- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus

Reported speech
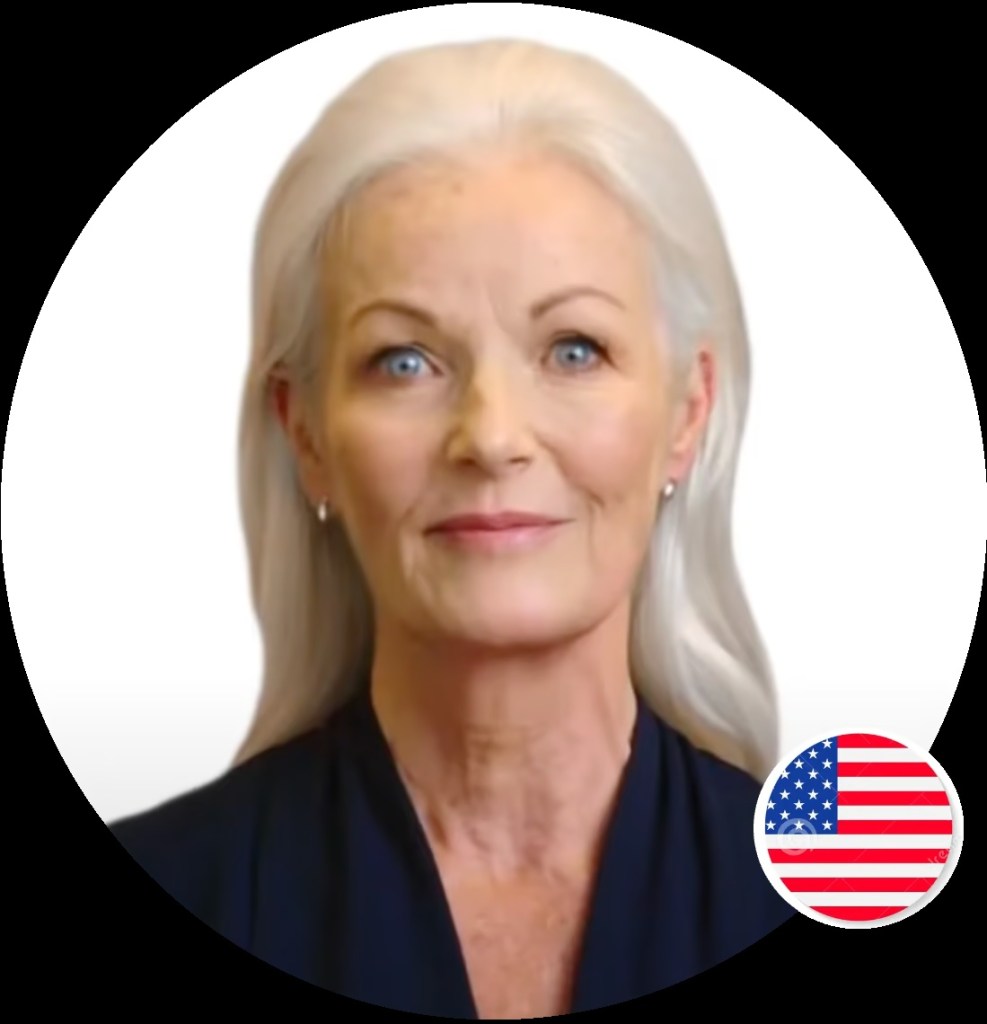
Reported speech is how we represent the speech of other people or what we ourselves say. There are two main types of reported speech: direct speech and indirect speech.
Direct speech repeats the exact words the person used, or how we remember their words:
Barbara said, “I didn’t realise it was midnight.”
In indirect speech, the original speaker’s words are changed.
Barbara said she hadn’t realised it was midnight .
In this example, I becomes she and the verb tense reflects the fact that time has passed since the words were spoken: didn’t realise becomes hadn’t realised .
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words:
“I’m sorry,” said Mark. (direct)
Mark apologised . (indirect: report of a speech act)
In a similar way, we can report what people wrote or thought:
‘I will love you forever,’ he wrote, and then posted the note through Alice’s door. (direct report of what someone wrote)
He wrote that he would love her forever , and then posted the note through Alice’s door. (indirect report of what someone wrote)
I need a new direction in life , she thought. (direct report of someone’s thoughts)
She thought that she needed a new direction in life . (indirect report of someone’s thoughts)
Reported speech: direct speech
Reported speech: indirect speech
Reported speech: reporting and reported clauses
Speech reports consist of two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. The reporting clause includes a verb such as say, tell, ask, reply, shout , usually in the past simple, and the reported clause includes what the original speaker said.
Reported speech: punctuation
Direct speech.
In direct speech we usually put a comma between the reporting clause and the reported clause. The words of the original speaker are enclosed in inverted commas, either single (‘…’) or double (“…”). If the reported clause comes first, we put the comma inside the inverted commas:
“ I couldn’t sleep last night, ” he said.
Rita said, ‘ I don’t need you any more. ’
If the direct speech is a question or exclamation, we use a question mark or exclamation mark, not a comma:
‘Is there a reason for this ? ’ she asked.
“I hate you ! ” he shouted.
We sometimes use a colon (:) between the reporting clause and the reported clause when the reporting clause is first:
The officer replied: ‘It is not possible to see the General. He’s busy.’
Punctuation
Indirect speech
In indirect speech it is more common for the reporting clause to come first. When the reporting clause is first, we don’t put a comma between the reporting clause and the reported clause. When the reporting clause comes after the reported clause, we use a comma to separate the two parts:
She told me they had left her without any money.
Not: She told me, they had left her without any money .
Nobody had gone in or out during the previous hour, he informed us.
We don’t use question marks or exclamation marks in indirect reports of questions and exclamations:
He asked me why I was so upset.
Not: He asked me why I was so upset?
Reported speech: reporting verbs
Say and tell.
We can use say and tell to report statements in direct speech, but say is more common. We don’t always mention the person being spoken to with say , but if we do mention them, we use a prepositional phrase with to ( to me, to Lorna ):
‘I’ll give you a ring tomorrow,’ she said .
‘Try to stay calm,’ she said to us in a low voice.
Not: ‘Try to stay calm,’ she said us in a low voice .
With tell , we always mention the person being spoken to; we use an indirect object (underlined):
‘Enjoy yourselves,’ he told them .
Not: ‘Enjoy yourselves,’ he told .
In indirect speech, say and tell are both common as reporting verbs. We don’t use an indirect object with say , but we always use an indirect object (underlined) with tell :
He said he was moving to New Zealand.
Not: He said me he was moving to New Zealand .
He told me he was moving to New Zealand.
Not: He told he was moving to New Zealand .
We use say , but not tell , to report questions:
‘Are you going now?’ she said .
Not: ‘Are you going now?’ she told me .
We use say , not tell , to report greetings, congratulations and other wishes:
‘Happy birthday!’ she said .
Not: Happy birthday!’ she told me .
Everyone said good luck to me as I went into the interview.
Not: Everyone told me good luck …
Say or tell ?
Other reporting verbs
The reporting verbs in this list are more common in indirect reports, in both speaking and writing:
Simon admitted that he had forgotten to email Andrea.
Louis always maintains that there is royal blood in his family.
The builder pointed out that the roof was in very poor condition.
Most of the verbs in the list are used in direct speech reports in written texts such as novels and newspaper reports. In ordinary conversation, we don’t use them in direct speech. The reporting clause usually comes second, but can sometimes come first:
‘Who is that person?’ she asked .
‘It was my fault,’ he confessed .
‘There is no cause for alarm,’ the Minister insisted .
Verb patterns: verb + that -clause

Word of the Day
on the road
If a vehicle is on the road, it is working as it should and can be legally used.

