
What Are Logos, Pathos & Ethos?
A straight-forward explainer (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | June 2023
If you spend any amount of time exploring the wonderful world of philosophy, you’re bound to run into the dynamic trio of rhetorical appeals: logos , ethos and pathos . But, what exactly do they mean and how can you use them in your writing or speaking? In this post, we’ll unpack the rhetorical love triangle in simple terms, using loads of practical examples along the way.
Overview: The Rhetorical Triangle
- What are logos , pathos and ethos ?
- Logos unpacked (+ examples)
- Pathos unpacked (+ examples)
- Ethos unpacked (+ examples)
- The rhetorical triangle
What are logos, ethos and pathos?
Simply put, logos, ethos and pathos are three powerful tools that you can use to persuade an audience of your argument . At the most basic level, logos appeals to logic and reason, while pathos appeals to emotions and ethos emphasises credibility or authority.
Naturally, a combination of all three rhetorical appeals packs the biggest punch, but it’s important to consider a few different factors to determine the best mix for any given context. Let’s look at each rhetorical appeal in a little more detail to understand how best to use them to your advantage.

Logos appeals to the logical, reason-driven side of our minds. Using logos in an argument typically means presenting a strong body of evidence and facts to support your position. This evidence should then be accompanied by sound logic and well-articulated reasoning .
Let’s look at some examples of logos in action:
- A friend trying to persuade you to eat healthier might present scientific studies that show the benefits of a balanced diet and explain how certain nutrients contribute to overall health and longevity.
- A scientist giving a presentation on climate change might use data from reputable studies, along with well-presented graphs and statistical analyses to demonstrate the rising global temperatures and their impact on the environment.
- An advertisement for a new smartphone might highlight its technological features, such as a faster processor, longer battery life, and a high-resolution camera. This could also be accompanied by technical specifications and comparisons with competitors’ models.
In short, logos is all about using evidence , logic and reason to build a strong argument that will win over an audience on the basis of its objective merit . This contrasts quite sharply against pathos, which we’ll look at next.

Contrasted to logos, pathos appeals to the softer side of us mushy humans. Specifically, it focuses on evoking feelings and emotions in the audience. When utilising pathos in an argument, the aim is to cultivate some feeling of connection in the audience toward either yourself or the point that you’re trying to make.
In practical terms, pathos often uses storytelling , vivid language and personal anecdotes to tap into the audience’s emotions. Unlike logos, the focus here is not on facts and figures, but rather on psychological affect . Simply put, pathos utilises our shared humanness to foster agreement.
Let’s look at some examples of pathos in action:
- An advertisement for a charity might incorporate images of starving children and highlight their desperate living conditions to evoke sympathy, compassion and, ultimately, donations.
- A politician on the campaign trail might appeal to feelings of hope, unity, and patriotism to rally supporters and motivate them to vote for his or her party.
- A fundraising event may include a heartfelt personal story shared by a cancer survivor, with the aim of evoking empathy and encouraging donations to support cancer research.
As you can see, pathos is all about appealing to the human side of us – playing on our emotions to create buy-in and agreement.

Last but not least, we’ve got ethos. Ethos is all about emphasising the credibility and authority of the person making the argument, or leveraging off of someone else’s credibility to support your own argument.
The ethos card can be played by highlighting expertise, achievements, qualifications and accreditations , or even personal and professional associations and connections. Ultimately, the aim here is to foster some level of trust within the audience by demonstrating your competence, as this will make them more likely to take your word as fact.
Let’s look at some examples of ethos in action:
- A fitness equipment brand might hire a well-known athlete to endorse their product.
- A toothpaste brand might make claims highlighting that a large percentage of dentists recommend their product.
- A financial advisor might present their qualifications, certifications and professional memberships when meeting with a prospective client.
As you can see, using ethos in an argument is largely about emphasising the credibility of the person rather than the logical soundness of the argument itself (which would reflect a logos-based approach). This is particularly helpful when there isn’t a large body of evidence to support the argument.
Ethos can also overlap somewhat with pathos in that positive emotions and feelings toward a specific person can oftentimes be extended to someone else’s argument. For example, a brand that has nothing to do with sports could still benefit from the endorsement of a well-loved athlete, just because people feel positive feelings about the athlete – not because of that athlete’s expertise in the product they’re endorsing.

How to use logos, pathos and ethos
Logos, pathos and ethos combine to form the rhetorical triangle , also known as the Aristotelian triangle. As you’d expect, the three sides (or corners) of the triangle reflect the three appeals, but there’s also another layer of meaning. Specifically, the three sides symbolise the relationship between the speaker , the audience and the message .
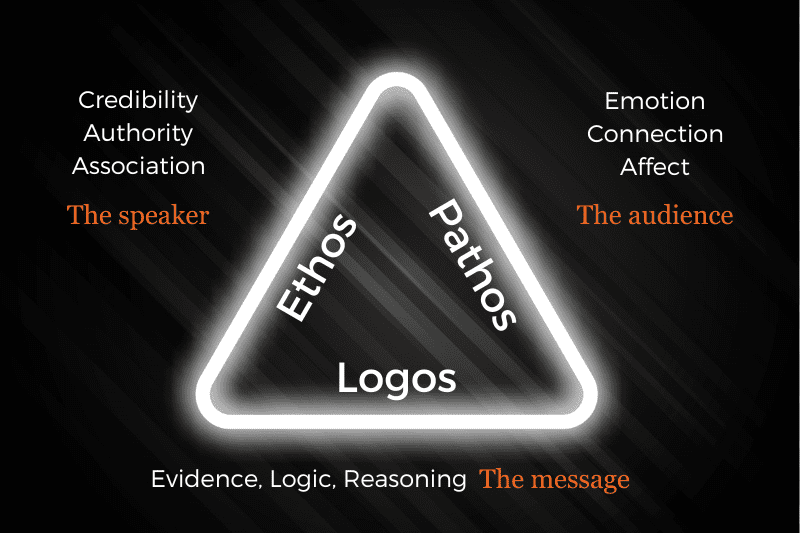
Without getting too philosophical, the key takeaway here is that logos, pathos and ethos are all tools that you can use to present a persuasive argument . However, how much you use each tool needs to be informed by careful consideration of who your audience is and what message you’re trying to convey to them.
For example, if you’re writing a research paper for a largely scientific audience, you’ll likely lean more heavily on the logos . Conversely, if you’re presenting a speech in which you argue for greater social justice, you may lean more heavily on the pathos to win over the hearts and minds of your audience.
Simply put, by understanding the relationship between yourself (as the person making the argument), your audience , and your message , you can strategically employ the three rhetorical appeals to persuade, engage, and connect with your audience more effectively in any context. Use these tools wisely and you’ll quickly notice what a difference they can make to your ability to communicate and more importantly, to persuade .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos – A Simple Guide

4-minute read
- 12th April 2023
Ethos, logos, and pathos are three essential components of persuasive communication . They’ve been used for centuries by great communicators to influence the beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors of their audiences. In this simple guide, we’ll take a closer look at these three components using examples from famous writing and speeches.
What Is Ethos?
Ethos is a persuasive appeal based on the credibility or character of the speaker or writer. It refers to the trustworthiness, expertise, or authority that they bring to the argument. It’s crucial in establishing the credibility of the speaker or writer and can be built in through a variety of means, such as reputation and sources, or language and tone.
How To Use Ethos
Ethos can be established through the speaker or writer’s reputation: if they are known for being knowledgeable, honest, and trustworthy, this can lend credibility to their argument. For example, in his famous “I Have a Dream” speech, Martin Luther King Jr. established his ethos by highlighting his role as a civil rights leader and his personal experience with racial injustice.
Another way you can achieve ethos in speech or writing is through the use of credible sources. For example, Rachel Carson established ethos in her book Silent Spring by providing extensive scientific evidence to support her argument that pesticides were harming the environment.
Finally, ethos can be accomplished through the use of language and tone . Using a professional and respectful tone can create the impression of credibility and authority. For instance, in his second inaugural address, President Abraham Lincoln employed ethos by using a solemn, reflective tone to convey the gravity of the situation.
What Is Logos?
Logos is a persuasive appeal based on logic and reasoning. It refers to the use of evidence and logical arguments to support the speaker or writer’s position.
How To Use Logos
One way you can implement logos in your speech or writing is through the use of statistics and data. When writing, or constructing a speech, try to incorporate reliable and credible stats or figures to strengthen your claims or argument and persuade your audience.
You can also employ examples and analogies to achieve logos. These can make your argument more accessible and understandable to a wider audience. For example, in his book The Tipping Point , Malcolm Gladwell uses the example of “the broken windows” theory to illustrate his argument that small changes can have a big impact on social behavior.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Finally, logos can be established through the use of logical arguments . To ensure you have a logical argument, you should have a clear statement with definitions, examples, and evidence to support it. For instance, in his essay “Civil Disobedience,” Henry David Thoreau made a logical argument that individuals have a moral obligation to resist unjust laws.
What Is Pathos?
Pathos is a persuasive appeal based on emotion. It refers to the use of language and imagery that elicits an emotional response. Pathos can be used to create a sense of urgency, inspire empathy, or evoke a particular mood.
How To Use Pathos
Vivid imagery is a great way in which a writer or speaker can implement pathos. Using descriptive language to paint a picture in your audience’s mind is a powerful and persuasive skill. For example, in his poem “Dulce et Decorum Est,” Wilfred Owen used vivid imagery to describe the horrors of war and elicit an emotional response in his readers.
Pathos can also be accomplished by using personal anecdotes. The power of storytelling is an invaluable skill for any writer or speaker because it creates rapport and an emotional connection with your audience. For example, in her TED talk “The Power of Vulnerability,” Brene Brown shares personal stories about her struggles with shame and vulnerability to inspire empathy and connection with her audience.
Finally, pathos can be established through the use of rhetorical questions and appeals to shared values. A good example can be heard in Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech. He poses his biggest question to his audience (and the world): “Now, what does all of this mean in this great period of history?” In response to this rhetorical question, he beautifully tries to persuade the audience to work together toward a common goal, stating, “It means that we’ve got to stay together. We’ve got to stay together and maintain unity.”
Ethos, logos, and pathos are powerful tools for persuasive speech and writing. By establishing credibility, using logical arguments, and appealing to emotion, speakers and writers can influence the beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors of their audiences. When used effectively, these elements can help to create meaningful and lasting change in the world.
Interested in learning how to elevate your writing with more literary devices? Check our other articles .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
6 Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined
By melanie gagich and emilie zickel.
Rhetoric is the way that authors use and manipulate language in order to persuade an audience. Once we understand the rhetorical situation out of which a text is created (why it was written, for whom it was written, by whom it was written, how the medium in which it was written creates certain constraints or perhaps freedoms of expression), we can look at how all of those contextual elements shape the author’s creation of the text .
We can look first at the classical rhetorical appeals, which are the three ways to classify authors’ intellectual, moral, and emotional approaches to getting the audience to have the reaction that the author hopes for.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeals refer to ethos, pathos, and logos. These are classical Greek terms, dating back to Aristotle, who is traditionally seen as the father of rhetoric. To be rhetorically effective (and thus persuasive), an author must engage the audience in a variety of compelling ways, which involves carefully choosing how to craft their argument so that the outcome, audience agreement with the argument or point, is achieved. Aristotle defined these modes of engagement and gave them the terms that we still use today: logos, pathos, and ethos.
Logos: Appeal to Logic
Logic. Reason. Rationality. Logos is brainy and intellectual, cool, calm, collected, objective .
When an author relies on logos, it means that they are using logic, careful structure, and objective evidence to appeal to the audience. An author can appeal to an audience’s intellect by using information that can be fact checked (using multiple sources ) and thorough explanations to support key points. Additionally, providing a solid and non-biased explanation of one’s argument is a great way for an author to invoke logos.
For example, if I were trying to convince my students to complete their homework, I might explain that I understand everyone is busy and they have other classes (non-biased), but the homework will help them get a better grade on their test (explanation). I could add to this explanation by providing statistics showing the number of students who failed and didn’t complete their homework versus the number of students who passed and did complete their homework (factual evidence).
Logical appeals rest on rational modes of thinking , such as
- Comparison – including a comparison between one thing (with regard to your topic ) and another similar thing to help support your claim . It is important that the comparison is fair and valid–the things being compared must share significant traits of similarity.
- Cause/effect thinking – arguing that X has caused Y, or that X is likely to cause Y to help support your claim . Be careful with the latter–it can be difficult to predict that something will happen in the future.
- Deductive reasoning – starting with a broad, general claim /example and using it to support a more specific point or claim
- Inductive reasoning – using several specific examples or cases to make a broad generalization
- Exemplification – using many examples or a variety of evidence to support a single point
- Elaboration – moving beyond just including a fact but explaining the significance or relevance of that fact
- Coherent thought – maintaining a well-organized line of reasoning; not repeating ideas or jumping around
Pathos: Appeal to Emotions
When an author relies on pathos, it means that they are trying to tap into the audience’s emotions to get them to agree with the author’s claim . An author using pathetic appeals wants the audience to feel something: anger, pride, joy, rage, or happiness. For example, many of us have seen the ASPCA commercials that use photographs of injured puppies or sad-looking kittens and slow, depressing music to emotionally persuade their audience to donate money.
Pathos-based rhetorical strategies are any strategies that get the audience to “open up” to the topic , the argument, or the author. Emotions can make us vulnerable, and an author can use this vulnerability to get the audience to believe that their argument is a compelling one.
Pathetic appeals might include
- Expressive descriptions of people, places, or events that help the reader to feel or experience those events
- Vivid imagery of people, places, or events that help the reader to feel like they are seeing those events
- Personal stories that make the reader feel a connection to, or empathy for, the person being described
- Emotion-laden vocabulary as a way to put the reader into that specific emotional mindset (What is the author trying to make the audience feel? And how are they doing that?)
- Information that will evoke an emotional response from the audience . This could involve making the audience feel empathy or disgust for the person/group/event being discussed or perhaps connection to or rejection of the person/group/event being discussed.
When reading a text , try to locate when the author is trying to convince the reader using emotions because, if used to excess, pathetic appeals can indicate a lack of substance or emotional manipulation of the audience. See the links below about fallacious pathos for more information.
Ethos: Appeal to Values/Trust
Ethical appeals have two facets: audience values and authorial credibility/character.
On the one hand, when an author makes an ethical appeal, they are attempting to tap into the values or ideologies that the audience holds , for example, patriotism, tradition, justice, equality, dignity for all humankind, self-preservation, or other specific social, religious or philosophical values (Christian values, socialism, capitalism, feminism, etc.). These values can sometimes feel very close to emotions, but they are felt on a social level rather than only on a personal level. When an author evokes the values that the audience cares about to justify or support their argument, we classify that as ethos. The audience will feel that the author is making an argument that is “right” (in the sense of moral “right”-ness, i.e., “My argument rests upon the values that matter to you. Therefore, you should accept my argument”). This first part of the definition of ethos, then, is focused on the audience’s values.
On the other hand, this sense of referencing what is “right” in an ethical appeal connects to the other sense of ethos: the author. Ethos that is centered on the author revolves around two concepts: the credibility of the author and their character.
- Credibility of the speaker/author is determined by their knowledge and expertise in the subject at hand. For example, if you are learning about Einstein’s Theory of Relativity, would you rather learn from a professor of physics or a cousin who took two science classes in high school 30 years ago? It is fair to say that, in general, the professor of physics would have more credibility to discuss the topic of physics. To establish their credibility, an author may draw attention to who they are or what kinds of experience they have with the topic being discussed as an ethical appeal (i.e., “Because I have experience with this topic –and I know my stuff– you should trust what I am saying about this topic ”). Some authors do not have to establish their credibility because the audience already knows who they are and that they are credible.
- Character is another aspect of ethos. Character is different from credibility because it involves personal history and even personality traits. A person can be credible but lack character or vice versa. For example, in politics, sometimes the most experienced candidates–those who might be the most credible candidates–fail to win elections because voters do not accept their character. Politicians take pains to shape their character as leaders who have the interests of the voters at heart. The candidate who successfully proves to the voters (the audience) that they have the type of character that the audience can trust is more likely to win.
Thus, ethos comes down to trust. How can the author gain the audience’s trust so that the audience will accept their argument? How can the author make him or herself appear as a credible speaker who embodies the character traits that the audience values? In building ethical appeals, we see authors referring either directly or indirectly to the values that matter to the intended audience (so that the audience will trust the speaker). Authors use language, phrasing, imagery, or other writing styles common to people who hold those values, thereby “talking the talk” of people with those values (again, so that the audience is inclined to trust the speaker). Authors refer to their experience and/or authority with the topic as well (and therefore demonstrate their credibility).
When reading, you should think about the author’s credibility regarding the subject as well as their character. Here is an example of a rhetorical move that connects with ethos: when reading an article about abortion, the author mentions that she has had an abortion. That is an example of an ethical move because the author is creating credibility via anecdotal evidence and first-person narrative. In a rhetorical analysis project, it would be up to you, the analyzer, to point out this move and associate it with a rhetorical strategy.
Rhetorical Appeals Misuse
When writers misuse logos, pathos, or ethos, arguments can be weakened. Above, we defined and described what logos, pathos, and ethos are and why authors may use those strategies. Sometimes, using a combination of logical, pathetic, and ethical appeals leads to a sound, balanced, and persuasive argument. It is important to understand, though, that using rhetorical appeals does not always lead to a sound, balanced argument. In fact, any of the appeals could be misused or overused. And when that happens, arguments can be weakened.
To see what a misuse of logical appeals might consist of, see Logical Fallacies.
To see how authors can overuse emotional appeals and turn-off their target audience, visit the following link from WritingCommons.org : Fallacious Pathos .
To see how ethos can be misused or used in a manner that may be misleading, visit the following link to WritingCommons.org : Fallacious Ethos
Attributions
“Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined” by Melanie Gagich, Emilie Zickel is licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0
Writing Arguments in STEM Copyright © by Jason Peters; Jennifer Bates; Erin Martin-Elston; Sadie Johann; Rebekah Maples; Anne Regan; and Morgan White is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Feedback/errata.
Comments are closed.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.2: Logos, Ethos, and Pathos
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 118683

