Creative Problem-Solving
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2023
- Cite this reference work entry

- Gerard J. Puccio 2 ,
- Barry Klarman 2 &
- Pamela A. Szalay 2
121 Accesses
Life and work in the beginning of the twenty-first century has been described as volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous. In this fast changing, innovation-driven environment, Creative Problem-Solving has been identified as a fundamental skill for success. In contrast to routine problem-solving, with straightforward and repeatable solution paths, today’s problems are described as being complex and wicked. To generate the possibilities that can effectively address complex problems, individuals need to draw on the highest level of human thought – creativity. Creative Problem-Solving explicitly draws on, and promotes, effective creative thinking. The purpose of this entry is to describe and distinguish Creative Problem-Solving from other forms of problems-solving. Moreover, as Creative Problem-Solving is a deliberate creativity methodology, this chapter also provides a description of the more specific thinking skills that are embodied by the higher-order skill of creative thinking and are explicitly called on in Creative Problem-Solving. Complex problems require complex thinking, and Creative Problem-Solving provides a structured process that allows individuals to more easily and efficiently deploy their creative thinking skills.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.

Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Anderson, L. W., & Krathwohl, D. R. (Eds.). (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching and assessing: A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives: Complete edition . New York: Longman.
Google Scholar
Basadur, M. (1994). Simplex. Buffalo, NY: The Creative Education Foundation.
Brackett, M. (2019). Permission to feel: Unlocking the power of emotions to help our kids, ourselves, and our society thrive . New York: Celadon Books.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1990). Flow: The psychology of optimal experience . New York: HarperPerennial.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1996). Creativity: Flow and the psychology of discovery and invention . New York: HarperCollins.
Darwin, C. (2003). The origin of species: By means of natural selection of the preservation of favoured races in the struggle for life (p. 252). New York: Signet Classics.
Goleman, D. (1995). Emotional intelligence: Why it can matter more than IQ . New York: Bantam.
Isaksen, S. G., & Treffinger, D. J. (1985). Creative problem solving: The basic course. Buffalo, NY: Bearly Limited.
Isaksen, S. G., Dorval, K. B., & Treffinger, D. J. (1994). Creative approaches to problem solving. Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt.
Isaksen, S. G., Dorval, K. B. & Treffinger, D. J. (2000). Creative approaches to problem solving (2nd ed.). Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt Publishing.
Johnson, B. (1996). Polarity management: Identifying and managing unsolvable problem . Amherst: HRD Press.
Miller, J. C. (2004). The transcendent function: Jung’s model of psychological growth through dialogue with the unconscious . Albany: State University of New York Press.
Morriss-Kay, G. M. (2010). The evolution of human artistic creativity. Journal of Anatomy, 216 , 158–176.
Article Google Scholar
Mumford, M. D., Zaccaro, S. J., Harding, F. D., Jacobs, T. O., & Fleishman, E. A. (2000). Leadership skills for a changing world: Solving complex problems. Leadership Quarterly, 11 , 11–35.
Osborn, A. F. (1953). Applied imagination: Principles and procedures of creative problem-solving . New York: Scribner.
Osborn, A. F. (1963). Applied imagination: Principles and procedures of creative problem-solving (3rd ed.). New York: Scribner.
Otani, A. (2015, January). These are the skills you need if you want to be headhunted. Retrieved on 27 July 2015 from Osborn, A. F. (1953). Applied imagination: Principles and procedures of creative problem-solving . New York: Scribner.
Parnes, S. J. (1967). Creative behavior workbook. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
Parnes, S. J. (1988). Visionizing. East Aurora, NY: D.O.K. Publishers.
Parnes, S. J. (1992). Creative problem solving and visionizing. In S.J. Parnes (Ed.), Sourcebook for creative problem solving (pp. 133–154). Buffalo, NY: Creative Education Press.
Parnes, S. J., & Biondi, A. M. (1975). Creative behavior: A delicate balance. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 9 , 149–158.
