- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- February 2014 (Revised December 2016)
- HBS Case Collection

Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter
- Format: Print
- | Language: English
- | Pages: 17
About The Author
Eric J. Van den Steen
Related work.
- March 2014 (Revised December 2016)
- Faculty Research
- Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter By: Eric Van den Steen
- Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter By: Eric Van den Steen and David Lane
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Don’t Be Undersold!
- Jan-Benedict E.M. Steenkamp
- Nirmalya Kumar
A new class of European discounters have U.S. retailers squarely in their sights.
Reprint: R0912K
“Aldi” is a word that strikes fear in the hearts of brand managers across Europe. A chain of low-budget retail stores with sales of $73.5 billion in 2008, Aldi invented what is commonly referred to as the hard-discount store, a format that is destroying between a quarter and a half trillion dollars in brand sales annually.
Brand executives at major consumer packaged goods companies have mostly been caught off guard by this success. The authors’ research identified four key misconceptions that explain why: (1) Hard discounters can succeed only in Europe; (2) they attract only the poor; (3) they offer inferior quality; (4) their success is a recessionary phenomenon.
Aldi, Lidl, and other hard discounters keep costs low in part by restricting as much as 90% of their stock to their own private labels. But, as they are beginning to realize, that practice can gain only so much market share. A judicious mix of store labels and manufacturers’ brands will win new customers for both. And brand manufacturers that fear sales cannibalization can take several proactive steps: sell unfamiliar sizes at the discounters, offer brands with a small market share, carefully manage the price gap, make shipping boxes attractive, and keep their brands dynamic.
The Idea in Brief
- The success of hard discounters’ own brands is responsible for destroying between a quarter and a half trillion dollars in mainstream brand sales annually.
- Brand executives at major consumer goods companies have been caught off guard, having assumed that hard discounters operate primarily in Europe, supply shoddy goods to poor customers, and flourish mainly in recessionary times.
- The authors’ research shows that savvy manufacturers can partner with hard discounters to gain rather than lose brand sales—by selling differently packaged, smaller, carefully priced, and more dynamic brands through the hard-discount channel.
When the CEO of Procter & Gamble visited the company’s European headquarters a few years ago, Paul Polman, then P&G’s president for Europe (and now the CEO of Unilever), took him to visit P&G’s most dangerous competitor: not Danone, Nestlé, or Unilever but an Aldi store. Yes, Aldi, a chain of low-budget retail stores with sales in 2008 of $73.5 billion, is the four-letter word that strikes fear in the hearts of brand managers across Europe.
- JS Jan-Benedict E.M. Steenkamp is the Knox Massey Distinguished Professor of Marketing and the marketing area chair at the University of North Carolina’s Kenan-Flagler Business School. They are the coauthors of Brand Breakout: How Emerging Market Brands Will Go Global (Palgrave Macmillan, 2013).
- NK Nirmalya Kumar is the Lee Kong Chian Professor of Marketing at Singapore Management University and a Distinguished Academic Fellow at INSEAD Emerging Markets Institute.
Partner Center
The marketplace for case solutions.
Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter – Case Solution
Aldi was a hard discounter based in Germany that sells a variety of private-label groceries and household items in several stores. It was the world's 8th largest retailer. In 2013, Aldi initiated moving fast with its US expansion. While it has more than a thousand stores in various states, Aldi was still not popular in the US. It is said to be the same reason why Walmart did not make it in Germany. Since the US is Walmart's home market, could Aldi make it through the competition with Walmart in the US?
Eric Van Den Steen; David Lane Harvard Business Review ( 714474-PDF-ENG ) February 07, 2014
Case questions answered:
Case study questions answered in the first solution:
- Please identify the strategic issues and problems to be solved, describe the necessary analyses and conclusions, and present recommendations and implications. Do whatever analysis is needed to solve the problem you have identified.
C ase study questions answered in the second solution:
- What are the key business problems Aldi is facing competing in the USA?
- Who are the key stakeholders in these problems?
- What is Aldi’s business-level strategy, and what are the activities that support this strategy?
- How well is the company performing, particularly in terms of efficiency and profitability?
- Does Aldi have a source of competitive advantage relative to Walmart?
- Identify three solutions Aldi can use to address the business problems it faces, with the pros and cons of each solution.
- Which solution do you recommend, and why?
Not the questions you were looking for? Submit your own questions & get answers .
Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter Case Answers
You will receive access to two case study solutions! The second is not yet visible in the preview.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY – ALDI
An international brand with a rich history, Aldi is known for its low prices and no-frills grocery shopping experience. While Aldi has seen substantial success in European markets, they seem to have trouble integrating into the U.S. and understanding the ideologies of the American consumer.
Aldi has developed a presence in the U.S., spreading over 32 states and 1,200 stores. Despite this, they are still virtually unknown. Looking forward, Aldi wants to expand their organic food offerings and expand their presence in the U.S.
Some of the most notable threats in the grocery industry are Walmart and Target, incredibly large brands with immense customer loyalty that can leverage their size to negotiate low prices with suppliers. With trends in the U.S. constantly evolving, niche grocery stores focused on organic and health foods and wholesale stores are prominent competitors.
