

Persuasive Writing In Three Steps: Thesis, Antithesis, Synthesis
April 14, 2021 by Ryan Law in

Great writing persuades. It persuades the reader that your product is right for them, that your process achieves the outcome they desire, that your opinion supersedes all other opinions. But spend an hour clicking around the internet and you’ll quickly realise that most content is passive, presenting facts and ideas without context or structure. The reader must connect the dots and create a convincing argument from the raw material presented to them. They rarely do, and for good reason: It’s hard work. The onus of persuasion falls on the writer, not the reader. Persuasive communication is a timeless challenge with an ancient solution. Zeno of Elea cracked it in the 5th century B.C. Georg Hegel gave it a lick of paint in the 1800s. You can apply it to your writing in three simple steps: thesis, antithesis, synthesis.
Use Dialectic to Find Logical Bedrock
“ Dialectic ” is a complicated-sounding idea with a simple meaning: It’s a structured process for taking two seemingly contradictory viewpoints and, through reasoned discussion, reaching a satisfactory conclusion. Over centuries of use the term has been burdened with the baggage of philosophy and academia. But at its heart, dialectics reflects a process similar to every spirited conversation or debate humans have ever had:
- Person A presents an idea: “We should travel to the Eastern waterhole because it’s closest to camp.”
- Person B disagrees and shares a counterargument: “I saw wolf prints on the Eastern trail, so we should go to the Western waterhole instead.”
- Person A responds to the counterargument , either disproving it or modifying their own stance to accommodate the criticism: “I saw those same wolf prints, but our party is large enough that the wolves won’t risk an attack.”
- Person B responds in a similar vein: “Ordinarily that would be true, but half of our party had dysentery last week so we’re not at full strength.”
- Person A responds: “They got dysentery from drinking at the Western waterhole.”
This process continues until conversational bedrock is reached: an idea that both parties understand and agree to, helped by the fact they’ve both been a part of the process that shaped it.

Dialectic is intended to help draw closer to the “truth” of an argument, tempering any viewpoint by working through and resolving its flaws. This same process can also be used to persuade.
Create Inevitability with Thesis, Antithesis, Synthesis
The philosopher Georg Hegel is most famous for popularizing a type of dialectics that is particularly well-suited to writing: thesis, antithesis, synthesis (also known, unsurprisingly, as Hegelian Dialectic ).
- Thesis: Present the status quo, the viewpoint that is currently accepted and widely held.
- Antithesis: Articulate the problems with the thesis. (Hegel also called this phase “the negative.”)
- Synthesis: Share a new viewpoint (a modified thesis) that resolves the problems.
Hegel’s method focused less on the search for absolute truth and more on replacing old ideas with newer, more sophisticated versions . That, in a nutshell, is the same objective as much of content marketing (and particularly thought leadership content ): We’re persuading the reader that our product, processes, and ideas are better and more useful than the “old” way of doing things. Thesis, antithesis, synthesis (or TAS) is a persuasive writing structure because it:
- Reduces complex arguments into a simple three-act structure. Complicated, nuanced arguments are simplified into a clear, concise format that anyone can follow. This simplification reflects well on the author: It takes mastery of a topic to explain it in it the simplest terms.
- Presents a balanced argument by “steelmanning” the best objection. Strong, one-sided arguments can trigger reactance in the reader: They don’t want to feel duped. TAS gives voice to their doubts, addressing their best objection and “giv[ing] readers the chance to entertain the other side, making them feel as though they have come to an objective conclusion.”
- Creates a sense of inevitability. Like a story building to a satisfying conclusion, articles written with TAS take the reader on a structured, logical journey that culminates in precisely the viewpoint we wish to advocate for. Doubts are voiced, ideas challenged, and the conclusion reached feels more valid and concrete as a result.
There are two main ways to apply TAS to your writing: Use it beef up your introductions, or apply it to your article’s entire structure.
Writing Article Introductions with TAS
Take a moment to scroll back to the top of this article. If I’ve done my job correctly, you’ll notice a now familiar formula staring back at you: The first three paragraphs are built around Hegel’s thesis, antithesis, synthesis structure. Here’s what the introduction looked like during the outlining process . The first paragraph shares the thesis, the accepted idea that great writing should be persuasive:

Next up, the antithesis introduces a complicating idea, explaining why most content marketing isn’t all that persuasive:

Finally, the synthesis shares a new idea that serves to reconcile the two previous paragraphs: Content can be made persuasive by using the thesis, antithesis, synthesis framework. The meat of the article is then focused on the nitty-gritty of the synthesis.

Introductions are hard, but thesis, antithesis, synthesis offers a simple way to write consistently persuasive opening copy. In the space of three short paragraphs, the article’s key ideas are shared , the entire argument is summarised, and—hopefully—the reader is hooked.
Best of all, most articles—whether how-to’s, thought leadership content, or even list content—can benefit from Hegelian Dialectic , for the simple reason that every article introduction should be persuasive enough to encourage the reader to stick around.
Structuring Entire Articles with TAS
Harder, but most persuasive, is to use thesis, antithesis, synthesis to structure your entire article. This works best for thought leadership content. Here, your primary objective is to advocate for a new idea and disprove the old, tired way of thinking—exactly the use case Hegel intended for his dialectic. It’s less useful for content that explores and illustrates a process, because the primary objective is to show the reader how to do something (like this article—otherwise, I would have written the whole darn thing using the framework). Arjun Sethi’s article The Hive is the New Network is a great example.

The article’s primary purpose is to explain why the “old” model of social networks is outmoded and offer a newer, better framework. (It would be equally valid—but less punchy—to publish this with the title “ Why the Hive is the New Network.”) The thesis, antithesis, synthesis structure shapes the entire article:
- Thesis: Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram grew by creating networks “that brought existing real-world relationships online.”
- Antithesis: As these networks grow, the less useful they become, skewing towards bots, “celebrity, meme and business accounts.”
- Synthesis: To survive continued growth, these networks need to embrace a new structure and become hives.
With the argument established, the vast majority of the article is focused on synthesis. After all, it requires little elaboration to share the status quo in a particular situation, and it’s relatively easy to point out the problems with a given idea. The synthesis—the solution that needs to reconcile both thesis and antithesis—is the hardest part to tackle and requires the greatest word count. Throughout the article, Arjun is systematically addressing the “best objections” to his theory and demonstrating why the “Hive” is the best solution:
- Antithesis: Why now? Why didn’t Hives emerge in the first place?
- Thesis: We were limited by technology, but today, we have the necessary infrastructure: “We’re no longer limited to a broadcast radio model, where one signal is received by many nodes. ...We sync with each other instantaneously, and all the time.”
- Antithesis: If the Hive is so smart, why aren’t our brightest and best companies already embracing it?
- Thesis: They are, and autonomous cars are a perfect example: “Why are all these vastly different companies converging on the autonomous car? That’s because for these companies, it’s about platform and hive, not just about roads without drivers.”
It takes bravery to tackle objections head-on and an innate understanding of the subject matter to even identify objections in the first place, but the effort is worthwhile. The end result is a structured journey through the arguments for and against the “Hive,” with the reader eventually reaching the same conclusion as the author: that “Hives” are superior to traditional networks.
Destination: Persuasion
Persuasion isn’t about cajoling or coercing the reader. Statistics and anecdotes alone aren’t all that persuasive. Simply sharing a new idea and hoping that it will trigger an about-turn in the reader’s beliefs is wishful thinking. Instead, you should take the reader on a journey—the same journey you travelled to arrive at your newfound beliefs, whether it’s about the superiority of your product or the zeitgeist-changing trend that’s about to break. Hegelian Dialectic—thesis, antithesis, synthesis— is a structured process for doing precisely that. It contextualises your ideas and explains why they matter. It challenges the idea and strengthens it in the process. Using centuries-old processes, it nudges the 21st-century reader onto a well-worn path that takes them exactly where they need to go.

Ryan is the Content Director at Ahrefs and former CMO of Animalz.
Why ‘Vertical Volatility’ Is the Missing Link in Your Keyword Strategy
Get insight and analysis on the world's top SaaS brands, each and every Monday morning.
Success! Now check your email to confirm your subscription.
There was an error submitting your subscription. Please try again.

- Organizations
- Planning & Activities
- Product & Services
- Structure & Systems
- Career & Education
- Entertainment
- Fashion & Beauty
- Political Institutions
- SmartPhones
- Protocols & Formats
- Communication
- Web Applications
- Household Equipments
- Career and Certifications
- Diet & Fitness
- Mathematics & Statistics
- Processed Foods
- Vegetables & Fruits
Difference Between Thesis and Antithesis
• Categorized under Miscellaneous | Difference Between Thesis and Antithesis
Thesis and antithesis are literary techniques used to make a point during a debate or a lecture or discourse about a topic. The thesis is the theory or the definition of the point under discussion. Antithesis is the exact opposite of the point made in the thesis. Anti is a prefix meaning against. The antithesis therefore goes against the thesis to create an opposition effect. The antithesis creates a clash of ideas or opinions and is a rhetorical device used to sway the opinions of the reader. The two opposite statements highlight a point in literature, politics and other forums of debate. Hearing the two sides of an argument has to have more impact on the reader or listener. The two opposing ideas make the writer’s point more definite and obvious.

Definition of Thesis
The thesis is the beginning of the study or debate. It is the introduction to the topic. The thesis is the normal way of looking at the subject matter. The thesis is the accepted way of thinking or viewing an issue to be discussed or written about. It is often the theory that is presented by philosophers and usually believed by the majority. A thesis can be used in a written document or as a speech. The thesis study looks at the positive side of the topic to be presented or discussed. The subject matter is usually what readers consider normal. In a political context it may be what is seen as the status quo. Not necessarily the right situation for the times politically, but what has been the norm, and what has been established before change must take place.

Definition of Antithesis
The antithesis is the opposite or opposition to the thesis. Anti being the prefix, and when it is added to thesis, spells antithesis. Anti changes the meaning of the word thesis. Opposition or an opposing statement or word, is the role that the antithesis plays. The antithesis helps to bring out the reason behind a debate or an emotive statement. Looking at the opposing theme and comparing the thesis and the antithesis highlights the mental picture through the anti aspect of the word antithesis. For example, when Neil Armstrong told the world he had made one small step for man and a giant leap for mankind he used the normal step he took as the thesis, and used the antithesis as a giant leap to create the picture of how great this step was for mankind. This created a memorable image, and shows the enormity of the first man walking on the moon. Antithesis is a form of rhetoric and a useful way of persuading people and igniting emotional reactions. Antithesis has been used by writers and politicians to stir emotions and bring home an important point.
What is the connection between Thesis, Antithesis and synthesis?
Thesis, together with antithesis results in a synthesis, according to philosopher Hegel. Hegel’s dialectics is a philosophical method involving a contradictory series of events between opposing sides. He describes the thesis as being the starting point, the antithesis is the reaction and the synthesis is the outcome from the reaction. Karl Marx used this philosophy to explain how communism came about. According to Marx’s theory:
The thesis was capitalism, the way Russia was run at the time.
The antithesis was the Proletariat, the industrial workers and labor force, at that time. The Proletariat decided to revolt against the capitalists, because they were being exploited. This reaction is the antithesis, or the opposition.
The synthesis results from these two groups opposing one another and there is an outcome, a synthesis. The outcome is a new order of things and new relationships. The new order was Communism. I t was a direct result of the antithesis or political opposition. The connection is therefore between the perceived ‘normal’ or starting point against the opposition, the antithesis, to create a new order of doing things.
How is Thesis and Antithesis used in literary circles?
Dramatic effect and contrasts of character are created through an antithesis. The writer uses the normal character matched with the completely opposite character to create an understanding or the different personalities or the different environment. Snow White and the wicked queen, who is the stepmother, are a shining example of antithesis. Hamlet’’s soliloquy, to be or not to be, sums up his dilemma at the time and creates a confusion of thought. Charles Dickens uses this rhetorical technique in a Tale of Two Cities as he describes ‘It was the best of times and the worst of times,’ when chapter one begins. The reader is immediately drawn into the story and the upsetting times of the French Revolution that is the scene for the book.
How are Thesis and Antithesis used in the political arena?
Well known politicians have used thesis and antithesis in their propaganda and speeches to rouse their followers. The well known Gettysburg address, given by Abraham Lincoln, used the antithesis of little and long at Gettysburg at the dedication to national heroism. Lincoln said:
“The world will little note, nor long remember, what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here.” This speech has gone down in history as one of the most important speeches and it has definitely been remembered.
Antithesis in a speech helps to advertise sentiments and rally crowds together due to its emotional power. Martin Luther King used antithesis to sway a crowd by saying unless people chose to live together as brothers they would surely perish as fools.
How does Thesis and Antithesis form part of a debate?
Formal debates make good use of the opposition concept brought about by the use of antithesis. The debate will start with the presentation of the thesis, followed by the antithesis and summed up in the synthesis. For example, a debate about eating meat could open with the points for eating meat. The next section of the debate argues for not eating meat and finally the points for and against could sum up eating meat, but as small portions of a persons dietary needs. The conflict of the argument comes between the thesis and the antithesis. The summary for the listeners to take away is the synthesis of the points made in the debate.
What makes Antithesis a rhetorical device?
The antithesis conjures up a more emotive response because of the opposition factor. Adding in the opposite or exaggerated form of a word in a statement makes more impact for the listener. In the event of a man walking on the moon, for example, this was not just a small event happening when a rocket went to the moon. No, this was a gigantic expedition to another planet. Whether it was intentional or not this statement has stood the test of time. It has become one of the most well known quotes highlighting a particular event. The clever use of the antithesis of a giant leap as part of the statement has made these words stand out in asthey marked this occasion. They bring the impact of these steps to the world as a great vision and achievement for mankind.
Chart to compare Thesis and Antithesis
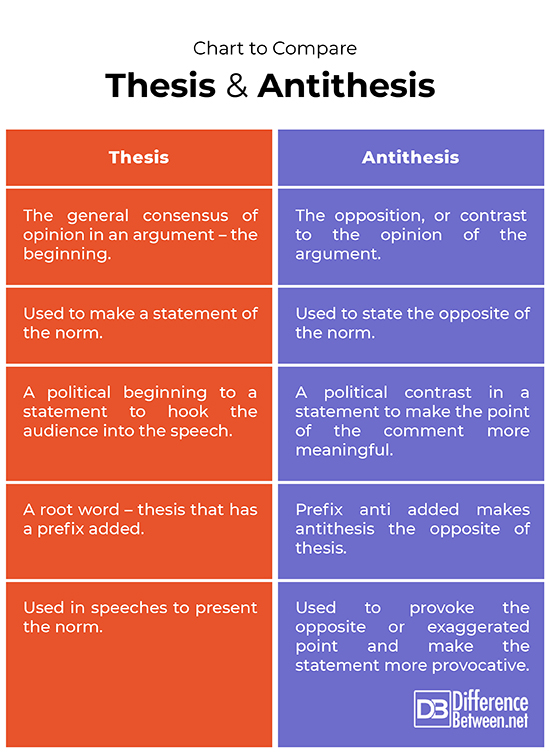
Summary of Thesis and Antithesis:
- Thesis and antithesis are literary devices that highlight themes or emotional rhetorical situations.
- Well known events, using thesis and antithesis, show how this form of rhetoric creates an emotional response from readers or audiences. Neil Armstrong’s comment upon landing and walking on the moon for the first time in history is a shining example.
- The use of thesis and antithesis in literature enable the author to give more emphasis to an event or a theme in a story or play.
- Karl Marx used the thesis, antithesis and conclusion of a synthesis, to explain the evolution of communism.
- Using this format in debate helps to understand how two opposing ideals, around one debatable topic, can help the speakers provide their arguments. The debate is then wrapped up in a synthesis of ideas and the conclusion of the debate leading to a consensus of opinion.
- When well known politicians make a statement using thesis and antithesis, the statement is more powerful. These rhetorical statements become part of our history and become famous for the impact they made using just a few words to express a life changing situation.
- Recent Posts
- Difference Between Lagoon and Bay - October 20, 2021
- Difference Between Futurism and Preterism - August 12, 2021
- Difference Between Dichotomy and Paradox - August 7, 2021
Sharing is caring!
- Pinterest 3
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
- Difference Between Antithesis and Oxymoron
- Difference Between Thesis and Dissertation
- Difference Between Analysis and Synthesis
- Difference Between Full Moon and New Moon
- Difference Between Lunar Eclipse And New Moon
Cite APA 7 Wither, C. (2020, November 23). Difference Between Thesis and Antithesis. Difference Between Similar Terms and Objects. http://www.differencebetween.net/miscellaneous/difference-between-thesis-and-antithesis/. MLA 8 Wither, Christina. "Difference Between Thesis and Antithesis." Difference Between Similar Terms and Objects, 23 November, 2020, http://www.differencebetween.net/miscellaneous/difference-between-thesis-and-antithesis/.
Leave a Response
Name ( required )
Email ( required )
Please note: comment moderation is enabled and may delay your comment. There is no need to resubmit your comment.
Notify me of followup comments via e-mail
References :
Advertisments, more in 'miscellaneous'.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary
- Difference Between an Arbitrator and a Mediator
- Difference Between Cellulite and Stretch Marks
- Difference Between Taliban and Al Qaeda
- Difference Between Kung Fu and Karate
Top Difference Betweens
Get new comparisons in your inbox:, most emailed comparisons, editor's picks.
- Difference Between MAC and IP Address
- Difference Between Platinum and White Gold
- Difference Between Civil and Criminal Law
- Difference Between GRE and GMAT
- Difference Between Immigrants and Refugees
- Difference Between DNS and DHCP
- Difference Between Computer Engineering and Computer Science
- Difference Between Men and Women
- Difference Between Book value and Market value
- Difference Between Red and White wine
- Difference Between Depreciation and Amortization
- Difference Between Bank and Credit Union
- Difference Between White Eggs and Brown Eggs
Definition of Antithesis
Examples of antithesis in everyday speech, common examples of antithesis from famous speeches, examples of proverbs featuring antithesis, utilizing antithesis in writing, antithesis and parallelism, antithesis and juxtaposition, use of antithesis in sentences , examples of antithesis in literature, example 1: hamlet (william shakespeare).
Give every man thine ear, but few thy voice ; Take each man’s censure, but reserve thy judgment.
Example 2: Paradise Lost (John Milton)
Here at least We shall be free; the Almighty hath not built Here for his envy, will not drive us hence: Here we may reign secure, and in my choice To reign is worth ambition though in Hell: Better to reign in Hell, than serve in Heaven.
Example 3: Fire and Ice (Robert Frost)
Some say the world will end in fire, Some say in ice. From what I’ve tasted of desire I hold with those who favor fire. But if it had to perish twice, I think I know enough of hate To say that for destruction ice Is also great And would suffice.
Example 4: The Gettysburg Address by Abraham Lincoln
We have come to dedicate a portion of that field, as a final resting place for those who here gave their lives so that nation might live.
The brave men, living and dead, who struggled here, have consecrated it, far above our poor power to add or detract.
The world will little note, nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here.
Function of Antithesis
Synonyms of antithesis, post navigation.

