreaks in Bangladesh. Environ Sci Pol. 2020;114:253–5.
Sharma P, Singh AK, Agrawal B, Sharma A. Correlation between weather and COVID-19 pandemic in India: an empirical investigation. J Public Aff. 2020;20(4)
Fu S, Wang B, Zhou J, Xu X, Liu J, Ma Y, et al. Meteorological factors, governmental responses and COVID-19: evidence from four European countries. Environ Res. 2021;194:110596.
Mecenas P, Bastos RT, Vallinoto AC, Normando D. Effects of temperature and humidity on the spread of COVID-19: A systematic review. PLoS One. 2020;15:1–21.
Malki Z, Atlam ES, Hassanien AE, Dagnew G, Elhosseini MA, Gad I. Association between weather data and COVID-19 pandemic predicting mortality rate: machine learning approaches. Chaos, Solitons Fractals. 2020;138:110137.
Sasikumar K, Nath D, Nath R, Chen W. Impact of extreme hot climate on COVID-19 outbreak in India. GeoHealth. 2020;4(12)
Kodera S, Rashed EA, Hirata A. Correlation between COVID-19 morbidity and mortality rates in Japan and local population density, temperature, and absolute humidity. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(15):1–14.
Sobral MFF, Duarte GB, da Penha Sobral AIG, Marinho MLM, de Souza Melo A. Association between climate variables and global transmission oF SARS-CoV-2. Sci Total Environ. 2020;729:138997.
Patel SK, Pathak M, Tiwari R, Yatoo MI, Malik YS. A vaccine is not too far for COVID-19 coronavirus pandemic A vaccine is not too far for COVID-19. May; 2020.
Nicola M, Neill NO, Sohrabi C, Khan M, Agha M, Agha R. Evidence based management guideline for the COVID-19 pandemic - review article. Int J Surg. 2020;77:206–16.
Atangana E, Atangana A. Facemasks simple but powerful weapons to protect against COVID-19 spread: can they have sides effects? Results in Physics. 2020;19:103425.
Sarmadi M, Moghanddam VK, Dickerson AS, Martelletti L. Association of COVID-19 distribution with air quality, sociodemographic factors, and comorbidities: an ecological study of US states. Air Qual Atmos Health. 2021;14(4):455–65.
Chung CJ, Nazif TM, Wolbinski M, Hakemi E, Lebehn M, Brandwein R, et al. The restructuring of structural heart disease practice during The Covid-19 pandemic. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020; InPress
Bukhari Q, Massaro JM, D’agostino RB, Khan S. Effects of weather on coronavirus pandemic. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(15):1–12.
Sun C, Zhai Z. The efficacy of social distance and ventilation effectiveness in preventing COVID-19 transmission. Sustain Cities Soc. 2020;62:102390.
Nair N, Selvaraj P. Using a cultural and social identity lens to understand pandemic responses in the US and India. Int J Cross-cult Manag. 2021;21(3):545–68.
Cetron M, Landwirth J. Public health and ethical considerations in planning for quarantine. Yale J Biol Med. 2005;78(5):325–30.
Jernigan DB. Update: public health response to the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak—United States, February 24, 2020. MMWR. Morbidity and mortality weekly report, 69. 2020.
Stasi C, Fallani S, Voller F, Silvestri C. Treatment for COVID-19: an overview. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;889:173644.
Foad CAKK, Xun N, Pejman J, Nataraj RC. Nonlinear dynamic analysis of an epidemiological model for COVID-19 including public behavior and government action. Nonlinear Dynamics. 2020;101(3):1545–59.
Sun Z, Zhang H, Yang Y, Wan H, Wang Y. Science of the Total environment impacts of geographic factors and population density on the COVID-19 spreading under the lockdown policies of China. Sci Total Environ. 2020;746(666):141347.
Abdullah S, Mansor AA, Napi NNLM, Mansor WNW, Ahmed AN, Ismail M, et al. Air quality status during 2020 Malaysia movement control order (MCO) due to 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) pandemic. Sci Total Environ. 2020;729:139022.
Menhat M, Yusuf Y. Factors influencing the choice of performance measures for the oil and gas supply chain - exploratory study. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 2018;342(1)
Ćirkovića MM, Vukotića B. Long-term prospects: mitigation of supernova and gamma-ray burst threat to intelligent beings. Acta Astronautica. 2016;129:438–46.
Asyary A, Veruswati M. Science of the Total environment sunlight exposure increased Covid-19 recovery rates : A study in the central pandemic area of Indonesia. Sci Total Environ. 2020;729:139016.
Jayaweeraa M, Pererab H, Gunawardanaa B, Manatungea J. Transmission of COVID-19 virus by droplets and aerosols: A critical review on the unresolved dichotomy. Environ Res. 2020;188:1–18.