Puccio, G. J. (2017). From the dawn of humanity to the 21st century: Creativity as an enduring survival skill. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 51 , 330–334. https://doi.org/10.1002/jocb.203 .
Puccio, G. J., Murdock, M. C., & Mance, M. (2005). Current developments in creative problem solving for organizations: A focus on thinking skills and styles. The Korean Journal of Thinking & Problem Solving, 15 , 43–76.
Puccio, G. J., Mance, M., & Murdock, M. (2011). Creative leadership: Skills that drive change (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks: SAGE.
Puccio, G. J., Mance, M., Switalski, B., & Reali, P. (2012). Creativity rising: Creative thinking and problem solving in the 21st century . Buffalo: ICSC Press.
Puccio, G. J., Burnett, C., Acar, S., Yudess, J. A., Holinger, M., & Cabra, J. F. (2018). Creative problem solving in small groups: The effects of creativity training on idea generation, solution creativity, and leadership effectiveness. The Journal of Creative Behavior . Advance online publication. [not sure of order]. https://doi.org/10.1002/jocb.381 .
Scott, G. M., Leritz, L. E., & Mumford, M. D. (2004). The effectiveness of creativity training: A meta-analysis. Creativity Research Journal, 16 , 361–388.
Stokes, P. D. (2013). Crossing disciplines: A constraint-based model of the creative/innovative process. The Journal of Product Innovation Management, 31 (2), 247–228. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12093 .
Trilling, B., & Fadel, C. (2009). 21st century skills: Learning for life in our times . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Vehar, J. R., Firestien, R. L., & Miller, B. (1997). Creativity unbound. Williamsville, NY: Innovation Systems Group.
Wagner, T. (2008). The global achievement gap: Why even our best schools don’t teach the new survival skills our children need – And what we can do about it . New York: Basic Books.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
International Center for Studies in Creativity, The State University of New York, Buffalo, NY, USA
Gerard J. Puccio, Barry Klarman & Pamela A. Szalay
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gerard J. Puccio .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Dublin City University, Dublin, Ireland
Vlad Petre Glăveanu
Section Editor information
No affiliation provided
Sergio Agnoli
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Puccio, G.J., Klarman, B., Szalay, P.A. (2022). Creative Problem-Solving. In: Glăveanu, V.P. (eds) The Palgrave Encyclopedia of the Possible. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90913-0_41
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90913-0_41
Published : 26 January 2023
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-90912-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-90913-0
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 10 min read
Creative Problem Solving
Finding innovative solutions to challenges.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Imagine that you're vacuuming your house in a hurry because you've got friends coming over. Frustratingly, you're working hard but you're not getting very far. You kneel down, open up the vacuum cleaner, and pull out the bag. In a cloud of dust, you realize that it's full... again. Coughing, you empty it and wonder why vacuum cleaners with bags still exist!
James Dyson, inventor and founder of Dyson® vacuum cleaners, had exactly the same problem, and he used creative problem solving to find the answer. While many companies focused on developing a better vacuum cleaner filter, he realized that he had to think differently and find a more creative solution. So, he devised a revolutionary way to separate the dirt from the air, and invented the world's first bagless vacuum cleaner. [1]
Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of solving problems or identifying opportunities when conventional thinking has failed. It encourages you to find fresh perspectives and come up with innovative solutions, so that you can formulate a plan to overcome obstacles and reach your goals.
In this article, we'll explore what CPS is, and we'll look at its key principles. We'll also provide a model that you can use to generate creative solutions.
About Creative Problem Solving
Alex Osborn, founder of the Creative Education Foundation, first developed creative problem solving in the 1940s, along with the term "brainstorming." And, together with Sid Parnes, he developed the Osborn-Parnes Creative Problem Solving Process. Despite its age, this model remains a valuable approach to problem solving. [2]
The early Osborn-Parnes model inspired a number of other tools. One of these is the 2011 CPS Learner's Model, also from the Creative Education Foundation, developed by Dr Gerard J. Puccio, Marie Mance, and co-workers. In this article, we'll use this modern four-step model to explore how you can use CPS to generate innovative, effective solutions.