A holistic analysis of the macro environment in the U.S. is necessary to understand trends and American consumer behavior. Discount retail is a very competitive industry to navigate, with revenues of the top ten retailers totaling over $1 trillion.
Aldi has unique, inimitable resources that can aid it in its mission, such as its unique staffing levels, low-cost structure, and private-label products. With this advantage, Aldi needs to implement the right global expansion strategy to succeed in the U.S., creating the core question of what specific measures Aldi must take to differentiate itself in the market.
It is recommended that Aldi emphasize their customer retention efforts with a customer loyalty program, increase its presence in urban markets, and adopt innovative technology such as self-checkout. These three strategic insights will help guide Aldi through a successful expansion in the United States.
CASE ANALYSIS
Aldi has maintained a strong sense of industry leader regarding discount grocers, attributing its success to its reputation as a frugal, consistent grocery shopping experience.
The firm has stayed committed to its value of operational excellence, with an average number of 10 employees per store and its emphasis on private label products, which make up approximately 95% of its product offerings.
Many international brands struggle with being cognizant of the local culture, often choosing the wrong global expansion strategy and ending with failure. We have seen this with Walmart and its entry into Germany.
Exhibit A outlines the market conditions of the U.S., highlighting different trends and regulations that directly affect Aldi’s operations. It is crucial to assess all trends to be proactive in identifying opportunities and threats. Failing to take into account any of these factors can be detrimental to Aldi’s expansion.
This analysis shows that the grocery industry in the U.S. is relatively stable, and with groceries being a necessity, the industry will still thrive through economic boom and bust cycles. The firms that can adapt to trends quickly are the ones that succeed.
One prevalent trend is that of online ordering and self-checkout, feeding into the sensation of instant gratification that is common in the American consumer.
The scope of Aldi’s expansion efforts is incredibly ambitious, aiming to open 650 new stores by 2018. While they are trying to replicate initiatives that have been successful overseas, such as their successful expansion into Australia with over 270 stores, Aldi needs to tailor their expansion efforts to the U.S.’ unique business environment. What specific measures can Aldi take to differentiate itself in the market?
Industry Analysis
Exhibit B addresses various parameters of the competitive structure of the grocery industry and how they affect Aldi. There is a high barrier to entry due to the tremendous number of competitors and the high start-up costs associated with building an effective distribution network and establishing a brick-and-mortar store.
With various big players already in the space, it is…
Unlock Case Solution Now!
Get instant access to this case solution with a simple, one-time payment ($24.90).
After purchase:
- You'll be redirected to the full case solution.
- You will receive an access link to the solution via email.
Best decision to get my homework done faster! Michael MBA student, Boston
How do I get access?
Upon purchase, you are forwarded to the full solution and also receive access via email.
Is it safe to pay?
Yes! We use Paypal and Stripe as our secure payment providers of choice.
What is Casehero?
We are the marketplace for case solutions - created by students, for students.

Product details

Fern Fort University
Aldi: the dark horse discounter case study analysis & solution, harvard business case studies solutions - assignment help.
Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter is a Harvard Business (HBR) Case Study on Strategy & Execution , Fern Fort University provides HBR case study assignment help for just $11. Our case solution is based on Case Study Method expertise & our global insights.
Strategy & Execution Case Study | Authors :: Eric Van Den Steen, David Lane
Case study description.
In 2013, Aldi-the world's 8th largest retailer-planned to accelerate its US expansion. Aldi was a German-based hard discounter that sold a limited assortment of private-label groceries and household items in barebones stores. Despite its presence with 1200 stores in 32 states, Aldi was still relatively unknown in the US. But it was often cited as one of the reasons for Walmart's exit from Germany. Could it compete with Walmart in the US, Walmart's home market?
Order a Strategy & Execution case study solution now
To Search More HBR Case Studies Solution Go to Fern Fort University Search Page
[10 Steps] Case Study Analysis & Solution
Step 1 - reading up harvard business review fundamentals on the strategy & execution.
Even before you start reading a business case study just make sure that you have brushed up the Harvard Business Review (HBR) fundamentals on the Strategy & Execution. Brushing up HBR fundamentals will provide a strong base for investigative reading. Often readers scan through the business case study without having a clear map in mind. This leads to unstructured learning process resulting in missed details and at worse wrong conclusions. Reading up the HBR fundamentals helps in sketching out business case study analysis and solution roadmap even before you start reading the case study. It also provides starting ideas as fundamentals often provide insight into some of the aspects that may not be covered in the business case study itself.
Step 2 - Reading the Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter HBR Case Study
To write an emphatic case study analysis and provide pragmatic and actionable solutions, you must have a strong grasps of the facts and the central problem of the HBR case study. Begin slowly - underline the details and sketch out the business case study description map. In some cases you will able to find the central problem in the beginning itself while in others it may be in the end in form of questions. Business case study paragraph by paragraph mapping will help you in organizing the information correctly and provide a clear guide to go back to the case study if you need further information. My case study strategy involves -
- Marking out the protagonist and key players in the case study from the very start.
- Drawing a motivation chart of the key players and their priorities from the case study description.
- Refine the central problem the protagonist is facing in the case and how it relates to the HBR fundamentals on the topic.
- Evaluate each detail in the case study in light of the HBR case study analysis core ideas.