Leung K, Shum MHH, Leung GM, Lam TTY, Wu JT. Early transmissibility assessment of the N501Y mutant strains of SARS-CoV-2 in the United Kingdom, October to November 2020. Euro Surveill. 2020;26(1)
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would also like to acknowledge the Editors and an anonymous reviewer, who contributed immensely to improving the quality of this publication and a special thanks to Muhammad Hafiy Nauwal Effi Helmy, that contributed an excellent idea through singing during the COVID-19 lockdown period.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Maritime Studies, Universiti Malaysia Terengganu, 21030, Kuala Nerus, Terengganu, Malaysia
Masha Menhat
Institute of Oceanography and Environment, Universiti Malaysia Terengganu, 21030, Kuala Nerus, Terengganu, Malaysia
Effi Helmy Ariffin, Junainah Zakaria & Mohd Fadzil Akhir
Faculty of Science and Marine Environment, Universiti Malaysia Terengganu, 21030, Kuala Nerus, Terengganu, Malaysia
Wan Shiao Dong & Aminah Ismailluddin
Institute for Social Science Studies, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400, Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
Hayrol Azril Mohamed Shafril
Social, Environmental and Developmental Sustainability Research Center, Faculty of Social Sciences and Humanities, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600, Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia
Mahazan Muhammad
Institute of Geology Malaysia, Board of Geologists, 62100, Putrajaya, Malaysia
Ahmad Rosli Othman
Executive Office, Proofreading By A UK PhD, 51-1, Biz Avenue II, 63000, Cyberjaya, Malaysia
Thavamaran Kanesan
Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Malaya, 50603, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Suzana Pil Ramli
Faculty of Applied Sciences, Uva Wellassa University, Badulla, 90000, Sri Lanka
Amila Sandaruwan Ratnayake
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors have been involved in writing this editorial and contributing to the review of the manuscript. MM and EHA contribute to conceptualization. IA and ARO have made the figure.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Effi Helmy Ariffin .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not Applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Menhat, M., Ariffin, E.H., Dong, W.S. et al. Rain, rain, go away, come again another day: do climate variations enhance the spread of COVID-19?. Global Health 20 , 43 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12992-024-01044-w
Download citation
Received : 27 July 2023
Accepted : 22 April 2024
Published : 14 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12992-024-01044-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Coronavirus
- Solar radiation
- Temperature
- Social distancing
Globalization and Health
ISSN: 1744-8603
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
China’s Approach to Foreign Policy Gets Largely Negative Reviews in 24-Country Survey
Still, views of china – and its soft power – are more positive in middle-income countries, table of contents.
- Road map to the report
- How views of China have changed in recent years
- Views of China by age group
- How views of China’s international behavior have changed over time
- Most say China does not contribute to world peace and stability
- China seen as interventionist
- How opinions about which country is the world’s top economy have changed in recent years
- Many who see China as the world’s leading economic power also see it as a good thing
- Chinese investment seen as an economic benefit
- How views of Chinese soft power vary by age
- Views of Chinese technology
- How confidence in Xi has changed over time
- How confidence in Xi varies by age
- Acknowledgments
- Methodology

This Pew Research Center analysis focuses on public opinion of China and President Xi Jinping in 24 countries in North America, Europe, the Middle East, the Asia-Pacific region, sub-Saharan Africa and Latin America. The report explores views of China’s role in the world, including as an economic power, and perceptions of Chinese soft power. This is the first year since 2019 that the Global Attitudes Survey has included countries from Africa and Latin America, which were not included more recently due to the coronavirus outbreak .
For non-U.S. data, this report draws on nationally representative surveys of 27,285 adults conducted from Feb. 20 to May 22, 2023. All surveys were conducted over the phone with adults in Canada, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, South Korea, Spain, Sweden and the United Kingdom. Surveys were conducted face to face in Argentina, Brazil, Hungary, India, Indonesia, Israel, Kenya, Mexico, Nigeria, Poland and South Africa. In Australia, we used a mixed-mode probability-based online panel.
In the United States, we surveyed 3,576 U.S. adults from March 20 to 26, 2023. Everyone who took part in this survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for the report , along with responses, and the survey methodology .
Views of China are broadly negative across 24 countries in a new Pew Research Center survey: A median of 67% of adults express unfavorable views of the country, while 28% have a favorable opinion.
Negative views extend to evaluations of China’s international actions. Despite several high-profile diplomatic initiatives by Beijing over the past year – such as brokering a peace deal between Saudi Arabia and Iran and issuing a 12-point proposal for the end of violence in Ukraine – a median of 71% think China does not contribute to global peace and stability.
Most people also think China does not take into account the interests of other countries in its foreign policy (76%) and a median of 57% say China interferes in the affairs of other nations a great deal or fair amount.
Still, attitudes toward China are somewhat rosier in middle-income than high-income countries. Across eight middle-income countries – places Pew Research Center has not surveyed since 2019 due to the challenges of conducting face-to-face interviews during the pandemic – India stands out as the only middle-income country in which a majority has unfavorable views of China. And in three middle-income countries – Kenya, Mexico and Nigeria – a majority even gives China a positive rating.
Fewer in these middle-income countries also criticize China’s global behavior, and many more see China’s “soft power” appeal. Indeed, publics in these middle-income countries offer relatively favorable ratings for China’s entertainment products, its universities and its standard of living – while few in most high-income countries agree.
