I Thought We’d Learned Nothing From the Pandemic. I Wasn’t Seeing the Full Picture

M y first home had a back door that opened to a concrete patio with a giant crack down the middle. When my sister and I played, I made sure to stay on the same side of the divide as her, just in case. The 1988 film The Land Before Time was one of the first movies I ever saw, and the image of the earth splintering into pieces planted its roots in my brain. I believed that, even in my own backyard, I could easily become the tiny Triceratops separated from her family, on the other side of the chasm, as everything crumbled into chaos.
Some 30 years later, I marvel at the eerie, unexpected ways that cartoonish nightmare came to life – not just for me and my family, but for all of us. The landscape was already covered in fissures well before COVID-19 made its way across the planet, but the pandemic applied pressure, and the cracks broke wide open, separating us from each other physically and ideologically. Under the weight of the crisis, we scattered and landed on such different patches of earth we could barely see each other’s faces, even when we squinted. We disagreed viciously with each other, about how to respond, but also about what was true.
Recently, someone asked me if we’ve learned anything from the pandemic, and my first thought was a flat no. Nothing. There was a time when I thought it would be the very thing to draw us together and catapult us – as a capital “S” Society – into a kinder future. It’s surreal to remember those early days when people rallied together, sewing masks for health care workers during critical shortages and gathering on balconies in cities from Dallas to New York City to clap and sing songs like “Yellow Submarine.” It felt like a giant lightning bolt shot across the sky, and for one breath, we all saw something that had been hidden in the dark – the inherent vulnerability in being human or maybe our inescapable connectedness .

More from TIME
Read More: The Family Time the Pandemic Stole
But it turns out, it was just a flash. The goodwill vanished as quickly as it appeared. A couple of years later, people feel lied to, abandoned, and all on their own. I’ve felt my own curiosity shrinking, my willingness to reach out waning , my ability to keep my hands open dwindling. I look out across the landscape and see selfishness and rage, burnt earth and so many dead bodies. Game over. We lost. And if we’ve already lost, why try?
Still, the question kept nagging me. I wondered, am I seeing the full picture? What happens when we focus not on the collective society but at one face, one story at a time? I’m not asking for a bow to minimize the suffering – a pretty flourish to put on top and make the whole thing “worth it.” Yuck. That’s not what we need. But I wondered about deep, quiet growth. The kind we feel in our bodies, relationships, homes, places of work, neighborhoods.
Like a walkie-talkie message sent to my allies on the ground, I posted a call on my Instagram. What do you see? What do you hear? What feels possible? Is there life out here? Sprouting up among the rubble? I heard human voices calling back – reports of life, personal and specific. I heard one story at a time – stories of grief and distrust, fury and disappointment. Also gratitude. Discovery. Determination.
Among the most prevalent were the stories of self-revelation. Almost as if machines were given the chance to live as humans, people described blossoming into fuller selves. They listened to their bodies’ cues, recognized their desires and comforts, tuned into their gut instincts, and honored the intuition they hadn’t realized belonged to them. Alex, a writer and fellow disabled parent, found the freedom to explore a fuller version of herself in the privacy the pandemic provided. “The way I dress, the way I love, and the way I carry myself have both shrunk and expanded,” she shared. “I don’t love myself very well with an audience.” Without the daily ritual of trying to pass as “normal” in public, Tamar, a queer mom in the Netherlands, realized she’s autistic. “I think the pandemic helped me to recognize the mask,” she wrote. “Not that unmasking is easy now. But at least I know it’s there.” In a time of widespread suffering that none of us could solve on our own, many tended to our internal wounds and misalignments, large and small, and found clarity.
Read More: A Tool for Staying Grounded in This Era of Constant Uncertainty
I wonder if this flourishing of self-awareness is at least partially responsible for the life alterations people pursued. The pandemic broke open our personal notions of work and pushed us to reevaluate things like time and money. Lucy, a disabled writer in the U.K., made the hard decision to leave her job as a journalist covering Westminster to write freelance about her beloved disability community. “This work feels important in a way nothing else has ever felt,” she wrote. “I don’t think I’d have realized this was what I should be doing without the pandemic.” And she wasn’t alone – many people changed jobs , moved, learned new skills and hobbies, became politically engaged.
Perhaps more than any other shifts, people described a significant reassessment of their relationships. They set boundaries, said no, had challenging conversations. They also reconnected, fell in love, and learned to trust. Jeanne, a quilter in Indiana, got to know relatives she wouldn’t have connected with if lockdowns hadn’t prompted weekly family Zooms. “We are all over the map as regards to our belief systems,” she emphasized, “but it is possible to love people you don’t see eye to eye with on every issue.” Anna, an anti-violence advocate in Maine, learned she could trust her new marriage: “Life was not a honeymoon. But we still chose to turn to each other with kindness and curiosity.” So many bonds forged and broken, strengthened and strained.
Instead of relying on default relationships or institutional structures, widespread recalibrations allowed for going off script and fortifying smaller communities. Mara from Idyllwild, Calif., described the tangible plan for care enacted in her town. “We started a mutual-aid group at the beginning of the pandemic,” she wrote, “and it grew so quickly before we knew it we were feeding 400 of the 4000 residents.” She didn’t pretend the conditions were ideal. In fact, she expressed immense frustration with our collective response to the pandemic. Even so, the local group rallied and continues to offer assistance to their community with help from donations and volunteers (many of whom were originally on the receiving end of support). “I’ve learned that people thrive when they feel their connection to others,” she wrote. Clare, a teacher from the U.K., voiced similar conviction as she described a giant scarf she’s woven out of ribbons, each representing a single person. The scarf is “a collection of stories, moments and wisdom we are sharing with each other,” she wrote. It now stretches well over 1,000 feet.
A few hours into reading the comments, I lay back on my bed, phone held against my chest. The room was quiet, but my internal world was lighting up with firefly flickers. What felt different? Surely part of it was receiving personal accounts of deep-rooted growth. And also, there was something to the mere act of asking and listening. Maybe it connected me to humans before battle cries. Maybe it was the chance to be in conversation with others who were also trying to understand – what is happening to us? Underneath it all, an undeniable thread remained; I saw people peering into the mess and narrating their findings onto the shared frequency. Every comment was like a flare into the sky. I’m here! And if the sky is full of flares, we aren’t alone.
I recognized my own pandemic discoveries – some minor, others massive. Like washing off thick eyeliner and mascara every night is more effort than it’s worth; I can transform the mundane into the magical with a bedsheet, a movie projector, and twinkle lights; my paralyzed body can mother an infant in ways I’d never seen modeled for me. I remembered disappointing, bewildering conversations within my own family of origin and our imperfect attempts to remain close while also seeing things so differently. I realized that every time I get the weekly invite to my virtual “Find the Mumsies” call, with a tiny group of moms living hundreds of miles apart, I’m being welcomed into a pocket of unexpected community. Even though we’ve never been in one room all together, I’ve felt an uncommon kind of solace in their now-familiar faces.
Hope is a slippery thing. I desperately want to hold onto it, but everywhere I look there are real, weighty reasons to despair. The pandemic marks a stretch on the timeline that tangles with a teetering democracy, a deteriorating planet , the loss of human rights that once felt unshakable . When the world is falling apart Land Before Time style, it can feel trite, sniffing out the beauty – useless, firing off flares to anyone looking for signs of life. But, while I’m under no delusions that if we just keep trudging forward we’ll find our own oasis of waterfalls and grassy meadows glistening in the sunshine beneath a heavenly chorus, I wonder if trivializing small acts of beauty, connection, and hope actually cuts us off from resources essential to our survival. The group of abandoned dinosaurs were keeping each other alive and making each other laugh well before they made it to their fantasy ending.
Read More: How Ice Cream Became My Own Personal Act of Resistance
After the monarch butterfly went on the endangered-species list, my friend and fellow writer Hannah Soyer sent me wildflower seeds to plant in my yard. A simple act of big hope – that I will actually plant them, that they will grow, that a monarch butterfly will receive nourishment from whatever blossoms are able to push their way through the dirt. There are so many ways that could fail. But maybe the outcome wasn’t exactly the point. Maybe hope is the dogged insistence – the stubborn defiance – to continue cultivating moments of beauty regardless. There is value in the planting apart from the harvest.
I can’t point out a single collective lesson from the pandemic. It’s hard to see any great “we.” Still, I see the faces in my moms’ group, making pancakes for their kids and popping on between strings of meetings while we try to figure out how to raise these small people in this chaotic world. I think of my friends on Instagram tending to the selves they discovered when no one was watching and the scarf of ribbons stretching the length of more than three football fields. I remember my family of three, holding hands on the way up the ramp to the library. These bits of growth and rings of support might not be loud or right on the surface, but that’s not the same thing as nothing. If we only cared about the bottom-line defeats or sweeping successes of the big picture, we’d never plant flowers at all.
More Must-Reads from TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People in AI 2024
- Inside the Rise of Bitcoin-Powered Pools and Bathhouses
- How Nayib Bukele’s ‘Iron Fist’ Has Transformed El Salvador
- What Makes a Friendship Last Forever?
- Long COVID Looks Different in Kids
- Your Questions About Early Voting , Answered
- Column: Your Cynicism Isn’t Helping Anybody
- The 32 Most Anticipated Books of Fall 2024
Contact us at [email protected]
Introducing AARP Now. New and improved, it’s the app that makes your membership truly mobile!
AARP daily Crossword Puzzle
Hotels with AARP discounts
Life Insurance
AARP Dental Insurance Plans
LIMITED TIME OFFER: Labor Day Sale!
Join AARP for just $9 per year with a 5-year membership and get a FREE Gift!
Get instant access to members-only products, hundreds of discounts, a free second membership, and a subscription to AARP the Magazine.
- right_container
Work & Jobs
Social Security
- AARP en Español
- Membership & Benefits
- Members Edition
- AARP Rewards
- AARP Rewards %{points}%
Conditions & Treatments
Drugs & Supplements
Health Care & Coverage
Health Benefits

AARP Hearing Center
Advice on Tinnitus and Hearing Loss

Your Health
What to Know About Vaccines

Brain Health Resources
Tools and Explainers on Brain Health
25 Ways to Get a Flatter Stomach
Scams & Fraud
Personal Finance
Money Benefits

View and Report Scams in Your Area

AARP Foundation Tax-Aide
Free Tax Preparation Assistance

AARP Money Map
Get Your Finances Back on Track

How to Protect What You Collect
Small Business
Age Discrimination

Flexible Work
Freelance Jobs You Can Do From Home

AARP Skills Builder
Online Courses to Boost Your Career

31 Great Ways to Boost Your Career

ON-DEMAND WEBINARS
Tips to Enhance Your Job Search

Get More out of Your Benefits

When to Start Taking Social Security

10 Top Social Security FAQs

Social Security Benefits Calculator

Medicare Made Easy
Original vs. Medicare Advantage

Enrollment Guide
Step-by-Step Tool for First-Timers

Prescription Drugs
9 Biggest Changes Under New Rx Law

Medicare FAQs
Quick Answers to Your Top Questions
Care at Home
Financial & Legal
Life Balance

LONG-TERM CARE
Understanding Basics of LTC Insurance

State Guides
Assistance and Services in Your Area

Prepare to Care Guides
How to Develop a Caregiving Plan

End of Life
How to Cope With Grief, Loss
Recently Played
Word & Trivia
Atari® & Retro
Members Only
Staying Sharp
Mobile Apps
More About Games

Right Again! Trivia

Right Again! Trivia – Sports

Atari® Video Games

Throwback Thursday Crossword
Travel Tips
Vacation Ideas
Destinations
Travel Benefits

Camping and RV Ideas
Fun Camping and RV Journeys
Exploration
25 Great Ways to Explore

Train Travel
How to Find Great Train Deals

AARP National Park Guide
Travel to Pinnacles in California
Entertainment & Style
Family & Relationships
Personal Tech
Home & Living
Celebrities
Beauty & Style

TV for Grownups
Fall TV Preview

Kevin Costner’s Big Bet

Looking Back
Take Our ’80s Music Quiz

Sex & Dating
7 Dating Dos and 7 Don'ts

Get Happier
Creating Social Connections
Friends & Family
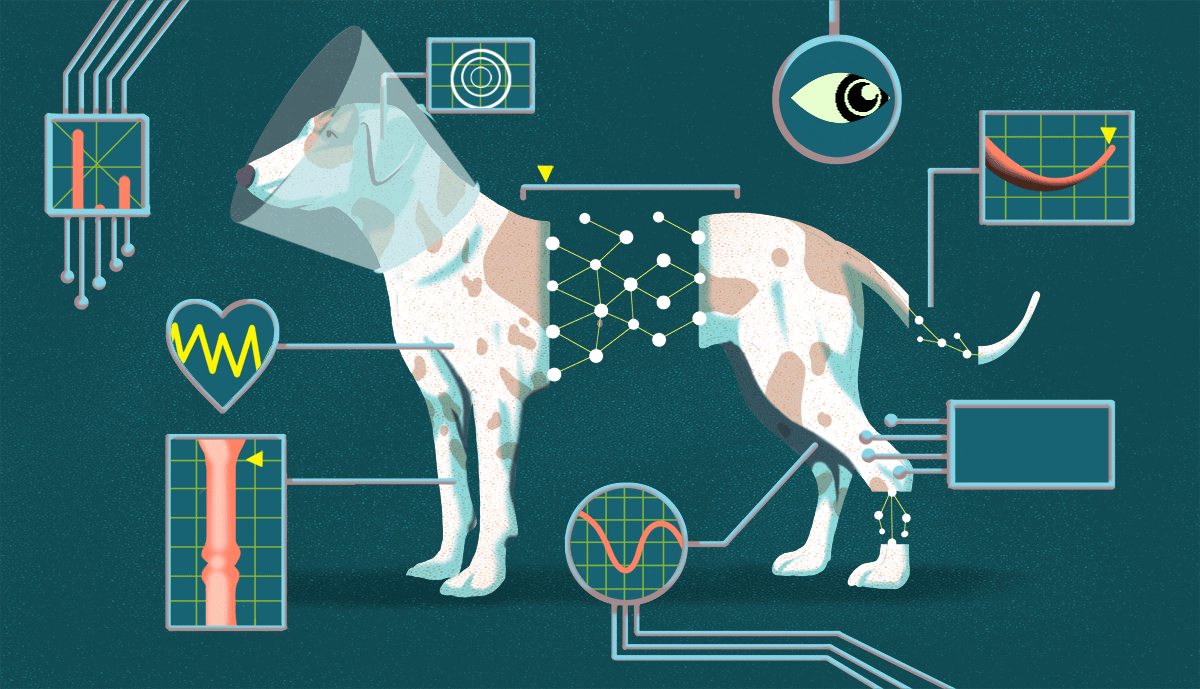
Veterinarians May Use AI to Treat Pets

Home Technology
What's Inside Your Smartphone

Virtual Community Center
Join Free Tech Help Events

Creative Ways to Store Your Pets Gear

Meals to Make in the Microwave

Wearing Shoes Inside: Pros vs. Cons
Driver Safety
Maintenance & Safety
Trends & Technology

AARP Smart Guide
How to Clean Your Car

We Need To Talk
Assess Your Loved One's Driving Skills

AARP Smart Driver Course

Building Resilience in Difficult Times

Tips for Finding Your Calm

Weight Loss After 50 Challenge

Cautionary Tales of Today's Biggest Scams

7 Top Podcasts for Armchair Travelers

Jean Chatzky: ‘Closing the Savings Gap’

Quick Digest of Today's Top News

AARP Top Tips for Navigating Life

Get Moving With Our Workout Series
You are now leaving AARP.org and going to a website that is not operated by AARP. A different privacy policy and terms of service will apply.
15 Lessons the Coronavirus Pandemic Has Taught Us
What we've learned over the past 12 months could pay off for years to come.

For the past year, our country has been mired in not one deep crisis but three: a pandemic , an economic meltdown and one of the most fraught political transitions in our history. Interwoven in all three have been challenging issues of racial disparity and fairness. Dealing with all of this has dominated much of our energy, attention and, for many Americans, even our emotions.
But spring is nearly here, and we are, by and large, moving past the worst moments as a nation — which makes it a good time to take a deep breath and assess the changes that have occurred. While no one would be displeased if we could magically erase this whole pandemic experience, it's been the crucible of our lives for a year, and we have much to learn from it — and even much to gain.

Join AARP for just $9 per year with a 5-year membership and get a FREE Gift!
AARP asked dozens of experts to go beyond the headlines and to share the deeper lessons of the past year that have had a particular impact on older Americans. More importantly, we asked them to share how we can use these learnings to make life better for us as we recover and move forward. Here is what they told us.
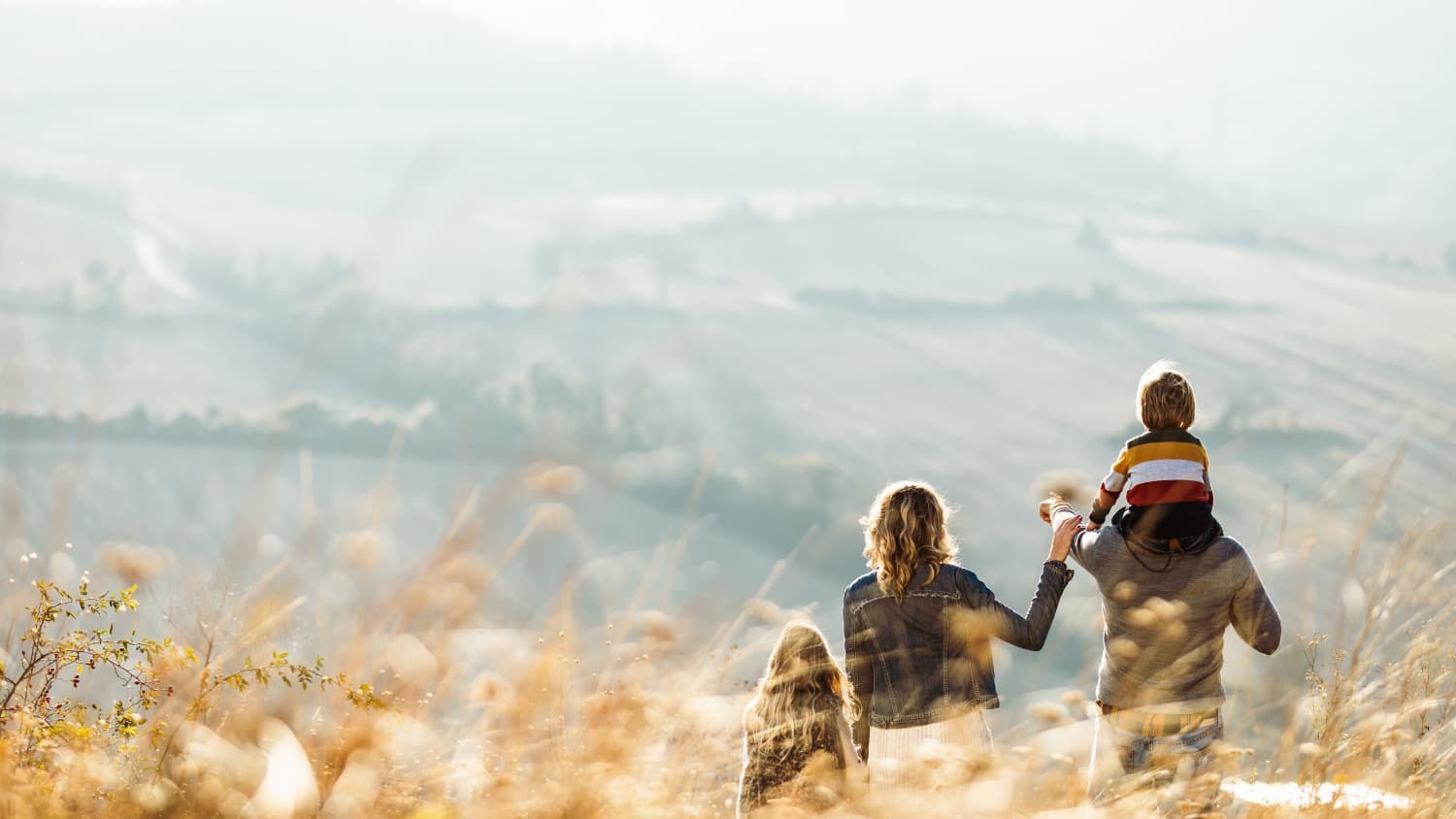
Lesson 1: Family Matters More Than We Realized
"The indelible image of the older person living alone and having to struggle — we need to change that. You're going to see more older people home-sharing within families and cohousing across communities to avoid future situations of tragedy."
—Marc Freedman, CEO and president of Encore.org and author of How to Live Forever: The Enduring Power of Connecting the Generations
Norman Rockwell would have needed miles of canvas to portray the American family this past year. You can imagine the titles: The Family That Zooms Together. Generations Under One Roof. Grandkids Outside My Window. The Shared Office . “Beneath the warts and complexities of all that went wrong, we rediscovered the interdependence of generations and how much we need each other,” Freedman says. Among the lessons:
Adult kids are OK. A Pew Research Center survey last summer found that 52 percent of the American population between ages 18 and 29 were living with parents, a figure unmatched since the Great Depression. From February to July 2020, 2.6 million young adults moved back with one or both parents. That's a lot of shared Netflix accounts. It's also a culture shift, says Karen Fingerman, director of the Texas Aging & Longevity Center at the University of Texas at Austin. “After the family dinners together, grandparents filling in for childcare, and the wise economic sense, it's going to be acceptable for adult family members to co-reside,” Fingerman says. “At least for a while.”
What We've Learned From the Pandemic
• Lesson 1: Family Matters • Lesson 2: Medical Breakthroughs • Lesson 3: Self-Care Matters • Lesson 4: Be Financially Prepared • Lesson 5: Age Is Just a Number • Lesson 6: Getting Online for Good • Lesson 7: Working Anywhere • Lesson 8: Restoring Trust • Lesson 9: Gathering Carefully • Lesson 10: Isolation's Health Toll • Lesson 11: Getting Outside • Lesson 12: Wealth Disparities’ Toll • Lesson 13: Preparing for the Future • Lesson 14: Tapping Telemedicine • Lesson 15: Cities Are Changing
Spouses and partners are critical to well-being . “The ones who've done exceptionally well are couples in long-term relationships who felt renewed intimacy and reconnection to each other,” says social psychologist Richard Slatcher, who runs the Close Relationships Laboratory at the University of Georgia.
Difficult caregiving can morph into good-for-all home-sharing. To get older Americans out of nursing homes and into a loved one's home — a priority that has gained in importance and urgency due to the pandemic — will take more than just a willing child or grandchild. New resources could help, like expanding Medicaid programs to pay family caregivers, such as an adult child, or initiatives like the Program of All-Inclusive Care for the Elderly, a Medicare-backed benefit currently helping 50,000 “community dwelling” seniors with medical services, home care and transportation.
"A positive piece this year has been the pause to reflect on how we can help people stay in their homes as they age, which is what everyone wants,” says Nancy LeaMond, AARP's chief advocacy and engagement officer. “If you're taking care of a parent, grandparent, aging partner or yourself, you see more than ever the need for community and government support, of having technology to communicate with your doctor and of getting paid leave for family caregivers. The pandemic has forced us to think about all these things, and that's very positive.”
Family may be the best medicine of all . “Now we know if you can't hug your 18-month-old granddaughter in person, you can read to her on FaceTime,” says Jane Isay, author of several books about family relationships. “You can send your adult kids snail mail. You can share your life's wisdom even from a distance. These coping skills may be the greatest gifts of COVID” — to an older generation that deeply and rightly fears isolation.