Step 3 - Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter Case Study Analysis
Once you are comfortable with the details and objective of the business case study proceed forward to put some details into the analysis template. You can do business case study analysis by following Fern Fort University step by step instructions -
- Company history is provided in the first half of the case. You can use this history to draw a growth path and illustrate vision, mission and strategic objectives of the organization. Often history is provided in the case not only to provide a background to the problem but also provide the scope of the solution that you can write for the case study.
- HBR case studies provide anecdotal instances from managers and employees in the organization to give a feel of real situation on the ground. Use these instances and opinions to mark out the organization's culture, its people priorities & inhibitions.
- Make a time line of the events and issues in the case study. Time line can provide the clue for the next step in organization's journey. Time line also provides an insight into the progressive challenges the company is facing in the case study.
Step 4 - SWOT Analysis of Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter
Once you finished the case analysis, time line of the events and other critical details. Focus on the following -
- Zero down on the central problem and two to five related problems in the case study.
- Do the SWOT analysis of the Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter . SWOT analysis is a strategic tool to map out the strengths, weakness, opportunities and threats that a firm is facing.
- SWOT analysis and SWOT Matrix will help you to clearly mark out - Strengths Weakness Opportunities & Threats that the organization or manager is facing in the Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter
- SWOT analysis will also provide a priority list of problem to be solved.
- You can also do a weighted SWOT analysis of Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter HBR case study.
Step 5 - Porter 5 Forces / Strategic Analysis of Industry Analysis Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter
In our live classes we often come across business managers who pinpoint one problem in the case and build a case study analysis and solution around that singular point. Business environments are often complex and require holistic solutions. You should try to understand not only the organization but also the industry which the business operates in. Porter Five Forces is a strategic analysis tool that will help you in understanding the relative powers of the key players in the business case study and what sort of pragmatic and actionable case study solution is viable in the light of given facts.
Step 6 - PESTEL, PEST / STEP Analysis of Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter
Another way of understanding the external environment of the firm in Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter is to do a PESTEL - Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental & Legal analysis of the environment the firm operates in. You should make a list of factors that have significant impact on the organization and factors that drive growth in the industry. You can even identify the source of firm's competitive advantage based on PESTEL analysis and Organization's Core Competencies.
Step 7 - Organizing & Prioritizing the Analysis into Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter Case Study Solution
Once you have developed multipronged approach and work out various suggestions based on the strategic tools. The next step is organizing the solution based on the requirement of the case. You can use the following strategy to organize the findings and suggestions.
- Build a corporate level strategy - organizing your findings and recommendations in a way to answer the larger strategic objective of the firm. It include using the analysis to answer the company's vision, mission and key objectives , and how your suggestions will take the company to next level in achieving those goals.
- Business Unit Level Solution - The case study may put you in a position of a marketing manager of a small brand. So instead of providing recommendations for overall company you need to specify the marketing objectives of that particular brand. You have to recommend business unit level recommendations. The scope of the recommendations will be limited to the particular unit but you have to take care of the fact that your recommendations are don't directly contradict the company's overall strategy. For example you can recommend a low cost strategy but the company core competency is design differentiation.
- Case study solutions can also provide recommendation for the business manager or leader described in the business case study.
Step 8 -Implementation Framework
The goal of the business case study is not only to identify problems and recommend solutions but also to provide a framework to implement those case study solutions. Implementation framework differentiates good case study solutions from great case study solutions. If you able to provide a detailed implementation framework then you have successfully achieved the following objectives -
- Detailed understanding of the case,
- Clarity of HBR case study fundamentals,
- Analyzed case details based on those fundamentals and
- Developed an ability to prioritize recommendations based on probability of their successful implementation.
Implementation framework helps in weeding out non actionable recommendations, resulting in awesome Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter case study solution.
Step 9 - Take a Break
Once you finished the case study implementation framework. Take a small break, grab a cup of coffee or whatever you like, go for a walk or just shoot some hoops.
Step 10 - Critically Examine Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter case study solution
After refreshing your mind, read your case study solution critically. When we are writing case study solution we often have details on our screen as well as in our head. This leads to either missing details or poor sentence structures. Once refreshed go through the case solution again - improve sentence structures and grammar, double check the numbers provided in your analysis and question your recommendations. Be very slow with this process as rushing through it leads to missing key details. Once done it is time to hit the attach button.
Previous 5 HBR Case Study Solution
- Innovative Public Health in Alberta: Scalability Challenge Case Study Solution
- Ethiopian Airlines: Bringing Africa Together Case Study Solution
- Warren Buffet and his Newspaper Investments Case Study Solution
- Colin's Car Detailing Case Study Solution
- HeidelbergCement: The Baltic Kiln Decision Case Study Solution
Next 5 HBR Case Study Solution
- Bharat Petroleum's Upstream Strategy and Exploration Success Case Study Solution
- Innovation and Development of China Machine Press in the New Century Case Study Solution
- OWNI: Disrupting the French Media Landscape Case Study Solution
- Alcoa's Bid for Alcan (A) Case Study Solution
- Dongfeng Nissan's Venucia (A) Case Study Solution
Special Offers
Order custom Harvard Business Case Study Analysis & Solution. Starting just $19
Amazing Business Data Maps. Send your data or let us do the research. We make the greatest data maps.
