You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.

73 ESL Writing Activities to Spark Your Students’ Creativity and Imagination
From a student’s point of view, writing assignments are something to dread.
But from an ESL teacher’s point of view, they should be a challenge worth accepting.
The challenge for you is to motivate your students enough to actually be excited about writing.
Sounds impossible? It’s actually quite simple.
The key is a strong pre-writing activity that boosts their confidence and adds to their vocabulary at the same time.
So, how do you get your students’ writing off to a great start?
In this post, we’ll look at some different ESL writing activities that will transform your students from hesitant writers to confident wordsmiths in their own right.
Writing Assignments Based on Stories
Writing activities prompted by music, writing practice exercises based on images or pictures, writing assignments based on food, writing activities based on mysteries, exercises to practice writing emails, activities to practice writing advertisements, assignments to practice writing reports, creative writing activity: class newsletter/newspaper.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
People of all ages love a well-told story, and using stories to teach ESL is a sure winner.
A story for a pre-writing activity could be in the form of:
- A movie . It could be a biography, sci-fi film, thriller, action-packed adventure, fairy tale or even a cartoon.
- A story read aloud from a book. If you’re using this, read in a way that brings the characters’ voices to life (including the narrator’s), hold the book up to show any pictures within or scan them and project onto a screen as you read. You can also search YouTube videos of famous authors or celebrities reading a book aloud, and show these in class.
- A story from the news . It could be from the TV, radio, newspaper or an online news site .
- A story read by your students. In this case, you could let them read a story silently or with a partner, and take as long as they like to think about the important parts.
No matter what you choose, it’ll be a great lead-in to the ESL writing exercises below.
1. Re-tell the story as is, or summarize it. (This works best for beginners, who are still getting their feet wet in the waters of English comprehension.)
2. After watching “Finding Nemo” : Tell the story from the point of view of the whale, the dentist’s daughter or Bruce the shark.
3. Explain to Marlin how he should take care of Nemo better.
4. Make up a story about a farm animal/zoo animal/jungle animal. What if a baby ___ was lost? What if a child was lost in the city? What if you found a lost child?
5. After the story of “Goldilocks” : Tell the story from the baby bear’s point of view.
6. What if the baby bear and Goldilocks became best buds? What would happen?
7. After discussing “The Gingerbread Man” : Tell the story from the fox’s or gingerbread man’s point of view.
8. What did the old woman do wrong that made the gingerbread man run away?
9. How do you make a gingerbread man? What other shapes could be made instead?
10. After “Little Red Riding Hood” : Write the story in the first person—from the point of view of either Red Riding Hood or the wolf.
11. What should Red Riding Hood have done when she met the wolf?
12. After watching a “Lord of the Rings” movie: What would you do if you had the One Ring? Write about a magical quest you and several friends would have if you could.
13. After watching a “Pirates of the Caribbean” movie: What if you were a pirate? What adventures would you have if you were a pirate?
14. After watching “Titanic” : Write about what you discover when you dive onto the wreck. Or imagine you were on the ship when it sank, and talk about how you escaped.
15. Whose fault was it that so many people drowned on the Titanic? What should they have done?
16. After watching a “Star Wars” movie: Imagine you’re a space explorer and write about what happens when you meet some characters from “Star Wars.”
17. After watching a “Terminator” movie: Imagine your teacher is a robot that has come back from the future. Or imagine you have come back from the future—what would it be like?
18. After watching a “Harry Potter” movie: Make up some magic spells and explain how you’d use them.
Everybody loves music! Watch your students’ faces light up as soon as they realize that they’re about to be treated to some songs rather than chalk-and-talk. Music stirs the emotions, after all, and can get your students excited about writing.
Here are some ideas for music you can incorporate into ESL writing activities:
- Classical music. There are some pieces of well-known classical music that specifically tell a story , and many of these are available on YouTube.
- “Fantasia 2000,” particularly “Rhapsody in Blue.” This wonderful, wordless animated story can kick off so much great writing!
- Movie music. The music that goes with a movie tells watchers how they should be feeling, and could be a good jumping-off point for some writing.
- Popular songs and music. Self-explanatory. Check out the most popular or trending artists on YouTube or Spotify for ideas.
- Kids’ songs . There’s something about singing a catchy little tune that makes the words stick in your mind more than just saying them. These can lead to some interesting writing, too.
19. After Prokofiev’s “Peter and the Wolf” : Tell the story from Peter’s point of view.
20. After Saint-Saëns’ “The Carnival of the Animals” : Imagine walking through the scenes with the animals and interacting with them. Write a story from the point of view of one of the animals.
21. Describe the animals in “The Carnival of the Animals.”
22. After Tchaikovsky’s “Romeo and Juliet” : Re-tell this classic Shakespeare story, adding a twist.
23. After watching and listening to “Rhapsody in Blue” : Tell all/part of the story.
24. If you were the main character in “Rhapsody in Blue,” what would you do?
25. Listen to a piece of classical/instrumental music and tell the story that it might be a background to. Imagine that it’s the background music for a movie.
26. Tell the story (real or made up) behind some popular songs like Taylor Swift’s “Wildest Dreams.”
27. Describe meeting someone special like in the aforementioned Taylor Swift song.
28. What happens in your wildest dreams?
29. What if you were a famous pop star or musician? What would it be like? What would you do?
30. Give instructions on how to find your favorite song on the Internet, both music and lyrics.
31. If you play an instrument, or have a relative who plays one, write about some of the basics of how to play. (This could also work as a speaking and listening activity, and then the whole class could write about it.)
32. What is your favorite genre of music, and why? (Be sure to explain what “genre” means !)
33. Do you think young children should be allowed to freely watch music videos?
Some pictures you can use for ESL writing activities include:
- Pictures from social media. If you use social media at all, you doubtless have a barrage of amazing photos and videos on your feed, all of which make for excellent writing prompts.
- Pictures from Google Images . A quick Google search on any (classroom-safe) image will turn up plenty.
- Cartoons . If you have young students, they’ll definitely enjoy this one.
- Pictures selected by your students. Not sure what to choose? Have your students pick their own pictures to write about. You’ll be pleasantly surprised at how vibrant their writing can be when they’re writing about subjects they actually care about.
Regardless of the picture you (or your students) choose, here are some writing prompts you can consider.
34. Tell a story—real or imagined—of what is happening in the picture.
35. Write about what happens next from the pictured moment.
36. Write about what was happening just before the pictured incident.
37. What if that was you in the picture?
38. What if you were the person who took the picture?
39. What if you knew the people in the picture? What would you say to them?
40. Describe all of the elements in the picture. This is great for vocabulary practice.
41. Describe how someone in the picture might be feeling.
42. Explain how to get into a pictured predicament (for example, in the picture here , how did he get into the boat without the crocodile eating him?) as well as how to get out of it.
43. Express an opinion about the rights and wrongs of the pictured situation. For example, for the same picture above: Should crocodiles be hunted and killed? What should happen if a crocodile kills someone?
Many of your students likely enjoy thinking and talking about food. So why wouldn’t they be motivated to write about it?
How you integrate food into your ESL writing assignments depends on your classroom arrangements and the amount of time you’re willing to put into preparation.
In any case, here are some ideas:
- Start with the preparation and sharing of food before writing about it.
- Look at pictures of food, and talk about them before moving on to writing.
- Have students research food-related topics on the internet.
- Start with a story about food.
Here are the specific food writing prompts:
44. After the story of “The Gingerbread Man”: Think about food that develops a life of its own, and what would happen with it. (This can also open up a discussion about cultural foods.) For example, make up a similar story about another piece of food (e.g., spaghetti or rice that comes alive). What if you felt something moving in your mouth after you bit into your burger?
45. Write a story (real or imagined) about being very hungry and/or finding/buying/stealing food to meet a desperate need.
46. Write a story about trying a new, unfamiliar kind of food—maybe in a (relevant) cross-cultural setting.
47. Write a story about finding and eating a food that has magical properties. (Maybe read or watch some or all of “Alice in Wonderland” first.)
48. Describe interesting/disgusting/unusual/delicious/colorful foods, especially after a class tasting lesson. (Prepare students first with suitable taste vocabulary .)
49. Describe a food that’s unfamiliar to most students in the class. (This is particularly helpful for classes where there are students belonging to minority groups who hesitate to speak up.)
50. Describe an imaginary magical food.
51. Give instructions for preparing a particular recipe.
52. After a class activity or demonstration involving food: Write down what you have learned.
53. Give instructions for producing food—growing vegetables, keeping animals, etc.
54. Give instructions for buying the best food—what to look for, looking at labels, checking prices and the like.
55. Write about your opinion on food and health in First World and Third World countries. (Explain what makes a country “First,” “Second” or “Third World” first.)
56. Write about your opinion on the cost of food.
57. Write about your opinion on GMOs or genetically engineered foods .
There’s nothing quite like a good “whodunnit,” and students will always enjoy a good puzzle. You can base various pre-writing activities around the two games below to get the class warmed up for ESL writing practice.
- Conundrum. This is an example of a game that can be played as a speaking and listening activity, and can lead into some good writing. The game starts with a simple statement or description of a situation like the ones described in situation puzzles . Students ask questions and receive yes/no answers until they work out the explanation for the situation.
After Conundrum, here are some of the activities your students can do:
58. Write a story about the sequence of events involved in a situation brought up in the game.
59. Devise and describe your own situation puzzle.
- Putting their hands inside a cloth bag (or just feeling the outside) to guess what an object is.
- Smelling substances in opaque jars with perforated lids, and trying to guess what they are.
- Tasting mystery foods on plastic spoons (with blindfolds).
- Looking at pictures of mysterious objects from obscure angles.
- Listening to and guessing the origins of sound effects. (You can record your own, or use some from the Internet .)
(Important: Make sure that whatever you’re using for your guessing game is safe for your students, especially if they involve having to touch, taste or smell the object.)
After a guessing game, your students can:
60. Write about a possible mystery object and a magical quality it could possess.
61. Describe what you thought you saw, heard, felt, tasted or smelled.
For both games, here are some writing prompts you can do:
62. Give instructions for playing one of the games.
63. Give instructions for the perfect crime.
64. Give your opinion about a recent crime and the punishment for it.
Emailing can often be a scary task for your students, especially if they’re using a new, strange language like English. You can utilize an email writing activity to help your students build confidence and get more comfortable writing in English.
Email can also teach your students things like proper language (formal or informal), structure and format. Email-related writing activities for ESL students can offer ample opportunities to teach all of these three aspects.
Since emails involve two parties (the sender and the receiver), you’ll need to pair your students up for this activity. Here’s how to prepare for it:
- Create one set of worksheets explaining details relevant to the sender. For example, it could contain information about a sender’s upcoming birthday party that they want to invite the receiver to.
- Create another set of worksheets with the receiver’s details. The worksheets could contain questions about food dishes or gifts, or it could say that the receiver can’t make it for one reason or other.
Once the above has been done, give one set of worksheets to the “senders” and the other to the “receivers.” Then, here’s what your students will do:
65. Based on the senders’ worksheets, write an email inviting the receiver and explaining the key aspects of the event featured in the worksheet.
66. Based on the receivers’ worksheets, write an email explaining why you can or cannot make it to the party, and/or what other information you need about the event.
Advertisements are everywhere, and you can bet that your students have a few favorite ads of their own. Advertisement-related writing activities work across age groups and can be adapted to most students and their needs.
This great ESL writing assignment can help your students put the adjectives they’ve learned into good use, as well as showcase their creative writing and persuasion skills.
You can find advertisements everywhere, including:
- YouTube videos
- Newspapers and magazines
You can also bring an object (or handful of objects) to class that your students can write ads about.
67. After your students carefully examine the object(s) you brought into class: Write all the adjectives you can think of about it.
68. For a more challenging writing exercise: Write an ad about the object. How would you persuade someone who knows nothing about the object whatsoever to buy it? (Your students may or may not use the adjectives they wrote down earlier. Encourage them to be creative!)
Your students have likely already done some kind of report during the course of their studies. Also, writing reports is a skill that’ll be useful to them once they enter college or the corporate world (if they aren’t in it already). If you feel that they need a little more practice in this area, use this ESL writing assignment.
First, discuss how research and structure matter to reports—and perhaps show them a few samples. Then, give them a few questions to base their reports on, like:
69. What can you say about (insert topic here) in terms of (insert specific angle here)? (For example, “What can you say about the government’s efforts to improve the local park in terms of its impact on the general public?” Of course, you should adapt this question to the level of your students.)
70. After talking about a YouTube video on bears eating salmon : What would happen to the bears if the salmon ran out?
This ESL writing activity is a bit more intensive and will allow your students to employ many different aspects of their ESL knowledge. Crafting a class newsletter will build collaboration, communication, listening, speaking and, of course, writing skills. If they’re not sure how to build a newsletter or newspaper from scratch, they can always swipe from premade templates like this one .
The newsletter/newspaper can follow a specific theme, or the articles can consist of a hodgepodge of random topics based on questions like:
71. What is the most interesting thing that happened in school this year? It can be the funniest/scariest/most heartwarming incident. Write a feature article about it. (Make sure to explain what a “feature article” is .)
72. Write a report highlighting the key events in some recent local festivals or concerts.
73. Going off of the last exercise, write an ad inviting the reader to buy a product or attend an event.
Once all of the articles are done, you can start putting them together. Make sure to walk your students through these newspaper layout tips . And when the newsletter/newspaper is finally published and circulated out there for the world to see, remember to congratulate your students for a job well done!
No matter what writing assignments you choose, make sure to keep the excitement level high so that your students are enthusiastic for your next writing session.
Whether they write by hand or type on a computer, remember to encourage them as much as you can by focusing on the good points rather than just running all over their mistakes with a red pen.
Lastly, find ways for them to share their efforts—whether online, on the classroom wall, bound together in a book to be passed around, etc.
They can also read aloud to each other, share with their parents and siblings and even share with other classes!
For more ESL assignment ideas, check out this post:
Great ESL homework ideas can be difficult to come up with. So check out these 13 great ideas for ESL homework assignments that your students will love. Not only are they…
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe

- Teaching Tips
20 Interactive Classroom Activities for College Students [Plus: Free List of 45+ Activities]
Planning to use interactive classroom activities intentionally can really transform the learning dynamic. Here are 20 activities to get you started.
Top Hat Staff
![assignment activities examples 20 Interactive Classroom Activities for College Students [Plus: Free List of 45+ Activities]](https://tophat.com/wp-content/uploads/TopHat_Blog_Classroom-Activities_B.jpg)
How interactive are your classroom activities? Do you have less energy for class than you used to? Do you find student grades declining? And are the teaching methods you’ve always relied on not working as well as they once did? We spoke to two college instructors, Chris Merlo and Monika Semma. Their strategies for interactive classroom activities will energize your class and get the discussion moving again.
Table of contents
- Why are interactive activities important in college?
6 community-building activities
5 communication activities for college students, 3 motivational activities for college students.
- 6 team-building activities for college students
Interactive classroom activities, in short
Why are interactive classroom activities important.
Merlo, a computer science teacher, says that interactive classroom activities are not new to students, and one main reason why teachers have trouble connecting is that they fail to adapt to their students’ perspectives.
“My six-year-old son doesn’t find iPads amazing; to him, they’ve always just existed. Similarly, to a lot of students today, experiences like team exercises and flipped classrooms, while foreign to many instructors are not new.
“If we care about reaching today’s students, who seem to have a different idea of student responsibilities than we had, perhaps we have to reach them on their terms.
“In my thirties, I could still find a lot of similarities with my twenty-something students. But now, in my forties? Not so much. What I’ve started to realize is that it isn’t just the little things, like whether they’ve seen Ghostbusters. (They haven’t.) It’s the big things, like how they learn.”
Semma, a humanities TA, found that the chalk-and-talk approach failed on her first day in front of a class. “It was a lot like parallel parking in front of 20 people,” she said. “I looked more like a classmate. I dropped the eraser on my face whilst trying to write my name on the board. One of my students called me ‘mom.’”
“I chalked it up to first day jitters, but that same quietness crept its way back into my classroom for the next tutorial, and the next tutorial and the next. While nearly silent in class, my students were rather vocal in the endless stream of emails that flooded my inbox. That way I knew they wanted to learn. I also knew that I had to find a way to make tutorials more engaging.”
From these experiences, Merlo and Semma now share some interactive classroom activities for students and for teachers that can turn a quiet classroom full of people unwilling to speak up to a hive of debate, making the student learning experience more collaborative for everyone.
Energize your college classroom and get discussions flowing. Download The Best Classroom Activities for College Courses to engage and motivate students.
1. Open-ended questions
Chris Merlo: Open-ended questions don’t take any planning. All they take is a class with at least one student who isn’t too shy. I remember a class a few semesters ago that started with nine students. Due to a couple of medical conditions and a job opportunity, three of the students had to drop the semester. The problem was that these three students were the ones I counted on to ask questions and keep the class lively! Once I was left with six introverted people, conversations during class seemed to stop.
By luck, I stumbled on something that got the students talking again. I said, “What has been the most difficult thing about [the project that was due soon]?” This opened the floodgates—students love to complain, especially about us and our demands. This one simple question led to twenty minutes of discussion involving all six students. I wasn’t even sure what a couple of these students’ voices sounded like, but once I gave them an open-ended opportunity to complain about an assignment, they were off to the races. A truly successful classroom activity.
2. What’s wrong with this example?
Chris Merlo: Students also love to find a professor’s mistakes—like me, I’m sure you’ve found this out the hard way. When I teach computer science, I will make up a program that, for instance, performs the wrong arithmetic, and have students find the bug. In a particularly quiet or disengaged class, you can incentivize students with five points on the next exam, or something similar.
If you teach history, you might use flawed examples that change a key person’s name, such as “King Henry VIII (instead of King John) signed the Magna Carta in 1215,” or match a person to an incorrect event: “Gavrilo Princip is considered to have fired the first shot in the Spanish Civil War (instead of World War I).” Beam these examples on the whiteboard, and let the students’ competitiveness drive them to get the right answer before their classmates.
3. Let students critique each other
Chris Merlo: This can go badly if you don’t set some ground rules for civility, but done well, classroom activities like this really help open up collaborative learning. One of my colleagues devised a great exercise: First, give students about half of their class time to write instructions that an imaginary robot can understand to draw a recognizable picture, like a corporate logo, without telling students what will happen later. Then assign each student’s instructions to a randomly chosen classmate, and have the classmate pretend to be the robot, attempting to follow the instructions and draw the same logo.
After a few minutes, introduce a specific student who can share their results with the class, then ask their partner to share the initial instructions. This method gives students a chance to communicate with each other (“That’s not what I meant!”) and laugh and bond, while learning an important lesson.
This exercise teaches computer science students the difficulty and importance of writing clear instructions. I have seen this exercise not only teach pairs of such students meaningful lessons but encourage friendships that extended beyond my classroom.
Get students participating with these 45 classroom activities
4. Pass the “mic”
Monika Semma: As an instructor, it’s amazing how much information you can gather from a student-centered review session. Specifically, if you leave the review in the hands of your students, you can get an easy and thorough assessment of what is being absorbed, and what is being left by the wayside. The more you encourage participation, the more you’ll see where your class is struggling and the more comfortable students will become with course material. Here’s how to transform a standard review into one of your more popular classroom activities:
- A week before the review, ask students to email you two to five key terms or theories that they feel they need to brush up on. Take all that data and compress it until you have a solid working list of what students want to review most.
- In class, provide students with visual access to the list (I found writing all the terms on a chalkboard to be most effective). Instruct the class to have their notes out in front of them, with a pad of paper or blank Word document at their fingertips, and encourage them to take notes as the review is in progress.
- A trinket of sorts (I highly recommend a plush ball), used as a “microphone,” helps to give students equal opportunity to direct the review without putting individuals on the spot too aggressively. The rules are simple: she or he who holds the “mic” can pick one term from the list and using their notes, can offer up what they already know about the term or concept, what they are unsure of, or what they need more elaboration on.
- Actively listen to the speaker and give them some positive cues if they seem unsure; it’s okay to help them along the way, but important to step back and let this review remain student-centered. Once the speaker has said their piece, open the floor to the rest of the class for questions or additional comments. If you find that the discussion has taken a departure from the right direction, re-center the class and provide further elaboration if need be.
- Erase each term discussed from the list as you go, and have the speaker pass (or throw) on the “mic” to a fellow classmate, and keep tossing the ball around after each concept/term is discussed.
Students will have a tendency to pick the terms that they are most comfortable speaking about and those left consistently untouched will give you a clear assessment of the subjects in which your class is struggling, and where comprehension is lacking. Once your class has narrowed down the list to just a few terms, you can switch gears into a more classic review session. Bringing a bit of interaction and fun into a review can help loosen things up during exam time, when students and teachers alike are really starting to feel the pressure.
5. Use YouTube for classroom activities
Monika Semma: Do you remember the pure and utter joy you felt upon seeing your professor wheel in the giant VHS machine into class? Technology has certainly changed—but the awesome powers of visual media have not. Making your students smile can be a difficult task, but by channeling your inner Bill Nye the Science Guy you can make university learning fun again.
A large part of meaningful learning is finding interactive classroom activities that are relevant to daily life—and I can think of no technology more relevant to current students than YouTube.
A crafty YouTube search can yield a video relevant to almost anything in your curriculum and paired with an essay or academic journal, a slightly silly video can go a long way in helping your students contextualize what they are learning.
Even if your comedic attempts plunge into failure, at the very least, a short clip will get the class discussion ball rolling. Watch the video as a class and then break up into smaller groups to discuss it. Get your students thinking about how the clip they are shown pairs with the primary sources they’ve already read.
6. Close reading
Monika Semma: In the humanities, we all know the benefits of close reading activities—they get classroom discussion rolling and students engaging with the material and open up the floor for social and combination learners to shine. “Close reading” is a learning technique in which students are asked to conduct a detailed analysis or interpretation of a small piece of text. It is particularly effective in getting students to move away from the general and engage more with specific details or ideas.
If you’re introducing new and complex material to your class, or if you feel as though your students are struggling with an equation, theory, or concept; giving them the opportunity to break it down into smaller and more concrete parts for further evaluation will help to enhance their understanding of the material as a whole.
And while this technique is often employed in the humanities, classroom activities like this can be easily transferred to any discipline. A physics student will benefit from having an opportunity to break down a complicated equation in the same way that a biology student can better understand a cell by looking at it through a microscope.
In any case, evaluating what kinds of textbooks, lesson plans and pedagogy we are asking our students to connect with is always a good idea.
Brainwriting
Group size: 10 students (minimum)
Course type: Online (synchronous), in-person
This activity helps build rapport and respect in your classroom. After you tackle a complex lecture topic, give students time to individually reflect on their learnings. This can be accomplished through guided prompts or left as an open-ended exercise. Once students have gathered their thoughts, encourage them to share their views either through an online discussion thread or a conversation with peers during class time.
Concept mapping
Collaborative concept mapping is the process of visually organizing concepts and ideas and understanding how they relate to each other. This exercise is a great way for students to look outside of their individual experiences and perspectives. Groups can use this tactic to review previous work or to help them map ideas for projects and assignments. For in-person classes, you can ask students to cover classroom walls with sticky notes and chart paper. For online classes, there are many online tools that make it simple to map out connections between ideas, like Google Docs or the digital whiteboard feature in Zoom.
Group size: Groups of 5–10 students
Propose a topic or issue to your class. Group students together (or in breakout rooms if you’re teaching remotely) according to the position they take on the specific issue. Ask the groups of students to come up with a few arguments or examples to support their position. Write each group’s statements on the virtual whiteboard and use these as a starting point for discussion. A natural next step is to debate the strengths and weaknesses of each argument, to help students improve their critical thinking and analysis skills.
Make learning active with these 45 interactive classroom activities
Compare and contrast
Group size: Groups of 5–10 students
Ask your students to focus on a specific chapter in your textbook. Then, place them in groups and ask them to make connections and identify differences between ideas that can be found in course readings and other articles and videos they may find. This way, they can compare their ideas in small groups and learn from one another’s perspectives. In online real-time classes, instructors can use Zoom breakout rooms to put students in small groups.
Assess/diagnose/act
This activity will improve students’ problem-solving skills and can help engage them in more dynamic discussions. Start by proposing a topic or controversial statement. Then follow these steps to get conversations going. In online classes, students can either raise their hands virtually or use an online discussion forum to engage with their peers.
- Assessment: What is the issue or problem at hand?
- Diagnosis: What is the root cause of this issue or problem?
- Action: How can we solve the issue?
Moral dilemmas
Group size: Groups of 3–7 students
Provide students with a moral or ethical dilemma, using a hypothetical situation or a real-world situation. Then ask them to explore potential solutions as a group. This activity encourages students to think outside the box to develop creative solutions to the problem. In online learning environments, students can use discussion threads or Zoom breakout rooms.
Conversation stations
Group size: Groups of 4–6 students
Course type: In-person
This activity exposes students’ ideas in a controlled way, prompting discussions that flow naturally. To start, share a list of discussion questions pertaining to a course reading, video or case study. Put students into groups and give them five-to-ten minutes to discuss, then have two students rotate to another group. The students who have just joined a group have an opportunity to share findings from their last discussion, before answering the second question with their new group. After another five-to-ten minutes, the students who haven’t rotated yet will join a new group.
This or that
Course type: Online (synchronous or asynchronous), in-person
This activity allows students to see where their peers stand on a variety of different topics and issues. Instructors should distribute a list of provocative statements before class, allowing students to read ahead. Then, they can ask students to indicate whether they agree, disagree or are neutral on the topic in advance, using an online discussion thread or Google Doc. In class, use another discussion thread or live chat to have students of differing opinions share their views. After a few minutes, encourage one or two members in each group to defend their position amongst a new group of students. Ask students to repeat this process for several rounds to help familiarize themselves with a variety of standpoints.
6 team-building classroom activities for college students
Snowball discussions .
Group size: 2–4 students per group
Assign students a case study or worksheet to discuss with a partner, then have them share their thoughts with the larger group. Use breakout rooms in Zoom and randomly assign students in pairs with a discussion question. After a few minutes, combine rooms to form groups of four. After another five minutes, combine groups of four to become a larger group of eight—and so on until the whole class is back together again.
Make it personal
Group size: Groups of 2–8 students
After you’ve covered a topic or concept in your lecture, divide students into small discussion groups (or breakout rooms online). Ask the groups questions like “How did this impact your prior knowledge of the topic?” or “What was your initial reaction to this source/article/fact?” to encourage students to reflect on their personal connections to the course concepts they are learning.
Philosophical chairs
Group size: 20–25 students (maximum)
A statement that has two possible responses—agree or disagree—is read out loud. Depending on whether they agree or disagree with this statement, students move to one side of the room or the other. After everyone has chosen a side, ask one or two students on each side to take turns defending their positions. This allows students to visualize where their peers’ opinions come from, relative to their own.
Get more interactive classroom activities here
Affinity mapping
Group size: Groups of 3–8 students
Course type: Online (synchronous)
Place students in small groups (or virtual breakout rooms) and pose a broad question or problem to them that is likely to result in lots of different ideas, such as “What was the greatest innovation of the 21st century?” or “How would society be different if _____ never occurred?” Ask students to generate responses by writing ideas on pieces of paper (one idea per page) or in a discussion thread (if you’re teaching online). Once lots of ideas have been generated, have students begin grouping their ideas into similar categories, then label the categories and discuss why the ideas fit within them, how the categories relate to one another and so on. This allows students to engage in higher-level thinking by analyzing ideas and organizing them in relation to one another.
Socratic seminar
Group size: 20 students (minimum)
Ask students to prepare for a discussion by reviewing a course reading or group of texts and coming up with a few higher-order discussion questions about the text. In class, pose an introductory, open-ended question. From there, students continue the conversation, prompting one another to support their claims with evidence from previous course concepts or texts. There doesn’t need to be a particular order to how students speak, but they are encouraged to respectfully share the floor with their peers.
Concentric circles
Group size: 20 students (maximum)
Students form two circles: an inner circle and an outer circle. Each student on the inside is paired with a student on the outside; they face each other. Pose a question to the whole group and have pairs discuss their responses with each other. After three-to-five minutes, have students on the outside circle move one space to the right so they are standing in front of a new person. Pose a new question, and the process is repeated, exposing students to the different perspectives of their peers.
Making your classes more interactive should help your students want to come to class and take part in it. Giving them a more active role will give them a sense of ownership, and this can lead to students taking more pride in their work and responsibility for their grades.
Use these 45 classroom activities in your course to keep students engaged
A more interactive class can also make things easier for you—the more work students do in class, the less you have to do. Even two minutes of not talking can re-energize you for the rest of the class.
Plus, these six methods outlined above don’t require any large-scale changes to your class prep. Set up a couple of activities in advance here and there, to support what you’ve been doing, and plan which portion of your class will feature them.
The reality remains that sometimes, students do have to be taught subject matter that is anything but exciting. That doesn’t mean that we can’t make it more enjoyable to teach or learn. It may not be possible to incorporate classroom activities into every lecture, but finding some room for these approaches can go a long way in facilitating a positive learning environment.
And let’s not forget, sometimes even an educator needs a brief departure from the everyday-ordinary-sit-and-listen-to-me-lecture regimen.
Recommended Readings

