Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.

The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
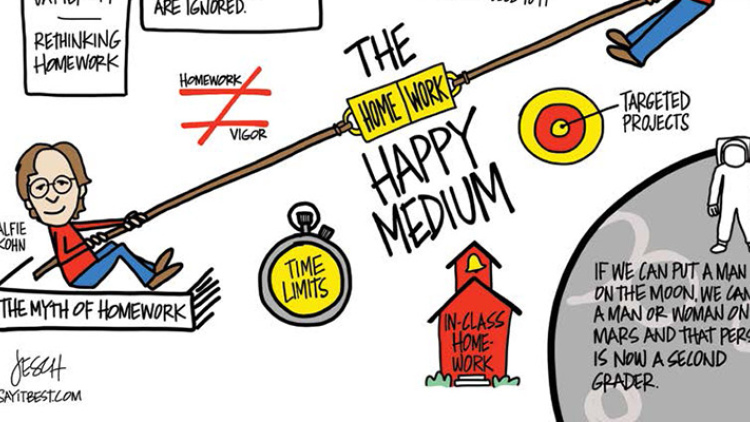
Are You Down With or Done With Homework?
- Posted January 17, 2012
- By Lory Hough

The debate over how much schoolwork students should be doing at home has flared again, with one side saying it's too much, the other side saying in our competitive world, it's just not enough.
It was a move that doesn't happen very often in American public schools: The principal got rid of homework.
This past September, Stephanie Brant, principal of Gaithersburg Elementary School in Gaithersburg, Md., decided that instead of teachers sending kids home with math worksheets and spelling flash cards, students would instead go home and read. Every day for 30 minutes, more if they had time or the inclination, with parents or on their own.
"I knew this would be a big shift for my community," she says. But she also strongly believed it was a necessary one. Twenty-first-century learners, especially those in elementary school, need to think critically and understand their own learning — not spend night after night doing rote homework drills.
Brant's move may not be common, but she isn't alone in her questioning. The value of doing schoolwork at home has gone in and out of fashion in the United States among educators, policymakers, the media, and, more recently, parents. As far back as the late 1800s, with the rise of the Progressive Era, doctors such as Joseph Mayer Rice began pushing for a limit on what he called "mechanical homework," saying it caused childhood nervous conditions and eyestrain. Around that time, the then-influential Ladies Home Journal began publishing a series of anti-homework articles, stating that five hours of brain work a day was "the most we should ask of our children," and that homework was an intrusion on family life. In response, states like California passed laws abolishing homework for students under a certain age.
But, as is often the case with education, the tide eventually turned. After the Russians launched the Sputnik satellite in 1957, a space race emerged, and, writes Brian Gill in the journal Theory Into Practice, "The homework problem was reconceived as part of a national crisis; the U.S. was losing the Cold War because Russian children were smarter." Many earlier laws limiting homework were abolished, and the longterm trend toward less homework came to an end.
The debate re-emerged a decade later when parents of the late '60s and '70s argued that children should be free to play and explore — similar anti-homework wellness arguments echoed nearly a century earlier. By the early-1980s, however, the pendulum swung again with the publication of A Nation at Risk , which blamed poor education for a "rising tide of mediocrity." Students needed to work harder, the report said, and one way to do this was more homework.
For the most part, this pro-homework sentiment is still going strong today, in part because of mandatory testing and continued economic concerns about the nation's competitiveness. Many believe that today's students are falling behind their peers in places like Korea and Finland and are paying more attention to Angry Birds than to ancient Babylonia.
But there are also a growing number of Stephanie Brants out there, educators and parents who believe that students are stressed and missing out on valuable family time. Students, they say, particularly younger students who have seen a rise in the amount of take-home work and already put in a six- to nine-hour "work" day, need less, not more homework.
Who is right? Are students not working hard enough or is homework not working for them? Here's where the story gets a little tricky: It depends on whom you ask and what research you're looking at. As Cathy Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework , points out, "Homework has generated enough research so that a study can be found to support almost any position, as long as conflicting studies are ignored." Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth and a strong believer in eliminating all homework, writes that, "The fact that there isn't anything close to unanimity among experts belies the widespread assumption that homework helps." At best, he says, homework shows only an association, not a causal relationship, with academic achievement. In other words, it's hard to tease out how homework is really affecting test scores and grades. Did one teacher give better homework than another? Was one teacher more effective in the classroom? Do certain students test better or just try harder?
"It is difficult to separate where the effect of classroom teaching ends," Vatterott writes, "and the effect of homework begins."
Putting research aside, however, much of the current debate over homework is focused less on how homework affects academic achievement and more on time. Parents in particular have been saying that the amount of time children spend in school, especially with afterschool programs, combined with the amount of homework given — as early as kindergarten — is leaving students with little time to run around, eat dinner with their families, or even get enough sleep.
Certainly, for some parents, homework is a way to stay connected to their children's learning. But for others, homework creates a tug-of-war between parents and children, says Liz Goodenough, M.A.T.'71, creator of a documentary called Where Do the Children Play?
"Ideally homework should be about taking something home, spending a few curious and interesting moments in which children might engage with parents, and then getting that project back to school — an organizational triumph," she says. "A nag-free activity could engage family time: Ask a parent about his or her own childhood. Interview siblings."

Instead, as the authors of The Case Against Homework write, "Homework overload is turning many of us into the types of parents we never wanted to be: nags, bribers, and taskmasters."
Leslie Butchko saw it happen a few years ago when her son started sixth grade in the Santa Monica-Malibu (Calif.) United School District. She remembers him getting two to four hours of homework a night, plus weekend and vacation projects. He was overwhelmed and struggled to finish assignments, especially on nights when he also had an extracurricular activity.
"Ultimately, we felt compelled to have Bobby quit karate — he's a black belt — to allow more time for homework," she says. And then, with all of their attention focused on Bobby's homework, she and her husband started sending their youngest to his room so that Bobby could focus. "One day, my younger son gave us 15-minute coupons as a present for us to use to send him to play in the back room. … It was then that we realized there had to be something wrong with the amount of homework we were facing."
Butchko joined forces with another mother who was having similar struggles and ultimately helped get the homework policy in her district changed, limiting homework on weekends and holidays, setting time guidelines for daily homework, and broadening the definition of homework to include projects and studying for tests. As she told the school board at one meeting when the policy was first being discussed, "In closing, I just want to say that I had more free time at Harvard Law School than my son has in middle school, and that is not in the best interests of our children."
One barrier that Butchko had to overcome initially was convincing many teachers and parents that more homework doesn't necessarily equal rigor.
"Most of the parents that were against the homework policy felt that students need a large quantity of homework to prepare them for the rigorous AP classes in high school and to get them into Harvard," she says.
Stephanie Conklin, Ed.M.'06, sees this at Another Course to College, the Boston pilot school where she teaches math. "When a student is not completing [his or her] homework, parents usually are frustrated by this and agree with me that homework is an important part of their child's learning," she says.
As Timothy Jarman, Ed.M.'10, a ninth-grade English teacher at Eugene Ashley High School in Wilmington, N.C., says, "Parents think it is strange when their children are not assigned a substantial amount of homework."
That's because, writes Vatterott, in her chapter, "The Cult(ure) of Homework," the concept of homework "has become so engrained in U.S. culture that the word homework is part of the common vernacular."
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn.
"Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of time that children will have to do something every night (or several times a week). … This commitment to the idea of homework in the abstract is accepted by the overwhelming majority of schools — public and private, elementary and secondary."
Brant had to confront this when she cut homework at Gaithersburg Elementary.
"A lot of my parents have this idea that homework is part of life. This is what I had to do when I was young," she says, and so, too, will our kids. "So I had to shift their thinking." She did this slowly, first by asking her teachers last year to really think about what they were sending home. And this year, in addition to forming a parent advisory group around the issue, she also holds events to answer questions.
Still, not everyone is convinced that homework as a given is a bad thing. "Any pursuit of excellence, be it in sports, the arts, or academics, requires hard work. That our culture finds it okay for kids to spend hours a day in a sport but not equal time on academics is part of the problem," wrote one pro-homework parent on the blog for the documentary Race to Nowhere , which looks at the stress American students are under. "Homework has always been an issue for parents and children. It is now and it was 20 years ago. I think when people decide to have children that it is their responsibility to educate them," wrote another.
And part of educating them, some believe, is helping them develop skills they will eventually need in adulthood. "Homework can help students develop study skills that will be of value even after they leave school," reads a publication on the U.S. Department of Education website called Homework Tips for Parents. "It can teach them that learning takes place anywhere, not just in the classroom. … It can foster positive character traits such as independence and responsibility. Homework can teach children how to manage time."
Annie Brown, Ed.M.'01, feels this is particularly critical at less affluent schools like the ones she has worked at in Boston, Cambridge, Mass., and Los Angeles as a literacy coach.
"It feels important that my students do homework because they will ultimately be competing for college placement and jobs with students who have done homework and have developed a work ethic," she says. "Also it will get them ready for independently taking responsibility for their learning, which will need to happen for them to go to college."
The problem with this thinking, writes Vatterott, is that homework becomes a way to practice being a worker.
"Which begs the question," she writes. "Is our job as educators to produce learners or workers?"
Slate magazine editor Emily Bazelon, in a piece about homework, says this makes no sense for younger kids.
"Why should we think that practicing homework in first grade will make you better at doing it in middle school?" she writes. "Doesn't the opposite seem equally plausible: that it's counterproductive to ask children to sit down and work at night before they're developmentally ready because you'll just make them tired and cross?"
Kohn writes in the American School Board Journal that this "premature exposure" to practices like homework (and sit-and-listen lessons and tests) "are clearly a bad match for younger children and of questionable value at any age." He calls it BGUTI: Better Get Used to It. "The logic here is that we have to prepare you for the bad things that are going to be done to you later … by doing them to you now."
According to a recent University of Michigan study, daily homework for six- to eight-year-olds increased on average from about 8 minutes in 1981 to 22 minutes in 2003. A review of research by Duke University Professor Harris Cooper found that for elementary school students, "the average correlation between time spent on homework and achievement … hovered around zero."
So should homework be eliminated? Of course not, say many Ed School graduates who are teaching. Not only would students not have time for essays and long projects, but also teachers would not be able to get all students to grade level or to cover critical material, says Brett Pangburn, Ed.M.'06, a sixth-grade English teacher at Excel Academy Charter School in Boston. Still, he says, homework has to be relevant.
"Kids need to practice the skills being taught in class, especially where, like the kids I teach at Excel, they are behind and need to catch up," he says. "Our results at Excel have demonstrated that kids can catch up and view themselves as in control of their academic futures, but this requires hard work, and homework is a part of it."
Ed School Professor Howard Gardner basically agrees.
"America and Americans lurch between too little homework in many of our schools to an excess of homework in our most competitive environments — Li'l Abner vs. Tiger Mother," he says. "Neither approach makes sense. Homework should build on what happens in class, consolidating skills and helping students to answer new questions."
So how can schools come to a happy medium, a way that allows teachers to cover everything they need while not overwhelming students? Conklin says she often gives online math assignments that act as labs and students have two or three days to complete them, including some in-class time. Students at Pangburn's school have a 50-minute silent period during regular school hours where homework can be started, and where teachers pull individual or small groups of students aside for tutoring, often on that night's homework. Afterschool homework clubs can help.
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.) Other schools offer an extended day that allows teachers to cover more material in school, in turn requiring fewer take-home assignments. And for others, like Stephanie Brant's elementary school in Maryland, more reading with a few targeted project assignments has been the answer.
"The routine of reading is so much more important than the routine of homework," she says. "Let's have kids reflect. You can still have the routine and you can still have your workspace, but now it's for reading. I often say to parents, if we can put a man on the moon, we can put a man or woman on Mars and that person is now a second-grader. We don't know what skills that person will need. At the end of the day, we have to feel confident that we're giving them something they can use on Mars."
Read a January 2014 update.
Homework Policy Still Going Strong
Ed. Magazine
The magazine of the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Commencement Marshal Sarah Fiarman: The Principal of the Matter

Making Math “Almost Fun”
Alum develops curriculum to entice reluctant math learners