- Scholarly Community Encyclopedia
- Log in/Sign up

| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | handwiki | -- | 1044 | 2022-10-31 01:38:44 |
Video Upload Options
- MDPI and ACS Style
- Chicago Style
In philosophy, the triad of thesis, antithesis, synthesis (German: These, Antithese, Synthese; originally: Thesis, Antithesis, Synthesis) is a progression of three ideas or propositions. The first idea, the thesis, is a formal statement illustrating a point; it is followed by the second idea, the antithesis, that contradicts or negates the first; and lastly, the third idea, the synthesis, resolves the conflict between the thesis and antithesis. It is often used to explain the dialectical method of German philosopher Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, but Hegel never used the terms himself; instead his triad was concrete, abstract, absolute. The thesis, antithesis, synthesis triad actually originated with Johann Fichte.
1. History of the Idea
Thomas McFarland (2002), in his Prolegomena to Coleridge's Opus Maximum , [ 1 ] identifies Immanuel Kant's Critique of Pure Reason (1781) as the genesis of the thesis/antithesis dyad. Kant concretises his ideas into:
- Thesis: "The world has a beginning in time, and is limited with regard to space."
- Antithesis: "The world has no beginning and no limits in space, but is infinite, in respect to both time and space."
Inasmuch as conjectures like these can be said to be resolvable, Fichte's Grundlage der gesamten Wissenschaftslehre ( Foundations of the Science of Knowledge , 1794) resolved Kant's dyad by synthesis, posing the question thus: [ 1 ]
- No synthesis is possible without a preceding antithesis. As little as antithesis without synthesis, or synthesis without antithesis, is possible; just as little possible are both without thesis.
Fichte employed the triadic idea "thesis–antithesis–synthesis" as a formula for the explanation of change. [ 2 ] Fichte was the first to use the trilogy of words together, [ 3 ] in his Grundriss des Eigentümlichen der Wissenschaftslehre, in Rücksicht auf das theoretische Vermögen (1795, Outline of the Distinctive Character of the Wissenschaftslehre with respect to the Theoretical Faculty ): "Die jetzt aufgezeigte Handlung ist thetisch, antithetisch und synthetisch zugleich." ["The action here described is simultaneously thetic, antithetic, and synthetic." [ 4 ] ]
Still according to McFarland, Schelling then, in his Vom Ich als Prinzip der Philosophie (1795), arranged the terms schematically in pyramidal form.
According to Walter Kaufmann (1966), although the triad is often thought to form part of an analysis of historical and philosophical progress called the Hegelian dialectic, the assumption is erroneous: [ 5 ]
Whoever looks for the stereotype of the allegedly Hegelian dialectic in Hegel's Phenomenology will not find it. What one does find on looking at the table of contents is a very decided preference for triadic arrangements. ... But these many triads are not presented or deduced by Hegel as so many theses, antitheses, and syntheses. It is not by means of any dialectic of that sort that his thought moves up the ladder to absolute knowledge.
Gustav E. Mueller (1958) concurs that Hegel was not a proponent of thesis, antithesis, and synthesis, and clarifies what the concept of dialectic might have meant in Hegel's thought. [ 6 ]
"Dialectic" does not for Hegel mean "thesis, antithesis, and synthesis." Dialectic means that any "ism" – which has a polar opposite, or is a special viewpoint leaving "the rest" to itself – must be criticized by the logic of philosophical thought, whose problem is reality as such, the "World-itself".
According to Mueller, the attribution of this tripartite dialectic to Hegel is the result of "inept reading" and simplistic translations which do not take into account the genesis of Hegel's terms:
Hegel's greatness is as indisputable as his obscurity. The matter is due to his peculiar terminology and style; they are undoubtedly involved and complicated, and seem excessively abstract. These linguistic troubles, in turn, have given rise to legends which are like perverse and magic spectacles – once you wear them, the text simply vanishes. Theodor Haering's monumental and standard work has for the first time cleared up the linguistic problem. By carefully analyzing every sentence from his early writings, which were published only in this century, he has shown how Hegel's terminology evolved – though it was complete when he began to publish. Hegel's contemporaries were immediately baffled, because what was clear to him was not clear to his readers, who were not initiated into the genesis of his terms. An example of how a legend can grow on inept reading is this: Translate "Begriff" by "concept," "Vernunft" by "reason" and "Wissenschaft" by "science" – and they are all good dictionary translations – and you have transformed the great critic of rationalism and irrationalism into a ridiculous champion of an absurd pan-logistic rationalism and scientism. The most vexing and devastating Hegel legend is that everything is thought in "thesis, antithesis, and synthesis." [ 7 ]
Karl Marx (1818–1883) and Friedrich Engels (1820–1895) adopted and extended the triad, especially in Marx's The Poverty of Philosophy (1847). Here, in Chapter 2, Marx is obsessed by the word "thesis"; [ 8 ] it forms an important part of the basis for the Marxist theory of history. [ 9 ]
2. Writing Pedagogy
In modern times, the dialectic of thesis, antithesis, and synthesis has been implemented across the world as a strategy for organizing expositional writing. For example, this technique is taught as a basic organizing principle in French schools: [ 10 ]
The French learn to value and practice eloquence from a young age. Almost from day one, students are taught to produce plans for their compositions, and are graded on them. The structures change with fashions. Youngsters were once taught to express a progression of ideas. Now they follow a dialectic model of thesis-antithesis-synthesis. If you listen carefully to the French arguing about any topic they all follow this model closely: they present an idea, explain possible objections to it, and then sum up their conclusions. ... This analytical mode of reasoning is integrated into the entire school corpus.
Thesis, Antithesis, and Synthesis has also been used as a basic scheme to organize writing in the English language. For example, the website WikiPreMed.com advocates the use of this scheme in writing timed essays for the MCAT standardized test: [ 11 ]
For the purposes of writing MCAT essays, the dialectic describes the progression of ideas in a critical thought process that is the force driving your argument. A good dialectical progression propels your arguments in a way that is satisfying to the reader. The thesis is an intellectual proposition. The antithesis is a critical perspective on the thesis. The synthesis solves the conflict between the thesis and antithesis by reconciling their common truths, and forming a new proposition.
- Samuel Taylor Coleridge: Opus Maximum. Princeton University Press, 2002, p. 89.
- Harry Ritter, Dictionary of Concepts in History. Greenwood Publishing Group (1986), p.114
- Williams, Robert R. (1992). Recognition: Fichte and Hegel on the Other. SUNY Press. p. 46, note 37.
- Fichte, Johann Gottlieb; Breazeale, Daniel (1993). Fichte: Early Philosophical Writings. Cornell University Press. p. 249.
- Walter Kaufmann (1966). "§ 37". Hegel: A Reinterpretation. Anchor Books. ISBN 978-0-268-01068-3. OCLC 3168016. https://archive.org/details/hegelreinterpret00kauf.
- Mueller, Gustav (1958). "The Hegel Legend of "Thesis-Antithesis-Synthesis"". Journal of the History of Ideas 19 (4): 411–414. doi:10.2307/2708045. https://dx.doi.org/10.2307%2F2708045
- Mueller 1958, p. 411.
- marxists.org: Chapter 2 of "The Poverty of Philosophy", by Karl Marx https://www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1847/poverty-philosophy/ch02.htm
- Shrimp, Kaleb (2009). "The Validity of Karl Marx's Theory of Historical Materialism". Major Themes in Economics 11 (1): 35–56. https://scholarworks.uni.edu/mtie/vol11/iss1/5/. Retrieved 13 September 2018.
- Nadeau, Jean-Benoit; Barlow, Julie (2003). Sixty Million Frenchmen Can't Be Wrong: Why We Love France But Not The French. Sourcebooks, Inc.. p. 62. https://archive.org/details/sixtymillionfren00nade_041.
- "The MCAT writing assignment.". Wisebridge Learning Systems, LLC. http://www.wikipremed.com/mcat_essay.php. Retrieved 1 November 2015.

- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Advisory Board


- Ask LitCharts AI
- Discussion Question Generator
- Essay Prompt Generator
- Quiz Question Generator