Educators In Conversation: How to Help Students ‘Do’ Sociology

A 6-Step Exercise for Discussing AI In Education
Subscribe to the top hat blog.
Join more than 10,000 educators. Get articles with higher ed trends, teaching tips and expert advice delivered straight to your inbox.
Teaching, Learning, & Professional Development Center
- Teaching Resources
- TLPDC Teaching Resources
How Do I Create Meaningful and Effective Assignments?
Prepared by allison boye, ph.d. teaching, learning, and professional development center.
Assessment is a necessary part of the teaching and learning process, helping us measure whether our students have really learned what we want them to learn. While exams and quizzes are certainly favorite and useful methods of assessment, out of class assignments (written or otherwise) can offer similar insights into our students' learning. And just as creating a reliable test takes thoughtfulness and skill, so does creating meaningful and effective assignments. Undoubtedly, many instructors have been on the receiving end of disappointing student work, left wondering what went wrong… and often, those problems can be remedied in the future by some simple fine-tuning of the original assignment. This paper will take a look at some important elements to consider when developing assignments, and offer some easy approaches to creating a valuable assessment experience for all involved.
First Things First…
Before assigning any major tasks to students, it is imperative that you first define a few things for yourself as the instructor:
- Your goals for the assignment . Why are you assigning this project, and what do you hope your students will gain from completing it? What knowledge, skills, and abilities do you aim to measure with this assignment? Creating assignments is a major part of overall course design, and every project you assign should clearly align with your goals for the course in general. For instance, if you want your students to demonstrate critical thinking, perhaps asking them to simply summarize an article is not the best match for that goal; a more appropriate option might be to ask for an analysis of a controversial issue in the discipline. Ultimately, the connection between the assignment and its purpose should be clear to both you and your students to ensure that it is fulfilling the desired goals and doesn't seem like “busy work.” For some ideas about what kinds of assignments match certain learning goals, take a look at this page from DePaul University's Teaching Commons.
- Have they experienced “socialization” in the culture of your discipline (Flaxman, 2005)? Are they familiar with any conventions you might want them to know? In other words, do they know the “language” of your discipline, generally accepted style guidelines, or research protocols?
- Do they know how to conduct research? Do they know the proper style format, documentation style, acceptable resources, etc.? Do they know how to use the library (Fitzpatrick, 1989) or evaluate resources?
- What kinds of writing or work have they previously engaged in? For instance, have they completed long, formal writing assignments or research projects before? Have they ever engaged in analysis, reflection, or argumentation? Have they completed group assignments before? Do they know how to write a literature review or scientific report?
In his book Engaging Ideas (1996), John Bean provides a great list of questions to help instructors focus on their main teaching goals when creating an assignment (p.78):
1. What are the main units/modules in my course?
2. What are my main learning objectives for each module and for the course?
3. What thinking skills am I trying to develop within each unit and throughout the course?
4. What are the most difficult aspects of my course for students?
5. If I could change my students' study habits, what would I most like to change?
6. What difference do I want my course to make in my students' lives?
What your students need to know
Once you have determined your own goals for the assignment and the levels of your students, you can begin creating your assignment. However, when introducing your assignment to your students, there are several things you will need to clearly outline for them in order to ensure the most successful assignments possible.
- First, you will need to articulate the purpose of the assignment . Even though you know why the assignment is important and what it is meant to accomplish, you cannot assume that your students will intuit that purpose. Your students will appreciate an understanding of how the assignment fits into the larger goals of the course and what they will learn from the process (Hass & Osborn, 2007). Being transparent with your students and explaining why you are asking them to complete a given assignment can ultimately help motivate them to complete the assignment more thoughtfully.
- If you are asking your students to complete a writing assignment, you should define for them the “rhetorical or cognitive mode/s” you want them to employ in their writing (Flaxman, 2005). In other words, use precise verbs that communicate whether you are asking them to analyze, argue, describe, inform, etc. (Verbs like “explore” or “comment on” can be too vague and cause confusion.) Provide them with a specific task to complete, such as a problem to solve, a question to answer, or an argument to support. For those who want assignments to lead to top-down, thesis-driven writing, John Bean (1996) suggests presenting a proposition that students must defend or refute, or a problem that demands a thesis answer.
- It is also a good idea to define the audience you want your students to address with their assignment, if possible – especially with writing assignments. Otherwise, students will address only the instructor, often assuming little requires explanation or development (Hedengren, 2004; MIT, 1999). Further, asking students to address the instructor, who typically knows more about the topic than the student, places the student in an unnatural rhetorical position. Instead, you might consider asking your students to prepare their assignments for alternative audiences such as other students who missed last week's classes, a group that opposes their position, or people reading a popular magazine or newspaper. In fact, a study by Bean (1996) indicated the students often appreciate and enjoy assignments that vary elements such as audience or rhetorical context, so don't be afraid to get creative!
- Obviously, you will also need to articulate clearly the logistics or “business aspects” of the assignment . In other words, be explicit with your students about required elements such as the format, length, documentation style, writing style (formal or informal?), and deadlines. One caveat, however: do not allow the logistics of the paper take precedence over the content in your assignment description; if you spend all of your time describing these things, students might suspect that is all you care about in their execution of the assignment.
- Finally, you should clarify your evaluation criteria for the assignment. What elements of content are most important? Will you grade holistically or weight features separately? How much weight will be given to individual elements, etc? Another precaution to take when defining requirements for your students is to take care that your instructions and rubric also do not overshadow the content; prescribing too rigidly each element of an assignment can limit students' freedom to explore and discover. According to Beth Finch Hedengren, “A good assignment provides the purpose and guidelines… without dictating exactly what to say” (2004, p. 27). If you decide to utilize a grading rubric, be sure to provide that to the students along with the assignment description, prior to their completion of the assignment.
A great way to get students engaged with an assignment and build buy-in is to encourage their collaboration on its design and/or on the grading criteria (Hudd, 2003). In his article “Conducting Writing Assignments,” Richard Leahy (2002) offers a few ideas for building in said collaboration:
• Ask the students to develop the grading scale themselves from scratch, starting with choosing the categories.
• Set the grading categories yourself, but ask the students to help write the descriptions.
• Draft the complete grading scale yourself, then give it to your students for review and suggestions.
A Few Do's and Don'ts…
Determining your goals for the assignment and its essential logistics is a good start to creating an effective assignment. However, there are a few more simple factors to consider in your final design. First, here are a few things you should do :
- Do provide detail in your assignment description . Research has shown that students frequently prefer some guiding constraints when completing assignments (Bean, 1996), and that more detail (within reason) can lead to more successful student responses. One idea is to provide students with physical assignment handouts , in addition to or instead of a simple description in a syllabus. This can meet the needs of concrete learners and give them something tangible to refer to. Likewise, it is often beneficial to make explicit for students the process or steps necessary to complete an assignment, given that students – especially younger ones – might need guidance in planning and time management (MIT, 1999).
- Do use open-ended questions. The most effective and challenging assignments focus on questions that lead students to thinking and explaining, rather than simple yes or no answers, whether explicitly part of the assignment description or in the brainstorming heuristics (Gardner, 2005).
- Do direct students to appropriate available resources . Giving students pointers about other venues for assistance can help them get started on the right track independently. These kinds of suggestions might include information about campus resources such as the University Writing Center or discipline-specific librarians, suggesting specific journals or books, or even sections of their textbook, or providing them with lists of research ideas or links to acceptable websites.
- Do consider providing models – both successful and unsuccessful models (Miller, 2007). These models could be provided by past students, or models you have created yourself. You could even ask students to evaluate the models themselves using the determined evaluation criteria, helping them to visualize the final product, think critically about how to complete the assignment, and ideally, recognize success in their own work.
- Do consider including a way for students to make the assignment their own. In their study, Hass and Osborn (2007) confirmed the importance of personal engagement for students when completing an assignment. Indeed, students will be more engaged in an assignment if it is personally meaningful, practical, or purposeful beyond the classroom. You might think of ways to encourage students to tap into their own experiences or curiosities, to solve or explore a real problem, or connect to the larger community. Offering variety in assignment selection can also help students feel more individualized, creative, and in control.
- If your assignment is substantial or long, do consider sequencing it. Far too often, assignments are given as one-shot final products that receive grades at the end of the semester, eternally abandoned by the student. By sequencing a large assignment, or essentially breaking it down into a systematic approach consisting of interconnected smaller elements (such as a project proposal, an annotated bibliography, or a rough draft, or a series of mini-assignments related to the longer assignment), you can encourage thoughtfulness, complexity, and thoroughness in your students, as well as emphasize process over final product.
Next are a few elements to avoid in your assignments:
- Do not ask too many questions in your assignment. In an effort to challenge students, instructors often err in the other direction, asking more questions than students can reasonably address in a single assignment without losing focus. Offering an overly specific “checklist” prompt often leads to externally organized papers, in which inexperienced students “slavishly follow the checklist instead of integrating their ideas into more organically-discovered structure” (Flaxman, 2005).
- Do not expect or suggest that there is an “ideal” response to the assignment. A common error for instructors is to dictate content of an assignment too rigidly, or to imply that there is a single correct response or a specific conclusion to reach, either explicitly or implicitly (Flaxman, 2005). Undoubtedly, students do not appreciate feeling as if they must read an instructor's mind to complete an assignment successfully, or that their own ideas have nowhere to go, and can lose motivation as a result. Similarly, avoid assignments that simply ask for regurgitation (Miller, 2007). Again, the best assignments invite students to engage in critical thinking, not just reproduce lectures or readings.
- Do not provide vague or confusing commands . Do students know what you mean when they are asked to “examine” or “discuss” a topic? Return to what you determined about your students' experiences and levels to help you decide what directions will make the most sense to them and what will require more explanation or guidance, and avoid verbiage that might confound them.
- Do not impose impossible time restraints or require the use of insufficient resources for completion of the assignment. For instance, if you are asking all of your students to use the same resource, ensure that there are enough copies available for all students to access – or at least put one copy on reserve in the library. Likewise, make sure that you are providing your students with ample time to locate resources and effectively complete the assignment (Fitzpatrick, 1989).
The assignments we give to students don't simply have to be research papers or reports. There are many options for effective yet creative ways to assess your students' learning! Here are just a few:
Journals, Posters, Portfolios, Letters, Brochures, Management plans, Editorials, Instruction Manuals, Imitations of a text, Case studies, Debates, News release, Dialogues, Videos, Collages, Plays, Power Point presentations
Ultimately, the success of student responses to an assignment often rests on the instructor's deliberate design of the assignment. By being purposeful and thoughtful from the beginning, you can ensure that your assignments will not only serve as effective assessment methods, but also engage and delight your students. If you would like further help in constructing or revising an assignment, the Teaching, Learning, and Professional Development Center is glad to offer individual consultations. In addition, look into some of the resources provided below.
Online Resources
“Creating Effective Assignments” http://www.unh.edu/teaching-excellence/resources/Assignments.htm This site, from the University of New Hampshire's Center for Excellence in Teaching and Learning, provides a brief overview of effective assignment design, with a focus on determining and communicating goals and expectations.
Gardner, T. (2005, June 12). Ten Tips for Designing Writing Assignments. Traci's Lists of Ten. http://www.tengrrl.com/tens/034.shtml This is a brief yet useful list of tips for assignment design, prepared by a writing teacher and curriculum developer for the National Council of Teachers of English . The website will also link you to several other lists of “ten tips” related to literacy pedagogy.
“How to Create Effective Assignments for College Students.” http:// tilt.colostate.edu/retreat/2011/zimmerman.pdf This PDF is a simplified bulleted list, prepared by Dr. Toni Zimmerman from Colorado State University, offering some helpful ideas for coming up with creative assignments.
“Learner-Centered Assessment” http://cte.uwaterloo.ca/teaching_resources/tips/learner_centered_assessment.html From the Centre for Teaching Excellence at the University of Waterloo, this is a short list of suggestions for the process of designing an assessment with your students' interests in mind. “Matching Learning Goals to Assignment Types.” http://teachingcommons.depaul.edu/How_to/design_assignments/assignments_learning_goals.html This is a great page from DePaul University's Teaching Commons, providing a chart that helps instructors match assignments with learning goals.
Additional References Bean, J.C. (1996). Engaging ideas: The professor's guide to integrating writing, critical thinking, and active learning in the classroom . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Fitzpatrick, R. (1989). Research and writing assignments that reduce fear lead to better papers and more confident students. Writing Across the Curriculum , 3.2, pp. 15 – 24.
Flaxman, R. (2005). Creating meaningful writing assignments. The Teaching Exchange . Retrieved Jan. 9, 2008 from http://www.brown.edu/Administration/Sheridan_Center/pubs/teachingExchange/jan2005/01_flaxman.pdf
Hass, M. & Osborn, J. (2007, August 13). An emic view of student writing and the writing process. Across the Disciplines, 4.
Hedengren, B.F. (2004). A TA's guide to teaching writing in all disciplines . Boston: Bedford/St. Martin's.
Hudd, S. S. (2003, April). Syllabus under construction: Involving students in the creation of class assignments. Teaching Sociology , 31, pp. 195 – 202.
Leahy, R. (2002). Conducting writing assignments. College Teaching , 50.2, pp. 50 – 54.
Miller, H. (2007). Designing effective writing assignments. Teaching with writing . University of Minnesota Center for Writing. Retrieved Jan. 9, 2008, from http://writing.umn.edu/tww/assignments/designing.html
MIT Online Writing and Communication Center (1999). Creating Writing Assignments. Retrieved January 9, 2008 from http://web.mit.edu/writing/Faculty/createeffective.html .
Contact TTU

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that he or she will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove her point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, he or she still has to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and she already knows everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality she or he expects.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Columbia University in the City of New York
- Office of Teaching, Learning, and Innovation
- University Policies
- Columbia Online
- Academic Calendar
- Resources and Technology
- Instructional Technologies
- Teaching in All Modalities
Designing Assignments for Learning
The rapid shift to remote teaching and learning meant that many instructors reimagined their assessment practices. Whether adapting existing assignments or creatively designing new opportunities for their students to learn, instructors focused on helping students make meaning and demonstrate their learning outside of the traditional, face-to-face classroom setting. This resource distills the elements of assignment design that are important to carry forward as we continue to seek better ways of assessing learning and build on our innovative assignment designs.
On this page:
Rethinking traditional tests, quizzes, and exams.
- Examples from the Columbia University Classroom
- Tips for Designing Assignments for Learning
Reflect On Your Assignment Design
Connect with the ctl.
- Resources and References

Cite this resource: Columbia Center for Teaching and Learning (2021). Designing Assignments for Learning. Columbia University. Retrieved [today’s date] from https://ctl.columbia.edu/resources-and-technology/teaching-with-technology/teaching-online/designing-assignments/
Traditional assessments tend to reveal whether students can recognize, recall, or replicate what was learned out of context, and tend to focus on students providing correct responses (Wiggins, 1990). In contrast, authentic assignments, which are course assessments, engage students in higher order thinking, as they grapple with real or simulated challenges that help them prepare for their professional lives, and draw on the course knowledge learned and the skills acquired to create justifiable answers, performances or products (Wiggins, 1990). An authentic assessment provides opportunities for students to practice, consult resources, learn from feedback, and refine their performances and products accordingly (Wiggins 1990, 1998, 2014).
Authentic assignments ask students to “do” the subject with an audience in mind and apply their learning in a new situation. Examples of authentic assignments include asking students to:
- Write for a real audience (e.g., a memo, a policy brief, letter to the editor, a grant proposal, reports, building a website) and/or publication;
- Solve problem sets that have real world application;
- Design projects that address a real world problem;
- Engage in a community-partnered research project;
- Create an exhibit, performance, or conference presentation ;
- Compile and reflect on their work through a portfolio/e-portfolio.
Noteworthy elements of authentic designs are that instructors scaffold the assignment, and play an active role in preparing students for the tasks assigned, while students are intentionally asked to reflect on the process and product of their work thus building their metacognitive skills (Herrington and Oliver, 2000; Ashford-Rowe, Herrington and Brown, 2013; Frey, Schmitt, and Allen, 2012).
It’s worth noting here that authentic assessments can initially be time consuming to design, implement, and grade. They are critiqued for being challenging to use across course contexts and for grading reliability issues (Maclellan, 2004). Despite these challenges, authentic assessments are recognized as beneficial to student learning (Svinicki, 2004) as they are learner-centered (Weimer, 2013), promote academic integrity (McLaughlin, L. and Ricevuto, 2021; Sotiriadou et al., 2019; Schroeder, 2021) and motivate students to learn (Ambrose et al., 2010). The Columbia Center for Teaching and Learning is always available to consult with faculty who are considering authentic assessment designs and to discuss challenges and affordances.
Examples from the Columbia University Classroom
Columbia instructors have experimented with alternative ways of assessing student learning from oral exams to technology-enhanced assignments. Below are a few examples of authentic assignments in various teaching contexts across Columbia University.
- E-portfolios: Statia Cook shares her experiences with an ePorfolio assignment in her co-taught Frontiers of Science course (a submission to the Voices of Hybrid and Online Teaching and Learning initiative); CUIMC use of ePortfolios ;
- Case studies: Columbia instructors have engaged their students in authentic ways through case studies drawing on the Case Consortium at Columbia University. Read and watch a faculty spotlight to learn how Professor Mary Ann Price uses the case method to place pre-med students in real-life scenarios;
- Simulations: students at CUIMC engage in simulations to develop their professional skills in The Mary & Michael Jaharis Simulation Center in the Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and the Helene Fuld Health Trust Simulation Center in the Columbia School of Nursing;
- Experiential learning: instructors have drawn on New York City as a learning laboratory such as Barnard’s NYC as Lab webpage which highlights courses that engage students in NYC;
- Design projects that address real world problems: Yevgeniy Yesilevskiy on the Engineering design projects completed using lab kits during remote learning. Watch Dr. Yesilevskiy talk about his teaching and read the Columbia News article .
- Writing assignments: Lia Marshall and her teaching associate Aparna Balasundaram reflect on their “non-disposable or renewable assignments” to prepare social work students for their professional lives as they write for a real audience; and Hannah Weaver spoke about a sandbox assignment used in her Core Literature Humanities course at the 2021 Celebration of Teaching and Learning Symposium . Watch Dr. Weaver share her experiences.
Tips for Designing Assignments for Learning
While designing an effective authentic assignment may seem like a daunting task, the following tips can be used as a starting point. See the Resources section for frameworks and tools that may be useful in this effort.
Align the assignment with your course learning objectives
Identify the kind of thinking that is important in your course, the knowledge students will apply, and the skills they will practice using through the assignment. What kind of thinking will students be asked to do for the assignment? What will students learn by completing this assignment? How will the assignment help students achieve the desired course learning outcomes? For more information on course learning objectives, see the CTL’s Course Design Essentials self-paced course and watch the video on Articulating Learning Objectives .
Identify an authentic meaning-making task
For meaning-making to occur, students need to understand the relevance of the assignment to the course and beyond (Ambrose et al., 2010). To Bean (2011) a “meaning-making” or “meaning-constructing” task has two dimensions: 1) it presents students with an authentic disciplinary problem or asks students to formulate their own problems, both of which engage them in active critical thinking, and 2) the problem is placed in “a context that gives students a role or purpose, a targeted audience, and a genre.” (Bean, 2011: 97-98).
An authentic task gives students a realistic challenge to grapple with, a role to take on that allows them to “rehearse for the complex ambiguities” of life, provides resources and supports to draw on, and requires students to justify their work and the process they used to inform their solution (Wiggins, 1990). Note that if students find an assignment interesting or relevant, they will see value in completing it.
Consider the kind of activities in the real world that use the knowledge and skills that are the focus of your course. How is this knowledge and these skills applied to answer real-world questions to solve real-world problems? (Herrington et al., 2010: 22). What do professionals or academics in your discipline do on a regular basis? What does it mean to think like a biologist, statistician, historian, social scientist? How might your assignment ask students to draw on current events, issues, or problems that relate to the course and are of interest to them? How might your assignment tap into student motivation and engage them in the kinds of thinking they can apply to better understand the world around them? (Ambrose et al., 2010).
Determine the evaluation criteria and create a rubric
To ensure equitable and consistent grading of assignments across students, make transparent the criteria you will use to evaluate student work. The criteria should focus on the knowledge and skills that are central to the assignment. Build on the criteria identified, create a rubric that makes explicit the expectations of deliverables and share this rubric with your students so they can use it as they work on the assignment. For more information on rubrics, see the CTL’s resource Incorporating Rubrics into Your Grading and Feedback Practices , and explore the Association of American Colleges & Universities VALUE Rubrics (Valid Assessment of Learning in Undergraduate Education).
Build in metacognition
Ask students to reflect on what and how they learned from the assignment. Help students uncover personal relevance of the assignment, find intrinsic value in their work, and deepen their motivation by asking them to reflect on their process and their assignment deliverable. Sample prompts might include: what did you learn from this assignment? How might you draw on the knowledge and skills you used on this assignment in the future? See Ambrose et al., 2010 for more strategies that support motivation and the CTL’s resource on Metacognition ).
Provide students with opportunities to practice
Design your assignment to be a learning experience and prepare students for success on the assignment. If students can reasonably expect to be successful on an assignment when they put in the required effort ,with the support and guidance of the instructor, they are more likely to engage in the behaviors necessary for learning (Ambrose et al., 2010). Ensure student success by actively teaching the knowledge and skills of the course (e.g., how to problem solve, how to write for a particular audience), modeling the desired thinking, and creating learning activities that build up to a graded assignment. Provide opportunities for students to practice using the knowledge and skills they will need for the assignment, whether through low-stakes in-class activities or homework activities that include opportunities to receive and incorporate formative feedback. For more information on providing feedback, see the CTL resource Feedback for Learning .
Communicate about the assignment
Share the purpose, task, audience, expectations, and criteria for the assignment. Students may have expectations about assessments and how they will be graded that is informed by their prior experiences completing high-stakes assessments, so be transparent. Tell your students why you are asking them to do this assignment, what skills they will be using, how it aligns with the course learning outcomes, and why it is relevant to their learning and their professional lives (i.e., how practitioners / professionals use the knowledge and skills in your course in real world contexts and for what purposes). Finally, verify that students understand what they need to do to complete the assignment. This can be done by asking students to respond to poll questions about different parts of the assignment, a “scavenger hunt” of the assignment instructions–giving students questions to answer about the assignment and having them work in small groups to answer the questions, or by having students share back what they think is expected of them.
Plan to iterate and to keep the focus on learning
Draw on multiple sources of data to help make decisions about what changes are needed to the assignment, the assignment instructions, and/or rubric to ensure that it contributes to student learning. Explore assignment performance data. As Deandra Little reminds us: “a really good assignment, which is a really good assessment, also teaches you something or tells the instructor something. As much as it tells you what students are learning, it’s also telling you what they aren’t learning.” ( Teaching in Higher Ed podcast episode 337 ). Assignment bottlenecks–where students get stuck or struggle–can be good indicators that students need further support or opportunities to practice prior to completing an assignment. This awareness can inform teaching decisions.
Triangulate the performance data by collecting student feedback, and noting your own reflections about what worked well and what did not. Revise the assignment instructions, rubric, and teaching practices accordingly. Consider how you might better align your assignment with your course objectives and/or provide more opportunities for students to practice using the knowledge and skills that they will rely on for the assignment. Additionally, keep in mind societal, disciplinary, and technological changes as you tweak your assignments for future use.
Now is a great time to reflect on your practices and experiences with assignment design and think critically about your approach. Take a closer look at an existing assignment. Questions to consider include: What is this assignment meant to do? What purpose does it serve? Why do you ask students to do this assignment? How are they prepared to complete the assignment? Does the assignment assess the kind of learning that you really want? What would help students learn from this assignment?
Using the tips in the previous section: How can the assignment be tweaked to be more authentic and meaningful to students?
As you plan forward for post-pandemic teaching and reflect on your practices and reimagine your course design, you may find the following CTL resources helpful: Reflecting On Your Experiences with Remote Teaching , Transition to In-Person Teaching , and Course Design Support .
The Columbia Center for Teaching and Learning (CTL) is here to help!
For assistance with assignment design, rubric design, or any other teaching and learning need, please request a consultation by emailing [email protected] .
Transparency in Learning and Teaching (TILT) framework for assignments. The TILT Examples and Resources page ( https://tilthighered.com/tiltexamplesandresources ) includes example assignments from across disciplines, as well as a transparent assignment template and a checklist for designing transparent assignments . Each emphasizes the importance of articulating to students the purpose of the assignment or activity, the what and how of the task, and specifying the criteria that will be used to assess students.
Association of American Colleges & Universities (AAC&U) offers VALUE ADD (Assignment Design and Diagnostic) tools ( https://www.aacu.org/value-add-tools ) to help with the creation of clear and effective assignments that align with the desired learning outcomes and associated VALUE rubrics (Valid Assessment of Learning in Undergraduate Education). VALUE ADD encourages instructors to explicitly state assignment information such as the purpose of the assignment, what skills students will be using, how it aligns with course learning outcomes, the assignment type, the audience and context for the assignment, clear evaluation criteria, desired formatting, and expectations for completion whether individual or in a group.
Villarroel et al. (2017) propose a blueprint for building authentic assessments which includes four steps: 1) consider the workplace context, 2) design the authentic assessment; 3) learn and apply standards for judgement; and 4) give feedback.
References
Ambrose, S. A., Bridges, M. W., & DiPietro, M. (2010). Chapter 3: What Factors Motivate Students to Learn? In How Learning Works: Seven Research-Based Principles for Smart Teaching . Jossey-Bass.
Ashford-Rowe, K., Herrington, J., and Brown, C. (2013). Establishing the critical elements that determine authentic assessment. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education. 39(2), 205-222, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2013.819566 .
Bean, J.C. (2011). Engaging Ideas: The Professor’s Guide to Integrating Writing, Critical Thinking, and Active Learning in the Classroom . Second Edition. Jossey-Bass.
Frey, B. B, Schmitt, V. L., and Allen, J. P. (2012). Defining Authentic Classroom Assessment. Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. 17(2). DOI: https://doi.org/10.7275/sxbs-0829
Herrington, J., Reeves, T. C., and Oliver, R. (2010). A Guide to Authentic e-Learning . Routledge.
Herrington, J. and Oliver, R. (2000). An instructional design framework for authentic learning environments. Educational Technology Research and Development, 48(3), 23-48.
Litchfield, B. C. and Dempsey, J. V. (2015). Authentic Assessment of Knowledge, Skills, and Attitudes. New Directions for Teaching and Learning. 142 (Summer 2015), 65-80.
Maclellan, E. (2004). How convincing is alternative assessment for use in higher education. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education. 29(3), June 2004. DOI: 10.1080/0260293042000188267
McLaughlin, L. and Ricevuto, J. (2021). Assessments in a Virtual Environment: You Won’t Need that Lockdown Browser! Faculty Focus. June 2, 2021.
Mueller, J. (2005). The Authentic Assessment Toolbox: Enhancing Student Learning through Online Faculty Development . MERLOT Journal of Online Learning and Teaching. 1(1). July 2005. Mueller’s Authentic Assessment Toolbox is available online.
Schroeder, R. (2021). Vaccinate Against Cheating With Authentic Assessment . Inside Higher Ed. (February 26, 2021).
Sotiriadou, P., Logan, D., Daly, A., and Guest, R. (2019). The role of authentic assessment to preserve academic integrity and promote skills development and employability. Studies in Higher Education. 45(111), 2132-2148. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2019.1582015
Stachowiak, B. (Host). (November 25, 2020). Authentic Assignments with Deandra Little. (Episode 337). In Teaching in Higher Ed . https://teachinginhighered.com/podcast/authentic-assignments/
Svinicki, M. D. (2004). Authentic Assessment: Testing in Reality. New Directions for Teaching and Learning. 100 (Winter 2004): 23-29.
Villarroel, V., Bloxham, S, Bruna, D., Bruna, C., and Herrera-Seda, C. (2017). Authentic assessment: creating a blueprint for course design. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education. 43(5), 840-854. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2017.1412396
Weimer, M. (2013). Learner-Centered Teaching: Five Key Changes to Practice . Second Edition. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Wiggins, G. (2014). Authenticity in assessment, (re-)defined and explained. Retrieved from https://grantwiggins.wordpress.com/2014/01/26/authenticity-in-assessment-re-defined-and-explained/
Wiggins, G. (1998). Teaching to the (Authentic) Test. Educational Leadership . April 1989. 41-47.
Wiggins, Grant (1990). The Case for Authentic Assessment . Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation , 2(2).
Wondering how AI tools might play a role in your course assignments?
See the CTL’s resource “Considerations for AI Tools in the Classroom.”
This website uses cookies to identify users, improve the user experience and requires cookies to work. By continuing to use this website, you consent to Columbia University's use of cookies and similar technologies, in accordance with the Columbia University Website Cookie Notice .
- Sign Up for Mailing List
- Search Search
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Resources for Teachers: Creating Writing Assignments
This page contains four specific areas:
Creating Effective Assignments
Checking the assignment, sequencing writing assignments, selecting an effective writing assignment format.
Research has shown that the more detailed a writing assignment is, the better the student papers are in response to that assignment. Instructors can often help students write more effective papers by giving students written instructions about that assignment. Explicit descriptions of assignments on the syllabus or on an “assignment sheet” tend to produce the best results. These instructions might make explicit the process or steps necessary to complete the assignment. Assignment sheets should detail:
- the kind of writing expected
- the scope of acceptable subject matter
- the length requirements
- formatting requirements
- documentation format
- the amount and type of research expected (if any)
- the writer’s role
- deadlines for the first draft and its revision
Providing questions or needed data in the assignment helps students get started. For instance, some questions can suggest a mode of organization to the students. Other questions might suggest a procedure to follow. The questions posed should require that students assert a thesis.
The following areas should help you create effective writing assignments.
Examining your goals for the assignment
- How exactly does this assignment fit with the objectives of your course?
- Should this assignment relate only to the class and the texts for the class, or should it also relate to the world beyond the classroom?
- What do you want the students to learn or experience from this writing assignment?
- Should this assignment be an individual or a collaborative effort?
- What do you want students to show you in this assignment? To demonstrate mastery of concepts or texts? To demonstrate logical and critical thinking? To develop an original idea? To learn and demonstrate the procedures, practices, and tools of your field of study?
Defining the writing task
- Is the assignment sequenced so that students: (1) write a draft, (2) receive feedback (from you, fellow students, or staff members at the Writing and Communication Center), and (3) then revise it? Such a procedure has been proven to accomplish at least two goals: it improves the student’s writing and it discourages plagiarism.
- Does the assignment include so many sub-questions that students will be confused about the major issue they should examine? Can you give more guidance about what the paper’s main focus should be? Can you reduce the number of sub-questions?
- What is the purpose of the assignment (e.g., review knowledge already learned, find additional information, synthesize research, examine a new hypothesis)? Making the purpose(s) of the assignment explicit helps students write the kind of paper you want.
- What is the required form (e.g., expository essay, lab report, memo, business report)?
- What mode is required for the assignment (e.g., description, narration, analysis, persuasion, a combination of two or more of these)?
Defining the audience for the paper
- Can you define a hypothetical audience to help students determine which concepts to define and explain? When students write only to the instructor, they may assume that little, if anything, requires explanation. Defining the whole class as the intended audience will clarify this issue for students.
- What is the probable attitude of the intended readers toward the topic itself? Toward the student writer’s thesis? Toward the student writer?
- What is the probable educational and economic background of the intended readers?
Defining the writer’s role
- Can you make explicit what persona you wish the students to assume? For example, a very effective role for student writers is that of a “professional in training” who uses the assumptions, the perspective, and the conceptual tools of the discipline.
Defining your evaluative criteria
1. If possible, explain the relative weight in grading assigned to the quality of writing and the assignment’s content:
- depth of coverage
- organization
- critical thinking
- original thinking
- use of research
- logical demonstration
- appropriate mode of structure and analysis (e.g., comparison, argument)
- correct use of sources
- grammar and mechanics
- professional tone
- correct use of course-specific concepts and terms.
Here’s a checklist for writing assignments:
- Have you used explicit command words in your instructions (e.g., “compare and contrast” and “explain” are more explicit than “explore” or “consider”)? The more explicit the command words, the better chance the students will write the type of paper you wish.
- Does the assignment suggest a topic, thesis, and format? Should it?
- Have you told students the kind of audience they are addressing — the level of knowledge they can assume the readers have and your particular preferences (e.g., “avoid slang, use the first-person sparingly”)?
- If the assignment has several stages of completion, have you made the various deadlines clear? Is your policy on due dates clear?
- Have you presented the assignment in a manageable form? For instance, a 5-page assignment sheet for a 1-page paper may overwhelm students. Similarly, a 1-sentence assignment for a 25-page paper may offer insufficient guidance.
There are several benefits of sequencing writing assignments:
- Sequencing provides a sense of coherence for the course.
- This approach helps students see progress and purpose in their work rather than seeing the writing assignments as separate exercises.
- It encourages complexity through sustained attention, revision, and consideration of multiple perspectives.
- If you have only one large paper due near the end of the course, you might create a sequence of smaller assignments leading up to and providing a foundation for that larger paper (e.g., proposal of the topic, an annotated bibliography, a progress report, a summary of the paper’s key argument, a first draft of the paper itself). This approach allows you to give students guidance and also discourages plagiarism.
- It mirrors the approach to written work in many professions.
The concept of sequencing writing assignments also allows for a wide range of options in creating the assignment. It is often beneficial to have students submit the components suggested below to your course’s STELLAR web site.
Use the writing process itself. In its simplest form, “sequencing an assignment” can mean establishing some sort of “official” check of the prewriting and drafting steps in the writing process. This step guarantees that students will not write the whole paper in one sitting and also gives students more time to let their ideas develop. This check might be something as informal as having students work on their prewriting or draft for a few minutes at the end of class. Or it might be something more formal such as collecting the prewriting and giving a few suggestions and comments.
Have students submit drafts. You might ask students to submit a first draft in order to receive your quick responses to its content, or have them submit written questions about the content and scope of their projects after they have completed their first draft.
Establish small groups. Set up small writing groups of three-five students from the class. Allow them to meet for a few minutes in class or have them arrange a meeting outside of class to comment constructively on each other’s drafts. The students do not need to be writing on the same topic.
Require consultations. Have students consult with someone in the Writing and Communication Center about their prewriting and/or drafts. The Center has yellow forms that we can give to students to inform you that such a visit was made.
Explore a subject in increasingly complex ways. A series of reading and writing assignments may be linked by the same subject matter or topic. Students encounter new perspectives and competing ideas with each new reading, and thus must evaluate and balance various views and adopt a position that considers the various points of view.
Change modes of discourse. In this approach, students’ assignments move from less complex to more complex modes of discourse (e.g., from expressive to analytic to argumentative; or from lab report to position paper to research article).
Change audiences. In this approach, students create drafts for different audiences, moving from personal to public (e.g., from self-reflection to an audience of peers to an audience of specialists). Each change would require different tasks and more extensive knowledge.
Change perspective through time. In this approach, students might write a statement of their understanding of a subject or issue at the beginning of a course and then return at the end of the semester to write an analysis of that original stance in the light of the experiences and knowledge gained in the course.
Use a natural sequence. A different approach to sequencing is to create a series of assignments culminating in a final writing project. In scientific and technical writing, for example, students could write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic. The next assignment might be a progress report (or a series of progress reports), and the final assignment could be the report or document itself. For humanities and social science courses, students might write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic, then hand in an annotated bibliography, and then a draft, and then the final version of the paper.
Have students submit sections. A variation of the previous approach is to have students submit various sections of their final document throughout the semester (e.g., their bibliography, review of the literature, methods section).
In addition to the standard essay and report formats, several other formats exist that might give students a different slant on the course material or allow them to use slightly different writing skills. Here are some suggestions:
Journals. Journals have become a popular format in recent years for courses that require some writing. In-class journal entries can spark discussions and reveal gaps in students’ understanding of the material. Having students write an in-class entry summarizing the material covered that day can aid the learning process and also reveal concepts that require more elaboration. Out-of-class entries involve short summaries or analyses of texts, or are a testing ground for ideas for student papers and reports. Although journals may seem to add a huge burden for instructors to correct, in fact many instructors either spot-check journals (looking at a few particular key entries) or grade them based on the number of entries completed. Journals are usually not graded for their prose style. STELLAR forums work well for out-of-class entries.
Letters. Students can define and defend a position on an issue in a letter written to someone in authority. They can also explain a concept or a process to someone in need of that particular information. They can write a letter to a friend explaining their concerns about an upcoming paper assignment or explaining their ideas for an upcoming paper assignment. If you wish to add a creative element to the writing assignment, you might have students adopt the persona of an important person discussed in your course (e.g., an historical figure) and write a letter explaining his/her actions, process, or theory to an interested person (e.g., “pretend that you are John Wilkes Booth and write a letter to the Congress justifying your assassination of Abraham Lincoln,” or “pretend you are Henry VIII writing to Thomas More explaining your break from the Catholic Church”).
Editorials . Students can define and defend a position on a controversial issue in the format of an editorial for the campus or local newspaper or for a national journal.
Cases . Students might create a case study particular to the course’s subject matter.
Position Papers . Students can define and defend a position, perhaps as a preliminary step in the creation of a formal research paper or essay.
Imitation of a Text . Students can create a new document “in the style of” a particular writer (e.g., “Create a government document the way Woody Allen might write it” or “Write your own ‘Modest Proposal’ about a modern issue”).
Instruction Manuals . Students write a step-by-step explanation of a process.
Dialogues . Students create a dialogue between two major figures studied in which they not only reveal those people’s theories or thoughts but also explore areas of possible disagreement (e.g., “Write a dialogue between Claude Monet and Jackson Pollock about the nature and uses of art”).
Collaborative projects . Students work together to create such works as reports, questions, and critiques.
- BookWidgets Teacher Blog