Lessons Learned: Zid Mancenido, Ph.D.'22
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/71970990/05_nohomework_Jiayue_Li.0.jpg)
Filed under:
- The Highlight
Nobody knows what the point of homework is
The homework wars are back.
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: Nobody knows what the point of homework is
As the Covid-19 pandemic began and students logged into their remote classrooms, all work, in effect, became homework. But whether or not students could complete it at home varied. For some, schoolwork became public-library work or McDonald’s-parking-lot work.
Luis Torres, the principal of PS 55, a predominantly low-income community elementary school in the south Bronx, told me that his school secured Chromebooks for students early in the pandemic only to learn that some lived in shelters that blocked wifi for security reasons. Others, who lived in housing projects with poor internet reception, did their schoolwork in laundromats.
According to a 2021 Pew survey , 25 percent of lower-income parents said their children, at some point, were unable to complete their schoolwork because they couldn’t access a computer at home; that number for upper-income parents was 2 percent.
The issues with remote learning in March 2020 were new. But they highlighted a divide that had been there all along in another form: homework. And even long after schools have resumed in-person classes, the pandemic’s effects on homework have lingered.
Over the past three years, in response to concerns about equity, schools across the country, including in Sacramento, Los Angeles , San Diego , and Clark County, Nevada , made permanent changes to their homework policies that restricted how much homework could be given and how it could be graded after in-person learning resumed.
Three years into the pandemic, as districts and teachers reckon with Covid-era overhauls of teaching and learning, schools are still reconsidering the purpose and place of homework. Whether relaxing homework expectations helps level the playing field between students or harms them by decreasing rigor is a divisive issue without conclusive evidence on either side, echoing other debates in education like the elimination of standardized test scores from some colleges’ admissions processes.
I first began to wonder if the homework abolition movement made sense after speaking with teachers in some Massachusetts public schools, who argued that rather than help disadvantaged kids, stringent homework restrictions communicated an attitude of low expectations. One, an English teacher, said she felt the school had “just given up” on trying to get the students to do work; another argued that restrictions that prohibit teachers from assigning take-home work that doesn’t begin in class made it difficult to get through the foreign-language curriculum. Teachers in other districts have raised formal concerns about homework abolition’s ability to close gaps among students rather than widening them.
Many education experts share this view. Harris Cooper, a professor emeritus of psychology at Duke who has studied homework efficacy, likened homework abolition to “playing to the lowest common denominator.”
But as I learned after talking to a variety of stakeholders — from homework researchers to policymakers to parents of schoolchildren — whether to abolish homework probably isn’t the right question. More important is what kind of work students are sent home with and where they can complete it. Chances are, if schools think more deeply about giving constructive work, time spent on homework will come down regardless.
There’s no consensus on whether homework works
The rise of the no-homework movement during the Covid-19 pandemic tapped into long-running disagreements over homework’s impact on students. The purpose and effectiveness of homework have been disputed for well over a century. In 1901, for instance, California banned homework for students up to age 15, and limited it for older students, over concerns that it endangered children’s mental and physical health. The newest iteration of the anti-homework argument contends that the current practice punishes students who lack support and rewards those with more resources, reinforcing the “myth of meritocracy.”
But there is still no research consensus on homework’s effectiveness; no one can seem to agree on what the right metrics are. Much of the debate relies on anecdotes, intuition, or speculation.
Researchers disagree even on how much research exists on the value of homework. Kathleen Budge, the co-author of Turning High-Poverty Schools Into High-Performing Schools and a professor at Boise State, told me that homework “has been greatly researched.” Denise Pope, a Stanford lecturer and leader of the education nonprofit Challenge Success, said, “It’s not a highly researched area because of some of the methodological problems.”
Experts who are more sympathetic to take-home assignments generally support the “10-minute rule,” a framework that estimates the ideal amount of homework on any given night by multiplying the student’s grade by 10 minutes. (A ninth grader, for example, would have about 90 minutes of work a night.) Homework proponents argue that while it is difficult to design randomized control studies to test homework’s effectiveness, the vast majority of existing studies show a strong positive correlation between homework and high academic achievement for middle and high school students. Prominent critics of homework argue that these correlational studies are unreliable and point to studies that suggest a neutral or negative effect on student performance. Both agree there is little to no evidence for homework’s effectiveness at an elementary school level, though proponents often argue that it builds constructive habits for the future.
For anyone who remembers homework assignments from both good and bad teachers, this fundamental disagreement might not be surprising. Some homework is pointless and frustrating to complete. Every week during my senior year of high school, I had to analyze a poem for English and decorate it with images found on Google; my most distinct memory from that class is receiving a demoralizing 25-point deduction because I failed to present my analysis on a poster board. Other assignments really do help students learn: After making an adapted version of Chairman Mao’s Little Red Book for a ninth grade history project, I was inspired to check out from the library and read a biography of the Chinese ruler.
For homework opponents, the first example is more likely to resonate. “We’re all familiar with the negative effects of homework: stress, exhaustion, family conflict, less time for other activities, diminished interest in learning,” Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth, which challenges common justifications for homework, told me in an email. “And these effects may be most pronounced among low-income students.” Kohn believes that schools should make permanent any moratoria implemented during the pandemic, arguing that there are no positives at all to outweigh homework’s downsides. Recent studies , he argues , show the benefits may not even materialize during high school.
In the Marlborough Public Schools, a suburban district 45 minutes west of Boston, school policy committee chair Katherine Hennessy described getting kids to complete their homework during remote education as “a challenge, to say the least.” Teachers found that students who spent all day on their computers didn’t want to spend more time online when the day was over. So, for a few months, the school relaxed the usual practice and teachers slashed the quantity of nightly homework.
Online learning made the preexisting divides between students more apparent, she said. Many students, even during normal circumstances, lacked resources to keep them on track and focused on completing take-home assignments. Though Marlborough Schools is more affluent than PS 55, Hennessy said many students had parents whose work schedules left them unable to provide homework help in the evenings. The experience tracked with a common divide in the country between children of different socioeconomic backgrounds.
So in October 2021, months after the homework reduction began, the Marlborough committee made a change to the district’s policy. While teachers could still give homework, the assignments had to begin as classwork. And though teachers could acknowledge homework completion in a student’s participation grade, they couldn’t count homework as its own grading category. “Rigorous learning in the classroom does not mean that that classwork must be assigned every night,” the policy stated . “Extensions of class work is not to be used to teach new content or as a form of punishment.”
Canceling homework might not do anything for the achievement gap
The critiques of homework are valid as far as they go, but at a certain point, arguments against homework can defy the commonsense idea that to retain what they’re learning, students need to practice it.
“Doesn’t a kid become a better reader if he reads more? Doesn’t a kid learn his math facts better if he practices them?” said Cathy Vatterott, an education researcher and professor emeritus at the University of Missouri-St. Louis. After decades of research, she said it’s still hard to isolate the value of homework, but that doesn’t mean it should be abandoned.
Blanket vilification of homework can also conflate the unique challenges facing disadvantaged students as compared to affluent ones, which could have different solutions. “The kids in the low-income schools are being hurt because they’re being graded, unfairly, on time they just don’t have to do this stuff,” Pope told me. “And they’re still being held accountable for turning in assignments, whether they’re meaningful or not.” On the other side, “Palo Alto kids” — students in Silicon Valley’s stereotypically pressure-cooker public schools — “are just bombarded and overloaded and trying to stay above water.”
Merely getting rid of homework doesn’t solve either problem. The United States already has the second-highest disparity among OECD (the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) nations between time spent on homework by students of high and low socioeconomic status — a difference of more than three hours, said Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University and author of No More Mindless Homework .
When she interviewed teachers in Boston-area schools that had cut homework before the pandemic, Bempechat told me, “What they saw immediately was parents who could afford it immediately enrolled their children in the Russian School of Mathematics,” a math-enrichment program whose tuition ranges from $140 to about $400 a month. Getting rid of homework “does nothing for equity; it increases the opportunity gap between wealthier and less wealthy families,” she said. “That solution troubles me because it’s no solution at all.”
A group of teachers at Wakefield High School in Arlington, Virginia, made the same point after the school district proposed an overhaul of its homework policies, including removing penalties for missing homework deadlines, allowing unlimited retakes, and prohibiting grading of homework.
“Given the emphasis on equity in today’s education systems,” they wrote in a letter to the school board, “we believe that some of the proposed changes will actually have a detrimental impact towards achieving this goal. Families that have means could still provide challenging and engaging academic experiences for their children and will continue to do so, especially if their children are not experiencing expected rigor in the classroom.” At a school where more than a third of students are low-income, the teachers argued, the policies would prompt students “to expect the least of themselves in terms of effort, results, and responsibility.”
Not all homework is created equal
Despite their opposing sides in the homework wars, most of the researchers I spoke to made a lot of the same points. Both Bempechat and Pope were quick to bring up how parents and schools confuse rigor with workload, treating the volume of assignments as a proxy for quality of learning. Bempechat, who is known for defending homework, has written extensively about how plenty of it lacks clear purpose, requires the purchasing of unnecessary supplies, and takes longer than it needs to. Likewise, when Pope instructs graduate-level classes on curriculum, she asks her students to think about the larger purpose they’re trying to achieve with homework: If they can get the job done in the classroom, there’s no point in sending home more work.
At its best, pandemic-era teaching facilitated that last approach. Honolulu-based teacher Christina Torres Cawdery told me that, early in the pandemic, she often had a cohort of kids in her classroom for four hours straight, as her school tried to avoid too much commingling. She couldn’t lecture for four hours, so she gave the students plenty of time to complete independent and project-based work. At the end of most school days, she didn’t feel the need to send them home with more to do.
A similar limited-homework philosophy worked at a public middle school in Chelsea, Massachusetts. A couple of teachers there turned as much class as possible into an opportunity for small-group practice, allowing kids to work on problems that traditionally would be assigned for homework, Jessica Flick, a math coach who leads department meetings at the school, told me. It was inspired by a philosophy pioneered by Simon Fraser University professor Peter Liljedahl, whose influential book Building Thinking Classrooms in Mathematics reframes homework as “check-your-understanding questions” rather than as compulsory work. Last year, Flick found that the two eighth grade classes whose teachers adopted this strategy performed the best on state tests, and this year, she has encouraged other teachers to implement it.
Teachers know that plenty of homework is tedious and unproductive. Jeannemarie Dawson De Quiroz, who has taught for more than 20 years in low-income Boston and Los Angeles pilot and charter schools, says that in her first years on the job she frequently assigned “drill and kill” tasks and questions that she now feels unfairly stumped students. She said designing good homework wasn’t part of her teaching programs, nor was it meaningfully discussed in professional development. With more experience, she turned as much class time as she could into practice time and limited what she sent home.
“The thing about homework that’s sticky is that not all homework is created equal,” says Jill Harrison Berg, a former teacher and the author of Uprooting Instructional Inequity . “Some homework is a genuine waste of time and requires lots of resources for no good reason. And other homework is really useful.”
Cutting homework has to be part of a larger strategy
The takeaways are clear: Schools can make cuts to homework, but those cuts should be part of a strategy to improve the quality of education for all students. If the point of homework was to provide more practice, districts should think about how students can make it up during class — or offer time during or after school for students to seek help from teachers. If it was to move the curriculum along, it’s worth considering whether strategies like Liljedahl’s can get more done in less time.
Some of the best thinking around effective assignments comes from those most critical of the current practice. Denise Pope proposes that, before assigning homework, teachers should consider whether students understand the purpose of the work and whether they can do it without help. If teachers think it’s something that can’t be done in class, they should be mindful of how much time it should take and the feedback they should provide. It’s questions like these that De Quiroz considered before reducing the volume of work she sent home.
More than a year after the new homework policy began in Marlborough, Hennessy still hears from parents who incorrectly “think homework isn’t happening” despite repeated assurances that kids still can receive work. She thinks part of the reason is that education has changed over the years. “I think what we’re trying to do is establish that homework may be an element of educating students,” she told me. “But it may not be what parents think of as what they grew up with. ... It’s going to need to adapt, per the teaching and the curriculum, and how it’s being delivered in each classroom.”
For the policy to work, faculty, parents, and students will all have to buy into a shared vision of what school ought to look like. The district is working on it — in November, it hosted and uploaded to YouTube a round-table discussion on homework between district administrators — but considering the sustained confusion, the path ahead seems difficult.
When I asked Luis Torres about whether he thought homework serves a useful part in PS 55’s curriculum, he said yes, of course it was — despite the effort and money it takes to keep the school open after hours to help them do it. “The children need the opportunity to practice,” he said. “If you don’t give them opportunities to practice what they learn, they’re going to forget.” But Torres doesn’t care if the work is done at home. The school stays open until around 6 pm on weekdays, even during breaks. Tutors through New York City’s Department of Youth and Community Development programs help kids with work after school so they don’t need to take it with them.
As schools weigh the purpose of homework in an unequal world, it’s tempting to dispose of a practice that presents real, practical problems to students across the country. But getting rid of homework is unlikely to do much good on its own. Before cutting it, it’s worth thinking about what good assignments are meant to do in the first place. It’s crucial that students from all socioeconomic backgrounds tackle complex quantitative problems and hone their reading and writing skills. It’s less important that the work comes home with them.
Jacob Sweet is a freelance writer in Somerville, Massachusetts. He is a frequent contributor to the New Yorker, among other publications.
Will you help keep Vox free for all?
Millions rely on Vox’s journalism to understand the coronavirus crisis. We believe it pays off for all of us, as a society and a democracy, when our neighbors and fellow citizens can access clear, concise information on the pandemic. But our distinctive explanatory journalism is expensive. Support from our readers helps us keep it free for everyone. If you have already made a financial contribution to Vox, thank you. If not, please consider making a contribution today from as little as $3.
We accept credit card, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. You can also contribute via
Can we protect and profit from the oceans?
Sometimes kids need a push. here’s how to do it kindly., who gets to flourish, sign up for the newsletter today, explained, thanks for signing up.
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.
Is Homework Good for Kids? Here’s What the Research Says
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.
The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in Texas went viral last week , earning praise from parents across the country who lament the heavy workload often assigned to young students. Brandy Young told parents she would not formally assign any homework this year, asking students instead to eat dinner with their families, play outside and go to bed early.
But the question of how much work children should be doing outside of school remains controversial, and plenty of parents take issue with no-homework policies, worried their kids are losing a potential academic advantage. Here’s what you need to know:
For decades, the homework standard has been a “10-minute rule,” which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 minutes of homework each night. High school seniors should complete about two hours of homework each night. The National PTA and the National Education Association both support that guideline.
But some schools have begun to give their youngest students a break. A Massachusetts elementary school has announced a no-homework pilot program for the coming school year, lengthening the school day by two hours to provide more in-class instruction. “We really want kids to go home at 4 o’clock, tired. We want their brain to be tired,” Kelly Elementary School Principal Jackie Glasheen said in an interview with a local TV station . “We want them to enjoy their families. We want them to go to soccer practice or football practice, and we want them to go to bed. And that’s it.”
A New York City public elementary school implemented a similar policy last year, eliminating traditional homework assignments in favor of family time. The change was quickly met with outrage from some parents, though it earned support from other education leaders.
New solutions and approaches to homework differ by community, and these local debates are complicated by the fact that even education experts disagree about what’s best for kids.
The research
The most comprehensive research on homework to date comes from a 2006 meta-analysis by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper, who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was stronger for older students—in seventh through 12th grade—than for those in younger grades, for whom there was a weak relationship between homework and performance.
Cooper’s analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school, self-discipline, inquisitiveness and independent problem solving skills. On the other hand, some studies he examined showed that homework can cause physical and emotional fatigue, fuel negative attitudes about learning and limit leisure time for children. At the end of his analysis, Cooper recommended further study of such potential effects of homework.
Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing two hours of homework each night, he said, but they also shouldn’t be doing no homework.
Not all education experts agree entirely with Cooper’s assessment.
Cathy Vatterott, an education professor at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, supports the “10-minute rule” as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary school.
“Correlation is not causation,” she said. “Does homework cause achievement, or do high achievers do more homework?”
Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs , thinks there should be more emphasis on improving the quality of homework tasks, and she supports efforts to eliminate homework for younger kids.
“I have no concerns about students not starting homework until fourth grade or fifth grade,” she said, noting that while the debate over homework will undoubtedly continue, she has noticed a trend toward limiting, if not eliminating, homework in elementary school.
The issue has been debated for decades. A TIME cover in 1999 read: “Too much homework! How it’s hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.” The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push for better math and science education in the U.S. The ensuing pressure to be competitive on a global scale, plus the increasingly demanding college admissions process, fueled the practice of assigning homework.
“The complaints are cyclical, and we’re in the part of the cycle now where the concern is for too much,” Cooper said. “You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness.”
Cooper acknowledged that some students really are bringing home too much homework, and their parents are right to be concerned.
“A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements,” he said. “If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.”
More Must-Reads From TIME
- Biden’s Campaign Is In Trouble. Will the Turnaround Plan Work?
- Why We're Spending So Much Money Now
- The Financial Influencers Women Actually Want to Listen To
- Breaker Sunny Choi Is Heading to Paris
- The UAE Is on a Mission to Become an AI Power
- Why TV Can’t Stop Making Silly Shows About Lady Journalists
- The Case for Wearing Shoes in the House
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Katie Reilly at [email protected]
You May Also Like
- Subscribe to BBC Science Focus Magazine
- Previous Issues
- Future tech
- Everyday science
- Planet Earth
- Newsletters
Should homework be banned?
Social media has sparked into life about whether children should be given homework - should students be freed from this daily chore? Dr Gerald Letendre, a professor of education at Pennsylvania State University, investigates.
We’ve all done it: pretended to leave an essay at home, or stayed up until 2am to finish a piece of coursework we’ve been ignoring for weeks. Homework, for some people, is seen as a chore that’s ‘wrecking kids’ or ‘killing parents’, while others think it is an essential part of a well-rounded education. The problem is far from new: public debates about homework have been raging since at least the early-1900s, and recently spilled over into a Twitter feud between Gary Lineker and Piers Morgan.
Ironically, the conversation surrounding homework often ignores the scientific ‘homework’ that researchers have carried out. Many detailed studies have been conducted, and can guide parents, teachers and administrators to make sensible decisions about how much work should be completed by students outside of the classroom.
So why does homework stir up such strong emotions? One reason is that, by its very nature, it is an intrusion of schoolwork into family life. I carried out a study in 2005, and found that the amount of time that children and adolescents spend in school, from nursery right up to the end of compulsory education, has greatly increased over the last century . This means that more of a child’s time is taken up with education, so family time is reduced. This increases pressure on the boundary between the family and the school.
Plus, the amount of homework that students receive appears to be increasing, especially in the early years when parents are keen for their children to play with friends and spend time with the family.
Finally, success in school has become increasingly important to success in life. Parents can use homework to promote, or exercise control over, their child’s academic trajectory, and hopefully ensure their future educational success. But this often leaves parents conflicted – they want their children to be successful in school, but they don’t want them to be stressed or upset because of an unmanageable workload.
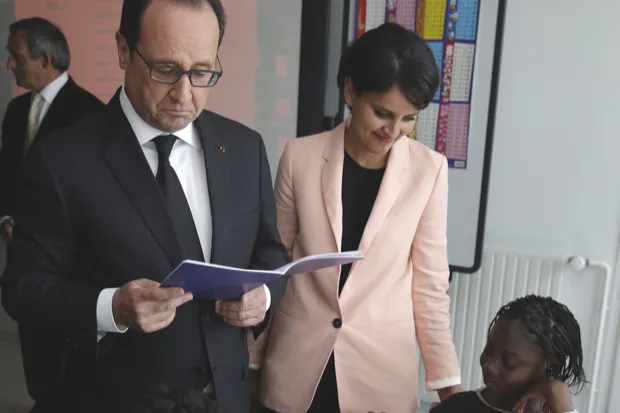

