
Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
The “Golden Thread” Explained Simply (+ Examples)
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022
The research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.

Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Research Questions, Objectives and Hypotheses
Published by Alberta Bridges Modified over 8 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Research Questions, Objectives and Hypotheses"— Presentation transcript:

Chapter 2 The Process of Experimentation

Critical Reading Strategies: Overview of Research Process

Yiu-fai Cheung, MD Department of Paediatrics and Adolescent Medicine LKS Faculty of Medicine The University of Hong Kong Hong Kong, China Sharing in GRF.

Research Questions & Hypotheses. Overview What is a research question? How does one develop one? How does one evaluate one?

Study Objectives and Questions for Observational Comparative Effectiveness Research Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ)

Protocol Development.

Donald T. Simeon Caribbean Health Research Council

What You Will Learn From These Sessions

The Anatomy of Research Presented by: Shahrzad Bazargan-Hejazi, PhD September

DECO3008 Design Computing Preparatory Honours Research KCDCC Mike Rosenman Rm 279

introduction to MSc projects

NIH Mentored Career Development Awards (K Series) Part 4

Chapter 3 Preparing and Evaluating a Research Plan Gay and Airasian

Copyright © 2013 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Statistical Methods for Health Care Research Chapter 1 Using Research and Statistics.

Research Methodologies in Allied Health SAHP 418/518 Research Planning Sandra Gunselman, Ph.D.

Research problem, Purpose, question

WRITING A RESEARCH PROPOSAL

How to Improve your Grant Proposal Assessment, revisions, etc. Thomas S. Buchanan.

RESEARCH DESIGN.

Writing a Research Proposal
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research
How to Make a Successful Research Presentation
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor’s standpoint. I’ve presented my own research before, but helping others present theirs taught me a bit more about the process. Here are some tips I learned that may help you with your next research presentation:
More is more
In general, your presentation will always benefit from more practice, more feedback, and more revision. By practicing in front of friends, you can get comfortable with presenting your work while receiving feedback. It is hard to know how to revise your presentation if you never practice. If you are presenting to a general audience, getting feedback from someone outside of your discipline is crucial. Terms and ideas that seem intuitive to you may be completely foreign to someone else, and your well-crafted presentation could fall flat.
Less is more
Limit the scope of your presentation, the number of slides, and the text on each slide. In my experience, text works well for organizing slides, orienting the audience to key terms, and annotating important figures–not for explaining complex ideas. Having fewer slides is usually better as well. In general, about one slide per minute of presentation is an appropriate budget. Too many slides is usually a sign that your topic is too broad.

Limit the scope of your presentation
Don’t present your paper. Presentations are usually around 10 min long. You will not have time to explain all of the research you did in a semester (or a year!) in such a short span of time. Instead, focus on the highlight(s). Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
You will not have time to explain all of the research you did. Instead, focus on the highlights. Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
Craft a compelling research narrative
After identifying the focused research question, walk your audience through your research as if it were a story. Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling.
- Introduction (exposition — rising action)
Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story. Introduce the key studies (characters) relevant in your story and build tension and conflict with scholarly and data motive. By the end of your introduction, your audience should clearly understand your research question and be dying to know how you resolve the tension built through motive.
- Methods (rising action)
The methods section should transition smoothly and logically from the introduction. Beware of presenting your methods in a boring, arc-killing, ‘this is what I did.’ Focus on the details that set your story apart from the stories other people have already told. Keep the audience interested by clearly motivating your decisions based on your original research question or the tension built in your introduction.
- Results (climax)
Less is usually more here. Only present results which are clearly related to the focused research question you are presenting. Make sure you explain the results clearly so that your audience understands what your research found. This is the peak of tension in your narrative arc, so don’t undercut it by quickly clicking through to your discussion.
- Discussion (falling action)
By now your audience should be dying for a satisfying resolution. Here is where you contextualize your results and begin resolving the tension between past research. Be thorough. If you have too many conflicts left unresolved, or you don’t have enough time to present all of the resolutions, you probably need to further narrow the scope of your presentation.
- Conclusion (denouement)
Return back to your initial research question and motive, resolving any final conflicts and tying up loose ends. Leave the audience with a clear resolution of your focus research question, and use unresolved tension to set up potential sequels (i.e. further research).
Use your medium to enhance the narrative
Visual presentations should be dominated by clear, intentional graphics. Subtle animation in key moments (usually during the results or discussion) can add drama to the narrative arc and make conflict resolutions more satisfying. You are narrating a story written in images, videos, cartoons, and graphs. While your paper is mostly text, with graphics to highlight crucial points, your slides should be the opposite. Adapting to the new medium may require you to create or acquire far more graphics than you included in your paper, but it is necessary to create an engaging presentation.
The most important thing you can do for your presentation is to practice and revise. Bother your friends, your roommates, TAs–anybody who will sit down and listen to your work. Beyond that, think about presentations you have found compelling and try to incorporate some of those elements into your own. Remember you want your work to be comprehensible; you aren’t creating experts in 10 minutes. Above all, try to stay passionate about what you did and why. You put the time in, so show your audience that it’s worth it.
For more insight into research presentations, check out these past PCUR posts written by Emma and Ellie .
— Alec Getraer, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on October 26, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
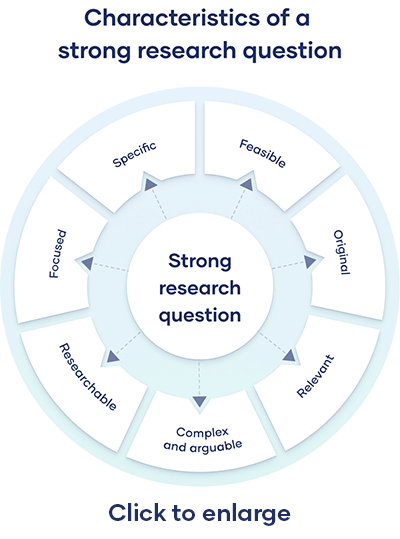
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, using sub-questions to strengthen your main research question, research questions quiz, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
Using your research problem to develop your research question
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
Feasible and specific, complex and arguable, relevant and original.
Chances are that your main research question likely can’t be answered all at once. That’s why sub-questions are important: they allow you to answer your main question in a step-by-step manner.
Good sub-questions should be:
- Less complex than the main question
- Focused only on 1 type of research
- Presented in a logical order
Here are a few examples of descriptive and framing questions:
- Descriptive: According to current government arguments, how should a European bank tax be implemented?
- Descriptive: Which countries have a bank tax/levy on financial transactions?
- Framing: How should a bank tax/levy on financial transactions look at a European level?
Keep in mind that sub-questions are by no means mandatory. They should only be asked if you need the findings to answer your main question. If your main question is simple enough to stand on its own, it’s okay to skip the sub-question part. As a rule of thumb, the more complex your subject, the more sub-questions you’ll need.
Try to limit yourself to 4 or 5 sub-questions, maximum. If you feel you need more than this, it may be indication that your main research question is not sufficiently specific. In this case, it’s is better to revisit your problem statement and try to tighten your main question up.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (“ x affects y because …”).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses . In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.

Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 21). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-questions/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

How to formulate research questions

Related Papers
Dr. Jayanta Ghosh
Rebekka Tunombili
Writing for Publication
Christian Dueñas
A group of higher education faculty members from different colleges and departments were participating in a 3-day professional development institute on writing for professional publication. The pressure to publish was on at their institution, newly categorized as a university. Prior to the mid-morning break on the fi rst day, the presenter asked the participants to write their concerns about publishing on Post-it notes and then read and categorized them before the group reconvened. The great majority of the participants were worried about their ability to fulfi ll the scalating expectations for faculty. Only a few had published previously and they ondered if they were capable of writing well enough to publish their work. As away to allay their fears, the presenter offered to assess a short writing sample from each participant that evening and return it the next day.
Pavel Collado
Sebastian Garcia
Cristian Perez
Tola Boeurt
COURSE DURATION: 63 Hours, 42 sessions, 21 weeks LECTURER: BOEURT CHANTOLA I. COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is designed for advanced level English Learners who wish to effectively find information on every aspect. This course will provide all learners the knowledge of how to collect the information from the different resources. Specifically, the research methodology will seek to enable all learners the comprehensive knowledge of research such as; processing of research, formulating the research problem, conceptualizing a research design, constructing on instrument for collecting the data, writing a research proposal, processing the data, and writing a research report. II. STRATEGIC OBJECTIVES By the end of the course, all the students will be able to: Work independently to develop complex research project Analyze critically the structure, argumentation and quality of the thesis or practical project Identify the methodological approaches employed in the a spirit of intellectual openness and generosity Present the outline of specific questions developing out their research III. INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon completion of the course, students will be able:
Dr. Krishnanaik Vankdoth
Research methods and presentation is a broad term. While methods of data collection and data analysis represent the core of research methods. The most important elements of research methodology expected to be covered in business dissertation at Bachelor’s, Master’s and PhD levels include research philosophy
Davida Scharf
See review in Library Journal. http://reviews.libraryjournal.com/2013/11/reference/wiki-literacy/
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Francisco Javier Leal López
Chitu Okoli
Malehe pourkazemi
Ágnes Szokolszky
Jazmín Guillén
Penny Beile
mnkeni africanus
Proceedings of the International Conference …
Hiroaki Ogata
Aksha Memon
Educational Technology & Society
Lung-Hsiang Wong , Chee Lay Tan , Chee-Kuen Chin
Gwo-dong Chen
Prof.Dr. Bahadır Erişti
Sarada Dhakal
Tùng McLeonard
Xianzhong He
Tejaswini Kotian
glenda crosling
Donald J. Kochan
Veiko Locos
Greg Stoner
US-China Education Review A & B
Dr Dare E Ajayi
Xerxes Daji
Ridwan Osman
Abdilahi Adam Mohamoud
Zahori Conferencista Internacional
Roohullah Nawandish
Dondon B. Buensuceso
Sadman Sakib
Susan Searing
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Home Blog Presentation Ideas How to Create and Deliver a Research Presentation
How to Create and Deliver a Research Presentation

Every research endeavor ends up with the communication of its findings. Graduate-level research culminates in a thesis defense , while many academic and scientific disciplines are published in peer-reviewed journals. In a business context, PowerPoint research presentation is the default format for reporting the findings to stakeholders.
Condensing months of work into a few slides can prove to be challenging. It requires particular skills to create and deliver a research presentation that promotes informed decisions and drives long-term projects forward.
Table of Contents
What is a Research Presentation
Key slides for creating a research presentation, tips when delivering a research presentation, how to present sources in a research presentation, recommended templates to create a research presentation.
A research presentation is the communication of research findings, typically delivered to an audience of peers, colleagues, students, or professionals. In the academe, it is meant to showcase the importance of the research paper , state the findings and the analysis of those findings, and seek feedback that could further the research.
The presentation of research becomes even more critical in the business world as the insights derived from it are the basis of strategic decisions of organizations. Information from this type of report can aid companies in maximizing the sales and profit of their business. Major projects such as research and development (R&D) in a new field, the launch of a new product or service, or even corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives will require the presentation of research findings to prove their feasibility.
Market research and technical research are examples of business-type research presentations you will commonly encounter.
In this article, we’ve compiled all the essential tips, including some examples and templates, to get you started with creating and delivering a stellar research presentation tailored specifically for the business context.
Various research suggests that the average attention span of adults during presentations is around 20 minutes, with a notable drop in an engagement at the 10-minute mark . Beyond that, you might see your audience doing other things.
How can you avoid such a mistake? The answer lies in the adage “keep it simple, stupid” or KISS. We don’t mean dumbing down your content but rather presenting it in a way that is easily digestible and accessible to your audience. One way you can do this is by organizing your research presentation using a clear structure.
Here are the slides you should prioritize when creating your research presentation PowerPoint.
1. Title Page
The title page is the first thing your audience will see during your presentation, so put extra effort into it to make an impression. Of course, writing presentation titles and title pages will vary depending on the type of presentation you are to deliver. In the case of a research presentation, you want a formal and academic-sounding one. It should include:
- The full title of the report
- The date of the report
- The name of the researchers or department in charge of the report
- The name of the organization for which the presentation is intended
When writing the title of your research presentation, it should reflect the topic and objective of the report. Focus only on the subject and avoid adding redundant phrases like “A research on” or “A study on.” However, you may use phrases like “Market Analysis” or “Feasibility Study” because they help identify the purpose of the presentation. Doing so also serves a long-term purpose for the filing and later retrieving of the document.
Here’s a sample title page for a hypothetical market research presentation from Gillette .

2. Executive Summary Slide
The executive summary marks the beginning of the body of the presentation, briefly summarizing the key discussion points of the research. Specifically, the summary may state the following:
- The purpose of the investigation and its significance within the organization’s goals
- The methods used for the investigation
- The major findings of the investigation
- The conclusions and recommendations after the investigation
Although the executive summary encompasses the entry of the research presentation, it should not dive into all the details of the work on which the findings, conclusions, and recommendations were based. Creating the executive summary requires a focus on clarity and brevity, especially when translating it to a PowerPoint document where space is limited.
Each point should be presented in a clear and visually engaging manner to capture the audience’s attention and set the stage for the rest of the presentation. Use visuals, bullet points, and minimal text to convey information efficiently.