20 interactive teaching activities for in the interactive classroom

Interactive teaching is all about instructing the students in a way they are actively involved with their learning process. There are different ways to create an involvement like this. Most of the time it’s through
- teacher-student interaction
- student-student interaction
- the use of audio, visuals, video
- hands-on demonstrations and exercises
You encourage your students to be active members of your class, thinking on their own, using their brains, resulting in long-term memory retention . Not only the students’ knowledge will improve, but their interest, strength, knowledge, team spirit and freedom of expression will increase as well.
In this blog post, I will talk about the use of interactive methods for teaching, encouraging more dedication towards the lesson material. We will see some interactive teaching tools, interactive teaching ideas, and interactive teaching games. Not only will I talk about the use of interactive methods of teaching, but I’ll also give you some examples of methods used in the present classroom as well.
Ready? Let’s find out some interactive classroom activities to engage your pupils!
3 Effective interactive teaching strategies to encourage speech in your classroom
First, I want to put some activities in the spotlight. The following interactive student activities are three of the most effective ways to encourage more speech in your classroom.
1. Think, pair and share

2. Brainstorming

3. Buzz session

Of course, there are many other interactive teaching ideas as well. I split up the activities in different categories:
Individual student activities
Student pair activities, student group activities, interactive game activities, 4. exit slips.

5. Misconception check

6. Circle the questions

Create corners concerning different questions that were circled. Let your students work on the extra exercises and explanation in the corners, individually. As your students will all have circled different questions, you have to give each student a different and personalized order to visit the corners.
7. Ask the winner

8. Pair-share-repeat

9. Teacher and student

10. Wisdom from another

11. Forced debate

Variation: one half of the class takes one position, the other half takes the other position. Students line up and face each other. Each student may only speak once so that all students on both sides can engage the issue.
12. Optimist/Pessimist

13. Peer review writing task

14. Board rotation

15. Pick the Winner

16. Movie Application

Create an interactive classroom full of interactive learning games. Games are so much fun for students since it doesn’t feel like learning. With BookWidgets, you can make interactive learning games like crossword puzzles, pair matching games, bingo games, jigsaw puzzles, memory games, and many more in minutes (and there’s a Google Classroom integration as well).
17. Crossword puzzle

18. Scrabble

19. Who/what am I?

Want to create a bingo game yourself? You can start for free right here:
Create a Bingo Game
That’s it! Like in any list, you could add many other interactive lesson ideas. I could go on for quite a while myself. But what about you? Share your creative, interactive classroom ideas in our Facebook Group . This way, we can build out this article with many more great ideas!
One more thing… Don’t forget to follow us on Twitter ! 😉

Join hundreds of thousands of subscribers, and get the best content on technology in education.
BookWidgets enables teachers to create fun and interactive lessons for tablets, smartphones, and computers.

Center for Teaching Innovation
Ideas for group & collaborative assignments, why collaborative learning.
Collaborative learning can help
- students develop higher-level thinking, communication, self-management, and leadership skills
- explore a broad range of perspectives and provide opportunities for student voices/expression
- promote teamwork skills & ethics
- prepare students for real life social and employment situations
- increase student retention, self-esteem, and responsibility
Collaborative activities & tools
Group brainstorming & investigation in shared documents.
Have students work together to investigate or brainstorm a question in a shared document (e.g., structured Google doc, Google slide, or sheet) or an online whiteboard, and report their findings back to the class.
- Immediate view of contributions
- Synchronous & asynchronous group work
- Students can come back to the shared document to revise, re-use, or add information
- Google workspace (Google Docs, Sheets, Forms, & Slides)
- Microsoft 365 (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Teams)
- Cornell Box (document storage)
- Whiteboarding tools ( Zoom , JamBoard , Miro , Mural , etc.)
Considerations
- Sharing settings
- Global access
- Accessibility
Group discussions with video conferencing and chat
Ask students to post an answer to a question or share their thoughts about class content in the Zoom chat window (best for smaller classes). For large classes, ask students in Zoom breakout rooms to choose a group notetaker to post group discussion notes in the chat window after returning to the main class session.
You can also use a discussion board for asynchronous group work.
- Students can post their reflections in real time and read/share responses
- If group work is organized asynchronously, students can come back to the discussion board at their own time
Synchronous group work:
- Zoom Breakout rooms
- Microsoft Teams
- Canvas Conferences
- Canvas Group Discussions
- Ed Discussion
- Stable access to WiFi and its bandwidth
- Clear expectations about participation and pace for asynchronous discussion boards
- Monitoring discussion boards
Group projects: creation
Students retrieve and synthesize information by collaborating with their peers to create something new: a written piece, an infographic, a piece of code, or students collectively respond to sample test questions.
- Group projects may benefit from features offered by shared online space (ability to chat, do video conferencing, share files and links, post announcements and discussion threads, and build content)
- Canvas groups with all available tools
Setting up groups and group projects for success may require the following steps:
- Introduce group or peer work early in the semester
- Establishing ground rules for participation
- Plan for each step of group work
- Explain how groups will function and the grading
Peer learning, critiquing, giving feedback
Students submit their first draft of an essay, research proposal, or a design, and the submitted work is distributed for peer review. If students work on a project in teams, they can check in with each other through a group member evaluation activity. Students can also build on each other’s knowledge and understanding of the topic in Zoom breakout room discussions or by sharing and responding in an online discussion board.
When providing feedback and critiquing, students have to apply their knowledge, problem-solving skills, and develop feedback literacy. Students also engage more deeply with the assignment requirements and/or the rubric.
- FeedbackFruits Peer Review and Group Member Evaluation
- Canvas Peer Review
- Turnitin PeerMark
- Zoom breakout rooms
- Canvas discussions, and other discussion tools
- Peer review is a multistep activity and may require careful design and consideration of requirements to help students achieve the learning outcomes. The assignment requirements will inform which platform is best to use and the best settings for the assignment
- We advise making the first peer review activity a low-stakes assignment for the students to get used to the platform and the flow.
- A carefully written rubric helps guide students through the process of giving feedback and yields more constructive feedback.
- It helps when the timing for the activity is generous, so students have enough time to first submit their work and then give feedback.
Group reflection & social annotation activities
Students can annotate, highlight, discuss, and collaborate on text documents, images, video, audio, and websites. Instructors can post guiding questions for students to respond to, and allow students to post their own questions to be answered by peers. This is a great reading activity leading up to an inperson discussion.
- Posing discussion topics and/or questions for students to answer as they read a paper
- Students can collaboratively read and annotate synchronously and asynchronously
- Collaborative annotation helps students to acknowledge some parts of reading that they could have neglected otherwise
- Annotating in small groups
- FeedbackFruits
- Interactive Media (annotations on document, video, and audio)
- Providing students with thorough instructions
- These are all third-party tools, so the settings should be selected thoughtfully
- Accessibility (Perusall)
Group learning with polling and team competitions
Instructors can poll students while they are in breakout rooms using Poll Everywhere. This activity is great for checking understanding and peer learning activities, as students will be able to discuss solutions.
- Students can share screen in a breakout room and/or answer questions together
- This activity can be facilitated as a competition among teams
- Poll Everywhere competitions, surveys, and polls facilitated in breakout rooms
- Careful construction of questions for students
- Students may need to be taught how to answer online questions
- It requires appropriate internet connection and can experience delays in response summaries.
More information
- Group work & collaborative learning
- Collaboration tools
- Active learning
- Active learning in online teaching
- Prodigy Math
- Prodigy English
- Is a Premium Membership Worth It?
- Promote a Growth Mindset
- Help Your Child Who's Struggling with Math
- Parent's Guide to Prodigy
- Assessments
- Math Curriculum Coverage
- English Curriculum Coverage
- Game Portal
8 Active Learning Strategies and Examples [+ Downloadable List]

Written by Justin Raudys
Engage your students, get time-saving tools and differentiate learning with Prodigy.
- Teaching Strategies
- Teaching Tools
- 8 Active Learning Strategies
The Teacher’s Role in the Active Learning Classroom
Active learning techniques: key questions, making space for active learning strategies.
As a teacher, one of your biggest challenges is to plan lessons that inspire your students to stay actively involved in the learning process.
But you’ve probably noticed that traditional, teacher-centered learning plans aren’t always conducive to achieving that inspiration.
That’s where active learning strategies come into play. You can use them to empower, engage, and stimulate a classroom by putting students at the center of the learning process.
Get inspired by these 8 strategies that will help students talk more openly, think more creatively and -- ultimately -- become more engaged in the process of learning.
This article is accompanied by a downloadable list of active learning strategies to keep at your desk for quick reference.
Active Learning Strategies
1. reciprocal questioning.
Use reciprocal questioning to encourage an open dialogue in which students take on the role of the teacher and create their own questions about a topic, reading section, or lesson.

After covering a topic of your choice in class -- or after assigning a reading selection -- divide the class into pairs or small groups and have students come up with a few questions for discussion with the rest of the class. To facilitate the process, you can provide students with “question stems,” which provide a foundation for a question but still require students to think critically about a lesson, text, or other section of material by completing the query. Consider the examples below.
Comprehension Question Stems
Describe x in your own words. What does y mean? Why is z important? How could x be used to y ?
Connector Question Stems
Explain how x and why z. In what ways are x and y similar? In what ways are x and y different? How does x tie in with that we learned before?
Use these question stems to anchor and explore concepts in course material, helping students investigate a range of new topics and points of view associated with your lesson.
Much like student-generated test questions -- a type of of experiential learning activity -- reciprocal questioning involves students in the learning process to help build their comprehension of course material.
Reciprocal questioning can be particularly useful when:
- Preparing for tests or exams
- Introducing a new topic or section of course content
- Discussing reading or writing materials in greater detail
2. Three step interviews
A cooperative learning strategy , the three step interview encourages students to develop active listening skills by quizzing one another, sharing their thoughts, and taking notes.

To use the three step interview process, divide students into groups of three, and assign three roles: interviewer, interviewee, and notetaker.
After also assigning a theme or topic of discussion, have students participate in a five to 10 minute interview to discuss what they found to be the key information relating to the topic.
After each interview, have students rotate roles. Depending on factors including the grade level of your students and their experience with the strategy, you may adjust the length of the time for each interview.

One interpretation of the three-step interview process. Feel free to experiment with the duration and number of students involved in these steps. Image courtesy: Kagan Publishing
Before using the strategy, you may find it useful to have students explore the types of questions reporters ask in interviews and at what point in an interview they ask them. You may also want to provide recording sheets to use when they are assigned the “reporter” role.
The three-step interview confers benefits including:
- Helping students learn and apply different questioning strategies
- Strengthening students’ connection with course material in a creative and engaging way
- Producing a sense of accountability, with students working together to complete a task and grasp a lesson
3. The pause procedure
Use the pause procedure to intersperse strategic pauses into your class lectures and enhance student understanding of teaching materials.

To use the pause procedure, arrange for pauses of two to three minutes between every 10 to 15 minutes of lecture time.
During these brief breaks, encourage students to discuss or rework their notes in pairs to clarify key points covered, raise questions, and solve problems posed by the instructor.
Alternatively, students can work together to write a paragraph that connects or highlights key ideas set out in their partner’s notes.
A 2014 study concluded that breaking a lecture into brief pauses can increase student attention and learning outcomes. The pause procedure, the study determined, is “a good active learning strategy which helps students review their notes, reflect on them, discuss and explain the key ideas with their partners.”
The use of the pause procedure involves a minimal amount of extra time, but can confer significant benefits in comparison to lectures that continue without breaks.
4. The muddiest point technique
The muddiest point technique involves asking students to write notes on the most unclear or most confusing element of a given homework assignment, lecture, or class discussion.

The Muddiest Point: Sample Phrasing What have you found to be the muddiest point so far in this assignment? What topic do you find to be the least clear?
Asking students to write down what they find to be the least clear is a powerful exercise because it compels them to grade or rate their own knowledge of a topic.
In short, the exercise helps students reflect on the lesson and identify concepts needing further examination or study.

Example of a "muddiest point" handout to issue to students. Image source: TeachersPayTeachers .
From your perspective, the activity can serve as an insightful source of feedback.
For example, if more than a quarter of the class mentions the same “muddiest point,” you may wish to schedule a further time to discuss that topic, or create a new lesson plan or assignment to tackle it.
5. The devil's advocate approach
The devil's advocate approach asks one or more students to take the opposing side of a predominant argument or point of view being discussed during a lesson.

Once you have completed an assignment or lesson plan, select a topic that is suitable for discussion and debate. The topic should serve as an appropriate subject for providing arguments from both sides.
The activity is flexible and should be tailored to suit your students' grade level. In its simplest form, divide the class into two sections and coordinate a class-wide debate based on a selected topic. Alternatively, you may have students annotate reading texts and respond to contentions by creating counterarguments. Then, have students debate the proposals discussed during a mock town hall meeting.
While this approach can be used across a number of grade levels and subjects, consider this list of thematic claims used as primers for a devil’s advocate activity in a secondary ELA class.
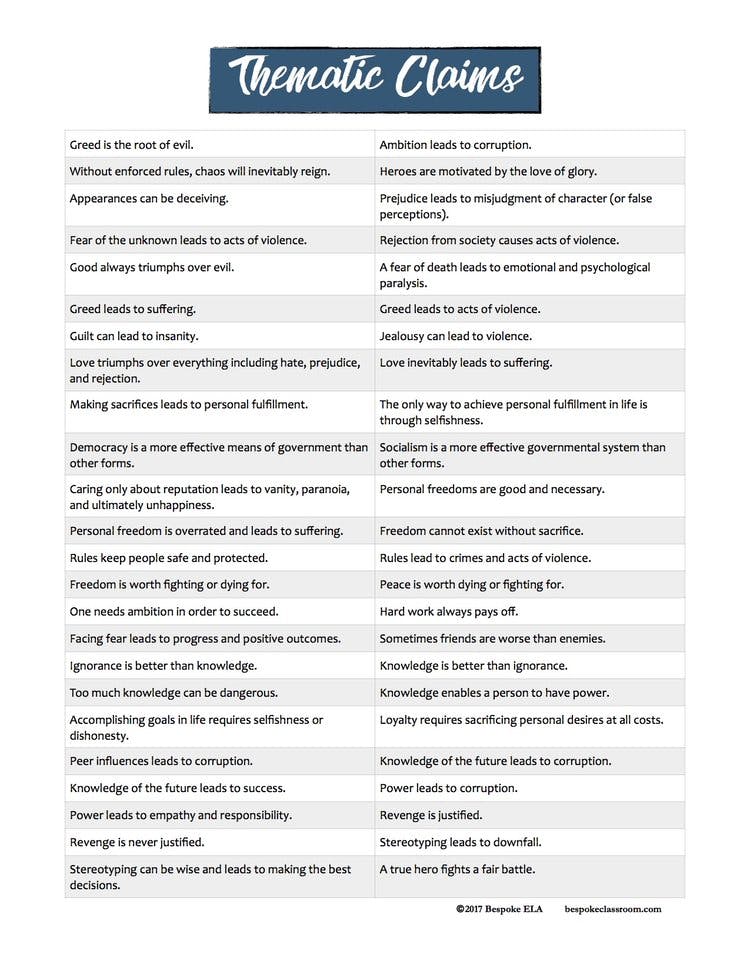
Image source: Bespoke Classroom .
This approach can help cultivate active learning in the classroom by encouraging students to:
- Think more critically , challenging participants to expand their understanding of the perspectives surrounding an issue and to view it through a different lens
- Become more engaged, fostering involvement by drawing out opinions to explore the complexity of an issue being studied
- Produce a deeper understanding of topics or issues, using rigorous analysis to collectively clarify, probe, and pose alternatives to problems being discussed
According to a study published in the Journal of Theory, Research and Action in Urban Education , the devil’s advocate approach can help students become “more familiar with a...topic and its multifaceted viewpoints.” The same study concludes that a classroom using this strategy can:
“provide students with multiple perspectives, and challenge students with tough questions. In such a classroom, students will become more engaged and students’ critical thinking and writing skills will be enriched.”
6. Peer teaching activities
A flexible and multi-faceted approach to active learning, peer instruction encompasses a range of scenarios where students instruct skills or explain concepts to classmates .

Some popular options include:
- Reading buddies — A cooperative learning strategy that pairs two students who work together to read an assigned text.
- Cross-age peer tutoring — A peer learning strategy involving students in different grades, wherein which one student instructs another on the material in which the first student is advanced and the second student is a novice.
- Role play — A group of students is split into smaller groups and given a specific task to complete, like in small group work. However, in addition to working on a specific task, the members of each group are asked to play a certain “role”. Unlike in traditional role-play, all members of one group play the same role, not individually assigned roles.
Peer teaching activities help boost vital skills and behaviors including student interaction, accountability, group processing.
7. Game-based learning platforms
Game-based learning platforms and depth and differentiation to the educational process and allow students to work with their instructors to achieve their learning objectives.

Eric Sheninger, a principal, author, and Senior Fellow at the International Center for Leadership in Education (ICLE), writes passionately about the use of technology as an active learning tool. In his article " Shifting From Passive to Active Learning ," he writes:
It is really about how students use devices to create artifacts of learning that demonstrate conceptual mastery through relevant application and evaluation...Give kids challenging problems to solve that have more than one right answer and let them use technology to show that they understand. This is the epitome of active learning...
Math games and websites are at the forefront of delivering active learning through technology. One example is Prodigy, a platform that constantly adjusts questions to tackle student trouble spots and delivers math problems with words, charts pictures, and numbers. Better yet, educational content is free to access and aligned with curricula for grades 1 to 8 teachers.
Create and sign into your free teacher account.
8. Rotating chair group discussions
Rotating chair group discussions encourage students to actively listen to selected speakers who follow a pattern of guiding class discussion and summarizing previous points. Students lead and stimulate class discussion as they “rotate” roles, repeatedly selecting the following speaker.

To use this strategy effectively, ensure that students adhere to the following pattern:
- When a student wishes to participate, they must raise their hand
- The student who is speaking calls on the next speaker, ideally someone who has not yet contributed
- The student who has been called upon briefly summarizes what the previous student said before developing the idea further
This process can be repeated across a variety of topics, with your guidance to stay on track and help stuck students.
The benefits of rotating chair group discussions are not only limited to the speakers. Knowing that they may be called upon to summarize the previous topic, all students are engaged in attentive listening, frequently jotting down notes and ideas to stay on track in the spaces between speaking.
Moreover, students are put into a scenario where they learn from their colleagues’ ideas, sparking new considerations of material in an active and engaging way.
This strategy is rewarding for students because it encourages powerful and direct engagement with course material.
While active learning places an emphasis on the student’s role in the learning experience, there is no doubt that the success of any active learning strategy starts with the thought and planning of a conscientious instructor.

"Overall," a 2011 study found , "teachers play an influential role in increasing students' situational interest in the active-learning classroom," while factors like a teacher's social connection with students and subject matter expertise "significantly influence the level of students' situational interest in the active learning classroom."
And, critically, the benefits of active learning go both ways, helping teachers as well as students.
As active learning advocate James Ballencia writes,
With the goal of teaching mindful learners who actively pursue knowledge, teachers become more actively engaged in how they teach the curriculum and how they develop each student's learning potential. They mix and match a variety of ... tactics to ensure that students not only learn more, better, and faster -- they also learn smarter.
As many of the techniques above are open-ended, the active learning strategies underpinning them may differentiate for different types of learners. Be sure to consider how you can differentiate instruction while still enjoying the benefits of these active learning strategies.
To help the success of these strategies, put yourself in your students’ position and imagine how they might experience it. This will help you get a feel for the lesson.

When applying any of these strategies for your course, be sure to ask yourself:
- Will this be engaging and exciting for my students?
- Can this activity deploy formative assessment strategies ?
- Is the student placed at the center of this learning strategy?
- Will this encourage my students to discuss a topic with one another?
- Am I giving students the opportunity to reflect on the learning process?
- Is this activity getting my students to think deeply and critically about a topic or lesson or is it simply a comprehension exercise?
While all of the active learning strategies outlined above can be deployed in traditional, lecture-oriented classrooms, the physical arrangement of your room and the number of students in the class can make some of them difficult to perform easily.

