Developing a Thesis Statement
Many papers you write require developing a thesis statement. In this section you’ll learn what a thesis statement is and how to write one.
Keep in mind that not all papers require thesis statements . If in doubt, please consult your instructor for assistance.

What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement . . .
- Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic.
- Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper.
- Is focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Is generally located near the end of the introduction ; sometimes, in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or in an entire paragraph.
- Identifies the relationships between the pieces of evidence that you are using to support your argument.
Not all papers require thesis statements! Ask your instructor if you’re in doubt whether you need one.
Identify a topic
Your topic is the subject about which you will write. Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic; or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper.
Consider what your assignment asks you to do
Inform yourself about your topic, focus on one aspect of your topic, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts, generate a topic from an assignment.
Below are some possible topics based on sample assignments.
Sample assignment 1
Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II.
Identified topic
Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis
This topic avoids generalities such as “Spain” and “World War II,” addressing instead on Franco’s role (a specific aspect of “Spain”) and the diplomatic relations between the Allies and Axis (a specific aspect of World War II).
Sample assignment 2
Analyze one of Homer’s epic similes in the Iliad.
The relationship between the portrayal of warfare and the epic simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64.
This topic focuses on a single simile and relates it to a single aspect of the Iliad ( warfare being a major theme in that work).
Developing a Thesis Statement–Additional information
Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic, or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper. You’ll want to read your assignment carefully, looking for key terms that you can use to focus your topic.
Sample assignment: Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II Key terms: analyze, Spain’s neutrality, World War II
After you’ve identified the key words in your topic, the next step is to read about them in several sources, or generate as much information as possible through an analysis of your topic. Obviously, the more material or knowledge you have, the more possibilities will be available for a strong argument. For the sample assignment above, you’ll want to look at books and articles on World War II in general, and Spain’s neutrality in particular.
As you consider your options, you must decide to focus on one aspect of your topic. This means that you cannot include everything you’ve learned about your topic, nor should you go off in several directions. If you end up covering too many different aspects of a topic, your paper will sprawl and be unconvincing in its argument, and it most likely will not fulfull the assignment requirements.
For the sample assignment above, both Spain’s neutrality and World War II are topics far too broad to explore in a paper. You may instead decide to focus on Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis , which narrows down what aspects of Spain’s neutrality and World War II you want to discuss, as well as establishes a specific link between those two aspects.
Before you go too far, however, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts. Try to avoid topics that already have too much written about them (i.e., “eating disorders and body image among adolescent women”) or that simply are not important (i.e. “why I like ice cream”). These topics may lead to a thesis that is either dry fact or a weird claim that cannot be supported. A good thesis falls somewhere between the two extremes. To arrive at this point, ask yourself what is new, interesting, contestable, or controversial about your topic.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times . Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Derive a main point from topic
Once you have a topic, you will have to decide what the main point of your paper will be. This point, the “controlling idea,” becomes the core of your argument (thesis statement) and it is the unifying idea to which you will relate all your sub-theses. You can then turn this “controlling idea” into a purpose statement about what you intend to do in your paper.
Look for patterns in your evidence
Compose a purpose statement.
Consult the examples below for suggestions on how to look for patterns in your evidence and construct a purpose statement.
- Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis
- Franco turned to the Allies when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from the Axis
Possible conclusion:
Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: Franco’s desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power.
Purpose statement
This paper will analyze Franco’s diplomacy during World War II to see how it contributed to Spain’s neutrality.
- The simile compares Simoisius to a tree, which is a peaceful, natural image.
- The tree in the simile is chopped down to make wheels for a chariot, which is an object used in warfare.
At first, the simile seems to take the reader away from the world of warfare, but we end up back in that world by the end.
This paper will analyze the way the simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64 moves in and out of the world of warfare.
Derive purpose statement from topic
To find out what your “controlling idea” is, you have to examine and evaluate your evidence . As you consider your evidence, you may notice patterns emerging, data repeated in more than one source, or facts that favor one view more than another. These patterns or data may then lead you to some conclusions about your topic and suggest that you can successfully argue for one idea better than another.
For instance, you might find out that Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis, but when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from them, he turned to the Allies. As you read more about Franco’s decisions, you may conclude that Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: his desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power. Based on this conclusion, you can then write a trial thesis statement to help you decide what material belongs in your paper.
Sometimes you won’t be able to find a focus or identify your “spin” or specific argument immediately. Like some writers, you might begin with a purpose statement just to get yourself going. A purpose statement is one or more sentences that announce your topic and indicate the structure of the paper but do not state the conclusions you have drawn . Thus, you might begin with something like this:
- This paper will look at modern language to see if it reflects male dominance or female oppression.
- I plan to analyze anger and derision in offensive language to see if they represent a challenge of society’s authority.
At some point, you can turn a purpose statement into a thesis statement. As you think and write about your topic, you can restrict, clarify, and refine your argument, crafting your thesis statement to reflect your thinking.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Compose a draft thesis statement
If you are writing a paper that will have an argumentative thesis and are having trouble getting started, the techniques in the table below may help you develop a temporary or “working” thesis statement.
Begin with a purpose statement that you will later turn into a thesis statement.
Assignment: Discuss the history of the Reform Party and explain its influence on the 1990 presidential and Congressional election.
Purpose Statement: This paper briefly sketches the history of the grassroots, conservative, Perot-led Reform Party and analyzes how it influenced the economic and social ideologies of the two mainstream parties.
Question-to-Assertion
If your assignment asks a specific question(s), turn the question(s) into an assertion and give reasons why it is true or reasons for your opinion.
Assignment : What do Aylmer and Rappaccini have to be proud of? Why aren’t they satisfied with these things? How does pride, as demonstrated in “The Birthmark” and “Rappaccini’s Daughter,” lead to unexpected problems?
Beginning thesis statement: Alymer and Rappaccinni are proud of their great knowledge; however, they are also very greedy and are driven to use their knowledge to alter some aspect of nature as a test of their ability. Evil results when they try to “play God.”
Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main idea: The reason some toys succeed in the market is that they appeal to the consumers’ sense of the ridiculous and their basic desire to laugh at themselves.
Make a list of the ideas that you want to include; consider the ideas and try to group them.
- nature = peaceful
- war matériel = violent (competes with 1?)
- need for time and space to mourn the dead
- war is inescapable (competes with 3?)
Use a formula to arrive at a working thesis statement (you will revise this later).
- although most readers of _______ have argued that _______, closer examination shows that _______.
- _______ uses _______ and _____ to prove that ________.
- phenomenon x is a result of the combination of __________, __________, and _________.
What to keep in mind as you draft an initial thesis statement
Beginning statements obtained through the methods illustrated above can serve as a framework for planning or drafting your paper, but remember they’re not yet the specific, argumentative thesis you want for the final version of your paper. In fact, in its first stages, a thesis statement usually is ill-formed or rough and serves only as a planning tool.
As you write, you may discover evidence that does not fit your temporary or “working” thesis. Or you may reach deeper insights about your topic as you do more research, and you will find that your thesis statement has to be more complicated to match the evidence that you want to use.
You must be willing to reject or omit some evidence in order to keep your paper cohesive and your reader focused. Or you may have to revise your thesis to match the evidence and insights that you want to discuss. Read your draft carefully, noting the conclusions you have drawn and the major ideas which support or prove those conclusions. These will be the elements of your final thesis statement.
Sometimes you will not be able to identify these elements in your early drafts, but as you consider how your argument is developing and how your evidence supports your main idea, ask yourself, “ What is the main point that I want to prove/discuss? ” and “ How will I convince the reader that this is true? ” When you can answer these questions, then you can begin to refine the thesis statement.
Refine and polish the thesis statement
To get to your final thesis, you’ll need to refine your draft thesis so that it’s specific and arguable.
- Ask if your draft thesis addresses the assignment
- Question each part of your draft thesis
- Clarify vague phrases and assertions
- Investigate alternatives to your draft thesis
Consult the example below for suggestions on how to refine your draft thesis statement.
Sample Assignment
Choose an activity and define it as a symbol of American culture. Your essay should cause the reader to think critically about the society which produces and enjoys that activity.
- Ask The phenomenon of drive-in facilities is an interesting symbol of american culture, and these facilities demonstrate significant characteristics of our society.This statement does not fulfill the assignment because it does not require the reader to think critically about society.
Drive-ins are an interesting symbol of American culture because they represent Americans’ significant creativity and business ingenuity.
Among the types of drive-in facilities familiar during the twentieth century, drive-in movie theaters best represent American creativity, not merely because they were the forerunner of later drive-ins and drive-throughs, but because of their impact on our culture: they changed our relationship to the automobile, changed the way people experienced movies, and changed movie-going into a family activity.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast-food establishments, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize America’s economic ingenuity, they also have affected our personal standards.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast- food restaurants, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize (1) Americans’ business ingenuity, they also have contributed (2) to an increasing homogenization of our culture, (3) a willingness to depersonalize relationships with others, and (4) a tendency to sacrifice quality for convenience.
This statement is now specific and fulfills all parts of the assignment. This version, like any good thesis, is not self-evident; its points, 1-4, will have to be proven with evidence in the body of the paper. The numbers in this statement indicate the order in which the points will be presented. Depending on the length of the paper, there could be one paragraph for each numbered item or there could be blocks of paragraph for even pages for each one.
Complete the final thesis statement
The bottom line.
As you move through the process of crafting a thesis, you’ll need to remember four things:
- Context matters! Think about your course materials and lectures. Try to relate your thesis to the ideas your instructor is discussing.
- As you go through the process described in this section, always keep your assignment in mind . You will be more successful when your thesis (and paper) responds to the assignment than if it argues a semi-related idea.
- Your thesis statement should be precise, focused, and contestable ; it should predict the sub-theses or blocks of information that you will use to prove your argument.
- Make sure that you keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Change your thesis as your paper evolves, because you do not want your thesis to promise more than your paper actually delivers.
In the beginning, the thesis statement was a tool to help you sharpen your focus, limit material and establish the paper’s purpose. When your paper is finished, however, the thesis statement becomes a tool for your reader. It tells the reader what you have learned about your topic and what evidence led you to your conclusion. It keeps the reader on track–well able to understand and appreciate your argument.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
How to Write a Master's Thesis: A Guide to Planning Your Thesis, Pursuing It, and Avoiding Pitfalls
#scribendiinc
Part 1: Initial Considerations
Who needs to write a master’s thesis.
Thesis writing is one of the more daunting challenges of higher education. That being said, not all master's students have to write a thesis. For example, fields that place a stronger emphasis on applied knowledge, such as nursing, business, and education, tend to have projects and exams to test students on the skills and abilities associated with those fields. Conversely, in disciplines that require in-depth research or highly polished creative abilities, students are usually expected to prove their understanding and independence with a thesis.
What's Your Goal?
Do you want to write a thesis? The process is a long one, often spanning years. It's best to know exactly what you want before you begin. Many people are motivated by career goals. For example, hiring managers may see a master's degree as proof that the candidate is an expert within their field and can lead, motivate, and demonstrate initiative for themselves and others. Others dream of earning their doctorate, and they see a master's degree as a stepping stone toward their Ph.D .

No matter what your desired goal is, you should have one before you start your thesis. With your goal in mind, your work will have a purpose, which will allow you to measure your progress more easily.
Major Types of Theses
Once you've carefully researched or even enrolled in a master's program—a feat that involves its own planning and resources —you should know if you are expected to produce a quantitative (which occurs in many math and science programs), qualitative (which occurs in many humanities programs), or creative (which occurs in many creative writing, music, or fine arts programs) thesis.
Time and Energy Considerations
Advanced degrees are notoriously time and energy consuming. If you have a job, thesis writing will become your second job. If you have a family, they will need to know that your thesis will take a great deal of your attention, energy, and focus.

