- Original Article
- Open access
- Published: 19 December 2017

GOOGLE: a reflection of culture, leader, and management
- Sang Kim Tran 1 , 2
International Journal of Corporate Social Responsibility volume 2 , Article number: 10 ( 2017 ) Cite this article
414k Accesses
12 Citations
4 Altmetric
Metrics details
This paper provides a viewpoint of the culture and subcultures at Google Inc., which is a famous global company, and has a huge engineering staff and many talented leaders. Through its history of development, it has had positive impacts on society; however; there have been management challenges. The Board of Directors (BoDs) developed and implemented a way to measure the abilities of their managers, which helped to identify problems. This paper will analyze the case study of Harvard Business Review, Oxygen Project, and clarify the management problem in Google’s organization. It will also compare Google with Zappos, a much smaller organization, and present how the BoDs of Zappos assesses its culture and subcultures. In this paper, we will recommend eight important points to building an organizational culture that is positive for stable growth of a company. We believe that much of what be learned could be useful to other business leaders, regardless of company scale.
Introduction
In a large society, each company is considered a miniature society (Mawere 2011 ). Similar to large societies with large cultures, small societies also need to build their own cultures. A culture is influenced by many factors and determines if it is a great culture. Corporate culture requires both the attention to the efficiency of production and business and to the relationship among people in the organization closely (Bhagat et al. 2012 ). Regardless if it is a large or a small organization, it must encounter issues of cooperation among individuals and groups. There are many factors leading to the success of business process re-engineering in higher education (BPR), the main four elements are culture, processes, structure, and technology. Culture is listed as number one (Ahmad et al. 2007 ). Hence, culture becomes the most important factor to the success of the development of a business. Organizational culture is the set of shared beliefs (Steiber and Alänge 2016 ), values, and norms that influence the way members think, feel, and behave. Culture is created by means of terminal and instrumental values, heroes, rites and rituals, and communication networks (Barman n.d. ). The primary methods of maintaining organizational culture are through the socialization process by which an individual learns the values, expected behaviors, and necessary social knowledge to assume their roles in the organization. In addition, (Gupta and Govindarajan 2000 ) and Fig. 1 in (Ismail Al-Alawi et al. 2007 ) illustrates that culture was established by six major factors, such as information systems, people, process, leadership, rewarding system, and organization structure. Therefore, there is a wide variety of combined and sophisticated cultures in the workplace, especially in big corporations like Google, Facebook, Proctor & Gamble, etc. Each organization tends to have a common goal, which is to create a culture that is different from other companies and to promote their teams to be creative in developing a distinctive culture (Stimpson and Farquharson 2014 ). Clearly, we can see that Google’s culture is different than others. What makes this company unique and different from others, as well as the dominant cultures and subcultures existing at this company? How do leadership behaviors impact the organizational culture? By operating a case study of a Harvard Business Review to analyze its organizational culture, subsequently, having compared it with Zappos’ culture, this paper will clarify the similarities and differences in managing organizational cultures between them and consider whether the solutions for the problems can be applied to other business models, and for tomorrow leaders or not?
Trends of using product by information searching
Company overview
This part shows how Google became famous in the world and its culture and subcultures made it a special case for others to take into consideration. Google is one of the few technology companies which continue to have one of the fastest growth rates in the world. It began by creating a search engine that combined PageRank system, developed by Larry Page (ranking the importance of websites based on external links), and Web search engine, created by Sergey Brin (accessing a website and recording its content), two co-founders of the company (Jarvis 2011 ; Downes 2007 ). Google’s achievements absolutely do not come from any luck. Google has made extra efforts in creating an index of a number of websites, which have been up to 25 billion websites. This also includes 17 million images and one billion messages to Usenet group (Downes 2007 ). Besides searching for websites, Google users are able to search for PDF files, PostScript, documents, as well as Microsoft, Lotus, PowerPoint and Shockwave files. Google processes nearly 50% of search queries all over the world. Moreover, it is the number one search option for web users and is one of the top five websites on the Internet, which have more than 380 million users and 28 billion visits every month, and more than 50% of access from countries outside the US (Desjardins 2017 ). Google’s technology is rather special: it can analyze millions of different variables of users and businesses who place advertisements. It then connects them with millions of potential advertisements and gives messages of advertisement, which is closest to objects in less than one second. Thus, Google has the higher rate of users clicking advertisements than its opponent Yahoo, from 50 to 100%, and it dominates over 70% market share of paid advertisements (Rosenberg 2016 ). Google’s self-stated mission: “to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful (Alves n.d. ).” Nowadays, it is believed that people in the world like “Google” with words “the useful-lively information storage”.
Predominant culture at Google
The dominant culture in the organization depends on the environment in which the company operates the organization’s objectives, the belief system of the employees, and the company’s management style. Therefore, there are many organizational cultures (Schein 2017 ). The Exhibit 3.1 at page 39 in (Schein 2009 ) provides what culture is about. For example, employee follows a standard procedure with a strict adherence to hierarchy and well-defined individual roles and responsibilities. Those in competitive environments, such as sales may forget strict hierarchies and follow a competitive culture where the focus is on maintaining strong relationships with external parties. In this instance, the strategy is to attain competitive advantages over the competition. The collaborative culture is yet another organizational way of life. This culture presents a decentralized workforce with integrated units working together to find solutions to problems or failure.
Why do many large companies buy its innovation? Because its dominant culture of 99% defect-free operational excellence squashes any attempts at innovation, just like a Sumo wrestler sitting on a small gymnast (Grossman-Kahn and Rosensweig 2012 ). They cannot accept failures. In fact, failure is a necessary part of innovation and Google took this change by Oxygen Project to measure the abilities of their multicultural managers. This means that Google itself possesses multiple different cultures (see Google’s clips). Like Zappos, Google had established a common, organizational culture for the whole offices that are distinctive from the others. The predominant culture aimed at Google is an open culture, where everybody and customer can freely contribute their ideas and opinions to create more comfortable and friendly working environment (Hsieh 2010a ).
The fig. 2 .1 in chapter two of (Schein 2009 ) and page 17 in part one of (Schein 2017 ) provide us three levels of culture which are Artifacts, Espoused values and Underlying assumptions helping us to understand the culture at Google. At page 84, in (Schein 2009 ), the “artifacts” are identified such as dress codes, level of formality in authority relationships, working hours, meeting (how often, how run, timing), how are decisions made, communication, social events, jargon, uniforms, identity symbols, rites and rituals, disagreements and conflicts, balance between work and family . It seems that Google is quite open in these artifacts by showing a respect for uniform and national culture of each staff individually and giving them the right to wear traditional clothes.
Ad Blocking Incidence
Working at Google, employees enjoy free food served throughout the day, a volleyball court, a swimming pool, a car wash, an oil change, a haircut, free health care, and many other benefits. The biggest benefit for the staff is to be picked up on the day of work. As assessed by many traffic experts, the system set up by Google is considered to be a great transport network. Tad Widby, a project manager and a traffic system researcher throughout the United States, said: “I have not seen any larger projects in the Bay Area as well as in urban areas across the country” (Helft 2007 ). Of course, it is impossible for Google to “cover up the sky”, so Yahoo also started implementing the bus project for employees in 2005. On peak days, Yahoo’s bus also took off. Pick up about 350 employees in San Francisco, as well as Berkeley, Oakland, etc. These buses run on biofuels and have Wi-Fi coverage. Yet, Danielle Bricker, the Yahoo bus coordinator of Yahoo, has also admitted that the program is “indirectly” inspired by Google’s initiative (Helft 2007 ). Along with that, eBay recently also piloted shuttle bus transfers at five points in San Francisco. Some other corporations are also emerging ideas for treatment of staff is equally unique. Facebook is an example, instead of facilitating employees far from the workplace; it helps people in the immediate neighborhood by offering an additional $10,000 for an employee to live close to the pillar within 10 miles, nearby the Palo Alto Department (Hall 2015 ).
When it comes to Google, people often ask what the formula for success is. The answer here is the employees of Google. They create their own unique workplace culture rules to create an effective work environment for their employees. And here are the most valuable things to learn from Google’s corporate culture (Scott 2008 ) that we should know:
Tolerate with mistakes and help staff correct
At Google, paying attention to how employees work and helping them correct mistakes is critical. Instead of pointing out the damage and blaming a person who caused the mistake, the company would be interested in what the cause of the problem was and how to fix it as quickly and efficiently as possible.
Also as its culture, we understand that if we want to make breakthroughs in the workplace, we need to have experimentation, failure and repeat the test. Therefore, mistakes and failures are not terrible there. We have the right to be wrong and have the opportunity to overcome failure in the support of our superiors and colleagues. Good ideas are always encouraged at Google. However, before it is accepted and put into use, there is a clear procedure to confirm whether it is a real new idea and practical or not?
Exponential thought
Google developed in the direction of a holding company - a company that does not directly produce products or provide services but simply invest in capital by buying back capital. In the company, the criteria for setting the ten exponential function in lieu of focusing only on the change in the general increase. This approach helps Google improve its technology and deliver great products to consumers continuously.
Of course, every company wants to hire talented people to work for them. However, being talented is an art in which there must be voluntary work and enthusiasm for the work of the devotees. At page 555 in (Saffold 1988 ) illustrated that distinctive cultures dramatically influencing performance do exist. Likewise, Google, Apple, Netflix, and Dell are 40% more productive than the average company which attracts top-tier employees and high performers (Vozza 2017 ). Recognizing this impact, Google created a distinctive corporate culture when the company attracted people from prestigious colleges around the world (West 2016 ; Lazear and Gibbs 2014 ).
Build a stimulating work environment
When it comes to the elements that create creativity and innovation, we can easily recognize that the working environment is one of the most important things. Google has succeeded in building an image of a creative working. Google offices are individually designed, not duplicated in any type of office. In fact, working environment at Google is so comfortable so that employees will not think of it as a working room, with a full area of work, relaxation, exercise, reading, watching movies. Is the orientation of Google’s corporate culture to stimulate creativity and to show interest in the lives of employees so that volunteers contribute freely (Battelle 2011 )?
Subculture is also a culture, but for a smaller group or community in a big organization (Crosset and Beal 1997 ). Google, known as the global company with many more offices, so there are many subcultures created among groups of people who work together, from subcultures among work groups to subcultures among ethnic groups and nations, multi-national groups, as well as multiple occupations, functions, geographies, echelons in the hierarchy and product lines. For example, six years ago, when it bought 100 Huffys for employees to use around the sprawling campus, has since exploded into its own subculture. Google now has a seven-person staff of bicycle mechanics that maintains a fleet of about 1300 brightly-colored Google bikes. The company also encourages employees to cycle to work by providing locker rooms, showers and places to securely park bikes during working hours. And, for those who want to combine meetings with bike-riding, Googlers can use one of several seven-person (Crowley 2013 ).
Leadership influences on the culture at Google
From the definition of leadership and its influence on culture; so what does leader directly influence the culture existed? According to Schein, “culture and leadership are two sides of the same coin and one cannot understand one without the other”, page three in (Schein 2009 ). If one of us has never read the article “Google and the Quest to create a better boss” in the New York Times, it is listed in a priority reading. It breaks the notion that managers have no change. The manager really makes a difference (Axinn 1988 ; Carver 2011 ). In fact, a leader has a massive impact on the culture of the company, and Google is not an exception. The leaders of Google concerned more about the demands and abilities of each individual, the study of the nature of human being, an appreciation their employees as their customers. At Google, the founders thought they could create a company that people would want to work at when creating a home-like environment. It is real that they focus on the workplace brings the comfort to staff creatively and freely (Lebowitz 2013 ).
In my opinion, a successful business cannot be attributed solely from a single star; that needs the brightness of all employees. It depends very much on the capacity and ability to attract talented people. It is the way in which the leader manages these talents, is the cornerstone of corporate culture. One thing that no one can deny is that a good leader must be a creator of a corporate culture so that the employees can maximize capabilities themselves (Driscoll and McKee 2007 ; Kotter 2008 ).
To brief, through the view of Google’s culture, BoDs tended and designed to encourage loyalty and creativity, based on an unusual organizational culture because culture is not only able to create an environment, but it also adapts to diverse and changes circumstances (Bulygo 2013 ).
Company growth and its impact
“Rearrange information around the world, make them accessible everywhere and be useful.” This was one of the main purposes set by Larry Page and Sergey Brin when they first launched Google on September 4th, 1998, as a private company (Schmidt and Rosenberg 2014 ). Since then, Google has expanded its reach, stepped into the mobile operating system, provided mapping services and cloud computing applications, launched its own hardware, and prepared it to enter the wearable device market. However, no matter how varied and rich these products are, they are all about the one thing, the root of Google: online searching.
1998–2001: Focus on search
In its early years, Google.com was simply one with extreme iconic images: a colorful Google logo, a long text box in the middle of the screen, a button to execute. One button for searching and the other button are “I’m feeling lucky” to lead users to a random Google site. By May 2000, Google added ten additional languages to Google.com , including French, German, Italian, Swedish, Finnish, Spanish, Portuguese, Dutch, Norwegian and Danish, etc. This is one of the milestones in Google’s journey into the world. Google.com is available in over 150 languages (Scott 2008 ; Lee 2017 ).
2001–2007: Interface card
A very important event with Google around this time was the sale of shares to the public (IPO). In October 2003, Microsoft heard news of the IPO, so it quickly approached Google to discuss a buyout or business deal. Nevertheless, that intention was not materialized. In 2004, it was also the time when Google held a market share of 84.7% globally through collaboration with major Internet companies, such as Yahoo, AOL, and CNN. By February 2004, Yahoo stopped working with Google and separately stood out for engine search. This has led Google to lose some market share, but it has shown the importance and distinctness of Google. Nowadays, the term “Google” has been used as a verb just by visiting Google.com and doing an online search (Smith 2010 ). Not stopping at the homepage search, Google’s interface tag began to be brought to Gmail and Calendar with the links at the top of the page. Google homepage itself continues to use this style.
In 2006, Google also made an important acquisition to buy YouTube for $1.65 billion (Burgess and Green 2013 ). However, the company decided to keep YouTube as a separate brand and not to include it in Google Video search. Thanks to the backing of an Internet industry giant, YouTube has grown to become the world’s largest online video sharing service (Cha et al. 2007 ).
2007–2012: Navigation bar, Google menu, Google now
Google began to deploy a new navigation bar located at the edge of the screen. It includes links to a place where to look for photos, videos, news, maps, as well as buttons to switch to Gmail, Calendar, and other services developed by the company. In the upper left corner, Google added a box displaying Google + notifications and user accounts’ image. Google Now not only appeared on Android and it’s also brought to Chrome on a computer as well as iOS. All have the same operating principle, and the interface card still appears as Android it is.
2013–2014: Simplified interface
Google has moved all of the icons that lead to its other applications and services to an App Drawer button in the upper right hand, at the corner of the screen. In addition, Google.com also supports better voice search through the Chrome browser. Google has experimented with other markets, such as radio and print publications, and in selling advertisements from its advertisers within offline newspapers and magazines. As of November 2014, Google operates over 70 offices over 40 countries (Jarvis 2011 ; Vise 2007 ).
2014–2017: Chrome development and facing challenges
In 2015, Google would turn HTTPS into the default. The better website is, the more users will trust search engine. In 2016, Google announced Android version 7, introduced a new VR platform called Daydream, and its new virtual assistant, Google Assistant.
Most of Google’s revenue comes from advertising (Rosenberg 2016 ). However, this “golden” business is entering a difficult period with many warning signs of its future. Google Search is the dominant strength of Google and bringing great revenue for the company. Nonetheless, when Amazon surpassed Google to become the world’s leading product in the search engine in last December, this advantage began to wobble. This is considered a fatal blow to Google when iOS devices account for 75% of their mobile advertising revenue (Rosenberg 2016 ).
By 2016, the number of people installing software to block ads on phones has increased 102% from 2015. Figure 1 illustrates that by the year’s end, about 16% of smart phone users around the world blocked their ads whilst surfing the web. These were also two groups having the most time on the Internet, high-earners and young people; however, these people have disliked ads (see Fig. 1 ).
Figure 2 shows the young people have the highest ad blocking rates. It is drawing a gloomy picture for the sustainable development of the online advertising industry in general and Google in particular. Therefore, in early 2017, Google has strategies to build an ad blocking tool, built into the Chrome browser. This tool allows users to access ads that have passed the “Coalition for Better Ads” filter so as to limit the sense of discomfort (see Fig. 2 ).
For the company impact, the history shows that speedy development of Google creates both economic and social impacts to followers in a new way of people connection (Savitz 2013 ). In this modern world, it seems that people cannot spend a day without searching any information in Google (Chen et al. 2014 ; Fast and Campbell 2004 ), a tool serves human information seeking needs. Even though when addressing this paper, it is also in need the information from Google search and uses it as a supporting tool. Nobody can deny the convenience of Google as a fast and easy way to search (Schalkwyk et al. 2010 ; Jones 2001 ; Langville and Meyer 2011 ).
Research question and methodology
In order to get the most comprehensive data and information for this case analysis, a number of methods are used, including:
Research data and collect information were mostly from the Harvard Study (Project Oxygen), which has been selected because it is related to the purpose of our study.
Data collection and analysis has been taken from Google Scholar and various websites related researches. We look at the history of appearance, development, and recognize the impacts of this company, as well as the challenges and the way the Board of Directors measures the abilities of their manager when the problem is found.
Analyzing: It was begun by considering expectations from the Harvard Study. Subsequently, considering the smaller organization (Zappos) in comparison of how its cultures and subcultures are accessed as well. Since then, the paper has clarified the management problem that Google and Zappos confront and deal with it so as to help other businesses apply this theoretical practice and achieve its goal beyond expectations.
