
- MJC Library & Learning Center
- Research Guides

Format Your Paper & Cite Your Sources
- Harvard Style
- Citing Sources
- Avoid Plagiarism
- MLA Style (8th/9th ed.)
- APA Style, 7th Edition
- Chicago Style
What is Harvard Style?
What you need to know, harvard style tutorial.
- Other Styles
- Annotated Bibliographies
- How to Create an Attribution
Harvard Style
The Harvard referencing system is known as the Author-Date style . It emphasizes the name of the creator of a piece of information and the date of publication, with the list of references in alphabetical order at the end of your paper.
Unlike other citation styles, there is no single, definitive version of Harvard Style. Therefore, you may see a variation in features such as punctuation, capitalization, abbreviations, and the use of italics.
Always check with your instructor and follow the rules he or she gives you.
- Harvard Style Guidelines Your class handout
- Harvard Referencing Quick Guide From Staffordshire University
Harvard Style will affect your paper in two places:
- In-text citations in the body of your paper, and
- The reference list at the end of your paper
- All in-text citations should be listed in the reference list at the end of your paper.
- Reference list entries need to contain all the information that someone reading your paper would need in order to find your source.
- Reference lists in Harvard Style are arranged alphabetically by first author.
- Begin your Reference list on a new page after your text and number it consecutively.
Sample References List:

Click on the Links Below to See Additional Examples:
- Sample Paper Paper provided by Kurt Olson
- Harvard Citation Examples Document created by The University of Western Australia
Click on the image below to launch this tutorial that was created by the University of Leeds. The section on Citing in Text is especially useful.

- << Previous: Chicago Style
- Next: Other Styles >>
- Last Updated: May 1, 2024 2:04 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mjc.edu/citeyoursources
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 and CC BY-NC 4.0 Licenses .

Library Services
UCL LIBRARY SERVICES
- Guides and databases
- Library skills
Published report
- A-Z of Harvard references
- Citing authors with Harvard
- Page numbers and punctuation
- References with missing details
- Secondary referencing
- Example reference list
- Journal article
- Magazine article
- Newspaper article
- Online video
- Radio and internet radio
- Television advertisement
- Television programme
- Ancient text
- Bibliography
- Book (printed, one author or editor)
- Book (printed, multiple authors or editors)
- Book (printed, with no author)
- Chapter in a book (print)
- Collected works
- Dictionaries and Encyclopedia entries
- Multivolume work
- Religious text
- Thesis or dissertation
- Translated work
- Census data
- Financial report
- Mathematical equation
- Scientific dataset
- Book illustration, Figure or Diagram
- Inscription on a building
- Installation
- Painting or Drawing
- Interview (on the internet)
- Interview (newspaper)
- Interview (radio or television)
- Interview (as part of research)
- Act of the UK parliament (statute)
- Bill (House of Commons/Lords)
- Birth/Death/Marriage certificate
- British standards
- Command paper
- European Union publication
- Government/Official publication
- House of Commons/Lords paper
- Legislation from UK devolved assemblies
- Statutory instrument
- Military record
- Film/Television script
- Musical score
- Play (live performance)
- Play script
- Song lyrics
- Conference paper
- Conference proceedings
- Discussion paper
- Minutes of meeting
- Personal communication
- PowerPoint presentation
- Student's own work
- Tutor materials for academic course
- Unpublished report
- Working paper
- Referencing glossary
To be made up of:
- Author or organisation.
- Year of publication (in round brackets).
- Title of report (in italics).
- Place of publication: publisher.
If accessed on the internet, add:
- Available at: URL.
- (Accessed: date).
In-text citation:
(BSkyB Ltd, 2012)
Reference list:
BSkyB Ltd (2012). Annual report 2012 . Available at: https://www.annualreports.com/HostedData/AnnualReportArchive/b/LSE_BSY_2012.pdf (Accessed: 9 January 2020).
Quick links
- Harvard references A-Z
Published reports are reports which an individual or organisation have distributed, either electronically or in print, to the wider public. This can include annual reports and research reports.
Unpublished reports , such as internal reports, are referenced differently to published reports.
Reports by government departments should be referenced as Official publications .
- Reference an unpublished report
- Reference an official publication
- << Previous: PowerPoint presentation
- Next: Student's own work >>
- Last Updated: Feb 28, 2024 12:08 PM
- URL: https://library-guides.ucl.ac.uk/harvard

Harvard Citation Guide: Getting Started
- Getting Started
- How do I Cite?
- In-Text Citations
- Reference List
- Additional Resources
Header Image

What is Harvard Style?
Harvard style is a set of rules for research papers and publications. It is one of the most widely used styles in the world.
In Harvard, you must cite sources that you have paraphrased, quoted, or consulted to write your research paper. Cite your sources in two places:
- In the body of your paper (in-text citation).
- In the Reference list at the end of your paper (full bibliographic reference).
Digital Object Identifiers (DOI)
Also known as a permalink, a DOI, or digital object identifier , is an article's permanent online location. DOIs are used for a variety of academic and non-academic sources that are located online.
Include a DOI for all works that have a DOI. If an online work has both a DOI and a URL, include only the DOI; if the source only has a URL, include the URL.
Cite Them Right 11th edition
Many of the disciplines and institutions that favor Harvard style use Cite Them Right 11th edition as their primary manual.
Cite Them Right This is the official website for Cite Them Right.
- Next: How do I Cite? >>
- Last Updated: Jun 24, 2022 12:36 PM
- URL: https://paperpile.libguides.com/harvard
Harvard Citation Style: All Examples
- Introduction
- Books / E-Books
- Company Information
- Conference Proceedings
- Internet / Websites
- Journal Articles
- Lecture Notes
- Multi-Media Formats
- Patents and Standards
- All Examples
- Writing Support
- Citation Support
In-text citations
Two or more works cited at one point in the text
If two or more works by different authors or authoring bodies are cited at one point in the text, use a semi-colon to separate them:
(Larsen 2000; Malinowski 1999)
The authors should be listed in alphabetical order.
Two or three authors or authoring bodies
When citing a work by two or three authors or authoring bodies, cite the names in the order in which they appear on the title page:
(Malinowski, Miller & Gupta 1995)
In-Text & Reference List Examples
- << Previous: Theses
- Next: Writing Support >>

- Last Updated: Feb 6, 2024 10:18 AM
- URL: https://guides.himmelfarb.gwu.edu/harvard_citation

- Himmelfarb Intranet
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
- GW is committed to digital accessibility. If you experience a barrier that affects your ability to access content on this page, let us know via the Accessibility Feedback Form .
- Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library
- 2300 Eye St., NW, Washington, DC 20037
- Phone: (202) 994-2850
- [email protected]
- https://himmelfarb.gwu.edu
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Cite a Report in Harvard Referencing

