
- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons

Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

9.3: The Argumentative Essay
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 58378
- Lumen Learning
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Examine types of argumentative essays
Argumentative Essays
You may have heard it said that all writing is an argument of some kind. Even if you’re writing an informative essay, you still have the job of trying to convince your audience that the information is important. However, there are times you’ll be asked to write an essay that is specifically an argumentative piece.
An argumentative essay is one that makes a clear assertion or argument about some topic or issue. When you’re writing an argumentative essay, it’s important to remember that an academic argument is quite different from a regular, emotional argument. Note that sometimes students forget the academic aspect of an argumentative essay and write essays that are much too emotional for an academic audience. It’s important for you to choose a topic you feel passionately about (if you’re allowed to pick your topic), but you have to be sure you aren’t too emotionally attached to a topic. In an academic argument, you’ll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you’ll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions.

Argumentative essays are quite common in academic writing and are often an important part of writing in all disciplines. You may be asked to take a stand on a social issue in your introduction to writing course, but you could also be asked to take a stand on an issue related to health care in your nursing courses or make a case for solving a local environmental problem in your biology class. And, since argument is such a common essay assignment, it’s important to be aware of some basic elements of a good argumentative essay.
When your professor asks you to write an argumentative essay, you’ll often be given something specific to write about. For example, you may be asked to take a stand on an issue you have been discussing in class. Perhaps, in your education class, you would be asked to write about standardized testing in public schools. Or, in your literature class, you might be asked to argue the effects of protest literature on public policy in the United States.
However, there are times when you’ll be given a choice of topics. You might even be asked to write an argumentative essay on any topic related to your field of study or a topic you feel that is important personally.
Whatever the case, having some knowledge of some basic argumentative techniques or strategies will be helpful as you write. Below are some common types of arguments.
Causal Arguments
- In this type of argument, you argue that something has caused something else. For example, you might explore the causes of the decline of large mammals in the world’s ocean and make a case for your cause.
Evaluation Arguments
- In this type of argument, you make an argumentative evaluation of something as “good” or “bad,” but you need to establish the criteria for “good” or “bad.” For example, you might evaluate a children’s book for your education class, but you would need to establish clear criteria for your evaluation for your audience.
Proposal Arguments
- In this type of argument, you must propose a solution to a problem. First, you must establish a clear problem and then propose a specific solution to that problem. For example, you might argue for a proposal that would increase retention rates at your college.
Narrative Arguments
- In this type of argument, you make your case by telling a story with a clear point related to your argument. For example, you might write a narrative about your experiences with standardized testing in order to make a case for reform.
Rebuttal Arguments
- In a rebuttal argument, you build your case around refuting an idea or ideas that have come before. In other words, your starting point is to challenge the ideas of the past.
Definition Arguments
- In this type of argument, you use a definition as the starting point for making your case. For example, in a definition argument, you might argue that NCAA basketball players should be defined as professional players and, therefore, should be paid.
https://assessments.lumenlearning.co...essments/20277
Essay Examples
- Click here to read an argumentative essay on the consequences of fast fashion . Read it and look at the comments to recognize strategies and techniques the author uses to convey her ideas.
- In this example, you’ll see a sample argumentative paper from a psychology class submitted in APA format. Key parts of the argumentative structure have been noted for you in the sample.
Link to Learning
For more examples of types of argumentative essays, visit the Argumentative Purposes section of the Excelsior OWL .
Contributors and Attributions
- Argumentative Essay. Provided by : Excelsior OWL. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/rhetorical-styles/argumentative-essay/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of a man with a heart and a brain. Authored by : Mohamed Hassan. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : pixabay.com/illustrations/decision-brain-heart-mind-4083469/. License : Other . License Terms : pixabay.com/service/terms/#license
- Clerc Center | PK-12 & Outreach
- KDES | PK-8th Grade School (D.C. Metro Area)
- MSSD | 9th-12th Grade School (Nationwide)
- Gallaudet University Regional Centers
- Parent Advocacy App
- K-12 ASL Content Standards
- National Resources
- Youth Programs
- Academic Bowl
- Battle Of The Books
- National Literary Competition
- Youth Debate Bowl
- Youth Esports Series
- Bison Sports Camp
- Discover College and Careers (DC²)
- Financial Wizards
- Immerse Into ASL
- Alumni Relations
- Alumni Association
- Homecoming Weekend
- Class Giving
- Get Tickets / BisonPass
- Sport Calendars
- Cross Country
- Swimming & Diving
- Track & Field
- Indoor Track & Field
- Cheerleading
- Winter Cheerleading
- Human Resources
- Plan a Visit
- Request Info

- Areas of Study
- Accessible Human-Centered Computing
- American Sign Language
- Art and Media Design
- Communication Studies
- Data Science
- Deaf Studies
- Early Intervention Studies Graduate Programs
- Educational Neuroscience
- Hearing, Speech, and Language Sciences
- Information Technology
- International Development
- Interpretation and Translation
- Linguistics
- Mathematics
- Philosophy and Religion
- Physical Education & Recreation
- Public Affairs
- Public Health
- Sexuality and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Theatre and Dance
- World Languages and Cultures
- B.A. in American Sign Language
- B.A. in Art and Media Design
- B.A. in Biology
- B.A. in Communication Studies
- B.A. in Communication Studies for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Deaf Studies
- B.A. in Deaf Studies for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Education with a Specialization in Early Childhood Education
- B.A. in Education with a Specialization in Elementary Education
- B.A. in English
- B.A. in Government
- B.A. in Government with a Specialization in Law
- B.A. in History
- B.A. in Interdisciplinary Spanish
- B.A. in International Studies
- B.A. in Interpretation
- B.A. in Mathematics
- B.A. in Philosophy
- B.A. in Psychology
- B.A. in Psychology for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Social Work (BSW)
- B.A. in Sociology
- B.A. in Sociology with a concentration in Criminology
- B.A. in Theatre Arts: Production/Performance
- B.A. or B.S. in Education with a Specialization in Secondary Education: Science, English, Mathematics or Social Studies
- B.S in Risk Management and Insurance
- B.S. in Accounting
- B.S. in Accounting for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.S. in Biology
- B.S. in Business Administration
- B.S. in Business Administration for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.S. in Information Technology
- B.S. in Mathematics
- B.S. in Physical Education and Recreation
- B.S. In Public Health
- General Education
- Honors Program
- Peace Corps Prep program
- Self-Directed Major
- M.A. in Counseling: Clinical Mental Health Counseling
- M.A. in Counseling: School Counseling
- M.A. in Deaf Education
- M.A. in Deaf Education Studies
- M.A. in Deaf Studies: Cultural Studies
- M.A. in Deaf Studies: Language and Human Rights
- M.A. in Early Childhood Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in Early Intervention Studies
- M.A. in Elementary Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in International Development
- M.A. in Interpretation: Combined Interpreting Practice and Research
- M.A. in Interpretation: Interpreting Research
- M.A. in Linguistics
- M.A. in Secondary Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in Sign Language Education
- M.S. in Accessible Human-Centered Computing
- M.S. in Speech-Language Pathology
- Master of Social Work (MSW)
- Au.D. in Audiology
- Ed.D. in Transformational Leadership and Administration in Deaf Education
- Ph.D. in Clinical Psychology
- Ph.D. in Critical Studies in the Education of Deaf Learners
- Ph.D. in Hearing, Speech, and Language Sciences
- Ph.D. in Linguistics
- Ph.D. in Translation and Interpreting Studies
- Ph.D. Program in Educational Neuroscience (PEN)
- Individual Courses and Training
- Summer On-Campus Courses
- Summer Online Courses
- Certificates
- Certificate in Sexuality and Gender Studies
- Educating Deaf Students with Disabilities (online, post-bachelor’s)
- American Sign Language and English Bilingual Early Childhood Deaf Education: Birth to 5 (online, post-bachelor’s)
- Peer Mentor Training (low-residency/hybrid, post-bachelor’s)
- Early Intervention Studies Graduate Certificate
- Online Degree Programs
- ODCP Minor in Communication Studies
- ODCP Minor in Deaf Studies
- ODCP Minor in Psychology
- ODCP Minor in Writing
- Online Degree Program General Education Curriculum
- University Capstone Honors for Online Degree Completion Program
Quick Links
- PK-12 & Outreach
- NSO Schedule

Guide to Different Kinds of Essays
202.448-7036
An essay is a paper that discusses, describes or analyzes one topic. It can discuss a subject directly or indirectly, seriously or humorously. It can describe personal opinions, or just report information. An essay can be written from any perspective, but essays are most commonly written in the first person ( I ), or third person (subjects that can be substituted with the he, she, it, or they pronouns).
There are many different kinds of essays. The following are a some of the most common ones:
Descriptive Cause/Effect Argumentative Definition Narrative Critical Compare/Contrast Process
Descriptive:
Examples: A descriptive essay could describe . . .
The descriptive essay provides details about how something looks, feels, tastes, smells, makes one feel, or sounds. It can also describe what something is, or how something happened. These essays generally use a lot of sensory details. The essay could be a list-like description that provides point by point details. Or, it could function as a story, keeping the reader interested in the plot and theme of the event described.
Definition:
Examples: A definition essay may try and define . . .
A definition essay attempts to define a specific term. It could try to pin down the meaning of a specific word, or define an abstract concept. The analysis goes deeper than a simple dictionary definition; it should attempt to explain why the term is defined as such. It could define the term directly, giving no information other than the explanation of the term. Or, it could imply the definition of the term, telling a story that requires the reader to infer the meaning.
Compare/Contrast:
Examples:A compare/contrast essay may discuss . . .
The compare/contrast essay discusses the similarities and differences between two things, people, concepts, places, etc. The essay could be an unbiased discussion, or an attempt to convince the reader of the benefits of one thing, person, or concept. It could also be written simply to entertain the reader, or to arrive at an insight into human nature. The essay could discuss both similarities and differences, or it could just focus on one or the other. A comparison essay usually discusses the similarities between two things, while the contrast essay discusses the differences.
Cause/Effect:
Examples:A cause/effect essay may explain . . .
The cause/effect essay explains why or how some event happened, and what resulted from the event.
This essay is a study of the relationship between two or more events or experiences. The essay could discuss both causes and effects, or it could simply address one or the other. A cause essay usually discusses the reasons why something happened. An effect essay discusses what happens after a specific event or circumstance.
The example below shows a cause essay, one that would explain how and why an event happened.
If this cause essay were about a volcanic eruption, it might go something like this: “Pressure and heat built up beneath the earth’s surface; the effect of this was an enormous volcanic eruption.”
The next example shows an effect essay, one that would explain all the effects that happened after a specific event, like a volcanic eruption.
If this effect essay were about a volcanic eruption again, it might go something like this:
“The eruption caused many terrible things to happen; it destroyed homes, forests, and polluted the atmosphere.”
Examples:A narrative essay could tell of . . .
The narrative essay tells a story. It can also be called a “short story.” Generally, the narrative essay is conversational in style and tells of a personal experience. It is most commonly written in the first person (uses I ). This essay could tell of a single, life-shaping event, or simply a mundane daily experience.
Examples: A process essay may explain . . .
A process essay describes how something is done. It generally explains actions that should be performed in a series. It can explain in detail how to accomplish a specific task, or it can show how an individual came to a certain personal awareness. The essay could be in the form of step-by-step instructions, or in story form, with the instructions/explanations subtly given along the way.
Argumentative:
Examples: An argumentative essay may persuade a reader that . . .
An argumentative essay is one that attempts to persuade the reader to the writer’s point of view. The writer can either be serious or funny, but always tries to convince the reader of the validity of his or her opinion. The essay may argue openly, or it may attempt to subtly persuade the reader by using irony or sarcasm.
Examples: A critical essay may analyze . . .
A critical essay analyzes the strengths, weaknesses, and methods of someone else’s work. Generally, these essays begin with a brief overview of the main points of the text, movie, or piece of art, followed by an analysis of the work’s meaning. It should then discuss how well the author/creator accomplishes his/her goals and makes his/her points. A critical essay can be written about another essay, story, book, poem, movie, or work of art.
202-448-7036
At a Glance
- Quick Facts
- University Leadership
- History & Traditions
- Accreditation
- Consumer Information
- Our 10-Year Vision: The Gallaudet Promise
- Annual Report of Achievements (ARA)
- The Signing Ecosystem
- Not Your Average University
Our Community
- Library & Archives
- Technology Support
- Interpreting Requests
- Ombuds Support
- Health and Wellness Programs
- Profile & Web Edits
Visit Gallaudet
- Explore Our Campus
- Virtual Tour
- Maps & Directions
- Shuttle Bus Schedule
- Kellogg Conference Hotel
- Welcome Center
- National Deaf Life Museum
- Apple Guide Maps
Engage Today
- Work at Gallaudet / Clerc Center
- Social Media Channels
- University Wide Events
- Sponsorship Requests
- Data Requests
- Media Inquiries
- Gallaudet Today Magazine
- Giving at Gallaudet
- Financial Aid
- Registrar’s Office
- Residence Life & Housing
- Safety & Security
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- University Communications
- Clerc Center

Gallaudet University, chartered in 1864, is a private university for deaf and hard of hearing students.
Copyright © 2024 Gallaudet University. All rights reserved.
- Accessibility
- Cookie Consent Notice
- Privacy Policy
- File a Report
800 Florida Avenue NE, Washington, D.C. 20002

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)

We define an argumentative essay as a type of essay that presents arguments about both sides of an issue. The purpose is to convince the reader to accept a particular viewpoint or action. In an argumentative essay, the writer takes a stance on a controversial or debatable topic and supports their position with evidence, reasoning, and examples. The essay should also address counterarguments, demonstrating a thorough understanding of the topic.
Table of Contents
- What is an argumentative essay?
- Argumentative essay structure
- Argumentative essay outline
- Types of argument claims
How to write an argumentative essay?
- Argumentative essay writing tips
- Good argumentative essay example
How to write a good thesis
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay with Paperpal?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an argumentative essay.
An argumentative essay is a type of writing that presents a coherent and logical analysis of a specific topic. 1 The goal is to convince the reader to accept the writer’s point of view or opinion on a particular issue. Here are the key elements of an argumentative essay:
- Thesis Statement : The central claim or argument that the essay aims to prove.
- Introduction : Provides background information and introduces the thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs : Each paragraph addresses a specific aspect of the argument, presents evidence, and may include counter arguments.
Articulate your thesis statement better with Paperpal. Start writing now!
- Evidence : Supports the main argument with relevant facts, examples, statistics, or expert opinions.
- Counterarguments : Anticipates and addresses opposing viewpoints to strengthen the overall argument.
- Conclusion : Summarizes the main points, reinforces the thesis, and may suggest implications or actions.