3. Introduction/ Project Description Slides
In this section, your goal is to provide your audience with the information that will help them understand the details of the presentation. Provide a detailed description of the project, including its goals, objectives, scope, and methods for gathering and analyzing data.
You want to answer these fundamental questions:
- What specific questions are you trying to answer, problems you aim to solve, or opportunities you seek to explore?
- Why is this project important, and what prompted it?
- What are the boundaries of your research or initiative?
- How were the data gathered?
Important: The introduction should exclude specific findings, conclusions, and recommendations.

4. Data Presentation and Analyses Slides
This is the longest section of a research presentation, as you’ll present the data you’ve gathered and provide a thorough analysis of that data to draw meaningful conclusions. The format and components of this section can vary widely, tailored to the specific nature of your research.
For example, if you are doing market research, you may include the market potential estimate, competitor analysis, and pricing analysis. These elements will help your organization determine the actual viability of a market opportunity.
Visual aids like charts, graphs, tables, and diagrams are potent tools to convey your key findings effectively. These materials may be numbered and sequenced (Figure 1, Figure 2, and so forth), accompanied by text to make sense of the insights.

5. Conclusions
The conclusion of a research presentation is where you pull together the ideas derived from your data presentation and analyses in light of the purpose of the research. For example, if the objective is to assess the market of a new product, the conclusion should determine the requirements of the market in question and tell whether there is a product-market fit.
Designing your conclusion slide should be straightforward and focused on conveying the key takeaways from your research. Keep the text concise and to the point. Present it in bullet points or numbered lists to make the content easily scannable.

6. Recommendations
The findings of your research might reveal elements that may not align with your initial vision or expectations. These deviations are addressed in the recommendations section of your presentation, which outlines the best course of action based on the result of the research.
What emerging markets should we target next? Do we need to rethink our pricing strategies? Which professionals should we hire for this special project? — these are some of the questions that may arise when coming up with this part of the research.
Recommendations may be combined with the conclusion, but presenting them separately to reinforce their urgency. In the end, the decision-makers in the organization or your clients will make the final call on whether to accept or decline the recommendations.

7. Questions Slide
Members of your audience are not involved in carrying out your research activity, which means there’s a lot they don’t know about its details. By offering an opportunity for questions, you can invite them to bridge that gap, seek clarification, and engage in a dialogue that enhances their understanding.
If your research is more business-oriented, facilitating a question and answer after your presentation becomes imperative as it’s your final appeal to encourage buy-in for your recommendations.
A simple “Ask us anything” slide can indicate that you are ready to accept questions.
1. Focus on the Most Important Findings
The truth about presenting research findings is that your audience doesn’t need to know everything. Instead, they should receive a distilled, clear, and meaningful overview that focuses on the most critical aspects.
You will likely have to squeeze in the oral presentation of your research into a 10 to 20-minute presentation, so you have to make the most out of the time given to you. In the presentation, don’t soak in the less important elements like historical backgrounds. Decision-makers might even ask you to skip these portions and focus on sharing the findings.
2. Do Not Read Word-per-word
Reading word-for-word from your presentation slides intensifies the danger of losing your audience’s interest. Its effect can be detrimental, especially if the purpose of your research presentation is to gain approval from the audience. So, how can you avoid this mistake?
- Make a conscious design decision to keep the text on your slides minimal. Your slides should serve as visual cues to guide your presentation.
- Structure your presentation as a narrative or story. Stories are more engaging and memorable than dry, factual information.
- Prepare speaker notes with the key points of your research. Glance at it when needed.
- Engage with the audience by maintaining eye contact and asking rhetorical questions.
3. Don’t Go Without Handouts
Handouts are paper copies of your presentation slides that you distribute to your audience. They typically contain the summary of your key points, but they may also provide supplementary information supporting data presented through tables and graphs.
The purpose of distributing presentation handouts is to easily retain the key points you presented as they become good references in the future. Distributing handouts in advance allows your audience to review the material and come prepared with questions or points for discussion during the presentation.
4. Actively Listen
An equally important skill that a presenter must possess aside from speaking is the ability to listen. We are not just talking about listening to what the audience is saying but also considering their reactions and nonverbal cues. If you sense disinterest or confusion, you can adapt your approach on the fly to re-engage them.
For example, if some members of your audience are exchanging glances, they may be skeptical of the research findings you are presenting. This is the best time to reassure them of the validity of your data and provide a concise overview of how it came to be. You may also encourage them to seek clarification.
5. Be Confident
Anxiety can strike before a presentation – it’s a common reaction whenever someone has to speak in front of others. If you can’t eliminate your stress, try to manage it.
People hate public speaking not because they simply hate it. Most of the time, it arises from one’s belief in themselves. You don’t have to take our word for it. Take Maslow’s theory that says a threat to one’s self-esteem is a source of distress among an individual.
Now, how can you master this feeling? You’ve spent a lot of time on your research, so there is no question about your topic knowledge. Perhaps you just need to rehearse your research presentation. If you know what you will say and how to say it, you will gain confidence in presenting your work.
All sources you use in creating your research presentation should be given proper credit. The APA Style is the most widely used citation style in formal research.
In-text citation
Add references within the text of your presentation slide by giving the author’s last name, year of publication, and page number (if applicable) in parentheses after direct quotations or paraphrased materials. As in:
The alarming rate at which global temperatures rise directly impacts biodiversity (Smith, 2020, p. 27).
If the author’s name and year of publication are mentioned in the text, add only the page number in parentheses after the quotations or paraphrased materials. As in:
According to Smith (2020), the alarming rate at which global temperatures rise directly impacts biodiversity (p. 27).
Image citation
All images from the web, including photos, graphs, and tables, used in your slides should be credited using the format below.
Creator’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Image.” Website Name, Day Mo. Year, URL. Accessed Day Mo. Year.
Work cited page
A work cited page or reference list should follow after the last slide of your presentation. The list should be alphabetized by the author’s last name and initials followed by the year of publication, the title of the book or article, the place of publication, and the publisher. As in:
Smith, J. A. (2020). Climate Change and Biodiversity: A Comprehensive Study. New York, NY: ABC Publications.
When citing a document from a website, add the source URL after the title of the book or article instead of the place of publication and the publisher. As in:
Smith, J. A. (2020). Climate Change and Biodiversity: A Comprehensive Study. Retrieved from https://www.smith.com/climate-change-and-biodiversity.
1. Research Project Presentation PowerPoint Template

A slide deck containing 18 different slides intended to take off the weight of how to make a research presentation. With tons of visual aids, presenters can reference existing research on similar projects to this one – or link another research presentation example – provide an accurate data analysis, disclose the methodology used, and much more.
Use This Template
2. Research Presentation Scientific Method Diagram PowerPoint Template

