An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychiatry

Metasynthesis: An Original Method to Synthesize Qualitative Literature in Psychiatry
Jonathan lachal.
1 AP-HP, Cochin Hospital, Maison de Solenn, Paris, France
2 Université Paris Descartes, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Paris, France
3 CESP, Faculté de médecine, Université Paris-Sud, Faculté de médecine, Université de Versailles Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines (UVSQ), INSERM, Université Paris-Saclay, Villejuif, France
Anne Revah-Levy
4 Service Universitaire de Psychiatrie de l’Adolescent, Centre Hospitalier Argenteuil, Argenteuil, France
5 ECSTRA Team, UMR-1153, INSERM, Paris Diderot University, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Paris, France
Massimiliano Orri
6 Université Paris-Sud, Paris, France
Marie Rose Moro
Metasynthesis—the systematic review and integration of findings from qualitative studies—is an emerging technique in medical research that can use many different methods. Nevertheless, the method must be appropriate to the specific scientific field in which it is used. The objective is to describe the steps of a metasynthesis method adapted from Thematic Synthesis and phenomenology to fit the particularities of psychiatric research.
We detail each step of the method used in a metasynthesis published in 2015 on adolescent and young adults suicidal behaviors. We provide clarifications in several methodological points using the latest literature on metasyntheses. The method is described in six steps: define the research question and the inclusion criteria, select the studies, assess their quality, extract and present the formal data, analyze the data, and express the synthesis.
Metasyntheses offer an appropriate balance between an objective framework, a rigorously scientific approach to data analysis and the necessary contribution of the researcher’s subjectivity in the construction of the final work. They propose a third level of comprehension and interpretation that brings original insights, improve the global understanding in psychiatry, and propose immediate therapeutic implications. They should be included in the psychiatric common research toolkit to become better recognized by clinicians and mental health professionals.
The use of qualitative research is proliferating in medical research ( 1 ). Over the past two decades, numerous studies in the field of psychiatry have used a qualitative protocol ( 2 , 3 ), and it has been recognized as a valuable way to “ obtain knowledge that might not be accessible by other methods and to provide extensive data on how people interpret and act upon their illness symptoms ” ( 4 ). What matters most is the respondent’s perspective and the joint construction by the respondent and the researcher of a context-dependent, multiple, and complex reality ( 5 ). In this respect, the qualitative approach is close to that of the psychiatrist: what is important is what the patient feels and experiences and what emerges during the interaction between the patient and the psychiatrist. Indeed, the subjective coconstruction inherent to most of qualitative methods seems especially close to the psychiatric clinical meeting. Both are useful for building up local theory that helps to increase two important aspects of theory: individually relevant theory for clinical work and field-specific general theory for research ( 6 ). Qualitative research offers a thick description (one that encompass all the complexity of the phenomenon, behavior, or context) of a phenomenon and attempts to document the complexity and multiplicity of its experience ( 6 ). Similarly, in their day-to-day clinical work, psychiatrists attribute great importance to complexity and try to place symptoms within the patient’s history, in all of its intricate context—which again plays a crucial role in therapeutic choices.
Some have expressed concern, however, that because qualitative studies are isolated and rarely used to contribute to practical knowledge, they do not play a significant role in the movement toward evidence-based medicine ( 5 ). To alleviate this concern and enable qualitative work to contribute to this movement, an increasing number of teams have worked to develop and apply synthesis methods to these data. Qualitative syntheses refer to a collection of different methods for systematically reviewing and integrating findings from qualitative studies ( 7 ). The aims of such methods are to capture the increasing volume of qualitative research, to facilitate the transfer of knowledge to improve healthcare, and to bring together a broad range of participants and descriptions ( 8 , 9 ). Qualitative syntheses require not only a systematic approach to collecting, analyzing, and interpreting results across multiple studies, but also to develop overarching interpretation emerging from the joint interpretation of the primary studies included in the synthesis ( 10 , 11 ). Therefore, it involves going beyond the findings of any individual study to make the “whole into something more than the parts alone imply” ( 12 ).
Qualitative syntheses are now recognized as valuable tools for examining participants’ meanings, experiences, and perspectives, both deeply (because of the qualitative approach) and broadly (because of the integration of studies from different healthcare contexts and participants). They have been shown to be particularly useful to identify research gaps, to inform the development of primary studies, and to provide evidence for the development, implementation, and evaluation of health interventions ( 13 ). Because of this growing importance, an important work has been done in the last ten years, in order to ensure the quality of qualitative syntheses, such as: describing the methods to ensure reproducibility, develop tools for assessing the quality of the primary articles, and establish reporting guidelines [see, for example, the ENTREQ statement ( 13 ), the GRADE-Cerqual protocol ( 14 ), and the Cochrane or EVIDENT works ( 15 , 16 )].
However, despite some qualitative syntheses have been successfully conducted in the field of mental health ( 2 , 3 , 17 – 20 ), no study considers the methodological specificities inherent to psychiatric epistemological stance ( 7 ). Filling this gap has been one of the aims of our team since 2011. In this methodological article, we aimed to discuss the challenge of implementing metasynthesis to improve the understanding of youths suicide. In this study, we adapted the Thematic Synthesis developed by Thomas and Harden and incorporate a phenomenological approach in order to deal with new rigor with general as well as psychiatric issues ( 21 ). We will present each step of the method (Figure (Figure1) 1 ) and will propose methodological discussions. The detailed description of the findings can be found elsewhere ( 22 ).

Distribution in time for articles included in the metasynthesis.
Conducting a Metasynthesis
Before start—constitution of a research group.
The constitution of the research group and the definition of the study method are an important step before engaging in any synthesis work. The researcher must work in collaboration with researchers of diverse backgrounds ( 9 ). A collaborative approach improves quality and rigor and subjects the analytical process to group reflexivity ( 11 ). The research team should include members trained in qualitative synthesis as well as those expert in the topic being studied ( 23 ). As there are many ways to do qualitative syntheses, the research team will have to choose one of them adapted to the research question and to the expertise of the group ( 15 ).
Our team is composed of adolescent and child psychiatrists and psychologists from France and elsewhere (Italy, Chile, and Brazil) and focuses on developing qualitative research ( 24 – 26 ) and metasynthesis in adolescent psychiatry and related fields ( 22 , 27 , 28 ). Our method is adapted from thematic synthesis ( 21 ), which combines and adapts approaches from both metaethnography and grounded theory ( 10 ). Metaethnography, as well as Thematic Synthesis, takes place in six or seven steps from data collection to text coding and finally writing the synthesis. Original authors of metaethnography were trained in grounded theory, a qualitative method developed in the social sciences, laying on conceptual coding combine to construct a new theory. Thematic synthesis allows the researcher to include much more studies in the synthesis and to use tools coming from quantitative reviews, as systematic literature searches. This method perfectly suits to psychiatric research: user-friendliness for both researchers and readers; standardized in its most subjective steps but flexible, to make it adaptable to various patients or situations, such as children, patients with psychological disabilities or psychotic disorders, and to different researchers’ backgrounds (e.g., phenomenology, psychology, or psychoanalysis). We add a phenomenological perspective with a coding close to Smith’s interpretative phenomenological analysis (IPA) ( 29 ). IPA is also a qualitative method of coding a text, laying on phenomenology and hermeneutics. The level of coding is what makes sense to the reader (for example, a letter, a word, a sentence, the absence of a word, or a sentence). Phenomenology allows avoiding never-ending debates about theories of the psyche and focuses on the patient experience which is at the heart of psychiatric care. We understand that published manuscripts provide only thin data sets that are not eligible for a complete phenomenological analysis. Rather we tried to let ourselves guided by the impressions the text generated in us. It was like one article was assimilated as one participant, as it is mainly the voice of the main writer. We applied Smith’s tips on how reading and coding the data.
Define the Research Question and the Selection Criteria
Defining the research question is a crucial substep ( 9 ). This question must be broad enough to be of interest but small enough to be manageable ( 5 , 23 ) and has already been explored by enough studies ( 30 ). Inclusion and exclusion criteria may be fixed on methodological aspects, on participants selected, on thematic focuses or language specificities ( 9 , 31 ).
Youths suicide is a focus that were suitable for qualitative methods. We chose this subject because youth suicide is a major public health issue worldwide as well as a complex disorder that encompasses medical, sociological, anthropological, cultural, psychological, and philosophical issues. It has been widely explored by qualitative research. The lack of effectiveness of current care let us think that new insights could be expected by qualitative exploration. A first selection of articles, as well as an existing literature review on the topic, served to specify some starting information and enable initial decisions, including the definition of the research question, specification of the scope and the inclusion criteria. Then, the questions were constructed through reading and confronting these articles with our first qualitative study in the theme and our clinical knowledge of the theme.
As we wanted to study the therapeutic relationship and barriers to effective care, we decided to include research concerning not only the population being treated (the adolescents and young adults, and their parents), but also the healthcare professionals who care for these patients. A first screening of the literature showed us that optimal scope required a large range of ages, from 15 to 30 years old. The common thread linking all these youths was the importance of their parents in their everyday life. We chose to include only qualitative research, because it remains unclear how to deal with mixed method (combining qualitative and quantitative datasets) ( 23 ). Although databases contain articles in different languages, we chose to include only articles published in English (as most studies are now published in English) and French (as it is our first language) ( 22 , 27 ).
Study Selection
There is a debate on the choice of sampling method, some authors using an exhaustive sampling, some others, an expansive one ( 30 ). We privileged exhaustive systematic searches ( 32 ) since our method allowed large samples and because our target audience was the mental health community, which is accustomed to quantitative systematic reviews ( 9 ). Only journal articles were included, as most scientific data are published in this form ( 33 ). The first selection of articles served to specify the choice of keywords and databases for the electronic search. To ensure both sensitivity and specificity, we decided to use a combined approach of thesaurus terms and free-text terms. This technique maximizes the number of potentially relevant articles retrieved and ensures the highest level of rigor ( 34 ). Keywords were established during research team meetings, and were reported in the article or as supplemental material for more clarity ( 35 ). As each database has its own thesaurus terms, and as keywords encompasses different meanings in each discipline ( 36 ), the keywords were specific for each one.