Apples and oranges (Talking about differences, Part 2)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

What is Reported Speech and how to use it? with Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
Reported speech and indirect speech are two terms that refer to the same concept, which is the act of expressing what someone else has said.
On this page:
Reported speech is different from direct speech because it does not use the speaker’s exact words. Instead, the reporting verb is used to introduce the reported speech, and the tense and pronouns are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. There are two main types of reported speech: statements and questions.
1. Reported Statements: In reported statements, the reporting verb is usually “said.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and any pronouns referring to the speaker or listener are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. For example, “I am going to the store,” becomes “He said that he was going to the store.”
2. Reported Questions: In reported questions, the reporting verb is usually “asked.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and the word order changes from a question to a statement. For example, “What time is it?” becomes “She asked what time it was.”
It’s important to note that the tense shift in reported speech depends on the context and the time of the reported speech. Here are a few more examples:
- Direct speech: “I will call you later.”Reported speech: He said that he would call me later.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
- Direct speech: “I love pizza.”Reported speech: They said that they loved pizza.
When do we use reported speech?
Reported speech is used to report what someone else has said, thought, or written. It is often used in situations where you want to relate what someone else has said without quoting them directly.
Reported speech can be used in a variety of contexts, such as in news reports, academic writing, and everyday conversation. Some common situations where reported speech is used include:
News reports: Journalists often use reported speech to quote what someone said in an interview or press conference.
Business and professional communication: In professional settings, reported speech can be used to summarize what was discussed in a meeting or to report feedback from a customer.
Conversational English: In everyday conversations, reported speech is used to relate what someone else said. For example, “She told me that she was running late.”
Narration: In written narratives or storytelling, reported speech can be used to convey what a character said or thought.
How to make reported speech?
1. Change the pronouns and adverbs of time and place: In reported speech, you need to change the pronouns, adverbs of time and place to reflect the new speaker or point of view. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the store now,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then.
In this example, the pronoun “I” is changed to “she” and the adverb “now” is changed to “then.”
2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet me at the park the next day.
In this example, the present tense “will” is changed to the past tense “would.”
3. Change reporting verbs: In reported speech, you can use different reporting verbs such as “say,” “tell,” “ask,” or “inquire” depending on the context of the speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
In this example, the reporting verb “asked” is changed to “said” and “did” is changed to “had.”
Overall, when making reported speech, it’s important to pay attention to the verb tense and the changes in pronouns, adverbs, and reporting verbs to convey the original speaker’s message accurately.
How do I change the pronouns and adverbs in reported speech?
1. Changing Pronouns: In reported speech, the pronouns in the original statement must be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. Generally, the first person pronouns (I, me, my, mine, we, us, our, ours) are changed according to the subject of the reporting verb, while the second and third person pronouns (you, your, yours, he, him, his, she, her, hers, it, its, they, them, their, theirs) are changed according to the object of the reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I love chocolate.” Reported speech: She said she loved chocolate.
Direct speech: “You should study harder.” Reported speech: He advised me to study harder.
Direct speech: “She is reading a book.” Reported speech: They noticed that she was reading a book.
2. Changing Adverbs: In reported speech, the adverbs and adverbial phrases that indicate time or place may need to be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech: She said she was going to the cinema that night.
Direct speech: “He is here.” Reported speech: She said he was there.
Note that the adverb “now” usually changes to “then” or is omitted altogether in reported speech, depending on the context.
It’s important to keep in mind that the changes made to pronouns and adverbs in reported speech depend on the context and the perspective of the new speaker. With practice, you can become more comfortable with making these changes in reported speech.
How do I change the tense in reported speech?
In reported speech, the tense of the reported verb usually changes to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here are some guidelines on how to change the tense in reported speech:
Present simple in direct speech changes to past simple in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I like pizza.” Reported speech: She said she liked pizza.
Present continuous in direct speech changes to past continuous in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I am studying for my exam.” Reported speech: He said he was studying for his exam.
Present perfect in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I have finished my work.” Reported speech: She said she had finished her work.
Past simple in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I visited my grandparents last weekend.” Reported speech: She said she had visited her grandparents the previous weekend.
Will in direct speech changes to would in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I will help you with your project.” Reported speech: He said he would help me with my project.
Can in direct speech changes to could in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I can speak French.” Reported speech: She said she could speak French.
Remember that the tense changes in reported speech depend on the tense of the verb in the direct speech, and the tense you use in reported speech should match the time frame of the new speaker’s perspective. With practice, you can become more comfortable with changing the tense in reported speech.
Do I always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech?
No, you do not always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech. However, using a reporting verb can help to clarify who is speaking and add more context to the reported speech.
In some cases, the reported speech can be introduced by phrases such as “I heard that” or “It seems that” without using a reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She said she was going to the cinema tonight. Reported speech without a reporting verb: It seems that she’s going to the cinema tonight.
However, it’s important to note that using a reporting verb can help to make the reported speech more formal and accurate. When using reported speech in academic writing or journalism, it’s generally recommended to use a reporting verb to make the reporting more clear and credible.
Some common reporting verbs include say, tell, explain, ask, suggest, and advise. For example:
Direct speech: “I think we should invest in renewable energy.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She suggested that they invest in renewable energy.
Overall, while using a reporting verb is not always required, it can be helpful to make the reported speech more clear and accurate
How to use reported speech to report questions and commands?
1. Reporting Questions: When reporting questions, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “What time is the meeting?” Reported speech: She asked what time the meeting was.
Note that the question mark is not used in reported speech.
2. Reporting Commands: When reporting commands, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “ordered” or “told” followed by the person, to + infinitive, and any additional information. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Clean your room!” Reported speech: She ordered me to clean my room.
Note that the exclamation mark is not used in reported speech.
In both cases, the tense of the reported verb should be changed accordingly. For example, present simple changes to past simple, and future changes to conditional. Here are some examples:
Direct speech: “Will you go to the party with me?”Reported speech: She asked if I would go to the party with her. Direct speech: “Please bring me a glass of water.”Reported speech: She requested that I bring her a glass of water.
Remember that when using reported speech to report questions and commands, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
How to make questions in reported speech?
To make questions in reported speech, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here are the steps to make questions in reported speech:
Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb in the sentence. Common reporting verbs used to report questions include “asked,” “inquired,” “wondered,” and “wanted to know.”
Change the tense and pronouns: Next, you need to change the tense and pronouns in the sentence to reflect the shift from direct to reported speech. The tense of the verb is usually shifted back one tense (e.g. from present simple to past simple) in reported speech. The pronouns should also be changed as necessary to reflect the shift in perspective from the original speaker to the reporting speaker.
Use an appropriate question word: If the original question contained a question word (e.g. who, what, where, when, why, how), you should use the same question word in the reported question. If the original question did not contain a question word, you can use “if” or “whether” to introduce the reported question.
Change the word order: In reported speech, the word order of the question changes from the inverted form to a normal statement form. The subject usually comes before the verb, unless the original question started with a question word.
Here are some examples of reported questions:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: He wanted to know if I had finished my homework. Direct speech: “Where are you going?”Reported speech: She wondered where I was going.
Remember that when making questions in reported speech, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
Here you can find more examples of direct and indirect questions
What is the difference between reported speech an indirect speech?
In reported or indirect speech, you are retelling or reporting what someone said using your own words. The tense of the reported speech is usually shifted back one tense from the tense used in the original statement. For example, if someone said, “I am going to the store,” in reported speech you would say, “He/she said that he/she was going to the store.”
The main difference between reported speech and indirect speech is that reported speech usually refers to spoken language, while indirect speech can refer to both spoken and written language. Additionally, indirect speech is a broader term that includes reported speech as well as other ways of expressing what someone else has said, such as paraphrasing or summarizing.
Examples of direct speech to reported
- Direct speech: “I am hungry,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was hungry.
- Direct speech: “Can you pass the salt, please?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked her to pass the salt.
- Direct speech: “I will meet you at the cinema,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet her at the cinema.
- Direct speech: “I have been working on this project for hours,” she said. Reported speech: She said she had been working on the project for hours.
- Direct speech: “What time does the train leave?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked what time the train left.
- Direct speech: “I love playing the piano,” she said. Reported speech: She said she loved playing the piano.
- Direct speech: “I am going to the grocery store,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to the grocery store.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” the teacher asked. Reported speech: The teacher asked if he had finished his homework.
- Direct speech: “I want to go to the beach,” she said. Reported speech: She said she wanted to go to the beach.
- Direct speech: “Do you need help with that?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked if she needed help with that.
- Direct speech: “I can’t come to the party,” he said. Reported speech: He said he couldn’t come to the party.
- Direct speech: “Please don’t leave me,” she said. Reported speech: She begged him not to leave her.
- Direct speech: “I have never been to London before,” he said. Reported speech: He said he had never been to London before.
- Direct speech: “Where did you put my phone?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked where she had put her phone.
- Direct speech: “I’m sorry for being late,” he said. Reported speech: He apologized for being late.
- Direct speech: “I need some help with this math problem,” she said. Reported speech: She said she needed some help with the math problem.
- Direct speech: “I am going to study abroad next year,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to study abroad the following year.
- Direct speech: “Can you give me a ride to the airport?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked him to give her a ride to the airport.
- Direct speech: “I don’t know how to fix this,” he said. Reported speech: He said he didn’t know how to fix it.
- Direct speech: “I hate it when it rains,” she said. Reported speech: She said she hated it when it rained.
Share this:
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Going to and present continuous for future plans and arrangements, difference between present simple vs. present continuous with example, questions in present continuous tense with examples, present continuous negative sentences with examples, present continuous sentences with examples, present perfect vs past perfect exercises with answers, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Reported Speech – Rules, Examples & Worksheet
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.
What Does Reported Speech Mean?
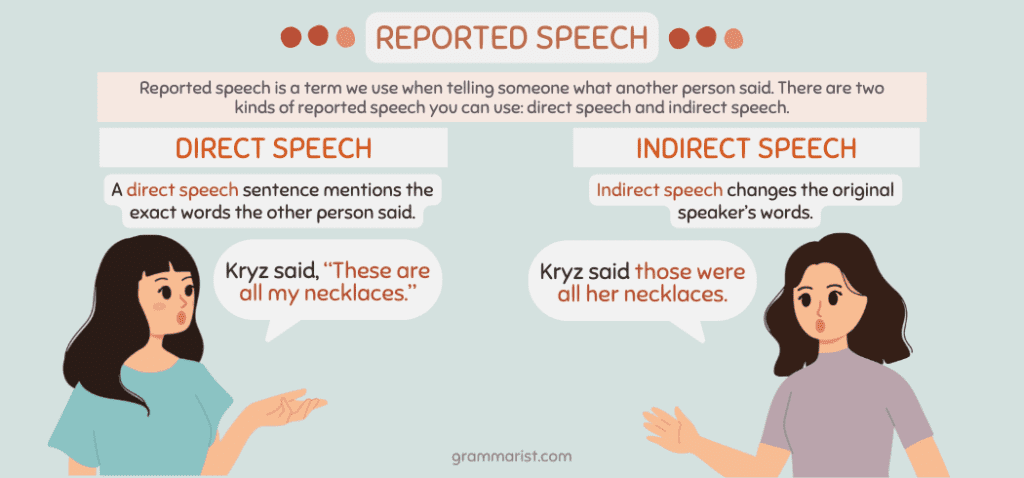
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.
Using Modals
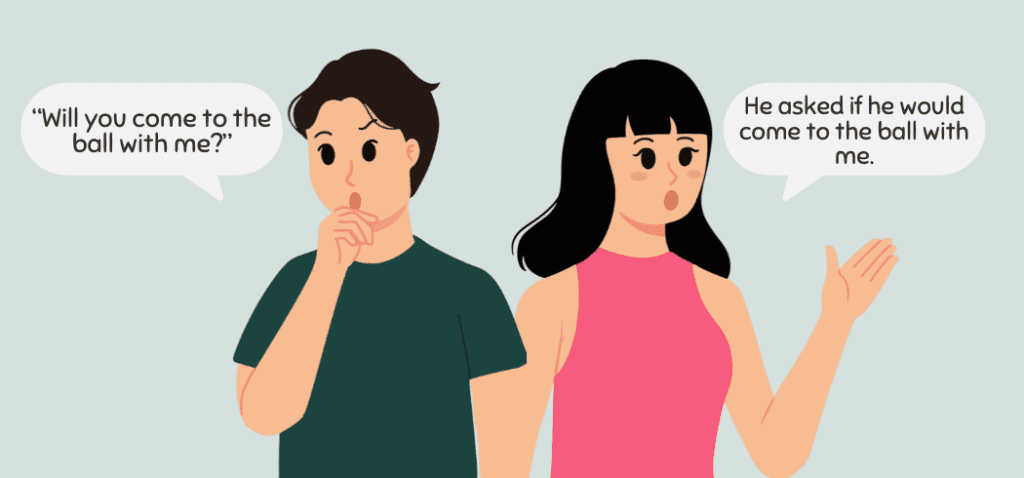