In our paper, we mainly use the inductive method approach by compiling and describing the other authors’ theories of corporate culture, especially Google and Zappos in merging and comparing, analyzing them and making our own results.
From the aspects of the research, the questions are suggested as below:
What is the most instrumental element found from the Harvard study?
Is there any difference and similarity between a huge company and a smaller enterprise in perspective of culture and subculture?
What makes Google different from others, the dominant cultures as well as subcultures existing? How do leadership behaviors impact on the organizational culture?
How organizational culture impacts on business achievements?
The Harvard study
Project oxygen summary.
This project began in 2009 known as “the manager project” with the People and Innovation Lab (PiLab) team researching questions, which helped the employee of Google become a better manager. The case study was conducted by Garvin (2013) about a behavior measurement to Google’s manager, why managers matter and what the best manager s do. In early days of Google, there are not many managers. In a flat structure, most employees are engineers and technical experts. In fact, in 2002 a few hundred engineers reported to only four managers. But over time and out of necessity, the number of managers increased. Then, in 2009, people and team culture at Google noticed a disturbing trend. Exit interview data cited low satisfaction with their manager as a reason for leaving Google. Because Google has accessed so much online data, Google’s statisticians are asked to analyze and identify the top attributes of a good manager mentioned with an unsolved question: “Do managers matter?” It always concerns all stakeholders at Google and requires a data-based survey project called Project Oxygen to clarify employees’ concern, to measure key management behaviors and cultivate staff through communication and training (Bryant 2011 ; Garvin et al. 2013 ). Research −1 Exit Interviews, ratings, and semiannual reviews. The purpose is to identify high-scoring managers and low-scoring managers resulted in the former, less turnover on their teams, and its connection (manager quality and employee’s happiness). As for “what the best managers do”, Research-2 is to interview high and low scoring managers and to review their performance. The findings with 8 key behaviors illustrated by the most effective managers.
The Oxygen Project mirrors the managers’ decision-making criteria, respects their needs for rigorous analysis, and makes it a priority to measure impact. In the case study, the findings prove that managers really have mattered. Google, initially, must figure out what the best manager is by asking high and low scoring managers such questions about communication, vision, etc. Its project identifies eight behaviors (Bulygo 2013 ; Garvin et al. 2013 ) of a good manager that considered as quite simple that the best manager at Google should have. In a case of management problem and solution, as well as discussing four- key theoretical concepts, they will be analyzed, including formal organizational training system, how culture influences behavior, the role of “flow” and building capacity for innovation, and the role of a leader and its difference from the manager.
Formal organizational training system to create a different culture: Ethical culture
If the organizational culture represents “how we do things around here,” the ethical culture represents “how we do things around here in relation to ethics and ethical behavior in the organization” (Key 1999 ). Alison Taylor (The Five Levels of an Ethical Culture, 2017) reported five levels of an ethical culture, from an individual, interpersonal, group, intergroup to inter-organizational (Taylor 2017 ). In (Nelson and Treviño 2004 ), ethical culture should be thought of in terms of a multi-system framework included formal and informal systems, which must be aligned to support ethical judgment and action. Leadership is essential to driving the ethical culture from a formal and informal perspective (Schwartz 2013 ; Trevino and Nelson 2011 ). Formally, a leader provides the resources to implement structures and programs that support ethics. More informally, through their own behaviors, leadership is a role model whose actions speak louder than their words, conveying “how we do things around here.” Other formal systems include selection systems, policies and codes, orientation and training programs, performance management systems, authority structures, and formal decision processes. On the informal side are the organization’s role models and heroes, the norms of daily behavior, organizational rituals that support or do not support ethical conduct, the stories people tell about the organization and their implications for conduct, and the language people use, etc. Is it okay to talk about ethics? Or is ethical fading the norm?
The formal and informal training is very important. The ethical context in organizations helps the organizational culture have a tendency to the positive or negative viewpoints (Treviño et al. 1998 ). The leader should focus on providing an understanding of the nature and reasons for the organization’s values and rules, on providing an opportunity for question and challenge values for sincerity/practicality, and on teaching ethical decision-making skills related to encountered issues commonly. The more specific and customized training, the more effective it is likely to be. Google seemed to apply this theory when addressed the Oxygen Project.
How culture influences behavior
Whenever we approach a new organization, there is no doubt that we will try to get more about the culture of that place, the way of thinking, working, as well as behavior. And it is likely that the more diverse culture of a place is, the more difficult for outsiders to assess its culture becomes (Mosakowski 2004 ).
Realizing culture in (Schein 2009 ) including artifacts, espoused valued and shared underlying assumptions. It is easier for outsiders to see the artifacts (visual objects) that a group uses as the symbol for a group; however, it does not express more about the espoused values, as well as tacit assumptions. In (Schein et al. 2010 ), the author stated: “For a culture assessment to be valuable, it must get to the assumptions level. If the client system does not get to assumptions, it cannot explain the discrepancies almost always surface between the espoused values and the observed behavioral artifacts” (Schein et al. 2010 ). Hence, in order to be able to assess other cultures well, it is necessary for us to learn each other’s languages, as well as adapt to a common language. Moreover, we also need to look at the context of working, the solution for shared problems because these will facilitate to understand the culture better.
According to the OCP (Organizational Culture Profile) framework (Saremi and Nejad 2013 ), an organization is with possessing the innovation of culture, flexible and adaptable with fresh ideas, which is figured by flat hierarchy and title. For instance, Gore-Tex is an innovative product of W. L. Gore & Associates Inc., considered as the company has the most impact on its innovative culture (Boudreau and Lakhani 2009 ). Looking at the examples of Fast Company, Genentech Inc., and Google, they also encourage their employees to take challenges or risks by allowing them to take 20% of their time to comprehend the projects of their own (Saremi and Nejad 2013 ). In (Aldrich n.d. ), it is recorded that 25%–55% of employees are fully encouraged and giving a maximum value.
The famous quote by Peter Drucker , “Culture eats strategy for Breakfast” at page 67 has created a lot of interest in (Manning and Bodine 2012 ; Coffman and Sorensen 2013 ; Bock 2015 ). Despite we all know how important culture is, we have successively failed to address it (O'Reilly et al. 1991 ). The organizational research change process from the view of Schein ( 2009 ); it is a fact that whenever an organization has the intention of changing the culture, it really takes time. As we all acknowledge, to build an organizational culture, both leader and subordinate spend most of their time on learning, relearning, experiencing, as well as considering the most appropriate features. Sometimes, some changes are inevitable in terms of economic, political, technological, legal and moral threats, as well as internal discomfort (Kavanagh and Ashkanasy 2006 ; Schein 1983 ). As the case in (Schein 2009 ), when a CEO would like to make an innovation which is proved no effective response, given that he did not get to know well about the tacit implications at the place he has just come. It is illustrated that whatsoever change should need time and a process to happen (Blog 2015 ; Makhlouk and Shevchuk 2008 ). In conclusion, a new culture can be learned (Schein 1984 ), but with an appropriate route and the profits for all stakeholders should be concerned by the change manager (Sathe 1983 ).
It is true that people’s behavior managed by their types of culture (Kollmuss and Agyeman 2002 ). All tacit assumptions of insiders are not easy for outsiders to grasp the meaning completely (Schein 2009 ). It is not also an exception at any organization. Google is an example of the multicultural organization coming from various regions of the world, and the national or regional cultures making this multicultural organization with an official culture for the whole company.
In this case, the organizational culture of Google has an influence on the behaviors of manager and employee. In addition, as for such a company specializes in information technology, all engineers prefer to work on everything with data-evidence to get them involved in the meaningful survey about manager (Davenport et al. 2010 ). Eventually, Google discovered 8 good behaviors of manager, which effect to the role of “flow” also (Bulygo 2013 ; Garvin et al. 2013 ).
The role of the “flow” and building capacity for innovation
More and more people are using the term of “patient flow”. This overview describes patient flow and links to theories about flow. Patient flow underpins many improvement tools and techniques. The term “flow” describes the progressive movement of products, information, and people through a sequence of the process. In simple terms, flow is about uninterrupted movement (Nave 2002 ), like driving steadily along the motorway without interruptions or being stuck in a traffic jam. In healthcare, flow is the movement of patients, information or equipment between departments, office groups or organizations as a part of a patient’s care pathway (Bessant and Maher 2009 ). In fact, flow plays a vital role in getting stakeholders involved in working creatively and innovatively (Adams 2005 ; Amabile 1997 ; Forest et al. 2011 ). An effective ethical leader must create flow in work before transfer it to employees for changing the best of their effort to maintain, keep and develop “flow” in an engineering job, which job be easier to get stress. Definitely, Google gets it done very well.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the knowledge from my Master course, a credit of managing culture which helps me to write this paper. The author also gratefully acknowledges the helpful comments and suggestions of the reviewers and Associate Professor Khuong- Ho Van, who provided general technical help that all have improved the article.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Center for Predoctoral Training, Vietnam National University–HCMC, Quarter 6, Linh Trung Ward, Thu Duc District, Ho Chi Minh, HCMC, Vietnam
Sang Kim Tran
Department of Research, Galaxy, 4/62 Nguyen Thi Minh Khai, Hoa Lan 1, Thuan Giao Ward, Binh Duong, 820000, Viet Nam
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The completed paper is solely written by the corresponding author.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sang Kim Tran .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
I obviously inform that there is not any competing interest to this paper.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Tran, S.K. GOOGLE: a reflection of culture, leader, and management. Int J Corporate Soc Responsibility 2 , 10 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40991-017-0021-0
Download citation
Received : 16 May 2017
Accepted : 15 November 2017
Published : 19 December 2017
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40991-017-0021-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Organizational culture
- Management style
- Oxygen project
Get inspired.
Omni Hotels boosts conversions 4X by ditching cookies for Display & Video 360’s PAIR
From its roots in grand historic hotels to its collection of modern resort destinations, Omni Hotels & Resorts has been shaping the hospitality landscape for decades. With over 40 locations spanning across North America, Omni has continued to build upon its rich legacy that blends time-honored elegance with personalized experiences, offering guests a taste of genuine luxury. To navigate the privacy-focused landscape, Omni partnered with PMG, MiQ, and LiveRamp, adopting Google's Display & Video 360 Publisher Advertiser Identity Reconciliation (PAIR) solution to deliver relevant ads without compromising user data. This resulted in a remarkable 4X increase in ad conversion rates compared to traditional cookie-based methods, demonstrating success in delivering relevant experiences while respecting user privacy.
Get the latest, delivered.
Our monthly newsletter puts the latest success stories, insights, and product news right into your inbox.
- Ads Data Hub
- Analytics 360
- Campaign Manager 360
- Connected TV
- Custom Bidding
- Display & Video 360
- Google Cloud
- Google Marketing Platform
- Search Ads 360
- Tag Manager
- Tag Manager 360
No matching results
Enterprise Brand SAS embraces custom bidding to strategically reach connected TV viewers
Sky TV Italia uses Display & Video 360 together with Campaign Manager 360 to boost video performance
Reckitt US boosts its connected TV strategy with Display & Video 360
Mitsubishi Motors Canada uses propensity modeling to increase conversion rate
Riot Games uses Google Marketing Platform to level-up their player base
Men in Green cuts their creative production time in half with Ads Creative Studio
McDonald’s Hong Kong uses Google Analytics 4 to increase in-app orders by 550%
Uber Eats delivers a 10% increase in campaign reach with Display & Video 360
Charlotte Tilbury Beauty reduces CPA by 29% with Custom Bidding
Claro Shop uses Google Analytics 4 to increase in-app purchases in time for the holiday season
Square improves conversion measurement securely with Server-Side Tagging
Banco Azteca increases financial product sales by 178% with Google Marketing Platform
How The North Face used Tag Manager 360 to increase conversions by 3X
How PepsiCo moved from mass demographic marketing to a consumer-centric marketing approach
Nemlig gathers new insights and grows conversions by 40%
Líder drives in-app purchases at a lower CPA with Google Analytics
How OMD and the Guardian used Programmatic Guaranteed to increase efficiency for their direct deals.
How first-party data helped Deckers Brands see which customer trends were taking off
United Overseas Bank drives 3x increase in applications with Google Marketing Platform
Deckers Brands drives business growth with Google Marketing Platform and Google Cloud
TUI UK drives 13% higher return on ad spend by investing in digital maturity
Adidas uses Display & Video 360’s connected TV solutions to show the world it is “Ready for Change”
Samsung increases return on ad spend by over 2x with data-driven creatives
412 Food Rescue uses the new Google Analytics to cut reporting time by 50%
Salesforce unlocks marketing insights faster with Google Analytics 360
L'Oréal Taiwan uses predictive insights to reach the right customers
L’Oréal Taiwan increases offline revenue 2.5x with Google Cloud and Google Marketing Platform
Mondelēz International improves cross-functional collaboration with Campaign Manager 360
Booking.com Evolves Their Measurement with Ads Data Hub
Essence Develops New Measurement Solutions for Customers with Ads Data Hub
How Suntory PepsiCo Vietnam Beverage maximized reach and reduced waste
Nestlé UK Drives Incremental Reach with Audio Ads
Groupe Renault boosts sales and reduces cost per lead with Google and Salesforce
Toyota Canada sees 6X boost in conversions using Google Marketing Platform and Google Cloud
How Samsung found success in Indonesia’s smartphone-savvy market
SAS increases online bookings by 34% in partnership with Google
How did L’Oréal make one creative idea work 100K+ different ways? With a little help from Display & Video 360, Studio and GWD.
Rituals Grows Their Brand with Google Marketing Platform
Rituals Boosts Sales by 85% with Google Marketing Platform
With Display & Video 360, Google Media Lab brings the best of programmatic to its linear TV ad buys
Australia’s Qantas uses Display & Video 360 to reach frequent flyers with relevant ads
Major League Baseball speeds up its marketing game with Google Marketing Platform
Columbus efficiently boosts conversions with a Search Ads 360 Smart Bidding strategy
adidas brings teams together around insights with Google Marketing Platform
Scotiabank boosts mobile conversions with Google Search Ads 360
BookIt moves new users through the funnel with insights-driven creative
OMD revs up high-value traffic for Nissan with Google Display & Video 360
Dune London teamed up with NMPi to boost its Google Shopping revenue by 72%
Scotiabank makes a winning investment with Google Display & Video 360
Moncler hits 72% rise in revenue with Google Marketing Platform’s full stack digital marketing solution
iProspect boosts Thon Hotels' revenue 147% with Google Search Ads 360
IPG Mediabrands improves time spent on Le Petit Marseillais website
L’Oréal Paris puts a fresh face forward with Google Display & Video 360
Walks of Italy boosts revenue and ROI with data-driven attribution and automated bidding
Avon paints a pretty picture with native ad engagement from Google Display & Video 360
Zoopla increases leads with Google Search Ads 360
Audi’s dynamic creative ads reinforce car customization possibilities
IKEA boosts ad spend ROI through Google Search Ads 360
Jellyfish increases agency efficiency with Google Search Ads 360
Using Google Marketing Platform, Novartis customer experience is the picture of health on a global scale
AIDA Cruises speeds ahead with scaled insights and efficiencies from Google Marketing Platform
With Google Tag Manager 360, GoPro discovers freedom and adventure in marketing
Jobs2Careers doubles conversions and increases workflow efficiency using Google Tag Manager
Airbnb improves vendor data collection to 90% with Google Tag Manager
Rail Europe accelerates page load speed by 20%

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.1 Decision-Making Culture: The Case of Google
Figure 11.1

Wikimedia Commons – public domain.
Google (NASDAQ: GOOG) is one of the best-known and most admired companies around the world, so much so that “googling” is the term many use to refer to searching information on the Web. What started out as a student project by two Stanford University graduates—Larry Page and Sergey Brin—in 1996, Google became the most frequently used Web search engine on the Internet with 1 billion searches per day in 2009, as well as other innovative applications such as Gmail, Google Earth, Google Maps, and Picasa. Google grew from 10 employees working in a garage in Palo Alto to 10,000 employees operating around the world by 2009. What is the formula behind this success?
Google strives to operate based on solid principles that may be traced back to its founders. In a world crowded with search engines, they were probably the first company that put users first. Their mission statement summarizes their commitment to end-user needs: “To organize the world’s information and to make it universally accessible and useful.” While other companies were focused on marketing their sites and increasing advertising revenues, Google stripped the search page of all distractions and presented users with a blank page consisting only of a company logo and a search box. Google resisted pop-up advertising, because the company felt that it was annoying to end-users. They insisted that all their advertisements would be clearly marked as “sponsored links.” This emphasis on improving user experience and always putting it before making more money in the short term seems to have been critical to their success.
Keeping their employees happy is also a value they take to heart. Google created a unique work environment that attracts, motivates, and retains the best players in the field. Google was ranked as the number 1 “Best Place to Work For” by Fortune magazine in 2007 and number 4 in 2010. This is not surprising if one looks closer to how Google treats employees. On their Mountain View, California, campus called the “Googleplex,” employees are treated to free gourmet food options including sushi bars and espresso stations. In fact, many employees complain that once they started working for Google, they tend to gain 10 to 15 pounds! Employees have access to gyms, shower facilities, video games, on-site child care, and doctors. Google provides 4 months of paternal leave with 75% of full pay and offers $500 for take-out meals for families with a newborn. These perks create a place where employees feel that they are treated well and their needs are taken care of. Moreover, they contribute to the feeling that they are working at a unique and cool place that is different from everywhere else they may have worked.