We used four clusters of keywords: (i) those that concern the topic of interest (such as suicide, obesity, or anorexia nervosa), (ii) those that concern the participants (gender, age, profession, etc.), (iii) those that concern qualitative research (such as qualitative research, interviews, focus groups , or content analysis ), and (iv) those that concern perceptions and understanding, often called “views” ( 33 ) (such as knowledge, perception, self-concept, feeling , or attitude ). The last cluster takes all its importance in the phenomenological perspective of the analysis. An example of the final algorithm used (in the PubMed Web search) is provided in Table Table1 1 .
Algorithm used in the PubMed Web search from Ref. ( 22 ).
Similar work was conducted to select the databases. After consulting reference articles ( 33 , 37 , 38 ), we decided to conduct the search in five electronic databases covering medical, psychological, social, and nursing sciences: MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Social Science Citation Index (SSCI). Not long ago, CINAHL was the most important database for finding qualitative research, but as qualitative research proliferates in medical research, more and more qualitative articles are referenced in MEDLINE ( 33 ) and EMBASE. PsycINFO was a good database for finding qualitative articles with a psychological approach. We decided to add SSCI to broaden and complexity the outlook with a sociological point of view. We followed recommendations published on MEDLINE ( 39 ), CINAHL ( 40 ), EMBASE ( 41 ), and PsycINFO ( 42 ) for choosing search terms. Finally, we decided not to use the methodological databases’ filters for qualitative research, as these have undergone little replication and validation ( 43 ).
We decided to include articles published only in or after 1990. Two points impelled this decision: first, there was very little qualitative research on suicide before the year 2000 and even less before the 1990s (Figure (Figure2). 2 ). Second, we chose to consider as outdated research findings and results published more than 20 years ago were outdated, given the evolution of medical practices ( 44 ). However, this choice must be adapted to the topic of metasynthesis.

Flowchart of the metasynthesis steps.
The results of database searches were entered into a bibliographic software program (Zotero©) for automatic removal of duplicates. Then, two authors independently screened all titles and abstracts and selected the studies according to our inclusion criteria (defined earlier). If the abstract was not sufficient, we read the full text. Disagreements were resolved during working group meetings. Full texts of potentially relevant articles were then examined, and a second selection was performed. At this phase, we also checked each article’s reference list looking for new articles we might have overlooked. The final selection represented from 2 to 3% of the total initially obtained. This rate is consistent with the findings of other metasyntheses ( 23 ). For clarity, the selection process was also presented in a flowchart (Figure (Figure3). 3 ). We referred to STARLITE principles to report our literature search ( 45 ) (Table (Table2 2 ).

Flowchart for selecting studies from Ref. ( 22 ).
STARLITE principles applied to the literature search report of Ref. ( 22 ).
Quality Assessment of Included Studies
There is no consensus about whether quality criteria should be applied to qualitative research, or, for those who think they should be, about which criteria to use and how to apply them. Nevertheless a growing number of researchers are choosing to appraise studies for metasyntheses ( 46 ) and some authors state that a good metasynthesis can no longer avoid this methodological step ( 7 ). The reasons and methods for quality assessment fit into three general approaches: assessment of study conduct, appraisal of study reporting, and an implicit judgment of the content and utility of the findings for theory development ( 13 ). There is certainly not one best appraisal tool, but rather a wide choice of good ones ( 8 ).
We chose the Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP) ( 47 ), which is the most frequently used instrument ( 46 ), addresses all the principles and assumptions underpinning qualitative research ( 13 ). It is one of the instruments recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration ( 48 ) and has been used in several important thematic analyses of medical topics. As proposed by Boeije et al., we weighted our assessment by applying a three-point scale to each criterion (0 = criterion not met; 1/P = criterion partially met; 2/T = criterion totally met) ( 49 ) (Table (Table3 3 ).
Evaluation of the quality of the studies according to the Critical Appraisal Skill Programme (CASP) from Ref. ( 22 ).
a Number of studies .
We have not excluded any study on quality criteria. We think that the goal of the quality assessment is not to help selecting the more rigorous article. Either, this step is important to improve the overall rigor of the metasynthesis: by easily evaluating the quality of each article, the readers will have the possibility to make their own evaluation of the quality of the results of the metasynthesis ( 9 ). To enhance the rigor of the synthesis, we published the full results of this assessment ( 50 ).
Extracting and Presenting the Formal Data
To understand the context of each study, readers need the formal data about each study: the number and type of participants in each study, its location, and the method of data collection and of analysis. These data must be extracted and presented in a way that enables readers to form their own opinions about the studies included. We presented these data systematically, in a table with the following headings:
- – Identification of the study.
- – Summary of the study’s aim.
- – Country where the study took place.
- – Details about the participants: age, gender, type, and number.
- – Method of data collection (e.g., semistructured interviews or focus groups).
- – Analysis method (grounded theory, phenomenology, thematic, etc.).
Data Analysis
This step is probably the most subjective: its performance is highly influenced by the authors’ backgrounds ( 13 ). There are many ways to analyze, as many as there are authors. All researchers build on their personal knowledge and background for the analysis, sometimes described as bricolage , following Claude Levi-Strauss: “ the bricoleur combines techniques, methods, and materials to work on any number of projects and creations. Whereas a typical construction process might be limited by the history or original use of individual pieces, the bricoleur works outside of such limitations, reorganizing pieces to construct new meaning. In other words, unlike linear, step-by-step processes, the bricoleur steps back and works without exhaustive preliminary specifications ” ( 51 , 52 ). The synthesis will inevitably be only one possible interpretation of the data ( 9 ), as it depends on the authors’ judgment and insights ( 21 ). The qualitative synthesis does not result simply from a coding process, but rather from the researchers’ configuration of segments of coded data “ assembled into a novel whole ” ( 53 ).
In this process, the multidisciplinary team is essential to assess rigor and develop richer and more complex understandings. Triangulation of the analyses is enhanced when researchers with diverse background consider the same data set ( 11 ). “ Collaborative working not only improve quality and rigour, but subjects the analytical process to group reflexivity ” ( 54 ).
The first step of this process involved carefully reading and rereading each study ( 21 ). It is an active reading, with the intention of appraising, familiarizing, identifying, extracting, recording, organizing, comparing, relating, mapping, stimulating and verifying. In other words, it is reading with “ the intention of collating a synthesizable set of accounts ” ( 11 ).
The second step was coding: at least two different researchers coded each part of the data (whole manuscripts), performing a line-by-line coding, close to the phenomenological analysis described by Smith et al. ( 29 ).
In the third step, the codes were grouped and categorized into a hierarchical tree structure. This step is very close to the translation work described by Noblit and Hare ( 12 ). It involves comparing themes across articles to match themes from one article with those from another while ensuring that each key theme captured similar themes from different articles. We obtained a list of descriptive themes very close to the data.
In our example, we highlighted the sentence “You’re going to school, you’re getting an education, but you’re depressed” and coded it depressed . The code is then combined with others in a theme named “The experience of distress.”
Finally, in the last and most subjective step of the analysis, we generated analytical themes, which depended largely on the “judgment and insights of the reviewers” ( 21 ). This step is very similar the development of third-order interpretations—“ the synthesis of both first and second order constructs into a new model or theory about a phenomenon ” ( 23 )—and requires going beyond the content of original studies to achieve a higher level of interpretation and going beyond the descriptive synthesis to propose a more conceptual line-of-argument ( 21 , 23 ). This work has two types of underlying aims. The first type may be theoretical, by enabling a higher level of comprehension of a phenomenon; in medical science, this may be to better describe and understand a pathology. The second type may be to answer clinical questions about pathology and care directly.
In our example, we clearly fulfilled the second aim. The results leaded us to discuss new insights about suicidal youths’ care. The experience of incomprehension shared by all the protagonists of the care interferes with the capacity for empathy of both family members and professionals. We could use the concepts of intersubjectivity to witness the violence driven by the suicidal act.
Writing the Synthesis
Throughout the analysis process, the authors build themes that take place in the story they are telling about the participant’s experience ( 21 ). Then, the expression of the synthesis is our story of the studied phenomenon.
The results of the metasynthesis consist of the themes that we developed in the analysis. They are built by first and second order constructs. We did not define actual third-order themes; rather, third-order constructs helped us to build the synthesis into a story. We organized the themes into superordinate themes, which are interpretations of the themes and can be considered third-order interpretations.
For example, in one of the developed theme called the experience of distress we described that the young people experienced depressive symptoms. The participants described feelings of sadness, sorrow, mental pain, despair, detachment, anger, and irritability . The authors interpreted that as despair . We organized all these closed related feeling into the individual experience of distress . We decide not to speak about depression , first because some healthcare professionals repeated that they may diagnose depression “ but certainly not on a routine basis ” ( 22 ), then because we adopted a phenomenological approach and we felt that distress encompasses a broader and more complex experience.
Metasynthesis results prepare the framework for the discussion, the most interpretative part of the review, where hypothesis and proposals are presented. We offer our understanding of the participants’ experience. Both our presentation and our discourse are influenced by our aim: to answer clinical questions by suggesting specific actions or considerations for care; the discussion and the answers are intended to be useful for the readers of our article, as well as for us ( 23 ).
Our conclusion is that “ the violence of the message of a suicidal act and the fears associated with death lead to incomprehension and interfere with the capacity for empathy of both family members and professionals. The issue in treatment is to be able to witness this violence so that the patient feels understood and heard, and thus to limit recurrences ” ( 22 ). This issue is clear and simple and it leads to an immediate application to clinical practice which is described in the implication for practice chapter.