Across all 24 countries surveyed, however, there is more agreement about China’s technology. A median of 69% describe China’s technological achievements as the best or above average relative to other wealthy nations, with similar shares in high- and middle-income countries. A median of 54% also see China’s military as among the best in the world.
But views of the country as the world’s foremost economic power have faltered somewhat in recent years. More people now name the United States as the top economic power than China (a median of 42% vs. 33%, respectively). Much of this shift has come in high-income countries, where the share naming China has fallen in nearly every surveyed country – including by double digits in Germany, the Netherlands, Poland and Sweden.
In the U.S., where equal shares (43%) called China and the U.S. the world’s leading economic power in 2022, views have shifted significantly over the past year ; now, Americans are 10 percentage points more likely to name the U.S. than China (48% vs. 38%). (For more on American views of China, read “ Americans are Critical of China’s Global Role – as Well as Its Relationship With Russia ”.)
These findings come from a new Pew Research Center survey conducted from Feb. 20 to May 22, 2023, among more than 30,000 people in 24 countries. Below are some of the other findings regarding China’s overall image, views of Chinese foreign policy, ratings of President Xi Jinping, opinions about Chinese soft power and its economic power.
Overall ratings for China
Across many high-income countries surveyed, which are in North America, Western Europe and parts of the Asia-Pacific region, a large majority has unfavorable views of China, as has been the case for multiple years . Indeed, in almost every high-income country surveyed, negative views currently stand at or near historic highs. In most countries, this does not reflect a significant increase over last year; rather, negative views have simply remained high in recent years. One notable exception is Poland, where negative views have increased 12 points during a period of strained bilateral relations , perhaps related to China’s handling of the war in Ukraine.
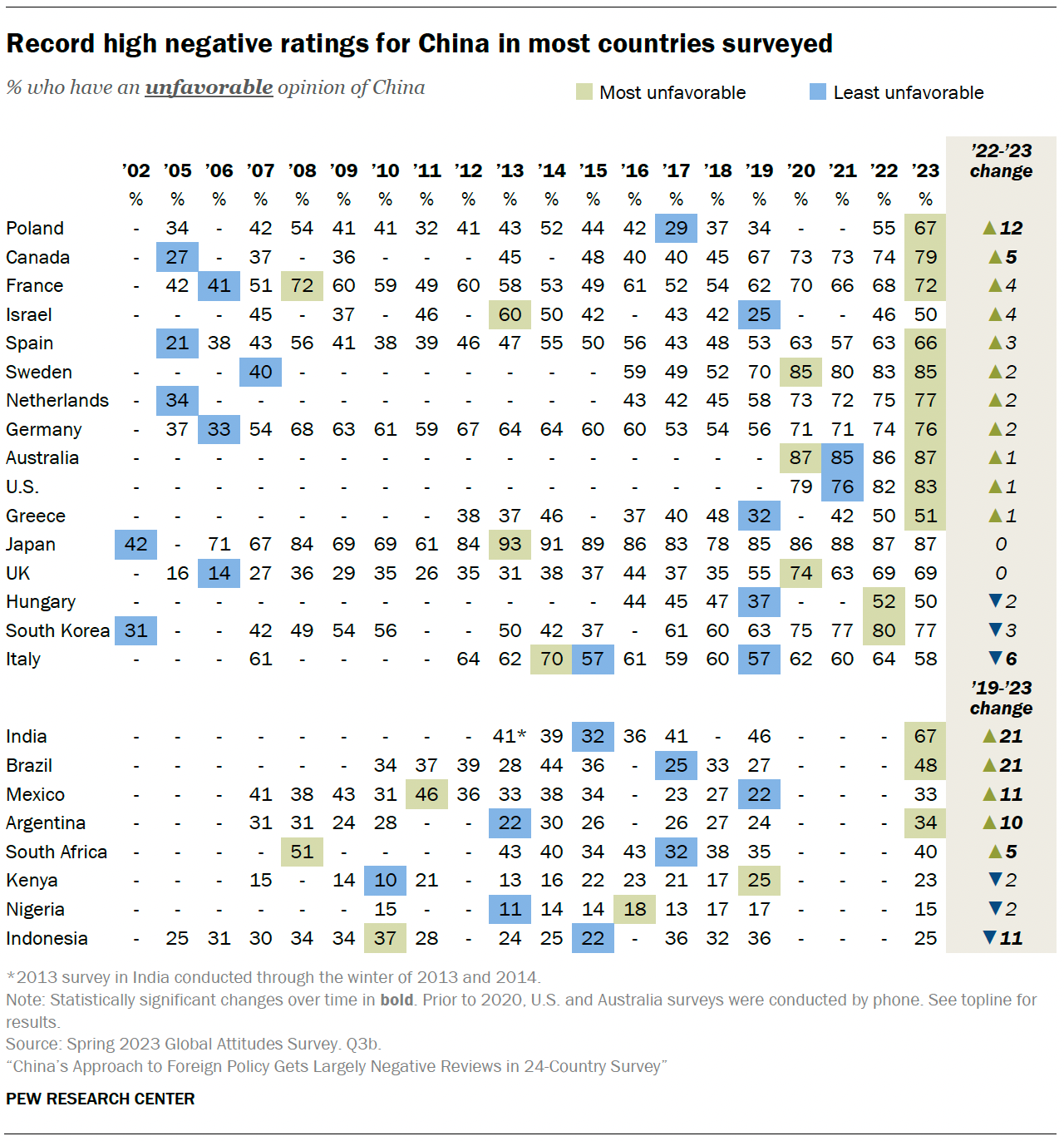
Views of China in middle-income countries are relatively more positive. Still, negative ratings in most of these countries have also grown since the countries were last surveyed, pre-pandemic. In South Africa and Mexico, for example, opinions have turned somewhat more negative since 2019, and in Argentina, Brazil and India, negative views have even reached historic highs. In India, military conflicts along a contested border may have contributed to the 21 percentage point increase in unfavorable opinion.