- Literature Guides
- Poetry Guides
- Shakespeare Translations
- Literary Terms

Antithesis Definition
What is antithesis? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
Antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two contrasting or opposing ideas, usually within parallel grammatical structures. For instance, Neil Armstrong used antithesis when he stepped onto the surface of the moon in 1969 and said, "That's one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind." This is an example of antithesis because the two halves of the sentence mirror each other in grammatical structure, while together the two halves emphasize the incredible contrast between the individual experience of taking an ordinary step, and the extraordinary progress that Armstrong's step symbolized for the human race.
Some additional key details about antithesis:
- Antithesis works best when it is used in conjunction with parallelism (successive phrases that use the same grammatical structure), since the repetition of structure makes the contrast of the content of the phrases as clear as possible.
- The word "antithesis" has another meaning, which is to describe something as being the opposite of another thing. For example, "love is the antithesis of selfishness." This guide focuses only on antithesis as a literary device.
- The word antithesis has its origins in the Greek word antithenai , meaning "to oppose." The plural of antithesis is antitheses.
How to Pronounce Antithesis
Here's how to pronounce antithesis: an- tith -uh-sis
Antithesis and Parallelism
Often, but not always, antithesis works in tandem with parallelism . In parallelism, two components of a sentence (or pair of sentences) mirror one another by repeating grammatical elements. The following is a good example of both antithesis and parallelism:
To err is human , to forgive divine .
The two clauses of the sentence are parallel because each starts off with an infinitive verb and ends with an adjective ("human" and "divine"). The mirroring of these elements then works to emphasize the contrast in their content, particularly in the very strong opposite contrast between "human" and "divine."
Antithesis Without Parallelism
In most cases, antitheses involve parallel elements of the sentence—whether a pair of nouns, verbs, adjectives, or other grammar elements. However, it is also possible to have antithesis without such clear cut parallelism. In the Temptations Song "My Girl," the singer uses antithesis when he says:
"When it's cold outside , I've got the month of May ."
Here the sentence is clearly cut into two clauses on either side of the comma, and the contrasting elements are clear enough. However, strictly speaking there isn't true parallelism here because "cold outside" and "month of May" are different types of grammatical structures (an adjective phrase and a noun phrase, respectively).
Antithesis vs. Related Terms
Three literary terms that are often mistakenly used in the place of antithesis are juxtaposition , oxymoron , and foil . Each of these three terms does have to do with establishing a relationship of difference between two ideas or characters in a text, but beyond that there are significant differences between them.
Antithesis vs. Juxtaposition
In juxtaposition , two things or ideas are placed next to one another to draw attention to their differences or similarities. In juxtaposition, the pairing of two ideas is therefore not necessarily done to create a relationship of opposition or contradiction between them, as is the case with antithesis. So, while antithesis could be a type of juxtaposition, juxtaposition is not always antithesis.
Antithesis vs. Oxymoron
In an oxymoron , two seemingly contradictory words are placed together because their unlikely combination reveals a deeper truth. Some examples of oxymorons include:
- Sweet sorrow
- Cruel kindness
- Living dead
The focus of antithesis is opposites rather than contradictions . While the words involved in oxymorons seem like they don't belong together (until you give them deeper thought), the words or ideas of antithesis do feel like they belong together even as they contrast as opposites. Further, antitheses seldom function by placing the two words or ideas right next to one another, so antitheses are usually made up of more than two words (as in, "I'd rather be among the living than among the dead").
Antithesis vs. Foil
Some Internet sources use "antithesis" to describe an author's decision to create two characters in a story that are direct opposites of one another—for instance, the protagonist and antagonist . But the correct term for this kind of opposition is a foil : a person or thing in a work of literature that contrasts with another thing in order to call attention to its qualities. While the sentence "the hare was fast, and the tortoise was slow" is an example of antithesis, if we step back and look at the story as a whole, the better term to describe the relationship between the characters of the tortoise and the hare is "foil," as in, "The character of the hare is a foil of the tortoise."
Antithesis Examples
Antithesis in literature.
Below are examples of antithesis from some of English literature's most acclaimed writers — and a comic book!
Antithesis in Charles Dickens' A Tale of Two Cities
In the famous opening lines of A Tale of Two Cities , Dickens sets out a flowing list of antitheses punctuated by the repetition of the word "it was" at the beginning of each clause (which is itself an example of the figure of speech anaphora ). By building up this list of contrasts, Dickens sets the scene of the French Revolution that will serve as the setting of his tale by emphasizing the division and confusion of the era. The overwhelming accumulation of antitheses is also purposefully overdone; Dickens is using hyperbole to make fun of the "noisiest authorities" of the day and their exaggerated claims. The passage contains many examples of antithesis, each consisting of one pair of contrasting ideas that we've highlighted to make the structure clearer.
It was the best of times , it was the worst of times , it was the age of wisdom , it was the age of foolishness , it was the epoch of belief , it was the epoch of incredulity , it was the season of Light , it was the season of Darkness , it was the spring of hope , it was the winter of despair , we had everything before us, we had nothing before us, we were all going direct to Heaven , we were all going direct the other way —in short, the period was so far like the present period, that some of its noisiest authorities insisted on its being received, for good or for evil, in the superlative degree of comparison only.
Antithesis in John Milton's Paradise Lost
In this verse from Paradise Lost , Milton's anti-hero , Satan, claims he's happier as the king of Hell than he could ever have been as a servant in Heaven. He justifies his rebellion against God with this pithy phrase, and the antithesis drives home the double contrast between Hell and Heaven, and between ruling and serving.
Better to reign in Hell than serve in Heaven.
Antithesis in William Shakespeare's Othello
As the plot of Othello nears its climax , the antagonist of the play, Iago, pauses for a moment to acknowledge the significance of what is about to happen. Iago uses antithesis to contrast the two opposite potential outcomes of his villainous plot: either events will transpire in Iago's favor and he will come out on top, or his treachery will be discovered, ruining him.
This is the night That either makes me or fordoes me quite .
In this passage, the simple word "either" functions as a cue for the reader to expect some form of parallelism, because the "either" signals that a contrast between two things is coming.
Antithesis in William Shakespeare's Hamlet
Shakespeare's plays are full of antithesis, and so is Hamlet's most well-known "To be or not to be" soliloquy . This excerpt of the soliloquy is a good example of an antithesis that is not limited to a single word or short phrase. The first instance of antithesis here, where Hamlet announces the guiding question (" to be or not to be ") is followed by an elaboration of each idea ("to be" and "not to be") into metaphors that then form their own antithesis. Both instances of antithesis hinge on an " or " that divides the two contrasting options.
To be or not to be , that is the question: Whether 'tis nobler in the mind to suffer The slings and arrows of outrageous fortune Or to take arms against a sea of troubles, And by opposing end them ...
Antithesis in T.S. Eliot's "Four Quartets"
In this excerpt from his poem "Four Quartets," T.S. Eliot uses antithesis to describe the cycle of life, which is continuously passing from beginning to end, from rise to fall, and from old to new.
In my beginning is my end . In succession Houses rise and fall , crumble, are extended, Are removed, destroyed, restored, or in their place Is an open field, or a factory, or a by-pass. Old stone to new building , old timber to new fires ...
Antithesis in Green Lantern's Oath
Comic book writers know the power of antithesis too! In this catchy oath, Green Lantern uses antithesis to emphasize that his mission to defeat evil will endure no matter the conditions.
In brightest day , in blackest night , No evil shall escape my sight. Let those who worship evil's might Beware my power—Green lantern's light!
While most instances of antithesis are built around an "or" that signals the contrast between the two parts of the sentence, the Green Lantern oath works a bit differently. It's built around an implied "and" (to be technical, that first line of the oath is an asyndeton that replaces the "and" with a comma), because members of the Green Lantern corps are expressing their willingness to fight evil in all places, even very opposite environments.
Antithesis in Speeches
Many well-known speeches contain examples of antithesis. Speakers use antithesis to drive home the stakes of what they are saying, sometimes by contrasting two distinct visions of the future.
Antithesis in Patrick Henry's Speech to the Second Virginia Convention, 1775
This speech by famous American patriot Patrick Henry includes one of the most memorable and oft-quoted phrases from the era of the American Revolution. Here, Henry uses antithesis to emphasize just how highly he prizes liberty, and how deadly serious he is about his fight to achieve it.
Is life so dear, or peace so sweet, as to be purchased at the price of chains and slavery? Forbid it, Almighty God! I know not what course others may take: but as for me, give me liberty or give me death .
Antithesis in Martin Luther King Jr.'s Oberlin Commencement Address
In this speech by one of America's most well-known orators, antithesis allows Martin Luther King Jr. to highlight the contrast between two visions of the future; in the first vision, humans rise above their differences to cooperate with one another, while in the other humanity is doomed by infighting and division.
We must all learn to live together as brothers —or we will all perish together as fools .
Antithesis in Songs
In songs, contrasting two opposite ideas using antithesis can heighten the dramatic tension of a difficult decision, or express the singer's intense emotion—but whatever the context, antithesis is a useful tool for songwriters mainly because opposites are always easy to remember, so lyrics that use antithesis tend to stick in the head.
Antithesis in "Should I Stay or Should I Go" by The Clash (1981)
In this song by The Clash, the speaker is caught at a crossroads between two choices, and antithesis serves as the perfect tool to express just how confused and conflicted he is. The rhetorical question —whether to stay or to go—presents two opposing options, and the contrast between his lover's mood from one day (when everything is "fine") to the next (when it's all "black") explains the difficulty of his choice.
One day it's fine and next it's black So if you want me off your back Well, come on and let me know Should I stay or should I go ? Should I stay or should I go now? Should I stay or should I go now? If I go, there will be trouble If I stay it will be double ...
Antithesis in "My Girl" by the Temptations (1965)
In this song, the singer uses a pair of metaphors to describe the feeling of joy that his lover brings him. This joy is expressed through antithesis, since the singer uses the miserable weather of a cloudy, cold day as the setting for the sunshine-filled month of May that "his girl" makes him feel inside, emphasizing the power of his emotions by contrasting them with the bleak weather.
I've got sunshine on a cloudy day When it's cold outside I've got the month of May Well I guess you'd say, What can make me feel this way? My girl, my girl, my girl Talkin' bout my girl.
Why Do Writers Use Antithesis?
Fundamentally, writers of all types use antithesis for its ability to create a clear contrast. This contrast can serve a number of purposes, as shown in the examples above. It can:
- Present a stark choice between two alternatives.
- Convey magnitude or range (i.e. "in brightest day, in darkest night" or "from the highest mountain, to the deepest valley").
- Express strong emotions.
- Create a relationship of opposition between two separate ideas.
- Accentuate the qualities and characteristics of one thing by placing it in opposition to another.
Whatever the case, antithesis almost always has the added benefit of making language more memorable to listeners and readers. The use of parallelism and other simple grammatical constructions like "either/or" help to establish opposition between concepts—and opposites have a way of sticking in the memory.
Other Helpful Antithesis Resources
- The Wikipedia page on Antithesis : A useful summary with associated examples, along with an extensive account of antithesis in the Gospel of Matthew.
- Sound bites from history : A list of examples of antithesis in famous political speeches from United States history — with audio clips!
- A blog post on antithesis : This quick rundown of antithesis focuses on a quote you may know from Muhammad Ali's philosophy of boxing: "Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee."

- Climax (Figure of Speech)
- Figure of Speech
- Juxtaposition
- Parallelism
- Protagonist
- Rhetorical Question
- Flat Character
- Bildungsroman
- Antimetabole
- Rising Action
- Colloquialism
- Connotation
- Deus Ex Machina
- Anadiplosis
- Tragic Hero
- Round Character
- Polysyndeton

- Quizzes, saving guides, requests, plus so much more.
Is MasterClass right for me?
Take this quiz to find out.
How to Use Antithesis in Your Writing: Definition and Examples of Antithesis as a Literary Device
Written by MasterClass
Last updated: Sep 29, 2021 • 3 min read
The English language is full of literary devices that can enliven your writing. One tool used often in literature and politics is called antithesis.

- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- How to Use Antithesis
I. What is an Antithesis?
“Antithesis” literally means “opposite” – it is usually the opposite of a statement, concept, or idea. In literary analysis, an antithesis is a pair of statements or images in which the one reverses the other. The pair is written with similar grammatical structures to show more contrast. Antithesis (pronounced an-TITH-eh-sis) is used to emphasize a concept, idea, or conclusion.
II. Examples of Antithesis
That’s one small step for a man – one giant leap for mankind . (Neil Armstrong, 1969)
In this example, Armstrong is referring to man walking on the moon. Although taking a step is an ordinary activity for most people, taking a step on the moon, in outer space, is a major achievement for all humanity.
To err is human ; to forgive , divine . (Alexander Pope)
This example is used to point out that humans possess both worldly and godly qualities; they can all make mistakes, but they also have the power to free others from blame.
The world will little note , nor long remember , what we say here, but it can never forget what they did (Abraham Lincoln, The Gettysburg Address )
In his speech, Lincoln points out that the details of that moment may not be memorable, but the actions would make history, and therefore, never entirely forgotten.
Antithesis can be a little tricky to see at first. To start, notice how each of these examples is separated into two parts . The parts are separated either by a dash, a semicolon, or the word “but.” Antithesis always has this multi-part structure (usually there are two parts, but sometimes it can be more, as we’ll see in later examples). The parts are not always as obvious as they are in these examples, but they will always be there.
Next, notice how the second part of each example contains terms that reverse or invert terms in the first part: small step vs. giant leap; human vs. divine; we say vs. they do. In each of the examples, there are several pairs of contrasted terms between the first part and the second, which is quite common in antithesis.
Finally, notice that each of the examples contains some parallel structures and ideas in addition to the opposites. This is key! The two parts are not simply contradictory statements. They are a matched pair that have many grammatical structures or concepts in common; in the details, however, they are opposites.
For example, look at the parallel grammar of Example 1: the word “one,” followed by an adjective, a noun, and then the word “for.” This accentuates the opposites by setting them against a backdrop of sameness – in other words, two very different ideas are being expressed with very, very similar grammatical structures.
To recap: antithesis has three things:
- Two or more parts
- Reversed or inverted ideas
- (usually) parallel grammatical structure
III. The Importance of Verisimilitude
Antithesis is basically a complex form of juxtaposition . So its effects are fairly similar – by contrasting one thing against its opposite, a writer or speaker can emphasize the key attributes of whatever they’re talking about. In the Neil Armstrong quote, for example, the tremendous significance of the first step on the moon is made more vivid by contrasting it with the smallness and ordinariness of the motion that brought it about.
Antithesis can also be used to express curious contradictions or paradoxes. Again, the Neil Armstrong quote is a good example: Armstrong is inviting his listeners to puzzle over the fact that a tiny, ordinary step – not so different from the millions of steps we take each day – can represent so massive a technological accomplishment as the moon landing.
Paradoxically, an antithesis can also be used to show how two seeming opposites might in fact be similar.
IV. Examples of Verisimilitude in Literature
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); Forgive us this day our trespasses as we forgive those who trespass against us . (The Lord’s Prayer)
The antithesis is doing a lot of work here. First, it shows the parallel between committing an evil act and being the victim of one. On the surface, these are opposites, and this is part of the antithesis, but at the same time they are, in the end, the same act from different perspectives. This part of the antithesis is basically just an expression of the Golden Rule.
Second, the antithesis displays a parallel between the speaker (a human) and the one being spoken to (God). The prayer is a request for divine mercy, and at the same time a reminder that human beings should also be merciful.
All the joy the world contains has come through wanting happiness for others . All the misery the world contains has come through wanting pleasure for yourself . (Shantideva, The Way of the Bodhisattva )
The antithesis here comes with some pretty intense parallel structure. Most of the words in each sentence are exactly the same as those in the other sentence. (“All the ___ the world contains has come through wanting ____ for ____.”) This close parallel structure makes the antithesis all the more striking, since the words that differ become much more visible.
Another interesting feature of this antithesis is that it makes “pleasure” and “happiness” seem like opposites, when most of us might think of them as more or less synonymous. The quote makes happiness seem noble and exalted, whereas pleasure is portrayed as selfish and worthless.
The proper function of man is to live , not to exist . I shall not waste my days in trying to prolong (Jack London, Credo )
The opening antithesis here gets its punch from the fact that we think of living and existing as pretty similar terms. But for London, they are opposites. Living is about having vivid experiences, learning, and being bold; simply existing is a dull, pointless thing. These two apparently similar words are used in this antithesis to emphasize the importance of living as opposed to mere existing.
The second antithesis, on the other hand, is just the opposite – in this case, London is taking two words that seem somewhat opposed (waste and prolong), and telling us that they are in fact the same . Prolonging something is making it last; wasting something is letting it run out too soon. But, says London, when it comes to life, they are the same. If you try too hard to prolong your days (that is, if you’re so worried about dying that you never face your fears and live your life), then you will end up wasting them because you will never do anything worthwhile.
V. Examples of Verisimilitude in Pop Culture
Everybody doesn’t like something, but nobody doesn’t like Sara Lee. (Sara Lee pastry advertisement)
This classic ad uses antithesis to set up a deliberate grammatical error. This is a common technique in advertising, since people are more likely to remember a slogan that is grammatically incorrect. (Even if they only remember it because they found it irritating, it still sticks in their brain, which is all that an ad needs to do.) The antithesis helps make the meaning clear, and throws the grammatical error into sharper relief.
What men must know , a boy must learn . (The Lookouts)
Here’s another example of how parallel structure can turn into antithesis fairly easily. (The structure is noun-“must”-verb. ) The antithesis also expresses the basic narrative of The Lookouts , which is all about kids learning to fend for themselves and become full-fledged adults.
Shut Your Mouth and Open Your Eyes (the band “AFI” – album title)
The antithesis here is a juxtaposition of two different actions (opening and shutting) that are actually part of the same sort of behavior – the behavior of somebody who wants to understand the world rather than be the center of attention. It’s basically a restatement of the old adage that “those who speak the most often have the least to say.”
VI. Related Terms
- Juxtaposition
Antithesis is basically a form of juxtaposition . Juxtaposition, though, is a much broader device that encompasses any deliberate use of contrast or contradiction by an author. So, in addition to antithesis, it might include:
- The scene in “The Godfather” where a series of brutal murders is intercut with shots of a baptism, juxtaposing birth and death.
- “A Song of Ice and Fire” (George R. R. Martin book series)
- Heaven and Hell
- Mountains and the sea
- Dead or alive
- “In sickness and in health”
Antithesis performs a very similar function, but does so in a more complicated way by using full sentences (rather than single words or images) to express the two halves of the juxtaposition.
Here is an antithesis built around some of the common expressions from above
- “ Sheep go to Heaven ; goats go to Hell .”
- “Beethoven’s music is as mighty as the mountains and as timeless as the sea .”
- “In sickness he loved me; in health he abandoned ”
Notice how the antithesis builds an entire statement around the much simpler juxtaposition. And, crucially, notice that each of those statements exhibits parallel grammatical structure . In this way, both Juxtaposition and parallel structures can be used to transform a simple comparison, into antithesis.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website

Literature Review Survival Library Guide: Thesis, antithesis and synthesis
- What is a literature review?
- Thesis, antithesis and synthesis
- 1. Choose your topic
- 2. Collect relevant material
- 3. Read/Skim articles
- 4. Group articles by themes
- 5. Use citation databases
- 6. Find agreement & disagreement
- Review Articles - A new option on Google Scholar
- How To Follow References
- Newspaper archives
- Aditi's Humanities Referencing Style Guide
- Referencing and RefWorks
- New-version RefWorks Demo
- Tracking Your Academic Footprint This link opens in a new window
- Finding Seminal Authors and Mapping the Shape of the Literature
- Types of Literature Review, including "Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide"
- Research Data Management
- Tamzyn Suleiman's guide to Systematic Reviews
- Danielle Abrahamse's Search String Design and Search Template
Thesis, antithesis, synthesis
The classic pattern of academic arguments is:
Thesis, antithesis, synthesis.
An Idea (Thesis) is proposed, an opposing Idea (Antithesis) is proposed, and a revised Idea incorporating (Synthesis) the opposing Idea is arrived at. This revised idea sometimes sparks another opposing idea, another synthesis, and so on…
If you can show this pattern at work in your literature review, and, above all, if you can suggest a new synthesis of two opposing views, or demolish one of the opposing views, then you are almost certainly on the right track.
Next topic: Step 1: Choose your topic
- << Previous: What is a literature review?
- Next: 1. Choose your topic >>
- Last Updated: Apr 2, 2024 12:22 PM
- URL: https://libguides.lib.uct.ac.za/litreviewsurvival