Finally, we discuss the limitation of the findings. The principal limitations were methodological (with our method, the access to participants’ data is partial), and in the sampling (we didn’t take in consideration the influence of gender on the experience of suicidal behavior). That exercise enhances the credibility of the publication, enabling readers to measure the importance and generalizability of the findings.
The written synthesis has to fulfill the standard for reporting synthesis of qualitative research. We chose to refer to Tong and al. ENTREQ statement ( 13 ) attached to the publication.
Our method is based on Thomas and Harden Thematic Synthesis ( 21 ). After a broad-scale review of literature on the topic of metasynthesis, we have decided to clarify the definition of some aspects of the method and modify or expand others, because we wanted both a medical and a psychological approach. For example, we opted to use a systematic search method and a weighted version of the CASP to assess quality.
Most metasynthesis authors argue that these reviews achieve a third-order level of interpretation, that is, that they are more than the sum of their results. If, as we think, qualitative research can achieve a moderate level of generalization with clinical implications, metasyntheses may transform these findings into more highly abstracted and generalizable theoretical frameworks. We “ push their findings toward the nomothetic end of the idiographic-nomothetic continuum ” ( 44 ). Qualitative specialists certainly do not shy away from stressing the importance of context in their studies, or from arguing that the context of one study may not be applicable to others. It is true that, in a way, metasyntheses decontextualize concepts to attain greater generalizability ( 44 ). But we can relate this act to the response of clinicians reading a qualitative article: they will try to apply the concepts to their own situations ( 21 ). Authors of metasyntheses are proposing their own interpretation of the concept and its generalizability. The scientific value of metasynthesis lies in its role as a summary of several studies and as the interpretation of varying context, as well as in its ability to weight each result and to propose greater generalizability.
Qualitative research is an invaluable method for gaining new insights into mental disorders ( 6 ). Its development in recent years requires that we improve methods for synthesizing their results. We think this way of doing metasynthesis is appropriate to psychiatric research in its intermediate position that stresses both progress in the general comprehension of disorders and direct clinical implications. It offers an appropriate balance between three components: an objective framework, which includes the selection, inclusion, and appraisal of studies; a rigorously scientific approach to data analysis; and the necessary contribution of the researcher’s subjectivity in the construction of the final work. The balance for a qualitative metasynthesis is, we think, very similar to the clinical approach to each patient. It necessitates a robust scientific background, a rigorous step-by-step—symptom by symptom—progression, and finally a part of art that depends on each clinician: the subjective part of therapy.
Finally, we think that metasyntheses enable insights that no other method can provide. Qualitative research sheds new light on scientific questions by emphasizing the participants’ subjective understanding and experience ( 6 ). Metasynthesis proposes a third level of comprehension and interpretation that brings original insights. In our study ( 22 ), we emphasized an original point in the relationship that was no found in any result from each primary study: the difficulty of professionals and parents to understand and cope with suicide as an obstacle to the care of the suicidal adolescent. Therefore, our study’s analysis went deeper and proposed original results.
Author Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments and final approval: JL, AR-L, MO, and MM. Conducted the literature review: JL and MO. Performed the experiments: JL, MO, and AR-L. Wrote the article: JL (all the article), AR-L (analysis), MO (introduction and analysis), and MM (discussion).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Jo Ann Cahn for revising our English.
Meta-Synthesis of Qualitative Research
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 24 February 2018
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Angela J. Dawson 2
564 Accesses
1 Citations
A meta-synthesis of qualitative health research is a structured approach to analyzing primary data across the findings sections of published peer-reviewed papers reporting qualitative research. A meta-synthesis of qualitative research provides evidence for health care and service decision-making to inform improvements in both policy and practice. This chapter will provide an outline of the purpose of the meta-synthesis of qualitative health research, a historical overview, and insights into the value of knowledge generated from this approach. Reflective activities and references to examples from the literature will enable readers to:
Summarize methodological approaches that can be applied to the analysis of qualitative research.
Define the scope of and review question for a meta-synthesis of qualitative research.
Undertake a systematic literature search using standard tools and frameworks.
Examine critical appraisal tools for assessing the quality of research papers.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Banning JH. Ecological triangulation: an approach for qualitative meta-synthesis. US Department of Education, School of Education, Colorado State University, Colorado; 2005.
Google Scholar
Barnett-Page E, Thomas J. Methods for the synthesis of qualitative research: a critical review, Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Co-ordinating (EPPI) Centre, Social Science Research Unit Institute of Education, London 01/09; 2007.
Bayliss K, Starling B, Raza K, Johansson EC, Zabalan C, Moore S, Skingle D, Jasinski T, Thomas S, Stack R. Patient involvement in a qualitative meta-synthesis: lessons learnt. Res Involv Engagem. 2016;2:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-016-0032-0 .
Article Google Scholar
Chatfield SL, DeBois K, Nolan R, Crawford H, Hallam JS. Hand hygiene among healthcare workers: a qualitative meta summary using the GRADE-CERQual process. J Infect Prev. 2017;18(3):104–20.
Cherryholmes CH. Notes on pragmatism and scientific realism. Educ Res. 1992;21(6):13–7.
Cooke A, Smith D, Booth A. Beyond PICO: the SPIDER tool for qualitative evidence synthesis. Qual Health Res. 2012;22(10):1435–43.
Crandell JL, Voils CI, Chang Y, Sandelowski M. Bayesian data augmentation methods for the synthesis of qualitative and quantitative research findings. Qual Quant. 2011;45(3):653–69.
Crotty M. The foundations of social research: meaning and perspective in the research process. St Leonards: Sage; 1998.
Dawson AJ, Buchan J, Duffield C, Homer CS, Wijewardena K. Task shifting and sharing in maternal and reproductive health in low-income countries: a narrative synthesis of current evidence. Health Policy Plan. 2013;29(3):396–408.
Dawson A, Nkowane A, Whelan A. Approaches to improving the contribution of the nursing and midwifery workforce to increasing universal access to primary health care for vulnerable populations: a systematic review. Hum Resour Health. 2015;13:97. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12960-015-0096-1 .
Denzin NK, Lincoln YS. The Sage handbook of qualitative research. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 2011.
Elfenbein DM. Confidence crisis among general surgery residents: a systematic review and qualitative discourse analysis. JAMA Surg. 2016;151(12):1166–75.
Fegran L, Hall EO, Uhrenfeldt L, Aagaard H, Ludvigsen MS. Adolescents’ and young adults’ transition experiences when transferring from paediatric to adult care: a qualitative metasynthesis. Int J Nurs Stud. 2014;51(1):123–35.
France E, Ring N, Noyes J, Maxwell M, Jepson R, Duncan E, Turley R, Jones D, Uny I. Protocol-developing meta-ethnography reporting guidelines (eMERGe). BMC Med Res Methodol. 2015;15:103. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-015-0068-0 .
France EF, Wells M, Lang H, Williams B. Why, when and how to update a meta-ethnography qualitative synthesis. Systematic reviews. 2016;5(44). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-13016-10218-13644 . https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0218-4
Franzen SR, Chandler C, Lang T. Health research capacity development in low and middle income countries: reality or rhetoric? A systematic meta-narrative review of the qualitative literature. BMJ Open. 2017;7(1):e012332. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012332 .
Glenton C, Colvin CJ, Carlsen B, Swartz A, Lewin S, Noyes J, Rashidian A. Barriers and facilitators to the implementation of lay health worker programmes to improve access to maternal and child health: qualitative evidence synthesis. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev. 2013;10. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010414.pub2 .
Gough D, Thomas J, Oliver S. Clarifying differences between review designs and methods. Syst Rev. 2012;1:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-1-28 .
Greenhalgh T, Annandale E, Ashcroft R, Barlow J, Black N, Bleakley A, Boaden R, Braithwaite J, Britten N, Carnevale F. An open letter to The BMJ editors on qualitative research. BMJ. 2016;352:i563. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i563 .
Guba EG. The paradigm dialog. Newberry Park: Sage; 1990.
Hannes K, Harden A. Multi-context versus context-specific qualitative evidence syntheses: combining the best of both. Res Synth Methods. 2011;2(4):271–8.
Hannes K, Lockwood C. Pragmatism as the philosophical foundation for the Joanna Briggs meta-aggregative approach to qualitative evidence synthesis. J Adv Nurs. 2011;67(7):1632–42.
Hannes K, Lockwood C. Qualitative evidence synthesis: choosing the right approach. West Sussex: Wiley-Blackwell; 2012.
Hannes K, Macaitis K. A move to more systematic and transparent approaches in qualitative evidence synthesis: update on a review of published papers. Qual Res. 2012;12(4):402–42.
Hannes K, Pearson A. Obstacles to the implementation of evidence-based practice in Belgium: a worked example of meta-aggregation. In: Synthesizing qualitative research: choosing the right approach. Chichester: Wiley; 2012. p. 21–39.
Chapter Google Scholar
Hannes K, Behrens J, Bath-Hextall F. There is no such thing as a one dimensional hierarchy of evidence: a critique and a perspective. Vienna, Austria: Paper presented at the Cochrane Colloquium; 2015.
Harden A, Thomas J, Cargo M, Harris J, Pantoja T, Flemming K, Booth A, Garside R, Hannes K, Noyes J. Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group guidance paper 4: methods for integrating qualitative and implementation evidence within intervention effectiveness reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017;In Press, Accepted Manuscript. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.11.029 .
Harris JL, Booth A, Cargo M, Hannes K, Harden A, Flemming K, Garside R, Pantoja T, Thomas J, Noyes J. Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group guidance series-paper 6: methods for question formulation, searching and protocol development for qualitative evidence synthesis. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017;In Press, Corrected Proof. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.10.023 .