Your studies should not consume you, but they also should not take a back seat to everything else. You will be expected to attend classes, conduct research, source relevant literature, and schedule meetings with various people as you pursue your master's, so it's important to let those you care about know what's going on.
As a general note, most master's programs expect students to finish within a two-year period but are willing to grant extra time if requested, especially if that time is needed to deal with unexpected life events (more on those later).
Part 2: Form an Initial Thesis Question, and Find a Supervisor
When to begin forming your initial thesis question.
Some fields, such as history, may require you to have already formed your thesis question and to have used it to create a statement of intent (outlining the nature of your research) prior to applying to a master’s program. Others may require this information only after you've been accepted. Most of the time, you will be expected to come up with your topic yourself. However, in some disciplines, your supervisor may assign a general research topic to you.
Overall, requirements vary immensely from program to program, so it's best to confirm the exact requirements of your specific program.
What to Say to Your Supervisor
You will have a supervisor during your master's studies. Have you identified who that person will be? If yes, have you introduced yourself via email or phone and obtained information on the processes and procedures that are in place for your master's program? Once you've established contact, request an in-person meeting with him or her, and take a page of questions along with you. Your questions might include:
- Is there a research subject you can recommend in my field?
- I would like to pursue [target research subject] for my thesis. Can you help me narrow my focus?
- Can you give me an example of a properly formatted thesis proposal for my program?
Don't Be Afraid to Ask for Help (to a Degree)
Procedures and expectations vary from program to program, and your supervisor is there to help remove doubt and provide encouragement so you can follow the right path when you embark on writing your thesis. Since your supervisor has almost certainly worked with other graduate students (and was one at some point), take advantage of their experience, and ask questions to put your mind at ease about how to write a master’s thesis.
That being said, do not rely too heavily on your supervisor. As a graduate student, you are also expected to be able to work independently. Proving your independent initiative and capacity is part of what will earn you your master's degree.
Part 3: Revise Your Thesis
Read everything you can get your hands on.
Whether you have a question or need to create one, your next step is simple and applies to all kinds of theses: read.

Seek Out Knowledge or Research Gaps
Read everything you can that relates to the question or the field you are studying. The only way you will be able to determine where you can go is to see where everyone else has been. After you have read some published material, you will start to spot gaps in current research or notice things that could be developed further with an alternative approach. Things that are known but not understood or understood but not explained clearly or consistently are great potential thesis subjects. Addressing something already known from a new perspective or with a different style could also be a potentially valuable project. Whichever way you choose to do it, keep in mind that your project should make a valuable contribution to your field.

Talk with Experts in Your Field (and Don't Be Afraid to Revise Your Thesis)
To help narrow down your thesis topic, talk to your supervisor. Your supervisor will have an idea of what is current in your field and what can be left alone because others are already working on it. Additionally, the school you are attending will have programs and faculty with particular areas of interest within your chosen field.
On a similar note, don't be surprised if your thesis question changes as you study. Other students and researchers are out there, and as they publish, what you are working on can change. You might also discover that your question is too vague, not substantial enough, or even no longer relevant. Do not lose heart! Take what you know and adjust the question to address these concerns as they arise. The freedom to adapt is part of the power you hold as a graduate student.
Part 4: Select a Proposal Committee
What proposal committees are and why they're useful.
When you have a solid question or set of questions, draft a proposal.

You'll need an original stance and a clear justification for asking, and answering, your thesis question. To ensure this, a committee will review your thesis proposal. Thankfully, that committee will consist of people assigned by your supervisor or department head or handpicked by you. These people will be experts who understand your field of study and will do everything in their power to ensure that you are pursuing something worthwhile. And yes, it is okay to put your supervisor on your committee. Some programs even require that your supervisor be on your committee.
Just remember that the committee will expect you to schedule meetings with them, present your proposal, respond to any questions they might have for you, and ultimately present your findings and thesis when all the work is done. Choose those who are willing to support you, give constructive feedback, and help address issues with your proposal. And don't forget to give your proposal a good, thorough edit and proofread before you present it.
How to Prepare for Committee Meetings
Be ready for committee meetings with synopses of your material for committee members, answers for expected questions, and a calm attitude. To prepare for those meetings, sit in on proposal and thesis defenses so you can watch how other graduate students handle them and see what your committee might ask of you. You can even hold rehearsals with friends and fellow students acting as your committee to help you build confidence for your presentation.

Part 5: Write Your Thesis
What to do once your proposal is approved.
After you have written your thesis proposal and received feedback from your committee, the fun part starts: doing the work. This is where you will take your proposal and carry it out. If you drafted a qualitative or quantitative proposal, your experimentation or will begin here. If you wrote a creative proposal, you will now start working on your material. Your proposal should be strong enough to give you direction when you perform your experiments, conduct interviews, or craft your work. Take note that you will have to check in with your supervisor from time to time to give progress updates.

Thesis Writing: It's Important to Pace Yourself and Take Breaks
Do not expect the work to go quickly. You will need to pace yourself and make sure you record your progress meticulously. You can always discard information you don't need, but you cannot go back and grab a crucial fact that you can't quite remember. When in doubt, write it down. When drawing from a source, always create a citation for the information to save your future self time and stress. In the same sense, you may also find journaling to be a helpful process.
Additionally, take breaks and allow yourself to step away from your thesis, even if you're having fun (and especially if you're not). Ideally, your proposal should have milestones in it— points where you can stop and assess what you've already completed and what's left to do. When you reach a milestone, celebrate. Take a day off and relax. Better yet, give yourself a week's vacation! The rest will help you regain your focus and ensure that you function at your best.
How to Become More Comfortable with Presenting Your Work
Once you start reaching your milestones, you should be able to start sharing what you have. Just about everyone in a graduate program has experience giving a presentation at the front of the class, attending a seminar, or watching an interview. If you haven't (or even if you have), look for conferences and clubs that will give you the opportunity to learn about presenting your work and become comfortable with the idea of public speaking. The more you practice talking about what you are studying, the more comfortable you'll be with the information, which will make your committee defenses and other official meetings easier.
Published authors can be called upon to present at conferences, and if your thesis is strong, you may receive an email or a phone call asking if you would share your findings onstage.
Presenting at conferences is also a great way to boost your CV and network within your field. Make presenting part of your education, and it will become something you look forward to instead of fear.
What to Do If Your Relationship with Your Supervisor Sours
A small aside: If it isn't already obvious, you will be communicating extensively with others as you pursue your thesis. That also means that others will need to communicate with you, and if you've been noticing things getting quiet, you will need to be the one to speak up. Your supervisor should speak to you at least once a term and preferably once a week in the more active parts of your research and writing. If you give written work to your supervisor, you should have feedback within three weeks.
If your supervisor does not provide feedback, frequently misses appointments, or is consistently discouraging of your work, contact your graduate program advisor and ask for a new supervisor. The relationship with your supervisor is crucial to your success, especially if she or he is on your committee, and while your supervisor does not have to be friendly, there should at least be professional respect between you.
What to Do If a Crisis Strikes
If something happens in your life that disrupts everything (e.g., emotional strain, the birth of a child, or the death of a family member), ask for help. You are a human being, and personal lives can and do change without warning. Do not wait until you are falling apart before asking for help, either. Learn what resources exist for crises before you have one, so you can head off trauma before it hits. That being said, if you get blindsided, don't refuse help. Seek it out, and take the time you need to recover. Your degree is supposed to help you become a stronger and smarter person, not break you.
Part 6: Polish and Defend Your Master's Thesis
How to write a master’s thesis: the final stages.
After your work is done and everything is written down, you will have to give your thesis a good, thorough polishing. This is where you will have to organize the information, draft it into a paper format with an abstract, and abbreviate things to help meet your word-count limit. This is also where your final editing and proofreading passes will occur, after which you will face your final hurdle: presenting your thesis defense to your committee. If they approve your thesis, then congratulations! You are now a master of your chosen field.
Conclusion and Parting Thoughts
Remember that you do not (and should not) have to learn how to write a master’s thesis on your own. Thesis writing is collaborative, as is practically any kind of research.

While you will be expected to develop your thesis using your own initiative, pursue it with your own ambition, and complete it with your own abilities, you will also be expected to use all available resources to do so. The purpose of a master's thesis is to help you develop your own independent abilities, ensuring that you can drive your own career forward without constantly looking to others to provide direction. Leaders get master's degrees. That's why many business professionals in leadership roles have graduate degree initials after their last names. If you already have the skills necessary to motivate yourself, lead others, and drive change, you may only need your master's as an acknowledgement of your abilities. If you do not, but you apply yourself carefully and thoroughly to the pursuit of your thesis, you should come away from your studies with those skills in place.
A final thought regarding collaboration: all theses have a section for acknowledgements. Be sure to say thank you to those who helped you become a master. One day, someone might be doing the same for you.
Image source: Falkenpost/Pixabay.com
We’re Masters at Master’s Theses! Make Yours Shine.
Let our expert academic editors perfect your writing, or get a free sample, about the author.

A Scribendi in-house editor, Anthony is happily putting his BA in English from Western University to good use with thoughtful feedback and incisive editing. An avid reader and gamer, he can be found during his off hours enjoying narrative-driven games and obscure and amusing texts, as well as cooking for his family.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation

Selecting a Thesis Committee

Thesis/Dissertation Writing Series: How to Write a Literature Review
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).


Chapter 2: Evidence
Constructing Your Essay Blueprint
With your data and observational paragraph in front of you, read the original text again. This may seem like an exercise in redundancy, but re-reading with the seeds of your own interpretation in mind will help you to confirm or revise your reading of some passages and elements. Reading the text again may also help you find less obvious support that will strengthen and make your reading or analysis more complex. As you read, you should ask yourself, “What is the purpose of this text? What is the central argument? How does the author support the central argument?”
Draft your blueprint: Once you have extracted and compressed the essential material in the original text, it is time to begin structuring your blueprint. You do not necessarily need to present the author’s ideas in the order they originally appear. You may want to begin your blueprint by stating the author’s central thesis, even if it does not appear at the beginning of the original article. However, it is best to avoid a point-by-point analysis of the text as that will result inevitably in summary, which you most certainly want to avoid at this level.
You should begin your analysis with an examination of what you believe to be the most important and revealing piece (or pieces) of evidence. Was there a moment in the text or a key repetition or consistent contrast that confirmed for you what this text was really about? Begin with that. Using that strong base, you can move to your second and third strongest pieces of evidence. Continue with all your evidence, building your analysis until you reach your final points which should examine the less-than-obvious supportive aspects of the text. A close reading doesn’t just rely on one or two obvious statement that prove you are “right.” Imagine that you are luring your reader into your understanding of the text: “Do you agree with my reading of the first piece of evidence? The second? The third? Well, then perhaps you would like to consider what I have to say about this part of the text that you may be surprised to find in this argument.”
Understand that not every essay you analyze will let you apply this formula, but the exercise of pushing your claim to consider all aspects of the text is always worthwhile.
In your blueprint, be sure to cite keywords and terms from the original text. Cite those words or phrases that you believe are pivotal to the author’s delivery of his or her main message and explain why. While quoting the author is expected at this level, you never want to let these passages stand alone without analysis. So include the analysis of the selected quotations in your blueprint. While you do not want to rush to your purposeful analysis and interpretation of the text while conducting the information-gathering exercise detailed in Chapter One, it is good to start your meaningful interaction with the text in these pre-drafting stages of organization.
Review and Revise Your Essay Blueprint: Remember that a blueprint is an outline for the essay you will eventually construct. Its purpose is to organize the information or evidence you’ve gathered from your annotated reading of the text and to begin structuring your analysis of the author’s purpose and argument. Don’t just rush into your essay after you’ve completed your blueprint. Reread the article then review your blueprint. Have you included everything you believe will lead to your most interesting and controversial reading of the text? As you revise your blueprint, ensure that you have:
- captured the main argument presented in the original text
- highlighted the article’s main points (including any key concepts or theories) and eliminated all extraneous or minor details
- presented clearly your interpretation and interaction with the text. Is it obvious that you understand the text you are analyzing? Is your interpretation of the text presented clearly?
Write Here, Right Now: An Interactive Introduction to Academic Writing and Research Copyright © 2018 by Ryerson University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