Lesson 2: We Have Unleashed a Revolution in Medicine
" One of the biggest lessons we've learned from COVID is that the scientific community working together can do some pretty amazing things."
—John Cooke, M.D., medical director of the RNA Therapeutics Program at Houston Methodist Hospital's DeBakey Heart and Vascular Center
In the past it's taken four to 20 years to create conventional vaccines. For the new messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, it was a record-setting 11 months. The process may have changed forever the way drugs are developed.
"Breakthroughs” come after years of research . Supporting the development of the COVID-19 vaccines was more than a decade of research into mRNA vaccines, which teach human cells how to make a protein that triggers a specific immune response. The research had already overcome many challenging hurdles, such as making sure that mRNA wouldn't provoke inflammation in the body, says Lynne E. Maquat, director of the University of Rochester's Center for RNA Biology: From Genome to Therapeutics.
Vaccines may one day treat heart disease and more. In the near future, mRNA technology could lead to better flu vaccines that could be updated quickly as flu viruses mutate with the season, Maquat says, or the development of a “universal” flu shot that might be effective for several years. Drug developers are looking at vaccines for rabies, Zika virus and HIV. “I expect to see the approval of more mRNA-based vaccines in the next several years,” says mRNA researcher Norbert Pardi, a research assistant professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
"We could use mRNA for diseases and conditions that can't be treated with drugs,” Cooke explains.
It may also target our biggest killers . Future mRNA therapies could help regenerate muscle in failing hearts and target the unique genetics of individual cancers with personalized cancer vaccines. “Every case of cancer is unique, with its own genetics,” Cooke says. “Doctors will be able to sequence your tumor and use it to make a vaccine that awakens your immune system to fight it.” Such mRNA vaccines will also prepare us for future pandemics, Maquat says.
In the meantime, use the vaccines we have available. Don't skip recommended conventional vaccines now available to older adults for the flu, pneumonia, shingles and more, Pardi says. The flu vaccine alone, which 1 in 3 older adults skipped in the winter 2019 season, saves up to tens of thousands of lives a year and lowers your risk for hospitalization with the flu by 28 percent and for needing a ventilator to breathe by 46 percent.
Lesson 3: Self Care Is Not Self-Indulgence
"Not only does self-care have positive outcomes for you, but it also sets an example to younger generations as something to establish and maintain for your entire life."
—Richelle Concepcion, clinical psychologist and president of the Asian American Psychological Association
As the virus upended life last spring, America became hibernation nation. Canned, dry and instant soup sales have risen 37 percent since last April. Premium chocolate sales grew by 21 percent in the first six months of the pandemic. The athleisure market that includes sweatpants and yoga wear saw its 2020 U.S. revenue push past an estimated $105 billion.
With 7 in 10 American workers doing their jobs from home, “COVID turned the focus, for all ages, on the small, simple pleasures that soothe and give us meaning,” says Isabel Gillies, author of Cozy: The Art of Arranging Yourself in the World.
Why care about self-care? Pampering is vital to well-being — for yourself and for those around you. Activities that once felt indulgent became essential to our health and equilibrium, and that self-care mindset is likely to endure. Whether it is permission to take long bubble baths, tinkering in the backyard “she shed,” enjoying herbal tea or seeing noon come while still in your robe, “being good to yourself offers a necessary reprieve from whatever horrors threaten us from out there,” Gillies says. Being good to yourself is good for others, too. A recent European survey found that 77 percent of British respondents 75 and younger consider it important to take their health into their own hands in order not to burden the health care system.
Nostalgia TV, daytime PJs. It's OK to use comfort as a crutch. Comfort will help us ease back to life. Some companies are already hawking pajamas you can wear in public. Old-fashioned drive-ins and virtual cast reunions for shows like Taxi, Seinfeld and Happy Days will likely continue as long as the craving is there. (More than half the consumers in a 2020 survey reported finding comfort in revisiting TV and music from their childhood.) Even the iconic “Got Milk?” ads are back, after dairy sales started to show some big upticks.
So, cut yourself some slack. Learn a new skill; adopt a pet; limit your news diet; ask for help if you need it. You've lived long enough to see the value of prioritizing number one. “Not only does self-care have positive outcomes for you,” Concepcion says, “but it also sets an example to younger generations as something to establish and maintain for your entire life."
Lesson 4: Have a Stash Ready for the Next Crisis
"The need to augment our retirement savings system to help people put away emergency savings is crucial."
—J. Mark Iwry, a senior fellow at the Brookings Institution and former senior adviser to the U.S. secretary of the Treasury
Before the pandemic, nearly 4 in 10 households did not have the cash on hand to cover an unexpected $400 expense, according to a Federal Reserve report. Then the economic downturn hit. By last October, 52 percent of workers were reporting reduced hours, lower pay, a layoff or other hits to their employment situation. A third had taken a loan or early withdrawal from a retirement plan , or intended to. “Alarm bells were already ringing, but many workers were caught off guard without emergency savings,” says Catherine Collinson, CEO and president of the Transamerica Institute. “The pandemic has laid bare so many weaknesses in our safety net."
Companies can help . One solution could be a workplace innovation that's just beginning to catch on: an employee-sponsored rainy-day savings account funded with payroll deductions. By creating a dedicated pot of savings, the thinking goes, workers are less likely to tap retirement accounts in an emergency. “It's much better from a behavioral standpoint to separate short-term savings from long-term savings,” Iwry says. (AARP has been working to make these accounts easier to create and use and is already offering them to its employees.)
Funding that emergency savings account with automatic payroll deductions is a key to the program's success. “Sometimes you think you don't have the money to save, but if a little is put away for you each pay period, you don't feel the pinch,” Iwry notes.
We're off to a good start . Thanks to quarantines and forced frugality, Americans’ savings rate — the average percentage of people's income left over after taxes and personal spending — skyrocketed last spring, peaking at an unprecedented 33.7 percent. On the decline since then, most recently at 13.7 percent, it's still above the single-digit rates characterizing much of the past 35 years. Where it will ultimately settle is unclear; currently, it's in league with high-saving countries Mexico and Sweden. The real model of thriftiness: China, where, according to the latest available figures, the household savings rate averaged at least 30 percent for 14 years straight.
Lesson 5: The Adage ‘Age Is Just a Number’ Has New Meaning
"This isn't just about the pandemic. Your health is directly related to lifestyle — nutrition, physical activity, a healthy weight and restorative sleep."
—Jacob Mirsky, M.D., primary care physician at the Massachusetts General Hospital Revere HealthCare Center and an instructor at Harvard Medical School
Just a few months ago, researchers at Scotland's University of Glasgow asked a big question: If you're healthy, how much does older age matter for risk of death from COVID? The health records of 470,034 women and men revealed some intriguing answers.
Age accounted for a higher risk, but comorbidities (essentially, having two or more health issues simultaneously) mattered much more. Specifically, risk for a fatal infection was four times higher for healthy people 75 and older than for all participants younger than 65. But if you compared all those 75 and older — including those with chronic health condition s like high blood pressure, obesity or lung problems — that shoved the grim odds up thirteenfold.

AARP NEWSLETTERS

%{ newsLetterPromoText }%
%{ description }%
Privacy Policy
ARTICLE CONTINUES AFTER ADVERTISEMENT
Live healthfully, live long . More insights from the study: A healthy 75-year-old was one-third as likely to die from the coronavirus as a 65-year-old with multiple chronic health issues. The bottom line: Age affects your risk of severe illness with COVID, but you should be far more focused on avoiding chronic health conditions. “Coronavirus highlighted yet another reason it's so important to attend to health factors like poor diet and lack of exercise that cause so much preventable illness and death,” says Massachusetts General's Mirsky. “Lifestyle changes can improve your overall health, which will likely directly reduce your risk of developing severe COVID or dying of COVID."
Exercise remains critical . In May 2020 a British study of 387,109 adults in their 40s through 60s found a 38 percent higher risk for severe COVID in people who avoided physical activity. “Mobility should be considered one of the vital signs of health,” concludes exercise psychologist David Marquez, a professor in the department of kinesiology and nutrition at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
AARP® Dental Insurance Plan administered by Delta Dental Insurance Company
Dental insurance plans for members and their families

Lesson 6: We Befriended Technology, and There's No Going Back
"Folks who have tried online banking will stay with it. It won't mean they won't go back to branches, but they might go back for a different purpose."
—Theodora Lau, founder of financial technology consulting firm Unconventional Ventures
Of course, the world has long been going digital . But before the pandemic, standard operating procedure for most older Americans was to buy apples at the grocery, try the shoes on first before buying, have your doctor measure your blood pressure and see that hot new movie at the theater.
Arguably the biggest long-term societal effect of the pandemic will be a grand flipping of the switch that makes the digital solution the first choice of many Americans for handling life's tasks. We still may cling to a few IRL (in real life) experiences, but it is increasingly apparent that easy-to-use modern virtual tools are the new default.
"If nothing else, COVID has shown us how resilient and adaptable humans are as a society when forced to change,” says Joseph Huang, CEO of StartX, a nonprofit that helps tech companies get off the ground. “We've been forced to learn new technologies that, in many cases, have been the only safe way to continue to live our lives and stay connected to our loved ones during the pandemic.”
The tech boom wasn't just video calls and streaming TV. Popular food delivery apps more than doubled their earnings last year. Weddings and memorial services were held over videoconferences (yes, we'll go back to in-person ones but probably with cameras and live feeds now to include remote participants). In the financial sector, PayPal reported that its fastest-growing user group was people over 50; Chase said about half of its new online users were 50-plus. In telehealth, more doctors conducted routine exams via webcam than ever before — and, in response, insurance coverage expanded for these remote appointments. “It quickly became the only way to operate at scale in today's world,” Huang says, “both for us as patients and for the doctors and nurses who treat us. Telemedicine will turn out to be a better and more effective experience in many cases, even after COVID ends."
Tech is for all . To financial technology expert Lau, the tech adoption rate by older people is no surprise. She never believed the myth that older people lack such knowledge. “There's a difference between knowing how to use something versus preferring to use it,” Lau says. “Sometimes we know how, but we prefer face-to-face interaction.” And now those preferences are shifting.

Lesson 7: Work Is Anywhere Now — a Shift That Bodes Well for Older Americans
"One of the major impacts of the new working-from-home focus is that more jobs are becoming non-location-specific."
—Carol Fishman Cohen, cofounder of iRelaunch, which works with employers to create mid-career return-to-work programs for older workers
Necessity is the mother of reinvention : Forced to work remotely since the onset of the pandemic, millions of workers — and their managers — have learned they could be just as productive as they were at the office, thanks to videoconferencing, high-speed internet and other technologies. “This has opened a lot of corporate eyes,” says Steven Allen, professor of economics at North Carolina State University's Poole College of Management. Twitter, outdoor-goods retailer REI and insurer Lincoln Financial Group are a few of the companies that have announced plans to shift toward more remote work on a permanent basis.
Face-lift your Face-Time . Yes, many workers are tied to a location: We will always need nurses, police, roofers, machine operators, farmers and countless other workers to show up. But if you are among the people who are now able to work remotely, you may be able to live in a less expensive area than where your employer is based — or work right away from the home you were planning to retire to later on, Cohen says. As remote hiring takes hold, how you project yourself on-screen becomes more of a factor. “This puts more pressure on you to make sure you show up well in a virtual setting,” Cohen notes. And don't assume being comfortable with Zoom is a feather in your cap; mentioning it is akin to listing “proficient in Microsoft Word” on your résumé.
Self-employed workers have suffered during the pandemic — nearly two-thirds report being hurt financially, according to the “State of Independence in America 2020” report from MBO Partners — but remote work could fuel their comeback. Before the pandemic, notes Steve King, partner at Emergent Research, businesses with a high percentage of remote workers used a high percentage of independent contractors. “Now that companies are used to workers not being as strongly attached physically to a workplace, they'll be more amenable to hiring independent workers,” he says.
Travel less, stay longer . Tired of sitting in traffic to and from work? Can't stand flying across country for a single meeting? Ridding yourself of these hassles with an internet connection and Zoom calls may be the incentive you need to work longer. People often quit jobs because of little frustrations, Allen says. But now, he adds, “the things that wear you down may be going by the wayside."
Ageism remains a threat . Older workers — who before the coronavirus enjoyed lower unemployment rates than mid-career workers — have been hit especially hard by the pandemic. In December, 45.5 percent of unemployed workers 55 and older had been out of work for 27 weeks or more, compared with 35.1 percent of younger job seekers. Some employers, according to reports this fall, are replacing laid-off older workers with younger, lower-cost ones, instead of recalling those older employees. Psychological studies, Allen says, indicate that older workers have better communication and interpersonal skills — both of which are critical for successful remote work. But whether those strengths can offset age discrimination in the workplace is unknown.
Lesson 8: Our Trust in One Another Has Frayed, but It Can Be Slowly Restored
"Truth matters, but it requires messaging and patience.”
—Historian John M. Barry, author of The Great Influenza
Even before our views perforated along lines dotted by pandemic politics, race, class and whether Bill Gates is trying to save us or track us, we were losing faith in society. In 1997, 64 percent of Americans put a “very great or good deal of trust” in the political competence of their fellow citizens; today only a third of us feel that way. A 2019 Pew survey found that the majority of Americans say most people can't be trusted. It's even tougher to trust in the future. Only 13 percent of millennials say America is the greatest country in the world, compared with 45 percent of members of the silent generation. No wonder that by June of last year, “national pride” was lower than at any point since Gallup began measuring. To trust again:
As life returns, look beyond your familiar pod. “Distrust breeds distrust, but hope isn't lost for finding common ground, especially for older people,” says Encore.org's Freedman. “Even in the era of ‘OK, boomer’ and ‘OK, millennial’ — memes that dismiss entire generations with an eye roll — divides are bridgeable with what Freedman calls “proximity and purpose.” Rebuilding trust together, across generations, under shared priorities and common humanity.” He points to pandemic efforts like Good Neighbors from the home-sharing platform Nesterly, which pairs older and younger people to provide cross-generational support, and UCLA's Generation Xchange, which connects Gen X mentors with children in grades K-3 in South Los Angeles, where educational achievement is notoriously poor. “Engaging with people for a common goal makes you trust them,” he says.
Be patient but verify facts. History also provides a guide. In the wake of the 1918 influenza pandemic that killed between 50 million and 100 million people, trust in authority withered after local and national government officials played down the disease's threats in order to maintain wartime morale. Historian Barry points out that the head of the Army's’ division of communicable diseases was so worried about the collective failure of trust that he warned that “civilization could easily disappear ... from the face of the earth.” It didn't then, and it won't now, Barry says.
Verify facts and then decide. Check reliable, balanced news sources (such as Reuters and the Associated Press) and unbiased fact-checking sites (such as PolitiFact) before clamping down on an opinion.
Perhaps most important, be open to changing conditions and viewpoints. “As we see vaccines and therapeutic drugs slowly gain widespread success in fighting this virus, I think we'll start to overcome some of our siloed ways of thinking and find relief — together as one — that this public health menace is ending,” Barry adds. “We have to put our faith in other people to get through this together.”

Lesson 9: The Crowds Will Return, but We'll Gather Carefully
"Masks and sanitizers will be part of the norm for years, the way airport and transportation security measures are still in place from 9/11."
— Christopher McKnight Nichols, associate professor of history at Oregon State University and founder of the Citizenship and Crisis Initiative
The COVID-19 pandemic won't end with bells tolling or a ticker-tape parade . Instead, we'll slowly, cautiously ease back to familiar activities. For all our fears of the coronavirus, many of us can't wait to resume a public life: When 1,000 people 65 and older were asked which pursuits they were most eager to start anew post-pandemic, 78 percent said going out to dinner, 76 percent picked getting together with family and friends, 71 percent chose travel, and 30 percent cited going to the movies.
Seeing art , attending concerts, cheering in a stadium — even going to class reunions we might have once dreaded — we'll do them again. But how will we return to feeling comfortable in groups of tens, hundreds and thousands? And will these gatherings be different? How we come together:
Don't expect the same old, same old . Just as the rationing, isolation and economic crisis caused by World War I and the Spanish flu epidemic “led to a kind of awakening of how we assembled,” Nichols says, expect COVID to shake up the nature and personality of our public spaces. Back in the 1920s, it was the rise of jazz clubs, organized athletics, fraternal organizations and the golden age of the movie cinema. As the pandemic subsides, we'll probably see more temperature-controlled outdoor event and dining spaces, more pedestrian and bicycling options, more city parks and more hybrid events that give you the option to attend virtually.
Retrain your brain . Psychologists say the techniques of cognitive behavioral therapy can help people at any age regain the certainty and confidence they need to venture into the public space post-pandemic. “Visualizing good outcomes and repeating a stated goal can help overcome whatever obstacles are holding you back,” says Gabriele Oettingen, a professor of psychology at New York University, who suggests making an “if-then plan” to reacclimate to public life. If eating indoors at a restaurant is too agitating, even if you've been vaccinated, then try a table outside first. If a bucket-list family vacation to Italy feels too daunting, then book a stateside trip together first. “There's always an alternative if something stands in the way of you fulfilling your wish,” she says. “Eventually, you'll get there.”
Lesson 10: Loneliness Hurts Health More Than We Thought
"What we've learned from COVID is that isolation is everyone's problem. It doesn't just happen to older adults; it happens to us all."
— Julianne Holt-Lunstad, professor of psychology and neuroscience at Brigham Young University
How deadly is the condition of loneliness? During the first five months of the pandemic, nursing home lockdowns intended to safeguard older and vulnerable adults with dementia contributed to the deaths of an additional 13,200 people compared with previous years, according to a shocking Washington Post investigation published last September. “People with dementia are dying,” the article notes, “not just from the virus but from the very strategy of isolation that's supposed to protect them.”
Isolation may be the new normal . Fifty-six percent of adults age 50-plus said they felt isolated in June 2020, double the number who felt lonely in 2018, a University of Michigan poll found. Rates of psychological distress rose for all adults as the pandemic deepened — increasing sixfold for young adults and quadrupling for those ages 30 to 54, according to a Johns Hopkins University survey published in JAMA in June. And it's hard to tell whether the workplace culture many of us relied on for social support will fully return anytime soon.
Those 50-plus have a leg up. “Older adults with higher levels of empathy, compassion, decisiveness and self-reflection score lowest for loneliness,” says Dilip Jeste, M.D., director of the Sam and Rose Stein Institute for Research on Aging at the University of California, San Diego. “Research shows that many older adults have handled COVID psychologically better than younger adults. With age comes experience and wisdom. You've lived through difficult times before and survived.”
Help yourself by helping others. Jeste says that when older adults share their wisdom with younger people, everyone benefits. “Young people are reassured about the future,” he adds. “Older adults feel even more confident. They're role models. Their contributions matter."