Lewin S, Glenton C, Munthe-Kaas H, Carlsen B, Colvin CJ, Gülmezoglu M, Noyes J, Booth A, Garside R, Rashidian A. Using qualitative evidence in decision making for health and social interventions: an approach to assess confidence in findings from qualitative evidence syntheses (GRADE-CERQual). PLoS Med. 2015;12(10):e1001895. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed .
Martsolf DS, Draucker CB, Cook CB, Ross R, Stidham AW, Mweemba P. A meta-summary of qualitative findings about professional services for survivors of sexual violence. Qual Rep. 2010;15(3):489–506.
Melendez-Torres GJ, Grant S, Bonell C. A systematic review and critical appraisal of qualitative metasynthetic practice in public health to develop a taxonomy of operations of reciprocal translation. Res Synth Methods. 2015;6(4):357–71.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed .
Noblit GW, Hare RD. Meta-ethnography: synthesizing qualitative studies. Newbury Park: Sage; 1988.
Book Google Scholar
Noyes J, Popay J. Directly observed therapy and tuberculosis: how can a systematic review of qualitative research contribute to improving services? A qualitative meta-synthesis. J Adv Nurs. 2007;57(3):227–43.
Noyes J, Hannes K, Booth A, Harris J, Harden A, Popay J, Pearson A, Cargo M, Pantoja T. Qualitative research and cochrane reviews. In: Higgins J, Green S, editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.3.0. The Cochrane Collaboration. 2015. http://qim.cochrane.org/supplemental-handbook-guidance
Noyes J, Booth A, Flemming K, Garside R, Harden A, Lewin S, Pantoja T, Hannes K, Cargo M, Thomas J. Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group guidance paper 2: methods for assessing methodological limitations, data extraction and synthesis, and confidence in synthesized qualitative findings. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017;In Press, Corrected Proof. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.06.020 .
Oishi A, Murtagh FE. The challenges of uncertainty and interprofessional collaboration in palliative care for non-cancer patients in the community: a systematic review of views from patients, carers and health-care professionals. Palliat Med. 2014;28(9):1081–98.
Oliver K, Rees R, Brady L-M, Kavanagh J, Oliver S, Thomas J. Broadening public participation in systematic reviews: a case example involving young people in two configurative reviews. Research Synthesis Methods. 2015;6(2):206–217. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1145
Onwuegbuzie AJ, Leech NL, Collins KM. Qualitative analysis techniques for the review of the literature. Qual Rep. 2012;17(28):1–28.
Pawson R, Tilley N. Realistic evaluation. London: Sage; 1997.
Rodríguez-Prat A, Balaguer A, Booth A, Monforte-Royo C. Understanding patients’ experiences of the wish to hasten death: an updated and expanded systematic review and meta-ethnography. BMJ Open. 2017;7(9):e016659. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016528 .
Röing M, Holmström IK, Larsson J. A metasynthesis of phenomenographic articles on understandings of work among healthcare professionals. Qual Health Res. 2017;28(2):273–91. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732317719433 .
Sager F, Andereggen C. Dealing with complex causality in realist synthesis: the promise of qualitative comparative analysis. Am J Eval. 2012;33(1):60–78.
Sandelowski M, Barroso J. Handbook for synthesizing qualitative research. New York: Springer; 2006.
Schreiber R, Crooks D, Stern PN. Qualitative meta-analysis. In: Morse M, editor. Completing a qualitative project: details and dialogue. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 1997. p. 311–26.
Seymour KC, Addington-Hall J, Lucassen AM, Foster CL. What facilitates or impedes family communication following genetic testing for cancer risk? A systematic review and meta-synthesis of primary qualitative research. J Genet Couns. 2010;19(4):330–42.
Shaw R. Conducting literature reviews. In: Forreste MA, editor. Doing qualitative research in psychology: a practical guide. London: Sage; 2010. p. 39–56.
Stansfield C, Thomas J, Kavanagh J. ‘Clustering’ documents automatically to support scoping reviews of research: a case study. Res Synth Methods. 2013;4(3):230–41.
Thomas J, McNaught J, Ananiadou S. Applications of text mining within systematic reviews. Res Synth Methods. 2011;2(1):1–14.
Thomas J, O’Mara-Eves A, Brunton G. Using qualitative comparative analysis (QCA) in systematic reviews of complex interventions: a worked example. Syst Rev. 2014;3:67. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-3-67 .
Thorne S, Jensen L, Kearney MH, Noblit G, Sandelowski M. Qualitative metasynthesis: reflections on methodological orientation and ideological agenda. Qual Health Res. 2004;14(10):1342–65.
Tomlin G, Borgetto B. Research pyramid: a new evidence-based practice model for occupational therapy. Am J Occup Ther. 2011;65(2):189–96.
Tong A, Flemming K, McInnes E, Oliver S, Craig J. Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research: ENTREQ. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2012;12:181. https://doi.org/10.1186/471-2288-12-181 .
Voils C, Hassselblad V, Crandell J, Chang Y, Lee E, Sandelowski M. A Bayesian method for the synthesis of evidence from qualitative and quantitative reports: the example of antiretroviral medication adherence. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2009;14(4):226–33.
Walder K, Molineux M. Occupational adaptation and identity reconstruction: a grounded theory synthesis of qualitative studies exploring adults’ experiences of adjustment to chronic disease, major illness or injury. J Occup Sci. 2017;24(2):225. https://doi.org/10.1080/14427591.2016.1269240 .
Wong G, Greenhalgh T, Westhorp G, Pawson R. Development of methodological guidance, publication standards and training materials for realist and meta-narrative reviews: the RAMESES (Realist and Meta-narrative Evidence Syntheses–Evolving Standards) project. Health Serv Deliv Res. 2014;2(30):1. https://doi.org/10.3310/hsdr02300 .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Australian Centre for Public and Population Health Research, University of Technology Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Angela J. Dawson
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Angela J. Dawson .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Health, Locked Bag 1797, CA.02.35, Western Sydney Univ, School of Science & Health, Locked Bag 1797, CA.02.35, Penrith, New South Wales, Australia
Pranee Liamputtong
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Dawson, A.J. (2018). Meta-Synthesis of Qualitative Research. In: Liamputtong, P. (eds) Handbook of Research Methods in Health Social Sciences . Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2779-6_112-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2779-6_112-1
Received : 28 January 2018
Accepted : 12 February 2018
Published : 24 February 2018
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-10-2779-6
Online ISBN : 978-981-10-2779-6
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Social Sciences Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Reviewing the literature
- Scoping reviews
- Systematic reviews
- Meta-analysis
Meta-synthesis
- Rapid reviews
- Resources and references
- Protocol content
- Register your protocol
- Where and how to search
- Evaluate your search
- Export results to EndNote
- Assessing the evidence
- Retracted studies
- Reporting the screening
- Screening programs
- All reviews
To help the library continually improve, please use the form below if you wish to give feedback or suggestions about this guide.
Writing reviews guide feedback form
Meta-syntheses integrate and interpret research results from multiple qualitative primary studies (Erwin et al., 2011; Leary & Walker, 2018; Lockwood et al., 2015; MacEntee, 2019).
What is a meta-synthesis?
Meta-syntheses contribute to:
- Bridging of research gaps and practice (Erwin et al., 2011)
- Improved decision making in evidence-based practice (Erwin et al., 2011; Korhonen et al., 2013)
- Representing participants' perspectives, behaviours, emotions, beliefs, and experiences (Korhonen et al., 2013; Lachal et al., 2017; Tong et al., 2012)
- Understanding patient responses to various interventions (Lockwood et al., 2015; MacEntee, 2019)
- Comparison of a variety of healthcare contexts (Lachal et al., 2017; Tong et al., 2012)
- Stronger results because the source of evidence comes from many different scholars and primary studies (Korhonen et al., 2013; Leary & Walker, 2018)
- Generation of new primary research and knowledge (Erwin et al., 2011; Lachal et al., 2017; Leary & Walker, 2018; Tong et al., 2012)
- Meta-synthesis (Temple University Library)
- Origins, methods and advances in qualitative meta-synthesis
- Meta-analysis and meta-synthesis methodologies: Rigorously piecing together research
- Meta-synthesis of qualitative case studies: An approach to theory building
- Meta-synthesis of qualitative research: The challenges and opportunities
- The acceptability of physical activity interventions to older adults: A systematic review and meta-synthesis
- Digitized patient–provider interaction: How does it matter? A qualitative meta-synthesis
- Health practitioners' readiness to address domestic violence and abuse: A qualitative meta-synthesis.