Whenever you intend to raise questions, expose the methodology you used for your research, or even suggest a scientific method approach for future analysis, this circular wheel diagram is a perfect fit for any presentation study.
Customize all of its elements to suit the demands of your presentation in just minutes.
3. Thesis Research Presentation PowerPoint Template

If your research presentation project belongs to academia, then this is the slide deck to pair that presentation. With a formal aesthetic and minimalistic style, this research presentation template focuses only on exposing your information as clearly as possible.
Use its included bar charts and graphs to introduce data, change the background of each slide to suit the topic of your presentation, and customize each of its elements to meet the requirements of your project with ease.
4. Animated Research Cards PowerPoint Template

Visualize ideas and their connection points with the help of this research card template for PowerPoint. This slide deck, for example, can help speakers talk about alternative concepts to what they are currently managing and its possible outcomes, among different other usages this versatile PPT template has. Zoom Animation effects make a smooth transition between cards (or ideas).
5. Research Presentation Slide Deck for PowerPoint

With a distinctive professional style, this research presentation PPT template helps business professionals and academics alike to introduce the findings of their work to team members or investors.
By accessing this template, you get the following slides:
- Introduction
- Problem Statement
- Research Questions
- Conceptual Research Framework (Concepts, Theories, Actors, & Constructs)
- Study design and methods
- Population & Sampling
- Data Collection
- Data Analysis
Check it out today and craft a powerful research presentation out of it!
A successful research presentation in business is not just about presenting data; it’s about persuasion to take meaningful action. It’s the bridge that connects your research efforts to the strategic initiatives of your organization. To embark on this journey successfully, planning your presentation thoroughly is paramount, from designing your PowerPoint to the delivery.
Take a look and get inspiration from the sample research presentation slides above, put our tips to heart, and transform your research findings into a compelling call to action.

Like this article? Please share
Academics, Presentation Approaches, Research & Development Filed under Presentation Ideas
Related Articles

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 29th, 2024

How to Make a Fundraising Presentation (with Thermometer Templates & Slides)
Meet a new framework to design fundraising presentations by harnessing the power of fundraising thermometer templates. Detailed guide with examples.

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 15th, 2024
How to Create a 5 Minutes Presentation
Master the art of short-format speeches like the 5 minutes presentation with this article. Insights on content structure, audience engagement and more.
Leave a Reply
Home Collections Medical Science Research Research Objectives Presentation
Free - Research Objectives PPT Presentation And Google Slides

Research Objectives Presentation Slides
Features of the templates:.
- 100% customizable slides and easy to download
- The slides contained 16:9 and 4:3 formats.
- Easy to change the slide colors quickly.
- Planets animation inserted template.
- Ready-made nodes are given to you.
- science research
- Objectives Operations Research
- Research Objectives
- Research Questions
- Key Objectivies
- Project Objectives
- Research Proposal
- Business Objectives
- Google Slides

666+ Templates
-594.webp)
124+ Templates

Science & Research
182+ Templates

Telemedicine
40+ Templates

320+ Templates

86+ Templates

115+ Templates

44+ Templates

191+ Templates
You May Also Like These PowerPoint Templates


Writing Research Question and Research Objectives
Jan 05, 2020
90 likes | 93 Views
Writing Research Question and Research Objectives. Selecting and Defining a Problem. This marks the beginning of a research study and is the most difficult and important step. This involves : (1). identifying and stating the problem in specific terms;
Share Presentation
- research questions
- research strategy
- case study research
- generating tentative guesses hypotheses

Presentation Transcript
Selecting and Defining a Problem This marks the beginning of a research study and is the most difficult and important step. This involves : (1). identifying and stating the problem in specific terms; (2). identifying the variables in the problem situation and defining them adequately; (3). generating tentative guesses (hypotheses) about therelation of the variables or in other words the solution of the problem, or writing explicitly the questions (research questions) for which answers are sought; and (4). evaluating the problem for its research ability.
Selecting and Defining a Problem • To achieve this, you review the literature related to the problem to know what other researchers have done and discovered and to identify the possible methodology for conducting the research.
Overall Research Questions • They tell you what you want to focus on and what you want to know • They set the rough boundaries of the research: you will study some issues in some context with some actors • They are oriented towards action and process • The way they are (implicitly) formulated will determine research strategy later on • They set the vision for the research project and helps focusing activities
MyOverall Research Questions • How does the emergence of new industrial principles take place in expert supplier firms? • What is the place and role of expert suppliers in the automotive supply chain? • What lean production techniques are used and how are they adopted for satisfying the needs of the organisation? • How in practice takes integrated component development place? • How are organisations and processes designed to support integration?
Research Objective One can distinguish between mainly three objectives or purposes with a research project: • To explain the causality between different observations or the reasons behind a certain situation concerning the phenomenon • To explore a vague problem or a new area of research • To describe, i.e., observe and visualise the situation of certain phenomena The research objective does not automatically define a quantitative or qualitative logic
Research Objective The research questions implicitly determine the research objective, and together they indicate quantitative vs. qualitative research: • WHAT questions of descriptive nature in the sense “how much” or “how many” call for a quantitative approach • WHAT questions of explanatory or exploratory nature call for a qualitative approach • HOW questions and WHY questions call for a qualitative approach Qualitative research is needed when we want to come to terms with the meaning, not the “right” or “wrong” with the phenomena under investigation
Research Strategy Five Basic Strategies: • Experiment • Survey • Archival Analysis • History • Case Study
Sources • Van Maanen, J., (1983), Qualitative Methodology, Beverley Hills, CA: Sage Publications. • Yin, R., K., (2003), Case Study Research, Design and Methods, 3rd edition, Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications.
- More by User

Research question
Mobility, National Sovereignty and Changing Relations: The Nigerian Migrants in Southern Cameroons/Anglophone Cameroon Tangie Nsoh Fonchingong University of Buea -Cameroon. Research question
313 views • 19 slides

Research: Conducting Research and Writing REsearch
Research: Conducting Research and Writing REsearch. In your “Writer’s Notebook”, respond to the following. Title: Better Readers and Writers Close reading helps you become a better reader and writer, because close reading forces you to pay attention to every aspect of a written text.
447 views • 22 slides

RESEARCH QUESTION
Katherine Jernigan River Poze ENVS 220 Daphne Hamilton Fall 2012 Erin Scheibe. Green Building in the Land Down Under. Vertical Development and Compaction of Green Buildings in Australian Cities. BACKGROUND
91 views • 1 slides

Research Question
Research Question. Does a student’s race and gender impact their relationship with others?. Descriptive Statistics. Inferential Statistics.
139 views • 6 slides
Research and objectives
Tackling biological complexity with BetaWB. Lorenzo Dematt é The Microsoft Research – University of Trento Centre for Computational and Systems Biology. Complexity in software.
89 views • 1 slides