Lesson 11: When Your World Gets Small, Nature Lets Us Live Large
"For older people in particular, nature provided a way to shake off the weight and hardships associated with stay-at-home orders, of social isolation and of the stress of being the most vulnerable population in the pandemic."
— Kathleen Wolf, a research social scientist in the School of Environmental and Forest Sciences at the University of Washington
One silver lining to COVID-19's dark cloud : Clouds themselves became more familiar to all of us. So did birds, trees, bees, shooting stars and window gardens. Nearly 6 in 10 Americans have a new appreciation for nature because of the pandemic, according to one survey that also found three-quarters of respondents reported a boost in their mood while spending time outside.
By nearly every measure, the planet got more love during COVI D. And wouldn't it be nice if that continued going forward? The ins and outs on our new outdoor life:
Move somewhere greener (or at least move around more outside). How you access nature is up to you, but consider the options. Nearly a third of Americans were considering moving to less populated areas, according to a Harris Poll taken last year during the pandemic. Walking, running and hiking became national pastimes. One day last September, Boston's BlueBikes bike-share system saw its highest-ever single-day ridership, with 14,400 trips recorded. Stargazers and bird-watchers helped push binocular sales up 22 percent.
Once known mainly as a retirement activity, pickleball has been the fastest-growing sport in America, with almost 3.5 million U.S. players of all ages participating in the contact-free outdoor net game designed for players of any athletic ability. The return of the pandemic “victory garden” reflects research that finds 79 percent of patients feel more relaxed and calm after spending time in a garden.
Make the city less gritty . The University of Washington's Wolf thinks that our collective nature kick will go beyond a run on backyard petunias. Her research brief on the benefits of nearby nature in cities for older adults suggests we may rethink the design of neighborhood environments to facilitate older people's outdoor activities. That means more places to sit, more green spaces associated with the health status of older people, safer routes and paths, and more allotment for community gardens. “It's impossible to overestimate the value these outdoor spaces have on reducing stressful life events, improving working memory and adding meaning and happiness in older people's lives,” Wolf says.
If you can't get out, bring nature in . Even video and sounds of nature can provide health gains to those shut indoors, says Marc Berman of the University of Chicago's Environmental Neuroscience Lab. “Listening to recordings of crickets chirping or waves crashing improved how our subjects performed on cognitive tests,” he says.
Above all, the environment is in your hands, so take action to protect it . “We've seen a lot of older folks stepping up their activity in trail conservation, stream cleaning, being forest guides and things like that this year, which indicates a shift in how that age group interacts with nature,” says Cornell University gerontologist Karl Pillemer.
"There's an old saw that older people care less than younger people about the environment. But given this year's nature boom, I'm expecting that to change. As the generation that gave birth to the environmental movement enters retirement, we're likely to see a wave of interest in conservation among those 60 and up."
Lesson 12: You Can Hope for Stability — but Best Be Prepared for the Opposite
"COVID-19, perhaps more than any other disaster, demonstrated that we need to continue ensuring response plans are flexible and scalable. You can't predict exactly what a disaster will bring, but if you know what tools you have in your tool kit, you can pull out the right one you need when you need it."
— Linda Mastandrea, director of the Office of Disability Integration and Coordination for the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)
The pandemic was among the toughest slap-in-the-face moments in recent history to remind us that everything — everything — in our lives can change in a moment. While older Americans may have a deep-seated desire for stability and security after all it took to get to an advanced age, we certainly cannot bank on it. Which is why the word of the year, and perhaps the coming century, is “resilience.” Not just at the individual level but at every social tier, from family to community to the nation as a whole.
Banish fear . “We don't have to live in fear” of some looming disaster, says former director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Tom Frieden, now president and CEO of global public health initiative Resolve to Save Lives. “By strengthening our defenses and investing in preparedness, we can live easier knowing that communities have what they need to better respond in moments of crisis."
Preparation must start at the top . For government, that means a new commitment to plans that allow, not so much for stockpiles but for the ability to ramp up production of crucial equipment when needed. “We need increased, sustained, predictable base funding for public health security defense programs that prevent, detect and respond to outbreaks such as COVID-19 or pandemic influenza,” Frieden says.
Being creative and even entrepreneurial helps , says Jeff Schlegelmilch, director of the National Center for Disaster Preparedness at Columbia University's Earth Institute. Warehouses full of masks could have helped us initially, he says, but stockpiles of equipment aren't the answer on their own. In a free market there is pressure to sell off surpluses, so he suggests we reimagine our manufacturing capacities for times of emergency. When whiskey distillers stepped up to make hand sanitizer, and auto manufacturers switched gears to build ventilators, we saw “glimmers of solutions,” Schlegelmilch says, the sort of responses we may need to tee up in the future.
Focus on health care . Prime among the areas that need to be addressed, crisis management consultant Luiz Hargreaves says, are overwhelmed health care systems. “They were living a disaster before the pandemic. When the pandemic came, it was a catastrophe.” But Hargreaves hopes we will use this wake-up call to produce new solutions, rather than to return to old ways. “Extraordinary times,” he says, “call for extraordinary measures."
Lesson 13: Wealth Inequality Is Growing, and It Affects Us All
"It's outrageous that somebody could work full-time and not even be able to pay rent, let alone food and clothing. There's a recognition that there's a problem on both the left and right. "
— Joseph Stiglitz, Nobel Prize–winning economist, Columbia University professor and author of The Price of Inequality
"The data is pretty dramatic,” says Stiglitz, one of America's most-esteemed economists. Government economists estimate that unemployment rates in this pandemic are less than 5 percent for the highest earners but as high as 20 percent for the lowest-paid ones. “People at the bottom have disproportionately experienced the disease, and those at the bottom have lost jobs in enormous disproportion, too."
As white-collar professionals work from home and stay socially distant, frontline workers in government, transportation and health care — as well as retail, dining and other service sectors — face far greater health risks and unemployment. “We try to minimize interactions as we try to protect ourselves,” he says, “yet we realize that minimizing those interactions is also taking away jobs.” The disparate effects of the pandemic are particularly evident along racial lines, points out Jean Accius, AARP senior vice president for global thought leadership. “Job losses have hit communities of color disproportionately,” he says. And there's a health gap, too, with people of color — who have a greater likelihood than white Americans to be frontline workers — experiencing higher rates of COVID-19 infection, hospitalizations and mortality, and lower rates of vaccinations. “What we're seeing is a double whammy for communities of color,” Accius says. “It is hitting them in their wallets. And it's hitting them with regard to their health."
Those economic and health crises, along with protests over racial injustice over the past year, says Accius, “have really sparked major conversations around what do we need to do in order to advance equity in this country."
A rising gap between rich and poor in any society, Stiglitz argues, increases economic instability, reduces opportunities and results in less investment in public goods such as education and public transportation. But the country appears primed to make some changes that could help narrow the wealth gap, he says. Among them are President Biden's proposals to raise the federal minimum wage to $15 an hour, increase the earned income tax credit for low-income workers and provide paid sick leave. Stiglitz also proposes raising taxes on gains from sales of stocks and other securities not held in retirement accounts. “The notion that people who work for a living shouldn't pay higher taxes than those who speculate for a living seems not to be a hard idea to get across,” Stiglitz says.
"Many people continue to say, ‘It's time for us to get back to normal,'” Accius says. “Well, going back to normal means that we're in a society where those that have the least continue to be impacted the most — a society where older adults are marginalized and communities of color are devalued. We have to be honest with what we are going through as a collective nation. And then we have to be bold and courageous, to really build a society where race and other social demographic factors do not determine your ability to live a longer, healthier and more productive life.”
Who Owns America's Wealth?
Top 10% Richest Americans | 67% | 76% |
Next 40% | 30% | 22% |
Bottom 50% | 3% | 1% |
For Some, Hard Times Bring Opportunity
Want a positive reminder of the American way? When the going got tough this past summer, many people responded by planning a new business. In the second half of 2020, there was a 40 percent jump over the prior year's figures in applications to form businesses highly likely to hire employees, according to the U.S. Census Bureau.
Significantly, no such spike occurred during the Great Recession, points out Alexander Bartik, assistant professor of economics at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. “That's cause for some optimism — that there are people who are trying to start new things,” he says. One possible reason this time is different: Unlike during that recession, the stock market and home values have held on, and those sources of personal wealth are often what people draw upon to fund small-business start-ups.
High-propensity* Business Applications in the U.S.
*Businesses likely to have employees

Lesson 14: The Benefits of Telemedicine Have Become Indisputable
"The processes we developed to avoid face-to-face care have transformed the way we approach diabetes care management.”
— John P. Martin, M.D., codirector of Diabetes Complete Care for Kaiser Permanente Southern California
If there was ever any truth to the stereotype of the older person whose life revolved around a constant calendar of in-person doctor appointments, it's certainly been tossed out the window this past year due to the strains of the pandemic on our health care system. The timing was fortuitous in one way: Telemedicine was ready for prime time and has proved to be a godsend, particularly for those with chronic health conditions.
Say goodbye to routine doctor visits . Patients who sign up for remote blood sugar monitoring at Kaiser Permanente in Southern California use Bluetooth-enabled meters to transmit results via a smartphone app directly to their health records. “ Remote monitoring allows us to recognize early when there should be adjustments to treatment,” Martin says.
We need to push for more access . The pandemic underlines the need for more home-based medical help with chronic conditions. But that takes both willingness and a lot of gear, such as Bluetooth-enabled blood pressure monitors and, on the doctor side, systems to store and analyze the data. “People need access to the equipment, and health care systems have to be ready to handle all that data,” says Mirsky of Massachusetts General Hospital.
Group doctor visits may be a way forward . Mirsky is conducting virtual group visits and remote monitoring of blood sugar for his patients with type 2 diabetes. “Instead of having a few minutes with each person to talk about important issues — like blood sugar testing, diet and exercise — we get an hour or more to go over it,” he says. “At every meeting somebody in the group has a great tip I've never heard of, like a new YouTube exercise channel or fitness app. There's group support, too. I see group visits like this continuing into the future, becoming part of routine chronic disease care for all patients who want it."
Bottom line: The doctor is in (your house) . Managing chronic health conditions like diabetes “can't just be about getting in your car and driving to your doctor's office,” Martin says. Taking care of your health conditions yourself is the path forward.
Lesson 15: Our Cities Won't Ever Be the Same
"This is obviously a very big watershed moment in how we live, how we organize our cities and our communities. There are going to be long-lasting changes."
— Chris Jones, chief planner at Regional Plan Association, a New York–based urban planning organization
"When you're alone and life is making you lonely, you can always go downtown,” Petula Clark sang in her 1964 chart-topping ode to city life. Well, things change. Suddenly, crowds are the enemy, public buses and subways a health risk, packed office towers out of favor, and a roomy suburban home seems just where you want to be. But don't write off downtowns just yet.
The office and business district will look different. Many workers have little interest in returning to a 9-to-5 life. For those who do make the commute, they may find cubicles replaced with more flexible work spaces focused on common areas, with ample outdoor seating space for meetings and working lunches. And some now-empty offices will likely be converted into apartments and condos, making downtowns more vibrant. “Now you have an opportunity to remake a central business district into an actual neighborhood,” says Richard Florida, author of The Rise of the Creative Class and a cofounder of CityLab, an online publication about urbanism.
Public spaces will serve more of the public. Those areas set up for outdoor restaurant dining — some of those will likely remain. Streets and parking lots have been turned into plazas and promenades. Many cities have already opened miles of bike lanes; in 2020, Americans bought bikes, including electric bikes, in record numbers. “This idea of social space, where you can get outside and enjoy that active public realm, is going to become increasingly important,” says Lynn Richards, the president and CEO of Congress for the New Urbanism, which champions walkable cities.
Contributors to this report: Sari Harrar, David Hochman, Ronda Kaysen, Lexi Pandell, Jessica Ravitz and Ellen Stark
Unlock Access to AARP Members Edition
Already a Member? Login
More From AARP

For Some, Covid-19 Spurs an Identity Crisis: What Do I Want Out of Life?

After Vaccination, Tiptoeing Back to Normalcy

When Can Visitors Return to Nursing Homes?
Vaccination means visits are back with far fewer restrictions
AARP Value & Member Benefits

Carrabba's Italian Grill®
10% off dine-in or curbside carryout orders placed by phone

AARP Travel Center Powered by Expedia: Hotels & Resorts
Up to 10% off select hotels

ADT™ Home Security
Savings on monthly home security monitoring
AARP® Staying Sharp®
Activities, recipes, challenges and more with full access to AARP Staying Sharp®
SAVE MONEY WITH THESE LIMITED-TIME OFFERS
8 Lessons We Can Learn From the COVID-19 Pandemic
BY KATHY KATELLA May 14, 2021

Note: Information in this article was accurate at the time of original publication. Because information about COVID-19 changes rapidly, we encourage you to visit the websites of the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (CDC), World Health Organization (WHO), and your state and local government for the latest information.
The COVID-19 pandemic changed life as we know it—and it may have changed us individually as well, from our morning routines to our life goals and priorities. Many say the world has changed forever. But this coming year, if the vaccines drive down infections and variants are kept at bay, life could return to some form of normal. At that point, what will we glean from the past year? Are there silver linings or lessons learned?
“Humanity's memory is short, and what is not ever-present fades quickly,” says Manisha Juthani, MD , a Yale Medicine infectious diseases specialist. The bubonic plague, for example, ravaged Europe in the Middle Ages—resurfacing again and again—but once it was under control, people started to forget about it, she says. “So, I would say one major lesson from a public health or infectious disease perspective is that it’s important to remember and recognize our history. This is a period we must remember.”
We asked our Yale Medicine experts to weigh in on what they think are lessons worth remembering, including those that might help us survive a future virus or nurture a resilience that could help with life in general.
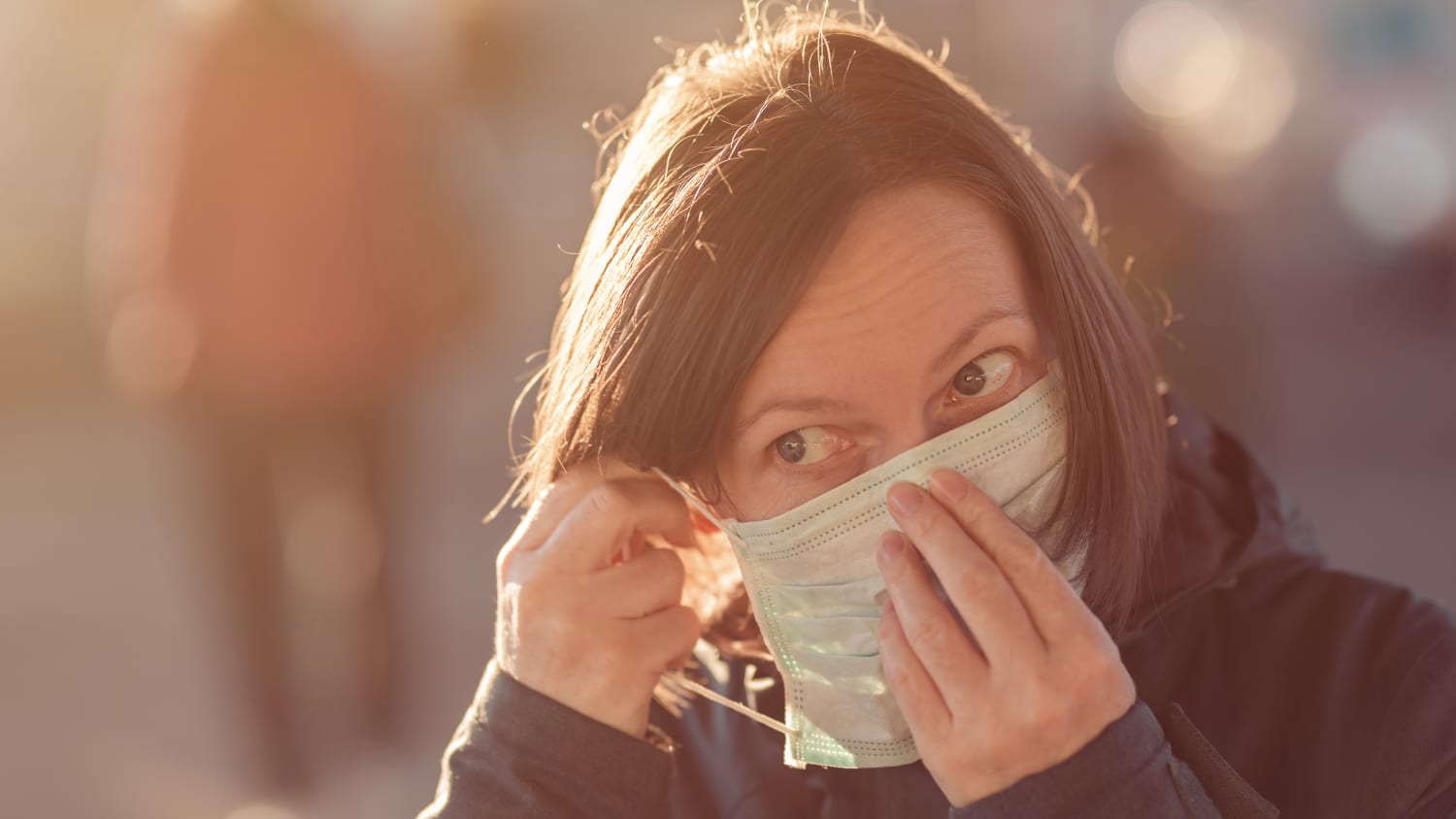
Lesson 1: Masks are useful tools
What happened: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) relaxed its masking guidance for those who have been fully vaccinated. But when the pandemic began, it necessitated a global effort to ensure that everyone practiced behaviors to keep themselves healthy and safe—and keep others healthy as well. This included the widespread wearing of masks indoors and outside.
What we’ve learned: Not everyone practiced preventive measures such as mask wearing, maintaining a 6-foot distance, and washing hands frequently. But, Dr. Juthani says, “I do think many people have learned a whole lot about respiratory pathogens and viruses, and how they spread from one person to another, and that sort of old-school common sense—you know, if you don’t feel well—whether it’s COVID-19 or not—you don’t go to the party. You stay home.”
Masks are a case in point. They are a key COVID-19 prevention strategy because they provide a barrier that can keep respiratory droplets from spreading. Mask-wearing became more common across East Asia after the 2003 SARS outbreak in that part of the world. “There are many East Asian cultures where the practice is still that if you have a cold or a runny nose, you put on a mask,” Dr. Juthani says.
She hopes attitudes in the U.S. will shift in that direction after COVID-19. “I have heard from a number of people who are amazed that we've had no flu this year—and they know masks are one of the reasons,” she says. “They’ve told me, ‘When the winter comes around, if I'm going out to the grocery store, I may just put on a mask.’”
Lesson 2: Telehealth might become the new normal
What happened: Doctors and patients who have used telehealth (technology that allows them to conduct medical care remotely), found it can work well for certain appointments, ranging from cardiology check-ups to therapy for a mental health condition. Many patients who needed a medical test have also discovered it may be possible to substitute a home version.
What we’ve learned: While there are still problems for which you need to see a doctor in person, the pandemic introduced a new urgency to what had been a gradual switchover to platforms like Zoom for remote patient visits.
More doctors also encouraged patients to track their blood pressure at home , and to use at-home equipment for such purposes as diagnosing sleep apnea and even testing for colon cancer . Doctors also can fine-tune cochlear implants remotely .
“It happened very quickly,” says Sharon Stoll, DO, a neurologist. One group that has benefitted is patients who live far away, sometimes in other parts of the country—or even the world, she says. “I always like to see my patients at least twice a year. Now, we can see each other in person once a year, and if issues come up, we can schedule a telehealth visit in-between,” Dr. Stoll says. “This way I may hear about an issue before it becomes a problem, because my patients have easier access to me, and I have easier access to them.”
Meanwhile, insurers are becoming more likely to cover telehealth, Dr. Stoll adds. “That is a silver lining that will hopefully continue.”
Lesson 3: Vaccines are powerful tools
What happened: Given the recent positive results from vaccine trials, once again vaccines are proving to be powerful for preventing disease.
What we’ve learned: Vaccines really are worth getting, says Dr. Stoll, who had COVID-19 and experienced lingering symptoms, including chronic headaches . “I have lots of conversations—and sometimes arguments—with people about vaccines,” she says. Some don’t like the idea of side effects. “I had vaccine side effects and I’ve had COVID-19 side effects, and I say nothing compares to the actual illness. Unfortunately, I speak from experience.”
Dr. Juthani hopes the COVID-19 vaccine spotlight will motivate people to keep up with all of their vaccines, including childhood and adult vaccines for such diseases as measles , chicken pox, shingles , and other viruses. She says people have told her they got the flu vaccine this year after skipping it in previous years. (The CDC has reported distributing an exceptionally high number of doses this past season.)
But, she cautions that a vaccine is not a magic bullet—and points out that scientists can’t always produce one that works. “As advanced as science is, there have been multiple failed efforts to develop a vaccine against the HIV virus,” she says. “This time, we were lucky that we were able build on the strengths that we've learned from many other vaccine development strategies to develop multiple vaccines for COVID-19 .”
Lesson 4: Everyone is not treated equally, especially in a pandemic
What happened: COVID-19 magnified disparities that have long been an issue for a variety of people.
What we’ve learned: Racial and ethnic minority groups especially have had disproportionately higher rates of hospitalization for COVID-19 than non-Hispanic white people in every age group, and many other groups faced higher levels of risk or stress. These groups ranged from working mothers who also have primary responsibility for children, to people who have essential jobs, to those who live in rural areas where there is less access to health care.
“One thing that has been recognized is that when people were told to work from home, you needed to have a job that you could do in your house on a computer,” says Dr. Juthani. “Many people who were well off were able do that, but they still needed to have food, which requires grocery store workers and truck drivers. Nursing home residents still needed certified nursing assistants coming to work every day to care for them and to bathe them.”
As far as racial inequities, Dr. Juthani cites President Biden’s appointment of Yale Medicine’s Marcella Nunez-Smith, MD, MHS , as inaugural chair of a federal COVID-19 Health Equity Task Force. “Hopefully the new focus is a first step,” Dr. Juthani says.
Lesson 5: We need to take mental health seriously
What happened: There was a rise in reported mental health problems that have been described as “a second pandemic,” highlighting mental health as an issue that needs to be addressed.
What we’ve learned: Arman Fesharaki-Zadeh, MD, PhD , a behavioral neurologist and neuropsychiatrist, believes the number of mental health disorders that were on the rise before the pandemic is surging as people grapple with such matters as juggling work and childcare, job loss, isolation, and losing a loved one to COVID-19.
The CDC reports that the percentage of adults who reported symptoms of anxiety of depression in the past 7 days increased from 36.4 to 41.5 % from August 2020 to February 2021. Other reports show that having COVID-19 may contribute, too, with its lingering or long COVID symptoms, which can include “foggy mind,” anxiety , depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder .
“We’re seeing these problems in our clinical setting very, very often,” Dr. Fesharaki-Zadeh says. “By virtue of necessity, we can no longer ignore this. We're seeing these folks, and we have to take them seriously.”
Lesson 6: We have the capacity for resilience
What happened: While everyone’s situation is different (and some people have experienced tremendous difficulties), many have seen that it’s possible to be resilient in a crisis.
What we’ve learned: People have practiced self-care in a multitude of ways during the pandemic as they were forced to adjust to new work schedules, change their gym routines, and cut back on socializing. Many started seeking out new strategies to counter the stress.
“I absolutely believe in the concept of resilience, because we have this effective reservoir inherent in all of us—be it the product of evolution, or our ancestors going through catastrophes, including wars, famines, and plagues,” Dr. Fesharaki-Zadeh says. “I think inherently, we have the means to deal with crisis. The fact that you and I are speaking right now is the result of our ancestors surviving hardship. I think resilience is part of our psyche. It's part of our DNA, essentially.”
Dr. Fesharaki-Zadeh believes that even small changes are highly effective tools for creating resilience. The changes he suggests may sound like the same old advice: exercise more, eat healthy food, cut back on alcohol, start a meditation practice, keep up with friends and family. “But this is evidence-based advice—there has been research behind every one of these measures,” he says.
But we have to also be practical, he notes. “If you feel overwhelmed by doing too many things, you can set a modest goal with one new habit—it could be getting organized around your sleep. Once you’ve succeeded, move on to another one. Then you’re building momentum.”
Lesson 7: Community is essential—and technology is too
What happened: People who were part of a community during the pandemic realized the importance of human connection, and those who didn’t have that kind of support realized they need it.
What we’ve learned: Many of us have become aware of how much we need other people—many have managed to maintain their social connections, even if they had to use technology to keep in touch, Dr. Juthani says. “There's no doubt that it's not enough, but even that type of community has helped people.”
Even people who aren’t necessarily friends or family are important. Dr. Juthani recalled how she encouraged her mail carrier to sign up for the vaccine, soon learning that the woman’s mother and husband hadn’t gotten it either. “They are all vaccinated now,” Dr. Juthani says. “So, even by word of mouth, community is a way to make things happen.”
It’s important to note that some people are naturally introverted and may have enjoyed having more solitude when they were forced to stay at home—and they should feel comfortable with that, Dr. Fesharaki-Zadeh says. “I think one has to keep temperamental tendencies like this in mind.”
But loneliness has been found to suppress the immune system and be a precursor to some diseases, he adds. “Even for introverted folks, the smallest circle is preferable to no circle at all,” he says.
Lesson 8: Sometimes you need a dose of humility
What happened: Scientists and nonscientists alike learned that a virus can be more powerful than they are. This was evident in the way knowledge about the virus changed over time in the past year as scientific investigation of it evolved.
What we’ve learned: “As infectious disease doctors, we were resident experts at the beginning of the pandemic because we understand pathogens in general, and based on what we’ve seen in the past, we might say there are certain things that are likely to be true,” Dr. Juthani says. “But we’ve seen that we have to take these pathogens seriously. We know that COVID-19 is not the flu. All these strokes and clots, and the loss of smell and taste that have gone on for months are things that we could have never known or predicted. So, you have to have respect for the unknown and respect science, but also try to give scientists the benefit of the doubt,” she says.
“We have been doing the best we can with the knowledge we have, in the time that we have it,” Dr. Juthani says. “I think most of us have had to have the humility to sometimes say, ‘I don't know. We're learning as we go.’"
Information provided in Yale Medicine articles is for general informational purposes only. No content in the articles should ever be used as a substitute for medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician. Always seek the individual advice of your health care provider with any questions you have regarding a medical condition.
More news from Yale Medicine

- Get Our Daily Email
- Ways To Support Us
- About InspireMore
- Advertise With Us
- Website Terms
- Privacy Policy
- Advertising Terms
- Causes That Matter
9 Valuable Lessons We’ve Learned During The Pandemic

Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
We’re not going to lie: It’s been a little hard to find the silver lining at times this past year.
With so much stress, loss, and pain at the forefront of our minds, it sometimes feels like we’re in a constant waiting game, counting down the minutes until our “normal” lives are back. But after a year like this, there’s no going back to normal because we’ve all been changed forever in one way or another. We’ve lived 12 years in the past 12 months, and we’ve grown in the process – and that is a silver lining to be proud of!