- Meta-ethnography in healthcare research: A guide to using A meta-ethnographic approach for literature synthesis
- Meta‐synthesis on migraine management
- The nurse's role in palliative care: A qualitative meta‐synthesis
- Proposed teacher competencies to support effective nature of science instruction: A meta-synthesis of the literature
- What’s the meaning of the concept of caring? A meta‐synthesis
- Women’s psychological experiences of physiological childbirth: A meta-synthesis
Erwin, E. J., Brotherson, M. J., & Summers, J. A. (2011). Understanding qualitative metasynthesis: Issues and opportunities in early childhood intervention research . Journal of early intervention, 33(3), 186-200. https://doi.org/10.1177/1053815111425493
Korhonen, A., Hakulinen-Viitanen, T., Jylhä, V., & Holopainen, A. (2013). Meta-synthesis and evidence-based health care: A method for systematic review . Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences, 27(4), 1027-1034. https://doi.org/10.1111/scs.12003
Lachal, J., Revah-Levy, A., Orri, M., & Moro, M. R. (2017). Metasynthesis: An original method to synthesize qualitative literature in psychiatry . Frontiers in Psychiatry, 8 , Article 269. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00269
Leary, H., & Walker, A. (2018). Meta-Analysis and meta-synthesis methodologies: Rigorously piecing together research . TechTrends, 62 (5), 525-534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-018-0312-7
Lockwood, C., Munn, Z., & Porritt, K. (2015). Qualitative research synthesis: methodological guidance for systematic reviewers utilizing meta-aggregation. JBI Evidence Implementation, 13 (3). https://journals.lww.com/ijebh/Fulltext/2015/09000/Qualitative_research_synthesis__methodological.10.aspx
MacEntee, M. I. (2019). A typology of systematic reviews for synthesising evidence on health care. Gerodontology, 36 (4), 303-312. https://doi.org/10.1111/ger.12439
Tong, A., Flemming, K., McInnes, E., Oliver, S., & Craig, J. (2012). Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research: ENTREQ . BMC Medical Research Methodology, 12 (1), 181-181. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-12-181
- << Previous: Meta-analysis
- Next: Rapid reviews >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 10:56 AM
- URL: https://libguides.federation.edu.au/reviewingtheliterature
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 08 January 2021
Meta-ethnography in healthcare research: a guide to using a meta-ethnographic approach for literature synthesis
- Raabia Sattar ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1003-9772 1 , 2 ,
- Rebecca Lawton 1 , 2 ,
- Maria Panagioti 3 &
- Judith Johnson 1 , 2
BMC Health Services Research volume 21 , Article number: 50 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
36k Accesses
99 Citations
41 Altmetric
Metrics details
Qualitative synthesis approaches are increasingly used in healthcare research. One of the most commonly utilised approaches is meta-ethnography. This is a systematic approach which synthesises data from multiple studies to enable new insights into patients’ and healthcare professionals’ experiences and perspectives. Meta-ethnographies can provide important theoretical and conceptual contributions and generate evidence for healthcare practice and policy. However, there is currently a lack of clarity and guidance surrounding the data synthesis stages and process.
This paper aimed to outline a step-by-step method for conducting a meta-ethnography with illustrative examples.
A practical step-by-step guide for conducting meta-ethnography based on the original seven steps as developed by Noblit & Hare (Meta-ethnography: Synthesizing qualitative studies.,1998) is presented. The stages include getting started, deciding what is relevant to the initial interest, reading the studies, determining how the studies are related, translating the studies into one another, synthesising the translations and expressing the synthesis.
We have incorporated adaptations and developments from recent publications. Annotations based on a previous meta-ethnography are provided. These are particularly detailed for stages 4–6, as these are often described as being the most challenging to conduct, but with the most limited amount of guidance available.
Meta-ethnographic synthesis is an important and increasingly used tool in healthcare research, which can be used to inform policy and practice. The guide presented clarifies how the stages and processes involved in conducting a meta-synthesis can be operationalised.
Peer Review reports
The range of different methods for synthesising qualitative research has grown in recent years [ 1 ]. There are now a number of different qualitative synthesis methods including qualitative meta-synthesis, narrative synthesis, thematic synthesis, interpretative synthesis, grounded theory and meta-ethnography. A qualitative synthesis is defined as ‘any methodology whereby study findings are systematically interpreted through a series of expert judgements to represent the meaning of the collected work’ [ 2 ] .. In a qualitative synthesis the findings of qualitative studies are pooled [ 2 ] . The use of some types of qualitative syntheses allow for the inclusion of mixed-methods and quantitative research studies alongside qualitative studies. A qualitative synthesis approach can be used to examine the available literature, and review and integrate the primary research studies related to a specific question or phenomenon, to reveal deeper insights or explanations that would not be possible from a single study [ 3 ]. The various qualitative synthesis approaches mentioned above differ in their purposes, philosophical traditions and whether they primarily aggregate or re-interpret the study findings [ 4 , 5 ]. Meta-ethnography is an inductive, interpretative approach upon which most interpretative qualitative synthesis methods are based [ 6 ] and is the most commonly utilised qualitative synthesis approach in healthcare research [ 7 ].
Meta-ethnography is particularly suited to developing conceptual models and theories [ 8 ]. This method of qualitative synthesis is often chosen over alternative approaches as it is more suitable for the development of analytical rather than descriptive findings [ 9 ]. A meta-ethnography differs from other qualitative synthesis approaches as the reviewer re-interprets the conceptual data (themes, concepts or metaphors) created by the authors of the primary study whilst taking into account the primary data (participant quotes) using a unique translation synthesis method in order to transcend the findings of individual study accounts and create higher order themes [ 10 , 11 ]. Meta-ethnographic reviews offer greater description of methods and higher order interpretation compared to conventional narrative literature reviews [ 12 ]. In health sciences, meta-ethnographies can be used to generate evidence for healthcare and policy [ 13 ]. A meta-ethnographic synthesis approach is suitable when researchers are interested in conceptual or theoretical understandings of a particular phenomenon. Unlike some qualitative synthesis approaches which allow the inclusion of mixed-methods design studies (such as thematic synthesis and interpretative synthesis), a meta-ethnographic approach enables only the inclusion of qualitative studies. A meta-ethnography can include multiple study designs, whereas other approaches such as grounded theory require only the inclusion of similar study approaches [ 14 ].
Although meta-ethnography is a widely used qualitative literature synthesis method within healthcare research, it is poorly demarcated and there is a lack of clarity surrounding the description of the data analysis process. A number of reviews have used this approach [ 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 ] but do not provide a fully rigorous description of the stages involved in the analysis process. Given the value of qualitative meta-synthesis in integrating the findings from multiple studies into a higher conceptual level, it is important to provide detailed guidance on each of the steps involved in conducting a meta-ethnography. This paper aims to fill this gap by outlining a step-by-step method for conducting meta-ethnography. We describe our interpretation of each of the seven steps outlined by Noblit & Hare [ 10 ] who first proposed this approach. We also incorporate adaptations and developments by recent researchers [ 21 ] and provide annotations where applicable to assist in describing the stages involved.
The worked example we are using is a published meta-ethnography (reference and author names omitted for author anonymity during peer review). Where applicable, illustrative examples from this review are provided alongside the each phase to demonstrate the process.
Within a meta-ethnographic synthesis, the process of translation is key and unique. It is defined as ‘comparing the metaphors and concepts in one account with the metaphors and concepts in others’ [ 10 ]. A meta-ethnography should involve a reciprocal and refutational translation, where possible combined with a line of argument synthesis [ 22 , 23 ]. Reciprocal translation occurs when concepts in one study can incorporate those of another [ 22 ], whereas a refutational translation explains and explores differences, exceptions, incongruities and inconsistencies [ 1 , 22 , 24 ]. Reviewers often overlook refutational translation [ 24 , 25 ]; however studies may refute each other [ 26 , 27 ] or concepts within studies may refute one another [ 27 , 28 ]. Therefore it may be possible to conduct both a reciprocal and refutational translation [ 22 ]. A line of argument synthesis is not an alternative to conducting a translation but is viewed as the next stage of analysis [ 23 ]. A line of argument synthesis is the translation of accounts that interpret different aspects of the same phenomenon under study, which results in producing a whole that is greater than the sum of its individual parts [ 10 , 15 ]. Although Noblit & Hare [ 10 ] describe meta-ethnography as a seven step process, it is important to acknowledge that this process is iterative and the phases are not discrete but may overlap and run in parallel [ 10 ]. A meta-ethnography reporting tool, eMERGE has very recently been developed, and provides a framework for reviewers to follow when reporting the important aspects of a meta-ethnography [ 22 ].
In order to identify relevant literature to inform the present guide, we searched for articles which described an evaluation or discussed methodological issues in conducting a meta-ethnography or provided guidance for reporting a meta-ethnography. We then scanned the reference lists of relevant articles to identify further relevant literature. We also drew on the results from two recent systematic reviews [ 23 , 29 ]. As such, while the searches conducted for the present article were not systematic, the guide reflects recent methodological recommendations in the wider methodological literature. All relevant articles were read and recommendations were noted; where any disagreement between authors of papers was apparent, guidance which was based on systematic reviews of the evidence rather than individual reflections was prioritised.
Doing a meta-ethnographic synthesis: a step-by-step guide with illustrated examples
Phase 1: getting started.
The initial stage requires the authors to identify an area of interest [ 10 ]. The reviewers need to consider if a synthesis of the topic is required and whether a qualitative synthesis and the meta-ethnographic approach fits with the research question [ 30 ]. E.g. A meta-ethnographic synthesis approach is suitable when researchers are interested in conceptual or theoretical understandings of a particular phenomenon. It is also important to determine whether there is a large and growing body of qualitative research in this area, and whether synthesizing qualitative findings can contribute valuable knowledge to the existing literature [ 31 ]. As proposed by Campbell and colleagues [ 32 ], we emphasize, that at this stage, it is important to establish a team of researchers who have different approaches, opinions and the key skills to conduct the meta-ethnography, as this will add rigour to the meta-ethnographic review.
We were interested in the disclosure of adverse events within healthcare; specifically in the perceptions and experiences of patients and healthcare professionals relating to these events. We were aware of the large and growing body of qualitative research in this area. Our searches revealed that there was no qualitative synthesis specific to the experiences of adverse event disclosure. We believed that synthesizing the views, attitudes and experiences of both groups (patients and healthcare professionals) would enable us to understand what patients require from the disclosure conversation and what healthcare professionals currently offer. Our motivation for synthesizing the body of qualitative evidence was to inform future disclosure interventions which were acceptable to patients and practical for healthcare professionals to deliver. Synthesizing qualitative findings can make valuable knowledge accessible to healthcare professionals and policy makers [ 31 ].
Phase 2: deciding what is relevant to the initial interest
Once you have chosen your topic of interest, phase 2 involves the following steps: a) defining the focus of the synthesis, b) selecting studies for inclusion in the synthesis and locating relevant studies, c) developing inclusion and exclusion criteria and d) quality assessment of the included studies [ 12 ].