Research Question. As publishing houses develop graphic novel imprints geared specifically towards a YA audience, how will the concept of verisimilitude – a key component in YA fiction – play a role in the depiction of the adolescent female body?. Scholarly Resources.
93 views • 3 slides

Selection of irrigation duration for high performance furrow irrigation on cracking clay soils Rod Smith, Jasim Uddin , Malcolm Gillies. Research question. Is there a simple objective way of estimating time to cut-off for furrows in real-time &
183 views • 12 slides

Identifying a research question and study objectives
Knowledge, attitude and practices about HIV in the rural areas of the 24 Parganas district, West Bengal. Identifying a research question and study objectives. 1. Background on HIV in West Bengal. The HIV pandemic continues to expand
207 views • 10 slides

WRITING A RESEARCH QUESTION
WRITING A RESEARCH QUESTION. Adapted from 11 th grade PLC. What is a research question?. a clear, focused, concise, complex and arguable question around which you center your research. Why is it important?. It helps writers focus their research by providing a path for research
414 views • 17 slides

WRITING A RESEARCH QUESTION. What is a research question?. a clear , focused, concise, complex and arguable question around which you center your research. Why is it important?. focused research by providing a path for research
262 views • 13 slides
Research Question. Data Set . Data Set. Data Set. Implications for Classroom Practice. Research Question. Data Set. Data Set. Data Set. Implications for Classroom Practice. Analysis. Research Question. Data Set. Data Set. Data Set. Implications for Classroom Practice. Analysis.
148 views • 9 slides

Research Question. What Makes a Good Question?. Consider…. Is it specific enough? Is it testable? Do you already know the answer? Does it indicate a clear independent variable? Does it allow for possible dependent variables?. Some Questions….
132 views • 4 slides
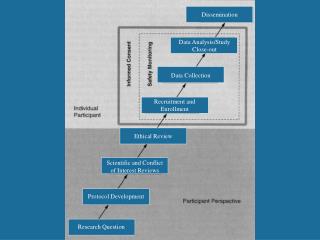
Dissemination. Data Analysis/Study Close-out. Data Collection. Recruitment and Enrollment. Ethical Review. Scientific and Conflict of Interest Reviews. Protocol Development. Research Question. Responsible Research. Overarching Goal for National System Protect Every Research Participant
246 views • 13 slides

Gertrud Tarp, PhD CALPIU conference, Roskilde University, December 15-17 2008 Student voices/agendas in intercultural learning projects Learning outside the classroom
323 views • 19 slides

Children’s Understanding of Polarity Items Ming Xiang, Anastasia Conroy, Jeff Lidz and Andrea Zukowski. University of Maryland Linguistics Department. AmLap 2006. RESEARCH QUESTION. Experiment 1. Two possibilities to interpret Expt 1 results:.
82 views • 1 slides
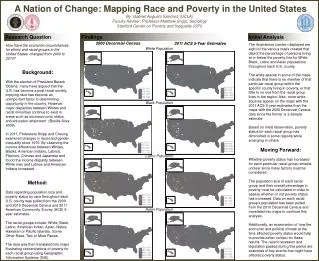
Research Question:
Analysis The illustrations (center) displayed are eight of the various maps created that depict the percentage of persons living at or below the poverty line for White, Black, Latino and Asian populations throughout each U.S. county.
70 views • 1 slides

Research Question. Does the race and gender of college students impact their relationship with students of other ethnic groups?. Group 2B: Kimberly Sheppard, Joy Singleton, Dawn Revere, E. Anne Roycroft. Descriptive Statistics. Inferential Statistics. Results.
127 views • 6 slides

Title Authors Associated institutions. Procedures/Variables/Definitions. Analyses. Discussion (continued). Research Question. Specify the specific aims for your study.

Research Question.
A Comparison of Picture, Video and Written Instruction on the Proper Performance and Compliance of HEP for Patients With Rotator Cuff Disease/ Impingement Syndrome. Cool Springs Focus Team 2008/2009. Research Question.
239 views • 17 slides

Real-Time Measure of Analyst Beliefs Jason V. Chen University of Michigan Venky Nagar University of Michigan Jordan Schoenfeld University of Michigan. Research Question. Analysts provide EPS forecasts, price targets, and stock recommendations to capital market participants
291 views • 18 slides

Research question …
“How do we develop and sustain a professional learning community for teachers in small, rural schools?”. Research question …. Our Research Claims. Professional Learning Communities, such as Smurals, are an effective model of school improvement
364 views • 36 slides
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.53(4); 2010 Aug