Why Use Creative Problem Solving?
Dealing with obstacles and challenges is a regular part of working life, and overcoming them isn't always easy. To improve your products, services, communications, and interpersonal skills, and for you and your organization to excel, you need to encourage creative thinking and find innovative solutions that work.
CPS asks you to separate your "divergent" and "convergent" thinking as a way to do this. Divergent thinking is the process of generating lots of potential solutions and possibilities, otherwise known as brainstorming. And convergent thinking involves evaluating those options and choosing the most promising one. Often, we use a combination of the two to develop new ideas or solutions. However, using them simultaneously can result in unbalanced or biased decisions, and can stifle idea generation.
For more on divergent and convergent thinking, and for a useful diagram, see the book "Facilitator's Guide to Participatory Decision-Making." [3]
Core Principles of Creative Problem Solving
CPS has four core principles. Let's explore each one in more detail:
- Divergent and convergent thinking must be balanced. The key to creativity is learning how to identify and balance divergent and convergent thinking (done separately), and knowing when to practice each one.
- Ask problems as questions. When you rephrase problems and challenges as open-ended questions with multiple possibilities, it's easier to come up with solutions. Asking these types of questions generates lots of rich information, while asking closed questions tends to elicit short answers, such as confirmations or disagreements. Problem statements tend to generate limited responses, or none at all.
- Defer or suspend judgment. As Alex Osborn learned from his work on brainstorming, judging solutions early on tends to shut down idea generation. Instead, there's an appropriate and necessary time to judge ideas during the convergence stage.
- Focus on "Yes, and," rather than "No, but." Language matters when you're generating information and ideas. "Yes, and" encourages people to expand their thoughts, which is necessary during certain stages of CPS. Using the word "but" – preceded by "yes" or "no" – ends conversation, and often negates what's come before it.
How to Use the Tool
Let's explore how you can use each of the four steps of the CPS Learner's Model (shown in figure 1, below) to generate innovative ideas and solutions.
Figure 1 – CPS Learner's Model
Explore the Vision
Identify your goal, desire or challenge. This is a crucial first step because it's easy to assume, incorrectly, that you know what the problem is. However, you may have missed something or have failed to understand the issue fully, and defining your objective can provide clarity. Read our article, 5 Whys , for more on getting to the root of a problem quickly.
Gather Data
Once you've identified and understood the problem, you can collect information about it and develop a clear understanding of it. Make a note of details such as who and what is involved, all the relevant facts, and everyone's feelings and opinions.
Formulate Questions
When you've increased your awareness of the challenge or problem you've identified, ask questions that will generate solutions. Think about the obstacles you might face and the opportunities they could present.
Explore Ideas
Generate ideas that answer the challenge questions you identified in step 1. It can be tempting to consider solutions that you've tried before, as our minds tend to return to habitual thinking patterns that stop us from producing new ideas. However, this is a chance to use your creativity .
Brainstorming and Mind Maps are great ways to explore ideas during this divergent stage of CPS. And our articles, Encouraging Team Creativity , Problem Solving , Rolestorming , Hurson's Productive Thinking Model , and The Four-Step Innovation Process , can also help boost your creativity.
See our Brainstorming resources within our Creativity section for more on this.
Formulate Solutions
This is the convergent stage of CPS, where you begin to focus on evaluating all of your possible options and come up with solutions. Analyze whether potential solutions meet your needs and criteria, and decide whether you can implement them successfully. Next, consider how you can strengthen them and determine which ones are the best "fit." Our articles, Critical Thinking and ORAPAPA , are useful here.
4. Implement
Formulate a plan.
Once you've chosen the best solution, it's time to develop a plan of action. Start by identifying resources and actions that will allow you to implement your chosen solution. Next, communicate your plan and make sure that everyone involved understands and accepts it.
There have been many adaptations of CPS since its inception, because nobody owns the idea.