2a. Defining the focus of the synthesis
An important decision involves deciding whether to include all the studies within your chosen area of interest. It is necessary to find a balance between a review which has a broad scope, and a focus which will yield a manageable number of studies. The scope of a meta-ethnography is more restricted compared to other qualitative narrative reviews. This is due to the avoidance of making gross generalisations across disparate fields [ 10 , 26 ]. There is currently no agreement to how many studies should be included in the synthesis. Some researchers argue that synthesizing a large number of studies may interfere with the ability to produce a useful interpretative output and could result in an aggregative synthesis [ 23 ]. Synthesizing too few studies can result in underdeveloped theories/concepts [ 24 , 28 ]. A large number of studies have varied from 40 [ 32 ] to over 100 [ 24 ]. The volume of data, rather than just the number of studies is important and team size and resources will affect the ability to manage this data [ 22 ]. It is recognised that focusing on a particular aspect of your chosen topic interest and excluding certain aspects may result in some papers being overlooked. However it is important to make this choice to ensure that you have manageable number of studies [ 12 ].
Our systematic review question focused on ‘The views and experiences of patients and healthcare professionals on the disclosure of adverse events’. We focused on studies which examined the views and experiences of patients (and/or family members, members of the general public) and healthcare professionals. We found that qualitative research in the area of adverse event disclosure was limited. As this was an under-researched area, we were able to include all the available qualitative studies in this research area (enabling us to include both patients’ and healthcare professionals’ views on adverse event disclosure).
Phase 2b: locating relevant studies
The second important step involves locating potentially relevant qualitative studies by conducting a systematic search of the literature. In order to conduct a systematic search, a well-constructed and comprehensive search strategy needs to be developed. Qualitative searches can yield a large number of search results, which can be daunting and time consuming to screen. One of the ways to make your search strategy more specific is through the use of qualitative search filters. Empirically tested search filters for qualitative studies have been developed [ 33 , 34 , 35 ]. However it is possible that some of the potentially relevant studies may be missed when using such filters. Decisions regarding your search strategy and screening depend on your aims and resources available. We advise the use of a librarian for reaching decisions on the content of searches. Multiple databases are utilised to locate relevant articles and this can be further supplemented by hand searching. This is important as it can locate relevant articles which are not indexed or inaccurately indexed, and minimises the risk of missing relevant studies [ 24 ].
Some argue that a more purposive sampling approach may be more appropriate [ 36 , 37 ], which aims to provide a holistic interpretation of a phenomenon, where the extent of searching is driven by the need to reach theoretical saturation rather than to identify all eligible studies [ 24 , 38 ]. Detailed information on purposive sampling technique is available [ 24 , 28 ]. Also, to avoid the potential problem of having too few descriptively or conceptually-rich studies, knowledge-building and theory-generating systematic reviewers can conduct expansive searches of the literature [ 28 ]. We do not describe here how to conduct a systematic search of the literature, however there are a number of papers which describe this process [ 39 , 40 , 41 ].
We searched five electronic databases, and our search strategy included a combination of the three major concepts (disclosure, safety incident and experience). We also supplemented the database searches by hand searching relevant journals and reference lists. We chose not to apply qualitative filters in order to capture all the possible relevant articles.
Phase 2c: decisions to include studies
A number of factors should be considered when deciding whether to include or exclude studies from the synthesis. An important consideration is the expertise of the review authors and the time available to complete the review [ 36 ]. Reviewers should consider the likelihood of excluding valuable insights on the basis of quality, and the contribution of these studies to the development and interpretation of findings. Would excluding such studies affect the coherence of qualitative synthesized findings? [ 36 ]. Also, an important consideration is the nature of the primary data which is available to synthesise [ 23 ]. Including predominantly thin descriptive data can be problematic as it is difficult to further interpret data which lacks depth [ 23 ]. Conceptually rich data which is explanatory, or rich descriptive data which provides sufficient detail to be further developed is suitable for meta-ethnography. Therefore selecting studies based on this suitability is one of the approaches reviewers should consider. Further discussion on decisions to include studies is available [ 36 ].
Phase 2d: quality appraisal
There is a lack of agreement surrounding the use of quality appraisal for qualitative studies [ 30 ]. Some researchers argue there are difficulties with quality appraisal as some aspects of qualitative research are difficult to appraise and therefore depend on subjective judgement [ 5 ]. Although this debate continues, we argue that at least some quality appraisal of studies needs to be considered to give an indication of the credibility of the included studies. Critically appraising the studies and assigning numerical scores to indicate level of quality is also useful as it can be used as a way to order the studies for analysis. Previous published qualitative reviews have either used the highest scoring paper as the ‘index study’ [ 15 ] or have arranged all the papers in chronological order by date, and used the most recently published paper as the ‘index study’ [ 42 ]. One of the limitations is of assigning numerical scores using CASP and the use the highest scoring as an index study is that it focuses on the methodological rather than conceptual strength. Other reviewers have chosen a ‘conceptually rich’ index account [ 43 , 44 ] however it is unclear how this ‘conceptually rich’ index account should be selected. The different ways of ordering study accounts has yet to be formally empirically compared and there is no guidance for reviewers [ 23 ]. However the order could affect the synthesis output [ 11 , 12 , 24 , 45 ]. There are different perspectives to the use of tools in the quality assessment of qualitative research [ 46 ]. Some recommend the exclusion of studies based on a low-quality assessment and others refute this view and suggest that such tools may not truly assess the meaningfulness and potential impact of qualitative findings [ 47 ]. However, we believe that these checklists can equip novice qualitative researchers with the resources to evaluate qualitative research efficiently.
Two common and widely used quality assessment tools are the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) and the Qualitative Assessment and Review Instrument (JBI-QARI). The Critical Appraisal Skills Checklist (CASP) provides detailed instructions and decision rules on how to interpret the criteria [ 48 ]. This checklist contains a number of questions which help the reviewer to assess the rigour, credibility and relevance of each study [ 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 ]. All studies are critically appraised and each study is assigned a numerical score out of ten, where a higher score is correlated to a higher quality [ 15 ]. The two studies ranked with the highest scores are used as index studies, and can be used as the first studies from which concepts are translated into other studies and therefore shaping the analysis [ 12 ]. Similarly, the Qualitative Assessment and Review Instrument (JBI-QARI) is a 10 item checklist which assesses the methodological quality of a study, and determines the extent to which a study has addressed the possibility of bias in its design, conduct and analysis [ 53 ]. Some researchers provide guidelines for determining and excluding studies which have major methodological flaws [ 54 ]. However, it can be argued that excluding studies based on quality criteria may result in the exclusion of insightful studies. GRADE-CERQual is a recently developed approach which provides guidance for assessing how much confidence to place in findings from systematic reviews of qualitative research [ 55 ]. The application of GRADE-CERQual can be helpful for appraising the overall quality of the qualitative synthesis [ 55 ] but a quality appraisal of primary studies is required before applying the CERQual tool.
We used the CASP checklist to assess the quality of included studies. We chose to use the CASP as it propagates a systematic process through which the strengths and weaknesses of a research study can be identified [ 56 ]. The CASP guidelines are easy to follow, especially for novice researchers [ 56 ]. We made a decision in advance not to exclude studies with low quality scores. We believed that although some authors may have failed to describe the methods in sufficient detail for us to determine that quality criteria had been met, lack of reporting did not necessarily mean it was poorly conducted research [ 12 ]. We did however use the quality rating of the studies in our synthesis approach. The study ranked with the highest score was used as the ‘index study’ and was the first study from which concepts were translated into other studies and therefore shaping the analysis [ 12 ].
Phase 3: Reading the studies
It is during this phase where the synthesis process begins. First, this involves repeatedly reading the included studies and familiarising yourself with the key concepts and metaphors. It is important at this stage to become as familiar as possible with the content and detail of the included studies. A concept is defined as ‘having some analytical or conceptual power, unlike more descriptive themes [ 26 ]. It is important to acknowledge that reading the studies is not a discrete phase; reading occurs throughout the synthesis process. The notion of first, second order and third order constructs [ 26 ] are useful in distinguishing the ‘data’ of the meta-ethnography which are defined in Table 1 below.
Once you have read through the chosen studies, the next step involves extracting the ‘raw data’ from the studies for the synthesis. The raw data for a meta-ethnographic synthesis are the first and second order constructs [ 29 , 31 ]. The data needs to be extracted from each of the studies, which can be done by using a standardised data extraction form [ 11 ]. Alternative ways to extract data include creating a list of metaphors and themes [ 32 ] or coding concepts in Nvivo; a software programme for the analysis of qualitative data [ 31 ]. The data should be extracted verbatim, so there is no risk of losing important data [ 12 ] and to preserve the original terminology used by the primary authors. However, some authors of a previous meta-ethnography chose to record summaries of primary author interpretations due to the large number of studies included in their synthesis [ 12 ]. However, one of the drawbacks of recording such summaries is that there is the risk of potentially losing important detail.
It is essential at this stage to extract information on study characteristics for each study, using a separate data extraction form as it provides context for interpretations and explanation of each study [ 57 ]. This includes information on study sample, data collection methods, data analysis methods, study outcomes and study conclusions.
We have provided an example of a data extraction table we used to extract the raw data (Fig. 1 ).

Example of a data extraction table
Phase 4: determining how the studies are related
During this stage, the relationships between the key concepts from the different papers need to be considered. A concept is described as a ‘ meaningful idea that develops by comparing particular instances’ [ 29 , 45 ]. It is also important that concepts explain and do not only describe the data [ 29 , 45 ] as one of the aims of qualitative analysis is to develop concepts which help to understand an experience and not just describe it [ 58 ]. In order to consider the relationship between concepts from the different studies, you are required to look across the studies for common and recurring concepts. This can be done by creating a list of the themes [ 10 ]. These are then juxtaposed against each other to examine the relationships between the key concepts and metaphors these themes reflect and to identify common and recurring concepts. From this list, the themes from the different studies are then clustered into relevant categories, where we grouped common concepts from studies according to the common underlying metaphors, an approach which has previously been used [ 12 , 31 , 59 ]. During this phase it is essential to examine the contextual data about each study. This includes settings, aims and focuses. These newly formed categories are labelled using terminology which encompasses all the relevant concepts they contain. This phase is likely to be iterative, and clusters may be revised through discussions within the review team of how they are related and by making reference to the original text.