- Tanya Long Bennett
- University of North Georgia via GALILEO Open Learning Materials
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
In order to persuade a particular audience of a particular point, a writer makes decisions about how best to convince the reader. Aristotle recognized three basic appeals that a writer (or orator) should consider when presenting an argument: logos, ethos, and pathos .
Consider this hypothetical plea from Zach to his father: “Dad, could you loan me money for gas until I get my paycheck at the end of the week? If you do, I’ll be able to haul your junk pile to the dump as well as drive myself back and forth to work. I’ll pay you back as soon as I get my check!”
Logos , a Latin term referring to logic, appeals to the reader’s intellect. As readers, we test arguments for their soundness. Does the writer make false assumptions? Are there gaps in the argument? Does the writer leap to conclusions without sufficient evidence to back up his claims? As writers, it is our job to build a solid, well-explained, sufficiently supported argument. In academic texts, logos is usually considered the most important appeal since scholarly research is supposed to be objective and thus more dependent on logic than on emotion (pathos) or on the reputation of the scholar (ethos). What about Zach’s argument above? Essentially, he asserts that a loan from his father would benefit both Zach and his dad. Does the argument seem sound? We do not know why Zach is short on cash this week—his father may be aware that Zach spent most of last week’s check on the newest iPhone, so he does not have enough to cover his gas this week. Thus, there may be factors that undermine Zach’s implication that his request is motivated by responsibility. However, he does offer evidence that the loan will allow him to fulfill his obligations.
Logic is based on either inductive or deductive reasoning. Understanding these types of logic can help us test the soundness of arguments, both our own and those of others.
Inductive Reasoning
You likely use inductive reasoning every day. By this kind of logic, we form conclusions based on samples. Lab experiments, for example, must be repeatable in order for scientists to gather a convincing amount of data to prove a hypothesis. If a scientist hypothesizes that addiction to a particular drug causes a certain, predictable behavior, the experiment must be carefully controlled, and must be repeated hundreds of times in order to prove that the behavior is consistently associated with the addiction and that other possible causes of that behavior have been ruled out. If we observe enough examples of an event occurring under similar circumstances, we can employ inductive reasoning to draw a conclusion about the pattern. For example, if we pay less each time we buy apples at Supermart than when we purchase apples at Pete’s Grocery, we will likely conclude, inductively, that apples are less expensive at Supermart.
Literary argument is often based on inductive reasoning. Here are two illustrations of such reasoning:
- In Robert Frost’s sonnet “Design,” the color white is used ironically to suggest that only a devious designer would clothe the universe’s evil in so much beauty. The “dimpled spider, fat and white”; the “white heal-all” flower that “hold[s] up” the moth for the spider’s feast; and the rhyming of “blight” with “white” and “right” work together to generate the poem’s disturbing sense that the innocence implied in the whiteness of the natural scene is deceptive.
As powerful evidence of the irreversible destruction of war, Hemingway’s The Sun Also Rises presents Jake Barnes’s struggles to overcome the damage incurred during his service as a soldier in World War I. Jake’s difficulty coping with his injury, his tendency to self-medicate with alcohol, his inability to pray, and his failure to sustain an intimate relationship with another person all exemplify the terrible destruction inflicted on him by the war.
When writing a literary analysis essay, such as the paper that might develop from the second argument above, you will need to provide enough examples to support your assertion that the pattern you observed in the text does, indeed, exist.
Deductive Reasoning
Deductive reasoning, on the other hand, is drawing a conclusion based on a logical equation . It can be argued that we see deduction in its purest form in the context of scientific or mathematical reasoning. A logical equation of this sort is based on a proven assumption and/or clearly and inflexibly-defined terms. Commonly manifesting these conditions, computer programs accomplish tasks through deductive logic. For example, Mary, an art major who has completed 24 credit hours, cannot register for English 4500 . This statement is true because the university course enrollment system is governed by the following logic: Only English majors with 30 or more credit hours may register for English 4500. Students who have not officially declared as English majors and/or whose records do not exhibit completion of credit hours equal to or greater than 30 will be automatically prevented from registering for English 4500. Similarly, the following statement is based on deductive logic: Glyptol paint cannot be cleaned up with water only. This conclusion is based on the fact that Glyptol contains alkyds, which are not water soluble. Therefore, clean-up of any paint containing alkyds will require turpentine or another petroleum-based solvent.
Having examined deductive reasoning in its pure form, however, we can see that argument will rarely be required in such a context. Investigation may be required in order to determine the characteristic and/ or definition of a material, but once the facts are ascertained, scientists will not need to debate whether or not alkyds are water-soluble. Persuasion becomes relevant when the issue moves beyond proven facts. As we explore issues of ethics and values, logical reasoning can seem a bit mushy, yet rather than throw up their hands in abandonment of deductive reasoning, humanities scholars generally work hard to establish valid assumptions, or generally agreed-upon notions, that can be used to help humans move closer to reasonable, or logical, social and political beliefs and behaviors.
Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s famous fictional detective Sherlock Holmes is famous for employing deductive reasoning to solve mysteries. In “Five Orange Pips,” Holmes uses deductive reasoning to work as far as possible toward solving John Openshaw’s case, based on the facts Holmes and Watson have been given:
Now let us consider the situation and see what may be deduced from it. In the first place, we may start with a strong presumption that Colonel Openshaw had some very strong reason for leaving America. Men at his time of life do not change all their habits and exchange willingly the charming climate of Florida for the lonely life of an English provincial town. His extreme love of solitude in England suggests the idea that he was in fear of someone or something, so we may assume as a working hypothesis that it was fear of someone or something which drove him from America. As to what it was he feared, we can only deduce that by considering the formidable letters which were received by himself and his successors. Did you remark the postmarks of those letters?
Equations such as the ones being forwarded by Holmes, when seen in their complete form, comprise a three part logical statement called a syllogism .
The statement includes
- A general statement , or major premise : Middle-aged men do not readily embrace change.
- A minor premise : Colonel Openshaw is a middle-aged man.
- And a conclusion : Colonel Openshaw would not have changed his circumstances without a strong impetus.
Although some might argue that Holmes came to the major premise through inductive reasoning (observing the behavior of many, many middle-aged men), in the above passage, he asserts the major premise as the basis for his deductive logical equation proving that Colonel Openshaw must have had a strong impetus for leaving America. If we agree with Holmes’s premise , we are likely to trust his conclusion .
Here is a more questionable logical equation, considered by the characters of Stephen Crane’s short story “The Open Boat”:
If I am going to be drowned—if I am going to be drowned—if I am going to be drowned, why, in the name of the seven mad gods who rule the sea, was I allowed to come thus far and contemplate sand and trees? Was I brought here merely to have my nose dragged away as I was about to nibble the sacred cheese of life? It is preposterous. If this old ninny-woman, Fate, cannot do better than this, she should be deprived of the management of men’s fortunes. She is an old hen who knows not her intention. If she has decided to drown me, why did she not do it in the beginning and save me all this trouble. The whole affair is absurd.... But, no, she cannot mean to drown me. She dare not drown me. She cannot drown me. Not after all this work.
The following syllogism reflects the men’s attitude:
- Major premise: The world is just and reasonable.
- Minor premise: All of the men in the life-boat are good men and are working hard to survive.
- Conclusion: All of the men should survive.
You can see in the latter example that some times syllogisms are flawed, or illogical. Most of us doubt, at least some of the time, that the universe is indeed just and reasonable, at least by human standards. If it is not just, then the men’s conclusion that they ought to survive may be incorrect.
The occurrence of flawed logic is most problematic when we find an equation in its incomplete form: an enthymeme . If we consider the major premise as the underlying assumption, and recognize that this premise often goes unstated, we see that the enthymeme is a type of elliptical statement that sometimes “leaps” to its conclusion unreasonably. Consider the following examples:
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
- Enthymeme: Sarah, don’t eat that beef; it came from Bob’s Café.
- Major premise: All food from Bob’s Café is bad.
- Minor premise: That beef came from Bob’s Café.
- Conclusion: That beef is bad.
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
- Enthymeme: Lisa Harmon would be a good hire for our company; she has a degree from Harvard University.
- Major premise: Anyone with a degree from Harvard University would be a good employee for our company.
- Minor premise: Lisa has a degree from Harvard University.
- Conclusion: Lisa would be a good employee for our company.
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
- Enthymeme: Kill Bill is a chick flick.
- Major premise: Any movie that features a female protagonist is a chick flick.
- Minor premise: Kill Bill features a female protagonist.
- Conclusion: Kill Bill is a chick flick.
As you test the major premises above, how do they fare? Are they true? If a writer asserted the above enthymemes, would you, as the reader, agree with the major premise of each? Why or why not? What is the danger of reading (or hearing) only the enthymeme and not testing the underlying (unspoken) assumption which would complete the syllogism?
Logical Fallacies
Whether an assertion is based on inductive or deductive reasoning, when we test a claim, it helps to know about the following logical fallacies commonly found in weak arguments:
Bandwagon Argument
This claim encourages us to agree with a particular opinion because “everyone else agrees with it.” Frost’s “Design” implies an evil creator; several important critics agree that this is Frost’s message . Does the text itself support this theory?
Single Cause
This kind of argument suggests that a problem results from one particular cause when the causes may actually be complex and multiple: In The Great Gatsby, it is Gatsby’s decision to pursue a decadent woman like Daisy that leads to his downfall. Are there any other factors that might lay the groundwork for the tragic events of the novel?
This type of statement implies that there are only two options: Roethke’s poem “My Papa’s Waltz” either points to abuse, or it emphasizes the love between father and son. Is it possible for both to be true?
Slippery Slope
In this kind of argument, the writer warns that one step in the “wrong” direction will result in complete destruction: If the instructor curves the grade for this assignment, students will expect a curve on all assignments, and they will lose their motivation to work hard toward their own learning. Is the compromised course grade inevitable as the result of one curved assignment grade? A similar argument is the following: If the government gives welfare to poor citizens, those citizens will become permanently dependent on “handouts” and will lose their motivation to work for a living.
In this approach, the writer holds up an extreme and usually easyto-defeat example of the opposition as the general representative of that opposition instead of considering the opposition’s most reasonable arguments. Senator Jill Campbell was convicted of bribery, confirming that politicians can’t be trusted . Are there any ethical politicians? If so, this conclusion is logically flawed.
False Cause
Here, the writer offers a cause that seems linked to the problem but does not actually establish the causal relationship. T he university cut three class days due to snow, and now I’m failing history; therefore, the university should have added three extra days to the semester.
As you listen to and read arguments forwarded by others, test the claims carefully to ensure that you are not accepting an illogical line of thinking. Also, carefully review your own arguments to avoid forwarding faulty logic yourself!
Ethos, an appeal based on the credibility of the author, can affect a reader’s willingness to trust the writer. This credibility is often generated by the author’s apparent ethics. If the reader perceives that she shares important values with the writer, the door of communication opens wider than if the writer and reader seem to lack common values. Reflecting back to Zach’s request for a loan from his father, Zach does remind his father subtly that the loan will allow him to work, both at his job and at home. This respect for work is likely a value held by Zach’s father, so it becomes important common ground for the argument.
Consider again the previously presented thesis about Hemingway’s The Sun Also Rises :
Hopefully, the writer, let’s call him Bill, will go on to support, with evidence from the text, the claim that the portrayal of Jake’s struggles promotes anti-war sentiment. Beyond the logical soundness of the argument, however, the reader will inevitably react on a personal level to the values underlying the statement. Bill, in his decision to focus on this aspect of the text, seems to appreciate the anti-war stance he observes in the novel. If the reader is sympathetic to this position, she may be more open to Bill’s argument as a whole.
Aside from the writer’s ethics, ethos can also be generated by the author’s credibility, which is usually based on (1) the ability to forward a logical argument (hence, ethos can be affected by logos!), (2) thoroughness of significant research, and (3) credentials proving the writer’s expertise. If Bill is not an expert in the field of literary studies yet, but is a sophomore English Major, he may have no recognizable credentials to persuade the reader in his favor. But if he has been careful and thorough in his presentation of evidence (passages and examples from the text itself) and has considered (and possibly integrated) material from scholarly articles and books to help define and support his argument, his ethos is likely to be strong.
What about pathos , or the appeal to the reader’s emotions? Certainly, Zach’s father will be affected by his feelings for his son Zach as he considers whether to loan Zach the money for gas, but what about in a more academic or professional context? Even though the goal of an academic writer is to approach a research topic as objectively as possible, even scholars are people, and people are emotional creatures. Bill’s awareness of this fact leads him to choose some particularly poignant passages from Hemingway’s novel to support his point:
The damage caused by Jake’s war experience is not only physical but also psychological. For example, after looking in the mirror at the scar from his wound, he lies in bed unable to sleep:
I lay awake thinking and my mind jumping around. Then I couldn’t keep away from it, and I started to think about Brett and all the rest of it went away. I was thinking about Brett and my mind stopped jumping around and started to go in sort of smooth waves. Then all of a sudden I started to cry. Then after a while it was better and I lay in bed and listened to the heavy trams go by and way down the street, and then I went to sleep. (Hemingway 31)
Although Jake makes a convincing show in public of dealing with his trauma, this passage reveals the challenge he faces in trying to cope.
Although Bill’s readers will critically consider whether this passage logically supports Bill’s claim, it is likely that they will also react emotionally to Jake’s anguish, thus reinforcing the persuasive effectiveness of Bill’s argument.
Rhetorical Analysis Sample Essay
Harriet Clark
Ms. Rebecca Winter
13 Feb. 2015
Not Quite a Clean Sweep: Rhetorical Strategies in
Grose's "Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier”
A woman’s work is never done: many American women grow up with this saying and feel it to be true. 1 One such woman, author Jessica Grose, wrote “Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier,” published in 2013 in the New Republic, 2 and she argues that while the men recently started taking on more of the childcare and cooking, cleaning still falls unfairly on women. 3 Grose begins building her credibility with personal facts and reputable sources, citing convincing facts and statistics, and successfully employing emotional appeals; however, toward the end of the article, her attempts to appeal to readers’ emotions weaken her credibility and ultimately, her argument. 4
In her article, Grose first sets the stage by describing a specific scenario of house-cleaning with her husband after being shut in during Hurricane Sandy, and then she outlines the uneven distribution of cleaning work in her marriage and draws a comparison to the larger feminist issue of who does the cleaning in a relationship. Grose continues by discussing some of the reasons that men do not contribute to cleaning: the praise for a clean house goes to the woman; advertising and media praise men’s cooking and childcare, but not cleaning; and lastly, it is just not fun. Possible solutions to the problem, Grose suggests, include making a chart of who does which chores, dividing up tasks based on skill and ability, accepting a dirtier home, and making cleaning more fun with gadgets. 5
Throughout her piece, Grose uses many strong sources that strengthen her credibility and appeal to ethos, as well as build her argument. 6 These sources include, “sociologists Judith Treas and Tsui-o Tai,” “a 2008 study from the University of New Hampshire,” and “P&G North America Fabric Care Brand Manager, Matthew Krehbiel” (qtd. in Grose). 7 Citing these sources boosts Grose’s credibility by showing that she has done her homework and has provided facts and statistics, as well as expert opinions to support her claim. She also uses personal examples from her own home life to introduce and support the issue, which shows that she has a personal stake in and first-hand experience with the problem. 8
Adding to her ethos appeals, Grose uses strong appeals to logos, with many facts and statistics and logical progressions of ideas. 9 She points out facts about her marriage and the distribution of household chores: “My husband and I both work. We split midnight baby feedings ...but ... he will admit that he’s never cleaned the bathroom, that I do the dishes nine times out of ten, and that he barely knows how the washer and dryer work in the apartment we’ve lived in for over eight months.” 10 These facts introduce and support the idea that Grose does more household chores than her husband. Grose continues with many statistics:
[A]bout 55 percent of American mothers employed full time do some housework on an average day, while only 18 percent of employed fathers do. ... [W]orking women with children are still doing a week and a half more of “second shift” work each year than their male partners. ... Even in the famously gender-neutral Sweden, women do 45 minutes more housework a day than their male partners. 11
These statistics are a few of many that logically support her claim that it is a substantial and real problem that men do not do their fair share of the chores. The details and numbers build an appeal to logos and impress upon the reader that this is a problem worth discussing. 12
Along with strong logos appeals, Grose effectively makes appeals to pathos in the beginning and middle sections. 13 Her introduction is full of emotionally-charged words and phrases that create a sympathetic image; Grose notes that she “was eight months pregnant” and her husband found it difficult to “fight with a massively pregnant person.” 14 The image she evokes of the challenges and vulnerabilities of being so pregnant, as well as the high emotions a woman feels at that time effectively introduce the argument and its seriousness. Her goal is to make the reader feel sympathy for her. Adding to this idea are words and phrases such as, “insisted,” “argued,” “not fun,” “sucks” “headachey,” “be judged,” “be shunned” (Grose). All of these words evoke negative emotions about cleaning, which makes the reader sympathize with women who feel “judged” and shunned”—very negative feelings. Another feeling Grose reinforces with her word choice is the concept of fairness: “fair share,” “a week and a half more of ‘second shift’ work,” “more housework,” “more gendered and less frequent.” These words help establish the unfairness that exists when women do all of the cleaning, and they are an appeal to pathos, or the readers’ feelings of frustration and anger with injustice. 15
However, the end of the article lacks the same level of effectiveness in the appeals to ethos. 16 For example, Grose notes that when men do housework, they are considered to be “’enacting “small instances of gender heroism,” or ‘SIGH’s’—which, barf.” 17 The usage of the word “barf” is jarring to the reader; unprofessional and immature, it is a shift from the researched, intelligent voice she has established and the reader is less likely to take the author seriously. This damages the strength of her credibility and her argument. 18
Additionally, her last statement in the article refers to her husband in a way that weakens the argument. 19 While returning to the introduction’s hook in the conclusion is a frequently-used strategy, Grose chooses to return to her discussion of her husband in a humorous way: Grose discusses solutions, and says there is “a huge, untapped market ... for toilet-scrubbing iPods. I bet my husband would buy one.” 20 Returning to her own marriage and husband is an appeal to ethos or personal credibility, and while that works well in the introduction, in the conclusion, it lacks the strength and seriousness that the topic deserves and was given earlier in the article. 21
Though Grose begins the essay by effectively persuading her readers of the unfair distribution of home-maintenance cleaning labor, she loses her power in the end, where she most needs to drive home her argument. Readers can see the problem exists in both her marriage and throughout the world; however, her shift to humor and sarcasm makes the reader not take the problem as seriously in the end. 22 Grose could have more seriously driven home the point that a woman’s work could be done: by a man. 23
Works Cited
Grose, Jessica. “Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier.” New Republic. The New Republic, 19 Mar. 2013. Web. 28 Mar. 2014.
- Article author's claim or purpose
- Summary of the article's main point in the second paragraph (could also be in the introduction)
- Third paragraph begins with a transition and topic sentence that reflects the first topic in the thesis
- Quotes illustrate how the author uses appeals to ethos
- Analysis explains how the quotes show the effective use of ethos as noted in the thesis
- Transition and topic sentence about the second point from the thesis
- Quote that illustrates appeals to logos
- Analysis explains how the quotes show the effective use of logos, as noted in the thesis
- Transition and topic sentence about the third point from the thesis
- Quotes that illustrate appeals to pathos
- Analysis explains how the quotes show the effective use of pathos, as noted in the thesis
- Transition and topic sentence about fourth point from the thesis
- Quote illustrates how the author uses appeal to ethos
- Analysis explains how quote supports thesis
- Transition and topic sentence about fourth point from thesis
- Conclusion returns to the ideas in the thesis and further develops them
- Last sentence returns to the hook in the introduction
Learn more about the " Rhetorical Analysis Graphic Organizer ."
Learn more about " Pathos, Logos, and Ethos ."
Understand The Difference Between Ethos, Pathos, And Logos To Make Your Point
- What Is Ethos?
- What Is Pathos?
- What Is Logos?
- Examples Of Each
- What Are Mythos And Kairos?
During an argument, people will often say whatever is necessary to win. If that is the case, they would certainly need to understand the three modes of persuasion, also commonly known as the three rhetorical appeals: ethos , pathos , and logos . In short, these three words refer to three main methods that a person can use to speak or write persuasively. As you’re about to find out, the modes of persuasion are important because a speaker who knows how to effectively use them will have a significant advantage over someone who doesn’t.
The terms ethos , pathos , and logos and the theory of their use can be traced back to ancient Greece to the philosophy of Aristotle . Aristotle used these three concepts in his explanations of rhetoric , or the art of influencing the thought and conduct of an audience. For Aristotle, the three modes of persuasion specifically referred to the three major parts of an argument: the speaker ( ethos ), the argument itself ( logos ), and the audience ( pathos ). In particular, Aristotle focused on the speaker’s character, the logic and reason presented by an argument, and the emotional impact the argument had on an audience.
While they have ancient roots, these modes of persuasion are alive and well today. Put simply, ethos refers to persuasion based on the credibility or authority of the speaker, pathos refers to persuasion based on emotion, and logos refers to persuasion based on logic or reason.
By effectively using the three modes of persuasion with a large supply of rhetorical devices, a speaker or writer can become a master of rhetoric and win nearly any argument or win over any audience. Before they can do that, though, they must know exactly what ethos , pathos , and logos mean. Fortunately, we are going to look closely at each of these three ideas and see if they are really as effective as they are said to be.
⚡️ Quick summary
Ethos , pathos , and logos are the three classical modes of persuasion that a person can use to speak or write persuasively. Specifically:
- ethos (character): known as “the appeal to authority” or “the appeal to credibility.” This is the method in which a person relies on their credibility or character when making an appeal or an argument.
- pathos (emotions): known as “the appeal to emotion.” Pathos refers to the method of trying to persuade an audience by eliciting some kind of emotional reaction.
- logos (logic): known as “the appeal to reason.” This method involves using facts and logical reasoning to support an argument and persuade an audience.
What is ethos ?
The word ethos comes straight from Greek. In Greek, ethos literally translates to “habit,” “custom,” or “character.” Ethos is related to the words ethic and ethical , which are typically used to refer to behavior that is or isn’t acceptable for a particular person.
In rhetoric, the word ethos is used to refer to the character or reputation of the speaker. As a rhetorical appeal, ethos is known as “the appeal to authority” or “the appeal to credibility.” When it comes to ethos , one important consideration is how the speaker carries themself and how they present themselves to the audience: Does it seem like they know what they are talking about? Do they even believe the words they are saying? Are they an expert? Do they have some experience or skills that tell us we should listen to them?
Ethos is important in rhetoric because it often influences the opinion or mood of the audience. If a speaker seems unenthusiastic, unprepared, or inexperienced, the audience is more likely to discount the speaker’s argument regardless of what it even is. On the other hand, a knowledgeable, authoritative, confident speaker is much more likely to win an audience over.
Ethos often depends on more than just the argument itself. For example, a speaker’s word choice, grammar, and diction also contribute to ethos ; an audience may react more favorably toward a professional speaker who has a good grasp of industry jargon and enunciates clearly versus a speaker who lacks the necessary vocabulary and fails to enunciate. Ethos can also be influenced by nonverbal factors as well, such as posture, body language, eye contact, and even the speaker’s choice of clothing. For example, a military officer proudly wearing their uniform bedecked with medals will go a long way to establishing ethos without them saying a single word.
Here as a simple example of ethos :
- “As a former mayor of this city, I believe we can solve this crisis if we band together.”
The speaker uses ethos by alerting the audience of their credentials and experience. By doing so, they rely on their reputation to be more persuasive. This “as a…” method of establishing ethos is common, and you have probably seen it used in many persuasive advertisements and speeches.
What are open-ended questions and how can you use them effectively? Find out here.
What is pathos ?
In Greek, pathos literally translates to “suffering, experience, or sensation.” The word pathos is related to the words pathetic , sympathy , and empathy , which all have to do with emotions or emotional connections. Aristotle used the word pathos to refer to the emotional impact that an argument had on an audience; this usage is still mainly how pathos is used in rhetoric today.
As a rhetorical appeal, pathos is referred to as “the appeal to emotion.” Generally speaking, an author or speaker is using pathos when they are trying to persuade an audience by causing some kind of emotional reaction. When it comes to pathos , any and all emotions are on the table: sadness, fear, hope, joy, anger, lust, pity, etc.
As you probably know from your own life, emotions are a powerful motivating factor. For this reason, relying on pathos is often a smart and effective strategy for persuading an audience. Both positive and negative emotions can heavily influence an audience: for example, an audience will want to support a speaker whose position will make them happy, a speaker who wants to end their sadness, or a speaker who is opposed to something that makes them angry.
Here is a simple example of pathos :
- “Every day, the rainforests shrink and innocent animals are killed. We must do something about this calamitous trend before the planet we call our home is damaged beyond repair.”
Here, the author is trying to win over an audience by making them feel sad, concerned, or afraid. The author’s choice of words like “innocent” and “calamitous” enforce the fact that they are trying to rely on pathos .
What is logos ?
In Greek, the word logos literally translates to “word, reason, or discourse.” The word logos is related to many different words that have to do with reason, discourse, or knowledge, such as logic , logical , and any words that end in the suffixes -logy or -logue .
As a mode of persuasion and rhetorical appeal, logos is often referred to as “the appeal to reason.” If a speaker or author is relying on logos , they are typically reciting facts or providing data and statistics that support their argument. In a manner of speaking, logos does away with all of the bells and whistles of ethos and pathos and cuts to the chase by trying to present a rational argument.
Logos can be effective in arguments because, in theory, it is impossible to argue against truth and facts. An audience is more likely to agree with a speaker who can provide strong, factual evidence that shows their position is correct. On the flip side, an audience is less likely to support an argument that is flawed or entirely wrong. Going further, a speaker that presents a lot of supporting evidence and data to the audience is likely to come across as knowledgeable and someone to be listened to, which earns bonus points in ethos as well.
While Aristotle clearly valued an argument based on reason very highly, we know that logos alone doesn’t always effectively persuade an audience. In your own life, you have likely seen a rational, correct speaker lose an argument to a charismatic, authoritative speaker who may not have the facts right.
Here is a simple example of logos :
- “According to market research, sales of computer chips have increased by 300% in the last five years. Analysis of the industry tells us that the market share of computer chips is dominated by Asian manufacturers. It is clear that the Asian technology sector will continue to experience rapid growth for the foreseeable future.”
In this paragraph, the author is using data, statistics, and logical reasoning to make their argument. They clearly hope to use logos to try to convince an audience to agree with them.
Do you need persuading to take this quiz on identifying ethos, pathos, and logos? We think you’ll be a champion at it.
Examples of ethos , pathos , and logos
Ethos , pathos , and logos can all be employed to deliver compelling and persuasive arguments or to win over an audience. Let’s look at a variety of examples to see how different speakers and authors have turned to these modes of persuasion over the years.
“Come I to speak in Caesar’s funeral. He was my friend, faithful and just to me […] You all did see that on the Lupercal I thrice presented him a kingly crown, Which he did thrice refuse: was this ambition?” —Marc Antony, Julius Caesar by William Shakespeare
In this scene, Marc Antony is trying to win over the Roman people, so Shakespeare has Antony rely on ethos . Antony is establishing himself as both a person of authority in Rome (having the power to offer Caesar a crown) and an expert on Caesar’s true character (Antony was Caesar’s close friend and advisor).
“During the next five years, I started a company named NeXT, another company named Pixar, and fell in love with an amazing woman who would become my wife. Pixar went on to create the world’s first computer animated feature film, Toy Story , and is now the most successful animation studio in the world. In a remarkable turn of events, Apple bought NeXT, I returned to Apple, and the technology we developed at NeXT is at the heart of Apple’s current renaissance.” —Steve Jobs, 2005
Here, Steve Jobs is providing his background–via humblebrag – of being a major figure in several different highly successful tech companies. Jobs is using ethos to provide substance to his words and make it clear to the audience that he knows what he is talking about and they should listen to him.
Make Your Writing Shine!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
“Moreover, though you hate both him and his gifts with all your heart, yet pity the rest of the Achaeans who are being harassed in all their host; they will honour you as a god, and you will earn great glory at their hands. You might even kill Hector; he will come within your reach, for he is infatuated, and declares that not a Danaan whom the ships have brought can hold his own against him.” —Ulysses to Achilles, The Iliad by Homer
In this plea, Ulysses is doing his best to pile on the pathos . In one paragraph, Ulysses is attempting to appeal to several of Achilles’s emotions: his hatred of Hector, his infamous stubborn pride, his sympathy for civilians, and his desire for vengeance.
“I am not unmindful that some of you have come here out of great trials and tribulations. Some of you have come fresh from narrow jail cells. Some of you have come from areas where your quest—quest for freedom left you battered by the storms of persecution and staggered by the winds of police brutality.” —Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., 1963
In this excerpt from his “I Have A Dream” speech, King is using pathos to accomplish two goals at once. First, he is connecting with his audience by making it clear is aware of their plight and suffering. Second, he is citing these examples to cause sadness or outrage in the audience. Both of these effects will make an audience interested in what he has to say and more likely to support his position.
Dr. King’s “I Have A Dream” speech is recognizable and noteworthy for many reasons, including the rhetorical device he employs. Learn about it here.
“Let it be remembered how powerful the influence of a single introduced tree or mammal has been shown to be. But in the case of an island, or of a country partly surrounded by barriers, into which new and better adapted forms could not freely enter, we should then have places in the economy of nature which would assuredly be better filled up if some of the original inhabitants were in some manner modified; for, had the area been open to immigration, these same places would have been seized on by intruders. In such case, every slight modification, which in the course of ages chanced to arise, and which in any way favoured the individuals of any of the species, by better adapting them to their altered conditions, would tend to be preserved; and natural selection would have free scope for the work of improvement.” —Charles Darwin, On the Origin of the Species , 1859
In this passage, Darwin is using logos by presenting a rational argument in support of natural selection. Darwin connects natural selection to established scientific knowledge to argue that it makes logical sense that animals would adapt to better survive in their environment.
“I often echo the point made by the climate scientist James Hansen: The accumulation of carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gases—some of which will envelop the planet for hundreds and possibly thousands of years—is now trapping as much extra energy daily as 500,000 Hiroshima-class atomic bombs would release every 24 hours. This is the crisis we face.” —Al Gore, “The Climate Crisis Is the Battle of Our Time, and We Can Win,” 2019
In this call to action, Al Gore uses logos to attempt to convince his audience of the significance of climate change. In order to do this, Gore both cites an expert in the field and provides a scientifically accurate simile to explain the scale of the effect that greenhouse gases have on Earth’s atmosphere.
What are mythos and kairos ?
Some modern scholars may also use terms mythos and kairos when discussing modes of persuasion or rhetoric in general.
Aristotle used the term mythos to refer to the plot or story structure of Greek tragedies, i.e., how a playwright ordered the events of the story to affect the audience. Today, mythos is most often discussed as a literary or poetic term rather than a rhetorical one. However, mythos may rarely be referred to as the “appeal to culture” or the “appeal to myth” if it is treated as an additional mode of persuasion. According to this viewpoint, a speaker/writer is using mythos if they try to persuade an audience using shared cultural customs or societal values.
A commonly cited example of mythos is King’s “I Have a Dream” speech quoted earlier. King says:
“When the architects of our republic wrote the magnificent words of the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence, they were signing a promissory note to which every American was to fall heir. This note was a promise that all men—yes, black men as well as white men—would be guaranteed the ‘unalienable rights’ of ‘life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness.’ ”
Throughout the speech, King repeatedly uses American symbols and American history ( mythos ) to argue that all Americans should be outraged that Black Americans have been denied freedom and civil rights.
Some modern scholars may also consider kairos as an additional mode of persuasion. Kairos is usually defined as referring to the specific time and place that a speaker chooses to deliver their speech. For written rhetoric, the “place” instead refers to the specific medium or publication in which a piece of writing appears.
Unlike the other modes of persuasion, kairos relates to the context of a speech and how the appropriateness (or not) of a setting affects how effective a speaker is. Once again, King’s “I Have a Dream” speech is a great example of the use of kairos . This speech was delivered at the steps of the Lincoln Memorial during the 100th anniversary of the Emancipation Proclamation at the end of the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. Clearly, King intended to use kairos to enhance the importance and timeliness of this landmark speech.
Make your communication as smooth as can be by learning about filler words and when you should, and shouldn't, use them.