China’s role on the world stage
Majorities in most countries do not think China takes into account the interests of countries like theirs. In Canada, France, Israel, Spain and Sweden, around half or more say China doesn’t consider them at all . Only in the three sub-Saharan African countries surveyed, as well as in Indonesia, does around half or more of the public feel like China listens to their country.
A median of 71% also think China does little or nothing at all to contribute to global peace and stability, compared with a median of 23% who say it is doing a great deal or a fair amount. Australians, Canadians, Indians, Israelis and South Koreans are particularly likely to say China is doing nothing at all to help with global peace and stability.
Most also see China as an interventionist power. A median of 57% say China does interfere a great deal or a fair amount in the affairs of other countries, while a median of 35% say it does not do so much or at all. Around seven-in-ten or more in Australia, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Spain and the U.S. see China getting involved in the affairs of other countries – and many of these places also stood out for the high share who said China’s involvement in domestic politics in their own country was a very serious problem in a 2022 Pew Research Center survey .
But the country which is most likely to see China interfering in the affairs of other countries in this year’s survey is Italy (82%). Italy, which was the only G7 country to join China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) , was debating leaving the initiative at the time that the survey was conducted, but treading delicately for fear of stoking possible Chinese retribution against Italian businesses.
Attitudes toward Xi
Few in the 24 countries surveyed have confidence in Chinese President Xi Jinping to do the right thing regarding world affairs. Across most of Western Europe, the U.S., Canada and much of the Asia-Pacific region, around half in each country say they have no confidence in him at all . Indonesia, Kenya, Nigeria and South Africa stand out as the only countries where a majority or plurality have confidence in his leadership.