In addition, Google encourages employee risk taking and innovation. How is this done? When a vice president in charge of the company’s advertising system made a mistake costing the company millions of dollars and apologized for the mistake, she was commended by Larry Page, who congratulated her for making the mistake and noting that he would rather run a company where they are moving quickly and doing too much, as opposed to being too cautious and doing too little. This attitude toward acting fast and accepting the cost of resulting mistakes as a natural consequence of working on the cutting edge may explain why the company is performing much ahead of competitors such as Microsoft and Yahoo! One of the current challenges for Google is to expand to new fields outside of their Web search engine business. To promote new ideas, Google encourages all engineers to spend 20% of their time working on their own ideas.
Google’s culture is reflected in their decision making as well. Decisions at Google are made in teams. Even the company management is in the hands of a triad: Larry Page and Sergey Brin hired Eric Schmidt to act as the CEO of the company, and they are reportedly leading the company by consensus. In other words, this is not a company where decisions are made by the senior person in charge and then implemented top down. It is common for several small teams to attack each problem and for employees to try to influence each other using rational persuasion and data. Gut feeling has little impact on how decisions are made. In some meetings, people reportedly are not allowed to say “I think…” but instead must say “the data suggest….” To facilitate teamwork, employees work in open office environments where private offices are assigned only to a select few. Even Kai-Fu Lee, the famous employee whose defection from Microsoft was the target of a lawsuit, did not get his own office and shared a cubicle with two other employees.
How do they maintain these unique values? In a company emphasizing hiring the smartest people, it is very likely that they will attract big egos that may be difficult to work with. Google realizes that its strength comes from its “small company” values that emphasize risk taking, agility, and cooperation. Therefore, they take their hiring process very seriously. Hiring is extremely competitive and getting to work at Google is not unlike applying to a college. Candidates may be asked to write essays about how they will perform their future jobs. Recently, they targeted potential new employees using billboards featuring brain teasers directing potential candidates to a Web site where they were subjected to more brain teasers. Each candidate may be interviewed by as many as eight people on several occasions. Through this scrutiny, they are trying to select “Googley” employees who will share the company’s values, perform at high levels, and be liked by others within the company.
Will this culture survive in the long run? It may be too early to tell, given that the company was only founded in 1998. The founders emphasized that their initial public offering (IPO) would not change their culture and they would not introduce more rules or change the way things are done in Google to please Wall Street. But can a public corporation really act like a start-up? Can a global giant facing scrutiny on issues including privacy, copyright, and censorship maintain its culture rooted in its days in a Palo Alto garage? Larry Page is quoted as saying, “We have a mantra: don’t be evil, which is to do the best things we know how for our users, for our customers, for everyone. So I think if we were known for that, it would be a wonderful thing.”
Based on information from Elgin, B., Hof, R. D., & Greene, J. (2005, August 8). Revenge of the nerds—again. BusinessWeek . Retrieved April 30, 2010, from http://www.businessweek.com/technology/content/jul2005/tc20050728 _5127_tc024.htm ; Hardy, Q. (2005, November 14). Google thinks small. Forbes, 176 (10); Lashinky, A. (2006, October 2). Chaos by design. Fortune , 154 (7); Mangalindan, M. (2004, March 29). The grownup at Google: How Eric Schmidt imposed better management tactics but didn’t stifle search giant. Wall Street Journal , p. B1; Lohr, S. (2005, December 5). At Google, cube culture has new rules. New York Times . Retrieved April 30, 2010, from http://www.nytimes.com/2005/12/05/technology/05google.html ; Schoeneman, D. (2006, December 31). Can Google come out to play? New York Times . Retrieved April 30, 2010, from http://www.nytimes.com/2006/12/31/fashion/31google.html ; Warner, M. (2004, June). What your company can learn from Google. Business 2.0, 5 (5).
Discussion Questions
- Do you think Google’s decision-making culture will help or hurt Google in the long run?
- What are the factors responsible for the specific culture that exists in Google?
- What type of decision-making approach has Google taken? Do you think this will remain the same over time? Why or why not?
- Do you see any challenges Google may face in the future because of its emphasis on risk taking?
Organizational Behavior Copyright © 2017 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Our Customers
From small businesses to Fortune 500 corporations, see how teams use Google Workspace to work better together.
Dive into Google Workspace featured resources
Watch Champions of Change
Celebrate heroes behind the new era of work in this global video series.
Explore the User Love series
Learn why customers choose Google Workspace.
Read more customer stories
Dive into our blog to see how customers do their best work using Google Workspace.
We help our customers achieve measurable results
Reduction in spam thanks to built-in AI features within Gmail 1
Hours per year saved in employee productivity 2
Increase in user adoption in first year 3
Explore customer stories
Unilever: can technology help employees feel more valued.
ACB Securities Champions of Change
ACDC Express: Taking a growing national franchise to the next level
AKRON: Connecting frontline employees to head office with Google Workspace
ATB Financial: Reimagining work with Google Workspace
AVEVE Group: Coordinating an agricultural supplier with Google Workspace tools
Achères, France: Helping municipal workers serve their community better with Google Workspace
Adler Planetarium: Discovering avenues for workflow improvement
Adobe: Streamlines collaboration and helps teams bring beautiful design to life
Adore Me: Redefining Productivity in the New Era of Gen AI
Adore Me: Working in unison across four time zones to make fashion a force for good
Aerotech: Developing precision productivity
Africa GreenTec: Electrifying off-grid Africa with cross-continental teamwork on Google Workspace
AirAsia’s BIG Rewards: Accelerating forecasting and budgeting and increasing agility with Connected Sheets
Airbus: Google Workspace and Google Cloud help build the future of work
Airbus: Keep your data safe and compliant with Google Workspace
Al Shirawi: Helping one of the Middle East's biggest industrial groups work more collaboratively
Alfamart: Spreading minimart convenience across the Philippines with Google Workspace
All Nippon Airways
Allen Institute: Collaborative research in immunology with Google Cloud
Amstelring: Bringing caregivers closer to those who need them most
Andela: Partnering with Africa's tech community
AnyMind Group: Using Google Cloud technologies to grow professionals, businesses, and industries
Appian: Helping drive process efficiency and automation with intuitive, low-code technology
Article: How Article enhances user experiences and IT security with JumpCloud and Google Workspace
Arvika Municipality: Securing a digital classroom learning platform with Google Workspace
Asana: Enabling effortless coordination of work with Google Workspace
Ascend Money: Using Google Cloud Platform and Google Workspace to reduce costs
Ascend Money: Using Google Cloud Platform and Google Workspace to reduce costs, automate activities, and improve collaboration
Ascension: Redefining collaboration across the continuum of care
Atlantic Housing Foundation: Supporting families in need with help from Google Workspace
Atlassian: Stimulates collaboration, creativity, and problem-solving with Jamboard**
Augmented Human Lab: Inspiring curiosity for science in kids with Google Cloud solutions
BHI: Embracing Google Workspace and AppSheet to transform the workplace

BMI Group: Bringing digital innovation to the employee and manufacturing experience
BPER Banca: Banking on Google Cloud to improve collaboration and simplify search
Back Market: Going global in the refurbished electronics market with Google Workspace
Banco Davivienda: Driving a digital transformation strategy with Google Workspace
Banco Macro: Banking on team collaboration to support customers on and offline
Bci: Transforming banking from the inside out with Google Workspace
Big chicken: see how shaq uses google workspace to help run his successful business.
Blank Label: Tailoring high-touch customized fitting experiences for men’s clothing
Bluebell Group: Transforming the way luxury brands do business in Asia
Brabantzorg: transforms patient care in months with google workspace and adapta.
Britam: Helping a leading pan-African insurer support its clients at every stage of life
Broadcom: Advancing mass transformation through better connectivity
Brown University: Safeguarding communication channels for faculty, students, and staff
Buffalo Tours
Building a stronger work culture using Google Chat
Bushel: Ensuring seamless collaboration, anytime, anywhere
Buurtzorg: Empowering nurses to provide effective care with Google Workspace
C.C. Content Commercial Champions of Change
CENTURY 21 Canada: Enabling best-in-class real estate customer experiences with Google Workspace
Cuf: securely enabling agile world class medical and patient care.
Cambridge Health Alliance: Collaborating in the service of community health
Camper: Creating fashion-forward footwear through advanced collaboration and analytics
Canada Games Council: Inspiring dreams and building champions
Canam Group: Constructing a faster productivity solution
Canva: Democratizing design and collaborating closely with Google Workspace
Cargills Bank: Transforming workflows and empowering employees with Google Cloud
Carrefour: shaping the future of work for frontline workers.
Celestica: Improving global productivity and collaboration with Google Workspace
Cello Zorg: Connecting caregivers and communities test
Centro Medico Santagostino: Taking healthcare to the cloud
Chantelle Lingerie: Real-time collaboration, from factory to boutique
Chas Everitt: Saving on travel and IT support with Google Workspace
Choice Hotels helps hoteliers do their best work with Google Workspace
Choice Hotels, Korean Air: Stay secure & improve efficiency for your frontline with Google Workspace
City of Chattanooga: Innovating government services to support Tennesseans
City of Linköping: Flexibly collaborating on Google Workspace to better serve its citizens
City of Los Angeles: Using Google Maps to inform and empower citizens
Clarkstown Police Department: Catalyst for a culture shift
Cloud & Ground: Encouraging better community living with the support of Google Workspace
Cloud Next Recap: 20 ways our customers outdo themselves using Google Workspace
CodePath: Generative AI tools to transform work for the better
Coin: digitizing internal processes developing their own apps, coindcx champions of change.
Colgate-Palmolive: Empowering global collaboration with Google Workspace to better serve millions of families worldwide
Comanche County Memorial Hospital: Enhancing patient care and security
Comdata: Delivering outstanding Customer Experience using Google Workspace
Comune di Bergamo: enabling a cohesive, collaborative workforce with Google Workspace
Comune di Bologna: Creating community in a 21st-century smart city with Google Workspace
Conrad Electronic: Disrupting online retail
Covisian: Driving the international growth of its outsourcing business using Google Workspace
Custom Ink: Managing rapid growth through an always-connected collaborative culture
DFS: Staying connected, from the sales floor to the living room floor
DTDC Champions of Change
DTDC Express: Achieving a tenfold increase in collaboration and speed of decision-making with Google Workspace
Dassana secures businesses with Google Workspace, Google Cloud
Deliveroo: Delivering record-breaking growth with the right tools
Design Within Reach
Developing a corporate data transaction app and using task automation with Appsheet
Developing onboarding and asset management apps using appsheet.
Devoteam: Helping companies of all sizes to adapt and thrive in challenging times, with Google Workspace
Discovery: Creating world-class entertainment with anywhere, anytime collaboration tools
DocuSign: Providing customers seamless access to eSignature within Google Workspace apps.
Driving cultural transformation in the workplace with equifax, commonspirit, and hcl software.
EDUA Group: Innovating via Google Workspace to bring teachers, courses, and students together online
EULEN: Delivering excellence in care and sanitary service through collaboration
Eagle County, Colorado: Powering real-time emergency response through cloud collaboration
Eagle county: how it's coordinated and cultivated with google workspace, easypark accelerates onboarding, supports 60% annual growth with google workspace.
Eaux de Vienne: Improving the flow of information with collaborative tools on Google Workspace
Economist Impact: Launching a global brand during lockdown
Electronica Finance Limited: Creating, updating, and fine-tuning machine loans in real time
Entelgy: Creating a workplace that is more transparent, more efficient, and more collaborative
Environmental Dynamics Inc.: Enabling digital productivity in the field, in the office, and at home
Euroclean: Gaining more flexibility in one clean sweep with Google Workspace, Google Cloud Platform, and Chrome Enterprise
Evergen: Powering remote teams with effective collaboration on Google Workspace and cloud apps
Exterro: Connecting global teams at scale with Google Chat and Google Workspace
FM Logistic: An integrated digital workplace with Google Workspace and LumApps
Feralpi: Forging a culture of communication, collaboration, and innovation with Google Workspace
Finding fresh perspectives at LafargeHolcim: Enabling true collaboration with Google Workspace
Fleetsmith: Easier, more secure fleet management with Google Workspace
Footway: How a small workforce powers big retail with Google Workspace
GANT: Suiting up for global growth with Google Workspace
General Mobile: Making the call to improve collaboration
Generali Hungary: Transforming sales network communication with Google Workspace
Geneva Business School: Empowering the business leaders of tomorrow with collaborative mindsets
Georgia Department of Community Supervision: Better supporting communities through remote work
Global Payments: Disrupting tools to foster innovation
Gobierno del Estado de Puebla: Delivering the future of digital government
Governors’ Camp: Combining adventure and innovation for the ideal safari
Guidion: Building a more secure infrastructure with Google Workspace
Gulbene Municipality: Keeping community services running with modern collaboration tools
HK01: Connecting teams and data insights on Google Cloud to build a top lifestyle platform
HMH: Modernizing healthcare IT and collaboration for better patient and practitioner experiences
Hackensack Meridian Health, Sanmina, Sports Basement: Bring it all together: Google's Ecosystem Powers the Future of AI at Work
Hackensack meridian health: modernizing healthcare, hackensack meridian health: modernizing healthcare with google workspace, chromeos, and citrix.
Hackney Council: Empowering 4,000 staff to keep serving their community from home
Hamaya: Transforming traditional ways of work seamlessly with Google Workspace
Hamilton Beach
Harim Group: An integrated communication tool that binds more than 20 subsidiaries, and establishes a horizontal work culture
Herron todd white champions of change.

Hijra: Empowering Indonesians to lead better lives through digital Islamic finance solutions

Holtzbrinck Publishing Group: Stimulating innovation through collaboration with Google Workspace
Homer Central School District: Transforming student learning
Homesale Realty: Empowering independent agents to do their best work from anywhere
How Businesses are using Gemini for Google Workspace
How Globe Telecom applied the democracy model for citizen development
How google workspace strengthened mercado libre as a leader, how just add honey uses google workspace and pixel 6.
How Kisan Network uses Google Workspace to help Indian farmers reap more profits from their crops
How pwc migrated 275,000+ users to g suite, how sports basement uses google workspace and pixel 8 pro, how teams of all sizes connect, create, and collaborate with google workspace, hsin hsin galaxy champions of change.
Hunterdon Healthcare: Achieving higher-quality, more cost-effective care
Hurley Medical Center: Providing the best healthcare using advanced technologies
IT Convergence: More intuitive, enterprise collaboration with Google Workspace
Ibibo Group: Improving customer experiences with Google Maps Platform and Google Cloud
Idex: Enhances services that nurture sustainability goals inside and out
Imerys: Powering the digital transformation of a global mineral giant
Impress: Digitizing the orthodontics experience with secure collaboration on Google Workspace
Improving collaboration and saving time with Google Chat
Insurance agency StreetSmart modernizes its family business with Google Workspace
Intellect Design Arena: Enabling agile design thinking with seamless collaboration
Ippen digital: onboarding employees 34% faster with google workspace.
Iron Mountain: Protecting critical data and assets with the help of Google Workspace
JBGoodwin REALTORS: Finding a home for better productivity
Jain Irrigation Systems: Empowering farmers across the globe with sustainable innovation on Google Workspace
Jeni's Splendid Ice Creams
KAESER COMPRESSORS
KBZ Bank: Building reputation and competitiveness in Myanmar
KKday: Ensuring efficient and secure global collaboration to deliver unique travel experiences
KPJ Healthcare: Using Google Workspace to enable business continuity and introduce new ways of medical consultation in APAC
Karkinos healthcare: making cancer detection and care delivery highly available with a scalable cloud infrastructure.

Kawan Lama Group: Transforming the workplace with secure, seamless collaboration tools
Khon kaen university champions of change.
Kings Transport: Enhancing collaboration and compliance with Google Workspace
Kingston and Sutton London Borough Councils: Empowering smart teams
Kirloskar group champions of change.
Klarahill: Bringing local funeral homes together to thrive in a competitive and changing market
Koenig & Bauer: Staying innovative by making knowledge and idea sharing easy with Google Workspace
Kumu Champions of Change
Kärcher: Bringing more than 85 years of tradition to the cloud with Google Workspace
L&T Finance: Providing opportunities for small businesses with quicker loan processing
L&t financial services: offering loans in rural india.
La Virginia powers real-time collaboration with Google Workspace and aeros
Lalamove: Building affordable, versatile global on-demand delivery with Google Workspace tools
Lamor Corporation: Collaborating seamlessly with localized teams to help clean the world
Latentview analytics ltd. champions of change.
Le Biscuit: Digitizing 50 years of retail tradition
Les Grands Chais de France: Finding new ways to offer a virtual taste of French wine culture
LifeCell: Nurturing life sciences solutions to build a healthier future
Linear Clinical Research: Supporting remote working, BYOD and data loss prevention with Google Workspace
Liu Jo UOMO: Accelerated growth and increased mobility with Google Workspace
Long Shot's development breakthrough and user growth surge using Appsheet
Lucent bio: google workspace helps boost collaboration and sustainability.
Lush: the beauty of enabling 9,000 global employees to collaborate and grow via Google Workspace
Léon Grosse: Bringing offices and building sites closer, with collaborative Google Workspace solutions
L’Appart Fitness: Reaching its best shape with Google Workspace to continue expanding
Mm pakistan champions of change.
MMP: Creating a new work culture and systems for consulting excellence
Mantech: leading the way to google workspace, mantel group: making client collaboration easier and more convenient at a lower cost.
Mass Rapid Transit Corporation: Delivering stability and empowering staff with Google Workspace
Mastersystem Infotama: Transforming the workplace with secure, seamless collaboration tools
Maven Wave: Helping enterprises disrupt instead of being disrupted
McClatchy: Real-time collaboration to drive real-time news
MediaNews Group: Competing in the fast-paced news business through better collaboration
Mercer International: Enabling collaboration via Google Workspace and migrating 2K+ staff during COVID-19
Mercury Promotions & Fulfillment: Employee collaboration from anywhere
Migrating data and applications with Appsheet
MinTIC improves digital government initiatives with the support of Google Workspace and Xertica
Ministério Público do Estado do Amapá enhances citizen support using Google Workspace
Mobile premier league champions of change.