3-minute read
- 23rd March 2023
When writing an essay, you may find yourself using a report as a source for your research. If you’re using the Harvard referencing style , you’ll need to include an in-text citation and a reference list entry to credit the source properly.
The Harvard style has many variations, so be sure to check your own style guide to verify that you’re doing things correctly. In today’s post, we’ll look at citing a report in the Open University style. Read on to learn more!
Creating an In-Text Citation for a Report
In the Open University style of Harvard referencing, an in-text citation includes the author’s last name and the year of publication in parentheses, like this:
If you provide a direct quotation, you’ll need to include the page numbers as well:
If the source has two authors, include both names, separated by “and.” If the source has three or more authors, though, include the first name only, followed by “ et al. ”
Adding a Reference List Entry for a Report
At the end of your paper, you’ll need to compile a list of the sources you used, including any reports from which you pulled information. Fortunately, the Open University style makes this easy, as the reference list requirements for a report are the same as those for a book, following this format:
Author, X. (year). Title. Place of publication: Publisher.
In practice, then, we would cite the report from our example this way:
Barnes, T. (2014). American Animal Shelters Report. New York: Collins Publishing.
If you found the report online, you can follow the same format you’d use for an eBook:
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Author, X. (year). Title [Online]. Place of publication if available: Publisher if available. Available at: URL (Accessed date).
Our example, then, would look like this:
Barnes, T. (2014). American Animal Shelters Report [Online]. New York: Collins Publishing. Available at: www.AASR.org (Accessed March 1, 2023).
We hope this post has helped you with citing reports in your work. Remember, the Harvard style varies across institutions, so although we’ve used the Open University style today, be sure to check your own style guide to verify that you’ve met the requirements.
And before you submit your paper, make sure someone proofreads it for you! Our editors will ensure flawless grammar, spelling, punctuation, references , and more. Try it out for free today.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you format an in-text citation for a report in harvard.
To create an in-text citation for a report, include the author’s name and the date of publication in parentheses. If the source has two authors, include both names. If the source has three, include the first name only, followed by “et al.”
How do you format a reference list entry for a report in Harvard?
A reference list item for a report in Harvard looks like this: Author, X. (year). Title. Place of publication: Publisher.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Referencing
- Harvard Referencing for Journal Articles | Templates & Examples
Harvard Referencing for Journal Articles | Templates & Examples
Published on 20 May 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 7 November 2022.
In Harvard style, to reference a journal article, you need the author name(s), the year, the article title, the journal name, the volume and issue numbers, and the page range on which the article appears.
If you accessed the article online, add a DOI (digital object identifier) if available.
Scribbr’s free Harvard reference generator can instantly create accurate references for a wide variety of source types:
Harvard Reference Generator
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Online-only journal articles, articles with multiple authors, referencing a whole issue of a journal, referencing a preprint journal article, frequently asked questions about referencing journal articles in harvard style.
To reference an online journal article with no print version, always include the DOI if available. No access date is necessary with a DOI. Note that a page range may not be available for online-only articles; in this case, simply leave it out, as in this example.
Online-only article with no DOI
When you need to reference an online-only article which doesn’t have a DOI, use a URL instead – preferably the stable URL often listed with the article. In this case, you do need to include an access date.
Note that if an online article has no DOI but does have a print equivalent, you don’t need to include a URL. The details of the print journal should be enough for the reader to locate the article.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Journal articles often have multiple authors. In both your in-text citations and reference list, list up to three authors in full. Use the first author’s name followed by ‘ et al. ’ when there are four or more.
When you want to reference an entire issue of a journal instead of an individual article, you list the issue editor(s) in the author position and give the title of the issue (if available) rather than of an individual article.
When you reference an article that’s been accepted for publication but not yet published, the format changes to acknowledge this.
If it’s unknown where or whether the article will be published, omit this information:
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
In Harvard referencing, up to three author names are included in an in-text citation or reference list entry. When there are four or more authors, include only the first, followed by ‘ et al. ’
In Harvard style , when you quote directly from a source that includes page numbers, your in-text citation must include a page number. For example: (Smith, 2014, p. 33).
You can also include page numbers to point the reader towards a passage that you paraphrased . If you refer to the general ideas or findings of the source as a whole, you don’t need to include a page number.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, November 07). Harvard Referencing for Journal Articles | Templates & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/referencing/harvard-journal-article-reference/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, a quick guide to harvard referencing | citation examples, harvard style bibliography | format & examples, harvard in-text citation | a complete guide & examples, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

- How it works

How to Cite a Report in Harvard Style?
Published by Alaxendra Bets at August 30th, 2021 , Revised On August 23, 2023
A report is an official document that summarises some sort of information for a specific audience. It serves a highly specific objective, too. Reports are mostly in written form, although their summaries might be presented orally.
Companies, banks, accountants and industry groups, etc. are mostly the ones who make the most use of reports in their daily work routine. Some reports are meant to present minor project details every now and then.
But reports on a larger scale are to be presented to a certain audience in a company meeting, for example. Such large-scale reports might even go on to become published on a company’s official platform.
Additionally, reports might also be published in higher-order platforms, such as databases. Commonly used reports databases include Business Source Premier, Factiva, DataAnalysis, etc.
In-text Citation and Reference Formats with Examples
Harvard style follows this basic format for referencing and citing a report from a company’s website, a database and even for a company profile (if it’s in the form of a report).
In-text citation: (Author Surname, Year Published)
Reference list entry: Author Surname, Author Initial. (Year Published). Title of the Report in italics. Series Number. [online] City: Publisher, p.# for a single page or pp.# for page range. Available at: http://Website URL [Accessed Date Accessed].
In case the author’s surname is missing, the title of the report is written in place of the author’s name instead (exemplified further below).
For example:
In-text citation: 9 (GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS: SCREENING, DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW UP, 2014)
Reference list entry: GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS: SCREENING, DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW UP. (2014). NHS Diabetes.
Citing a report from a Database
In such a case, the name of the database is considered as the author’s name. The format for citing such a source is:
In-text citation: ( Author Surname Year) OR
(Author Surname Year, Page number)
Reference list entry: Author Surname, Initial(s), Year, Title of the Report in italics, viewed Day Month Year, Name of the Database.
In-text citation: (Datamonitor 2010) OR
(Datamonitor 2010, p. 13)
Reference list entry: Datamonitor 2010, Rio Tinto SWOT analysis , viewed 20 January 2012, Business Source Premier, EBSCOhost.
Citing a report from a Company Profile or Website
In this case, the name of the report’s creator is mentioned. The format for citing such a source in Harvard style is the same as that of a report obtained from a database.
Here is an example of a report cited from an Australian company platform called IBISWorld. Its report that is being cited here, mentions the report analyst (surname Stephen) who created it.
In-text citation: (Stephen 2012) OR
(Stephen 2012, p. 24)
Reference list entry: Stephen, T 2012, IBISWorld Industry Report L7714. Retail Property Operators in Australia , viewed 20 January 2013, IBISWorld.
Citing an annual report
Citing an annual report in print form
The basic format for such a source in Harvard style is:
In-text citation: (Corporate author Year) OR
(Corporate author Year, page)
Reference list entry: Corporate Author, Year, Full title of the annual report in italics, Publisher, Place of Publication.
In-text citation: (Tabcorp 2012) OR
(Tabcorp 2012, p. 2)
Reference list entry: Tabcorp 2012, Annual report 2012 , Tabcorp Holdings Limited, Melbourne.
Citing an online annual report
In case it’s an online annual report, the citation format remains the same, whereas the reference list entry format becomes:
Corporate Author, Year, Full title of the annual report in italics, viewed Day Month Year, <URL>.
In-text citation: (Woolworths Limited 2015) OR
(Woolworths Limited, p. 12)
Reference list entry: Woolworths Limited 2015, Annual report 2015 , viewed 10 December 2015, <http://www.woolworthslimited.com.au/ annualreport/2015/files/Woolworths_AR_2015.pdf>.
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

Frequently Asked Questions
To cite a report in Harvard style:
- Author(s) last name, first initial.
- Year of publication.
- Title of report in italics.
- Report series or number (if applicable).
- URL (if accessed online). Example: Smith, J. (2023). Report Title. Report Series No. Publisher. URL
You May Also Like
This guide discusses how to cite a website in Harvard style. When citing information from the Internet, it is of utmost importance to cite a source carefully, since information on the Internet can vary widely. Your reference should be accurate to lead the reader directly to the accurate source.
In academia, you may need to cite a patent. This article shows you how to do this in Harvard Referencing,
To cite a press release in Harvard Style, follow the format: Title. (Year Published). [online] Available at: http://Website URL [Accessed Date Accessed].
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Cite A Report in Harvard style
Powered by chegg.
- Select style:
- Archive material
- Chapter of an edited book
- Conference proceedings
- Dictionary entry
- Dissertation
- DVD, video, or film
- E-book or PDF
- Edited book
- Encyclopedia article
- Government publication
- Music or recording
- Online image or video
- Presentation
- Press release
- Religious text
Use the following template or our Harvard Referencing Generator to cite a report. For help with other source types, like books, PDFs, or websites, check out our other guides. To have your reference list or bibliography automatically made for you, try our free citation generator .