Confidence in Xi is closely related to views of China more broadly. In each country surveyed people with unfavorable views of China are more likely to have little confidence in the Chinese president, and vice versa.
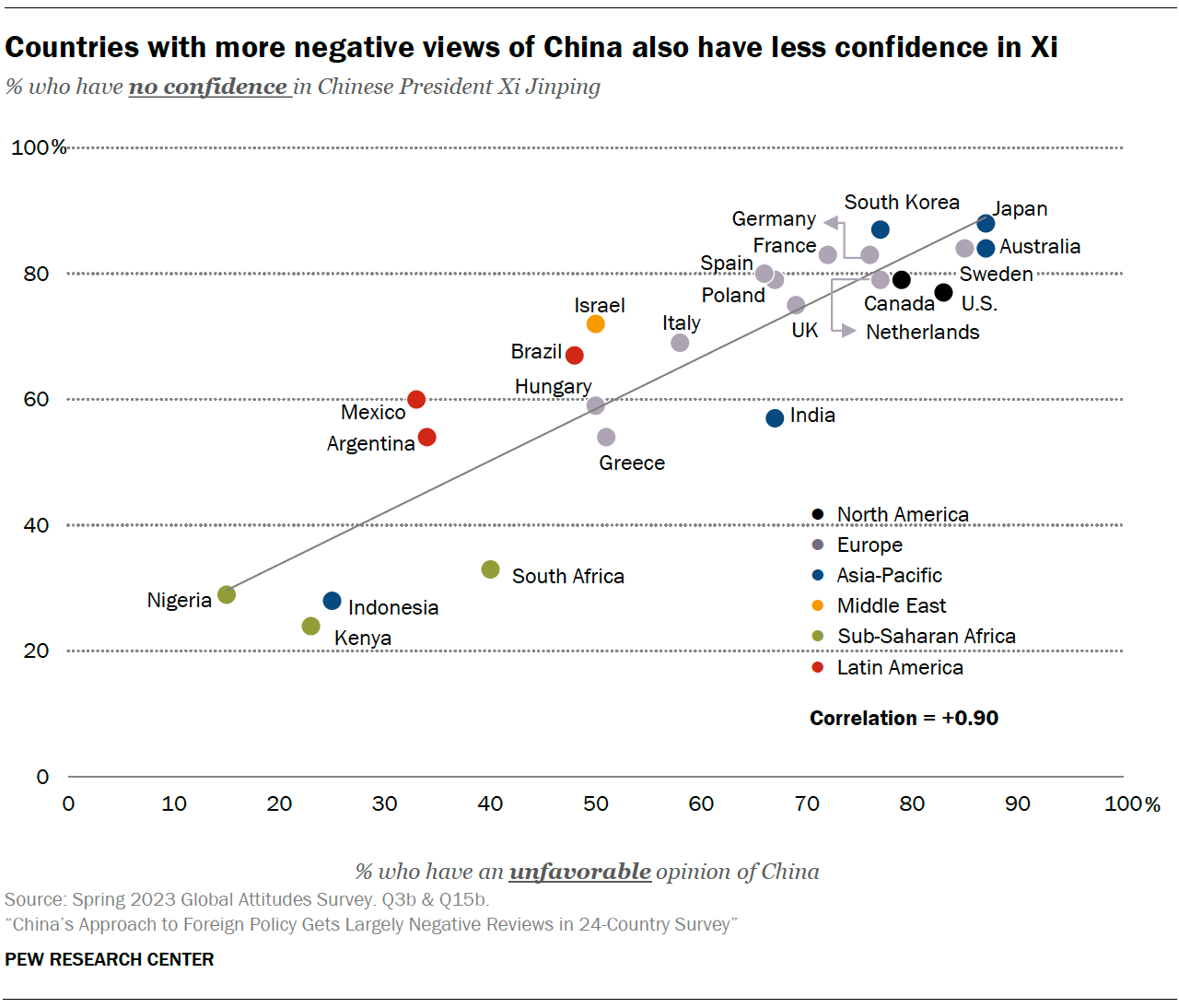
Chinese soft power
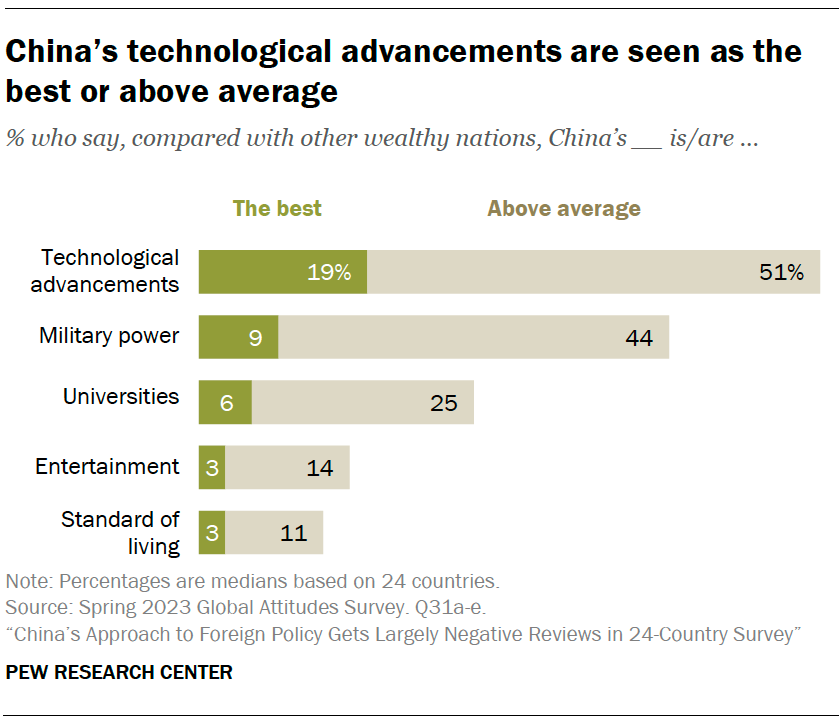
When it comes to elements often considered part of a country’s “soft power,” China’s technological achievements receive high marks, though fewer say the same about its universities, entertainment products or standard of living.
In fact, outside of South Korea, nearly half or more in every country say Chinese technological advancements are the best in the world or above average relative to other wealthy nations. And in many of the middle-income countries, around four-in-ten call Chinese technology the best in the world.
Middle-income countries – many of which are increasingly reliant on Chinese companies like Huawei for components of their 4G and 5G systems – were also asked specifically about technology such as phones, tablets or computers made by Chinese companies. Across these eight countries, there is a relatively widespread sense that these products are well-made. Middle-income publics are more divided when it comes to their cost: A median of 50% describe them as inexpensive, while 44% call them costly.
They are also somewhat divided when it comes to whether technological products made by Chinese companies protect people’s personal data (a median of 45%) or make their data unsafe (40%). (Americans were asked a different but related question about Chinese social media companies; large majorities have little confidence that they will use personal information responsibly or follow privacy policies.)
In every country, at least a plurality – and often a majority – also see China’s “hard power,” its military, as one of the best in the world or above average.
Chinese economic power
Fewer name China as the world’s leading economic power than the U.S. (a median of 33% vs. 42%). And, in many countries, the share naming China as the world’s leading economy has gone down in recent years.