Ways To Say
Synonym of the day

Ethos, Pathos & Logos — Definition and Examples of Persuasive Advertising Techniques
- What is Pathos
- What is Logos
- What is Telos
- What is Kairos
- What is Ethos
- Ethos, Pathos & Logos
- What is an EPK
- What is a Creative Director
- What is Branded Content
- What is a Creative Brief
- How to Pitch a TV Show Like a Pro
- How Does Rotten Tomatoes Work?
- How to Make a Movie Poster
- The Filmmaker’s Guide to The Clio Advertising Awards
- A Complete Guide To The Funniest Commercials
- How to Make a Commercial
- How to Develop Your Brand
- Complete Guide to Advertising on Instagram
- How Does Instagram Promotion Work and Is It Worth It?
- How Can You Kickstart Your Social Media Advertising?
- Small Business Advertising Ideas from LeBron James Commercials
- How To Create a Successful Branded Content Campaign
- How and Why To Make Facebook Video Ads That Work
- How to Make a Commercial People Will Actually Share
- Video Branding Strategies to Get More Followers Right Now
- Social Media and Digital Communications for Successful Short Films
- Digital Advertising Trends
- Most Inspiring Ads
- Best Movie Taglines
- Best Marketing and Advertising Campaigns
- Best Creative Brief Template
- Best Explainer Video Trends for Your Brand
E thos, pathos and logos are techniques of persuasion that form the rhetorical triangle. A compelling argument, sales pitch, speech, or commercial ideally uses elements of all three strategies. We’ll show you how to employ each of the techniques and present some awesome examples along the way.
Ethos, Pathos and Logos: How to Create Persuasive Ads
Ethos, Pathos, Logos, Definition
The rhetorical triangle.
Rhetoric is a type of communication a writer or speaker uses to persuade, inform or motivate. We can see rhetoric everywhere — politics, law, advertising, creative writing, and even our everyday conversations.
Rhetorical devices include irony , metaphor , hyperbole and many other techniques writers and speakers employ to great effect.
A subset of these devices are known as rhetorical appeals , often attributed to Aristotle, and include: ethos , pathos and logos .
This is also known as the Rhetorical Triangle and we still depend on it today.
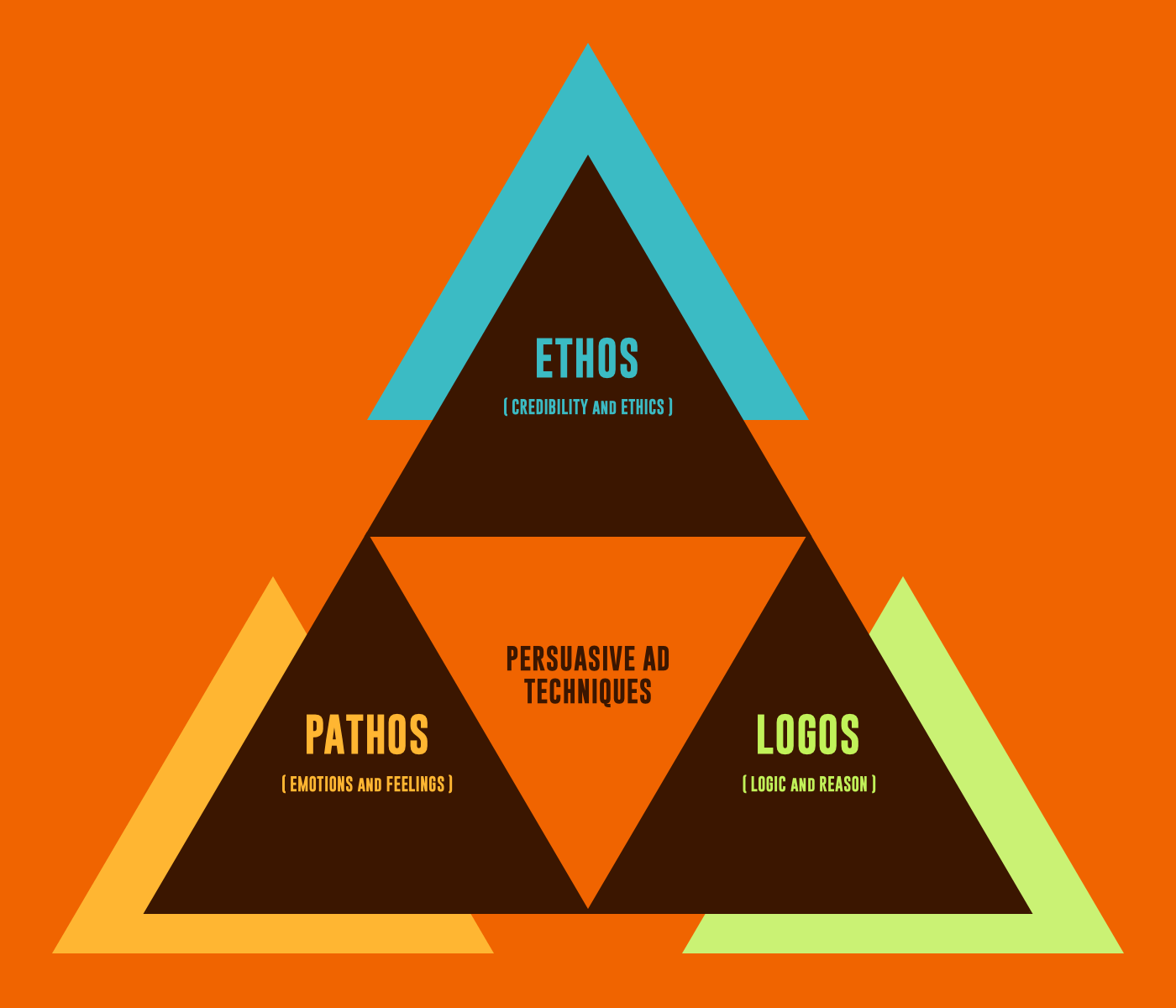
Ethos, pathos and logos are the three categories of persuasive advertising techniques
Each category invokes a different appeal between speaker and audience.
Ethos calls upon the ethics, or what we'd call the values, of the speaker. Pathos elicits emotions in the audience. Finally, logos puts logic into play by using evidence and facts.
Good persuasive advertising technique is when you balance all three.
But using ethos, pathos and logos in commercials sometimes means featuring one advertising technique prominently.
Learn More Logos Ethos and Pathos
Comparing other techniques.
There are many types of rhetorical strategies. To get a full picure on how they work together, or when to use which rhetorical strategies, explore the full guide below.
Everything About Rhetorical Appeals
Basics & terminology, appeal to credibility , appeal to emotion, appeal to logic, appeal to purpose, appeal to timeliness.
Each of these rhetorical strategies can be effective in its own way. When combined, their potential effects grow exponentially. To fully understand the power of persusaion, these are the tools you need.
ETHOS DEFINITION
What is ethos.
Ethos is the persuasive technique that appeals to an audience by highlighting credibility. Ethos advertisement techniques invoke the superior “character” of a speaker, presenter, writer, or brand.
Ethos examples aim to convince the audience that the advertiser is reliable and ethical. It’s easier to make a decision when someone you respect signs off on it, right? This is broadly the function of ethos in commercials.
When an esteemed public figure endorses a product, it validates it to the end consumer. An ethos advertisement plays off the consumer’s respect for a given spokesperson.
Through that respect, the spokesperson appears convincing, authoritative and trustworthy enough to listen to. Of the types of persuasive techniques in advertising, ethos is best used to unlock trust.
USE OF ETHOS IN ADVERTISING
How is ethos used in advertising.
So what does ethos mean?
It’s all about credibility. Famous people enjoy a high status in our society. So they’re the ones selling products to us — whether or not they have product-specific expertise.
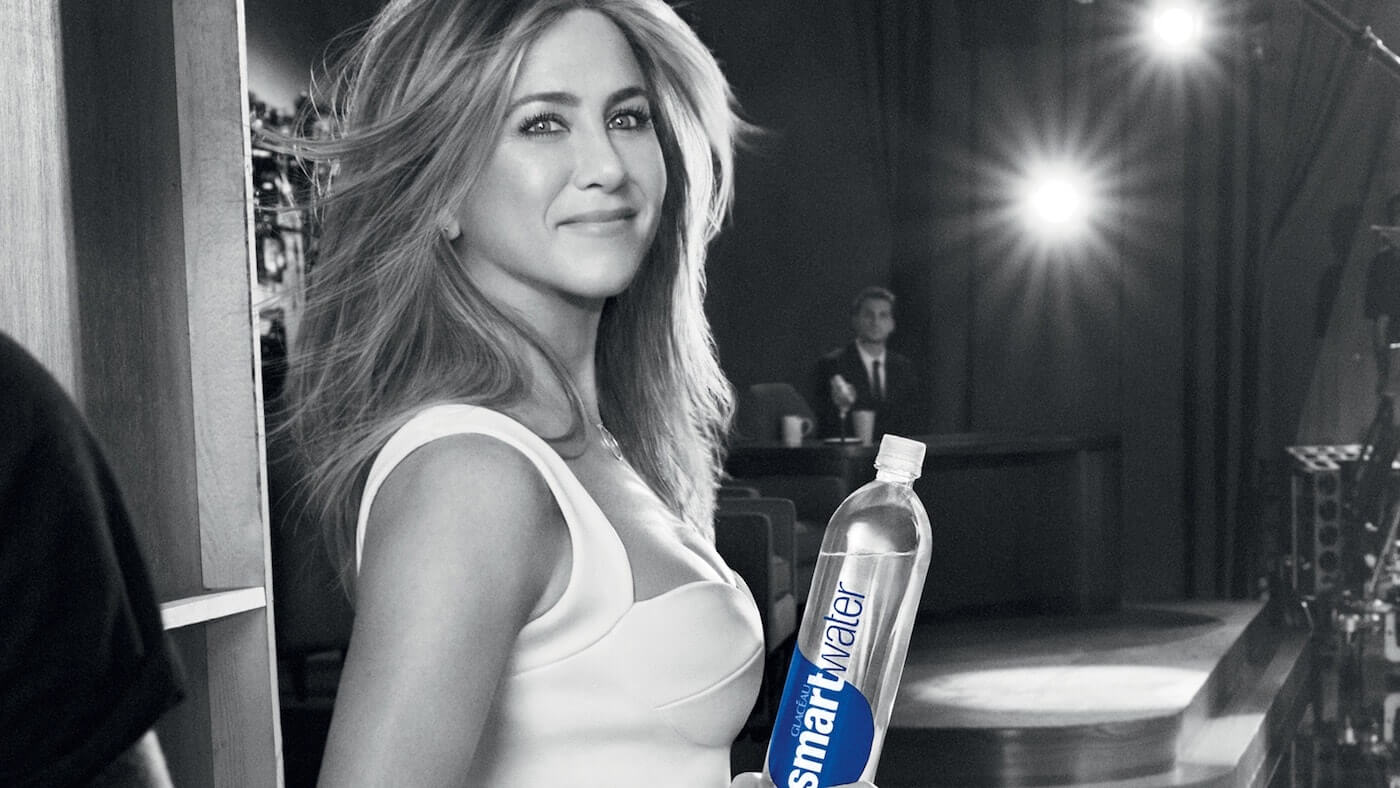