Monstarlab: Empowering talent anywhere with a global workforce united by Google Workspace
Moûtiers: Keeping citizens safe and informed through an innovative approach to local government
Mullenlowe group: bringing creative minds together on google workspace.
Multnomah County: Keeping its employees connected using Google Workspace—on site or on the road
MyGate: Securing devices and data during rapid growth with Google Workspace, Chrome OS and Android Enterprise
MyRepublic: Powering a lean, agile alternative to traditional telcos
Nba superstar dwyane wade is dropping dimes daily using duet ai in google workspace.
NII Holdings: Standardizing on Google Workspace for savings and security
NTUC Enterprise: Keeping living costs sustainable for Singaporeans with better collaboration tools
National Institute for Health Research: Forging a framework for world-class biomedical research
NewMotion: Powering an electric vehicle revolution with Google Workspace
Nielsen: Collaborating across 100 countries for better consumer insights
Nielsen: Scores high ratings from users after deploying Google Workspace and Salesforce
Nineleaps: Improving collaboration and teamwork to efficiently create software solutions for companies
Noberasco: Sows the seeds for success with Google Workspace
Nordward: Uniting four brands on one platform to deliver on a shared sustainability mission
Nova Post: Driving international expansion with risk-free information exchange
Nubian Skin: Scaling more inclusive fashion with help from Google Workspace
Nutresa group: connected we work better.
O2 Care Services: Using Google Meet to connect, collaborate, and keep caring
OIC Onlus: Delivering better care with Google Chromebooks
OLX Group: Building a global community with Google Workspace
OT Group: Delivering everyday consumables to millions of Indonesians with Google Workspace
Ohio Department of Rehabilitation and Correction: Creating a secure virtual classroom
Optimizing employee productivity using Appsheet
OrangeTee: Using Google Workspace to help secure sensitive data and streamline document editing
Origami: Accomodating a shift in business demands with easy-to-use Google communication tools
Ospedali Riuniti di Ancona: Delivering first class healthcare around the clock with Google Workspace
Ovo, UNFPA, Air Liquide: Keep your data private and compliant with Gemini for Google Workspace
PGA of America: Seeing green with modernized collaboration
POPULAR VEHICLES: Driving secure, seamless collaboration across the organization
Pegadaian: Steering a digital transformation program toward workflow efficiency, with Google Workspace
Picnic health: revolutionizing healthcare with google workspace and google cloud.
Picnic: Delivering on its next-day promise with easy collaboration on Google Workspace
Piramis: Connecting TLC with clients from north to south with a more personal touch
PrestaShop: Building a flexible “work-from-anywhere” culture with Google Workspace
Pulse Secure: Growing and protecting revenue with Google Cloud Platform Marketplace
Questrade Financial Group (QFG): Maintaining a people-focused company culture of care
Quimmco: Elevating team collaboration during a pandemic and beyond
RLE International
RSPCA: Rescuing animals with the help of Google Workspace
RZB: Putting innovation and collaboration in the spotlight with Google Workspace
Raisely: expanding digital channels to help nonprofits reach more donors and maximize fundraising.
Randstad: Applying HR expertise through Google Workspace features
Rawson Properties: Adding tech value for real estate franchisees
Red Hat: Instant access to enterprise knowledge improves performance
RedDoorz: Boosting work productivity via collaborative and secure workspaces enabled by Google Workspace
RelianceUnited: Boosting productivity and patient experience, with Google Workspace and Google Cloud
Rentokil Initial
Revolut revolutionizes the financial services industry to make money management easy and accessible for all
Revolutionizing production control with Appsheet
Rovaniemi: Collaboration in the Finnish Arctic with Google Workspace
Royal Government of Bhutan: Enabling sustainable development and social well-being with Google Workspace
SADA Systems: Building a successful business on Google Cloud
SADA: Driving real transformation for thousands of global companies with Google Workspace
SCL Health: Modernizing patient and provider experiences with advanced productivity and collaboration tools
SDIS 41: Providing Loir-et-Cher's volunteer firefighters with equal access to collaborative tools
SGAG: Creating engaging content to put a smile on Singaporean faces
Safetec: Helping customers thrive, grow, and save with Google Workspace
Salesforce: Driving business and positive change through collaboration
Samudera Indonesia: Consolidating email and enhancing collaboration with Google Workspace
Sanmina: Making collaboration a competitive advantage
Savoir Faire Ensemble: Building the fabric of COVID-19 protection with Google Workspace
Schnucks: Improving operational efficiency with seamless collaboration
Scienaptic: Safeguarding data assets with Google Workspace to drive the future of global credit
Seeff Properties: Building better communications with Google Workspace
Shaw Industries
Sheboygan County: Embracing new tools for county responsiveness
Simplifying Healthcare Communication: The Power of Gmail
Singapore Press Holdings: Going paperless and generating efficiencies with Google Workspace and Google Cloud
Snap: Prevent, identify, and respond to threats in Gmail and Google Workspace
Sompo Insurance (Hong Kong): Expanding into retail insurance business
Sony Pictures Imageworks: Making cinematic magic through modern collaboration
Southern Cross Care (SA, NT & VIC) Inc: Transforming the aged care experience with Google Cloud and Google Workspace
Southern cross care champions of change, southern cross care: solving for providing consistent care to patients.
SproutLoud: Transforming channel marketing with cloud IT
St. luke’s medical center: delivering quality healthcare with secure online collaboration to keep patients and staff safe.
State of Arizona: Enhancing productivity and security with cloud collaboration
State of Guanajuato: Improving fiscal audit efficiency with Google Workspace automation
Supr Daily: Empowering teams to streamline processes and improve morning grocery deliveries with AppSheet
TCG: Streamlining loan approval processes with team collaboration on Google Workspace to help more SMEs receive funding
Telus and google cloud partner to create a more sustainable future.
Team Olivia: Creating cost-efficient collaboration with Google Workspace
Teréga: Designing a productivity platform for better collaboration and mobility
Testing and launching applications faster using Appsheet
The F.C. Tucker Company: Revolutionizing real estate sales in Indiana
The FA: Transforming the world’s oldest football association
The Government of Tamaulipas: Example of innovation with Google Workspace and AppSheet
The knot worldwide starts testing duet ai in google workspace.
The Printers Mysore: Bringing 70 years of journalism tradition to the digital age with Google Workspace
The Roche Group
The Scotts Miracle-Gro Company: Planting a cloud-based future
The case for change: a business-value framework for technology choices, the new era of work with gemini for google workspace with etsy, fox sports, and thoughtworks.
Thirdware: Unifying 25 years of knowledge to give technology services a competitive advantage
Thoughtworks: Delivering Software Solutions from the Cloud to Clients
Tiger analytics champions of change.
Toho Gas: Creating a safe mobile work environment and gaining foothold to a broader DX business expansion
Tradebridge: Connecting three businesses with one cloud culture
TransContainer: Saving time and money to build a better workforce with Google Workspace
Transforming to a collaborative enterprise with Google Workspace
Transworld Group Singapore: Improving communication between customers and employees to speed up container shipping
Travis Perkins PLC transforms the workspace and embraces a digital future
Treebo Hotels: Transforming India's budget hotel experience with a pioneering digital platform
Trimble, FinQuery: Level up your productivity at work with Gemini for Google Workspace
Trondheim Kommune: Working smarter, easier, and together in the cloud
TrueCar: Making work a smooth drive
Twinkl: Getting top marks for global growth with Google Workspace and Hire by Google
U.s. army chooses google workspace to deliver cutting-edge collaboration, u.s. navy: building bridges (and ships).
Uber, Verizon, Golden State Warriors, Randstad: Level-up your Sales, Marketing & Customer Service with Gemini for Google Workspace
Uber: Enhancing productivity by using AppSheet to automate key administrative processes
Ukrgasbank: how ukraine’s fourth largest bank relies on google workspace during unprecedented times, uniformed services university plans for a digital medical workforce with generative ai.
Unify: Uniting top online brands on one collaboration platform
Unlocking productivity and collaboration with Google Workspace
Uplers solutions pvt. ltd. champions of change, vtech gives its global development teams a new way to collaborate.
Veolia Australia and New Zealand: Improving employee collaboration, mobility and security more effectively with technology
Verizon: Google’s productivity expert on getting to your personal “uptime”
Vichy Catalan Corporation rejuvenates its workforce with more than mineral water
Vidio: Innovating the future of video streaming for Indonesia with Google Workspace
Viessmann: Promoting global collaboration to build tomorrow’s sustainable energy solutions
Virgin Active: Building a culture of collaboration with Google Workspace
Vodafone idea limited champions of change.
Vonage: Driving productivity and sales through digital transformation
Wayfair: Furnishing personalized online buying experiences through cloud collaboration
Wayfair: google workspace | how it’s done, webfx: redefining productivity in the new era of gen ai.
Weiss + Appetito: Matching mobility with peace of mind
Xero: Delivering communications and collaboration at scale with Google Workspace including Google Meet hardware
York: Behind every good outcome
ZALORA: Supporting sustainable, secure business expansion with Google Workspace
Zerodha: improving the retail investment experience with seamless collaboration on google workspace, acommerce champions of change.
eir: Supporting staff to keep more than 2 million customers connected, from home
flaconi: Giving collaboration a makeover with an innovative, customer-first solution on Google Workspace
Ifood: google workspace | how it’s done.

iOPEX Technologies: Driving digital transformation for large enterprises with enhanced security and increased team productivity
kfzteile24: Reducing costs and boosting productivity with Google Workspace
Nurture.farm champions of change, how teams of all sizes connect, create and collaborate.
1. Google Workspace Customer Story: HMH
2. Google Workspace Customer Story: Celestica
3. Google Workspace Customer Story: MullenLowe Group
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Google’s Scientific Approach to Work-Life Balance (and Much More)
- Laszlo Bock
A new longitudinal survey seeks to quantify worker satisfaction, teamwork, and more.
More than 65 years ago in Massachusetts, doctors began a longitudinal study that would transform our understanding of heart disease. The Framingham Heart Study , which started with more than 5,000 people and continues to this day, has become a data source for not just heart disease, but also for insights about weight loss (adjusting your social network helps people lose weight), genetics (inheritance patterns), and even happiness (living within a mile of a happy friend has a 25% chance of making you happier).
- LB Laszlo Bock is the CEO and co-founder of Humu, an HR software company using people science to help people do their best work. He is the former SVP of People Operations at Google and the author of Work Rules!: Insights from Inside Google That Will Transform How You Live and Lead . He donates 100% of his book income to charity.
Partner Center
Case Study: How Google Boosts its Employees’ Engagement
You might have heard about this mantra: ‘happy employees produce better results.’ this is the mindset of google to keep its employees productive and satisfied. this article explains more..
Let’s say you’re a company providing software development services . If your developer’s team isn’t enthusiastic about their projects every day, you’re not going to achieve excellence. This is productivity’s power. But remember productivity is dependent on the company’s culture.
Why is everyone talking about Google’s culture or work environment? We know that Google is one of the most influential and powerful companies around the globe. The company follows a pretty well unique culture instead of corporate culture.
It has something that every big organisation needs to follow to level up their employees’ engagement or morale. The culture of any company is vital to its success and Google is perfectly right on the track.
It has one sole purpose: Keep the employees happy and keep up the productivity.
Google has been at number ONE place from the past six years and featured on Fortune’s annual list of ‘Best Companies to Work For.’ And this is not it. Google has also been named as the tech company with the best culture. (Reported by Forbes) Furthermore, Google has a 4.4 rating on Glassdoor based on 6000+ employees reviews.
Google’s morale
This is what the employees of Google answered the questions asked about their work culture.
- Acknowledged for the efforts?
Yes: 61 % Employees
Get started for free today.
No: 39% Employees
- Job Security?
Very Secure: 34 % Employees
Neutral: 19% Employees
Insecure: 8% Employees
Very insecure: 5% Employees
- Work Environment?
Positive: 85% Employees
Negative: 15% Employees
- Excited about going to work daily?
Yes: 80% Employees
No: 20% Employees
So, without further ado, let’s move towards the ways Google uses to boost its employees’ engagement .
“There are way easier places to work, but nobody ever changed the world on 40 hours a week. But if you love what you do, it (mostly) doesn’t feel like work.”- Elon Musk.
How Google Keeps Its Employees Productive And Engaged?
Exclusive perks.
Today, employees want a job in a company that makes them love what they do. Never for financial benefit or intellectual recognition. Yet instead of chance to add to the common good.
The major differentiator is to make a real difference.
Google offers different perks to its employees to show them that they are not only investing in their overall health but their future as well.
- Chef-prepared free organic food (breakfast, lunch, and dinner);
- Free dental and health checkup;
- Free and unlimited dry cleaning;
- Subsidised massages;
- Several foosball, ping pong, video games stations;
- On-site physicians;
- Gyms/swimming pools memberships;
- Free haircuts from professional hairdressers;
- In-house nap pods;
- Death benefits to deceased employees’ families, and;
- Hybrid car subsidies.
Flexibility
Google has been one of the very first companies that had a vision of understanding the employees’ needs. It lets its workers have a flexible schedule so that they can work on their terms and enhance creativity and productivity. They have given their employees complete freedom to work in a way that is most suitable to them.
Knowing the employees well
Google had gone through a series of laboratory tests to figure out the productivity of their employees. They had four different experiments that included 700 participants. All the employees were treated to free drinks, fruits, and chocolates or shown a comedy movie clip.
They also enquired some of the participants about the family tragedies as a part of their assessment. After this, they found that happiness is the reason for 12% more productivity.
Google promotes an innovative and diverse organisational culture that has been a part of its employee’s life. A positive creative atmosphere and a safe working space offered by Google to its workers keep them comfortable and happy at work. The concept that being a part of Google is about being smart and wise encourages the employees to think openly and keeps them productive.
Nowadays, there are different creative coworking spaces which are known to be a perfect alternate to a workplace. These spaces are believed to deliver various advantages such as strong networking and increased engagement.
Google’s founders were researchers who had a belief in innovation and freedom of thinking. This is one of the main factors that influenced the style of Google’s leadership.
According to Brassfield, 2013, a positive leadership style stimulates inspiring and motivating employees to develop innovative ideas and inventions.
Keeping people inspired
Future Workplace, in 2017, demonstrated in a study that one of the biggest threats to employees’ engagement is employee burnout. It has also been found out that many proficient workers are often overburdened with the tasks that lead to halted innovation, incomplete work, etc.
What does Google do about keeping its employees productive, inspired, or motivated? Google’s strategy for this is 20% time . Every employee devours up to 20% of his time at work each week on ventures that inspire him.
This concept inspires employees as it allows them to concentrate on things they love or are passionate about. It can prevent burnout, decrease turnover, increase engagement.

Image: Pexels
Career development
Google provides an extensive professional growth program that is successful and creative and guarantees long-term performance for all the employees. The career development program of Google is one that ensures incentives are provided to employees to meet their professional and personal progression.
Google has adopted a unique way to promote the professional development of all its employees. CareerGuru is a career coaching that provides all the details to the employees by Google’s leaders about working at a specific role in the company.
Creativity Encouragement
The companies that believe in fostering a culture of creativity have happy, satisfied, and motivated employees. Google leads the way in promoting creativity in their employees.
They are free to express their ideas as a solution to any problem. Moreover, employees are encouraged to work wherever they are comfortable in the workplace. Google has a set up where rather than just considering an applicant’s professional background, they look to recruit people who are normally inquisitive and fond of learning.
Trusting Employees
Google believes in trusting their workers because trusted employees feel more valuable. It can also boost the sense of job satisfaction and can also decrease the rate of staff turnover.
In a survey by PwC, reliable employees are 76% more engaged in their work than those in a low trusting environment. Trusted employees are happier and they have the urge to go the extra miles.
Culture based on qualitative data
Google has always been searching out different ways to optimise the performance of its employees while ensuring their happiness and satisfaction. Everything done at Google is based on real data. They use the qualitative and quantitative facts to set up processes and every single rule that is streamlined.
Google has additionally performed researches to discover how much paid time off new mothers would need and ways of building an improvised and better culture.
Fun workplace
Have you ever been allowed to design your own workstation at your company?
Probably not. But Google does it. It lets the employees design their desks or workstations.
When you see the pictures of the workplace, it seems an interesting adult play and work area and not a dull and lifeless space.
Google has always tried to push the boundaries of its workspace.
Collaboration of coworkers
At Google, the employees are urged to collaborate. They have a program called ‘Googler to Googler’ to keep them productive and promote skills such as management, public speaking, orientation, or extracurricular activities.
It is crucial to build a sense of community to create a positive culture. The company has arranged several micro kitchens around the whole workspace where coworkers can have a little chit-chat session. No one has to spend time on deciding where to eat because Google has various break-out spaces for lunch.
Google’s way of listening
Google employees have developed great software and projects that include Gmail, AdSense, Google News, etc. and all these big projects were originated because of its staff productivity approach. Google has a way of collecting employees’ feedback and listening to their suggestions that is gDNA.
- The employees utilise a device ‘Google Moderator’ , the result of 20% time strategy, to inquire about something and vote on inquiries of others;
- The company holds a meeting, every Friday, where the managers react to the most famous inquiries of the week;
- Leaders or managers utilise a charting instrument called Google-O-Meter to measure the prominence of various worker bits of advice;
- Leaders likewise plan “Fixits” to comprehend huge, critical issues; and,
- Fixits are 24-hour runs where team members give their full focus around discovering solutions for explicit issues.
So, can Google teach us anything?