A Writer's Handbook
- Introduction
- Purpose & Audience
- Opening Sentences
- Linking Sentences
General Thesis
Other thesis types notes.
- Finished Introduction
- Topic Sentences
- Development
- Conclusion Sentences
- Conclusion Paragraphs for Essays
- Essay Writing Organization: The Outline
- Annotating Readings
- General Writing Idea Development
- Rhetorical and Visual Analysis Idea Development
- Character Analysis Idea Development
- Theme Analysis Idea Development
- Theory Analysis
- Using the Library
- Using Sources for Illustration or Support
- Using Research for Essays
- Writing About Research
- MLA Handbook Summary for Citations
- Final Thoughts on Essays
- Literary Element Index
- Appendix of Example Papers
Most important sentence in the introduction
- Structure for the entire paper
- Suggests your point of view or argument
Two different types
- Very specifically lays out the 3 or more points in the body
- Follows specific “blueprint”
- Lays out general argument that allows for a little bit of freedom in the organization of the body paragraphs
- No specific “blueprint”
- X, Y, and Z refer to the three or more body paragraph topics a writer wishes to discuss within the paper
- "Topical argument/stance on topic" + body topic X, body topic Y, and body topic Z.
Although many people think of addiction as drug or alcohol related, Jane’s story shows that "even work can be an addiction" because it ruins relationships , creates mental suffering , and causes health problems .
"Topical argument/stance on topic: even "work" can be an addiction"
Body topic X: ruins relationships
Body topic Y: creates mental suffering
Body topic Z: causes health problems
- A general thesis sentence carries no specific blueprint but still holds the idea of the entire paper
- Although there are no specific points to follow, a general thesis will have logical body paragraph topics that will fall in line under the thesis argument
Although many people think of addiction as something geared toward alcohol or drugs, Jane’s story illustrates how "work can become an addiction."
"Idea of paper: work can become an addiction"
Compare and Contrast
- Whichever--compare or contrast--you will be focusing on the most will need to be in the last part of the sentence, and the other will need to be mentioned first
- Example: If you want to focus on the differences between two cars:
Although the Camaro and the Tahoe are both vehicles made by Chevrolet, they differ in price, body style, and performance. (X, Y, Z thesis)
Cause and Effect
- Same rule as above: whichever topic your paper will be focusing more on will need to be the last mentioned
- Example: If you want to focus on the effects of smoking:
Due to the smoking in most restaurants, even the non-smoking guests are turning up with lung disease and other problems caused by smoking. (General Thesis)
- Same rule as above: whichever side of the argument you will be more focused on will need to be the last mentioned
- Example: The pros and cons of tougher immigration laws with a heavier argument toward the pros:
Many people who are against immigration policy think the laws violate civil and human rights; however, tougher immigration laws would decrease crime instances and provide better access to citizenship for those who legally enter the country.
- Example: The pros and cons of tougher immigration laws with a heavier argument toward the cons:
Although people argue that tougher immigration laws may decrease crime rate, the new immigration policy under discussion is a violation of many human beings’ basic civil rights.
- If you are writing about a piece of literature, always include the name of the author and the name of the work in the thesis statement
- If you are comparing and contrasting items or talking about two different ideas within one paper, be sure to mention both ideas or both items in the thesis
- As a general rule, a thesis is ALWAYS the last sentence of the introduction
- A thesis is NEVER a quote or a question
- A thesis NEVER uses the phrase(s) “This paper will show you…” or “I will now tell you about…” etc.
- Even if a thesis does not have a blue print, it MUST have a point or argument
- << Previous: Linking Sentences
- Next: Finished Introduction >>
- Last Updated: Jan 3, 2023 9:01 AM
- URL: https://library.jeffersonstate.edu/AWH
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer

Elite Editing
You write it. We right it.™

How to Write a Thesis Proposal
If you want to build a house, step one is not wandering over to the next vacant lot with a hammer, some nails, and a pile of boards. Your first step is probably finding an appealing place to build your house—an empty plot of land where the roads are good and where you can pretty easily connect the gas, electricity, and water. Step two is drawing up a blueprint for what you plan to build.
If a thesis is a house, then a thesis proposal is your blueprint. It’s you figuring out how your thesis will fit into the space you’ve found, how you’ll build it, and whether it will stand up to the harsh winds of your thesis adviser’s opinions and the tremors of a difficult defense. A thesis proposal allows you to clearly define—and even more crucially, limit—the focus and scope of your research. Producing an excellent thesis blueprint means that you won’t accidentally find you’re trying to build a skyscraper when you should be aiming at a bungalow—and that you have all the supplies and equipment you need.
But how do you create a research proposal? How do you know what it should include? The style and length of your thesis proposal will vary a bit depending on your school’s requirements and the type of thesis you will eventually produce, but the fundamentals will always be the same, and those are what we’re going to cover here. So let’s look at how to write a thesis proposal.
Choosing a Topic
The first step (a step that you must take before figuring out how to write a thesis proposal or even a thesis proposal outline) is choosing a topic for your thesis. The point of embarking on this kind of project is that you’ll first find and then fill a gap in the established, preexisting research in your field. You’re looking for a manageable topic—something focused enough that you can cover it within your word limit but broad enough that you actually have something to write about.
Undergraduate theses are often less revolutionary and more about surveying or analyzing the existing research on a particular topic. This is appropriate because these projects are shorter in length—and you have much less time (typically months rather than years) to work on them. An undergraduate thesis can run anywhere from ten to thirty pages. A master’s thesis is typically forty to eighty pages and might present some original research, or it might be a significant reinterpretation of preexisting research.
A doctoral thesis is (naturally) the longest of these three, and the research it presents should be more groundbreaking and challenging to complete. That investment of time and mental energy is what’s going to earn you the right to demand that everyone call you “Doctor.”
Tips for Choosing a Thesis Topic
- Consider your interests. What makes you sit up and your brain feel fizzy? You’re about to spend a lot of time working on this topic. It had better be something that fascinates you.
- Explore open-ended questions. How or why questions offer you more scope and flexibility than what or who questions.
- Consider the time. How long will your project take to complete? Make sure you have enough time to get from here to there.
- Research any funding you’ll need. Will you need to travel or establish an experimental protocol? If so, can you get the funding for these projects? How do these affect your projected timeline? Save the long-view research for your later career, and find something you can finish.
- If it’s a controversial topic, choose wisely. Be realistic about whether you’re likely to encounter stiff resistance during your defense. Something that goes against all existing research will demand greater rigor and effort from you than something that challenges only a part of what is currently considered established knowledge.
- Make it publishable. Are all possible outcomes to your research interesting and academically publishable? Or is there a potential dead end that you can avoid by shifting your focus now?
- Think long term. How will the project affect (and improve) your marketability for the future? There is life after your thesis, after all. Where do you want to be, and how can your work now help get you there?
Structuring Your Thesis Proposal
A thesis proposal usually includes some or all of the following elements:
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Literature review or annotated bibliography
- Approach/methods
- Preliminary results and discussion
- Work plan and schedule
- Research implications
The thesis proposal outline above shows one potential way to order the parts, but (and this is important) you won’t work on those elements in that order. For example, that table of contents? It’s probably the last thing you’ll work on. Similarly, you can’t write the abstract until you’ve written everything else.

Let’s look at how to write a thesis proposal in greater detail.
Title Page and Creating a Title
The title of your project is likely to be a brief statement of your research topic, approach, and intent. It will be far easier to write a title once you’ve written a thesis statement (see below) because it is likely to restate or incorporate your thesis statement.
Violence and Redemption in Modern Afghani Literature: A Marxist Analysis of Power Structures in The Kite Runner and The Wasted Vigil
Living the Fantasy: Addiction and Social Identity in World of Warcraft
Your title page will include this title, your name, your department and institution, your adviser, your adviser’s institution, and the date you’re submitting the proposal.
Writing an Abstract
An abstract is a short summary of your full proposal, usually about a page in length. It hits the highlights of the proposal as a whole, including your title, your thesis statement, a quick summary of your plan of research, and a statement about why this project matters.
Table of Contents
If you’re writing your table of contents, you’re minutes away from a celebratory “Woo-hoo!” because you’re almost finished. A table of contents will list all the headings and subheadings of your proposal with lovely indentations and the correct page numbers. If you’re using MS Word, and you’ve been formatting your headings in the appropriate styles, you can automatically generate a table of contents that will make everything look very pretty indeed.

Writing the Thesis Statement
It’s not a simple question: How do you write a good thesis statement? Your thesis statement may well be the hardest sentence (or two—three at the most) you ever have to write. Despairing tears or frustrated anger are not out of the question. However, once you formulate that thesis statement, you will be off and running because now you have a beautifully clear and specific goal to head for.
A thesis statement should clearly define the scope and intent of your project. It might be a hypothesis or a question, or it might be a firm statement. The hours of work that will become your thesis will then prove (or possibly disprove, though hopefully in a deeply productive way) your thesis statement, so it should be something provable—something that can in some way be measured.
Let’s look at some examples of how to write a good thesis statement.
Not so good:
Taking a year off between high school and college is a good idea.
A “good idea” is vague and indefensible. Good by whose standards? How can you prove that?
Students who take a year off between high school and college are more academically successful than their peers.
This is better because it limits the scope of the project to academics, but it’s still rather vague and unwieldy. It also doesn’t suggest what metrics will be used to judge “academically successful.”
Better still:
Students who take a year off between high school and college are significantly more likely than their peers to graduate within four years with a B average or better.
This thesis statement works because it is concrete and measurable. The data you collect will either clearly prove the statement or disprove it.
How does the internet affect social behavior?
Wow, that’s a huge question. Also, there is nothing to prove, measure, or evaluate. It’s a topic rather than a thesis. It might be what you’re generally interested in, but you have yet to find the aspect of this topic that you can effectively research.
The internet has changed how American teens approach gender.
At least this is a statement, but it’s still too vague. “Changed” how? And what does “approach” mean?
The social media profiles of American teens thirteen to eighteen years old reflect this demographic’s increasing comfort with fluid sexual and gender identities.
This thesis statement could probably still be improved, but it is getting toward something measurable and provable.
Writing a Thesis Proposal Introduction
Your introduction will do just that—introduce your readers to your topic and thesis. Don’t mistake this for an introductory paragraph, however. This is where you’ll summarize your project in the hopes of intriguing and engaging the committee that will either approve your thesis project or send you back to the drawing board. Your writing should be as clear, straightforward, and free from jargon as possible. You’ll contextualize your project within the broader scope of the topic, perhaps exploring the papers, research, or work that led to your formulation of your thesis. You’ll explain why your project excites you. You’ll illustrate your competence to embark on this project. Basically, you’ll sell your proposal.
Literature Review or Annotated Bibliography
You might be able to quickly cover the most relevant literature in your proposal introduction, but if there are many articles or books relevant to your research, your thesis proposal might include an annotated bibliography or a literature review (which is slightly more informal and conversational in approach). Here is where you’d not only list the most influential and crucial texts that underpin your research but also explain why they matter—that is, how they fit into your project. This is a way to show that gap in the research that you will be filling with your thesis project.
Explain Your Proposed Methods or Approach
Most thesis projects demand original research of some kind, and for degrees in the sciences (including the social sciences), that research may very well take the form of an experiment or raw data collection. Here is where you should describe your proposed methodology. What materials will you use? How will you collect your data? How will you analyze the data once it’s collected? Are you taking a qualitative or quantitative approach? Why? Will you need outside funding (for travel or other costs), and how do you propose to acquire that funding? Do you need space and equipment to conduct your research?
Provide Preliminary Results
It may be that you have already been testing the viability of your thesis project with some preliminary research (which is not a bad idea). If so, here is where you should provide the results of that research and your tentative interpretation of those results. Clearly show how this work fits into your larger project—and how it proves that you’re heading down a productive road of inquiry.
Design a Work Plan
Even if your particular program or professor doesn’t require you to include a work plan in your thesis proposal, you should still make one. There’s nothing more likely than a schedule—with deadlines!—to keep you on track and get your thesis done on time.
This section should
- lay out your plan,
- list the various stages of your project,
- set deadlines for the completion of each stage, and
- detail any work you’ve already completed.
In addition, your work plan should take into account any challenges (personal, practical, or institutional) that may affect the completion of the study.
Discuss Research Implications
Here, you are striving to answer this question: Why does this project matter in this place and at this time? It’s actually a wonderful exercise in focusing your own thoughts and evaluating the worth of your proposed project. Are you remedying a misunderstanding that might affect how to treat a particular medical condition? Are you exploring the dynamics of a culture that is (socially or politically) especially relevant at the moment? Are you providing new insight into a classic work of literature or music that will reinvigorate teachers and academics? Your research might have implications for the entire world or it might be of interest only to other specialists in your subject, but that really doesn’t matter. The point is to figure out and clearly state how your research will enhance the sum total of knowledge.
Notes and Bibliography
All statements in this thesis proposal need to be supported with data, whether that data is derived from your own research or gleaned from a third party. Using whatever citation style is most appropriate to your field, you should give credit to all your sources, primary or secondary. Note that this is separate from your literature review in that you’re only going to cite the sources you’ve used in your proposal.
Thesis Proposal Defense / Thesis Proposal Presentation
Your college or university may require you to appear in person at a thesis proposal defense or to make a thesis proposal presentation. In both cases, however, you’ll be presenting your proposal to your thesis committee (and possibly others) and then potentially answering their questions about your project. While this might seem alarming, this event is actually an excellent opportunity to pick your committee’s brain about possible obstacles or objections you will need to overcome while working on your project. Better to know right now that they’d rather you took a quantitative approach than do all the work and then discover their preference. It will also help focus you since knowing something is one level of understanding it—but explaining it to someone else can take your understanding to a much deeper level.
You should now have a much deeper understanding of how to write a thesis proposal. A clear, thorough, well-thought-out thesis proposal allows you to see the entire shape of your project before you invest huge amounts of time and energy into research that might end up leading nowhere. Your thesis proposal sets the stage for the success of your project as a whole, and it should reflect and predict the quality you intend to produce in your final thesis. That’s why your thesis proposal presentation also matters. In addition, remember that proofreading counts. It’s extremely important to carefully review your finished proposal for spelling, grammar, and structural errors.
With your thesis proposal completed and approved, you’re well on your way to embarking on what might be the most important project of your life to date. We wish you all the best with your studies, and if you decide you want an editor to cast an expert eye over any part—large or small—of your project, we here at Elite are happy to help!
Want more? Check out this post on credible online sources and how to find them.
Other Resources You Might Like

