Brought to you by:


What IKEA Do We Want?
By: Juan Alcacer, Cynthia A. Montgomery, Emilie Billaud, Vincent Dessain
In 2018, Swedish furniture maker IKEA was undergoing a significant transformation. Challenged by the rise of online shopping and changing consumer behavior, and mourning the death of its founder, the…
- Length: 34 page(s)
- Publication Date: Jun 16, 2020
- Discipline: Strategy
- Product #: 720429-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
In 2018, Swedish furniture maker IKEA was undergoing a significant transformation. Challenged by the rise of online shopping and changing consumer behavior, and mourning the death of its founder, the Company's top executives knew they had to step out of their comfort zones and embrace new strategic initiatives to stay relevant. But which initiatives, executed where, when and how, would enable IKEA to achieve its goals in a way that was profitable while creating an IKEA they would want to pass on to the next generation of co-workers and customers?
Learning Objectives
Strategy Identification and Evaluation: Learn to identify the key elements of a firm's strategy, and why it is effective or ineffective. Students are asked to identify IKEA's historic strategy, its key supporting elements, and what made it successful for so long. Added-Value: Learn to de-compose a firm's added-value. Did IKEA increase customers' willingness to pay, reduce the total cost of supply, or both? How did it do it? Environment and Competitive Analysis: Understand the key factors in the external landscape that impact a firm's success and the ways those factors can change over time. What is notable about the macro environment, the furniture industry, and consumer behavior and preferences at the time IKEA's initial strategy was developed? Globally, what has changed? What are the implications for IKEA? Change at an Iconic Firm: Iconic firms are set apart by their distinctiveness. Often, their strategies are developed over years and reflected in a host of unique, interconnected elements, a system of advantage. This case gives students an opportunity to consider when, as a leader, you might want to change a strategy, or key elements of a strategy; the possible risks and benefits of doing so; and how one might want to proceed.
Jun 16, 2020
Discipline:
Geographies:
China, India, Netherlands, Sweden, United States
Industries:
Retail and consumer goods
Harvard Business School
720429-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .

- Business Case Studies
- HBS Global Research Center: Europe Research Center
Strategy & Execution

What IKEA Do We Want?

What IKEA Do We Want? ^ 720429
Want to buy more than 1 copy? Contact: [email protected]
Product Description
Publication Date: June 16, 2020
Industry: Retail and consumer goods
Source: Harvard Business School
In 2018, Swedish furniture maker IKEA was undergoing a significant transformation. Challenged by the rise of online shopping and changing consumer behavior, and mourning the death of its founder, the Company's top executives knew they had to step out of their comfort zones and embrace new strategic initiatives to stay relevant. But which initiatives, executed where, when and how, would enable IKEA to achieve its goals in a way that was profitable while creating an IKEA they would want to pass on to the next generation of co-workers and customers?

This Product Also Appears In
Buy together, related products.

What Do Men Want?

What Do Customers Really Want?

What Do Your Customers Want in 2023?
Copyright permissions.
If you'd like to share this PDF, you can purchase copyright permissions by increasing the quantity.
Order for your team and save!

Digital Innovation and Transformation
Mba student perspectives.
- Assignments
- Assignment: Machine Learning
IKEA’s Leap Forward with Data and AI