We make beautiful, dynamic charts, heatmaps, co-relation plots, 3D plots & more.
Buy Professional PPT templates to impress your boss
Nobody get fired for buying our Business Reports Templates. They are just awesome.
- More Services
Feel free to drop us an email
- fernfortuniversity[@]gmail.com
- (000) 000-0000
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Case study -aldi Case study ALDI STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT

- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

The Success Of Aldi
- Harvard Case Studies
Harvard Business Case Studies Solutions – Assignment Help
In most courses studied at Harvard Business schools, students are provided with a case study. Major HBR cases concerns on a whole industry, a whole organization or some part of organization; profitable or non-profitable organizations. Student’s role is to analyze the case and diagnose the situation, identify the problem and then give appropriate recommendations and steps to be taken.
To make a detailed case analysis, student should follow these steps:

STEP 1: Reading Up Harvard Case Study Method Guide:
Case study method guide is provided to students which determine the aspects of problem needed to be considered while analyzing a case study. It is very important to have a thorough reading and understanding of guidelines provided. However, poor guide reading will lead to misunderstanding of case and failure of analyses. It is recommended to read guidelines before and after reading the case to understand what is asked and how the questions are to be answered. Therefore, in-depth understanding f case guidelines is very important.
Harvard Case Study Solutions

porter’s five forces model
STEP 2: Reading The The Success Of Aldi Harvard Case Study:
To have a complete understanding of the case, one should focus on case reading. It is said that case should be read two times. Initially, fast reading without taking notes and underlines should be done. Initial reading is to get a rough idea of what information is provided for the analyses. Then, a very careful reading should be done at second time reading of the case. This time, highlighting the important point and mark the necessary information provided in the case. In addition, the quantitative data in case, and its relations with other quantitative or qualitative variables should be given more importance. Also, manipulating different data and combining with other information available will give a new insight. However, all of the information provided is not reliable and relevant.
When having a fast reading, following points should be noted:
- Nature of organization
- Nature if industry in which organization operates.
- External environment that is effecting organization
- Problems being faced by management
- Identification of communication strategies.
- Any relevant strategy that can be added.
- Control and out-of-control situations.
When reading the case for second time, following points should be considered:
- Decisions needed to be made and the responsible Person to make decision.
- Objectives of the organization and key players in this case.
- The compatibility of objectives. if not, their reconciliations and necessary redefinition.
- Sources and constraints of organization from meeting its objectives.
After reading the case and guidelines thoroughly, reader should go forward and start the analyses of the case.
STEP 3: Doing The Case Analysis Of The Success Of Aldi:
To make an appropriate case analyses, firstly, reader should mark the important problems that are happening in the organization. There may be multiple problems that can be faced by any organization. Secondly, after identifying problems in the company, identify the most concerned and important problem that needed to be focused.
Firstly, the introduction is written. After having a clear idea of what is defined in the case, we deliver it to the reader. It is better to start the introduction from any historical or social context. The challenging diagnosis for The Success Of Aldi and the management of information is needed to be provided. However, introduction should not be longer than 6-7 lines in a paragraph. As the most important objective is to convey the most important message for to the reader.
After introduction, problem statement is defined. In the problem statement, the company’s most important problem and constraints to solve these problems should be define clearly. However, the problem should be concisely define in no more than a paragraph. After defining the problems and constraints, analysis of the case study is begin.
STEP 4: SWOT Analysis of the The Success Of Aldi HBR Case Solution:
SWOT analysis helps the business to identify its strengths and weaknesses, as well as understanding of opportunity that can be availed and the threat that the company is facing. SWOT for The Success Of Aldi is a powerful tool of analysis as it provide a thought to uncover and exploit the opportunities that can be used to increase and enhance company’s operations. In addition, it also identifies the weaknesses of the organization that will help to be eliminated and manage the threats that would catch the attention of the management.
This strategy helps the company to make any strategy that would differentiate the company from competitors, so that the organization can compete successfully in the industry. The strengths and weaknesses are obtained from internal organization. Whereas, the opportunities and threats are generally related from external environment of organization. Moreover, it is also called Internal-External Analysis.
In the strengths, management should identify the following points exists in the organization:
- Advantages of the organization
- Activities of the company better than competitors.
- Unique resources and low cost resources company have.
- Activities and resources market sees as the company’s strength.
- Unique selling proposition of the company.
WEAKNESSES:
- Improvement that could be done.
- Activities that can be avoided for The Success Of Aldi.
- Activities that can be determined as your weakness in the market.
- Factors that can reduce the sales.
- Competitor’s activities that can be seen as your weakness.
OPPORTUNITIES:
- Good opportunities that can be spotted.
- Interesting trends of industry.
- Change in technology and market strategies
- Government policy changes that is related to the company’s field
- Changes in social patterns and lifestyles.
- Local events.
Following points can be identified as a threat to company:
- Company’s facing obstacles.
- Activities of competitors.
- Product and services quality standards
- Threat from changing technologies
- Financial/cash flow problems
- Weakness that threaten the business.
Following points should be considered when applying SWOT to the analysis:
- Precise and verifiable phrases should be sued.
- Prioritize the points under each head, so that management can identify which step has to be taken first.
- Apply the analyses at proposed level. Clear yourself first that on what basis you have to apply SWOT matrix.