If you are planning to adopt these learnings at your organisation just like Google keeps its employees productive, it’s essential to test the progressions first and measure the results.
It’s a great deal of work, however, the engagement advantages will make the difficult function admirably justified.
About the Author
Usman Akram is a digital marketer and SEO specialist who’s passionate about experimenting and discovering new SEO tactics and strategies to dominate search rankings while bringing an unmatched user-experience. As of now Usman is serving Buzz Interactive , a leading digital marketing agency as the head of SEO.
Related articles

Post navigation
The Case of Strategic Analysis of Google Inc. Case Study
Introduction, company overview, the google inc. strategic issue, external environment, porter’s five forces analysis, company situation, recommendations.
The Google Inc. is a giant Internet search engine technology provider incorporated in Delaware. It was founded in 1996 by Larry page and Sergey Brin. The company has grown over time to become one of the most successful and highly admired organizations in the world. Today, the company offers more than just mere search engine technology. Google’s strategy entails becoming the world’s leading Internet search engine by increasing ads to cover markets outside the US including emerging Russia and China.
The company’s strategy has been focusing on the acquisition of companies Motorola Mobility Center and Keyhole that helped in the diversification of its products. The Google Inc. adopts an exceptional business model that continues to influence unmatched growth and profitability. This paper provides a strategic analysis of the Google Inc. case including a SWOT, five forces analysis, strategy road map, and financial analysis with a view of pointing out its key success factors.
The birth of the giant search engine technology is attributed to the Stanford University where its two computer science graduate students, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, worked in partnership in 1996. Initially, the company was named the BackRub. The name changed to the Google Inc. in 1998, imitating the word googol that mathematically means the digit one (1) followed by a hundred (100) zeroes.
The search engine giant’s headquarters are based in Mountain View, CA, with various office locations around the world. Executives and a Board of Directors (BoD) manage the company. Its growth has been catapulted by its rapid innovations including wireless search technologies, search capabilities in more than ten languages, and the Google Toolbar browser plug-in that made it possible for users to enjoy the Internet search service without first visiting a Google-affiliated web portal.
Additional products by the end of 2004 included Google News, Google Product search, Google Local, and the Google Scholar. Additionally, Google’s web pages index increased to eight billion besides its country domains reaching one hundred and fifty by the year ending 2004.
The most historical success story of the Google Inc. was recorded on the first day of public offering. At the end of its first day of trading, the company’s shares appreciated by 18% making the two co-founders over $3.8 billion richer. At this time, its workforce had expanded reaching over 900 employees each approximately worth $1 million.
The Google Inc. has not restricted its services to the Internet search technology only. Since 2005, the company has introduced numerous products through its robust innovations and the vast financial reserves. Through various strategic acquisitions, it developed new Internet applications to provide advertising opportunities that underpin the giant’s enormous success today. Notably, the acquisition of Keyhole, which was a digital mapping company, enabled the launching of the Google earth in 2005.
Additionally, Google acquired the Motorola Mobility for $12.5 billion in 2012. This acquisition placed the company in the hardware market offering competition to the Apple Inc. Having launched the Android operating system in 2008, venturing into the hardware segment will promote the integration of the software as seen in companies such as the Apple Inc. In 2007, Google maps were enhanced when the company added street-view images taken by traveling Google camera cars.
The technological strategy enabled users to link digital images, webcam feds, and videos to locations displayed by the Google maps software. Additionally, the company made it possible to link real estate listings and short personal messages to the Google Maps locations. The Google Maps received a major enhancement in 2010 when the earth-view mode was included allowing users to view 3D images of different locales from the ground level.
Google strategy included dominating the Internet advertising and the becoming the world’s leading search engine. In light of this strategy it enabled online ads with more than 41 languages around the world. As a result, a half of its 2012 revenues came outside the United States. In 2013, the company strategy focused on venturing into emerging markets including Russia and China.
However, entering the largest emerging market, China, faced tough challenges. The greatest threat in China was stiff competition from local search providers such as Baidu. Second, tough government’s requirements that included censoring search results. Disagreements with the government saw Google controlling only 3% of the Chinese market.
Google’s PESTEL Analysis
This PESTEL analysis section seeks to provide an in-depth insight into Google’s success factors from the macro-environment that serve as both opportunities and threats. These factors influence the company’s strategy formulation. Addressing the threats whilst taking up opportunities availed by the remote environment is vital for the growth and performance of the organization. In so doing, the company will sustain its competitive position as the world’s leading online search engine.
Political Factors
The political factors in the macro-environment influence Google’s decisions ad operations. Opportunities offered by the political factors globalization and the stable political climate in a booster markets. The major threat is the state-sponsored online competitors. Globalization has offered a prime opportunity for the Mountain View, CA-based search engine to exploit the vast online market from a more informed global population.
It also helps in the spreading of information, awakening, and changes from traditional practices amongst consumers and organizations. In a knowledge-guided economy, the Google Inc. plays a vital role in changing lives as it rolls over its new products across borders. Moreover, the stable political climate in booster markets creates the favorable environment for Google to maximize profits.
Economic Factors
According to the PESTEL analysis, external economic factors play the role of influencing opportunities available for organizations. The Google Inc. thrives under economic stability of its major markets and the rigorous growth of developing and emerging economies. These factors are viable opportunities for the Google Inc.
They create new momentum for the company to explore and invest. In fact, company can expand globally owing to these economic factors. The increasing gross domestic product for most countries including South Africa, China, India, and the United Kingdom is good news for the Google Inc. The increase in GDP for these countries among others indicates an economic growth.
Changes in interest rates affect investment companies, especially those that target global markets. However, it is worth noting that economic factors have little impact on technology and online investors such as the Google Inc. The company is isolated from economic forces since it relies on virtual investments via the Internet. As such, economic turbulence and financial crises have little impact on the Google’s business model.
Socio-Cultural Factors
Socio-cultural factors refer to the overall customers’ response to Google’s products. These factors can act as either opportunities or barriers to the company’s growth. The rising diversity of internet users represents an opportunity whereas the increasing use of social media is a threat to Google’s business.
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected through the Internet’s communication capabilities, Google’s business stands to thrive even higher than before. The increased connectivity through smartphones and tablets is an opportunity that has changed people’s beliefs and perceptions over time. Today, people utilize the Google Maps feature available in mobile platforms to search for directions, restaurants, and drive-ins among other locations.
Additionally, people can download free MP3s music and videos besides keeping in touch with their favorite sport events, scores, and fixtures. Google is well positioned since it targets the young population user-base with its fascinating products such as the Mobile Google App and the Android OS that are both user-friendly and interactive. Most of the Google’s applications are downloadable across all mobile platforms including the Apple IPhone and BlackBerry among others.
Internet use is gender-neutral. In light of this cultural factor, gender issues less affect the Google Inc.’s business. In addition, changes in gender ratios do not adversely affect its interventions at all. As such, Google’s business model remains strong across the majority of socio-cultural spectrums. Instead, the company benefits when people abandon their traditional ways and start using the Internet.
Technological Factors
Google’s technological capacity improves with every bit of advancement as a strategy to remain relevant. For instance, the company is known for using cheap computer components that can be swapped with upgraded ones. This phenomenon indicates a high level of grand strategy.
Google’s business is shielded from geographic dependence since the applicability of the Internet is universal across most cultures. In this regard, the company has offices in both the United States and many countries around the world. According to the PESTEL analysis, technological factors are deemed as either enhancers or breakers of business.
Two chief external technological factors underpin Google’s growth. These factors include the rapid growth of internet users in developing countries and the increasing evolution of smartphones in the global market. Google taps these opportunities as it designs its products to suit the mobile platform (see Figure 7 in the appendix).
Legal Factors
The legal factors have far-reaching impacts on the limits of what organizations can do. Google’s macro-environment is influenced by the growing concerns and regulations of the Internet on its privacy issues. Second, regulations of intellectual property influence the extent of the company’s operations.
However, it builds on these legal factors by improving the protection of people’s information archived in their online storage avenues. Again, the company can develop robust approaches to deter people’s violation of the intellectual property rights through its innovative capabilities.
The Porter’s Five Forces Model is a tool used by organizations to gain insight into the macro-environment with a view of aligning its strategic objectives. Given the ever-changing business landscape, uncertainty, and the wave of globalization, it is important for organizations to improve their external environments.
The tool enables one to analyze the environment with a view of identifying potential issues that are likely to influence the organization’s strategic growth. As coined by Michael E. Porter in 1979, the tool takes a close account of rival players in the industry in which the given organization falls. Factors such as supplier power, barriers to entry, competitive rivalry, threat of substitutes, and buyers’ power closely influence the Google’s external environment (Gamble, 2013).
The Google Inc. witnesses fierce competition that can limit its growth capabilities. The company ought to take into account various external factors based on the market competition including the number and diversity of firms besides the low switching costs that exert moderate to strong force.
Google’s chief rivals include Yahoo, Bing, Apple, and Comcast among others. The company has diversified into numerous product lines including advertising, the Google Glass, Google Fiber, Mobile Android OS, and Chromecast among others. This product diversification has attracted stiff competition. However, the Google Inc. has managed to achieve an unmatched competitive edge over its rivals through its innovation and product differentiation.
The bargaining power of Google’s customers is weak; hence, it provides the company an opportunity to control both the demand and supply of its products. Several factors underpin the weak bargaining power for Google’s products. At the outset, the small size of individual buyers, which represents a weak force, exerts minimal effects on the giant search engine.
Individual buyers have little contribution to the company’s revenue. Secondly, the high and increasing demand for online products of the Google Inc. and its rivals makes individual customers put little force on the company.
Suppliers’ bargaining is weak since Google has numerous alternatives products. This weak bargaining power of suppliers is attributable to various factors including the high number of suppliers and their high availability in the industry. The two factors lower the bargaining power since Google can select from a large pool at controlled costs. This situation makes it possible for the company to switch from one supplier to another. The suppliers are diverse as they correspond to Google’s array of products.
The Google Inc. experiences a low to moderate threat of product substitution. Some of the substitutes include the traditional advertising channels such as television, radio, and print media. The moderate threat of substitutes stems from low switching costs and the medium to high availability of those alternatives.
The fact that customers can move away from Google’s ads exerts little force on the company. Moreover, there is a moderate threat of new entry that influences Google’s business in a number of ways. First, the moderate cost of doing business for startups and new ventures imply that Google stands the risk of increased competition. However, due to the high cost of brand development, new ventures find it difficult to enter the Internet advertising and other online businesses.
Google’s SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It seeks to provide a company’s microenvironment and macro-environment factors that surround it as a business entity. This section provides a detailed SWOT analysis for the Google Inc. (Gamble, 2013). Figure 3 on the appendices shows the Google’s SWOT analysis chart.
The Google Inc. boasts several strengths of its internal environment. First, the company incorporates its mission (reorganizing the world’s information making it universally accessible and useful) in each product. Open source products and services for Google including Google Maps, web-based calendars, drive, OS, and the hardware devices are deemed to have exceptional quality.
Its openness gives the company flexibility to innovate in any direction without restricting its expertise to one line of business. Second, the company offers high-quality customer experience. All its products are built to ensure premium experience to its customers. The organization ensures that its products solve practical needs to the customers. For instance, linking Google Maps with digital images to indicate locations and other features helps customers to keep track of photography moments at different events and localities.
The financial position of the Google Inc. is vast enough to support all its operations and ambitions. The company’s financial data on profitability and liquidity for the years between 2001 and 2006 (shown in figures 3, 4, and 5 respectively). The company is one of the most profitable businesses in the world with earnings approximated at $ 49.99 billion and more than $10.99 billion profits (21.9%). Its liquidity reaches over $47 billion and a debt of nearly $.6.9 billion only.
This vast financial position provides a major thrust for the company to invest in technology and the best human capital. Its online advertising is very successful as it is the top revenue earner for the giant search engine. The company strikes exciting deals with online sites that allow Google Ads to appear for customer to view.
Viral advertising is a magical phenomenon for Google that has leveraged its high profitability year in year out. Google’s performance has been rapidly growing relative to its rivals as indicated in the appendix (See Figure 5). Figure 6 shows the Financial Ration analysis of the Google Inc.
The Google Inc. also has unbeatable strong patents portfolio. In fact, the addition of more than 1150 patents back in 2012 placed the company at position 21 on the world’s patents ranking (Gamble, 2013). Intellectual property for the Google Inc. is the most vital component that leverages the attainment of a competitive edge over its rivals.
The Motorola’s acquisition gave Google a strong advantage relative to its rivals. Further, product integration is one of the most significant Google’s internal strengths. The integration of all its products with each other forms a viable ecosystem for excellent customer experience. The purchasing of one product creates the need for another. This integration is rare with most of the major tech-organizations in the entire world.
Google faces several internal limitations. First, it relies on a single source of income, advertising. As at 2013, online advertising had grown with double digits that grew the company’s income. Second, Google has only a single search box. This phenomenon makes it hard for the company to change context from a finder to a producer.
The company has been criticized based on online privacy. Critics say that users can view other users’ profile information in accounts including YouTube, Picasa, and Orkut. Besides, the litigations facing the company are costly and resource consuming. It is a source of distraction from its business errands.
Opportunities
The Internet industry is ever growing. The bust of smartphones has presented the Google Inc. with prime opportunities for growth and success. Today, the number of internet users is enormous, especially with the evolution of smartphones. The company has seized the growing smartphone industry to increase its online services.
In addition, the Google Inc. has numerous unexploited opportunities including the creation of an independent browser that can speed up Internet downloads and upgrading of its systems to enhance real-time feedback to its infinite customer base. With the growing number of smartphone manufacturers around the world, Google stands to gain through extended deals.
Its independent database software can organize databases for improved refined search for customers. In addition, the company continues to tap into continued network expansions. Besides, Google News functionality stands to grow as local news become more important to communities. The emerging markets such as China present prime opportunities for the company to extend its services for additional growth.
The Google Inc. faces a variety of threats such as copyright lawsuits and issues on music, books, and movies, and legal issues affecting YouTube. In addition, the public’s perception of the storage of their private data by Google is a serious threat to the growth of its customers’ base. The presence of the anti-spyware software and programs threaten to block Google cookies. This situation can influence the growth of AdWords and AdSense capabilities.
Moreover, the security of the Google’s servers is not guaranteed as the access by hackers can result in massive devastation. The rumored partnership of Microsoft and Yahoo! is a serious peril to the Google Inc. Its free services continue to burden the company since they trigger losses. The introduction of unprofitable or low value products can cause its profits to plummet in the near future.
Google’s Generic Strategy
Google’s strategic choices are directly related with its core business objectives and the overall aspects of the industry. Its generic strategy is an all-encompassing influence on the company’s activities. Google’s generic strategy has greatly affected the highly competitive environment.
It is based on product differentiation, market development, and innovation. Based on the Porter’s model, the company’s generic strategy is mainly differentiation. This peculiar business technique has continually acted as a major impetus for Google’s competitive advantage. The company distinguishes itself from its competitors through product differentiation. Innovation has also been the company’s strength. The Google Inc. has added new products such as the Google Fiber and Google Glass through its proactive innovations.
It is worth noting that the Google’s algorithm evolves over time to spur competitiveness and growth. Researchers argue that the continued evolution of the Google’s algorithm out wins the Yahoo! and Bing search engines, which are the closest rivals. Continued innovation makes the Google Inc. unique and unbeatable.
The generic strategy of differentiation is aligned with the company’s objective of product development. Additionally, the company ensures that its existing products are continually improved to sustain the company’s market share and profitability (Gamble, 2013). Through its generic strategy of differentiation, the company remains highly competitive relative to other players in the industry.
Google’s Grand Strategy
A grand strategy entails the comprehensive frameworks that help in laying out strategic actions of an organization. They focus on the long-term course of a business. Some of the Google’s grand strategies include concentrated growth, market and product development, innovation, concentric and conglomerate diversification, and strategic alliances.
Google’s momentum of growth will continue following its exceptional performance. Its ambitious scanning of global high-tech innovations is a key impetus of this growth. The company is the most admired employer in the world. Market growth is a low-risk strategy since it focuses on developing the market base of the existing product rather than research and product development (Gamble, 2013).
Just like Facebook, Google runs the web like a cartel where it sets both the demand and supply of its products. This way, the company boasts the opportunity to increase demand for its existing products. Google’s swim strategy enhanced fifteen acquisitions, one of which paid approximately $1billion.
The Waze, an Israeli traffic report application paid the amount that demonstrated Google’s strength of its grand strategy. The acquisitions help the company to invest in broadening its expertise in engineering, technology, and product offerings. Additionally, its mission of being everywhere underpins Google’s grand strategy. This way, the swimming strategy enables the company to be successful in each innovation.
Product development is one of the Google Inc.’s grand strategies. Through its unbeatable innovative capabilities, the company’s enthusiasts continue to grin as it launches new products one after another. For instance, the launching of the Android operating system (the leading mobile user interface), the Chromecast device, and the Nexus 7 tablet are significant strategies for the company’s long-term growth and sustainability.
However, the company has grown past ads. Today, it has a myriad of exciting products that customers throughout the world have developed unshakable loyalty (Gamble, 2013). For instance, the Android OS for mobile smartphones and tablets tops the list of the most popular operating systems beating the Apple Inc.’s IOS and BlackBerry that ruled before.
Market Development (Using the 4Ps)
Google’s market penetration is the main strategy for its intensive growth abroad. Outside the United States, Google competes with other giant search engines and online advertising. The company utilizes market penetration to compete with these companies. It continues to strive for a bigger share of the global Internet advertising market.
Market development is a key intensive strategy for Google Inc. In the US, the company adopts the intensive strategy for the Google Fiber product and cable television. This approach has worked for the company in various states including Kansas, Missouri, Texas, and Utah. The market development plan will leverage the launch of fiber product and cable television in additional states and abroad.