Example of ethos in advertising: Jennifer Aniston in a campaign for Glaceau Smart Water
For example, an Infiniti commercial featured Steph Curry. Even though he’s not known for his taste in vehicles, his stature validates the product.
This is ethos in commercials at work.
Example of ethos in commercials: Steph Curry in a recent spot for Infiniti
Ethos rhetoric is also invoked to tie a brand to fundamental rights.
Brands build trust with their audience when they stand with an important cause. Anheuser-Busch illustrated this in their “Born the Hard Way” ad.
Ethos examples: This ethos advertisement by Anheuser-Busch underscores the value of multiculturalism
This spot focuses on the origin story of Anheuser-Busch’s founders.
It shows Busch’s turbulent immigration from Germany to St. Louis, and speaks to the importance of immigration and multiculturalism.
This is how ethos rhetoric is used in advertising.
Of the many types of persuasive advertising techniques in advertising, ethos is best for playing up the strength of a brand or spokesperson’s character.
ETHOS EXAMPLE IN COMMERCIALS
Ethos advert case study.
If you want a really strong example of ethos that also has a pretty funny meta quality to it, check out the shot list for this Heineken spot. See how many times they use foreground elements and OTS shots in this spot:
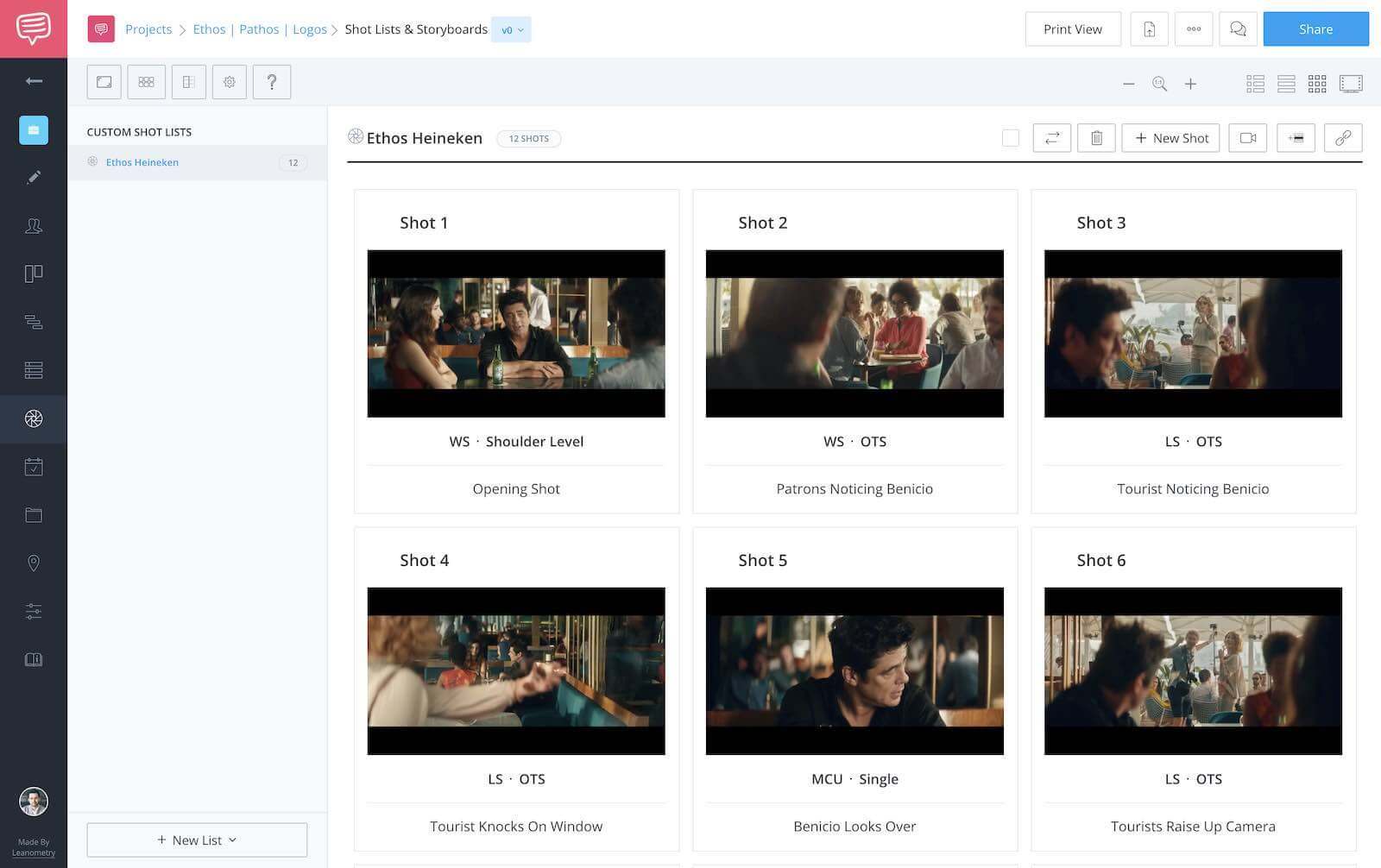
Ethos Examples • Shot Listed in StudioBinder
This Heineken commercial shows famous actor Benicio Del Toro at the bar enjoying a Heineken. Benicio chats about how both he, and Heineken, are world famous and instantly recognizable.
Then, a pair of goofy tourists spot him in the bar, and they call out for him to pose for a photo, but... they actually think he's Antonio Banderas.
Ethos Example in Heineken Commercial
This commercial not only uses ethos as a way to tie the celebrity of Benicio to the celebrity of Heineken, but it uses humor and the bold faced usage of ethos to make fun of the brand, people, and fame.
THE "PLAIN FOLKS" PERSUASIVE ADVERTISING TECHNIQUE
How is "plain folks" used in ads.
Ethos rhetoric often employs imagery of everyday, ordinary people.
Known as the Plain Folks persuasive advertising technique, in this approach a spokesperson or brand appears as an Average Joe to feel common and sensible. In doing so, they appear concerned and cut from the same cloth as you.
This approach is very common in political ads. Consider the “Family Strong” ad from Hillary Clinton’s 2016 presidential campaign.
Ethos Examples: Hillary Clinton underscores the “Plain Folks” definition in her campaign videos.
Despite her status and wealth, Clinton draws on imagery of her family and upbringing to make her feel more relatable. In this way, “Plain” folks is propaganda and also a logical fallacy.
But it’s also an effective and persuasive advertising technique.
Of the types of persuasive techniques in advertising, Plain Folks aligns your brand with the values of the everyday consumer.
Related Posts
- Creative Digital Advertising Trends →
- Steps to Make a Persuasive Commercial →
- Learn: How to Make a Storyboard in 9 Steps →
Pathos DEFINITION
What is pathos.
Pathos is persuasive technique that try to convince an audience through emotions. Pathos advertisement techniques appeal to the senses, memory, nostalgia, or shared experience. Pathos examples pull at the heartstrings and make the audience feel.
A quick way to appeal to a viewer’s emotions? A cute animal. A devastated family. A love story. Overcoming great odds. An inspirational song and imagery. A good zinger.
Emotions create responses and, in our increasingly consumer-driven culture, the response is to buy something. Pathos appeals to an audience’s basic emotions like joy, fear, and envy. All are easily triggered in many ways.
So what is pathos?
Well, it's a model enjoying a refreshing Coke. Or a frustrated infomercial character desperate for a better remedy. And "tired" of the "same old blah-blah-blah."
The many different pathos advertisement examples not only evoke your feelings but anticipate your responses too. If you want to explore pathos in advertising, language is the best place to start.
Because the words we hear and read trigger specific feelings. Positive words conjure feelings of love, excitement and wonder.

What is pathos? Cutting to the emotional core, really
Look at how General Mills and Cheerios achieved this in their “Good Goes Round” campaign.
Example of pathos: This Cheerios pathos advertisement injects good vibes with positive words
We see sunshine, smiles and bright colors while we hear the words “good goes around.” It invites positivity and encourages us to associate Cheerios accordingly.
On the other hand, pathos advertisements can also employ unpleasant emotions like fear and worry just as effectively.
Pathos examples: this somber pathos advertisement says don’t let heart disease happen to you
This ad by the British Heart Foundation underscores the dangers of heart disease. As the spot unfolds, you start to realize that the narrator suddenly died at her sister’s wedding.
Her tragic story encourages you to not let it happen to you.

Pathos examples: BMW warns against drinking and driving in this pathos advertisement example
Pathos example in commercials, pathos advert case study.
If you want a really strong example of pathos is an advertisement, check out this shot list from a particularly emotional Zillow spot. Notice how the shots on the son are often singles and medium close-ups :
Pathos Examples • Shot Listed in StudioBinder
This Zillow commercial shows a father and son who have just suffered the terrible loss of their wife/mother. The father tries to cheer his son up by finding a new home, one preferably near the boy's grandparents.
The son seems disinterested, but then the father finds his son and the family dog looking up at the stars, one of which is particularly bright. The son decides that the star is his mother, looking down on him.
That gives the father an idea:
Pathos example in Zillow Commercial
The father searches on Zillow, finds a home, and buys it. We then learn that the home is not only close to the grandparents, but it also has a skylight in the son's room, allowing him to see his Mother's star at night.
This commercial uses the emotions of the father, the son, the grandparents, and of course the viewer to suggest that Zillow is the type of website that can balm grief through its functionality.
USE OF PATHOS IN ADVERTISING
The appeal of pathos in advertising.
Sex appeal is of course also hugely successful among the pathos advertising techniques. Open any Cosmopolitan magazine and you’ll find scantily clad models, muscular men and sexual innuendo.
Although the common expression “sex sells” has been debated, sexually provocative ads do leave a lasting impression. Mr. Clean , for example, spiced up their eponymous mascot for comedic effect.
Pathos Examples: This Mr. Clean pathos advertisement gave their mascot a sexy upgrade
Their brawny Mr. Clean upgrade wears tight clothes and turns mopping the floor into something more... sensual?
Humor, patriotism and snob appeal are also all common in pathos advertisement examples. The pathos definition even extends to nostalgia and the strategic use of music in ads.
Pathos Examples: The pathos definition extends to evoking emotions with music ... even *NSYNC
The bandwagon advertising technique, what is the "bandwagon advertising".
“Bandwagon advertising” is commonly categorized under pathos advertisement examples. While it may sound unfamiliar, you're probably pretty familiar with it. It creates that impression that using certain product will put you on the “winning team.” It adheres to the pathos definition because it plays off your fear... of being left out.
Old Spice used this in their “The Man Your Man Could Smell Like” spot.
Bandwagon advertising: to be The Man Your Man Could Smell Like, you buy Old Spice
In its comical way, it puts pressure on men to smell as good as the Old Spice Guy. Like the “Plain Folks” technique, Bandwagon advertising is a very popular form of propaganda.
Of the persuasive advertising techniques, “Bandwagon” puts your brand on the right side of popular opinion. Remember the "Be like Mike" Ads?
Pathos example: Talk about putting the consumer on the "winning team"
- Learn from the Best Marketing and Ad Campaigns →
- Stock Video Sites That’ll Make Your Clients Happy →
- Storyboard your video with StudioBinder →
LOGOS DEFINITION
What is logos.
Logos is the persuasive technique that aims to convince an audience by using logic and reason. Also called “the logical appeal,” logos examples in advertisement include the citation of statistics, facts, charts, and graphs.

Logos Examples: This Samsung ad puts the Logos persuasive advertising technique to work
Ever told someone to “listen to reason” during an argument? This is what logos does. The best logos advertisement examples are when a speaker appeals to logic. Statistics, surveys, facts, and historical data can make a product seem like a more reasonable decision. Whether the data is sound or not is another story.
LOGOS EXAMPLE IN COMMERCIALS
Logos advert case study.
If you want a really strong example of logos is an advertisement, check out this shot list from a recent Nissan Commercial. You'll notice how the camera angles and shot size change when the "ProPilot" system clicks on:

Logos Advertisment Examples • Shot Listed in StudioBinder
This Nissan commercial shows a daughter and father driving on a highway. The daughter is about to drive past some scary construction, but then the father uses his sage like wisdom to instruct her to turn on the "ProPilot" system that Nissan now features in their cars.
Once the daughter does this, we see a Star Wars battle scene playing out in front of out eyes, and she becomes so distracted that she begin to veer off the road... but guess what? The "ProPilot" system saves her by auto-correcting the trajectory of the car based on the sensor system.
So how is this logos? Well, the commercial places the daughter in a relatively common situation and uses the machine logic behind having a guided system in the car to keep your distracted children safe.
Now... is it logical that this Star Wars homage suggests the daughter reach out to use the force by using a guided machine? Of course not! That's the opposite of what Luke does in the movie. Is it logical for your kid to be scared of driving past construction at 40mph? Of course not!
Is there anything in this spot that is logical? The basic fact that young drivers get distracted, and the Nissan "ProPilot" system might just save their lives one day, well that is how you use logic to sell cars.
- The Most Inspiring Ads That Every Agency Should See →
- Shot list your video with StudioBinder →
- Creative YouTube Video Ideas to Try on Your Channel →
LOGOS TECHNIQUES
How is logos being used in advertising.
Technology advertisements use logos because their goal is to showcase cool new features. Consider the example of logos in Apple’s ad for the iPhone:
A logos advertisement example: In Apple’s iPhone spot, the features pop out at you
In logos rhetoric, you have to the sell best reasons to buy your product..
How does Apple do that?
They have their new innovative features pop out at you. From durable glass to Face ID software. It effectively asks you why you would choose any phone but iPhone. Logos often use buzzwords to sell the product.
What's a great example of this?
Food companies capitalizing on the rising demand for healthy choices.
Logos Examples: I Can’t Believe It’s Not Butter underscore the health benefits
This I Can’t Believe It’s Not Butter ad hinges on the health benefits to prove their point. Of the types of persuasive techniques in advertising, logos will build your brand as the most logical, functional and helpful option.
Explore more rhetorical devices
Ethos , pathos , and logos are highly effective rhetorical appeals but there is much more to explore, including kairos and telos . Or dive into more rhetorical devices that help construct and support these appeals, including metaphor , hyperbole , and metonymy . When you've mastered these techniques, your ability to convince and persuade in your writing will be unmatched.
Up Next: Rhetorical Devices Index →
Showcase your vision with elegant shot lists and storyboards..
Create robust and customizable shot lists. Upload images to make storyboards and slideshows.
Learn More ➜
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- VFX vs. CGI vs. SFX — Decoding the Debate
- What is a Freeze Frame — The Best Examples & Why They Work
- TV Script Format 101 — Examples of How to Format a TV Script
- Best Free Musical Movie Scripts Online (with PDF Downloads)
- What is Tragedy — Definition, Examples & Types Explained
- 57.8K Facebook
- 240 Pinterest
- 7.2K LinkedIn
Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Ethos Pathos And Logos
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos - Structure, Usage & Examples
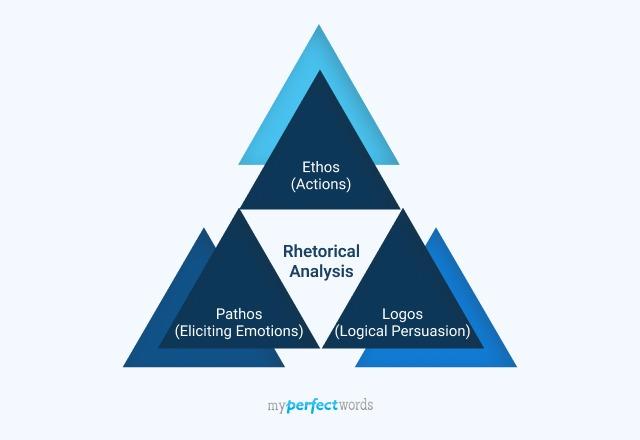
People also read
Rhetorical Analysis Essay - A Complete Guide With Examples
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Topics – 120+ Unique Ideas
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example - Free Samples
Crafting an Effective Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline - Free Samples!
Are your arguments falling flat? Struggling to persuade your audience effectively? You're not alone!
Many students face this challenge when trying to convey their ideas convincingly. Whether it's in a class discussion, a persuasive essay , or a presentation, the art of persuasion often seems elusive.
But fear not!
In this blog, we're going to delve deep into the world of ethos, pathos, and logos, the three pillars of persuasive communication.
By the end, you'll not only understand these concepts but also know how to wield them skillfully.
Let’s get started!
- 1. Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Definition
- 2. Usage of Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
- 3. How To Identify Whether An Author Is Using Ethos, Pathos, Or Logos While Analyzing A Text?
- 4. Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Examples
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Definition
Ethos, pathos, and logos are three essential components in rhetorical analysis . It can be a very effective tool for influencing and convincing others.
These concepts have been employed by great speakers, writers, and thinkers throughout history and continue to play a pivotal role in communication today.
Here are the key differences between ethos, pathos, and logos:
Let's break down each section one at a time, getting to know what ethos, pathos, and logos mean.
Ethos
Ethos is all about establishing credibility and trustworthiness. When you use ethos in your argument, you aim to convince your audience that you are a credible and reliable source of information. It also means you have the expertise needed to speak on a particular subject.
This can be achieved through the use of references to your qualifications, expertise, or by citing reputable sources to support your claims.
Pathos
Pathos appeals to the emotions and feelings of your audience. When you employ pathos, you're aiming to elicit an emotional response, whether it's sympathy, anger, happiness, or any other emotion that can strengthen any type of argument .
This is often achieved through storytelling, vivid language, and relatable anecdotes that connect with the audience on a personal level.
Logos is the appeal to logic and reason. When you use logos, you provide your audience with clear, rational, and well-structured arguments supported by evidence, facts, and statistics.
This appeals to the logical side of your audience's thinking, encouraging them to see the soundness of your position and the validity of your claims.
Usage of Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
Understanding the definitions of ethos, pathos, and logos is a solid foundation, but knowing how to apply these modes of persuasion effectively is equally important.
In this section, we'll delve into practical examples and strategies for utilizing ethos, pathos, and logos to make your persuasive communication more compelling.
Ethos in Action
One of the most common ways to establish ethos is by citing credible sources. Whether you're writing an academic paper or delivering a persuasive speech , referencing reputable experts, institutions, or publications can lend authority to your argument.
If you have personal expertise in the subject matter, don't be shy about showcasing it. Share your qualifications, relevant experiences, or your journey of learning and growth to build trust with your audience.
The following examples of the usage of ethos in the content will help you understand the concept better.
- "My three decades of experience in public service, my tireless commitment to the people of this community, and my willingness to reach across the aisle and cooperate with the opposition make me the ideal candidate for your mayor."
- "Our expertise in roofing contracting is evidenced not only by our 50 years in the business and our staff of qualified technicians. But in the decades of satisfied customers who have come to expect nothing but the best."
- "Based on the dozens of archaeological expeditions I've made all over the world, I am confident that those potsherds are Mesopotamian in origin."
2. Eliciting Emotions with Pathos
Personal anecdotes or emotionally charged stories can engage your audience on a deeper level. They create a connection by allowing the audience to empathize with the characters or situations in your narrative.
Use descriptive language that paints a vivid picture in the minds of your audience. This can help evoke specific emotions and make your message more memorable.
Here are some examples of how to use pathos for persuasion:
- "They've worked against everything we've worked so hard to build, and they don't care who gets hurt in the process. Make no mistake, they're the enemy, and they won't stop until we're all destroyed."
- "You will never be satisfied in life if you don't seize this opportunity. Do you want to live the rest of your year’s yearning to know what would have happened if you just jumped when you had the chance?"
- "After years of this type of disrespect from your boss, countless hours wasted, and birthdays missed, it's time that you took a stand."