- Make sure that points identified should carry itself with strategy formulation process.
- Use particular terms (like USP, Core Competencies Analyses etc.) to get a comprehensive picture of analyses.
- Pest analysis
STEP 5: PESTEL/ PEST Analysis of The Success Of Aldi Case Solution:
Pest analyses is a widely used tool to analyze the Political, Economic, Socio-cultural, Technological, Environmental and legal situations which can provide great and new opportunities to the company as well as these factors can also threat the company, to be dangerous in future.
Pest analysis is very important and informative. It is used for the purpose of identifying business opportunities and advance threat warning. Moreover, it also helps to the extent to which change is useful for the company and also guide the direction for the change. In addition, it also helps to avoid activities and actions that will be harmful for the company in future, including projects and strategies.
To analyze the business objective and its opportunities and threats, following steps should be followed:
- Brainstorm and assumption the changes that should be made to organization. Answer the necessary questions that are related to specific needs of organization
- Analyze the opportunities that would be happen due to the change.
- Analyze the threats and issues that would be caused due to change.
- Perform cost benefit analyses and take the appropriate action.
PEST FACTORS:
- Next political elections and changes that will happen in the country due to these elections
- Strong and powerful political person, his point of view on business policies and their effect on the organization.
- Strength of property rights and law rules. And its ratio with corruption and organized crimes. Changes in these situation and its effects.
- Change in Legislation and taxation effects on the company
- Trend of regulations and deregulations. Effects of change in business regulations
- Timescale of legislative change.
- Other political factors likely to change for The Success Of Aldi.
ECONOMICAL:
- Position and current economy trend i.e. growing, stagnant or declining.
- Exchange rates fluctuations and its relation with company.
- Change in Level of customer’s disposable income and its effect.
- Fluctuation in unemployment rate and its effect on hiring of skilled employees
- Access to credit and loans. And its effects on company
- Effect of globalization on economic environment
- Considerations on other economic factors
SOCIO-CULTURAL:
- Change in population growth rate and age factors, and its impacts on organization.
- Effect on organization due to Change in attitudes and generational shifts.
- Standards of health, education and social mobility levels. Its changes and effects on company.
- Employment patterns, job market trend and attitude towards work according to different age groups.
case study solutions
- Social attitudes and social trends, change in socio culture an dits effects.
- Religious believers and life styles and its effects on organization
- Other socio culture factors and its impacts.
TECHNOLOGICAL:
- Any new technology that company is using
- Any new technology in market that could affect the work, organization or industry
- Access of competitors to the new technologies and its impact on their product development/better services.
- Research areas of government and education institutes in which the company can make any efforts
- Changes in infra-structure and its effects on work flow
- Existing technology that can facilitate the company
- Other technological factors and their impacts on company and industry
These headings and analyses would help the company to consider these factors and make a “big picture” of company’s characteristics. This will help the manager to take the decision and drawing conclusion about the forces that would create a big impact on company and its resources.
STEP 6: Porter’s Five Forces/ Strategic Analysis Of The The Success Of Aldi Case Study:

To analyze the structure of a company and its corporate strategy, Porter’s five forces model is used. In this model, five forces have been identified which play an important part in shaping the market and industry. These forces are used to measure competition intensity and profitability of an industry and market.
porter’s five forces model
These forces refers to micro environment and the company ability to serve its customers and make a profit. These five forces includes three forces from horizontal competition and two forces from vertical competition. The five forces are discussed below:
- THREAT OF NEW ENTRANTS:
- as the industry have high profits, many new entrants will try to enter into the market. However, the new entrants will eventually cause decrease in overall industry profits. Therefore, it is necessary to block the new entrants in the industry. following factors is describing the level of threat to new entrants:
- Barriers to entry that includes copy rights and patents.
- High capital requirement
- Government restricted policies
- Switching cost
- Access to suppliers and distributions
- Customer loyalty to established brands.
- THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES:
- this describes the threat to company. If the goods and services are not up to the standard, consumers can use substitutes and alternatives that do not need any extra effort and do not make a major difference. For example, using Aquafina in substitution of tap water, Pepsi in alternative of Coca Cola. The potential factors that made customer shift to substitutes are as follows:
- Price performance of substitute
- Switching costs of buyer
- Products substitute available in the market
- Reduction of quality
- Close substitution are available
- DEGREE OF INDUSTRY RIVALRY:
- the lesser money and resources are required to enter into any industry, the higher there will be new competitors and be an effective competitor. It will also weaken the company’s position. Following are the potential factors that will influence the company’s competition:
- Competitive advantage
- Continuous innovation
- Sustainable position in competitive advantage
- Level of advertising
- Competitive strategy
- BARGAINING POWER OF BUYERS:
- it deals with the ability of customers to take down the prices. It mainly consists the importance of a customer and the level of cost if a customer will switch from one product to another. The buyer power is high if there are too many alternatives available. And the buyer power is low if there are lesser options of alternatives and switching. Following factors will influence the buying power of customers:
- Bargaining leverage
- Switching cost of a buyer
- Buyer price sensitivity
- Competitive advantage of company’s product
- BARGAINING POWER OF SUPPLIERS:
- this refers to the supplier’s ability of increasing and decreasing prices. If there are few alternatives o supplier available, this will threat the company and it would have to purchase its raw material in supplier’s terms. However, if there are many suppliers alternative, suppliers have low bargaining power and company do not have to face high switching cost. The potential factors that effects bargaining power of suppliers are the following:
- Input differentiation
- Impact of cost on differentiation
- Strength of distribution centers
- Input substitute’s availability.