Argumentative essay structure
Aristotelian, Rogerian, and Toulmin are three distinct approaches to argumentative essay structures, each with its principles and methods. 2 The choice depends on the purpose and nature of the topic. Here’s an overview of each type of argumentative essay format.
Have a looming deadline for your argumentative essay? Write 2x faster with Paperpal – Start now!
Argumentative essay outline
An argumentative essay presents a specific claim or argument and supports it with evidence and reasoning. Here’s an outline for an argumentative essay, along with examples for each section: 3
1. Introduction :
- Hook : Start with a compelling statement, question, or anecdote to grab the reader’s attention.
Example: “Did you know that plastic pollution is threatening marine life at an alarming rate?”
- Background information : Provide brief context about the issue.
Example: “Plastic pollution has become a global environmental concern, with millions of tons of plastic waste entering our oceans yearly.”
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position.
Example: “We must take immediate action to reduce plastic usage and implement more sustainable alternatives to protect our marine ecosystem.”
2. Body Paragraphs :
- Topic sentence : Introduce the main idea of each paragraph.
Example: “The first step towards addressing the plastic pollution crisis is reducing single-use plastic consumption.”
- Evidence/Support : Provide evidence, facts, statistics, or examples that support your argument.
Example: “Research shows that plastic straws alone contribute to millions of tons of plastic waste annually, and many marine animals suffer from ingestion or entanglement.”
- Counterargument/Refutation : Acknowledge and refute opposing viewpoints.
Example: “Some argue that banning plastic straws is inconvenient for consumers, but the long-term environmental benefits far outweigh the temporary inconvenience.”
- Transition : Connect each paragraph to the next.
Example: “Having addressed the issue of single-use plastics, the focus must now shift to promoting sustainable alternatives.”
3. Counterargument Paragraph :
- Acknowledgement of opposing views : Recognize alternative perspectives on the issue.
Example: “While some may argue that individual actions cannot significantly impact global plastic pollution, the cumulative effect of collective efforts must be considered.”
- Counterargument and rebuttal : Present and refute the main counterargument.
Example: “However, individual actions, when multiplied across millions of people, can substantially reduce plastic waste. Small changes in behavior, such as using reusable bags and containers, can have a significant positive impact.”
4. Conclusion :
- Restatement of thesis : Summarize your main argument.
Example: “In conclusion, adopting sustainable practices and reducing single-use plastic is crucial for preserving our oceans and marine life.”
- Call to action : Encourage the reader to take specific steps or consider the argument’s implications.
Example: “It is our responsibility to make environmentally conscious choices and advocate for policies that prioritize the health of our planet. By collectively embracing sustainable alternatives, we can contribute to a cleaner and healthier future.”

Types of argument claims
A claim is a statement or proposition a writer puts forward with evidence to persuade the reader. 4 Here are some common types of argument claims, along with examples:
- Fact Claims : These claims assert that something is true or false and can often be verified through evidence. Example: “Water boils at 100°C at sea level.”
- Value Claims : Value claims express judgments about the worth or morality of something, often based on personal beliefs or societal values. Example: “Organic farming is more ethical than conventional farming.”
- Policy Claims : Policy claims propose a course of action or argue for a specific policy, law, or regulation change. Example: “Schools should adopt a year-round education system to improve student learning outcomes.”
- Cause and Effect Claims : These claims argue that one event or condition leads to another, establishing a cause-and-effect relationship. Example: “Excessive use of social media is a leading cause of increased feelings of loneliness among young adults.”
- Definition Claims : Definition claims assert the meaning or classification of a concept or term. Example: “Artificial intelligence can be defined as machines exhibiting human-like cognitive functions.”
- Comparative Claims : Comparative claims assert that one thing is better or worse than another in certain respects. Example: “Online education is more cost-effective than traditional classroom learning.”
- Evaluation Claims : Evaluation claims assess the quality, significance, or effectiveness of something based on specific criteria. Example: “The new healthcare policy is more effective in providing affordable healthcare to all citizens.”
Understanding these argument claims can help writers construct more persuasive and well-supported arguments tailored to the specific nature of the claim.
If you’re wondering how to start an argumentative essay, here’s a step-by-step guide to help you with the argumentative essay format and writing process.
- Choose a Topic: Select a topic that you are passionate about or interested in. Ensure that the topic is debatable and has two or more sides.
- Define Your Position: Clearly state your stance on the issue. Consider opposing viewpoints and be ready to counter them.
- Conduct Research: Gather relevant information from credible sources, such as books, articles, and academic journals. Take notes on key points and supporting evidence.
- Create a Thesis Statement: Develop a concise and clear thesis statement that outlines your main argument. Convey your position on the issue and provide a roadmap for the essay.
- Outline Your Argumentative Essay: Organize your ideas logically by creating an outline. Include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each body paragraph should focus on a single point that supports your thesis.
- Write the Introduction: Start with a hook to grab the reader’s attention (a quote, a question, a surprising fact). Provide background information on the topic. Present your thesis statement at the end of the introduction.
- Develop Body Paragraphs: Begin each paragraph with a clear topic sentence that relates to the thesis. Support your points with evidence and examples. Address counterarguments and refute them to strengthen your position. Ensure smooth transitions between paragraphs.
- Address Counterarguments: Acknowledge and respond to opposing viewpoints. Anticipate objections and provide evidence to counter them.
- Write the Conclusion: Summarize the main points of your argumentative essay. Reinforce the significance of your argument. End with a call to action, a prediction, or a thought-provoking statement.
- Revise, Edit, and Share: Review your essay for clarity, coherence, and consistency. Check for grammatical and spelling errors. Share your essay with peers, friends, or instructors for constructive feedback.
- Finalize Your Argumentative Essay: Make final edits based on feedback received. Ensure that your essay follows the required formatting and citation style.
Struggling to start your argumentative essay? Paperpal can help – try now!
Argumentative essay writing tips
Here are eight strategies to craft a compelling argumentative essay:
- Choose a Clear and Controversial Topic : Select a topic that sparks debate and has opposing viewpoints. A clear and controversial issue provides a solid foundation for a strong argument.
- Conduct Thorough Research : Gather relevant information from reputable sources to support your argument. Use a variety of sources, such as academic journals, books, reputable websites, and expert opinions, to strengthen your position.
- Create a Strong Thesis Statement : Clearly articulate your main argument in a concise thesis statement. Your thesis should convey your stance on the issue and provide a roadmap for the reader to follow your argument.
- Develop a Logical Structure : Organize your essay with a clear introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Each paragraph should focus on a specific point of evidence that contributes to your overall argument. Ensure a logical flow from one point to the next.
- Provide Strong Evidence : Support your claims with solid evidence. Use facts, statistics, examples, and expert opinions to support your arguments. Be sure to cite your sources appropriately to maintain credibility.
- Address Counterarguments : Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and counterarguments. Addressing and refuting alternative perspectives strengthens your essay and demonstrates a thorough understanding of the issue. Be mindful of maintaining a respectful tone even when discussing opposing views.
- Use Persuasive Language : Employ persuasive language to make your points effectively. Avoid emotional appeals without supporting evidence and strive for a respectful and professional tone.
- Craft a Compelling Conclusion : Summarize your main points, restate your thesis, and leave a lasting impression in your conclusion. Encourage readers to consider the implications of your argument and potentially take action.

Good argumentative essay example
Let’s consider a sample of argumentative essay on how social media enhances connectivity:
In the digital age, social media has emerged as a powerful tool that transcends geographical boundaries, connecting individuals from diverse backgrounds and providing a platform for an array of voices to be heard. While critics argue that social media fosters division and amplifies negativity, it is essential to recognize the positive aspects of this digital revolution and how it enhances connectivity by providing a platform for diverse voices to flourish. One of the primary benefits of social media is its ability to facilitate instant communication and connection across the globe. Platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram break down geographical barriers, enabling people to establish and maintain relationships regardless of physical location and fostering a sense of global community. Furthermore, social media has transformed how people stay connected with friends and family. Whether separated by miles or time zones, social media ensures that relationships remain dynamic and relevant, contributing to a more interconnected world. Moreover, social media has played a pivotal role in giving voice to social justice movements and marginalized communities. Movements such as #BlackLivesMatter, #MeToo, and #ClimateStrike have gained momentum through social media, allowing individuals to share their stories and advocate for change on a global scale. This digital activism can shape public opinion and hold institutions accountable. Social media platforms provide a dynamic space for open dialogue and discourse. Users can engage in discussions, share information, and challenge each other’s perspectives, fostering a culture of critical thinking. This open exchange of ideas contributes to a more informed and enlightened society where individuals can broaden their horizons and develop a nuanced understanding of complex issues. While criticisms of social media abound, it is crucial to recognize its positive impact on connectivity and the amplification of diverse voices. Social media transcends physical and cultural barriers, connecting people across the globe and providing a platform for marginalized voices to be heard. By fostering open dialogue and facilitating the exchange of ideas, social media contributes to a more interconnected and empowered society. Embracing the positive aspects of social media allows us to harness its potential for positive change and collective growth.
- Clearly Define Your Thesis Statement: Your thesis statement is the core of your argumentative essay. Clearly articulate your main argument or position on the issue. Avoid vague or general statements.
- Provide Strong Supporting Evidence: Back up your thesis with solid evidence from reliable sources and examples. This can include facts, statistics, expert opinions, anecdotes, or real-life examples. Make sure your evidence is relevant to your argument, as it impacts the overall persuasiveness of your thesis.
- Anticipate Counterarguments and Address Them: Acknowledge and address opposing viewpoints to strengthen credibility. This also shows that you engage critically with the topic rather than presenting a one-sided argument.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay with Paperpal?
Writing a winning argumentative essay not only showcases your ability to critically analyze a topic but also demonstrates your skill in persuasively presenting your stance backed by evidence. Achieving this level of writing excellence can be time-consuming. This is where Paperpal, your AI academic writing assistant, steps in to revolutionize the way you approach argumentative essays. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use Paperpal to write your essay:
- Sign Up or Log In: Begin by creating an account or logging into paperpal.com .
- Navigate to Paperpal Copilot: Once logged in, proceed to the Templates section from the side navigation bar.
- Generate an essay outline: Under Templates, click on the ‘Outline’ tab and choose ‘Essay’ from the options and provide your topic to generate an outline.
- Develop your essay: Use this structured outline as a guide to flesh out your essay. If you encounter any roadblocks, click on Brainstorm and get subject-specific assistance, ensuring you stay on track.
- Refine your writing: To elevate the academic tone of your essay, select a paragraph and use the ‘Make Academic’ feature under the ‘Rewrite’ tab, ensuring your argumentative essay resonates with an academic audience.
- Final Touches: Make your argumentative essay submission ready with Paperpal’s language, grammar, consistency and plagiarism checks, and improve your chances of acceptance.
Paperpal not only simplifies the essay writing process but also ensures your argumentative essay is persuasive, well-structured, and academically rigorous. Sign up today and transform how you write argumentative essays.
The length of an argumentative essay can vary, but it typically falls within the range of 1,000 to 2,500 words. However, the specific requirements may depend on the guidelines provided.
You might write an argumentative essay when: 1. You want to convince others of the validity of your position. 2. There is a controversial or debatable issue that requires discussion. 3. You need to present evidence and logical reasoning to support your claims. 4. You want to explore and critically analyze different perspectives on a topic.
Argumentative Essay: Purpose : An argumentative essay aims to persuade the reader to accept or agree with a specific point of view or argument. Structure : It follows a clear structure with an introduction, thesis statement, body paragraphs presenting arguments and evidence, counterarguments and refutations, and a conclusion. Tone : The tone is formal and relies on logical reasoning, evidence, and critical analysis. Narrative/Descriptive Essay: Purpose : These aim to tell a story or describe an experience, while a descriptive essay focuses on creating a vivid picture of a person, place, or thing. Structure : They may have a more flexible structure. They often include an engaging introduction, a well-developed body that builds the story or description, and a conclusion. Tone : The tone is more personal and expressive to evoke emotions or provide sensory details.
- Gladd, J. (2020). Tips for Writing Academic Persuasive Essays. Write What Matters .
- Nimehchisalem, V. (2018). Pyramid of argumentation: Towards an integrated model for teaching and assessing ESL writing. Language & Communication , 5 (2), 185-200.
- Press, B. (2022). Argumentative Essays: A Step-by-Step Guide . Broadview Press.
- Rieke, R. D., Sillars, M. O., & Peterson, T. R. (2005). Argumentation and critical decision making . Pearson/Allyn & Bacon.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
Make Your Research Paper Error-Free with Paperpal’s Online Spell Checker
The do’s & don’ts of using generative ai tools ethically in academia, you may also like, how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to ace grant writing for research funding..., powerful academic phrases to improve your essay writing , how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples .
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Argumentative Essays

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
What is an argumentative essay?
The argumentative essay is a genre of writing that requires the student to investigate a topic; collect, generate, and evaluate evidence; and establish a position on the topic in a concise manner.
Please note : Some confusion may occur between the argumentative essay and the expository essay. These two genres are similar, but the argumentative essay differs from the expository essay in the amount of pre-writing (invention) and research involved. The argumentative essay is commonly assigned as a capstone or final project in first year writing or advanced composition courses and involves lengthy, detailed research. Expository essays involve less research and are shorter in length. Expository essays are often used for in-class writing exercises or tests, such as the GED or GRE.
Argumentative essay assignments generally call for extensive research of literature or previously published material. Argumentative assignments may also require empirical research where the student collects data through interviews, surveys, observations, or experiments. Detailed research allows the student to learn about the topic and to understand different points of view regarding the topic so that she/he may choose a position and support it with the evidence collected during research. Regardless of the amount or type of research involved, argumentative essays must establish a clear thesis and follow sound reasoning.
The structure of the argumentative essay is held together by the following.
- A clear, concise, and defined thesis statement that occurs in the first paragraph of the essay.
In the first paragraph of an argument essay, students should set the context by reviewing the topic in a general way. Next the author should explain why the topic is important ( exigence ) or why readers should care about the issue. Lastly, students should present the thesis statement. It is essential that this thesis statement be appropriately narrowed to follow the guidelines set forth in the assignment. If the student does not master this portion of the essay, it will be quite difficult to compose an effective or persuasive essay.
- Clear and logical transitions between the introduction, body, and conclusion.
Transitions are the mortar that holds the foundation of the essay together. Without logical progression of thought, the reader is unable to follow the essay’s argument, and the structure will collapse. Transitions should wrap up the idea from the previous section and introduce the idea that is to follow in the next section.
- Body paragraphs that include evidential support.
Each paragraph should be limited to the discussion of one general idea. This will allow for clarity and direction throughout the essay. In addition, such conciseness creates an ease of readability for one’s audience. It is important to note that each paragraph in the body of the essay must have some logical connection to the thesis statement in the opening paragraph. Some paragraphs will directly support the thesis statement with evidence collected during research. It is also important to explain how and why the evidence supports the thesis ( warrant ).
However, argumentative essays should also consider and explain differing points of view regarding the topic. Depending on the length of the assignment, students should dedicate one or two paragraphs of an argumentative essay to discussing conflicting opinions on the topic. Rather than explaining how these differing opinions are wrong outright, students should note how opinions that do not align with their thesis might not be well informed or how they might be out of date.
- Evidential support (whether factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal).
The argumentative essay requires well-researched, accurate, detailed, and current information to support the thesis statement and consider other points of view. Some factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal evidence should support the thesis. However, students must consider multiple points of view when collecting evidence. As noted in the paragraph above, a successful and well-rounded argumentative essay will also discuss opinions not aligning with the thesis. It is unethical to exclude evidence that may not support the thesis. It is not the student’s job to point out how other positions are wrong outright, but rather to explain how other positions may not be well informed or up to date on the topic.
- A conclusion that does not simply restate the thesis, but readdresses it in light of the evidence provided.
It is at this point of the essay that students may begin to struggle. This is the portion of the essay that will leave the most immediate impression on the mind of the reader. Therefore, it must be effective and logical. Do not introduce any new information into the conclusion; rather, synthesize the information presented in the body of the essay. Restate why the topic is important, review the main points, and review your thesis. You may also want to include a short discussion of more research that should be completed in light of your work.
A complete argument
Perhaps it is helpful to think of an essay in terms of a conversation or debate with a classmate. If I were to discuss the cause of World War II and its current effect on those who lived through the tumultuous time, there would be a beginning, middle, and end to the conversation. In fact, if I were to end the argument in the middle of my second point, questions would arise concerning the current effects on those who lived through the conflict. Therefore, the argumentative essay must be complete, and logically so, leaving no doubt as to its intent or argument.
The five-paragraph essay
A common method for writing an argumentative essay is the five-paragraph approach. This is, however, by no means the only formula for writing such essays. If it sounds straightforward, that is because it is; in fact, the method consists of (a) an introductory paragraph (b) three evidentiary body paragraphs that may include discussion of opposing views and (c) a conclusion.
Longer argumentative essays
Complex issues and detailed research call for complex and detailed essays. Argumentative essays discussing a number of research sources or empirical research will most certainly be longer than five paragraphs. Authors may have to discuss the context surrounding the topic, sources of information and their credibility, as well as a number of different opinions on the issue before concluding the essay. Many of these factors will be determined by the assignment.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Praxis Core Writing
Course: praxis core writing > unit 1, argumentative essay | quick guide.
- Source-based essay | Quick guide
- Revision in context | Quick guide
- Within-sentence punctuation | Quick guide
- Subordination and coordination | Quick guide
- Independent and dependent Clauses | Video lesson
- Parallel structure | Quick guide
- Modifier placement | Quick guide
- Shifts in verb tense | Quick guide
- Pronoun clarity | Quick guide
- Pronoun agreement | Quick guide
- Subject-verb agreement | Quick guide
- Noun agreement | Quick guide
- Frequently confused words | Quick guide
- Conventional expressions | Quick guide
- Logical comparison | Quick guide
- Concision | Quick guide
- Adjective/adverb confusion | Quick guide
- Negation | Quick guide
- Capitalization | Quick guide
- Apostrophe use | Quick guide
- Research skills | Quick guide
Argumentative essay (30 minutes)
- states or clearly implies the writer’s position or thesis
- organizes and develops ideas logically, making insightful connections between them
- clearly explains key ideas, supporting them with well-chosen reasons, examples, or details
- displays effective sentence variety
- clearly displays facility in the use of language
- is generally free from errors in grammar, usage, and mechanics
- organizes and develops ideas clearly, making connections between them
- explains key ideas, supporting them with relevant reasons, examples, or details
- displays some sentence variety
- displays facility in the use of language
- states or implies the writer’s position or thesis
- shows control in the organization and development of ideas
- explains some key ideas, supporting them with adequate reasons, examples, or details
- displays adequate use of language
- shows control of grammar, usage, and mechanics, but may display errors
- limited in stating or implying a position or thesis
- limited control in the organization and development of ideas
- inadequate reasons, examples, or details to explain key ideas
- an accumulation of errors in the use of language
- an accumulation of errors in grammar, usage, and mechanics
- no clear position or thesis
- weak organization or very little development
- few or no relevant reasons, examples, or details
- frequent serious errors in the use of language
- frequent serious errors in grammar, usage, and mechanics
- contains serious and persistent writing errors or
- is incoherent or
- is undeveloped or
- is off-topic
How should I build a thesis?
- (Choice A) Kids should find role models that are worthier than celebrities because celebrities may be famous for reasons that aren't admirable. A Kids should find role models that are worthier than celebrities because celebrities may be famous for reasons that aren't admirable.
- (Choice B) Because they profit from the admiration of youths, celebrities have a moral responsibility for the reactions their behaviors provoke in fans. B Because they profit from the admiration of youths, celebrities have a moral responsibility for the reactions their behaviors provoke in fans.
- (Choice C) Celebrities may have more imitators than most people, but they hold no more responsibility over the example they set than the average person. C Celebrities may have more imitators than most people, but they hold no more responsibility over the example they set than the average person.
- (Choice D) Notoriety is not always a choice, and some celebrities may not want to be role models. D Notoriety is not always a choice, and some celebrities may not want to be role models.
- (Choice E) Parents have a moral responsibility to serve as immediate role models for their children. E Parents have a moral responsibility to serve as immediate role models for their children.
How should I support my thesis?
- (Choice A) As basketball star Charles Barkley stated in a famous advertising campaign for Nike, he was paid to dominate on the basketball court, not to raise your kids. A As basketball star Charles Barkley stated in a famous advertising campaign for Nike, he was paid to dominate on the basketball court, not to raise your kids.
- (Choice B) Many celebrities do consider themselves responsible for setting a good example and create non-profit organizations through which they can benefit youths. B Many celebrities do consider themselves responsible for setting a good example and create non-profit organizations through which they can benefit youths.
- (Choice C) Many celebrities, like Kylie Jenner with her billion-dollar cosmetics company, profit directly from being imitated by fans who purchase sponsored products. C Many celebrities, like Kylie Jenner with her billion-dollar cosmetics company, profit directly from being imitated by fans who purchase sponsored products.
- (Choice D) My ten-year-old nephew may love Drake's music, but his behaviors are more similar to those of the adults he interacts with on a daily basis, like his parents and teachers. D My ten-year-old nephew may love Drake's music, but his behaviors are more similar to those of the adults he interacts with on a daily basis, like his parents and teachers.
- (Choice E) It's very common for young people to wear fashions similar to those of their favorite celebrities. E It's very common for young people to wear fashions similar to those of their favorite celebrities.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to write an a+ argumentative essay.
Miscellaneous