The Google Inc.’s robust marketing mix has largely leveraged its success. The giant search engine has developed numerous products including the Google Glass and Google Fiber. The company’s marketing mix embraces varied approaches to suit its diversified products. The Google Inc. expanded from a mere web-based firm to provide mobile smartphone devices such as the Nexus and Chromecast media devices, Android operating systems, desktop applications, and mobile apps among other services.
This product diversification is a clear indication of the company’s growth and market expansion. The generic strategy helps the company to expand its market share for existing products such as the Google AdWords and Nexus among others. The 4Ps stand for place, product, promotion, and placement.
The Google’s place component of its marketing mix is typically online locations. The platform is used for the distribution of products in a way that customers can access them via the Internet. For instance, customers from any physical locations around the word can download the Google Maps app so long as they have internet connectivity.
The utility of the internet across borders helps the company to market its digital products to customers far away without face-to-face interaction. It utilizes retail stores as the main distributors of hardware products such as the Nexus smartphones. For such items, Google chooses largely established retailers to increase the sales volumes and extensive access by large populations of potential buyers.
Google’s promotion component of the marketing mix is not very proactive since its reputation and market dominance plays that role. However, minimal product promotions are carried out through online advertisements such as the Gmail for work ads that frequent many sites.
Google’s prices and pricing strategies are diversified in accordance with the different product lines. Examples of such strategies include freemium, marketing-oriented, penetration, and value-based pricing. First, Google uses the freemium pricing strategy to offer free products as it sells their premium or add-on features. The product sold under this strategy is the Gmail. Second, the market-oriented pricing approach determines product prices based on the characteristics of the target market.
The Chromecast is priced using market-oriented approach. Third, the penetration pricing entails providing new products at low prices in a market dominated by strong competitors. This approach helps Google to gain market share through low pricing of its products. This strategy has worked for the Google Fiber Internet and cable television service.
Finally yet importantly, the value-based method determines the product’s prices based on its customers’ perceived value. For instance, the strategy works best for AdWords online adverting service since advertisers bidding is determined by their perceived significance of advertising their products.
Product Development
The product development strategy for Google is implemented through its proactive innovation. The development of new products such as the Google Glass, the driverless car, and Nexus mobile devices puts the company above its rivals in the technology industry. This intensive strategy has helped the Google Inc. to create additional sources of revenue generation. These grand strategies correspond to the company’s strategic objectives.
Google’s Key Success Factors
The company’s key success factors include a coordinated leadership group, commitment to cutting edge, wise expansion, and subtle marketing. Google boasts a strongly coordinated classic leadership molecule of three leaders including the founders Brin and Page, and the Chief Executive Officer, Schmidt. It integrates high-tech into its business that ensures that customers enjoy high quality services including the Universal search, Real-time search, and Google Instant.
These new tech capabilities promote customer convenience and satisfaction. The company has provided a stepping-stone to its diversification outside the search engine business through its acquisition strategies. Moreover, it adopts a proactive marketing strategy for its brand name in distinguished ways. For instance, the Google letters that appear on the home page and the Google doodle, mostly seen during holidays, are under-the-radar marketing techniques.
The Google Inc. is the leading online advertising firm in the world. Founded by two Stanford undergraduate students, the company has revolutionized the advertising business in the world. Through its generic and grand strategies, it has continued to grow and command the largest market share across the global markets. The Google Inc. boasts its control over both the demand and supply of its products.
Recently, the company diversified its products portfolio ranging from virtual desktop and mobile apps to the Nexus mobile, and the world’s most popular Android Operating system. This strategic analysis has adopted various tools including Porter’s Five Model, SWOT analysis, and the PESTEL/PESTLE analysis to address Google’s both micro and macro-environments. With the growing demand for
Internet services, especially in the knowledge-driven world economy, the number of searches is expected to rise markedly. The business model makes the company seldom affected by economic, political, legal, and socio-cultural factors. The Google Inc. can increase its competitiveness through investing in app development. With the increasing demand for mobile apps in other sectors including banking, healthcare, and insurance, Google can utilize its innovative capabilities to fill this market gap.
Figure 1: Porter’s Five Forces Model
Figure 2: Google’s Marketing Mix
Figure 3: Google’s SWOT Analysis
Figure 4: Google’s Profitability analysis
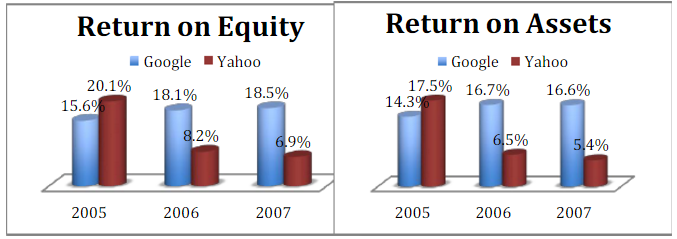
Figure 5: Google’s Liquidity analysis
Google’s annual growth and performance between 2001 and 2006
Figure 6: Google’s Financial ratios for the year 2013
Figure 7: Google’s Strategic Map
Gamble, J. (2013). Google’s Strategy in 2013. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, May 31). The Case of Strategic Analysis of Google Inc. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-case-of-strategic-analysis-of-google-inc/
"The Case of Strategic Analysis of Google Inc." IvyPanda , 31 May 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/the-case-of-strategic-analysis-of-google-inc/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'The Case of Strategic Analysis of Google Inc'. 31 May.
IvyPanda . 2019. "The Case of Strategic Analysis of Google Inc." May 31, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-case-of-strategic-analysis-of-google-inc/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Case of Strategic Analysis of Google Inc." May 31, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-case-of-strategic-analysis-of-google-inc/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Case of Strategic Analysis of Google Inc." May 31, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-case-of-strategic-analysis-of-google-inc/.
- Google Company Overview
- Google: External Threats and Prospects
- Google’s Competitive Strategy
- How to Measure Innovation: DUBAL Company
- Emirates Identity Authority Strategy
- Business Plan: Coffee Shop Report
- Analyzing Firm Strategy: Lipton Tea
- Southwest Airlines Business Strategy

Hacking the Case Interview

If you are interviewing for a business strategy or operations role at Google, there is a high chance that you will be given at least one case interview or case study interview. Roles at Google that have case interviews as part of the interview process include:
- Strategy & Operations
- Product Management
- Business Partnerships
- Business Analyst
In order to land these jobs at Google, you will need to pass every single one of your case interviews. While Google case interviews may seem ambiguous and intimidating at first, know that they can be conquered with the right preparation and practice.
If you are unfamiliar with how to solve or prepare for Google case interviews, we have you covered. In this comprehensive Google case interview guide, we’ll cover:
- What is a Google case interview
- Why Google uses case interviews
- The 6 steps to ace any Google case interview
- Google case interview examples and answers
- Google case interview tips
- Recommended Google case interview resources
If you’re looking for a step-by-step shortcut to learn case interviews quickly, enroll in our case interview course . These insider strategies from a former Bain interviewer helped 30,000+ land tech and consulting offers while saving hundreds of hours of prep time.
What is a Google Case Interview?
Google case interviews, also known as Google case study interviews, are 30- to 45-minute exercises in which you are placed in a hypothetical business situation and are asked to find a solution or make a recommendation.
To do this, you’ll create an overall framework that shows what approach you would take to solve the case. Then, you’ll collaborate with the interviewer, answering a mix of quantitative and qualitative questions that will give you the information and data needed to develop an answer. At the end of the case, you’ll deliver your recommendation.
Case interviews have traditionally been used by consulting firms to assess a candidate’s potential to become a successful consultant, but many companies with ex-consultants now use them to assess an interview candidate’s capabilities. Since Google hires so many former consultants in its business roles, you’ll likely encounter at least one case interview in your interview process.
The business problems that you’ll be given in a Google case interview will likely be real challenges that Google faces today:
- How can Google increase its revenues from enterprise businesses?
- How can Google reduce costs among its customer service call centers while maintaining customer satisfaction?
- Google has seen a steep decline in the number of Google searches in Japan. What is causing this decline and what should Google do to address this?
- How can Google improve customer retention among small and medium-sized businesses?
Depending on what team at Google you are interviewing for, you’ll likely be given a business problem that is relevant to that specific team.
Although there is a wide range of business problems you could possibly be given in your Google case interview, the fundamental case interview strategies to solve each problem is the same. If you learn the right strategies and get enough practice, you’ll be able to solve any Google case interview.
Why does Google Use Case Interviews?
Google uses case interviews because your performance in a case interview is a measure of how well you would do on the job. Google case interviews assess a variety of different capabilities and qualities needed to successfully complete job duties and responsibilities.
Google’s case interviews assess five major qualities:
- Logical, structured thinking : Can you structure complex problems in a clear, simple way?
- Analytical problem solving : Can you read, interpret, and analyze data well?
- Business acumen : Do you have sound business judgment and intuition?
- Communication skills : Can you communicate clearly, concisely, and articulately?
- Personality and cultural fit : Are you coachable and easy to work with?
Since all of these qualities can be assessed in just a 30- to 45-minute case, Google case interviews are an effective way to assess a candidate’s capabilities.
The 6 Steps to Solve Any Google Case Interview
In general, there are six steps to solve any Google case interview or case study interview.
1. Understand the case
Your Google case interview will begin with the interviewer giving you the case background information. While the interviewer is speaking, make sure that you are taking meticulous notes on the most important pieces of information. Focus on understanding the context of the situation and the objective of the case.
Don’t be afraid to ask clarifying questions if you do not understand something. You may want to summarize the case background information back to the interviewer to confirm your understanding of the case.
The most important part of this step is to verify the objective of the case. Not answering the right business question is the quickest way to fail a case interview.
2. Structure the problem
The next step is to develop a framework to help you solve the case. A framework is a tool that helps you structure and break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable components. Another way to think about frameworks is brainstorming different ideas and organizing them into different categories.
For a complete guide on how to create tailored and unique frameworks for each case, check out our article on case interview frameworks .
Before you start developing your framework, it is completely acceptable to ask the interviewer for a few minutes so that you can collect your thoughts and think about the problem.
Once you have identified the major issues or areas that you need to explore, walk the interviewer through your framework. They may ask a few questions or provide some feedback.
3. Kick off the case
Once you have finished presenting your framework, you’ll start diving into different areas of your framework to begin solving the case. How this process will start depends on whether the case interview is candidate-led or interviewer-led.
If the case interview is a candidate-led case, you’ll be expected to propose what area of your framework to start investigating. So, propose an area and provide a reason for why you want to start with that area. There is generally no right or wrong area of your framework to pick first.
If the case interview is interviewer-led, the interviewer will tell you what area of the framework to start in or directly give you a question to answer.
4. Solve quantitative problems
Google case interviews typically have some quantitative aspect to them. For example, you may be asked to calculate a certain profitability or financial metric. You could also be asked to estimate the size of a particular market or to estimate a particular figure.
The key to solving quantitative problems is to lay out a structure or approach upfront with the interviewer before doing any math calculations. If you lay out and present your structure to solve the quantitative problem and the interviewer approves of it, the rest of the problem is just simple execution of math.
5. Answer qualitative questions
Google case interviews will also typically have qualitative aspects to them. You may be asked to brainstorm a list of potential ideas. You could also be asked to provide your opinion on a business issue or situation.
The key to answering qualitative questions is to structure your answer. When brainstorming a list of ideas, develop a structure to help you neatly categorize all of your ideas. When giving your opinion on a business issue or situation, provide a summary of your stance or position and then enumerate the reasons that support it.
6. Deliver a recommendation
In the last step of the Google case interview, you’ll present your recommendation and provide the major reasons that support it. You do not need to recap everything that you have done in the case, so focus on only summarizing the facts that are most important.
It is also good practice to include potential next steps that you would take if you had more time or data. These can be areas of your framework that you did not have time to explore or lingering questions that you do not have great answers for.
Google Case Interview Examples and Answers
Example #1: What differences would you take into account when selling a product to a client in India versus a client in Argentina?
Sample solution: To answer this, create a framework that shows the most important characteristics or qualities of each country that you would want to look into. For example, one potential framework may look into the customer needs and preferences, the competitive landscape, market trends, and Google’s capabilities across the two countries.
Example #2: If you were a Google Search competitor entering a new market and had a small market share, how would you convince advertisers to advertise with you?
Sample solution: To answer this question, you should be familiar with Google Search. You can create a framework that outlines the product’s strengths and weaknesses so that you can identify gaps in customer needs.
At a high level, the strengths of Google Search is that it has the widest reach since it is the most used search engine. It also has high targeting specificity since it has lots of data on long-tail keywords. However, the main drawback is how competitive and expensive it can be for advertisers to use. Customer service can also be slow for smaller customers given the number of customers Google services. Finally, the product can be complicated for advertisers to set up initially. Therefore, when entering a new market as a Google Search competitor, it may make sense to target customers with smaller budgets and sell them on low-prices, fast customer service, and ease of set up.
Example #3: What are three areas that Google should invest in?
Sample solution: To answer this question, it may be helpful to clarify what Google’s primary objective is. Are they looking to increase profits, revenues, or number of users? The ideas that you brainstorm may vary depending on their actual goals. Next, develop a framework to organize your ideas. You may want to think about areas of investments as short-term investments, medium-term investments, and long-term investments.
Example #4: If you were the CEO of AdSense, what would be your strategy to improve the product?
Sample solution: As always, create a framework to help you organize your ideas in a clear and easy to follow way. To improve AdSense, you can think about improving the product for advertisers, improving the product for search users, and improving the product for Google’s profitability. Using a framework like this one will help you consider all of the different ways that AdSense can be improved.
Example #5: How much money do you think YouTube makes daily from ads?
Sample solution: This is an estimation question. Before doing any math calculations, make sure to lay out a structure or approach for how you would estimate this figure.
You may want to start by estimating the number of people in the world, the percentage that use YouTube, the percentage that use YouTube on any given day, the average amount of time spent on YouTube in a day, the number of ads seen for that period of time, and then estimating the amount YouTube earns per ad that is shown. Multiplying all of these figures will give you your answer.
Example #6: How would you set the price for the YouTube masthead? The YouTube masthead is a digital billboard placed on YouTube’s homepage for 24 hours, reaching about 60 million people.
Sample solution: In general, there are three ways to price a product: pricing by the cost to produce the product, pricing by the economic value the product provides customers, and pricing by the price of competitors’ similar products.
Since the cost of putting up a digital billboard is minimal, the first pricing strategy is not helpful. Looking at the second pricing strategy, you can price the digital billboard based on how much it would have cost the potential customer to get 60 million ad impressions. Looking at the third pricing strategy, you can look into how much other types of advertising that reach a similar number of people costs. For example, you could look into how much Super Bowl ads cost.
Example #7: How would you market the Google Ads product to a potential client?
Sample solution: To develop an effective marketing strategy, you may want to look into the client’s needs, competitor offerings, and Google Ads’ features or benefits. Exploring these three areas will help you identify the features or benefits of Google Ads that are superior to competitor products that the client values.
Example #8: How would you estimate the market size of Google display ads on websites?
Sample solution: This is another estimation question. As always, outline a structure before you begin doing any math calculations.
You may want to start by estimating the global population, estimating the percentage that have internet, estimate the average number of sites visited per day, estimate the percentage of websites that have ads, estimate the percentage of these websites that use Google display ads, estimate the revenue Google generates per ad. If you multiply the product of these figures by 365 days in a year, you’ll get an estimate of the market size of Google display ads.
Example #9: How would you determine the number of staff members needed in the customer support team next year?
Sample solution: One potential approach for solving this question could look like the following.
Start with Google’s annual revenues and estimate the average revenue generated per customer to determine the number of customers Google services. For each customer, estimate the frequency in which they call customer support and the average length of a support call. Assuming that a staff member works eight hours per day, you can estimate the number of staff members you’d need to meet the volume of support calls.
You may need to grow this number by Google’s historical growth rate to account for expected revenue growth next year.
Example #10: If you were setting up a new ecommerce business, what are the things you would look at?
Sample solution: This is a market entry case. Potential areas you should consider looking into in your framework include: the attractiveness of the market, the competitive landscape, the company’s capabilities, and the expected profitability.
Example #11 : How should YouTube deal with spam?
Sample solution: There are many different ways to deal with spam. To ensure that you brainstorm ideas in a clear and comprehensive way, develop a framework to categorize all of the different ways of dealing with spam. You may want to think about this as: preventing spam from being posted, detecting spam, and removing spam.
Example #12 : Let’s say that Google is considering acquiring iRobot, a company that builds consumer robots, such as the Roomba. What would you consider when deciding whether to make this acquisition?
Sample solution: This is an acquisition case. To determine whether or not this is an attractive acquisition, you may want to look into: the attractiveness of the consumer robots market, the attractiveness of iRobot as a company, the potential synergies from the acquisition, and the financial implications of the acquisition.
Example #13 : Estimate the time it takes a Google Street View car to collect footage in a city.
Sample solution: To answer this question, first clarify which city the interviewer is talking about. Then, outline your approach for how you would do this calculation.
You might want to start by estimating the length and width of the city area. Then, estimate how wide a street is and the average distance between streets. If you think of a city as a grid that consists of vertical and horizontal lines, you can use these estimates to calculate the total street length in the city.
Afterwards, estimate the average speed of a Google Street View car, taking into traffic and stoplights. Dividing the total street length by the average speed of a Google Street View car will get you an estimate of how long it would take to collect footage.
Example #14 : How would you define the strategy for YouTube over the next 5 years?
Sample solution: This question is very similar to Example #3. Before answering, it may be helpful to clarify what YouTube’s primary objective is. Are they looking to increase profits, increase number of users, or increase user engagement? You may want to think about strategy as short-term strategy and long-term strategy.