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
Reported Speech
Perfect english grammar.

Reported Statements
Here's how it works:
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: I like ice cream.
- Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'. (As I'm sure you know, often, we can choose if we want to use 'that' or not in English. I've put it in brackets () to show that it's optional. It's exactly the same if you use 'that' or if you don't use 'that'.)
But , if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech:
- Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream.
* doesn't change.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
Click here for a mixed tense exercise about practise reported statements. Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.
Reported Questions
So now you have no problem with making reported speech from positive and negative sentences. But how about questions?
- Direct speech: Where do you live?
- Reported speech: She asked me where I lived.
- Direct speech: Where is Julie?
- Reported speech: She asked me where Julie was.
- Direct speech: Do you like chocolate?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
Click here to practise reported 'wh' questions. Click here to practise reported 'yes / no' questions. Reported Requests
There's more! What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)? For example:
- Direct speech: Close the window, please
- Or: Could you close the window please?
- Or: Would you mind closing the window please?
- Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
- Direct speech: Please don't be late.
- Reported speech: She asked us not to be late.
Reported Orders
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
- Click here for an exercise to practise reported requests and orders.
- Click here for an exercise about using 'say' and 'tell'.
- Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of reported speech noun from the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
- reported speech
- In reported speech, ‘“I'll come later,” he said.’ becomes ‘He said he'd come later.’
- Certain grammatical rules must be followed when describing a conversation in reported speech.
Definitions on the go
Look up any word in the dictionary offline, anytime, anywhere with the Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary app.

👉 Quiz 1 / Quiz 2
Advanced Grammar Course
What is reported speech?
“Reported speech” is when we talk about what somebody else said – for example:
- Direct Speech: “I’ve been to London three times.”
- Reported Speech: She said she’d been to London three times.
There are a lot of tricky little details to remember, but don’t worry, I’ll explain them and we’ll see lots of examples. The lesson will have three parts – we’ll start by looking at statements in reported speech, and then we’ll learn about some exceptions to the rules, and finally we’ll cover reported questions, requests, and commands.

So much of English grammar – like this topic, reported speech – can be confusing, hard to understand, and even harder to use correctly. I can help you learn grammar easily and use it confidently inside my Advanced English Grammar Course.
In this course, I will make even the most difficult parts of English grammar clear to you – and there are lots of opportunities for you to practice!

Backshift of Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called “backshift.”
Here are some examples in different verb tenses:
Reported Speech (Part 1) Quiz
Exceptions to backshift in reported speech.
Now that you know some of the reported speech rules about backshift, let’s learn some exceptions.
There are two situations in which we do NOT need to change the verb tense.
No backshift needed when the situation is still true
For example, if someone says “I have three children” (direct speech) then we would say “He said he has three children” because the situation continues to be true.
If I tell you “I live in the United States” (direct speech) then you could tell someone else “She said she lives in the United States” (that’s reported speech) because it is still true.
When the situation is still true, then we don’t need to backshift the verb.

He said he HAS three children
But when the situation is NOT still true, then we DO need to backshift the verb.
Imagine your friend says, “I have a headache.”
- If you immediately go and talk to another friend, you could say, “She said she has a headache,” because the situation is still true
- If you’re talking about that conversation a month after it happened, then you would say, “She said she had a headache,” because it’s no longer true.
No backshift needed when the situation is still in the future
We also don’t need to backshift to the verb when somebody said something about the future, and the event is still in the future.
Here’s an example:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Friday .”
- “She said she ‘ll call me on Friday”, because Friday is still in the future from now.
- It is also possible to say, “She said she ‘d (she would) call me on Friday.”
- Both of them are correct, so the backshift in this case is optional.
Let’s look at a different situation:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Tuesday .”
- “She said she ‘d call me on Tuesday.” I must backshift because the event is NOT still in the future.