For example, Scott Isaksen and Donald Treffinger formed The Creative Problem Solving Group Inc . and the Center for Creative Learning , and their model has evolved over many versions. Blair Miller, Jonathan Vehar and Roger L. Firestien also created their own version, and Dr Gerard J. Puccio, Mary C. Murdock, and Marie Mance developed CPS: The Thinking Skills Model. [4] Tim Hurson created The Productive Thinking Model , and Paul Reali developed CPS: Competencies Model. [5]
Sid Parnes continued to adapt the CPS model by adding concepts such as imagery and visualization , and he founded the Creative Studies Project to teach CPS. For more information on the evolution and development of the CPS process, see Creative Problem Solving Version 6.1 by Donald J. Treffinger, Scott G. Isaksen, and K. Brian Dorval. [6]
Creative Problem Solving (CPS) Infographic
See our infographic on Creative Problem Solving .

Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of using your creativity to develop new ideas and solutions to problems. The process is based on separating divergent and convergent thinking styles, so that you can focus your mind on creating at the first stage, and then evaluating at the second stage.
There have been many adaptations of the original Osborn-Parnes model, but they all involve a clear structure of identifying the problem, generating new ideas, evaluating the options, and then formulating a plan for successful implementation.
[1] Entrepreneur (2012). James Dyson on Using Failure to Drive Success [online]. Available here . [Accessed May 27, 2022.]
[2] Creative Education Foundation (2015). The CPS Process [online]. Available here . [Accessed May 26, 2022.]
[3] Kaner, S. et al. (2014). 'Facilitator′s Guide to Participatory Decision–Making,' San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
[4] Puccio, G., Mance, M., and Murdock, M. (2011). 'Creative Leadership: Skils That Drive Change' (2nd Ed.), Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
[5] OmniSkills (2013). Creative Problem Solving [online]. Available here . [Accessed May 26, 2022].
[6] Treffinger, G., Isaksen, S., and Dorval, B. (2010). Creative Problem Solving (CPS Version 6.1). Center for Creative Learning, Inc. & Creative Problem Solving Group, Inc. Available here .
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Action learning sets.
Solving Problems by Doing and Discussing

Cause and Effect Analysis
Identifying the Likely Causes of Problems
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 30% off your first year of Mind Tools
Great teams begin with empowered leaders. Our tools and resources offer the support to let you flourish into leadership. Join today!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

The Role of a Facilitator

How to Manage Passive-Aggressive People
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
How can i manage passive-aggressive team members.
Dealing with passive aggression when it takes over your team
Written Communication
Discover how to construct an effective message, and test and hone your writing skills
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Matrix management.
An Outline of Approaches to Matrix Management With Guidance Around the Issues Involved
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Creative Problem-Solving & Why Is It Important?

- 01 Feb 2022
One of the biggest hindrances to innovation is complacency—it can be more comfortable to do what you know than venture into the unknown. Business leaders can overcome this barrier by mobilizing creative team members and providing space to innovate.
There are several tools you can use to encourage creativity in the workplace. Creative problem-solving is one of them, which facilitates the development of innovative solutions to difficult problems.
Here’s an overview of creative problem-solving and why it’s important in business.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Creative Problem-Solving?
Research is necessary when solving a problem. But there are situations where a problem’s specific cause is difficult to pinpoint. This can occur when there’s not enough time to narrow down the problem’s source or there are differing opinions about its root cause.
In such cases, you can use creative problem-solving , which allows you to explore potential solutions regardless of whether a problem has been defined.
Creative problem-solving is less structured than other innovation processes and encourages exploring open-ended solutions. It also focuses on developing new perspectives and fostering creativity in the workplace . Its benefits include:
- Finding creative solutions to complex problems : User research can insufficiently illustrate a situation’s complexity. While other innovation processes rely on this information, creative problem-solving can yield solutions without it.
- Adapting to change : Business is constantly changing, and business leaders need to adapt. Creative problem-solving helps overcome unforeseen challenges and find solutions to unconventional problems.