Crafting Timeless Content

Mastering the Art of Persuasive White Papers

Writing Effective Press Releases in a Digital Age
Get elite updates straight to your inbox..
- Content Writing
- Marketing and Sales Enablement
- Program Management
- AI Implementation
Who We Help
- Thought Leaders
- Cybersecurity
- Health Care
- Full-Time Careers
- Freelance Opportunities
- Press and Awards
- Success Stories
- About Elite
In the News
- Elite Creative Makes the Inc. 5000 for the Third Year in a Row


Blueprints for Academic Research Projects
Today's post is written by Dr. Ben Ellway, the founder of www.academic-toolkit.com . Ben completed his Ph.D. at The University of Cambridge and created the Research Design Canvas , a multipurpose tool for learning about academic research and designing a research project.
Based on requests from students for examples of completed research canvases, Ben created the Research Model Builder Canvas .
This canvas modifies the original questions in the nine building blocks to enable students to search for key information in a journal article and then reassemble it on the canvas to form a research model — a single-page visual summary of the journal article which captures how the research was designed and conducted.
Ben’s second book, Building Research Models, explains how to use the Research Model Builder Canvas to become a more confident and competent reader of academic journal articles, while simultaneously building research models to use as blueprints to guide the design of your own project .
Ben has created a template for Stormboard based on this tool and this is his brief guide on how to begin using it.
Starting with a blank page can be daunting
The Research Design Canvas brings together the key building blocks of academic research on a single page and provides targeted questions to help you design your own project. However, starting with a blank page can be a daunting prospect!
Academic research is complex as it involves multiple components, so designing and conducting your own project can be overwhelming, especially if you lack confidence in making decisions or are confused about how the components of a project fit together. It is much easier to start a complex task and long process such as designing a research project when you have an existing research model or ‘blueprint’ to work from.
Starting with a ‘blueprint’ — tailored to your topic area — is much easier
Using the Research Model Builder Canvas, you can transform a journal article in your topic into a research model or blueprint — a single-page visualization of how a project was designed and conducted.
The research model — and equally importantly the process of building it — will improve your understanding of academic research, and will also provide you with a personalized learning resource for your Thesis. You can use the research model as a blueprint to refer to specific decisions and their justification, and how components of research fit together, to help you begin to build your own project.
Obviously, each project is unique so you’ll be using the blueprint as a guide rather than as a ‘cookie cutter’ solution. Seeing the components of a completed research project together on a single page (which you produced from a ten or twenty-page journal article) — is a very powerful learning resource to have on your academic research journey.
Build research models on Stormboard
If you prefer to work digitally rather than with paper and pen, you can use the Research Model Builder Canvas Template in Stormboard.
By using the Stormboard template, you’ll be able to identify key content and points from the journal article and then quickly summarize these on digital sticky notes. You can easily edit the sticky notes to rearrange, delete, or expand upon the ideas and points. You can then refer back to the permanent visual research model you created, share it with fellow students, or discuss it with your supervisors.
What are the building blocks of the research model?
The template has nine building blocks.
The original questions in the building blocks of the research design canvas are modified in the research model builder canvas. They are designed to help you locate the most important points, decisions, and details in a journal article.
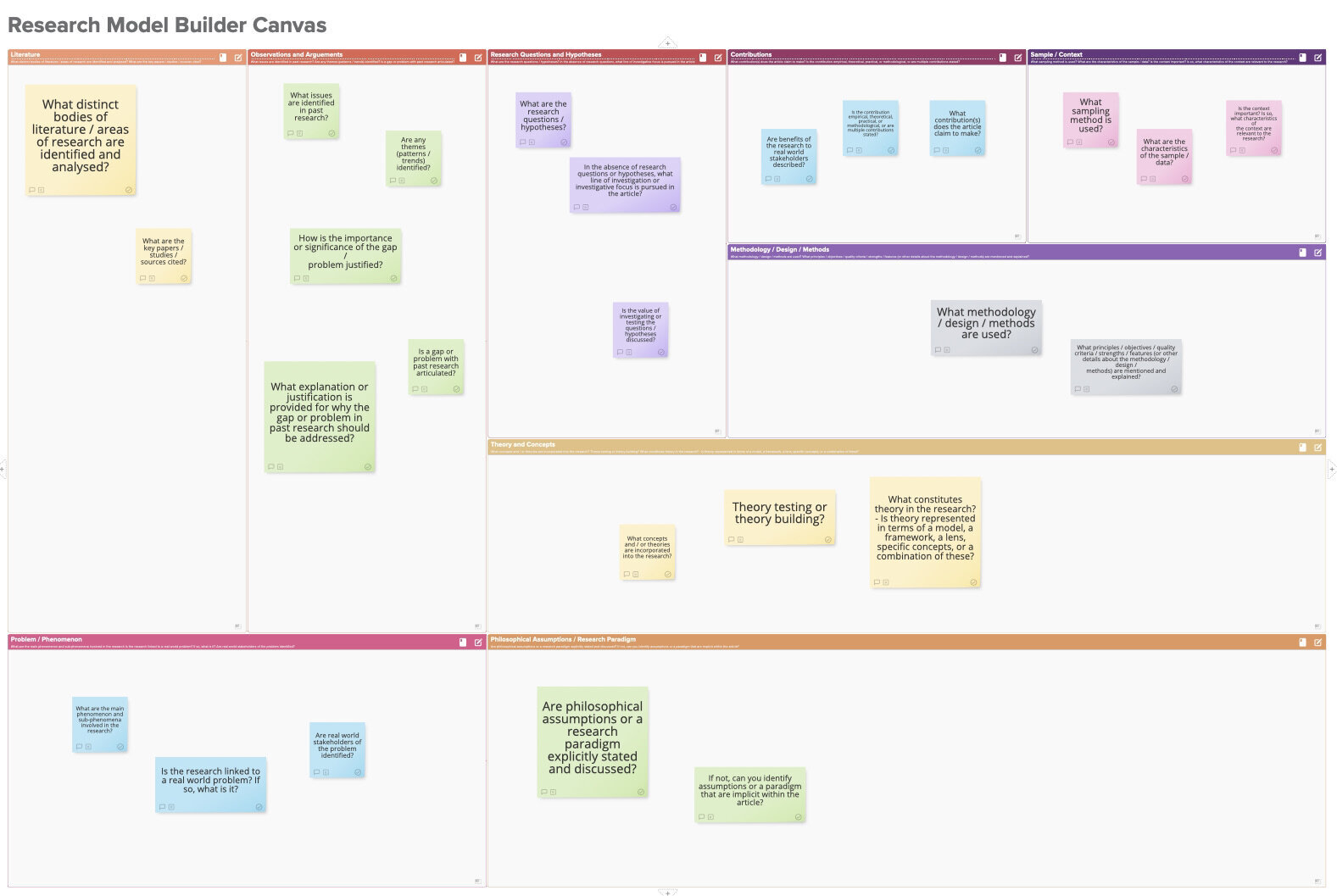
A brief introduction to the purpose of each building block is provided below to help you familiarize yourself with the research model you will build.
Phenomenon / Problem
What does the research focus on? What were the main ‘things’ investigated and discussed in the journal article? Did the research involve a real-world problem?
What area (or areas) of past literature are identified and introduced? Which sources are especially important?
Observations & Arguments
What are the most crucial points made by the authors in their analysis of past research? What evidence, issues, and themes are the focus of the literature review? Is a gap in past research identified?
Research Questions / Hypotheses
What are the research questions and/or hypotheses? How are they justified? If none are stated, what line of investigation is pursued?
Theory & Concepts
Does the research involve a theoretical or conceptual component? If so, what are the key concepts / theory? What role do they play in the research?
Methodology / Design / Methods
What methods and data were used? How are the decisions justified?
Sample / Context
What sampling method is used? Is the research context important?
Contributions
What contribution(s) do the authors claim that their research makes? Is the value-add more academically or practically-oriented? Are real-world stakeholders and the implications for them mentioned?
Philosophical Assumptions / Research Paradigm
These are not usually mentioned or discussed in journal articles. Indeed, this building block can be confusing if you are not familiar with research philosophy or are confused by its seemingly abstract focus. If you understand these ideas, can you identify any implicit assumptions or a research paradigm in the article?
Compare two research models to appreciate the diversity of research
The easiest way to increase your appreciation of the different types and ways of conducting academic research is to build multiple research models.
Start by building two models. Compare and contrast them. Which decisions and aspects are similar and which are different? What can you learn from each research model and how can this help you when designing your own research and Thesis?
Building research models will help you to appreciate the diversity in the different types of research conducted in your topic area.
Transforming a ten or twenty-page journal article into a single-page visual summary is a powerful way to learn about how academic research is designed and conducted — and also what a completed research project looks like.
The Stormboard template makes the process of building research models easy, and the ability to save, edit, and share them ensures that you’ll be able to refer back to these blueprints at various stages throughout your research journey and Thesis writing process.
When you get confused, become stuck, or feel overwhelmed by the complexity of academic research, you can fall back on the research models you created to guide you and get you back on track. Good luck!
Are you interested in trying the Research Model Builder Canvas? Sign up for a free trial now!
Keep reading.

Discover the latest advancements in StormAI, the industry's first augmented intelligence collaborator, with exciting updates that enhance its capabilities. Learn about the innovative features and improvements that make StormAI 2.0 a groundbreaking technology for collaborative work.