However, the issue isn’t simply down to the opinions of parents, children and their teachers – governments also like to get involved. In the autumn of 2012, French president François Hollande hit world headlines after making a comment about banning homework, ostensibly because it promoted inequality. The Chinese government has also toyed with a ban, because of concerns about excessive academic pressure being put on children.
The problem is, some politicians and national administrators regard regulatory policy in education as a solution for a wide array of social, economic and political issues, perhaps without considering the consequences for students and parents.
Does homework work?
Homework seems to generally have a positive effect for high school students, according to an extensive range of empirical literature. For example, Duke University’s Prof Harris Cooper carried out a meta-analysis using data from US schools, covering a period from 1987 to 2003. He found that homework offered a general beneficial impact on test scores and improvements in attitude, with a greater effect seen in older students. But dig deeper into the issue and a complex set of factors quickly emerges, related to how much homework students do, and exactly how they feel about it.
In 2009, Prof Ulrich Trautwein and his team at the University of Tübingen found that in order to establish whether homework is having any effect, researchers must take into account the differences both between and within classes . For example, a teacher may assign a good deal of homework to a lower-level class, producing an association between more homework and lower levels of achievement. Yet, within the same class, individual students may vary significantly in how much homework improves their baseline performance. Plus, there is the fact that some students are simply more efficient at completing their homework than others, and it becomes quite difficult to pinpoint just what type of homework, and how much of it, will affect overall academic performance.
Over the last century, the amount of time that children and adolescents spend in school has greatly increased
Gender is also a major factor. For example, a study of US high school students carried out by Prof Gary Natriello in the 1980s revealed that girls devote more time to homework than boys, while a follow-up study found that US girls tend to spend more time on mathematics homework than boys. Another study, this time of African-American students in the US, found that eighth grade (ages 13-14) girls were more likely to successfully manage both their tasks and emotions around schoolwork, and were more likely to finish homework.
So why do girls seem to respond more positively to homework? One possible answer proposed by Eunsook Hong of the University of Nevada in 2011 is that teachers tend to rate girls’ habits and attitudes towards work more favourably than boys’. This perception could potentially set up a positive feedback loop between teacher expectations and the children’s capacity for academic work based on gender, resulting in girls outperforming boys. All of this makes it particularly difficult to determine the extent to which homework is helping, though it is clear that simply increasing the time spent on assignments does not directly correspond to a universal increase in learning.
Can homework cause damage?
The lack of empirical data supporting homework in the early years of education, along with an emerging trend to assign more work to this age range, appears to be fuelling parental concerns about potential negative effects. But, aside from anecdotes of increased tension in the household, is there any evidence of this? Can doing too much homework actually damage children?
Evidence suggests extreme amounts of homework can indeed have serious effects on students’ health and well-being. A Chinese study carried out in 2010 found a link between excessive homework and sleep disruption: children who had less homework had better routines and more stable sleep schedules. A Canadian study carried out in 2015 by Isabelle Michaud found that high levels of homework were associated with a greater risk of obesity among boys, if they were already feeling stressed about school in general.
For useful revision guides and video clips to assist with learning, visit BBC Bitesize . This is a free online study resource for UK students from early years up to GCSEs and Scottish Highers.
It is also worth noting that too much homework can create negative effects that may undermine any positives. These negative consequences may not only affect the child, but also could also pile on the stress for the whole family, according to a recent study by Robert Pressman of the New England Centre for Pediatric Psychology. Parents were particularly affected when their perception of their own capacity to assist their children decreased.
What then, is the tipping point, and when does homework simply become too much for parents and children? Guidelines typically suggest that children in the first grade (six years old) should have no more that 10 minutes per night, and that this amount should increase by 10 minutes per school year. However, cultural norms may greatly affect what constitutes too much.
A study of children aged between 8 and 10 in Quebec defined high levels of homework as more than 30 minutes a night, but a study in China of children aged 5 to 11 deemed that two or more hours per night was excessive. It is therefore difficult to create a clear standard for what constitutes as too much homework, because cultural differences, school-related stress, and negative emotions within the family all appear to interact with how homework affects children.
Should we stop setting homework?
In my opinion, even though there are potential risks of negative effects, homework should not be banned. Small amounts, assigned with specific learning goals in mind and with proper parental support, can help to improve students’ performance. While some studies have generally found little evidence that homework has a positive effect on young children overall, a 2008 study by Norwegian researcher Marte Rønning found that even some very young children do receive some benefit. So simply banning homework would mean that any particularly gifted or motivated pupils would not be able to benefit from increased study. However, at the earliest ages, very little homework should be assigned. The decisions about how much and what type are best left to teachers and parents.
As a parent, it is important to clarify what goals your child’s teacher has for homework assignments. Teachers can assign work for different reasons – as an academic drill to foster better study habits, and unfortunately, as a punishment. The goals for each assignment should be made clear, and should encourage positive engagement with academic routines.

Parents should inform the teachers of how long the homework is taking, as teachers often incorrectly estimate the amount of time needed to complete an assignment, and how it is affecting household routines. For young children, positive teacher support and feedback is critical in establishing a student’s positive perception of homework and other academic routines. Teachers and parents need to be vigilant and ensure that homework routines do not start to generate patterns of negative interaction that erode students’ motivation.
Likewise, any positive effects of homework are dependent on several complex interactive factors, including the child’s personal motivation, the type of assignment, parental support and teacher goals. Creating an overarching policy to address every single situation is not realistic, and so homework policies tend to be fixated on the time the homework takes to complete. But rather than focusing on this, everyone would be better off if schools worked on fostering stronger communication between parents, teachers and students, allowing them to respond more sensitively to the child’s emotional and academic needs.
- Five brilliant science books for kids
- Will e-learning replace teachers?
Follow Science Focus on Twitter , Facebook , Instagram and Flipboard
Share this article

- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
- Code of conduct
- Magazine subscriptions
- Manage preferences
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Book Bracket Template. For March and Beyond!
Should We Ban Homework?
The cons of homework are starting to outweigh the pros.