IKEA using data and AI to achieve digital innovation and transformation
IKEA’s Digital Transformation
Before becoming the largest furniture retailer in the world, Ingvar Kamprad started IKEA as a mail-order sales business in Sweden 1943. IKEA is now a global conglomerate or a multi-industry and multi-sector business organization. The success of this organization can be attributed to specific business strategies and tactics that revolve around offering well-designed and functional products at affordable prices.
Currently, IKEA is in the middle of a transformation of its business model that made it successful on a global scale. Specifically, for many decades IKEA’s business strategy was primarily based on having giant out-of-town warehouses, where shoppers pick their own furniture and then build it at home. But now it is looking increasingly at city-center stores, online shopping, home delivery and assembly, and more radical ideas such as leasing furniture.
Barbara Martin Coppola, CDO at IKEA Retail mentioned in Harvard Business Review:
Pathways to a Just Digital Future
“Digital transformation is not a goal in and of itself, and it is so much more than technology. We are transforming our business: We are exploring potential new offers to customers, new ways to bring our offers to customers, and new ways to operate our business. And in order to be successful, digital needs to be embedded in every aspect of IKEA. Digital is a way of working, making decisions, and managing the company.”
IKEA has been on the digital transformation journey and the supply chain has been part of it. Its online sales have boosted during lockdowns, and digital transformation has helped make the company sustainable. Artificial Intelligence-powered product recommendations and a more scientific approach to data have seen IKEA lift average order value (AOV) by 2% worldwide.
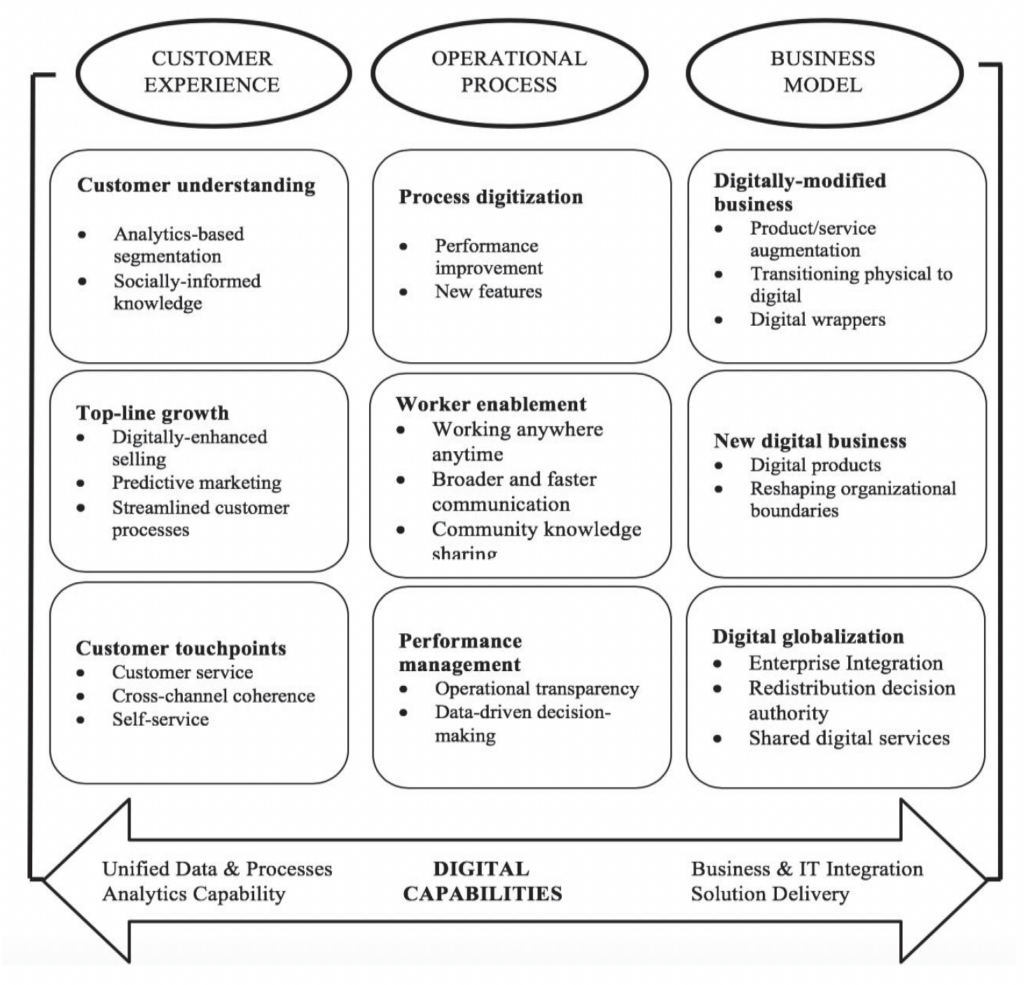
IKEA Utilizing Data + AI
1. Decision Making
The first step IKEA made was to radically improve its ability to get high-quality quantitative information to understand how its ‘ recommendation’ solutions affected personalization . IKEA did this through high volume A/B testing on customer behavior and after initial experimentation, IKEA had a few key learnings: first, the mix of both UX and algorithms are really important for a cohesive customer experience; and second, the quality of personalization cannot be measured in silos. Statistical significance could be attained by testing several groups of recommendations at once.
2. Data for Personalization
Utilization of qualitative and psychographic data to understand its customers better and delve deeper to develop personalized experiences for its customers distinguish IKEA from its competitors. The qualitative data helps IKEA to understand that when a customer buys a piece of furniture, for example a sofa, the customer is bound to make other changes — the domino effect, to ensure the matching of the couch with the room, like lamps, curtains, and pillow covers. Like many modern businesses, IKEA’s digital strategy relies on customer data. However, the company understands the concerns around it and thus launched the Customer Data Promise to help customers understand, provide control, and the ability to make decisions about their data – for psychographic data.