Reference list
Place this part in your bibliography or reference list at the end of your assignment.
In-text citation
Place this part right after the quote or reference to the source in your assignment.
Popular Harvard Citation Guides
- How to cite a Book in Harvard style
- How to cite a Website in Harvard style
- How to cite a Journal in Harvard style
- How to cite a DVD, video, or film in Harvard style
- How to cite a Online image or video in Harvard style
Other Harvard Citation Guides
- How to cite a Archive material in Harvard style
- How to cite a Artwork in Harvard style
- How to cite a Blog in Harvard style
- How to cite a Broadcast in Harvard style
- How to cite a Chapter of an edited book in Harvard style
- How to cite a Conference proceedings in Harvard style
- How to cite a Court case in Harvard style
- How to cite a Dictionary entry in Harvard style
- How to cite a Dissertation in Harvard style
- How to cite a E-book or PDF in Harvard style
- How to cite a Edited book in Harvard style
- How to cite a Email in Harvard style
- How to cite a Encyclopedia article in Harvard style
- How to cite a Government publication in Harvard style
- How to cite a Interview in Harvard style
- How to cite a Legislation in Harvard style
- How to cite a Magazine in Harvard style
- How to cite a Music or recording in Harvard style
- How to cite a Newspaper in Harvard style
- How to cite a Patent in Harvard style
- How to cite a Podcast in Harvard style
- How to cite a Presentation or lecture in Harvard style
- How to cite a Press release in Harvard style
- How to cite a Religious text in Harvard style
- How to cite a Report in Harvard style
- How to cite a Software in Harvard style
- Formatting Your Dissertation
- Introduction
Harvard Griffin GSAS strives to provide students with timely, accurate, and clear information. If you need help understanding a specific policy, please contact the office that administers that policy.
- Application for Degree
- Credit for Completed Graduate Work
- Ad Hoc Degree Programs
- Acknowledging the Work of Others
- Advanced Planning
- Dissertation Advisory Committee
- Dissertation Submission Checklist
- Publishing Options
- Submitting Your Dissertation
- English Language Proficiency
- PhD Program Requirements
- Secondary Fields
- Year of Graduate Study (G-Year)
- Master's Degrees
- Grade and Examination Requirements
- Conduct and Safety
- Financial Aid
- Non-Resident Students
- Registration
On this page:
Language of the Dissertation
Page and text requirements, body of text, tables, figures, and captions, dissertation acceptance certificate, copyright statement.
- Table of Contents
Front and Back Matter
Supplemental material, dissertations comprising previously published works, top ten formatting errors, further questions.
- Related Contacts and Forms
When preparing the dissertation for submission, students must follow strict formatting requirements. Any deviation from these requirements may lead to rejection of the dissertation and delay in the conferral of the degree.
The language of the dissertation is ordinarily English, although some departments whose subject matter involves foreign languages may accept a dissertation written in a language other than English.
Most dissertations are 100 to 300 pages in length. All dissertations should be divided into appropriate sections, and long dissertations may need chapters, main divisions, and subdivisions.
- 8½ x 11 inches, unless a musical score is included
- At least 1 inch for all margins
- Body of text: double spacing
- Block quotations, footnotes, and bibliographies: single spacing within each entry but double spacing between each entry
- Table of contents, list of tables, list of figures or illustrations, and lengthy tables: single spacing may be used
Fonts and Point Size
Use 10-12 point size. Fonts must be embedded in the PDF file to ensure all characters display correctly.
Recommended Fonts
If you are unsure whether your chosen font will display correctly, use one of the following fonts:
If fonts are not embedded, non-English characters may not appear as intended. Fonts embedded improperly will be published to DASH as-is. It is the student’s responsibility to make sure that fonts are embedded properly prior to submission.
Instructions for Embedding Fonts
To embed your fonts in recent versions of Word, follow these instructions from Microsoft:
- Click the File tab and then click Options .
- In the left column, select the Save tab.
- Clear the Do not embed common system fonts check box.
For reference, below are some instructions from ProQuest UMI for embedding fonts in older file formats:
To embed your fonts in Microsoft Word 2010:
- In the File pull-down menu click on Options .
- Choose Save on the left sidebar.
- Check the box next to Embed fonts in the file.
- Click the OK button.
- Save the document.
Note that when saving as a PDF, make sure to go to “more options” and save as “PDF/A compliant”
To embed your fonts in Microsoft Word 2007:
- Click the circular Office button in the upper left corner of Microsoft Word.
- A new window will display. In the bottom right corner select Word Options .
- Choose Save from the left sidebar.
Using Microsoft Word on a Mac:
Microsoft Word 2008 on a Mac OS X computer will automatically embed your fonts while converting your document to a PDF file.
If you are converting to PDF using Acrobat Professional (instructions courtesy of the Graduate Thesis Office at Iowa State University):
- Open your document in Microsoft Word.
- Click on the Adobe PDF tab at the top. Select "Change Conversion Settings."
- Click on Advanced Settings.
- Click on the Fonts folder on the left side of the new window. In the lower box on the right, delete any fonts that appear in the "Never Embed" box. Then click "OK."
- If prompted to save these new settings, save them as "Embed all fonts."
- Now the Change Conversion Settings window should show "embed all fonts" in the Conversion Settings drop-down list and it should be selected. Click "OK" again.
- Click on the Adobe PDF link at the top again. This time select Convert to Adobe PDF. Depending on the size of your document and the speed of your computer, this process can take 1-15 minutes.
- After your document is converted, select the "File" tab at the top of the page. Then select "Document Properties."
- Click on the "Fonts" tab. Carefully check all of your fonts. They should all show "(Embedded Subset)" after the font name.
- If you see "(Embedded Subset)" after all fonts, you have succeeded.
The font used in the body of the text must also be used in headers, page numbers, and footnotes. Exceptions are made only for tables and figures created with different software and inserted into the document.
Tables and figures must be placed as close as possible to their first mention in the text. They may be placed on a page with no text above or below, or they may be placed directly into the text. If a table or a figure is alone on a page (with no narrative), it should be centered within the margins on the page. Tables may take up more than one page as long as they obey all rules about margins. Tables and figures referred to in the text may not be placed at the end of the chapter or at the end of the dissertation.
- Given the standards of the discipline, dissertations in the Department of History of Art and Architecture and the Department of Architecture, Landscape Architecture, and Urban Planning often place illustrations at the end of the dissertation.
Figure and table numbering must be continuous throughout the dissertation or by chapter (e.g., 1.1, 1.2, 2.1, 2.2, etc.). Two figures or tables cannot be designated with the same number. If you have repeating images that you need to cite more than once, label them with their number and A, B, etc.
Headings should be placed at the top of tables. While no specific rules for the format of table headings and figure captions are required, a consistent format must be used throughout the dissertation (contact your department for style manuals appropriate to the field).
Captions should appear at the bottom of any figures. If the figure takes up the entire page, the caption should be placed alone on the preceding page, centered vertically and horizontally within the margins.
Each page receives a separate page number. When a figure or table title is on a preceding page, the second and subsequent pages of the figure or table should say, for example, “Figure 5 (Continued).” In such an instance, the list of figures or tables will list the page number containing the title. The word “figure” should be written in full (not abbreviated), and the “F” should be capitalized (e.g., Figure 5). In instances where the caption continues on a second page, the “(Continued)” notation should appear on the second and any subsequent page. The figure/table and the caption are viewed as one entity and the numbering should show correlation between all pages. Each page must include a header.
Landscape orientation figures and tables must be positioned correctly and bound at the top so that the top of the figure or table will be at the left margin. Figure and table headings/captions are placed with the same orientation as the figure or table when on the same page. When on a separate page, headings/captions are always placed in portrait orientation, regardless of the orientation of the figure or table. Page numbers are always placed as if the figure were vertical on the page.
If a graphic artist does the figures, Harvard Griffin GSAS will accept lettering done by the artist only within the figure. Figures done with software are acceptable if the figures are clear and legible. Legends and titles done by the same process as the figures will be accepted if they too are clear, legible, and run at least 10 or 12 characters per inch. Otherwise, legends and captions should be printed with the same font used in the text.
Original illustrations, photographs, and fine arts prints may be scanned and included, centered between the margins on a page with no text above or below.
Use of Third-Party Content
In addition to the student's own writing, dissertations often contain third-party content or in-copyright content owned by parties other than you, the student who authored the dissertation. The Office for Scholarly Communication recommends consulting the information below about fair use, which allows individuals to use in-copyright content, on a limited basis and for specific purposes, without seeking permission from copyright holders.
Because your dissertation will be made available for online distribution through DASH , Harvard's open-access repository, it is important that any third-party content in it may be made available in this way.
Fair Use and Copyright
What is fair use?
Fair use is a provision in copyright law that allows the use of a certain amount of copyrighted material without seeking permission. Fair use is format- and media-agnostic. This means fair use may apply to images (including photographs, illustrations, and paintings), quoting at length from literature, videos, and music regardless of the format.
How do I determine whether my use of an image or other third-party content in my dissertation is fair use?
There are four factors you will need to consider when making a fair use claim.
1) For what purpose is your work going to be used?
- Nonprofit, educational, scholarly, or research use favors fair use. Commercial, non-educational uses, often do not favor fair use.
- A transformative use (repurposing or recontextualizing the in-copyright material) favors fair use. Examining, analyzing, and explicating the material in a meaningful way, so as to enhance a reader's understanding, strengthens your fair use argument. In other words, can you make the point in the thesis without using, for instance, an in-copyright image? Is that image necessary to your dissertation? If not, perhaps, for copyright reasons, you should not include the image.
2) What is the nature of the work to be used?
- Published, fact-based content favors fair use and includes scholarly analysis in published academic venues.
- Creative works, including artistic images, are afforded more protection under copyright, and depending on your use in light of the other factors, may be less likely to favor fair use; however, this does not preclude considerations of fair use for creative content altogether.
3) How much of the work is going to be used?
- Small, or less significant, amounts favor fair use. A good rule of thumb is to use only as much of the in-copyright content as necessary to serve your purpose. Can you use a thumbnail rather than a full-resolution image? Can you use a black-and-white photo instead of color? Can you quote select passages instead of including several pages of the content? These simple changes bolster your fair use of the material.
4) What potential effect on the market for that work may your use have?
- If there is a market for licensing this exact use or type of educational material, then this weighs against fair use. If however, there would likely be no effect on the potential commercial market, or if it is not possible to obtain permission to use the work, then this favors fair use.
For further assistance with fair use, consult the Office for Scholarly Communication's guide, Fair Use: Made for the Harvard Community and the Office of the General Counsel's Copyright and Fair Use: A Guide for the Harvard Community .
What are my options if I don’t have a strong fair use claim?
Consider the following options if you find you cannot reasonably make a fair use claim for the content you wish to incorporate:
- Seek permission from the copyright holder.
- Use openly licensed content as an alternative to the original third-party content you intended to use. Openly-licensed content grants permission up-front for reuse of in-copyright content, provided your use meets the terms of the open license.