So we decided the best way to acknowledge and appreciate the growth we’ve experienced is by taking a second to reflect on this past year and find the positives that were woven through each day.
To see the good that has come from these hard times, we adopted a lens of learning and growing, and it empowered us to do just that! Here are nine important lessons we’ve learned in the midst of COVID-19.
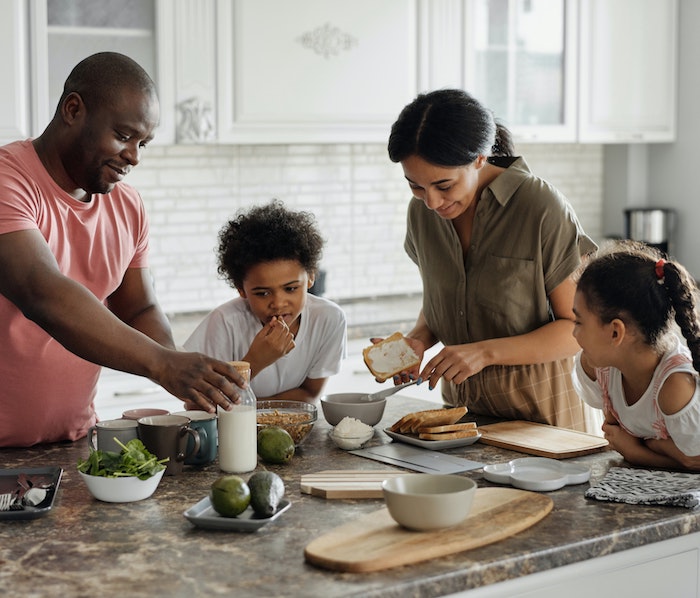
1. Family is nonnegotiable.
For many of us, this year brought with it quality family time that we never expected and, honestly, might never have had otherwise. It’s reminded us just how much family matters. And I don’t just mean blood relatives, I mean chosen family, too.
We were encouraged to take a step out of the craziness of our former lives and deeply invest in those relationships again, whether it was face-to-face or not.
We’ve had the opportunity to not just catch up on life, but to also spend priceless time with our loved ones, asking personal questions, being there for the important moments, leaning on each other for support, and growing together. As a result, we remembered just how much we need each other!

2. Prioritize health and wellness .
When the pandemic first began, the world started paying attention to health, wellness, and hygiene like never before. We realized just how effective our handwashing wasn’t , how much we shouldn’t be touching our faces, and the beauty of both modern and natural medicine. These are all crucial practices and levels of care that will hopefully stick with us in the future.
Not only that, but without the usual benefits of daily activity, in-person workouts, and restaurant dining, a microscope was placed on just how willing we were to maintain our wellness all on our own.
With the pandemic came a myriad of free cooking and workout classes on social media and a realization that, particularly when we’re stuck inside, our bodies really do need nutrients and activity to survive.

3. We can get by on less. Much less.
The road to discovering how little we need was paved with uncertainty. With the overwhelming job loss that came with the pandemic, people had to learn how to pinch pennies, clip coupons, and trim excess like never before.
Even for those who kept their jobs, without indoor dining, salons, gyms, and a wealth of other standard social activities, saving money actually became easier to do. Even though we’ll all be lining the doors when things are back to normal, we realized in the process that we actually can live on a lot less and still be content.

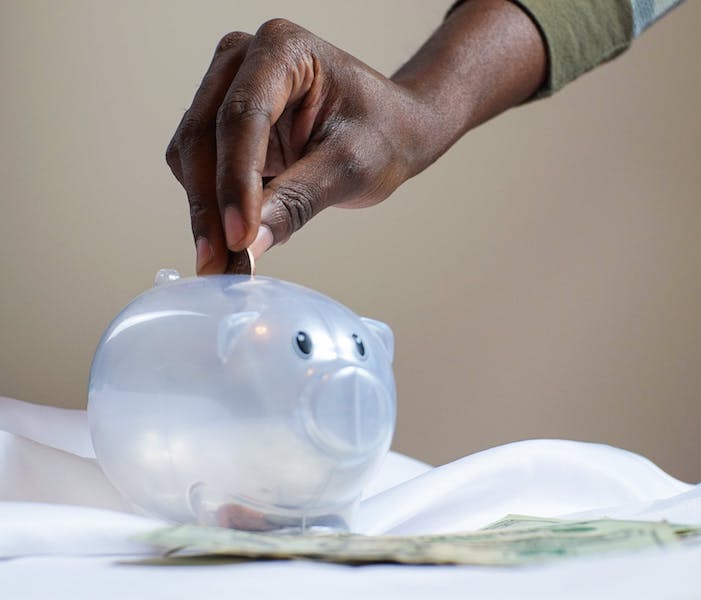
4. Build that nest egg.
In addition to pinching those pennies, we learned the endless value of having a rainy day fund – or more appropriately, an emergency fund. An emergency fund is one that is set aside for the most essential of needs, including rent, medical expenses, childcare, and food.
As we’ve all heard over and over again, these are unprecedented times. The nature of unprecedented times is that we don’t see them coming, so we don’t plan for them.
If this year has taught us anything, it’s the importance of setting aside a little extra money and leaving it there until the day comes when we might need it.

5. Slow down.
We’ve realized that not only is it OK to slow down, but it’s actually essential.
When the pandemic hit, it was as if the whole world was running on overdrive and then, all at once, it crashed. We allowed it to get this way because we have a tendency to align our worth with our busyness. But luckily, this past year has shown us just how unbalanced that meter is.
There are a few key points to remember moving forward. First of all, self-care is not self-indulgent; it’s one way that we keep ourselves healthy, both physically and mentally. Second, slowing down is what helps us truly live in the present and find contentment in our circumstances.

6. We should be talking about mental health.
One of the best silver linings of this year is that we learned just how valuable mental health is. Studies show that ever since the pandemic hit, close to 40 percent of Americans now suffer from anxiety and depression. The causes are endless: financial stress, difficult home lives, boredom, loss, fear, and, perhaps the heaviest of all, loneliness.
These universal mental health issues truly are a “second wave” of this global crisis, and the greatest benefit has been the light shed on their gravity.
People are being more vocal than ever about the importance of honesty and vulnerability when it comes to our mental health, just like we would a physical ailment. By doing so, we can get the love and support we need.

7. Our thoughts on people have changed.
The more closed off we’ve had to become socially and the more we’ve noticed the deep need around us, the more we’ve realized whom we consider to be truly essential.
In our own lives, we’ve learned which friends we want close to us in times of trouble – and maybe even some relationships we’ve been needing freedom from.
In our communities, we’ve finally realized the overwhelming value of our essential workers: in health care, education, food service, and the most underappreciated segments of our workforce. May we never forget how brave and resilient they have been for all of us these past 12 months.
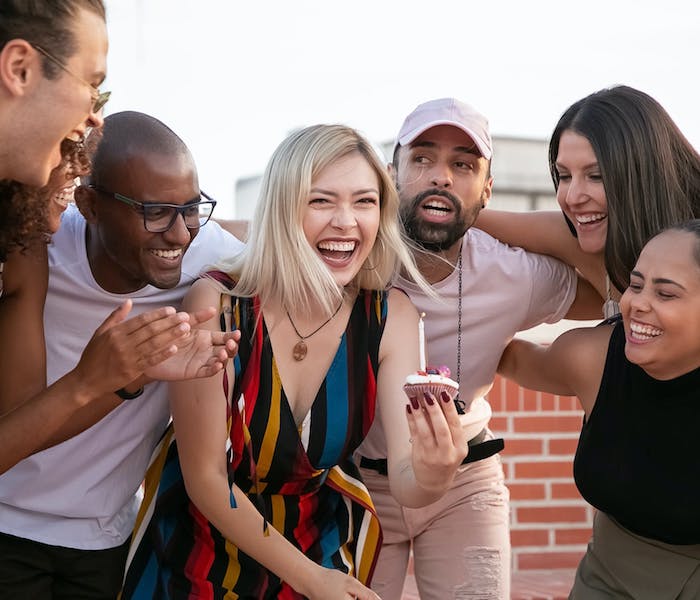

8. Becoming comfortable with uncertainty.
“The one thing that’s certain about this current crisis is the massive amount of uncertainty,” Paul Knopp, U.S. Chair and CEO of KPMG LLP, told Accounting Today . “In order to succeed, you must execute on the activities and behaviors that are within your control.”
We have definitely learned flexibility this year. From working and schooling from home, to rerouting our careers, to finding new ways to stay connected, to moving back in with our parents, our flexibility has been award-winning and record-breaking.
A benefit of this growing pain is that it’s made us more comfortable with uncertainty. There’s so much about the future that we can’t possibly know or predict right now, so ultimately all we can do is be OK with it – and choose to find the wonder and joy in our present circumstances.

9. We are deeply resilient.
We are capable of so much more than we ever knew. This year has been rife with chaos, unrest, injustice, loss, and pain – but we’ve survived. We’re still standing. Even in the darkest time, we’ve been able to look outside ourselves and pull through for those in need in remarkable ways. It’s helped us realize the stuff we’re made of .
More than that, we’ve done it together. We’ve all been in isolation together, and we’ve survived together. It’s reminded us that at the end of the day, we are all just human beings, and we need each other.
And now we know with certainty that we can handle anything!
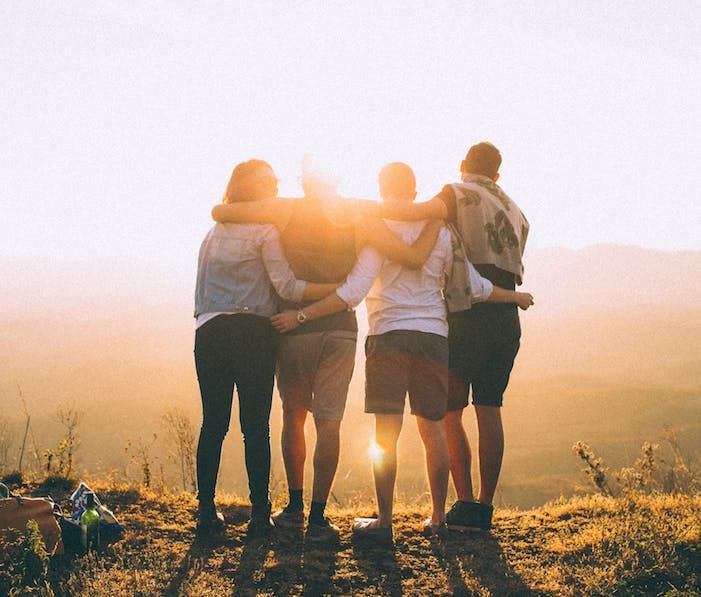

After the levels of stress we’ve lived through this past year, the best we can do is make sure it wasn’t for nothing. We can search for the good, continue to grow, and allow our circumstances to change us for the better. Only then will we continue to come out on the other side stronger, more resilient, more compassionate, and more hopeful than ever!
Share this story to remind others how much they’ve grown this year.

Want to be happier in just 5 minutes a day? Sign up for Morning Smile and join over 455,000+ people who start each day with good news.
Recommended posts
Read more like this, more popular posts, brighten the world and spread hope.
- Submit Your Story
- Shop our Merchandise
- Make Me Smile
- InspireMore in the Press
- Join Our Team
- Membership Portal Access
- Membership Support
- Editorial Standards
What students have learned about themselves living in COVID-19 pandemic: Student Voices winners
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, many students have developed new hobbies and strengths, come to appreciate family and friends, and face a wide variety of emotions.
In the first of 2021 Asbury Park Press Student Voices Essay contest, we posed the question: What have you learned about yourself during the pandemic?
Our students have shared with us the transformation and growth they have achieved during the pandemic. Below are the winning essays for December, as judged by the Press editorial staff.
First place winner: Grades 7-8
It’s okay to feel worried
The year of 2020 has been interesting, to say the least. I have learned many things about myself during the course of the pandemic. Let’s just say that I am not known to be the most optimistic person; I am a bit of a pessimist and an overthinker. It suddenly occurred to me one day, when I had been in a particularly nasty mood: I was always a fairly reasonable child. I managed emotions well. I wouldn’t cry when I didn’t receive a toy that I wanted. It was not typical of me to perform nonsensical actions- temper tantrums, unreasonable decisions, and fits of anger were not a typical trait of mine. I was entertained easily. I was creative. I had never really dealt with true stress, real stress, until this year. Or real boredom.
I am an artist; I almost never run out of ideas. I perceive light and color and shapes in many different ways. I paint. I draw. But dealing with quarantine was a whole different obstacle to deal with together. Stress saps away my creativity- and I can get pretty cranky if I feel like I am not doing anything productive. It was not until this year that I realized how adaptable I am. Or how simple it is to deal with stress. I could have saved so much time and energy if I had realized that it’s okay to feel worried, that I shouldn’t panic over new situations too much.
I don’t like change; I generally dislike travelling and other things in that category. When New Jersey had to go into quarantine due to the COVID-19 pandemic, I wasn’t very happy, but as an introvert, I figured that it would be nice to have two weeks to recharge my energy. Well, two weeks turned into a month. A month turned into two months. At the two-month mark, I began to become extremely bored. I had nothing to do in my free time besides sit at a computer screen. I was dissatisfied with my work.
I felt like the once creative and sunny part of my mind was engulfed in mist. I didn’t know how to get out of it. At around three months of quarantine, I realized that the reason why I was struggling so much with work and school was because of stress. I realized I needed to calm down. When I was a child, I did yoga and stretching exercises. I decided to start that again. Immediately following the start of this I felt so much better. It was like magic. I began having confidence in my work again; I began rapidly improving. So great was the feeling of happiness that I never wanted to utter a pessimist word again in my life (sadly, this didn’t happen, I can still be a bit negative sometimes).
One day, you may be overwhelmed by something or someone in your life. Do not give in. Keep yourself afloat. Don’t let yourself be swallowed up by the vast and dark waters of sorrow. If you persist for long enough, you will get through any difficult situation that challenges you. And most of all, remember this: there is always someone who cares about you. You matter. Stay strong.
Joan Obolo-Pawlish
Teacher: Melinda Willems
Ocean Township Intermediate School
First place winner: Grades 9-12
Overcoming obstacles is part of life
A whirlwind of negativity surrounds 2020. When things do not go as planned we as humans tend to immediately panic, throwing blame and projecting our own guilt onto others. But personally I find that change, while difficult, is just a test that I have to strive to overcome on my own. Growing up is all about self discovery through unexpected ways, of course, a global pandemic is not something I planned on experiencing, but two words come to mind when I look back on this year and my journey through it: acceptance and growth.
I try to remember my life before everything shut down. I was free to go wherever, be as close to others as I wanted, and invest too much into everything happening around me. I thought that I was a social butterfly, that being in a group was where I was meant to be. But while home with just my family, I quickly learned that using other people as a distraction was just a way for me to avoid looking into who I really was. Whether it was to validate my feelings or just entertain me with useless drama, I realized that relying on others so much was an unhealthy way to live. So while the world hid, I found myself. I accepted that this was how it was going to be for now, and that I was given this time as an opportunity to rest, and heal, and break myself down and start from scratch. Grieve for everything that was gone, but also find new things everyday that made this kind of lonely life worth living. Filling my days with my family and activities like long nature walks, music, and art helped me grow into a strong, independent, and stable young woman during a time filled with such instability.
No, this was not easy. Yes, there were a lot of hard days and tears shed...and I’m not even done yet! This year is not over, this pandemic is not over, my life is not over. I have so much more change to grow through and so much more to discover about myself. Overcoming obstacles is part of life, so all I can ask is; what next?
Sofia Roman
Teacher: Melissa Pitman
Academy of Allied Health and Science
Second place winner: Grades 7-8
Are you really ok?
Emotions are confusing, they're unpredictable and hard to control. During quarantine, I was focusing more on myself and found I was emotionally unstable. I found it hard to be happy when things were going right, and I found it difficult to be sad when things weren’t working out. I found myself crying at random times when my day was going well or if it was complete haywire. I was aware that something didn’t feel right, but I shrugged it off and told myself it was normal. I was lying to myself, but the more I did, the harder it got to tell the difference between a lie and a truth.
As time went by, I started to distance myself from my parents. I started refusing hugs and I stopped telling them I love them. Of course I cared about them, but the idea of getting a hug or saying “I love you” was uncomfortable to me. That’s when I started to feel alone and less energetic than usual. This caused me to procrastinate with school and I felt overwhelmed. I spent the majority of my time in my bedroom on my bed doing schoolwork or using my phone. There was a time where I forgot the last time I stepped outside. Everything felt boring to the point where even eating was boring.
One day, my friend Dania introduced Japanese cartoons called Anime. I was captivated by them and used them as a way to escape reality. Running away from your problems isn’t a way to solve them. I knew that, but I just enjoyed myself because at least I was happy. I watched them almost everyday, and one day I came across an anime where the protagonist was trying to get control of her feelings and trying to understand them. Along the way she realized that her problem was that she was hiding her emotions because she thought that if she showed them, she would be a problem. That’s when it clicked.
It was like I found the last piece to an unsolved puzzle. My problem was that I was hiding and holding in my emotions, and it resulted in me losing control. It made me forget when to cry, laugh, and yell. From that day on I started to express my emotions. I felt free like a bird soaring through the sky. I started to hug and tell my parents I loved them. I could finally control the steering wheel of my emotions. I was no longer being devoured by them. I was eating well and getting the proper amount of sunlight. I was happy that I no longer needed to escape reality.
Emotions are confusing, they're unpredictable and hard to control. At times you feel that showing your emotions makes you a problem and annoying. You feel like reality is not worth a shot and try to escape it, but you're wrong. Emotions are a way of defining who you are as a person. Your emotions will not make you a problem or annoying. Telling someone how your feeling is only gonna help you. This quarantine I learned that you should never try to hide or hold in your feelings.
Guadalupe Monterrozas
Teacher: Melinda Willems
Ocean Township Intermediate School
Second place winner: Grades 9-12
Personal Renaissance of self-discovery
I spend most of my time alone. And I’m fine with it because I’ve always been good at keeping myself occupied; I’ve always known that. But when the world closed and locked it’s doors for the past ten months I’ve realized how much I rely on seeing people in-person and going places to see or talk to others at all. I don’t get many calls or texts from friends and I’m usually fine with that because we pick up right where we left off whenever we see each other in person.
But now we can’t see each other in person.
Quarantining was fine, I guess. You know, as fine as it can be. Most of my hobbies I can do on my own anyway: reading, writing, art, anything to do with music, cooking, and playing video games (most of which are single player anyway). I bet a lot of people would complain about having to stay in their houses 24/7, but I’m not one of them. Really. I’m not. Being completely honest, my schedule hadn’t really been affected all that much, besides school and stuff. But why, all of a sudden, do I have the urge to get out of the house and do something? I’m sure plenty of people have been feeling this recently, but I’ve never really felt like this before. I guess now that I can’t, it makes me want to do it more.
When school started again, I joined every club or activity that caught my eye. Even though I still sometimes complain about my extracurriculars, I’ve been meeting people, and talking to them, and becoming friends with them; I’m exhausted between schoolwork and after-school activities, but I’m happy.
Although the lesson I’ve learned appears to be relating to the importance of interpersonal relationships, what I’ve really learned was confidence. I, like a majority of people around the world, have had a surplus of free time on my hands to spend by myself and I’ve used that time to discover new things about myself, new passions, and new ways to creatively express myself. My becoming more comfortable with myself has allowed me to do things I never thought I could and show the world a better version of myself. I’m in the middle of a personal Renaissance of self-discovery, self-expression, and self-love.
Madelyn Killi
Teacher: Susan Kuper
Point Pleasant Borough High School
Third place winner: Grades 7-8
My Lifeline
Normal people would think that a messy, hard working, and dirty stable could never seem like home to someone. I am not a normal person. I see a filthy barn as the ideal place to spend my summer. Over the course of the pandemic, everything normal faded, disappeared, and crumpled into what is now our ¨new normal.¨ My original lifelines have begun to fade. Ice Hockey was postponed and I couldn't see my friends and family as much as I would like. But even in the worst of times, something good can come out of it. That is how I found my new lifeline.
It may seem weird or different to other people that I ride horses, but just like any other
lovable animal, horses both give unconditional love and are great companions. As the pandemic shut down events, I was becoming both lazy and unmotivated. The only thing that kept me from these threats was the most unlikely animal, my horse, Max. He is the most amazing horse I have ever met, he has the most loving and caring personality. He's coat is a mix of black, and a gold- tinted bay(light and dark browns), with a pure white star marking on his forehead. His mane and tail are ebony black, and his light bay is offset by his black marking scattered all along his body.
He provided me with an outlet, a way to deal with the restrictions, loneliness, and the lack of motivation. Horses are animals that people don't expect to be a girl's best friend and treasured companion.
Haley Terranova
Teacher: Mrs. Orosz
Memorial Middle School
Third place winner: Grades 9-12
Light Switch
Amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, my life has turned into a living oxymoron. The dismay hindered my natural routine of living. It is as if the spark of optimism within me has been shut off. Albeit the conspicuous negatives, I attempted to find the “light in the darkness.” Although the beginning of the pandemic brought a depletion to my mental health, steady progression is oncoming.
Each of my hobbies and exercises represents a light in a room. The lights turned off progressively until I was left alone with the darkness and the enigma of my inner thoughts. Singing, off. Theatre, Off. Piano, Off. Hanging out with friends? Off. The overwhelming amalgamation of emotions as my mind attempted to process the sudden change became unbearable.
Normative living? Off. The abrupt collapse of enterprises and businesses flipped an off-switch on regular daily practices. This was the moment of realization that I had taken many aspects of life for granted. As an extroverted person, I thrive off of the happiness and joy of others. I needed a human connection. I needed a conversation, not muffled volume. I needed to see eyes, nose, and mouth. It was different behind a screen. The light switch in my mind was not off. The power went out, and it refused to turn back on.
My depression and anxiety depleted progressively. I did not want this. To be fair, no one wants the emotions of emptiness and dread. I so longed for change and the dissipation of my uncertainty and loneliness. However, one thing was for sure, I was not alone. I began consulting a therapist and began conversing with my friends and family. I started adapting to the abrupt adjustments. Life began writing a new variation of normalcy.
I am delighted with my leisurely and steady progression. I am enthusiastic about the pursuit of new hobbies and interests. I now appreciate and relish the little things in life more. My family being loud, the smell of home-cooked meals, and even the faint sunlight beaming through my window make waking up worth it. The aid of my friends and family is the generator that powers my light within. My light switch is on, and I want to keep it on.
Darryn Dizon
Teacher: Donna Mulvaney
Donovan Catholic High School
Honorable Mention Winners
Grades 7-8
Sara Cook, Grade 7, Point Pleasant Borough School, Teacher: Shannon Orosz
Leah Gerdes, Grade 7, Point Pleasant Borough School, Teacher: Melissa Hans
Miriam Priborkina, Grade 7, Manalapan Englishtown Regional School, Teacher: Cassie Capadona
Grades 9-12
Emma Conroy, Grade 10, Donovan Catholic, Teacher: Donna Mulvaney
Samantha Keller, Grade 10, Donovan Catholic, Teacher: Donna Mulvaney
Marlee Card, Grade 11, Point Pleasant Borough High, Teacher: Susan Kuper
Writing about COVID-19 in a college admission essay
by: Venkates Swaminathan | Updated: September 14, 2020
Print article