Review: Reported Speech, Backshift, & Exceptions
Quick review:
- Normally in reported speech we backshift the verb, we put it in a verb tense that’s a little bit further in the past.
- when the situation is still true
- when the situation is still in the future
Reported Requests, Orders, and Questions
Those were the rules for reported statements, just regular sentences.
What about reported speech for questions, requests, and orders?
For reported requests, we use “asked (someone) to do something”:
- “Please make a copy of this report.” (direct speech)
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. (reported speech)
For reported orders, we use “told (someone) to do something:”
- “Go to the bank.” (direct speech)
- “He told me to go to the bank.” (reported speech)
The main verb stays in the infinitive with “to”:
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. She asked me make a copy of the report.
- He told me to go to the bank. He told me go to the bank.
For yes/no questions, we use “asked if” and “wanted to know if” in reported speech.
- “Are you coming to the party?” (direct)
- He asked if I was coming to the party. (reported)
- “Did you turn off the TV?” (direct)
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.” (reported)
The main verb changes and back shifts according to the rules and exceptions we learned earlier.
Notice that we don’t use do/does/did in the reported question:
- She wanted to know did I turn off the TV.
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.
For other questions that are not yes/no questions, we use asked/wanted to know (without “if”):
- “When was the company founded?” (direct)
- She asked when the company was founded.” (reported)
- “What kind of car do you drive?” (direct)
- He wanted to know what kind of car I drive. (reported)
Again, notice that we don’t use do/does/did in reported questions:
- “Where does he work?”
- She wanted to know where does he work.
- She wanted to know where he works.
Also, in questions with the verb “to be,” the word order changes in the reported question:
- “Where were you born?” ([to be] + subject)
- He asked where I was born. (subject + [to be])
- He asked where was I born.

Reported Speech (Part 2) Quiz
Learn more about reported speech:
- Reported speech: Perfect English Grammar
- Reported speech: BJYU’s
If you want to take your English grammar to the next level, then my Advanced English Grammar Course is for you! It will help you master the details of the English language, with clear explanations of essential grammar topics, and lots of practice. I hope to see you inside!
I’ve got one last little exercise for you, and that is to write sentences using reported speech. Think about a conversation you’ve had in the past, and write about it – let’s see you put this into practice right away.
Master the details of English grammar:


More Espresso English Lessons:
About the author.
Shayna Oliveira
Shayna Oliveira is the founder of Espresso English, where you can improve your English fast - even if you don’t have much time to study. Millions of students are learning English from her clear, friendly, and practical lessons! Shayna is a CELTA-certified teacher with 10+ years of experience helping English learners become more fluent in her English courses.

Reported Speech
Direct speech and reported speech (indirect speech), reported speech table of contents:, overview and definitions, reporting verbs.
- Using the word THAT
Reported speech – changes
Third person singular verbs, place and time expressions, tense backshift, no tense backshift, reporting questions, reporting orders and requests.
Click Here for Step-by-Step Rules, Stories and Exercises to Practice All English Tenses

- She says we should go.
- They told us to bring our stuff.
- He asked them the time.
- I explained the rules to her.
The word THAT
- She says they are full = She says that they are full
- I told them we could help = I told them that we could help
- I suggest we start = I suggest that we start
How to report
So when reporting speech we must apply this rule., a list of common place and time expressions.
Do online exercises and download a free worksheet.
Get the Reported Speech Illustrated Workbook: The easy way to teach and learn direct and reported speech. 148 pages of explanations, rules, exercises, stories, and lots of hands-on practice.
Get this illustrated workbook and you will receive the following items:
- Step-by-Step Workbook (148 pages)
- Full Answer Key (51 pages)
- Class Activities (52 pages)
- Final Test (10 pages)
- Rule Summary (23 pages)
Get Updates, Special Offers, and English Resources
Download your free gift (the first two chapters of english short stories book and workbook ) as soon as you join.

By submitting your email, you consent to receiving updates and newsletters from us and to the sharing of your personal data with third parties for the purposes of sending you communications. We will not spam you. You can unsubscribe at any time. For more information, please see our privacy policy .
Return from Direct Speech and Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) to Easy English Grammar
Really Learn English Home
Top of this page
Please share this page with others:
- Spanish Version
- Textbooks and Workbooks
- Why Learn English
Downloads & Products
- English Short Stories Book and Workbook
- Stories and Exercises to Practice Grammar
- Online English Courses
Videos & Tips
- Learn English Videos
- ESL Lessons
Speaking & Pronunciation
- Learn To Speak English
- English Pronunciation
- English Reading Practice
- English Short Stories
- English Reading Comprehension
- Learn to Write in English
- Writing Tips
- Vocabulary Activities
- Building Vocabulary
- Vocabulary Games
- English Dictionaries
- English Spelling Rules
- Confusing Words
- English Grammar Center
- English Grammar Exercises
- English Tenses
- English Parts of Speech
- Parts of a Sentence
- Gerunds and Infinitives
- English Modal Verbs
Teaching Center
- How to Teach English
- Tips & Resources
Keep in Touch
- Ask Questions
- Learn English Blog
- About This Site
- Affiliate Program
- Useful Links
- Privacy Policy

- English Short Stories Book & Workbook
- ESL/EFL Resources for Teachers
- Free ESL/EFL Downloads
- Spanish Version (Español)
Downloads & Products:
Videos & tips:, speaking & pronunciation:, vocabulary:, teaching center:, keep in touch:.
Online English Courses: Interactive and Fun
Copyright © 2010-2023 Really-Learn-English.com. All rights reserved.


30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Reported Speech: Definition, Rules, Usage with Examples, Tips, Exercises for Students