Contradiction
Do I contradict myself? Very well, then, I contradict myself. (I am large, I contain multitudes.) —Walt Whitman, “Song of Myself”
Vorrei e non vorrei. —Zerlina, “Là ci darem la mano”, Don Giovanni
This entry outlines the role of the law of non-contradiction (LNC) as the foremost among the first (indemonstrable) principles of Aristotelian philosophy and its heirs, and depicts the relation between LNC and LEM (the law of excluded middle) in establishing the nature of contradictory and contrary opposition. §1 presents the classical treatment of LNC as an axiom in Aristotle's “First Philosophy” and reviews the status of contradictory and contrary opposition as schematized on the Square of Opposition. §2 explores in further detail the possible characterizations of LNC and LEM, including the relevance of future contingent statements in which LEM (but not LNC) is sometimes held to fail. In §3 I briefly discuss the mismatch between the representation of contradictory negation as a propositional operator and its varied realization within natural language. §4 deals with several challenges to LNC within Western philosophy, including the paradoxes, and the relation between systems with truth-value gaps (violating LEM) and those with truth-value gluts (violating LNC). Finally, in §5, the tetralemma of Buddhist logic is discussed within the context of gaps and gluts; it is argued that apparent violations of LNC in this tradition and others can in be attributed to either differing viewpoints of evaluation (as foreseen by Aristotle) or to intervening modal and epistemic operators.
1. LNC as Indemonstrable
2. lem and lnc, 3. contradictory negation in term and propositional logic, 4. gaps and gluts: lnc and its discontents, 5. lnc and the buddhist tetralemma, bibliography, other internet resources, related entries.
The twin foundations of Aristotle's logic are the law of non-contradiction (LNC) (also called the law of contradiction) and the law of excluded middle (LEM). In Metaphysics Book Gamma, LNC—“the most certain of all principles”—is defined as follows:
It is impossible that the same thing can at the same time both belong and not belong to the same object and in the same respect, and all other specifications that might be made, let them be added to meet local objections (1005b19-23).
For Aristotle, the status of LNC as a first, indemonstrable principle is obvious. Those who stubbornly demand a proof of LNC simply “lack education”: since “a demonstration of everything is impossible”, resulting in infinite regress, at least some principles must be taken as primitive axiomata rather than derived from other propositions—and what principle more merits this status than LNC? (1006a6-12). In first philosophy, as in mathematics, an axiom is both indemonstrable and indispensable; without LNC, “a is F ” and “a is not F ” are indistinguishable and no argumentation is possible. While Sophists and “even many physicists” may claim that it is possible for the same thing to be and not to be at the same time and in the same respect, such a position self-destructs “if only our opponent says something”, since as soon as he opens his mouth to make an assertion, any assertion, he must accept LNC. But what if he does not open his mouth? Against such an individual “it is ridiculous to seek an argument” for he is no more than a vegetable (1006a1-15).
The role of LNC as the basic, indemonstrable “first principle” is affirmed by Leibniz, for whom LNC is taken as interdefinable with another of Aristotle's axiomata, the Law of Identity: “Nothing should be taken as first principles but experiences and the axiom of identity or (what is the same thing) contradiction, which is primitive, since otherwise there would be no difference between truth and falsehood, and all investigation would cease at once, if to say yes or no were a matter of indifference” (Leibniz 1696/Langley 1916: 13-14). For Leibniz, everybody—even “barbarians”—must tacitly assume LNC as part of innate knowledge implicitly called upon at every moment, thus demonstrating the insufficiency of Locke's empiricism (ibid., 77). [ 1 ]
In accounting for the incompatibility of truth and falsity, LNC lies at the heart of the theory of opposition, governing both contradictories and contraries. (See traditional square of opposition .) Contradictory opposites (“She is sitting”/“She is not sitting”) are mutually exhaustive as well as mutually inconsistent; one member of the pair must be true and the other false. As it was put by the medievals, contradictory opposites divide the true and the false between them; for Aristotle, this is the primary form of opposition. [ 2 ] Contrary opposites (“He is happy”/“He is sad”) are mutually inconsistent but not necessarily exhaustive; they may be simultaneously false, though not simultaneously true. LNC applies to both forms of opposition in that neither contradictories nor contraries may belong to the same object at the same time and in the same respect ( Metaphysics 1011b17-19). What distinguishes the two forms of opposition is a second indemonstrable principle, the law of excluded middle (LEM): “Of any one subject, one thing must be either asserted or denied” ( Metaphysics 1011b24). Both laws pertain to contradictories, as in a paired affirmation (“ S is P ”) and denial (“ S isn't P ”): the negation is true whenever the affirmation is false, and the affirmation is true when the negation is false. Thus, a corresponding affirmation and negation cannot both be true , by LNC, but neither can they both be false , by LEM. But while LNC applies both to contradictory and contrary oppositions, LEM holds only for contradictories: “Nothing can exist between two contradictories, but something may exist between contraries” ( Metaphysics 1055b2): a dog cannot be both black and white, but it may be neither.
As Aristotle explains in the Categories, the opposition between contradictories— “statements opposed to each other as affirmation and negation”—is defined in two ways. First, unlike contrariety, contradiction is restricted to statements or propositions; terms are never related as contradictories. Second, “in this case, and in this case only, it is necessary for the one to be true and the other false” (13b2-3).
Opposition between terms cannot be contradictory in nature, both because only statements (subject-predicate combinations) can be true or false ( Categories 13b3-12) and because any two terms may simultaneously fail to apply to a given subject. [ 3 ] But two statements may be members of either a contradictory or a contrary opposition. Such statements may be simultaneously false, although (as with contradictories) they may not be simultaneously true. The most striking aspect of the exposition for a modern reader lies in Aristotle's selection of illustrative material. Rather than choosing an uncontroversial example involving mediate contraries, those allowing an unexcluded middle (e.g. “This dog is white”/“This dog is black”; “Socrates is good”/“Socrates is bad”), Aristotle offers a pair of sentences containing immediate contraries, “Socrates is sick”/“Socrates is well”. These propositions may both be false, even though every person is either ill or well: “For if Socrates exists, one will be true and the other false, but if he does not exist, both will be false; for neither ‘Socrates is sick’ nor ‘Socrates is well’ will be true, if Socrates does not exist at all” (13b17-19). But given a corresponding affirmation and negation, one will always be true and the other false; the negation “Socrates is not sick” is true whether the philosopher is healthy or non-existent: “for if he does not exist, ‘he is sick’ is false but ‘he is not sick’ true” (13b26-35).
Members of a canonical pair of contradictories are formally identical except for the negative particle:
An affirmation is a statement affirming something of something, a negation is a statement denying something of something…It is clear that for every affirmation there is an opposite negation, and for every negation there is an opposite affirmation…Let us call an affirmation and a negation which are opposite a contradiction ( De Interpretatione 17a25-35).
But this criterion, satisfied simply enough in the case of singular expressions, must be recast in the case of quantified expressions, both those which “signify universally” (“every man”, “no man”) and those which do not (“some man”, “not every man”).
For such cases, Aristotle shifts from a formal to a semantically based criterion of opposition (17b16-25). The A / O pair (“Every man is white”, “Not every man is white”) and I / E pair (“Some man is white”, “No man is white”) are contradictories because in any state of affairs one member of each pair must be true and the other false. (See traditional square of opposition .) Similarly, the A / E pair—“Every man is just”, “No man is just”—are contraries, since these cannot be true together. The contradictories of two contraries (“Not every man is just”, “Some man is just”) can be simultaneously true with reference to the same subject; (17b23-25). The last opposition of I and O statements, later to be dubbed subcontraries because they appear below the contraries on the traditional square, is a peculiar opposition indeed; Aristotle elsewhere ( Prior Analytics 63b21-30) sees I and O as “only verbally opposed”, given the mutual consistency of “Some Greeks are bald” and “Some Greeks aren't bald”.
The same relations obtain for modal propositions, those involving binary connectives like “and” and “or”, quantificational adverbs, and a range of other expressions that can be mapped in analogous ways (see Horn 1989). Thus for example we have the following modal square, based on De Interpretatione 21b10ff. and Prior Analytics 32a18-28:
(1) Modal Square
In the twelfth century, Peter of Spain (1972: 7) offers a particularly elegant formulation in his Tractatus ; it will be seen that these apply to the modal propositions in (1) as well as to the quantificational statements in the original square:
- Each contradictory is equivalent to the negation of the other.
- Each contradictory entails and is entailed by the negation of the other.
- Each contrary statement entails the negation of the other but not vice versa. [E.g. “I am happy” unilaterally entails “I am not unhappy”; “It is necessary that Φ” unilaterally entails “It is not impossible that Φ”.]
- The law of subcontraries is such that if one is false the other is true but not vice versa.
The law of excluded middle, LEM, is another of Aristotle's first principles, if perhaps not as first a principle as LNC. Just as Heraclitus's anti-LNC position, “that everything is and is not, seems to make everything true”, so too Anaxagoras's anti-LEM stance, “that an intermediate exists between two contradictories, makes everything false” ( Metaphysics 1012a25-29). Of any two contradictories, LEM requires that one must be true and the other false ( De Interpretatione 18a31)—or does it? In a passage that has launched a thousand treatises, Aristotle ( De Interpretatione , Chapter 9) addresses the difficulties posed by apparently contradictory contingent statements about future events, e.g. (2a,b).
(2a) There will be a sea-battle tomorrow. (2b) There will not be a sea-battle tomorrow.
Clearly, (2a) and (2b) cannot both be true; LNC applies to future contingents as straightforwardly as to any other pair of contradictories. But what of LEM? Here is where the difficulties begin, culminating in the passage with which Aristotle concludes and (apparently) summarizes his account:
It is necessary for there to be or not to be a sea-battle tomorrow; but it not necessary for a sea-battle to take place tomorrow, nor for one not to take place—though it is necessary for one to take place or not to take place. So, since statements are true according to how the actual things are, it is clear that wherever these are such as to allow of contraries as chance has it, the same necessarily holds for the contradictories also. This happens with things that are not always so or are not always not so. With these it is necessary for one or the other of the contradictories to be true or false—not, however, this one or that one, but as chance has it; or for one to be true rather than the other, yet not already true or false. Clearly, then it is not necessary that of every affirmation and opposite negation one should be true and the other false. For what holds for things that are does not hold for things that are not but may possibly be or not be; with these it is as we have said ( De Interpretatione 19a30-b4).
Unfortunately, given the systematic ambiguity and textual variations in the Greek text, the difficulty of telling when Aristotle is speaking with his own voice or characterizing an opponent's argument, and the lack of formal devices for the essential scopal distinctions at issue, it has never been clear exactly just what has been said here and in the chapter more generally. Some, including Boethius and Lukasiewicz, have seen in this text an argument for rejecting LEM for future contingent statements, which are therefore to be assigned a non-classical value (e.g. “Indeterminate”) or no truth-value at all. [ 4 ] Their reasoning is based in part on the premise that the alternative position seems to require the acceptance of determinism. Others, however, read Aristotle as rejecting not simple bivalence for future contingents but rather determinacy itself. This interpretive tradition, endorsed by al-Fârâbi, Saint Thomas, and Ockham, is crystallized in this passage from Abelard's Dialectica (210-22) cited by Kneale and Kneale (1962: 214):
No proposition de contingenti futuro can be determinately true or determinately false…, but this is not to say that no such proposition can be true or false. On the contrary, any such proposition is true if the outcome is to be true as it states, even though this is unknown to us.
Even if we accept the view that Aristotle is uncomfortable with assigning truth (or falsity) to (2a) and (2b), their disjunction in (3a) is clearly seen as true, and indeed as necessarily true. But the modal operator must be taken to apply to the disjunction as a whole as in (3b) and not to each disjunct as in (3c).
(3a) Either there will be or there will not be a sea-battle tomorrow. (3b) □ (Φ ∨ ¬Φ) (3c) □ Φ ∨ □ ¬Φ
For Aristotle, LNC is understood not as the principle of propositional logic that no statement can be true simultaneously with its negation, but as a prima facie rejection of the possibility that any predicate F could both hold and not hold of a given subject (at the same time, and in the same respect). A full rendering of the version of LNC appearing at Metaphysics 1006b33-34—“It is not possible to truly say at the same time of a thing that it is a man and that it is not a man”—would require a representation involving operators for modality and truth and allowing quantification over times. [ 5 ] In the same way, LEM is not actually the principle that every statement is either true or has a true negation, but the law that for any predicate F and any entity x , x either is F or isn't F .
But these conceptualizations of LNC and LEM must be generalized, since the principle that it is impossible for a to be F and not to be F will not apply to statements of arbitrary complexity. We can translate the Aristotelian language, with some loss of faithfulness, into the standard modern versions in (4a,b) respectively, ignoring the understood modal and temporal modifications:
(4a) LNC: ¬(Φ & ¬Φ) (4b) LEM: Φ ∨ ¬Φ
Taking LNC and LEM together, we obtain the result that exactly one proposition of the pair {Φ, ¬Φ} is true and exactly one is false, where ¬ represents contradictory negation.
Alternatively, the laws can be recast semantically as in (5), again setting aside the usual qualifications:
(5a) LNC: No proposition may be simultaneously true and false. (5b) LEM: Every proposition must be either true or false.
Not every natural language negation is a contradictory operator, or even a logical operator. A statement may be rejected as false, as unwarranted, or as inappropriate—misleading, badly pronounced, wrongly focused, likely to induce unwanted implicatures or presuppositions, overly or insufficiently formal. Only in the first of these cases, as a toggle between truth and falsity, is it clear that contradictory negation is involved (Horn 1989, Smiley 1993). But is every contradictory negation sentential?
Within propositional logic, contradictory negation is a self-annihilating operator: ¬(¬Φ) is equivalent to Φ. This is explicitly recognized in the proto-Fregean Stoic logic of Alexander of Aphrodisias: “‘Not: not: it is day’ differs from ‘it is day’ only in manner of speech” (Mates 1953: 126). The Stoics' apophatikon directly prefigures the iterating and self-cancelling propositional negation of Frege and Russell. As Frege puts it (1919: 130), “Wrapping up a thought in double negation does not alter its truth value.” The corresponding linguistic principle is expressed in the grammarians' bromide, “Duplex negatio affirmat.”
Not all systems of propositional logic accept a biconditional law of double negation (LDN), ¬(¬Φ) ≡ Φ. In particular, LDN, along with LEM, is not valid for the Intuitionists, who reject ¬(¬Φ) → Φ while accepting its converse, Φ → ¬(¬Φ). But the very possibility of applying negation to a negated statement presupposes the analysis of contradictory negation as an iterative operator (one capable of applying to its own output), or as a function whose domain is identical to its range. Within the categorical term-based logic of Aristotle and his Peripatetic successors, every statement—whether singular or general—is of subject-predicate form. Contradictory negation is not a one-place operator taking propositions into propositions, but rather a mode of predication , a way of combining subjects with predicates: a given predicate can be either affirmed or denied of a given subject. Unlike the apophatikon or propositional negation connective introduced by the Stoics and formalized in Fregean and Russellian logic, Aristotelian predicate denial, while toggling truth and falsity and yielding the semantics of contradictory opposition, does not apply to its own output and hence does not syntactically iterate. In this respect, predicate denial both anticipates the form of negation in Montague Grammar and provides a more plausible representation of contradictory negation in natural language, whether Ancient Greek or English, where reflexes of the iterating one-place connective of the Stoics and Fregeans (“Not: not: the sun is shining”) are hard to find outside of artificial constructs like the “it is not the case” construction (Horn 1989, §7.2). In a given natural language, contradictory negation may be expressed as a particle associated with a copula or a verb, as an inflected auxiliary verb, as a verb of negation, or as a negative suffix or prefix.
In addition, there is a widespread pragmatically motivated tendency for a formal or semantic contradictory negation to be strengthened to a contrary through such processes as litotes (“I don't like prunes” conveying that I dislike prunes) and so-called negative raising (“I don't think that Φ” conveying “I think that ¬Φ”); similarly, the adjective-forming prefixal negation in such words as “unhappy” or “unfair” is understood as a contrary rather than contradictory (not-Adj) of its base. These phenomena have been much discussed by rhetoricians, logicians, and linguists (see Horn 1989: Chap. 5).
In addition to predicate denial, in which a predicate F is denied of a subject a , Aristotelian logic allows for narrow-scope predicate term negation , in which a negative predicate not-F is affirmed of a . The relation of predicate denial and predicate term negation to a simple affirmative proposition can be schematized on a generalized square of opposition ( De Interpretatione 19b19-30, Prior Analytics Chapter 46):
(6) Negation Square
If Socrates doesn't exist, “Socrates is wise” ( A ) and its contrary “Socrates is not-wise” ( E ) are both automatically false (since nothing—positive or negative—can be truly affirmed of a non-existent subject), while their respective contradictories “Socrates is not wise” ( O ) and “Socrates is not not-wise” ( I ) are both true. Similarly, for any object x , either x is red or x is not red—but x may be neither red nor not-red; if, for instance, x is a unicorn or a prime number.
While Russell (1905), without acknowledgment, echoed Aristotle's ambiguist analysis of negation as either contradictory (“external”) or contrary (“internal”), by virtue of the two logical forms assigned to “The king of France is not bald” (see descriptions ), such propositionalized accounts are bought at a cost of naturalness, as singular sentences of subject-predicate grammatical form are assigned the logical form of an existentially quantified conjunction and as names are transmuted into predicates.
In addition to the future contingent statements discussed, vacuous subjects like those in (7a,b) have sometimes been taken to yield a violation of LEM through the emergence of a truth-value gap.
(7a) {The present king of France/King Louis} is bald. (7b) {The present king of France/King Louis} isn't bald.
While Aristotle would see a republican France as rendering (7a) false and (7b) automatically true, Frege (1892) and Strawson (1950) reject the notion that either of these sentences can be used to make a true or false assertion. Instead, both statements presuppose the existence of a referent for the singular term; if the presupposition fails, so does the possibility of classical truth assignment. Note, however, that such analyses present a challenge to LEM only if (7b) is taken as the true contradictory of (7a), an assumption not universally shared. Russell, for example, allows for one reading of (7b) on which it is, like (7a), false in the absence of a referent for the subject term.
In those systems that do embrace truth value gaps (Strawson, arguably Frege) or non-classically-valued systems (Lukasiewicz, Bochvar, Kleene), some sentences or statements are not assigned a (classical) truth value; in Strawson's famous dictum, the question of the truth value of “The king of France is wise”, in a world in which France is a republic, simply fails to arise. The negative form of such vacuous statements, e.g. “The king of France is not wise”, is similarly neither true nor false. This amounts to a rejection of LEM, as noted by Russell 1905. In addition to vacuous singular expressions, gap-based analyses have been proposed for future contingents (following one reading of Aristotle's exposition of the sea-battle; cf. §2 above) and category mistakes (e.g. “The number 7 likes/doesn't like to dance”).
While LNC has traditionally remained more sacrosanct, reflecting its position as the primus inter pares of the indemonstrables, transgressing this final taboo has become increasingly alluring in recent years. The move here involves embracing not gaps but truth value gluts , cases in which a given sentence and its negation are taken to be both true, or alternatively cases in which a sentence may be assigned more than one (classical) truth value, i.e. both True and False. Parsons (1990) observes that the two non-classical theories are provably logically equivalent, as gluts arise within one class of theories precisely where gaps do in the other. Further, dialetheism escapes the charge of incoherence by avoiding the logical armageddon of Ex Contradictione Quodlibet, the inference in (8):
(8) p , ¬ p _____ ∴ q
Far from reduced to the silence of a vegetable, as Aristotle ordained, the proponents of true contradictions, including self-avowed dialetheists like Sylvan (né Routley) and Priest have been eloquent.
Is the status of Aristotle's “first principle” as obvious as he believed? Adherents of the dialetheist view that there are true contradictories (Priest 1987, 1998, 2002; see also dialetheism and paraconsistent logic ) would answer firmly in the negative. [ 6 ] In the Western tradition, the countenancing of true contradictions is typically—although not exclusively—motivated on the basis of such classic logical paradoxes as “This sentence is not true” and its analogues (the Liar, the Barber, Russell's paradox), each of which is true if and only if it is not true. As Smiley (1993: 19) has remarked, “Dialetheism stands to the classical idea of negation like special relativity to Newtonian mechanics: they agree in the familiar areas but diverge at the margins (notably the paradoxes).”
In addition to the Liar, another locus classicus is the problem of omnipotence as crystallized in the Paradox of the Stone. One begins by granting the basic dilemma, as an evident instance of LEM: either God is omnipotent or God is not omnipotent. With omnipotence, He can do anything, and in particular He can create a stone x so heavy that even He cannot lift it. But then there is something He cannot do, viz. (ex hypothesi) lift x . But this is an instance of LNC: God can lift x and God cannot lift x .
This paradox, and the potential challenge it offers to either LNC or the possibility of omnipotence, has been recognized since Aquinas, who opted for retaining the Aristotelian law by understanding omnipotence as the capacity to do only what is not logically impossible. (Others, including Augustine and Maimonides, have noted that in any case God is “unable” to do what is inconsistent with His nature, e.g. commit sin.) For Descartes, on the other hand, an omnipotent God is by definition capable of any task, even those yielding contradictions. Mavrodes (1963), Kenny, and others have sided with Aquinas in taking omnipotence to extend only to those powers it is possible to possess; Frankfurt (1964), on the other hand, essentially adopt the Cartesian line: Yes, of course God can indeed construct a stone that He cannot lift—and what's more, He can lift it! (See also Savage 1967 for a related solution.)
Within Western philosophy, Hegel has often been depicted as a leading LNC-skeptic, but in fact for Hegel an unresolved contradiction is a sign of error. The contradiction between thesis and antithesis results in Aufhebung, the dialectical resolution or superseding of the contradiction between opposites as a higher-level synthesis that eventually generates its own antithesis. Rather than repudiating LNC, Hegel's dialectic rests upon it. In Marxist theory, too, contradictories do not simply cancel out but are dynamically resolved ( aufgehoben ) at a higher level in a way that both preserves and supersedes the contradiction, motivating the historical dialectic. (See Horn 1989: §1.3.2.)
For Freud, there is a realm in which LNC is not so much superseded but dissolved. On the primary, infantile level, reflected in dreams and neuroses, there is no not : “‘No’ seems not to exist as far as dreams are concerned. Anything in a dream can mean its contrary” (Freud 1910: 155). When the analysand insists of a dream character “It's not my mother”, the analyst silently translates, “So it is his mother!”
Given Aristotle's observation that “even some physicists” deny LNC and affirm that is indeed possible for the same thing to be and not to be at the same time and in the same respect, he would not have been surprised to learn that quantum mechanics has made such challenges fashionable again. Thus, we have Schrödinger's celebrated cat, placed (within the context of a thought experiment) inside a sealed box along with radioactive material and a vial of poison gas that will be released if that material decays. Given quantum uncertainty, an atom inhabits both states—decayed and non-decayed—simultaneously, rendering the cat (in the absence of an observer outside the system) both alive and dead. Where speculative consensus breaks down is on whether Schrödinger's paradox arises only when the quantum system is isolated from the environment.
Aristotle himself anticipated many of the challenges that have since been raised against LNC. Thus whether it is the ambivalence of Zerlina's “Vorrei e non vorrei”, Strawson's exchange (1952: 7)
—Were you pleased? —Well, I was and I wasn't.
or the observation of Jainists two millennia ago that “ S is P ” and “ S is not P ” can both be true from different standpoints (Raju 1954: 698-701; Balcerowicz 2003), we have ample opportunity to reflect on the foresight of Aristotle's rider: “ S is P ” and “ S is not P ” cannot both hold in the same sense, at the same time, and in the same respect .
Outside the Western canon, the brunt of the battle over LNC has been largely borne by the Buddhists, particularly in the exposition by Nâgârjuna of the catuskoti or tetralemma (c. 200 A.D.; cf. Bochenski 1961: Part VI, Raju 1954, Garfield 1995, Tillemans 1999, Garfield & Priest 2002), also known as the four-cornered or fourfold negation. Consider the following four possible truth outcomes for any statement and its (apparent) contradictory:
(9) (i) S is P (ii) S is not P (iii) S is both P and not- P (iv) S is neither P nor not- P
For instances of the positive tetralemma, all four statement types can or must be accepted, e.g.:
Everything is real and not real. Both real and not real. Neither real nor not real. That is Lord Buddha's teaching. — Mûla-madhyamaka-kârikâ 18:8, quoted in Garfield (1995: 102)
Such cases arise only when we are beyond the realm to which ordinary logic applies, when “the sphere of thought has ceased.” On the other hand, much more use is made of the negative tetralemma, in which all four of the statements in (9) can or must be rejected. Is this tantamount, as it appears, to the renunciation of LEM and LNC, the countenancing of both gaps and gluts, and thus—in Aristotle's view—the overthrow of all bounds of rational argument?
It should first be noted that the axiomatic status of LNC and LEM is as well-established within the logical traditions of India as it is for the Greeks and their epigones. [ 7 ] And indeed, Garfield (1995) and Tillemans (1999) convincingly refute the claim that Nâgârjuna was an “irrationalist”. [ 8 ] In the first place, if Nâgârjuna simply rejected LNC, there would be no possibility of reductio arguments, which hinge on the establishment of untenable contradictions, yet such arguments are standardly employed in his logic. In fact, he overtly prohibits virodha (contradiction). Crucially, it is only in the realm of the Absolute or Transcendent, where we are contemplating the nature of the ultimate, that contradictions are embraced; in the realm of ordinary reality, LNC operates and classical logic holds. In this sense, the logic of Nâgârjuna and of the Buddhist tradition more generally can be seen not as inconsistent but paraconsistent.
One aspect of the apparent paradox is precisely parallel to that arising with some of the potential counterexamples to the LNC arising in Western thought. In various Buddhist and Jainist systems of thought, the apparent endorsement of Fa & ¬ Fa (or, in propositional terms, Φ & ¬Φ) is upon closer examination qualified in precisely the way foreseen by the codicils in Aristotle's statement of the law: “From a certain viewpoint, Φ (e.g. Nirvana exists); from a certain viewpoint, ¬Φ (e.g. Nirvana does not exist).
To further explore the status of truth-value gluts, in which both classical values are simultaneously assigned to a given proposition (e.g. “ x is real”), let us consider the analogous cases involving gaps. Recall, for example, the case of future contingents as in (2a,b) above: we need not maintain that “Iraq will become a secular democracy” is neither true nor false when uttered today, but only that neither this statement nor its contradictory “Iraq will not become a secular democracy” is assertable today in the absence of foreknowledge. Similarly for past unknowables, such as (to adapt an example from Quine) the proposition that the number of blades of grass on the Old Campus lawn during the 2005 Yale commencement exercises was odd. This is again more plausibly viewed as unassertable than as truth-valueless, even though its truth-value will never be known. To take a third example, we can argue, with Grice (1989: 80ff.), that a negation outside the scope of a conditional is generally intended as a refusal (or hesitation) to assert “if p then q ” rather than as the contradictory negation of a conditional, whose truth value is determined in accord with the standard material equivalence:
(10) ¬( p → q ) ≡ ( p & ¬ q )
Thus, in denying your conditional “If you give her penicillin, she will get better”, I am allowing for the possibility that giving her penicillin might have no effect on her, but I am not predicting that you will administer the penicillin and she will fail to recover. Nor does denying the apothegm (typically though inaccurately attributed to Dostoyevsky or Nietzsche) that if God is dead everything is permitted commit one to the conjoined proposition that God is dead and something is forbidden. As Dummett (1973: 328-30) puts the point, we must distinguish negation outside the scope of a Fregean assertion operator, not (⊢ p ), from the assertion of a negative proposition, ⊢(not p ). The former interpretation “might be taken to be a means of expressing an unwillingness to assert” p , in particular when p is a conditional:
(11) X : If it rains, the match will be canceled. Y : That's not so. ( or, I don't think that's the case.)
Y 's contribution here does not constitute a negation of X 's content; rather, we can paraphrase Y as conveying (11′a) or (11′b):
(11′a) If it rains, the match won't necessarily be canceled. (11′b) It may [ epistemic ] happen that it rains and yet the match is not canceled.
Dummett observes, “We have no negation of the conditional of natural language, that is, no negation of its sense: we have only a form for expressing refusal to assent to its assertion.”
Similarly with disjunction. Consider the exchange in (12) preceding the 2000 election, updated from an example of Grice:
(12) X : Bush or Gore will be elected. Y : That's not so: Bush or Gore or Nader will be elected.
Y 's rejoinder cannot be a contradictory of the content of X 's claim, since the (de jure) election of Bush rendered both X 's and Y 's statements true. Rather, Y objects on the grounds that X is not in an epistemic position to assert the binary disjunction.
Unassertability can be read as the key to the apparent paradox of the catuskoti as well. The venerable text in Majjhima-nikâya 72, relating the teachings of the historical Buddha, offers a precursor for Nâgârjuna's doctrine of the negative tetralemma. Gotama is responding to a monk's question concerning the doctrine of rebirth (quoted in Robinson 1967: 54):
Gotama, where is the monk reborn whose mind is thus freed? Vaccha, it is not true to say that he is reborn. Then, Gotama, he is not reborn. Vaccha, it is not true to say that he is not reborn. Then, Gotama, he is both reborn and not reborn. Vaccha, it is not true to say that he is both reborn and not reborn. Then, Gotama, he is neither reborn nor not reborn. Vaccha, it is not true to say that he is neither reborn nor not reborn.
Note the form of the translation here, or similarly that of the standard rendering of the negative catuskoti that “it profits not” to assert Φ, to assert ¬Φ, to assert both Φ and ¬Φ, or to assert neither Φ nor ¬Φ: the relevant negation can be taken to operate over an implicit modal, in particular an epistemic or assertability operator. If so, neither LEM nor LNC is directly at stake in the tetralemma: you can have your Aristotle and Buddha too.
We tend to recalibrate apparent violations of LNC as conforming to a version of the law that incorporates the Aristotelian qualifications: a sincere defense of “ p and not- p ” plausibly involves a change in the context of evaluation or a shift in viewpoint, or alternatively a suppression of modal or epistemic operators. This practice can be seen as an instance of a general methodological principle associated with Davidson and Quine that has come to be called the principle of charity (or, alternately, the principle of rational accommodation ): when it is unclear how to interpret another's argument, interpret it in a way that makes the most sense. At the same time, this procedure evokes the standard Gricean mode of explanation: granted the operation of the Cooperative Principle and, more broadly, the premise of Rationality, we reinterpret apparent violations of valid principles or maxims so as to conserve the assumption that one's interlocutor is a rational and cooperative agent. As Aristotle would remind us, no principle is more worthy of conservation than the Law of Non-Contradiction.
- Aristotle. Categories and De Interpretatione , J. N. Ackrill, ed., Oxford: Clarendon, 1963.
- Aristotle. Metaphysics , Hippocrates Apostle, ed., Bloomington: Indiana U. Press, 1966.
- Aristotle. Prior and Posterior Analytics , W. D. Ross, ed., Oxford: Clarendon, 1957.
- Balcerowicz, Piotr (2003). "Some remarks on the Naya method," in Essays in Jaina Philosophy and Religion. Warsaw Indological Studies , Vol. 2, pp. 37-68.
- Barnes, Jonathan (1969). "The law of contradiction," Philosophical Quarterly 19: 302-309.
- Bochenski, I. M. (1961). A History of Formal Logic , Ivo Thomas, ed. and trans., Notre Dame: U. of Notre Dame Press.
- Dummett, Michael (1973). Frege: philosophy of language , London: Duckworth.
- Frankfurt, Harry (1964). "The logic of omnipotence," Philosophical Review 73: 262-63.
- Frege, Gottlob (1892). "On sense and reference", in Translations from the Philosophical Writings of Gottlob Frege , P. Geach and M. Black, eds., Oxford: Blackwell, 1952, pp. 56-78.
- Frege, Gottlob (1919). "Negation," in Translations from the Philosophical Writings of Gottlob Frege , P. Geach and M. Black, eds., Oxford: Blackwell, 1952, pp. 117-35.
- Freud, Sigmund (1910). "The antithetical sense of primal words," in J. Strachey (ed.), The Standard Edition of the Complete Psychological Works of Sigmund Freud , Vol. 11, 155-61. London: Hogarth Press, 1957.
- Garfield, Jay (1995). The fundamental wisdom of the middle way: Nâgârjuna's Mûlamadhyamakakârikâ , Translation and commentary by Jay L. Garfield. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Garfield, Jay and Graham Priest (2002). "Nâgârjuna and the limits of thought," in Priest (2002), pp. 249-70.
- Geach, P. T. (1972). Logic Matters , reprinted Berkeley: U. of California Press, 1980.
- Grice, H. P. (1989). Studies in the Way of Words , Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
- Horn, Laurence (1989). A Natural History of Negation , Chicago: U. of Chicago Press. Reissue edition, Stanford: CSLI, 2001.
- Kneale, William and Martha Kneale (1962). The Development of Logic , Oxford: Clarendon.
- Kumârila Bhatta, The Mîmânsâ-sloka-vârtika , R. Talainga, ed., Benares: Freeman & Co., 1899.
- Lear, Jonathan (1980). Aristotle and Logical Theory , Cambridge: Cambridge U. Press.
- Leibniz, Gottfried (1696). New Essays Concerning Human Understanding by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz , A. G. Langley, ed. and trans., 2d ed., Chicago: Open Court, 1916.
- Lukasiewicz, Jan ([1910] 1971). "On the principle of contradiction in Aristotle", trans. by V. Wedin, Review of Metaphysics 24: 485-509.
- Mates, Benson (1953). Stoic Logic , Berkeley and Los Angeles: U. of California Press.
- Mavrodes, George (1963). "Some puzzles concerning omnipotence," Philosophical Review 72: 221-23.
- Parsons, Terry (1990). "True Contradictions," Canadian Journal Philosophy 20: 335-53.
- Peter of Spain, Tractatus, called afterwards Summulae Logicales , L. M. de Rijk, ed., Assen: van Gorcum, 1972.
- Priest, Graham (1987). In Contradiction , Dordrecht: M. Nijhoff.
- ––– (1998). "To be and not to be—that is the answer. On Aristotle on the law of non-contradiction," Philosophiegeschichte und logische Analyse 1: 91-130.
- ––– (2002). Beyond the Limits of Thought , Oxford: Oxford U. Press.
- Priest, Graham, J. C. Beall, and Bradley Armour-Garb, eds. (2004). The Law of Non-Contradiction: New Philosophical Essays , Oxford: Clarendon.
- Raju, P. T. (1954). "The principle of four-cornered negation in Indian philosophy," Review of Metaphysics 7: 694-713.
- Robinson, Richard (1967). Early Mâdhyamika in India and China , Madison: U. of Wisconsin Press.
- Russell, Bertrand (1905). "On descriptions", Mind 14: 479-93.
- Savage, C. Wade (1967). "The paradox of the stone," Philosophical Review 76: 74-79.
- Smiley, Timothy (1993). "Can contradictions be true?," Aristotelian Society Supplement Volume 67: 17-33.
- Strawson, P. F. (1952). Introduction to Logical Theory , London: Methuen.
- Tillemans, Tom (1999). "Is Buddhist Logic non-classical or deviant?," Chapter 9 in Scripture, Logic, Language , Boston: Wisdom Publications.
[Please contact the author with suggestions.]
Aristotle, General Topics: logic | Aristotle, General Topics: metaphysics | dialetheism [dialethism] | Russell's paradox | square of opposition
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to an anonymous reader and to Professor Piotr Balcerowicz for very helpful comments.
What are you looking for?
Quick links.
Click here to find all our contact information
What is antithesis? A guide with examples
Find out how to use antithesis to improve your writing and see examples of antithesis being used in literature, poetry and advertising.