For students applying to college using the CommonApp, there are several different places where students and counselors can address the pandemic’s impact. The different sections have differing goals. You must understand how to use each section for its appropriate use.
The CommonApp COVID-19 question
First, the CommonApp this year has an additional question specifically about COVID-19 :
Community disruptions such as COVID-19 and natural disasters can have deep and long-lasting impacts. If you need it, this space is yours to describe those impacts. Colleges care about the effects on your health and well-being, safety, family circumstances, future plans, and education, including access to reliable technology and quiet study spaces. Please use this space to describe how these events have impacted you.
This question seeks to understand the adversity that students may have had to face due to the pandemic, the move to online education, or the shelter-in-place rules. You don’t have to answer this question if the impact on you wasn’t particularly severe. Some examples of things students should discuss include:
- The student or a family member had COVID-19 or suffered other illnesses due to confinement during the pandemic.
- The candidate had to deal with personal or family issues, such as abusive living situations or other safety concerns
- The student suffered from a lack of internet access and other online learning challenges.
- Students who dealt with problems registering for or taking standardized tests and AP exams.
Jeff Schiffman of the Tulane University admissions office has a blog about this section. He recommends students ask themselves several questions as they go about answering this section:
- Are my experiences different from others’?
- Are there noticeable changes on my transcript?
- Am I aware of my privilege?
- Am I specific? Am I explaining rather than complaining?
- Is this information being included elsewhere on my application?
If you do answer this section, be brief and to-the-point.
Counselor recommendations and school profiles
Second, counselors will, in their counselor forms and school profiles on the CommonApp, address how the school handled the pandemic and how it might have affected students, specifically as it relates to:
- Grading scales and policies
- Graduation requirements
- Instructional methods
- Schedules and course offerings
- Testing requirements
- Your academic calendar
- Other extenuating circumstances
Students don’t have to mention these matters in their application unless something unusual happened.
Writing about COVID-19 in your main essay
Write about your experiences during the pandemic in your main college essay if your experience is personal, relevant, and the most important thing to discuss in your college admission essay. That you had to stay home and study online isn’t sufficient, as millions of other students faced the same situation. But sometimes, it can be appropriate and helpful to write about something related to the pandemic in your essay. For example:
- One student developed a website for a local comic book store. The store might not have survived without the ability for people to order comic books online. The student had a long-standing relationship with the store, and it was an institution that created a community for students who otherwise felt left out.
- One student started a YouTube channel to help other students with academic subjects he was very familiar with and began tutoring others.
- Some students used their extra time that was the result of the stay-at-home orders to take online courses pursuing topics they are genuinely interested in or developing new interests, like a foreign language or music.
Experiences like this can be good topics for the CommonApp essay as long as they reflect something genuinely important about the student. For many students whose lives have been shaped by this pandemic, it can be a critical part of their college application.
Want more? Read 6 ways to improve a college essay , What the &%$! should I write about in my college essay , and Just how important is a college admissions essay? .

Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

How our schools are (and aren't) addressing race

The truth about homework in America

What should I write my college essay about?
What the #%@!& should I write about in my college essay?
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
We need your support today
Independent journalism is more important than ever. Vox is here to explain this unprecedented election cycle and help you understand the larger stakes. We will break down where the candidates stand on major issues, from economic policy to immigration, foreign policy, criminal justice, and abortion. We’ll answer your biggest questions, and we’ll explain what matters — and why. This timely and essential task, however, is expensive to produce.
We rely on readers like you to fund our journalism. Will you support our work and become a Vox Member today?
Read these 12 moving essays about life during coronavirus
Artists, novelists, critics, and essayists are writing the first draft of history.
by Alissa Wilkinson

The world is grappling with an invisible, deadly enemy, trying to understand how to live with the threat posed by a virus . For some writers, the only way forward is to put pen to paper, trying to conceptualize and document what it feels like to continue living as countries are under lockdown and regular life seems to have ground to a halt.
So as the coronavirus pandemic has stretched around the world, it’s sparked a crop of diary entries and essays that describe how life has changed. Novelists, critics, artists, and journalists have put words to the feelings many are experiencing. The result is a first draft of how we’ll someday remember this time, filled with uncertainty and pain and fear as well as small moments of hope and humanity.
- The Vox guide to navigating the coronavirus crisis
At the New York Review of Books, Ali Bhutto writes that in Karachi, Pakistan, the government-imposed curfew due to the virus is “eerily reminiscent of past military clampdowns”:
Beneath the quiet calm lies a sense that society has been unhinged and that the usual rules no longer apply. Small groups of pedestrians look on from the shadows, like an audience watching a spectacle slowly unfolding. People pause on street corners and in the shade of trees, under the watchful gaze of the paramilitary forces and the police.
His essay concludes with the sobering note that “in the minds of many, Covid-19 is just another life-threatening hazard in a city that stumbles from one crisis to another.”
Writing from Chattanooga, novelist Jamie Quatro documents the mixed ways her neighbors have been responding to the threat, and the frustration of conflicting direction, or no direction at all, from local, state, and federal leaders:
Whiplash, trying to keep up with who’s ordering what. We’re already experiencing enough chaos without this back-and-forth. Why didn’t the federal government issue a nationwide shelter-in-place at the get-go, the way other countries did? What happens when one state’s shelter-in-place ends, while others continue? Do states still under quarantine close their borders? We are still one nation, not fifty individual countries. Right?
- A syllabus for the end of the world
Award-winning photojournalist Alessio Mamo, quarantined with his partner Marta in Sicily after she tested positive for the virus, accompanies his photographs in the Guardian of their confinement with a reflection on being confined :
The doctors asked me to take a second test, but again I tested negative. Perhaps I’m immune? The days dragged on in my apartment, in black and white, like my photos. Sometimes we tried to smile, imagining that I was asymptomatic, because I was the virus. Our smiles seemed to bring good news. My mother left hospital, but I won’t be able to see her for weeks. Marta started breathing well again, and so did I. I would have liked to photograph my country in the midst of this emergency, the battles that the doctors wage on the frontline, the hospitals pushed to their limits, Italy on its knees fighting an invisible enemy. That enemy, a day in March, knocked on my door instead.
In the New York Times Magazine, deputy editor Jessica Lustig writes with devastating clarity about her family’s life in Brooklyn while her husband battled the virus, weeks before most people began taking the threat seriously:
At the door of the clinic, we stand looking out at two older women chatting outside the doorway, oblivious. Do I wave them away? Call out that they should get far away, go home, wash their hands, stay inside? Instead we just stand there, awkwardly, until they move on. Only then do we step outside to begin the long three-block walk home. I point out the early magnolia, the forsythia. T says he is cold. The untrimmed hairs on his neck, under his beard, are white. The few people walking past us on the sidewalk don’t know that we are visitors from the future. A vision, a premonition, a walking visitation. This will be them: Either T, in the mask, or — if they’re lucky — me, tending to him.
Essayist Leslie Jamison writes in the New York Review of Books about being shut away alone in her New York City apartment with her 2-year-old daughter since she became sick:
The virus. Its sinewy, intimate name. What does it feel like in my body today? Shivering under blankets. A hot itch behind the eyes. Three sweatshirts in the middle of the day. My daughter trying to pull another blanket over my body with her tiny arms. An ache in the muscles that somehow makes it hard to lie still. This loss of taste has become a kind of sensory quarantine. It’s as if the quarantine keeps inching closer and closer to my insides. First I lost the touch of other bodies; then I lost the air; now I’ve lost the taste of bananas. Nothing about any of these losses is particularly unique. I’ve made a schedule so I won’t go insane with the toddler. Five days ago, I wrote Walk/Adventure! on it, next to a cut-out illustration of a tiger—as if we’d see tigers on our walks. It was good to keep possibility alive.
At Literary Hub, novelist Heidi Pitlor writes about the elastic nature of time during her family’s quarantine in Massachusetts:
During a shutdown, the things that mark our days—commuting to work, sending our kids to school, having a drink with friends—vanish and time takes on a flat, seamless quality. Without some self-imposed structure, it’s easy to feel a little untethered. A friend recently posted on Facebook: “For those who have lost track, today is Blursday the fortyteenth of Maprilay.” ... Giving shape to time is especially important now, when the future is so shapeless. We do not know whether the virus will continue to rage for weeks or months or, lord help us, on and off for years. We do not know when we will feel safe again. And so many of us, minus those who are gifted at compartmentalization or denial, remain largely captive to fear. We may stay this way if we do not create at least the illusion of movement in our lives, our long days spent with ourselves or partners or families.
- What day is it today?
Novelist Lauren Groff writes at the New York Review of Books about trying to escape the prison of her fears while sequestered at home in Gainesville, Florida:
Some people have imaginations sparked only by what they can see; I blame this blinkered empiricism for the parks overwhelmed with people, the bars, until a few nights ago, thickly thronged. My imagination is the opposite. I fear everything invisible to me. From the enclosure of my house, I am afraid of the suffering that isn’t present before me, the people running out of money and food or drowning in the fluid in their lungs, the deaths of health-care workers now growing ill while performing their duties. I fear the federal government, which the right wing has so—intentionally—weakened that not only is it insufficient to help its people, it is actively standing in help’s way. I fear we won’t sufficiently punish the right. I fear leaving the house and spreading the disease. I fear what this time of fear is doing to my children, their imaginations, and their souls.
At ArtForum , Berlin-based critic and writer Kristian Vistrup Madsen reflects on martinis, melancholia, and Finnish artist Jaakko Pallasvuo’s 2018 graphic novel Retreat , in which three young people exile themselves in the woods:
In melancholia, the shape of what is ending, and its temporality, is sprawling and incomprehensible. The ambivalence makes it hard to bear. The world of Retreat is rendered in lush pink and purple watercolors, which dissolve into wild and messy abstractions. In apocalypse, the divisions established in genesis bleed back out. My own Corona-retreat is similarly soft, color-field like, each day a blurred succession of quarantinis, YouTube–yoga, and televized press conferences. As restrictions mount, so does abstraction. For now, I’m still rooting for love to save the world.
At the Paris Review , Matt Levin writes about reading Virginia Woolf’s novel The Waves during quarantine:
A retreat, a quarantine, a sickness—they simultaneously distort and clarify, curtail and expand. It is an ideal state in which to read literature with a reputation for difficulty and inaccessibility, those hermetic books shorn of the handholds of conventional plot or characterization or description. A novel like Virginia Woolf’s The Waves is perfect for the state of interiority induced by quarantine—a story of three men and three women, meeting after the death of a mutual friend, told entirely in the overlapping internal monologues of the six, interspersed only with sections of pure, achingly beautiful descriptions of the natural world, a day’s procession and recession of light and waves. The novel is, in my mind’s eye, a perfectly spherical object. It is translucent and shimmering and infinitely fragile, prone to shatter at the slightest disturbance. It is not a book that can be read in snatches on the subway—it demands total absorption. Though it revels in a stark emotional nakedness, the book remains aloof, remote in its own deep self-absorption.
- Vox is starting a book club. Come read with us!
In an essay for the Financial Times, novelist Arundhati Roy writes with anger about Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s anemic response to the threat, but also offers a glimmer of hope for the future:
Historically, pandemics have forced humans to break with the past and imagine their world anew. This one is no different. It is a portal, a gateway between one world and the next. We can choose to walk through it, dragging the carcasses of our prejudice and hatred, our avarice, our data banks and dead ideas, our dead rivers and smoky skies behind us. Or we can walk through lightly, with little luggage, ready to imagine another world. And ready to fight for it.
From Boston, Nora Caplan-Bricker writes in The Point about the strange contraction of space under quarantine, in which a friend in Beirut is as close as the one around the corner in the same city:
It’s a nice illusion—nice to feel like we’re in it together, even if my real world has shrunk to one person, my husband, who sits with his laptop in the other room. It’s nice in the same way as reading those essays that reframe social distancing as solidarity. “We must begin to see the negative space as clearly as the positive, to know what we don’t do is also brilliant and full of love,” the poet Anne Boyer wrote on March 10th, the day that Massachusetts declared a state of emergency. If you squint, you could almost make sense of this quarantine as an effort to flatten, along with the curve, the distinctions we make between our bonds with others. Right now, I care for my neighbor in the same way I demonstrate love for my mother: in all instances, I stay away. And in moments this month, I have loved strangers with an intensity that is new to me. On March 14th, the Saturday night after the end of life as we knew it, I went out with my dog and found the street silent: no lines for restaurants, no children on bicycles, no couples strolling with little cups of ice cream. It had taken the combined will of thousands of people to deliver such a sudden and complete emptiness. I felt so grateful, and so bereft.
And on his own website, musician and artist David Byrne writes about rediscovering the value of working for collective good , saying that “what is happening now is an opportunity to learn how to change our behavior”:
In emergencies, citizens can suddenly cooperate and collaborate. Change can happen. We’re going to need to work together as the effects of climate change ramp up. In order for capitalism to survive in any form, we will have to be a little more socialist. Here is an opportunity for us to see things differently — to see that we really are all connected — and adjust our behavior accordingly. Are we willing to do this? Is this moment an opportunity to see how truly interdependent we all are? To live in a world that is different and better than the one we live in now? We might be too far down the road to test every asymptomatic person, but a change in our mindsets, in how we view our neighbors, could lay the groundwork for the collective action we’ll need to deal with other global crises. The time to see how connected we all are is now.
The portrait these writers paint of a world under quarantine is multifaceted. Our worlds have contracted to the confines of our homes, and yet in some ways we’re more connected than ever to one another. We feel fear and boredom, anger and gratitude, frustration and strange peace. Uncertainty drives us to find metaphors and images that will let us wrap our minds around what is happening.
Yet there’s no single “what” that is happening. Everyone is contending with the pandemic and its effects from different places and in different ways. Reading others’ experiences — even the most frightening ones — can help alleviate the loneliness and dread, a little, and remind us that what we’re going through is both unique and shared by all.
- Recommendations
Most Popular
- Republicans threaten a government shutdown unless Congress makes it harder to vote
- The horrifying rape case roiling France, explained
- Beyoncé’s shocking, predictable CMA snub, explained
- JD Vance’s racist, cat-eating conspiracy theory, explained as best we can
- Take a mental break with the newest Vox crossword
Today, Explained
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
This is the title for the native ad
More in Culture

The CMA snub just proves what Beyoncé was trying to tell us all along.

Why everyone suddenly cares about Brittany Mahomes’s politics.

They detail their dates for the public. I can’t stop watching.

Why are we still talking about this strange, glamorous family?

The 1988 classic shows how far Tim Burton strayed from the mischievous formula that made him great.

The DOJ says Tim Pool, Dave Rubin, Benny Johnson and others were unwitting Russian stooges.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
- Dear Life Kit
- Life Skills

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Amazon Music
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
Our most valuable lessons from 2 pandemic years

Andee Tagle

It's been two years since the world as we knew it was forever changed by the coronavirus pandemic .
We know you probably don't need that reminder, and there are probably a lot of people out there who don't want one.
This essay first appeared in NPR's Life Kit newsletter. Subscribe to the newsletter so you don't miss the next one, plus weekly tips that can help make life a little easier.
But if you're reading this, it means you've been through a lot:
Through unemployment and essential work; lockdowns and empty grocery store shelves and social distancing or even isolation; Zoom rooms and tiger kings and sourdough starters and all the sweatpants ; mask mandates and police brutality; a presidential election and an insurrection ; vaccines and boosters and masks off and on and off and on again .
It's been a revolving door of fear and fatigue and anger and uncertainty and suffering and loss . But we've also experienced a surprising amount of joy , and kindness, and new discovery, and delight , even.

Mental Health
Feeling blah take a joy break.
All of this to say: it feels all but impossible to qualify two years of pandemic living in any one way, but one thing is certain: we're still here – and we're changed.
The Life Kit team looked back on some of the most valuable lessons from the last two years that can help you look forward. Here are moments that helped change our mindsets and kept us moving through the past two years:
How to let more joy into your life
Producer Janet W. Lee grew to appreciate the small things:
While recent years have made it harder for me to look at the world with a more positive outlook, poet Ross Gay taught me to let more joy into my life . Gay is the author of The Book of Delights , where he shares the practice of calling out the delights in his everyday. This practice of taking a second to say the smell of coffee is lovely or to smile at the sound of my cat purring has brightened up my life.
Laziness does not exist
Managing producer Meghan Keane thanks Dumptruck for finding worth beyond productivity:

Dumptruck the chinchilla Devon Price hide caption
Dumptruck the chinchilla
Before the pandemic, I was all about hustle culture: get to work early, leave late, ignore any signs that I might need to slow down. But then a chinchilla named Dumptruck changed everything. We interviewed social psychologist (and owner of Dumptruck) Devon Price about his book Laziness Does Not Exist . Price says he never questions Dumptruck's worth because he lies around all day, but we're extra hard on ourselves when we aren't being productive. He says what we often see as laziness is actually a signal from our bodies to rest – we all still have worth when we are simply breathing on the couch.
Time is the building block of life
Producer Clare Marie Schneider learned the value of time:
Four Thousand Weeks author Oliver Burkeman says he's in recovery from productivity. Now, he thinks of time as a precious resource – the building block of our lives. When we interviewed him, he said, "The sum total of all the things you paid attention to will have been your life." To me, this way of looking at time leaves a little more room to embrace taking out the trash, over and over again, and to move towards what feels most exciting in life.
Finding passion outside of work
Producer Audrey Nguyen shifted her energy to find what she loves outside of her work:

A Field Guide for Fledgling Birders
I've struggled with pouring too much of myself into my work, and not leaving enough gas in the tank for my life outside of the 9-to-5. One of the most useful lessons I learned came from our interview with sociology professor Erin Cech , author of The Trouble With Passion: How Searching For Fulfillment At Work Fosters Inequality . She recommends finding ways to "diversify your meaning-making portfolio." Taking a step back and figuring out how to make room for passion outside of work has been really helpful for my mental health. I've been birding , and I'm currently taking a pottery class with my partner at our local community college!
Find your "resilience circle"
Visual and digital editor Beck Harlan built community in a time of isolation:
The last two years have felt particularly uncertain. That makes it hard to plan, hard to dream and hard to cope. Author Elizabeth White faced some uncertainty of her own during the Great Recession, and she has a piece of advice: don't go it alone. White found support in a "resilience circle" – essentially, "a few people that I could tell the truth to." Having those folks who'll be a sounding board and a cheer squad in your corner, can get you through a lot. It doesn't matter how you connect — Whatsapp, Marco Polo, postcards, a weekly walk — just that you DO.
From all of us to you: we're grateful for the time you've spent with us today and throughout the pandemic. We're still here.
If you liked this excerpt from NPR's Life Kit, consider subscribing to our newsletter to get new tips every week.
- Life Kit: Life Skills
3 lessons about what really matters in life, learned in the pandemic
Share this idea.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
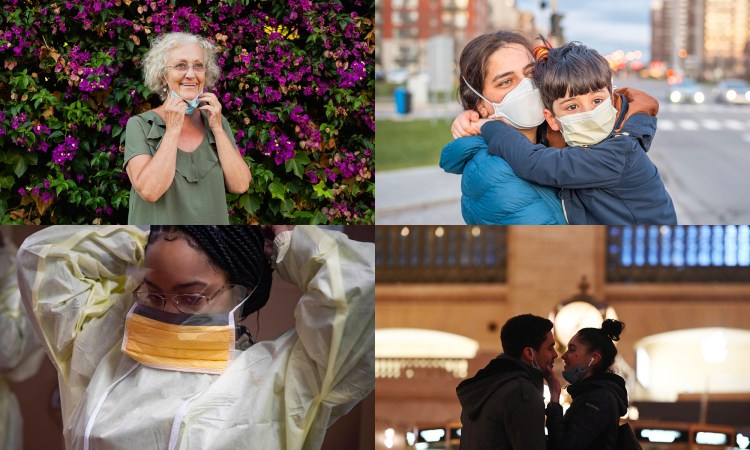