While a flexible seating classroom arrangement may ease this challenge, such a solution is not always possible. Plan these exercises with the limitations of your physical space carefully, being mindful of the environmental constraints posed by the unique arrangements of some of the strategies above.
Final Thoughts on Active Learning Strategies
Active learning plainly puts the focus on the learner: what the learner does, what the learner thinks, and how the learner behaves.
But, crucially, active learning doesn't simply happen with a few simple instructions: it occurs in the classroom where the teacher is committed to a learning environment that makes active learning possible .
Ultimately, these active learning strategies will help build understanding rather than memorization of facts, giving students the confidence to apply learning to different problems and contexts and achieve greater autonomy over their learning.
And, after all, that’s exactly makes active learning “active”: putting students at the center of the learning process as they take the initiative to learn .
Downloadable List of the 8 Active Learning Strategies
Click here to download the list of strategies to print and keep at your desk.
Create or log in to your teacher account on Prodigy -- a game-based learning platform that assesses student progress and performance as they play. Aligned with a growing list of curricula across the world, over 800,000 teachers and 30 million students have signed up to Prodigy Math Game .
Learning Activities and Assignments: How to Maximize Their Effectiveness
Clearly communicate to students your goals for any assignment or learning activity . Don't assume that students will know what the pedagogical purpose of the assignment is. Have a discussion about your goals and desired learning outcomes, and help students understand how specific aspects of the assignment fit these goals. Be open to making some changes if students have ideas to offer. After the discussion has taken place, summarize it and post it in the learning management system for students to revisit as they work on their assignments.
Inform your students of assignments as early as possible in a semester, and help them schedule and plan for them.
Give your students examples of "typical" exemplary assignments from past students, but also of submissions that were both exemplary and unique , so that students can see what you are looking for, but also so that they realize a range of possibilities.
Scaffold smaller activities and assignments towards large assignments so that students understand the trajectory of their work. This helps students build on their growing knowledge, but also helps them move forward: it's easier for them to continue a learning process than to start a new one. It also combats procrastination and plagiarism, and encourages time on task.
Consider creating flexible intermediate deadlines. That is, provide deadlines for when particular stages or parts of the assignment should be completed, so that students can understand the ideal pace of their work flow.
If possible, allow students to share draft work with you and with their peers. They can then use your feedback, and their peer's feedback, to revise and improve their work.
Offer students performative options. In other words, allow students to demonstrate their understanding or skill acquisition in alternative or diverse ways. For example, rather than a traditional essay, could a student create a podcast or screencast? Instead of submitting a written assignment, could a student do an in-class poster presentation?
Meet with students one-on-one as much as possible to assist with every step in the process, from clarifying the assignment, to brainstorming, to polishing.
Help your students appreciate the importance of formative feedback . Many students are interested only in the grade that an assignment receives (the summative assessment), and will spend little time on the formative feedback that you also provide on their assignments. Help them understand that carefully reviewing the formative feedback will improve their performance in the future.
Discuss your own working process : the ideal scene for your work, the personal supports you have or try to create, your own blocks and difficulties. Students can benefit from seeing how their instructors work. At the same time, recognize that there are many different learning styles, and that most students won't work the same way that their teachers do, and that this is a good thing.
Use the learning management system to support students as they work on their assignments. For example, create on online discussion forum where students can ask questions about their assignments, or where they can post drafts of their work in order to receive feedback from peers.
Be sensitive to cultural differences that might impact student learning processes and the "products" they create.
Ask students to help you revise assignment prompts for the next time you teach the class , and/or to write down some advice they would give to future students for succeeding at an assignment.
Consider having your program, department, or faculty implement an ePortfolio program for students . Students can use the ePortfolio to archive drafts of their assignments, to reflect on specific assignments or their overall progress, to showcase their best assignments, and more.
Consider providing verbal feedback on student assignments using new technologies. For example, the latest (free) version of Adobe Acrobat makes it easy to add audio comments to specific parts of a document. Narrating your comments might be easier than typing them, and you can also be more nuanced with verbal comments than with written comments.
Make large-print copies of all materials available. These are beneficial not only for visually impaired students who are registered with AccessAibility Services , but for any student who is experiencing some degree of vision impairment.
If you would like support applying these tips to your own teaching, CTE staff members are here to help. View the CTE Support page to find the most relevant staff member to contact.
This Creative Commons license lets others remix, tweak, and build upon our work non-commercially, as long as they credit us and indicate if changes were made. Use this citation format: Learning Activities and Assignments: How to Maximize Their Effectiveness. Centre for Teaching Excellence, University of Waterloo .
Catalog search
Teaching tip categories.
- Assessment and feedback
- Blended Learning and Educational Technologies
- Career Development
- Course Design
- Course Implementation
- Inclusive Teaching and Learning
- Learning activities
- Support for Student Learning
- Support for TAs
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Assignment is a task given to students by a teacher or professor, usually as a means of assessing their understanding and application of course material. Assignments can take various forms, including essays, research papers, presentations, problem sets, lab reports, and more.
Assignments are typically designed to be completed outside of class time and may require independent research, critical thinking, and analysis. They are often graded and used as a significant component of a student’s overall course grade. The instructions for an assignment usually specify the goals, requirements, and deadlines for completion, and students are expected to meet these criteria to earn a good grade.
History of Assignment
The use of assignments as a tool for teaching and learning has been a part of education for centuries. Following is a brief history of the Assignment.
- Ancient Times: Assignments such as writing exercises, recitations, and memorization tasks were used to reinforce learning.
- Medieval Period : Universities began to develop the concept of the assignment, with students completing essays, commentaries, and translations to demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of the subject matter.
- 19th Century : With the growth of schools and universities, assignments became more widespread and were used to assess student progress and achievement.
- 20th Century: The rise of distance education and online learning led to the further development of assignments as an integral part of the educational process.
- Present Day: Assignments continue to be used in a variety of educational settings and are seen as an effective way to promote student learning and assess student achievement. The nature and format of assignments continue to evolve in response to changing educational needs and technological innovations.
Types of Assignment
Here are some of the most common types of assignments:
An essay is a piece of writing that presents an argument, analysis, or interpretation of a topic or question. It usually consists of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Essay structure:
- Introduction : introduces the topic and thesis statement
- Body paragraphs : each paragraph presents a different argument or idea, with evidence and analysis to support it
- Conclusion : summarizes the key points and reiterates the thesis statement
Research paper
A research paper involves gathering and analyzing information on a particular topic, and presenting the findings in a well-structured, documented paper. It usually involves conducting original research, collecting data, and presenting it in a clear, organized manner.
Research paper structure:
- Title page : includes the title of the paper, author’s name, date, and institution
- Abstract : summarizes the paper’s main points and conclusions
- Introduction : provides background information on the topic and research question
- Literature review: summarizes previous research on the topic
- Methodology : explains how the research was conducted
- Results : presents the findings of the research
- Discussion : interprets the results and draws conclusions
- Conclusion : summarizes the key findings and implications
A case study involves analyzing a real-life situation, problem or issue, and presenting a solution or recommendations based on the analysis. It often involves extensive research, data analysis, and critical thinking.
Case study structure:
- Introduction : introduces the case study and its purpose
- Background : provides context and background information on the case
- Analysis : examines the key issues and problems in the case
- Solution/recommendations: proposes solutions or recommendations based on the analysis
- Conclusion: Summarize the key points and implications
A lab report is a scientific document that summarizes the results of a laboratory experiment or research project. It typically includes an introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
Lab report structure:
- Title page : includes the title of the experiment, author’s name, date, and institution
- Abstract : summarizes the purpose, methodology, and results of the experiment
- Methods : explains how the experiment was conducted
- Results : presents the findings of the experiment
Presentation
A presentation involves delivering information, data or findings to an audience, often with the use of visual aids such as slides, charts, or diagrams. It requires clear communication skills, good organization, and effective use of technology.
Presentation structure:
- Introduction : introduces the topic and purpose of the presentation
- Body : presents the main points, findings, or data, with the help of visual aids
- Conclusion : summarizes the key points and provides a closing statement
Creative Project
A creative project is an assignment that requires students to produce something original, such as a painting, sculpture, video, or creative writing piece. It allows students to demonstrate their creativity and artistic skills.
Creative project structure:
- Introduction : introduces the project and its purpose
- Body : presents the creative work, with explanations or descriptions as needed
- Conclusion : summarizes the key elements and reflects on the creative process.
Examples of Assignments
Following are Examples of Assignment templates samples:
Essay template:
I. Introduction
- Hook: Grab the reader’s attention with a catchy opening sentence.
- Background: Provide some context or background information on the topic.
- Thesis statement: State the main argument or point of your essay.
II. Body paragraphs
- Topic sentence: Introduce the main idea or argument of the paragraph.
- Evidence: Provide evidence or examples to support your point.
- Analysis: Explain how the evidence supports your argument.
- Transition: Use a transition sentence to lead into the next paragraph.
III. Conclusion
- Restate thesis: Summarize your main argument or point.
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your essay.
- Concluding thoughts: End with a final thought or call to action.
Research paper template:
I. Title page
- Title: Give your paper a descriptive title.
- Author: Include your name and institutional affiliation.
- Date: Provide the date the paper was submitted.
II. Abstract
- Background: Summarize the background and purpose of your research.
- Methodology: Describe the methods you used to conduct your research.
- Results: Summarize the main findings of your research.
- Conclusion: Provide a brief summary of the implications and conclusions of your research.
III. Introduction
- Background: Provide some background information on the topic.
- Research question: State your research question or hypothesis.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of your research.
IV. Literature review
- Background: Summarize previous research on the topic.
- Gaps in research: Identify gaps or areas that need further research.
V. Methodology
- Participants: Describe the participants in your study.
- Procedure: Explain the procedure you used to conduct your research.
- Measures: Describe the measures you used to collect data.
VI. Results
- Quantitative results: Summarize the quantitative data you collected.
- Qualitative results: Summarize the qualitative data you collected.
VII. Discussion
- Interpretation: Interpret the results and explain what they mean.
- Implications: Discuss the implications of your research.
- Limitations: Identify any limitations or weaknesses of your research.
VIII. Conclusion
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your paper.
Case study template:
- Background: Provide background information on the case.
- Research question: State the research question or problem you are examining.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of the case study.
II. Analysis
- Problem: Identify the main problem or issue in the case.
- Factors: Describe the factors that contributed to the problem.
- Alternative solutions: Describe potential solutions to the problem.
III. Solution/recommendations
- Proposed solution: Describe the solution you are proposing.
- Rationale: Explain why this solution is the best one.
- Implementation: Describe how the solution can be implemented.
IV. Conclusion
- Summary: Summarize the main points of your case study.
Lab report template:
- Title: Give your report a descriptive title.
- Date: Provide the date the report was submitted.
- Background: Summarize the background and purpose of the experiment.
- Methodology: Describe the methods you used to conduct the experiment.
- Results: Summarize the main findings of the experiment.
- Conclusion: Provide a brief summary of the implications and conclusions
- Background: Provide some background information on the experiment.
- Hypothesis: State your hypothesis or research question.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of the experiment.
IV. Materials and methods
- Materials: List the materials and equipment used in the experiment.
- Procedure: Describe the procedure you followed to conduct the experiment.
- Data: Present the data you collected in tables or graphs.
- Analysis: Analyze the data and describe the patterns or trends you observed.
VI. Discussion
- Implications: Discuss the implications of your findings.
- Limitations: Identify any limitations or weaknesses of the experiment.
VII. Conclusion
- Restate hypothesis: Summarize your hypothesis or research question.
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your report.
Presentation template:
- Attention grabber: Grab the audience’s attention with a catchy opening.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of your presentation.
- Overview: Provide an overview of what you will cover in your presentation.
II. Main points
- Main point 1: Present the first main point of your presentation.
- Supporting details: Provide supporting details or evidence to support your point.
- Main point 2: Present the second main point of your presentation.
- Main point 3: Present the third main point of your presentation.
- Summary: Summarize the main points of your presentation.
- Call to action: End with a final thought or call to action.
Creative writing template:
- Setting: Describe the setting of your story.
- Characters: Introduce the main characters of your story.
- Rising action: Introduce the conflict or problem in your story.
- Climax: Present the most intense moment of the story.
- Falling action: Resolve the conflict or problem in your story.
- Resolution: Describe how the conflict or problem was resolved.
- Final thoughts: End with a final thought or reflection on the story.
How to Write Assignment
Here is a general guide on how to write an assignment:
- Understand the assignment prompt: Before you begin writing, make sure you understand what the assignment requires. Read the prompt carefully and make note of any specific requirements or guidelines.
- Research and gather information: Depending on the type of assignment, you may need to do research to gather information to support your argument or points. Use credible sources such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites.
- Organize your ideas : Once you have gathered all the necessary information, organize your ideas into a clear and logical structure. Consider creating an outline or diagram to help you visualize your ideas.
- Write a draft: Begin writing your assignment using your organized ideas and research. Don’t worry too much about grammar or sentence structure at this point; the goal is to get your thoughts down on paper.
- Revise and edit: After you have written a draft, revise and edit your work. Make sure your ideas are presented in a clear and concise manner, and that your sentences and paragraphs flow smoothly.
- Proofread: Finally, proofread your work for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. It’s a good idea to have someone else read over your assignment as well to catch any mistakes you may have missed.
- Submit your assignment : Once you are satisfied with your work, submit your assignment according to the instructions provided by your instructor or professor.
Applications of Assignment
Assignments have many applications across different fields and industries. Here are a few examples:
- Education : Assignments are a common tool used in education to help students learn and demonstrate their knowledge. They can be used to assess a student’s understanding of a particular topic, to develop critical thinking skills, and to improve writing and research abilities.
- Business : Assignments can be used in the business world to assess employee skills, to evaluate job performance, and to provide training opportunities. They can also be used to develop business plans, marketing strategies, and financial projections.
- Journalism : Assignments are often used in journalism to produce news articles, features, and investigative reports. Journalists may be assigned to cover a particular event or topic, or to research and write a story on a specific subject.
- Research : Assignments can be used in research to collect and analyze data, to conduct experiments, and to present findings in written or oral form. Researchers may be assigned to conduct research on a specific topic, to write a research paper, or to present their findings at a conference or seminar.
- Government : Assignments can be used in government to develop policy proposals, to conduct research, and to analyze data. Government officials may be assigned to work on a specific project or to conduct research on a particular topic.
- Non-profit organizations: Assignments can be used in non-profit organizations to develop fundraising strategies, to plan events, and to conduct research. Volunteers may be assigned to work on a specific project or to help with a particular task.
Purpose of Assignment
The purpose of an assignment varies depending on the context in which it is given. However, some common purposes of assignments include:
- Assessing learning: Assignments are often used to assess a student’s understanding of a particular topic or concept. This allows educators to determine if a student has mastered the material or if they need additional support.
- Developing skills: Assignments can be used to develop a wide range of skills, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, research, and communication. Assignments that require students to analyze and synthesize information can help to build these skills.
- Encouraging creativity: Assignments can be designed to encourage students to be creative and think outside the box. This can help to foster innovation and original thinking.
- Providing feedback : Assignments provide an opportunity for teachers to provide feedback to students on their progress and performance. Feedback can help students to understand where they need to improve and to develop a growth mindset.
- Meeting learning objectives : Assignments can be designed to help students meet specific learning objectives or outcomes. For example, a writing assignment may be designed to help students improve their writing skills, while a research assignment may be designed to help students develop their research skills.
When to write Assignment
Assignments are typically given by instructors or professors as part of a course or academic program. The timing of when to write an assignment will depend on the specific requirements of the course or program, but in general, assignments should be completed within the timeframe specified by the instructor or program guidelines.
It is important to begin working on assignments as soon as possible to ensure enough time for research, writing, and revisions. Waiting until the last minute can result in rushed work and lower quality output.
It is also important to prioritize assignments based on their due dates and the amount of work required. This will help to manage time effectively and ensure that all assignments are completed on time.
In addition to assignments given by instructors or professors, there may be other situations where writing an assignment is necessary. For example, in the workplace, assignments may be given to complete a specific project or task. In these situations, it is important to establish clear deadlines and expectations to ensure that the assignment is completed on time and to a high standard.
Characteristics of Assignment
Here are some common characteristics of assignments:
- Purpose : Assignments have a specific purpose, such as assessing knowledge or developing skills. They are designed to help students learn and achieve specific learning objectives.
- Requirements: Assignments have specific requirements that must be met, such as a word count, format, or specific content. These requirements are usually provided by the instructor or professor.
- Deadline: Assignments have a specific deadline for completion, which is usually set by the instructor or professor. It is important to meet the deadline to avoid penalties or lower grades.
- Individual or group work: Assignments can be completed individually or as part of a group. Group assignments may require collaboration and communication with other group members.
- Feedback : Assignments provide an opportunity for feedback from the instructor or professor. This feedback can help students to identify areas of improvement and to develop their skills.
- Academic integrity: Assignments require academic integrity, which means that students must submit original work and avoid plagiarism. This includes citing sources properly and following ethical guidelines.
- Learning outcomes : Assignments are designed to help students achieve specific learning outcomes. These outcomes are usually related to the course objectives and may include developing critical thinking skills, writing abilities, or subject-specific knowledge.
Advantages of Assignment
There are several advantages of assignment, including:
- Helps in learning: Assignments help students to reinforce their learning and understanding of a particular topic. By completing assignments, students get to apply the concepts learned in class, which helps them to better understand and retain the information.
- Develops critical thinking skills: Assignments often require students to think critically and analyze information in order to come up with a solution or answer. This helps to develop their critical thinking skills, which are important for success in many areas of life.
- Encourages creativity: Assignments that require students to create something, such as a piece of writing or a project, can encourage creativity and innovation. This can help students to develop new ideas and perspectives, which can be beneficial in many areas of life.
- Builds time-management skills: Assignments often come with deadlines, which can help students to develop time-management skills. Learning how to manage time effectively is an important skill that can help students to succeed in many areas of life.
- Provides feedback: Assignments provide an opportunity for students to receive feedback on their work. This feedback can help students to identify areas where they need to improve and can help them to grow and develop.
Limitations of Assignment
There are also some limitations of assignments that should be considered, including:
- Limited scope: Assignments are often limited in scope, and may not provide a comprehensive understanding of a particular topic. They may only cover a specific aspect of a topic, and may not provide a full picture of the subject matter.
- Lack of engagement: Some assignments may not engage students in the learning process, particularly if they are repetitive or not challenging enough. This can lead to a lack of motivation and interest in the subject matter.
- Time-consuming: Assignments can be time-consuming, particularly if they require a lot of research or writing. This can be a disadvantage for students who have other commitments, such as work or extracurricular activities.
- Unreliable assessment: The assessment of assignments can be subjective and may not always accurately reflect a student’s understanding or abilities. The grading may be influenced by factors such as the instructor’s personal biases or the student’s writing style.
- Lack of feedback : Although assignments can provide feedback, this feedback may not always be detailed or useful. Instructors may not have the time or resources to provide detailed feedback on every assignment, which can limit the value of the feedback that students receive.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
Teaching for Learning @ McGill University
Discussing what matters in higher education.
What’s an assignment that really helped you learn?
That was the question McGill University’s Teaching and Learning Services (TLS) asked students on campus in 2018 and again in a campus-wide survey in 2019. Understanding students’ perceptions of how they learn can inform our development of instructor support resources, such as workshops, webinars and resource documents.
When students described assignments that helped them learn, a number of themes emerged. For example, students believe their learning is supported through real-world activities and creative assignments that foster their critical thinking skills. Students also expressed that short, regular assignments that make them stay up to date with course work reinforce their learning.

We thought readers might be interested in seeing examples of assignments—assessment strategies, from instructors’ perspective—that students believe help them learn. So, we decided to add some of the strategies that students told us about in the survey to the Beyond Grading: Strategies from McGill Instructors web page. This online collection of assessment strategies intends to provide colleagues with a go-to place when they’re seeking inspiration for their teaching. (You can read more about this online collection in an earlier post .)
The newly-added strategies call upon students to develop their critical thinking skills in the context of real-world activities: 10 Questions, 10 Answers (W. Archambault), In-class Debate (S. Burgos), and Scientific Source Evaluation (S. Woolley and T. Western). The Hands-on Creative Project (C. Bradley) was deemed a “unique” alternative to the traditional research paper in that it allows students to demonstrate their learning through a variety of media.
COVID-19 has imposed upon many in higher education the need to implement less familiar assessment strategies. If you’re looking for ideas, we hope you’ll check out the strategies from McGill instructors, many of which can be adapted for remote teaching.
More strategies will be added to the online collection in the coming weeks. In the meantime:
- Read our blog series on Assessment for Learning https://teachingblog.mcgill.ca/tag/beyond-grading/ , which highlights interviews with students describing assignments that help them learn.
- Hear directly from students about assignments that help them learn in this video playlist .
Carolyn Samuel
Associate Director, Faculty and Teaching Development, and Senior Academic Associate, at McGill's Teaching and Learning Services; former Senior Faculty Lecturer at the McGill Writing Centre; area of specialization: Second Language Education; loves teaching and learning!
(Photo credit: Owen Egan)
- Carolyn Samuel https://teachingblog.mcgill.ca/author/carolynsamuel/ Preparing for Winter 2024: Seven strategies for success
- Carolyn Samuel https://teachingblog.mcgill.ca/author/carolynsamuel/ Terrific teaching tales
- Carolyn Samuel https://teachingblog.mcgill.ca/author/carolynsamuel/ Seven+ inclusive teaching strategies to support student learning
- Carolyn Samuel https://teachingblog.mcgill.ca/author/carolynsamuel/ What do you do when you’re in the classroom and things go awry in a way you weren’t expecting?
Share this:
0 comments on “ what’s an assignment that really helped you learn ”, leave a reply cancel reply, discover more from teaching for learning @ mcgill university.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
You must be logged in to post a comment.

25 Examples Of Cooperative Learning Activities

Affiliate Disclaimer
As an affiliate, we may earn a commission from qualifying purchases. We get commissions for purchases made through links on this website from Amazon and other third parties.
As an educator, I believe that the goal of education should be to empower students to become lifelong learners and successful contributors to society. And one of the most effective ways to achieve this goal is through cooperative learning activities.
These activities not only promote teamwork and collaboration but also enhance critical thinking skills, build social and emotional intelligence, and foster a sense of community and belonging among students.
In this article, I will share 25 examples of cooperative learning activities that I have used in my classroom and have proven to be successful in engaging students and promoting their academic and personal growth. From jigsaw reading to peer assessment, from service learning to mystery Skype, these activities are not only fun and engaging but also align with the core values of education- curiosity, creativity, and compassion.
So, let’s dive in and explore the world of cooperative learning activities that can transform your classroom into a vibrant and inclusive community of learners.
Table of Contents
Examples of cooperative learning activities that you can use in the classroom, 1. jigsaw reading.
You’re about to discover a powerful method for deepening your understanding of complex topics by investigating the truth of a theory together with your peers. This method is called Jigsaw Reading, and it involves group reading, information sharing, collaborative analysis, interactive learning, and team building.
Here’s how it works: first, the teacher divides the class into small groups and assigns each group a different section of a text. Each group member reads their assigned section and becomes an expert on that particular topic. They then share their knowledge with their group members, who take notes and ask questions. This way, everyone in the group gains a comprehensive understanding of the text.
Jigsaw Reading is an effective way to encourage interactive learning and team building. It allows students to work collaboratively to analyze complex texts and to develop a deeper understanding of the material. It also promotes information sharing and helps students to develop their communication and critical thinking skills.
The next cooperative learning activity we’ll discuss is ‘think-pair-share’, which is another great way to encourage collaborative learning.
2. Think-Pair-Share
In Think-Pair-Share, I make my students interact with their peers and learn from their perspectives. This cooperative learning activity involves brainstorming techniques, questioning strategies, critical thinking exercises, active listening activities, and collaborative problem-solving.
It begins with me posing a question or a topic related to the lesson. Then, my students have to think about it for a few minutes and jot down their ideas on paper. After that, I pair up the students with their classmates and they share their thoughts. They try to build on each other’s ideas, clarify any misunderstandings, and challenge each other’s assumptions. Finally, they present their findings to the class.
To make the most out of Think-Pair-Share, here are three tips that I find helpful:
- Active Listening – When my partner is speaking, I make sure to give them my full attention. I listen to their words, tone, and body language . I ask follow-up questions and seek clarification if needed. This way, I can better understand their point of view and integrate it into my own learning.
- Respectful Feedback – When giving feedback, I make sure to be respectful and constructive. I focus on the ideas presented, not the person presenting them. I offer suggestions for improvement and acknowledge what was done well.
- Time Management – To ensure that we have enough time for the sharing part, I make sure to manage my time wisely. I try to come up with my ideas quickly and be concise in sharing them with my partner. This way, we have more time to discuss and collaborate on our findings.
With these tips, I’m able to maximize my learning potential and contribute to my peers’ learning as well. In the next section, I’ll discuss the benefits of group presentations.
3. Group Presentations
Get ready to impress your classmates with your group presentation skills! Collaborative planning is key to a successful group presentation.
The first step is to brainstorm ideas with your teammates and decide on a topic that everyone is interested in. Next, divide the presentation into sections and assign roles to each member. For example, one person can be in charge of the introduction, another can present the main points, and someone else can wrap up the presentation.
During the presentation, audience participation is crucial. Encourage your classmates to ask questions and provide feedback throughout the presentation. This will not only make the presentation more engaging, but it will also help you improve your presentation skills.
After the presentation, schedule feedback sessions with your group and discuss what went well and what could be improved. Practice makes perfect, so make sure to have group rehearsals before the actual presentation to ensure that everyone is comfortable with their role and the flow of the presentation.
Now, let’s move on to the next section about ’roundtable discussions’.
4. Roundtable Discussions
You’ll love participating in roundtable discussions, where you can share your thoughts and opinions with others in a respectful and engaging environment. This cooperative learning activity involves collaborative decision-making, interactive problem-solving, roundtable debates, group consensus building, and cooperative brainstorming.
Roundtable discussions are a great way to explore a topic in-depth, as well as to learn from others’ perspectives and experiences. In a roundtable discussion, everyone has a chance to speak and be heard. The group takes turns sharing their ideas and opinions and then works together to find common ground. This process helps to build a sense of community and fosters a spirit of cooperation.
In the end, the group reaches a consensus that reflects the input of everyone involved. Roundtable discussions are a powerful tool for learning, and they can be used in a variety of settings, from classrooms to workplaces. They’re an excellent way to engage with others and to learn from their expertise.
Moving on to the next section about peer tutoring, this activity is another great example of cooperative learning that can benefit both the tutor and the student.
5. Peer Tutoring
As a peer tutor, I’ve found that the role reversal of being a teacher and a student can be incredibly rewarding.
Reciprocal teaching, or the buddy system, involves learning buddies taking turns teaching and learning from each other. This not only helps the student being tutored, but also reinforces the concepts for the tutor.
Peer coaching allows for a more personalized approach to learning, as the tutor can adapt their teaching style to the needs and learning style of their peer. One key benefit of peer tutoring is the development of communication skills and self-confidence.
Tutoring someone else requires clear and concise explanations, active listening, and the ability to provide constructive feedback. Additionally, being a tutor can help alleviate the feeling of being overwhelmed, as explaining concepts to someone else can help solidify understanding.
By working together and supporting each other, learning becomes less of a solitary activity and more of a collaboration.
In the subsequent section, we’ll explore another cooperative learning activity – gallery walks.
6. Gallery Walks
Let’s take a stroll through the gallery and explore how we can learn and engage with our peers in a fun and interactive way. Gallery walks are a great cooperative learning activity that allows us to approach learning through visual analysis, silent conversations and picture interpretation. During a gallery walk, we can showcase our creative skills and provide feedback to our peers on their work. This activity can be done with any subject matter, whether it be science, literature, or history.
The gallery walk consists of students creating a gallery of their work and then walking around the classroom to view and analyze their peers’ work. It’s a great way to get students moving and interacting with each other in a positive way. Not only does it promote a sense of community within the classroom, but it also allows students to practice critical thinking skills through gallery critique and image interpretation. As we participate in this activity, we can gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter and learn from our peers. Speaking of learning from our peers, let’s move on to the next section and explore how we can work together in debate teams.
7. Debate Teams
If you want to truly understand a subject and challenge your own beliefs, join a debate team and engage in lively discussions with your peers. Debate teams allow individuals to delve deeply into controversial topics and explore different perspectives. Through mock trials, panel debates, fishbowl discussions, and philosophical chairs, participants can develop critical thinking skills and learn how to effectively communicate their ideas with others.
Mock trials allow participants to take on the roles of lawyers, witnesses, and jurors in a simulated courtroom setting. Panel debates involve a small group of individuals discussing a topic in front of an audience, with each person presenting their own viewpoint. Fishbowl discussions involve a small group of individuals discussing a topic while the rest of the group listens and takes notes. Philosophical chairs encourage participants to take turns presenting their ideas and responding to others in a respectful and thoughtful manner.
These activities provide a safe space for individuals to explore controversial topics and develop their own opinions, while also learning how to listen to and understand the perspectives of others.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about ‘role play’, individuals can also develop empathy and understanding through participating in role play activities.
8. Role Play
The Role Play section of cooperative learning activities offers an immersive and interactive way to develop empathy and understanding. Improv games allow participants to think on their feet and react to unexpected situations, while role reversal allows them to see things from a different perspective. Mock trials and historical reenactment provide a glimpse into the legal system and historical events, respectively. Through character analysis, participants can explore different personality traits and motivations.
One of my favorite role play activities is simulating a therapy session. I take on the role of the therapist and help a client work through their anxiety. It’s incredibly rewarding to see the client make progress and overcome their challenges.
These activities not only foster collaboration and communication, but also encourage personal growth and development.
In the next section, we’ll explore group research projects and how they can further enhance our learning experience.
9. Group Research Projects
Group research projects provide an opportunity for collaborative analysis, group exploration, team discovery, joint investigation, and collective examination. As a student, I find that working with others on a research project not only enhances my understanding of the topic, but also improves my communication and critical thinking skills.
Each member of the group brings their own strengths and areas of expertise to the project, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. Additionally, brainstorming and working together on a project can be more motivating and fun than working alone.
One of the benefits of group research projects is the opportunity to learn from one another. Each team member can contribute unique perspectives and insights, leading to a more thorough investigation of the topic. Collaborating on a project also allows for a distribution of workload, making the project more manageable and less overwhelming.
Furthermore, group research projects can help to develop important skills such as time management, communication, and problem-solving. Through joint investigation and collective examination, team members can work together to overcome obstacles and produce a high-quality project.
Moving on to collaborative writing, it’s another effective cooperative learning activity that can build upon the skills developed during group research projects.
10. Collaborative Writing
You can enhance your writing skills by collaborating with others in order to produce a more engaging and effective final product. Collaborative outlining is a great way to start a writing project. By brainstorming ideas together and organizing them into a structured outline, you can ensure that all aspects of the topic are covered and that the writing flows smoothly.
Joint blogging is another effective way to collaborate on writing. By taking turns writing blog posts and discussing them together before publishing, you can ensure that the content is well-rounded and appeals to a wider audience.
Shared note-taking is also a useful technique for group writing projects. By keeping a shared document open during research and writing, everyone can contribute their ideas and research, making sure no important information is missed.
Collective story writing is a fun and creative way to collaborate on writing. Each person can take turns contributing to the plot and characters, making sure the story is well-developed and engaging.
Finally, team editing is essential for any writing project. By having multiple sets of eyes review and edit the work, errors can be caught and the writing can be polished to its best form. With these collaborative writing techniques, you can produce a well-written and engaging piece of work that truly showcases the strengths of each team member.
Now, let’s move on to the next section about problem-based learning.