- Updated on
- Jan 10, 2024

Reported Speech: Reported Speech or also known as indirect speech, is typically used to convey what has been said by someone at a particular point of time. However, owing to the nuances of the systems involved, English grammar may be a complicated language to learn and understand. But once you get hold of the grammar fundamentals , you can be a pro. It’s these fundamentals that will help you create a solid base. The rest of the journey becomes much easier once you get a good grip on the english grammar for competitive exams . So, today, we’re going to talk about one of those basics that is an important part of English grammar, i.e., Reported Speech with multiple definition, usage with examples and numerous practise exercicses.
This Blog Includes:
What is reported speech, definition of reported speech, reported speech rules, rules for modal verbs, rules for pronouns, rules for change in tenses, rules for changing statements into reported speech, rules for changing interrogative sentences into reported speech, rules for changing commands and requests into indirect speech, tips to practise reported speech, fun exercises for reported speech with answers.
When we use the exact words spoken by someone, it is known as Direct Speech or Reported Speech. Reporting speech is a way to effectivley communication something that has been spoken, usually in the past, by the speaker. It is also possible to describe it from the speaker’s perspective from the third person. Since you are only communicating the message and are not repeating the speaker’s exact words, you do not need to use quotation marks while using this type of speaking.
For example: Rita said to Seema, “ I am going to bake a cake ”
Here we are using the exact words spoken by Rita, however, reported or Indirect speech is used when we are reporting something said by someone else but we do not use the exact words. So, we use this form of speech to talk about the past. For example:
Rita told Seema that she was going to bake a cake
In this case, we haven’t used the exact words of Rita but conveyed her message.
Difference Between Reporting Clause and Reported Speech
The words that come before the inverted commas are known as the reporting clause, in the example given above, the reporting clause will be – Rita said to Seema, where ‘said’ is the verb and is known as the reporting clause/verb . The words written within the inverted commas are known as the Reported speech, in the above example, the reported speech is “I am going to bake a cake” .
Also Read: 55+ Phrases with Meaning to Boost Your Vocabulary
Here are some common definitions of reported speech for your reference:
➡️ An Oxford Learner’s Dictionary definition of reported speech is “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.”
➡️ Reporter speech is described as “speech which tells you what someone said but does not use the person’s actual words” by the Collins Dictionary.
➡️ “The act of reporting something that was said, but not using the same words,” according to the Cambridge Dictionary.
➡️ Reported speech is defined as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said” by the Macmillan Dictionary.
Also Read: Adjective: Definition, Usage, Example, Forms, Types
Now let us take a look at the rules for changing direct speech to indirect or reported speech –
➡️ First and foremost, we do not use inverted commas in reported speech which must be clear from the example given above.
➡️ We use conjunctions like ‘if’, and ‘whether’ after the reporting verb in reported speech
➡️ The reporting verb’s tense is never altered.
➡️ The verb of reporting varies according to sense: it can be told, inquired, asked, etc.
For example: Direct : Mohan said to Sohan, “I am going to school” Reported : Mohan told Sohan that he is going to school
Also Read: Useful Idioms for IELTS Exams That Will Boost Your Score
Modal words are used to show a sense of possibility, intent, necessity or ability. Some common examples of verbs can include should, can and must. These words are used to express hypothetical conditions. Check the table of contents below for rules with examples of modal verbs.
Also Read: Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises With Answers for Class 12
Listed below are some common rules followed in pronouns using reported speech:
✏️ We change the first-person pronouns (I, my, us, our, me, we) as per the subject of the reporting verb in the reported speech. ✏️ We change the second-person pronouns (you, your, yourself) as per the object of the reporting verb in the reported speech. ✏️ There is no change in the third-person pronouns.
For example:
Direct : Rita said, “I like the book.” Reported : Rita said that she likes the book.
Direct : Arun said to me, “Do you like to eat cakes?” Reported : Arun asked me if I liked eating cakes.
Direct : Ravi said, “I enjoy fishing.” Reported : Ravi said that he enjoys fishing.
Also Read: Reported Speech Interrogative: Rules, Examples & Exercise
Here are some common ruled used for change in tenses:
✏️ The tense of the reported speech is not changed if the reporting verb is in the present or the future tense. ✏️ If a historical fact, a universal reality or a habitual fact is conveyed in a direct speech. The indirect speech tense will not change. ✏️ If the reporting verb is in the past tense, then it will change the tense of the reported speech as follows:
Direct : Reema says, “I am going out.” Reported : Reema says that she is going out.
Direct : Ramesh said, “Honesty is the best policy.” Reported : Ramesh said that honesty is the best policy.
Direct : Vishnu said that, “India gained independence in 1947.” Reported : Vishnu said that India gained independence in 1947.
Direct : Akshat will say, “I want a slice of cake.” Reported : Akshat will say that he wants a slice of cake.
Direct : Reena said, “I am writing a novel.” Reported : Reena said that she was writing a novel.
Direct : Ayushi said, “I was working on my project.” Reported : Ayushi said that she had been working on her project.
Also Read: Exploring the Types of Reported Speech: A Complete Guide
Here are some common rules for changing statements into reported speech:
✏️ The “said to” reporting verb is changed to “told,” “replied,” “remarked,” ✏️ We do not change the object i.e., the reporting verb is not followed by an object. ✏️ We drop the inverted commas and use a conjunction to join the reporting clause and speech/ ✏️ The laws are followed for the changing of pronouns, tenses, etc.
Direct: Ramu said, “I saw a lion in the forest.” Indirect: Ramu said that he had seen a lion in the forest.
Direct : Satish said to me, “I am very happy here.” Indirect : Satish told me that he was very happy there.
Direct : He said, “I can do this work.” Indirect: He said that he could do that work.
50 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech Interrogative Sentences
Here are some common rules followed for changing interrogative sentences into reported speech:
✏️ The reporting verb “say” is transformed into “ask, inquire,” ✏️ By inserting the subject before the verb, the interrogative clause is converted into a declaration and the full stop is inserted at the end of the sentence. ✏️ The wh-word is repeated in the sentence if the interrogative sentence has a wh-word (who, where, where, how, why, etc). This works as a conjunction. ✏️ If the asking phrase is a yes-no answer style phrase (with auxiliary verbs are, were, were, do, did, have, shall, etc.), then if or whether is used as a conjunction. ✏️ In the reported speech, the auxiliaries do, did, does drop in a positive question. ✏️ The conjunction after the reporting clause is not used.
Direct: I said to him, “Where are you going?” Indirect: Tasked him where he was going.
Direct: He said to me, “Will you go there?” Indirect: He asked me if I would go there.
Direct: My friend said to Deepak, “Have you ever been to Agra?” Indirect: My friend asked Deepak if he had ever been to Agra.
How to Change Sentences into Indirect Speech
The reporting verb is changed into command, order, say, enable, submit, etc. in imperative sentences that have commands.
✏️ By positioning it before the verb, the imperative mood is converted into the infinitive mood. The auxiliary ‘do’ is dropped in the case of negative sentences, and ‘to’ is substituted after ‘not
Direct: She said to me, “Open the window.” Indirect: She ordered me to open the window.
Direct: The captain said to the soldiers, “Attack the enemy.” Indirect: The captain commanded the soldiers to attack the enemy.
Direct: I said to him, “Leave this place at once.” Indirect: I told him to leave that place at once.
Also Read: Direct And Indirect Speech Questions
Indirect speech, sometimes referred to as reported speech, is used to communicate ideas without directly quoting another person. The following advice will help you become proficient in reported speech:
👉 Understand the Basics : Ensure you have a solid understanding of direct speech (quoting exact words) before moving on to reported speech.
👉 Identify Reporting Verbs : Recognize common reporting verbs such as “say,” “tell,” “ask,” “inform,” etc. These verbs are often used to introduce reported speech.
👉 Practice with Various Tenses : Work on reported speech with different tenses (present, past, future) to become comfortable with each.
👉 Use Reporting Words Appropriately : Experiment with different reporting words to convey the speaker’s attitude or emotion accurately. For example, “complain,” “admit,” “suggest.”
👉 Write Dialogues : Create dialogues and convert them into reported speech. This will help you practice both creating and transforming speech.
👉 Use Authentic Materials : Practice reported speech by reading books, articles, or watching videos. Try to convert the direct speech in these materials into reported speech.
Here are a few exercises for reported speech along with answers:
Change the following sentences from direct speech to reported speech.
- Answer: She said that she loved watching movies.
- Answer: He told me not to forget to buy some milk on my way home.
- Answer: Peter said that he would visit his grandparents the following weekend.
- Answer: She announced that she had finished her homework.
- Answer: They exclaimed that they were going to the beach the next day.
Reported Speech Exercises For Class 9
Combine the following sentences into reported speech.
- Answer: Mary said that she was going to the store because she needed some groceries.
- Answer: He remarked that it was raining outside.
- Answer: She explained that she couldn’t attend the meeting because she had a doctor’s appointment.
- Answer: They assured us that they would finish the project by Friday.
- Answer: He admitted that he had never been to Paris.
Transform the sentences into reported speech.
- Answer: She asked why I was late.
- Answer: He requested me to help him with that heavy box.
- Answer: She inquired if I could pass her the salt.
- Answer: The guide told the visitors not to touch the paintings.
- Answer: He said that he must finish that report that day.
Direct And Indirect Speech Questions: Comprehensive Guide with Examples
Reporting speech is the way we present our own or other people’s words. Direct speech and indirect speech are the two primary categories of reported speech. Direct communication restates the speaker’s precise words or their words as we recall them: “I didn’t realize it was midnight,” Barbara remarked.
The speech that is being reported may be declarative, interrogative, exclamatory, or imperative.
Quote marks are not used when putting the speaker’s words or ideas into a sentence in reported speech. Typically, noun clauses are employed. When reading a reported speech, the reader should not assume that the words are exactly what the speaker said; frequently, they are paraphrased.
The reported speech can be Assertive/Declarative, Imperative, Interrogative, and Exclamatory.
We hope that this blog helped you learn about the basics of Reported Speech. Planning for English proficiency exams like IELTS or TOEFL ? Our Leverage Edu experts are here to guide you through your exam preparation with the best guidance, study materials and online classes! Sign up for a free demo with us now!
Vaishnavi has 2+ years of experience in SEO and Content Marketing. She is highly proficient in English, possessing exceptional language skills and a deep understanding of English grammar and communication. Currently working on Ed Tech, Finance, Lifestyle, and other niches. All her works are infused with love for writing!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
i visited this website during my exams so it was really helpful.. my dounts are cleared… Thanks alot to leverageedu.. i will also suggest this website to my frnds..
Thank you Hansini! Your comment just made our day!
I love it, it like the best to me