Recent research shows that teenagers have doubled the amount of time they spend on homework since the 1990s. This is in spite of other, well-documented research that calls the efficacy of homework into question, albeit in the younger grades. Why are students spending so much time on homework if the impact is zero (for younger kids) or moderate (for older ones)? Should we ban homework? These are the questions teachers, parents, and lawmakers are asking.
Bans proposed and implemented in the U.S. and abroad
The struggle of whether or not to assign homework is not a new one. In 2017, a Florida superintendent banned homework for elementary schools in the entire district, with one very important exception: reading at home. The United States isn’t the only country to question the benefits of homework. Last August, the Philippines proposed a bill to ban homework completely, citing the need for rest, relaxation, and time with family. Another bill there proposed no weekend homework, with teachers running the risk of fines or two years in prison. (Yikes!) While a prison sentence may seem extreme, there are real reasons to reconsider homework.
Refocus on mental health and educate the “whole child”
Prioritizing mental health is at the forefront of the homework ban movement. Leaders say they want to give students time to develop other hobbies, relationships, and balance in their lives.
This month two Utah elementary schools gained national recognition for officially banning homework. The results are significant, with psychologist referrals for anxiety decreasing by 50 percent. Many schools are looking for ways to refocus on wellness, and homework can be a real cause of stress.
[contextly_auto_sidebar]
Research supports a ban for elementary schools
Supporters of a homework ban often cite research from John Hattie, who concluded that elementary school homework has no effect on academic progress. In a podcast he said, “Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it’s larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It’s one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, ‘Is it really making a difference?'”
In the upper grades, Hattie’s research shows that homework has to be purposeful, not busy work. And the reality is, most teachers don’t receive training on how to assign homework that is meaningful and relevant to students.
Parents push back, too
In October this Washington Post article made waves in parenting and education communities when it introduced the idea that, even if homework is assigned, it doesn’t have to be completed for the student to pass the class. The writer explains how her family doesn’t believe in homework, and doesn’t participate. In response, other parents started “opting out” of homework, citing research that homework in elementary school doesn’t further intelligence or academic success.
Of course, homework has its defenders, especially in the upper grades
“I think some homework is a good idea,” says Darla E. in our WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook. “Ideally, it forces the parents to take some responsibility for their child’s education. It also reinforces what students learn and instills good study habits for later in life.”
Jennifer M. agrees. “If we are trying to make students college-ready, they need the skill of doing homework.”
And the research does support some homework in middle and high school, as long as it is clearly tied to learning and not overwhelming.
We’d love to hear your thoughts—do you think schools should ban homework? Come and share in our WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
Plus, why you should stop assigning reading homework.

You Might Also Like

We Just Can’t With These Embarrassing Teacher Moments 🙈
Be glad you're not them. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
21 Reasons Why Homework Should Be Banned

The homework debate has strong arguments on both sides. Commonly-cited reasons why homework should be banned include the idea that it is often counterproductive, stifles students’ creativity, and limits their freedom outside the classroom.
Students already have up to 7 hours of schoolwork to complete 5 days a week; adding more contributes to increased anxiety, burnout, and overall poor performance.
But arguments for homework include the fact it does increase student grades (Cooper, Robinson & Patall, 2006), it instils discipline, and it helps to reinforce what was learned into long-term memory.
The following are common arguments for banning homework – note that this is an article written to stimulate debate points on the topic, so it only presents one perspective. For the other side of the argument, it’s worth checking out my article on the 27 pros and cons of homework .
Reasons Why Homework Should Be Banned
1. it contributes to increased anxiety.
If there’s one word that describes middle-school and high-school students, it’s anxiety. In my homework statistics article , I cite research showing that 74% of students cite homework as a source of stress.
They have so much to juggle, from the novelty of adolescence to the realization that they must soon start preparing for college and their life after (Pressman et al., 2015).
It’s a lot to manage, and adding homework that reduces their free time and makes them even more restricted is downright harmful. The natural outcome of this dogpile of pressure is anxiety, and many students often feel overwhelmed, both by the hours and hours of coursework in a day and the extensive homework they are assigned (Galloway, Conner & Pope, 2013).
Because teachers often don’t communicate with one another over curricula, major assignments can overlap such that students have to tackle numerous large projects at once, which contributes to severe anxiety over good grades.
In response to this, some students check out of school entirely, letting their academic future go to waste. While, of course, it’s not fair to strawman and say that homework is to blame for all these cases, it may indeed by a contributing factor.
2. It Offers Less Social Time
Homework cuts out free time. Children already spend the better part of their day learning in a school environment, and when they come home, they need to socialize.
Whether it’s family or friends, a social balance is important. Depending on the coursework they’re assigned, homework can detrimentally affect students’ social life, which feed back into more of our first gripe about homework: its anxiety-inducing nature.
Furthermore, social time is extremely important for children to grow up well-balanced and confident. If a child is highly intelligent (book smart) but lacks to social skills we might call street smarts , they may struggle in adulthood.
3. It Detracts from Play Time
Play is extremely important for children’s physical, social, and cognitive development . In fact, children naturally learn through play .
So, when children get home from school, they need a few hours to play. They’re actually learning when playing! If playing with friends, they’re learning social skills; but playing alone also stimulates creative and analytical thinking skills.
Play is also a different type of learning than the learning that commonly happens at school. So, allowing children to play at home gives their brain a break from ‘school learning’ and lets them learn through active and even relaxing methods.
4. It Discourages Physical Exercise and Contributes to Obesity
Exercise is an important part of life for everyone, but especially for children. Developing a positive self-image and disciplining oneself is an important skill to learn, one that becomes much more difficult when homework is in the picture.
Homework can demand a lot of attention that kids could be spending exercising or socializing. These two important life pursuits can be left by the wayside, leaving students feeling confused, depressed, and anxious about the future.
Physical exercise should be considered a key feature of a child’s holistic development. It helps keep children healthy, can reduce anxiety, and support healthy immune systems. It also helps with physical development such as supporting fine and gross motor skills .
In fact, some scholars (Ren et al., 2017) have even identified excessive homework as a contributing factor for childhood obesity.
5. It Disrupts Sleep Patterns
Everyone knows the trope of a college student staying up late to finish their homework or cram for a test.
While it would be unfair to credit homework exclusively for an unhealthy sleep schedule, the constant pressure to finish assignments on time often yields one of two results.
Students can either burn the midnight oil to make sure their homework is done, or they can check out of school entirely and ignore their academic interests. Neither is an acceptable way to live.
This point is particularly pertinent to teenagers. They are not lazy; teens need 12-13 hours of sleep every day because their bodies are changing so dramatically.
To pile additional homework on them that interferes with the circadian rhythm is not just unhelpful—it may be downright harmful (Yeo et al., 2020).
6. It Involves Less Guidance
If there’s one thing that’s beneficial about the in-person learning experience, it’s the ability to raise one’s hand and let the teacher know when something is unclear or difficult to understand.
That handheld process isn’t available for homework; in fact, homework matters little in the grand scheme of learning. It’s just busywork that’s supposed to help students consolidate their knowledge.
In reality, homework becomes something that students resent and can fill them with feelings of frustration—something that would be much more readily addressed if the same content was covered in-person with a teacher to guide the student through the assignment.
7. It’s Regularly Rote Learning
In most subjects, homework isn’t reflective of the skills students need to learn to thrive in the workforce. Instead, it often simply involves rote learning (repetition of tasks) that is not seen as the best way to learn.
A main goal of education is to train up vocational professionals with defined skills. But more often than not, homework winds up as a bland set of word problems that have no basis in the real world.
Walking through real-world examples under the guidance of a teacher is much more beneficial to student learning.
8. It Can Detract from a Love of Learning
If you know what it’s like to doze off during a boring class or meeting, then you can relate to the difficulty students have paying attention in class.
That motivation starts to dwindle when students must complete assignments on their own time, often under immense pressure.
It’s not a healthy way to inspire kids to learn about different subjects and develop a love of learning.
Students already need to sit through hours and hours of class on end in-person. This learning time should be used more effectively to eliminate the need for home.
When children finally get out of class at the end of the day, they need to socialize and exercise, not spend even longer staring at a book to complete a bunch of unhelpful practice questions.
9. It Convolutes the Subject
Another important consideration about homework is that it can often be counterproductive.
That’s because teachers don’t always use the full curriculum material for their teaching, and they may choose to develop their own homework rather than to use the resources offered by the curriculum provider.
This homework can often be off-subject, extremely niche, or unhelpful in explaining a subject that students are studying.
Students who don’t understand a subject and don’t have resources to rely on will eventually give up. That risk becomes even more prevalent when you factor in the scope, complexity, and type of assignment.
Students need to be taught in a safe environment where they can feel free to ask questions and learn at their own pace. Of course, there’s no fairytale way to perfect this ideal, but what is clear is that homework is not beneficial to the learning environment for many students.
10. It’s Not What Kids Want
Lastly, homework should be banned because it’s generally not what students want. From elementary to college level, most students harbor some sort of resentment towards homework.
It might be easy to dismiss this to say that the students “aren’t living in the real world.” The truth of the matter is that the real world is a lot more nuanced, creative, and diverse than the repetitive, broad, and often stagnant homework.
It’s easy to understand why most students wish that more time in school had been spent on learning how to live rather than trying to figure out how many apples Johnny had. Subjects like car maintenance, entrepreneurship, computer skills, socialization, networking, tax filing, finances, and survival are touched on at best and ignored at worst.
It’s not enough for students to be able to regurgitate information on a piece of paper; in the end, the education system should teach them how to be self-sufficient, something that might be much easier to do if resources were divested from homework and poured into more beneficial subject material.
Consider these 11 Additional Reasons
- Decreases time with parents – Homework may prevent parents and children from spending quality time together.
- Hidden costs – Families often feel pressure to purchase internet and other resources to help their children to complete their homework.
- Is inequitable – some children have parents to help them while others don’t. Similarly, some children have internet access to help while others don’t (see: Kralovec & Buell, 2001).
- Easy to cheat – Unsupervised homework time makes it easy for children to simply cheat on their work so they can get on with play time!
- Lack of downtime – Children need time where they aren’t doing anything. Time that is unstructured helps them to develop hobbies and interests .
- Detracts from reading – Children could be spending their time reading books and developing their imaginations rather than working on repetitive homework tasks.
- Take up parental time – Parents, who have just spent all day working, are increasingly expected to spend their time doing ‘teaching’ with their children at home.
- Discourages club membership – If children are too busy with homework, they may not be able to join clubs and sporting groups that can help them make friends and develop extracurricular skills.
- Makes it hard for college students to make a living – In college, where homework is extensive, students often can’t juggle homework with their weekend and night-time jobs. As a result, it pushes them further into student poverty.
- Contributes to poor work-life culture – From early ages, we’re sending a message to children that they should take their work home with them. This can spill over into the workplace, where they’ll be expected to continue working for their company even after the workday ends.
- Can reinforce faulty learning – When children learn in isolation during homework time, they may end up practicing their work completely wrong! They need intermittent support to make sure their practice is taking them down the right path.
Students may need to demonstrate their understanding of a topic to progress; that, at least, is a reflection of the real world. What’s not helpful is when students are peppered day and night with information that they need to regurgitate on a piece of paper.
For positive outcomes to come from homework, parents and teachers need to work together. It depends a lot on the type of homework provided as well as the age of the student and the need to balance homework with time to do other things in your life.
Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003. Review of educational research , 76 (1), 1-62.
Galloway, M., Conner, J., & Pope, D. (2013). Nonacademic effects of homework in privileged, high-performing high schools. The journal of experimental education , 81 (4), 490-510. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00220973.2012.745469
Kralovec, E., & Buell, J. (2001). The end of homework: How homework disrupts families, overburdens children, and limits learning . Beacon Press.
Pressman, R. M., Sugarman, D. B., Nemon, M. L., Desjarlais, J., Owens, J. A., & Schettini-Evans, A. (2015). Homework and family stress: With consideration of parents’ self confidence, educational level, and cultural background. The American Journal of Family Therapy , 43 (4), 297-313. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01926187.2015.1061407
Ren, H., Zhou, Z., Liu, W., Wang, X., & Yin, Z. (2017). Excessive homework, inadequate sleep, physical inactivity and screen viewing time are major contributors to high paediatric obesity. Acta Paediatrica , 106 (1), 120-127. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.13640
Yeo, S. C., Tan, J., Lo, J. C., Chee, M. W., & Gooley, J. J. (2020). Associations of time spent on homework or studying with nocturnal sleep behavior and depression symptoms in adolescents from Singapore. Sleep Health , 6 (6), 758-766. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2020.04.011

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
5 thoughts on “21 Reasons Why Homework Should Be Banned”
very helpful website thanks
my topic on publics speaking is on banning homework it really helps
Very helpful cheers mate
This really helped my debate team
It is very helpful for me.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Thanks for visiting! GoodRx is not available outside of the United States. If you are trying to access this site from the United States and believe you have received this message in error, please reach out to [email protected] and let us know.
Debate Nirvana
Homework should be banned.