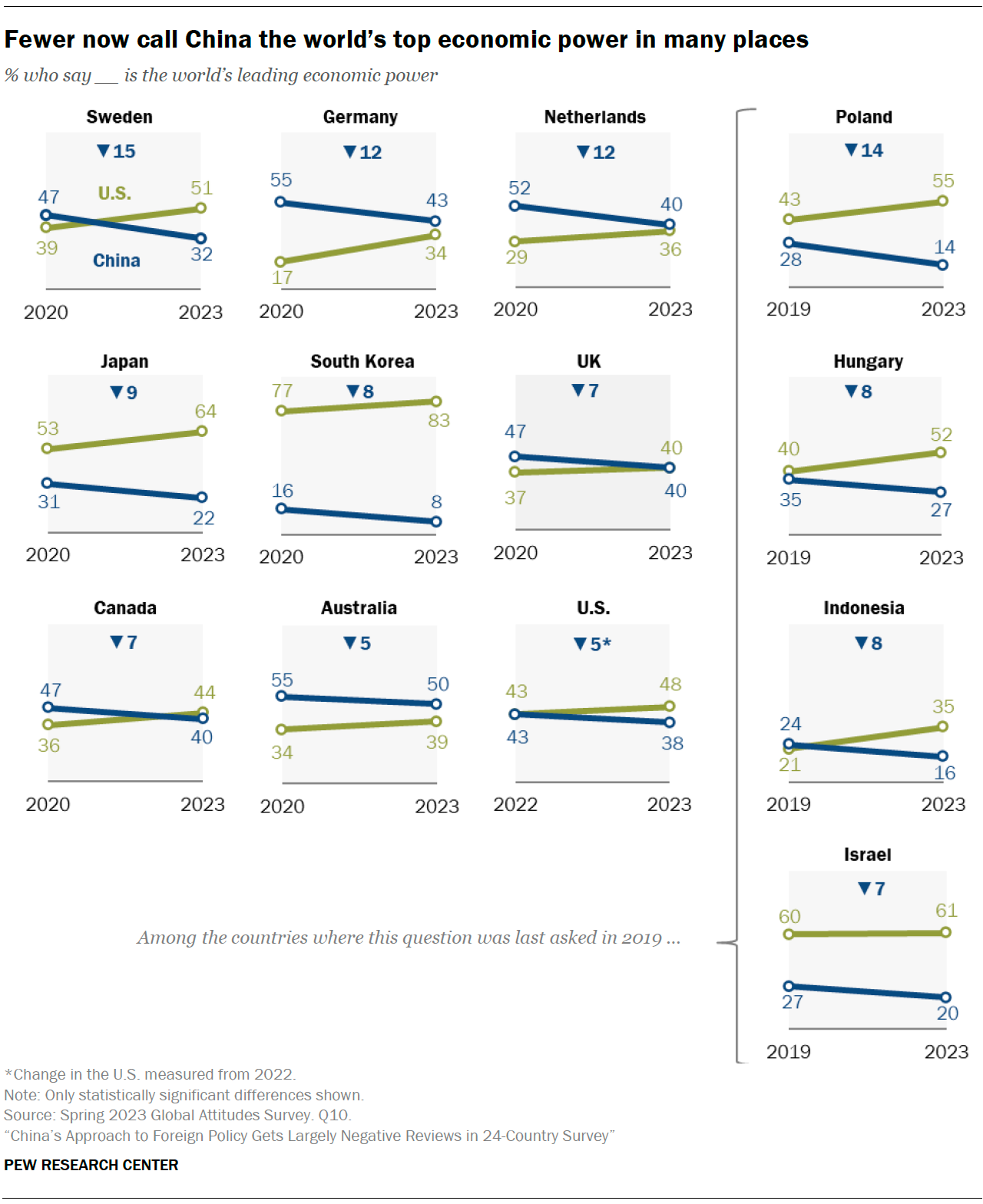
Interestingly, China’s image as an economic superpower is stronger in high-income countries than middle-income ones. Italy, for example, is the only country where a majority (55%) calls China the leading economic power.
Still, people in middle-income countries do recognize economic benefits from their relations with China. A different survey question, asked only in these countries, finds that around half or more in six middle-income countries say their nation’s economy has benefited a great deal or a fair amount from Chinese investment. In Nigeria, Kenya and South Africa, around seven-in-ten or more say this.
In the U.S., Americans were also asked to name the country which poses the top threat to the U.S. Not only was China the top answer, by far, but Americans see it as both an economic and a national security threat – in sharp contrast to Russia, which is primarily seen as a security threat. To read more about this related analysis, see “ Americans name China as the top threat facing the U.S. ”
The chapters that follow discuss these findings and others in more detail:
- Chapter 1 looks at overall opinion of China across the countries surveyed, including how perceptions have shifted over the years
- Chapter 2 considers the negative and positive roles China plays in international affairs
- Chapter 3 reviews global public opinion about which country is the world’s leading economic power
- Chapter 4 explores perceptions of Chinese soft power, summarizing how people across 24 countries rate China compared with other wealthy nations
- Chapter 5 examines confidence in Chinese President Xi Jinping to do the right thing in world affairs
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- China Global Image
- Global Balance of Power
- Global Economy & Trade
- World Leaders
Americans Remain Critical of China
How people in hong kong view mainland china and their own identity, in east asia, many people see china’s power and influence as a major threat, u.s.-germany relationship remains solid, but underlying policy differences begin to show, how views of the u.s., china and their leaders have changed over time, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center

A Simple Technique for Removing Microplastics from Drinking Water Revealed by Research
A s microplastic fragments increasingly infiltrate our systems, largely through consumption of contaminated food and drink, scientists are seeking effective solutions to combat this issue.