Other authors have used diagrams [ 11 , 32 ] or coding using qualitative analysis software [ 31 ]. The use of lists or tables in phase 4 is useful when synthesising a small number of studies, however such an approach would be unwieldy when there are hundreds of concepts, whereas coding in NVivo is efficient [ 23 ]. However, the recording of links between concepts within primary studies may be difficult when using NVivo [ 23 ].
During this phase, for our review we created a list of the themes from each paper (Fig. 2 ) listed under each study name. As we had included both healthcare professional and patient studies, we also labelled whether the study had included patients, healthcare professionals or both groups.
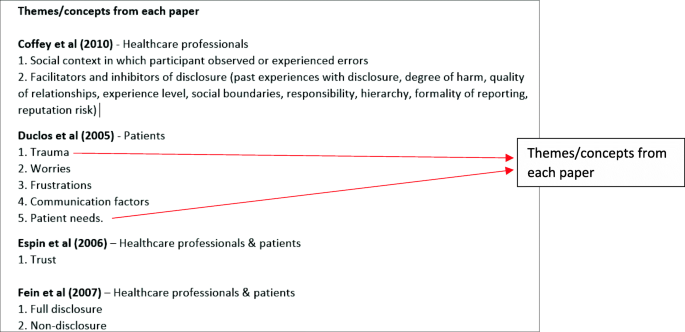
List of key metaphors/concepts from each study
The next step involved reducing the themes from the different studies into relevant categories (Fig. 3 ).

Reducing themes into relevant categories
It is important to note that the category labels you create during this phase are not the higher third order constructs, but are descriptive labels. The third order constructs are developed within the next two phases. However, the data within each category forms the basis of reciprocal translation or refutational synthesis in the next stages. This approach can work well when you have a manageable number of studies, however this can prove to be challenging when you have a larger number of studies. In previous meta-ethnographies where a large number of studies have been included, a thematic analysis of themes was carried out instead [ 12 ].
Phase 5: translating the studies into one another
The original method of meta-ethnography suggests that this phase involves ‘comparing the metaphors and concepts in one account with the metaphors and concepts in others’ [ 10 ]. However, despite a number of meta-ethnographies being conducted, it is unclear how this should be done and how this phase of the analysis should be recorded. To address this lack of clarity, we will now outline below one way in which this can be done. During this phase, each concept from each paper is compared with all the other papers to check for the presence or absence of commonality. Doing this highlights the similarities and differences between the concepts and metaphors and allows the researcher to organise them into further conceptual categories, which results in the development of the higher third order constructs.
This phase is approached by arranging the studies either chronologically [ 32 ] from the highest scoring paper to the lowest scoring paper (where the scores are generated during the quality appraisal process [ 15 ]. Arranging the studies chronologically is advised when you are including a large number of papers over a large time span [ 12 , 29 ]. The order in which studies are compared may influence the synthesis, as earlier papers will have a strong influence on the subsequent development of ideas [ 60 ]. The reviewer first starts by summarising the themes and concepts from paper 1. Summarising involves comparing and contrasting the concepts taking into account study contexts. They then summarise the themes and concepts from paper 2, commenting first on what is similar with paper 1 and then what paper 2 may add to paper 1 or where its findings diverge from paper 1 [ 12 , 29 ]. Next, paper 3 is summarised, considering what is similar to papers 1 and 2, and then noting any areas of divergence and anything that paper 3 adds to the knowledge offered in papers 1 and 2. This process continues until you have synthesised all the papers and produces a synthesis of the primary author interpretations (see Fig. 4 ) which are useful in aiding with the development of the third order constructs in the next stage.

Primary data synthesis of the primary author interpretations
Examining the key concepts within and across the studies is similar to the method of constant comparison [ 29 ]. During this phase, it is important to refer back to the table of study characteristics you recorded earlier, (country, sample, recruitment method, gender, publication date etc.) to use as a context for the comparisons [ 15 ] as well the full papers. This process can also be supported by creating a translations table, as this is a useful way to display this level of synthesis [ 61 ] (see Fig. 5 for an example of a translations table). Maintaining a personal journal during this phase of the analysis can help to ensure that the researcher is aware of their position from a theoretical point of view [ 62 ]. Discussing the key concepts and their meanings with team members can result in collaborative interpretations.
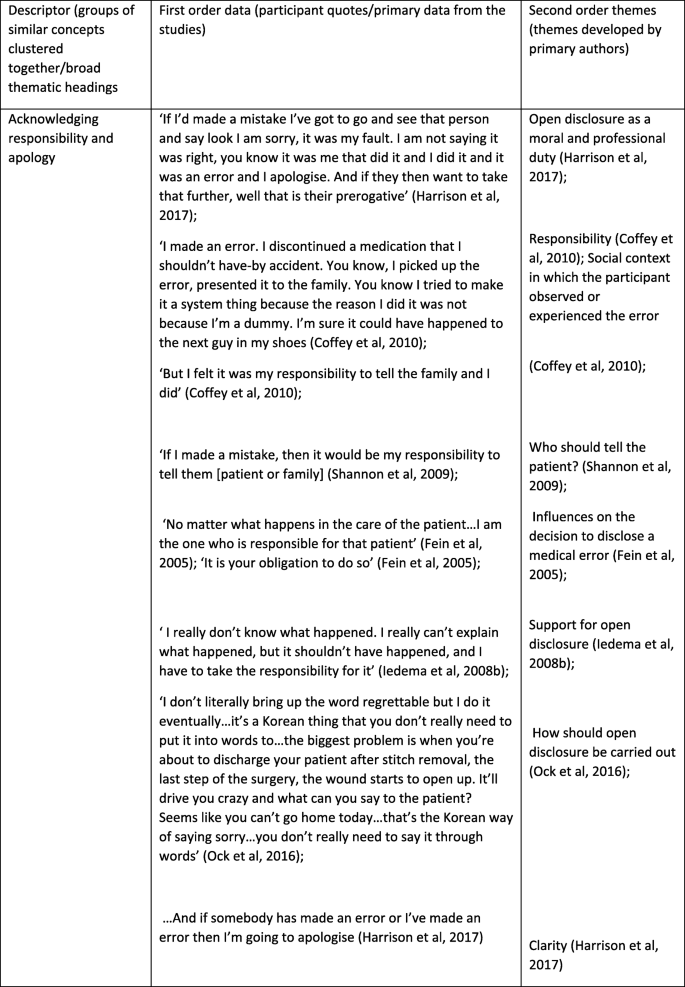
Example of a translations table
We conducted two separate syntheses; one for the views of patients and one for healthcare professionals, and conducted a line of argument synthesis of all the included studies, therefore we found it useful to have two separate translation tables; one for each group. Part of the translation table for healthcare professionals is shown in Fig. 5 (see example of table below).
Phase 6: Synthesising the translations
This phase is described by [ 10 ] as ‘making the whole into something more than the parts alone imply’. However, similar to Phase 5, there has been no clear guidance on how to carry out this phase. During this phase, the studies are now viewed as a ‘whole’ with the aim of developing a framework [ 29 , 31 ]. When writing about how the studies are related, reviewers can present this in a narrative and/or diagrammatic form [ 30 ]. Phase 6 can be broken down into the following two stages; (a) reciprocal and refutational synthesis and (b) line of argument synthesis.
(A) Reciprocal and refutational synthesis
This stage of the synthesis involves deciding whether the studies are sufficiently similar in their focus to allow for a reciprocal translation synthesis. Alternatively, the studies may refute each other in which case a refutational synthesis is conducted. It is possible to conduct both types of synthesis to discuss similar accounts (reciprocal translation synthesis) and also explore any contradictions between the studies (refutational synthesis) [ 23 ]. Generally, reciprocal translation syntheses are conducted more frequently in reviews than refutational syntheses and guidance on how to conduct a refutational synthesis is currently limited [ 23 ]. Below we first discuss how to carry out a reciprocal translation and then describe the way a refutational synthesis can be conducted. Referring to the translations table of data developed in the stages above allows reviewers to establish the relationship between the studies and consider how to approach a reciprocal and refutational synthesis.
Reciprocal translation
It is during this phase where the shared themes across the studies are summarised by juxtaposing the first and second order constructs. This leads to the generation of new concepts which provide a fuller account of the given phenomenon and resolve any contradictions [ 63 ]. These are known as the original third order constructs developed by the review authors and provide a new understanding of the phenomena [ 15 ]. To put briefly, this can be achieved by reading the primary data synthesis (Fig. 4 ) alongside the translations table (Fig. 5 ) and drawing out the main points to form the reciprocal translations and therefore developing the third order constructs. It is important to constantly check the summary and third order constructs you are developing against the translations table to ensure it is consistent with the original data.
Refutational synthesis
There are limited published examples of refutational synthesis [ 25 , 45 ] as reviewers often focus on reciprocal translations [ 25 ]. Also reviewers may conduct a refutational synthesis, but not label it as such [ 23 ]. There are two published examples of refutational synthesis [ 43 , 64 ]. This is not surprising given the lack of guidance available on how to conduct a refutational synthesis. The purpose of a refutational synthesis is to explore and explain the differences, exceptions, incongruities and inconsistencies in concepts across the studies [ 1 , 24 ]. Refutational synthesis focuses on identifying, understanding and reconciling the contradictions, rather than developing concepts around the similarities. Similar to reciprocal translation, reviewers are required to refer back to the primary data synthesis and translations table in order to develop third order constructs. The contradictions between the concepts across the studies may be explained by differences in participants, settings or study design. During this phase, it is helpful to refer back to the study characteristics table as this can help provide context for interpretations and explanations [ 57 ]. It has been suggested that a refutational translation can be approached by placing two refutational concepts at either end of a continuum and proceed by analysing the differences between the concepts [ 22 , 28 ]. In order to express the refutational findings, a narrative can be created so that the findings ‘are placed into context’ [ 28 ].