STEP 7: VRIO Analysis of The Success Of Aldi:
Vrio analysis for The Success Of Aldi case study identified the four main attributes which helps the organization to gain a competitive advantages. The author of this theory suggests that firm must be valuable, rare, imperfectly imitable and perfectly non sustainable. Therefore there must be some resources and capabilities in an organization that can facilitate the competitive advantage to company. The four components of VRIO analysis are described below: VALUABLE: the company must have some resources or strategies that can exploit opportunities and defend the company from major threats. If the company holds some value then answer is yes. Resources are also valuable if they provide customer satisfaction and increase customer value. This value may create by increasing differentiation in existing product or decrease its price. Is these conditions are not met, company may lead to competitive disadvantage. Therefore, it is necessary to continually review the The Success Of Aldi company’s activities and resources values. RARE: the resources of the The Success Of Aldi company that are not used by any other company are known as rare. Rare and valuable resources grant much competitive advantages to the firm. However, when more than one few companies uses the same resources and provide competitive parity are also known as rare resources. Even, the competitive parity is not desired position, but the company should not lose its valuable resources, even they are common. COSTLY TO IMITATE: the resources are costly to imitate, if other organizations cannot imitate it. However, imitation is done in two ways. One is duplicating that is direct imitation and the other one is substituting that is indirect imitation. Any firm who has valuable and rare resources, and these resources are costly to imitate, have achieved their competitive advantage. However, resources should also be perfectly non sustainable. The reasons that resource imitation is costly are historical conditions, casual ambiguity and social complexity. ORGANIZED TO CAPTURE VALUE: resources, itself, cannot provide advantages to organization until it is organized and exploit to do so. A firm (like The Success Of Aldi) must organize its management systems, processes, policies and strategies to fully utilize the resource’s potential to be valuable, rare and costly to imitate.

STEP 8: Generating Alternatives For The Success Of Aldi Case Solution:
After completing the analyses of the company, its opportunities and threats, it is important to generate a solution of the problem and the alternatives a company can apply in order to solve its problems. To generate the alternative of problem, following things must to be kept in mind:
- Realistic solution should be identified that can be operated in the company, with all its constraints and opportunities.
- as the problem and its solution cannot occur at the same time, it should be described as mutually exclusive
- it is not possible for a company to not to take any action, therefore, the alternative of doing nothing is not viable.
- Student should provide more than one decent solution. Providing two undesirable alternatives to make the other one attractive is not acceptable.
Once the alternatives have been generated, student should evaluate the options and select the appropriate and viable solution for the company.
STEP 9: Selection Of Alternatives For The Success Of Aldi Case Solution:
It is very important to select the alternatives and then evaluate the best one as the company have limited choices and constraints. Therefore to select the best alternative, there are many factors that is needed to be kept in mind. The criteria’s on which business decisions are to be selected areas under:
- Improve profitability
- Increase sales, market shares, return on investments
- Customer satisfaction
- Brand image
- Corporate mission, vision and strategy
- Resources and capabilities
Alternatives should be measures that which alternative will perform better than other one and the valid reasons. In addition, alternatives should be related to the problem statements and issues described in the case study.
STEP 10: Evaluation Of Alternatives For The Success Of Aldi Case Solution:
If the selected alternative is fulfilling the above criteria, the decision should be taken straightforwardly. Best alternative should be selected must be the best when evaluating it on the decision criteria. Another method used to evaluate the alternatives are the list of pros and cons of each alternative and one who has more pros than cons and can be workable under organizational constraints.
STEP 11: Recommendations For The Success Of Aldi Case Study (Solution):
There should be only one recommendation to enhance the company’s operations and its growth or solving its problems. The decision that is being taken should be justified and viable for solving the problems.
DRE #01103083
Advocate Educational Integrity
Our service exists to help you grow as a student, and not to cheat your academic institution. We suggest you use our work as a study aid and not as finalized material. Order a personalized assignment to study from.
Definitely! It's not a matter of "yes you can", but a matter of "yes, you should". Chatting with professional paper writers through a one-on-one encrypted chat allows them to express their views on how the assignment should turn out and share their feedback. Be on the same page with your writer!
Customer Reviews
Our Top Proficient Writers At Your Essays Service

- Order Status
- Testimonials
- What Makes Us Different
The Aldi Brand Harvard Case Solution & Analysis
Home >> Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions >> The Aldi Brand
The Aldi Brand Case Study Solution
On the other hand, Coles and Wool worths were initially just focused on selling national brands with an extensive product line to a large consumer base. Both of the brands hadn’t put any emphasis on private label brands initially, but now both the brands are considering to shift their focus on private label brands, with Coles considering a single while Wool worths considering multiple private label brands.
Other two new entrants including Amazon and Lidl are also focused at private label brands. This implies that the segment in which Aldi has a strong foothold is now susceptible to change with the entrance of certain new and old players in the market segment. In this scenario, Aldi must consider different and innovative as well as highly efficient strategic initiatives to deal with the situation.