Logos for Logical Persuasion
Logos require you to incorporate relevant data, statistics, and evidence to support your claims. This provides a logical foundation for your argument and demonstrates that your position is well-informed and substantiated.
Using logos can be a bit hard compared to the other two devices, but the following examples can help you understand.
- "Ladies and gentlemen of the jury: we have not only the fingerprints, the lack of an alibi, a clear motive, and an expressed desire to commit the robbery. We also have a video of the suspect breaking in. The case could not be more open and shut."
- "More than one hundred peer-reviewed studies have been conducted over the past decade. None of them suggests that this is an effective treatment for hair loss."
- "Research compiled by analysts from NASA, as well as organizations from five other nations with space programs, suggests that a moon colony is viable with international support."

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
How To Identify Whether An Author Is Using Ethos, Pathos, Or Logos While Analyzing A Text?
Identifying whether an author is using Ethos, Pathos, or Logos in a text involves a careful analysis of the writing's persuasive techniques.
Here's how to recognize each of these elements:
- Look for the author's credentials, expertise, or reputation. Do they cite reputable sources, and are they qualified to speak on the subject?
- Assess whether the author employs a professional and trustworthy tone throughout the text.
- Check for citations and references to authoritative figures, institutions, or research.
- Identify emotionally charged language, vivid imagery, or personal anecdotes that elicit feelings in the reader.
- Pay attention to words that trigger empathy, sympathy, or strong emotional responses.
- Notice if the author appeals to values, hopes, fears, or desires to sway the reader's emotions.
- Analyze the use of statistics, data, and facts in the text. Does the author support their argument with evidence?
- Look for clear and structured reasoning. Is the argument well-organized and does it follow a logical sequence?
- Consider whether the author uses syllogisms, analogies, or deductive reasoning to make their point.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Examples
Still uncertain about making a try on your argumentative essay or analysis paper?
Here are some additional examples of ethos, pathos, and logos to help you make your content convincing and persuasive.
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos in Advertising
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Worksheet
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos in Movies
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos in Speeches
Ethos, Pathos, Logos Kairos Example
In summary, using ethos, pathos, and logos is essential to strengthen your point and persuade the audience. Without using these rhetorical devices, the readers will not understand the frame of mind of the writer.
If you are still unclear about the concept and its usage, it is advised to get help from expert analytical essay writer. MyPerfectWords.com is an expert essay writer service that helps students with all their academic assignments.
Be it a rhetorical paper or a persuasive speech, our analytical essay writing service knows how to assist students. Simply place an order at our college paper writing service to get in touch with an expert writer at the most reasonable price.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can logos build ethos.
Logos are appealing to logic by offering evidence in support of your argument. It also makes you look knowledgeable because the information demonstrates intelligence on your part, developing ethos for yourself.
Which is more important: ethos logos or pathos?
Aristotle believed that logos should be the most important of three persuasive appeals. As a philosopher and master of logical reasoning, he thought it was unnecessary to use either ethos or pathos if you present your argument with good reason supported by facts.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


Ethos Definition
What is ethos? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
Ethos , along with logos and pathos , is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Ethos is an argument that appeals to the audience by emphasizing the speaker's credibility and authority. If the speaker has a high-ranking position, is an expert in his or her field, or has had life experience relevant to a particular topic, anything the speaker says or does to ensure that the audience knows about and remembers these qualifications is an example of ethos .
Some additional key details about ethos:
- Ethos shares a root with the word "ethics ." This is helpful to remember because speakers often try to establish their own strong moral character by using ethos.
- The word "ethos" is also often used to refer to a community or organization's characteristic belief or spirit, as in the sentence, "We will not give you a larger bonus than your coworkers: that is against our company's ethos of fairness." However, this guide focuses specifically on the rhetorical technique of ethos used in literature and public speaking.
- The three "modes of persuasion"— pathos , logos , and ethos —were originally defined by Aristotle.
- While ethos appeals to an audience's instinctive respect for authority, logos appeals to the audience's sense of reason, and pathos appeals to the audience's emotions.
- Ethos is used in advertising just as often as it is used in public speaking and literature. Any commercial in which a celebrity endorses a product, for example, hopes to persuade its target audience by cultivating an aura of authority or expertise through its association with the celebrity—and is therefore an example of ethos.
How to Pronounce Ethos
Here's how to pronounce ethos: ee -thos
Ethos Explained
Aristotle (the ancient Greek philosopher and scientist) first defined e thos , along with logos and pathos , in his treatise on rhetoric, Ars Rhetorica. Together, he referred to e thos , logos , and pathos as the three modes of persuasion, or sometimes simply as "the appeals." Aristotle believed that in order to have ethos a good speaker must demonstrate three things:
- Phronesis : Sound reasoning, and relevant experience or expertise.
- Arete : Moral character.
- Eunoia : Good intentions towards the audience.
Aristotle argued that a speaker in possession of these three attributes will naturally impress the audience with his or her ethos , and as a result will be better able to influence that audience. Over time, however, the definition of ethos has broadened, and the significance of the three qualities Aristotle named is now lost on anyone who hasn't studied classical Greek. So it may give more insight into the meaning of ethos to translate Aristotle's three categories into a new set of categories that make more sense in the modern era. A speaker or writer's credibility can be said to rely on each of the following:
- Within literature, it's interesting to notice when characters attempt to invoke their own authority and enhance their ethos by reminding other characters of the titles they possess. Often, this can be an indication that the character citing his or her own credentials actually feels his or her authority being threatened or challenged.
- In literature, this form of ethos is particularly relevant with respect to narrators. Authors often have their narrators profess impartiality or objectivity at the outset of a book in order to earn the reader's trust in the narrator's reliability regarding the story he or she is about to tell.
- This type of ethos translates into literature quite easily, in the sense that characters' opinions are often evaluated within the framework of their professions.
- Literary characters often use ethos to communicate similarity or likemindedness to other characters, and you can detect this by certain changes in their speech. In these situations, characters (as well as real-life speakers) often use a shibboleth— a specialized term or word used by a specific group of people—to show that they belong. For example, if you knew the name of a special chemical used to make jello, and you wanted to impress the head of a jello company, the name of that chemical would count as a shibboleth and saying it would help you show the jello executive that you're "in the know."
The Stagecraft of Ethos
In order to impress their positive personal qualities upon audiences, public speakers can use certain techniques that aren't available to writers. These include:
- Speaking in a certain manner or even with a certain accent.
- Demonstrating confident stage presence.
- Having reputable people to introduce the speaker in a positive light.
- Listing their credentials and achievements.
Put another way, the ethos of a speech can be heavily impacted by the speaker's confidence and manner of presenting him or herself.
Ethos and Ad Hominem
An ad hominem argument is a specific type of argument which involves attacking someone else's character or ethos, rather than attacking that person's position or point of view on the subject being discussed. Ad hominem attacks usually have the goal of swaying an audience away from an opponent's views and towards one's own by degrading the audience's perception of the opponent's character. For instance, if one politician attacks another as being "elite," the attacker may be seeking to make voters question whether the other politician is trustworthy or actually has the public's interest at heart. But the first politician is not in any way attacking their opponent's positions on matters of policy.
An ad hominem argument is not necessarily "wrong" or even a bad strategy, but it's generally seen as more dignified (another component of ethos ) for speakers to focus on strengthening their own ethos, and to debate their opponents based on the substance of the opposition's counterarguments. When a literary character uses an ad hominem argument, this can sometimes indicate that he or she is insecure about his or her own position regarding a certain issue.
Ethos Examples
Examples of ethos in literature.
Characters in novels often use ethos , as well as logos and pathos , to convince one another of certain arguments in the same way that a speaker in reality might use these techniques. In addition, authors often use a subtler form of ethos when establishing a narrator's reliability at the outset of a novel.
Ethos in Ayn Rand's Atlas Shrugged
In Atlas Shrugged, a group of pioneering American industrialists, financiers, and artists go on strike against a corrupt government. As the strike nears its end, its leader—John Galt—delivers a speech to the nation about his ideals. He promises that the strike will end only if Americans allow him to remake the country according to his moral code, which he explains in the following lines:
Just as I support my life, neither by robbery nor alms, but by my own effort, so I do not seek to derive my happiness from the injury or the favor of others, but earn it by my own achievement. Just as I do not consider the pleasure of others as the goal of my life, so I do not consider my pleasure as the goal of the lives of others. Just as there are no contradictions in my values and no conflicts among my desires—so there are no victims and no conflicts of interest among rational men, men who do not desire the unearned and do not view one another with a cannibal's lust, men who neither make sacrifices nor accept them.
Galt not only creates an impression of moral rectitude, but also emphasizes his own self-sufficiency. He assures his audience that he expects nothing in return from them for sharing his personal views. In this way, his ability to cultivate an aura of impartiality and objectivity enhances his ethos.
Ethos in Nathaniel Hawthorne's The Scarlet Letter
The Scarlet Letter opens with a chapter called "The Custom-House," in which the unnamed narrator—who has a similar biography to Hawthorne—describes his job in a Custom House, a place where taxes were paid on imports in 18th century Massachusetts. The narrator's stories about his job have no relation to the actual narrative of The Scarlet Letter, except that he finds the scarlet letter of the title in the Custom House attic. This discovery inspired him to research the life of the woman who wore the embroidered letter, and to tell her story. By presenting himself as someone who merely discovered, researched, and "edited" the story the reader is about to begin, the narrator effectively creates the impression that his is a reliable historical account, thereby strengthening his ethos.
It will be seen, likewise, that this Custom-House sketch has a certain propriety, of a kind always recognised in literature, as explaining how a large portion of the following pages came into my possession, and as offering proofs of the authenticity of a narrative therein contained. This, in fact—a desire to put myself in my true position as editor, or very little more, of the most prolix among the tales that make up my volume—this, and no other, is my true reason for assuming a personal relation with the public.
Ethos in F. Scott Fitzgerald's The Great Gatsby
In the opening lines of The Great Gatsby , the narrator, Nick Carraway, claims that he has followed one piece of his father's advice throughout his life:
In my younger and more vulnerable years my father gave me some advice that I've been turning over in my mind ever since. 'Whenever you feel like criticizing any one,' he told me, just remember that all the people in this world haven't had the advantages that you've had.'... In consequence I'm inclined to reserve all judgements, a habit that has opened up many curious natures to me and also made me the victim of not a few veteran bores. The abnormal mind is quick to detect and attach itself to this quality when it appears in a normal person, and so it came about that in college I was unjustly accused of being a politician, because I was privy to the secret griefs of wild, unknown men...
Nick's tendency to reserve judgement makes him an ideal, objective narrator, while his awareness of his own economic and social advantages makes him a perfect guide to the privileged world of The Great Gatsby. Though he describes his non-judgmental, "neutral" affect with self-deprecating humor, it's a subtle way of strengthening his ethos as a narrator, and of causing the reader to eagerly anticipate hearing the stories that "wild, unknown men" have shared with him.
Examples of Ethos in Political Speeches
Every politician recognizes that a speaker must earn an audience's respect and trust if he or she expects to be listened to. As a result, it's difficult to find a political speech that doesn't contain an example of ethos. It's particularly easy to spot ethos in action when listening to speeches by candidates for office.
Ethos in Mitt Romney's Acceptance Speech at the 2012 Republican National Convention
When he accepted the Republican presidential nomination in 2012, Romney pointed to his business success as relevant experience that would serve him well if he were to take office:
I learned the real lessons about how America works from experience. When I was 37, I helped start a small company. My partners and I had been working for a company that was in the business of helping other businesses. So some of us had this idea that if we really believed our advice was helping companies, we should invest in companies. We should bet on ourselves and on our advice. So we started a new business called Bain Capital...That business we started with 10 people has now grown into a great American success story. Some of the companies we helped start are names you know. An office supply company called Staples – where I'm pleased to see the Obama campaign has been shopping; The Sports Authority, which became a favorite of my sons. We started an early childhood learning center called Bright Horizons that First Lady Michelle Obama rightly praised.
In addition to strengthening his ethos by pointing to his past achievements, Romney also hopes to portray himself as principled, rational, and daring when he explains how his company decided to "bet on ourselves and on our advice."
Ethos in John Kasich's 2016 Ohio Primary Victory Speech
After winning his first campaign victory, 2016 presidential candidate John Kasich told his supporters about his disadvantaged yet hardworking relatives to contextualize his own rise to success:
And you know, ladies and gentlemen, my whole life has been about trying to create a climate of opportunity for people. You know, as my father carried that mail on his back and his father was a coal miner, and you know, I was just told by my cousin—I didn't realize this—that my mother, one of four [children]‚ was the only one to graduate from high school. The other three barely made it out of the eighth grade because they were poor... And you know, as I've traveled the country and I look into your eyes... You want to believe that your children are going to have ultimately a better America than what we got from our mothers and fathers. That's the great American legacy: that our kids will be better than we are.
By saying that he comes from a modest background, Kasich hopes to convey that he is "just a regular American" and that he will advocate for other hard working Americans.
Ethos in Winston Churchill's 1941 Address to Joint Session of the US Congress
In this speech to the US Congress during World War II, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill enhances the ethos of his speech by emphasizing both the qualities he shares in common with the American people and the American Democratic values instilled in him by his parents:
I am a child of the House of Commons. I was brought up in my father's house to believe in democracy. "Trust the people." That was his message. I used to see him cheered at meetings and in the streets by crowds of workingmen way back in those aristocratic Victorian days when as Disraeli said "the world was for the few, and for the very few." Therefore I have been in full harmony all my life with the tides which have flowed on both sides of the Atlantic against privilege and monopoly and I have steered confidently towards the Gettysburg ideal of government of the people, by the people, for the people.
Examples of Ethos in Advertisements
Advertisers often attempt to use ethos to influence people to buy their product. Dressing up an actor as a doctor who then extols the benefits a medication is a way that advertisers used to try to gin up a little ethos , but such obvious practices of what might be called "fake ethos" are now regularly mocked. However, any celebrity endorsement or testimonial from an expert are also attempts to build up ethos around a product's endorsement. For instance, here's a Prudential Financial commercial that ups its ethos with an appearance by Harvard social psychologist Dan Gilbert.
Why Do Writers Use Ethos?
Politicians, activists, and advertisers use ethos because they recognize that it is impossible to convince an audience of anything if its members do not believe in the speaker's credibility, morality, or authority.
The use of e thos in fiction is often different from real-world examples. Authors are not usually trying to directly influence their audience in the way politicians or advertisers are. Rather, authors often show one of their characters making use of ethos . In doing so, the author gives insight into characters' perceptions of one another, their values, and their motives.
In addition, e thos is an especially useful tool for authors looking to establish a narrator's credibility. Having a credible narrator is hugely important to the success of a literary work. Books with narrators that never establish a reasonable claim to an objective viewpoint are nearly impossible to read because everything they say is cast in doubt, so that readers come to feel like they're being lied to or "jerked around," which is fatiguing. Although often enough readers simply assume that a narrator has credibility , if you've ever read a book where you felt you simply didn't like the narrator very much—or watched a television show where you felt that none of the characters were likable or believable—that might be another sign that the writer has failed to establish a character's ethos . There are circumstances in which a writer creates an unreliable narrator —a narrator who is either purposefully or subconsciously offering a slanted narrative—but ethos is just as crucial in creating such a narrator: the author must first establish the narrator's ethos and then slowly undermine it over the course of the book.
Other Helpful Ethos Resources
- The Wikipedia Page on Ethos: An in-depth explanation of ethos , and how the concept has changed over time.
- The Dictionary Definition of Ethos: A definition and etymology of the term, which comes from the Greek ethos meaning "character, custom, or habit."
- Ethos on Youtube: An excellent video from TED-Ed about the three modes of persuasion.

- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1929 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,694 quotes across 1929 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
- Dynamic Character
- Blank Verse
- Figure of Speech
- Juxtaposition
- Bildungsroman
- Connotation
- Figurative Language
- Deus Ex Machina
- Rhetorical Question
- External Conflict


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
III. Rhetorical Situation
3.6 Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined
Melanie Gagich; Emilie Zickel; and Terri Pantuso
Rhetoric, as the previous sections have discussed, is the way that authors use and manipulate language in order to persuade an audience. Once we understand the rhetorical situation out of which a text is created (why it was written, for whom it was written, by whom it was written, how the medium in which it was written creates certain constraints, or perhaps freedom of expression), we can look at how all of those contextual elements shape the author’s creation of the text.
We can look first at the classical rhetorical appeals which are the three ways to classify an author’s intellectual, moral, and emotional approaches to getting the audience to react in the manner in which the author may have intended.
Rhetorical Appeals
In composition studies, the term rhetorical appeals refers to the use of ethos, pathos, and logos. These are classical Greek terms dating back to Aristotle who is traditionally viewed as the creator of rhetoric. To be rhetorically effective (and thus persuasive), an author must engage the audience in a variety of compelling ways which involves carefully choosing how to craft their argument so that the intended outcome is achieved. Often that outcome occurs when the audience agrees with the argument or point being presented. Aristotle defined these modes of engagement and gave them the terms that we still use today: logos, pathos, and ethos.
Logos: Appeal to Logic
Logic. Reason. Rationality. Logos is brainy and intellectual, cool, calm, collected, objective.
When an author relies on logos, it means that they are using logic, careful structure, and objective evidence to appeal to the audience. Objective evidence is anything that can be proven with statistics or other facts via more than one source. Oftentimes that evidence has been validated by more than one authority in the field of study.
For example, if Dr. Smith was trying to convince her students to complete their homework, she might explain that she understands everyone is busy and they have other classes (non-biased), but that completing their homework will help them get a better grade on their test (explanation). She could add to this explanation by providing statistics showing the number of students who failed and didn’t complete their homework versus the number of students who passed and did complete their homework (factual evidence). This is an example of logos employed for the purposes of argument and persuasion.
Logical appeals rest on rational modes of thinking , such as:
- Comparison: a comparison between one thing (with regard to your topic) and another, similar thing to help support your claim. It is important that the comparison is fair and valid – the things being compared must share significant traits of similarity.
- Cause/effect thinking: you argue that X has caused Y, or that X is likely to cause Y to help support your claim. Be careful with the latter – it can be difficult to predict that something “will” happen in the future.
- Deductive reasoning: starting with a broad, general claim/example and using it to support a more specific point or claim (picture an hourglass where the sands gather in the middle)
- Inductive reasoning: using several specific examples or cases to make a broad generalization (consider the old question of “if your friend jumped off of a bridge, would you” to make the sweeping claim that all young people are easily persuaded to follow the crowd)
- Analogical reasoning: moves from one particular claim/example to another, seemingly sequential (sometimes this line of reasoning is used to make a guilt by association claim)
- Exemplification: use of many examples or a variety of evidence to support a single point
- Elaboration: moving beyond just including a fact, but explaining the significance or relevance of that fact
- Coherent thought: maintaining a well-organized line of reasoning; not repeating ideas or jumping around
Pathos: Appeal to Emotions
When an author relies on pathos, it means that they are trying to tap into the audience’s emotions to get them to agree with the author’s claim. An author using pathos appeals wants the audience to feel something: anger, pride, joy, rage, or happiness. For example, many of us have seen the ASPCA commercials that use photographs of injured puppies, or sad-looking kittens, and slow, depressing music to emotionally persuade their audience to donate money. This is a classic example of the use of pathos in argument.
Pathos-based rhetorical strategies are any strategies that get the audience to “open up” to the topic, the argument, or to the author through an emotional connection. Emotions can make us vulnerable and an author can use this vulnerability to get the audience to believe that their argument is a compelling one.
Pathos appeals might include:
- Expressive descriptions of people, places, or events that help the reader to feel or experience those events
- Vivid imagery of people, places or events that help the reader to feel like they are seeing those events
- Sharing personal stories that make the reader feel a connection to, or empathy for, the person being described
- Using emotion-laden vocabulary as a way to put the reader into that specific emotional mindset (what is the author trying to make the audience feel? and how are they doing that?)
- Using any information that will evoke an emotional response from the audience. This could involve making the audience feel empathy or disgust for the person/group/event being discussed, or perhaps connection to or rejection of the person/group/event being discussed.
When reading a text, try to locate where the author is trying to convince the reader by strictly using emotions because, if used to excess, pathos appeals can indicate a lack of substance or emotional manipulation of the audience. If the only way in which an author can persuade the reader is by making him/her sad or angry, does that make for a solid, valid argument?
Ethos: Appeal to Values/Trust
Appeals using ethos are typically two faceted focusing on audience values and authorial credibility/character.
On the one hand, when an author makes an ethical appeal, they are attempting to tap into the values or ideologies that the audience holds. Examples include patriotism, tradition, justice, equality, dignity for all humankind, self-preservation, or other specific social, religious or philosophical values (Christian values, socialism, capitalism, feminism, etc.). These values can sometimes feel very close to emotions, but they are felt on a social level rather than only on a personal level. When an author evokes the values that the audience cares about as a way to justify or support their argument, we classify that as ethos. The audience will feel that the author is making an argument that is “right” (in the sense of moral “right”-ness, i.e., My argument rests upon the values that matter to you. Therefore, you should accept my argument ). This first part of the definition of ethos, then, is focused on the audience’s values.
On the other hand, this sense of referencing what is “right” in an ethical appeal connects to the other sense of ethos, the author. Ethos that is centered on the author revolves around two concepts: the credibility of the author and their character.
Credibility of the speaker/author is determined by their knowledge and expertise in the subject at hand. For example, if you are learning about Einstein’s Theory of Relativity, would you rather learn from a professor of physics or a cousin who took two science classes in high school thirty years ago? It is fair to say that, in general, the professor of physics would have more credibility to discuss the topic of physics than your cousin. To establish their credibility, an author may draw attention to who they are or what kinds of experience they have with the topic being discussed as an ethical appeal (i.e., Because I have experience with this topic – and I know my stuff! – you should trust what I am saying about this topic ). Some authors do not have to establish their credibility because the audience already knows who they are and that they are credible.
Character is another aspect of ethos that is different from credibility because it involves personal history and sometimes personality traits. A person can be credible but lack character or vice versa. For example, in politics, sometimes the most experienced candidates – those who might be the most credible candidates – fail to win elections because voters do not accept their character. Politicians take pains to shape their character as leaders who have the interests of the voters at heart. The candidate who successfully proves to the voters (the audience) that they have the type of character that they can trust is more likely to win.
Thus, ethos comes down to trust. How can the author get the audience to trust him or her so that they will accept their argument? How can the author make himself or herself appear as a credible speaker who embodies the character traits that the audience values?
In building ethical appeals, we may see authors:
- Referring either directly or indirectly to the values that matter to the intended audience (so that the audience will trust the speaker)
- Using language, phrasing, imagery, or other writing styles common to people who hold those values, thereby “talking the talk” of people with those values (again, so that the audience is inclined to trust the speaker)
- Referring to their experience and/or authority with the topic (and therefore demonstrating their credibility)
- Referring to their own character, or making an effort to build their character in the text
When reading, you should always think about the author’s credibility regarding the subject as well as their character. Here is an example of a rhetorical move that connects with ethos: when reading an article about abortion, the author mentions that she has had an abortion. That is an example of an ethical move because the author is creating credibility via anecdotal evidence and first person narrative. In a rhetorical analysis project, it would be up to you, the analyzer, to point out this move and associate it with a rhetorical strategy.
When Writers Misuse Logos, Pathos, or Ethos, Arguments can be Weakened
Above, we defined and described what logos, pathos, and ethos are and why authors may use those strategies. Sometimes, using a combination of appeals leads to a sound, balanced, and persuasive argument. It is important to understand, though, that using rhetorical appeals does not always lead to a sound, balanced argument. In fact, any of the appeals could be misused or overused. When that happens, arguments can be weakened.
Using a social media platform, find a topic that is trending for today and create an argument using ethos, pathos, and logos for that topic.
Practice Activity
This section contains material from:
Gagich, Melanie and Emilie Zickel. “Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined.” In A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing , by Melanie Gagich and Emilie Zickel. Cleveland: MSL Academic Endeavors. Accessed July 2019. https://pressbooks.ulib.csuohio.edu/csu-fyw-rhetoric/chapter/rhetorical-strategies-building-compelling-arguments/ Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . Archival link: https://web.archive.org/web/20201027010216/https://pressbooks.ulib.csuohio.edu/csu-fyw-rhetoric/chapter/rhetorical-strategies-building-compelling-arguments/
Logical, reasonable, or sensible; having good sense; to be sane or lucid; usually refers to a state of mind.
Sequence; the order in which things occur.
3.6 Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined Copyright © 2023 by Melanie Gagich; Emilie Zickel; and Terri Pantuso is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
22 Ethos, Pathos, & Logos
Using rhetorical appeals to support your argument.
In addition to choosing an effective rhetorical mode (see Rhetorical Modes for Paragraphs & Essays for details) for an essay, you need to think about the most effective rhetorical appeal , or way of persuading your audience.
Writers are generally most successful with their audiences when they can skillfully and appropriately balance the three core types of rhetorical appeals. These appeals are referred to by their Greek names: ethos , pathos , and logos .