- Fueling innovation and growth : In addition to solutions, creative problem-solving can spark innovative ideas that drive company growth. These ideas can lead to new product lines, services, or a modified operations structure that improves efficiency.

Creative problem-solving is traditionally based on the following key principles :
1. Balance Divergent and Convergent Thinking
Creative problem-solving uses two primary tools to find solutions: divergence and convergence. Divergence generates ideas in response to a problem, while convergence narrows them down to a shortlist. It balances these two practices and turns ideas into concrete solutions.
2. Reframe Problems as Questions
By framing problems as questions, you shift from focusing on obstacles to solutions. This provides the freedom to brainstorm potential ideas.
3. Defer Judgment of Ideas
When brainstorming, it can be natural to reject or accept ideas right away. Yet, immediate judgments interfere with the idea generation process. Even ideas that seem implausible can turn into outstanding innovations upon further exploration and development.
4. Focus on "Yes, And" Instead of "No, But"
Using negative words like "no" discourages creative thinking. Instead, use positive language to build and maintain an environment that fosters the development of creative and innovative ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving and Design Thinking
Whereas creative problem-solving facilitates developing innovative ideas through a less structured workflow, design thinking takes a far more organized approach.
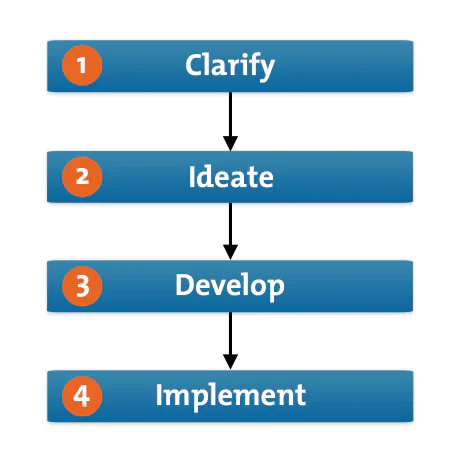
Design thinking is a human-centered, solutions-based process that fosters the ideation and development of solutions. In the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar leverages a four-phase framework to explain design thinking.
The four stages are:

- Clarify: The clarification stage allows you to empathize with the user and identify problems. Observations and insights are informed by thorough research. Findings are then reframed as problem statements or questions.
- Ideate: Ideation is the process of coming up with innovative ideas. The divergence of ideas involved with creative problem-solving is a major focus.
- Develop: In the development stage, ideas evolve into experiments and tests. Ideas converge and are explored through prototyping and open critique.
- Implement: Implementation involves continuing to test and experiment to refine the solution and encourage its adoption.
Creative problem-solving primarily operates in the ideate phase of design thinking but can be applied to others. This is because design thinking is an iterative process that moves between the stages as ideas are generated and pursued. This is normal and encouraged, as innovation requires exploring multiple ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving Tools
While there are many useful tools in the creative problem-solving process, here are three you should know:
Creating a Problem Story
One way to innovate is by creating a story about a problem to understand how it affects users and what solutions best fit their needs. Here are the steps you need to take to use this tool properly.
1. Identify a UDP
Create a problem story to identify the undesired phenomena (UDP). For example, consider a company that produces printers that overheat. In this case, the UDP is "our printers overheat."
2. Move Forward in Time
To move forward in time, ask: “Why is this a problem?” For example, minor damage could be one result of the machines overheating. In more extreme cases, printers may catch fire. Don't be afraid to create multiple problem stories if you think of more than one UDP.
3. Move Backward in Time
To move backward in time, ask: “What caused this UDP?” If you can't identify the root problem, think about what typically causes the UDP to occur. For the overheating printers, overuse could be a cause.
Following the three-step framework above helps illustrate a clear problem story:
- The printer is overused.
- The printer overheats.
- The printer breaks down.
You can extend the problem story in either direction if you think of additional cause-and-effect relationships.
4. Break the Chains
By this point, you’ll have multiple UDP storylines. Take two that are similar and focus on breaking the chains connecting them. This can be accomplished through inversion or neutralization.