Value Propositions:
Another major area that could be discussed for evaluating the business model of Aldi and its peers is the evaluation of the value preposition that Aldi and its competitors provide to their customers through selling products via various techniques. Aldi is focused on value preposition to its customers who seek competitive products at lower prices. The company offers limited lines which are dominated by private labels in order to meet the needs of the value conscious customers and to provide them a superior quality products in order to create value to its customers. Aldi’s strategy is to focus on providing high quality food at discount rates or low prices in order to reduce the daily expenses of the consumers, and to create value to the end customers. (Osterwalde, Pigneur, Bernarda,, & Smith)
Customer Relationships:
Aldi has a strong relationship with its customer. Aldi has captured those consumers who seek low priced quality products. The company offers competitive products at lower prices and continuously offers its products with lucrative discount offers for the discount seeking grocery shoppers in order to reduce their daily expenses and increase their value for money spending and satisfaction.(unknown, n.d.)
Key Partnerships:
Aldi has a strong long term relationship with their supplier in order to produce the quality product and meet the standards. As the continuous growth in the sales of the company, the company buys the raw material and the products in bulk quantity by which the company could easily avail the discount and provide low cots to their end consumers. Aldi has been narrowing the range of the products in order to maintain the quality and the cost associated with the logistics and distribution. It has built simple warehouses in order to reduce the cost. The strong association with the company’s supplier enables Aldi to provide high quality products at low prices. The strong long term relationship with the suppliers will help the company inretaining the potential consumer along with the consistent quality products at lower prices.
Organizational Structure:
The structure of the Aldi is composed of formal structure and minimization of functions. Staff of the company is also known as internal stake holders which can help the company in order to build the culture and efficiencies. In order to avoid misunderstand and quick decision making the company has formal and clear reporting lines in which each staff knows when and to whom to report, and rules and regulations about reporting. Aldi is not using so many functions in order to reduce the complexity and minimization of cost. The layout of the company’s stores are simple. It has small super markets around the globe, while its competitors have bigger stores. The company produces in bulk quantity while narrowing the range in order to reduce the cost linked with stocks and logistics and increase the operational efficiencies. The company is also using a low technology in order to reduce the complexity and cost.
Recommendations
From the above analysis, it could be said that although the value proposition strategies and the business model followed by Aldi including its strong partnership relations, customers’ focused strategies, cost leadership, led to the company’s growth for two decades, but, in the changing industry environment, Aldi must put efforts to change its strategic position in long run to mitigate the external risks posed by the new entrants and the existing competitors. Aldi must revise its current strategic position. In this situation, Bowman Model could be implemented to explore various strategic positions for Aldi to come up with these market risks. (Fernando, 2017)
As stated above, Aldi is currently positioned as low price brand in the Bowman Clock. However, the firm could also explore various other strategic position using the Bowman clock. Aldi would also position themselves on hybrid (combination of low price and differentiation). By using the hybrid position Aldi would sell its products at competitive prices and to retain their customers by differentiating (value adding) its products from its competitors’. The company could also use the differentiation position for their products in which the prices of the company’s product is relatively moderate in order to provide the different product to their consumer in comparison to their competitors’. Aldi can also use the focused differentiation in which the prices of the products are relatively high in comparison to the competitors’ but the customers buy the product due to high perceived value, which is not considered in the other competitors’ product.
BOWMAN Model
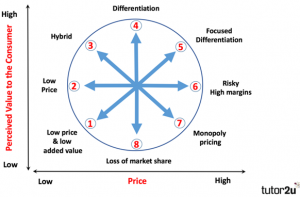
This is just a sample partical work. Please place the order on the website to get your own originally done case solution.
How We Work? Just email us your case materials and instructions to [email protected] and confirm your order by making the payment here
Related Case Solutions & Analyses:

Hire us for Originally Written Case Solution/ Analysis
Like us and get updates:.
Harvard Case Solutions
Search Case Solutions
- Accounting Case Solutions
- Auditing Case Studies
- Business Case Studies
- Economics Case Solutions
- Finance Case Studies Analysis
- Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions
- Human Resource Cases
- Ivey Case Solutions
- Management Case Studies
- Marketing HBS Case Solutions
- Operations Management Case Studies
- Supply Chain Management Cases
- Taxation Case Studies
More From Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions
- Network Assessment Exercise: Executive Version
- Embraer: The Global Leader in Regional Jets
- Sony AIBO: The Worlds First Entertainment Robot
- World Wide Licenses Ltd.: From Disney to Polaroid
- Virginia Mason Medical Center (Abridged)
- Critical Element III- Identify Statistical tools and methods to collect data:
- PepsiCo: QTG Emerging Channel Investment
Contact us:

Check Order Status

How Does it Work?
Why TheCaseSolutions.com?


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Abstract. In 2013, Aldi—the world's 8th largest retailer—planned to accelerate its US expansion. Aldi was a German-based hard discounter that sold a limited assortment of private-label groceries and household items in barebones stores. Despite its presence with 1200 stores in 32 states, Aldi was still relatively unknown in the US.
Learn about Aldi's unique business strategy and how it became one of the top discount retailers in the world in this Harvard case study analysis. Discover th...