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Indirect Speech Definition and Examples
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Indirect speech is a report on what someone else said or wrote without using that person's exact words (which is called direct speech). It's also called indirect discourse or reported speech .
Direct vs. Indirect Speech
In direct speech , a person's exact words are placed in quotation marks and set off with a comma and a reporting clause or signal phrase , such as "said" or "asked." In fiction writing, using direct speech can display the emotion of an important scene in vivid detail through the words themselves as well as the description of how something was said. In nonfiction writing or journalism, direct speech can emphasize a particular point, by using a source's exact words.
Indirect speech is paraphrasing what someone said or wrote. In writing, it functions to move a piece along by boiling down points that an interview source made. Unlike direct speech, indirect speech is not usually placed inside quote marks. However, both are attributed to the speaker because they come directly from a source.
How to Convert
In the first example below, the verb in the present tense in the line of direct speech ( is) may change to the past tense ( was ) in indirect speech, though it doesn't necessarily have to with a present-tense verb. If it makes sense in context to keep it present tense, that's fine.
- Direct speech: "Where is your textbook? " the teacher asked me.
- Indirect speech: The teacher asked me where my textbook was.
- Indirect speech: The teacher asked me where my textbook is.
Keeping the present tense in reported speech can give the impression of immediacy, that it's being reported soon after the direct quote,such as:
- Direct speech: Bill said, "I can't come in today, because I'm sick."
- Indirect speech: Bill said (that) he can't come in today because he's sick.
Future Tense
An action in the future (present continuous tense or future) doesn't have to change verb tense, either, as these examples demonstrate.
- Direct speech: Jerry said, "I'm going to buy a new car."
- Indirect speech: Jerry said (that) he's going to buy a new car.
- Direct speech: Jerry said, "I will buy a new car."
- Indirect speech: Jerry said (that) he will buy a new car.
Indirectly reporting an action in the future can change verb tenses when needed. In this next example, changing the am going to was going implies that she has already left for the mall. However, keeping the tense progressive or continuous implies that the action continues, that she's still at the mall and not back yet.
- Direct speech: She said, "I'm going to the mall."
- Indirect speech: She said (that) she was going to the mall.
- Indirect speech: She said (that) she is going to the mall.
Other Changes
With a past-tense verb in the direct quote, the verb changes to past perfect.
- Direct speech: She said, "I went to the mall."
- Indirect speech: She said (that) she had gone to the mall.
Note the change in first person (I) and second person (your) pronouns and word order in the indirect versions. The person has to change because the one reporting the action is not the one actually doing it. Third person (he or she) in direct speech remains in the third person.
Free Indirect Speech
In free indirect speech, which is commonly used in fiction, the reporting clause (or signal phrase) is omitted. Using the technique is a way to follow a character's point of view—in third-person limited omniscient—and show her thoughts intermingled with narration.
Typically in fiction italics show a character's exact thoughts, and quote marks show dialogue. Free indirect speech makes do without the italics and simply combines the internal thoughts of the character with the narration of the story. Writers who have used this technique include James Joyce, Jane Austen, Virginia Woolf, Henry James, Zora Neale Hurston, and D.H. Lawrence.
- Question Mark Definition and Examples
- Figure of Speech: Definition and Examples
- Indirect Speech in the English Language
- Direct Speech Definition and Examples
- French Grammar: Direct and Indirect Speech
- How to Teach Reported Speech
- Definition and Examples of Direct Quotations
- How to Use Indirect Quotations in Writing for Complete Clarity
- What Is Attribution in Writing?
- Backshift (Sequence-of-Tense Rule in Grammar)
- Indirect Question: Definition and Examples
- Reported Speech
- Using Reported Speech: ESL Lesson Plan
- Constructed Dialogue in Storytelling and Conversation
- The Subjunctive Present in German
- What Are Reporting Verbs in English Grammar?
Definition of 'reported speech'
- reported speech
reported speech in British English
Examples of 'reported speech' in a sentence reported speech, trends of reported speech.
View usage over: Since Exist Last 10 years Last 50 years Last 100 years Last 300 years
Browse alphabetically reported speech
- reported question
- reported recently
- reported sighting
- reporter activity
- All ENGLISH words that begin with 'R'
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

Wordle Helper

Scrabble Tools

- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
Advertisement
reported speech
- another term for indirect speech
Discover More
Example sentences.
As for lowlights, an under-reported speech by Judge Roy Moore took the Wingnut prize.
His longest reported speech will be found in the Parliamentary History, vol.
Indirect discourse means reported speech,—the thoughts of a writer or speaker put in the words of the one reporting them.
She was quoting from his last reported speech, and her spirits rose as she felt how glad she was to have been ready.
A fully reported speech was therein described as perhaps the greatest oratorical masterpiece ever delivered outside Hyde Park.
Lincoln's remarks on the resolution form his first reported speech.
Advertisement
Trump Posts, Then Takes Down, Video Online With Headlines About a ‘Unified Reich’
The 30-second video shared from Donald Trump’s Truth Social account, which included references to “the creation of a unified Reich” was denounced by President Biden as using “Hitler’s language.”
- Share full article

By Chris Cameron
- Published May 20, 2024 Updated May 22, 2024
Former President Donald J. Trump posted a video on Monday afternoon that features images of hypothetical newspaper articles celebrating a 2024 victory for him and referring to “the creation of a unified Reich” under the headline “What’s next for America?”
The 30-second video, which Mr. Trump posted on his social media site, Truth Social, features several articles styled like newspapers from the early 1900s — and apparently recycling text from reports on World War I, including references to “German industrial strength” and “peace through strength.” One article in the video asserts that Mr. Trump would deport 15 million migrants in a second term, while text onscreen lists the start and end days of World War I.
Another headline in the video suggests that Mr. Trump in a second term would reject “globalists,” using a term that has been widely adopted on the far right and that scholars say can be used as a signal of antisemitism .
The Trump campaign said in a statement that the video had been posted by a staff member while Mr. Trump was in his criminal trial in Manhattan . The video was still up on his account early Tuesday, and his campaign did not respond to a question late Monday about why it had not been taken down. It was then deleted sometime Tuesday morning.
“This was not a campaign video, it was created by a random account online and reposted by a staffer who clearly did not see the word, while the President was in court,” Karoline Leavitt, a campaign spokeswoman, said in a statement. “The real extremist is Joe Biden.”
President Biden’s campaign denounced the video soon after it was first reported by The Associated Press late Monday. Mr. Biden then personally addressed the matter in his own video response on Tuesday, which was posted on social media.
“A unified Reich? That’s Hitler’s language, that’s not America’s,” Mr. Biden said, who also expressed disbelief that the video was posted on Mr. Trump’s “official account.”
The clip was originally posted early Monday morning by a member of a group of video producers who call themselves the Dilley Meme Team , after its founder, Brenden Dilley. The group has close ties to Mr. Trump, who frequently reposts their content and has praised their efforts on numerous occasions.
It is not the first time that a video created by the meme team and used by Mr. Trump has stirred up controversy. In the lead-up to the Iowa caucuses in January, Mr. Trump posted a video called “God Made Trump” and then played it at several campaign rallies. Some religious leaders found the video, which depicted the candidate as a messianic figure , to be offensive.
Mr. Trump has repeatedly denounced Jews who vote for Democrats , accusing them of hating their religion and Israel . In one video this month, he said that “if Jewish people are going to vote for Joe Biden, they have to have their head examined.”
Mr. Trump, whose advisers have been crafting plans for a second term that would be more radical than his first , has also drawn criticism during this campaign for echoing the language of past authoritarian leaders , dehumanizing his political opponents as “vermin” and promising that he would not be a dictator “ except for Day 1 .”
In November 2022, Mr. Trump had dinner with Nick Fuentes , an outspoken antisemite who is one of the country’s most prominent white supremacists. He has also tried to downplay the violent white supremacist rally in Charlottesville, Va., in 2017, describing the episode as “a big hoax.” One woman was killed and nearly 40 people were injured when an avowed neo-Nazi plowed his car into a crowd .
Mr. Biden’s campaign also accused Mr. Trump of echoing Nazi Germany by posting the clip, saying in a statement on social media that the video was “foreshadowing a second Trump term.”
On his podcast on Tuesday, Mr. Dilley, a former congressional candidate and life coach, laughed off the matter, saying Democrats were “trying to stir up controversy.” He added that “there is nothing scary or racist about what is there. You can imagine that until you’re blue in the face.”
The term “Reich” is often associated with Germany’s Nazi government under Adolf Hitler, who established a “Third Reich” that succeeded its first two counterparts, the medieval Holy Roman Empire and the German Empire of 1871-1918 , which lost World War I to the Allied powers .
The sentence referring to “the creation of a unified Reich” is used three times in the video. It reads, in full, “German industrial strength significantly increased after 1871, driven by the creation of a unified Reich.” In the beginning of the video, as an announcer asks, “What’s next for America,” the text is partly visible, including the words “the creation of a unified Reich.”
The German Empire that fought in World War I was founded when many different German-speaking states and regions were unified — some by force — into a single, powerful nation in 1871. That empire was dismantled at the end of World War I, and Hitler stoked resentment against the loss of former German territories, and against the Jewish people, as he rose to power in the lead-up to World War II.
The anonymous person who made the clip, who uses the handle @ramble_rants, has since posted multiple times that the background imagery came from a template they did not create and was “not a secret hidden message.” Other members of the meme team have noted the template came from a company, Envato, that offers dozens of downloadable templates with images of newspapers that can be used as video backgrounds.
The template in the video made by the meme team appears to be one that comes with headlines such as “Man Arrested,” “World War II Begins” and “Cold War Over?” Those headlines, accompanying photos and most of the background — including the “unified Reich” language — can be changed by the person who downloads the template.
Maggie Astor and Ken Bensinger contributed reporting.
An earlier version of this article incorrectly described which parts of Envato’s templates are customizable. Users can alter the background text, where the “unified Reich” language appears, not just the headlines and photos.
How we handle corrections
Chris Cameron covers politics for The Times, focusing on breaking news and the 2024 campaign. More about Chris Cameron
Our Coverage of the 2024 Election
Presidential Race: News and Analysis
President Biden’s campaign released a new advertisement aimed at Black voters . It comes as Donald Trump railed against Biden and the migrant crisis at a rally in the Bronx , the latest in a series of stops campaigning in New York City in a push to win his home state.
Trump has baselessly and publicly cast doubt about the fairness of the 2024 election about once a day, on average, a significant escalation since he announced his candidacy for president.
A state dinner held in honor of Kenya, with Barack Obama as a surprise guest , was more about keeping Democratic allies close as campaign season intensifies. Here is the full guest list .
Trump praised Nikki Haley , once his bitter rival for the Republican nomination, a day after she said that she would vote for him , opening the door to bringing Haley into his circle.
Special Legislative Session: Gov. Mike DeWine of Ohio has called a special session to resolve an issue that would prevent Biden from being placed on the November ballot there.
Protest Zone Clash: The Republican National Committee, alarmed by what it sees as a significantly worsening security threat, asked that the director of the Secret Service intervene and move a designated protest zone farther away at an upcoming convention.
A.I.’s Role: The era of A.I. has officially arrived on the campaign trail. But so far, the political uses of the much-anticipated, and feared, technology are more theoretical than transformational .
Trump shares video suggesting his victory will bring 'unified Reich'
Former President Donald Trump 's Truth Social account shared a video Monday that referred to a "unified Reich" as being among possible developments if he were to win re-election in November , drawing criticism from President Joe Biden and his campaign.
Trump's account posted a 30-second video to his Truth Social platform Monday afternoon that asked "what happens after Donald Trump wins?" and "what's next for America?" The video was also posted to his Instagram account.
The background is made up of hypothetical newspaper front pages with headlines including "BORDER IS CLOSED — 15 MILLION ILLEGAL ALIENS DEPORTED" and "ECONOMY BOOMS." Twice in the clip, slightly blurred text appears beneath the headlines that reads: "Industrial strength significantly increased ... driven by the creation of a unified Reich."
The post was deleted from Truth Social on Tuesday morning. It was also removed from Trump's Instagram account.
"Reich," meaning "realm," "kingdom" or "empire," is often considered to be a reference to Hitler's Third Reich regime, which emerged in 1930s Nazi Germany — and its inclusion in the video was condemned by Biden.
"Is this on his official account? Wow!" Biden said Tuesday in a video of his own . "A 'unified Reich?' That's Hitler's language, that's not America's. He cares about holding on to power. I care about you."
Biden made similar remarks Tuesday at a campaign event in Boston.
James Singer, a spokesman for Biden’s re-election campaign, said in a statement that Trump’s post “is part of a pattern of his praise for dictators and echoing antisemitic tropes. He’s a threat to our democracy and Americans must reject him and stand up for our democracy this November.”
Trump’s campaign dismissed the allegation and said Trump — who is on trial in New York — was not aware the word appeared in the video.
“This was not a campaign video, it was created by a random account online and reposted by a staffer who clearly did not see the word, while the President was in court," Karoline Leavitt, the Trump campaign's spokeswoman, said in a statement.
"The real extremist is Joe Biden who has turned his back on Israel and the Jewish people by bowing down to radical anti-semites and terrorist sympathizers in his party like Ilhan Omar and Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez," she added.
At a separate campaign event Tuesday, Biden dismissed the Trump campaign's explanation.
"We got some lame excuse that a staffer did it. And we already know Trump personally controls his social media account, because he brags so much about control," Biden said.
While Hitler did discuss creating an enlarged German empire in his autobiographical manifesto, "Mein Kampf," the text from the video shared on Truth Social appears to have been taken from the Wikipedia page for World War I .
The site reads: “German industrial strength and production had significantly increased after 1871, driven by the creation of a unified Reich.”
The unification of Germany in 1871 brought together an assortment of German-speaking kingdoms and duchies that had been left independent the Holy Roman Empire collapsed in 1806.
Another sentence in the video reads: "First World War (often abbreviated as WW1 or WWI) Causes of World War I."
Trump has used 20th century German historical comparisons to attack his opponents: He compared the Biden administration this month to the Gestapo, Nazi Germany's secret police force.
Late last year, he said immigrants were " poisoning the blood " of America, echoing parts of "Mein Kampf," but he said he was unaware that Hitler had used similar language and denied the comments were racist.
Patrick Smith is a London-based editor and reporter for NBC News Digital.