Introduction
This blog post is part of the Semantix copywriters’ toolkit, which is a great resource for writing professionals and all those looking to improve their writing, including language and marketing students. Firstly, we’ll discuss the definition of antithesis, including how it differs from similar rhetorical devices . Then, we’ll look at how other writers have used antithesis to set contrast and add impact to their work, including some famous examples of antithesis in literature, poetry and marketing.
What is antithesis?
The word antithesis is sometimes used to mean ‘opposite’. For example, “She is slim and sporty – the very antithesis of her brother”. However, ‘antithesis’ (or ‘antitheses’ if plural) is also the name given to a particular rhetorical or literary device. In this blog post, we’ll be looking at ‘antithesis’ in its role as the rhetorical and literary device.
The word ‘antithesis’ comes from the Greek for ‘setting opposite’. It means to express a concept by creating contrast. This can be done in different ways according to different definitions: either using only the content of the expression, or the content and the grammatical structure. Using the content can be as simple as using words with opposite meanings in close proximity to each other, or more complex by describing concepts that contrast with one another. This draws the reader’s attention to the differences between the two things.
Antithesis often presents opposing ideas and presents those ideas in a parallel grammatical structure. This is unlike general parallelism, which presents a balance of elements in a structure (sentence, clause or other) without necessarily involving the content. Antithesis is usually created in two parts, but can also be formed by three or more opposing clauses.
Writers can use antithesis to communicate a concept that is best expressed through opposites. It’s a simple yet effective way to really drive a point home. As with other literary devices , the rules aren’t set in stone, it’s more about using the device in ways that create impact and bring the words to life.
Examples of antithesis in literature
What makes a good piece of writing truly great? You might argue that the key ingredients include memorability, impact and the beauty of a rhythmical grammatical structure – deliverables that can be served skillfully with antitheses.
When you put two antithetical concepts together in a short phrase, you get drama. And drama is what keeps the reader turning the pages.
In addition, the parallel structure often used in antithesis makes the words stand out from the other text on a page. Working like a mental stop sign, it compels the reader to notice the contrasting ideas and consider the meaning of that contrast.
Using antithesis, writers can present contradictions by balancing opposing words and statements. This builds contrasting images in a reader’s mind and creates a powerful impression of either a character or circumstance.
A good portion of the best-known writers in history have been masters of antithesis. For example, antithesis plays a big part in the language used by William Shakespeare. In fact, nearly every character he created uses it. For example, in Mac beth the witches chant, “Fair is foul, and foul is fair” – a simple but dramatic antithesis. One of the best-known Shakespearean quotes of all time is an antithesis from the play Hamlet , when the prince says, “To be, or not to be...”. In just six words Shakespeare creates a perfect contrast between existing and not existing, inviting the audience to ponder the meaning of life itself.
Another famous use of antithesis is the expression, “To err is human; to forgive, divine”, which was written in 1711 by English poet Alexander Pope in ‘ An Essay on Criticism, Part II ’. After the original creation of the statement, further iterations have added the word ‘is’ so, “To err is human; to forgive is divine”, which, arguably, improves the rhythm by creating an equal number of words in each part of the sentence.
And it’s not just the writers of old who wield the sword of antithesis so well: their modern counterparts are equally aware of its power. For example, the Green Lantern comic writers use antithesis at the start of Green Lantern’s oath in order to emphasise his mission to defeat evil at all costs:
In brightest day , in blackest night , No evil shall escape my sight. Let those who worship evil’s might Beware my power – Green Lantern’s light!
Antithesis in poetry.
Poetry is perhaps the writing genre where we find the most graceful use of words. That’s why there are lots of antitheses used in poetry throughout history.
Take a look at the two-part structures and conceptual contrasts from some of the world’s best-known poems:
"Better to reign in Hell , then serve in Heav’n" – Paradise Lost , John Milton, 1667
“much madness is divinest sense ” – 620, emily dickinson, “some say the world will end in fire / some say in ice ” – fire and ice, robert frost, 1920.
Occasionally, a writer might even make use of a triple antithesis:
“Herein lives wisdom, beauty , and increase ; / Without this, folly, age , and cold decay ” – Sonnet 11, William Shakespeare, 1609
Antithesis in speeches.
Of course, what works on paper often works in its spoken form too. Some of the best speeches of all time can thank, at least in part, antithesis for their success.
“That’s one small step for a man – one giant leap for mankind” – Neil Armstrong, 1969
“we must learn to live together as brothers or perish together as fools ” – martin luther king jr, 1964, “on this day, we gather because we have chosen hope over fear, unity of purpose over conflict and discord ” – barack obama, 2009, antithesis in advertising.
Marketers love to make us remember how truly wonderful their services or products are. Antithesis provides marketers with a powerful tool: contrast to underline a unique selling proposition (USP) and a memorable rhythm. That’s why you’ll find the path to marketing gold is littered with antitheses: the antithesis is the life-blood of the tagline or slogan.
Take a look at how each of these taglines uses a parallel structure and creates opposition:
“ Small business. Big future” – Santander
“ heavy on features. light on price” – apple, “ tough on stains. gentle on skin” – persil, “ less calories; more taste” – so good, “inspired by yesterday , built for tomorrow ” – nokia, “ all of the taste. none of the sugars” – alpro, “ smart listens to the head. stupid listens to the heart” – diesel, antithesis, chiasmus and parallelism – what are the differences.
Parallelism, sometimes called parallel structure or parallel construction, is the repetition of grammatical structures in a piece of writing in order to create a balanced, harmonious effect.
Parallelism requires only the repeated grammatical structure, while antithesis uses the content – you can’t set up opposing concepts by only using the structure!
Look at this example, “They have plundered our seas, ravaged our coasts, burnt our towns – all while caring for their own oceans and cities.” The beginning of this statement repeats the same structure while changing the verbs and nouns. It doesn’t create a contrast between each clause or suggest any form of opposition. That’s the key difference between other forms of parallelism and antithesis: parallelism doesn’t need to present opposites, but antithesis is all about the opposites.
If a similar phrase was written using antitheses, it might read something like this. “They have plundered our seas; but have nurtured their seas. They ravaged our coasts; they cared for their own. They burnt our towns while they built their cities.” In the ‘antithesis version’, each clause is juxtaposed with another concept to create impact. You can hear how much more powerful the second phrase is if you read both versions out loud.
While antithesis is parallelism, not all parallelism is antithesis! For example, chiasmus is also a form of parallelism. In fact, it’s sometimes described as an inverted parallelism and happens when word order or grammatical structure is reversed in two phrases. For example, the phrase, “Do I love you because you are beautiful? Or are you beautiful because I love you?” qualifies as a parallelism and a chiasmus but there’s no opposition so it’s not an antithesis.
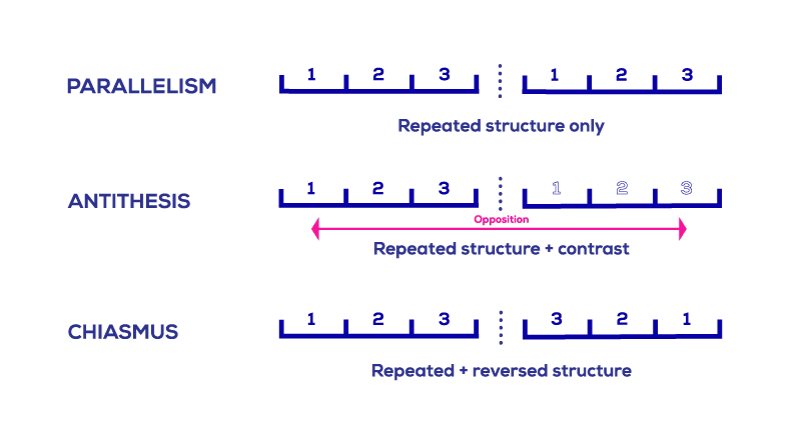