Example #15 : Let’s say that Google is considering getting into the ride share business. What should they consider when making the decision on whether or not to enter?
Sample solution: This is a market entry case and the approach is similar to Example #10. Potential areas you should consider looking into in your framework include: the attractiveness of the ride share market, the competitive landscape, the company’s capabilities, and the expected profitability.
Google Case Interview Tips
Below are eight of our best tips to help you perform your best during your Google case interviews.
1. Familiarize yourself with Google’s business model
If you don’t understand Google’s business model, it will be challenging for you to do well in their case interviews. Therefore, you should know that Google makes the majority of its revenue by selling advertising and you should be familiar with the products and services that Google offers for the specific team you are interviewing for.
2. Read recent news articles on Google
Often, the cases you’ll see in a Google case interview are real business issues that the company faces. Reading up on the latest news on Google will give you a sense of what Google’s biggest challenges are and what major business decisions they face today. There may be a good chance that you’ll be given a case that is similar to something that you have read in the news.
3. Verify the objective of the case
Answering the wrong business problem will waste a lot of time during your Google case interview. Therefore, the most critical step of the case interview is to verify the objective of the case with the interviewer. Make sure that you understand what the primary business issue is and what overall question you are expected to answer at the end of the case.
4. Ask clarifying questions
Do not be afraid to ask questions. You will not be penalized for asking questions that are important and relevant to the case.
Great questions to ask include asking for the definition of an unfamiliar term, asking questions that clarify the objective of the issue, and asking questions to strengthen your understanding of the business situation.
5. Do not use memorized frameworks
Interviewers can tell when you are using memorized frameworks from popular case interview prep books. Google values creativity and intellect. Therefore, make every effort to create a custom, tailored framework for each case that you get.
6. Always connect your answers to the case objective
Throughout the case, make sure you are connecting each of your answers back to the overall business problem or question. What implications does your answer have on the overall business problem?
Many candidates make the mistake of answering case questions correctly, but they don’t take the initiative to tie their answer back to the case objective.
7. Communicate clearly and concisely
In a Google case interview, it can be tempting to answer the interviewer’s question and then continue talking about related topics or ideas. However, you have a limited amount of time to solve a Google case, so it is best to keep your answers concise and to the point.
Answer the interviewer’s question, summarize how it impacts the case objective, and then move onto the next important issue or question.
8. Be enthusiastic
Google wants to hire candidates that love their job and will work hard. Displaying enthusiasm shows that you are passionate about working at Google. Having a high level of enthusiasm and energy also makes the interview more enjoyable for the interviewer. They’ll be more likely to have a positive impression of you.
Recommended Google Case Interview Resources
Here are the resources we recommend to learn the most robust, effective case interview strategies in the least time-consuming way:
- Comprehensive Case Interview Course (our #1 recommendation): The only resource you need. Whether you have no business background, rusty math skills, or are short on time, this step-by-step course will transform you into a top 1% caser that lands multiple consulting offers.
- Hacking the Case Interview Book (available on Amazon): Perfect for beginners that are short on time. Transform yourself from a stressed-out case interview newbie to a confident intermediate in under a week. Some readers finish this book in a day and can already tackle tough cases.
- The Ultimate Case Interview Workbook (available on Amazon): Perfect for intermediates struggling with frameworks, case math, or generating business insights. No need to find a case partner – these drills, practice problems, and full-length cases can all be done by yourself.
- Case Interview Coaching : Personalized, one-on-one coaching with former consulting interviewers
- Behavioral & Fit Interview Course : Be prepared for 98% of behavioral and fit questions in just a few hours. We'll teach you exactly how to draft answers that will impress your interviewer
- Resume Review & Editing : Transform your resume into one that will get you multiple interviews
Land Multiple Tech and Consulting Offers
Complete, step-by-step case interview course. 30,000+ happy customers.
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Management Case Studies » Case Study: Analysis of Organizational Culture at Google
Case Study: Analysis of Organizational Culture at Google
Google Inc came to life with the two brilliant people as the founder of the company. Those two were Larry Page and Sergey Brin . Both of them are a PhDs holder in computer science in Stanford University California. In their research project, they came out with a plan to make a search engine that ranked websites according to the number of other websites that linked to that site. Before Google was established, search engines had ranked site simply by the number of times the search term searched for appeared on the webpage. By the brilliant mind of Larry and Sergey, they develop the technology called PageRank algorithm . PageRank is a link analysis algorithm that assigns a numerical weighting to each element of a hyperlinked set of document, such as the World Wide Web, with the purpose of measuring its relative importance within the set. All this in-depth research leads to a glorious day which is on September 15, 1997 where Google.com domain was registered. Soon after that, on September 4, 1998, they formally incorporated their company, Google Inc, at a friend’s garage in Menlo Park California. The name Google originates from “Googol” which refers to the mathematical equivalent of the number one followed by a hundred zeros. In March 1999, the company moved into offices at 165 University Avenue in Palo Alto. After that, the company leased a complex of buildings in Mountain View. Ever since then, the location of the headquarter remain unchanged.
Google’s core business is to provide a search engine for the cyber user who would like to go to their desire site. The Google search engine attracted a number of internet users by its sleek and simple design but result in amazing search result. After the initial stage of Google establishing itself in the world, it began selling advertisements associated with the search keywords. The advertisements were text-based in order to maximize the page loading speed. Most of the Google Inc revenue relies on the advertisement and they had been successfully with the help of AdWords and AdSense in their system. After having some experience in the industry, Google itself launched its own free web-based email service, known as Gmail in 2004. This service is established to meet the need of the cyber user in order to store and send their document through online. In the same year, one of the most captivating technologies that Google had launched is the Google Earth. Google Earth is an amazing creation that is a map of the earth based on the satellite image. It requires you to type the desire location that you want to view and it will process the image for you. Furthermore, Google Inc made a new partnership with NASA with even enhances the Google technologies. Google also had its own Google Video which allows user to search the internet for videos. One of the most important things in the Google Inc is that they have a strong organizational culture which brings them closer and stronger compare with other firms. The values that they emphasis on are creativity, simplicity and innovation in order to gain competitive advantage against their competitor.
The Google Culture
Google is well known for their organizational cultures distinctiveness and uniqueness compared to their immediate competitors. On the Google corporate website, they have listed down 10 core principles that guide the actions of the entire organization. These are the values and assumptions shared within the organization. These values are also termed as ‘espoused values’, where it is not necessarily what the organization actually values even though the top executives of the company embrace them.
In Google, the daily organizational life is distinctive and is one that thrives on informal culture. The rituals that portray the organization’s culture as unique and possesses a small-company feel are portrayed daily at lunchtime, where almost all employees eat together at the many various office cafes while at the same time having an open, relaxed conversations with fellow Googlers that come from different teams. Also, because one of the Google culture’s main pillars are the pillar of innovation, every Googler are very comfortable at sharing ideas, thoughts, and opinions with one another in a very informal working environment. Every employee is a hands-on contributor and everyone wears several hats. Sergey and Brin also plays a big part of laying the foundation on what the Google culture is and the founders have continued to maintain the Google Way by organizing a weekly all-hands “TGIF” meetings for employees to pose questions directly at them.
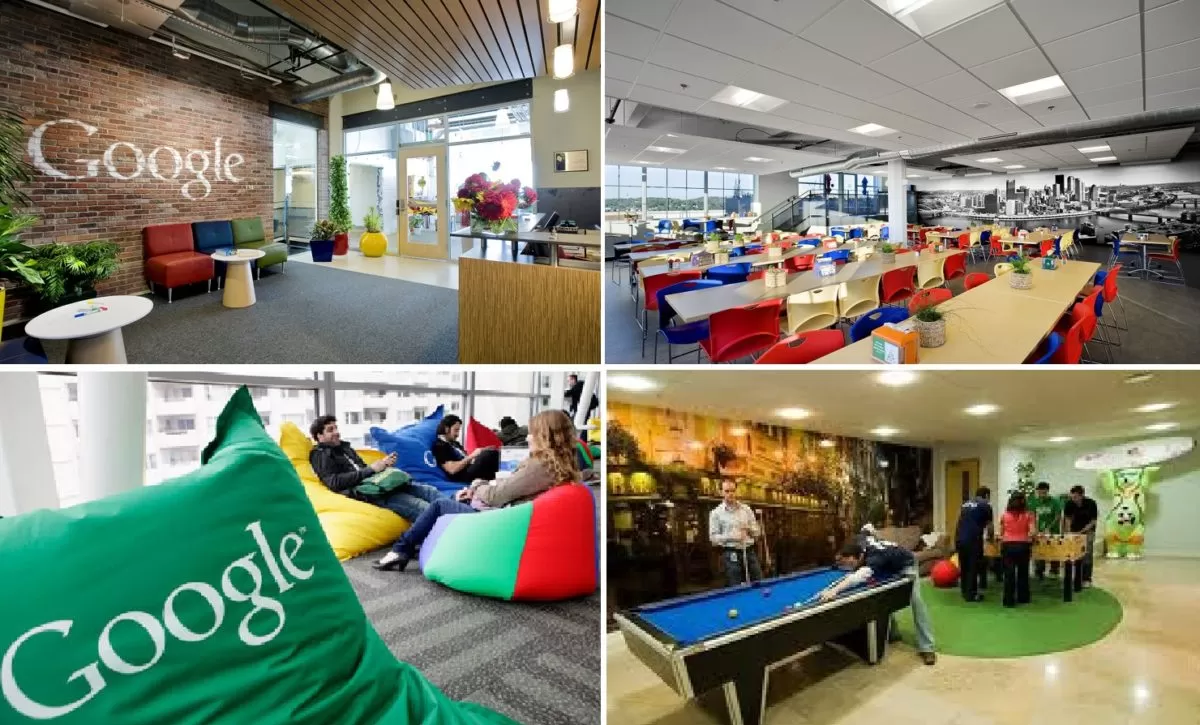

Here are some of a few of their core principles which will provide a look into Google’s management philosophy and the type of culture they want to possess:
In Google, the motivated employees who ‘live’ the Google brand and are aligned to the company call themselves ‘Googlers’. Even former employees of Google have a name which they refer to themselves as ‘Xooglers’. This shows that in Google, their employees are so involved in the organization that they have their own symbolic name that mirrors the organization’s name and image, which is a sure sign of existing strong cultural values that are present within the company.
After tremendous growth in Google, the organization moved from a humble office building in Palo Alto, California back in its early days to its current office complex bought over from Silicon Graphics. The complex is popularly known as the Googleplex, which is a blend of the word ‘Google’ and ‘complex’. Googleplex is the result of a careful selection that serves to establish Google’s unique and individualistic culture in the eyes of the employees and the public. The corporate campus is built to provide a very fun, relaxed and colorful environment both inside and outside. Innovative design decisions provides Google employees 2000 car lots underground so that open spaces above and surrounding the building are filled with unique and interesting architectures that includes an on-site organic garden that supplies produces for Google’s various cafes, a bronze casting of a dinosaur fossil, a sand volleyball court, heated “endless pools” and also electric scooters along with hundreds of bikes scattered throughout the complex for Googlers to get to meetings across campuses. Googleplex is a significant departure from typical corporate campuses, challenging conventional thinking about private and public space. This also points out the alignment of values that are present in Google’s culture such as innovation, fun, laid-back, creativity and uniqueness that clearly shows that their organizational culture is truly unique and different from that of their competitors and other organizations.
Within the Googleplex, a truly attractive, fun and extraordinary workplace environment exists for Google employees. The interior of the headquarters is furnished with items like lava lamps and giant rubber balls while sofas, Google color coded chairs, and pool tables can be found at lounges and bar counters to express Google’s laid-back working atmosphere. The lobby contains a grand piano and a projection of current live Google search queries. The employees’ various needs are also taken care of by facilities such as the 19 cafes on campus which serves a variety of food choices for their diverse workforce, a gym, massage parlor, laundromats, and even micro kitchens, which provides snacks for employees who want a quick bite. This ensures that employees can be more productive and happy without ever leaving the workplace. A manifestation of Google’s creative and innovative culture is shown by the unconventional building design with high ceilings to let natural light in, durable floors made of tiny quartz stones, working British phone booths splashed in Google colors, and lounges that also serve as DIY libraries with cleverly placed low-reach book racks adorned with colorful Lego sets and cubes. All these innovative, creative and colorful designs are symbols of Google’s unique organizational culture that emphasizes on continuous innovation.
Google engages their employees by applying adaptive culture in the organization. From their core competency in search engine technology, Google has responded to customers change in needs by expanding onto the mobile market. The employees analyze, anticipate and seek out the opportunities to improve the organization’s performance by being proactive and quick in coming out with new technologies and solutions for mobile services. It aims to help people all over the world to do more tasks on their phone, not to mention the several different ways to access their Google search engine on a mobile phone. In addition, Google recently entered the smartphone market by launching the Google Nexus One smartphone in response to customer’s increasing need for smartphones, which is gaining ground on popularity because everyone is going mobile in the Information Age. This is the result of Google employees’ common mental model that the organization’s success depends on continuous change to support the stakeholders and also that they are solely responsible for the organization’s performance. The employees also believe that by entering into other markets beyond their core competency, the change is necessary and inevitable to keep pace with an ever changing and volatile technological market.
Google’s organizational culture places a huge importance of trust and transparency by having an informal corporate motto namely “Don’t be evil”. This slogan has become a central pillar to their identity and a part of their self-proclaimed core principles. It also forms the ethical codes of the organization where Google establishes a foundation for honest decision-making that disassociates Google from any and all cheating. Its ethical principles means that Google sets guiding principles for their advertising programs and practices, which is where most of their revenues come from. Google doesn’t breach the trust of its users so it doesn’t accept pop-up advertising, which is a disruptive form of advertisement that hinders with the user’s ability to see the content that they searched. And because they don’t manipulate rankings to put any of their partners higher in their search results or allow anyone to buy their way up the PageRank, the integrity of their search results are not compromised. This way, users trust Google’s objectivity and their ethical principles is one of the reasons why Google’s ad business had become so successful. The founders of Google believe strongly that ‘in the long term we will be better served, as shareholders and in all other ways, by a company that does good things for the world even if we forgo some short term gains.’
Analysis of Google Culture
Satisfied employees not only increase productivity and reduce turnover, but also enhance creativity and commitment. Google is already having a playful variation culture in the organization for the employees. This can enable the employees to have an enjoyment environment and this will be able enhance the relationship between the employees and strengthen their bond to work as a team. An enjoyment environment definitely can let the employees to feel satisfied and subsequently will increase productivity. Apart from that, this will shape a convenient work process for the employees that will smoothen the decision making process for the management team. Google already identified the employees are the organization’s internal customers and this is the reason why it has been constantly giving employees a sense of purpose, enhancing their self-esteem and sense of belonging for being a part of the organization. The company was reorganized into small teams that attacked hundreds of projects all at once. The founders give the employees great latitude, and they take the same latitude for themselves. Eric Schmidt says that Google merely appears to be disorganized. “We say we run the company chaotically. We run it at the edge. This can adapt the culture Google and therefore they can individually to generate the ideas on their own.
On the other hand, Google hires employees that have good academic results but without practical experience and this will be a threat to Google in terms of their organization’s operation. Google is a results-driven organization and if employees with only creative ideas but lacking of skills to realize the ideas they have initially planned, this will absolutely reduce the productivity of the organizations. Google had been public listed on year 2004 and therefore Google had to take the shareholders’ views into consideration before making any decision. The shareholders had been strongly emphasizing on reducing the employee benefits due to the high cost invested on it. This leads to the organizational culture would be degraded and the employees would feel less satisfied and affect their produced results. Employees are very important asset the Google while the shareholders also the contributor of funds for Google. The management team has to weight the importance of both of the stakeholders for the Google as this will create a different organizational culture .
Related posts:
- Case Study: Organizational Structure and Culture of Virgin Group
- Case Study: Google’s Competitive Advantage
- Case Study: Google’s Acquisition of Motorola Mobility
- Case Study: Google’s Quest for Competitive Advantage
- Case Study of Johnson & Johnson: Creating the Right Fit between Corporate Communication and Organizational Culture
- Case Study: Google’s Recruitment and Selection Process
- Case Study: Success Story of Google Search Engine
- Case Study of Starbucks: Creating a New Coffee Culture
- Case Study of Procter and Gamble (P&G): Structure and Culture
- Case Study: Henry Ford’s Contributions to Organizational Behavior and Leadership
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
- Deutschland
- Asia, Australia & New Zealand
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- United States & Canada
- Latinoamérica
Google Analytics Performance Marketing Case Studies
When you change the way data is collected and analyzed, you gain insights into your customers and their purchase behaviors. The brands in the section below, including Westwing, Travelocity and PBS, did just that with products such as Google Analytics Premium and Universal Analytics.
Share this page
Lenovo: a radically new view of results, accuweather measures holistic analytics with google analytics premium, watchfinder clocks 1,300% roi using precision remarketing with google analytics, westwing uses universal analytics to better understand customers' purchase path, rooms to go improves the shopper experience by integrating google analytics premium.
- Español – América Latina
- Português – Brasil
On: Staying competitive for the long haul with a unified big data platform
On was born in the Swiss Alps with one goal: to revolutionize the sensation of running by empowering all to run on clouds. Fueled by customer recommendation, On’s award-winning CloudTec ® innovation, purposeful design, and groundbreaking strides in sportswear’s circular economy have attracted a fast-growing global fan base across more than 60 countries worldwide.
Tell us your challenge. We're here to help.
By unifying ecommerce information on scalable data infrastructure, the sports shoe experts at on ensure they understand what their customers want, even as the company expands., google cloud results.