- Use content in the public domain, as this content is not in-copyright and is therefore free of all copyright restrictions. Whereas third-party content is owned by parties other than you, no one owns content in the public domain; everyone, therefore, has the right to use it.
For use of images in your dissertation, please consult this guide to Finding Public Domain & Creative Commons Media , which is a great resource for finding images without copyright restrictions.
Who can help me with questions about copyright and fair use?
Contact your Copyright First Responder . Please note, Copyright First Responders assist with questions concerning copyright and fair use, but do not assist with the process of obtaining permission from copyright holders.
Pages should be assigned a number except for the Dissertation Acceptance Certificate . Preliminary pages (abstract, table of contents, list of tables, graphs, illustrations, and preface) should use small Roman numerals (i, ii, iii, iv, v, etc.). All pages must contain text or images.
Count the title page as page i and the copyright page as page ii, but do not print page numbers on either page .
For the body of text, use Arabic numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, etc.) starting with page 1 on the first page of text. Page numbers must be centered throughout the manuscript at the top or bottom. Every numbered page must be consecutively ordered, including tables, graphs, illustrations, and bibliography/index (if included); letter suffixes (such as 10a, 10b, etc.) are not allowed. It is customary not to have a page number on the page containing a chapter heading.
- Check pagination carefully. Account for all pages.
A copy of the Dissertation Acceptance Certificate (DAC) should appear as the first page. This page should not be counted or numbered. The DAC will appear in the online version of the published dissertation. The author name and date on the DAC and title page should be the same.
The dissertation begins with the title page; the title should be as concise as possible and should provide an accurate description of the dissertation. The author name and date on the DAC and title page should be the same.
- Do not print a page number on the title page. It is understood to be page i for counting purposes only.
A copyright notice should appear on a separate page immediately following the title page and include the copyright symbol ©, the year of first publication of the work, and the name of the author:
© [ year ] [ Author’s Name ] All rights reserved.
Alternatively, students may choose to license their work openly under a Creative Commons license. The author remains the copyright holder while at the same time granting up-front permission to others to read, share, and (depending on the license) adapt the work, so long as proper attribution is given. (By default, under copyright law, the author reserves all rights; under a Creative Commons license, the author reserves some rights.)
- Do not print a page number on the copyright page. It is understood to be page ii for counting purposes only.
An abstract, numbered as page iii , should immediately follow the copyright page and should state the problem, describe the methods and procedures used, and give the main results or conclusions of the research. The abstract will appear in the online and bound versions of the dissertation and will be published by ProQuest. There is no maximum word count for the abstract.
- double-spaced
- left-justified
- indented on the first line of each paragraph
- The author’s name, right justified
- The words “Dissertation Advisor:” followed by the advisor’s name, left-justified (a maximum of two advisors is allowed)
- Title of the dissertation, centered, several lines below author and advisor
Dissertations divided into sections must contain a table of contents that lists, at minimum, the major headings in the following order:
- Front Matter
- Body of Text
- Back Matter
Front matter includes (if applicable):
- acknowledgements of help or encouragement from individuals or institutions
- a dedication
- a list of illustrations or tables
- a glossary of terms
- one or more epigraphs.
Back matter includes (if applicable):
- bibliography
- supplemental materials, including figures and tables
- an index (in rare instances).
Supplemental figures and tables must be placed at the end of the dissertation in an appendix, not within or at the end of a chapter. If additional digital information (including audio, video, image, or datasets) will accompany the main body of the dissertation, it should be uploaded as a supplemental file through ProQuest ETD . Supplemental material will be available in DASH and ProQuest and preserved digitally in the Harvard University Archives.
As a matter of copyright, dissertations comprising the student's previously published works must be authorized for distribution from DASH. The guidelines in this section pertain to any previously published material that requires permission from publishers or other rightsholders before it may be distributed from DASH. Please note:
- Authors whose publishing agreements grant the publisher exclusive rights to display, distribute, and create derivative works will need to seek the publisher's permission for nonexclusive use of the underlying works before the dissertation may be distributed from DASH.
- Authors whose publishing agreements indicate the authors have retained the relevant nonexclusive rights to the original materials for display, distribution, and the creation of derivative works may distribute the dissertation as a whole from DASH without need for further permissions.
It is recommended that authors consult their publishing agreements directly to determine whether and to what extent they may have transferred exclusive rights under copyright. The Office for Scholarly Communication (OSC) is available to help the author determine whether she has retained the necessary rights or requires permission. Please note, however, the Office of Scholarly Communication is not able to assist with the permissions process itself.
- Missing Dissertation Acceptance Certificate. The first page of the PDF dissertation file should be a scanned copy of the Dissertation Acceptance Certificate (DAC). This page should not be counted or numbered as a part of the dissertation pagination.
- Conflicts Between the DAC and the Title Page. The DAC and the dissertation title page must match exactly, meaning that the author name and the title on the title page must match that on the DAC. If you use your full middle name or just an initial on one document, it must be the same on the other document.
- Abstract Formatting Errors. The advisor name should be left-justified, and the author's name should be right-justified. Up to two advisor names are allowed. The Abstract should be double spaced and include the page title “Abstract,” as well as the page number “iii.” There is no maximum word count for the abstract.
- The front matter should be numbered using Roman numerals (iii, iv, v, …). The title page and the copyright page should be counted but not numbered. The first printed page number should appear on the Abstract page (iii).
- The body of the dissertation should be numbered using Arabic numbers (1, 2, 3, …). The first page of the body of the text should begin with page 1. Pagination may not continue from the front matter.
- All page numbers should be centered either at the top or the bottom of the page.
- Figures and tables Figures and tables must be placed within the text, as close to their first mention as possible. Figures and tables that span more than one page must be labeled on each page. Any second and subsequent page of the figure/table must include the “(Continued)” notation. This applies to figure captions as well as images. Each page of a figure/table must be accounted for and appropriately labeled. All figures/tables must have a unique number. They may not repeat within the dissertation.
- Any figures/tables placed in a horizontal orientation must be placed with the top of the figure/ table on the left-hand side. The top of the figure/table should be aligned with the spine of the dissertation when it is bound.
- Page numbers must be placed in the same location on all pages of the dissertation, centered, at the bottom or top of the page. Page numbers may not appear under the table/ figure.
- Supplemental Figures and Tables. Supplemental figures and tables must be placed at the back of the dissertation in an appendix. They should not be placed at the back of the chapter.
- Permission Letters Copyright. permission letters must be uploaded as a supplemental file, titled ‘do_not_publish_permission_letters,” within the dissertation submission tool.
- DAC Attachment. The signed Dissertation Acceptance Certificate must additionally be uploaded as a document in the "Administrative Documents" section when submitting in Proquest ETD . Dissertation submission is not complete until all documents have been received and accepted.
- Overall Formatting. The entire document should be checked after all revisions, and before submitting online, to spot any inconsistencies or PDF conversion glitches.
- You can view dissertations successfully published from your department in DASH . This is a great place to check for specific formatting and area-specific conventions.
- Contact the Office of Student Affairs with further questions.
CONTACT INFO
Katie riggs, explore events.
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / Harvard Referencing / Harvard Referencing Style Examples / Formatting page numbers in Harvard referencing style
Formatting page numbers in Harvard referencing style
Harvard-style referencing is one of the systems that a student, researcher, or writer may use to cite sources in their works.
Depending on what you are citing, you may or may not need numbered pages in your citation or reference.
In-text citations
In-text citations only require a page number under two conditions:
- The source has page numbers.
- You are citing a direct quotation.
If these two requirements are not both fulfilled, then you do not need to include page numbers in your in-text citation.
If you do need to include page numbers, the page number will go at the end of the in-text citation following a comma. To create the in-text citation, you will need this information:
- Author surname
- Publication year
- Page number(s)
There are two different in-text citation formats you could use:
(Author surname, publication year, p. no.)
Author surname (publication year, p. no.)
Examples:
“Proper gender roles become boundaries in the national iconography” (Mostov, 2008, p. 42).
In Soft Borders , Julie Mostov argues that “proper gender roles become boundaries in the national iconography” (2008, p. 42).
If you are citing a range of pages instead of one page, use ‘pp.’ in the citation.
“Every quality teacher is both a subject matter expert and good at teaching. These are two different skills. A teacher who connects well with his students but doesn’t know the subject matter isn’t going to be an effective teacher” (Stolar, 2020, pp. 4-5).
Even if page numbers are included in an in-text citation, it doesn’t necessarily mean they need to be included in the reference. In order for page numbers to be required for a reference, the cited source must meet the first criteria and either the second or third criteria:
- The cited source is complete work that is part of a larger work.
- The larger work involves different authors.
Common sources that require page numbers include journals.
Example scenarios:
- A quote from the book For Whom the Bell Tolls would require page numbers in the in-text citation, but since the book only has one author, the reference would not need page numbers.
- An edited book has several chapters written by various authors. You use information from a single chapter. That chapter would be cited and its reference would include page numbers.
- A single journal has several articles written by different authors. So, usually, when you cite a journal, you must include the page numbers of the particular article you’re using.
- A book is a collection of short stories by a single author, and you use a quote from just one of the stories. You would cite that story within the larger collection and the full reference would include page numbers.
If you do have to add page numbers to the reference, here are a few tips to follow:
- Use ‘p. nn ’ to cite a single page.
- Use ‘pp. nn – nn ’ to cite a range of pages.
- Print sources: place page numbers at the end of the citation for print sources.
- Online sources: place the page numbers before the URL or DOI.
Chapter in an edited book example:
Barondes, S. (2012) ‘ Each of us is ordinary, yet one of a kind’, in Brockman, J. (ed.) This will make you smarter . New York: Harper Perennial, p. 32.
Online journal article example:
Steinkuehler, C. (2010) ‘Video games and digital literacies’, Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy , 54(1), pp. 61–63. Available at: www.jstor.org/stable/20749077 (Accessed 16 October 2020).
Other cases
Most electronic sources, such as websites, videos, and audio recordings, do not have page numbers. Therefore, you do not need to list a location (page number) within your in-text citations.
Instead of page numbers, online sources usually have a URL or DOI number, which should be included in the reference to indicate the source location.
Published October 29, 2020.
Harvard Formatting Guide
Harvard Formatting
- et al Usage
- Direct Quotes
- In-text Citations
- Multiple Authors
- Page Numbers
- Writing an Outline
- View Harvard Guide
Reference Examples
- View all Harvard Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Harvard Referencing Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