You'll no doubt have to write a number of argumentative essays in both high school and college, but what, exactly, is an argumentative essay and how do you write the best one possible? Let's take a look.
A great argumentative essay always combines the same basic elements: approaching an argument from a rational perspective, researching sources, supporting your claims using facts rather than opinion, and articulating your reasoning into the most cogent and reasoned points. Argumentative essays are great building blocks for all sorts of research and rhetoric, so your teachers will expect you to master the technique before long.
But if this sounds daunting, never fear! We'll show how an argumentative essay differs from other kinds of papers, how to research and write them, how to pick an argumentative essay topic, and where to find example essays. So let's get started.
What Is an Argumentative Essay? How Is it Different from Other Kinds of Essays?
There are two basic requirements for any and all essays: to state a claim (a thesis statement) and to support that claim with evidence.
Though every essay is founded on these two ideas, there are several different types of essays, differentiated by the style of the writing, how the writer presents the thesis, and the types of evidence used to support the thesis statement.
Essays can be roughly divided into four different types:
#1: Argumentative #2: Persuasive #3: Expository #4: Analytical
So let's look at each type and what the differences are between them before we focus the rest of our time to argumentative essays.
Argumentative Essay
Argumentative essays are what this article is all about, so let's talk about them first.
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance.
An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the factually and logically correct one. This means that an argumentative essay must use only evidence-based support to back up a claim , rather than emotional or philosophical reasoning (which is often allowed in other types of essays). Thus, an argumentative essay has a burden of substantiated proof and sources , whereas some other types of essays (namely persuasive essays) do not.
You can write an argumentative essay on any topic, so long as there's room for argument. Generally, you can use the same topics for both a persuasive essay or an argumentative one, so long as you support the argumentative essay with hard evidence.
Example topics of an argumentative essay:
- "Should farmers be allowed to shoot wolves if those wolves injure or kill farm animals?"
- "Should the drinking age be lowered in the United States?"
- "Are alternatives to democracy effective and/or feasible to implement?"
The next three types of essays are not argumentative essays, but you may have written them in school. We're going to cover them so you know what not to do for your argumentative essay.
Persuasive Essay
Persuasive essays are similar to argumentative essays, so it can be easy to get them confused. But knowing what makes an argumentative essay different than a persuasive essay can often mean the difference between an excellent grade and an average one.
Persuasive essays seek to persuade a reader to agree with the point of view of the writer, whether that point of view is based on factual evidence or not. The writer has much more flexibility in the evidence they can use, with the ability to use moral, cultural, or opinion-based reasoning as well as factual reasoning to persuade the reader to agree the writer's side of a given issue.
Instead of being forced to use "pure" reason as one would in an argumentative essay, the writer of a persuasive essay can manipulate or appeal to the reader's emotions. So long as the writer attempts to steer the readers into agreeing with the thesis statement, the writer doesn't necessarily need hard evidence in favor of the argument.
Often, you can use the same topics for both a persuasive essay or an argumentative one—the difference is all in the approach and the evidence you present.
Example topics of a persuasive essay:
- "Should children be responsible for their parents' debts?"
- "Should cheating on a test be automatic grounds for expulsion?"
- "How much should sports leagues be held accountable for player injuries and the long-term consequences of those injuries?"
Expository Essay
An expository essay is typically a short essay in which the writer explains an idea, issue, or theme , or discusses the history of a person, place, or idea.
This is typically a fact-forward essay with little argument or opinion one way or the other.
Example topics of an expository essay:
- "The History of the Philadelphia Liberty Bell"
- "The Reasons I Always Wanted to be a Doctor"
- "The Meaning Behind the Colloquialism ‘People in Glass Houses Shouldn't Throw Stones'"
Analytical Essay
An analytical essay seeks to delve into the deeper meaning of a text or work of art, or unpack a complicated idea . These kinds of essays closely interpret a source and look into its meaning by analyzing it at both a macro and micro level.
This type of analysis can be augmented by historical context or other expert or widely-regarded opinions on the subject, but is mainly supported directly through the original source (the piece or art or text being analyzed) .
Example topics of an analytical essay:
- "Victory Gin in Place of Water: The Symbolism Behind Gin as the Only Potable Substance in George Orwell's 1984"
- "Amarna Period Art: The Meaning Behind the Shift from Rigid to Fluid Poses"
- "Adultery During WWII, as Told Through a Series of Letters to and from Soldiers"

There are many different types of essay and, over time, you'll be able to master them all.
A Typical Argumentative Essay Assignment
The average argumentative essay is between three to five pages, and will require at least three or four separate sources with which to back your claims . As for the essay topic , you'll most often be asked to write an argumentative essay in an English class on a "general" topic of your choice, ranging the gamut from science, to history, to literature.
But while the topics of an argumentative essay can span several different fields, the structure of an argumentative essay is always the same: you must support a claim—a claim that can reasonably have multiple sides—using multiple sources and using a standard essay format (which we'll talk about later on).
This is why many argumentative essay topics begin with the word "should," as in:
- "Should all students be required to learn chemistry in high school?"
- "Should children be required to learn a second language?"
- "Should schools or governments be allowed to ban books?"
These topics all have at least two sides of the argument: Yes or no. And you must support the side you choose with evidence as to why your side is the correct one.
But there are also plenty of other ways to frame an argumentative essay as well:
- "Does using social media do more to benefit or harm people?"
- "Does the legal status of artwork or its creators—graffiti and vandalism, pirated media, a creator who's in jail—have an impact on the art itself?"
- "Is or should anyone ever be ‘above the law?'"
Though these are worded differently than the first three, you're still essentially forced to pick between two sides of an issue: yes or no, for or against, benefit or detriment. Though your argument might not fall entirely into one side of the divide or another—for instance, you could claim that social media has positively impacted some aspects of modern life while being a detriment to others—your essay should still support one side of the argument above all. Your final stance would be that overall , social media is beneficial or overall , social media is harmful.
If your argument is one that is mostly text-based or backed by a single source (e.g., "How does Salinger show that Holden Caulfield is an unreliable narrator?" or "Does Gatsby personify the American Dream?"), then it's an analytical essay, rather than an argumentative essay. An argumentative essay will always be focused on more general topics so that you can use multiple sources to back up your claims.
Good Argumentative Essay Topics
So you know the basic idea behind an argumentative essay, but what topic should you write about?
Again, almost always, you'll be asked to write an argumentative essay on a free topic of your choice, or you'll be asked to select between a few given topics . If you're given complete free reign of topics, then it'll be up to you to find an essay topic that no only appeals to you, but that you can turn into an A+ argumentative essay.
What makes a "good" argumentative essay topic depends on both the subject matter and your personal interest —it can be hard to give your best effort on something that bores you to tears! But it can also be near impossible to write an argumentative essay on a topic that has no room for debate.
As we said earlier, a good argumentative essay topic will be one that has the potential to reasonably go in at least two directions—for or against, yes or no, and why . For example, it's pretty hard to write an argumentative essay on whether or not people should be allowed to murder one another—not a whole lot of debate there for most people!—but writing an essay for or against the death penalty has a lot more wiggle room for evidence and argument.
A good topic is also one that can be substantiated through hard evidence and relevant sources . So be sure to pick a topic that other people have studied (or at least studied elements of) so that you can use their data in your argument. For example, if you're arguing that it should be mandatory for all middle school children to play a sport, you might have to apply smaller scientific data points to the larger picture you're trying to justify. There are probably several studies you could cite on the benefits of physical activity and the positive effect structure and teamwork has on young minds, but there's probably no study you could use where a group of scientists put all middle-schoolers in one jurisdiction into a mandatory sports program (since that's probably never happened). So long as your evidence is relevant to your point and you can extrapolate from it to form a larger whole, you can use it as a part of your resource material.
And if you need ideas on where to get started, or just want to see sample argumentative essay topics, then check out these links for hundreds of potential argumentative essay topics.
101 Persuasive (or Argumentative) Essay and Speech Topics
301 Prompts for Argumentative Writing
Top 50 Ideas for Argumentative/Persuasive Essay Writing
[Note: some of these say "persuasive essay topics," but just remember that the same topic can often be used for both a persuasive essay and an argumentative essay; the difference is in your writing style and the evidence you use to support your claims.]