Discover the contrasting views within the Agile community regarding spilled stories (or spillover) in sprint cycles and delve into strategies adopted by different teams. Gain insights into the pros and cons of each approach to better inform your Agile methodology.

Discover how groupthink poses a significant threat to innovation within agile teams, hindering the emergence of new ideas and impeding progress throughout the scrum cycle. Explore strategies for agile team management to mitigate the impact of groupthink and foster a culture of creativity and innovation.

Discover how technology enables cohesive collaboration for remote web development teams, with 4 out of 5 developers working remotely. Explore the top collaboration tools empowering seamless workflows and website building, regardless of location.

In a fast-paced business world marked by evolving customer needs and technological advancements, staying ahead demands adaptability. Discover how fostering an agile workplace culture can empower your team to innovate, collaborate, and swiftly respond to change, driving efficiency and securing a competitive edge.
Learn how DevOps is revolutionizing development and operations workflows, enhancing product delivery speed and cost-efficiency. Explore the critical role of continuous security auditing in DevOps to mitigate vulnerabilities and safeguard against threats.

Project management challenges are inevitable. Here are some common problems and how you can stay ahead of them in 2024.

Explore the transformative landscape of 2023 as Stormboard, riding the generative AI wave, celebrates its most significant year yet. Uncover how Stormboard's core product enhancements and advanced workflow integrations respond to the evolving needs of modern businesses, empowering enterprises to reimagine their technology strategy for a dynamic future.

Unlock innovation and embrace diversity in team brainstorming! Learn strategies to navigate cultural differences and create an inclusive environment for effective ideation while overcoming boundaries and enhancing diversity in collaboration sessions.

Explore Stormboard's Q3 highlights: Discover how user feedback shapes our evolution, and explore Q3 highlights with new features and enhanced UX for global organizations.

Discover how crafting buyer personas can elevate your marketing strategy, making your website more effective and enhancing customer interactions in the competitive business landscape.
How to Track Your Team’s Workflow Remotely
Archive - 2021 business trends.
blog @ precision
Chapter 1: creating the blueprint for your dissertation.
The first chapter of your dissertation can be challenging to complete, and as many of our dissertation assistance clients have shared, it can even be difficult to start! This is because the introduction to the dissertation provides a blueprint for the rest of the study, laying out key aspects of your proposed research that will be covered in more depth in subsequent chapters.

This means that in addition to mastering the fine art of APA editing and formatting, you need to have a fairly solid understanding of the applications of quantitative or qualitative research methods, an in-depth appraisal of the current literature on your topic, and a firm grasp of the concept of alignment to write your first chapter. Understandably, this might seem a bit intimidating for first-time researchers! We hope that the following section-by-section overview helps to ease you into this first major chapter in your dissertation.
Background: What Is the Overall Aim of This Section?
All studies, dissertations included, contribute to the larger body of research on a particular topic, and your aim with this section is to help the reader understand the specific literature context for your dissertation. As you may already know, you will complete an in-depth discussion of the research literature related to your topic in your literature review chapter; however, a brief background section in your first chapter helps to orient the reader to the current research related to your dissertation topic.
When writing the background section, include at least one paragraph on each key element of your topic (Sampson, 2012). For example, if you plan to conduct statistical analysis to determine the relationship between exposure to trauma, substance misuse, and homelessness in men with schizophrenia, your background will need to cover the four key elements of: (a) trauma exposure, (b) substance misuse, (c) homelessness, and (d) men who experience schizophrenia.
What Are the Essential Elements of the Background Section?
- Brief summary of relevant research on key elements of your topic
- Description of gap in research that your study will help to address
- Explanation of the reason the study is needed
Problem Statement: What Is the Overall Aim of This Section?
Although the problem statement i s fairly short, usually running 250 to 350 words, many of our dissertation consulting clients have expressed that they found it to be the most challenging section of Chapter 1 to write. This short section is the centerpiece of the topic development process, as it helps to illustrate the need for your study by explaining the problem that you will address with your dissertation, including whom the problem affects and how. Because your dissertation must contribute to an existing gap in the research, it is important that you draw only from very recent sources (i.e., those published within the last 3 to 5 years) when developing the problem statement.
A common mistake we encourage our dissertation assistance clients to avoid is equating a lack of research with the research gap; these are not the same thing. Instead, the research gap actually consists of at least three other recent studies that express a need for additional quantitative or qualitative research in a particular area. Another common error is to use this section to describe what you intend to investigate through your study or to explain what type of statistical analysis or qualitative analysis you have planned; but, save that information for later in the chapter and just focus on the problem for now.
What Are the Essential Elements of the Problem Statement Section?
- Description of problem of interest, including whom it affects and how
- Prevalence statistic (i.e., how widespread is the problem?)
- Citations of 12-15 recent (i.e., published within last 3-5 years) sources that document the existence of the problem
- Citations of at least three current studies that note a need for additional research on the topic
Purpose: What Is the Overall Aim of This Section?
In this very short section of the chapter, your goal is to help the reader understand the aims of your dissertation. The first sentence—or purpose statement—should contain all key information on how you intend to address the problem you articulated in the previous section (Bloomberg & Volpe, 2008). As the purpose statement is presented verbatim throughout the dissertation, it helps to be thorough and yet concise, stating the method, design, variables or phenomena of interest, population, and often, location of the study. Our dissertation assistance clients often find that they need to go through a few rounds of committee review and editing in order to get the phrasing of the purpose statement just right.

An important note is that the verbs you choose for the purpose statement must align with the research method and design . For example, you might say that the purpose of a qualitative research study is to explore the lived experiences of your participants with regard to some specific phenomenon. On the other hand, you would not use the verb “explore” if you’re planning a study that involves statistical analysis of relationships between variables. For quantitative studies, use verbs such as “examine” or “investigate.” As an example, you might say that the purpose of a quantitative correlational study is to examine the relationship between two or more variables of interest.
What Are the Essential Elements of the Purpose Section?
- Specify the method and design
- Use a verb that aligns with method and design
- Specify variables when using quantitative method, or phenomenon of interest for qualitative research
Research Questions: What Is the Overall Aim of This Section?
In this section, your aim is to help readers understand the specific questions that you will answer through your dissertation. These are your research questions, which must convey “all methodological aspects of the research” (Sampson, 2012, p. 28). Because of this, they need to align with your purpose statement, using the same terminology for population and variables/phenomena of interest.
Research questions must also be carefully worded so that they reflect the research approach and intended analysis. For example, statistical analysis terminology such as “relationship” and “difference” should not be used in qualitative research questions, as qualitative analysis cannot determine relationships or differences between variables. As with your dissertation’s purpose statement, perfecting the research questions may require a few rounds of committee review and editing because every word matters.

If you are planning to conduct qualitative research, it may help to understand that the research questions are not the same as the interview questions that you will later ask your participants. This is a common misunderstanding among our dissertation consulting clients who are conducting qualitative research for the first time. For example, imagine that you are planning a qualitative analysis of African American executives’ experiences of ascent to leadership positions. Although you might be interested in asking your participants questions about their early experiences, education, mentorship, training, and networking, you wouldn’t write research questions for each of these topics. Instead, you would create one or two very broad research questions that refer to the phenomenon of interest (i.e., experiences of ascent to leadership positions for African American executives), which create an “umbrella” for the more specific interview questions that will guide data collection for your dissertation.
What Are the Essential Elements of the Research Questions Section?
- Align the research questions with the purpose statement
- Align the research questions with research method and design
- Present the research questions with hypotheses if using a quantitative method
Theoretical Framework: What Is the Overall Aim of This Section?
In this section, your aim is to help the reader understand the explanatory structure that will hold your dissertation together logically. With a theoretical framework, you base this structure on established theories that help to explain how specific variables or dimensions relate to each other; with a conceptual framework, you base the structure on your own literature-based analysis of how key variables or phenomena relate to one another. To provide an appropriate explanatory structure, the theoretical or conceptual framework needs to align with your problem, purpose, and research questions (Grant & Osanloo, 2014). Whether you are conducting qualitative analysis or statistical analysis, you will also need to interpret your dissertation’s findings through the lens of your framework in your discussion chapter .
What Are the Essential Elements of the Theoretical Framework Section?
- Cite the originators of the theory
- Explain the key tenets of the theory
- Explain how the framework makes sense for your study, given its topic

Nature of the Study: What Is the Overall Aim of This Section?
When developing this section, your aim is to help the reader to understand the proposed methodological plan for your dissertation. In addition to specifying the research method and research design, you must also present your rationale for choosing this approach (Bloomberg & Volpe, 2008). For example, if you have selected a qualitative research method , you will need to explain not only why this method aligns with your purpose but also why statistical analysis (i.e., a quantitative method) would not be suitable for answering your research questions. Although you will cover this in greater depth in your methods chapter, this section should also briefly discuss your sample and data collection, along with the specific type of statistical analysis or qualitative analysis you will use to analyze your data.
What Are the Essential Elements of the Nature of the Study Section?
- Provide rationale for choice of method
- Provide rationale for choice of research design
- Briefly describe sample, data collection, data analysis
Assumptions: What Is the Overall Aim of This Section?
Your objective in this section is to help readers understand the assumptions that it was necessary for you to make to conduct your study; these are aspects of your dissertation that you believe—but cannot prove—to be true. One common assumption is that participants will respond to questions honestly and accurately. Note that for quantitative studies, there will also be assumptions that are related to the statistical analysis regarding properties of the data, such as independence of observations, normality of the distribution, and homogeneity of variances. Our statisticians often help with developing appropriate assumptions for our dissertation assistance clients who are completing quantitative studies.
What Are the Essential Elements of the Assumptions Section?
- Only include those assumptions that are essential to the particular study
- Explain why it is necessary to make those assumptions
Scope and Delimitations: What Is the Overall Aim of This Section?
In writing this section, your aim is to help the reader to understand the specific aspects of the problem you will investigate through your dissertation (i.e., its scope) and also aspects of the problem that you will not examine (i.e., its delimitations). For example, imagine that you are conducting qualitative research to explore perspectives on cognitive-behavior therapy among persons who experience depression. You would explain this focus and why you selected it, additionally specifying populations (e.g., persons with co-occurring mental health diagnoses) and treatments (e.g., mindfulness-based therapies) that you have chosen not to focus on in your dissertation.
What Are the Essential Elements of the Scope and Delimitations Section?
- Specific focus of study and why you chose this
- Aspects of topic, populations, or frameworks that you will not investigate
Limitations: What Is the Overall Aim of This Section?
Your aim in this section is to help readers understand the potential shortcomings of your study. Limitations may arise from your dissertation’s methodology or procedures, and they typically relate to either internal validity or external validity (Price & Murnan, 2004). For example, internal validity may be threatened if you are using an instrument with incomplete or inadequate psychometric properties, and procedures such as convenience sampling may limit the external validity (i.e., generalizability) of your results. The small, purposive samples typically used in qualitative research also limit generalizability, and even though this is normal and expected, it is still important to acknowledge this limitation formally.
What Are the Essential Elements of the Limitations Section?
- Aspects of the study that could limit generalizability
- Potential sources of bias
- Steps you will take to minimize these limitations

Significance: What Is the Overall Aim of This Section?
When preparing the significance section, your aim is to help readers understand how your dissertation’s findings might benefit specific individuals or the general public by reducing or eliminating the issue you described in your problem statement. By demonstrating the social significance of your proposed study in this section, you justify the investment in time and resources that you, your committee, and your university will make over the course of the study (Sampson, 2012).
As an example, imagine that your plan is to use your dissertation to help address the general problem of teacher attrition in rural school districts, and your specific problem is lack of effective mentorship in such settings. An outcome that you would hope for, given this general and specific problem, is that your dissertation’s findings would help to increase the quality of mentorship for new teachers in rural areas, thereby increasing retention. Note that it is important to keep your significance statements reasonable, considering the scope and boundaries of your dissertation. Although you might hope that increasing teacher retention would help to increase high school students’ graduation rates and college readiness, these student-specific implications would be outside of the bounds of your specific study.
What Are the Essential Elements of the Significance Section?
- Explain potential contributions to knowledge and practice
- Align implications for positive social change with the field of study
- Keep implications reasonable, given the scope of the study