3. Smarter Demand Forecasting
Optimizing stock across various in-store and online channels requires real-time analysis of customers’ buying behavior to minimize the demand and supply gap. To that end, IKEA created an innovative Demand Sensing, an AI-based tool that optimizes stock levels to ensure the consistency of shopping experiences for its customers. To create projections and predict future demand more intelligently and effectively, the tool leverages up to 200 data sources for each product. The system considers various influencing elements, like festival purchasing preferences, the impact of seasonal changes on purchase patterns, and weather forecasts, among others. It can even detect an increase in in-store visits during the month.
4. AR and VR for Visualization
IKEA Kreativ uses virtual and mixed-reality room design technology to let customers use the app to scan and design their space and bring products into their homes. Once the customer is happy with the design, they can add everything to their online cart and check out. Or, they can save everything to a shopping list and go to the store for pickup. IKEA Kreativ brings machine learning and 3D technology into something that is immediately applicable and helpful for customers. Both mobile and web applications connect to a scalable, containerized, cloud-based platform of microservices and AI pipelines, hosted by the Google Cloud Platform.

Results and Lessons
COVID influenced IKEA to commit to its digital transformation journey three years ago with a root and branch review of the company’s digital strategy, encompassing everything from back-office IT systems to how consumers experienced the buying process on their smart devices . IKEA visualizes key consumer data from around the world in real time, sharing insights across departments, markets, and nations. As a result, IKEA can be far more adaptable and proactive in its social efforts.
With more personalized and real-time recommendations with AI, IKEA was able to increase the number of relevant recommendations displayed on a page by +400%. Even though IKEA previously already had well-tuned recommendations of several types, with ‘Recommendations AI’ IKEA measured a +30% improvement in click-through rates as well. Average order value saw a +2% surge with numerous examples of how Recommendations AI could help customers find both attractive and directly complementary products, expanding the customer purchase from a single product to an entire home furnishing solution.
- Milne, R. (2019) “Inter Ikea’s Torbjorn Loof: making the vision clear” Financial Times, Available at: https://www.ft.com/content/6b250c0a-2486-11e9-b329-c7e6ceb5ffdf
- https://hbr.org/2021/06/inside-ikeas-digital-transformation
- https://www.architectmagazine.com/technology/ikea-launches-augmented-reality-application
- https://www.pymnts.com/news/retail/2022/inflation-stokes-recession-fears-while-slamming-retail-earnings/
- https://digiday.com/marketing/ikeas-chief-digital-officer-on-how-its-using-ai-to-personalized-online-shopping-working-with-influencers/
- https://newatlas.com/around-the-home/ikea-kreativ-ai-room-design-app/
- https://biz.crast.net/ikeas-chief-digital-officer-explains-how-hes-using-ai-for-personalized-online-shopping-working-with-influencers/