Semantix’s copywriting toolkit
Our copywriting toolkit is a valuable resource for anyone aiming to improve their writing skills. It contains definitions and examples of rhetorical devices in action, with guidelines on how and why they are used.
Using rhetorical devices, such as antitheses, is a time-proven method of taking your writing to another level and making sure that your words are impactful, memorable and effective. Whether you’re writing for pleasure or writing for business, they create drama and keep your readers or listeners engaged.
Semantix’s copywriting services
As the leading language solution provider in the Nordics, language is our passion. Every day, we help our clients reach new target audiences and enter new global marketplaces. We believe that language should be used as an opportunity to boost business and never be seen as a barrier.
Our copywriting services are available in more than 200 languages, and we only work with native-speaking translators . By matching you with a multilingual copywriter with experience in your specific industry, we’ll help you make every word work hard for your business in every language.
Want to find out more about our multilingual copywriting services?
Further reading.
- A Handlist Of Rhetorical Terms – Richard Lanham, University of California Press, 2013
- Simplified Glossary Of Literary Terms/Devices: An Easy-To-Use Source Of Definitions, Examples And Exercises For Students And Teachers – Victor Igiri, 2022
- The Oxford Dictionary Of Literary Terms (Oxford Quick Reference) 4th Edition – Chris Baldick, OUP Oxford, 2015
- The Elements Of Eloquence – Mark Forsyth, Icon Books, 2013
- The Elements Of Rhetoric – Ryan N S Topping, Angelico Press, 2016
- The Penguin Dictionary Of Literary Terms And Literary Theory – J A Cuddon, Penguin, 2014
- The Rhetorical Device: Literary Resources For The Writer Vol. 1 of 2 – Paul F Kisak, CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform, 2016
- Writing With Clarity And Style: A Guide To Rhetorical Devices For Contemporary Writers – Robert A Harris, Routledge, 2017
- The Use Of Rhetorical Devices In Selected Speeches by Clinton & Trump: Discourse From The Electoral Campaign 2016 – Larissa Wolf, AV Akademikerverlag, 2018
- American rhetoric (online) Antithesis blog post
- Studiobinder (online) ‘What is antithesis’ blog post
- The Oxford Dictionary O f Literary Terms (Oxford Quick Reference) 4th Edition – Chris Baldick, OUP Oxford, 2015
- Voltaire, The Project Gutenberg EBook Of A Philosophical Dictionary, Volume 4 (of 10).
- Toastmasters (online) ‘The Crafting of Eloquence’ blog post .
Related content

A guide to the literary device anaphora – for professional wordsmiths

Literary devices list: examples of literary devices and how to use them

- Scriptwriting
What is Antithesis — Definition & Examples in Literature & Film
I f you’ve ever heard sentence structure, met characters, or witnessed ideas that seem diametrically opposed, you’re actually pretty familiar with the idea of the antithesis. But there is more to it than just juxtaposing ideas. Read on to learn exactly what is antithesis, how this tool is used, and how you can include an antithesis in your next project.
Antithesis Definition
First, let’s define antithesis.
There are a number of terms often confused for antithesis (like paradox or oxymoron ). But an antithesis has a particular grammatical structure that helps differentiate it from the rest. So, here’s the antithesis definition and then we'll look at specific examples:
ANTITHESIS DEFINITION
What is antithesis.
An antithesis is a rhetorical and literary device with parallel grammar structure but which establishes a nearly complete or exact opposition in ideas or characters. It can be effective in emphasizing drastic differences between opposing concepts.
How to pronounce antithesis: [an-TITH-uh-sis]
Familiar antithesis examples:
- “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.”
- “No pain, no gain.”
- “Out of sight, out of mind.”
The word “antithesis” comes from the Greek word meaning “setting opposite,” which is an idea that has been used in various forms. Let’s look at those various forms in more antithesis examples.
Antitheses Examples
How do we use antithesis today.
The purpose of antithetical language is not just mentioning the existence of opposing ideas, but rather emphasizing the stark differences between them. The often lyrical and rhythmic nature of this device helps accentuate the parallel grammatical structure.
Watch the video below to learn more about how we use antitheses today.
Antithesis Definition, Examples and Techniques
We use this device in that pure form today (see the examples above) in everyday turns of phrase. But there are more in-depth ways (in actions and story in general) that fit the antithesis definition.
People and characters can act in an antithetical manner to their beliefs.
Antithesis Examples in Behavior:
- A character who says they love animals but wears real fur coats.
- Someone who says they are vegetarian but eats a big steak for dinner.
- A person who uses a “Shop Small” tote bag but does their holiday shopping at Walmart.
In addition, characters in literary or scripted works, much like people, can be antitheses to each other in and of themselves. In fact, this is often how great villains are created.
Check out the video below to see more on writing great villains , and how antagonists can mirror or juxtapose protagonists .
Page to Picture: How to Write a Villain • Subscribe on YouTube
Protagonists can be an “antihero,” or the villain of a story can be portrayed separately as a parallel to the protagonist; therefore, the protagonist and antagonist highlight each other’s strengths and weaknesses, and evil and benevolent qualities. Some classic examples of this pseudo-mirrored antagonist concept are:
Snow White and the Queen
Batman and Joker
Dumbledore and Voldemort
As you can see, the antithesis is typically the ultimate antagonist, even if the character they are meant to parallel isn’t the protagonist, as is the case in the Harry Potter series.
Both a strong example of antithesis and nuanced portrayal of complicated character relationships, the Harry Potter series showcases a number of moral ambiguities as they pertain to Dumbledore and Voldemort.
We imported the script into StudioBinder’s screenwriting software to see exactly how this juxtaposition is first established.
Read Full Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone Script
Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone masterfully establishes the characteristics that Harry and Voldemort share, but it also establishes similarities between Dumbledore and Voldemort.
Throughout the series, these shared traits influence Dumbledore and Voldemort in their objectives and decisions.
For instance, in the Sorcerer’s Stone , we are introduced to how Voldemort and Dumbledore move through the world. Hagrid tells Harry early on about Voldemort’s rise to power: he was a wizard “who went as bad as you can go [...] anyone who stood up to him ended up dead.” Hagrid frames Voldemort as a powerful wizard, capable of massive destruction.