Final Thoughts
The potential contributions you can make to the world around you through your research are undoubtedly considerable, and our dissertation consultants would be thrilled to support you to bring your study to its full potential. We definitely recommend that you take the time to develop a top-notch Chapter 1, as this sets the tone for the remainder of your dissertation research. Best of luck with your research, and if we can help in any way, please let us know !
Bloomberg, L. D., & Volpe, M. (2008). Completing your qualitative dissertation: A roadmap from beginning to end . Sage. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781452226613.n1
Grant, C., & Osanloo, A. (2014). Understanding, selecting, and integrating a theoretical framework in dissertation research: Creating the blueprint for your “house”. Administrative Issues Journal , 4 (2), 12-26. https://doi.org/10.5929/2014.4.2.9
Price, J. H., & Murnan, J. (2004). Research limitations and the necessity of reporting them. American Journal of Health Education , 35 (2), 66-67. https://doi.org/10.1080/19325037.2004.10603611
Sampson, J. P. (2012). Guide to quantitative and qualitative dissertation research . Florida State University Libraries. https://diginole.lib.fsu.edu/islandora/object/fsu:405471/datastream/PDF/view
Paper 2: Thesis / Blueprint
14 comments.
does anyone know what command-line interfacing is?
also, I would like the Kindle on thursday
subject: virtual worlds and how they hinder and help society.
thesis to come tomorrow
Command line interface -- it's how we interacted with Deadline (the text adventure game) in class. The computer would display a prompt like c:>_ (with the underline symbol the equivalent of the vertical i-beam that marks the insertion point in Windows today), and the user would type a command like "word.exe myfile.doc" which would be the equivalent of double-clicking the "Word" icon and doing File -> Open -> "myfile.doc." Just as it was impossible to use graphics for games back in the day, it was impossible to use graphics in the operating system as well. To use a computer, you had to know what commands to type -- you couldn't just select options from a menu. So playing text-adventure games seemed a lot more natural to computer users 20 years ago, since reading a bit of text and typing a bit of text and getting the computer to give you a bit more text was the way that everyone was used to working with computers.
The command-line interface (CLI) was replaced by the graphic user interface (GUI), which is what most computer users are familiar with today.
Your topics sounds worthwhile, but remember the focus of this class is on the technology of reading and writing. There have been (and still are) virtual worlds that involve words along with images, and in-game text-based chat are important features of most virtual worlds. However, voice-based chat is another feature of some popular multiplayer combat games.
I don't plan on speaking about the voice -based game
A lot of the paper is on MUD's and the chatroom, which they evolved into....
My goal is to just get everything down on paper today. I plan on spending as much time revising as I do writing.
I don't think I should exclude the violence issue, since Dungeons and Dragons contained slaying and killing. I will just not mention the graphics
Dani, you know your own working style best, but I don't recommend that you write it all out now.
I recommend instead that you assemble quotes, and write things like [connect MUDs to violence] or other shorthands that announce what you plan to do. Then perhaps you can spend time reading more sources, instead of turning what you've got into the perfectly-crafted prose that I know you value.
Feedback from your classmates, and from me, might lead you to change your paper radically -- and that may mean overhauling or even completely cutting sections that you've carefully crafted.
The syllabus says that the first draft (which you seem to be trying to do now) is not actually due until Thursday, and that the revision of that will due the following Tuesday.
Again, only you know how your working style best fits into the schedule you're going to face over the next few weeks.
You can certainly mention graphics, and I agree that we can't ignore violence.
Dibbell's My Tiny Life (which expands on the "A Rape in Cyberspace" incident about the effect of a virtual assault in an online text-only community) is available for free on the author's site.
http://juliandibbell.com/news/2008_01_15_mtl_is_free.html
and here's the tie in to literacy and reading:
"literacy is about social power" () When people who cannot find power through traditional media, such as books, they turn to the interactive computer world, which provides oppurtunities for power and important that they would not ohtwise find. However....problems with power, etc.
I think the outline is best; although I have about 23 articles sitting in front of me, there may be some more sources out there.
I figure pulling quotes into an article by article outline is best. I'll start there.
the reason is wnated to mention graphical games is because we have been talking about orality into manuscript, manuscript into print, print into digital. Video games are what the inerative text game evolded into. As we have learned, there are always issues and problems when evolving.
I think now that it was rediculous for me to try and hammer outy something in an entire day. No matter if I have time or not-my brain gets fried. I guess I don't have to use the mixture of red bull and mountain dew I made now...
an extremely rough thesis. I know ther are faults; I see them, but if anyone has any feedback, they could possibly point me into anothjer direction. Again, very rough:
“In the 1980’s, ‘interactive’ technologies began to proliferate” (Mcmillan and Morrison 73). The creation of interactive games allowed people to create a community that allowed ‘”any symbolic pleasure imaginable” (Aarseth 114). The creation of these virtual worlds was a “convergance of utopia and dystopia” (Roberts 93). Interactive media pushes people apart and brings them together; it offers an escape for “those who struggle with what reality is” (Kennedy 17). The sometimes violent content offered an outlet for frustrations. They offer a person the chance to have control over a “life”; but too much control has spawned a new genre called “cyber crime”. The creation of interactive media equally benefits and hinders society.
my philosophy paper draft is pretty much there, my paper on Christopher duragn can be written in one night, so I will focus on this for the next week.
it offers an escape for “those who struggle with what reality is” (Kennedy 17)...
I suggest that you balance this with something like "and it also turns strangers into international collaborators" or some other statement that recognizes that good things can and do happen in virtual space.
This is fine for a working thesis, but you will probably want to come up with something more definite than "equally helps and hinders" -- maybe you could say "benefits societies but threatens individuality" or something like that. Of course, what you say will depend on what you find in your readings.
Yes, put aside the Red Bull and Mountain Dew for now.
A long paper is the result of a process, and you need time to sleep on your ideas so that your subconscious mind can find interesting details in your short-term memory and weave it into your deeper brain so it can jump out at you in those "aha!" moments that are impossible to have after 12 or 18 straight hours of work.
Sleep, or do laundry, or go sit under a tree with a blank pad of paper, or do something else to let your brain rest. You have the time to do a good job on this paper, and as you know I'll be happy to offer feedback as it progresses.
that comment really caught my intereest, and I have my thesis subconsciously. It just hasn't come out in thr right words yet.
I've found that it doesn't threaten individualyity as much as people think it would. The stereotype of the nerd alone at the computer is not as big a reality anymore. it's there, I'll have it tuesday, but tursday's paper certainly won't be gold.
23 articles in 22 hours takes a lot out of you.
I'm glad to hear it, Dani.
I'm thinking about going in a completely different direction.
I'm really interested in the durability of memory. Books as memory, but manipulatible memory. Reading Down and and Out just a little while ago, I see ample oppourtunity for manipulation when people have to fill in missing gaps. Plus, we were discussing method acting in F and A and it lead to a discussion about a recent experiment about how memories can be erased and prevented.
maybe on the fallibility and importance of memory, which is what I see Doctorow is heading in the direction of.
Memories are only what you THINK really happened; there is no certainity and no way to completely back it up.
By only backing up once a week, Jules is vulnerable.
it would be sort of a sequel to my last paper
So in the shower just now (best place for thinking because you're doing such robotic actions, in my opinion) I remembered my dad was in Army intelligence during the Vietnam era in Korea-- who better to talk to for ideas on my paper concerning information technology and how it changed warfare? DUH!
Jeremy, I'll find a way to get you some info too if you'd like. I haven't actually seen my dad since Thursday and I may not before tomorrow(sad when I live with him)...but I'm thinking about tape recording what he's got to say.
No point to posting this, just more as a reminder to myself and FYI for Jeremy. =)
I am definitely interested in what he has to say, Stormy.
Any help that you guys can give as far as feedback would be great. I am a little bit lost at the moment.
http://blogs.setonhill.edu/LeslieRodriguez/025474.html
Leave a comment
Type the characters you see in the picture above.
Recent Comments
50 Recent Peer Entries
Jeremy Barrick Daniella Choynowski David Cristello Dennis Jerz Stormy Knight Rachel Prichard Leslie Rodriguez Kayla Sawyer Christopher Ulicne
Biden administration plans to drastically change federal rules on marijuana
The Biden administration is poised to make a landmark change to the federal government's position on marijuana with a proposed plan that would no longer consider marijuana among the most dangerous and addictive substances .
In what would be the biggest change in marijuana policy the federal government has taken since pot was first outlawed, the Drug Enforcement Administration will take public comments on a plan to recategorize marijuana under the Controlled Substances Act, according to a source familiar with the process. The news was first reported by The Associated Press .
The Department of Justice will send its recommendation to reclassify marijuana from a Schedule I drug to a Schedule III drug to the White House Office of Management and Budget, according to the source, who was not authorized to speak publicly. The Justice Department is expected to transmit the recommendation today, the source said.
More: Trucker failed drug test after taking CBD supplement. Supreme Court to decide if he can sue
The plan wouldn't legalize marijuana at the federal level outright, but it would reclassify it from a Schedule I drug – believed highly dangerous, addictive and without medical use – to a Schedule III drug that can be lawfully prescribed as medication. Marijuana has been a Schedule I drug since the Controlled Substances Act was signed in 1970.
“It is significant for these federal agencies, and the DEA and FDA in particular, to acknowledge publicly for the first time what many patients and advocates have known for decades: that cannabis is a safe and effective therapeutic agent for tens of millions of Americans," said Paul Armentano, deputy director of the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws, or NORML, which advocates for cannabis to be removed altogether from the list of controlled substances.
This bureaucratic move is only a small step toward what advocates hope will be full legalization of the drug. However, the new proposed classification does not fully address the inconsistencies between federal restrictions and the laws in a growing number of states that have authorized medical and recreational use of pot.
Twenty-four states and Washington, D.C., have legalized the recreational use of marijuana, and 14 other states authorize it for medical use, according to the Pew Research Center .
“Rescheduling the cannabis plant to Schedule III fails to adequately address this conflict, as existing state legalization laws – both adult use and medical – will continue to be in conflict with federal regulations, thereby perpetuating the existing divide between state and federal marijuana policies," Armentano said in a statement.
The federal proposal to reschedule marijuana would have broad support among voters. A nationwide survey last fall commissioned by the Coalition for Cannabis Rescheduling Reform found nearly 60% of likely voters supported rescheduling, with 65% of younger voters 18 to 25 favoring it, the highest of any demographic group polled. Overall, the number of Americans who think marijuana should be legal reached a record high at 70%, according to a Gallup poll in the fall.
For decades, marijuana has been listed under the Controlled Substances Act as a Schedule I drug, alongside heroin, LSD and ecstasy. The act categorizes drugs based on their potential for abuse, addiction and medical use. Schedule I drugs are outlawed under federal law level and deemed to be without accepted medical use.
In 2022, President Joe Biden directed the Department of Health and Human Services to conduct a review of how marijuana is classified; and last year HHS recommended it be rescheduled to Schedule III, alongside drugs like Tylenol with codeine and anabolic steroids. The Justice Department did its own analysis and reached the same conclusion, the source said.
The proposal will undergo a public review period; the source did not say when the proposed rule would be open to public comment.
Rep. Andy Harris, R-Md., has previously criticized federal efforts to change Marijuana's classification . Harris was a physician at the Johns Hopkins Hospital, according to his online biography .
"Removing restrictions on an addictive gateway drug like Marijuana is a dangerous mistake. Numerous studies, including a recent and reputable study published by JAMA, points to the negative impact recreational marijuana has on the body and brain," Harris said in a Tuesday social media post on X, formerly known as Twitter.
Experts previously told USA TODAY that marijuana’s placement on Schedule I was not based on credible scientific evidence of its perils, but once it was listed, researchers and advocates faced a heavy burden trying to prove it shouldn’t face such stiff restrictions.
What exactly does rescheduling cannabis mean?
Placing marijuana in Schedule III puts it on par with drugs, such as ketamine, testosterone, anabolic steroids or Tylenol with codeine, that have “moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence,” according to the DEA.
Schedule III drugs can be legally prescribed by licensed health care providers and dispensed by licensed pharmacies. Rescheduling could also help resolve a massive federal tax burden that has been placed on cannabis companies – which were effectively seen as drug traffickers for tax purposes.
But rescheduling marijuana doesn’t make it legal to use recreationally, and it doesn’t change much about current state cannabis programs, said Jay Wexler, who teaches a seminar about marijuana laws at Boston University. It would still a controlled substance even with the new announcement
Wexler and other policy experts and advocates say rescheduling is not a solution, but it could be a sign the federal government is catching up with public opinion and consensus in the medical field that there are therapeutic benefits to marijuana, along with some risks.
"Rescheduling is a step forward, but it is not nearly enough. And there's no reason to keep cannabis in the Controlled Substances Act,” Wexler previously told USA TODAY.
What are the possible risks of marijuana?
Because of its classification, marijuana has been hard to study. But the move to reschedule marijuana is due in large part to its lower public health risk, federal scientists have said.
In a leaked HHS document , officials wrote to the DEA to support lowering its classification to Schedule III. Its risk for addiction was lower than other drugs and it had medical benefits, unlike Schedule I and II drugs, HHS researchers said.
Still, scientists said, users develop moderate to low physical dependence on it, and there is some risk of psychological dependence. However, they noted, the withdrawal symptoms are “relatively mild” compared with alcohol. Marijuana is more comparable to tobacco, they said.
There are no known deaths from a marijuana overdose, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse , or NIDA. But it does affect physical and mental health.
Marijuana can cause permanent IQ loss for people who begin using it at a young age, the institute said. Additionally, long-term use has been associated with temporary paranoia and hallucinations, and it can exacerbate symptoms with disorders such as schizophrenia, NIDA said.
Marijuana smoke has a similar health impact to tobacco smoke. NIDA found people who smoke marijuana frequently develop issues with breathing, akin to tobacco smokers.
Smoking cannabis, the most common way to consume the drug, may have additional risks because of particulate matter a person inhales, according to a recent study in the Journal of the American Heart Association . Researchers noted cannabis smoke isn’t all that different than tobacco smoke, the only difference being the added effect of the psychoactive drug THC in marijuana rather than nicotine in tobacco.
Respiratory issues include daily cough, phlegm and a higher risk of lung infections, however, the institute said it’s unclear if marijuana causes a greater risk of lung cancer.
Smoking marijuana also increases heart rate, which can increase the chance of heart attack, especially among older people and people with heart conditions. The Heart Association journal study linked increased cannabis use with an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
“Despite common use, little is known about the risks of cannabis use and, in particular, the cardiovascular disease risks,” the study’s lead author, Abra Jeffers, a data analyst at Boston’s Massachusetts General Hospital, said in a statement. “The perceptions of the harmfulness of smoking cannabis are decreasing, and people have not considered cannabis use dangerous to their health. However, previous research suggested that cannabis could be associated with cardiovascular disease.” She noted that smoking cannabis, which is the predominant way it is used, could pose other risks because it involves inhaling particulate matter.
In the study published in late February, researchers examined Centers for Disease Control and Prevention survey data of over 400,000 adults from 2016 to 2020, looking at self-reported cannabis use with cardiovascular outcomes, such as heart disease, heart attacks and strokes.
People who used marijuana daily had a 25% higher chance of having a heart attack and a 42% higher chance of stroke than those who didn’t use it at all.
Proposal reflects potential for health benefits
The cannabis plant has been used for medicinal purposes for centuries if not millennia. It appears to help with treating pain , insomnia, anxiety, and glaucoma, among other health conditions. Still, evidence is mixed and more research into its health benefits is needed, researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health said in August.
While the FDA hasn’t approved the cannabis plant for any medical use, federal regulators have approved several drugs containing cannabinoids, or substances such as THC or CBD found in the cannabis plant, according to the National Institutes of Health .
These include Epidiolex, a purified form of CBD ingested orally, that is FDA-approved to treat seizures associated with two severe forms of epilepsy. Marinol and Syndros both contain synthetic THC and are used to treat nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapy. Nabilone, another synthetic similar to THC, is approved as the brand name drug Cesamet for people with HIV/AIDS who experiencing weight loss and appetite loss.
A 2017 federal report found cannabis or cannabinoids were more likely to reduce pain symptoms for patients with chronic pain. Additionally, there is some evidence that cannabis is effective in treating symptoms of multiple sclerosis, particularly addressing the stiff or rigid muscles caused by the disease. One cannabinoid drug, nabiximol, a mouth spray that has both THC and CBD, has been approved in several countries but not in the U.S. Under the brand name Sativex, it has shown pain relief for people with cancer or multiple sclerosis.
Other research has examined cannabis’ uses to treat post-traumatic stress disorder, but the NIH said the evidence is mixed.
Biden administration plans to reclassify weed as a lower-risk drug. Here's what it means