- Study and research support
- Referencing
- Leeds Harvard referencing examples
Leeds Harvard: Report
Reference examples.
For paper copies of reports, reference these using the same format as book.
For online copies of reports, reference these using the same format as e-book.
For unpublished reports, reference these using the same format as unpublished document.
Common issues
When you're referencing with Leeds Harvard you may come across issues with missing details, multiple authors, edited books, references to another author's work or online items, to name a few. Here are some tips on how to deal with some common issues when using Leeds Harvard.
Skip straight to the issue that affects you:
- Online items
- URL web addresses
- Multiple authors
- Corporate author(s) or organisation(s)
- Multiple publisher details
- Editions and reprints
- Missing details
- Multiple sources with different authors
- Sources written by the same author in the same year
- Sources with the same author in different years
- Two authors with the same surname in the same year
- The work of one author referred to by another
- Anonymising sources for confidentiality
- Identifying the authors’ family name (surname)
- Free Tools for Students
- Harvard Referencing Generator
Free Harvard Referencing Generator
Generate accurate Harvard reference lists quickly and for FREE, with MyBib!
🤔 What is a Harvard Referencing Generator?
A Harvard Referencing Generator is a tool that automatically generates formatted academic references in the Harvard style.
It takes in relevant details about a source -- usually critical information like author names, article titles, publish dates, and URLs -- and adds the correct punctuation and formatting required by the Harvard referencing style.
The generated references can be copied into a reference list or bibliography, and then collectively appended to the end of an academic assignment. This is the standard way to give credit to sources used in the main body of an assignment.
👩🎓 Who uses a Harvard Referencing Generator?
Harvard is the main referencing style at colleges and universities in the United Kingdom and Australia. It is also very popular in other English-speaking countries such as South Africa, Hong Kong, and New Zealand. University-level students in these countries are most likely to use a Harvard generator to aid them with their undergraduate assignments (and often post-graduate too).
🙌 Why should I use a Harvard Referencing Generator?
A Harvard Referencing Generator solves two problems:
- It provides a way to organise and keep track of the sources referenced in the content of an academic paper.
- It ensures that references are formatted correctly -- inline with the Harvard referencing style -- and it does so considerably faster than writing them out manually.
A well-formatted and broad bibliography can account for up to 20% of the total grade for an undergraduate-level project, and using a generator tool can contribute significantly towards earning them.
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's Harvard Referencing Generator?
Here's how to use our reference generator:
- If citing a book, website, journal, or video: enter the URL or title into the search bar at the top of the page and press the search button.
- Choose the most relevant results from the list of search results.
- Our generator will automatically locate the source details and format them in the correct Harvard format. You can make further changes if required.
- Then either copy the formatted reference directly into your reference list by clicking the 'copy' button, or save it to your MyBib account for later.
MyBib supports the following for Harvard style:
🍏 What other versions of Harvard referencing exist?
There isn't "one true way" to do Harvard referencing, and many universities have their own slightly different guidelines for the style. Our generator can adapt to handle the following list of different Harvard styles:
- Cite Them Right
- Manchester Metropolitan University (MMU)
- University of the West of England (UWE)