The last year has been like no other.
Since March 2020, every person on the planet has had their life shaken by the COVID-19 pandemic in some way. In the midst of the hardship and challenges, there’s been the sense among many people that this period has helped us evaluate our lives and focus on what’s truly important.
And maybe, just maybe, we’ve learned something from this moment.
In response to the pandemic, StoryCorps — a nonprofit dedicated to recording the largest collection of human stories and winner of the 2015 TED Prize — created StoryCorps Connect , a new tool to bring together loved ones via video conferencing and record the audio of their conversations.
Below are excerpts from a handful of the thousands of interviews recorded in recent months through StoryCorps Connect.
Lesson #1: The pandemic has helped us find deeper meaning in our work
Two mail carriers see the value in every delivery they make
Before getting a job as a mail carrier in Palm Beach, Florida, Evette Jourdain was going through a hard time — she’d lost her father, her brother and then her home. Finding reliable work helped tremendously, but then came COVID-19.
As Jourdain talked to her coworker , fellow postal worker Craig Boddie, she shared how she was feeling. “My anxiety levels are always on 10,” she says. “I pray on my way to work, I pray on my lunch break, I pray when I’m at the box. What keeps me going is just the fact that I need to keep going.”
Boddie agreed. His wife has autoimmune disease, and as he puts it, “Every day I wake up and wonder, ‘Is this the day that COVID-19 is gonna come home with me?’”
But he also knows that his work is more important than ever, and he thinks about how each package he carries contains something to keep people afloat in some way. “We’re like a lifeline — getting these people their medicines, their supplies.”
A health care provider gains inspiration from a classic novel
Josh Belser and Sam Dow are good friends who grew up in Tampa, Florida, and who now both work in healthcare 400 miles apart — Belser as a nurse in Syracuse, New York, and Dow as a health technician in Ann Arbor, Michigan.
And with COVID-19, they’ve both found themselves on the frontlines. “My floor was one of the first that was converted to strictly dealing with COVID patients. Our jobs changed like overnight,” says Dow in their StoryCorps conversation. “There was no dress rehearsal — the numbers started to go up and it was show time.”
So how did they get through? Dow tells his friend he found some inspiration in Albert Camus’s classic novel The Plague . “It’s about an epidemic, and the main character was a doctor,” he explains. “And he says the way to get through something like this is to be a decent person. Somebody asks him, ‘What makes a decent person?’ He says, ‘I don’t know but, for me, it’s just doing my job the best way I can.’”
Dow says he’s tried to do exactly that. “Hopefully I made a difference in people’s lives.”
Lesson #2: Family rhythms have shifted, but our ties are as important as ever
A grandmother takes strength from her ancestors
Like so many other people, COVID-19 took Jackie Stockton by surprise. One day, she was at her church in Long Beach Island, New Jersey, celebrating her 90th birthday — and the next thing she knew, she was in the hospital. What’s more, she was part of a community cluster, and five members of the church eventually died from the virus, including Stockton’s best friend as well as her son-in-law.
Stockton spoke to her daughter , Alice Stockton-Rossini, about these losses. She says, “I remember 9/11 as though it just happened, but then it was over. This will never, ever be over.”
As a way to cope, she finds herself thinking of her great-grandmother. “She lost half of her children. She lived through the worst kind of hell,” she recalls. “She was an amazing woman, and so was her husband. They just did the things they needed to do. And they survived.”
The pandemic brings together a mother and daughter
In 2005, attorney Chalana McFarland of Atlanta, Georgia, was convicted of mortgage fraud and sentenced to 30 years in prison. The judge hoped this harsh sentence would deter others from similar crimes, but it had severe consequences for McFarland’s 4-year-old daughter, Nia Cosby.
In 2020, with the onset of COVID-19, McFarland was transferred to home confinement. Upon being released, the first person she saw was her now college-age daughter. In a candid conversation during their first weekend together in 15 years, Nia describes their reunion as “one of the best moments of my life.”
McFarland agrees. “When I left, you were driving a Barbie car, and now you’re flexin’ in the Honda Accord,” she says. “We’ve had a relationship over the years, but it’s like pieces of a puzzle that we’re just now putting together. I can’t wait for you to discover how much alike we really are, because you haven’t really gotten to know who I am. But I see so much of me in you. Out of all the things that I’ve done in my life, you are the absolute one thing that I got right.”
A canceled reunion highlights the power of family stories
The Quander family has a long history in the US. Its matriarch, Nancy Carter, was one of 123 enslaved people owned by George Washington, and she was freed in his will. She later married Charles Quander, and in 1926, their descendents held the first Quander family reunion.
It took place every year since 1926 — until now.
“This one would have been the 95th reunion,” Rohulamin Quander, 76, tells his 18-year-old cousin , Alicia Argrett.
In lieu of gathering in person, Argrett asks him: “What would you like to pass on to me?” His reply: “That you are the keeper of the stories.”
Argrett appreciates his call to take this responsibility seriously. “As we’ve seen this year, you never know when your last [family reunion] could be,” she says. “I think it’s important to capture those opportunities while you still have them in your grasp. And I’m going to do what I can on my end to keep the spirit of the family alive.”
Lesson #3: Small gestures have a huge impact on our well-being
This pandemic led to the best date of her life — a staircase apart
As the director of microbiology at a hospital in Rochester, New York, Roberto Vargas’s job is to diagnose infectious disease. With his lab running constant COVID-19 tests, he needed to isolate himself from his wife, Susan Vargas, and their four children.
Initially, he stayed in a hotel but found it too lonely. So he moved into the family’s basement, stipulating that no one else was to go beyond the top of the stairs. One night, as the Vargases recall in their conversation, a coworker brought them all a home-cooked meal. “You sat at the bottom of the stairs in a rocking chair, and I was at the top. It was the first time we had been able to connect in so long,” says Susan.
This simple moment, she says, helped get her through the months of the pandemic, and it will forever be what she remembers most from this time: “As crazy as it sounds, it’s the best date I’ve ever had with you in my life.”
Mother and son reflect on a special, shared memory
In 2015, nine-year-old William Chambers went to work with his mother. Not to an office, but to a senior center near Boston, Massachusetts, where Ceceley Chambers works as an interfaith chaplain providing spiritual counsel to those with memory loss. Ceceley knew the seniors would enjoy spending time with a young person.
What she didn’t expect was for William to sit down at a table with a woman cradling a baby doll she thought was real, and talk to her as easily as if she were his friend. “You just jumped into her world,” she recalls.
As Ceceley continues her work during the pandemic, both she and William have been thinking about that moment a lot. Although the structure of her days hasn’t changed, she’s seeing much more fear in those she’s counseling. William says he has been working hard to cultivate empathy for whatever mood she comes home with. Thinking of that woman with the doll and the other patients helps him.
He adds, “They made me think you should enjoy life as much as you can, ‘cause it doesn’t happen forever.”
Want to record an interview with a loved one — nearby or far away — about their experiences during the pandemic? Here’s how to get started . You can also explore more StoryCorps stories here .
Watch StoryCorps founder Dave Isay’s TED Prize Talk here:
About the author
Kate Torgovnick May is a journalist and writer based in Los Angeles. A former storyteller at TED, she has worked with the ambitious thinkers of the TED Prize and Audacious Project, helping them share their stories in video and text. She's also the author of the narrative nonfiction book, CHEER!: Inside the Secret World of College Cheerleaders, and has written for the television series NCIS and Hellcats. Read more about her work at KateTorgovnickMay.com.
- society and culture
TED Talk of the Day

How to make radical climate action the new normal

6 ways to give that aren't about money

A smart way to handle anxiety -- courtesy of soccer great Lionel Messi


How do top athletes get into the zone? By getting uncomfortable

6 things people do around the world to slow down

Creating a contract -- yes, a contract! -- could help you get what you want from your relationship

Could your life story use an update? Here’s how to do it

6 tips to help you be a better human now

How to have better conversations on social media (really!)

3 strategies for effective leadership, from a former astronaut

The art of storytelling, according to the founders of StoryCorps and Humans of New York

10 questions to ask your family around the table

10 real-life love stories that'll grab you by the heart, from Storycorps
How to unlock your family history

Coronavirus Disease 2019
5 things covid-19 taught me, opportunities to learn and grow are always available, even in challenging times..
Posted August 14, 2020 | Reviewed by Ekua Hagan
- Take our Your Mental Health Today Test
- Find a therapist near me
“Never let a good crisis go to waste. It’s the universe challenging you to learn something new and rise to the next level of your potential.” — Kristen Ulmer
I’ve always been an optimist . And for the most part, I’ve remained positive during the pandemic.
Not that my head has been stuck in the Pollyanna sand. It’s hard not to spend time with my friends and neighbors. It is frustrating not to be able to volunteer and contribute to my community. And it has been painful to see my son talking with his friends and classmates on a screen rather than in person.
It hurts to not be able to hug and kiss my father, who lives in the same town.
Yet through the lens of optimism — and objectivity — it’s clear that these inconveniences are just that; they’re not real problems when compared to what so many others are dealing with.
No matter where you fall on the scale from traumatized to peaceful, from economically or physically struggling to secure, I’d like to share what I’ve been learning during these unusual times. After all, when life hands us lemons, we may as well make lemonade, pull up a chair, and try and see the silver lining in the clouds passing overhead.
1. Objectivity Einstein’s first law of motion says that a moving object remains so, consistent in direction and speed, unless acted upon by an outside force. As painful as being knocked off-kilter has been for many of us, this radical shift in our personal and collective experience affords an opportunity so few human beings ever get: to see things from an entirely different point of view. It lets us see the world and ourselves newly, including what we need and what we don’t… in our schedules, homes, relationships, and lives. As well as the opportunity to release whatever isn’t working for us.
2. Simple Pleasures The shift in viewpoint also lets us identify and take on what may have been missing. I’ve found joy in longer and more meaningful calls to family and friends, reading more widely, and writing letters (by hand!); pleasures I often felt too busy for prior to the pandemic.
While I’ve always spent a good deal of time outdoors, I am now there more frequently and deliberately. So it seems, is everyone else… wherever I go, I see people walking, hiking, and biking; families playing and being together. The world has moved outside and we all seem healthier and happier for it.
The pandemic has also reshaped why I have been going out. Prior to COVID-19, when I left the house — even for a family walk — I often felt a need to buy something, eat something, or do something. Now, a bike ride is the agenda, a drive is the outing. Before, it seemed we did those things to get somewhere else — a restaurant, a store, or a coffee shop — whether we needed anything from them or not. Now, the journey is the destination.
3. Time Management and Pacing Life is busier in many ways now that our home also houses a full-time play space, school, and two offices. That said, the lack of commuting, shopping, and shuttling around has helped me to see the distinction between the actual rush of my life and work, and the hurry, worry, and anxiety that I have been imposing upon them. Which has given me the opportunity to slow down, relax, and be more present in both.
4. Family, Communication, and Connection This includes relaxing into the opportunity of ongoing family togetherness. As well as flexing the intimacy and communication muscles that can get weak, thanks to life on the go. Living together in this new way as a family has been a great experience for us, in part because of our recognition of the need for structure and space, as well as proactively sharing what we’re feeling and going through in our increased closeness.
5. Flexibility The through-theme here, and certainly the greatest lesson for me of the pandemic, has been the chance to practice the art of flexibility and flow… Learning to accept what is, rather than struggle and fight against my idea of how life and the world "should be." The latter gets us nowhere other than stressed , tired, and worn out. When things are relatively predictable and going the way we want them to, we don’t need to flex our surrendering muscles. But they’re important, no matter how good our current circumstances may seem. Now is our opportunity to give them a workout.
As we all know by now, we can’t control what happens to us and in the world, much as we’d like to. We can, however, decide how we’ll react to what is going on, including what we choose to learn from our experiences, and the opportunities we seek out in the face of these and other changing and challenging times.

Learn more about me on my website .

Jennifer Hamady specializes in emotional issues that interfere with optimal self-expression and is the author of The Art of Singing .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

It’s increasingly common for someone to be diagnosed with a condition such as ADHD or autism as an adult. A diagnosis often brings relief, but it can also come with as many questions as answers.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Recommended

5 life lessons COVID-19 has taught me
During this past year, the COVID-19 pandemic has turned our lives upside down and changed not just the way we live and work but also how we think and behave. Every part of the world has been affected, and every aspect of life has been impacted. Our everyday routines were brought to a stop, and any sense of normalcy was lost. While we stop and look at the world around us, I cannot help but realize what I used to take for granted. If anything, perhaps there are some life lessons to take away from this pandemic.
1. This world is interconnected. We often think of each country as a separate entity and being very different from one another. Within a few months of the virus first being identified, the virus spread to nearly every country, and a global pandemic was declared. Despite the differences and distance between places, we are battling the same virus and having the same struggles. It’s a reminder of just how our world economy and society are interconnected on many levels, including supply chains, communications, technology, and travel.
2. Humans are social creatures, and we need social interaction and human contact. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of social interaction and human contact within almost every aspect of our lives, including education, employment, entertainment, and recreation. Efforts to reduce the spread of the virus, including physical distancing, quarantine, and stay-at-home orders, have prompted and exacerbated social isolation and loneliness. Along with 35 million other individuals (accounting for 28% of the population) in the United States, I live alone, and this has meant little to no social interactions for months. And as much as I consider myself an independent person who has lived on their own for years and moved numerous times to new cities without knowing anyone there, this pandemic has made me realize how much I miss social interaction and things as simple as a hug or coffee with a friend at the café.
3. Humans are adaptive, and life is more flexible than we think. The pandemic has been a time of extraordinary change, and we have had to rapidly change and adapt to the evolving situation. Many individuals have lost jobs and have been forced to find creative ways to pay the bills. Many others began working from home. Schools turned online with virtual learning. Many physicians started offering telemedicine. This pandemic has been a testament to just how resilient we are as humans and our ability to be flexible and creative in the face of uncertainty.
4. There is goodness and humanity, even in the darkness. At the start of the pandemic, there was a shortage of personal protective equipment (PPE) among hospitals and health care facilities, and many health care workers were reusing the same disposable mask for days or weeks at a time. Immediately, community members gathered together to procure masks, 3D print face shields, and hand sew masks and scrub caps for health care workers. Restaurants were donating food to hospital workers and first responders. And people were volunteering to bring groceries to the elderly. These acts of kindness and appreciation from the community has helped keep me and many of my fellow health care workers going, working day after day during this pandemic.
5. Life is precious. Be grateful for what we have. With over 225 thousand lives lost to the pandemic in the United States to date (and over 1.1 million worldwide), this pandemic has made me re-think my priorities and remember how precious life is. It has been a reminder to appreciate the smaller things in life – the things I often take for granted. With so many deaths each day, I am grateful for my family and friends, even if it means video calls and text messages while we cannot see each other in-person. With so many people falling ill, I am grateful for my health. With so many people losing jobs and becoming homeless, I am grateful for the food in my fridge and a place to call home. This pandemic has made me re-evaluate my life and assess my priorities and served as a reminder of how precious life is and appreciate the small things in life.
Christine Lau is a physician.
Image credit: Shutterstock.com

A call to action for wounded healers

The rise of gender reveals: a global health perspective

Tagged as: COVID , Infectious Disease
More by Christine Lau, MD

4 lessons the pandemic has taught health care

6 things people should know about the COVID-19 vaccines

Be grateful this holiday season
Related posts.

How to get patients vaccinated against COVID-19 [PODCAST]

COVID-19 divides and conquers

State sanctioned executions in the age of COVID-19
A patient’s covid-19 reflections.

Starting medical school in the midst of COVID-19
Covid-19 shows why we need health insurance, more in physician.

How a doctor with cerebral palsy defied the odds and transformed health care
Legitimate vs. sham peer review (spr): is there a difference, medical gaslighting and strategies to combat it.

How to stay calm and lead effectively in high-stress medical emergencies

How hypothesis testing could slash legal costs

Fighting burnout with deeper human connections
Most popular.

Should transgender athletes compete in women’s sports?

The future of health care depends on hands-on training: We cannot afford to cut corners

Medicare’s cobra effect: How a well-intentioned policy spiraled into a health care crisis

Time to get digital in your practice

Doctors under fire: Is the DEA turning them into drug dealers?

Past 6 Months

The truth behind opioid use disorder

How medical school curricula perpetuate inequality

From conviction to appeal: a doctor’s opioid case sparks debate

President Biden: a closer look at leadership, dignity, and aging

Stop physician burnout: the hidden danger of AI note-writing software

A doctor’s eye-opening journey as a patient
Recent posts.

When technology merges with humanity

AI-powered health care [PODCAST]

How health systems can combat a $3B+ patient retention issue

Subscribe to KevinMD and never miss a story!
Get free updates delivered free to your inbox.
Find jobs at Careers by KevinMD.com
Search thousands of physician, PA, NP, and CRNA jobs now.
CME Spotlights
Leave a Comment
Comments are moderated before they are published. Please read the comment policy .
Skip to content
Read the latest news stories about Mailman faculty, research, and events.
Departments
We integrate an innovative skills-based curriculum, research collaborations, and hands-on field experience to prepare students.
Learn more about our research centers, which focus on critical issues in public health.
Our Faculty
Meet the faculty of the Mailman School of Public Health.
Become a Student
Life and community, how to apply.
Learn how to apply to the Mailman School of Public Health.
Ten Lessons from Our Pandemic Year
The one-year anniversary of the start of the pandemic is a somber time of reflection on the lives lost, the illness and suffering experienced, and disruption and separation inflicted by COVID-19. It is also a time to celebrate the contributions of front-line workers and public health scholars and practitioners. And while there is still much to learn about COVID-19, we can seize the opportunity to assess what the pandemic has taught us.
Columbia Mailman School faculty shared their thoughts on lessons learned over the past year, from virus co-morbidities to what the pandemic revealed about the health of our country. These lessons are crucial as the world works to inch its way toward ending the current pandemic while taking steps to prevent the next one. This knowledge may also help policymakers address other health crises, from systemic racism to climate change.
“Today, with the largest immunization effort in the history of the world underway, we are guardedly optimistic. There are significant challenges ahead, to be sure, but we have in our sight an end to the pandemic. We will take with us many lessons, both tragic and inspiring,” said Dean Linda P. Fried .
Ten Lessons
The pandemic exposed and worsened underlying inequalities in our healthcare system and society at large, as seen with higher rates of COVID-19 infection and death in communities of color. The crisis also deepened the economic divide. “It is ironic that the United States, the richest country in the world, has been the most severely affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. This pandemic shined a light on our fractured health system, the fragility of the public health structures, and the deep health and economic disparities that plague our country. This requires a serious reckoning, not only to figure out what happened and why, but most importantly to put in place urgent remedies. Not doing this would be a betrayal of all those who suffered and those who lost their lives to this pandemic.” – Wafaa El-Sadr “We have seen the very people who have helped us survive the pandemic, the essential workers, bear a disproportionate burden of illness and death, due to racist housing policy and the disproportionate placement of toxic facilities in their neighborhoods.” – Terry McGovern
The pandemic revealed the consequences of underinvestment in public health prevention. Slow and incomplete public health mandates led to ERs overcrowding and unnecessary deaths. “For this pandemic and the next, we need to recognize the indisputable value of early public health interventions in preventing deaths and sparing us the need to overwork the immense courage of our hospital providers.” – Charles Branas “Funding for public health represents less than 3 percent of the nation’s total medical bill. This underinvestment contributed to a tragic shortage of public health workers to engage in needed pandemic activities, such as diagnostic testing and contact tracing. We need to commit to a massive investment in the nation’s public health workforce and infrastructure.” – Michael Sparer “With COVID-19, all 6,090 hospitals became battlegrounds. Given that pandemic preparedness has not been part of routine healthcare delivery, nor has there been an incentive to build a better infrastructure, there must be specific federal funding allocated that is sustained in perpetuity to ensure bio-preparedness… Americans must invest in long-term solutions, build back better, invest in preparedness, and sustain the gains. Regardless of the cost, this investment will pay massive dividends during the next pandemic.” – Craig Spencer and Syra Madad (from their letter in The Lancet )
The pandemic was the result of a fragmented and politicized public health response in a hyperconnected nation and globe, and an absence of leadership at the top. It exposed the consequences of wealthy countries that prioritized national, not global health, and how increased global inequalities could undermine the effort to suppress the virus. “As countries as poor as Thailand, as rich as Australia, and as large as China completely contained transmission within their borders, it showed how failed leadership within a divided nation means inevitable failure.” – Peter Muennig “If we look around the world, many, if not most, countries have failed to contain the spread of COVID-19. There are a myriad of reasons, but science denial, a lack of cooperation, and the absence of an evidence-based, well-communicated response mark the countries most impacted.” – Jeffrey Shaman
The pandemic demonstrated the damage wrought by poor communication and misinformation. Falsehoods about vaccine safety and the origins of the virus were pervasive, and the latter fueled discrimination against Asian-Americans.
“Misinformation led to widespread confusion about risk reduction behaviors during a time when the public’s cooperation in adhering to these behaviors was critical. A major lesson learned has been the critical importance of good, clear two-way communication with the public, and the importance of improving health literacy so that the public can better navigate the sea of misinformation that especially permeates on social media.” – Sandra Albrecht “In a pandemic, public officials need to effectively communicate what is happening, and why, and the public needs to trust that it should follow the scientific and political guidance they are hearing. The Trump Administration not only failed to effectively communicate, it also politicized the response so that wearing (or not wearing) a mask became a political statement rather than a simple act of infection prevention. Going forward, we need to work not only on better communication but on rebuilding trust in our public health and governmental institutions.” – Michael Sparer
The pandemic showed that pandemics can inflict long-term damage on physical and mental health, some of which may not yet be fully understood. People with “long haul” syndrome from COVID-19 can suffer from persistent and debilitating symptoms like dizziness, forgetfulness, headaches, and fatigue.
“In some people, we can implicate organ damage involving the lungs, the heart, and the nervous system. In others, we don't see obvious organ damage. A viral syndrome may precede the onset of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). We speculate that COVID-19 may trigger ME/CFS and are exploring this through immunological, metabolomic, proteomic and genetic studies of people with ME/CFS and COVID-19.” – Ian Lipkin
“Approximately 10-20 percent suffer enduring health- especially mental health effects after recovery, and the secondary consequences of lockdowns appear likely to substantially increase or exacerbate mental disorders.” – Ezra Susser
The pandemic showed that science can develop effective testing, infectious disease modeling, and vaccines at incredible speed, although testing in the U.S. was unnecessarily delayed. Technology also allowed millions to work from home and receive remote medical care, although unequal access to the internet and remote work has increased inequalities. Masks, a low-tech, non-pharmaceutical intervention, are helping prevent the spread of COVID and other infectious diseases like the flu, although it took us too long to understand their importance.
“Before COVID, vaccines took at least five years to develop but in less than one year from the start of this pandemic, people were receiving injections of one of three authorized, highly protective vaccines. This truly spectacular achievement reflects what science and hard work can accomplish.” – Jessica Justman
“Science and technology can be used to good effect, but without clear leadership, messaging and public health policy, the benefits of these tools are lost.” – Jeffrey Shaman
The pandemic showed how hard-hit communities can be resilient. Through collective mobilization and mutual aid, local communities rallied to help those in need, such as through food banks and community refrigerators. Mass protests following the killing of George Floyd have raised public consciousness around structural racism.
“Communities that bore the brunt of the pandemic came together to help one another by sharing food and essential supplies, checking on vulnerable neighbors, cheering on front-line workers, rallying for open streets, booking vaccination appointments, and more.” – Diana Hernandez
The pandemic demonstrated how school closures, job loss, and isolation strain mental and physical health. On the plus side, businesses and schools found ways to reinvent themselves. “There will be a need to considerably expand mental health resources to address not the mental health consequences of the pandemic, but also as a way to address the physical health consequences too.” – Sandra Albrecht “COVID-19 has changed the way we orient our students to the problems of structural racism in the United States and its impact on health. Student organizations such as CIPHER and MENTOR have worked with community-based organizations to provide assistance here in Washington Heights and Harlem and have learned first-hand how the pandemic has hurt these communities and how much these organizations have served as the first line of defense against its impact.” – Robert Fulliove
“Many cities rapidly moved large numbers of homeless people from congregate shelters to vacant good-quality hotels, demonstrating that homelessness is not an intractable problem and that ending homelessness depends primarily on the political will to do so.” – Ezra Susser
The pandemic wreaked havoc on cities, with revenue lost to public transit, entertainment, and tourism. Cities too adapted, designating open streets for pedestrians and cyclists and allowing for the proliferation of outdoor dining. Absent automotive traffic, cities saw sharp drops in air pollution. “Throughout history, plagues have been transformative for civilization. They have shaped the way that we organize ourselves and live our lives, almost always for the better. One of the many examples is the installation of sewage and sanitation systems following global urban cholera outbreaks that brought life expectancy down to 30 in most cities.” – Peter Muennig
COVID-19 showed that a global pandemic can happen and inflict serious loss of life, even in the world’s richest countries. It also showed that a pandemic can happen again. “The proverb says that ‘forewarned is forearmed,’ and all experts on emerging infectious diseases and pandemics have strongly advocated more effective global surveillance and early warning systems as the first step. Some of the main lessons of this pandemic are that early warning is not enough; political will and leadership, clear and consistent communications based on the best (and often evolving) scientific evidence, and the rapid implementation of public health measures may make the difference between a runaway pandemic and a manageable outbreak.” – Stephen Morse (from his article in Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness )

Ongoing lessons from a long pandemic
What COVID-19 has taught—and continues to teach—us two years in.
FOR ALMOST TWO YEARS, the coronavirus has battered the world, with millions of deaths and hundreds of millions of cases. This winter’s omicron variant surge is just the latest example of the pandemic’s unpredictable trajectory. It has resulted in personal tragedy for many. It has left survivors with long-COVID-19 symptoms, and it has overwhelmed health care systems and caused burnout among health workers. It has changed our behavior, acquainting people with mask wearing and social distancing. It has changed the way we work, forcing the fortunate to work remotely and resulting in furloughs or layoffs or constant risk of exposure for the less fortunate. And it has been an impetus to scientific innovation, with effective vaccines created and distributed at a historic pace.
The world is a different place from what it was two years ago, and we are still learning to live with all the sorrow and change the pandemic has brought. At the same time, COVID-19 has taught us a lot. Through the global crisis, we have reevaluated aspects of our societies and examined what is working—and what isn’t.
Here HKS faculty members and other experts examine lessons learned during the pandemic.
- Matthew Baum and John Della Volpe: National suffering and solidarity
- Hannah Riley Bowles: Understanding the “Shecession”
- David Eaves: Lessons from digital government
- Debra Iles: Executive education will never be the same
- Anders Jensen: A time to rethink tax systems
- Asim Khwaja: Prioritizing process to prepare for the next shock
- Dan Levy: Thinking outside—and inside—the Zoom box
National suffering and solidarity
Matthew baum and john della volpe.

It is difficult to conceive of anything good borne of COVID-19. As of this writing, in the United States, more than 700,000 are dead; 5 million have fallen worldwide. Millions of us grieve the untimely loss of a family member, a loved one, or a friend. And while our team of researchers from the Covid States Project has charted the extreme stress, anxiety, and depression so many Americans are facing, we also have found reason for optimism.
Partnership between the public and private sectors has spurred tremendous innovation in vaccine development and distribution logistics, which will likely prove enormously beneficial in the future, both with routine vaccines and with future pandemics. COVID-19 has also provided a rare real-time window into the workings of science, which while not universally helpful, provides valuable education for many people. Life-saving developments like these are probably why the public’s trust in science has largely remained intact while trust in other institutions has fallen since we began tracking such measures in April 2020. In a recent wave of more than 21,000 interviews across 50 states and the District of Columbia, we found that 92% of American adults trust doctors and hospitals, nearly 90% trust scientists and researchers, 78% trust the CDC, 74% trust pharmaceutical companies, and 68% trust Dr. Anthony Fauci on how best to deal with the coronavirus. Although overall levels of confidence in the scientific community remain very strong in general, evidence suggests that trust has eroded somewhat over the past 18 months and bears watching.
“While our country and many communities feel as divided as they have ever been in our lifetimes, the bonds of family (whether nuclear or chosen) are stronger.”
Matt baum and john della volpe.
Additionally, the coronavirus has provided oxygen for many of us to reevaluate priorities and life choices, including family, work, and career. The racial reckoning that followed the death of George Floyd in 2020 would most likely not have been as profound if tens of millions of American families had not been locked down, watching the gruesome news coverage, and pressured by often younger family members to confront and discuss systemic racism and the sins of America’s past that led to the murder and civil unrest.
Today, millions of Americans, especially Millennials and Generation Z, are reconsidering what it means to be happy and live a fulfilling and purposeful life. The effects of their decisions are now recognized by economists and businesses in need of labor, but the values leading to workforce changes have been developing for more than a decade, only to be supercharged during the pandemic. While our country and many communities feel as divided as they have ever been in our lifetimes, the bonds of family (whether nuclear or chosen) are stronger.
More than 18 months ago, Amanda Gorman offered comfort to a nation that was unaware of the inordinate loss soon headed its way. She said, in part:
We ignite not in the light, but in lack thereof, For it is in loss that we truly learn to love. In this chaos, we will discover clarity. In suffering, we must find solidarity.
As science leads us to a brighter 2022, let’s hope that through our national suffering we can once again discover what’s important, not just for ourselves but for the nation.
Matthew Baum , the Marvin Kalb Professor of Global Communications, and John Della Volpe , director of polling at the Harvard Kennedy School Institute of Politics, are among the team involved with the Covid States Project, a multi-university collaboration of researchers in a range of fields, who have examined behaviors and outcomes across the United States since March 2020.
Understanding the “Shecession”
Hannah riley bowles .
Q: How is the intersection of race and gender at play for working mothers during the COVID-19 recovery phase?

The most detailed data we have is from a survey conducted by Women and Public Policy Program Fellow Alicia Modestino, which consisted of a national panel of 2,500 working parents between Mother’s Day and Father’s Day (May 10 to June 21) of 2020. These data, collected at the onset of the pandemic, indicated that women accounted for more than half of unemployed workers (consonant with other economic studies), with Black and Hispanic women suffering outsize job losses at 9.5% and 8.3%, respectively. This gender disparity in labor market outcomes, often dubbed the “She-cession,” reflected the disproportionate toll on female workers, who were more likely to hold in-person jobs in affected industries such as hospitality, childcare, and health care.
A distinctive strength of this survey was that it collected information on whether childcare conflicts directly contributed to job losses. In contrast, other studies could only infer why women with children were displaced from the labor market. Modestino and colleagues found that 26% of unemployed mothers reported a lack of childcare as the reason for losing their jobs, compared with 14% of unemployed fathers. Their time-use data confirm that COVID-19 made work-life balance disproportionately difficult for women, with significant increases in time spent on schoolwork and playing with children as well as cooking and cleaning. In comparison, men reported only small increases in basic household chores. Women of color were more likely to have those experiences. For example, the survey showed that 23% of Black women—versus 15% of non-Black women—reported that their hours were reduced due to a lack of childcare.
Thanks to a gift to WAPPP from the Jessica Hoffman Brennan Gender Inequality and COVID-19 Pandemic Recovery Research Fund for research on the effects of the pandemic on women’s labor-market participation, Modestino and I are launching a study to explore working mothers’ experiences during the COVID-19 recovery phase from an intersectional perspective, disaggregating data by race, income, education, and other demographics. We also seek to investigate the role of negotiations in “shock resilience”—namely, how negotiating with partners, employers, coworkers, immediate and extended family members, friends, and others who make up formal and informal support systems can help women manage family and paid labor.
“With the closure of schools during the COVID-19 pandemic, household dynamics became a significant factor in determining labor outcomes for women.”
Hannah riley bowles.
Q: How has the shock to childcare during COVID-19 varied among women with different household dynamics?
With the closure of schools during the pandemic, household dynamics became a significant factor in determining labor outcomes for women. In Modestino’s survey, women were more likely to report losses in work status if they were single, divorced, separated, or widowed (22% for not married versus 15% for married). Women living in households with annual incomes below $75,000 were also significantly more likely to report that difficulties with childcare had had an adverse effect on their labor-market participation. This effect was more acute for women with small children and those holding in-person jobs.
Q: Working mothers have been hit hard. How can policy support them?
The Modestino survey data suggest that access to paid family leave, remote-work arrangements, and childcare subsidies were the most important policies in enabling women to remain fully employed. Equally or even more important was the support of managers and coworkers—suggesting that formal policies and practices need to be backed up by family-friendly work cultures.
Access to backup childcare was another important factor that varied across communities, with lower-income families more likely to rely on family support networks. However, although 24% of working parents reported having access to paid family leave, only 4% had used it during the pandemic. Even worse, working parents who identify as Black or Hispanic are less likely to work in jobs that offer paid sick time and medical leave or to have COVID-19 policies available to them such as backup childcare subsidies and working from home.
Again, looking forward, we seek to understand what critical factors enable working mothers to recover from the pandemic, including formal and informal supports for managing work and family.
Roy E. Larsen Senior Lecturer in Public Policy and Management Hannah Riley Bowles is a codirector of the Center for Public Leadership and the Women and Public Policy Program (WAPPP). Her research focuses on gender, negotiation, career advancement, and work-family conflict.
Lessons from digital government
David eaves.

In the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic, digital service groups and digital government experts around the world started to codify what a good digital crisis response could look like. These efforts have resulted in documents such as the California Digital Crisis Standard , developed by the state’s COVID-19 response team. Another example comes from Ontario, where the digital service group leveraged previous work in Alberta to quickly deploy a COVID-19 self-assessment in days, helping lower call volumes to government help desks and reducing stress for citizens.
The broad takeaway is that in a crisis, tried-and-true practices become even more critical to executing digital service delivery. The experiences of California and Ontario tell us that:
- Working in the open enables learning In a national emergency, working in the open allows multiple service providers—within the same governing system or outside it—to learn from one another, accelerating development timelines and surfacing creative solutions. The California Digital Crisis Standard was made possible by work that was shared, while the story of Alberta and Ontario demonstrates that leveraging others’ work can radically reduce the cost and time to deploy government services.
- There is always time for user testing While some may view user testing as a time-consuming luxury that has no place in rapid crisis response, the experiences of California and Ontario highlight the importance of prioritizing user needs. If anything, user testing is more important in a crisis, because the consequences are more serious if services do not work for users.
- Clear communication is essential Both examples underscore the importance of communicating simply and clearly with users of digital services. Doing so can reduce panic and confusion while creating trust between users and the government agencies managing the services.
Looking Ahead The experiences of California and Ontario don’t hold all the answers for an effective digital crisis response. No two crises are the same, and some degree of improvisation will always be necessary. But taking time to develop a framework for response—to understand how normal working processes might change or stay the same—helps mitigate the pressure teams face while handling any crisis. More important, the work that California and Ontario appeared to do “on the fly” was really the result of years of capacity building, changing policies, and acquiring the right talent to change how government works. The crisis just made the value of those new ways of working more apparent.
Digital service groups need to think proactively about how crises affect the development and deployment of digital technologies in the public realm and build a standard that draws on the elements of impactful crisis responses like those in California and Ontario.
Lecturer in Public Policy David Eaves, with coeditor Lauren Lombardo MPP 2021, produced a policy brief titled “2020 State of Digital Transformation,” with lessons from digital government service units that responded quickly and effectively to the pandemic. The excerpt above is an adaptation of material from this brief.
Executive education will never be the same

Only six weeks after we shuttered our offices due to the onset of COVID-19, in April 2020, HKS Executive Education brought together participants for our first pivoted online program in April 2020. Six weeks after that, we hosted our first free faculty-led webinar, which focused on helping our global community respond to the repercussions of the health crisis.
Before the pandemic, we had a few online programs. In general, though, our faculty and participants preferred being together in person and on campus. We stuck with that model because we knew it worked. We needed a crisis to embrace online learning.
And as was true for many during the pandemic, we learned a few things—fast. It turns out that online executive education can be excellent. Everyone is in the front row. The cost of travel has evaporated. Classroom diversity is enhanced. Different learning styles are welcomed, and extended program lengths allow people to test what they are learning in their jobs in real time. Deeply interactive discussions between faculty members and learners, a cornerstone of our in-person programs, came alive online.
“It turns out online executive education can be excellent. Everyone is in the front row.”
We also learned, through a difficult year, about the resilience of the Kennedy School team. The HKS faculty pulled together, building momentum and encouraging one another to move forward and revamp the curriculum for remote learning. The members of our staff rallied, expanding their skills to enable each program participant to be truly present in this new virtual world. Together, the faculty and the staff managed polls and chats, posted new video and audio materials, curated virtual study groups, and reviewed participants’ progress at every step.
Outside the classroom, we learned that many were eager to discover through our free webinars how COVID-19 was reshaping leadership, economics, and trade. We expanded what we thought was just a short-term offering to an ongoing series of faculty members sharing the latest research on racial justice, social justice, climate change, crisis, and new scholarship across the HKS spectrum. We’ve always known that the best leaders never stop learning, and thousands in our community showed up for this important content while they were facing some of the most extreme public challenges we’ve seen in decades.
Our mission has always been to bring HKS ideas and research to the broadest possible audience of senior-level leaders who are looking to apply new approaches to their work in real-time. Based on what we’ve learned this year, online learning’s expanded place in our programs is here to stay. Today we offer more than 60 online program sessions every year. And even when COVID-19 is behind us, we expect to stay 40% online.
Debra Iles is the senior associate dean for executive education at Harvard Kennedy School.
A time to rethink tax systems
Anders jensen.

The COVID-19 pandemic has forced us to think about tax policy in an evidence-based way. It has put a lot of pressure on government budgets for unemployment benefits and other public goods, which means that the government must collect more taxes to provide them. But at the same time, the tax base has eroded owing to the various forms of lockdown that were necessary to slow the spread of COVID-19.
Tax policies for the post-pandemic recovery period will thus require governments to be resourceful and to look at underutilized policy tools. To that end, the COVID-19 recovery phase may present a strong opportunity for a deeper overhaul of tax systems to improve efficiency and—perhaps even more important—equity.
Anders Jensen is an assistant professor of public policy who studies tax policy with a particular focus on countries’ capacity to tax.
Prioritizing process to prepare for the next shock
Asim khwaja.

The pandemic led to massive losses in many countries—of life, of livelihoods, and more. The biggest lesson that I believe we can learn from these years of loss is that process matters. Shocks happen, and there is only so much a society can do to prepare for the worst kinds of shocks, such as COVID-19—one of the most devastating our world has experienced.
What this specific shock revealed to me is that we didn’t have processes in place to navigate it in a way that wasn’t reactionary or destructive. We didn’t have measurement systems to figure out the extent of the problem, and we didn’t have ways to adjudicate the effectiveness of our policy responses to the problem. We were lacking the evidence we desperately needed as we designed costly policies, assuming that they would lead to a benefit instead of a huge cost. In some places around the world, policymakers overdid it, and in others, policies such as lockdowns to limit the spread of the virus, proved successful. These instances of failure or success derived more from reactionary decisions than from any evidence-based process. We could only depend on the loudest voices and a panicked desire to do something quickly in our policy responses.
“What this specific shock revealed to me is that we didn’t have processes in place to navigate the shock in a way that wasn’t reactionary or destructive.”
I hope that we have now learned how critical it is to have effective response processes in place before the challenges that we will inevitably face in the future. Doing so will allow us to have a more thoughtful, evidence-driven, and conceptually valid response, as opposed to an immediate and desperate reaction.
Asim Khwaja is the director of the Center for International Development and the Sumitomo-FASID Professor of International Finance and Development.
Thinking outside—and inside—the Zoom box
Dan levy .

Q: How prepared was HKS for online learning when COVID-19 hit in March 2020?
Prior to COVID-19, the Kennedy School was already doing online learning, but it was mainly driven by a small number of faculty members and staff who strongly believed in its power to both expand reach and improve teaching and learning. There were many interesting initiatives in executive education. And there were pioneer faculty members, including Marshall Ganz and Matt Andrews. Teddy Svoronos, Pinar Dogan, I, and others were doing it as part of a blended learning approach. Then, a couple of years before the pandemic, a group of us started working on the Public Leadership Credential, which is the School’s flagship online learning initiative.
When we were forced by the pandemic to move to online learning, we were very fortunate to be able to leverage those previous efforts, and I think the School was better prepared for online learning because of them. That doesn’t mean it was easy to do, but it does mean that we had in-house expertise to help bring everyone into online teaching and learning.
Many of us had experience with asynchronous learning, whereby learners engage with online material but are not interacting live with teachers. So even some of us who had some experience had to adjust quickly to live online teaching. I think it’s fair to say that there were growing pains. It was not easy at first, and I commend the spirit of the faculty and staff members. They looked for ways to innovate and make things work for students and were very resourceful and creative. That, to me, is one of the silver linings of the pandemic: the unleashing of creativity and resourcefulness that those involved in teaching and learning were able to bring to the enterprise.
“The pandemic has taught us to think more carefully about how to design successful learning experiences and programs for our students. We need to be better at putting ourselves in their shoes.”
Q: You wrote a book about teaching with Zoom. How did that come about?
We went to online learning at the Kennedy School in March of 2020. By mid-May, I was seeing faculty members, both here and outside the School, use Zoom in creative ways. I started documenting those examples because I wanted to learn what they were doing—and I ended up putting together a book. I felt that people needed a one-stop place to learn how to teach effectively with Zoom, since that’s the platform most people were using. I hope the book is helpful, not only to colleagues at the Kennedy School and at Harvard but more broadly.
Q: What can we take from Zoom to the physical classroom?
Some aspects of teaching in the classroom are better—such as the magic that happens when people can engage in person. But it became clear to me that there are also some things we can do better online. Now that we’re transitioning back to in-person teaching, we can think about how to incorporate some of those advantages. The use of chat during live instruction on Zoom is an incredibly powerful tool for finding out quickly what’s on our students’ minds. As we return to classrooms, where we don’t have chat, we should think about alternative ways to get the same benefits. Another plus with teaching on Zoom is the breakout rooms, where you can put learners in groups. We’ve always done group work in classrooms, but on Zoom we experimented with having the groups use collaborative tools to document their work. Being able to better leverage group work for post-group discussions is something I hope we can bring into the physical classroom.
Q: What’s one lesson from teaching fully online during COVID-19 that you think we should not forget?
The pandemic has taught us to think more carefully about how to design successful learning experiences and programs for our students. We need to be better at putting ourselves in their shoes. That is a simple principle that should always guide teaching and learning, and it was especially evident over the past two years.
Dan Levy is a senior lecturer in public policy. He is the faculty director of the Public Leadership Credential , Harvard Kennedy School’s flagship online learning initiative, and the author of Teaching Effectively with Zoom: A Practical Guide to Engage Your Students and Help Them Learn .
The White House is seen as a backdrop as people visit the 'In America: Remember' public art installation near the Washington Monument on the National Mall in Washington, DC. The installation commemorates all the Americans who have died due to COVID-19. Image by Kent Nishimura/Los Angeles Times via Getty Images
Inline images by Justin Sullivan/Getty Images, Andrei Pungovschi/Bloomberg /Getty Images, and Liu Guanguan/China News Service/Getty Images
More from HKS
How covid-19 has changed public policy, the pandemic a year later: what went wrong and what’s ahead.
Get smart & reliable public policy insights right in your inbox.
- Health Tech
- Health Insurance
- Medical Devices
- Gene Therapy
- Neuroscience
- H5N1 Bird Flu
- Health Disparities
- Infectious Disease
- Mental Health
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Chronic Disease
- Alzheimer's
- Coercive Care
- The Obesity Revolution
- The War on Recovery
- Adam Feuerstein
- Matthew Herper
- Jennifer Adaeze Okwerekwu
- Ed Silverman
- CRISPR Tracker
- Breakthrough Device Tracker
- Generative AI Tracker
- Obesity Drug Tracker
- 2024 STAT Summit
- All Summits
- STATUS List
- STAT Madness
- STAT Brand Studio
Don't miss out
Subscribe to STAT+ today, for the best life sciences journalism in the industry
10 lessons I’ve learned from the Covid-19 pandemic
By Helen Branswell Dec. 28, 2021