Antithesis Example in Harry Potter • Read Full Scene
Alternatively, towards the end of the first film Dumbledore explains his tactics in his work with Nicolas Flamel on the Sorcerer’s Stone . “Only a person who wanted to find the stone—find it, but not use it—would be able to get it.” Dumbledore respects power and the laws of magic, and his actions reflect that.

Further into the series, in Order of the Phoenix , we see what happens when Dumbledore’s tremendous abilities collide with Voldemort’s formidable power in their epic Ministry of Magic duel.
Voldemort’s spells all aim to destruct, whereas Dumbledore’s are equally amazing, but meant to disarm, distinguish, or defend.
The series is a remarkable example of how antitheses can be essential to a story, and the respective backstories, unique abilities, and of course choices of Voldemort and Dumbledore prove it.
Implementing Antitheses
How to use antithesis.
With all the ways you can implement and define antithesis, it’s good to have a number of tricks or rules of thumb to keep in your back pocket. Whether you’re writing a short story or your next feature screenplay, here are some things you can keep in mind.
1. Aim for Moderation
If you’re using antithesis in the form of a rhetorical device, try to keep the number of antitheses to a minimum unless it’s a crucial character trait of the speaker. Using a similar literary device too often can leave your writing predictable or even annoying. The more you use a tool, like antithetical language, the less meaning it can have.
2. Similar Structure
Keep the structure of your antithesis as similar as possible if you want to highlight the differences more intensely. And try to keep the phrasing itself balanced. Both variables of the equation don’t have to be exact, but the lyrical phrasing can help your antithesis shine and stick long after the read.
3. Focus on Differences
Focus on contrast but remember to find ways to draw the parallels. How can the characters be compared to the point where their differences become obvious? How can their differences lead to conversation about how the characters may actually be similar?
Antitheses via characters and sentence structure can assist in not just interesting writing, but memorable writing. They can make your message more understandable and retainable, which should be a top goal in any written work. You never want to give you reader a reason to stop reading.
So, now that you’ve learned more about how an antithesis can strengthen your work, you can implement it into your next project like a pro.
After all, no guts, no glory.
What is Irony?
Antithesis is a rhetorical device you can use in everyday speech. Much like an antithesis, we encounter several types of irony in everyday life, too. Keep reading to learn about the types of irony and how they’re used in TV and Film.
Up Next: Irony Explained →
Write and produce your scripts all in one place..
Write and collaborate on your scripts FREE . Create script breakdowns, sides, schedules, storyboards, call sheets and more.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Pricing & Plans
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- What is a Femme Fatale — Definition, Characteristics, Examples
- What is Method Acting — 3 Different Types Explained
- How to Make a Mood Board — A Step-by-Step Guide
- What is a Mood Board — Definition, Examples & How They Work
- How to Make a Better Shooting Schedule with a Stripboard
- 0 Pinterest
Literary Devices
Literary devices, terms, and elements, definition of antithesis, difference between antithesis and juxtaposition, common examples of antithesis, significance of antithesis in literature, examples of antithesis in literature.
HAMLET: To be, or not to be, that is the question— Whether ’tis Nobler in the mind to suffer The Slings and Arrows of outrageous Fortune, Or to take Arms against a Sea of troubles, And by opposing, end them?
Arguably the most famous six words in all of Shakespeare’s work are an example of antithesis. Hamlet considers the important question of “to be, or not to be.” In this line, he is considering the very nature of existence itself. Though the line is quite simple in form it contrasts these very important opposite states. Hamlet sets up his soliloquy with this antithesis and continues with others, including the contrast between suffering whatever fortune has to offer or opposing his troubles. This is a good example of Shakespeare using antithesis to present to the audience or readers Hamlet’s inner life and the range of his thinking.
It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair, we had everything before us, we had nothing before us, we were all going direct to Heaven, we were all going direct the other way…
The opening paragraph of Charles Dickens’s A Tale of Two Cities employs many different literary devices all at once. There are many examples of antithesis back-to-back, starting with the first contrast between “the best of times” and “the worst of times.” Each pair of contrasting opposites uses a parallel structure to emphasize their differences. Dickens uses these antithetical pairs to show what a tumultuous time it was during the setting of his book. In this case, the use of antithesis is a rhetorical device that foreshadows the conflicts that will be central to the novel.
There was only one catch and that was Catch-22, which specified that a concern for one’s own safety in the face of dangers that were real and immediate was the process of a rational mind. Orr was crazy and could be grounded. All he had to do was ask; and as soon as he did, he would no longer be crazy and would have to fly more missions. Orr would be crazy to fly more missions and sane if he didn’t, but if he was sane he had to fly them. If he flew them he was crazy and didn’t have to; but if he didn’t want to he was sane and had to. Yossarian was moved very deeply by the absolute simplicity of this clause of Catch-22 and let out a respectful whistle.
In Joseph Heller’s classic anti-war novel Catch-22 , Heller uses a specific type of humor in which antithetical statements show the true absurdity of war. This very famous quote explains the concept of the “Catch-22,” which became a popular idiomatic expression because of the book. In fact, this example is not so much an antithetical statement but instead an antithetical situation. That is to say, the two possible outcomes for Orr are opposite: either he’s deemed crazy and would thus not be forced to fly any more combat missions, or he’s sane and then would indeed have to fly them. However, the one situation negates the possibility of the other, as only a sane man would be clear-headed enough to ask not to fly more missions.
This case is not a difficult one, it requires no minute sifting of complicated facts, but it does require you to be sure beyond all reasonable doubt as to the guilt of the defendant.
( To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee)
Test Your Knowledge of Antithesis
1. What is the correct antithesis definition? A. Using two very similar concepts and showing their subtle differences. B. Setting up a contrast between two opposite ideas or phrases in a balanced grammatical structure. C. Using words to convey an opposite meaning to their literal sense. [spoiler title=”Answer to Question #1″] Answer: B is the correct answer. A is one possible definition of juxtaposition, while C is one possible definition of irony.[/spoiler]
WITCHES: Fair is foul, and foul is fair: Hover through the fog and filthy air.
MACBETH: Is this a dagger which I see before me, The handle toward my hand?
WITCHES: Something wicked this way comes.
4. Which of the following quotes from Heller’s Catch-22 contains an example of antithesis? A. There are now fifty or sixty countries fighting in this war. Surely so many counties can’t all be worth dying for. B. He had decided to live forever or die in the attempt, and his only mission each time he went up was to come down alive. C. You’re inches away from death every time you go on a mission. How much older can you be at your age? [spoiler title=”Answer to Question #4″] Answer: B is the correct answer.[/spoiler]
What Is an Antithesis? Definition & 15+ Examples
Ever wondered how great writers and speakers create captivating contrasts to emphasize their points and leave you pondering?
The secret behind these mesmerizing moments often lies in the use of a powerful rhetorical tool called antithesis . This technique employs oppositional language to present contrasting ideas, which adds depth, color, and intrigue to language, leaving audiences eager for more.
From speeches to literature, antithesis has long been appreciated as a valuable component of persuasive and thought-provoking communication. Exploring these instances helps to deepen our understanding of how antithesis functions, as well as why it continues to be a beloved and effective rhetorical device in various forms of expression.
Let’s take a closer look:
Table of Contents
What Is Antithesis?
Antithesis is a figure of speech that uses parallelism to present opposing ideas. In essence, it is the juxtaposition of contrasting concepts, usually in balanced or parallel phrases, to create a heightened effect in a sentence or expression.
This rhetorical device can emphasize the differences between two opposing ideas, allowing the writer or speaker to deliver a powerful message more effectively.
In simple terms, “antithesis” is the opposition or contrast of ideas or words in a balanced construction. This technique is often employed to:
- Strengthen an argument.
- Emphasize a point.
- Create a vivid and memorable image for the reader or listener.
Antithesis can be found in various forms of literature, including poetry, prose, and speeches, and is often used to give emphasis to the importance of a particular idea or theme.
There are several ways in which antithesis can be presented:
- Word Antithesis: The use of opposing words or phrases, such as “love and hate” or “good and evil.”
- Ideological Antithesis: The expression of opposing beliefs or principles, such as “freedom versus tyranny” or “democracy versus totalitarianism.”
- Structural Antithesis: The arrangement of contrasting ideas in a parallel form, often using parallelism or repetition to highlight the contrast.
Employing antithesis can make language more expressive and engaging, drawing attention to the ideas being presented and making them more memorable. It serves as an effective tool for writers and speakers who seek to create a lasting impact on their audience through the power of opposing concepts.
Origins and History of Antithesis
Antithesis, derived from the Greek word “ antitithenai ,” which means “to set against,” is a figure of speech in which two opposing ideas are juxtaposed in a balanced, parallel manner. This deliberate contrast serves to heighten the impact of the ideas being presented and contributes to the overall strength and effectiveness of the argument.
Antithesis can be traced back to classical rhetoric , the art of effective and persuasive communication. It emerged prominently as a stylistic device in the works of ancient Greek and Roman orators and writers who sought to:
- Craft impactful arguments
- Create memorable phrases
The roots of antithesis lie in the use of parallelism , a rhetorical tool that involves expressing contrasting or opposing ideas in a balanced and parallel structure. This technique was employed by classical rhetoricians to emphasize the contrasts in their arguments and engage their audience effectively.
Throughout history, numerous famous orators and writers have demonstrated a mastery of antithesis. Here are some notable examples:
The ancient Greek philosopher was a skilled rhetorician, and his works often exemplified antithesis. In his work, Rhetoric , he provided a thorough analysis of various rhetorical techniques, including antithesis, to help his students persuasively convey their ideas.
As one of Rome’s greatest orators and a renowned lawyer, Cicero was well-versed in rhetorical devices. His speeches frequently utilized antithesis to emphasize particular points and create powerful statements that resonated with his audience.
William Shakespeare
The famous playwright often employed antithesis in his works, emphasizing contrasts and creating memorable lines. One of the most famous examples of antithesis in literature can be found in his play, Hamlet , with the line, “To be or not to be.”
Abraham Lincoln
The 16th President of the United States was also an adept user of antithesis. In his famous Gettysburg Address, Lincoln used antithesis to create a moving and poignant speech that resonates with audiences to this day.
These prominent figures from ancient Greece to modern times have utilized antithesis as an effective means of emphasizing contrasts and crafting impactful phrases, showcasing the enduring appeal of this rhetorical device.
Function and Purpose of Antithesis
It balances ideas, engages minds, and inspires reflection.
Antithesis serves several significant functions in both written and spoken language. Its primary purpose is to create balance , contrast , and emphasis , highlighting the differences between two opposing ideas or concepts.
By utilizing antithesis, writers, and speakers can effectively engage their readers or listeners and provoke thoughtful considerations of opposing viewpoints.
It Acts as a Catalyst for Deeper Understanding
The use of antithesis stimulates intellectual curiosity, prompting readers or listeners to ponder the implications of juxtaposing contrasting ideas.
This rhetorical device encourages deeper understanding and fuller appreciation of the complexities inherent in language and human thought. As a result, antithesis enhances the impact of a piece of writing or speech.
It Enhances Focus and Fosters Analytical Thinking
In addition, antithesis is an effective method for drawing attention to crucial points or ideas.
By bringing opposition to the forefront, it emphasizes the significance of contemplating various perspectives, which in turn fosters an open and analytical mindset. This technique is particularly beneficial in persuasive writing and speaking, as it can help sway the audience toward a specific stance or argument.
Examples of ways to employ antithesis include:
- Pairing opposite adjectives, such as “cold” and “hot,” to emphasize the extremity of the subject.
- Using contrasting phrases, like “sink or swim,” to underline the importance of a decision or action.
- Juxtaposing conflicting concepts or proposals, such as “peace” and “war,” to examine the consequences of each.
Types of Antithesis
Antithesis can be broadly divided into two categories: Verbal Antithesis and Conceptual Antithesis. Each type serves a different purpose in conveying opposing ideas or concepts in a piece of writing or speech.
Verbal Antithesis
Verbal Antithesis involves the use of words or phrases with opposite meanings in a single sentence or expression. This type of antithesis serves to emphasize the contrast between two opposing ideas by placing them in close proximity to one another.
Examples can include the use of:
- Oxymorons , where contradictory terms are combined.
- Parallelism , where contrasting words or phrases are structured similarly.
Some examples of Verbal Antithesis are:
- “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times.” (Charles Dickens)
- “To err is human, to forgive divine.” (Alexander Pope)
- “Give every man thy ear, but few thy voice.” (William Shakespeare)
Conceptual Antithesis
Conceptual Antithesis, on the other hand, does not rely on wordplay or linguistic contrasts. Instead, it focuses on presenting contrasting concepts or ideas in a larger context, such as within a narrative, argument, or theme.
This type of antithesis often involves juxtaposing characters, situations, or themes to highlight their differences and create tension or conflict. Examples can be found in various forms of literature and art, including:
- The opposing forces of good and evil in many religious texts.
- The conflicting moral perspectives in novels, such as in “To Kill a Mockingbird,” where Atticus Finch’s defense of Tom Robinson contrasts with the racism of the townspeople.
- The clashing beliefs and values in philosophical debates, like those between Socrates and the Sophists in ancient Greece.
Examples in Literature
Antithesis is a powerful literary device that writers have employed to create memorable works of poetry, prose, and drama. The use of antithesis not only heightens tension and deepens meaning within literature but it also heightens the reader’s experience and understanding.
Shakespeare
Known for his command of language, Shakespeare often employed antithesis in his plays and sonnets. One of the most famous examples is found in Hamlet’s soliloquy:
In this instance, the contrasting ideas of “ being ” and “not being” emphasize the central conflict of Hamlet’s character and the existential questions he grapples with throughout the play.
Charles Dickens
Antithesis can also be found in the opening lines of Charles Dickens’ celebrated novel, A Tale of Two Cities :
Dickens’ pairing of opposites establishes the novel’s social and political setting, which is characterized by paradoxical contrasts and deep divisions among the characters.
Jane Austen
Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice utilizes antithesis to highlight the differing perspectives of its main characters, Elizabeth Bennet and Mr. Darcy. Consider the following line:
This statement juxtaposes the idea of universal truth and personal desire, reflecting the novel’s themes of social expectations and individual choices.
Robert Frost
The celebrated poet Robert Frost deftly utilized antithesis in his work, such as in the poem Fire and Ice :
With the contrast between “ fire ” and “ ice ,” Frost explores the dual destructive forces of passion and indifference in human nature.
Examples in Speeches
Antithesis not only adds stylistic flair to speeches, but also enhances their rhetorical impact and persuasive effect. Below are examples from some famous speeches that demonstrate the use of antithesis.
Abraham Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address is considered one of the most powerful and well-crafted speeches in history. One effective example of antithesis in this speech is:
Lincoln contrasts words and actions, emphasizing the sacrificial deeds of the soldiers.
Winston Churchill
Winston Churchill’s speeches during World War II showcased his strong rhetorical skills. An example of antithesis in his famous Iron Curtain speech is:
Here, the physical location contrasts with the figurative iron curtain, underlining the division of eastern and western Europe.
Martin Luther King Jr.
In Martin Luther King Jr.’s I Have a Dream speech, he utilized antithesis to communicate his vision for a more inclusive and equal society. An example is:
King juxtaposes skin color and character, highlighting the content of one’s character as the more important factor for judgment.
John F. Kennedy
John F. Kennedy’s Inaugural Address also contains a well-known example of antithesis:
This statement reverses the expectations of the listener, placing emphasis on the civic responsibilities of citizens rather than government assistance.
Tips and Tricks: Mastering the Use of Antithesis
Mastering the use of antithesis can greatly enhance the effectiveness of writing and speech. In this section, we will discuss practical advice for incorporating antithesis effectively and ways to avoid common pitfalls.
Identifying Contrasting Ideas
Antithesis relies on the presentation of contrasting ideas to create emphasis and interest. To use this device effectively, one must first identify clear and meaningful contrasting ideas. Here are some suggestions:
- Consider the theme or topic of your writing or speech, and think about opposing viewpoints.
- Keep the contrasting ideas relevant to the central message.
- Identify contrasts in characterization, situation, or opinion.
Using Parallel Structures
Parallelism is a crucial aspect of using antithesis effectively. It serves to create balance and clarity in the presentation of contrasting ideas. To ensure parallelism:
- Identify the grammatical structure of the first half of the antithesis and maintain the same structure in the second half.
- Use similar syntax, word order, and punctuation to create a sense of symmetry.
- Maintain consistency in verb tense, voice, and mood throughout the antithesis.
Taking care to identify strong contrasting ideas and maintaining parallelism in the presentation of those ideas will ensure that antithesis is used effectively in writing and speech.
A Rich Tapestry: Related Terms and Concepts
In order to expand our understanding of antithesis, it is helpful to explore related rhetorical devices, such as oxymoron, paradox, and chiasmus. These terms may appear to be similar, but they each have distinct characteristics and functions within the realm of rhetoric and language:
An oxymoron occurs when two contradictory terms are placed side by side to form a new meaning. Examples of oxymorons include “deafening silence” and “bittersweet.”
A paradox is a statement or situation that seems to be contradictory but holds an element of truth. For instance, “less is more” and “I know that I know nothing” are paradoxical statements that reveal deeper truths.
Chiasmus involves the reversal of parallel grammatical structures, creating a crisscross pattern in a sentence or phrase. An example of chiasmus would be “Ask not what your country can do for you, but what you can do for your country.”
While these devices share the common trait of using contrast, their mechanisms and effects differ.
- In antithesis , opposing ideas are juxtaposed to emphasize the differences between them. For example, “To err is human; to forgive, divine.”
- Oxymoron is a condensed form of antithesis. It also focuses on contrast, but it conveys the opposing ideas through adjacent words rather than phrases or clauses.
- Paradox appears self-contradictory, but provides deeper insight upon closer examination. Unlike antithesis, which highlights the contrast between ideas, paradox seeks to reconcile the contradiction to reveal an underlying truth.
- Chiasmus creates a mirror-like structure in which elements are repeated in reverse order. While its primary function is to create balance and harmony, it can also be used to emphasize contrast, much like antithesis.
Case Studies: Analyzing the Use of Antithesis in Different Contexts
In this section, we will explore the use of antithesis in different fields including politics, advertising, and everyday conversation.
This rhetorical device is an effective means of creating a contrast to emphasize a particular point, and while it may be more commonly associated with literature and poetry, antithesis can be found throughout various forms of communication.
Politicians often use antithesis to draw attention to contrasting ideas and to emphasize their viewpoints.
For example, in his 1961 inaugural address, President John F. Kennedy employed antithesis when he urged Americans to:
By contrasting the individual’s responsibility toward their nation with the nation’s responsibility toward its citizens, Kennedy emphasized the significance of civic duty and personal responsibility in shaping the country’s future.
Advertising
In the world of advertising, antithesis is often used to create memorable slogans and to emphasize the unique selling points of a product or service. For example, a famous Mercedes-Benz tagline reads:
The contrasting phrases emphasize the idea that Mercedes-Benz automobiles stand out from the competition due to their engineering excellence. Such juxtaposition of opposing ideas helps reinforce the brand message and make it more memorable to potential consumers.
Everyday Conversation
Antithesis can also be found in our everyday conversations as it helps us emphasize contrasts, express humor, or simply make a point more clearly.
A common use of antithesis is in expressions like “ I t was the best of times, it was the worst of times,” taken from Charles Dickens’ A Tale of Two Cities . We also encounter antithesis when people use expressions like “You’re either with us, or against us,” highlighting the lack of middle ground in a situation.
These examples demonstrate how contrasting ideas, skillfully articulated through antithesis, can add depth and meaning to our daily interactions.
Understanding the Downside of Antithesis
While the use of antithesis can be an effective rhetorical strategy, it has certain drawbacks that are worth considering:
The Oversimplification Trap
One of the main concerns is the potential for oversimplification. When presenting two contrasting ideas, it can be easy to reduce complex issues into a simplistic binary choice, which may ignore important nuances.
Beware of False Dichotomies
Another downside is the risk of creating false dichotomies. In some cases, the use of antithesis may unintentionally reinforce the idea that only two opposing options exist, when in reality, alternative solutions or perspectives may be available. This can lead to limited critical thinking and hinder the exploration of other viewpoints.
Misrepresentation and Distortion
Additionally, the emphasis on opposition in antithesis can sometimes lead to a misrepresentation of the ideas being contrasted. The need to create a stark difference can encourage exaggeration or distortion of the original concepts, thereby weakening the overall argument.
Overuse: Striking a Balance
Lastly, overuse of antithesis can detract from the primary message of an argument or a text, by drawing attention away from the main points and focusing on the contrasts alone. As with any rhetorical device, moderation and careful consideration should be employed when using antithesis to communicate effectively.
Overuse and Misuse of Antithesis
While antithesis can be a powerful rhetorical device, it is essential to understand the potential pitfalls of overusing or misusing it in writing or speech.
- An overuse of antithesis may lead to the loss of its impact and may obscure the intended message.
- An misuse of antithesis can result in weak or illogical arguments.
Overuse Issues
One issue with the overuse of antithesis is that it can become repetitive and predictable. Similar to other rhetorical devices, antithesis works best when used sparingly and with purpose. Overusing antithesis can make the text monotonous and tedious to read, thus undermining the effectiveness of the arguments being presented.
Misuse Issues
When antithesis is misused, it can lead to the creation of false dichotomies or straw man arguments.
This occurs when a writer or speaker presents two opposing viewpoints in an attempt to create a strong contrast, but it ends up oversimplifying or misrepresenting the actual positions being debated. This weakens the overall argument and can make the writer or speaker seem less credible.
How to Avoid Them
To avoid overuse and misuse of antithesis, follow these guidelines:
- Use antithesis purposefully and strategically to emphasize a particular point.
- Be selective in the number of antitheses used in a piece of writing or speech to maintain effectiveness.
- Ensure that the contrasting ideas presented in the antithesis accurately represent the viewpoints being discussed.
- Avoid creating false dichotomies or straw man arguments by carefully examining the opposing ideas for nuances and common ground.
By adhering to these principles, writers, and speakers can utilize antithesis effectively, adding depth and impact to their arguments without sacrificing credibility.
Pros and Cons of Antithesis
Antithesis, a rhetorical device where opposing ideas are contrasted or balanced within a sentence or a phrase, is often employed to create emphasis and depth in writing. However, it has both advantages and disadvantages that writers should be aware of.
| Pros of Antithesis | Cons of Antithesis |
|---|---|
Pros of Antithesis:
- Emphasis on Key Points: Antithesis highlights the contrast between two opposing ideas or concepts, making it easier for the reader to focus on and understand the critical points.
- Stylistic Appeal: The use of antithesis adds an elegant and sophisticated touch to the writing, making it more engaging and thought-provoking for the reader.
- Memorability: By creating a distinct contrast, antithesis helps to make ideas or phrases more memorable, making the overall message of the text more likely to resonate with the audience.
Cons of Antithesis:
- Risk of Oversimplification: Antithesis can sometimes reduce complex ideas or issues to overly simplistic binaries, which may not fully represent the intricacies and nuances involved.
- Potential for Confusion: The contrast between opposing ideas may be difficult for some readers to comprehend, leading to potential misunderstandings or confusion.
- Overuse: Excessive use of antithesis in a piece of writing may make the text feel repetitive and heavy-handed, lessening the overall impact and effectiveness of the rhetorical device.
Writers can harness the strengths of antithesis by using it judiciously and avoiding overuse, ensuring that it adds value and depth to their work without compromising its integrity or clarity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is antithesis effective in persuasion.
Yes, antithesis can be an effective persuasion tool. In political speeches and other forms of rhetoric, the use of antithesis is often employed to highlight the contrasts between opposing viewpoints or ideologies, making the argument or position more compelling.
Can antithesis be used in a simile or metaphor?
Antithesis can be incorporated into similes and metaphors to enhance their impact. While the purpose of a simile or metaphor is to make a comparison, using antithesis can further emphasize the primary differences between the compared elements.
Can antithesis be overused?
As with any literary device, antithesis can lose its effectiveness if overused. Employing antithesis sparingly and strategically ensures that its purpose is clear and that it contributes to the overall impact and meaning of the text.
Antithesis, as a rhetorical device, has been a powerful tool in language and literature. It is characterized by contrasting two opposing ideas or phrases, typically within parallel structures. This technique effectively highlights the differences and creates a balanced yet opposing relationship between ideas, drawing the attention of the reader or audience.
Examples of antithesis can be found in various forms of literature, including speeches, poetry, and prose.
| Famous Examples | Work |
|---|---|
| John F. Kennedy’s Inauguration Speech | |
| Shakespeare’s | |
| George Orwell’s |
These works serve as testimony to the enduring influence and significance of antithesis in shaping ideas and engaging readers.
Experimenting with antithesis in one’s own writing and communication can lead to a deeper understanding of texts and a more engaging style. By employing opposing ideas and parallel structures, writers and speakers can create memorable expressions, emphasize contrasting concepts, and provoke thought and discussion.
Whether used artfully in literature or strategically in rhetoric, antithesis remains an essential technique to master for effective communication. Embracing its potential can enhance the clarity and impact of ideas, leaving a lasting impression on readers and audiences alike.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
As you found this post useful...
Share it on social media!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?