KO! Find that one argumentative essay topic you can absolutely conquer.
Argumentative Essay Format
Argumentative Essays are composed of four main elements:
- A position (your argument)
- Your reasons
- Supporting evidence for those reasons (from reliable sources)
- Counterargument(s) (possible opposing arguments and reasons why those arguments are incorrect)
If you're familiar with essay writing in general, then you're also probably familiar with the five paragraph essay structure . This structure is a simple tool to show how one outlines an essay and breaks it down into its component parts, although it can be expanded into as many paragraphs as you want beyond the core five.
The standard argumentative essay is often 3-5 pages, which will usually mean a lot more than five paragraphs, but your overall structure will look the same as a much shorter essay.
An argumentative essay at its simplest structure will look like:
Paragraph 1: Intro
- Set up the story/problem/issue
- Thesis/claim
Paragraph 2: Support
- Reason #1 claim is correct
- Supporting evidence with sources
Paragraph 3: Support
- Reason #2 claim is correct
Paragraph 4: Counterargument
- Explanation of argument for the other side
- Refutation of opposing argument with supporting evidence
Paragraph 5: Conclusion
- Re-state claim
- Sum up reasons and support of claim from the essay to prove claim is correct
Now let's unpack each of these paragraph types to see how they work (with examples!), what goes into them, and why.
Paragraph 1—Set Up and Claim
Your first task is to introduce the reader to the topic at hand so they'll be prepared for your claim. Give a little background information, set the scene, and give the reader some stakes so that they care about the issue you're going to discuss.
Next, you absolutely must have a position on an argument and make that position clear to the readers. It's not an argumentative essay unless you're arguing for a specific claim, and this claim will be your thesis statement.
Your thesis CANNOT be a mere statement of fact (e.g., "Washington DC is the capital of the United States"). Your thesis must instead be an opinion which can be backed up with evidence and has the potential to be argued against (e.g., "New York should be the capital of the United States").
Paragraphs 2 and 3—Your Evidence
These are your body paragraphs in which you give the reasons why your argument is the best one and back up this reasoning with concrete evidence .
The argument supporting the thesis of an argumentative essay should be one that can be supported by facts and evidence, rather than personal opinion or cultural or religious mores.
For example, if you're arguing that New York should be the new capital of the US, you would have to back up that fact by discussing the factual contrasts between New York and DC in terms of location, population, revenue, and laws. You would then have to talk about the precedents for what makes for a good capital city and why New York fits the bill more than DC does.
Your argument can't simply be that a lot of people think New York is the best city ever and that you agree.
In addition to using concrete evidence, you always want to keep the tone of your essay passionate, but impersonal . Even though you're writing your argument from a single opinion, don't use first person language—"I think," "I feel," "I believe,"—to present your claims. Doing so is repetitive, since by writing the essay you're already telling the audience what you feel, and using first person language weakens your writing voice.
For example,
"I think that Washington DC is no longer suited to be the capital city of the United States."
"Washington DC is no longer suited to be the capital city of the United States."
The second statement sounds far stronger and more analytical.
Paragraph 4—Argument for the Other Side and Refutation
Even without a counter argument, you can make a pretty persuasive claim, but a counterargument will round out your essay into one that is much more persuasive and substantial.
By anticipating an argument against your claim and taking the initiative to counter it, you're allowing yourself to get ahead of the game. This way, you show that you've given great thought to all sides of the issue before choosing your position, and you demonstrate in multiple ways how yours is the more reasoned and supported side.
Paragraph 5—Conclusion
This paragraph is where you re-state your argument and summarize why it's the best claim.
Briefly touch on your supporting evidence and voila! A finished argumentative essay.
Your essay should have just as awesome a skeleton as this plesiosaur does. (In other words: a ridiculously awesome skeleton)
Argumentative Essay Example: 5-Paragraph Style
It always helps to have an example to learn from. I've written a full 5-paragraph argumentative essay here. Look at how I state my thesis in paragraph 1, give supporting evidence in paragraphs 2 and 3, address a counterargument in paragraph 4, and conclude in paragraph 5.
Topic: Is it possible to maintain conflicting loyalties?
Paragraph 1
It is almost impossible to go through life without encountering a situation where your loyalties to different people or causes come into conflict with each other. Maybe you have a loving relationship with your sister, but she disagrees with your decision to join the army, or you find yourself torn between your cultural beliefs and your scientific ones. These conflicting loyalties can often be maintained for a time, but as examples from both history and psychological theory illustrate, sooner or later, people have to make a choice between competing loyalties, as no one can maintain a conflicting loyalty or belief system forever.
The first two sentences set the scene and give some hypothetical examples and stakes for the reader to care about.
The third sentence finishes off the intro with the thesis statement, making very clear how the author stands on the issue ("people have to make a choice between competing loyalties, as no one can maintain a conflicting loyalty or belief system forever." )
Paragraphs 2 and 3
Psychological theory states that human beings are not equipped to maintain conflicting loyalties indefinitely and that attempting to do so leads to a state called "cognitive dissonance." Cognitive dissonance theory is the psychological idea that people undergo tremendous mental stress or anxiety when holding contradictory beliefs, values, or loyalties (Festinger, 1957). Even if human beings initially hold a conflicting loyalty, they will do their best to find a mental equilibrium by making a choice between those loyalties—stay stalwart to a belief system or change their beliefs. One of the earliest formal examples of cognitive dissonance theory comes from Leon Festinger's When Prophesy Fails . Members of an apocalyptic cult are told that the end of the world will occur on a specific date and that they alone will be spared the Earth's destruction. When that day comes and goes with no apocalypse, the cult members face a cognitive dissonance between what they see and what they've been led to believe (Festinger, 1956). Some choose to believe that the cult's beliefs are still correct, but that the Earth was simply spared from destruction by mercy, while others choose to believe that they were lied to and that the cult was fraudulent all along. Both beliefs cannot be correct at the same time, and so the cult members are forced to make their choice.
But even when conflicting loyalties can lead to potentially physical, rather than just mental, consequences, people will always make a choice to fall on one side or other of a dividing line. Take, for instance, Nicolaus Copernicus, a man born and raised in Catholic Poland (and educated in Catholic Italy). Though the Catholic church dictated specific scientific teachings, Copernicus' loyalty to his own observations and scientific evidence won out over his loyalty to his country's government and belief system. When he published his heliocentric model of the solar system--in opposition to the geocentric model that had been widely accepted for hundreds of years (Hannam, 2011)-- Copernicus was making a choice between his loyalties. In an attempt t o maintain his fealty both to the established system and to what he believed, h e sat on his findings for a number of years (Fantoli, 1994). But, ultimately, Copernicus made the choice to side with his beliefs and observations above all and published his work for the world to see (even though, in doing so, he risked both his reputation and personal freedoms).
These two paragraphs provide the reasons why the author supports the main argument and uses substantiated sources to back those reasons.
The paragraph on cognitive dissonance theory gives both broad supporting evidence and more narrow, detailed supporting evidence to show why the thesis statement is correct not just anecdotally but also scientifically and psychologically. First, we see why people in general have a difficult time accepting conflicting loyalties and desires and then how this applies to individuals through the example of the cult members from the Dr. Festinger's research.
The next paragraph continues to use more detailed examples from history to provide further evidence of why the thesis that people cannot indefinitely maintain conflicting loyalties is true.
Paragraph 4
Some will claim that it is possible to maintain conflicting beliefs or loyalties permanently, but this is often more a matter of people deluding themselves and still making a choice for one side or the other, rather than truly maintaining loyalty to both sides equally. For example, Lancelot du Lac typifies a person who claims to maintain a balanced loyalty between to two parties, but his attempt to do so fails (as all attempts to permanently maintain conflicting loyalties must). Lancelot tells himself and others that he is equally devoted to both King Arthur and his court and to being Queen Guinevere's knight (Malory, 2008). But he can neither be in two places at once to protect both the king and queen, nor can he help but let his romantic feelings for the queen to interfere with his duties to the king and the kingdom. Ultimately, he and Queen Guinevere give into their feelings for one another and Lancelot—though he denies it—chooses his loyalty to her over his loyalty to Arthur. This decision plunges the kingdom into a civil war, ages Lancelot prematurely, and ultimately leads to Camelot's ruin (Raabe, 1987). Though Lancelot claimed to have been loyal to both the king and the queen, this loyalty was ultimately in conflict, and he could not maintain it.
Here we have the acknowledgement of a potential counter-argument and the evidence as to why it isn't true.
The argument is that some people (or literary characters) have asserted that they give equal weight to their conflicting loyalties. The refutation is that, though some may claim to be able to maintain conflicting loyalties, they're either lying to others or deceiving themselves. The paragraph shows why this is true by providing an example of this in action.
Paragraph 5
Whether it be through literature or history, time and time again, people demonstrate the challenges of trying to manage conflicting loyalties and the inevitable consequences of doing so. Though belief systems are malleable and will often change over time, it is not possible to maintain two mutually exclusive loyalties or beliefs at once. In the end, people always make a choice, and loyalty for one party or one side of an issue will always trump loyalty to the other.
The concluding paragraph summarizes the essay, touches on the evidence presented, and re-states the thesis statement.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 8 Steps
Writing the best argumentative essay is all about the preparation, so let's talk steps:
#1: Preliminary Research
If you have the option to pick your own argumentative essay topic (which you most likely will), then choose one or two topics you find the most intriguing or that you have a vested interest in and do some preliminary research on both sides of the debate.
Do an open internet search just to see what the general chatter is on the topic and what the research trends are.
Did your preliminary reading influence you to pick a side or change your side? Without diving into all the scholarly articles at length, do you believe there's enough evidence to support your claim? Have there been scientific studies? Experiments? Does a noted scholar in the field agree with you? If not, you may need to pick another topic or side of the argument to support.
#2: Pick Your Side and Form Your Thesis
Now's the time to pick the side of the argument you feel you can support the best and summarize your main point into your thesis statement.
Your thesis will be the basis of your entire essay, so make sure you know which side you're on, that you've stated it clearly, and that you stick by your argument throughout the entire essay .
#3: Heavy-Duty Research Time
You've taken a gander at what the internet at large has to say on your argument, but now's the time to actually read those sources and take notes.
Check scholarly journals online at Google Scholar , the Directory of Open Access Journals , or JStor . You can also search individual university or school libraries and websites to see what kinds of academic articles you can access for free. Keep track of your important quotes and page numbers and put them somewhere that's easy to find later.
And don't forget to check your school or local libraries as well!
#4: Outline
Follow the five-paragraph outline structure from the previous section.
Fill in your topic, your reasons, and your supporting evidence into each of the categories.
Before you begin to flesh out the essay, take a look at what you've got. Is your thesis statement in the first paragraph? Is it clear? Is your argument logical? Does your supporting evidence support your reasoning?
By outlining your essay, you streamline your process and take care of any logic gaps before you dive headfirst into the writing. This will save you a lot of grief later on if you need to change your sources or your structure, so don't get too trigger-happy and skip this step.
Now that you've laid out exactly what you'll need for your essay and where, it's time to fill in all the gaps by writing it out.
Take it one step at a time and expand your ideas into complete sentences and substantiated claims. It may feel daunting to turn an outline into a complete draft, but just remember that you've already laid out all the groundwork; now you're just filling in the gaps.
If you have the time before deadline, give yourself a day or two (or even just an hour!) away from your essay . Looking it over with fresh eyes will allow you to see errors, both minor and major, that you likely would have missed had you tried to edit when it was still raw.
Take a first pass over the entire essay and try your best to ignore any minor spelling or grammar mistakes—you're just looking at the big picture right now. Does it make sense as a whole? Did the essay succeed in making an argument and backing that argument up logically? (Do you feel persuaded?)
If not, go back and make notes so that you can fix it for your final draft.
Once you've made your revisions to the overall structure, mark all your small errors and grammar problems so you can fix them in the next draft.
#7: Final Draft
Use the notes you made on the rough draft and go in and hack and smooth away until you're satisfied with the final result.
A checklist for your final draft:
- Formatting is correct according to your teacher's standards
- No errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation
- Essay is the right length and size for the assignment
- The argument is present, consistent, and concise
- Each reason is supported by relevant evidence
- The essay makes sense overall
#8: Celebrate!
Once you've brought that final draft to a perfect polish and turned in your assignment, you're done! Go you!

Be prepared and ♪ you'll never go hungry again ♪, *cough*, or struggle with your argumentative essay-writing again. (Walt Disney Studios)
Good Examples of Argumentative Essays Online
Theory is all well and good, but examples are key. Just to get you started on what a fully-fleshed out argumentative essay looks like, let's see some examples in action.
Check out these two argumentative essay examples on the use of landmines and freons (and note the excellent use of concrete sources to back up their arguments!).
The Use of Landmines
A Shattered Sky
The Take-Aways: Keys to Writing an Argumentative Essay
At first, writing an argumentative essay may seem like a monstrous hurdle to overcome, but with the proper preparation and understanding, you'll be able to knock yours out of the park.
Remember the differences between a persuasive essay and an argumentative one, make sure your thesis is clear, and double-check that your supporting evidence is both relevant to your point and well-sourced . Pick your topic, do your research, make your outline, and fill in the gaps. Before you know it, you'll have yourself an A+ argumentative essay there, my friend.
What's Next?
Now you know the ins and outs of an argumentative essay, but how comfortable are you writing in other styles? Learn more about the four writing styles and when it makes sense to use each .
Understand how to make an argument, but still having trouble organizing your thoughts? Check out our guide to three popular essay formats and choose which one is right for you.
Ready to make your case, but not sure what to write about? We've created a list of 50 potential argumentative essay topics to spark your imagination.
Courtney scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT in high school and went on to graduate from Stanford University with a degree in Cultural and Social Anthropology. She is passionate about bringing education and the tools to succeed to students from all backgrounds and walks of life, as she believes open education is one of the great societal equalizers. She has years of tutoring experience and writes creative works in her free time.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Current students
- Staff intranet
- Find an event
- Academic writing
Types of academic writing
- Planning your writing
- Structuring written work
- Grammar, spelling and vocabulary
- Editing and proofreading
- Evidence, plagiarism and referencing
- Resources and support
The four main types of academic writing are descriptive, analytical, persuasive and critical. Each of these types of writing has specific language features and purposes.
In many academic texts you will need to use more than one type. For example, in an empirical thesis:
- you will use critical writing in the literature review to show where there is a gap or opportunity in the existing research
- the methods section will be mostly descriptive to summarise the methods used to collect and analyse information
- the results section will be mostly descriptive and analytical as you report on the data you collected
- the discussion section is more analytical, as you relate your findings back to your research questions, and also persuasive, as you propose your interpretations of the findings.
Descriptive
The simplest type of academic writing is descriptive. Its purpose is to provide facts or information. An example would be a summary of an article or a report of the results of an experiment.
The kinds of instructions for a purely descriptive assignment include: 'identify', 'report', 'record', 'summarise' and 'define'.
It’s rare for a university-level text to be purely descriptive. Most academic writing is also analytical. Analytical writing includes descriptive writing, but also requires you to re-organise the facts and information you describe into categories, groups, parts, types or relationships.
Sometimes, these categories or relationships are already part of the discipline, while in other cases you will create them specifically for your text. If you’re comparing two theories, you might break your comparison into several parts, for example: how each theory deals with social context, how each theory deals with language learning, and how each theory can be used in practice.
The kinds of instructions for an analytical assignment include: 'analyse', 'compare', 'contrast', 'relate', and 'examine'.
To make your writing more analytical:
- spend plenty of time planning. Brainstorm the facts and ideas, and try different ways of grouping them, according to patterns, parts, similarities and differences. You could use colour-coding, flow charts, tree diagrams or tables.
- create a name for the relationships and categories you find. For example, advantages and disadvantages.
- build each section and paragraph around one of the analytical categories.
- make the structure of your paper clear to your reader, by using topic sentences and a clear introduction.
In most academic writing, you are required to go at least one step further than analytical writing, to persuasive writing. Persuasive writing has all the features of analytical writing (that is, information plus re-organising the information), with the addition of your own point of view. Most essays are persuasive, and there is a persuasive element in at least the discussion and conclusion of a research article.
Points of view in academic writing can include an argument, recommendation, interpretation of findings or evaluation of the work of others. In persuasive writing, each claim you make needs to be supported by some evidence, for example a reference to research findings or published sources.
The kinds of instructions for a persuasive assignment include: 'argue', 'evaluate', 'discuss', and 'take a position'.
To help reach your own point of view on the facts or ideas:
- read some other researchers' points of view on the topic. Who do you feel is the most convincing?
- look for patterns in the data or references. Where is the evidence strongest?
- list several different interpretations. What are the real-life implications of each one? Which ones are likely to be most useful or beneficial? Which ones have some problems?
- discuss the facts and ideas with someone else. Do you agree with their point of view?
To develop your argument:
- list the different reasons for your point of view
- think about the different types and sources of evidence which you can use to support your point of view
- consider different ways that your point of view is similar to, and different from, the points of view of other researchers
- look for various ways to break your point of view into parts. For example, cost effectiveness, environmental sustainability, scope of real-world application.
To present your argument, make sure:
- your text develops a coherent argument where all the individual claims work together to support your overall point of view
- your reasoning for each claim is clear to the reader
- your assumptions are valid
- you have evidence for every claim you make
- you use evidence that is convincing and directly relevant.
Critical writing is common for research, postgraduate and advanced undergraduate writing. It has all the features of persuasive writing, with the added feature of at least one other point of view. While persuasive writing requires you to have your own point of view on an issue or topic, critical writing requires you to consider at least two points of view, including your own.
For example, you may explain a researcher's interpretation or argument and then evaluate the merits of the argument, or give your own alternative interpretation.
Examples of critical writing assignments include a critique of a journal article, or a literature review that identifies the strengths and weaknesses of existing research. The kinds of instructions for critical writing include: 'critique', 'debate', 'disagree' and 'evaluate'.
You need to:
- accurately summarise all or part of the work. This could include identifying the main interpretations, assumptions or methodology.
- have an opinion about the work. Appropriate types of opinion could include pointing out some problems with it, proposing an alternative approach that would be better, and/or defending the work against the critiques of others.
- provide evidence for your point of view. Depending on the specific assignment and the discipline, different types of evidence may be appropriate, such as logical reasoning, reference to authoritative sources and/or research data.
Critical writing requires strong writing skills. You need to thoroughly understand the topic and the issues. You need to develop an essay structure and paragraph structure that allows you to analyse different interpretations and develop your own argument, supported by evidence.
This material was developed by the Learning Hub (Academic Language and Learning), which offers workshops, face-to-face consultations and resources to support your learning. Find out more about how they can help you develop your communication, research and study skills .
See our Writing skills handouts .
Related links
- Learning Hub (Academic Language and Learning)
- Learning Hub (Academic Language and Learning) workshops
- Research skills for HDR students
- Reading and note taking
- Critical thinking
- Website feedback
Your feedback has been sent.
Sorry there was a problem sending your feedback. Please try again
You should only use this form to send feedback about the content on this webpage – we will not respond to other enquiries made through this form. If you have an enquiry or need help with something else such as your enrolment, course etc you can contact the Student Centre.
- Find an expert
- Media contacts
Student links
- How to log in to University systems
- Class timetables
- Our rankings
- Faculties and schools
- Research centres
- Campus locations
- Find a staff member
- Careers at Sydney
- Emergencies and personal safety

- Accessibility
How to Write an Argumentative Essay: Step By Step Guide
10 May, 2020
9 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
Being able to present your argument and carry your point in a debate or a discussion is a vital skill. No wonder educational establishments make writing compositions of such type a priority for all students. If you are not really good at delivering a persuasive message to the audience, this guide is for you. It will teach you how to write an argumentative essay successfully step by step. So, read on and pick up the essential knowledge.