PRO (6 arguments)
Links to more PRO research:
Homework and Its Role in Constructive Pedagogy
The site contains research and statistics on both sides of the homework debate.
Define :
Homework: a task set by teachers for students to complete outside of the time allotted for a normal school day.
Banned: Disallow homework in K-8 grades in the U.S. public schools
Homework produces large amount of pointless work of little educational value, but marking it ties up much of teachers’ time. Add in correcting it and the time it takes up in class going over it. Altogether, this leaves teachers tired and with little time to prepare more effective, inspiring lessons. Also, reversely, homework can function as a safety net for bad teachers in that they know that even if they do a poor job on their lessons and teaching during class they can always just pile on homework and hope that they can then use this as a sign that they are good teachers. A good teacher shouldn’t need to resort to homework to teach for them, which is why homework is unfair to the teachers who don’t need to assign it while the bad ones who do get credit for that from their employers.
“Teachers in many of the nations that outperform the U.S. on student achievement tests--such as Japan, Denmark and the Czech Republic--tend to assign less homework than American teachers, but instructors in low-scoring countries like Greece, Thailand and Iran tend to pile it on,” Time Magazine, The Myth About Homework
Time Magazine
Homework de-motivates kids to learn. Most see it as a consequence of going to school. Studies have shown that many children find doing homework very stressful, boring and tiring. Often teachers underestimate how long a task will take, or set an unrealistic deadline. Sometimes because a teacher has not explained something new well in class, the homework task is impossible. So children end up paying with their free time for the failings of their teachers. They also suffer punishments if work is done badly or late. After years of bad homework experiences, it is no wonder that many children come to dislike education and switch off, or drop out too early.
"It's one thing to say we are wasting kids' time and straining parent-kid relationships, but what's unforgivable is if homework is damaging our kids' interest in learning, undermining their curiosity." The Homework Myth by Alfie Kohn.
The Homework Myth by Alfie Kohn.
Homework is discriminatory in that it gives unfair advantages to certain types of people depending on their home environment. In school everyone is equal, but home is a different story. Middle-class families with books and computers will be able to help their children much more than poorer families can. This can mean working class children end up with worse grades and more punishments for undone or badly done homework. On the other hand pushy parents may even end up doing their kids’ homework for them – cheating. Even worse, kids who live in an abusive or volatile home environment (something completely out of the kids control) end up having their homework counting against them and compared to kids who benefit from doing work at home.
Common sense; there are plenty of homes where education is not the #1 priority and some where it is. This imbalance only comes out with homework and skewers results unfairly.
Homework takes up a lot of time, usually enough to push off many extracurricular a student might want to do. Being young is not just about doing schoolwork. It should also about being physically active, exploring the environment through play, doing creative things like music and art, and playing a part in the community. It is also important for young people to build bonds with others, especially family and friends, but homework often squeezes the time available for all these things.
According to the American Educational Research Association released this statement: “Whenever homework crowds out social experience, outdoor recreation, and creative activities, and whenever it usurps time that should be devoted to sleep, it is not meeting the basic needs of children and adolescents.”
Alos, Curt Dudley-Marlin, a professor at Boston College, interviewed dozens of families and found that, “the demands of homework disrupted…family relationships and led to stress and conflict.”
American Educational Research Association
Homework has little educational worth and adds nothing to the time spent in school. Some schools and some countries don’t bother with homework at all, and their results do not seem to suffer from it. Studies show that homework adds nothing to standardized test scores for primary/ elementary pupils. International comparisons of older students have found no positive relationship between the amount of homework set and average test scores. If anything, countries with more homework got worse results!
Harris Cooper, of Duke University, found that students in middle school who do more than 60-90 min. a night perform worse on standardized tests than those who do 20-30 min. a night.
Homework does little to develop good study skills. First off, many children, after a long and hard school day, end up plagiarizing off of either another student’s work or a professional manuscript. With the Internet, copying has just been made easier. All a student has to do is copy and paste a few paragraphs onto a blank word document and they have their report. This isn’t even considering the massive input parents have on their child’s homework, ranging from checking over answers to even writing a paper for their child. All of this is extremely prevalent in today’s society, and it makes teachers spend ten times as much effort deciding whether a student created a paper or copied off some one else than actually grading the work. Therefore, homework should be banned due to these unavoidable consequences that occur with it.
The pressure to complete homework can also lead to students cheating by copying from other students or obtaining help other than tutoring, such as getting their parents to complete it for them. Students who “perceive that achievement is defined by schools and teachers in terms of grades and performance, worry about school, and believe they can get rewards for doing well in class such as getting out of homework" are more likely to cheat, and to "avoid using deep level cognitive processing strategies such as trying different ways to solve a problem." The American Psychological Association (1998)
The American Psychological Association (1998)
Home | About | Topics | Articles | Blog | Privacy Policy | Login
25 Reasons Homework Should Be Banned (Busywork Arguments)

As students across the globe plow through heaps of homework each night, one question lingers in the minds of educators, parents, and students alike: should homework be banned?
This question is not new, yet it continues to spark lively debate as research findings, anecdotal evidence, and personal experiences paint a complex picture of the pros and cons of homework.
On one hand, proponents of homework argue that it reinforces classroom learning, encourages a disciplined work ethic, and provides teachers with valuable insight into student comprehension. They see homework as an extension of classroom instruction that solidifies and enriches learning while fostering important skills like time management and self-discipline. It also offers an opportunity for parents to be involved in their children's education.
However, some people say there are a lot of downsides. They argue that excessive homework can lead to stress and burnout, reduce time for extracurricular activities and family interactions, exacerbate educational inequalities, and even negatively impact students' mental health.

This article presents 25 reasons why we might need to seriously consider this radical shift in our educational approach. But first, lets share some examples of what homework actually is.
Examples of Homework
These examples cover a wide range of subjects and complexity levels, reflecting the variety of homework assignments students might encounter throughout their educational journey.
- Spelling lists to memorize for a test
- Math worksheets for practicing basic arithmetic operations
- Reading assignments from children's books
- Simple science projects like growing a plant
- Basic geography assignments like labeling a map
- Art projects like drawing a family portrait
- Writing book reports or essays
- Advanced math problems
- Research projects on various topics
- Lab reports for science experiments
- Reading and responding to literature
- Preparing presentations on various topics
- Advanced math problems involving calculus or algebra
- Reading classic literature and writing analytical essays
- Research papers on historical events
- Lab reports for advanced science experiments
- Foreign language exercises
- Preparing for standardized tests
- College application essays
- Extensive research papers
- In-depth case studies
- Advanced problem-solving in subjects like physics, engineering, etc.
- Thesis or dissertation writing
- Extensive reading and literature reviews
- Internship or practicum experiences
Lack of proven benefits

Homework has long been a staple of traditional education, dating back centuries. However, the actual efficacy of homework in enhancing learning outcomes remains disputed. A number of studies indicate that there's no conclusive evidence supporting the notion that homework improves academic performance, especially in primary education . In fact, research suggests that for younger students, the correlation between homework and academic achievement is weak or even negative .
Too much homework can often lead to increased stress and decreased enthusiasm for learning. This issue becomes particularly pressing when considering the common 'more is better' approach to homework, where the quantity of work given to students often outweighs the quality and effectiveness of the tasks. For instance, spending countless hours memorizing facts for a history test may not necessarily translate to better understanding or long-term retention of the subject matter.
However, it's worth noting that homework isn't completely devoid of benefits. It can help foster self-discipline, time management skills, and the ability to work independently. But, these positive outcomes are usually more pronounced in older students and when homework assignments are thoughtfully designed and not excessive in volume.
When discussing the merits and drawbacks of homework, it's critical to consider the nature of the assignments. Routine, repetitive tasks often associated with 'drill-and-practice' homework, such as completing rows of arithmetic problems or copying definitions from a textbook, rarely lead to meaningful learning. On the other hand, assignments that encourage students to apply what they've learned in class, solve problems, or engage creatively with the material can be more beneficial.
Increased stress

Homework can often lead to a significant increase in stress levels among students. This is especially true when students are burdened with large volumes of homework, leaving them with little time to relax or pursue other activities. The feeling of constantly racing against the clock to meet deadlines can contribute to anxiety, frustration, and even burnout.
Contrary to popular belief, stress does not necessarily improve performance or productivity. In fact, high levels of stress can negatively impact memory, concentration, and overall cognitive function. This counteracts the very purpose of homework, which is intended to reinforce learning and improve academic outcomes.
However, one might argue that homework can teach students about time management, organization, and how to handle pressure. These are important life skills that could potentially prepare them for future responsibilities. But it's essential to strike a balance. The pressure to complete homework should not come at the cost of a student's mental wellbeing.
Limited family time
Homework often infringes upon the time students can spend with their families. After spending the entire day in school, children come home to yet more academic work, leaving little room for quality family interactions. This limited family time can hinder the development of important interpersonal skills and familial bonds.
Moreover, family time isn't just about fun and relaxation. It also plays a crucial role in the social and emotional development of children. Opportunities for unstructured play, family conversations, and shared activities can contribute to children's well-being and character building.
Nonetheless, advocates of homework might argue that it can be a platform for parental involvement in a child's education. While this may be true, the involvement should not transform into parental control or cause friction due to differing expectations and pressures.
Reduced physical activity
Homework can often lead to reduced physical activity by eating into the time students have for sports, recreation, and simply being outdoors. Physical activity is essential for children's health, well-being, and even their academic performance. Research suggests that physical activity can enhance cognitive abilities, improve concentration, and reduce symptoms of ADHD .
Homework, especially when it's boring and repetitive, can deter students from engaging in physical activities, leading to a sedentary lifestyle. This lack of balance between work and play can contribute to physical health problems such as obesity, poor posture, and related health concerns.
Homework proponents might point out that disciplined time management could allow students to balance both work and play. However, given the demanding nature of many homework assignments, achieving this balance is often easier said than done.
Negative impact on sleep