Research questions, hypotheses and objectives
Patricia farrugia.
* Michael G. DeGroote School of Medicine, the
Bradley A. Petrisor
† Division of Orthopaedic Surgery and the
Forough Farrokhyar
‡ Departments of Surgery and
§ Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont
Mohit Bhandari
There is an increasing familiarity with the principles of evidence-based medicine in the surgical community. As surgeons become more aware of the hierarchy of evidence, grades of recommendations and the principles of critical appraisal, they develop an increasing familiarity with research design. Surgeons and clinicians are looking more and more to the literature and clinical trials to guide their practice; as such, it is becoming a responsibility of the clinical research community to attempt to answer questions that are not only well thought out but also clinically relevant. The development of the research question, including a supportive hypothesis and objectives, is a necessary key step in producing clinically relevant results to be used in evidence-based practice. A well-defined and specific research question is more likely to help guide us in making decisions about study design and population and subsequently what data will be collected and analyzed. 1
Objectives of this article
In this article, we discuss important considerations in the development of a research question and hypothesis and in defining objectives for research. By the end of this article, the reader will be able to appreciate the significance of constructing a good research question and developing hypotheses and research objectives for the successful design of a research study. The following article is divided into 3 sections: research question, research hypothesis and research objectives.
Research question
Interest in a particular topic usually begins the research process, but it is the familiarity with the subject that helps define an appropriate research question for a study. 1 Questions then arise out of a perceived knowledge deficit within a subject area or field of study. 2 Indeed, Haynes suggests that it is important to know “where the boundary between current knowledge and ignorance lies.” 1 The challenge in developing an appropriate research question is in determining which clinical uncertainties could or should be studied and also rationalizing the need for their investigation.
Increasing one’s knowledge about the subject of interest can be accomplished in many ways. Appropriate methods include systematically searching the literature, in-depth interviews and focus groups with patients (and proxies) and interviews with experts in the field. In addition, awareness of current trends and technological advances can assist with the development of research questions. 2 It is imperative to understand what has been studied about a topic to date in order to further the knowledge that has been previously gathered on a topic. Indeed, some granting institutions (e.g., Canadian Institute for Health Research) encourage applicants to conduct a systematic review of the available evidence if a recent review does not already exist and preferably a pilot or feasibility study before applying for a grant for a full trial.
In-depth knowledge about a subject may generate a number of questions. It then becomes necessary to ask whether these questions can be answered through one study or if more than one study needed. 1 Additional research questions can be developed, but several basic principles should be taken into consideration. 1 All questions, primary and secondary, should be developed at the beginning and planning stages of a study. Any additional questions should never compromise the primary question because it is the primary research question that forms the basis of the hypothesis and study objectives. It must be kept in mind that within the scope of one study, the presence of a number of research questions will affect and potentially increase the complexity of both the study design and subsequent statistical analyses, not to mention the actual feasibility of answering every question. 1 A sensible strategy is to establish a single primary research question around which to focus the study plan. 3 In a study, the primary research question should be clearly stated at the end of the introduction of the grant proposal, and it usually specifies the population to be studied, the intervention to be implemented and other circumstantial factors. 4
Hulley and colleagues 2 have suggested the use of the FINER criteria in the development of a good research question ( Box 1 ). The FINER criteria highlight useful points that may increase the chances of developing a successful research project. A good research question should specify the population of interest, be of interest to the scientific community and potentially to the public, have clinical relevance and further current knowledge in the field (and of course be compliant with the standards of ethical boards and national research standards).
FINER criteria for a good research question
Adapted with permission from Wolters Kluwer Health. 2
Whereas the FINER criteria outline the important aspects of the question in general, a useful format to use in the development of a specific research question is the PICO format — consider the population (P) of interest, the intervention (I) being studied, the comparison (C) group (or to what is the intervention being compared) and the outcome of interest (O). 3 , 5 , 6 Often timing (T) is added to PICO ( Box 2 ) — that is, “Over what time frame will the study take place?” 1 The PICOT approach helps generate a question that aids in constructing the framework of the study and subsequently in protocol development by alluding to the inclusion and exclusion criteria and identifying the groups of patients to be included. Knowing the specific population of interest, intervention (and comparator) and outcome of interest may also help the researcher identify an appropriate outcome measurement tool. 7 The more defined the population of interest, and thus the more stringent the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the greater the effect on the interpretation and subsequent applicability and generalizability of the research findings. 1 , 2 A restricted study population (and exclusion criteria) may limit bias and increase the internal validity of the study; however, this approach will limit external validity of the study and, thus, the generalizability of the findings to the practical clinical setting. Conversely, a broadly defined study population and inclusion criteria may be representative of practical clinical practice but may increase bias and reduce the internal validity of the study.
PICOT criteria 1
A poorly devised research question may affect the choice of study design, potentially lead to futile situations and, thus, hamper the chance of determining anything of clinical significance, which will then affect the potential for publication. Without devoting appropriate resources to developing the research question, the quality of the study and subsequent results may be compromised. During the initial stages of any research study, it is therefore imperative to formulate a research question that is both clinically relevant and answerable.
Research hypothesis
The primary research question should be driven by the hypothesis rather than the data. 1 , 2 That is, the research question and hypothesis should be developed before the start of the study. This sounds intuitive; however, if we take, for example, a database of information, it is potentially possible to perform multiple statistical comparisons of groups within the database to find a statistically significant association. This could then lead one to work backward from the data and develop the “question.” This is counterintuitive to the process because the question is asked specifically to then find the answer, thus collecting data along the way (i.e., in a prospective manner). Multiple statistical testing of associations from data previously collected could potentially lead to spuriously positive findings of association through chance alone. 2 Therefore, a good hypothesis must be based on a good research question at the start of a trial and, indeed, drive data collection for the study.
The research or clinical hypothesis is developed from the research question and then the main elements of the study — sampling strategy, intervention (if applicable), comparison and outcome variables — are summarized in a form that establishes the basis for testing, statistical and ultimately clinical significance. 3 For example, in a research study comparing computer-assisted acetabular component insertion versus freehand acetabular component placement in patients in need of total hip arthroplasty, the experimental group would be computer-assisted insertion and the control/conventional group would be free-hand placement. The investigative team would first state a research hypothesis. This could be expressed as a single outcome (e.g., computer-assisted acetabular component placement leads to improved functional outcome) or potentially as a complex/composite outcome; that is, more than one outcome (e.g., computer-assisted acetabular component placement leads to both improved radiographic cup placement and improved functional outcome).
However, when formally testing statistical significance, the hypothesis should be stated as a “null” hypothesis. 2 The purpose of hypothesis testing is to make an inference about the population of interest on the basis of a random sample taken from that population. The null hypothesis for the preceding research hypothesis then would be that there is no difference in mean functional outcome between the computer-assisted insertion and free-hand placement techniques. After forming the null hypothesis, the researchers would form an alternate hypothesis stating the nature of the difference, if it should appear. The alternate hypothesis would be that there is a difference in mean functional outcome between these techniques. At the end of the study, the null hypothesis is then tested statistically. If the findings of the study are not statistically significant (i.e., there is no difference in functional outcome between the groups in a statistical sense), we cannot reject the null hypothesis, whereas if the findings were significant, we can reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternate hypothesis (i.e., there is a difference in mean functional outcome between the study groups), errors in testing notwithstanding. In other words, hypothesis testing confirms or refutes the statement that the observed findings did not occur by chance alone but rather occurred because there was a true difference in outcomes between these surgical procedures. The concept of statistical hypothesis testing is complex, and the details are beyond the scope of this article.
Another important concept inherent in hypothesis testing is whether the hypotheses will be 1-sided or 2-sided. A 2-sided hypothesis states that there is a difference between the experimental group and the control group, but it does not specify in advance the expected direction of the difference. For example, we asked whether there is there an improvement in outcomes with computer-assisted surgery or whether the outcomes worse with computer-assisted surgery. We presented a 2-sided test in the above example because we did not specify the direction of the difference. A 1-sided hypothesis states a specific direction (e.g., there is an improvement in outcomes with computer-assisted surgery). A 2-sided hypothesis should be used unless there is a good justification for using a 1-sided hypothesis. As Bland and Atlman 8 stated, “One-sided hypothesis testing should never be used as a device to make a conventionally nonsignificant difference significant.”
The research hypothesis should be stated at the beginning of the study to guide the objectives for research. Whereas the investigators may state the hypothesis as being 1-sided (there is an improvement with treatment), the study and investigators must adhere to the concept of clinical equipoise. According to this principle, a clinical (or surgical) trial is ethical only if the expert community is uncertain about the relative therapeutic merits of the experimental and control groups being evaluated. 9 It means there must exist an honest and professional disagreement among expert clinicians about the preferred treatment. 9
Designing a research hypothesis is supported by a good research question and will influence the type of research design for the study. Acting on the principles of appropriate hypothesis development, the study can then confidently proceed to the development of the research objective.
Research objective
The primary objective should be coupled with the hypothesis of the study. Study objectives define the specific aims of the study and should be clearly stated in the introduction of the research protocol. 7 From our previous example and using the investigative hypothesis that there is a difference in functional outcomes between computer-assisted acetabular component placement and free-hand placement, the primary objective can be stated as follows: this study will compare the functional outcomes of computer-assisted acetabular component insertion versus free-hand placement in patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. Note that the study objective is an active statement about how the study is going to answer the specific research question. Objectives can (and often do) state exactly which outcome measures are going to be used within their statements. They are important because they not only help guide the development of the protocol and design of study but also play a role in sample size calculations and determining the power of the study. 7 These concepts will be discussed in other articles in this series.
From the surgeon’s point of view, it is important for the study objectives to be focused on outcomes that are important to patients and clinically relevant. For example, the most methodologically sound randomized controlled trial comparing 2 techniques of distal radial fixation would have little or no clinical impact if the primary objective was to determine the effect of treatment A as compared to treatment B on intraoperative fluoroscopy time. However, if the objective was to determine the effect of treatment A as compared to treatment B on patient functional outcome at 1 year, this would have a much more significant impact on clinical decision-making. Second, more meaningful surgeon–patient discussions could ensue, incorporating patient values and preferences with the results from this study. 6 , 7 It is the precise objective and what the investigator is trying to measure that is of clinical relevance in the practical setting.
The following is an example from the literature about the relation between the research question, hypothesis and study objectives:
Study: Warden SJ, Metcalf BR, Kiss ZS, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound for chronic patellar tendinopathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Rheumatology 2008;47:467–71.
Research question: How does low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) compare with a placebo device in managing the symptoms of skeletally mature patients with patellar tendinopathy?
Research hypothesis: Pain levels are reduced in patients who receive daily active-LIPUS (treatment) for 12 weeks compared with individuals who receive inactive-LIPUS (placebo).
Objective: To investigate the clinical efficacy of LIPUS in the management of patellar tendinopathy symptoms.
The development of the research question is the most important aspect of a research project. A research project can fail if the objectives and hypothesis are poorly focused and underdeveloped. Useful tips for surgical researchers are provided in Box 3 . Designing and developing an appropriate and relevant research question, hypothesis and objectives can be a difficult task. The critical appraisal of the research question used in a study is vital to the application of the findings to clinical practice. Focusing resources, time and dedication to these 3 very important tasks will help to guide a successful research project, influence interpretation of the results and affect future publication efforts.
Tips for developing research questions, hypotheses and objectives for research studies
- Perform a systematic literature review (if one has not been done) to increase knowledge and familiarity with the topic and to assist with research development.
- Learn about current trends and technological advances on the topic.
- Seek careful input from experts, mentors, colleagues and collaborators to refine your research question as this will aid in developing the research question and guide the research study.
- Use the FINER criteria in the development of the research question.
- Ensure that the research question follows PICOT format.
- Develop a research hypothesis from the research question.
- Develop clear and well-defined primary and secondary (if needed) objectives.
- Ensure that the research question and objectives are answerable, feasible and clinically relevant.
FINER = feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, relevant; PICOT = population (patients), intervention (for intervention studies only), comparison group, outcome of interest, time.
Competing interests: No funding was received in preparation of this paper. Dr. Bhandari was funded, in part, by a Canada Research Chair, McMaster University.