11.Problem-Based Learning
If you’re feeling stuck in your writing and want to challenge yourself to think critically and solve problems creatively, problem-based learning may be just the approach you need to take your skills to the next level.
Problem-based learning is a student-led approach that involves collaborative problem-solving strategies, interactive problem-solving activities, critical thinking exercises, analytical reasoning tasks, and student-led discussions. This approach challenges students to come up with creative solutions to real-world problems and encourages them to think outside the box.
By working together, students can learn from each other’s strengths and weaknesses, and develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Here are five ways that problem-based learning can benefit you:
- It encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- It promotes student engagement and active learning.
- It fosters collaboration and teamwork.
- It helps students develop analytical reasoning skills.
- It prepares students for real-world problem-solving challenges.
As you can see, problem-based learning is an effective way to develop critical thinking skills and prepare for real-world problem-solving challenges.
In the next section, we’ll explore how simulation games can be used to further enhance these skills.
12. Simulation Games
Get ready to level up your problem-solving skills with simulation games! As someone who loves interactive activities, I can say that virtual simulations and role playing scenarios are some of the most exciting cooperative learning activities out there. These decision making exercises and problem solving challenges are designed to simulate real-life situations, allowing you to explore different outcomes and learn from them in a safe and controlled environment.
To give you a better idea of what to expect, here’s a table that highlights the benefits of simulation games:
As you can see, simulation games offer a range of benefits that cater to different learning styles and levels. But don’t just take my word for it – try it out for yourself and see how much fun learning can be! Now, let’s move on to our next topic: case studies.
13. Case Studies
In the world of education, case studies are like a puzzle waiting to be solved. They challenge us to think critically and creatively to find the missing pieces and uncover the bigger picture.
Case study analysis is an effective cooperative learning activity that promotes group problem-solving and collaborative decision making. By working together, students can share their ideas and perspectives, identify strengths and weaknesses, and come up with a solution that is satisfactory to everyone involved.
Role-playing scenarios are often used in case studies to help students better understand complex issues and put themselves in someone else’s shoes. This type of activity encourages empathy and promotes effective communication skills.
Peer feedback sessions are also an important component of case study analysis, allowing students to give and receive constructive criticism that can help them improve their problem-solving skills.
Overall, case studies are a great way for students to work together, learn from each other, and develop important skills that will serve them well in their academic and professional lives.
Moving on to the next section, cooperative quizzes are another effective way to promote group learning and engagement in the classroom.
14. Cooperative Quizzes
Cooperative quizzes are an excellent method for students to collaborate and enhance their understanding of the material. Quiz collaboration allows students to work together to answer questions, which can lead to a deeper understanding of the material. Here are four reasons why cooperative quizzes are beneficial:
- Team Trivia: Students work together in teams to answer trivia questions. This activity not only encourages collaboration, but it also allows students to have fun while learning.
- Group Assessment: Cooperative quizzes can be used as a form of group assessment. Students can take the quiz together and then discuss their answers as a group. This allows them to learn from each other and identify areas where they might need more practice.
- Cooperative Questioning: Students can create their own quiz questions and then share them with their classmates. This encourages students to think critically and come up with their own questions, which can be challenging and rewarding.
- Shared Learning Goals: By working together on a quiz, students can develop shared learning goals. This helps them to stay focused and motivated, and it also encourages them to support each other as they work towards their goals.
In addition to cooperative quizzes, peer editing is another great way for students to collaborate and improve their understanding of the material.
15. Peer Editing
You’ll love how working together to improve each other’s writing can enhance your skills and lead to better results in the classroom. Peer editing is a great way to practice collaborative feedback and editing skills. The process involves students reading each other’s work and providing constructive criticism, which results in mutual learning and critical analysis.
Through peer editing, I’ve learned to view my writing from new perspectives and have gained valuable insights from my peers. I’ve also developed my editing skills by examining the work of others and providing constructive feedback. Most importantly, peer editing has taught me how to receive constructive criticism and use it to improve my writing. Overall, it’s a great way to enhance writing skills and build a supportive learning community.
Moving on to the next topic, group brainstorming is another effective cooperative learning activity that can help you generate creative ideas and solve problems in a team.
16. Group Brainstorming
Get ready to unleash your creativity and collaborate with your peers through dynamic group brainstorming sessions that will leave you feeling energized and inspired.
Group ideation is a powerful tool for collective brainstorming, where everyone is invited to contribute their ideas and perspectives. Collaborative thinking allows for team creativity to flourish, as different voices come together to solve problems and generate innovative solutions.
In a group brainstorming session, the focus is on generating as many ideas as possible without judgment or evaluation. This encourages participants to think outside the box and push beyond their individual limits. Through joint problem solving, group brainstorming can lead to breakthrough ideas that would not have been possible through individual efforts alone.
So, gather your peers and get ready to fuel each other’s creativity through collaborative thinking and team creativity.
Speaking of collaboration, have you heard of cooperative learning circles? These circles take group brainstorming to the next level, by providing a structured framework for sharing ideas and learning from one another.
17. Cooperative Learning Circles
Ready to take your group brainstorming to the next level? Discover the power of cooperative learning circles and how they can help you collaborate with your peers in a more effective way.
Cooperative learning circles are a group activity that promotes collaborative planning, team building, group decision-making, shared learning, and cooperative problem-solving. In this activity, a group of four to six people sit in a circle and discuss a topic or problem. Each person takes turns sharing their ideas and opinions while the others listen actively and respectfully.
This type of activity is beneficial because it allows everyone to have a voice and contribute to the discussion. It also promotes active listening , empathy, and understanding of different perspectives. Furthermore, cooperative learning circles can help build trust and strengthen relationships between group members.
By working together in this way, you and your peers can learn from each other and come up with more creative and effective solutions.
Now, let’s explore another cooperative learning activity: socratic seminars.
18. Socratic Seminars
In the Socratic Seminars, you’ll delve deep into thought-provoking discussions with your peers, challenging each other’s perspectives and ideas to gain a deeper understanding of complex topics.
Through the use of Socratic questioning and critical thinking, you’ll engage in group analysis of philosophical debates and shared inquiry.
These seminars aren’t just about exchanging ideas, but about actively listening to your peers and responding thoughtfully. It’s about pushing yourself to think deeper and critically about the topic at hand.
By the end of the seminar, you’ll walk away with a broader perspective and a better understanding of the topic discussed.
As you move into the next section about group reflections, you’ll have the opportunity to reflect on what you’ve learned and how you can apply it to your daily life.
19. Group Reflections
Let’s dive into group reflections, where we’ll take a moment to reflect on our thought-provoking discussions from the Socratic Seminars and explore how we can apply our newfound understanding to our daily lives.
Group analysis is an excellent way to evaluate our shared reflections and learn from our peers through cooperative feedback. Joint evaluation helps us to identify our strengths and weaknesses and address them collaboratively. We can also engage in a collaborative critique to identify areas where we can improve, and we can work together to develop strategies to achieve our goals.
Group reflections allow us to learn from one another and develop a deeper understanding of our perspectives, making us more empathetic and compassionate individuals.
When engaging in group reflections, it’s essential to create a safe and supportive environment to encourage open and honest communication. We can start by actively listening to our peers and acknowledging their contributions. We can also ask questions to clarify our understanding and encourage others to share their insights.
Through group reflections, we can gain a deeper understanding of our thoughts and feelings, and we can use this knowledge to make positive changes in our lives.
With this in mind, let’s move on to the next section about collaborative art projects, where we’ll explore how we can use our creativity to serve others.
20. Collaborative Art Projects
After reflecting on our group dynamics, I realized that creating art together could be a fun and productive way to foster collaboration. Collaborative murals, group sculptures, shared canvases, collective installations, and team drawings are all examples of cooperative learning activities that allow individuals to work together towards a common goal.
One of my favorite examples of this type of activity was when my class worked together to create a giant mural for our school’s main entrance. Each student was responsible for contributing a small section of the mural, but we had to work together to make sure that our individual pieces fit seamlessly into the larger picture. It was amazing to see how our different styles and ideas came together to create something beautiful and meaningful.
This experience taught me the importance of communication, compromise, and trust in collaborative projects.
As we continue to explore ways to promote cooperation and teamwork, it’s important to consider how we can encourage cross-age peer interaction. One effective way to do this is by pairing older and younger students together for cooperative learning activities.
21. Cross-Age Peer Interaction
The benefits of cross-age peer interaction are clear, as research shows that students who participate in these types of partnerships have higher academic achievement and improved social skills.
Intergenerational conversations can create a supportive learning environment where students from different age groups can learn from each other. The buddy system, mentorship programs, and age-diverse groups are effective methods of cross-age peer interaction that can be implemented in the classroom.
Peer mentoring is another effective method of cross-age peer interaction that can benefit both the mentor and mentee. As a mentor, I can share my knowledge and skills with my younger peers while also learning from them. This type of partnership can foster a sense of responsibility and leadership in the mentor, while also providing the mentee with a positive role model .
Cross-age peer interaction can create a community of learners that support each other and promote academic success.
Now, let’s move on to the next section about co-teaching.
22. Co-Teaching
In the previous subtopic, we discussed the benefits of cross-age peer interaction in cooperative learning activities. Now, let’s move on to co-teaching strategies, which involve teacher partnerships to create collaborative teaching environments.
Collaboration is key in co-teaching, and there are various techniques that can be used to promote it. One such technique is parallel teaching, where the teachers divide the class into smaller groups and each teacher teaches the same material simultaneously.
Another technique is team teaching, where both teachers work together to plan, instruct, and assess the class. Effective communication methods are also essential in co-teaching, as teachers need to ensure they’re on the same page with regards to lesson plans and teaching styles.
Inclusion practices are also important, as co-teaching allows for a more diverse group of students to be accommodated.
Here are five co-teaching strategies that can help promote collaboration and inclusion in the classroom:
- Parallel teaching
- Team teaching
- Station teaching
- One teach, one observe
- One teach, one assist
Co-teaching can be an effective way to improve student learning outcomes and promote collaboration among teachers. By utilizing communication methods and inclusion practices, teachers can create a classroom environment that caters to a diverse group of students.
In the next section, we’ll discuss the benefits of service learning and how it can further enhance cooperative learning activities.
23. Service Learning
Service learning offers a unique opportunity for students to engage with their community and develop practical skills while making a positive impact. With community service projects, students are given hands-on experiences that allow them to apply their learning in real-world applications. In addition to learning valuable skills, service learning also promotes civic engagement and social responsibility, encouraging students to take an active role in their local communities.
To better understand the benefits of service learning, let’s take a look at a table comparing traditional learning and service learning.
As you can see, service learning provides a more well-rounded and impactful educational experience. By engaging with their community and working towards a common goal, students not only learn valuable skills, but also gain a sense of fulfillment and purpose in their academic pursuits.
Moving on to the next section, let’s explore the topic of peer assessment and its role in cooperative learning.
24. Peer Assessment
Peer assessment allows me to take ownership of my own learning and develop valuable skills in evaluating my peers. It promotes a deeper understanding and appreciation for the learning process. Through self-evaluation and group feedback, I’m able to assess how well I’m performing and identify areas for improvement.
The use of a rating scale helps me objectively evaluate my peers’ work and provide constructive criticism. Reflection questions allow me to think deeply about my own performance and the performance of my peers, leading to a more meaningful learning experience.
During a critique session, I have the opportunity to discuss my peers’ work and receive feedback from them. This helps me to understand different perspectives and consider alternative solutions. Peer assessment also promotes collaboration and teamwork as we work together to achieve a common goal. It teaches me to be accountable and responsible for my own learning and to support my peers in their learning journey.
Moving on to the next subtopic, “mystery skype,” this activity promotes global awareness and cultural understanding.
25. Mystery Skype
Mystery Skype is a fun and engaging way for students to learn about different cultures and countries. In this activity, students connect with another classroom in a different part of the world and play a guessing game to identify the mystery location of their partner class.
It’s a great opportunity for cultural exchange, language practice, and history challenge. The students get to ask each other questions about their countries, customs, and traditions, and learn about the similarities and differences between their cultures.
Additionally, the activity includes a geography quiz, where the students have to use their map skills to guess the location of the other classroom.
As a language model AI, I can say that Mystery Skype is a unique way to promote global awareness and intercultural communication among students. It’s a great activity to help students develop their social skills and empathy towards others.
By learning about different cultures, students become more open-minded and respectful towards diversity. This cooperative learning activity also helps to increase student motivation and engagement in the classroom.
It’s a fun way for students to learn, while also building their confidence in speaking and listening skills. Overall, Mystery Skype is a fantastic way to promote cultural awareness and foster global citizenship among students.
Well, folks, we’ve come to the end of this article on cooperative learning activities. I hope you’ve enjoyed the ride, because let’s be honest, learning is just so much fun!
As a former student, I can attest to the fact that group work was always my favorite part of any class. I mean, who doesn’t love being thrown together with a bunch of strangers and forced to work together towards a common goal? It’s like a team-building exercise on steroids!
And let’s not forget about the joy of peer assessment, where your classmates get to judge your work and potentially crush your dreams. Ah, good times.
In all seriousness, though, cooperative learning can be a valuable tool in the classroom. It allows students to learn from each other, practice communication and collaboration skills, and gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
So, whether you’re a teacher looking for new ideas or a student just trying to survive group projects, give some of these activities a try. Who knows, you might just learn something!
About the author
Latest posts
Enhancing classroom communication with visual aids.
As a teacher, I’ve noticed that students often lose interest quickly. However, when I use visual aids in my lessons, the classroom becomes much more engaging. I want to share with you 15 effective ways that visual aids have made learning more exciting. These tools, which include interactive whiteboards and detailed mind maps, do more…
Boosting Student Participation: 13 Communication Tips for Success
As an educator, my goal is to find effective ways to increase student participation in the classroom. It’s important to understand that communication plays a crucial role in engaging students. In this article, I will share 13 communication tips that have proven to be successful in creating a positive classroom environment and fostering open dialogue…
Why Is Empathy Essential for Effective Classroom Communication?
Empathy is really important when we talk with our students. When we understand how they feel, it helps remove barriers and makes learning easier. Empathy builds trust, makes the classroom a supportive place, and gets students truly involved. When we pay attention to each student’s specific situation and treat them with respect, we’re doing more…
- By use case
- AI assisted videos
- Advertising video
- Animated video
- Animated logo video
- Animated text video
- Animation video
- Cartoon video
- Commercial video
- Business video
- Explainer video
- Infographic video
- Intro video
- Movie maker
- Photo to video
- Presentation video
- Short videos
- Trailer video
- Book trailer video
- YouTube video
- Diverse Workplace Scenes
- Leadership Skills Tips
- A Reason to Celebrate
- Frank Character Explainer
- Superpowers Girl
- Robot Character Explainer
- Team Birthdays
- Birthday Cake
- Birthday Calendar
- Birthday Greetings
- Funny Birthday
- Staff Birthday
- Workplace Announcement
- Business Explainer
- Employee Onboarding
- Business Ad
- Hybrid Work Policy
- Workplace Wellness Tips
- Explainer Script
- How to Change Your Password
- Snappy Explainer
- Mental Health for Employees
- Product Explainer
- E-Learning App Ad
- Infographics
- Industry Trend Update
- Real Estate Infographic
- Marketing Infographic
- Animated Infographics
- Infographic Explainer
- Infographic
- Introductions
- New Teammate
- New Employee Introduction
- Welcome New Team Member
- Warm Welcome
- New Team Members
- Meet the Team
- We're Hiring Manager
- Recruiting Ad
- We're Hiring IT Support
- Video Resume
- Now Hiring Product Engineer
- Job Offer Congratulations
- Dancing People Ad
- Eager Dog Ad
- Winter Sale
- Funky Sloth Ad
- Product Promo
- Book Trailer
- Thanks Group
- You Rock Employee
- Great Job Team
- You Rock Team
- Great Job Employee
- Great Job Group
- Weekly Update
- Company Update
- Product Launch
- Monthly Update
- News Update
- Year in Review
Ready to get started?
- Video Trimmer
- Remove audio from video
- Add music to video
- Add text to video
- Video merger
- Video resizer
- Convert image to video
- Montage maker
- Add image to video
- Watermark maker
- Add frame to video
- Video analytics
- Add button to video
- Image Resizer
- Convert video to GIF
- Convert GIF to MP4
- Extract audio from video
- Quick start guide
- Education , Inspiration
15 creative video project ideas for students (and their teachers)

Fall is here. The leaves are starting to change color and teachers everywhere are asking the same question: How do I come up with video project ideas for my students?
Video has been a staple learning tool for decades. But having students create, design, and edit video projects themselves is becoming a much more common classroom activity. Video projects are a great way to help students of all ages actively engage with subject matter and learn from one another.
Online apps like Biteable make it easy for students to turn video ideas for school into a reality. Templates and easy-to-use editing tools keep the process simple and offer plenty of inspiration for student video projects.
To help teachers and students alike leverage video as an educational tool , we’ve gathered our favorite creative video project ideas for students. Each idea comes with a ready-to-edit video template so you and your students can get started right away.
Create videos that drive action
Activate your audience with impactful, on-brand videos. Create them simply and collaboratively with Biteable.
Elementary student video project ideas
It can be tricky to keep young students interested and engaged all day long. Creating videos gives elementary students a fun, creative way to learn about anything. And student-created videos are an amazing classroom learning supplement. If a video is produced by their peers, interest will skyrocket.
1. Create a book trailer
Instead of a traditional book report, have students design a movie-style trailer that drums up excitement about a novel or a non-fiction book. Creating a book trailer gives students the opportunity to think creatively, share a story with their classmates, and reinforce their learning in a new way.
2. Give a video tour
To supplement social studies curriculum, students can create a video showing off a significant location or their favorite part of the school. If you have a field trip planned, ask students to share their experience by recording videos throughout the day and adding voice over narration.
A video tour of the school is also a great way to share the campus with new students and visitors. As a way to pass the torch before they leave for middle school, how about asking your fifth graders to collaborate on an orientation video for incoming kindergarteners?
3. Celebrate the holidays
There’s always something to celebrate, no matter what time of year it is. Have students film letters to Santa, make video Valentines for parents or grandparents, or make short educational videos about lesser known holidays. Students can even create simple, digital thank-you notes for classroom visitors or parent volunteers.
4. Recreate a moment in history
Learning about historical people and events? Have your students research and recreate major moments in history, like the story of Rosa Parks or the Oregon Trail.
Videos help students visualize and remember these important moments. It also gives students the opportunity to experiment with digital storytelling. And students will be challenged to bring each scene to life accurately.
5. Try stop-motion video
Video learning isn’t limited to literary or historical topics. Encourage students to use stop-motion or create their own slides to explain science experiments or other STEM projects. With the right footage, like Biteable’s extensive collection of clay animation footage, students won’t even need to build stop motion models. They can just focus on the presentation and storytelling in their video.
Video project ideas for middle and high school students
Video projects for high schoolers can be a little more advanced, as students should be practicing editing and narrative skills in addition to learning about new topics.
6. Create a news channel
To supplement learning in a current events class, have your students film a news broadcast covering both local and international events.
Ask students to take on certain roles in the newsroom: anchor, sports reporter, weather reporter, or entertainment correspondent. Doing a news segment helps everyone get involved and promotes teamwork.
7. Start a portfolio
Many high school students are thinking about college applications. Give them the chance to jumpstart their applications with a portfolio video project and showcase what makes them unique.
Art students can show off their best work and design skills. Students applying to traditional schools can answer an application question or create a video showcasing their community service and extracurriculars.
8. Promote a good cause
Rather than writing a traditional essay or report, have students create a video advocating for a cause that’s important to them. This helps students build their identity and develop persuasive skills. And students can share their promotional video with everyone, not just their teacher and classmates.
9. Questions for your future self
Think ahead with a video full of inspiring questions. This project is great for incoming freshmen. At the beginning of the year, have students create videos with questions for their future self or with goals for their life and career. At graduation, send the videos back to them. It’s a fun, positive way to celebrate their success throughout high school.
Higher ed video project ideas
Higher education might not seem like the place for student-made videos. But in the real world, businesses use video for all sorts of things. Video projects build plenty of resume-worthy skills that college students can take with them to the workforce.
10. Create a university promotion video
It’s easy to forget that colleges and universities are businesses, too. And they need help with promotion. A solid college or university promotion video could open opportunities for internships or college employment. Promoting something that they’re already familiar with is a great way for students to build video persuasion skills.
11. Record and edit interviews
Being able to conduct a good interview and edit it in a way that’s appropriate for the purpose of the interview is a valuable skill in multiple industries. And interviewing experts in the field is appropriate for just about any class.
12. Make a video self-assessment
Grades are important. But being able to self-assess is also an incredibly valuable way for students to incrementally improve at any skill.
Making video self-assessments gives students a more active role in the grading process and offers them a creative way to highlight the work they’ve put into a course. It also gives them a chance to make an argument for the grade they feel they deserve — a skill that easily correlates to performance reviews in their future workplace.
13. Film a job interview guide
For most people, the interview is the most nerve-wracking part of getting a job. Practicing interview questions is a great way to prepare. But most students don’t know how to prepare for a job interview.
Creating a job interview how-to guide is a perfect way for students to learn how to prepare for a job interview and help other students prepare at the same time.
14. Create a video presentation based on a written assignment
Written assignments are the backbone of a university education (in most disciplines, at least). However, the audience for most written assignments is limited to the professor and assistants. Creating presentation videos for their assignments gives students the opportunity to share their hard work with their fellow students, while also learning valuable video editing skills.
15. Build a video resume
For most students, the job search starts even before graduation. A video resume helps students highlight the skills they acquired and the experience they gained during college. And, given the global workforce, a video resume is a great supplement to a paper resume, especially when applying for remote or distant positions where an in-person interview may not be an option.
Take your video project from idea to reality with Biteable
Ready to get started making an education video project ?
Biteable has a huge library of video templates that help students get going fast rather than struggling to start from a blank screen. Drag-and-drop editing and easy to use tools let students focus on what’s important: the project assignment and delivering a thoughtful message.
Make stunning videos with ease.
Take the struggle out of team communication.
Try Biteable now.
- No credit card required
- No complicated design decisions
- No experience necessary
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
Designing Assessments of Student Learning
Image Hollie Nyseth Brehm, Associate Professor, Department of Sociology Professor Hollie Nyseth Brehm was a graduate student the first time she taught a class, “I didn’t have any training on how to teach, so I assigned a final paper and gave them instructions: ‘Turn it in at the end of course.’ That was sort of it.” Brehm didn’t have a rubric or a process to check in with students along the way. Needless to say, the assignment didn’t lead to any major breakthroughs for her students. But it was a learning experience for Brehm. As she grew her teaching skills, she began to carefully craft assignments to align to course goals, make tasks realistic and meaningful, and break down large assignments into manageable steps. "Now I always have rubrics. … I always scaffold the assignment such that they’ll start by giving me their paper topic and a couple of sources and then turn in a smaller portion of it, and we write it in pieces. And that leads to a much better learning experience for them—and also for me, frankly, when I turn to grade it .”
Reflect
Have you ever planned a big assignment that didn’t turn out as you’d hoped? What did you learn, and how would you design that assignment differently now?
What are students learning in your class? Are they meeting your learning outcomes? You simply cannot answer these questions without assessment of some kind.
As educators, we measure student learning through many means, including assignments, quizzes, and tests. These assessments can be formal or informal, graded or ungraded. But assessment is not simply about awarding points and assigning grades. Learning is a process, not a product, and that process takes place during activities such as recall and practice. Assessing skills in varied ways helps you adjust your teaching throughout your course to support student learning

Research tells us that our methods of assessment don’t only measure how much students have learned. They also play an important role in the learning process. A phenomenon known as the “testing effect” suggests students learn more from repeated testing than from repeated exposure to the material they are trying to learn (Karpicke & Roediger, 2008). While exposure to material, such as during lecture or study, helps students store new information, it’s crucial that students actively practice retrieving that information and putting it to use. Frequent assessment throughout a course provides students with the practice opportunities that are essential to learning.
In addition we can’t assume students can transfer what they have practiced in one context to a different context. Successful transfer of learning requires understanding of deep, structural features and patterns that novices to a subject are still developing (Barnett & Ceci, 2002; Bransford & Schwartz, 1999). If we want students to be able to apply their learning in a wide variety of contexts, they must practice what they’re learning in a wide variety of contexts .
Providing a variety of assessment types gives students multiple opportunities to practice and demonstrate learning. One way to categorize the range of assessment options is as formative or summative.
Formative and Summative Assessment
Opportunities not simply to practice, but to receive feedback on that practice, are crucial to learning (Ambrose et al., 2010). Formative assessment facilitates student learning by providing frequent low-stakes practice coupled with immediate and focused feedback. Whether graded or ungraded, formative assessment helps you monitor student progress and guide students to understand which outcomes they’ve mastered, which they need to focus on, and what strategies can support their learning. Formative assessment also informs how you modify your teaching to better meet student needs throughout your course.
Technology Tip
Design quizzes in CarmenCanvas to provide immediate and useful feedback to students based on their answers. Learn more about setting up quizzes in Carmen.
Summative assessment measures student learning by comparing it to a standard. Usually these types of assessments evaluate a range of skills or overall performance at the end of a unit, module, or course. Unlike formative assessment, they tend to focus more on product than process. These high-stakes experiences are typically graded and should be less frequent (Ambrose et al., 2010).
Using Bloom's Taxonomy
![assignment activities examples A visual depiction of the Bloom's Taxonomy categories positioned like the layers of a cake. [row 1, at bottom] Remember; Recognizing and recalling facts. [Row 2] Understand: Understanding what the facts mean. [Row 3] Apply: Applying the facts, rules, concepts, and ideas. [Row 4] Analyze: Breaking down information into component parts. [Row 5] Evaluate: Judging the value of information or ideas. [Row 6, at top] Create: Combining parts to make a new whole.](https://teaching.resources.osu.edu/sites/default/files/styles/max_960x960/public/2023-08/BloomsTaxonomy.jpeg?itok=1BcPgz2m)
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a common framework for thinking about how students can demonstrate their learning on assessments, as well as for articulating course and lesson learning outcomes .
Benjamin Bloom (alongside collaborators Max Englehart, Edward Furst, Walter Hill, and David Krathwohl) published Taxonomy of Educational Objectives in 1956. The taxonomy provided a system for categorizing educational goals with the intent of aiding educators with assessment. Commonly known as Bloom’s Taxonomy, the framework has been widely used to guide and define instruction in both K-12 and university settings. The original taxonomy from 1956 included a cognitive domain made up of six categories: Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation. The categories after Knowledge were presented as “skills and abilities,” with the understanding that knowledge was the necessary precondition for putting these skills and abilities into practice.
A revised Bloom's Taxonomy from 2001 updated these six categories to reflect how learners interact with knowledge. In the revised version, students can: Remember content, Understand ideas, Apply information to new situations, Analyze relationships between ideas, Evaluate information to justify perspectives or decisions, and Create new ideas or original work. In the graphic pictured here, the categories from the revised taxonomy are imagined as the layers of a cake.
Assessing students on a variety of Bloom's categories will give you a better sense of how well they understand your course content. The taxonomy can be a helpful guide to predicting which tasks will be most difficult for students so you can provide extra support where it is needed. It can also be used to craft more transparent assignments and test questions by honing in on the specific skills you want to assess and finding the right language to communicate exactly what you want students to do. See the Sample Bloom's Verbs in the Examples section below.
Diving deeper into Bloom's Taxonomy
Like most aspects of our lives, activities and assessments in today’s classroom are inextricably linked with technology. In 2008, Andrew Churches extended Bloom’s Taxonomy to address the emerging changes in learning behaviors and opportunities as “technology advances and becomes more ubiquitous.” Consult Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy for ideas on using digital tools to facilitate and assess learning across the six categories of learning.
Did you know that the cognitive domain (commonly referred to simply as Bloom's Taxonomy) was only one of three domains in the original Bloom's Taxonomy (1956)? While it is certainly the most well-known and widely used, the other two domains— psychomotor and affective —may be of interest to some educators. The psychomotor domain relates to physical movement, coordination, and motor skills—it might apply to the performing arts or other courses that involve movement, manipulation of objects, and non-discursive communication like body language. The affective domain pertains to feelings, values, motivations, and attitudes and is used more often in disciplines like medicine, social work, and education, where emotions and values are integral aspects of learning. Explore the full taxonomy in Three Domains of Learning: Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor (Hoque, 2017).
In Practice
Consider the following to make your assessments of student learning effective and meaningful.
Align assignments, quizzes, and tests closely to learning outcomes.
It goes without saying that you want students to achieve the learning outcomes for your course. The testing effect implies, then, that your assessments must help them retrieve the knowledge and practice the skills that are relevant to those outcomes.
Plan assessments that measure specific outcomes for your course. Instead of choosing quizzes and tests that are easy to grade or assignment types common to your discipline, carefully consider what assessments will best help students practice important skills. When assignments and feedback are aligned to learning outcomes, and you share this alignment with students, they have a greater appreciation for your course and develop more effective strategies for study and practice targeted at achieving those outcomes (Wang, et al., 2013).