The Biden administration could reclassify the federal government's position on marijuana , which would help decriminalize the drug.
The proposed plan would no longer consider cannabis a Schedule I drug – believed highly dangerous, addictive, and without medical use.
Here’s where the Biden administration's plan currently stands.
What is the Biden administration proposing?
The Drug Enforcement Administration’s proposal, which has to be reviewed by the White House Office of Management and Budget , would recognize the medical uses of cannabis, acknowledge it has less potential for abuse and reclassify cannabis as a Schedule III drug. It would not legalize cannabis for recreational use.
What is a scheduled drug?
According to the Texas State Board of Pharmacy , controlled (scheduled) drugs, substances, and certain chemicals are ones whose use and distribution are tightly controlled because of their abuse potential or risk. Controlled drugs are rated in the order of their abuse risk and placed in Schedules by the DEA.
Why is cannabis a Schedule 1 drug?
Recreational cannabis use in the U.S. has been around since the 20th century as well as movements to regulate its use, according to the National Institute of Health . However, in 1914, the Harrison Narcotics Tax Act was passed, which declared drug use a crime. There have been several laws that discouraged cannabis use and came with harsher penalties for doing so.
According to the NIH , California became the first State to make it illegal to possess cannabis. In the 1930s, the then U.S. Federal Bureau of Narcotics warned of the increasing abuse of cannabis, and by 1937, 23 States had criminalized possession. By 1970, the Controlled Substances Act passed, and the Federal government categorized marijuana as a Schedule I substance.
What are the current Schedule 1 drugs?
For decades, marijuana has been listed under the Controlled Substances Act as a Schedule I drug, alongside heroin, LSD and ecstasy. Schedule I drugs are outlawed under federal law level and deemed to be without accepted medical use.
According to the DEA , the following are examples of Schedule I drugs:
- Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)
- Methamphetamine
- Methaqualone (Quaalude)
See full list of controlled substances here.
What are schedule III drugs?
According to the DEA , the following are examples of Schedule III drugs:
- Anabolic steroids
- Testosterone
- Products containing less than 90mg of codeine per dosage unit
What's the difference between decriminalizing and legalizing weed?
There is a difference. According to the ACLU , drug decriminalization is the act of removing criminal sanctions against certain activities, including possession of drugs for personal use.
Legalization of marijuana would mean individuals 21 or older can possess certain amounts of cannabis freely under state or federal law, although it can still be regulated.
How many states have decriminalized cannabis?
According to the National Conference of State Legislatures, several states have passed legislation to decriminalize cannabis laws. "Although the law still classifies marijuana possession offenses as criminal, the offenses do not carry any threat of jail time," according to NORML .
Here are states that have decriminalized cannabis.
- New Jersey
- Connecticut
- New Mexico
- Rhode Island
- Massachusetts
- California
- District of Columbia
- Mississippi
- North Carolina
Is weed legal in Texas?
Recreational use is still not legal in Texas. But there is low-level use through the Compassionate-Use Act. In 2015, Texas passed the Compassionate-Use Act, which allowed the first legal use of low-THC cannabis products in the state for patients with intractable epilepsy. It was expanded in 2019 and 2021 to include other conditions.
Marijuana laws in Texas are confusing. Here's a guide to know what is and isn't legal
In 2019, Gov. Greg Abbott signed House Bill 1325 into law. The law allows the production, manufacture, retail sale, and inspection of industrial hemp crops and products in Texas, granted that they stay at 0.3% or less delta-9 THC level . This also includes products for consumable hemp products that contain cannabidiol (CBD), as well as other edible parts of the hemp plant.
Texas NORML has listed statutes that show the penalties for the amount of cannabis possession someone would have.
Texas cities and counties that have decriminalized marijuana
Here is a list of municipalities that have decriminalized local cannabis law.
- Bexar County
- Cedar Park
- Harker Heights
- Harris County
- Hays County
- Nueces County
- Plano County
- San Marcos
- Travis County
- Williamson County
A retired Microsoft exec and his wife fell in love with RVing during the pandemic. Now he's using AI to help you plan your next road trip.
- Scott Lengel, a former Microsoft CTO, launched an AI-powered RV road trip planner, AdventureGenie.
- He said when he got into RVing during the pandemic, he couldn't find a great planning tool.
- AdventureGenie recommends custom routes, campsites, and activities based on user preferences.