Authoritative Appeals = Ethos
Authors using authority to support their claims can use a variety of techniques. These include the following:
- personal anecdotes
- proof of deep knowledge on the issue
- citation of recognized experts on the issue
- testimony of those involved first-hand on the issue
Emotional Appeals = Pathos
Authors using emotion to support their claims also have many options to do so. These include the following:
- impact studies
Logical Appeals = Logos
Authors using logic to support their claims can incorporate a combination of different types of evidence. These include the following:
- established facts
- case studies
- experiments
- analogies and logical reasoning
As you can see, there is some overlap on these lists. One type of support may work in two or three different ways.
Many authors rely on one of the three as the primary method of support, but they may also draw upon one or two others at the same time. Consider your audience, purpose, and context to determine the best appeal(s) to use in your writing.
Activity A ~ Recognizing Rhetorical Appeals
Examine an article that you are reading for your research. Can you find examples of ethos, pathos, and/or logos? Discuss with a partner.
Watch “Nissan Leaf TM : Polar Bear” by clicking below (also found at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VdYWSsUarOg#action=share)
What appeal(s) did the authors of this video use?
Can you find other short videos which show rhetorical appeals?
Activity B ~ Choosing Rhetorical Appeals
A. Check in with your partners: What’s the difference between rhetorical modes and rhetorical appeals ?
B. Discuss the following topics with your partners, as we did in our chapter on rhetorical modes (patterns of organization). This time, think about which appeal(s) would be most effective for an essay about each topic. Why?
- Gender roles
- Race in America
- The value of art in society
- Travel as part of a well-rounded education
- Drugs and alcohol
- Advice to new parents
- Advice to teachers
- The value of making mistakes
- How you’d spend a million dollars
- What a tough day at work taught you about yourself or others
C. Consider the essay you are working on now. What rhetorical appeals would be most effective for your audience? Why? Discuss with your writing partners.
This chapter was modified from “ Logos, Ethos, Pathos ” from Developmental English: Introduction to College Composition under a CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike license.
Image of Persuasion. Authored by : Mrs. Adcock. Located at : https://agi241classes.wikispaces.com/Fifth+Grade . Project : Computer Class AGI241. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
Note : links open in new tabs.
moral character, credibility, trust, authority
emotion, feeling, beliefs
reasoning, logic
ENGLISH 087: Academic Advanced Writing Copyright © 2020 by Nancy Hutchison is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

The Rhetorical Triangle: Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
Introduction.
The Rhetorical Triangle is a simple, useful tool that can help you develop a strong and well thought-out essay, especially in persuasive writing and speeches. Each side of the triangle represents one of the three classical rhetorical approaches used to build informative, persuasive arguments that influence audiences in specific, powerful ways.
There are many visual representations of the Rhetorical Triangle available online, such as the following: https://i.pinimg.com/736x/d6/e9/29/d6e929c8d0e479a64a89e428491b296c.jpg
The Three Classical Appeals: Ethos, Pathos and Logos
Each of the three approaches attempts to prove arguments and persuade readers by emphasizing a specific type of appeal. These appeals are not mutually exclusive, and you will often find elements of all three working together in effective writing.
Ethos: Appeals to Credibility and Authority
To use this appeal, you might emphasize experience or educational background, your own or those of your sources, as the reason the reader should believe you. By citing credentials, the argument is being built on the word of experts. Your reader expects to acknowledge the qualifications of the individuals or organizations presented as capable of supporting an argument with valid, factual, and credible information.
Pathos: Appeals to Emotions
Although this appeal is not as commonly used in academic writing as the other two, it does appear regularly in literary work. Recognizing and using pathos appeals to personal values and emotions, which are some of the most powerful appeals.
Logos: Appeals to Logic and Reasoning
When you think about academic writing, you probably think of logic-based writing, which targets a reader’s intellect and often includes facts that build upon each other to support complex arguments. Because this appeal relies on a reader being able to follow well-constructed arguments, it is critical this writing is clear, organized, and focused. Extra information that does not directly support the logic of the arguments can distract and confuse a reader, and ultimately weaken an argument.
Identifying and Using Rhetorical Appeals in Your Projects
Now that you are familiar with each of the three rhetorical appeals, you can consider how you might use them in your writing, based on the specific rhetorical situation you are working with.
If your paper is discussing the effects of drinking and driving, you might include an interview with a veteran DPS Trooper who can discuss his fifteen years of experience working New Year’s Eve patrols. His professional credentials help your readers believe his observations and ideas are informed, relevant, and appropriate to the topic. By citing them, you are presenting your source’s DPS training, certifications, and experience as the reason your readers should accept your argument.
Incorporating topic information from reliable, well-informed sources strengthens your argument and makes it easier for your reader to accept. Writers present their source’s credentials through in-text citations as well as through their Works Cited listings. These citations provide your readers with the background and information they need to evaluate the quality and credibility of your sources.
If your goal is to get your reader to feel something, or to take a certain action, you may find this appeal highly effective. Think about the popular TV commercials that raise money for abused animals. Those commercials are designed to make viewers feel sadness by showing images of pain and suffering. By the end, they switch to hopeful images and dialogue to inspire viewers to take a specific action and become supporters of their cause. You can visit Youtube to view many ASPCA commercials as great examples of this appeal in use; be warned, you may become emotional!
Pathos is often used in literature. Think about stories that seem to come alive in some way. Perhaps it is a character to whom readers can genuinely relate or stories that make readers feel happy, sad, or angry. Writing that evokes emotion often uses Pathos. It is also commonly used in spoken word compositions like speeches, poetry, and theater. When possible, including thoughtfully chosen images and music is another way you can use pathos through sensory details to connect with your audience’s emotions.
To create logical support in your work, you might include data, case studies, statistics, lab reports, and other similar information. This is a popular appeal, and if you watch for it, you will find it used to support claims in everything from scientific reports to advertising, such as the familiar “Nine out of ten dentists recommend using an automatic toothbrush over regular brushing.”
Combining Rhetorical Appeals
As you start planning your essay, you may find that a combination of appeals works best. For example, you might decide that case studies and lab reports will provide the best data to support your claims, focusing on only highly-qualified sources that are well known in your field. By making these choices, you are employing the power of both Logos and Ethos into your essay, a combination that will result in a clear, organized, credible, and effective argument that conveys your message.
Page last updated July 12, 2023.

Chapter 6: Thinking and Analyzing Rhetorically
6.4 Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined
Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel
Rhetoric, as the previous chapters have discussed, is the way that authors use and manipulate language in order to persuade an audience. Once we understand the rhetorical situation out of which a text is created (why it was written, for whom it was written, by whom it was written, how the medium in which it was written creates certain constraints, or perhaps freedoms of expression), we can look at how all of those contextual elements shape the author’s creation of the text.
We can look first at the classical rhetorical appeals, which are the three ways to classify authors’ intellectual, moral, and emotional approaches to getting the audience to have the reaction that the author hopes for.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeals refer to ethos, pathos, and logos. These are classical Greek terms, dating back to Aristotle, who is traditionally seen as the father of rhetoric. To be rhetorically effective (and thus persuasive), an author must engage the audience in a variety of compelling ways, which involves carefully choosing how to craft his or her argument so that the outcome, audience agreement with the argument or point, is achieved. Aristotle defined these modes of engagement and gave them the terms that we still use today: logos, pathos, and ethos.
Logos: Appeal to Logic
Logic. Reason. Rationality. Logos is brainy and intellectual, cool, calm, collected, objective.
When an author relies on logos, it means that he or she is using logic, careful structure, and objective evidence to appeal to the audience. An author can appeal to an audience’s intellect by using information that can be fact checked (using multiple sources) and thorough explanations to support key points. Additionally, providing a solid and non-biased explanation of one’s argument is a great way for an author to invoke logos.
For example, if I were trying to convince my students to complete their homework, I might explain that I understand everyone is busy and they have other classes (non-biased), but the homework will help them get a better grade on their test (explanation). I could add to this explanation by providing statistics showing the number of students who failed and didn’t complete their homework versus the number of students who passed and did complete their homework (factual evidence).
Logical appeals rest on rational modes of thinking , such as
- Comparison – a comparison between one thing (with regard to your topic) and another, similar thing to help support your claim. It is important that the comparison is fair and valid – the things being compared must share significant traits of similarity.
- Cause/effect thinking – you argue that X has caused Y, or that X is likely to cause Y to help support your claim. Be careful with the latter – it can be difficult to predict that something “will” happen in the future.
- Deductive reasoning – starting with a broad, general claim/example and using it to support a more specific point or claim
- Inductive reasoning – using several specific examples or cases to make a broad generalization
- Exemplification – use of many examples or a variety of evidence to support a single point
- Elaboration – moving beyond just including a fact, but explaining the significance or relevance of that fact
- Coherent thought – maintaining a well organized line of reasoning; not repeating ideas or jumping around
Pathos: Appeal to Emotions
When an author relies on pathos, it means that he or she is trying to tap into the audience’s emotions to get them to agree with the author’s claim. An author using pathetic appeals wants the audience to feel something: anger, pride, joy, rage, or happiness. For example, many of us have seen the ASPCA commercials that use photographs of injured puppies, or sad-looking kittens, and slow, depressing music to emotionally persuade their audience to donate money.
Pathos-based rhetorical strategies are any strategies that get the audience to “open up” to the topic, the argument, or to the author. Emotions can make us vulnerable, and an author can use this vulnerability to get the audience to believe that his or her argument is a compelling one.
Pathetic appeals might include
- Expressive descriptions of people, places, or events that help the reader to feel or experience those events
- Vivid imagery of people, places or events that help the reader to feel like he or she is seeing those events
- Sharing personal stories that make the reader feel a connection to, or empathy for, the person being described
- Using emotion-laden vocabulary as a way to put the reader into that specific emotional mindset (what is the author trying to make the audience feel? and how is he or she doing that?)
- Using any information that will evoke an emotional response from the audience . This could involve making the audience feel empathy or disgust for the person/group/event being discussed, or perhaps connection to or rejection of the person/group/event being discussed.
When reading a text, try to locate when the author is trying to convince the reader using emotions because, if used to excess, pathetic appeals can indicate a lack of substance or emotional manipulation of the audience. See the links below about fallacious pathos for more information.
Ethos: Appeal to Values/Trust
Ethical appeals have two facets: audience values and authorial credibility/character.
On the one hand, when an author makes an ethical appeal, he or she is attempting to tap into the values or ideologies that the audience holds , for example, patriotism, tradition, justice, equality, dignity for all humankind, self preservation, or other specific social, religious or philosophical values (Christian values, socialism, capitalism, feminism, etc.). These values can sometimes feel very close to emotions, but they are felt on a social level rather than only on a personal level. When an author evokes the values that the audience cares about as a way to justify or support his or her argument, we classify that as ethos. The audience will feel that the author is making an argument that is “right” (in the sense of moral “right”-ness, i.e., “My argument rests upon that values that matter to you. Therefore, you should accept my argument”). This first part of the definition of ethos, then, is focused on the audience’s values.
On the other hand, this sense of referencing what is “right” in an ethical appeal connects to the other sense of ethos: the author. Ethos that is centered on the author revolves around two concepts: the credibility of the author and his or her character.
Credibility of the speaker/author is determined by his or her knowledge and expertise in the subject at hand. For example, if you are learning about Einstein’s Theory of Relativity, would you rather learn from a professor of physics or a cousin who took two science classes in high school thirty years ago? It is fair to say that, in general, the professor of physics would have more credibility to discuss the topic of physics. To establish his or her credibility, a n author may draw attention to who he or she is or what kinds of experience he or she has with the topic being discussed as an ethical appeal (i.e., “Because I have experience with this topic – and I know my stuff! – you should trust what I am saying about this topic”). Some authors do not have to establish their credibility because the audience already knows who they are and that they are credible.
Character is another aspect of ethos, and it is different from credibility because it involves personal history and even personality traits. A person can be credible but lack character or vice versa. For example, in politics, sometimes the most experienced candidates – those who might be the most credible candidates – fail to win elections because voters do not accept their character. Politicians take pains to shape their character as leaders who have the interests of the voters at heart. The candidate who successfully proves to the voters (the audience) that he or she has the type of character that they can trust is more likely to win.
Thus, ethos comes down to trust. How can the author get the audience to trust him or her so that they will accept his or her argument? How can the the author make him or herself appear as a credible speaker who embodies the character traits that the audience values?
In building ethical appeals, we see authors
- Referring either directly or indirectly to the values that matter to the intended audience (so that the audience will trust the speaker)
- Using language, phrasing, imagery, or other writing styles common to people who hold those values, thereby “talking the talk” of people with those values (again, so that the audience is inclined to trust the speaker)
- Referring to their experience and/or authority with the topic (and therefore demonstrating their credibility)
- Referring to their own character, or making an effort to build their character in the text
When reading, you should always think about the author’s credibility regarding the subject as well as his or her character. Here is an example of a rhetorical move that connects with ethos: when reading an article about abortion, the author mentions that she has had an abortion. That is an example of an ethical move because the author is creating credibility via anecdotal evidence and first person narrative. In a rhetorical analysis project, it would be up to you, the analyzer, to point out this move and associate it with a rhetorical strategy.
When writers misuse Logos, Pathos, or Ethos, arguments can be weakened
Above, we defined and described what logos, pathos, and ethos are and why authors may use those strategies. Sometimes, using a combination of logical, pathetic, and ethical appeals leads to a sound, balanced, and persuasive argument. It is important to understand, though, that using rhetorical appeals does not always lead to a sound, balanced argument.
In fact, any of the appeals could be misused or overused. When that happens, arguments can be weakened.
To see what a misuse of logical appeals might consist of, see the next chapter, Logical Fallacies.
To see how authors can overuse emotional appeals and turn-off their target audience, visit the following link from WritingCommons.org : Fallacious Pathos .
To see how ethos can be misused or used in a manner that may be misleading, visit the following link to WritingCommons.org : Fallacious Ethos
A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing by Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Feedback/Errata
Comments are closed.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, ethos, pathos, logos, kairos: the modes of persuasion and how to use them.
General Education

Ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos all stem from rhetoric—that is, speaking and writing effectively. You might find the concepts in courses on rhetoric, psychology, English, or in just about any other field!
The concepts of ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos are also called the modes of persuasion, ethical strategies, or rhetorical appeals. They have a lot of different applications ranging from everyday interactions with others to big political speeches to effective advertising.
Read on to learn about what the modes of persuasion are, how they’re used, and how to identify them!
What Are the Modes of Persuasion?
As you might have guessed from the sound of the words, ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos go all the way back to ancient Greece. The concepts were introduced in Aristotle’s Rhetoric , a treatise on persuasion that approached rhetoric as an art, in the fourth century BCE.
Rhetoric was primarily concerned with ethos, pathos, and logos, but kairos, or the idea of using your words at the right time, was also an important feature of Aristotle’s teachings.
However, kairos was particularly interesting to the Sophists, a group of intellectuals who made their living teaching a variety of subjects. The Sophists stressed the importance of structuring rhetoric around the ideal time and place.
Together, all four concepts have become the modes of persuasion, though we typically focus on ethos, pathos, and logos.

What Is Ethos?
Though you may not have heard the term before, ‘ethos’ is a common concept. You can think of it as an appeal to authority or character—persuasive techniques using ethos will attempt to persuade you based on the speaker’s social standing or knowledge. The word ethos even comes from the Greek word for character.
An ethos-based argument will include a statement that makes use of the speaker or writer’s position and knowledge. For example, hearing the phrase, “As a doctor, I believe,” before an argument about physical health is more likely to sway you than hearing, “As a second-grade teacher, I believe.”
Likewise, celebrity endorsements can be incredibly effective in persuading people to do things . Many viewers aspire to be like their favorite celebrities, so when they appear in advertisements, they're more likely to buy whatever they're selling to be more like them. The same is true of social media influencers, whose partnerships with brands can have huge financial benefits for marketers .
In addition to authority figures and celebrities, according to Aristotle, we’re more likely to trust people who we perceive as having good sense, good morals, and goodwill —in other words, we trust people who are rational, fair, and kind. You don’t have to be famous to use ethos effectively; you just need whoever you’re persuading to perceive you as rational, moral, and kind.