- Inversion: Inversion changes the relationship between two UDPs so the cause is the same but the effect is the opposite. For example, if the UDP is "the more X happens, the more likely Y is to happen," inversion changes the equation to "the more X happens, the less likely Y is to happen." Using the printer example, inversion would consider: "What if the more a printer is used, the less likely it’s going to overheat?" Innovation requires an open mind. Just because a solution initially seems unlikely doesn't mean it can't be pursued further or spark additional ideas.
- Neutralization: Neutralization completely eliminates the cause-and-effect relationship between X and Y. This changes the above equation to "the more or less X happens has no effect on Y." In the case of the printers, neutralization would rephrase the relationship to "the more or less a printer is used has no effect on whether it overheats."
Even if creating a problem story doesn't provide a solution, it can offer useful context to users’ problems and additional ideas to be explored. Given that divergence is one of the fundamental practices of creative problem-solving, it’s a good idea to incorporate it into each tool you use.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a tool that can be highly effective when guided by the iterative qualities of the design thinking process. It involves openly discussing and debating ideas and topics in a group setting. This facilitates idea generation and exploration as different team members consider the same concept from multiple perspectives.
Hosting brainstorming sessions can result in problems, such as groupthink or social loafing. To combat this, leverage a three-step brainstorming method involving divergence and convergence :
- Have each group member come up with as many ideas as possible and write them down to ensure the brainstorming session is productive.
- Continue the divergence of ideas by collectively sharing and exploring each idea as a group. The goal is to create a setting where new ideas are inspired by open discussion.
- Begin the convergence of ideas by narrowing them down to a few explorable options. There’s no "right number of ideas." Don't be afraid to consider exploring all of them, as long as you have the resources to do so.
Alternate Worlds
The alternate worlds tool is an empathetic approach to creative problem-solving. It encourages you to consider how someone in another world would approach your situation.
For example, if you’re concerned that the printers you produce overheat and catch fire, consider how a different industry would approach the problem. How would an automotive expert solve it? How would a firefighter?
Be creative as you consider and research alternate worlds. The purpose is not to nail down a solution right away but to continue the ideation process through diverging and exploring ideas.

Continue Developing Your Skills
Whether you’re an entrepreneur, marketer, or business leader, learning the ropes of design thinking can be an effective way to build your skills and foster creativity and innovation in any setting.
If you're ready to develop your design thinking and creative problem-solving skills, explore Design Thinking and Innovation , one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses. If you aren't sure which course is the right fit, download our free course flowchart to determine which best aligns with your goals.

About the Author

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
CPS is a comprehensive system built on our own natural thinking processes that deliberately ignites creative thinking and produces innovative solutions. Through alternating phases of divergent and convergent thinking, CPS provides a process for managing thinking and action, while avoiding premature or inappropriate judgment. It is built upon a ...
Because we all have to make critical decisions. Whether you're a student, a parent, or a professional, you face problems and opportunities every day — all of which can be addressed through Creative Problem Solving. CreativeEducationFoundation.org [email protected] Phone: +1.508.960.0000. CEF.
What is Creative Problem Solving? Creative Problem Solving (CPS) is a structured process for solving problems or finding opportunities, used when you want to go beyond conventional thinking and arrive at creative (novel and useful) solutions. A primary difference between CPS and other problem‐solving
What is Creative Problem Solving? CPS is a structured process for solving problems or finding opportunities, used when you want to go beyond conventional thinking and arrive at creative (novel and useful) solutions. A key point: although the process is depicted as
The Creative Problem-Solving Process . The creative problem-solving process. 1 . is a systematic approach to problem-solving that was first proposed by Alex Osborn in 1953 in his landmark book . Applied Imagination. The approach went through several refinements over a period of five years. Osborn began with a seven-
The purpose of this chapter is to describe what we mean by "creative approaches to prob - lem solving." As a result of reading this chapter, you will be able to do the following: 1. Describe the four basic elements of the system for understanding creativity. 2. Explain what the terms creativity, problem solving, and creative problem solving
the process of matching creative problem solving techniques to problems Creative action: putting in place the creative tech-niques that will provide the solutions we seek Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4. The Creative Problem Solver (CPS model): Stages 1 and 2 75 convergent characteristics. From running countless creative sessions,
to the process as everyone in the team will come up with ideas throughout. Putting up a Solution 'Car Park' to capture ideas as they occur allows all potential solutions to be captured whilst freeing up our brains to be truly creative. As per the diagram above, there are six steps in the CPS Process: 1. Explore and define the problem
As the name implies, CPS is a creative approach to problem-solving and therefore is focused on exploring what is possible, beyond what is known and demonstrable. This creative process methodology has been shaped by roughly 100 years of practice and is informed by insights derived from the field of creativity studies.