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.
Citation guides
All you need to know about citations
How to cite an online report in Harvard

To cite an online report in a reference entry in Harvard style include the following elements:
- Author or organization: Give the last name and initials (e. g. Watson, J.) of up to three authors with the last name preceded by 'and'. For four authors or more include the first name followed by et al., unless your institution requires referencing of all named authors.
- Year of publication: Give the year in round brackets.
- Title of the online report: Give the title as presented in the source. Only the first letter of the first word and proper nouns are capitalized.
- Place of publication: List the city and the US state using the two-letter abbreviation. Spell out country names if outside of the UK or the USA.
- Publisher: Give the name of the publisher.
- URL: Give the full URL of the web page including the protocol (http:// or https://).
- Date of access: Give the day month and year.
Here is the basic format for a reference list entry of an online report in Harvard style:
Author or organization . ( Year of publication ) Title of the online report . Place of publication : Publisher . Available at: URL (Accessed: Date of access ).
Take a look at our reference list examples that demonstrate the Harvard style guidelines in action:
A report retrieved online
Department of Making Pregnancy Safer . ( 2006 ) Annual report, 2005 . Available at: https://apps.who.int/ iris/bitstream/handle/10665/69505/WHO_MPS_07.01_eng.pdf (Accessed: 6 September 2010 ).
Bureau of Fiscal Service, Department of Treasury . ( 2018 ) Financial Report of the United States Government . Available at: https://fiscal.treasury.gov/files/reports-statements/financial-report/2018/03282019-FR(Final).pdf"> (Accessed: 2 September 2019 ).

This citation style guide is based on the Cite Them Right (10 th edition) Harvard referencing guide.
More useful guides
- UQ Harvard referencing style: Report
- Citing & Referencing: Harvard Style
- Harvard referencing tutorial
More great BibGuru guides
- AMA: how to cite an online journal article
- AMA: how to cite an online newspaper article
- Harvard: how to cite a film
Automatic citations in seconds
Citation generators
Alternative to.
- NoodleTools
- Getting started
From our blog
- 📚 How to write a book report
- 📝 APA Running Head
- 📑 How to study for a test
- Utility Menu
- Get Involved
- News & Events
qualtrics survey
Research report.