What Is Pathos?
Pathos, which comes from the Greek word for suffering or experience, is rhetoric that appeals to emotion. The emotion appealed to can be a positive or negative one, but whatever it is, it should make people feel strongly as a means of getting them to agree or disagree.
For example, imagine someone asks you to donate to a cause, such as saving rainforests. If they just ask you to donate, you may or may not want to, depending on your previous views. But if they take the time to tell you a story about how many animals go extinct because of deforestation, or even about how their fundraising efforts have improved conditions in the rainforests, you may be more likely to donate because you’re emotionally involved.
But pathos isn’t just about creating emotion; it can also be about counteracting it. For example, imagine a teacher speaking to a group of angry children. The children are annoyed that they have to do schoolwork when they’d rather be outside. The teacher could admonish them for misbehaving, or, with rhetoric, he could change their minds.
Suppose that, instead of punishing them, the teacher instead tries to inspire calmness in them by putting on some soothing music and speaking in a more hushed voice. He could also try reminding them that if they get to work, the time will pass quicker and they’ll be able to go outside to play.
Aristotle outlines emotional dichotomies in Rhetoric . If an audience is experiencing one emotion and it’s necessary to your argument that they feel another, you can counterbalance the unwanted emotion with the desired one . The dichotomies, expanded upon after Aristotle, are :
- Anger/Calmness
- Friendship/Enmity
- Fear/Confidence
- Shame/Shamelessness
- Kindness/Unkindness
- Pity/Indignation
- Envy/Emulation
Note that these can work in either direction; it’s not just about swaying an audience from a negative emotion to a positive one.
However, changing an audience's emotion based on false or misleading information is often seen as manipulation rather than persuasion. Getting into the hows and whys requires a dive into the ethics of rhetoric , but suffice to say that when you attempt to deceive an audience, that is manipulation.
If you really want to get an audience fired up about something, you can inspire righteous anger, which may or may not be manipulation. If somebody is offended that you’ve asked them for something, you can try making them feel sorry for you by turning indignation into pity— that’s manipulation.

What Is Logos?
Logos comes from a Greek word of multiple meanings, including “ground,” “speech,” and “reason.” In rhetoric, it specifically refers to having a sense of logic to your persuasion; logos-based rhetoric is founded in logic and reason rather than emotion, authority, or personality.
A logic-based argument appeals to a person’s sense of reason— good logos-based rhetoric will persuade people because the argument is well-reasoned and based in fact. There are two common approaches to logos: deductive and inductive arguments.
Deductive arguments build on statements to reach a conclusion —in effect, the conclusion is reached in reverse. A common method is to propose multiple true statements which are combined to reach a conclusion, such as the classic method of proving that Socrates is mortal.
All men are mortal, and Socrates is a man, therefore Socrates must be mortal.
That’s not really a case that needs to be argued, but we can apply the same framework to other arguments as well. For example, we need energy to live. Food gives the body energy. Therefore, we need food to live.
All of this is based on things we can prove, and results in a conclusion that is true , not just theorized. Deductive reasoning works on the assumption that A = B, B = C, so therefore A = C. But this also supposes that all the information is true, which is not always the case.
Sometimes the conclusions you reach with deductive reasoning can be valid, as in the reasoning makes sense, but the conclusion may not be necessarily true. If we return to the Socrates argument, we could propose that:
All men eat apples. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates must eat apples.
The problem is that we can’t prove that all men eat apples —some do, some don’t. Some might eat an apple once but never again. But based on our arguments, the conclusion that Socrates must eat apples is valid.
A strong deductive argument for logos-based reasoning will be composed of provable facts that can reach a provable conclusion. However, a valid but not entirely sound argument can also be effective—but be wary of shifting from persuasion to manipulation!
Another approach to logos-based rhetoric is inductive reasoning, which, unlike deductive reasoning, results in a probable argument rather than a definite one. That doesn’t mean that it is less effective—many scientific concepts we accept as truth are inductive theories simply because we cannot travel back in time and prove them— but rather that inductive reasoning is based on eliminating the impossible and ending in an argument that is based in sound logic and fact, but that may not necessarily be provable.
For example, all people with a cough have a cold. Kelly has a cough. Therefore, Kelly likely has a cold.
Our conclusion is likely , but not absolute. It’s possible that Kelly doesn’t have a cold—not because she doesn't have a cough, but because there are other possible causes, such as having allergies or having just breathed in some dust. The conclusion that she has a cold is likely based on data, but not absolute.
Another example would be that Kelly picks her nose. Kelly is a woman, therefore all women must pick their nose.
Inductive reasoning is based on generalizations. The first example, in which Kelly likely has a cold, makes sense because it’s based on something provable—that a sampling of people who have a cough have colds—and followed up with a likely conclusion. In the second example, this is a less sensible conclusion because it’s based on extrapolation from a single reference point.
If we reverse the claim and say that all women pick their noses, and Kelly is a woman, therefore Kelly must pick her nose, that would be more sound logic. Still not necessarily true—not all women pick their noses—but a more sound example of inductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning can still be incredibly effective in persuasion, provided that your information is well-reasoned. Inductive reasoning creates a hypothesis that can be tested; its conclusion is not necessarily true, but can be examined.
As always, be wary of venturing into manipulation, which is more likely to be based on erroneous or misleading facts.

What Is Kairos?
Kairos is the Greek word for the opportune moment, which is precisely what it means in rhetoric. According to this principle, the time in which an argument is deployed is as important as the argument itself. An argument at the wrong time or to the wrong audience will be wasted; to be effective, you must also consider when you are speaking and to whom.
In effect, kairos means choosing the correct rhetorical device to match the audience and space in which you’re attempting to persuade. If you wanted to persuade people to go vegetarian, the middle of a hot dog-eating contest is probably not the right time. Likewise, you’re probably not going to persuade a room of data-driven scientists of something by appealing to pathos or ethos; logos is probably your best bet.
In essence, kairos asks you to consider the context and atmosphere of the argument you’re making. How can you deploy your argument better considering time and space? Should you wait, or is time of the essence?
As Aristotle famously said, “Anybody can become angry—that is easy, but to be angry with the right person and to the right degree and at the right time and for the right purpose, and in the right way—that is not within everybody's power and is not easy.”
The goal of kairos is to achieve exactly that. Effective use of kairos strengthens your persuasion ability by considering how people are already feeling based on context. How can you influence or counteract that? Or maybe pathos isn’t the right approach—maybe cold hard facts, using logos, is more suited. Kairos works in conjunction with the other modes of persuasion to strengthen your argument, so as you’re putting a persuasive piece together, consider how and when it’ll be deployed!

How to Identify Ethos, Pathos, Logos, and Kairos
Understanding how the modes of persuasion work can make you better at identifying and picking them out. Not only is a better understanding of them useful for composing your own arguments, but it’s also beneficial when seeing other people’s arguments. When you understand how ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos work, you’re less susceptible to them.
Advertising is one of the places we see the modes of persuasion most often. Looking at each of these advertisements, you can see how they use each mode of persuasion to convince audiences to convince an audience of something.
Using celebrities is a classic example of ethos, which uses authority or recognition to convince an audience of something. In this case, celebrities like Michelle Obama, Lin-Manuel Miranda, and Janelle Monáe discuss the importance of voting.
It doesn’t matter that they’re not politicians or political scientists; audiences find them appealing and genuine. When they speak of the importance of voting, audiences listen because they like what these figures have to say . If talented, famous people like this are taking the time to vote, it must be important!
Historians or those well-versed in politics might make different arguments about why audiences should vote, but in this case, the goal is to inspire people. When we see people we admire doing things, we want to do them too; hence the reason that ethos works so well.
ASPCA’s commercials are some of the most infamous examples of pathos in advertising. Sarah McLachlan’s “Angel” plays over footage of abused animals in shelters, encouraging viewers to donate money to support the organization.
It’s not hard to understand why it works; both the song and the imagery are heartbreaking! You can’t help but feel sad when you see it, and that sadness, when followed up by a prompt to donate, encourages you to take immediate action. And these ads are effective— the campaign raised millions of dollars for ASPCA .
By appealing to our emotions and making us feel sad, this advertisement encourages us to act. That’s a classic use of ethos—it influences our feelings through the one-two punch of sad music and imagery, encouraging us to perform the desired action.
In some cases, emotion and authority aren’t the right tactic. Logos often appears in tech advertisements, such as this one for the iPhone XS and XR.
Notice how the advertisement focuses on product shots and technological terms. Most audiences won’t know what an A12 bionic neural engine is, but it sounds impressive. Likewise, that “12 MPf/1.8 wide-angle lens, with larger, deeper 1.4 micron pixels” is pretty meaningless to most people, but the numbers suggest that this phone is something special because it uses scientific-sounding language.
It doesn’t matter whether audiences really understand what’s being said or not. What matters is that they feel confident that the ad is selling them something they need —in this case, impressive technological specifications that make this phone an improvement over others.
Kairos should ideally factor into all uses of the modes of persuasion, but timeliness can also be a big selling point. In this Christmas-themed M&Ms advertisement, the company uses timely humor to forge a connection between the holidays and M&Ms.
Because these commercials have been running for such a long time, there’s also a nostalgic attachment to them. Just as people look forward to new Budweiser advertisements during the Super Bowl, others look forward to seeing M&Ms or the Coca-Cola polar bear during the holidays.
Though this commercial doesn’t go out of its way to tell you the benefits of M&Ms, it does forge a connection between M&Ms and Christmas, encouraging people to purchase them around the holidays.

Examples of the Modes of Persuasion
Now that you’ve had some exposure to how ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos function and what they can do, you can test your ability to recognize them using the images below!

There are a few things to notice about this image:
- The anonymous figure
- The language
- The use of a statistic
Can you figure out which mode of persuasion this represents?
The fact that the figure is anonymous tells us it’s probably not ethos. While we might be influenced by a person who’s in shape, there’s not really an appeal here based on the person—they’re just an image to support the ad.
“DOMINATE” is a pretty loaded word, suggesting that this may have elements of pathos.
However, take a look at that statistic. Whether it’s true or not, a hard statistic like that suggests that this ad is using logos to appeal to viewers. You can draw out an argument from there—75% of users lose weight within weeks. You’re a user. Therefore, you will likely lose weight within weeks.

What do you notice about this image?
- The way the text frames the woman’s body
- The name of the perfume
- The color choice
What mode of persuasion is this?
Again, we don’t know who the model is, and perfume isn’t going to make us look like her, so we can count ethos out.
The ad seems pretty intent on making us look at certain things—the woman’s lips and chest in particular. What is it trying to make us feel?
“FORBIDDEN FRUIT” has a connotation of sensuality.
Red is a color commonly associated with passion.
When you combine the photo, the framing, the perfume name, and the color, you get a strong sense of sex appeal from the advertisement. This makes it an example of pathos—the ad is trying to make us feel a certain way . If we buy this perfume, maybe we would feel attractive, too.

How about this advertisement?
- A serious-looking photo
- Text promising “no more back pain”
- “Doctor recommended.”
Seeing a doctor might make you tempted to think the answer is logos, but there’s no appeal to logic here.
“No more back pain,” is a nice promise, but there’s no attempt to appeal to emotions, so it can’t be pathos.
What’s important in this image is the combination of the doctor in the image and the line “doctor recommended.” This doctor might not be famous, but he does have authority, making this an example of ethos.
Our confidence in this treatment grows because we trust that a doctor understands how to address back pain.

What mode of persuasion is this? Think about:
- The framing
She does look fashionable and the ad mentions stylists, so it’s possible that this is ethos.
There are no statistics or arguments being made, so the answer probably isn’t logos.
Pathos is possible, but despite having a heavily made-up model, this ad is far less about sex appeal than the previous one.
But the text mentions a specific holiday—New Year’s—suggesting that this is kairos. Kairos can, and often should, be combined with all the modes of persuasion to be even more effective. In this case, the model’s appearance could suggest either ethos or pathos in addition to kairos. The message here is that you should act now, at the beginning of the year, to take advantage of the deal and to start the year off with a new style, much like the one the model is sporting.

Key Tips for Identifying Ethos, Pathos, Logos, and Kairos
Now that you know the difference between all the modes of persuasion, you’ll have a much easier time identifying them. If you run into trouble, you can always ask questions about what you’re seeing, hearing, or reading to understand what mode of persuasion it’s using.
#1: Is It Related to a Specific Time?
If the argument is based on a specific day or context, such as Valentine’s Day or appealing only to a select group of people, such as people with dogs, it’s more likely to be kairos.
#2: Does It Involve a Celebrity or Authority Figure?
Celebrities are often a dead giveaway that an argument is using ethos. But authority figures, such as doctors, dentists, or politicians, can also be used to appeal to ethos. Even regular, everyday people can work, particularly when combined with pathos, to appeal to you based on a mutual connection you have.
#3: Does It Involve Statistics?
Statistics are a huge clue that an argument is using logos. But logos can also just be a logical argument, such as that if plants need water, and it’s hard to remember to water them, you should buy an automatic plant waterer. It makes perfect sense, making you more likely to buy it, rather than changing your habits to remember to water your plants more frequently.
#4: Does It Influence Your Emotions?
If an argument tries to change your emotions, whether by making you sad, happy, angry, or something else entirely, it’s a good indicator that it’s using pathos. Sex appeal is one of the biggest examples of pathos in advertising, appearing everywhere from makeup ads to car commercials to hamburger advertisements.
What’s Next?
Need help understanding the historical context for The Great Gatsby to perfect your kairos-based argument?
You can always combine the modes of persuasion with literary devices to make your arguments even stronger!
Learn how to say "good morning" in Japanese ! Even if it's not a mode of persuasion, it's just good manners.

Melissa Brinks graduated from the University of Washington in 2014 with a Bachelor's in English with a creative writing emphasis. She has spent several years tutoring K-12 students in many subjects, including in SAT prep, to help them prepare for their college education.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Unlocking the Power of Persuasion: Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
This essay about the foundational principles of persuasion—ethos, pathos, and logos—details how these rhetorical strategies, established by Aristotle, function in influencing audiences. It discusses how ethos builds speaker credibility, pathos connects emotionally, and logos appeals through logic. Examples are provided from various fields, including advertising and influential speeches, illustrating the effective combination of these elements in practical scenarios to enhance communication and persuasive power.
How it works
Persuasion is an ancient art, refined through the centuries as a pivotal tool in the spheres of politics, education, and advertisement. At the core of this art lie three fundamental principles—ethos, pathos, and logos—introduced by Aristotle over 2,300 years ago. These rhetorical strategies offer a powerful framework through which we can understand and wield the art of persuasion more effectively in everyday interactions.
Ethos refers to the credibility or ethical appeal of the speaker. It encompasses the speaker’s character as the audience perceives it.
When we trust those who speak to us, their messages resonate more profoundly and their arguments become more convincing. Establishing ethos involves demonstrating competence, virtue, and goodwill. For example, a doctor discussing health issues naturally embodies ethos through their professional qualifications and experiences. Similarly, a teacher’s ethos is established through both their mastery of the subject and their dedication to students’ growth.
Pathos , on the other hand, appeals to the audience’s emotions. It aims to evoke feelings that prompt action. This emotional connection can be harnessed through storytelling, vivid imagery, or passionate delivery. It is often seen in advertising, where marketers create poignant narratives around their products to enhance desirability. For instance, charities use pathos effectively by showing heart-wrenching images of people in need to stimulate empathy and encourage donations. However, overuse or manipulation of emotional appeal can lead to skepticism and a loss of credibility.
Logos is the logical appeal based on reasoning. This aspect involves presenting clear, logical arguments that include facts, statistics, and undeniable data. Logical reasoning requires constructing a coherent argument that leads the audience to a rational conclusion. In academic or professional settings, logos is paramount as decisions need to be backed by solid evidence and clear thought processes. For instance, a business proposal that outlines potential returns on investment through detailed forecasts and market analysis utilizes logos to persuade stakeholders.
The most effective persuasive efforts typically combine these elements. A speaker might begin with an introduction that establishes their credibility (ethos), then appeal to the audience’s values and emotions (pathos), and conclude with compelling data and logical arguments (logos). This holistic approach can be seen in influential speeches like Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” where King established his ethos by aligning with moral and religious principles, invoked pathos through his passionate and poetic delivery, and used logos by referencing the American Constitution and the Emancipation Proclamation.
Understanding and mastering the use of ethos, pathos, and logos allows individuals to communicate more effectively and persuasively. In everyday life, being aware of these elements can help one discern the strategies behind the messages we receive from politicians, advertisers, or even friends and family, making us more informed and discerning listeners. Moreover, in crafting our messages, leveraging these pillars of rhetoric can enhance the impact of our communication, ensuring we convey our ideas in a manner that truly engages and moves our audience.
In conclusion, the power of persuasion lies in a balanced approach to building credibility, connecting emotionally, and reasoning logically. By enriching our understanding of ethos, pathos, and logos, we unlock the potential to influence, motivate, and persuade, paving the way for more meaningful and effective communication.
Cite this page
Unlocking the Power of Persuasion: Ethos, Pathos, and Logos. (2024, May 12). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/unlocking-the-power-of-persuasion-ethos-pathos-and-logos/
"Unlocking the Power of Persuasion: Ethos, Pathos, and Logos." PapersOwl.com , 12 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/unlocking-the-power-of-persuasion-ethos-pathos-and-logos/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Unlocking the Power of Persuasion: Ethos, Pathos, and Logos . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/unlocking-the-power-of-persuasion-ethos-pathos-and-logos/ [Accessed: 19 May. 2024]
"Unlocking the Power of Persuasion: Ethos, Pathos, and Logos." PapersOwl.com, May 12, 2024. Accessed May 19, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/unlocking-the-power-of-persuasion-ethos-pathos-and-logos/
"Unlocking the Power of Persuasion: Ethos, Pathos, and Logos," PapersOwl.com , 12-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/unlocking-the-power-of-persuasion-ethos-pathos-and-logos/. [Accessed: 19-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Unlocking the Power of Persuasion: Ethos, Pathos, and Logos . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/unlocking-the-power-of-persuasion-ethos-pathos-and-logos/ [Accessed: 19-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Nicholas Whaley

Aristotle, a student of the Greek philosopher Plato, is considered one of history’s greatest philosophers and the figure responsible for the three rhetorical appeals upon which modern rhetorical studies are built. Aristotle defined three distinct rhetorical appeals as they pertained to the art of persuasion: ethos (the rhetor’s credibility), logos (logic or rationality), and pathos (emotion).
Ethos in rhetoric is defined as “the role of the writer (speaker) in the argument and how credible his/her argument is” (“Rhetorical Triangle”). This definition can be further explicated as referring to how knowledgeable or wise the speaker is about their argument as well as how reputable the individual is morally in the eyes of their audience. Aristotle called this “persuasion through character,” as ethos primarily explores the characteristics of the speaker. Etiquette is also a factor in developing an effective ethos. This includes proper use of tone, word choice, and respect for the views of the audience.
Rather than being merely a translation of “logic,” logos refers to the content of an argument and its organization. Forming meaningful connections between facts, supporting claims through factual evidence and statistics, and even the use of historical or literal analogies to create logical connections between ideas are all elements of logos (St. Louis). Where its two counterparts, ethos and pathos, relate to the human qualities of the speaker and audience, logos refers primarily to the characteristics of the argument itself in both its formal structure and presentation.
To utilize pathos in one’s rhetoric means to appeal to the audience’s values and beliefs such that they are more likely to be emotionally swayed to favor the speaker’s argument. The goal when using pathos in rhetoric is to bring the audience into an emotional state in which they are more likely to hear out the speaker’s ideas and thus be more likely to consider the validity of said ideas. A speaker should understand the values and beliefs of their audience so as to avoid unintended offense or wrongful assumptions and to have adequate knowledge of their audience in order to present their argument in a manner listeners will find agreeable and worth supporting. Aristotle noted that human beings do, in fact, impart judgement differently depending on their emotional state. Consequently, it is in the speaker’s interest to design their speech so as to spark the appropriate emotional response from their listeners.
- Lutske, Jaclyn, and Mary F. Henggeler. “ The Rhetorical Triangle: Understanding and Using Logos, Ethos, and Pathos .” Indiana University School of Liberal Arts, 2009.
- St. Louis Community College Writing Center. “ Pathos, Logos, and Ethos .” Accessed 3 May 2022.
Open Rhetoric Copyright © by Nicholas Whaley is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
How to use Ethos, Pathos and Logos in a Persuasive Essay
Oct 21, 2023 | 0 comments