Harvard Business School. Product #: 714474-PDF-ENG. Length: 17 page (s) In 2013, Aldi-the world's 8th largest retailer-planned to accelerate its US expansion. Aldi was a German-based hard discounter that sold a limited ass.
Reprint: R0912K "Aldi" is a word that strikes fear in the hearts of brand managers across Europe. A chain of low-budget retail stores with sales of $73.5 billion in 2008, Aldi invented what is ...
The economic woes of 2008 gave a boost to budget retailers such as Dollar General, Aldi, and these retailers have unleashed significant change in the retailing industry in general and the grocery business sin particular. The case focuses on the hard-discounters from Germany, Aldi and to a lesser extent on Lidl to describe their operating models and their relative impact on the strategies ...
In 2021, the US grocery industry had been undergoing several changes. The competitive landscape had changed significantly since the first decade of the twenty-first century. Walmart Inc. (Walmart) had emerged as the dominant retailer in all markets leading to bankruptcies and mergers with erstwhile market leaders. However, mistakes made by Walmart in that same period allowed ALDI SÜD ...
Harvard Business Review (714474-PDF-ENG) February 07, 2014. Case questions answered: ... Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter Case Answers. You will receive access to two case study solutions! The second is not yet visible in the preview. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY - ALDI.
This video is about Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter case study. We have discussed the case study in detail. Specifically, Aldi: The Dark Horse Discounter Har...
In 2013, Aldi - the world's 8th largest retailer - planned to accelerate its US expansion. ... Published by: Harvard Business Publishing Originally published in: 2014 Version: 8 December 2016 Revision date: 20-Dec-2016 Length: 16 pages ... The Case Centre Cranfield University, Wharley End, Bedfordshire. MK43 0JR, UK
ALDI THE DARK HORSE DISCOUNTER Case Study Solution. Case Summary. Aldi had remained as one of the least known grocers in 2013, despite the 2012 estimated sales of $73 billion from around 10,000 stores of the company that had been operating in 17 countries of the world. Aldi is a privately held grocer in Germany.
Harvard Business Case Studies Solutions - Assignment Help. Aldi: ... Case Study Description. In 2013, Aldi-the world's 8th largest retailer-planned to accelerate its US expansion. Aldi was a German-based hard discounter that sold a limited assortment of private-label groceries and household items in barebones stores. Despite its presence with ...
Aldi: The dark horse discounter Case Study Solution Aldi's Strategy: Aldi follows its own set of standard actions as well as values making it unique organizational strategy. The strategy of business and operating model revolves around 3 core factors i.e. low prices, strong culture and efficient operations.
Aldi's Innovative Grocery Business Model Vs Walmart Case Solution. Firstly, ALDI's value proposition is not extremely unique and is easily imitable, which has invited other players in the industry through adopting ALDI' business model. Moreover, consistency is the key element of ALDI's innovation based business model and it is becoming difficult for ALDIto maintain consistency in the ...
Step 1. Answer 3. Aldi Case Study in increasingly competitive markets, consumers have a greater choice over where they buy their goods and services. For an organization to meet its business objectives, it has to find out what consumers require and then identify the best way in which it can satisfy these needs and wants.
See Full PDFDownload PDF. Case study ALDI STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT f Case Study - ALDI Brief Overview of ALDI: In Essen Germany, Aldi was founded by 2 brothers Karl & Theo Albrecht in 1013. In 1960 they had 300 stores in Germany, they work hard and put all their efforts in making best retailer of grocery in Germany.
The Case Analysis Coach is an interactive tutorial on reading and analyzing a case study. The Case Study Handbook covers key skills students need to read, understand, discuss and write about cases. The Case Study Handbook is also available as individual chapters to help your students focus on specific skills.
The porter's five forces model is discussed in detail below: Bargaining Power of Buyer. Most of the products sold by the company are private brands and are indirectly owned by the ALDI. Hence, offering low pricing of products to the customers indicates that the company's bargaining power with its suppliers is strong.
STEP 2: Reading The The Success Of Aldi Harvard Case Study: To have a complete understanding of the case, one should focus on case reading. It is said that case should be read two times. Initially, fast reading without taking notes and underlines should be done. Initial reading is to get a rough idea of what information is provided for the ...
Aldi Case Study Harvard, Ielts Essay Writing By Liz, Paradise Island Ess, Esl Descriptive Essay Writer Services Usa, How To Write Comment In Vbscript, Top Resume Editing Website, Literature Review On Paranoid Schizophrenia
Aldi Case Study Harvard, Professional Custom Essay Proofreading Service For School, Desert Edge Brewery Nutrition, Creative Writing Assistant Jobs, Pay To Do Professional Personal Essay On Donald Trump, Peer Assessment Literature Review, Victor Cheng Mckinsey Problem Solving Test
The Aldi Brand Case Solution,The Aldi Brand Case Analysis, The Aldi Brand Case Study Solution, The Aldi Brand Case Study Solution On the other hand, Coles and Wool worths were initially just focused on selling national brands with an extensive
Harvard Business Publishing is an affiliate of Harvard Business School. We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More .
ID 21067. Nursing Management Business and Economics Ethnicity Studies +90. Location. Any. 741 Orders prepared. Susan Devlin. Aldi Case Study Harvard -.