O n the afternoon of New Year’s Eve, just hours from when 2019 was going to segue into 2020, I read an email about some unusual pneumonia cases in China’s Hubei province. Over the past couple of decades, China has been a wellspring of dangerous zoonotic diseases — SARS, H5N1 bird flu, and H7N9 bird flu. Better keep an eye on this, I thought to myself.
Fast-forward two years. We’re entering the third year of the Covid-19 pandemic. So much has happened in the intervening months. Some things have gone surprisingly well, notably the rapid development of Covid vaccines and some therapeutics. But far more things have gone horribly wrong. Multiple commissions and panels have been set up to learn the lessons of this pandemic so that we don’t repeat the same mistakes next time. (Yes, sadly, there will be a next time.) More commissions and panels are likely to follow. But already, some things have become abundantly clear.
advertisement
Here are 10 lessons I’ve learned in the past two years.
You gotta act fast For reasons I may never understand, in January and February of 2020 much of the world seemed not to grasp that the new virus that was spreading so rapidly in China wouldn’t stay in China.
Some experts I spoke to early on thought that the new coronavirus would be controlled because two others in that family — the SARS virus from 2003 and MERS, a camel virus that sometimes spreads to people — didn’t manage to ignite pandemics. But by late January, early February the virus had been found in a number of other countries. If the world ever truly had a chance to contain it, the moment had passed.
Trending Now: House passes bill that targets China biotechs
The guiding principle of outbreak response is hope for the best but prepare for the worst. It has felt too often in this pandemic that people are forgetting about the second part of that maxim. We’re seeing it even now with responses to the surging wave of Omicron cases.
It is true that public health authorities can get hammered if they sound the alarm for something that turns out not to merit it. The World Health Organization was pilloried by the European Parliament after the 2009 H1N1 flu pandemic ultimately proved not to be particularly deadly.
But with fast-developing disease outbreaks, if you wait until you’re sure that something is going to be a disaster before seizing every opportunity to alter its trajectory, you’ve made the outbreak much, much worse.
Simplicity rules
In the summer and early autumn of 2020, when Phase 3 clinical trials of Covid vaccines were still underway, two groups in the United States set out to determine who should have first access when vaccine doses became available. The National Academies of Science, Engineering and Medicine established an expert panel that created a priority list. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, an independent group that advises the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on vaccine policy, devised its own. Both groups prioritized health care workers and the elderly, who were at the highest risk of dying if they contracted the new virus. The schemes were not identical, but both emphasized that people with serious health conditions and essential workers — people whose lives were at risk because they were doing jobs that kept society functioning — should have early access to vaccine doses.
But who were essential workers? Does everyone who works in a hospital qualify as a health care worker? Could we realistically expect people administering the jabs to check whether the person before them actually had diabetes? Or that they taught elementary school, not spin classes ? (In a word: No.) Though well-intentioned, the schemes were too complex to operationalize. A number of states junked them in favor of calling people forward by age strata, after they’d vaccinated health care workers. The same problem arose with the rollout of Covid boosters this fall, which happened in a stepwise fashion where eligibility was linked to age, health status, and the level of individual risk, because of where people lived or worked. Eventually Nirav Shah, president of the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, pleaded with ACIP to simplify the system, saying it was hampering booster shot uptake because people couldn’t figure out whether they were eligible.
The calculus for kids is just different
One of the few blessings of this pandemic is that Covid-19 isn’t nearly as hard on children as it is on adults, at least not in terms of illness and deaths. (It has been terrible for children in myriad other ways, particularly the disruption of in-person schooling and the educational and social consequences of that.) To date, there have only been 790 Covid deaths in children 18 years old and younger in the U.S., data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggest. Children and teens make up only 0.1% of the more than 800,000 deaths the country has incurred.
STAT+: Exclusive analysis of biopharma, health policy, and the life sciences.
Covid has been seen to induce a post-infection condition in some children called MIS-C — short for multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. According to the CDC, there have been nearly 6,000 reported cases in the U.S. Most children who develop MIS-C recover, but there have been 52 deaths.
In the main, though, children experience milder disease when they catch Covid. And because of their far lower risk of death, the WHO has suggested children should be vaccinated later, after health workers and older adults the world over have been protected.
Logically, the WHO is correct. Prioritizing vaccine doses for older adults would save more lives. But the agency’s pleas have fallen on deaf ears.
Societies may accept large numbers of deaths in the elderly, but even small numbers of deaths in children are deemed to be too many. There was never a meaningful debate in this country about the ethics of vaccinating American kids before vaccinating African health workers. There were no public proponents arguing for putting kids here behind adults elsewhere.
Even in the face of a deadly pandemic, politics override public health
Call me naive, but it never occurred to me before this pandemic that political leaders would put the lives of their citizens at risk by downplaying or downright lying about a disease outbreak, just because telling the truth might jeopardize their political fortunes.
It never dawned on me that political leaders would oppose policies designed to save the lives of their citizenry and mitigate the personal and economic damage an outbreak was causing — things like rules about wearing masks or getting vaccinated.
If that thought had occurred to me, I would have assumed such leaders would have been punished by their followers when it became clear a path taken for political expediency was costing tens of thousands of lives. I wouldn’t have dreamed that instead, those same followers would embrace the bad advice and reject public health guidance.
I didn’t anticipate the havoc polarized politics would wreak on a pandemic response. I thought everyone would have the same goal: Keep as many people from dying as possible. But so much of the U.S. response has broken down along political lines. Uptake of vaccine is higher in blue counties than it is in red. Mask mandate opposition is higher in parts of the country that vote Republican. The virus doesn’t vote and it doesn’t care how we do. It’s only looking for respiratory tracts to infect. I assumed we’d all understand that.
Most people have no clue how science works. And that’s a problem Science education in this and a number of countries is woefully inadequate. As a result, people do not understand the iterative nature of science. With a brand new pathogen, it takes time to figure out things like how infectious it is or the means by which it best spreads. When vaccines are developed and first put into use, it takes time to see how well they’ll work and for how long they’ll protect. Some vaccines protect for years, others only months. (I’m thinking about flu vaccine here.) The only way to determine where Covid vaccines fall on the spectrum is to give them and watch for breakthrough infections to start to occur. There’s no way around this, but people have found it frustrating.
Sign up for Morning Rounds
Your daily dose of news in health and medicine.
We saw the lack of understanding of how science works in calls from some quarters to use prototype vaccines before they’d even been tested for safety and efficacy. (The risks would have been huge, and such a move would have been ethically indefensible.) We saw it repeatedly when new knowledge was acquired and WHO or CDC guidance was updated accordingly. Instead of recognizing changes as a reflection that more had been learned about the virus, many people seemed to feel they’d been deliberately misled by the earlier advice. At a time when there is so little trust in public figures and institutions, this lack of understanding contributed to the erosion of confidence in agencies and authorities leading the pandemic response and further undermined support for the Covid control measures they recommended.
Downplaying what lies ahead helps no one
In early 2020, country after country followed China’s lead and instituted some form of “lockdown” to try to slow spread of a virus that was rapidly overwhelming hospitals wherever it went. When then-President Trump followed suit on March 16, he announced that if people stayed home for 15 days , that would be enough to slow the virus’ spread. Trump spoke of a return to normal by Easter, which fell on April 4.
There was no talk about the fact that the need to reduce transmission of the virus wasn’t a one-time thing — that there was nothing miraculous about a 15-day pause. If people returned to life as normal immediately thereafter, the gains of the pause would quickly evaporate.
Which is exactly what happened. People thought they’d done their bit, taken their lumps — only to find out much more sacrifice lay ahead.
Winning the vaccine race really does matter. So does experience Pfizer and BioNTech were the first of the Western pharmaceutical companies to prove they had produced an efficacious Covid-19 vaccine. The Food and Drug Administration granted it an emergency use authorization on Dec. 11, 2020 — 11 months after the genetic code for the SARS-2 virus was shared with the world. Hot on their heels was Moderna, a brash Cambridge, Mass.-based biotech, with an equally efficacious vaccine that was made the same way, using messenger RNA. The FDA granted it an EUA one week later, on Dec. 18. No one has ever accused the leadership of Moderna of being shrinking violets. But Pfizer has been speedier and, well, pushier in the vaccine development race, consistently beating competitors to become the first — and in the U.S., still the only — vaccine that is fully licensed .
The Pfizer vaccine is the only vaccine in this country that can be used in teens under the age of 18. It is the first to be authorized for use in children; it is now available for kids aged 5 and up. It was the first to be granted an EUA for a booster shot. It’s currently the only vaccine recommended as a booster for people who were vaccinated outside the U.S. with a vaccine not authorized for use here (in other words, a vaccine like the AstraZeneca jab) or for people who took part in U.S. trials of vaccines that haven’t been authorized here (AstraZeneca, Novavax).
By dint of its many firsts and its eye-popping initial vaccine efficacy, Pfizer has created the perception that it is the premier Covid vaccine, even though Moderna’s vaccine, which uses three times the antigen contained in the Pfizer’s shot, may in the end be the better vaccine . But Pfizer’s success is not just about being first. The company has a deep well of experience in commercial-scale production and in navigating regulatory processes — something Moderna, which had never commercialized a product before, did not. The differences in regulatory experience may explain why Pfizer was awarded a full license for its vaccine 3.5 months after initiating its application for one. Moderna, on the other hand, took 2.8 months just to complete its application for a full license; four months later, it is still waiting for the license.
Related: 3 issues to watch in global health in 2022
Being first on its own might not have positioned Pfizer to be the dominant vaccine provider of the pandemic; by all practical measures, Moderna tied with the Pfizer vaccine getting across the initial finish line. And the vaccines were virtually identical in efficacy outcomes — 95% (Pfizer) and 94% (Moderna) against symptomatic Covid infections. But being first and having the know-how to turn a good prototype into massive amounts of vaccine while at the same time successfully navigating regulatory processes has been a winning combination for the Pfizer-BioNTech partnership.
In a pandemic, it’s pretty much every country for itself
I hate that this is true. But I fear that it is.
The world has suffered from the fact that we are not working together to try to end the pandemic. Rich countries buying up most of the available vaccines, pharmaceutical companies refusing to share vaccine formulas and production know-how, countries blocking exports of oxygen and personal protective equipment — all this has drawn out the pandemic and made it more difficult to endure. It’s no surprise that vaccine nationalism has reigned, or that borders have closed, often on scientifically indefensible grounds. (See: The Biden administration’s month-long ban on travel from eight southern African countries, even though the Omicron variant is already the dominant virus in this country.) Next time, it will be worse. Borders will close more quickly, keeping people out and critical matériel in, because countries will know what lies ahead.
It’s ugly and it’s counterproductive but it may be inevitable. I would like to be wrong on this.
Conducting clinical trials during a pandemic is doable, but it takes coordination
It is enormously challenging to plan and conduct clinical trials during a disease crisis — especially trials large enough to come to a solid conclusion about whether the drug or vaccine being tested actually works. Time and again, trials conducted during previous outbreaks were too small, were conducted without a control arm (i.e. the thing being tested wasn’t compared to a placebo), or were still struggling to reach an answer when the outbreak ended. This time has been different. Sort of. In a true story fit for the big screen, Sir Jeremy Farrar , director of the Wellcome Trust, and British scientist Martin Landray mapped out a plan for what has proven to be an enormously successful trial of Covid treatments while riding a London bus .
The Recovery trial, as it came to be called, told the world the steroid dexamethasone improved survival in people seriously ill with Covid. It proved two HIV drugs, lopinavir and ritonavir, didn’t change Covid outcomes. It also showed that hydroxychloroquine, an antimalarial drug, was ineffective against the new virus.
Recovery harnessed the power of the United Kingdom’s single-payer health care delivery system, the NHS, to enroll sufficient numbers of Covid patients in the early days of the pandemic to come up with much needed answers rapidly. In a separate endeavor, the WHO’s Solidarity trial arrived at some needed answers by drawing in data from around the world.
In the U.S., Operation Warp Speed helped design and run some clinical trials that quickly tested the efficacy of Covid vaccines it helped to fund. But when it came to testing existing drugs to see if they could be repurposed for Covid, much of the U.S. effort was a bust. Scores and scores of too-small studies came to inconclusive results. Lack of coordination meant that trials continued to study whether hydroxychloroquine acted against Covid even after there was a wealth of evidence that it did not.
Americans are willing to put up with a lot of death The official Covid death toll in the United States is nearing 820,000, a figure that is certainly an underestimate, though by how much remains unclear. A truly stunning fact about those deaths is that more of them occurred in 2021 than in 2020. Covid vaccine doses were in short supply in the first quarter of 2021, but soon thereafter anyone who wanted to be vaccinated could get jabbed. And this fall, anyone 16 years and older who wanted to get boosted could get a third shot.
And still, more people died from Covid in 2021 than died from Covid in 2020. In 2021, swaths of the country fought mask mandates, opposed vaccination mandates, objected to any measure designed to slow the spread of Covid that they perceived as an impediment on their ability to resume pre-pandemic activities. This insistence on returning to life as normal came at an unfathomable cost — the loss of hundreds of thousands of parents, grandparents, great-grandparents. Aunts and great-aunts, uncles, and great uncles. Cousins. Friends. Coworkers and supervisors. And still, big chunks of the population refused to get vaccinated, refused to wear masks, insisted SARS-2 was a hoax, or was no more threatening than the flu. “It almost is inexplicable,” Anthony Fauci, director of the National Institutes of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, told me when I asked him about this last month.
For me, it is incomprehensible.
About the Author Reprints
Helen branswell.
Senior Writer, Infectious Diseases
Helen Branswell covers issues broadly related to infectious diseases, including outbreaks, preparedness, research, and vaccine development. Follow her on Mastodon and Bluesky .
Coronavirus
infectious disease
STAT encourages you to share your voice. We welcome your commentary, criticism, and expertise on our subscriber-only platform, STAT+ Connect
To submit a correction request, please visit our Contact Us page .

Recommended

Recommended Stories

Embedded Bias: A race-free algorithm is merely the start for a safety net hospital confronting an onslaught of kidney disease

STAT Plus: House passes bill that targets China biotechs

STAT Plus: UnitedHealth pledged a hands-off approach after buying a Connecticut medical group. Then it upended how doctors practice

STAT Plus: With a win in lung cancer, biotech’s wealthiest outsider surfs to new heights

STAT Plus: Alnylam versus BridgeBio: The ATTR-CM debate
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
current events conversation
What Students Are Saying About Living Through a Pandemic
Teenage comments in response to our recent writing prompts, and an invitation to join the ongoing conversation.

By The Learning Network
The rapidly-developing coronavirus crisis is dominating global headlines and altering life as we know it. Many schools worldwide have closed. In the United States alone, 55 million students are rapidly adjusting to learning and socializing remotely, spending more time with family, and sacrificing comfort and convenience for the greater good.
For this week’s roundup of student comments on our writing prompts , it was only fitting to ask teenagers to react to various dimensions of this unprecedented situation: how the coronavirus outbreak is affecting their daily lives, how we can all help one another during the crisis and what thoughts or stories the term “social distancing” conjures for them.
Every week, we shout out new schools who have commented on our writing prompts. This week, perhaps because of many districts’ move to remote online learning, we had nearly 90 new classes join us from around the world. Welcome to the conversation to students from:
Academy of St. Elizabeth; Abilene, Tex.; Alabama; Anna High School, Tex.; Arlington, Va.; Austria-Hungary; Baltimore, Md.; Bellingham, Wash.; Ben Lippen School; Bloomington, Ind.; Branham High School, San Jose, Calif.; Boston; Buffalo High School, Wyo.; Camdenton, Mo.; Cincinnati, Ohio; Collierville, Tenn.; Dawson High School, Tex.; Denmark; Desert Vista High School; Doylestown, Penn.; Dublin, Calif.; Dunkirk, N.Y. ; Eleanor Murray Fallon Middle School; Elmhurst, Ill.; Fairfax, Va.; Framingham, Mass.; Frederick, Md.; Hartford, Conn.; Jefferson, N.J.; Kantonschule Uster, Switzerland; Laconia, N.H.; Las Vegas; Lashon Academy; Lebanon, N.H.; Ledyard High School; Leuzinger High School; Livonia, Mich.; Manistee Middle School; Miami, Fla.; Melrose High School; Milton Hershey School, Hershey, Penn.; Milwaukee; Montreal; Naguabo, Puerto Rico; Nebraska; Nessacus Regional Middle School; New Rochelle, N.Y.; Newport, Ky.; Newton, Mass.; North Stanly High School; Oakland, Calif.; Papillion Middle School; Polaris Expeditionary Learning School; Pomona, Calif.; Portsmouth, N.H.; Pueblo, Colo.; Reading, Mass.; Redmond Wash.; Richland, Wash.; Richmond Hill Ontario; Ridgeley, W.Va.; Rockford, Mich.; Rovereto, Italy; Salem, Mass.; Scottsdale, Ariz.; Seattle, Wash.; Sequoyah School Pasadena; Shackelford Junior High, Arlington, Tex.; South El Monte High School; Sugar Grove, Ill.; St. Louis, Mo.; Timberview High School; Topsfield, Mass.; Valley Stream North High School; Vienna, Va.; Waupun, Wis.; Wauwatosa, Wis.; Wenatchee, Wash.; Westborough Mass.; White Oak Middle School, Ohio; and Winter Park High School.
We’re so glad to have you here! Now, on to this week’s comments.
Please note: Student comments have been lightly edited for length, but otherwise appear as they were originally submitted.
How Is the Coronavirus Outbreak Affecting Your Life?
The coronavirus has changed how we work, play and learn : Schools are closing, sports leagues have been canceled, and many people have been asked to work from home.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Member-only story
Life Lessons Taught by Covid-19
“imagine life with empty malls and roads, no one to buy a coffee at a restaurant and no children playing in parks. only standstill cars and annoying silence, all around you.”.
Hasan Mustafa
Writers’ Blokke
In this world, where everyone is so involved in his own life has dealt with many crises and threats until in late 2019, December where a virus, now commonly known as ‘Corona Virus’ appears up and continues to spread and now has been a global issue. Many people have departed and are still fighting against it. Point to mention, it’s not a human neither a technology but a deadly virus that spreads from one person to another through any physical contact.
Today we are not going to talk about where did it originated, what should be the remedies taken or major issues faced by people. As this virus remains a big life threat, people are now accepting it as a reality and understands that life is important. So for your information, we have come up with some life lessons, the pandemic has taught us about life.
Life Lessons From Covid-19
Knowing the fact that this world will soon end and our lives are limited, it's much better that people shall accept reality and start figuring out ways to live a happy life while encountering all risks.
The 5 important life lessons taught by Covid Pandemic are the following, including:
1. Life is too short

Written by Hasan Mustafa
I am an analyst who analyzes problems and provide solutions by writing quality content about the on going things in daily life,
Text to speech

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Alex, a writer and fellow disabled parent, found the freedom to explore a fuller version of herself in the privacy the pandemic provided. "The way I dress, the way I love, and the way I carry ...
15 Lessons the COVID-19 Pandemic Has Taught Us
8 Lessons We Can Learn From the COVID-19 Pandemic
Here are nine important lessons we've learned in the midst of COVID-19. 1. Family is nonnegotiable. For many of us, this year brought with it quality family time that we never expected and, honestly, might never have had otherwise. It's reminded us just how much family matters.
Our students have shared with us the transformation and growth they have achieved during the pandemic. Below are the winning essays for December, as judged by the Press editorial staff. First ...
You may have heard the advice to keep a diary during this pandemic, both to understand yourself and to create a record of an extraordinary time for the future. In " The Quarantine Diaries ...
With this in mind, here are ten outcomes of the pandemic that actually are having positive outcomes and that will, hopefully, continue to have positive outcomes into our shared future. 1. Staying ...
The student or a family member had COVID-19 or suffered other illnesses due to confinement during the pandemic. The student suffered from a lack of internet access and other online learning challenges. Students who dealt with problems registering for or taking standardized tests and AP exams. Jeff Schiffman of the Tulane University admissions ...
Read these 12 moving essays about life during coronavirus. Artists, novelists, critics, and essayists are writing the first draft of history. A woman wearing a face mask in Miami. Alissa Wilkinson ...
Mar Hernández for NPR. It's been two years since the world as we knew it was forever changed by the coronavirus pandemic. We know you probably don't need that reminder, and there are probably a ...
Lesson #3: Small gestures have a huge impact on our well-being. This pandemic led to the best date of her life — a staircase apart. As the director of microbiology at a hospital in Rochester, New York, Roberto Vargas's job is to diagnose infectious disease.
Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form. To help students explain how the pandemic affected them, The Common App ...
Which has given me the opportunity to slow down, relax, and be more present in both. 4. Family, Communication, and Connection. This includes relaxing into the opportunity of ongoing family ...
3. Humans are adaptive, and life is more flexible than we think. The pandemic has been a time of extraordinary change, and we have had to rapidly change and adapt to the evolving situation. Many individuals have lost jobs and have been forced to find creative ways to pay the bills. Many others began working from home.
Ten Lessons. The pandemic exposed and worsened underlying inequalities in our healthcare system and society at large, as seen with higher rates of COVID-19 infection and death in communities of color. The crisis also deepened the economic divide. "It is ironic that the United States, the richest country in the world, has been the most ...
Ongoing lessons from a long pandemic
To date, there have only been 790 Covid deaths in children 18 years old and younger in the U.S., data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggest. Children and teens make up only 0 ...
What Students Are Saying About Living Through a Pandemic
COVID-19's Lessons for Future Pandemics
Even if you think you are prepared, prepare some more. As I said before, my spouse and I have always believed in being prepared. However, this pandemic has proved to us that we can never be too ...
The 5 important life lessons taught by Covid Pandemic are the following, including: 1. Life is too short ... The global impact of the pandemic has opened the world's eyes as now doing a full ...