Will the Antisemitism Awareness Act repress free speech in the US?
We discuss how broadening the definition of anti-Semitism could impact activists and Jewish communities.
While Israel’s war on Gaza continues, the United States Senate is expected to vote on the Antisemitism Awareness Act after it passed the House of Representatives this month with a large majority.
Rights groups warn that the bill’s use of the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance’s definition will conflate criticism of Israel with anti-Semitism, which could stifle protests against Israel’s operations in the Palestinian territory.
So what could the legislation mean for the movement against Israel’s war on Gaza and to Jewish communities grappling with fear for their safety?
This week on UpFront , Marc Lamont Hill talks to contributing columnist at The Forward, Rabbi Jay Michaelson, and president of the Foundation for Middle East Peace, Lara Friedman, about efforts to expand anti-Semitism’s definition and the impact they could have.
trending now in US News

Maniac sets straphanger on fire inside NYC subway before being...

Haitian gangs shot, burned bodies of Missouri pol's missionary...

Napoleon's one-and-a-half inch long penis last known to be in the...

Off-duty NYPD officer, 25, killed in upstate NY crash

‘De-whiting NY’: North Africans, Middle Easterners would lose...

Mount Everest's filthy base camp conditions, thick traffic jams...

Six people contract 'brain worms' from eating undercooked bear...

Biden plans to address Trump ‘hush money’ verdict from the...
Nih official finally admits taxpayers funded gain-of-function research in wuhan — after years of denials.
- View Author Archive
- Get author RSS feed
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
It’s about time!
At long last, National Institutes of Health (NIH) principal deputy director Lawrence Tabak admitted to Congress Thursday that US taxpayers funded gain-of-function research at the Wuhan Institute of Virology in China in the months and years before the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Dr. Tabak,” asked Rep. Debbie Lesko (R-Ariz.) of the Select Subcommittee on the Coronavirus Pandemic, “did NIH fund gain-of-function research at the Wuhan Institute of Virology through [Manhattan-based nonprofit] EcoHealth [Alliance]?”
“It depends on your definition of gain-of-function research,” Tabak answered. “If you’re speaking about the generic term, yes, we did.”

The response comes after more than four years of evasions from federal public health officials — including Tabak himself and former National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) director Dr. Anthony Fauci — about the controversial research practice that modifies viruses to make them more infectious.
Tabak added that “this is research, the generic term [gain-of-function], is research that goes on in many, many labs around the country. It is not regulated. And the reason it’s not regulated is it poses no threat or harm to anybody.”
Dr. Bryce Nickels, a professor of genetics at Rutgers University and co-founder of the pandemic oversight group Biosafety Now, told The Post the exchange “was two people talking past each other.”
“Tabak was engaging in the usual obfuscation and semantic manipulation that is so frustrating and pointless,” Nickels said, adding that the NIH bigwig was resisting accountability for risky research that can create pathogens of pandemic potential.

“Instead of addressing this directly, Tabak launched into a useless response about how ‘gain-of-function’ encompasses many types of experiments,” he added.
In July 2023, the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) barred the Wuhan Institute of Virology from receiving federal grants for the next 10 years.
EcoHealth Alliance , whose mission statement declares it is “working to prevent pandemics,” had all of its grant funding pulled by HHS for the next three years on Tuesday.

EcoHealth Alliance president Dr. Peter Daszak, in a hearing earlier this month before the House Select Subcommittee on the Coronavirus Pandemic, testified that his organization “never has and did not do gain-of-function research, by definition.”
But that claim directly contradicted Daszak’s private correspondence, including a 2016 email in which he celebrated the end of an Obama administration pause on gain-of-function research.
The EcoHealth head was also called out in sworn testimony to the COVID panel by Dr. Ralph Baric, a leading coronavirologist who initiated the research himself and declared it was “absolutely” gain-of-function.