Callen, I., Carbonari, M. V., DeArmond, M., Dewey, D., Dizon-Ross, E., Goldhaber, D., Isaacs, J., et al. (2023). Summer School As a Learning Loss Recovery Strategy After COVID-19: Evidence from Summer 2022 . Abstract To make up for pandemic-related learning losses, many U.S. public school districts have increased enrollment in their summer school programs. We assess summer school as a strategy for COVID-19 learning recovery by tracking the academic progress of students who attended summer school in 2022 across eight districts serving 400,000 students. Based on students’ spring to fall progress, we find a positive impact for summer school on math test achievement (0.03 standard deviation, SD), but not on reading tests. These effects are predominantly driven by students in upper elementary grades. To put the results into perspective, if we assume that these districts have losses similar to those present at the end of the 2022–23 school year (i.e., approximately -0.2 SD), we estimate summer programming closed approximately 2% to 3% of the districts’ total learning losses in math, but none in reading.
We analyze data from approximately 7,800 school districts to describe variation in pandemic-related learning losses among communities and student subgroups. We attempt to understand mechanisms that led to learning losses, as well as explore how historical data from those districts can inform our expectations for how quickly districts will rebound from such losses. We show that learning losses during the pandemic were large and highly variable among communities. Similar to previous research, we find that losses were larger in lower-income and minority districts and in districts which remained remote or hybrid for longer periods during the 2020-21 school year. Among districts, the math learning loss per week of remote/hybrid instruction was larger in high-minority and high-poverty districts. Within districts, however, White students and non-economically disadvantaged students lost about the same amount of ground as Black, Hispanic and economically disadvantaged students. This suggests that the mechanisms driving losses operated at the district or community level, rather than household level. Several community-level characteristics were related to learning losses: broadband access, disruptions to social and economic activity, and trust in government institutions. However, no individual predictor provided strong explanatory power. Relative to historical years, losses during the pandemic were substantial, and an exploratory analysis of historical shocks to achievement suggests that the effects of the pandemic are likely to persist without continued concerted investments in student learning.
Teacher evaluation reform has been among the most controversial education reforms in recent years. It also is one of the costliest in terms of the time teachers and principals must spend on classroom observations. We conducted a randomized field trial at four sites to evaluate whether substituting teacher-collected videos for in-person observations could improve the value of teacher observations for teachers, administrators, or students. Relative to teachers in the control group who participated in standard in-person observations, teachers in the video-based treatment group reported that post-observation meetings were more “supportive” and they were more able to identify a specific practice they changed afterward. Treatment principals were able to shift their observation work to noninstructional times. The program also substantially increased teacher retention. Nevertheless, the intervention did not improve students’ academic achievement or self-reported classroom experiences, either in the year of the intervention or for the next cohort of students. Following from the literature on observation and feedback cycles in low-stakes settings, we hypothesize that to improve student outcomes schools may need to pair video feedback with more specific supports for desired changes in practice.
Click to read full text on MIT Press Journals
The project team is still awaiting student test data to complete the evaluation, but this brief provides a short update on survey results. Students of MQI-coached teachers report that their teachers ask more substantive questions, and require more use of mathematical vocabulary as compared to students of control teachers. Students in MQI-coached classrooms also reported more student talk in class. Teachers who received MQI Coaching tended to find their professional development significantly more useful than control teachers, and were also more likely to report that their mathematics instruction improved over the course of the year.
In Massachusetts, the charter school debate has centered on four concerns:
- that the achievement of the high-scoring charter schools is due to selective admission and retention policies and not the education that the charter schools provide,
- that charter schools are underserving English language learners and special education students,
- that charter schools are disciplining students at higher rates in order to drive troublesome students back to traditional schools, and
- that charter schools are undermining traditional public schools financially.
This report summarizes the evidence pertaining to these four concerns.
(2016). Findings from a National Study on Research Use Among School and District Leaders (Technical Report No. 1) . National Center for Research in Policy and Practice. Read the report (NCRPP Website)
Achievement Network (ANet) was founded in 2005 as a school-level intervention to support the use of academic content standards and assessments to improve teaching and learning. Initially developed within the Boston charter school sector, it has expanded to serve over 500 schools in nine geographic networks across the United States. The program is based on the belief that if teachers are provided with timely data on student performance from interim assessments tied to state standards, if school leaders provide support and create structures that help them use that data to identify student weaknesses, and if teachers have knowledge of how to improve the performance of students who are falling behind, then they will become more effective at identifying and addressing gaps in student learning. This will, in turn, improve student performance, particularly for high-need students.
In 2010, ANet received a development grant from the U.S. Department of Education’s Investing in Innovation (i3) Program. The grant funded both the expansion of the program to serve up to 60 additional schools in five school districts, as well as an external evaluation of the expansion. The Center for Education Policy Research (CEPR) at Harvard University partnered with ANet to design a matched-pair, school-randomized evaluation of their program’s impact on educator practice and student achievement in schools participating in its i3-funded expansion.
Subtle policy adjustments can induce relatively large “ripple effects.” We evaluate a College Board initiative that increased the number of free SAT score reports available to low-income students and changed the time horizon for using these score reports. Using a difference-in-differences analytic strategy, we estimate that targeted students were roughly 10 percentage points more likely to send eight or more reports. The policy improved on-time college attendance and 6-year bachelor’s completion by about 2 percentage points. Impacts were realized primarily by students who were competitive candidates for 4-year college admission. The bachelor’s completion impacts are larger than would be expected based on the number of students driven by the policy change to enroll in college and to shift into more selective colleges. The unexplained portion of the completion effects may result from improvements in nonacademic fit between students and the postsecondary institutions in which they enroll.
- Research Report (46)
- SDP Partner Diagnostic (27)
- Practictioner Resource (14)
- Technical Resource (4)
- Case Study (2)
- Newsletter (1)
- Presentation (4)
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 09 May 2024
Cubic millimetre of brain mapped in spectacular detail
- Carissa Wong
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
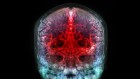
Rendering based on electron-microscope data, showing the positions of neurons in a fragment of the brain cortex. Neurons are coloured according to size. Credit: Google Research & Lichtman Lab (Harvard University). Renderings by D. Berger (Harvard University)
Researchers have mapped a tiny piece of the human brain in astonishing detail. The resulting cell atlas, which was described today in Science 1 and is available online , reveals new patterns of connections between brain cells called neurons, as well as cells that wrap around themselves to form knots, and pairs of neurons that are almost mirror images of each other.
The 3D map covers a volume of about one cubic millimetre, one-millionth of a whole brain, and contains roughly 57,000 cells and 150 million synapses — the connections between neurons. It incorporates a colossal 1.4 petabytes of data. “It’s a little bit humbling,” says Viren Jain, a neuroscientist at Google in Mountain View, California, and a co-author of the paper. “How are we ever going to really come to terms with all this complexity?”
Slivers of brain
The brain fragment was taken from a 45-year-old woman when she underwent surgery to treat her epilepsy. It came from the cortex, a part of the brain involved in learning, problem-solving and processing sensory signals. The sample was immersed in preservatives and stained with heavy metals to make the cells easier to see. Neuroscientist Jeff Lichtman at Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and his colleagues then cut the sample into around 5,000 slices — each just 34 nanometres thick — that could be imaged using electron microscopes.
Jain’s team then built artificial-intelligence models that were able to stitch the microscope images together to reconstruct the whole sample in 3D. “I remember this moment, going into the map and looking at one individual synapse from this woman’s brain, and then zooming out into these other millions of pixels,” says Jain. “It felt sort of spiritual.”
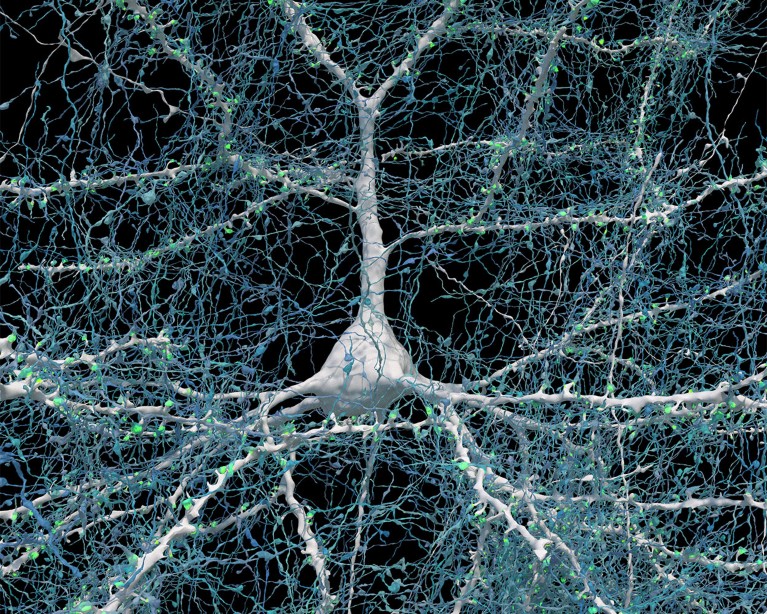
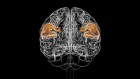
A single neuron (white) shown with 5,600 of the axons (blue) that connect to it. The synapses that make these connections are shown in green. Credit: Google Research & Lichtman Lab (Harvard University). Renderings by D. Berger (Harvard University)
When examining the model in detail, the researchers discovered unconventional neurons, including some that made up to 50 connections with each other. “In general, you would find a couple of connections at most between two neurons,” says Jain. Elsewhere, the model showed neurons with tendrils that formed knots around themselves. “Nobody had seen anything like this before,” Jain adds.
The team also found pairs of neurons that were near-perfect mirror images of each other. “We found two groups that would send their dendrites in two different directions, and sometimes there was a kind of mirror symmetry,” Jain says. It is unclear what role these features have in the brain.
Proofreaders needed
The map is so large that most of it has yet to be manually checked, and it could still contain errors created by the process of stitching so many images together. “Hundreds of cells have been ‘proofread’, but that’s obviously a few per cent of the 50,000 cells in there,” says Jain. He hopes that others will help to proofread parts of the map they are interested in. The team plans to produce similar maps of brain samples from other people — but a map of the entire brain is unlikely in the next few decades, he says.
“This paper is really the tour de force creation of a human cortex data set,” says Hongkui Zeng, director of the Allen Institute for Brain Science in Seattle. The vast amount of data that has been made freely accessible will “allow the community to look deeper into the micro-circuitry in the human cortex”, she adds.
Gaining a deeper understanding of how the cortex works could offer clues about how to treat some psychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases. “This map provides unprecedented details that can unveil new rules of neural connections and help to decipher the inner working of the human brain,” says Yongsoo Kim, a neuroscientist at Pennsylvania State University in Hershey.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-01387-9
Shapson-Coe, A. et al. Science 384 , eadk4858 (2024).
Article Google Scholar
Download references
Reprints and permissions
Related Articles
- Neuroscience
Temporal multiplexing of perception and memory codes in IT cortex
Article 15 MAY 24
Volatile working memory representations crystallize with practice
Evolution of a novel adrenal cell type that promotes parental care
Organoids merge to model the blood–brain barrier
Research Highlight 15 MAY 24