- Customer Favourites
Research Objective
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

- You're currently reading page 1

Stages // require(['jquery'], function ($) { $(document).ready(function () { //removes paginator if items are less than selected items per page var paginator = $("#limiter :selected").text(); var itemsPerPage = parseInt(paginator); var itemsCount = $(".products.list.items.product-items.sli_container").children().length; if (itemsCount ? ’Stages’ here means the number of divisions or graphic elements in the slide. For example, if you want a 4 piece puzzle slide, you can search for the word ‘puzzles’ and then select 4 ‘Stages’ here. We have categorized all our content according to the number of ‘Stages’ to make it easier for you to refine the results.
Category // require(['jquery'], function ($) { $(document).ready(function () { //removes paginator if items are less than selected items per page var paginator = $("#limiter :selected").text(); var itemsperpage = parseint(paginator); var itemscount = $(".products.list.items.product-items.sli_container").children().length; if (itemscount.
- Anatomy (2)
- Block Chain (1)
- Branding (1)
- Business Plan Word (56)
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches
infertility
30 templates

linguistics
89 templates
15 templates

28 templates

public health
35 templates

holy spirit
38 templates
Research Presentation templates
Customize our free themes and templates for google slides or powerpoint and explain what your research is about. these designs are easy to edit, so that will speed things up.

Formal Research Paper Slideshow
Have you seen these slides? They are perfect for presenting your research paper! First of all, because we have included all the necessary sections of this type of work, such as hypothesis, objectives, methodology, analysis and the conclusions of the paper. The second reason is that the formal style will...

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access
Research Methods Lesson
If you deal with Science, it’s important to learn more about research methods. Teach your students about them with this presentation full of illustrations and drawings related to labs. Use graphs, maps, tables and overview diagrams to support your lecture in a visual way!

Diseases Related to Stomach: Diverticulitis
Download the "Diseases Related to Stomach: Diverticulitis" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Taking care of yourself and of those around you is key! By learning about various illnesses and how they are spread, people can get a better understanding of them and make informed decisions about eating, exercise, and...

Medical Anatomy Poster
Download the "Medical Anatomy Poster" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Healthcare goes beyond curing patients and combating illnesses. Raising awareness about diseases, informing people about prevention methods, discussing some good practices, or even talking about a balanced diet—there are many topics related to medicine that you could be sharing...

Economics Thesis
If numbers, exchange rates, money and trading are your forte, odds are you’re already working on an economics thesis for your master’s degree. Defending your dissertation is the last step and the most difficult one, but Slidesgo can help you. Here’s our new free presentation template with a focus on...

Research Project Proposal
Before embarking yourself on a new project, especially if it’s about research, you need to set out a proposal to explain its viability. Here at Slidesgo we’re offering this theme that you can actually use for any kind of project, regardless of the topic.

Pregnancy Breakthrough
Giving birth to a baby is a beautiful occasion, a manifestation of love between two people. Obstetrics are key during pregnancy, so how about giving a presentation about the latest breakthrough in this field? Our free medical template will come in handy.

AP Research Defense for High School
AP, or Advanced Placement, is a North American educational program that offers a rigorous course designed to challenge and prepare high school students for their future careers and academic pursuits. It requires students to conduct independent research, write a lengthy academic paper, and present their findings to a panel of...
Excretory System Diseases
Download the "Excretory System Diseases" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Taking care of yourself and of those around you is key! By learning about various illnesses and how they are spread, people can get a better understanding of them and make informed decisions about eating, exercise, and seeking medical...