- Scales data solutions to match company growth, as On extends to 50 markets worldwide
- Unifies data with easy-to-use connections between Google Cloud tools
- Delivers accurate analysis on the true cost of campaigns using Google Sheets to manually add offline data
Connects data to identify precise customer clusters
Olivier Bernhard has done great things in running shoes. Twice world champion in the long-distance duathlon and eight times winner of Ironman triathlon competitions, Olivier spent more than a decade as a professional endurance athlete. So when he teamed up with David Allemann and Caspar Coppetti in 2010 to create the perfect running shoe, he brought a knowledgeable customer’s perspective to product development. Together, the three friends founded On , developing innovative footwear that is now sold in more than 60 countries worldwide.
“BigQuery is the cornerstone of our data strategy at On. It is secure, easy to use, and cost effective. Rich partner ecosystem and seamless integrations with other Google services have allowed us to move fast and focus on using the data and empowering all parts of the business."
In 2019, long-time On fan and Olympic gold medalist tennis player Roger Federer joined the On leadership team as an entrepreneur, bringing insights as a professional athlete to help create unique products and experiences for On customers around the world. The partnership was celebrated at a live event streamed globally on YouTube, where Roger himself revealed the results of his first project in the On Lab: a tennis-inspired sneaker collection designed for comfort and performance. While on set, Roger answered questions and interacted with the audience using Google Meet , to the delight of fans from all over the world.
On started life as a running shoe company, but its comfortable, light footwear soon attracted a diverse range of customers, from people looking for wearable, everyday shoes to those on the hunt for hiking apparel. Targeting new audiences in the US, Germany, and the UK, On recognized that a detailed understanding of customer needs is as vital for growth as it was for the design of that first running shoe.
The team at On had to manage different sources of data from different channels. But the team wanted to understand the way that everything in the company related to everything else. That’s why On created a centralized, scalable data warehouse on BigQuery with Looker , the modern business intelligence and data application platform that provides access to actionable insights on Google Cloud. This enabled the team to unify their data sources and compare performance across them. It has also made the process of growth manageable.
“Setting up an architecture is so easy with the intelligent connections between Google Cloud tools. In my experience, I’ve never worked with such a robust and coherent system. And with accounts managed through Google Workspace, it’s incredibly easy to onboard new starters, which is a real bonus for a fast-growing company.”
Connecting cloud tools to bring data together
As a company grows, it can become hard to maintain a clear idea of who its customers are, what they want, and how to give them what they need. For On, a diversifying product range and rapid expansion into multiple markets underlined the value of a unifying business intelligence solution that could scale at speed. On put together an architecture that does just that, built around BigQuery as a scalable data warehouse.
“BigQuery is the cornerstone of our data strategy at On. It is secure, easy to use, and cost-effective. Rich partner ecosystem and seamless integrations with other Google services have allowed us to move fast and focus on using the data and empowering all parts of the business." says Andrej Blaha, Head of Business Intelligence of On.
A wide array of data sources from across the company feed into BigQuery, including the campaign manager Display and Video 360 , On’s Google Ads , multiple social media sources, and Google Analytics 360 , which relays on-site user behavior. On also sends predictive modeling and segmentation, created with Apache Airflow run on Cloud Composer . Once in BigQuery, data is transformed with DBT data transformation tool and made available through Looker . “Setting up an architecture is so easy with the intelligent connections between Google Cloud tools,” says Sofia Cubillos, Head of Data Analytics at On. “In my experience, I’ve never worked with such a robust and coherent system to analyze, visualize, and act on the comprehensive business intelligence information we now have at hand.”
Using Google Workspace collaboration tools, teams can manually enter datasets into Google Sheets that connect directly to BigQuery. “If we’re running a campaign in the offline world, such as a direct mail campaign, we need to be able to compare the costs of those campaigns to the revenue that they generate on the webshop,” explains Sofia. “The digital marketing team on that campaign can upload its cost to a Google Sheet, which connects really nicely to all the other platforms through BigQuery, so we can get the full picture. And with accounts managed through Google Workspace, it’s incredibly easy to onboard new starters, which is a real bonus for a fast-growing company.”
Creating detailed audience clusters with machine learning
On uses its unified data architecture as the foundation for a wide range of projects, such as creating customer clusters in real time using AutoML . Using clusters to create audiences in Google Analytics 360, On is able to assign budgets to achieve the best returns on investment.
“We took all our data sources, including CRM data from Salesforce and behavioral data from Google Analytics 360, and we created 65 dimensions for each customer,” says Sofia, “such as country, transaction history, date of last session, etc. With AutoML, we created a clustering algorithm that put out seven clusters, such as ‘fans’ of the brand, or ‘Black Fridayers,’ who respond particularly well to promotions.” The team sends the clusters back to BigQuery, then identifies them in Google Analytics 360 through CRMint . Finally, sending the audiences to Display and Video 360 means On can create lookalike audiences and identify prospective customers.
“BigQuery fit our needs when we were a small company, and it fits our needs today. The infrastructure grows with us, so we haven't had to change systems or migrate data. We can just trust it to work. It’s a great jumping-off point for all our data projects.”
Laying the foundation for growth with a scalable data platform
On’s unified data platform on cloud infrastructure scales with the company, so that On can understand what customers want, even as it grows at speed. “By building this architecture with Google Cloud tools, we don't have to migrate everything in order to support rapid growth,” says Sofia. “Google Cloud scales our infrastructure for us.”
Now On is looking to build more predictive algorithms, using first-party data and machine learning tools. “We need to find the right balance between protecting user privacy and offering them the best service,” says Sofia. “To get that right, we need to use data.” Thanks to the architecture On has built on Google Cloud, that data is available, helping On outpace competitors and keep growth on track.
“BigQuery fit our needs when we were a small company, and it fits our needs today,” says Sofia. “The infrastructure grows with us, so we haven't had to change systems or migrate data. We can just trust it to work. It’s a great jumping-off point for all our data projects.”
Google's lawsuit history: The biggest legal cases against the search giant, including antitrust and class-action suits
- Google has faced numerous lawsuits over privacy, intellectual property, monopoly tactics, and more.
- Google is currently battling two key antitrust cases over its search engine and advertising tactics.
- Google also recently settled two class-action lawsuits concerning privacy and antitrust violations.

Google is one of the world's largest and most influential companies, and the most popular search engine by far. So it's no surprise that the search giant's rapidly evolving and boundary-pushing technology would attract litigation over the course of its 25-year history.
Google has been sued in dozens, if not hundreds of high-profile controversies over privacy, intellectual property, discrimination, advertising, and even defamation, and has racked up both wins and losses over the years.
Some of Google's most consequential legal cases have occurred in 2023 and 2024, including two major antitrust cases and several class-action lawsuits. Here's what you need to know about the biggest recent cases to land on Google's docket.
Why did the US government sue Google over antitrust violations?
The US government's battle against Google has resulted in two major antitrust cases that are both still ongoing.
One case culminated in a landmark monopoly trial in the fall of 2023, which is still awaiting a verdict. The dispute centered on whether Google has illegally abused its monopoly over the search engine industry, spending billions of dollars each year to suppress competition. The US government argued that Google's business dealings have blocked innovation in the search business to the detriment of internet users.
Google CEO Sundar Pichai testified in the antitrust trial in October 2023, and defended instances in which Google pushed companies like Apple and other smartphone makers into revenue-sharing agreements that would make Google the default search engine on phones and computers.
The Google CEO even acknowledged on the stand that company executives knew that becoming the default search engine on smartphones "would lead to increased usage of our products and services."
The second major antitrust case against Google concerns its online advertising strategies, and is set to go to trial in September 2024. The US government has alleged that Google illegally abused its monopoly over the digital advertising market by acquiring its competitors and forcing website publishers to adopt Google's tools, such as Google Ads , thereby suppressing the rise of rival technologies.
Google has denied any wrongdoing in both cases. The search giant argued during its 2023 trial that Google dominates the search business because it's superior to its rivals, not because of its business dealings. Google has similarly denied the claims in the advertising-related monopoly case, saying its acquisitions were legal and actually enable innovative new advertising technologies, and that the federal government's lawsuit could undo years of industry progress.
What happens if Google loses its antitrust cases?
It's unclear who will win the antitrust case on Google's search engine. Judge Amit Mehta will be the one to decide the outcome, rather than a jury, and Mehta vigorously questioned both sides during closing arguments in May 2024.
Related stories
If Google loses the lawsuit , Mehta is expected to take some sort of action that would boost competition in the search-engine business. Google could face consequences like orders to adjust its business practices, or even a total ban on its contracts to make Google the default search engine.
Both antitrust cases carry potentially massive implications for internet users — Google could face sanctions that alter its operations so dramatically that it loses its ubiquity in the search and advertising industries, paving the way for new companies and technologies to flourish.
Google's antitrust cases will also likely influence the outcomes of other antitrust lawsuits the US government has filed against major tech companies. Currently, Amazon , Apple, and Meta all face similar antitrust lawsuits against their business practices that could threaten their market dominance.
What to know about Google's class-action settlements and who can claim money
Google has been the subject of two major class-action lawsuits that were resolved or nearing resolution in late 2023 and 2024.
One of the most hotly anticipated resolutions was that of a class-action case involving personal data collected from 136 million Google Chrome users. The lawsuit accused Google of tracking the internet activity of users who had switched to Google's "incognito" setting.
As part of a settlement agreement, Google said it would delete the search data collected from those 136 million users, which Google said was merely "old personal technical data that was never associated with an individual and was never used for any form of personalization."
Lawyers initially sought a $5 billion payout for consumers, but anyone expecting to receive a chunk of that money will need to sue Google individually to receive any damages. The settlement agreement for the class-action case did not include any monetary damages to be paid out by Google.
Google does, however, have to pay out roughly $700 million as part of a separate class-action case involving the Google Play Store. Attorneys general from five states accused Google of using monopoly tactics to box out competitors to the Google Play Store and limited users' ability to download Android apps from other app stores.
An estimated 102 million consumers were affected between August 16, 2016, and September 30, 2023, and are entitled to compensation of at least $2, the settlement agreement stipulated. Consumers who are eligible for the Google settlement don't need to submit any sort of claim to get that money, however. Consumers will receive automatic payments through PayPal or Venmo.
Google's battle over Europe's "right to be forgotten" laws
One of Google's biggest legal battles in the 2010s concerned the European Court of Justice's "right to be forgotten" ruling and whether Google was responsible for personal data that appears in its search results. Google lost its case in 2014, and the EU court ruled that individuals have the right to remove information about themselves from search engine results.
Under the ruling, Google must respond to legitimate requests from individuals to delist webpages from its search results. Larry Page , one of Google's founders and a former CEO, spoke out vehemently against the EU court's "right to be forgotten" ruling at the time, warning that repressive foreign governments could abuse the ruling.
However, in 2019, Google won a "right to be forgotten" victory in a subsequent EU court ruling, which stipulated that Google only has to delist content from search results in Europe, and the "right to be forgotten" does not apply globally.
Recent research has suggested that Google and Microsoft together have received some 150,000 "right to be forgotten" requests to delist search results each year since the EU court's ruling in 2014. The vast majority of the links targeted for delisting were from Facebook , X, and YouTube .
On February 28, Axel Springer, Business Insider's parent company, joined 31 other media groups and filed a $2.3 billion suit against Google in Dutch court, alleging losses suffered due to the company's advertising practices.
Watch: Apple's antitrust lawsuit is just one of its major battles
- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Buy Copies. Google went public 10 years ago today, and since then has dramatically changed the way the world accesses information. It has also helped shape the practice of management. Staying true ...
This paper will analyze the case study of Harvard Business Review, Oxygen Project, and clarify the management problem in Google's organization. It will also compare Google with Zappos, a much smaller organization, and present how the BoDs of Zappos assesses its culture and subcultures. ... Rosenberg E. (2016, 27th June). The Business of ...
Abstract and Figures. This case study examines the disruptive nature of Google's strategy in the marketplace to assist researchers and practitioners in future endeavors. From this research ...
Google revenue model case study. Google case study : A summary of Google business strategy and background on Google technology for readers of my Digital Marketing and E-commerce books. End of case contains technical references on Google's approach to crawling, indexing and ranking results at the end of this case study page.
Read case studies from Google Marketing Platform customers who successfully use marketing analytics tools and intelligence to improve decision making. ... Deckers Brands drives business growth with Google Marketing Platform and Google Cloud. Read more Case Study. TUI UK drives 13% higher return on ad spend by investing in digital maturity ...
To promote new ideas, Google encourages all engineers to spend 20% of their time working on their own ideas. Google's culture is reflected in their decision making as well. Decisions at Google are made in teams. Even the company management is in the hands of a triad: Larry Page and Sergey Brin hired Eric Schmidt to act as the CEO of the ...
The case for change: A business-value framework for technology choices The new era of work with Gemini for Google Workspace with Etsy, Fox Sports, and Thoughtworks Thirdware: Unifying 25 years of knowledge to give technology services a competitive advantage
Edelman, Benjamin, and Thomas R. Eisenmann. "Google Inc." Harvard Business School Case 910-036, January 2010. (Revised April 2011.) (Winner of ECCH 2011 Award for Outstanding Contribution to the Case Method - Strategy and General Management.) Educators.
Google's Official Digital Marketing Publication. Learn how other brands have approached common marketing challenges. ... 3 key measurement considerations to drive business growth in 2024. Global Article. November, 2023. Holiday Shopping Insights: Keep momentum with devoted shoppers ... Case Study Learn how other brands have approached common ...
Artwork: Chad Hagen, Graphic Composition No. 1, 2009, digital. Since the early days of Google, people throughout the company have questioned the value of managers. That skepticism stems from a ...
Abstract. Beginning in 2017, technology (tech) company Google faced a series of employee-relations issues that threatened its unique culture of innovation and open communication. Issues included protests surrounding Google's contracts with the U.S. government, restrictions of employee speech, mistreatment of contract and temporary workers ...
Google Case Study: Defining the Issue. Larry Page and Sergey Brin created Google in 1998 during their college days at Stanford University. Over the last one decade, Google has grown into a globally acknowledged market force for its service provision, business model, efforts in development of technology, and human life influence.
Current is a financial technology company that offers a debit card and app made for teenagers. The app and card give teens hands-on learning with modern financial tools, and connects them with the people, brands, and experiences they value. Industries: Financial Services & Insurance. Location: United States. Products: Compute Engine, Kubernetes ...
The Framingham Heart Study, ... an HR software company using people science to help people do their best work. He is the former SVP of People Operations at Google and the author of Work Rules!:
CASE STUDY: GOOGLE. Google is a very successful information technology/web search company with more than 21,000 employees working in 77 offices located in 43 countries. It was founded in 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin. According to the Google website, Google has grown by leaps and bounds since then. From offering search in a single language ...
Google's strategy for this is 20% time. Every employee devours up to 20% of his time at work each week on ventures that inspire him. This concept inspires employees as it allows them to concentrate on things they love or are passionate about. It can prevent burnout, decrease turnover, increase engagement.
The Google Inc. is a giant Internet search engine technology provider incorporated in Delaware. It was founded in 1996 by Larry page and Sergey Brin. The company has grown over time to become one of the most successful and highly admired organizations in the world. Today, the company offers more than just mere search engine technology.
Google Case Interview: Strategies, Examples, and Answers. If you are interviewing for a business strategy or operations role at Google, there is a high chance that you will be given at least one case interview or case study interview. Roles at Google that have case interviews as part of the interview process include: Strategy & Operations.
Google's Official Digital Marketing Publication. Learn how other brands have approached common marketing challenges. ... Case Study Learn how other brands have approached common marketing challenges. Share this page Close. Email Copy Link Copied Linkedin Twitter Facebook Whatsapp Xing VK.
Business culture of corporate giant - a case study of Google company Akademia Zarządzania - 5(1)/2021 169 line with the values and shareholder's expectations and answer the questions: 'what
Case Study: Analysis of Organizational Culture at Google. Google Inc came to life with the two brilliant people as the founder of the company. Those two were Larry Page and Sergey Brin. Both of them are a PhDs holder in computer science in Stanford University California. In their research project, they came out with a plan to make a search ...
May 6, 2024 at 1:45 PM PDT. In its biggest antitrust challenge yet, Alphabet Inc. 's Google is being sued by the US Justice Department and state attorneys general in a case that could result in ...
Google Analytics Performance Marketing Case Studies. When you change the way data is collected and analyzed, you gain insights into your customers and their purchase behaviors. The brands in the section below, including Westwing, Travelocity and PBS, did just that with products such as Google Analytics Premium and Universal Analytics. Case Study.
15 Real-Life Case Study Examples. Now that you understand what a case study is, let's look at real-life case study examples. In this section, we'll explore SaaS, marketing, sales, product and business case study examples with solutions. Take note of how these companies structured their case studies and included the key elements.
A wide array of data sources from across the company feed into BigQuery, including the campaign manager Display and Video 360, On's Google Ads, multiple social media sources, and Google Analytics 360, which relays on-site user behavior. On also sends predictive modeling and segmentation, created with Apache Airflow run on Cloud Composer.
Google has faced numerous lawsuits over privacy, intellectual property, monopoly tactics, and more. Google is currently battling two key antitrust cases over its search engine and advertising ...
After Google's November core update to address E-E-A-T, the website saw a 99.3% decrease in traffic. Jump to the Casual.app Case Study. AI content risks violating Google spam policies. Google has spam policies to prevent people from manipulating search engines through shady tactics. Here are two spam policies that make the risks of AI copy ...
Chutney Bech Kar Khadi Kardi 5000 Cr Ki Company | Ching's Secret Case Study #shorts #chingssecret #casestudy #facts Follow us on :-Facebook:- https://www.fa...