Student comments on IKEA’s Leap Forward with Data and AI
I love this! Thank you for sharing Jiwon. It might be interesting to know if they have started to integrate online and offline experiences through data transformation. I am imagining a scenario like where a customer registers his/her visit to an offline store and scans the QR code of furniture that he or she is interested in (or even food order, which is impeccable for IKEA’s offline business!).
A very comprehensive blog post about Ikea’s business application of AI! The blog post focused more on the front-end AI applications and touched upon the back-stage digital operations as well. I wonder how interconnected the front and back ends are and what Ikea is thinking about as the next steps in the AI application!
Hi Jiwon, thank you for your Blog! It was intriguing to learn how IKEA is using artificial intelligence and data not only for their decision making and forecasting, but also to improve their customer experience. It also reminded me of the example of Starbucks. They are both collecting a lot of customer data to make seasonal changes and improve the experience compared to their competitors. I’m curious to see how the data collection is adapted to the local context and how IKEA is implementing all the new digital and technological aspects into their traditional business model step by step.
Thank you so much for this blogpost! It is impressive how IKEA was able to increase relevant recommendations by so much and how they make use of AI. I am wondering how far IKEA could take their strategy with using AI. I have some reservations, because I believe that many customers go to IKEA, because they love to walk around the store, only need one thing, and buy some candles and a hotdog on the way out. For IKEA, I think it would be necessary to focus on staying offline as well and focus on the warehouses as that is what at least in my head IKEA still stands for. On the other hand, I can see that using AI can improve the customer experience in other areas, for example if they are looking for anything specific.
Thank you for your blog! it’s really interesting to see that IKEA has introduced AR & VR technology to help customers to increase customer’s convenience. But I’m wondering how will the customer shopping behavior change after using AR & VR tech and its impact will be translated to the IKEA’s topline? Additionally, I’m curious to understand did IKEA make this move because of any existing competitive forces in the market, as I’m sure they aren’t the first mover in the furniture retail business to use the AR & VR tech. And really interested to see how this digital strategy pans out for IKEA.
This is an awesome post! I think like others here, I’m curious about how they can use the AI to actually improve their supply chain. I have often been frustrated after going really far outside the city to one of their stores to realize that they are out of stock of something and don’t know when it will be back in stock. It seems like some of their AI is gimicky but not actually addressing revenue-generating-issues that need to be addressed!
It’s always incredible to me when a store is able to find sources of data in person to be able to improve CX! I still think they’re a little behind the other furniture stores like Williams Sonoma etc. who have done several AR / VR acquisitions to help customers plan their homes and shopping better, but also think that might be because of their customer base / demographic. I also wonder how much they are integrated the in-store experience with more targeted email campaigns (something along the lines of ‘we saw you didn’t check out the bed you scanned twice and spent 10 minutes looking at, what were you looking for / here’s a discount, etc.)
Leave a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

- Order Status
- Testimonials
- What Makes Us Different
IKEA Harvard Case Solution & Analysis
Home >> Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions >> IKEA