What is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is a paper that gets the reader to recognize the author’s side of the argument as valid. The purpose of this specific essay is to pose a question and answer it with compelling evidence. At its core, this essay type works to champion a specific viewpoint. The key, however, is that the topic of the argumentative essay has multiple sides, which can be explained, weighed, and judged by relevant sources.
Check out our ultimate argumentative essay topics list!
This essay often explores common questions associated with any type of argument including:

Argumentative VS Persuasive Essay
It’s important not to confuse argumentative essay with a persuasive essay – while they both seem to follow the same goal, their methods are slightly different. While the persuasive essay is here to convince the reader (to pick your side), the argumentative essay is here to present information that supports the claim.
In simple words, it explains why the author picked this side of the argument, and persuasive essay does its best to persuade the reader to agree with your point of view.
Now that we got this straight, let’s get right to our topic – how to write an argumentative essay. As you can easily recognize, it all starts with a proper argument. First, let’s define the types of argument available and strategies that you can follow.
Types of Argument
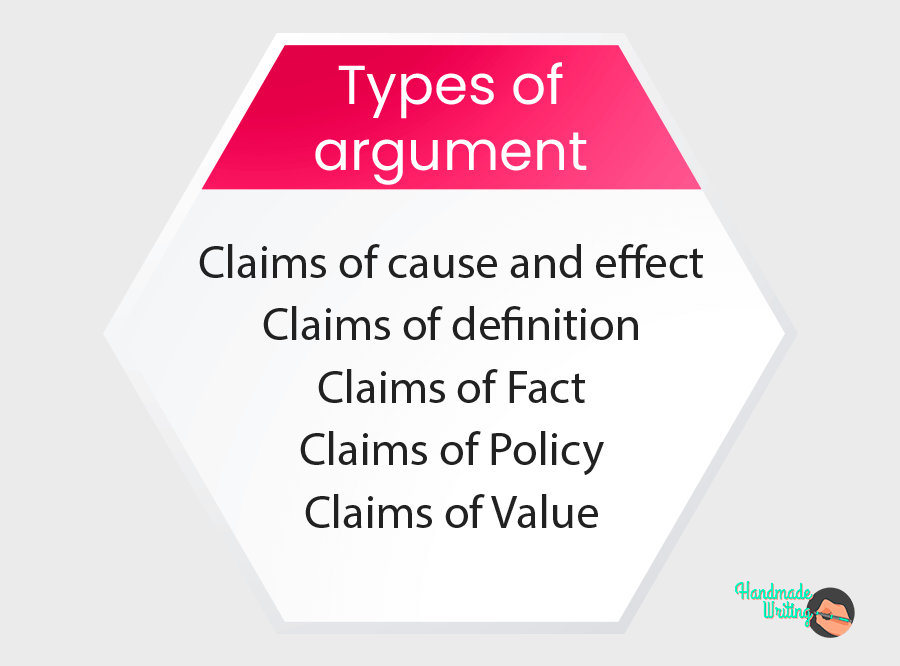
When delving into the types of argument, the vocabulary suddenly becomes quite “lawyerish”; and that makes sense since lawyers stake their whole livelihood on their ability to win arguments. So step into your lawyer shoes, and learn about the five kinds of arguments that you could explore in an argumentative paper:
Claims of cause and effect
This paper focuses on answering what caused the issue(s), and what the resulting effects have been.
Claims of definition
This paper explores a controversial interpretation of a particular definition; the paper delves into what the world really means and how it could be interpreted in different ways.
Claims of Fact
This argumentative paper examines whether a particular fact is accurate; it often looks at several sources reporting a fact and examines their veracity.
Claims of Policy
This is a favorite argumentative essay in government and sociology classes; this paper explores a particular policy, who it affects, and what (if anything) should be done about it.
Claims of Value
This essay identifies a particular value or belief and then examines how and why it is important to a particular cohort or a larger, general population.
The aim of argument, or of discussion, should not be victory, but progress. Joseph Joubert
Argument Strategies
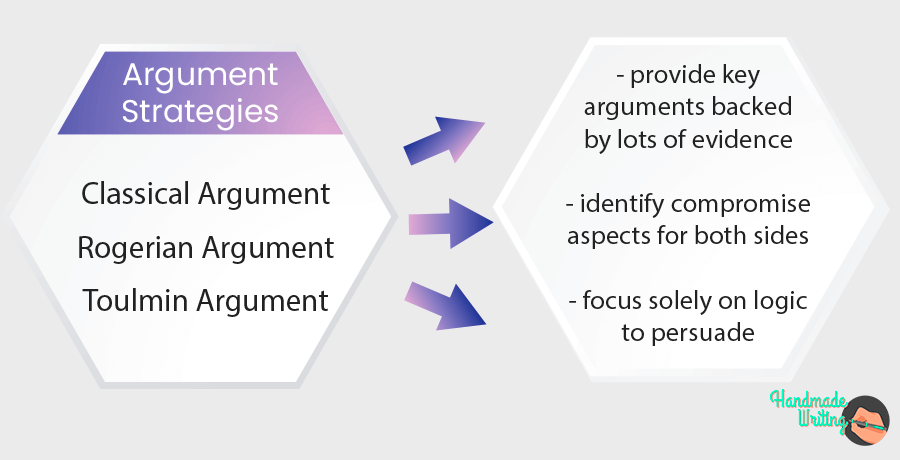
When mulling over how to approach your argumentative assignment, you should be aware that three main argument strategies exist regarding how exactly to argue an issue: classical, Rogerian, Toulmin.
Classical Argument
This argument structure dates back to the ancient Greeks and Romans. In this strategy, the arguer introduces the issue, provides context, clearly states their claim, provides key arguments backed by lots of evidence, and nullifies opposing arguments with valid data.
Rogerian Argument
Hate conflict? This may be the argumentative paper strategy for you. At its core, this strategy works to identify compromise aspects for both sides; this approach works to find commonality and an ultimate agreement between two sides rather than proclaiming a winner or loser. The focus in this argument is compromise and respect of all sides.

Toulmin Argument
Remember Spock? This is his type of strategy; the Toulmin approach focuses solely on logic to persuade the audience. It is heavy on data and often relies on qualities to narrow the focus of a claim and strengthen the writer’s stance. This approach also tends to rely on exceptions, which clearly set limits on the parameters of an argument, thus making a particular stance easier to agree with.
With that in mind, we can now organize our argument into the essay structure.
Have no time to write your essay? You can buy argumentative essay tasks at Handmade Writing. Our service is available 24/7.
Argumentative essay Example
Organizing the argumentative essay outline.
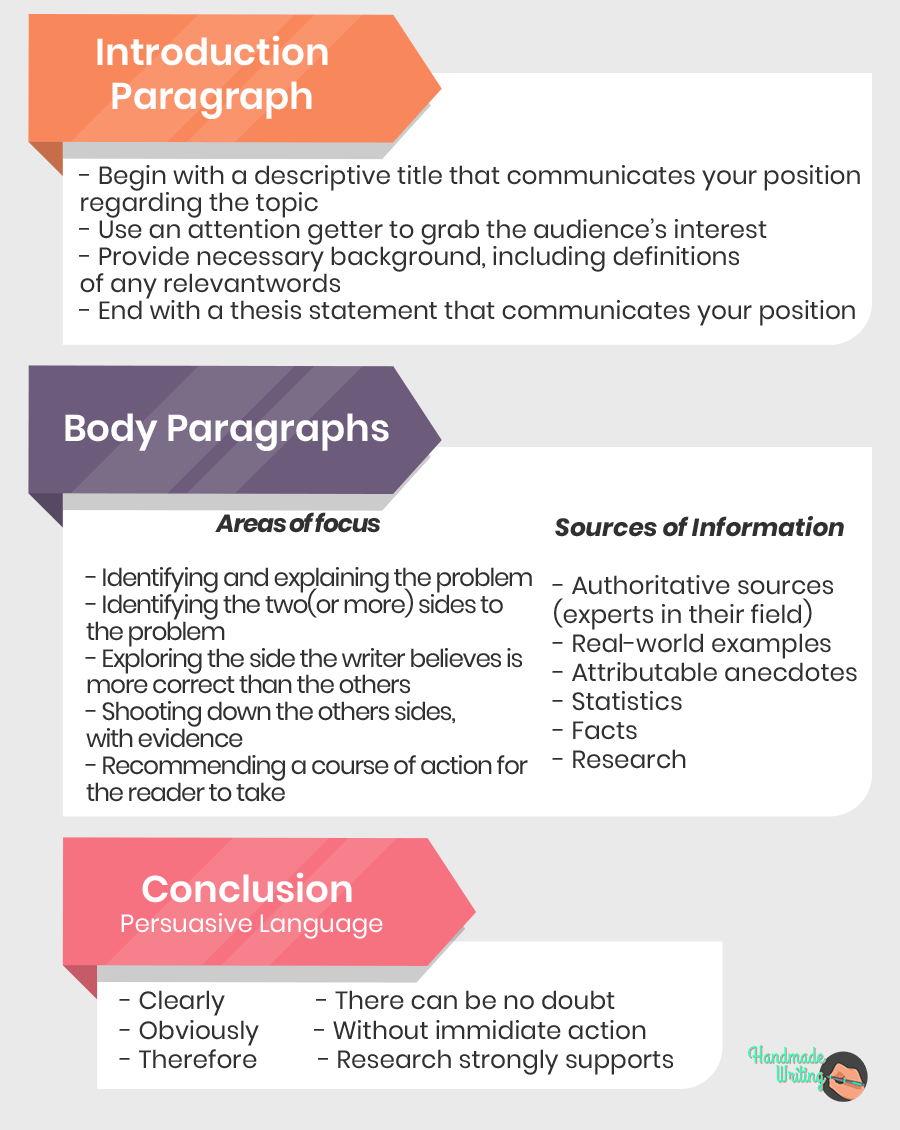
An argumentative essay follows the typical essay format: introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. However, the body paragraphs are structured a bit differently from other body paragraphs. Surely, not something you can see in a cause and effect essay outline .
While the introduction should still begin with an attention-grabbing sentence that catches the reader’s interest and compels him or her to continue reading and provides key background information, the following paragraphs focus on specific aspects of the argument.
Let’s begin with the introduction.
Related Post: How to write an Essay Introduction ?
Introduction Paragraph
As its name suggests, this paragraph provides all the background information necessary for a reader unfamiliar with the argumentative essay topic to understand what it’s about. A solid introduction should:
- Begin with a descriptive title that communicates your position regarding the topic
- Rhetorical question
- Personal anecdote
- Provide necessary background, including definitions of any relevant words
- End with a thesis statement that communicates your position
Stuck with your essay task? No more struggle! HandMadeWriting is the top essay writing service. Our online essay writer service not only guides you on writing papers, it can write a high-quality essay for you.
Body Paragraphs

Body paragraphs can range in size from six to fifteen or more sentences. The goal of these paragraphs is to support the thesis statement. Recommended areas of focus for the body paragraphs within an argumentative paper include:
- Identifying and explaining the problem
- Identifying the two (or more) sides to the problem
- Exploring the side the writer believes is more appropriate than the others
- Shooting down the other sides, with evidence
- Recommending a course of action for the reader
One important way how this essay differs from other kinds is its specific nature. At the end of reading such an essay, the audience should clearly understand the issue or controversy and have enough information to make an informed decision regarding the issue. But what compels an audience make an informed decision? Several things!
- Authoritative sources (experts in their field)
- Real-world examples
- Attributable anecdotes

In this paragraph, often the shortest of all the paragraphs, the writer reviews his or her most compelling reasons for taking a particular stance on an issue. The persuasion should be strong here, and the writer should use combative language including examples such as:
- “then” statements
- There can be no doubt
- Without immediate action
- Research strongly supports
It is also appropriate to refute potential opposition in the conclusion. By stating the objections readers could have, and show why they should be dismissed; the conclusion resonates more strongly with the reader.
Check our guide if you have any other questions on academic paper writing!
Argumentative Essay Sample
Be sure to check the sample essay, completed by our writers. Use it as an example to write your own argumentative essay. Link: Argumentative essay on white rappers’ moral rights to perform .
Remember : the key to winning any argument should be reliable sources — the better, the more trustworthy your sources, the more likely the audience will consider a viewpoint different from their own.
And while you may feel a deep passion towards a particular topic, keep in mind that emotions can be messy; this essay should present all sides to the argument respectfully and with a clear intention to portray each of them fairly.
Let the data, statistics, and facts speak loudly and clearly for themselves. And don’t forget to use opinionated language — using such diction is a must in any strong argumentative writing!

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
Difference between Expository & Argumentative Essays

When your teacher tells you to write an ‘expository’ or ‘argumentative’ essay, you might just freak out, clamp up, and say “What does the word expository even mean!?”
Sometimes these words just make it harder to understand what you need to do. So, in this article, I’m going to show you the exact difference between an expository and argumentative essay .
Let’s first look at what each of these essay types are and some examples of essay questions for each. Then, I will present you with a table clearly breaking down the differences into columns.
What is an Expository Essay?
An expository essay is the most common form of essay at university level.
‘Expository’ means, simply, to give an explanation of something.
But, it’s not that easy. If you just give a dictionary definition of an idea and move on, you’re not going to get a very good mark. Read on to learn how to get a top mark on an expository essay.
An expository essay presents an informative and balanced exploration of an issue. This type of essay does not require you to take a stance on an issue. Instead, you should present a range of evidence, facts and statistics on a topic.
Your teacher will ask you to write an expository essay in order to prove your deep knowledge and understanding of an issue. This is why these essays are so common at university level.
Let’s say the topic of your course is “Depression amongst Elderly People”. Your teacher will ask you to write an expository essay about depression amongst elderly people not to convince them that it is an issue (they already know that). The teacher just wants you to show-off how deep your knowledge is about the topic.
Therefore, you’re going to want to delve very deeply into the topic and explore some major themes. Here’s some tips the help go deep in your expository essay:
- Get Great Information. Use your lecture notes , assigned readings and readings you find from google scholar to show that you have a very deep and detailed understanding of the issue;
- Compare Ideas. Ensure you present two sides of an argument and compare them. Use critical thinking strategies like pros and cons lists and Venn diagrams to assist you in thinking deeply about the topic;
- Avoid dictionary definitions. Instead, use scholarly definitions from textbooks or journal articles . If there are multiple definitions of a term or topic , compare each of them.
- Be objective. You should avoid using first person language (I, we, us, you, our) and do not take a position on the issue. Your job is to inform, not convince.
The essay question in an expository essay usually asks you to compare, contrast, explain how things work, define concepts, or classify them. Note that it does not ask you to ‘convince’ or ‘take a side’, because all you’re doing is presenting your knowledge in an unbiased manner.
Expository Essay Examples
Here is a list of potential expository essay questions:
The ‘How To’ Expository Essay
- Explain how emergency room nurses triage patients based on need.
- Provide a clear explanation of how an internal combustion engine produces motion.
- Explore with evidence how carbon dating approximates the age of the earth.
- Examine, with examples, the ways in which nuclear engineers prevent nuclear meltdowns in power plants.
- Explore how the judicial system is designed to ensure justice is served in western democracies.
- Provide a clear and detailed explanation of how subjective mental health disorders are diagnosed and treated.
- Examine the process behind ensuring the structural integrity of bridges in the United States.
The ‘Classification’ Expository Essay
- What are the major types of rocks within the earth’s crust?
- What are the key fields of study under the broad umbrella of ‘Psychology’?
- Identify and classify the different animal species on earth today.
- What are the five most influential approaches to art theory in European history?
- Explore and explain the different learning styles proposed by Howard Gardner.
- How can the Bristol Stool Chart help to categorize and diagnose illness and disease?
- What are the main categories of financial assets that help produce wealth in Capitalist societies?
The ‘Cause and Effect’ Expository Essay
- How does the cash bail system in the United States disadvantage minorities?
- What are the effects of inserting fluoride into public water systems?
- What are the multiple projected effects of lowering the corporate tax rate?
- What impact does lowering the age of voting have on participatory democracy?
- What are the long-term impacts of the death of a parent when a child is very young?
- What are the impacts of stereotypical gender representations in Disney films?
- How would a carbon tax of $40 a tonne impact the economy?
The Comparative Expository Essay
- Compare modernist and post-modernist approaches to art.
- What are the major differences between socialism and communism?
- What are the key differences between string theory and quantum mechanics?
- Examine the advantages and disadvantages of moving from a manufacturing economy to a services economy.
- Explore the two major competing explanations for the fall of the Soviet Union.
- What are the core differences between Catholicism and Protestantism?
- Compare the healthcare systems of Canada and the United states on the key metrics of value for money, social justice, life expectancy and individual liberty.
The Problem and Solution Expository Essay
- Examine five potential solutions to the problem of automation taking the jobs of truck drivers in the mid-west.
- What solutions are on the horizon for bureaucratic bloat in the European Union?
- What are the three key ways society can overcome resource scarcity in the coming century?
- What are the major viable solutions to the opioid crisis in the United States?
- Which approaches to foreign policy could present a solution to the oppression of women in some East African nations?
- How can society help to increase the democratic participation of children?
- Explore three potential diets that could help prevent diabetes among middle-aged men.
What is an Argumentative Essay?