Provide authentic learning experiences.
Consider how far removed from “the real world” traditional assessments like academic essays, standard textbook problems, and multiple-choice exams feel to students. In contrast, assignments that are authentic resemble real-world tasks. They feel relevant and purposeful, which can increase student motivation and engagement (Fink, 2013). Authentic assignments also help you assess whether students will be able to transfer what they learn into realistic contexts beyond your course.
Integrate assessment opportunities that prepare students to be effective and successful once they graduate, whether as professionals, as global citizens, or in their personal lives.
To design authentic assignments:
- Choose real-world content . If you want students to be able to apply disciplinary methods, frameworks, and terminology to solve real-world problems after your course, you must have them engage with real-world examples, procedures, and tools during your course. Include actual case studies, documents, data sets, and problems from your field in your assessments.
- Target a real-world audience . Ask students to direct their work to a tangible reader, listener or viewer, rather than to you. For example, they could write a blog for their peers or create a presentation for a future employer.
- Use real-world formats . Have students develop content in formats used in professional or real-life discourse. For example, instead of a conventional paper, students could write an email to a colleague or a letter to a government official, develop a project proposal or product pitch for a community-based company, post a how-to video on YouTube, or create an infographic to share on social media.
Simulations, role plays, case studies, portfolios, project-based learning, and service learning are all great avenues to bring authentic assessment into your course.
Make sure assignments are achievable.
Your students juggle coursework from several classes, so it’s important to be conscious of workload. Assign tasks they can realistically handle at a given point in the term. If it takes you three hours to do something, it will likely take your students six hours or more. Choose assignments that assess multiple learning outcomes from your course to keep your grading manageable and your feedback useful (Rayner et al., 2016).
Scaffold assignments so students can develop knowledge and skills over time.
For large assignments, use scaffolding to integrate multiple opportunities for feedback, reflection, and improvement. Scaffolding means breaking a complex assignment down into component parts or smaller progressive tasks over time. Practicing these smaller tasks individually before attempting to integrate them into a completed assignment supports student learning by reducing the amount of information they need to process at a given time (Salden et al., 2006).
Scaffolding ensures students will start earlier and spend more time on big assignments. And it provides you more opportunities to give feedback and guidance to support their ultimate success. Additionally, scaffolding can draw students’ attention to important steps in a process that are often overlooked, such as planning and revision, leading them to be more independent and thoughtful about future work.
A familiar example of scaffolding is a research paper. You might ask students to submit a topic or thesis in Week 3 of the semester, an annotated bibliography of sources in Week 6, a detailed outline in Week 9, a first draft on which they can get peer feedback in Week 11, and the final draft in the last week of the semester.
Your course journey is decided in part by how you sequence assignments. Consider where students are in their learning and place assignments at strategic points throughout the term. Scaffold across the course journey by explaining how each assignment builds upon the learning achieved in previous ones (Walvoord & Anderson, 2011).
Be transparent about assignment instructions and expectations.
Communicate clearly to students about the purpose of each assignment, the process for completing the task, and the criteria you will use to evaluate it before they begin the work. Studies have shown that transparent assignments support students to meet learning goals and result in especially large increases in success and confidence for underserved students (Winkelmes et al., 2016).
To increase assignment transparency:

- Explain how the assignment links to one or more course learning outcomes . Understanding why the assignment matters and how it supports their learning can increase student motivation and investment in the work.
- Outline steps of the task in the assignment prompt . Clear directions help students structure their time and effort. This is also a chance to call out disciplinary standards with which students are not yet familiar or guide them to focus on steps of the process they often neglect, such as initial research.
- Provide a rubric with straightforward evaluation criteria . Rubrics make transparent which parts of an assignment you care most about. Sharing clear criteria sets students up for success by giving them the tools to self-evaluate and revise their work before submitting it. Be sure to explain your rubric, and particularly to unpack new or vague terms; for example, language like "argue," “close reading,” "list significant findings," and "document" can mean different things in different disciplines. It is helpful to show exemplars and non-exemplars along with your rubric to highlight differences in unacceptable, acceptable, and exceptional work.
Engage students in reflection or discussion to increase assignment transparency. Have them consider how the assessed outcomes connect to their personal lives or future careers. In-class activities that ask them to grade sample assignments and discuss the criteria they used, compare exemplars and non-exemplars, engage in self- or peer-evaluation, or complete steps of the assignment when you are present to give feedback can all support student success.
Technology Tip
Enter all assignments and due dates in your Carmen course to increase transparency. When assignments are entered in Carmen, they also populate to Calendar, Syllabus, and Grades areas so students can easily track their upcoming work. Carmen also allows you to develop rubrics for every assignment in your course.
Sample Bloom’s Verbs
Building a question bank, using the transparent assignment template, sample assignment: ai-generated lesson plan.
Include frequent low-stakes assignments and assessments throughout your course to provide the opportunities for practice and feedback that are essential to learning. Consider a variety of formative and summative assessment types so students can demonstrate learning in multiple ways. Use Bloom’s Taxonomy to determine—and communicate—the specific skills you want to assess.
Remember that effective assessments of student learning are:
- Aligned to course learning outcomes
- Authentic, or resembling real-world tasks
- Achievable and realistic
- Scaffolded so students can develop knowledge and skills over time
- Transparent in purpose, tasks, and criteria for evaluation
- Collaborative learning techniques: A handbook for college faculty (book)
- Cheating Lessons (book)
- Minds online: Teaching effectively with technology (book)
- Assessment: The Silent Killer of Learning (video)
- TILT Higher Ed Examples and Resource (website)
- Writing to Learn: Critical Thinking Activities for Any Classroom (guide)
Ambrose, S.A., Bridges, M.W., Lovett, M.C., DiPietro, M., & Norman, M.K. (2010). How learning works: Seven research-based principles for smart teaching . John Wiley & Sons.
Barnett, S.M., & Ceci, S.J. (2002). When and where do we apply what we learn? A taxonomy for far transfer. Psychological Bulletin , 128 (4). 612–637. doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.128.4.612
Bransford, J.D, & Schwartz, D.L. (1999). Rethinking transfer: A simple proposal with multiple implications. Review of Research in Education , 24 . 61–100. doi.org/10.3102/0091732X024001061
Fink, L. D. (2013). Creating significant learning experiences: An integrated approach to designing college courses . John Wiley & Sons.
Karpicke, J.D., & Roediger, H.L., III. (2008). The critical importance of retrieval for learning. Science , 319 . 966–968. doi.org/10.1126/science.1152408
Rayner, K., Schotter, E. R., Masson, M. E., Potter, M. C., & Treiman, R. (2016). So much to read, so little time: How do we read, and can speed reading help?. Psychological Science in the Public Interest , 17 (1), 4-34. doi.org/10.1177/1529100615623267
Salden, R.J.C.M., Paas, F., van Merriënboer, J.J.G. (2006). A comparison of approaches to learning task selection in the training of complex cognitive skills. Computers in Human Behavior , 22 (3). 321–333. doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2004.06.003
Walvoord, B. E., & Anderson, V. J. (2010). Effective grading: A tool for learning and assessment in college . John Wiley & Sons.
Wang, X., Su, Y., Cheung, S., Wong, E., & Kwong, T. (2013). An exploration of Biggs’ constructive alignment in course design and its impact on students’ learning approaches. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , 38 (4). 477–491. doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2004.06.003
Winkelmes, M., Bernacki, M., Butler, J., Zochowski, M., Golanics, J., & Weavil, K.H. (2016). A teaching intervention that increases underserved college students’ success. Peer Review , 18 (1/2). 31–36. Retrieved from https://www.aacu.org/peerreview/2016/winter-spring/Winkelmes
Related Teaching Topics
A positive approach to academic integrity, creating and adapting assignments for online courses, ai teaching strategies: transparent assignment design, designing research or inquiry-based assignments, using backward design to plan your course, universal design for learning: planning with all students in mind, search for resources.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Examining Sample Assignment 1: Summary and Analysis
In this chapter and in the next three, I walk through example assignments and how you might analyze them to better understand your task.
This assignment comes from one of my first-year writing classes. It’s a fairly typical early assignment in my first-year writing classes, one that asks students to read a text and engage with it in some way. In this case, the readings include the same one I use as a model in the first section of this book , though the actual assignment differs a bit.
The ability to read critically and summarize accurately is a crucial academic skill. The ability to use ideas from one text to guide understanding in another text is similarly crucial. This assignment helps you practice both of these skills.
Your summary will need to explain the key concepts in Mitchell’s article and to explain the main points in the article that you choose to work with. In class, we will work specifically on critical reading strategies to understand how authors make claims and connect those claims to one another. We will also work on techniques for writing strong summaries that accurately represent an author’s work.
Your summaries of these texts should be between 300 and 400 words of your final paper.
In this part of your paper, you will make connections between Mitchell’s concepts and the specific situation described in the article you have chosen. Specifically, you must try to explain the situation in your article using the terms “segregated coexistence” and “living in community” as Mitchell explains them. Think about questions like the following:
- Does the article you have chosen describe a situation that could be considered “segregated coexistence”? If so, what is that situation and how well does it align with “segregated coexistence” as Mitchell describes it?
- Similarly, does the article you have chosen describe a situation that could be considered “living in community”? If so, what is that situation and how well does it align with “living in community” as Mitchell describes it?
- Are there ways in which Mitchell’s terms don’t apply or don’t cover the issue well enough? How so?
Note that this part of your paper should be between 400 and 500 words long, longer than your summaries. While accurately summarizing is important, readers at the college level are more interested in seeing your thinking, so this part should be longer than your summary.
When I comment on your summary and analysis, I will be looking to see how well you have met the goals of the assignment. That is, I will be looking for how accurately and thoroughly you have summarized the articles and how well you have explained and provided support for your analysis. If you only provide summaries of the articles without analysis, your project will not be successful. Instead, your project should demonstrate your critical reading and thinking skills.
Your summary and analysis will also need to meet the standard expectations of good college-level academic writing, which we will be working on during the term. Your purpose and focus will need to be clear and well explained. You will need to provide your reader with sufficient detail in your summary and your response so that your explanations are clear and thorough. You will also need to provide structural cues that enable your reader to follow the logic of your thinking. And your prose will need to be well written both stylistically and grammatically.
Examining the Verbs in Key Sentences
When I read this assignment, I find three key sentences that tell us what we’re supposed to do in this assignment.
Before going on, try to find the key sentences in the Summary and Analysis assignment. Then, read on to see if you agree with my choices.
Let’s look at them.
First Sentence for Examination
To start, there is a sentence summarizing the assignment at the top. Sentences pulled out like this are often important:
Summarize the ideas of “segregated coexistence” and “living in community” from Mitchell’s essay and analyze how those ideas apply to the situation described in an additional article (see sources below).
The verbs here are pretty direct: summarize and analyze.
- What are you summarizing? Mitchell’s ideas
- What are you analyzing? How those ideas apply to the situation in the second article you have chosen
Second Sentence for Examination
There’s another key sentence at the beginning of the “Summaries” section:
Your summary will need to explain the key concepts in Mitchell’s article and to explain the main points in the article that you choose to work with.
The verbs here are less helpful, at least until we look at the words around them.
When someone tells you that you “will need” to do something, you know that they mean that you “must” do it. If we substitute “must” for “will need,” we get a bit more help:
Your summary must explain the key concepts in Mitchell’s article and must explain the main points in the article that you choose to work with.
“Choose” is not terribly important for our purposes because it’s just identifying the second source that we are working with. “Explain,” however, seems to be very important.
Here we get a focus for our summary work:
- Explain the key concepts in Mitchell’s article (which have been identified in the first sentence we analyzed)
- Explain the main points in the article we’ve chosen
In this sentence, we have more detail about what “summarizing” looks like for this assignment.
Third Sentence for Examination
To understand the “analyzing” part of the assignment, we have a couple of sentences at the beginning of the “Analysis” section. I’m including two sentences since the second sentence begins with “specifically,” which indicates that it’s providing more detail about the first:
In this part of your paper, you will make connections between Mitchell’s concepts and the specific situation described in the article you have chosen . Specifically, you must try to explain the situation in your article using the terms “segregated coexistence” and “living in community” as Mitchell explains them.
These verbs require a bit of adjustment before our task will be clear. “Will make” doesn’t tell us much without the following word “connections,” without which we don’t know what we are making. However, “will make connections” can also be understood as simply “connect.” Here’s the sentence with this adjustment (eliminating a few more words to make the sentence grammatically correct:
In this part of your paper, you will connect Mitchell’s concepts and the specific situation described in the article you have chosen . Specifically, you must try to explain the situation in your article using the terms “segregated coexistence” and “living in community” as Mitchell explains them.
Similarly, “must try” doesn’t help us until we look at the words that tell us what we are trying to do. In this case, “must try to explain” is the idea we need to focus on. “Must try” in this sentence is an indication that our professor wants us to make effort, but explaining is really the work here:
In this part of your paper, you will connect Mitchell’s concepts and the specific situation described in the article you have chosen . Specifically, you must explain the situation in your article using the terms “segregated coexistence” and “living in community” as Mitchell explains them.
As with the sentence earlier, “have chosen” just indicates our second article, which is why I skipped that one.
The last “explains” is worth looking at in a bit more detail. In this case, the verb is not about your doing the explaining, but rather the fact that Mitchell has done some. From this sentence, we know that we must use the two identified terms in the same way that Mitchell does.
So, in the analysis part of our paper, we need to do the following:
- Connect Mitchell’s concepts, which we summarized in the summary section of the paper, to the situation in our second article.
- To do this effectively, we need to use Mitchell’s terms.
Applying Bloom
Having done this analysis, we now have a better sense of the intellectual work of this assignment:
- Summary Part 1: Explain Mitchell’s key ideas
- Summary Part 2: Explain the main points in our second article
- Analysis: Use Mitchell’s ideas to explain the situation in our second article.
Before jumping into the next section, take what you know about the task in the sample assignment and see which types of knowledge and which cognitive processes you believe the assignment is looking for.
After you read the rest of this chapter, decide whether or not you agree with my analysis.
Kinds of Cognitive Processes
First, the verbs.
The summary section of the assignment focused on explaining the key ideas in both articles. It can be helpful to move “up” the pyramid or the side of the grid with the cognitive processes to help us figure this out.
We aren’t being asked to remember, since we can look up the information, but we are being asked to understand both Mitchell’s concepts and the main points from the second article. Notice that on the grid version, summarizing appears at the intersection of factual knowledge and the cognitive process of understanding.
When we look at connections, though, “understanding” doesn’t seem to be enough. Yes, we have to understand, but we’re trying to make those connections (remember the original wording?), and “understanding” seems to be more about making sense of ideas that others have already put together.
The next step is “ applying .” If we look only at the grid, applying doesn’t seem to work, but the pyramids explain this one a bit differently. If applying means to “use information in new situations” or “use information in a new (but similar) form,” the term seems to work, right? The assignment asks us to use Mitchell’s terms to explain the situation in the second article. That sounds like an application to me!
But what about “analysis” in the title of the assignment? Look at the explanation of analyzing on the grid: “Break material into constituent parts and determine how parts relate to one another and to an overall structure of purpose.” Similarly, the pyramids describe analyzing as making connections and exploring relationships.
We aren’t doing this kind of work if we look only at Mitchell’s article; there, we are simply explaining what Mitchell means (i.e., summarizing). But when we get to the second article, we have to do more than just apply Mitchell’s terms. We have to divide up the ideas in that article into ideas that are connected to “segregated coexistence” and ideas that are connected to “living in community.”
To do this successfully, we need to explain how these connections work. This means that it’s not enough to identify specific ideas as either one or the other. We also need to make those connections clear to our reader. Those explanations are kinds of analysis .
The verbs in the assignment do not ask us to make arguments or critique ideas, so Bloom’s “evaluate” doesn’t apply in this assignment. Similarly, we aren’t really “creating” something new, beyond the vague idea that what we write should be in our own words for the most part. These two cognitive processes don’t apply much, if at all, here.
To summarize, looking at the verbs and assignment, we seem to be working in the cognitive realms of understanding, applying, and analyzing.
Kinds of Knowledge
While the verbs tell us about the cognitive processes that we are being asked to use, the examination of those key sentences can also help us focus on the information that we will need to complete the task. While much of this was obvious as we explored the verbs, I’ll break it down a bit here to complete the example.
In this case, we will need to know/understand the following:
- Mitchell’s key terms (“segregated coexistence” and “living in community”)
- The main ideas in our second article
- The connections between Mitchell’s concepts and the ideas in our second article
The first two would be factual knowledge, according to Bloom’s Taxonomy. We should be able to go to the article and find those ideas. We aren’t developing those terms or ideas; we are simply recording them. To do that, we have to understand them, but that’s a cognitive process, and we’ll come back to that in a minute.
The connections, however, aren’t factual. Our chosen article doesn’t use Mitchell’s terms directly, so we have to create those connections ourselves. If you look at the descriptions, you’ll see that this type of knowledge is called “ conceptual ,” which specifically is about organizing factual knowledge.
I don’t see anything here that is asking us to work with procedural (how to) knowledge or metacognition (thinking about thinking), so we are just working with the first two types of information.
Putting It Together
In this assignment, we are being asked to use factual and conceptual knowledge to understand, apply, and analyze.
The assignment comes in two parts. The first part is focused on summarizing Mitchell’s two key concepts and the main points from the second article. This part, then, stays firmly in the factual realm. We’re not supposed to talk about our opinions of any of these ideas or start making connections between them in this section. If we fail to present the factual information (e.g., we are missing one summary or the other; or we misread the article so our summary isn’t accurate), we will not succeed at this part. Also, because this is the more basic part of the assignment (lower on the pyramids and grid), if we don’t do this part accurately, odds are good that our analysis part won’t be as successful as we would like.
The second part, what the assignment calls “analysis,” is really a combination of applying and analyzing. We have to understand the main points, too, but mostly, we would do that in the first part of the assignment. In the “analysis,” we need to explain how the ideas in the second article can be categorized using Mitchell’s terms. We’re applying Mitchell, but we also have to explain if our assignment is going to be successful.
At this point, I have beaten this assignment into submission, but I’m hoping you can see the value in taking an assignment apart like this.
Reading and Writing Successfully in College: A Guide for Students Copyright © 2023 by Patricia Lynne is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Poetry Worksheet Bundle! Perfect for National Poetry Month.
30 Lesson Plan Examples for Every Grade Level and Subject
Lots of ways to prepare for top-notch learning.

Writing lessons might be a fun activity for you (all the things you’ll do!) or it may be a necessary evil (so many boxes to fill). Either way, it’s an important part of teaching and can make or break your week, month, and year. Whether you’re a brand-new teacher or an experienced educator looking for some new ideas, these lesson plan examples offer inspiration for every subject and every grade level.
Lesson Plan Sections
Preschool lesson plan examples, elementary school lesson plan examples, middle and high school lesson plan examples.
Many lesson plans include some or all of the following sections.
- Objective : These should be specific and measurable. Often they align with Common Core or other learning standards.
- Materials: List any items you’ll need, including worksheets or handouts, school supplies, etc.
- Activities: This is usually the longest section, where you’ll lay out what the lesson and its activities look like. Some teachers write these in great detail. Others include just an overview to help them plan.
- Assessment: How will you assess your students’ learning? This could be a formal assessment or something simple like an exit ticket. ( Get lots of formative assessment ideas here. )
- Differentiation: Describe how you’ll vary the level of difficulty for students at all levels, including any enrichment for early finishers.
Some people think preschool is just playtime, but pre-K teachers know better! Here are some of the ways preschool teachers plan for their lessons.
Weekly Lesson Plan
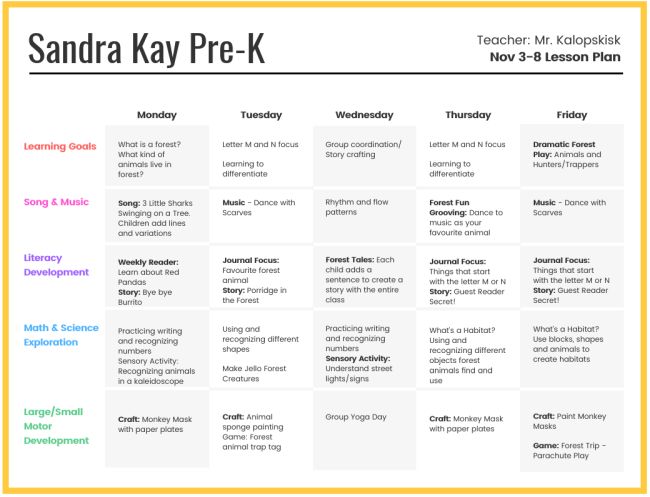
Venngage/pre-K lesson plan via Venngage.com
Weekly preschool lesson planning helps you plan each day and ensure you’re tackling all the most important skills.
Learn more: Venngage Pre-K Weekly Lesson Plan Template
Pre-K Theme Lesson Plan
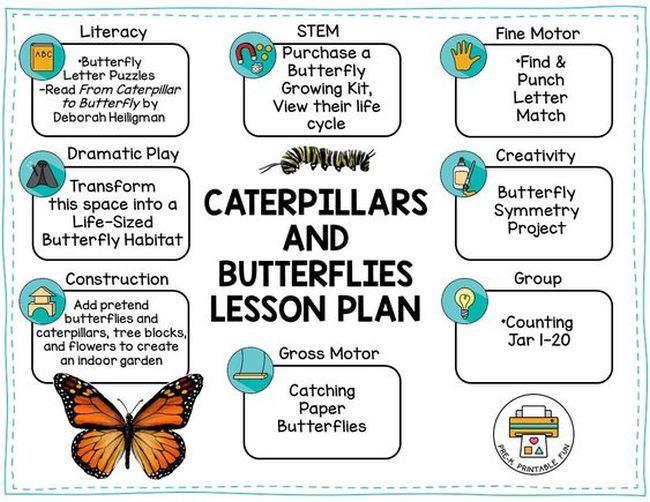
Pre-K Printable Fun/Caterpillar and Butterfly Lesson Plan via PreKPrintableFun.com
If you like to plan by theme, try a template like this. It includes space for a variety of activities that fit your topic.
Learn more: Pre-K Printable Fun
Alphabet Letter Lesson Plan
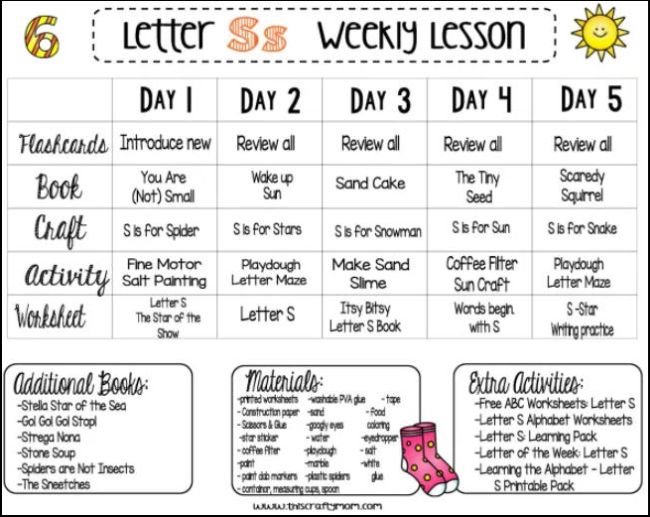
This Crafty Mom/Letter S Lesson Plan via ThisCraftyMom.com
If you’re focusing on a new letter of the alphabet each week, try lesson planning like this. You can see the week at a glance, including all the materials and books you’ll need.
Learn more: Alphabet Letter Lesson Plan by This Crafty Mom
Centers Lesson Plan

Pocket of Preschool/Centers Lesson Plans via PocketofPreschool.com
Your centers need some planning too! Whether you change them out weekly, monthly, or as needed, use plans like these to stay prepared.
Learn more: Pocket of Preschool
Weekly Unit Lesson Plan

This Crafty Mom/weather unit lessons via ThisCraftyMom.com
Adding pops of color and a few images can make it easier to locate the lesson plan you’re looking for in a snap!
Learn more: Weekly Weather Unit Lesson Plan by This Crafty Mom
Since elementary teachers tackle multiple subjects every day, their lesson plans might look like a general overview. Or they may prepare more detailed lesson plans for each topic to help them stay on track. The choice is up to you.
Weekly Overview Lesson Plan
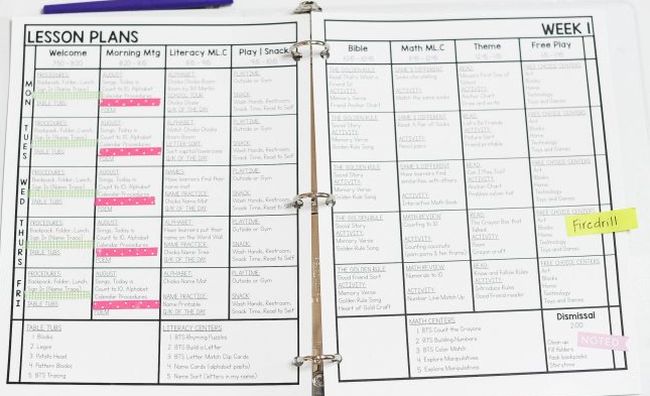
Mrs. Jones Creation Station/lesson plan example via MrsJonesCreationStation.com
Don’t be afraid to write out your lesson plans by hand! A side-by-side setup like this lets you see a whole week at once. We love the use of color to highlight special things like fire drills.
Learn more: Mrs. Jones Creation Station
Yearlong Schedule
Planning a whole year may seem daunting, but it can show you where you’re going to need to stretch a unit and where you can circle back and review. Mrs. D from Mrs. D’s Corner has ideas on how to structure a yearlong lesson plan using Google Sheets.
Learn more: Mrs. D’s Corner
Guided Math Lesson Plan

Tunstall’s Teaching Tidbits/Guided Math lesson plan example via TunstallsTeachingTidbits.com
This example on adding three numbers together can be altered to fit any math lesson plan.
Learn more: Tunstall’s Teaching Tidbits
Art Lesson Plan

Artsy Blevs/lesson plans via TeachandShoot.com
While these are elementary art lesson plan examples, you can easily use this style for teaching art at upper levels too.
Learn more: Artsy Blevs
Special Education Lesson Plans
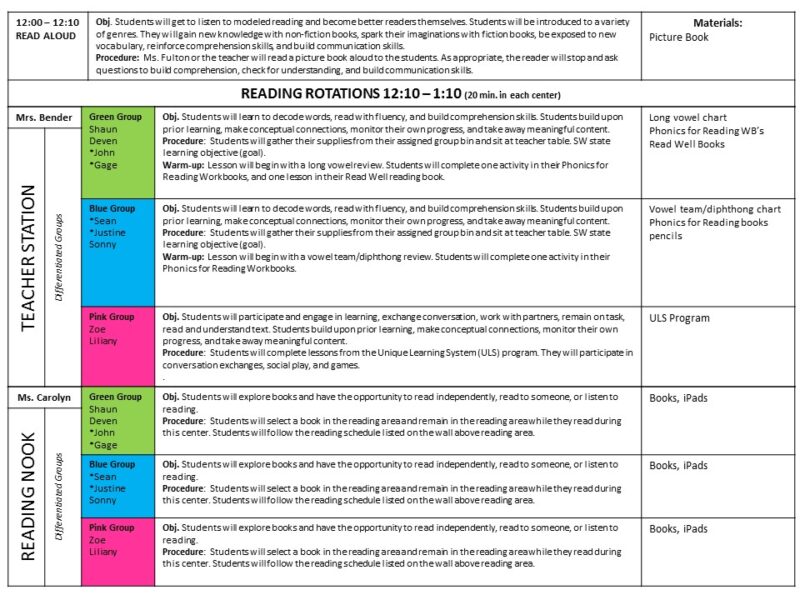
The Bender Bunch/lesson plan example via TheBenderBunch.com
Lesson planning for special education looks different than general classroom lessons in that the lessons have to cover specific IEP goals and include lots and lots of progress monitoring. The Bender Bunch starts each lesson with independent work (read: IEP practice) and then heads into mini-lessons and group work.
Learn more: The Bender Bunch
Interactive Read-Aloud Plan

The Colorful Apple/interactive read-aloud lesson plan example via TheColorfulApple.com
Interactive read-alouds aren’t something that should be “on the fly.” The Colorful Apple explains how to choose a book, get to know it, and get ready to teach it. Once you’re in the book, sticky notes may be the best lesson-planning tool you have for marking questions and vocabulary words you want to point out to students.
Learn more: The Colorful Apple
Social Studies Lesson Plan

Mrs. Jones’s Class/social studies lesson plan example via MrsJonessClass.com
Including images of your anchor charts is a great idea! That way, you can pull one out and have it ready to go in advance.
Learn more: Mrs. Jones’s Class
5E Lesson Plan for Elementary School

What I Have Learned Teaching/example from 5E lesson planning via WhatIHaveLearnedTeaching.com
The 5Es stand for Engagement, Exploration, Explanation, Elaborate, Evaluate. This type of lesson planning can be helpful for students as they work through each of the 5Es related to the topic you’re studying.
Learn more: What I Have Learned Teaching
Science Lesson Plans

Venngage/Science lesson plan example via Venngage.com
If you like to plan your lessons in more detail, take a look at this elementary science lesson plan example.
Learn more: Venngage Science Lesson Plan Template
Reading Groups Lesson Plan
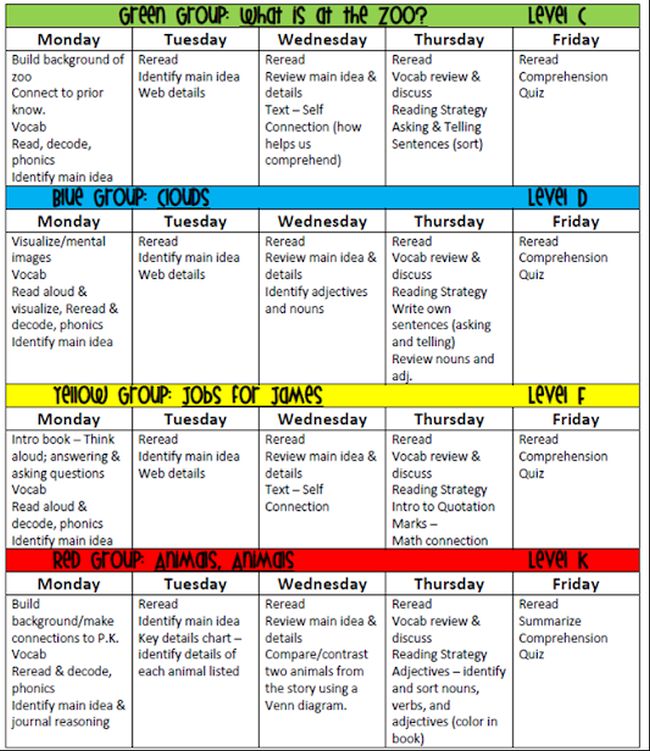
First Grade Fairy Tales/reading groups lesson plan via TheFirstGradeFairyTales.com
Lots of elementary schools have differentiated reading groups. Use a template like this one to plan for each one, all on one page.
Learn more: The First Grade Fairy Tales
P.E. Lesson Plan