INTRODUCTION
The Ingvar Kamprad established IKEA in the year 1943. At its starting stage, the company was selling the catalog of household goods given the discount on it. Later on in the year 1947, Kamprad started to sell the furnishing goods and after six years of selling, furnishing, goods Kamprad opened its first showroom. Afterwards, IKEA started to sell its own designed furniture and charge lower prices from customers.
In 1958, IKEA opened its largest store in Almhult, Sweden and it was the largest store in all of Scandinavia. Furthermore, IKEA opened its flagship store in the year 1965 in Stockholm and that flagship store became the prototype for all the retail outlets of IKEA.
IKEA become the prominent retail store in the world and this position was achieved by the year 2002. The brand of IKEA was one of the renowned brands, it creates value for the IKEA, and it was operating in 22 countries with the 154-retail stores in those countries. In the year 1985, IKEA opened its first retail store in America and it reached to 14 stores by the year 2002. However, IKEA wanted to establish 50 stores in America before 2013.
To identify that how IKEA would create the value for its customers, there is a need to analyze the IKEA’s value creation in terms of SWOT analysis.
SWOT Analysis:
IKEA’s cost effective business model is a key strength as IKEA is producing the furniture at lower cost and selling those furniture at lower prices that attract the price sensitive customers. IKEA’s distribution channel is very strong and it builds strong relationships with its suppliers and its customers.
IKEA’s product designs are modern and it provides the smooth packaging. Its brand image is strong as its stores are unique and provides all kinds of services regarding furniture. It provides a variety of products that made IKEA one stop shopping store.
Weaknesses:
IKEA is a Swedish company that is different from the American companies and customers preferred to purchase from American furniture stores. It has the difficulty to identify the Americans preferences regarding the furniture. IKEA offered product with the limited style and it provides unassembled furniture products, which is not the preferred product of America’s furniture customers.
IKEA stores are operating with the self-service environment that reduces the salespersons existence in the store for guiding the customers. On the other hand, Americans wanted to purchase from the sales person. IKEA did not provide delivery services to its customers. Durability of furniture is lower as IKEA focused on a cost leadership strategy to produce furniture.
Opportunity:
IKEA has the opportunity to target the price sensitive market such as students and middle upper class, this market segment is technology savvy customers, and they wanted to use furniture that could easily be used and move as well. IKEA has the opportunity to expand its operation into emerging markets such as Asia.
IKEA has the threat in terms of competition from the low-end furniture retail stores such as Wall mart, Costco, as these stores are widely existing in the American furniture market. High-end furniture retail stores such as specialty stores are also the threat for the IKEA. IKEA would also expose to the risks that, different companies could adapt its business model. American customers are not willing to change easily and adopt the new culture where furniture is not considered to have the lifetime durability rather it has the lowest price.
PROBLEM STATEMENT:
The problem of the IKEA was to enter into the American furniture market where the market was distributed into different segments and customers were reluctant to buy new furniture, as they preferred the furniture those have more life. Further challenges those are identified are that Customers are reluctant to change, and How to create value for the customers.
Customers of the American furniture market had the mindset that furniture must be purchased one time and it would last for a lifetime. This mindset was not aligned with the IKEA, as their products were durable products. IKEA must change the mindset of American customers regarding the purchase of furniture in order to increase its market share.
On the other hand, American customers of furniture had the preferences that furniture must be delivered for free of cost and this was creating the problem for IKEA as free of cost delivery was not the motto of IKEA. On the other hand, IKEA’s motto was to produce furniture at lower cost and customers should purchase the furniture and take it to home on their own..................
This is just a sample partial case solution. Please place the order on the website to order your own originally done case solution.
Related Case Solutions & Analyses:

Hire us for Originally Written Case Solution/ Analysis
Like us and get updates:.
Harvard Case Solutions
Search Case Solutions
- Accounting Case Solutions
- Auditing Case Studies
- Business Case Studies
- Economics Case Solutions
- Finance Case Studies Analysis
- Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions
- Human Resource Cases
- Ivey Case Solutions
- Management Case Studies
- Marketing HBS Case Solutions
- Operations Management Case Studies
- Supply Chain Management Cases
- Taxation Case Studies
More From Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions
- Korea First Bank (B)
- Sears, Roebuck And Co. Vs. Wal-Mart Stores
- Siemens Electric Motor Works (A): Process-Oriented Costing
- Teach for America 2005
- London Public Library
- Larkin bank
- Industry Note: Furniture
Contact us:

Check Order Status

How Does it Work?
Why TheCaseSolutions.com?