An argumentative essay is also often called a persuasive essay. Persuasive / argumentative essays take a position on an issue and try to convince their readers to accept your arguments.
In other words, the major difference between expository and argumentative essays is that argumentative essays try to convince, while expository essays do not.
In an argumentative essay you can take a position. You can say things like:
- “This essay will show that the best course of action is…”
- “It is evident that the best course of action is…”
- “The position of this essay is that…”
Argumentative Essay Tip #1: Avoiding Bias
Just because you need to take a position, that doesn’t mean you can be biased in an argumentative essay. ‘Bias’ means to be prejudiced or narrow-mindedly convinced by only one side, despite evidence to the contrary.
To avoid bias in argumentative essay, you need to convince your reader that you have taken a close and open-minded look at the evidence on both sides of an issue, weighed them up, and come to your conclusions based on an informed understanding of all the issues.
Argumentative Essay Tip #2: Going Deep
You should show deep insights into the topic to avoid bias in both expository and argumentative essays. To show an in-depth understanding of the topic in an argumentative essay, you can compare and contrast two ideas and then make a value judgement after showing all sides of the issue.
My favourite approach to help you go deep is to use a pros and cons list for each of the different sides of an argument. You could, for example, brainstorm different perspectives like this:
Here, you can brainstorm a ton of different things to discuss about the topic. Then, once you have shown a thoughtful discussion of both perspectives, you can take an informed position.
Showing deep understanding and comparing perspectives before taking a position makes your argumentative essay … more persuasive !
Argumentative Essay Examples
- Take a position on the argument between raising and lowering taxes on the wealthy.
- What is the best course of action for obtaining peace in Syria?
- Persuade your reader about the importance of decreasing the voting age to 16.
- Take a position on the statement: “There should be more men in nursing.”
- Are current drug laws good or bad for young men of colour?
- Who should be the next nominee for the Supreme Court and why?
- What is the most appropriate management style for improving productivity, health and job satisfaction in your workplace?
- What is the best course of action for decreasing the amount of plastics in the Pacific Ocean?
- Should there be laws mandating the installation of solar panels on all new homes built in California?
- Should GMOs be banned?
- Should there be limits to freedom of speech?
- Should Pluto’s status as a Planet be reinstated?
- How many refugees should the United Kingdom accept per year, and why?
- Convince your reader of the relevance or irrelevance of Freud’s ideas about child development for the 21 st
- Should financial advisors be forced to take a course on ethics before taking clients?
- After weighing up the benefits and negatives of the issue, take an issue on whether we should colonize Mars.
What’s the difference between Argumentative and Expository Essays?
Now, let’s take a look at a summary of the key differences and similarities between expository and argumentative essays:
As you can see, there are more similarities between an argumentative and persuasive essay than differences. Remember, your argumentative essay and expository essay both provide in-depth, balanced information on the topic. However, the argumentative essay goes one step further and lets you take a personal position on the issue once you have presented the key information.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Self-Actualization Examples (Maslow's Hierarchy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Forest Schools Philosophy & Curriculum, Explained!
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Montessori's 4 Planes of Development, Explained!
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Montessori vs Reggio Emilia vs Steiner-Waldorf vs Froebel
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Gradehacker
- Meet the Team
- Essay Writing
- Degree Accelerator
- Entire Class Bundle
- Learning Center
- Gradehacker TV
Argumentative Essay vs Narrative Essay | Everything You Need to Know
Santiago mallea.
- Writing Tips

Chief of Content At Gradehacker
Updated on April, 2023
Argumentative Essay vs. Narrative Essay is a comparison you need to have clear during college since these can be two of the most required types of essays for your tasks.
Each follows a completely different format since they are meant to achieve different things, but here we are about to show you how to differentiate them and make the best of them!
At Gradehacker, the non-traditional adult student #1 resource, we have years of experience helping students with their essays and getting the best grades for their academic success!
If you struggle with academic writing, understanding an essay’s purpose and rules can help you improve, so let’s see how you can start boosting your writing skills today!

What is an Argumentative Essay?
These are informative essays where you share an argument with evidence presenting your perspective on a particular issue . In your piece of writing, you’ll need to convince the reader about your arguments, meaning your point of view.
With this type of essay, you’ll have to:
- Develop a strong thesis statement
- Cite reliable sources to support it
- Refure an opposing point of view with strong arguments
Extensive research for your essay topic is necessary. You have to read all possible existing materials, and some might even require further investigation through observations, surveys, and interviews.
Argument essays are a common assignment that every college student has to face at some point in their academic journey, this is why it is so important to know how to write them well.
And if you have your doubts about how to do it and want the best tips, here you have our 5-step tutorial for creating outstanding ones !
What is a Narrative Essay?
A narrative essay is a genre of writing that tells a story .
The difference with a persuasive essay is that it is usually written from personal opinions and can be based on real-life experiences, fictional stories, or a combination of both.
These types of essays aim to engage with the reader’s emotions, and during the actual writing process, the writer can play with their imagination and tell a story whether they have been through it or not.
It often includes sensory details and vivid descriptions to help the reader visualize the events being described and should leave the reader with a sense of completeness or closure.
The Purpose Behind Each Essay Type
Argumentative essay.
As mentioned earlier, argumentative essay assignments require you to convince the reader to agree with your thesis statement.
That means that you need to have a well-supported argument for your debatable issue, which is why research is so important here.
The more relevant information and fact-based evidence you find, the more convincing your entire essay will be!
Narrative Essay
On the contrary, narrative essays are meant to tell a story .
You have to develop a compelling narrative where the reader not only understands the flow of the story but also feels connected to the writing.
Here, citing other academic papers or solid evidence are not necessary. The voice and experience of the writer is the only source of information needed.
The Right Structure For Your Essays
Argumentative essay structure is similar to the traditional style of essay containing and following: .
- An introduction
- A body (supporting points and refuting opposing arguments)
- A conclusion
As we’ve just stated, argumentative assignments have to persuade the reader into caring about your thesis statement . Besides having a strong opinion developed, it’s important to do extensive research first that backs up your argument.
The more relevant information you find, the more convincing your paper will be!
On the other hand, narrative essays have a structure related to storytelling, following:
- Body (Conflict and climax)
Introduction: Here, the introduction paragraph is about your characters and creating the setting of the story.
Body: The body will continue developing the plot until it evolves into the climax, where the central conflict occurs.
Conclusion: Lastly, the final paragraph must be the conclusion , where the narrative comes to an end.
Still, a narrative essay doesn’t have to be strictly divided into this storytelling structure . You need to have in mind that you should always start by setting up the narrative and finish by expressing the main point of your story.
Both types of essays are essential for college! They are meant to obtain different results, and if what you want is just to master and speed up your writing process, you can check how to use Chat GPT to write an essay in our video!
Finding a Voice: Tone And Language for Your Essays
As argumentative writing is meant to be written for an academic audience, the tone of your essay must be neutral . Although the audience is expected to be well-informed, the language used should not be overly formal or technical.
A great tip when thinking about who your audience is is, to imagine you are addressing peers in the same college level you are studying, who will understand your strong opinions and arguments.
Still, don’t assume everyone knows what you are talking about, so be sure always to explain your points in a clear and straightforward way.
Differently, narrative essays might be written for a broader audience. As the purpose of your writing is to evoke emotions, you can play more with the language.
From informal phrases to casual and specific vocabulary, your language style will help you shape a better-developed story. Depending on the setting of your story, your tone should reflect the emotions it aims to transmit .
Finding Precision: The Right Paper And Paragraph Length
First of all, it’s worth mentioning that your paper’s length will always depend on your class and the professor in charge.
However, as argumentative essays are evidence-based papers that want to inform the reader, they typically range from two to four double-spaced pages. Still, depending on your course and assignment type, it can be more.
For example, a course’s final essay where you have to prove a clear understanding of the topics discussed in class might require you to write a paper between six to ten double-spaced pages.
Regarding paragraph length, it’s key that each one has a similar length. This way, you’ll dedicate the same context to each supporting evidence of your thesis. But ideally, each paragraph should have six or seven sentences at minimum.
But If you struggle to come up with arguments or ideas when writing essays, there is an alternative method you can try !
We found that Chat GPT can assist you in crafting an argumentative essay. Check our tutorial and tips for achieving success in your writing!
Once again, the length of a narrative essay depends on the class and the professor .
But as these are creative exercises, they tend to be shorter assignments . While, on average, they need to be two or three pages long, some can be up to five pages.
Unlike argumentative essays, paragraphs don’t need to be the same length . Since you need to add to the development of your story, you can constantly change from long paragraphs to short sentences.
Remember, a well-developed thesis statement isn’t necessary for a narrative paper, just like you don’t need to be super creative to make a convincing argument in an essay.
Essential Tips For Exceptional Essay Writing
Each type of essay has its own set of requirements, and as a college student trying to improve your writing skills, you need the best tips on how to ace any academic essay.
Now that you understand the basics of how each essay type works let’s see what advice can take with you to improve your writing!
Don't be afraid of using too many sources
Many assignments give you a minimum of academic sources to meet. But don’t get limited by that! Always try to look for any piece of information that adds to your case .
Even if it’s only a single sentence or a statistic, each piece of evidence makes a difference.
As long as it provides more persuasive arguments, use as many reliable sources as you need!
Make sure they are trustworthy , such as academic journals, reputable news outlets, or expert analysis. To ensure that a source is credible, you can investigate the author’s credentials, affiliations, and any potential biases or conflicts of interest.
By incorporating reliable and reputable sources into your writing, you can strengthen your argument and make a solid case for your perspective on the topic.
In case you don’t know what sites you can use, we highly recommend checking out our list of best websites for scholarly sources.
Think of a clear and precise thesis statement
One of the most common problems students face is choosing a solid subject, which can lead to a confusing thesis statement. In this case, vague and simple topics are not enough, as they cover too much ground.
Try thinking of a research topic you like and find a more specific subject where you can develop a persuasive argument.
For example, a vague topic would be:
“Mental health care needs to be promoted”
Instead, a focused and more interesting thesis would be:
“Minority groups like African Americans and Latinos can’t access proper mental health care; hence the US government needs to promote new and better health policies…”
See the difference? Not only does it make for a better case that calls the reader to action, but it also gives you a more specific subject to investigate.
If you want more ideas like these for all subjects, you can check our list of essay topics or watch our videos!
One idea per paragraph
Don’t fill a paragraph with two or more ideas. The writing becomes more organized and understandable by thoroughly developing each topic separately.
You need to consider how topics are related so that you can transition from one paragraph to the next effectively. This can be achieved by using transitional phrases or sentences that connect the ideas in each paragraph while maintaining the flow of the writing.
By carefully structuring every paragraph only to include one main idea, your argument will be clearer and better communicated to the reader.
Don't introduce new ideas in the conclusion
Another common mistake is adding information to the conclusion that wasn’t explained before. Only readdress previously mentioned arguments.
Ensure that the conclusion effectively wraps up the story. This can include providing closure or resolution to any conflicts or issues in the essay.
The conclusion should also offer some final thought or reflection on the experience, leaving the reader with something to think about after finishing the essay.
Ultimately, the conclusion needs to include the message you want the reader to remember.
You can find more tips like this in our list of secrets to writing better conclusions .
Quick Summary
Argumentative essay vs narrative essay: nail your papers.
We know that to make the best essays, you must fulfill all their requirements, which can be hard.
Writing is a skill that you get better with every experience , but in order to successfully nail your academic papers, you need to understand their purpose and structure. By knowing its basics, improving is way easier!
After reading this article, we hope that next time you need to write an argumentative or narrative essay, you know what you need to do to create an outstanding paper!
But if you still feel blocked when writing and would like personal assistance, whether it’s an argumentative or narrative paper, you can always count on Gradehacker to have your back . We have assisted students with all types of essays and even accompanied them throughout their college journey .
If you are looking for more tips on how to improve your writing skills, check out some of our related articles:

What You Need For Your College Research Paper Outline

How to Come Up with an Eye-Catching Essay Title

5 Common Essay Mistakes and How to Avoid Them

Essay Service Honest Review 2023: The Good, The Bad, The Ugly
- Best Apps and Tools
- Financial Tips and Scholarships
- Career Planning
- Non-Traditional Students
- Student Wellness
- Cost & Pricing