A significant concern about homework is its impact on students' sleep patterns. Numerous studies have linked excessive homework to sleep deprivation in students. Children often stay up late to complete assignments, reducing the amount of sleep they get. Lack of sleep can result in a host of issues, from poor academic performance and difficulty concentrating to physical health problems like weakened immunity.
Even the quality of sleep can be affected. The stress and anxiety from a heavy workload can lead to difficulty falling asleep or restless nights. And let's not forget that students often need to wake up early for school, compounding the negative effects of late-night homework sessions.
On the other hand, some argue that homework can teach children time management skills, suggesting that effective organization could help prevent late-night work. However, when schools assign excessive amounts of homework, even the best time management might not prevent encroachment on sleep time.
Homework can exacerbate existing educational inequalities. Not all students have access to a conducive learning environment at home, necessary resources, or support from educated family members. For these students, homework can become a source of stress and disadvantage rather than an opportunity to reinforce learning.
Children from lower socio-economic backgrounds might need to contribute to household chores or part-time work, limiting the time they have for homework. This can create a gap in academic performance and grades, reflecting not on the students' abilities but their circumstances.
While homework is meant to level the playing field by providing additional learning time outside school, it often does the opposite. It's worth noting that students from privileged backgrounds can often access additional help like tutoring, further widening the gap.
Reduced creativity and independent thinking
Homework, particularly when it involves rote learning or repetitive tasks, can stifle creativity and independent thinking. Students often focus on getting the "right" answers to please teachers rather than exploring different ideas and solutions. This can hinder their ability to think creatively and solve problems independently, skills that are increasingly in demand in the modern world.
Homework defenders might claim that it can also promote independent learning. True, when thoughtfully designed, homework can encourage this. But, voluminous or repetitive tasks tend to promote compliance over creativity.
Diminished interest in learning
Overburdening students with homework can diminish their interest in learning. After long hours in school followed by more academic tasks at home, learning can begin to feel like a chore. This can lead to a decline in intrinsic motivation and an unhealthy association of learning with stress and exhaustion.
In theory, homework can deepen interest in a subject, especially when it involves projects or research. Yet, an excess of homework, particularly routine tasks, might achieve the opposite, turning learning into a source of stress rather than enjoyment.
Inability to pursue personal interests
Homework can limit students' ability to pursue personal interests. Hobbies, personal projects, and leisure activities are crucial for personal development and well-being. With heavy homework loads, students may struggle to find time for these activities, missing out on opportunities to discover new interests and talents.
Supporters of homework might argue that it teaches students to manage their time effectively. However, even with good time management, an overload of homework can crowd out time for personal interests.
Excessive workload
The issue of excessive workload is a common complaint among students. Spending several hours on homework after a full school day can be mentally and physically draining. This workload can lead to burnout, decreased motivation, and negative attitudes toward school and learning.
While homework can help consolidate classroom learning, too much can be counterproductive. It's important to consider the overall workload of students, including school, extracurricular activities, and personal time, when assigning homework.
Limited time for reflection
Homework can limit the time students have for reflection. Reflection is a critical part of learning, allowing students to digest and integrate new information. With the constant flow of assignments, there's often little time left for this crucial process. Consequently, the learning becomes superficial, and the true understanding of subjects can be compromised.
Although homework is meant to reinforce what's taught in class, the lack of downtime for reflection might hinder deep learning. It's important to remember that learning is not just about doing, but also about thinking.
Increased pressure on young children
Young children are particularly vulnerable to the pressures of homework. At an age where play and exploration are vital for cognitive and emotional development, too much homework can create undue pressure and stress. This pressure can instigate a negative relationship with learning from an early age, potentially impacting their future attitude towards education.
Advocates of homework often argue that it prepares children for the rigors of their future academic journey. However, placing too much academic pressure on young children might overshadow the importance of learning through play and exploration.
Lack of alignment with real-world skills
Traditional homework often lacks alignment with real-world skills. Assignments typically focus on academic abilities at the expense of skills like creativity, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence. These are crucial for success in the modern workplace and are often under-emphasized in homework tasks.
Homework can be an opportunity to develop these skills when properly structured. However, tasks often focus on memorization and repetition, rather than cultivating skills relevant to the real world.
Loss of motivation
Excessive homework can lead to a loss of motivation. The constant pressure to complete assignments and meet deadlines can diminish a student's intrinsic motivation to learn. This loss of motivation might not only affect their academic performance but also their love of learning, potentially having long-term effects on their educational journey.
Some believe homework instills discipline and responsibility. But, it's important to balance these benefits against the potential for homework to undermine motivation and engagement.
Disruption of work-life balance
Maintaining a healthy work-life balance is as important for students as it is for adults. Overloading students with homework can disrupt this balance, leaving little time for relaxation, socializing, and extracurricular activities. All of these are vital for a student's overall development and well-being.
Homework supporters might argue that it prepares students for the workloads they'll face in college and beyond. But it's also crucial to ensure students have time to relax, recharge, and engage in non-academic activities for a well-rounded development.
Impact on mental health
There's a growing body of evidence showing the negative impact of excessive homework on students' mental health. The stress and anxiety from heavy homework loads can contribute to issues like depression, anxiety, and even thoughts of suicide. Student well-being should be a top priority in education, and the impact of homework on mental health cannot be ignored.
While some might argue that homework helps students develop resilience and coping skills, it's important to ensure these potential benefits don't come at the expense of students' mental health.
Limited time for self-care
With excessive homework, students often find little time for essential self-care activities. These can include physical exercise, proper rest, healthy eating, mindfulness, or even simple leisure activities. These activities are critical for maintaining physical health, emotional well-being, and cognitive function.
Some might argue that managing homework alongside self-care responsibilities teaches students valuable life skills. However, it's important that these skills don't come at the cost of students' health and well-being.
Decreased family involvement
Homework can inadvertently lead to decreased family involvement in a child's learning. Parents often feel unqualified or too busy to help with homework, leading to missed opportunities for family learning interactions. This can also create stress and conflict within the family, especially when parents have high expectations or are unable to assist.
Some believe homework can facilitate parental involvement in education. But, when it becomes a source of stress or conflict, it can discourage parents from engaging in their child's learning.

Reinforcement of inequalities
Homework can unintentionally reinforce inequalities. Students from disadvantaged backgrounds might lack access to resources like private tutors or a quiet study space, placing them at a disadvantage compared to their more privileged peers. Additionally, these students might have additional responsibilities at home, further limiting their time to complete homework.
While the purpose of homework is often to provide additional learning opportunities, it can inadvertently reinforce existing disparities. Therefore, it's essential to ensure that homework doesn't favor students who have more resources at home.
Reduced time for play and creativity
Homework can take away from time for play and creative activities. These activities are not only enjoyable but also crucial for the cognitive, social, and emotional development of children. Play allows children to explore, imagine, and create, fostering innovative thinking and problem-solving skills.
Some may argue that homework teaches discipline and responsibility. Yet, it's vital to remember that play also has significant learning benefits and should be a part of every child's daily routine.
Increased cheating and academic dishonesty
The pressure to complete homework can sometimes lead to increased cheating and academic dishonesty. When faced with a large volume of homework, students might resort to copying from friends or searching for answers online. This undermines the educational value of homework and fosters unhealthy academic practices.
While homework is intended to consolidate learning, the risk of promoting dishonest behaviors is a concern that needs to be addressed.
Strained teacher-student relationships
Excessive homework can strain teacher-student relationships. If students begin to associate teachers with stress or anxiety from homework, it can hinder the development of a positive learning relationship. Furthermore, if teachers are perceived as being unfair or insensitive with their homework demands, it can impact the overall classroom dynamic.
While homework can provide an opportunity for teachers to monitor student progress, it's important to ensure that it doesn't negatively affect the teacher-student relationship.
Negative impact on family dynamics
Homework can impact family dynamics. Parents might feel compelled to enforce homework completion, leading to potential conflict, stress, and tension within the family. These situations can disrupt the harmony in the household and strain relationships.
Homework is sometimes seen as a tool to engage parents in their child's education. However, it's crucial to ensure that this involvement doesn't turn into a source of conflict or pressure.
Cultural and individual differences
Homework might not take into account cultural and individual differences. Education is not a one-size-fits-all process, and what works for one student might not work for another. Some students might thrive on hands-on learning, while others prefer auditory or visual learning methods. By standardizing homework, we might ignore these individual learning styles and preferences.
Homework can also overlook cultural differences. For students from diverse cultural backgrounds, certain types of homework might seem irrelevant or difficult to relate to, leading to disengagement or confusion.
Encouragement of surface-level learning
Homework often encourages surface-level learning instead of deep understanding. When students are swamped with homework, they're likely to rush through assignments to get them done, rather than taking the time to understand the concepts. This can result in superficial learning where students memorize information to regurgitate it on assignments and tests, instead of truly understanding and internalizing the knowledge.
While homework is meant to reinforce classroom learning, the quality of learning is more important than the quantity. It's important to design homework in a way that encourages deep, meaningful learning instead of mere rote memorization.
Related posts:
- Diathesis-Stress Model (Definition + Examples)
- HPA Axis (Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis)
- General Adaptation Syndrome Theory
- Careers in Psychology
- The Stress Response (General Adaptation Syndome)
Reference this article:
About The Author

Free Personality Test

Free Memory Test

Free IQ Test

PracticalPie.com is a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow Us On:
Youtube Facebook Instagram X/Twitter
Psychology Resources
Developmental
Personality
Relationships
Psychologists
Serial Killers
Psychology Tests
Personality Quiz
Memory Test
Depression test
Type A/B Personality Test
© PracticalPsychology. All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use

School Life Balance , Tips for Online Students
The Pros and Cons of Homework

Homework is a word that most students dread hearing. After hours upon hours of sitting in class , the last thing we want is more schoolwork over our precious weekends. While it’s known to be a staple of traditional schooling, homework has also become a rather divise topic. Some feel as though homework is a necessary part of school, while others believe that the time could be better invested. Should students have homework? Have a closer look into the arguments on both sides to decide for yourself.

Photo by energepic.com from Pexels
Why should students have homework, 1. homework encourages practice.
Many people believe that one of the positive effects of homework is that it encourages the discipline of practice. While it may be time consuming and boring compared to other activities, repetition is needed to get better at skills. Homework helps make concepts more clear, and gives students more opportunities when starting their career .
2. Homework Gets Parents Involved
Homework can be something that gets parents involved in their children’s lives if the environment is a healthy one. A parent helping their child with homework makes them take part in their academic success, and allows for the parent to keep up with what the child is doing in school. It can also be a chance to connect together.
3. Homework Teaches Time Management
Homework is much more than just completing the assigned tasks. Homework can develop time management skills , forcing students to plan their time and make sure that all of their homework assignments are done on time. By learning to manage their time, students also practice their problem-solving skills and independent thinking. One of the positive effects of homework is that it forces decision making and compromises to be made.
4. Homework Opens A Bridge Of Communication
Homework creates a connection between the student, the teacher, the school, and the parents. It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student.
5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can’t see it in the moment.
6. Homework Reduces Screen Time
Many students in North America spend far too many hours watching TV. If they weren’t in school, these numbers would likely increase even more. Although homework is usually undesired, it encourages better study habits and discourages spending time in front of the TV. Homework can be seen as another extracurricular activity, and many families already invest a lot of time and money in different clubs and lessons to fill up their children’s extra time. Just like extracurricular activities, homework can be fit into one’s schedule.