Researchers from China’s Guangzhou Medical University and Jinan University have discovered a straightforward method to extract these tiny plastic pieces from water.
The team experimented with both softened water and mineral-rich hard tap water , introducing nanoplastics and microplastics (NMPs) to the samples, following which they boiled and subsequently filtered the mixture to remove the remaining solids.
In some experiments, this boiling and filtering process successfully eliminated up to 90 percent of the NMPs, depending on the nature of the water being treated. This technique is especially convenient since it can be carried out using common kitchen equipment.
The research team states, “This uncomplicated boiling strategy can ‘decontaminate’ NMPs from household tap water, potentially reducing human consumption of NMPs from drinking water,” in their published work .
Hard water, well-known for its tendency to develop limescale, or calcium carbonate , upon heating, showed greater NMP removal. The kettle’s familiar white deposits capture the microplastics as the calcium carbonate separates from the water during boiling.
The method proved effective even with softened water, which contains less calcium carbonate—approximately one-quarter of the NMPs were caught in this case. Trapped within a calcium carbonate layer, these plastic particles were then filtered out using a simple tool, such as a thin stainless steel mesh typical for tea-straining, according to the researchers.
Previous research has detected traces of various plastics like polystyrene and polyethylene in drinking water, leading to routine ingestion. To test their solution further, the researchers introduced an excess of nanoplastics, which subsequently saw a reduced presence.
As stated by the researchers, “Drinking boiled water appears to be a feasible long-term solution for diminishing worldwide NMP exposure,” despite the fact that this practice is not common globally and is mostly traditional in a few regions. [source]
The study aims to encourage the habit of water boiling prior to consumption, especially with microplastic contamination on the rise globally.
While the exact health implications of microplastic ingestion remain to be fully understood, there is increasing concern regarding its contribution to disturbance of gut microbiota and antibiotic resistance in humans.
The authors of this study express a need for further exploration into the role of boiled water in preventing the introduction of synthetic materials into our systems and mitigating the alarming impacts of microplastics.
“Our outcomes affirm a highly practical approach to minimize human NMP exposure and contribute to the groundwork for conducting broader investigations involving a much larger sample collection,” the team shares .
The research was detailed in the journal Environmental Science & Technology Letters .
FAQ Section:
Q: What are microplastics?
A: Microplastics are small plastic fragments typically less than five millimeters in size, resulting from the breakdown of larger plastic debris or from manufactured products such as microbeads in personal care items.
Q: How do microplastics end up in drinking water?
A: Microplastics enter water systems through various sources, including industrial runoff, waste water discharge, and the breakdown of larger plastics in the environment. They have been found in both tap and bottled water.
Q: Is boiling water an effective way to remove microplastics?
A: Yes, according to the study by researchers from Guangzhou Medical University and Jinan University, boiling water and then filtering it can remove a significant portion of microplastics from drinking water.
Q: Are there health risks associated with consuming microplastics?
A: The health effects of consuming microplastics are not yet fully understood, but there is concern that they can lead to changes in the gut microbiome and increased antibiotic resistance.
Q: How can the average person remove microplastics from their drinking water at home?
A: Based on the study, individuals can boil their tap water and use a household filter, such as one made of stainless steel mesh typically used for straining tea, to remove any trapped microplastics.
Conclusion:
Microplastic contamination in drinking water is a growing concern with potential health implications. However, the study from Guangzhou Medical University and Jinan University offers a practical solution for individuals looking to reduce their exposure to microplastics. By boiling and filtering their water, people can take an active step toward limiting their intake of these synthetic particles. As research continues, there is a collective hope for broader acceptance of this water purification practice and a deeper understanding of the impacts of microplastics on human health.


COMMENTS
Generate the conclusion outline: After entering all necessary details, click on 'generate'. Paperpal will then create a structured outline for your conclusion, to help you start writing and build upon the outline. Write your conclusion: Use the generated outline to build your conclusion.
Table of contents. Step 1: Restate the problem. Step 2: Sum up the paper. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Research paper conclusion examples. Frequently asked questions about research paper conclusions.
Comprehensive: The conclusion should address all of the main points of the research paper, including the research question or problem, the methodology, the main results, and their implications. Future-oriented : The conclusion should provide insights and recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the research.
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research.
Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don't undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution. Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research.