Oct 21, 2023 | Blog | 0 comments
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos are three types of persuasion that an author or speaker can use to convince the audience. Ethos is the appeal to ethics, and it is a means of convincing someone of the character or credibility of the persuader. Pathos is the appeal to emotion, and it’s a way of convincing an audience of an argument by creating an emotional response. Logos is the appeal to logic, and it uses logical reasoning as its main tool for persuasion.
This article will discuss using these three modes when writing your essay. The difference between ethos, pathos, and logos will be elaborated by ethos, pathos, and logos examples.
People Also Read
- What Is a Blue Book?- All You Need to Know as a Student
- The Role Of Feedback And Reflection In Improving Diagnostic Essay Writing Skills
- Understanding the Limitations of Survey-based Studies
What Is Logos?
The third and final aspect of ethos, logos, is an appeal to logic. It attempts to persuade readers by using reason, rationality, and facts. You can use logos to present evidence for your thesis statement—using statistics or examples from the world around you—or it can be used as a standalone approach. Either way, logos are best when backed up by evidence from the real world.
Logos makes sense because it appeals to our rational minds: we use logic every day to make decisions (or not). We ask ourselves, “Is this a good idea?” or “Will this benefit me?” We weigh the pros and cons before acting on impulse; we think about consequences before making purchases; we run through a cost-benefit analysis before investing our time or money into something new. Logos tries its hardest not just because it makes sense but because it works!
Examples of Logos
Logos are often used in essays to support a claim, explain why something is true, or give an example. For example:
- “I can’t wait for our next meeting because it will be fun.” (explanation)
- “That’s not fair! You’re supposed to let me go first.” (reasoning)
Logos are especially useful when persuading someone or making your point clear. They’re also good for showing that you understand how things work or what makes them important. For example:
- “I know that many people think they need a degree to get a job in this field, but I think most employers value experience over education anyway.” (logical reasoning)
What Is Ethos
Ethos is an appeal to ethics, and it is a means of convincing someone of the character or credibility of the persuader. Ethos is the Greek word for “character.” The rhetoric must establish trust with an audience to persuade them effectively. Effective ethos will make your audience feel more comfortable with you and more likely to believe what you say.
To establish ethos, you can refer to other people who have similar credentials, experience, or knowledge as yourself or else provide evidence that shows how your expertise has been beneficial in similar situations before (this makes it easier for others to accept your knowledge because they know how much experience you have).
Examples of Ethos
Examples of Ethos:
- Speeches (e.g., Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech)
- Advertisements (e.g., Nike’s “Just Do It” campaign)
- Literature and poetry (e.g., Edgar Allan Poe’s “ The Raven “)
- Journalism (e.g., the New York Times’ coverage of Hurricane Harvey)
- Politics (e.g., Donald Trump’s presidential inauguration speech)
In daily life, you can use examples of ethos to persuade people to get what you want or do what you ask them to do.
What Is Pathos?
Pathos is all about the emotional connection between the speaker and the audience. It’s an appeal to the senses and feelings of an audience, often through pity or sympathy.
Essentially, pathos is all about persuasion through emotion: it’s how you can use pathos in your writing (and in life) to influence people—and get them on your side.
Because when we’re moved by something, whether it be a person’s suffering or a cause we believe in, we are more likely to act on that feeling than if there were no emotion.
So, what emotions does pathos evoke? There are many ways for writers and speakers alike to use pathos in their work—but these three methods of persuasion will probably come up most often: empathy, fear, guilt/shame.
Examples of Pathos
Here are some examples of how you can use pathos in various forms of writing:
- In advertising, an emotional appeal is often used to persuade viewers that a product will improve their lives. For example, one advertisement might portray a family enjoying time together using their new vacuum cleaner. Another advertisement might show a man alone at home watching TV and eating potato chips—but he could be happy if only he had this new brand of hot sauce!
- In speeches or debates, an emotional appeal is often used to encourage people to take action on something important to them or others. An activist might speak about how many animals have died yearly because they were trapped in animal testing labs—and ask everyone listening what they will do. A politician might talk about how his opponent’s policies won’t truly help people who need jobs; instead, he’ll ensure everyone has health insurance and gets paid more money for working full-time than if they were unemployed!
- Legal cases can include stories from witnesses or victims who experienced suffering because someone else committed wrongdoings against them (or even themselves). If you want someone else punished for stealing your car stereo system when all you did was walk outside your house one day and then come back later when there was nothing left where it should’ve been…then tell us why we should care!
Bonus: What Is Kairos?
Kairos is the right time to deliver your message.
It’s used in persuasive writing to take advantage of your audience’s current state of mind so they’re more likely to listen and act on whatever you’re trying to get across.
The best way to use kairos is by connecting with your reader emotionally—you want them to relate what you have written with their own experiences so that they can connect with what you are saying, whether it be about a product or an idea.
Examples of Kairos
Kairos is a Greek word meaning “the right or opportune moment (the supreme moment).” When the time is right, you do the right thing.
One of the most classic uses of kairos was in ancient Greece, when people would use it before speaking to kings and royalty. If someone had something important to say, they waited for a kairotic moment where both parties were available and in an appropriate mood to hear their speech.
You can use Kairos when you need to take advantage of an opportunity as soon as it arises. It’s similar to timeliness, but rather than just being on time, it’s more like jumping into action before anyone else has thought about doing so themselves! This can be useful when trying out new ideas or coming up with innovative solutions because you can come up with them before anyone else does, which means that other people will start thinking about them (which could give them ideas).
Final Thoughts on Ethos Pathos and Logos
Ethos, pathos, and logos are three important elements to consider when writing your essay.
- Ethos is the writer’s credibility, which you can establish by using facts and figures that are credible and relevant to the topic being discussed.
- Pathos is an appeal to emotion to create a connection with the reader, who will feel compelled to agree with your argument. Opening paragraphs of essays often use pathos because they set expectations for what will come later in the essay.
- Logos refers to appeals based on logic or reason rather than emotions or feelings—and, as such, relies on strong arguments supported by evidence (facts). You can use logos in any part of your essay, but especially at the end, where you want readers who did not initially agree with your point of view to change their minds after reading your supporting evidence.
Get Help from our Experts with your essay.
Our company is a professional writing service that helps students with essay writing. We have been offering this type of help to students for over 20 years, so we know what works and what does not in terms of academic success. Our team consists of highly qualified experts ready to provide you with the best possible assistance at any process stage, from initial brainstorming to final editing. In addition, we use advanced tools such as Grammarly to ensure that your written composition is flawless and fully consistent with all academic standards.
We can help you in many ways:
- Developing an outline for your essay by guiding how it should look and where each paragraph should go;
- Writing an entire paper from scratch if you don’t have enough time or confidence;
- Revising existing essays according to your instructions (you can find examples here);

I am dedicated to creating engaging blog posts that provide valuable insights and advice to help students excel in their studies. From study tips to time management strategies, my goal is to empower students to reach their full potential.
- Best 10 Persuasive Essay Examples for Students in 2024
- Essay writing: Fresh Revision Ideas

Most Popular Articles
Racism thesis statement example, how to rephrase a thesis statement, capstone project topic suggestions, how to write an abortion essay, should students wear school uniforms essay, list causal essay topics write, respect essay, signal words, great synonyms, informative speech examples, essay writing guide, introduction paragraph for an essay, argumentative essay writing, essay outline templates, write an autobiographical essay, personal narrative essay ideas, descriptive essay writing, how to write a reflective-essay, how to write a lab report abstract, how to write a grant proposal, point of view in an essay, debate topics for youth at church, theatre research paper topics, privacy overview.
- 1-844-845-1517
- 1-424-210-8369
- PLACE ORDER

- Logos, Ethos, Pathos May 18, 2024
- Being the Boss May 17, 2024
- End of Days May 16, 2024
- Human Trafficking May 15, 2024
Logos, Ethos, Pathos

A s a reader, it is essential to recognize how various writers and speakers use logos, ethos, and pathos as they communicate. For writers and communicators, it is important to understand how others are using logos, ethos, and pathos so that it can be easier to adapt the same when speaking and writing. When evaluating logos, you consider logic and how well the arguments are supported, mostly in terms of evidence. In essence, logos involves the use of logic and reasoning when crafting any writing to elevate the material and level of engagement with the readers. When evaluating ethos, you examine both authority and credibility and how they are established by the writer or the speaker (Lumen, 2020). On the other hand, pathos regards how the communicator enables the audience to find a personal connection. This is mostly achieved through evoking emotions. The story “That Time the Internet Sent a SWAT Team to My Mom’s House” by Caroline Sinders makes use of these elements to communicate with the audience and bring about the main message. This paper evaluates how logos, ethos, and pathos have been used in the story to communicate with the audience.

Throughout the story, the author has structured the arguments logically with support in terms of evidence. As a result, she builds logos which is why the audience tends to believe the opinions. Most of her arguments in the story are founded on a strong background in research (Lumen, 2020). The main concern for the author of the story is to understand online harassment as witnessed on social media platforms. She, for example, joints Twitter hashtags to understand and be closer to the source of online harassment. She retweets the anti-Gamergate tweets , most of which featured hashtags bearing the name Gamergate. By doing so, the author of the story understood, watched and documented what was going on with such hashtags. According to her, it is at this point that she began to notice some of her friends being harassed to a level enough to push them to a private corner within the Twitter social platform (Sinders, 2015). By “moving close to the sun,” the author was able to support her arguments regarding online harassment and other issues that may regard privacy. According to her online engagements, online harassment is not likely to end any time soon. Based on the extensive research on aspects that result in online harassment, it becomes easier for the author to communicate through logos. She gives evidence obtained from the study mostly to back her arguments.
The story’s first sentence indicates that the author had received an email from a reporter for a New Orleans newspaper. According to the author, the reporter had just come across the author’s name while researching an article. Although the author was not the main subject of the reporter’s research objective, coming across her name indicates her position and recognizability as a report. She even recognizes herself as “a budding researcher” on matters regarding online harassment (Sinders, 2015). This is part of her status that enables Sinders to build ethos and communicate to the audience. The fact that a report from a New Orleans newspaper had reached out gives Sinders the authority to get in touch with the audience. Although it was easier for the author to mention that she is a budding researcher on online harassment, she also says that she spent more than six months researching the area to understand how it works (Lumen, 2020). This is what Sinders uses to build credibility, which most audiences look after, especially when it is not easy to distinguish the truth from fake information due to the reporters’ objectivity. This is how the author builds ethos while communicating with the audience.
At the beginning of the story, and after reading the email, the author mentions how she had received an email about her mother being “swatted.” In many ways, Sinders appears to be sorry about the incident. Using a remorseful tone, she initially acknowledges that it was her fault that her mother was pranked – “swatted.” She says, “My mom had been swatted, and it was my fault (Sinders, 2015).” In response to that, and as a demonstration of how sorry she was, she stopped reading the email and immediately reached out to her mother through a call. She interrupts her mother as she tries to catch up with her on matters relating to their family and proceeds straight to her main concern – swatting. This is how the author builds pathos and creates a personal connection with the audience. Generally, people may not be interested in an issue until they find a way to connect to it (Lumen, 2020). To achieve this, Sinders evokes several emotions such as empathy, making it easy to communicate with the audience. After researching, the author then discovers that swatting can be attributed to gaming, which is another way of expressing its negative side. This argument is based on research allowing the author to gain more audience since her arguments are based on evidence.
References
Lumen. (2020). English Composition I: Evaluating Appeals to Ethos, Logos, and Pathos . Retrieved from Lumen: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/engcomp1-wmopen/chapter/text-evaluating-appeals-to-ethos-logos-and-pathos/
Sinders, C. (2015, 07 17). That Time the Internet Sent a SWAT Team to my Mom’s House . Retrieved from Narratively: https://narratively.com/that-time-the-internet-sent-a-swat-team-to-my-moms-house/
- Tags Ethos , Logos , Pathos

By Hanna Robinson
Hanna has won numerous writing awards. She specializes in academic writing, copywriting, business plans and resumes. After graduating from the Comosun College's journalism program, she went on to work at community newspapers throughout Atlantic Canada, before embarking on her freelancing journey.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Related Posts
College Essay Examples | January 24, 2022
Sweets Baby Guidelines
College Essay Examples | November 5, 2022
Media and Interpersonal Communication
College Essay Examples | September 18, 2017
DERIVING DUTIES FROM THE CATEGORICAL IMPERATIVE – KANT ESSAY SAMPLE
College Essay Examples | August 24, 2021
Blood Pressure Points
Begin typing your search term above and press enter to search. Press ESC to cancel.

8 Shockingly Easy Shortcuts to Get Your Essay Done Fast
Free 6-page report.

- Get your essay finished
- Submit your work on time
- Get a high grade
No thanks. I don't want the FREE report.
I’ll risk missing the deadline.
Get that Essay Finished in No Time


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Simply put, logos, ethos and pathos are three powerful tools that you can use to persuade an audience of your argument. At the most basic level, logos appeals to logic and reason, while pathos appeals to emotions and ethos emphasises credibility or authority. Naturally, a combination of all three rhetorical appeals packs the biggest punch, but ...
Aristotle developed the concept of "ethos," "logos," and "pathos.". Ethos, logos, and pathos are elements of writing that make it more effective and persuasive. While ethos establishes the writer's credibility, logos appeals to the audience's reason, and pathos appeals to their emotions. These three concepts, also known as the ...
Logos appeals to the audience's reason, building up logical arguments. Ethos appeals to the speaker's status or authority, making the audience more likely to trust them. Pathos appeals to the emotions, trying to make the audience feel angry or sympathetic, for example. Collectively, these three appeals are sometimes called the rhetorical ...
Conclusion. Ethos, logos, and pathos are powerful tools for persuasive speech and writing. By establishing credibility, using logical arguments, and appealing to emotion, speakers and writers can influence the beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors of their audiences. When used effectively, these elements can help to create meaningful and lasting ...
Rhetorical Appeals. Rhetorical appeals refer to ethos, pathos, and logos. These are classical Greek terms, dating back to Aristotle, who is traditionally seen as the father of rhetoric. To be rhetorically effective (and thus persuasive), an author must engage the audience in a variety of compelling ways, which involves carefully choosing how to ...
You may not know it but you need logos, ethos, pathos, and even kairos to come up with a good essay. Basically, these things, also called modes of persuasion, ethical strategies, or rhetorical appeals, can help you convince your audience and support your arguments. These four elements of persuasion were even described by Aristotle in his ...
Tips for Applying Logos in Your Writing. Strategy 1 — State the facts. Statistics, data, and other irrefutable facts make ideal evidence. "Twenty-seven percent of college students will experience back pain at some point due to the weight of their textbooks.". Strategy 2 — Show that it would be unreasonable not to take your side.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Ethos, Pathos, Logos Created by: Brandon Everett Summer 2019 An appeal is an author's attempt to earn audience approval. Authors will utilize specific devices and techniques to appeal to emotion, values, character, and reason in their writing in order to make their arguments more persuasive.
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos are three strategies commonly employed when attempting to persuade a reader. Pathos, or the appeal to emotion, means to persuade an audience by purposely evoking certain emotions to make them feel the way the author wants them to feel. Authors make deliberate word choices, use meaningful language, and use examples and ...
Read about pathos, ethos, and logos. Learn the definition of these modes of persuasion, identify how to use them to appeal to an audience, and view examples. Updated: 11/21/2023
Aside from the writer's ethics, ethos can also be generated by the author's credibility, which is usually based on (1) the ability to forward a logical argument (hence, ethos can be affected by logos!), (2) thoroughness of significant research, and (3) credentials proving the writer's expertise.
When writing your argumentative essay, consider implementing pathos, ethos, and logos based. approaches. All three approaches should be balanced throughout your paper in order to create a strong. point. Pathos the appeal to emotion, means to persuade an audience by purposely evoking certain emotions to make them feel the way the author wants ...
Quote illustrates how the author uses appeal to ethos; Analysis explains how quote supports thesis; Conclusion returns to the ideas in the thesis and further develops them; Last sentence returns to the hook in the introduction; Learn more about the "Rhetorical Analysis Graphic Organizer." Learn more about "Pathos, Logos, and Ethos."
Make sure your argument is persuasive by learning the three modes of persuasion—ethos, pathos, and logos—and how to effectively use them in communication.
Ethos, pathos and logos are the three categories of persuasive advertising techniques. Each category invokes a different appeal between speaker and audience. Ethos calls upon the ethics, or what we'd call the values, of the speaker. Pathos elicits emotions in the audience. Finally, logos puts logic into play by using evidence and facts.
In summary, using ethos, pathos, and logos is essential to strengthen your point and persuade the audience. Without using these rhetorical devices, the readers will not understand the frame of mind of the writer. If you are still unclear about the concept and its usage, it is advised to get help from expert analytical essay writer.
Ethos, along with logos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Ethos is an argument that appeals to the audience by emphasizing the speaker's credibility and authority. If the speaker has a high-ranking position, is an expert in his or her field, or has had life experience ...
When Writers Misuse Logos, Pathos, or Ethos, Arguments can be Weakened. Above, we defined and described what logos, pathos, and ethos are and why authors may use those strategies. Sometimes, using a combination of appeals leads to a sound, balanced, and persuasive argument.
22 Ethos, Pathos, & Logos Using Rhetorical Appeals to Support Your Argument. In addition to choosing an effective rhetorical mode (see Rhetorical Modes for Paragraphs & Essays for details) for an essay, you need to think about the most effective rhetorical appeal, or way of persuading your audience.. Writers are generally most successful with their audiences when they can skillfully and ...
Del Mar Home Offices and Departments Stone Writing Center Essay Writing and Research The Rhetorical Triangle: Ethos, Pathos, and Logos The Rhetorical Triangle: Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Introduction. The Rhetorical Triangle is a simple, useful tool that can help you develop a strong and well thought-out essay, especially in persuasive writing and speeches.
Logos appeals to the audience's reason, building up logical arguments. Ethos appeals to the speaker's status or authority, making the audience more likely to trust them. Pathos appeals to the emotions, trying to make the audience feel angry or sympathetic, for example. Collectively, these three appeals are sometimes called the rhetorical ...
4.10 A review of the five-paragraph essay; 4.11 Moving Beyond the five-paragraph format; Deeper Reading: "I Need You to Say I" Chapter 5: Writing a Summary and Synthesizing ... we defined and described what logos, pathos, and ethos are and why authors may use those strategies. Sometimes, using a combination of logical, pathetic, and ethical ...
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Definition and Examples. Ethos, Pathos, and Logos are modes of persuasion used to convince audiences. They are also referred to as the three artistic proofs (Aristotle coined the terms), and are all represented by Greek words. Ethos or the ethical appeal, means to convince an audience of the author's credibility or ...
The concepts of ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos are also called the modes of persuasion, ethical strategies, or rhetorical appeals. They have a lot of different applications ranging from everyday interactions with others to big political speeches to effective advertising. Read on to learn about what the modes of persuasion are, how they're ...
Essay Example: Persuasion is an ancient art, refined through the centuries as a pivotal tool in the spheres of politics, education, and advertisement. At the core of this art lie three fundamental principles—ethos, pathos, and logos—introduced by Aristotle over 2,300 years ago. These
Aristotle defined three distinct rhetorical appeals as they pertained to the art of persuasion: ethos (the rhetor's credibility), logos (logic or rationality), and pathos (emotion). Ethos. Ethos in rhetoric is defined as "the role of the writer (speaker) in the argument and how credible his/her argument is" ("Rhetorical Triangle").
4 Balance Act. Balancing logos, pathos, and ethos is more art than science. Think of your presentation as a meal: logos is the substance, pathos the flavor, and ethos the presentation. Too much ...
Ethos is the appeal to ethics, and it is a means of convincing someone of the character or credibility of the persuader. Pathos is the appeal to emotion, and it's a way of convincing an audience of an argument by creating an emotional response. Logos is the appeal to logic, and it uses logical reasoning as its main tool for persuasion.
In essence, logos involves the use of logic and reasoning when crafting any writing to elevate the material and level of engagement with the readers. When evaluating ethos, you examine both authority and credibility and how they are established by the writer or the speaker (Lumen, 2020). On the other hand, pathos regards how the communicator ...
6 Recognizing the Signs. To differentiate between ethos, pathos, and logos in writing, look for key indicators. Ethos often appears as credentials or ethical statements. Pathos can be identified ...