How does ChatGPT ‘think’? Psychology and neuroscience crack open AI large language models
News Feature 14 MAY 24
Brain-reading device is best yet at decoding ‘internal speech’
News 13 MAY 24
Postdoc in CRISPR Meta-Analytics and AI for Therapeutic Target Discovery and Priotisation (OT Grant)
APPLICATION CLOSING DATE: 14/06/2024 Human Technopole (HT) is a new interdisciplinary life science research institute created and supported by the...
Human Technopole
Research Associate - Metabolism
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Postdoc Fellowships
Train with world-renowned cancer researchers at NIH? Consider joining the Center for Cancer Research (CCR) at the National Cancer Institute
Bethesda, Maryland
NIH National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Faculty Recruitment, Westlake University School of Medicine
Faculty positions are open at four distinct ranks: Assistant Professor, Associate Professor, Full Professor, and Chair Professor.
Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Westlake University
PhD/master's Candidate
PhD/master's Candidate Graduate School of Frontier Science Initiative, Kanazawa University is seeking candidates for PhD and master's students i...
Kanazawa University
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Harvard referencing system is known as the Author-Date style. It emphasizes the name of the creator of a piece of information and the date of publication, with the list of references in alphabetical order at the end of your paper. Unlike other citation styles, there is no single, definitive version of Harvard Style.
www.communicate.gse.harvard.edu | 2 Writing the introduction As we've discussed, all introductions begin broadly. The audience, format, and purpose of your paper influence how broad it should be. You can expect more background knowledge from readers of a technical journal than you can from readers of a popular magazine.
Format for Harvard Referencing. Typically, a paper that uses Harvard referencing has the following format: 2.5 cm OR 1-inch margins on all sides; Recommended fonts: Arial 12 pt or Times New Roman, with double-spacing; Title is in the center of the page just above the text; Left-aligned text, with the first sentence of every paragraph indented ...
This guide introduces the Harvard referencing style and includes examples of citations. Skip to ... Title of report (in italics). Place of publication: publisher. ... have distributed, either electronically or in print, to the wider public. This can include annual reports and research reports. Unpublished reports, such as internal reports, are ...
When you cite a source with up to three authors, cite all authors' names. For four or more authors, list only the first name, followed by ' et al. ': Number of authors. In-text citation example. 1 author. (Davis, 2019) 2 authors. (Davis and Barrett, 2019) 3 authors.
By March 1 of your graduating year: Submit the following to [email protected] : Your mentor's approval of your scholarly report (emailed approval is appropriate to forward) A pdf of your scholarly report. Master's student report submission deadlines can be found below in the Scholarly Report Format section under Master's ...
Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples. Published on 1 May 2020 by Jack Caulfield.Revised on 7 November 2022. In Harvard style, the bibliography or reference list provides full references for the sources you used in your writing.. A reference list consists of entries corresponding to your in-text citations.; A bibliography sometimes also lists sources that you consulted for background ...
It is one of the most widely used styles in the world. In Harvard, you must cite sources that you have paraphrased, quoted, or consulted to write your research paper. Cite your sources in two places: In the body of your paper (in-text citation). In the Reference list at the end of your paper (full bibliographic reference).
Getting Started. There are two components to referencing: in-text citations in your paper and the reference list at the end of your paper. The in-text citation: Harvard is an 'author/date' system, so your in-text citation consists of author (s) and year of publication. In-text citation of a book (the same format applies for a journal article)
In-text citations. Two or more works cited at one point in the text. If two or more works by different authors or authoring bodies are cited at one point in the text, use a semi-colon to separate them: (Larsen 2000; Malinowski 1999) The authors should be listed in alphabetical order. Two or three authors or authoring bodies.
Fortunately, the Open University style makes this easy, as the reference list requirements for a report are the same as those for a book, following this format: Author, X. (year). Title. Place of publication: Publisher. In practice, then, we would cite the report from our example this way: Barnes, T. (2014). American Animal Shelters Report.
Title of the report: Give the title as presented in the source. Only the first letter of the first word and proper nouns are capitalized. Place of publication: List the city and the US state using the two-letter abbreviation. Spell out country names if outside of the UK or the USA. Publisher: Give the name of the publisher.
In Harvard style, to reference a journal article, you need the author name (s), the year, the article title, the journal name, the volume and issue numbers, and the page range on which the article appears. If you accessed the article online, add a DOI (digital object identifier) if available. In-text citation example. (Poggiolesi, 2016)
As you begin writing the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion of your Harvard referencing paper, these are formatting tips to keep in mind. Page headings: Center a page title. Do not bold, italicize, or underline it. Body: Left-aligned. Paragraphs: Indent the first line using the tab key. In-text citations: Include these citations ...
Text: double-spaced and left-aligned. Indent: first line of a paragraph has indent of 0.5 inch. Margins: 1 inch from each side. A Harvard style citation must have a Title page, header (or running head), headings and Reference list. We will take a closer look at formatting each section down below.
Harvard style follows this basic format for referencing and citing a report from a company's website, a database and even for a company profile (if it's in the form of a report). In-text citation: (Author Surname, Year Published) Reference list entry: Author Surname, Author Initial. (Year Published). Title of the Report in italics.
Cite A Report in Harvard style. Use the following template or our Harvard Referencing Generator to cite a report. For help with other source types, like books, PDFs, or websites, check out our other guides. To have your reference list or bibliography automatically made for you, try our free citation generator.
Depending on the size of your document and the speed of your computer, this process can take 1-15 minutes. After your document is converted, select the "File" tab at the top of the page. Then select "Document Properties." Click on the "Fonts" tab. Carefully check all of your fonts.
If you do have to add page numbers to the reference, here are a few tips to follow: Use 'p. nn ' to cite a single page. Use 'pp. nn - nn ' to cite a range of pages. Print sources: place page numbers at the end of the citation for print sources. Online sources: place the page numbers before the URL or DOI.
Leeds Harvard: Report Reference examples. For paper copies of reports, ... For unpublished reports, reference these using the same format as unpublished document. Common issues. When you're referencing with Leeds Harvard you may come across issues with missing details, multiple authors, edited books, references to another author's work or ...
A Harvard Referencing Generator solves two problems: It provides a way to organise and keep track of the sources referenced in the content of an academic paper. It ensures that references are formatted correctly -- inline with the Harvard referencing style -- and it does so considerably faster than writing them out manually.
To cite an online report in a reference entry in Harvard style include the following elements:. Author or organization: Give the last name and initials (e. g. Watson, J.) of up to three authors with the last name preceded by 'and'. For four authors or more include the first name followed by et al., unless your institution requires referencing of all named authors.
Center for Education Policy Research at Harvard University. Abstract. Read the report. (2016). DreamBox Learning Achievement Growth in the Howard County Public School System and Rocketship Education . Center for Education Policy at Harvard University. Read the key findings report. Read the technical appendix. (2016).
5. Research Report. Sometimes if you need to do some in-depth research, the best way to present that information is with a research report. Whether it's scientific findings, data and statistics from a study, etc., a research report is a great way to share your results. For the visuals in your research report, Visme offers millions of free stock ...
Credit: Google Research & Lichtman Lab (Harvard University). Renderings by D. Berger (Harvard University) ... and his colleagues then cut the sample into around 5,000 slices — each just 34 ...