Step 1: Explain your methodological approach. Step 2: Describe your data collection methods. Step 3: Describe your analysis method. Step 4: Evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made. Tips for writing a strong methodology chapter. Other interesting articles.
Research methodology refers to the system of procedures, techniques, and tools used to carry out a research study. It encompasses the overall approach, including the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and the interpretation of findings. Research methodology plays a crucial role in the field of research, as it ...
Revised on 10 October 2022. Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research.
Step 1: Restate the problem. Always begin by restating the research problem in the conclusion of a research paper. This serves to remind the reader of your hypothesis and refresh them on the main point of the paper. When restating the problem, take care to avoid using exactly the same words you employed earlier in the paper.
Step 1: Answer your research question. Step 2: Summarize and reflect on your research. Step 3: Make future recommendations. Step 4: Emphasize your contributions to your field. Step 5: Wrap up your thesis or dissertation. Full conclusion example. Conclusion checklist. Other interesting articles.
SCIENTIFIC METHODOLOGY AND ITS COMPONENTS. Methodologyin science refers to the diverse prin- ciples, procedures, and practices that govern empiri- cal research. It is useful to distinguish five major components to convey the scope of the topics and to organize the subject matter. 1.
The research design is a fundamental aspect of research methodology, outlining the overall strategy and structure of the study. It includes decisions regarding the research type (e.g., descriptive, experimental), the selection of variables, and the determination of the study's scope and timeframe. We must carefully consider the design to ...
Research methodology formats can vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project, but the following is a basic example of a structure for a research methodology section: ... Conclusion: This research aims to investigate the effectiveness of CBT in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. By using a randomized controlled ...
The conclusion is where you describe the consequences of your arguments by justifying to your readers why your arguments matter (Hamilton College, 2014). Derntl (2014) also describes conclusion as the counterpart of the introduction. Using the Hourglass Model (Swales, 1993) as a visual reference, Derntl describes conclusion as the part of the ...
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of your points or a re-statement of your research problem but a synthesis of key points. For most essays, one well-developed paragraph is sufficient for a conclusion ...
Background Methodological studies - studies that evaluate the design, analysis or reporting of other research-related reports - play an important role in health research. They help to highlight issues in the conduct of research with the aim of improving health research methodology, and ultimately reducing research waste. Main body We provide an overview of some of the key aspects of ...
2.7 Conclusion. In this chapter, you have learned about the processes involved in planning a research project. The process of research involves identifying a research problem or question, conducting a literature review to understand what is already known about the topic, formulating a hypothesis or research question, designing a study to test ...
The methodology used in this research is a descriptive method as it deliberates and defines the various parts of PhD methodology, results and conclusion writing process and elucidates the "how to do" in a very unpretentious and understanding manner.
Conclusion: Choosing an optimal research methodology is crucial for the success of any research project. The methodology you select will determine the type of data you collect, how you collect it, and how you analyse it. Understanding the different types of research methods available along with their strengths and weaknesses, is thus imperative ...
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
A conclusion is the final paragraph of a research paper and serves to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them. The conclusion of a conclusion should: Restate your topic and why it is important. Restate your thesis/claim. Address opposing viewpoints and explain why readers should align with your position.
Conclusive Research. Conclusive research design, as the name implies, is applied to generate findings that are practically useful in reaching conclusions or decision-making. In this type of studies research objectives and data requirements need to be clearly defined. Findings of conclusive studies usually have specific uses.
A scoping review was chosen as the appropriate method to synthesise the existing research regarding the barriers and facilitators to SSW practice to map the relevant literature and identify key concepts and knowledge gaps (Arksey and O'Malley, 2005; Levac et al., 2010; Munn et al., 2018). ... Conclusion. This scoping review examined the ...
The revolution and rotation of the Earth and the Sun supply heat and create differential heating on earth. The movements and the 23.5° inclination of the Earth [] separate the oblate-ellipsoid-shaped earth into northern and southern hemispheres.Consequently, the division results in various climatic zones at different latitudes and dissimilar local temperatures (see Fig. 1) and affects the ...
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design. When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make. First, decide how you will collect data. Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question:
In this article, the authors will describe a creative writing therapeutic group program they developed based on narrative therapy and narrative medicine principles. This was a Social Science and Humanities Research Council—Partnership Engagement Grant funded project, the aim of which was to develop a facilitator's manual for people interested in offering this group, titled "Journey ...
These findings come from a new Pew Research Center survey conducted from Feb. 20 to May 22, 2023, among more than 30,000 people in 24 countries. Below are some of the other findings regarding China's overall image, views of Chinese foreign policy, ratings of President Xi Jinping, opinions about Chinese soft power and its economic power.
The research team states, "This uncomplicated boiling strategy can 'decontaminate' NMPs from household tap water, potentially reducing human consumption of NMPs from drinking water," in ...
1.4 Market Research Methodology 1.5 Research Process and Data Source 1.6 Economic Indicators 1.7 Currency Considered. 2 Executive Summary 2.1 World Market Overview 2.1.1 Global POC and IVD Annual Sales 2017-2031 ... 14 Research Findings and Conclusion. Purchase this report ...