In an October 2021 letter to Congress, Tabak had acknowledged NIH funded a “limited experiment” at the Wuhan Institute of Virology that tested whether “spike proteins from naturally occurring bat coronaviruses circulating in China were capable of binding to the human ACE2 receptor in a mouse model.”
He did not describe it as gain-of-function research — but disclosed that EcoHealth “failed to report” the bat coronaviruses modified with SARS and MERS viruses had been made 10,000 times more infectious, in violation of its grant terms.
The NIH scrubbed its website of a longstanding definition for gain-of-function research the same day that the letter was sent.

Tabak also noted in his October 2021 letter that the “sequences of the viruses are genetically very distant” from COVID-19 — but other grant proposals from EcoHealth have since drawn scrutiny for their genetic similarities.
Fauci has repeatedly denied that the Wuhan lab research involved gain-of-function experiments, clashing with Republicans in high-profile hearings and “ playing semantics ” with the term during a closed-door interview with the House COVID panel earlier this year.
“He needs to define his definition of gain-of-function research, because as I have through this process in the last three years, read many, many published articles about gain-of-function research, or creation of a chimera, this is a new one,” COVID subcommittee Chairman Brad Wenstrup (R-Ohio) said following Fauci’s grilling in January .

The ex-NIAID head and White House medical adviser under President Biden was escorted by Capitol Police and his attorneys to and from the committee room for his two days of interviews — and repeatedly dodged The Post’s questions about gain-of-function research and pandemic lockdown restrictions.
In 2021, Sen. Rand Paul (R-Ky.) held Fauci’s feet to the fire over the evasions in several hearings.
“The NIH has not ever and does not now fund gain-of-function research in the Wuhan Institute of Virology,” Fauci declared that May.

In another House hearing the same month, then-NIH director Dr. Francis Collins testified that researchers at the Wuhan lab “were not approved by NIH for doing gain-of-function research .”
“We are, of course, not aware of other sources of funds or other activities they might have undertaken outside of what our approved grant allowed,” Collins added cautiously at the time.
That ignorance about what experiments came about as a result of the NIH grants was underscored by Daszak during his COVID subcommittee hearing last week.

The EcoHealth leader acknowledged he had not asked longtime collaborator and Wuhan Institute of Virology deputy director Shi Zhengli for any viral sequences since before the pandemic began.
In his own closed-door testimony to the House subcommittee released Thursday, Collins echoed Tabak’s comments but went further by saying there “is a generic description of gain-of-function which is utilized in scientific and public conversation, but is not appropriate to apply that to a circumstance where we’re talking about a potential pathogen.”
“We need to be highly cognizant of the risks of gain-of-function technology now that scientific capabilities exist for creating something in a lab that didn’t exist 100 years ago, or even 50 years ago,” Wenstrup told The Post following Thursday’s hearing.
“Drs. Fauci and Collins, over a decade ago, both conceded that there are risks associated with gain-of-function research.”
EcoHealth received more than half a million dollars for its work with the Wuhan Institute of Virology as part of a grant of more than $4 million to study the emergence of bat coronaviruses between 2014 and 2024.

That grant was revoked in 2020, reinstated in 2023 and finally suspended and proposed for debarment this week.
The House subcommittee is still investigating whether COVID-19 accidentally leaked out of a lab in Wuhan, which has been described as the most likely cause of the pandemic by the FBI, US Energy Department, ex-Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) director Dr. Robert Redfield and former Director of National Intelligence John Ratcliffe .
Nickels also slammed Tabak Thursday for still claiming the evidence points to SARS-CoV-2 originating in a “wild animal market in Wuhan.”
Start and end your day informed with our newsletters
Morning Report and Evening Update: Your source for today's top stories
Thanks for signing up!
Please provide a valid email address.
By clicking above you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Never miss a story.
“No credible scientist still believes this. In fact, the wet market theory has even been refuted by the world’s leading coronavirus expert, Ralph Baric, in his testimony from January,” Nickels said.
The Rutgers prof added that Thursday’s hearing highlighted the lack of oversight for scientific research on pathogens that poses a threat to humans, making it “up to the grantee to oversee themselves,” as Wenstrup put it.
“It’s pure insanity to continue to delegate responsibly for risk/benefit analysis of research that poses an existential threat to humanity to the scientist that will perform the work and their institutions,” Nickels claimed.
“We just had a devastating pandemic likely caused by creation of a [Pathogen with Enhanced Pandemic Potential] in a lab, and yet scientists want the public to trust them that they can police themselves?” he balked. “That’s just total and complete nonsense.”
Fauci is scheduled to answer questions about the gain-of-function research at the Wuhan lab and theories of the origin of the pandemic in a public subcommittee hearing set for June 3.
Share this article:

Advertisement

COMMENTS
Reported speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then. In this example, the pronoun "I" is changed to "she" and the adverb "now" is changed to "then.". 2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here's an example:
Definition of Reported Speech. Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner's Dictionary, is defined as "a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words." The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as "speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person's actual words." ...
We call them reported speech. Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language! Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything.
Watch my reported speech video: Here's how it works: We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence: Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
Reported Speech. Reported speech is the report of one speaker or writer on the words spoken, written, or thought by someone else. Also called reported discourse . Traditionally, two broad categories of reported speech have been recognized: direct speech (in which the original speaker's words are quoted word for word) and indirect speech (in ...
a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words. In reported speech, '"I'll come later," he said.' becomes 'He said he'd come later.' Certain grammatical rules must be followed when describing a conversation in reported speech. Topics Language b1
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called "backshift.". Here are some examples in different verb tenses: "I want to go home.". She said she wanted to go home. "I 'm reading a good book.". She said she was reading a good book. "I ate pasta for dinner last night.".
Reported speech: He asked if he would see me later. In the direct speech example you can see the modal verb 'will' being used to ask a question. Notice how in reported speech the modal verb 'will' and the reporting verb 'ask' are both written in the past tense. So, 'will' becomes 'would' and 'ask' becomes 'asked'.
Overview and definitions. Direct speech means to say exactly what someone else said. It is usually put inside quotation marks (". . ."). I have the package. He says, "I have the package." Reported speech (also called indirect speech ) means to say what someone else said, without actually quoting them.
Reported Speech (also called Indirect Speech) is used to communicate what someone else said, but without using the exact words. A few changes are necessary; often a pronoun has to be changed and the verb is usually moved back a tense, where possible. EG: He said that he was going to come. (The person's exact words were "I'm going to come.")
Here are some common definitions of reported speech for your reference: ️ An Oxford Learner's Dictionary definition of reported speech is "a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.". ️ Reporter speech is described as "speech which tells you what someone said but does not use the person's actual words ...
In free indirect speech, which is commonly used in fiction, the reporting clause (or signal phrase) is omitted. Using the technique is a way to follow a character's point of view—in third-person limited omniscient—and show her thoughts intermingled with narration.
Unlike direct speech, which relies on speech-marks to directly quote what someone has said, reported speech relays the same information without quoting the speaker. Examples. Direct speech 'I'm going to buy some milk.' Reported speech. He told me he was going to buy some milk. Direct speech 'Please help me unpack the shopping' Reported speech
reported speech. Reported speech is speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person's actual words: for example, `They said you didn't like it,' `I asked her what her plans were,' and `Citizens complained about the smoke.'. Collins COBUILD Advanced Learner's Dictionary.
Reported speech definition: another term for indirect speech. See examples of REPORTED SPEECH used in a sentence.
Former President Donald Trump posted a video on Monday showing images of a fake newspaper article that references a "unified Reich" if he's reelected in 2024.
The 30-second video shared from Donald Trump's Truth Social account, which included references to "the creation of a unified Reich" was denounced by President Biden as using "Hitler's ...
Biden made similar remarks Tuesday at a campaign event in Boston. James Singer, a spokesman for Biden's re-election campaign, said in a statement that Trump's post "is part of a pattern of ...
Rights groups warn that the bill's use of the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance's definition will conflate criticism of Israel with anti-Semitism, which could stifle protests ...
Note: content intended to incite violence against a protected category is prohibited under Violent Speech. Slurs and Tropes We prohibit targeting others with repeated slurs, tropes or other content that intends to degrade or reinforce negative or harmful stereotypes about a protected category.
National Institutes of Health (NIH) principal deputy director Lawrence Tabak admitted to Congress Thursday that US taxpayers funded gain-of-function research at the Wuhan Institute of Virology in C…