The Other Side: Why Homework Is Bad
1. homework encourages a sedentary lifestyle.
Should students have homework? Well, that depends on where you stand. There are arguments both for the advantages and the disadvantages of homework.
While classroom time is important, playground time is just as important. If children are given too much homework, they won’t have enough playtime, which can impact their social development and learning. Studies have found that those who get more play get better grades in school , as it can help them pay closer attention in the classroom.
Children are already sitting long hours in the classroom, and homework assignments only add to these hours. Sedentary lifestyles can be dangerous and can cause health problems such as obesity. Homework takes away from time that could be spent investing in physical activity.
2. Homework Isn’t Healthy In Every Home
While many people that think homes are a beneficial environment for children to learn, not all homes provide a healthy environment, and there may be very little investment from parents. Some parents do not provide any kind of support or homework help, and even if they would like to, due to personal barriers, they sometimes cannot. Homework can create friction between children and their parents, which is one of the reasons why homework is bad .
3. Homework Adds To An Already Full-Time Job
School is already a full-time job for students, as they generally spend over 6 hours each day in class. Students also often have extracurricular activities such as sports, music, or art that are just as important as their traditional courses. Adding on extra hours to all of these demands is a lot for children to manage, and prevents students from having extra time to themselves for a variety of creative endeavors. Homework prevents self discovery and having the time to learn new skills outside of the school system. This is one of the main disadvantages of homework.
4. Homework Has Not Been Proven To Provide Results
Endless surveys have found that homework creates a negative attitude towards school, and homework has not been found to be linked to a higher level of academic success.
The positive effects of homework have not been backed up enough. While homework may help some students improve in specific subjects, if they have outside help there is no real proof that homework makes for improvements.
It can be a challenge to really enforce the completion of homework, and students can still get decent grades without doing their homework. Extra school time does not necessarily mean better grades — quality must always come before quantity.
Accurate practice when it comes to homework simply isn’t reliable. Homework could even cause opposite effects if misunderstood, especially since the reliance is placed on the student and their parents — one of the major reasons as to why homework is bad. Many students would rather cheat in class to avoid doing their homework at home, and children often just copy off of each other or from what they read on the internet.
5. Homework Assignments Are Overdone
The general agreement is that students should not be given more than 10 minutes a day per grade level. What this means is that a first grader should be given a maximum of 10 minutes of homework, while a second grader receives 20 minutes, etc. Many students are given a lot more homework than the recommended amount, however.
On average, college students spend as much as 3 hours per night on homework . By giving too much homework, it can increase stress levels and lead to burn out. This in turn provides an opposite effect when it comes to academic success.
The pros and cons of homework are both valid, and it seems as though the question of ‘‘should students have homework?’ is not a simple, straightforward one. Parents and teachers often are found to be clashing heads, while the student is left in the middle without much say.
It’s important to understand all the advantages and disadvantages of homework, taking both perspectives into conversation to find a common ground. At the end of the day, everyone’s goal is the success of the student.
Related Articles
College life is an amazing period when most people find their soulmates, meet friends, obtain knowledge, study favorite subjects, and decide on the career path. Don’t you agree?
However, homework has always been the main stumbling block for most students who choose to keep a balance between studies, work, and personal life. While some teachers and parents agree that homework assignments help to improve knowledge and train theoretical skills. However, when kids have no experience in doing assignments out-of-class or school students who get many assignments , they spent hours of homework which led to stress, headache, and burnout. Obviously, parents see these negative effects and start thinking about whether the government should ban homework.
Since students want to enjoy their youth, it’s no wonder that more and more people ask themselves: should students have homework ?
Image Source
The debate over banning homework isn’t new, but it has gained in popularity over the last few years. Today, more and more schools and colleges in the USA and Canada implement the ‘no-homework’ policy.
In this article, we’re going to find out whether homework should be banned.
First things first: let’s find out why homework is bad . Here comes the list of the pros of banning homework.
1. Stay Interested in Subjects
It’s no secret that students spend at least five days a week at colleges, but when they come back home, they still have to work on their homework which also takes a lot of time. Since most teachers assign too much homework, students waste many days working on assignments, so they lack sleep and feel stressed. Why? They are afraid of completing their tasks on a bad level, and therefore getting bad marks. While kids study hard to be skilled and well-rounded, they waste a lot of time online and these factors lead to stress and mental health problems, so students are losing interest in subjects.
2. Keep a College-Life Balance
The college life is not just about attending lectures, hitting the books, and doing your homework. It’s an amazing period of life that most young people love as it helps them meet new friends and decide on their career paths if they keep a college-life balance. With the growing amount of homework assignments, it’s getting harder for responsible students to manage their time wisely. Not only do students spend much time working on their tasks and projects, but also teachers assign too much homework.
More and more famous people support the idea of a homework ban as they believe that working too much on homework assignments doesn’t allow kids to keep a college-life balance. Here’s a popular Tweet from Gary Lineker , for example:
Having a balance in life is crucial for every person, but when it comes to the youth, it’s even more important as it affects their productivity, performance, and overall well-being. To get great grades, students do their best to complete tasks on a good level, but they have to spend many days to complete their workload, so they can’t keep a balance.
3. Improve Mental Health
When students have to work on difficult assignments, they may get stress, headaches, and exhaustion. When kids have too much homework, it can result in lack of sleep and healthy relationships with peers and family. No matter how much they love various subjects, homework can negatively affect mental health which can lead to serious problems. The ‘no-homework’ movement helps to protect children from getting too much homework which also helps to improve mental health over the long haul.
Having too much homework is bad, but having no homework at all – is it good? Although more and more people want to implement the no-homework policy and discuss whether should homework be banned, working on assignments after classes is still a great way to obtain knowledge and improve skills. Let’s find out the cons of banning homework.
1. Have Poor Time Management Skills
Students get too much homework. At first blush, it seems to be a problem. However, it has a positive effect on their time management skills. With a desire to get great grades for their assignments without sacrificing personal life, most students find a homework routine that works best for them. In other words, this means they learn how to prioritize tasks, stay focused on their duties, and therefore improve time management skills which can help them in every aspect of life.
2. Increase Screen Time
The popularity of technologies has both advantages and disadvantages. While adults can make the most out of gadgets, younger people may have some problems using their smartphones/tablets. As specified in Common Sense Report , 59% of parents believe that their children are addicted to their devices. Since kids love gadgets so much, they always choose to get through the days playing video games or browsing social media networks unless they start working on homework assignments.
Gadgets have become a common problem most children face, so parents seek out alternative ways to occupy their kids . Believe it or not, homework reduces the amount of time the youth spends scrolling Facebook feeds or texting with peers. There’s a correlation between the amount of time people spend on education and screen time. The sum up? More education means less screen time:
Simply put, if you choose to ban homework, it may lead to serious problems caused by phone addiction. Thus, it’s a negative aspect of a homework ban that can become a global problem in the short term.
3. Damage Children-Parents Relationships
When it comes to homework, every student has asked their parents for help at least once in a lifetime. Since students seek out assignment help, it’s no wonder they turn to their parents. In most cases, parents do their best to help children get their questions answered. It’s psychologically proven that working together with parents on difficult tasks leads to better relationships, but when there’s no homework, students (especially teenagers) are less likely to contact their parents. In other words, this means a lack of communication between children and parents, which negatively affects their overall relationships.
Homework has both pros and cons, so it’s hard to say whether it should be banned or not. However, it’s obvious that teachers should take into account the amount of homework students get weekly and how many days they work on these tasks. Once teachers assign fewer tasks and students stop procrastinating on their homework, working on assignments at home will be more beneficial for everyone in the educational process.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- RANDOM QUIZ
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Study Skills
No More Homework: 12 Reasons We Should Get Rid of It Completely
Last Updated: February 16, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Finn Kobler . Finn Kobler graduated from USC in 2022 with a BFA in Writing for Screen/Television. He is a two-time California State Champion and record holder in Original Prose/Poetry, a 2018 finalist for the Los Angeles Youth Poet Laureate, and he's written micro-budget films that have been screened in over 150 theaters nationwide. Growing up, Finn spent every summer helping his family's nonprofit arts program, Showdown Stage Company, empower people through accessible media. He hopes to continue that mission with his writing at wikiHow. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 116,661 times. Learn more...
The amount of homework students are given has increased dramatically in the 21st century, which has sparked countless debates over homework’s overall value. While some have been adamant that homework is an essential part of a good education, it’s been proven that too much homework negatively affects students’ mood, classroom performance, and overall well-being. In addition, a heavy homework load can stress families and teachers. Here are 12 reasons why homework should be banned (or at least heavily reduced).
School is already a full-time job.

- For years, teachers have followed the “10-minute rule” giving students roughly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. However, recent studies have shown students are completing 3+ hours of homework a night well before their senior years even begin. [2] X Trustworthy Source American Psychological Association Leading scientific and professional organization of licensed psychologists Go to source
Homework negatively affects students’ health.

Homework interferes with student’s opportunities to socialize.

Homework hinders students’ chances to learn new things.

Homework lowers students’ enthusiasm for school.

Homework can lower academic performance.

Homework cuts into family time.

Homework is stressful for teachers.

Homework is often irrelevant and punitive.

- There are even studies that have shown homework in primary school has no correlation with classroom performance whatsoever. [9] X Research source
Homework encourages cheating.

Homework is inequitable.

Other countries have banned homework with great results.

- There are even some U.S. schools that have adopted this approach with success. [13] X Research source
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.edutopia.org/no-proven-benefits
- ↑ https://www.apa.org/monitor/2016/03/homework
- ↑ https://healthier.stanfordchildrens.org/en/health-hazards-homework/
- ↑ https://teensneedsleep.files.wordpress.com/2011/04/galloway-nonacademic-effects-of-homework-in-privileged-high-performing-high-schools.pdf
- ↑ https://time.com/4466390/homework-debate-research/
- ↑ https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00220485.2022.2075506?role=tab&scroll=top&needAccess=true&journalCode=vece20
- ↑ https://kappanonline.org/teacher-stress-balancing-demands-resources-mccarthy/
- ↑ https://www.chicagotribune.com/lifestyles/ct-life-homework-pros-cons-20180807-story.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6294446/
- ↑ https://www.theatlantic.com/business/archive/2016/06/homework-inequality-parents-schedules-grades/485174/
- ↑ https://www.bbc.com/news/education-37716005
- ↑ https://www.wsj.com/articles/no-homework-its-the-new-thing-in-u-s-schools-11544610600
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Leonardo F.
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Big debate club
Current debate, join for free, follow big debate club on twitter 🐦.
This website uses cookies. By continuing to browse you agree to this.
See our privacy policy.
Should Homework Be Banned Debate the Pros and Cons

Homework always seems like an inevitable side of the school. However, more schools realize that it might be a hurdle for students who struggle to find a balance between personal life, studies, and work. The homework should be banned debate has raised more worries as teachers and parents find themselves yet at another crossroads to give the students the best life. Read along to find out the pros and cons of why homework should be banned?
Should Homework Be Banned Essay?
This kind of essay piques interest of students as many engage in them . At Acemyhomework , we pride ourselves on providing the best essays on whichever topic you have. Our writers strive to ensure that your essay is a killer and they are just available at a click of a button.
Just like any essay, you will need a strong introduction with a killer hook and a focus on the thesis; the body needs to give the correct intentions and put in mind the pros and cons of why homework should be banned. The conclusion should focus on the thesis and recommendations and why it is essential.
Should homework be not banned? Is still a question that has left many parents and teachers with more questions than answers. While some arguments clearly show homework has been an impediment to many students, there is equally with the same vigor of studies that show homework has helped shape the future of students theoretically.
Why Should Homework Be Banned?
There is a significant debate on banning homework, and some parents are at the forefront of fighting for this as the adverse effects they experience from their children affect them due to the high amount of homework.
Here are some of the pros and cons of why homework should be banned:
Pros of Banning Homework
While this debate is still rising and many reasons are being given left, right, and center, it is good to know that anything in excess can have consequences and, in most cases, not a great one. See below, why homework should be banned 10 reasons?
- Mental Health
Students who keep on working on their many assignments tend to be stressed, exhausted, and have headaches and the result is burnout. When students have a lot on their plate, they forget to sleep and can hardly form functioning relationships with their families.
- Sometimes Homework Does Not Improve Academic Outcomes
Little to no scientific research has proved homework is practical; however, an analysis done in 2006 shows that for 6th and 7th graders, there was a correlation between homework and achievements. But as students get to higher levels, that is not the case as most people focus more on what they want in life.
- Less Interest in Subjects With Lots of Homework
It is a no-brainer that students spend more time in school than home. However, when they are back at home, there is no change of routine as they spend the most time working on their respective assignments. In most cases, students are afraid of performing poorly in various subjects leading them to do certain subjects repeatedly, and the result is a lack of interest in those subjects or courses.
- Homework Derange Family Life
As is known, students tend to spend more time with their teachers than parents. They spend more time doing assignments than having some family time with homework. In the end, the family bond is not as strong as they have little to no time to focus on family.
- Disrupts School-Life Balance
School life is not just about attending classes, doing your homework, and hitting the books. Especially in college, which is a perfect period when people evolve and decide on various career paths they love. With the growing amount of assignments, it is harder for students to manage their time well, missing crucial steps and opportunities that make life worth living.
- Homework Strains Extracurricular Activities
Students who are more engrossed in homework have zero to no time to focus on other activities like games that can improve their brain activity. As they say, work with no play makes John a dull boy.
- Health Issues
Aside from the mental health, physical fitness is also at risk. Some students do a lot of junk stress eating leading to obesity. In contrast, others do not eat, leading to loss of weight, both of which are a disturbance to an individual's health.
- Lack of a Home Environment for Some Students
Doing homework at home is okay until the setting is not conducive at all. For some, students face various challenges while doing their homework at home, such as noise, family problems, and chores, to mention a few.
- Homework Creates More Working Hours for Students
Like any typical job that has 8-12 hours of work with homework, it means students get to do more hours, which eventually leads to burnout and dropout.
- Retaining Data Is Difficult
Having homework might be okay until you have 100 questions that you must provide answers to within a stipulated period. Not only will that kill your morale, you are most likely to understand a fraction of it perfectly and swing your way through the rest.
People are considering banning homework but have you thought of having no task? Having homework has its benefits, as stated below:
- Homework Often Gets Parents Involved
Some parents realize what their kids are learning when allowed to assist their kids with homework.
- Screen Time
When students get a lot of homework, they tend to ignore devices that otherwise could be causing more harm than good; gadgets are a severe issue nowadays. Phone addiction is a serious issue and is on the rise.
- Time Management Skills
One way of being positive with homework is that students always work around time to do everything on assignment and still work around socializing and advancing their career. As a result, students learn the art of time management.
- Homework Helps in Tracking Students’ Performance and Understanding
The primary reason for homework is to track the student's grasp academically. It is also a less pressured environ than having students show what they know in a class setting.
- Improve Children and Parents Relationships
When kids turn to their parents for assistance, they develop a shared understanding and form trust, and by this, the relationship between parents and children evolve.
- Homework Nurtures Independent Learning and Study Skills
Practice requires discipline. With homework, the students learn to be patient and disciplined to complete and understand their work in time. By doing the assignment by themselves, they also become independent, skills that any person will benefit from along the road of success.
After learning the pros and cons of banning homework, some might still ask when will homework be banned. Ultimately, the decision lies with the various districts and educators. No matter your argument about homework banning, there is still more research to conduct. As of now, the issue is still more of an opinion.
Place Your Order Now & Ace Your Homework!
Need help with an assignment, essay, or online class?