- 2525 Ponce de Leon Blvd Suite 300 Coral Gables, FL 33134 USA
- Phone: (786) 991-9293
- Gradehacker 2525 Ponce de Leon Blvd Suite 300 Coral Gables, FL 33134 USA
About Gradehacker
Business hours.
Mon - Fri: 10:00 am - 7 pm ET Sat - Sun: 10 am - 3 pm ET
© 2024 Gradehacker LLC All Rights Reserved.
- Our Writers
- How to Order
- Assignment Writing Service
- Report Writing Service
- Buy Coursework
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Research Paper Writing Service
- All Essay Services
- Buy Research Paper
- Buy Term Paper
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Case study
- Buy Presentation
- Buy Personal statement
Argumentative Essay Guide
Types Of Argument
Learn the 3 Different Types of Argument and Multiple Argument Claims
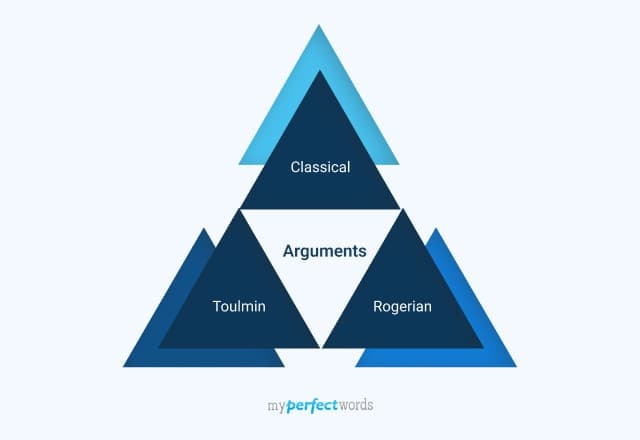
People also read
The Ultimate Guide to Argumentative Essay Writing
250+ Argumentative Essay Topic Ideas To Help You Out
Argumentative Essay Outline: How to Structure Your Argumentative Essay
Argumentative Essay Examples: Samples & Tips
An argument is a series of statements or facts intended to develop or support a point of view. It is usually known as a claim backed up with evidence, facts, and examples.
The way you structure the argument in your essay makes a huge difference. It will either set your paper apart or mix up with the other average papers without leaving an impact.
Recently, we created a complete guide to crafting an impressive argumentative essay from scratch. In this article, we will be focusing entirely on three core strategies and types of arguments.
Let’s learn how you can structure your essay with these 3 types of argument.
- 1. 3 Main Types of Argument
- 2. Types of Argument Claims
- 3. Steps to Structure an Argumentative Essay
3 Main Types of Argument
There are 3 types of arguments that you'll most likely encounter while writing an argumentative essay . These are:
Classical Argument
The Classical or Aristotelian model of argument is the most common type of argument. It was developed by the Greek philosopher and Rhetorician Aristotle.
In the classical model, both sides of an argument are analyzed , and one side is proven right using clear evidence .
This model efficiently utilizes Ethos (authenticity) + Pathos (emotion) + Logos (logic) to persuade an audience to a side of an argument.
The classical model argumentative essay takes into account the following things:
- Introduces the main claim or the argument of the essay.
- Present the writer's perspective on the argument. The reasons something is not working and why something should be done.
- Take into account the other side of the argument . Explain them in detail and refute them with the help of evidence.
- Provide clear evidence that proves that your side of the claim is true.
- Provide the conclusion which states the benefits of accepting your claim.
The structure of the classical model is as follows:
- Introduction - hook statement, brief background, thesis statement
- Body - topic sentence, facts & evidence to prove the argument
- Counter argument - opposing arguments, evidence and reasons to refute the counter-arguments
- Conclusion - restating the thesis statement, call to action and concluding remarks
Here is an example that follows this model:
Toulmin Argument
The Toulmin model for argumentative essays was developed by Stephen Toulmin. Unlike the classical model of argument, it presents only one side of the argument . This model works well when there is no clear truth or an absolute solution to a problem.
It breaks the argument into 6 basic components:
The structure of the Toulmin model is as follow:
- Introduction - thesis statement or the main claim
- Body - facts & evidence to support the argument
- Conclusion - rebuttal of counter-arguments
Here is an example outline of an argumentative essay about abortion in the Toulmin Model:
Rogerian Argument
The Rogerian model of argument was developed by Carl R. Rogers to provide a middle ground between opposing parties. This model works on collaboration and cooperation. It acknowledges that an argument can be looked at from different standpoints .
The objectives of the Rogerian model are:
- To show the reader that you have listened to their viewpoints and understood the complexities of the argument.
- To define the area where the writer acknowledges the reader's claim to be valid.
- Show the reader that you both share similar moral qualities and want to discover a solution that is mutually acceptable.
Each Rogerian model argumentative essay should define all of these aims.
The structure of the Rogerian model is as follow:
- Introduction - Introduction to the argument and thesis statement.
- Opposing position: An acknowledgment that there is another side of the argument.
- State your claim: Your own perspective about the argument.
- Provide a middle ground: Carefully bring both sides of the argument together and provide a compromised solution.
- Conclusion - Concluding remarks that state the benefits of a compromised solution.
Here’s a short example:
You can follow any of these 3 types of argument essay models in your argumentative essay. These models will help you to write an argumentative essay in a well-structured and persuasive way.
Types of Argument Claims
An argument claim, often simply referred to as a "claim," is a
“declarative statement or proposition put forward in an argument or discussion.”
It is the central point or thesis that the person making the argument is trying to prove or persuade others to accept.
Factual Claims
Factual claims are statements that assert something as a fact or reality. They are based on observable evidence and can be proven or disproven.
For example,
Value Claims
Value claims express personal opinions, preferences, or judgments about something. They are not about facts but about what someone believes is right, good, or important.
For instance,
Policy Claims
Policy claims propose a specific course of action or advocate for a change in the way things are done. They are often found in discussions about laws, regulations, or actions that should be taken.
An example would be,
Causal Claims
Causal claims assert a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more phenomena. They suggest that one thing is responsible for another.
For instance,
Definitional Claims
Definitional claims seek to clarify or establish the meaning of a term or concept. They aim to set a specific definition or understanding for a particular word or idea.
For example ,
Understanding these different types of argument claims can help you identify the nature of statements in discussions and debates. This makes it easier to analyze and respond to various arguments.
Steps to Structure an Argumentative Essay
You may have a very good and controversial argument in mind with strong evidence to prove it. However, if you haven't structured your argument properly, your argument is wasted.
Here are the easy steps that can help you structure your argument effectively:
- Choose a controversial and debatable topic from a comprehensive list of argumentative essay topics .
- Decide the type of claim that you want to make with your essay.
- Decide the type of argument structure you want to follow in your essay.
- Collect facts and evidence from credible sources and use them to support your claim.
- Develop a strong argumentative essay outline .
- Study some argumentative essay examples to get a deeper understanding of how to develop an argument in the essay.
- Begin your essay with an arguable claim or premises.
- Make sure your claim is logical and is developed coherently throughout the essay.
- Provide a conclusion that clearly matches the type of argument model you have followed.
Now that you've got the basics of different argument types, you're all set to start writing your argumentative essays.
However, if you still need expert help, you can hire a qualified writer from our custom essay writing online .
We know how to create strong and convincing arguments that will make your essays shine. Our argumentative essay writing service is available 24/7 to assist you with all of your argumentative writing needs.
Place your order today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
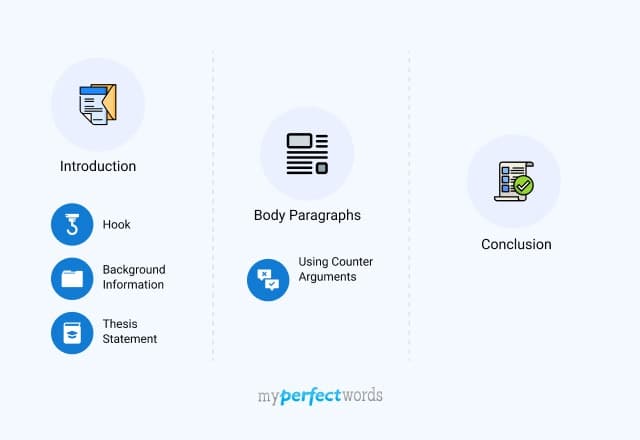

Differences Between Argumentative & Discursive Essay Writing

Argumentative and discursive writing form a large portion of the Paper 1 Syllabus, albeit often mistaken for each other due to their similarities and overlaps in writing techniques. In the first part of this two-part series, let us iron out the differences between these two text types so that we can tackle them better in our writing.
Neutrality vs Taking a Stand
The baseline difference between Argumentative and Discursive is innate to definition. As the terms imply, an argumentative essay requires you to argue towards an explicit stand. Its individual points and structure revolve around putting across and strengthening this stand to convince the reader. Discursive, on the other hand, requires you to discuss an issue as is, primarily to educate the reader. Thus, there isn’t a need to take an explicit stand or frame its points towards one.
It is important to distinguish this main difference between the two early-on; missing the purpose of the text type causes our writing to go haywire and become severely penalized.
Balance & Scope
The onus is on the writer in you to present the most holistic take on a topic as possible. However, both text types achieve the concept of balance and scope differently.
Discursive is generally neutral and free-for-all discussion; as such, we aim to maximize breadth and depth. There are 2 trains of thought to come up with a decent number of points to work with. The first way is to consider the dimensions of a topic. Most issues usually involve political, social and economic dimensions, and in some cases, technological, psychological, geographical and other applicable ones. We can dedicate one paragraph for a dimension and elaborate on it thoroughly. Secondly, we can analyze the topic at different scales – usually by considering how the topic affects the individual, group and society. Oftentimes, there are intermediate levels such as groups within an organization or groups of different backgrounds impacting each other.
Argumentative essays, on the other hand, achieve a balance between thesis and anti-thesis that support and refute your stand respectively. You must devise enough thesis points that are sufficiently in-depth standalone, while being sufficiently-varied to cover factors for scope. The anti-thesis is also essential; without it, only presenting a thesis makes your writing appear one-sided and stubborn or silent regarding the flaws of your argument. In contrast, acknowledging these gaps and being able to counter-argue against them is a sign of strength. Not only do you acknowledge potential holes and exceptions in the opposite arguments, you can also refute them confidently and thoroughly, thus making your argument more holistic.
Structure & Content Ratio
In timed examination conditions, you are expected to write an introduction, five body paragraphs and a conclusion to compose an essay of healthy length and completeness.
Based on our earlier reasoning, the optimal structure for Argumentative would be:
- State a stand in the introduction such that it is made strong and clear from the get-go
- Three body paragraphs supporting the thesis. It is sequentially logical to start the body text by substantiating it with your stand. It is also simpler to write more body paragraphs for the thesis than the anti-thesis so as to outnumber and overpower the latter.
- A signpost paragraph that separates the thesis and anti-thesis points. Generally, writing the thesis and anti-thesis points separately also makes the argument clearer and easier to follow (without the need for intermediate sign-postings and complex expressions, at least).
- Two body paragraphs supporting the anti-thesis, each ending with a counter-argument that furthers your thesis.
- A conclusion that reiterates your stand for a lasting impact on the reader. It also contains closing comments.
Discursive structure is less rigid, but your sequence of paragraphs must be justifiably logical. For instance, if we generate our points using the scaling method, it is sensible to write them in ascending scale ie. a body paragraph about the individual level, then the group, then the organization, and finally, the societal level.
Difficult Areas
Which of these two text types is easier? You may find the Discursive to be harder as it requires you to devise a wider range of points. Or that the Argumentative is easier if you feel strongly for a topic or can express your views more directly, albeit bearing a higher risk for not sounding critical, balanced or clear-stating of your stand. Difficulty also varies with the question and to an extent, your prior knowledge of the topic (and similar ones). Ultimately, the answer lies in your ability and knowledge. Every situation is a different scenario.
Do you have a preference for either text type? In the next part of our series, we shall zero-in on some smart ways to start each text type’s introduction.
Tuition Classes
English , Primary 4
English , Primary 5
English , Primary 6 (PSLE)
English , Secondary 1
English , Secondary 2
English , Secondary 3
English , Secondary 4 (O-Level)
Quick Links
SMART Sheets
Join Us (Jobs & Careers)
The Learning Board - English, Math & Science Tuition Centre In Singapore
Bishan Mall 501 Bishan Street 11 #01-366 Singapore 570501
The Midtown 1187 Upper Serangoon Road #01-67 Singapore 533971
Kembangan Court 5 Jalan Masjid #01-14 Singapore 418924

Business | Tech | Health | Sport
Argumentative vs Descriptive Essay: Basic Differences You Must Know!

An essay is a type of academic writing written mostly to inform or persuade someone. There are many different types of an essay. An argumentative and descriptive essay are two types of essays among those. An argumentative essay is focused on making arguments about a certain point of view and making things clear. On the other hand, a descriptive essay is aimed at describing things in a detailed manner. Read also schools in Bannerghatta .
As you are here, it is not difficult to guess that you do not know about the differences that exist between these two important types of essays. Well, you have just landed the right article. In today’s post, we are going to discuss the top differences that exist between an argumentative essay and a descriptive essay. However, before that, let’s define both essay types.
Table of Contents
What is an argumentative essay?
An argumentative essay is a type of essay in which the writer tries to prove a point with the support of concrete pieces of evidence. This type of essay is based on logic and reason. The writer gives examples and shreds of evidence in support of his point of view. It is up to the reader whether he agrees with the writer or disagrees. It is important to remember that there is no use of persuasion in this essay type.
What is a descriptive essay?
Descriptive writing or essay is another type of essay. This essay is aimed at describing the essay topic in detail. It provides the reader with a detailed sensory description of the essay topic. It means that through the content of the essay, the writer appeals to the five senses of the reader. A descriptive essay allows you to be more creative while writing it. For example, while describing a place, you can use some non-academic words. Also read about the India international school Bangalore .
Top differences between argumentative and descriptive essay
After reading the information above, it is now clear to you that argumentative and descriptive essays are two different types of writing. It is now time to discuss the differences that exist between them in detail. Hence, a brief description of the major differences is as follows:
1. The difference in balance and scope
The first difference between an argumentative and descriptive essay is of balance and scope. An argumentative essay does not have a balance of ideas. This essay requires you to take a side and refute the other. Also, an argumentative essay presents only one side of the story and asks you to take a stand. On the other hand, a descriptive essay is more balanced. Generally, this essay is neutral and just discusses the essay topic deeply.
2. The difference in complexity
Another difference that exists between these essay types is the difference in complexity. In general, writing an argumentative essay is easy. The reason is that all you need to do in this essay is take a side and present the arguments in support of that chosen side. In contrast, for writing a descriptive essay, you have to take a broader view of the topic into consideration. It requires extensive, and this is why it is difficult to craft.
3. The difference in the structure
There exists a minor difference in the rigidity of the structure of both essays. An argumentative essay is very strict about structure. As the writer, you have to craft the essay in three sections, i.e., introduction, body, and conclusion. In contrast, the descriptive essay is less rigid. The sequence of the sections remains the same, but the content ratio differs in this essay. If you still have any doubts about the structure, buy essay online and go through it.
4. The difference in the research bias
There is a difference between these two types of essays in terms of research bias. In an argumentative essay, you, as the writer, take a stand and present arguments in support of your stand. Hence, this essay is kind of biased in nature towards a point. On the other hand, the descriptive essay is not biased. In fact, you cannot think of bias in this essay. This essay just explains the topic, and that is it.
5. The difference in the tone
Another major difference that exists between these two types of essays is the difference in tone. The tone of an argumentative essay is very convincing. Although it is not a persuasive essay, its tone is similar to persuasive essays. On the other hand, the tone of a descriptive essay is very linear and constant. As the reader, you do not see any shift in the tone throughout the essay. Hence, it is a neutral essay. Also know about the Bangalore international school fees .
To sum up, argumentative and descriptive essay are two different types of academic essays. Both utilise different literary words and tones to express the information. Their purposes and aims are also different. In this guidepost, we have also discussed the major differences between them. So, read the information above and learn the differences.
I am Zoya Arya, and I have been working as Content Writer at Rananjay Exports for past 2 years. My expertise lies in researching and writing both technical and fashion content. I have written multiple articles on Gemstone Jewelry like Moonstone Ring and other stones over the past years and would love to explore more on the same in future. I hope my work keeps mesmerizing you and helps you in the future.
Share this:
Related posts.

Buy Premium Trading Courses: Your Path to Profitable Trading Education

How to Improve your Essay Writing Skills for Academic Performance?

School Management Software: Call of the Day
You May Have Missed!