Jessa Claire

Thesis vs. Antithesis — What's the Difference?
Difference Between Thesis and Antithesis
Table of contents, key differences, comparison chart, role in argument, position in dialectic, use in literature, compare with definitions, common curiosities, what is a thesis, can thesis and antithesis coexist in a debate, is antithesis necessary for a dialectical process, what is an antithesis, can a single statement be both thesis and antithesis, is the thesis always the truth, can antithesis lead to a resolution in an argument, how are thesis and antithesis used in arguments, does every academic paper have a thesis, is antithesis only used in formal debates, can a thesis change during the course of an argument, can antithesis be used in literature, are thesis and antithesis necessary for a compelling argument, how does antithesis enhance literature, can the terms thesis and antithesis apply to scientific research, share your discovery.

Author Spotlight
Popular Comparisons

Trending Comparisons

New Comparisons

Trending Terms

- Anatomy & Physiology
- Astrophysics
- Earth Science
- Environmental Science
- Organic Chemistry
- Precalculus
- Trigonometry
- English Grammar
- U.S. History
- World History
... and beyond
- Socratic Meta
- Featured Answers

What is Hegel's concept of thesis, antithesis and synthesis, in simple terms?


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Thesis: Present the status quo, the viewpoint that is currently accepted and widely held. Antithesis: Articulate the problems with the thesis. (Hegel also called this phase "the negative.") Synthesis: Share a new viewpoint (a modified thesis) that resolves the problems. Hegel's method focused less on the search for absolute truth and more ...
For G.R.G. Mure, for instance, the section on Cognition fits neatly into a triadic, thesis-antithesis-synthesis account of dialectics because the whole section is itself the antithesis of the previous section of Hegel's logic, the section on Life (Mure 1950: 270). Mure argues that Hegel's triadic form is easier to discern the more broadly ...
The thesis is the theory or the definition of the point under discussion. Antithesis is the exact opposite of the point made in the thesis. Anti is a prefix meaning against. The antithesis therefore goes against the thesis to create an opposition effect. The antithesis creates a clash of ideas or opinions and is a rhetorical device used to sway ...
Antithesis is an effective literary device and figure of speech in which a writer intentionally juxtaposes two contrasting ideas or entities. Antithesis is typically achieved through parallel structure, in which opposing concepts or elements are paired in adjacent phrases , clauses , or sentences.
In philosophy, the triad of thesis, antithesis, synthesis (German: These, Antithese, Synthese; originally: Thesis, Antithesis, Synthesis) is a progression of three ideas or propositions. The first idea, the thesis, is a formal statement illustrating a point; it is followed by the second idea, the antithesis, that contradicts or negates the ...
Antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two contrasting or opposing ideas, usually within parallel grammatical structures. For instance, Neil Armstrong used antithesis when he stepped onto the surface of the moon in 1969 and said, "That's one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind." This is an example of antithesis because ...
Antithesis (pronounced an-TITH-uh-sis) deals in opposites. The Merriam-Webster definition of antithesis is "the direct opposite," and in Greek the meaning is "setting opposite.". As a tool for writing, antithesis creates a juxtaposition of qualities using a parallel grammatical structure. In other words, it's setting opposites next to ...
Thesis, Antithesis and Synthesis Hegel's dialectic is based on the principle of thesis, antithesis and synthesis. Thesis and antithesis are two conflicting ideas, while synthesis is the result of their interaction. The dialectic process is a way of understanding how the world works, as it helps to explain the constant flux of ideas and events.
Writing How to Use Antithesis in Your Writing: Definition and Examples of Antithesis as a Literary Device. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Sep 29, 2021 • 3 min read
Antithesis performs a very similar function, but does so in a more complicated way by using full sentences (rather than single words or images) to express the two halves of the juxtaposition. Here is an antithesis built around some of the common expressions from above "Sheep go to Heaven; goats go to Hell."
An antithesis is just that—an "anti" "thesis.". An antithesis is used in writing to express ideas that seem contradictory. An antithesis uses parallel structure of two ideas to communicate this contradiction. Example of Antithesis: "Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee." -Muhammad Ali. This example of antithesis is a famous ...
Antithesis (pl.: antitheses; Greek for "setting opposite", from ἀντι- "against" and θέσις "placing") is used in writing or speech either as a proposition that contrasts with or reverses some previously mentioned proposition, or when two opposites are introduced together for contrasting effect. [1][2] Antithesis can be defined as "a ...
Thesis, antithesis, synthesis The classic pattern of academic arguments is: An Idea (Thesis) is proposed, an opposing Idea (Antithesis) is proposed, and a revised Idea incorporating (Synthesis) the opposing Idea is arrived at.
The contradiction between thesis and antithesis results in Aufhebung, the dialectical resolution or superseding of the contradiction between opposites as a higher-level synthesis that eventually generates its own antithesis. Rather than repudiating LNC, Hegel's dialectic rests upon it.
Antithesis (ann-TIH-thuh-suhs), put simply, means the absolute opposite of something. As a literary term, it refers to the juxtaposition of two opposing entities in parallel structure. Antithesis is an effective literary device because humans tend to define through contrast. Therefore, antithesis can help readers understand something by defining its opposite.
The word antithesis is sometimes used to mean 'opposite'. For example, "She is slim and sporty - the very antithesis of her brother". However, 'antithesis' (or 'antitheses' if plural) is also the name given to a particular rhetorical or literary device. In this blog post, we'll be looking at 'antithesis' in its role as ...
Familiar antithesis examples: "That's one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.". "No pain, no gain.". "Out of sight, out of mind.". The word "antithesis" comes from the Greek word meaning "setting opposite," which is an idea that has been used in various forms. Let's look at those various forms in more ...
Antithesis is the use of contrasting concepts, words, or sentences within parallel grammatical structures. This combination of a balanced structure with opposite ideas serves to highlight the contrast between them. For example, the following famous Muhammad Ali quote is an example of antithesis: "Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.".
Antithesis is a figure of speech that uses parallelism to present opposing ideas. In essence, it is the juxtaposition of contrasting concepts, usually in balanced or parallel phrases, to create a heightened effect in a sentence or expression. This rhetorical device can emphasize the differences between two opposing ideas, allowing the writer or ...
Thesis - a statement or theory that is put forward as a premise to be maintained or proved Antithesis - the negation or contradiction of the thesis Synthesis - the resolution of the conflict between thesis and antithesis. In CISC 497, the rationales must be backed up with facts found during research on the topic.
A thesis is a statement or theory put forward as a premise to be maintained or proved. Antithesis, in contrast, is the direct opposition or contrast to the thesis. In rhetoric, a thesis is the starting point of an argument, the claim you're making. Antithesis, on the other hand, introduces a contrasting idea to highlight differences.
In general terms a thesis is a starting point, an antithesis is a reaction to it and a synthesis is the outcome. Marx developed the concept of historical materialism whereby the history of man developed through several distinct stages, slavery, feudalism, capitalism and in the future communism.. The movement from one stage to another could be explained by using thesis, antithesis and synthesis.
Antithesis refers to the refutation of the idea. Synthesis is the moulding of the idea and its refutations into a new idea. For instance, I can crudely write an example like this: Thesis - There is a God. Antithesis - There is a lot of bad in the world. Synthesis - There is a God but His ways are mysterious. See below: A couple of things to ...