Elegant Black & White Thesis Defense
Present your research findings with grace and assertiveness through this template. Available for Google Slides and PowerPoint, this design set offers minimalistic charm with its simple, gray scale elegance. The template not only provides a polished platform to showcase your thesis but also ensures seamless and efficient delivery of your...

Cycle Diagrams Theme for a Case Report
Download the "Cycle Diagrams Theme for a Case Report" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. A clinical case is more than just a set of symptoms and a diagnosis. It is a unique story of a patient, their experiences, and their journey towards healing. Each case is an opportunity for...

Bariatric Surgery Breakthrough
Download the "Bariatric Surgery Breakthrough" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Treating diseases involves a lot of prior research and clinical trials. But whenever there’s a new discovery, a revolutionary finding that opens the door to new treatments, vaccines or ways to prevent illnesses, it’s great news. Should there be...
Project Research Infographics
Download the "Project Research Infographics" template for PowerPoint or Google Slides and discover the power of infographics. An infographic resource gives you the ability to showcase your content in a more visual way, which will make it easier for your audience to understand your topic. Slidesgo infographics like this set...

Nursing Capstone
In medical contexts, a capstone is often the final course in a nursing degree, a project of vital importance. It’s very demanding, so if you need help with the presentation, use this free professional template. Leave the design to us and focus on your data!

Soil Mechanics Research Project Proposal
Download the "Soil Mechanics Research Project Proposal" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. A well-crafted proposal can be the key factor in determining the success of your project. It's an opportunity to showcase your ideas, objectives, and plans in a clear and concise manner, and to convince others to invest...

Medical Disease Explained With Cycle Diagrams
Download the "Medical Disease Explained With Cycle Diagrams" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Taking care of yourself and of those around you is key! By learning about various illnesses and how they are spread, people can get a better understanding of them and make informed decisions about eating, exercise,...
SWOT Analysis Infographics
Discover the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of your own company performing a SWOT analysis. Use this basic strategic planning to evaluate your position with these new infographics created by Slidesgo.

Data Analysis for Marketing Strategies
With the amount of data available through various digital platforms, it's easier than ever to determine the trends and preferences of your target audience. By collecting and analyzing data, marketers can create highly personalized campaigns that align with the exact needs and wants of their customers. If you're trying to...
- Page 1 of 79
New! Make quick presentations with AI
Slidesgo AI presentation maker puts the power of design and creativity in your hands, so you can effortlessly craft stunning slideshows in minutes.

Register for free and start editing online

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research questions and research objectives. Mar 21, 2015 •. 75 likes • 180,263 views. National Institute of Technology Karnataka ( NITK ),Surathkal. Research questions are the starting point in any good research . They provide the road map to proceed and identify and focus on the research gaps . The research objectives are actions intended ...
19 likes • 19,770 views. Ashok Pandey. With the objective of To train the health professionals on health system research proposal development, To acquaint the participants with health research process, and To train basic managerial skills required to manage proposed health research. Research Questions, Objectives, and Hypothesis is important.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (collectively called the "golden thread") are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you're crafting a research proposal, dissertation or thesis.We receive questions almost every day about this "holy trinity" of research and there's certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we've crafted this post to help ...
RESEARCH QUESTIONS. Qualitative Approach. The use of Research Questions as opposed to objectives or hypothesis, is more frequent. Characteristics Use of words- what or how. Specify whether the study: discovers, seeks to understand, explores or describes the experiences. Use of non-directional wording in the question.
Define the overall research question: The first step in writing research objectives is to clearly define the overall research (SMART) question that the study aims to answer. Break it down into specific objectives: Once the overall research question has been defined, it should be broken down into objectives to guide the development of the research.
Research Questions, Objectives and Hypotheses Lecture by Dr Amna Rehana Siddiqui September 2013. SESSION OBJECTIVES Participants will be able to • Differentiate between goals & objectives • Learn formulation of research question • Define the specific objectives in terms of the stated problem 4. Describe the study hypothesis . GOALS and OBJECTIVES Goals: long-term benefits Objectives ...
Download ppt "Research Questions, Objectives and Hypotheses" Similar presentations . Chapter 2 The Process of Experimentation. Critical Reading Strategies: Overview of Research Process. Yiu-fai Cheung, MD Department of Paediatrics and Adolescent Medicine LKS Faculty of Medicine The University of Hong Kong Hong Kong, China Sharing in GRF.
Chapter 4Research Problems, Research Questions, and Hypotheses. Basic Terminology Research problem An enigmatic, perplexing, or troubling condition Problem statement A statement articulating the research problem and indicating the need for a study. Basic Terminology (cont'd) Research questions The specific queries the researcher wants to answer in addressing the research problem Hypotheses ...
Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling. Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story.
Formulating research objectives has the following five steps, which could help researchers develop a clear objective: 8. Identify the research problem. Review past studies on subjects similar to your problem statement, that is, studies that use similar methods, variables, etc.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
978-3-659-87517-5 RESEARCHBOOK.pdf. Dr. Krishnanaik Vankdoth. Research methods and presentation is a broad term. While methods of data collection and data analysis represent the core of research methods. The most important elements of research methodology expected to be covered in business dissertation at Bachelor's, Master's and PhD levels ...
It should include: The full title of the report. The date of the report. The name of the researchers or department in charge of the report. The name of the organization for which the presentation is intended. When writing the title of your research presentation, it should reflect the topic and objective of the report.
Shape your study's trajectory, articulate objectives with confidence, and captivate your audience with the strategic journey this template provides. Features of the templates: 100% customizable slides and easy to download. The slides contained 16:9 and 4:3 formats. Easy to change the slide colors quickly. Planets animation inserted template.
Writing Research Question and Research Objectives. Selecting and Defining a Problem This marks the beginning of a research study and is the most difficult and important step. This involves : (1). identifying and stating the problem in specific terms; (2). identifying the variables in the problem situation and defining them adequately; (3). generating tentative guesses (hypotheses) about ...
Research question. Interest in a particular topic usually begins the research process, but it is the familiarity with the subject that helps define an appropriate research question for a study. 1 Questions then arise out of a perceived knowledge deficit within a subject area or field of study. 2 Indeed, Haynes suggests that it is important to know "where the boundary between current ...
Project context and objectives for academic student research proposal ppt powerpoint tips. Slide 1 of 2. Project context and objectives for qualitative business research services ppt file slides. Slide 1 of 12. Pricing roadmap business objectives goals research implement opportunities. Slide 1 of 6.
Elegant Black & White Thesis Defense. Present your research findings with grace and assertiveness through this template. Available for Google Slides and PowerPoint, this design set offers minimalistic charm with its simple, gray scale elegance. The template not only provides a polished platform to showcase your thesis but also ensures seamless ...