We argue that creative problem-solving depends on the effective execution of a set of complex cognitive processes. Effective execution of these processes is, in turn, held to depend on the strategies employed in process execution and the knowledge being used in problem-solving. The implications of these observations for improving creative ...
Creative Problem Solving (CPS Version6.1™) is the latest version of Treffinger, Isaksen and Dorval's (2003) framework for solving problems and managing change. CPS Version 6.1™ includes the ...
There are many approaches to studying creativity and problem solving, including more than 100 defi nitions of creativity in the literature, for example (Treffi nger, 2000a). We have used the example of a lake to organize and explain many perspectives on the nature and sources of creativity (e.g., Treffi nger, Isaksen, & Firestien, 1983; Treffi ...
In defining the relationship between creativity and problem solving it is necessary to examine what makes creative problem solving creative. Such an examination necessitates an investigation into the creative process. One of the earliest models of the creative process was that espoused by Wallas (1926) and Hadamard (1945) early last century.
PDF | Organizational adaptability is modeled as a four stage creative problem solving process, with each stage involving a different kind of cognitive... | Find, read and cite all the research you ...
Key Points. Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of using your creativity to develop new ideas and solutions to problems. The process is based on separating divergent and convergent thinking styles, so that you can focus your mind on creating at the first stage, and then evaluating at the second stage.
The steps of _____ include (1) classifying and defining the problem or opportunity, (2) setting objectives and criteria, (3) generating creative and innovative alternatives, (4) analyzing alternatives and selecting the most feasible, (5) planning and implementing the decision, and (6) controlling the decision. 5.
Center for Creative Learning, Inc. Creative Problem Solving Group, Inc. P. O. Box 53169 P. O. Box 648 Sarasota, FL 34232 Orchard Park, NY 14127 941.342.9928 716.667.1324 ... and process planning to guide problem solvers in determining the appropriate approach and use of CPS.
Abstract. Creative Problem Solving (CPS) is a structured process for navigating complex, open-ended problems and achieving creative results (Puccio, Murdock, & Mance, 2011). Although CPS has been ...
Creative problem-solving primarily operates in the ideate phase of design thinking but can be applied to others. This is because design thinking is an iterative process that moves between the stages as ideas are generated and pursued. This is normal and encouraged, as innovation requires exploring multiple ideas.
Creative Problem Solving (CPS), an established process for navigating complex challenges that require imagination to resolve (Puccio, Murdock, & Mance, 2011), to address a challenge within a context of their choice. Because almost all students are mid-level managers, many conduct
The Six Step Problem Solving Model Problem solving models are used to address the many challenges that arise in the workplace. While many people regularly solve problems, there are a range of different approaches that can be used to find a solution. Complex challenges for teams, working groups and boards etc., are usually solved more quickly by ...
The purpose of this theoretical article is to present an instrument (the Creative Problem Solving Profile [CPSP]), which (1) measures these styles, (2) maps onto and interconnects directly with the four stages of this creative problem-solving process, (3) increases understanding of different cognitive creative problem-solving process
Abstract. This is a guide, supported by multimedia materials and practical vision, describing the Creative Problem Solving Methodology, explaining in details how to implement it in VET ...