Unraveling the Intrigues of “House of Zwide” A Journey Through Contemporary South African Drama

The Untold Secret To Faisal Town Phase 2 In Less Than Ten Minutes

Places Hosting Events For Everyone | Springfield IL Events

Fortnite Party: How to Plan the Ultimate Gaming Celebration
Narrative vs Descriptive Writing: Understanding the Key Differences
By: Author Paul Jenkins
Posted on May 13, 2023
Categories Storytelling , Writing
Narrative and descriptive writing are two of the most common writing styles used in literature. Both styles are used to convey a story, but they differ in their purpose and approach. Narrative writing is designed to tell a complete story, while descriptive writing conveys an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative writing involves telling a story with a beginning, middle, and end. It is often used in novels, short stories, and memoirs. Narrative writing can entertain, inform, or persuade the reader. It is a powerful tool for writers to convey their message and connect with their audience.
On the other hand, descriptive writing creates a vivid image in the reader’s mind. It is often used in poetry, descriptive essays, and travel writing. Descriptive writing allows the writer to use sensory details to create a picture in the reader’s mind. It is a powerful tool for writers to create a mood or atmosphere. Descriptive writing can entertain, inform, or persuade the reader.
Narrative Writing
Narrative writing is a style of writing that tells a story or describes an event. It can be fiction or non-fiction and is often written in the first-person point of view. The purpose of narrative writing is to entertain, inform or persuade the reader.
Narrative writing aims to engage the reader by telling a story that captures their attention. Narrative writing is often used in fiction writing, but it can also be used in non-fiction writing, such as memoirs or personal essays. The purpose of narrative writing is to create a vivid picture in the reader’s mind and make them feel like they are part of the story.
Narrative writing has several key elements that help to create a compelling story. These elements include characters, plot, point of view, narration, chronological order, action, setting, and theme. Characters are the people or animals that are involved in the story. The plot is the sequence of events that make up the story. Point of view is the perspective from which the story is told. Narration is how the story is told, such as first-person or third-person narration. Chronological order is the order in which events occur in the story. Action is the events that take place in the story. The setting is the time and place in which the story takes place. The theme is the underlying message or meaning of the story.
Examples of narrative writing include novels, short stories, and narrative essays. In fiction writing, the protagonist is the main character who drives the story forward. In a narrative essay, the writer tells a personal story that has a point or lesson to be learned. Narrative writing often uses first-person narration to create a more personal connection between the reader and the story.
In summary, narrative writing is a style of writing that tells a story or describes an event. It has several key elements that help to create a compelling story, including characters, plot, point of view, narration, chronological order, action, setting, and theme. Narrative writing can be used in fiction and non-fiction and is often used to entertain, inform, or persuade the reader.
Descriptive Writing
Descriptive writing is a type of writing that aims to provide a detailed description of a person, place, object, or event. It uses sensory details to create an image in the reader’s mind. The writer tries to make the reader feel like they are experiencing the scene.
Descriptive writing aims to create a vivid and detailed picture in the reader’s mind. It is often used to set the scene in a story or to provide a detailed description of a character or place. Descriptive writing can also create an emotional response in the reader.
Descriptive writing uses sensory details to create an image in the reader’s mind. It should be written in a logical order, so the reader can easily follow along. The following elements are commonly used in descriptive writing:
- Sensory detail (smell, taste, sight, sound, touch)
- Appearance and characteristics of the subject
- Description of the place or object
- Exposition of the subject
- Figurative language (metaphors, similes, onomatopoeia)
Here are a few examples of descriptive writing:
- The sun was setting over the mountains, casting a warm glow across the valley. The air was filled with the sweet scent of wildflowers and birds singing in the trees.
- The old house sat at the end of the street, its peeling paint and broken shutters a testament to its age. The front porch creaked as I stepped onto it, and the door groaned as I pushed it open.
- The chocolate cake was rich and decadent, with a moist crumb and a smooth, velvety frosting. Each bite was like a little slice of heaven, the flavors blending perfectly.
In conclusion, descriptive writing is a powerful tool for creating vivid and detailed images in the reader’s mind. The writer can transport the reader to another time and place using sensory details and logical order.
Narrative vs. Descriptive Writing
Differences.
Narrative writing and descriptive writing are two distinct forms of writing that have different purposes. Narrative writing is used to tell a story, while descriptive writing is used to describe something in detail. The following table summarizes some of the key differences between the two:
In narrative writing, the writer is trying to convey a specific message or theme through the story they are telling. In contrast, descriptive writing is more concerned with creating a sensory experience for the reader. Descriptive writing often uses figurative language, such as metaphors and similes, to create vivid images in the reader’s mind.
Similarities
Despite their differences, narrative writing and descriptive writing also share some similarities. Both forms of writing require the writer to use descriptive language to create a vivid picture in the reader’s mind. Both can also be used in both fiction and non-fiction writing.
Another similarity is that both forms of writing can create emotional connections with the reader. In narrative writing, this is achieved by creating relatable characters and situations. Descriptive writing is achieved by using sensory details to create a visceral experience for the reader.
In conclusion, while narrative writing and descriptive writing have different purposes, they require the writer to use descriptive language to create a vivid picture in the reader’s mind. Understanding the differences and similarities between these two forms of writing can help writers choose the appropriate style for their writing project.
Narrative Writing Techniques
Narrative writing is a form of storytelling that conveys a series of events or experiences through a particular perspective. This section will explore some of the key techniques used in narrative writing.
The narrator is the voice that tells the story. They can be a character within the story or an outside observer. The narrator’s perspective can greatly affect the reader’s interpretation of events. For example, a first-person narrator may provide a more personal and subjective account of events, while a third-person narrator may offer a more objective perspective.
Dialogue is the spoken or written words of characters within the story. It can reveal character traits, advance the plot, and provide insight into relationships between characters. Effective dialogue should sound natural and reflect the character’s personality and background.
Point of View
Point of view refers to the perspective from which the story is told. It can be first-person, third-person limited, or third-person omniscient. The choice of point of view can affect the reader’s understanding of the story and its characters.
The plot is the sequence of events that make up the story. It should have a clear beginning, middle, and end, with each event building upon the previous one. A well-crafted plot should be engaging and keep the reader interested.
Characterization
Characterization is the process of creating and developing characters within the story. This can be achieved through various techniques, including dialogue, actions, and inner thoughts. Effective characterization should create characters that are believable and relatable to the reader.
In conclusion, narrative writing techniques are essential for creating a compelling and engaging story. Using techniques such as a well-developed narrator, natural-sounding dialogue, and effective characterization, writers can create stories that captivate and entertain their readers.
Descriptive Writing Techniques
Sensory details.
One of the most critical aspects of descriptive writing is the use of sensory details. This means including information that appeals to the five senses: sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch. Sensory details help the reader experience the scene or object being described, making the writing more vivid and engaging.
For example, instead of simply stating that a flower is beautiful, a writer might describe the vibrant colors of its petals, the sweet fragrance it emits, and the soft texture of its petals. This level of detail allows the reader to fully imagine the flower and feel like they are experiencing it themselves.
Logical Order
Descriptive writing should also be organized in a logical order. This can mean starting with a general description and moving on to more specific details. For example, describing a room starts with an overview, then moves on to describe individual items.
It’s also important to consider the perspective of the reader. For example, if describing a landscape, the writer should consider the reader’s viewpoint and describe the scene from left to right, top to bottom, or in another logical order that makes sense for the reader.
Descriptive writing should create a clear mental image in the reader’s mind. This can be achieved through the use of vivid imagery and figurative language. For example, a writer might describe a sunset as a “golden blanket draped over the sky” or a forest as a “lush, green cathedral.”
It’s important to balance detailed descriptions and allow readers to use their imagination. The goal is to provide enough detail to create a mental image but not so much that the reader feels overwhelmed or bored.
Finally, descriptive writing should aim to evoke emotions in the reader. This can be achieved through descriptive language conveying a mood or feeling. For example, a writer might describe a storm as “fierce and unrelenting,” creating a sense of danger and foreboding.
It’s important to consider the emotions that the reader should feel based on the subject being described. For example, if describing a peaceful meadow, the writer should use language that conveys a sense of calm and relaxation.
By using these techniques, writers can create engaging and vivid descriptions that allow the reader to experience the scene or object being described fully.
Narrative vs. Descriptive Essays
When it comes to writing essays, there are two main types: narrative and descriptive. While they may seem similar, they have distinct differences in purpose, structure, and examples.
The purpose of a narrative essay is to tell a story. It typically includes characters, a plot, and a setting. It is meant to engage the reader and create an emotional response. Narrative essays can be based on real-life experiences or fictional stories.
On the other hand, the purpose of a descriptive essay is to provide a detailed description of a person, place, or thing. It is meant to paint a picture in the reader’s mind and create a sensory experience. Descriptive essays can be based on real-life experiences or imaginary scenarios.
Narrative essays typically have a chronological structure, meaning they follow a timeline. They often include dialogue and sensory details to create a vivid picture for the reader. The structure of a narrative essay can vary depending on the story being told.
On the other hand, descriptive essays typically have a spatial structure, meaning they describe something in a specific order. They often use sensory details and figurative language to create a vivid picture for the reader. The structure of a descriptive essay can vary depending on the topic being described.
A narrative essay example could be a personal experience, such as a memorable vacation or a life-changing event. It could also be a fictional story, such as a short story or novel.
A descriptive essay example could be describing a favorite place, such as a beach or a park. It could also be a description of a person, such as a family member or a celebrity.
In conclusion, narrative and descriptive essays have distinct differences in purpose, structure, and examples. It is important to understand these differences when deciding which type of essay to write.
Argumentative Essays
Argumentative essays are a type of writing that requires the writer to take a position on a topic and defend it using evidence and reasoning. This type of essay is often used in academic settings, such as in college courses or on standardized tests like the GRE or SAT.
An argumentative essay aims to persuade the reader to agree with the writer’s point of view. To do this, the writer must present a clear and compelling argument supported by evidence. The writer must also anticipate and address counterarguments to strengthen their argument.
An argumentative essay typically follows a five-paragraph structure, which includes an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The introduction should include a clear thesis statement that states the writer’s position on the topic. Each body paragraph should focus on a single point that supports the thesis statement. The conclusion should summarize the essay’s main points and restate the thesis statement in a new way.
Rhetorical Analysis
To write an effective argumentative essay, it is important to consider the rhetorical situation. This includes the audience, purpose, and context of the essay. The writer should also consider using ethos, pathos, and logos in their argument. Ethos refers to the writer’s credibility, pathos refers to emotional appeals, and logos refers to logical appeals.
Thesis Statement
The thesis statement is the most important part of an argumentative essay. It should be clear, concise, and specific. The thesis statement should state the writer’s position on the topic and provide a roadmap for the rest of the essay. It should also be arguable, meaning there should be evidence and reasoning to support the writer’s position.
Expository Essays
Expository essays are a common type of academic writing that aims to inform or explain a topic to the reader. This section will discuss the purpose, structure, and examples of expository essays.
The purpose of an expository essay is to present a balanced analysis of a topic or issue. The writer aims to explain or clarify the topic to the reader, using evidence and facts to support their arguments. Unlike narrative or descriptive writing, expository writing is focused on presenting information clearly and concisely.
The structure of an expository essay typically follows a five-paragraph format. The first paragraph is the introduction, which includes a thesis statement that summarizes the essay’s main point. The following three paragraphs are the body, which presents the evidence and arguments to support the thesis. Finally, the last paragraph is the conclusion, which restates the thesis and summarizes the essay’s main points.
Here are some examples of topics that could be covered in an expository essay:
- The causes and effects of climate change
- The history and significance of a particular event or invention
- The benefits and drawbacks of a particular technology or practice
- The process of learning a new skill or language
In conclusion, expository essays are academic writing that aims to inform or explain a topic to the reader. They follow a five-paragraph structure and present a balanced analysis using evidence and facts.
In conclusion, narrative and descriptive writing are two important styles of writing that serve different purposes. Narrative writing tells a story and conveys events, while descriptive writing paints a vivid picture of a person, place, or thing. Both styles can be used in various types of writing, such as fiction, poetry, biographies, and human interest stories.
When it comes to narrative writing, it is important to consider the basic elements of a story, such as the characters, plot, setting, and theme. Dialogue can also be used to add depth and realism to the story. On the other hand, descriptive writing focuses on sensory details, such as sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch, to create a vivid image in the reader’s mind.
It is important to note that narrative and descriptive writing are distinct styles, but they can also be used together to create a more engaging and compelling piece of writing. For example, a narrative essay can include descriptive elements to enhance the reader’s understanding and emotional connection to the story.
Overall, the key to effective narrative and descriptive writing is to use clear, concise, and engaging language. By mastering these styles, writers can create powerful and memorable works that resonate with readers long after they have finished reading.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
In an academic argument, you'll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you'll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions. Figure 1. When writing an argumentative essay, students must be able to separate emotion based arguments from logic based arguments in order to appeal to an academic audience.
The descriptive essay provides details about how something looks, feels, tastes, smells, makes one feel, or sounds. It can also describe what something is, or how something happened. These essays generally use a lot of sensory details. ... An argumentative essay is one that attempts to persuade the reader to the writer's point of view. The ...
An argumentative essay presents a specific claim or argument and supports it with evidence and reasoning. Here's an outline for an argumentative essay, along with examples for each section: 3. 1. Introduction: Hook: Start with a compelling statement, question, or anecdote to grab the reader's attention.
Expository essay. Purpose. Role of author. to present an original view on a topic. supports this view with good reasons. shows ability to invent and support an argumentative view. shows ability to think critically about this view. must show how the reasons provided establish your view as a convincing one.
3 Drafting: Write a rough draft of your essay. It helps to include any data and direct quotes as early as possible, especially with argumentative essays that often cite outside sources. 4 Revising: Polish your rough draft, optimize word choice, and restructure your arguments if necessary. Make sure your language is clear and appropriate for the ...
4. The balance: Acknowledging counterarguments for the argumentative essay. A well-rounded argumentative essay acknowledges that there are two sides to every story. Introducing counterarguments and opposing viewpoints in an argument essay is a strategic move that showcases your awareness of alternative viewpoints.
The argumentative essay is a genre of writing that requires the student to investigate a topic; collect, generate, and evaluate evidence; and establish a position on the topic in a concise manner. Please note: Some confusion may occur between the argumentative essay and the expository essay. These two genres are similar, but the argumentative ...
A. As basketball star Charles Barkley stated in a famous advertising campaign for Nike, he was paid to dominate on the basketball court, not to raise your kids. Many celebrities do consider themselves responsible for setting a good example and create non-profit organizations through which they can benefit youths. B.
Learn the Types of Writing: Expository, Descriptive, Persuasive, and Narrative. Catherine Traffis. Whether you write essays, business materials, fiction, articles, letters, or even just notes in your journal, your writing will be at its best if you stay focused on your purpose. While there are many reasons why you might be putting pen to paper ...
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance. An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the ...
Types of academic writing. The four main types of academic writing are descriptive, analytical, persuasive and critical. Each of these types of writing has specific language features and purposes. In many academic texts you will need to use more than one type. For example, in an empirical thesis: you will use critical writing in the literature ...
The goal of these paragraphs is to support the thesis statement. Recommended areas of focus for the body paragraphs within an argumentative paper include: Identifying and explaining the problem. Identifying the two (or more) sides to the problem. Exploring the side the writer believes is more appropriate than the others.
See Prices. You may have heard of the four essay types before: discursive, persuasive, narrative, and descriptive. It's important to know exactly what type of essay your assignment falls into - even before you start the planning and research. The essay type affects how you structure your essay, your writing style, the tone, the techniques ...
Tips for writing descriptively. The key to writing an effective descriptive essay is to find ways of bringing your subject to life for the reader. You're not limited to providing a literal description as you would be in more formal essay types. Make use of figurative language, sensory details, and strong word choices to create a memorable ...
In other words, the major difference between expository and argumentative essays is that argumentative essays try to convince, while expository essays do not. In an argumentative essay you can take a position. You can say things like: "This essay will show that the best course of action is…". "It is evident that the best course of ...
A narrative essay is a genre of writing that tells a story. The difference with a persuasive essay is that it is usually written from personal opinions and can be based on real-life experiences, fictional stories, or a combination of both. These types of essays aim to engage with the reader's emotions, and during the actual writing process ...
The classical model argumentative essay takes into account the following things: Introduces the main claim or the argument of the essay. Present the writer's perspective on the argument. The reasons something is not working and why something should be done. Take into account the other side of the argument. Explain them in detail and refute them ...
Argumentative essays, on the other hand, achieve a balance between thesis and anti-thesis that support and refute your stand respectively. You must devise enough thesis points that are sufficiently in-depth standalone, while being sufficiently-varied to cover factors for scope. The anti-thesis is also essential; without it, only presenting a ...
An argumentative essay does not have a balance of ideas. This essay requires you to take a side and refute the other. Also, an argumentative essay presents only one side of the story and asks you to take a stand. On the other hand, a descriptive essay is more balanced. Generally, this essay is neutral and just discusses the essay topic deeply. 2.
Revised on July 23, 2023. An essay outline is a way of planning the structure of your essay before you start writing. It involves writing quick summary sentences or phrases for every point you will cover in each paragraph, giving you a picture of how your argument will unfold. You'll sometimes be asked to submit an essay outline as a separate ...
Argumentative essays are a type of writing that requires the writer to take a position on a topic and defend it using evidence and reasoning. This type of essay is often used in academic settings, such as in college courses or on standardized tests like the GRE or SAT. Purpose. An argumentative essay aims to persuade the reader to agree with ...