American Coaching Academy/P.E. lesson plan via AmericanCoachingAcademy.com
Gym teachers will love this lesson plan idea, which includes directions for playing the games.
Learn more: American Coaching Academy
Music Class Lesson Plan
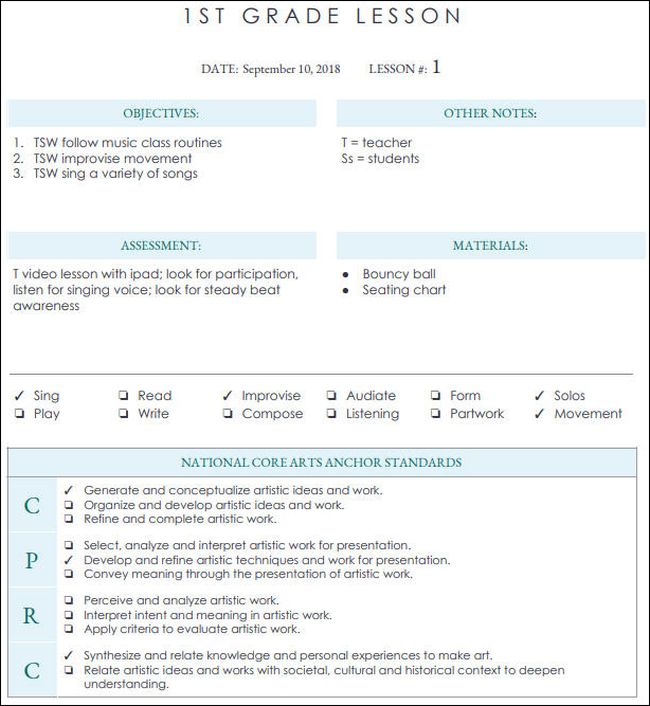
Victoria Boler/music lesson plan via VictoriaBoler.com
Plan out the skills and songs you’ll need for a meaningful music class with a lesson plan like this one.
Learn more: Victoria Boler
At the middle and high school levels, teachers often need more detailed plans for each class, which they may teach multiple times a day. Here are some examples to try.
Google Sheets Lesson Plans
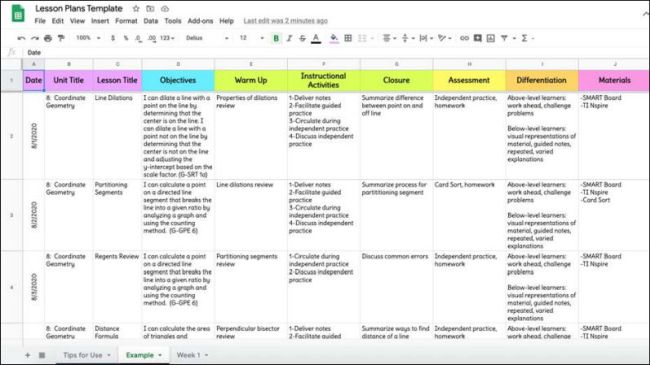
Busy Miss Beebe/Google sheets lesson plan example via BusyMissBeebe.com
Google Sheets (or Excel) is terrific for lesson planning! Create a new tab for each week, unit, or class.
Learn more: Busy Miss Beebe
Weekly History Plan
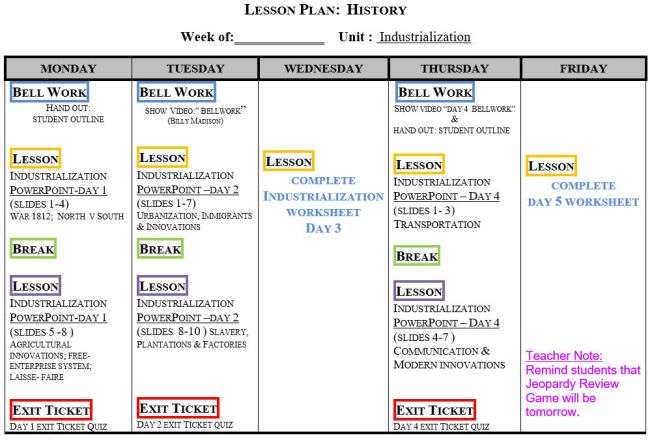
Teachers Pay Teachers/Coaching History lesson plan via TeachersPayTeachers.com
This example shows how you can plan out a week’s worth of lessons at once, and see the entire week all in one spot. This example is for history, but you could use this for math, ELA, or social studies too.
Learn more: Coaching History on Teachers Pay Teachers
Outline and Pacing Guide Lesson Plan
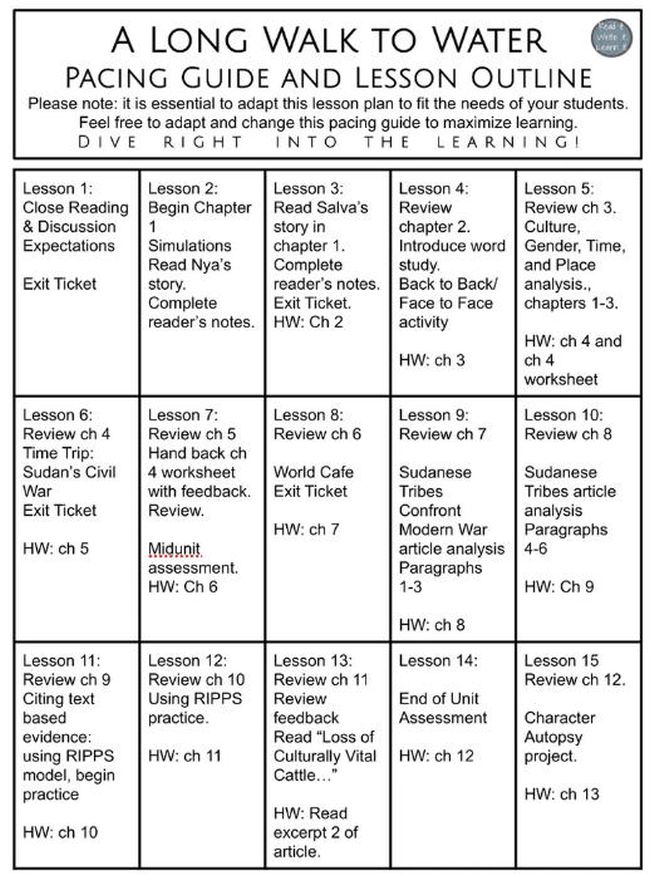
Read it. Write it. Learn it./pacing guide example via ReadItWriteItLearnIt.com
A pacing guide or outline works for both you and your students. Share it at the beginning of a unit to let them know what’s ahead.
Learn more: Read it. Write it. Learn it.
5E Lessons in Middle and High School

Teach Science With Fergy/5E lesson plan via TeachScienceWithFergy.com
5E lesson plans (Engagement, Exploration, Explanation, Elaborate, Evaluate) are great for middle and high school as well. This example is for science, but you can use the 5E structure across all lessons.
Learn more: Teach Science With Fergy
Math Intervention Plans
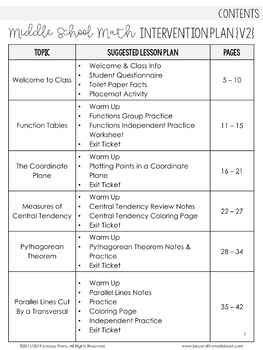
Lindsay Gould/middle school math lesson plan via TeachersPayTeachers.com
When students are in math intervention, they’re reviewing material they learned last week or last year. Lesson plans need to provide time for them to activate their prior knowledge (and make sure they’re remembering it all correctly) before reteaching and practice.
Buy it: Teachers Pay Teachers
The Sticky-Note Lesson Plan

The Wise & Witty Teacher/sticky note planner via WiseWittyTeacher.com
At some point, you’ll know what students are doing each day, you’ll just need some reminders for questions to ask and key points to cover. The nice thing about using sticky notes for lesson planning is if you get ahead or behind schedule, you can move the entire sticky note lesson to another day.
Learn more: The Wise & Witty Teacher
Read more ways to use sticky notes in the classroom .
Backwards Planning Lesson Plan
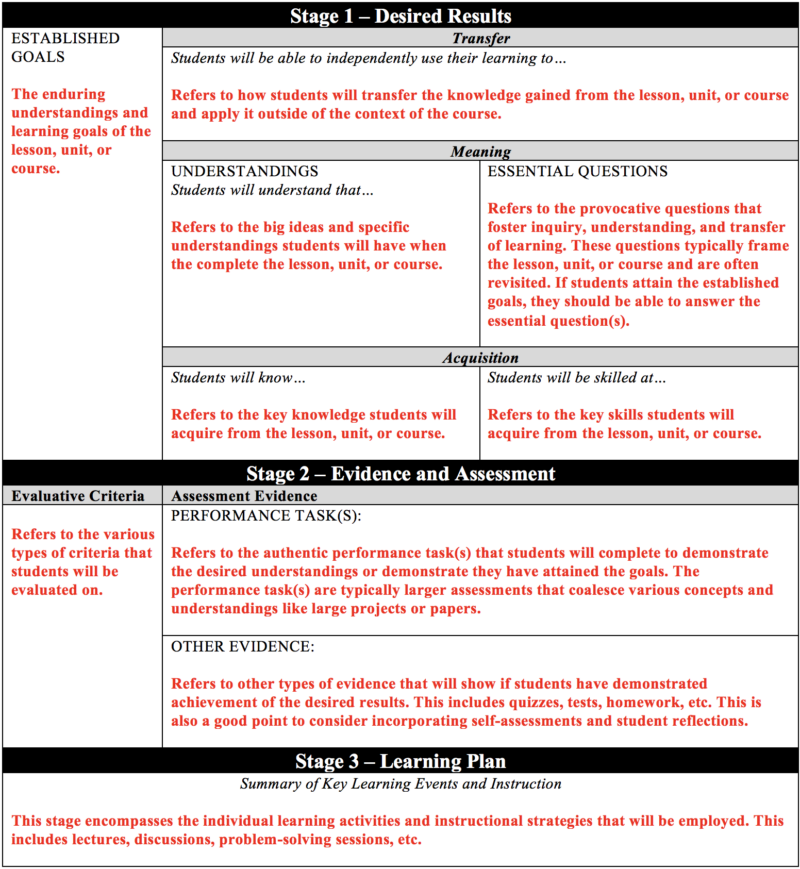
Vanderbilt University Center for Teaching/Understanding by Design lesson plan example via cft.vanderbilt.edu
If your school uses Understanding by Design or other backwards planning, you’ll be thinking about the outcome first and working back from there (rather than forward from an activity or task). Backwards planning lesson plans are intensive, but they’re also something you can use over and over, modifying them slightly for each group of students you have.
Learn more: Vanderbilt Center for Teaching
Visual Arts Lesson Plan

Venngage/visual art lesson plan example via Venngage.com
Detailed lesson plans take longer to prepare, but they make it easier on the day (especially if you wind up needing a sub).
Learn more: Venngage Visual Arts Lesson Plan Template
ESL or Foreign Language Lesson Plan

TeachEnglishAbroad.co/ESL lesson plan via TeachEnglishAbroad.co
Whether you’re teaching English as a second language (ESL) or a foreign language to English speakers, this lesson plan style is perfect.
Learn more: Teaching English Abroad
Music Lesson Plan
Melody Soup/lesson plan example via MelodySoup.Blogspot.com
Use a lesson plan like this for choir, orchestra, band, or individual music lessons.
Learn more: Melody Soup
Blended Learning Lesson Plan
Hot Lunch Tray/blended learning lesson plan example via HotLunchTray.com
If your instruction includes both computer-based and in-person elements, this lesson plan idea might be just what you need.
Learn more: Hot Lunch Tray
One-Sentence Lesson Plan

Norman Eng/Introducing the One-Sentence Lesson Plan via CultofPedagogy.com
This kind of lesson planning isn’t for everyone, but the extreme simplicity works well for some. Describe what students will learn, how they will learn it, and how they’ll demonstrate their knowledge.
Learn more: Cult of Pedagogy
Need more help with lesson planning? Come ask for ideas on the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook !
Plus, check out 40 ways to make time for more creativity in your lesson plans ..

WeAreTeachers
You Might Also Like

25 Formative Assessment Options Your Students Will Actually Enjoy
Get them excited to show you what they know! Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
39 best leadership activities and games

Good leaders can make or break a team. While more and more people are being asked to step into leadership roles, the path to becoming a good leader is long and not always straightforward . This is where leadership activities come in.
Leadership activities are a great way of developing the skills and competencies needed to be an effective leader . It's not easy to learn these skills, especially when so many leaders don't receive effective training or support. In this article, we'll explore the leadership activities you should master in order to lead a high-performing team and become a better leader!
Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
Learning the why and how of being a great leader alongside practical techniques and frameworks is one of the easiest ways to become a better leader.
Anyone in a leadership role has both a big influence and responsibility for their team. Some of the aspects they need to pay attention to in order to be a good leader are:
- Setting the climate of a workplace
- Making decisions
- Inspiring team members
- Setting values for their team
- Improving team spirit and cohesion
- Being responsible for their team’s communication and wellbeing
- Developing leadership skills in other team members
There are a number of tools to help you with leadership development. Coaching, peer support circles, and leadership development workshops can all help one to become a better leader.
Leadership activities such as those featured here are also effective at introducing leadership concepts and learning how to solve common leadership challenges . You might run these leadership training activities during a workshop, add them to an ongoing learning program or simply introduce them to managers as needed.
In this guide, we’ve grouped leadership activities by these core competencies, so you can choose the right activity to help yourself or others develop their leadership skills. Let’s dive in!
What are leadership activities?
Leadership activities are exercises designed to help develop leadership skills and enable leaders to be more effective in their roles. They can include activities that help train new leaders and improve core leadership skills like problem-solving, active listening, or effective group management.
You’ll also find that the best leadership development activities give leaders tools and techniques they can use on the job. It’s one thing to know that leaders need to be good listeners, but quite another to be given a framework and toolkit that means you are a great listener who always helps their team feel heard and understood.
The exercises below are not only great to use when training leaders, but they are practical techniques leaders can use with every team member immediately, whatever their leadership style.

What are leadership activities used for?
While managers might approach tasks differently based on their leadership style, there are skills and competencies that all leaders should learn in order to best service their team. Learning how to be a good leader can be difficult, so using exercises and activities to improve leadership skills in a safe, experiential environment can help leaders be more effective in their role.
If you’re running a leadership development program, you might use these activities during the training program. For example, after conducting a self-assessment and deciding how they want to develop as a leader, participants might work on improving their leadership skills with these activities.
Whether you’re running such a program and developing managers internally with workshops or simply want to brush up on your own leadership skills, these exercises are a great place to begin.
A bespoke leadership development workshop (like the one featured in this leadership template! ) is also a natural place to include these activities.
In SessionLab, it’s quick and easy to design a leadership workshop fit for your needs. Start by dragging and dropping blocks to design your outline. Add minute-perfect timing and instructions to each activity to refine your agenda.
When you’re ready to share with collaborators or participants, export your workshop agenda in PDF, Word, Powerpoint or invite them directly to the session.
Leadership training activities for building a positive work climate
Leaders are role models to their colleagues and organization. Their leadership styles, principles, and values determine the culture that drives their organization’s behavior.
That is why a competitive, paranoid leader can easily create an organization where team members are similarly competitive and less open to collaboration. While a leader who is open and inclusive will create a climate of openness and inclusiveness. How they behave, and what they consider the norm, also affects which kinds of behaviors are enforced and celebrated and which behaviors are punished.
The following leadership activities can help you in recognising important leadership behaviors that result in a productive workplace. They can also be used by leaders to set the stage for team bonding and a great workplace environment with their team. A must for all leaders!
Leadership Envelopes
Leadership games like this help groups translate abstract leadership principles into practical on-the-job behaviors. Participants work in groups to come up with real-life applications of different leadership principles.
The groups conduct multiple rounds of discussion to build upon each others’ ideas, and in the end, evaluate the best ideas to identify the most useful behaviors. This is also a great activity to run with all your team members. Seeing how they consider and respond to different leadership styles can help you focus on the right approach as a leader!
Leadership Envelopes #leadership #issue analysis #thiagi Leadership exercise in groups, working with practical leadership principles. This activity helps groups to translate abstract leadership principles into practical on-the-job behaviours. Participants work in groups to come up with real-life application of leadership principles. The groups take multiple rounds to build upon the ideas of each other, and in the end, evaluate the best ideas to identify the most useful behaviours.
Your Favourite Manager
In this activity, participants take on three different employee personas and list the behaviors of a positive leader or manager and a negative one from the perspectives of those employees. After some individual reflection, participants compare their lists, first in pairs and then in groups. Finally, they collect the ultimate do’s and don’ts for managers and leaders.
Any activity that encourages deep reflection on your own leadership style and those of your role models is a wonderful way to grow. I’ve been especially inspired by how some of my old bosses approach problem solving while I was a team member working beneath them.
My Favourite Manager #management #leadership #thiagi #teamwork #remote-friendly Participants work individually, assuming the roles of three different people and brainstorming their perceptions of three most favourite managers and three least favourite managers. Later, they work with a partner (and still later, in teams) to prepare a list of dos and don’t-s for improving employees’ perception of a manager’s style.
Leadership Pizza
This leadership development activity offers a self-assessment framework for people to first identify the skills, attributes and attitudes they find important for effective leadership, and then assess their own development in these areas. This framework is also a great tool to set individual leadership development goals in a coaching process.
We love activities that allow team members to reflect on different leadership styles and assess their own skills and preferences. The visual format makes it easy to share and reflect on leadership styles later too!
Leadership Pizza #leadership #team #remote-friendly This leadership development activity offers a self-assessment framework for people to first identify what skills, attributes and attitudes they find important for effective leadership, and then assess their own development and initiate goal setting.
Playing with Status
The best leadership training activities often allow managers to work on their leadership skills while also providing an opportunity to reflect on their leadership style and how it might affect other employees.
Playing with Status is a role playing game where pairs enact a job interview or coaching session and enact different versions of the conversation based on whether each person has high or low status. By experiencing the effect of status on the relationship, would-be leaders can consider how they interact with other members of their team and create a more positive workplace culture.
Playing with Status #teambuilding #communication #team #thiagi Participants are given a short script of 8-10 lines of neutral dialogue. The scene may depict a job interview (see the sample below) or a coaching session. Pairs take turns enacting the scene, playing with the status relationships through non-verbal behaviours.
Heard Seen Respected
Standing in the shoes of others, practicing empathy and ensuring that everyone on a team is able to be heard is a necessity for great leaders and your team in general. In this activity, participants shift between telling stories where they were not heard, seen or respected and then being listeners who do not pass judgment.
Remember that leadership training should often start with the fundamentals of respect and empathy. If you can’t respect and empathize with your team members, how can you expect them to do the same for you? Keeping things simple with an activity like Heard Seen Respected can be an especially effective option whether you’re working online or offline.
Heard, Seen, Respected (HSR) #issue analysis #empathy #communication #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can foster the empathetic capacity of participants to “walk in the shoes” of others. Many situations do not have immediate answers or clear resolutions. Recognizing these situations and responding with empathy can improve the “cultural climate” and build trust among group members. HSR helps individuals learn to respond in ways that do not overpromise or overcontrol. It helps members of a group notice unwanted patterns and work together on shifting to more productive interactions. Participants experience the practice of more compassion and the benefits it engenders.