Need help with an assignment , essay, or online class ?
538 Debate Club: Should TikTok be banned?
The pros and cons of a possible de facto TikTok ban.
Last week, the House of Representatives passed a bipartisan bill that would ban TikTok unless its owner, the Chinese company ByteDance, sells its stake in the app. This decision has ignited a national debate about TikTok and the effects of social media . So, in true 538 fashion, we’re reintroducing a segment we like to call ‘Debate Club’ to discuss the issue. In this installment of the 538 Politics podcast, Senior Elections Analyst Geoffrey Skelley, Podcast Intern Jala Everett, and Senior Editor and Senior Elections Analyst Nathaniel Rakich engage in a spirited debate. They'll defend their arguments on whether to ban TikTok, maintain the status quo or even consider banning social media altogether.
Top Stories

What we know about the Baltimore bridge collapse
- 2 hours ago

Diddy's Los Angeles, Miami homes raided by federal agents
- Mar 25, 5:10 PM

Baltimore bridge collapse live updates: At least 6 unaccounted for
- 15 minutes ago

'Heroic': Traffic onto Baltimore Key Bridge halted before collapse
- 4 hours ago

Judge in New York hush money case places limited gag order on Trump
- 2 minutes ago
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Why Are Lawmakers Trying to Ban TikTok Instead of Doing What Voters Actually Want?

By Julia Angwin
Ms. Angwin is a contributing Opinion writer and an investigative journalist.
America is politically polarized. But there is an issue on which both sides agree: We need more privacy, and TikTok should not be banned.
A record 72 percent of Americans want “more government regulation” of what companies can do with their data, according to an October report from Pew Research Center . And only 31 percent of Americans favor a nationwide ban on TikTok, according to a February Associated Press/NORC opinion poll .
Despite public sentiment, the U.S. House passed legislation on Wednesday by an overwhelming majority that could force TikTok to divest from control by its Chinese parent company or be banned. Its fate in the Senate is not clear.
TikTok’s parent company, ByteDance, is based in China, and American lawmakers say they are pursuing a ban in the name of protecting U.S. data from the Chinese government. But lawmakers are not pursuing comprehensive federal privacy legislation that would protect Americans’ data on all the apps they use.
This is, sadly, just more evidence of how removed federal lawmaking has become from the will of the people. Issues with wide popular support such as abortion access and gun control remain unaddressed at the federal level. And a majority of Americans say that government policies do not reflect public opinion on key issues.
Despite this growing divide, it is truly stunning that lawmakers feel comfortable pushing a TikTok ban during a high-stakes election year. After all, one-third of U.S. adults say they use the site , and one-third of U.S. adults under 30 say they regularly get their news on TikTok . Even President Biden, despite saying he would sign the ban into law if it made it to his desk, just started a TikTok channel for his re-election campaign .
Some members of Congress, such as Representative Jeff Jackson, a North Carolina Democrat, regularly use TikTok to communicate with their constituents. Mr. Jackson, who voted for the bill, has 2.5 million followers on the site. “My message to TikTok: break up with the Chinese Communist Party or lose access to your American users,” said Representative Mike Gallagher, a Wisconsin Republican and one of the bill’s sponsors.
The legislation seeks to bar the distribution within the United States of “foreign adversary controlled applications such as TikTok” unless it sells itself within six months to a buyer that is approved by the U.S. president.
The rush to pass this bill is particularly odd because the federal government already has a process for dealing with foreign entities buying stakes in domestic companies. The Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States is an interagency body that reviews foreign investments for national security concerns. For instance, it was a review by the committee that caused a Chinese buyer to reverse its acquisition of the dating app Grindr in 2020.
The committee and TikTok have been negotiating for years over how to mitigate the national security concerns. After Donald Trump while president ordered the committee to investigate , TikTok offered a plan that would have transferred all its data on U.S. citizens to a U.S. subsidiary that would be overseen by Oracle. Oracle would have also overseen TikTok’s algorithms and content takedown decisions on behalf of the U.S. government. But the U.S. government rejected it for reasons that have not been disclosed, and it appears the negotiations have reached an impasse.
But the tricky thing is that forcing TikTok to sell would not solve the problems that lawmakers claim they are trying to address. Selling TikTok to a big tech company such as Google, Meta or Microsoft — after all, who else could afford its estimated price of $84 billion ? — would not make U.S. users’ data more secure. In fact, it would simply give the tech giant buying it a new trove of information about all of us that the new owner could use to enhance its already astoundingly detailed portraits.
Right now, for example, Google has most of my email, my documents, my web-browsing behavior and my search queries. The videos I watch on TikTok are, in fact, among the few things it doesn’t have. Adding those videos would add valuable new data to its dossier on me and allow it to monetize it with advertisers, data brokers and anyone else that uses its self-service online advertising platforms and services.
Sure, maybe in the worst-case scenario, the Chinese government is spying on my viewing of TikTok videos. (TikTok, of course, says that its Chinese parent company is entirely separate from the U.S. entity.) But TikTok doesn’t have much more data than any other app; all it knows is that I spend too much time watching cooking videos and makeup tutorials. This information probably helps China in its endless quest to provide all of the material goods that I buy, from kitchen equipment to makeup brushes, but it was already manufacturing those goods anyway, so my feeling is that my viewing data is just additional information about potential future demand for products.
OK, fine, you say, but what about the Chinese propaganda that is being spread through TikTok? I’ve read the same scare stories, and all I can say is that they aren’t that convincing. Referring to the People’s Republic of China, the Office of the Director of National Intelligence stated in its February threat assessment that “TikTok accounts run by a P.R.C. propaganda arm reportedly targeted candidates from both political parties during the U.S. midterm election cycle in 2022.”
That sounds terrifying until you consider that anyone can set up a TikTok account to target anyone during an election. We know, for instance, that Russians set up accounts on Facebook to try to influence U.S. elections in 2016. And they didn’t have to buy Facebook to do that. It’s also worth noting that the threat assessment does not allege that TikTok’s algorithm promoted the People’s Republic of China accounts — and I’m guessing that if the director of national intelligence’s office had evidence of that, it would have stated it.
And it’s not clear that the intelligence community has better evidence that it is providing behind closed doors. After a national security briefing on TikTok for members of Congress, Representative Sara Jacobs, Democrat of California, told The Associated Press : “Not a single thing that we heard in today’s classified briefing was unique to TikTok. It was things that happen on every single social media platform.”
Meanwhile, China appears to be having plenty of success pushing its political agenda through influencers on YouTube, Facebook and Instagram , according to a 2022 Associated Press investigation.
And that’s my point. All of the social media platforms are information minefields, rife with deceptive content from state actors, corporations, paid influencers and others. Their algorithms fuel our worst impulses by highlighting content that promotes anger and outrage. They strip mine our data to make money.
Forcing TikTok to merge with another data-hungry social media platform won’t solve any of that. What will make a difference is establishing base-line privacy rules that prohibit companies from exploiting our data and that give us control over the algorithms used to manipulate us.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Julia Angwin, a contributing Opinion writer and the founder of Proof News , writes about tech policy. You can follow her on Twitter or Mastodon or her personal newsletter .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Should homework be banned? The big debate Homework is a polarising topic. It can cause students to feel stressed or anxious. It adds extra pressure on teachers, who are often already struggling with their workloads. And, some parents resent the way homework can cut into family time at home. Yet despite this,...
From dioramas to book reports, from algebraic word problems to research projects, whether students should be given homework, as well as the type and amount of homework, has been debated for over a century. []While we are unsure who invented homework, we do know that the word "homework" dates back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger asked his followers to practice their speeches at home.
A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can't ...
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night. "Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's ...
Many earlier laws limiting homework were abolished, and the longterm trend toward less homework came to an end. The debate re-emerged a decade later when parents of the late '60s and '70s argued that children should be free to play and explore — similar anti-homework wellness arguments echoed nearly a century earlier.
Beyond that point, kids don't absorb much useful information, Cooper says. In fact, too much homework can do more harm than good. Researchers have cited drawbacks, including boredom and burnout toward academic material, less time for family and extracurricular activities, lack of sleep and increased stress.
American high school students, in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found. It's time for an uprising. Already, small rebellions ...
In 1901, for instance, California banned homework for students up to age 15, and limited it for older students, ... Much of the debate relies on anecdotes, intuition, or speculation.
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.. The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in ...
Social media has sparked into life about whether children should be given homework - should students be freed from this daily chore? Dr Gerald Letendre, a professor of education at Pennsylvania State University, investigates.
Bans proposed and implemented in the U.S. and abroad. The struggle of whether or not to assign homework is not a new one. In 2017, a Florida superintendent banned homework for elementary schools in the entire district, with one very important exception: reading at home. The United States isn't the only country to question the benefits of ...
In the modern world of education, the debate over whether homework should be banned or not has gained significant attention. As a trusted source of information, we understand the importance of ...
Reasons Why Homework Should Be Banned. 1. It Contributes to Increased Anxiety. If there's one word that describes middle-school and high-school students, it's anxiety. In my homework statistics article, I cite research showing that 74% of students cite homework as a source of stress.
Pros of Homework Bans. 1. Homework May Not Improve Academic Outcomes. Unfortunately, as highly debated as homework is, there has been little conclusive or scientific research indicating its ...
Yes. Generally, the link between homework and achievement scores is stronger for math compared to subjects like English and history. For middle school students especially, math homework can strengthen school performance. There is not a lot of research into the quality of homework. Most experts agree that homework should be reinforcing what kids ...
All in all, perhaps homework shouldn't be banned completely, but it needs to be considered in a fair and balanced way. Here are some important points to remember that take the individual needs and resources of students into account: Everyone is different: Every person is unique, and each student learns differently.
Banned: Disallow homework in K-8 grades in the U.S. public schools. 1. Homework puts an unfair burden on teachers. Warrant: Homework produces large amount of pointless work of little educational value, but marking it ties up much of teachers' time. Add in correcting it and the time it takes up in class going over it.
Excessive workload. The issue of excessive workload is a common complaint among students. Spending several hours on homework after a full school day can be mentally and physically draining. This workload can lead to burnout, decreased motivation, and negative attitudes toward school and learning.
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can't see it in the moment. 6. Homework Reduces Screen Time.
Here comes the list of the pros of banning homework. 1. Stay Interested in Subjects. It's no secret that students spend at least five days a week at colleges, but when they come back home, they still have to work on their homework which also takes a lot of time. Since most teachers assign too much homework, students waste many days working on ...
Students spending all this time on homework limits meaningful interactions with family members, stifling those relationships. Parents are also more likely to excuse students from household chores when they have excessive schoolwork, making the home feel less like a team and increasing tension around the house. [7] 8.
Big Debate Club . How it works; Debate Library. All Debates; PSHE Debates; BDC in Lessons; Join for free; Big debate club. Aras and Arthur . Current debate. Should there be a legal age for teens to drink energy drinks? Participants so far: 0 . Start debate. Join for free ...
Should Homework Be Banned Debate the Pros and Cons. Homework always seems like an inevitable side of the school. However, more schools realize that it might be a hurdle for students who struggle to find a balance between personal life, studies, and work. The homework should be banned debate has raised more worries as teachers and parents find ...
March 17, 2024. By Joshua Hunt. Produced by Aaron Esposito and Jack D'Isidoro. Edited by John Woo. Original music by Aaron Esposito. Engineered by Daniel Farrell and Andrea Vancura.
Getty Images. Last week, the House of Representatives passed a bipartisan bill that would ban TikTok unless its owner, the Chinese company ByteDance, sells its stake in the app. This decision has ...
App stores that violate the legislation could be fined based on the number of users of a banned app. The bill establishes fines of $5,000 per user of a banned app. So, in the case of TikTok, Apple ...
In a pointed speech from the Senate floor this month, the majority leader, Chuck Schumer, called for Israel to hold a new election and for voters to oust the prime minister, Benjamin Netanyahu ...
March 25, 2024, 6:00 a.m. ET. Hosted by Sabrina Tavernise. Featuring Anton Troianovski. Produced by Will Reid and Rachelle Bonja. Edited by Patricia Willens. Original music by Dan Powell and ...
And only 31 percent of Americans favor a nationwide ban on TikTok, according to a February Associated Press/NORC opinion poll. Despite public sentiment, the U.S. House passed legislation on ...