This item appears in the following Collection(s)
- FAS Scholarly Articles [18295]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In 2018, Swedish furniture maker IKEA was undergoing a significant transformation. Challenged by the rise of online shopping and changing consumer behavior, and mourning the death of its founder, the Company's top executives knew they had to step out of their comfort zones and embrace new strategic initiatives to stay relevant. But which initiatives, executed where, when and how, would enable ...
Three years ago, IKEA Retail (Ingka Group) hired Barbara Martin Coppola — a veteran of Google, Samsung, and Texas Instruments — to guide the company through a digital transformation and help ...
Abstract. By 2014, IKEA Group was the largest home furnishing company, with EUR28.5 billion of sales, and planned to reach EUR50 billion by 2020, mainly from emerging markets. At the same time, IKEA Group had adopted in 2012 a new sustainability strategy that focused the company's efforts on its entire value chain from its raw materials ...
In they were so enamored amateurish creations that valued them as highly as made by experts. We also investigated the limits of the IKEA effect, showing that labor leads to higher valuation only when the labor is fruitful: When participants failed to complete an effortful task, the IKEA effect dissipated. research suggests that may be willing ...
Abstract. In 2018, Swedish furniture maker IKEA was undergoing a significant transformation. Challenged by the rise of online shopping and changing consumer behavior, and mourning the death of its founder, the Company's top executives knew they had to step out of their comfort zones and embrace new strategic initiatives to stay relevant.
Publication Date: June 16, 2020. Industry: Retail and consumer goods. Source: Harvard Business School. In 2018, Swedish furniture maker IKEA was undergoing a significant transformation. Challenged by the rise of online shopping and changing consumer behavior, and mourning the death of its founder, the Company's top executives knew they had to ...
Abstract and Figures. IKEA is the world-leading design-sell and ready-to-assemble furniture, applicants and accessories retailer, it was established in Sweden in 1948 and grown since then to have ...
IKEA Utilizing Data + AI. 1. Decision Making. The first step IKEA made was to radically improve its ability to get high-quality quantitative information to understand how its ' recommendation' solutions affected personalization.IKEA did this through high volume A/B testing on customer behavior and after initial experimentation, IKEA had a few key learnings: first, the mix of both UX and ...
Citation. Van den Steen, Eric, and Alon Galor. "IKEA." Harvard Business School Case 716-458, March 2016. (Revised January 2017.)
This is a critical response to the Harvard Business Review case- IKEA's Global Sourcing Challenge: Indian Rugs and Child Labor (A) by Christopher A. Bartlett, Vincent Marie Dessain and Anders Sjoman.
ment/ikea-iway-standard-.pdf__1364450371470.pdf. ... Harvard. Business Review, 9,1 ... a case study of IKEA was conducted. The study has also considered insights from previous researches on IKEA ...
Sustainability issues in the IKEA Group wood supply chain were especially challenging because the company sought to procure wood and wood products close to its consumer markets to minimize. Copying or posting is an infringement of copyright. [email protected] or 617-783- 7860. 515-033 Sustainability at IKEA Group.
This enabled IKEA to access to a potential 1bn customers in India whilst retaining 100% ownership in operations. Legal Regulations: • In September 2000, IKEA launched 'The IKEA way on purchasing home furnishing products', this is a three-page code of conduct for its 2,000 suppliers, this focuses on working conditions
Describes the innovative strategic and organizational changes Kamprad made to achieve success. In particular, focuses on his unique vision and values and the way they have become institutionalized as IKEA's binding corporate culture. The trigger issue revolves around whether this vital "corporate glue" can survive massive expansion into the ...
IKEA Harvard Case Solution & Analysis. INTRODUCTION. The Ingvar Kamprad established IKEA in the year 1943. At its starting stage, the company was selling the catalog of household goods given the discount on it. Later on in the year 1947, Kamprad started to sell the furnishing goods and after six years of selling, furnishing, goods Kamprad ...
IKEA was founded on 1943 by a 17 -year- old Swedish boy named Ingvar Kamprad. Initially he was selling Christm as g reeting cards, seeds, and pens from Kamprad's family. farm. From his childhood ...
DAN ARIELY*. *Michael I. Norton ([email protected]) is an Associate Professor of Business Administration in. the Marketing Unit at the Harvard Business School, Soldiers Field Road, Boston, MA, 02163. Daniel Mochon ([email protected]) is a Post-Doctoral Fellow in Marketing at the Rady.
Valuable understandings are created through these case studies, including the usage of tailored approaches, data-driven decision-making, and public involvement for successful policymaking in varied circumstances. en_US: dc.language.iso: en_US: en_US: dash.license: LAA: dc.title: Evidence Based Public Policy Making: A Comparative Case Study ...