Team building leadership activities
Every leader has an integral role in the formation of the teams they work with. Whether you are consciously working on it or not, your attitude and actions as a leader will significantly influence team cohesion, communication and the team spirit of the people you work with.
This comes through in small everyday actions, the way you share responsibilities, the way you empower colleagues, and the way you foster a cooperative work environment as opposed to a competitive one.
Sometimes, it can also be effective to run team building activities with your company that are expressly focused on helping teams come together and bond. Try using the following leadership team building activities with new teams, or groups that need to spend a little time getting to know each other better.
Marshmallow challenge
The Marshmallow Challenge is a team-building activity in which teams compete to build the tallest free-standing structure out of spaghetti sticks, tape, string, and the marshmallow that needs to be on the top. This leadership activity emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, collaboration, and innovation and problem-solving.
It’s a wonderful game that allows participants’s natural leadership qualities to shine through, and it helps teams have a lot of fun too!
Marshmallow challenge with debriefing #teamwork #team #leadership #collaboration In eighteen minutes, teams must build the tallest free-standing structure out of 20 sticks of spaghetti, one yard of tape, one yard of string, and one marshmallow. The marshmallow needs to be on top. The Marshmallow Challenge was developed by Tom Wujec, who has done the activity with hundreds of groups around the world. Visit the Marshmallow Challenge website for more information. This version has an extra debriefing question added with sample questions focusing on roles within the team.
Blind Square Rope Game
This activity is a tried and tested game that asks teams to communicate well and solve a problem as a team. Not only is this a fun team building activity, but it’s a great way for potential leaders to step up and help their team win! Start by tying a length of rope into a circle and then instruct participants they will have 20 minutes to turn it into a square, with fifteen minutes to plan their actions and five minutes to implement. Here’s the catch – no one may touch the rope until you begin, and every team member is blindfolded during implementation. This is an effective leadership game that is great with both small groups and larger teams separated into breakouts.
Blind Square – Rope game #teamwork #communication #teambuilding #team #energiser #thiagi #outdoor This is an activity that I use in almost every teambuilding session I run–because it delivers results every time. I can take no credit for its invention since it has existed from long before my time, in various forms and with a variety of names (such as Blind Polygon). The activity can be frontloaded to focus on particular issues by changing a few parameters or altering the instructions.
Tower of Power
All leaders need to work closely with other members of their organization in order to succeed. This leadership game encourages groups to work together in order to build a tower with specific (and sometimes tricky!) rules before than reflecting on what worked, what didn’t and what they would do next time.
It’s a wonderful activity for leadership training, as it provides an experiential way to explore leadership concepts, all wrapped in a fun game!
Tower of Power #team #teamwork #communication #leadership #teambuilding #skills This teamwork activity requires participants to work closely together to build a tower from a set of building blocks. The players need to coordinate their actions in order to be able to move the wooden blocks with the crane they have, and this can only be solved by precise planning, good communication and well-organised teamwork. You may use this exercise to emphasise the following themes and outcomes: In Leadership training : identifying interdependencies in systems, leadership communication, dealing with risk, giving feedback In Team building : communicating effectively, cooperating, being an active listener, maintaining the balance, working with values In Project management : simulating strategic planning, working under time pressure In Communication training : meta communication, facilitating, dealing with different perspectives
When teams work together well, something magic happens. But what elements constitute a high performing team? As a leader, how can you help ensure those conditions are met? In this leadership game, participants must work together to get every team member across an obstacle while blindfolded.
It’s a simple concept that creates a perfect space for exploring how teams operate and the role leaders have within them. Bring plenty of fun obstacles (squeaky toys are best) and encourage groups to think strategically for best results!
Minefield #teampedia #teamwork #action #team #icebreaker A fun activity that helps participants working together as a team while teaching the importance of communication, strategy and trust.
Crocodile River
The Crocodile River is a team-building activity in which group members need to support each other in a task to move from one end of a space to another. It requires working together creatively and strategically in order to solve a practical, physical problem. It tends to emphasize group communication, cooperation, leadership and membership, patience and problem-solving.
Crocodile River #hyperisland #team #outdoor A team-building activity in which a group is challenged to physically support one another in an endeavour to move from one end of a space to another. It requires working together creatively and strategically in order to solve a practical, physical problem. It tends to emphasize group communication, cooperation, leadership and membership, patience and problem-solving.
This is a simple game to help team members learn how to work together (better). It can also focus on the group’s understanding of communication, leadership, problem-solving, trust or persistence. Participants stand in a circle, close their eyes and put their hands into the circle to find two other hands to hold. Then they open their eyes and the group has to try to get back into a circle without letting go, though they can change their grip, of course.
Human Knot A physical-participation disentanglement puzzle that helps a group learn how to work together (self-organize) and can be used to illustrate the difference between self-organization and command-control management or simply as a get-to-know-you icebreaker. Standing in a circle, group members reach across to connect hands with different people. The group then tries to unravel the “human knot” by unthreading their bodies without letting go of each other people’s hands. As a management-awareness game to illustrate required change in behavior and leadership on a management level (e.g., illustrate the change from ‘task-oriented’ management towards ‘goal/value-oriented’ management).
Who are you? The pirate ship exercise
Every member of a group occupies a different position in the team. An effective team leader is one who considers their role and is aware of where employees also stand.
This leadership training activity is an effective method of getting a group to consider their roles with the metaphor of a pirate ship. Start by sharing the image and invite each person to consider which person on the deck they most identify with. Is it the captain, or perhaps is it the person repairing damage to the hull? What follows is an effective conversation on roles within a team.
Who are you? The pirate ship exercise (dinámica del barco pirata) #team alignment #team #remote-friendly #teamwork #warm up #icebreaker This an easy but powerful exercise to open a meeting or session and get participants to reflect on their attitudes or feelings about a topic, in the organization, team, or in the project.
Collaborative leadership activities
Whether you’re leading a small group or working across a massive organization, part of your role of a leader is to help their team work together more effectively. Removing obstacles to effective collaboration and creating frameworks for better teamwork is something you’ll be doing as a leader.
Use the activities below to develop the skills necessary to facilitate better collaboration and working habits between team members.
Circles of Influence
Effective teamwork is often about identifying where each member of a team can have the most impact and use their skills best. Leaders often need to find ways to identify where to direct their team and consider how different skills and working styles fit together to make a cohesive team. This activity makes it easy to facilitate this process and encourage employees to reflect and be proactive too!
We love that this leadership exercise encourages every team member to take responsibility and action. When looking for leadership qualities in a group and considering who you might want to develop into a future leader, this is also a great place to start!
Circles of Influence #hyperisland #team #team effectiveness A workshop to review team priorities and made choices about what to focus on individually and collectively. The workshop challenges members to reflect on where they can have the most impact and influence. Use this workshop to refine priorities and empower ownership among team members.
Team of Two
Whether you’re leading a team of just a few people or hundreds, the reality is that many of your discussions and interactions with the people you will lead will be interpersonal and one-on-one in nature. Developing the skillset you need to solve issues in your team when they arise and finding ways to ensure these conversations are productive is one of the most important things you can do as a leader.
Use Team of Two whether working online or as part of an in-person session to help your working pairs and interpersonal relationships go from strength to strength. By articulating needs and consequences clearly, this leadership exercise helps people communicate efficiently and see the results they need – a must for anyone in a leadership role!
Team of Two #communication #active listening #issue analysis #conflict resolution #issue resolution #remote-friendly #team Much of the business of an organisation takes place between pairs of people. These interactions can be positive and developing or frustrating and destructive. You can improve them using simple methods, providing people are willing to listen to each other. “Team of two” will work between secretaries and managers, managers and directors, consultants and clients or engineers working on a job together. It will even work between life partners.
What I Need From You
One of the most important leadership skills to cultivate is clarity: being clear in what you expect and need from others in your organisation or group is an integral component of high-functioning teams. With What I Need From You, each team member involved in the exchange is given the chance to articulate their core needs to others and respond in a structured way.
This kind of clear, direct action is great at unblocking conversational roadblocks in both large and small groups, and is something all leaders should have in their toolkit.
What I Need From You (WINFY) #issue analysis #liberating structures #team #communication #remote-friendly People working in different functions and disciplines can quickly improve how they ask each other for what they need to be successful. You can mend misunderstandings or dissolve prejudices developed over time by demystifying what group members need in order to achieve common goals. Since participants articulate core needs to others and each person involved in the exchange is given the chance to respond, you boost clarity, integrity, and transparency while promoting cohesion and coordination across silos: you can put Humpty Dumpty back together again!
Generative Relationships STAR
The relationships between the members of a team can make or break the work you do together. In this leadership training activity, leaders learn how to help a group understand their current working patterns and identify possible changes.
Each participant will individually rate the current performance of the group on the 4 points of the STAR compass tool included. Next, small groups will discuss their choices and find points of alignment and disagreement. Finally, the whole team will discuss the first steps they can take to improve relationships and performance for the group.
Generative Relationships STAR #team #liberating structures #teamwork You can help a group of people understand how they work together and identify changes that they can make to improve group performance. All members of the group diagnose current relationship patterns and decide how to follow up with action steps together, without intermediaries. The STAR compass tool helps group members understand what makes their relationships more or less generative. The compass used in the initial diagnosis can also be used later to evaluate progress in developing relationships that are more generative.
Team Canvas
When it comes to enabling true collaboration throughout your organization, it pays to involve your team members in helping shape the way you want to work together. Different leadership styles may call for a different approach to this process, but it’s always helpful to see a complete example of how you might define your team culture and working processes.
In this workshop template, you can see a complete agenda for a team canvas workshop. This will take a team through a process of co-creating and defining everything from your goals, values, assets, and rules. Effective leadership often means tapping into group intelligence and enabling your team to take shared ownership of their success. Team Canvas great way of achieving this!
Team Canvas Session #team alignment #teamwork #conflict resolution #feedback #teambuilding #team #issue resolution #remote-friendly The Team Canvas is Business Model Canvas for teamwork. It is an effective technique to facilitate getting teams aligned about their goals, values and purposes, and help team members find their role on the team.
Inspirational leadership activities
Great leaders inspire others. However, there are many different reasons why someone will find a leader inspirational. Developing the skills to inspire team members and lead with this energy is important, whatever your leadership style.
In order to grasp what facilitates inspiring leadership, try the following exercises. You’ll be surprised at how thinking more deeply about your own role models or what your values can help you in all of your leadership interactions!
Leadership Advice from your Role Model
Everyone is asked to think of a role model they look up to and ask themselves: If a young person would ask these role models for leadership advice and what kind of advice that would be.
Facilitate a group conversation where these pieces of advice are shared and contradicting points are discussed and reconciled. Given diverse enough responses, this structured sharing activity might be a good introduction to the concept of situational leadership.
Leadership Advice from Your Role Model #skills #leadership #thiagi #role playing This structured sharing activity provides a faster, cheaper, and better alternative to buying and reading a lot of books: You tap into the wisdom of the group—and of their role models.
Living Core Values
The core values of your organization are a great place to look when you want to inspire your team members. Leaders should be involved in defining and exemplifying their core values and also helping create space for the team to share how they’re living those values. The result is an inspiring leadership exercise that allows a leader to help the group celebrate their wins and also suggest places for improvement.
Start by choosing one of your core values and asking activity participants to share a story of how they have been practicing this core value. After sharing, ask the team to reflect on what inspired them from the story. As with any leadership development game, be the first one to share a story to help guide the discussion. Running this exercise will not only help inspire a team to greater heights but also surface any areas that need improvement – it’s a great method to have in your leadership toolbox!
Living Core Values #culture #values #core values, #connection #inspiration #virtual_friendly #team #team alignment #energizer #remote-friendly For use with a team, organization or any peer group forum. Can be done in person or virtual This is designed to create a conversation that brings Core Values alive. This is great for a team that knows what values they stand for. Through this exercise they will celebrate their values in action and therefore be energized to magnify them further. It will also help bring along anyone that is new so they can understand that the group really walks the talk
Throughout human history, stories have been a consistent source of inspiration. Whatever your leadership style, finding time to share more about your own story and create space for others to share theirs can be massively useful as a leader.
In Campfire, start by creating a selection of 10-20 sticky notes relating to a concept you wish to explore with the group. Put these on the wall and then invite your group to review them and consider stories they might tell related to one of those words. Start the storytelling session yourself and think about how you might inspire and elicit further stories from the rest of the team before passing the torch to the next person around the campfire!
This is a great activity to run during leadership training or when team building. Creating safe spaces for people to share their experiences is a leadership skill you absolutely want to cultivate and practice!
Campfire #gamestorming #team #remote-friendly #storytelling Campfire leverages our natural storytelling tendencies by giving players a format and a space in which to share work stories—of trial and error, failure and success, competition, diplomacy, and teamwork. Campfire is useful not only because it acts as an informal training game, but also because it reveals commonalities in employee perception and experience.
Letter from the Future
Leaders are often called upon to inspire their team members about the future of their product or organization. Employees who are excited about where you’re going are more likely to work together well and be energized to see results. This activity is useful for helping inspire a team, or even just to inspire yourself as a leader and get your vision for the future down on paper!
Begin by asking your team to speculate on what the world will look like in five years. Next, ask them to write a letter from the future detailing what the group has accomplished in that time and how they overcame any challenges.
Share the results to inspire the group for what you might accomplish and also start creating plans for how you’ll create your desired future. You might even find that running this activity solo is effective when thinking about how you want to develop as a team leader!
Letter from the Future #strategy #vision #thiagi #team #teamwork Teams that fail to develop a shared vision of what they are all about and what they need to do suffer later on when team members start implementing the common mandate based on individual assumptions. To help teams get started on the right foot, here is a process for creating a shared vision.
Leadership activities for personal development
A good leader is one who helps uplift and upskill the members of their team. These leadership activities are designed to help you encourage participants to be more autonomous, take initiative and work on their personal development.
If you’re new to a leadership role or trying on various leadership styles, these can also be great activities to practice on the road to leading a team. Growth and development is a vital aspect of employee happiness and fulfilment – be sure to bring ideas for enabling others to your leadership role.
Roles in a meeting
Learning by doing is an important aspect of effective leadership. Sometimes, you have to try something new and approach the task with an open mind while working to the best of your ability. This simple method is a great way of encouraging participants to take an important role during a meeting and also take part in developing and refining those roles.
If you’re running a leadership development program and want to start upskilling participants, this is a great way of delegating some simple leadership roles. Plus, it helps encourage the group to contribute and engage with how a successful meeting is put together too!
Roles in a meeting #meeting facilitation #remote-friendly #hybrid-friendly #skills Organize the day’s meeting by co-creating and assigning roles among participants.
Alignment & Autonomy
One of the most impactful things a leader can do is get out of a team’s way and allow them to perform more autonomously. Doing so effectively means people can take ownership of their work, be more invested, and develop their skills too. But how can you do this without creating chaos or misalignment?
In this activity, you first help every team member align on your goals and then reflect on where they can take more ownership and be more autonomous in their work while still contributing to the goals of the team. Not only is this a great way to help your team develop, but it also takes work off your plate as a leader and can enable you to get out of the trenches if necessary.
Alignment & Autonomy #team #team alignment #team effectiveness #hyperisland A workshop to support teams to reflect on and ultimately increase their alignment with purpose/goals and team member autonomy. Inspired by Peter Smith’s model of personal responsibility. Use this workshop to strengthen a culture of personal responsibility and build your team’s ability to adapt quickly and navigate change.
15% Solutions
One of the biggest barriers to personal development is being overwhelmed by what you need to do to achieve your goals. As a leader, you can help your team by enabling them to take the small, important actions that are within their control.
Start by asking participants to reflect on where they have the discretion and freedom to act and how they might make a small step towards a goal without needing outside help. By flipping the conversation to what 15% of a solution looks like, rather than 100%, employees can begin to make changes without fear of being overwhelmed.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
The GROW Coaching Model
The best leaders are often great coaches, helping individual team members achieve their potential and grow. This tried and test method is a wonderful way to help activate the development of everyone from a new start to an established leader.
Begin by teaching your mentee or group the GROW acronym (Goal, Reality, Obstacles/Options, and Will.) and guide them through a process of defining each section and collectively agreeing on how you’ll make progress. This is an effective leadership activity that is great for leadership training and is equally useful when it comes to help any team member grow.
The GROW Coaching Model #hyperisland #coaching #growth #goal setting The GROW Model is a coaching framework used in conversations, meetings, and everyday leadership to unlock potential and possibilities. It’s a simple & effective framework for structuring your coaching & mentoring sessions and great coaching conversations. Easy to use for both face-to-face and online meetings. GROW is an acronym that stands for Goal, Reality, Obstacles/Options, and Will.
Decision-making leadership activities
An important aspect of leadership development is learning how to make informed and intelligent decisions while also ensuring you listen to your team. A leader who bulldozes their team into a decision without first listening to their expertise is not going to make their team feel valued.
The outcomes of uninformed decisions are often poor or frustrating for those involved too. While leaders are justifiably responsible for making final decisions, it’s integral to find methods to do so in a well-reasoned way.
These leadership activities are useful when it comes to making good decisions while involving your team members in the process and developing a leadership style that creates space for others.
When solving problems as a team, it’s common to have various options for moving forward. As a leader, it often falls to you to make the decision for which solution or direction to pursue. But how can you do that while also creating space for the opinions of your team to be heard?
Dotmocracy is a tried and tested facilitation method for making informed decisions with the help of your team. After presenting the available options, give everyone on your team a number of dots to indicate which option they prefer. You’ll want to adjust the number of votes based on the number of options there are to choose from. A good rule of thumb is to have fewer dots than there are options, giving just a few for every team member.
Leaders want to be on hand to break any ties and to facilitate discussion around what is chosen, but when it comes to making decisions with your team, this method is hard to beat.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
Impact and Effort Matrix
The hallmark of a good decision making process is transparency. Leaders should know why a decision is made and should be able to clearly explain their thinking to team members. As such, the best decision making activities make the process open and easy to understand.
Start this activity by creating a 2×2 matrix and then place possible options on the matrix based on the expected impact and effort it would take to achieve them. This makes it easy to prioritize and compare possible decisions while also including team members in the process.
An inclusive leadership style means bringing your own knowledge to the table while also listening to the opinions of the team. When running this activity, be sure to combine these aspects to ensure items are placed in the appropriate place on the matrix.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
Level of influence
Making the right decision is often a process of weighing up various factors and prioritizing accordingly. While there are many methods for doing this, being an effective leader often means making this as simple as possible.
We love this decision making activity because it asks the group (and its leader!) some simple questions to narrow down possible options and makes it easy to prioritize too. Start by asking the level of influence a team has to make possible actions happen and ranking them accordingly.
Next, choose those items that you have the most influence on and then prioritize the ones you really want to happen. This simple, two-step process is a great activity for leadership development as it is something any leader can use with ease!
Level of Influence #prioritization #implementation #decision making #planning #online facilitation This is a simple method to prioritize actions as part of an action planning workshop, after a list of actions has been generated.
Fishbone Analysis
Making good decisions requires a complete knowledge of the problem at hand. For leaders who may no longer be on the frontlines of their department, it’s important to surface insights from their team and understand the root cause of any problem before making a decision.
In this leadership activity, start by choosing a problem area and adding it to the head of the fish. Next, brainstorm ideas that might cause the problem and add these as categories to the skeleton. Brainstorm on each of these categories and ask why is this happening in order to dive deeper and fully understand the issue at hand before making an informed decision as a group.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
Leadership exercises for setting team values
Usually, the values of a leader are mirrored in the organization. If shortcuts are common practice for the leader, then she will see shortcuts made by her team members all across their projects. But if learning and self-improvement are important to the leader, then this will be a good foundation for these values in the whole organization, too.
To be more aware of your own values as a leader and then bring these ideas to your team, try these leadership exercises!
Explore Your Values
Explore your Values is a group exercise for thinking on what your own and your team’s most important values are. It’s done in an intuitive and rapid way to encourage participants to follow their intuitions rather than over-thinking and finding the “correct” values.
It’s a good leadership game to use to initiate reflection and dialogue around personal values and consider how various leadership styles might chime with some values more than others.
Explore your Values #hyperisland #skills #values #remote-friendly Your Values is an exercise for participants to explore what their most important values are. It’s done in an intuitive and rapid way to encourage participants to follow their intuitive feeling rather than over-thinking and finding the “correct” values. It is a good exercise to use to initiate reflection and dialogue around personal values.
Your Leadership Coat of Arms
In this leadership development activity, participants are asked to draw their own coat of arms symbolising the most important elements of their leadership philosophy. The coat of arms drawings are then debriefed and discussed together with the group.
This activity works well with equally well with leadership and team members. Creating a visual representation of what you stand for in the form of a coat of arms can help create a memorable asset you can refer to and rally behind in the future.
Your Leadership Coat of Arms #leadership #leadership development #skills #remote-friendly #values In this leadership development activity, participants are asked to draw their own coat of arms symbolising the most important elements of their leadership philosophy. The coat of arms drawings are then debriefed and discussed together with the group. After the exercise you may prepare a coat of arms gallery, exhibiting the leadership approach and philosophy of group members
Team Purpose & Culture
Ensuring all group participants are aligned when it comes to purpose and cultural values is one of the jobs of a leader. Teams and organizations that have a shared and cohesive vision are often happier and more productive and by helping a group arrive at these conclusions, a good leader can help empower everyone to succeed. Even with multi-discipline teams and organizations with different leadership styles, this method is an effective way of getting everyone on the same page. This is a framework you’ll likely use again and again with different teams throughout your career.
Team Purpose & Culture #team #hyperisland #culture #remote-friendly This is an essential process designed to help teams define their purpose (why they exist) and their culture (how they work together to achieve that purpose). Defining these two things will help any team to be more focused and aligned. With support of tangible examples from other companies, the team members work as individuals and a group to codify the way they work together. The goal is a visual manifestation of both the purpose and culture that can be put up in the team’s work space.
Leadership communication activities
Leaders are usually viewed as the parents of the organization. It is expected from them that they take care of their people and make sure that proper norms and rules are followed. One of the key areas where a leader has a large influence is the style and amount of communication between people.

Active Listening and giving effective feedback are critical skills to have as a leader but are also crucial for your team members. In fact, the issue that leaders rank as one of the biggest barriers to successful leadership is avoiding tough conversations, including giving honest, constructive feedback .
Develop good communication practices with the following leadership games and activities.
Active Listening
This activity supports participants in reflecting on a question and generating their own solutions using simple principles of active listening and peer coaching. It’s an excellent introduction to active listening but can also be used with groups that are already familiar with this activity. Participants work in groups of three and take turns being “the subject” who will explore a question, “the listener” who is supposed to be totally focused on the subject, and “the observer” who will watch the dynamic between the other two.
Active Listening #hyperisland #skills #active listening #remote-friendly This activity supports participants to reflect on a question and generate their own solutions using simple principles of active listening and peer coaching. It’s an excellent introduction to active listening but can also be used with groups that are already familiar with it. Participants work in groups of three and take turns being: “the subject”, the listener, and the observer.
Trust battery
Every time you work together with someone, your trust battery – the trust you have towards a certain person, or the ‘emotional credit’ that person has in your eyes – either charges or depletes based on things like whether you deliver on what you promise and the social interaction you exhibit. A low trust battery is the core of many personal issues at the workplace.
This self-assessment activity allows you and your team members to reflect on the ‘trust battery’ they individually have towards each person on the team and encourages focus on actions that can charge the depleted trust batteries. It also works great when promoting virtual leadership and working with online teams!
Trust Battery #leadership #teamwork #team #remote-friendly This self-assessment activity allows you and your team members to reflect on the ‘trust battery’ they individually have towards each person on the team, and encourages focus on actions that can charge the depleted trust batteries.
Feedback: Start, Stop, Continue
Regular and constructive feedback is one of the most important ingredients for effective teams. Openness creates trust, and trust creates more openness. This is an activity for teams that have worked together for some time and are familiar with giving and receiving feedback. The objective of Start, Stop, Continue is to examine aspects of a situation or develop next steps by polling people on what to start, what to stop and what to continue doing.
For those in charge of online leadership, it’s vital to find ways of having difficult conversations in constructive ways virtually – try this method when working to resolve issues with your distributed team!
Feedback: Start, Stop, Continue #hyperisland #skills #feedback #remote-friendly Regular, effective feedback is one of the most important ingredients in building constructive relationships and thriving teams. Openness creates trust and trust creates more openness. Feedback exercises aim to support groups to build trust and openness and for individuals to gain self-awareness and insight. Feedback exercises should always be conducted with thoughtfulness and high awareness of group dynamics. This is an exercise for groups or teams that have worked together for some time and are familiar with giving and receiving feedback. It uses the words “stop”, “start” and “continue” to guide the feedback messages.
Reflection: Team
All leaders know the value of structured and considered reflection. Teams that take the time to reflect and improve are those that can grow and by creating an environment of reflection, team leaders and managers can help their group move forward together. This method is effective for both offline and virtual leadership development. It helps a group progress from individual reflection through to full group discussion in a way that encourages constructive thought and minimizes potential frustration or antagonistic conversation.
Reflection: Team #hyperisland #team #remote-friendly The purpose of reflecting as a team is for members to express thoughts, feelings and opinions about a shared experience, to build openness and trust in the team, and to draw out key learnings and insights to take forward into subsequent experiences. Team members generally sit in a circle, reflecting first as individuals, sharing those reflections with the group, then discussing the insights and potential actions to take out of the session. Use this session one or more times throughout a project or program.
Leadership conflict resolution activities
One of the most important leadership skills you’ll want to develop is the ability to mediate and resolve team conflicts. Even the most connected and effective teams can run into conflict and it will fall to managers and team leaders to help get things back on track.
Even for established leaders, navigating conflict can be difficult! These leadership development activities are designed to help groups manage and resolve conflicts more effectively.
Giving leaders a framework they can trust and use with their team right away is always a good use of time, and we’d recommend teaching these methods to all new leaders!
What, So What, Now What?
It’s easy to get lost in the woods when it comes to managing conflict. Helping a group see what happened objectively and without judgment is an important leadership skill, and this framework helps make this process easy.
Start by working with the group to collect facts about what happened before moving towards making sense of them. Once everywhere has been heard and given space to process these facts, you can then move towards suggesting practical actions. By following this kind of framework, you can manage a conflict in a pragmatic way that also ensures everyone in a group can contribute.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
Conflict Responses
All of us can be guilty of handling conflicts in a less than ideal manner. Part of developing as a leader is identifying when something didn’t go well before finding ways to do things better next time.
In this leadership activity, ask the group to provide examples of previous conflicts and then reflect on how they handled them. Next, ask everyone to reflect on how they might change their behavior for a better outcome in the future. As a leader, use this opportunity to lead the way and be honest and vulnerable. It’s your role to provide a model for interaction and its always worthwhile to see how you can do better as a people manager dealing with conflict too!
Conflict Responses #hyperisland #team #issue resolution A workshop for a team to reflect on past conflicts, and use them to generate guidelines for effective conflict handling. The workshop uses the Thomas-Killman model of conflict responses to frame a reflective discussion. Use it to open up a discussion around conflict with a team.
Bright Blurry Blind
Finding opportunities to reframe conflict as an opportunity to solve problems and create clarity is a very useful leadership quality. Often, conflict is a signifier of a deeper problem and so finding ways to surface and work on these issues as a team is a great way to move forward and bring a group together too.
In this leadership activity, start by asking the group to reflect on the central metaphor of bright to blind issues or topics, based on whether the problem is out in the open or unknown. Next, invite small groups to ideate on what issues facing the team are bright, blurry, or blind and then discuss them as a group. By working together to illuminate what is blurry or blind, you can create a one-team mentality and start resolving problems that can lead to conflict too.
Bright Blurry Blind #communication #collaboration #problem identification #issue analysis This is an exercise for creating a sense of community, support intra and inter departmental communication and breakdown of “Silos” within organizations. It allows participants to openly speak about current issues within the team and organization.
The Art of Effective Feedback Workshop
All leaders will need to give effective feedback in order to help their team develop and do great work. The best leaders also solicit feedback from their direct reports and use this is an opportunity to grow. But how can you teach these feedback skills and help leaders develop this important skill?
Check out our Effective Feedback Workshop template for a complete agenda you can use to develop this leadership skill. You’ll find a ready-to-go workshop with a guide and PowerPoint presentation you can use to help anyone in a leadership role give and receive better feedback.
Workshop design made easy
Designing and running effective workshops and meetings is an important leadership skill; whether it’s staying organized and on time during your daily stand-ups or planning more involved sessions.
With SessionLab, it’s easy to create engaging workshops that create impact while engaging every member of your team. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how you and your team might use SessionLab to design more effective sessions or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!
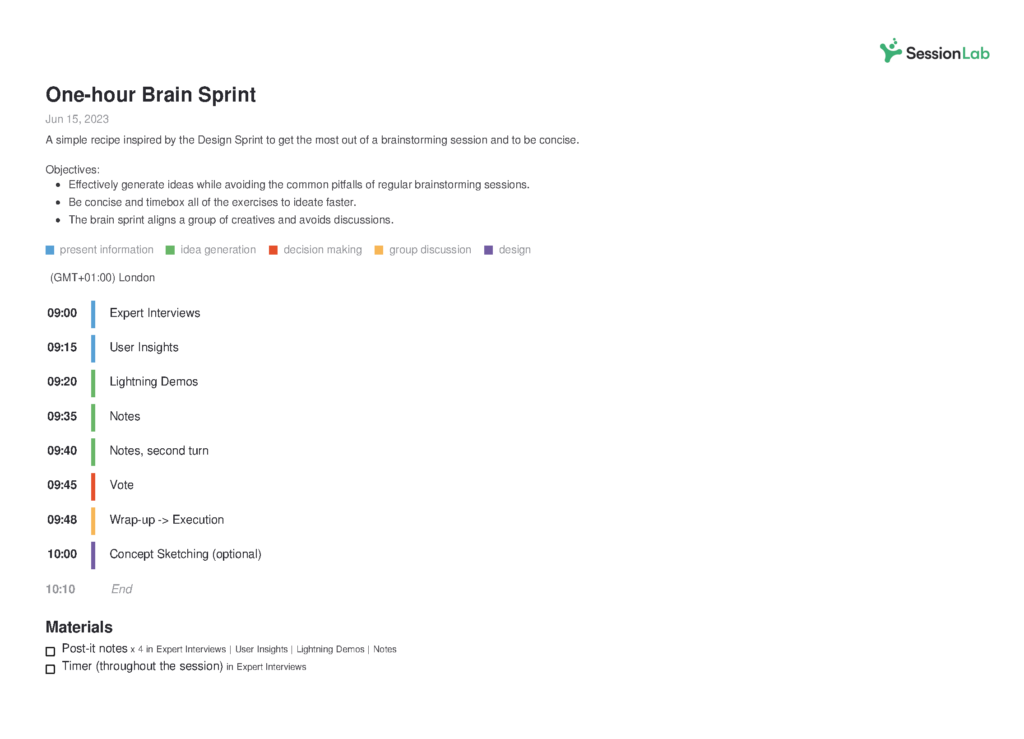
Now over to you…
I hope you have found some useful tips for leadership development workshops above. Now we’d love to hear from you!
What are your favorite leadership workshop ideas and training exercises for leadership development? Did you incorporate any of them into your facilitation practice?
Have you tried any of the activities above? Let us know about your experiences in the comments.
23 Comments
Thank you for sharing such great activity ideas. It is greatly appreciated and a perfect example of how the internet can and does serve the greater good!
Thank you, Jeanne! Great to see that you have found some useful ideas here!
Thank you this is very helpful in building new activities and revitalising teaching.
You’re welcome, Christine! Great to see that you’ve found the post helpful!
Thank you for the magnanimity of sharing these activities. We will choose and run and I am sure they will be very effective.
You are welcome, Roofi – enjoy using these activities at your sessions!
Thank you for sharing such great activity ideas. I will use in my leadership training programme
You are welcome man, happy to see that you’ve found some useful inspiration in this post!
Awesome resources for leadership coaching. Thank you so much! Cheers Marion (From Australia)
You’re welcome, Marion! I’m happy to hear you’ve found interesting the techniques above :-)
Thank you so much . I am really having a hard time thinking about what activities to include for my leadership training talk . This is of great help .
That’s nice to hear – I hope your training talk with go great! :-)
These exercises sound great. Does anyone have any feedback as to how these exercises have worked with their teams? Thanks!
Thank you for the question, Jennifer. We’ve used some of these activities at our own team meetings at SessionLab, and I’ve used other ones earlier on at different training workshops. Which one would you be interested to hear more about?
Thank you for these activities, I have used some of them already in my classes when teaching about leadership and leadership styles. Köszönöm!
That’s great to hear, you’re welcome, Réka! If you have any suggestion on how to tweak or run better these activities, we’d love to hear your thoughts :-)
Thank you for these activities. I was struggling to find activities to work on with groups as small as 1-5, but this should work well.
You’re welcome, Albert – Indeed, most of these activities do work well in small groups as well. Wishing best with your next sessions!
wow! this great! very helpful for trainers like me…. thanks you for sharing …
You’re welcome, I’m happy you’ve found these activities useful!
Hi I am trying to find an online simulation for a course I am designing for a college in Ontario, Canada. I am hoping to find something like your Leadership Envelope but in a virtual format or game. The ’rounds’ aspect is particularly interesting as I would like the students to work with one team over 14 weeks and then submit assigned work based on their experiences related to the course concepts.
Please let me know if you provide something like this or can help in any way.
Hey Rick! Thanks for your comment :)
Leadership Envelope is a great method! Sadly, there’s nothing quite like it in our remote-friendly section of the library currently, though there are a heap of virtual team building activities that could be adapted to go for multiple rounds.
We did have some thoughts on how you might perform the Leadership Envelope in a remote format, which I hope will help!
– Use breakout groups in Zoom for each group. – Have each team pass their virtual “envelope” with responses to the facilitator, either over Slack, PM or email – The facilitator then “passes” the leadership principle to the next team, though keeps the responses back – Play continues, with the facilitator collecting the responses under each leadership principle for later distribution – we’d recommend setting these up in an online whiteboard such as Mural or a Google Doc so teams can review them during the evaluation round – In the evaluation round, share the online whiteboard/Google Doc with the teams – they can then score them in the shared online space and present back to the group from there :) – For the final round, everyone returns to a single Zoom session, each team reclaims their cards (or the facilitator can distribute them back) and then you can debrief :)
Hope that helps, Rick! Using a shared online space such as Mural is also a great shout for an ongoing course, as you can collect and display artifacts generated by the teams throughout :)
Let us know how you get on!
Thank you for having the time and effort on sharing this amazing blog with us! I’ll probably read more of your articles.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Advertisement-related writing activities work across age groups and can be adapted to most students and their needs. This great ESL writing assignment can help your students put the adjectives they've learned into good use, as well as showcase their creative writing and persuasion skills. You can find advertisements everywhere, including:
Great activities and my students are enjoying using them." Out with the moans, groans, frustration, and suddenly urgent trips to the moon or anywhere outside of the classroom. Meaningful and engaging writing assignments include a dash of real-world, relevant writing opportunities, a pinch of skill transfer, and a sprinkling of creative freedom.
5 communication activities for college students Brainwriting. Group size: 10 students (minimum) Course type: Online (synchronous), in-person. This activity helps build rapport and respect in your classroom. After you tackle a complex lecture topic, give students time to individually reflect on their learnings.
Create four to five case studies of similar difficulty. Have students work in groups of four or five to work through and analyze their case study. Provide 10-15 minutes (or adequate time) to work through the cases. Walk around and address any questions. Call on groups randomly and ask that students share their analysis.
The example presented above from Dr. Yesilevskiy's teaching highlights how he scaffolded lab complexity, progressing from structured to student-driven. See the section below "Activities to Prepare Students for Creative Assignments" for sample activities to scaffold this work. Create opportunities for ongoing feedback. Provide feedback at ...
Some ideas and examples to follow can help. Having some plug-and-play activities to assign students can help, too -- even if you need to adjust them to fit your students' needs. We've got you covered. In this post, you'll find 100 elearning activities, templates and tutorials. They'll help you create elearning activities that lend themselves to ...
However, when introducing your assignment to your students, there are several things you will need to clearly outline for them in order to ensure the most successful assignments possible. First, you will need to articulate the purpose of the assignment. Even though you know why the assignment is important and what it is meant to accomplish, you ...
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
An authentic assessment provides opportunities for students to practice, consult resources, learn from feedback, and refine their performances and products accordingly (Wiggins 1990, 1998, 2014). Authentic assignments ask students to "do" the subject with an audience in mind and apply their learning in a new situation.
Instructors can often help students write more effective papers by giving students written instructions about that assignment. Explicit descriptions of assignments on the syllabus or on an "assignment sheet" tend to produce the best results. These instructions might make explicit the process or steps necessary to complete the assignment.
With BookWidgets, you can make interactive learning games like crossword puzzles, pair matching games, bingo games, jigsaw puzzles, memory games, and many more in minutes (and there's a Google Classroom integration as well). 17. Crossword puzzle. The crossword game is perfect to use as repetition activity.
Collaborative learning can help. students develop higher-level thinking, communication, self-management, and leadership skills. explore a broad range of perspectives and provide opportunities for student voices/expression. promote teamwork skills & ethics. prepare students for real life social and employment situations.
From your perspective, the activity can serve as an insightful source of feedback. For example, if more than a quarter of the class mentions the same "muddiest point," you may wish to schedule a further time to discuss that topic, or create a new lesson plan or assignment to tackle it. 5. The devil's advocate approach
Scaffold smaller activities and assignments towards large assignments so that students understand the trajectory of their work. This helps students build on their growing knowledge, but also helps them move forward: it's easier for them to continue a learning process than to start a new one. It also combats procrastination and plagiarism, and ...
Assignment is a task given to students by a teacher or professor, usually as a means of assessing their understanding and application of course material. Assignments can take various forms, including essays, research papers, presentations, problem sets, lab reports, and more. Assignments are typically designed to be completed outside of class ...
When students described assignments that helped them learn, a number of themes emerged. For example, students believe their learning is supported through real-world activities and creative assignments that foster their critical thinking skills. Students also expressed that short, regular assignments that make them stay up to date with course ...
8. Role Play. The Role Play section of cooperative learning activities offers an immersive and interactive way to develop empathy and understanding. Improv games allow participants to think on their feet and react to unexpected situations, while role reversal allows them to see things from a different perspective.
Create a promo video. 9. Questions for your future self. Think ahead with a video full of inspiring questions. This project is great for incoming freshmen. At the beginning of the year, have students create videos with questions for their future self or with goals for their life and career.
As educators, we measure student learning through many means, including assignments, quizzes, and tests. These assessments can be formal or informal, graded or ungraded. But assessment is not simply about awarding points and assigning grades. Learning is a process, not a product, and that process takes place during activities such as recall and ...
In this chapter and in the next three, I walk through example assignments and how you might analyze them to better understand your task. This assignment comes from one of my first-year writing classes. It's a fairly typical early assignment in my first-year writing classes, one that asks students to read a text and engage with it in some way.
30 Lesson Plan Examples for Every Grade Level and Subject. Lots of ways to prepare for top-notch learning. By Jill Staake, B.S., Secondary ELA Education. Aug 3, 2023. Writing lessons might be a fun activity for you (all the things you'll do!) or it may be a necessary evil (so many boxes to fill). Either way, it's an important part of ...
While all assignments can be considered activities, not all activities are assignments. For example, a teacher might assign a reading assignment for homework, which is a specific task with a deadline and contributes to the student's overall grade. However, the teacher might also have students participate in a classroom discussion as an ...
Making decisions. Inspiring team members. Setting values for their team. Improving team spirit and cohesion. Being responsible for their team's communication and wellbeing. Developing leadership skills in other team members. There are a number of tools to help you with leadership development.
CITY OF LONG BEACH - ADMINISTRATIVE ANALYST I-IV ASSIGNMENT EXAMPLES: DEPARTMENT PERSONNEL ADMINISTRATION Summary á The Administrative Analyst position may involve assisting with personnel management tasks such as recruitment and selection â onboarding, training, and employee relations â performance management and may assist with
The World Health Organization Thailand would like to invite institutions with relevant expertise for documentation and development of narratives to showcase public health achievements in various areas of work related to Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs), mental health and health promotion across the life course in Thailand.The deliverables of this assignment comprise of write-up of at least 8 ...