Scott Lengel and his wife, Lisa, were Marriott people.
After spending 23 years as a CTO at Microsoft , Lengel retired in 2017, at which point he and his wife knew they wanted to travel the world. They visited places like Cambodia, Vietnam, and India, typically traveling by plane and staying in hotels — often Marriotts.
Then the pandemic hit.
Suddenly, they were stuck at home in South Carolina. That's when the couple realized, "We really haven't seen the good old US of A."
Up until that point, they'd never even been camping .
"We figured if ever there was a time to go RVing, to go camping, this would be it," Lengel told Business Insider.
So they rented an RV and set off for Nashville with a couple of good friends. "We just had a blast," Lengel said. "Hanging around the campsite and the campfire and eating and beverages, and just the camaraderie. We just fell in love with the lifestyle of camping in one week."
Within six months, they purchased an RV of their own and started taking it all over. But when the couple tried to plan a six-week, multi-stop road trip to the national parks of the Southwest, they realized it was actually pretty challenging and that the existing resources were not great.
"There has to be a better way," they thought.
A couple of years later, in May 2023, Lengel launched AdventureGenie — an AI-powered RV trip planner. Lengel, who serves as chairman and CEO, said that in less than a year, AdventureGenie has attracted more than 10,000 users, and not just RVers, but also people traveling in cars on all kinds of road trips.
AI can customize trip planning
AdventureGenie is one of many AI-powered trip-planning tools that have popped up over the past couple of years. It's been featured on lists of the best RV- and road-trip planning AI tools.
Related stories
AdventureGenie is set up to help people plan their trips in three phases, which Lengel said was based on talking to thousands of people about how they plan their trips.
First, you can shape your trip. You can tell AdventureGenie things like where you want to start, where you want to end, how many miles you want to drive in a day, and any places you know you want to stop along the way. AdventureGenie will create a custom route based on your preferences and what the program knows about you, either from what you've told it or from past trips you've planned.
Second, you can select your campsites. AdventureGenie uses AI to compile information about campsites and make recommendations based on your preferences. In addition to generating an overall score on a campsite, AdventureGenie also generates a score that is unique to you, indicating how likely a specific campground is to meet your personal needs.
Third, is finding things to do. For instance, if it knows you like eating at local restaurants, hiking, and biking, as Lengel and his wife do, it can point out those attractions.
The biggest thing AI brings to AdventureGenie's trip planning is the customization, Lengel said. Instead of looking up a generic road trip planner that is the first hit served to everyone on Google, AdventureGenie can create itineraries that are unique to you.
"It feels as if you have a copilot or a travel planner sitting by your side and knows what you're looking for and customizes it for you," Lengel said.
He said that when RVers first use AdventureGenie the "jaw-dropping" moment for them is when it fills in the blanks on a trip with stops along the way.
In the past, if you wanted to road trip from South Carolina to Yellowstone, you'd have to look at a map and try to plot out stops based on how many miles a day you want to drive. But you'd also have to manually figure out whether those stops have campsites that suit your needs, or if they have any other attractions that make them worth passing through, or how far off the highway they are.
Lengel said new AdventureGenie users often say it saves them so much time planning their trip just by filling in their route.
"That's pretty darn rewarding for us," he said.
From Microsoft to tech startup
Lengel, who came out of retirement to launch AdventureGenie, said working on this startup has been a major change of pace from his days at Microsoft, which he also loved.
"We're a startup at our core, and it's a lot different than when I was working for an organization that had 150,000 employees and an incredible budget," he said. "We all wear lots of hats, which has been exciting, thrilling, and even challenging from time to time."
These days, he and his wife are on the road three out of four weeks a month, though now it's usually for work, visiting trade shows and meeting with RV user groups.
However, they do still make a point to do some fun things, too.
When Lengel spoke to BI, he was sitting in his RV in the Florida Keys, with a view of the ocean right out his window .
Watch: Marriott International's Tina Edmundson tells Insider that the travel mindset has changed since the pandemic
- Main content
More From Forbes
Trump’s plan to deport 11 million undocumented immigrants impossible.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Former U.S. President Donald Trump has big plans for undocumented immigrants in America (Photo by ... [+] Brandon Bell/Getty Images)
According to a Time cover story based on two interviews with the former president and conversations with more than a dozen of his closest advisors, if re-elected, one of Trump’s key concerns is immigration and the southern border. Apart from reinstating policies from his first term, such as the Remain in Mexico program for asylum seekers and Title 42 expelling migrants for health reasons without letting them apply for asylum, he will direct federal funding to resume construction of the border wall and introduce several other measures. Among all these initiatives, one particular plan Trump has merits special attention.
The Time article says, “The capstone of this program, advisers say, would be a massive deportation operation that would target millions of people. Trump made similar pledges in his first term, but says he plans to be more aggressive in a second. ‘People need to be deported,’ says Tom Homan, a top Trump adviser and former acting head of Immigration and Customs Enforcement. ‘No one should be off the table,’ use the military to round up, put in camps, and deport more than 11 million undocumented immigrants.”
The weakest link in the chain.
Weakest Link Problem
There is a saying that a chain is only as strong as its weakest link. And the weakest link in Trump’s chain of thinking on immigration is precisely this plan to round up 11 million undocumented immigrants.
Here is why.
First Deport Criminals
Firstly, it is important to distinguish between immigrants who simply entered this country unlawfully or have overstayed their period of authorized stay and criminals. To be more specific, of the 11 million undocumented immigrants in the United States, about one million have committed some sort of criminal offence. Of those, 300,000 have committed felonies . There is virtually no sympathy for immigrant felons, and even criminal aliens with lesser offences are not viewed with great sympathy by the general public. Trump would have little opposition to deporting most of these immigrants. But assuming we exclude those immigrants from this discussion, that leaves 10 million. How do we deal with the rest?
Your Best Look Yet At The New iPhone 16
Trump media stock djt at risk of a new short selling plunge, ryan garcia what s ostarine and how could a boxer use it to cheat, who are the rest.
Let’s look at them more closely. More than 60 percent of the 10 million undocumented immigrants, or some six million people, have lived in the United States for at least a decade . That’s a long time. We are talking about immigrants who, apart from their immigration status, live normal, decent lives and who have families and jobs in the United States and who, for 10 years, have been contributing to America through their work and taxes. Roughly 50 percent are Mexicans, many with close family or social and cultural ties to America. Some four million of them are parents of children born in the United States . These are the cold, hard facts about them. Do all such immigrants merit wholesale deportations?
A gavel and a name plate with the engraving Deportation
Past Massive Deportation Efforts Failed
In terms of deportations, while some previous Presidents have tried to deport unlawful immigrants from the USA, none came anywhere close to expelling as many as Trump is proposing. Not even President Eisenhower, who implemented Operation Wetback , came close to what Trump is proposing. A re-elected President Trump would soon discover that the task of removing undocumented immigrants is more difficult than it seems.
Constitutional Rights To Consider
Even undocumented immigrants in America have certain constitutional rights, particularly those who have been here for longer periods of time. For example, longer term noncitizens are entitled to the right to counsel, albeit at their own expense. They are also protected by at least the Fifth and Fourteenth Amendment rights to due process . These immigrants also have other legal protections . These constitutional rights mean that to remove illegal immigrants from America would require legal hearings in courtrooms. In addition to considering the rights of the defendants, this would create a logistical nightmare tying up the courts from dealing with other substantive issues. Judges, prosecutors, defence counsel as well as the persons concerned would all have to coordinate their calendars to schedule mutually agreeable dates for hearings before illegal immigrants could be deported. If you multiply this by some millions of cases you have a better idea of why legally removing these immigrants from America is going to take a long time and will be very expensive.
U.S. deportees not always welcome
Not Every Country Will Accept U.S. Deportees
Suppose, however, Trump were able to round up these people and overcome or simply ignore these constitutional protections. What then? There could be an even bigger problem to be faced. Not every country is ready to receive deported immigrants returning home from America. A Migration Policy Institute report indicated that America was not able to deport immigrants to many countries. “As of mid-2020, it considered 13 countries and territories recalcitrant: Bhutan, Burundi, Cambodia, China, Cuba, Eritrea, Hong Kong, India, Iran, Iraq, Laos, Pakistan, and Russia.” Furthermore, Myanmar, and Sierra Leone were publicly identified as being at risk of the classification. Add to that that in previous years, the United States has imposed visa penalties against Burundi, Ethiopia, the Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, and Guyana for similar reasons. Indeed, any review of country names in consideration of the likelihood they will cooperate on this kind of massive effort suggests that it is possible that as many as over 150 countries could at any moment refuse to accept the deportation from the U.S. of their nationals.
What is Trump going to do then? Beat up on all these countries to try to force them to comply? It does not take much to imagine how much chaos and angst will be involved.
On the other hand, President Biden seeks to establish a road to citizenship for these immigrants. Not everyone welcomes this approach, however. It is criticized for seeking to reward undocumented immigrants instead of punishing them for coming to America illegally. Some condemn Biden’s approach as nothing less than another unmerited amnesty. Concerns about the impetus such a policy would give to future migrants thinking about migrating to America are real. While also likely to encounter setbacks, such as defining how it would result in shutting down unlawful border crossings if implemented, at least Biden’s plan may be viewed as more consistent with America’s democratic essence. But it too, is not well thought out and remains a work in progress.
In the end, it will be for American voters to decide which vision of America when they vote in the November presidential election.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A thesis statement is the main idea that your essay supports. The thesis statement has 3 main parts: the limited subject, the precise opinion, and the blueprint .Hochstein, Jordan, and Jerz. A thesis reminder is a direct echo of the thesis statement. In a short paper, the topic sentence of each paragraph should repeat words or phrases from the ...
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
Your thesis statement, however, will present an argument about running and explain the significance. There are two types of thesis statements, blueprint and umbrella. • A blueprint thesis lists what will be discussed in your paper (EX: Running is important because A, B, and C.). While blueprint thesis statements are sometimes appropriate, you
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
Example 1: Passive construction. The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise. Example: Passive construction.
A thesis statement is the single, specific claim that your essay supports. A strong thesis answers the question you want to raise; it does so by presenting a topic, the position you wish to defend, and a reasoning blueprint that sketches out your defense of your chosen position. A good thesis is not merely a factual statement, an observation, a personal opinion or preference, or the question ...
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Thesis Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore needs
Part 2: Form an Initial Thesis Question, and Find a Supervisor When to Begin Forming Your Initial Thesis Question. Some fields, such as history, may require you to have already formed your thesis question and to have used it to create a statement of intent (outlining the nature of your research) prior to applying to a master's program. Others ...
The essay blueprint is NOT a summary (nor should it be confused with the essay roadmap, to be discussed in Chapter 4). Drafting an essay blueprint is an exercise that demonstrates clear understanding, meaningful citing and concise paraphrasing of the text's argument. In this sense, the essay blueprint is as much a reading comprehension ...
You may want to begin your blueprint by stating the author's central thesis, even if it does not appear at the beginning of the original article. However, it is best to avoid a point-by-point analysis of the text as that will result inevitably in summary, which you most certainly want to avoid at this level.
blueprint to make sure this happens! Before constructing an outline, you should review your research notes to develop a working thesis statement. For tips on crafting a thesis statement, see our tip sheet on "Overcoming the Thesis Statement." The Outlining Process 1. Organize your notes Begin by organizing your research notes.
XYZ Thesis. X, Y, and Z refer to the three or more body paragraph topics a writer wishes to discuss within the paper. Will have topic sentences corresponding to each of the points listed in this type of thesis: this is its blueprint. "Topical argument/stance on topic" + body topic X, body topic Y, and body topic Z. Example:
A thesis proposal allows you to clearly define—and even more crucially, limit—the focus and scope of your research. Producing an excellent thesis blueprint means that you won't accidentally find you're trying to build a skyscraper when you should be aiming at a bungalow—and that you have all the supplies and equipment you need.
For most grad students, preparing a thesis proposal is the first major step when writing a master's thesis. A strong thesis proposal: Acts as a project roadmap before major work begins. Outlines the research you plan to complete. Provides background, context, and qualifications. Limits and narrows the scope of the project.
The Stormboard template makes the process of building research models easy, and the ability to save, edit, and share them ensures that you'll be able to refer back to these blueprints at various stages throughout your research journey and Thesis writing process. When you get confused, become stuck, or feel overwhelmed by the complexity of ...
Tips for writing a clear "blueprint style" thesis!
The first chapter of your dissertation can be challenging to complete, and as many of our dissertation assistance clients have shared, it can even be difficult to start! This is because the introduction to the dissertation provides a blueprint for the rest of the study, laying out key aspects of your proposed research that will be covered in more depth in subsequent chapters.
Paper 2: Thesis / Blueprint. Come to class ready to discuss your thesis statement and a blueprint for the rest of your paper. Feel free to use this space to coordinate peer-reviews. You are also welcome to e-mail me. See the instructions for the April 17 thesis assignment for more about Paper 2. Categories: due_dates , in-class.
What's that balance between the short and long term? "It's a constant thing that we're always thinking about, and I think with the record that we have right now, it perhaps changes decisions compared to a different record. But there's also nothing that's set in stone at this point, and we're really thinking about that every day."
When starting your thesis or dissertation process, one of the first requirements is a research proposal or a prospectus. It describes what or who you want to examine, delving into why, when, where, and how you will do so, stemming from your research question and a relevant topic. The proposal or prospectus stage is crucial for the development ...
It is rare to get major presidential candidates - on either side of the political aisle - outside the confines of prepared remarks, stump speeches and friendly audiences, so it's worth ...
The plan wouldn't legalize marijuana at the federal level outright, but it would reclassify it from a Schedule I drug - believed highly dangerous, addictive and without medical use - to a ...
The proposed plan would no longer consider cannabis a Schedule I drug - believed highly dangerous, addictive, and without medical use. Here's where the Biden administration's plan currently ...
The Team plan is $30 per user per month, with a minimum of 5 seats. To get started with the Team plan, sign up here. iOS app. We're also announcing the launch of the Claude iOS app, so you can access Claude from anywhere, any time. The Claude iOS app features: Seamless syncing with web chats: Pick up where you left off across devices.
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Scott Lengel and his wife, Lisa, were Marriott people. After spending 23 years as a CTO at Microsoft, Lengel retired in 2017, at which point he and his wife knew they wanted to travel the world ...
Weakest Link Problem. There is a saying that a chain is only as strong as its weakest link. And the weakest link in Trump's chain of thinking on immigration is precisely this plan to round up 11 ...
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.