(B) A lines of argument synthesis
A lines of argument synthesis can then be created from the third order constructs, which involves ‘making a whole into something more than the parts alone imply’ (known as higher order interpretations) [ 10 ]. A lines of argument synthesis means that there is an ‘interpretation of the relationship between the themes, which further emphasises a key concept that may be hidden within individual studies in order to discover the whole from a set of parts’ [ 10 ]. This is classed as a further higher level of interpretative synthesis, and provides scope for developing new insights.
A lines of argument synthesis is achieved by constant comparison of the concepts and developing a ‘grounded theory that puts the similarities and differences between the studies into interpretative order’ [ 10 ]. Practically, reviewers can approach this phase by reading through the reciprocal translations and noting down the similarities and differences between each of the third-order constructs. These notes can then be used to construct interpretations of how each third order construct relates to the others in the analysis. These relationships can then be represented using a diagram to aid understanding. Each of the reviewers can carry out this stage independently, and merge their findings as a team to produce the final line of argument synthesis. Diagrams can be used to develop the line of argument synthesis and it is suggested that discussions between team members are vital to this process [ 29 , 30 ]. A lines of argument synthesis can be a useful way to bring together and explain the perspectives of two or more different groups and interpreting the relationship between the themes. This is particularly relevant for research in healthcare, where often the views of one or more groups are examined on a phenomenon (e.g. patients and healthcare professionals). An example of a line of argument synthesis from the worked example is presented in Fig. 6 .
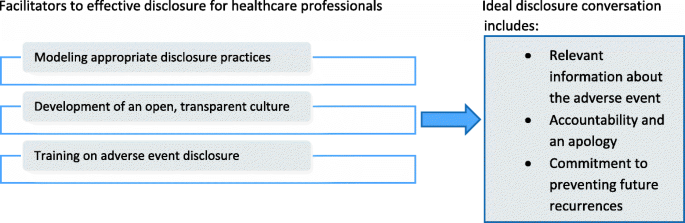
Example of a line of argument synthesis developed
We conducted separate reciprocal translations for the first- and second-order constructs relating to patients and healthcare professionals, resulting in third order constructs which related to solely either patients or professionals. Therefore, the synthesis process for our review consisted of three steps- (1) reciprocal translations of the patient studies to understand patients’ views and experiences of disclosure, (2) reciprocal translations of the healthcare professional studies to explore healthcare professionals views and experiences on disclosure and (3) a line of argument synthesis which contributed to the identification of both the key elements of an ideal disclosure desired by patients and the facilitators for healthcare professionals which can increase the likelihood of this taking place. We initially considered a refutational translation instead of a line-of-argument synthesis, but it was apparent during the synthesis that the concepts from the patient and healthcare professional studies were not contradictory in nature; rather they described alternate perspectives of the same phenomenon. Therefore we believed a line of argument synthesis was the most appropriate for the aim of our synthesis. During this stage of the analysis, we found it helpful to place all the third order constructs in a table to enable visual comparison (see Table 2 ).
The third order constructs should be theoretically rich. In our synthesis, although we found that the data we were dealing with was descriptive, it was rich descriptive data. This therefore provided us with sufficient detail to further interpret this and develop third order constructs [ 23 ]. The third order constructs we developed reflected the data we were dealing with, but allowed us to produce higher levels of analysis. Reviewers should take caution when dealing descriptive data. They need determine whether it is ‘thin descriptive data’ which could be problematic to further interpret due to lack of depth, or ‘rich descriptive data’ which can provide sufficient detail to be further interpreted [ 23 ].
Phase 7: expressing the synthesis
Reviewers should follow the eMERGE reporting guidance when writing up the synthesis [ 22 ] and the PRISMA guidelines may be used alongside this if systematic searches are conducted as many journals may require a PRISMA diagram [ 65 ]. In addition to these standard reporting methods as described by the eMERGE guidance [ 22 ] the final phase can be broken down into the following three stages; (a) summary of findings, (b) strengths, limitations & reflexivity and (c) recommendations and conclusions (refer to [ 22 ] where this phase is described in further detail).
Meta-ethnography is an evolving approach to synthesising qualitative research and is being increasingly used in healthcare research [ 29 ]. A meta-ethnographic approach offers a greater description of methods and higher-order interpretation (an overarching explanation of a phenomenon that goes beyond what the study parts alone imply), compared to a conventional narrative literature review [ 12 ]. The use of this approach can assist in generating evidence for healthcare staff, researchers and policy-makers. Although this approach is being used by numerous reviewers, transparency on how each of the stages should be conducted is still poor and there is a lack of clarity surrounding the exact stages reviewers utilise to reach their final synthesis [ 23 ]. The ultimate aim of qualitative research synthesis in healthcare is to contribute towards improvements in patient care and experience, as well as improving the processes for healthcare professionals involved [ 39 ]. In order for a meta-ethnography syntheses to be considered to be of high quality and useful, the meta-ethnographic approach needs to be rigorous and consistent. Therefore, a clear understanding of the steps included in a meta-ethnography is vital to produce a synthesis which is rigorous and comprehensive. Poorly reported methods of meta-ethnography can also make it challenging, particularly for early career qualitative researchers to conduct this synthesis. Therefore, we have provided a practical step-by-step guide to assist reviewers with conducting a meta-ethnographic synthesis of qualitative research. High quality qualitative research synthesis should not end with the final write up and further research needs to focus on how the impact of qualitative research can be maximised to improve healthcare.
Like any other method, the meta-ethnographic approach is not without its limitations. Within a meta-ethnography, although reviewers provide a synthesis, this is only one interpretation and as qualitative synthesis is subjective, several alternative interpretations are likely to be possible [ 66 ]. The subjective nature of a meta-ethnography may also affect the representativeness of the synthesis findings. To develop this guide, we searched for articles in a number of ways which is described in detail in the methods section. However, as a systematic literature search was not conducted to identify articles for the development of this guide, there is the potential that this may have resulted in the exclusion of some articles. Whilst we have provided guidance on how to conduct a meta-ethnographic synthesis, it is important to note that this is a flexible guide, which researchers can utilise and adapt the stages, according to their own research questions and the phenomenon under study. Some of the steps and challenges described in this guide hold true for systematic reviews in general. However, this guide aimed to offer practical step-by-step guidance on how to conduct meta-ethnography for even those researchers who may not be experienced in conducting systematic reviews as well as being unfamiliar with a meta-ethnographic approach. This guide was developed to assist with conducting a meta-ethnography within healthcare research. Although this guide would be potentially useful beyond healthcare research, there might be additional challenges and considerations in other research fields which may not be fully captured in this guide.
Conclusions
There was previously a lack of step-by-step guide to meta-ethnography conduct. In this paper, we have filled this gap by providing a practical step-by-step guide for conducting meta-ethnography based on the original seven steps as developed by Noblit & Hare [ 10 ]. We have incorporated adaptations and developments by recent publications and we provide detailed annotations, particularly for stages 4–6 which are often described as being the most challenging to conduct, yet the least amount of guidance is provided for conducting these stages. We have described each stage in relation to one of the previous meta-ethnographies we have conducted to aid understanding, and allows the reader to follow on from one step to the next easily.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Barnett-Page E, Thomas J. Methods for the synthesis of qualitative research: a critical review. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2009;9:59.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bearman M, Dawson P. Qualitative synthesis and systematic review in health professions education. Med Educ. 2013;47(3):252–60.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Erwin EJ, Brotherson MJ, Summers JA. Understanding qualitative metasynthesis: issues and opportunities in early childhood intervention research. J Early Interv. 2011;33(3):186–200.
Article Google Scholar
Gough D, Thomas J, Oliver S. Clarifying differences between review designs and methods. Syst Rev. 2012;1:28.
Dixon-Woods M, Booth A, Sutton AJ. Synthesizing qualitative research: a review of published reports. Qual Res. 2007;7:375–422.
Paterson BL. “It looks great but how do I know if it fits?”: an introduction to Meta-synthesis research. Synthesizing Qual Res: Choosing Right Approach. 2011;16:1–20.
Google Scholar
Hannes K, Macaitis K. A move to more systematic and transparent approaches in qualitative evidence synthesis: update on a review of published papers. Qual Res. 2012;12:402–42.
France EF, Wells M, Lang H, Williams B. Why, when and how to update a meta-ethnography qualitative synthesis. Syst Rev. 2016;5:44.
Daker-White G, Hays R, McSharry J, Giles S, Cheraghi-Sohi S, Rhodes P, Sanders C. Blame the patient, blame the doctor or blame the system? A meta-synthesis of qualitative studies of patient safety in primary care. PLoS One. 2015;10:128–329.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Noblit GW, Hare RD. Meta-ethnography: Synthesizing qualitative studies. California: Sage Publications Ltd; 1988.
Book Google Scholar
Malpass A, Shaw A, Sharp D, Walter F, Feder G, Ridd M, Kessler D. “Medication career” or “moral career”? The two sides of managing antidepressants: a meta-ethnography of patients’ experience of antidepressants. Soc Sci Med. 2009;68:154–68.
Atkins S, Lewin S, Smith H, Engel M, Fretheim A, Volmink J. Conducting a meta-ethnography of qualitative literature: lessons learnt. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2008;8:21.
Classen S, Alvarez L. Evidence-informed reviews- moving occupational therapy practice and science forward. OTJR: Occup, ParticipationHealth. 2015;35:199–203.
Soilemezi D, Linceviciute S. Synthesizing qualitative research: reflections and lessons learnt by two new reviewers. Int J Qual Methods. 2018;17(1):1–14.
Scott DA, Grant SM. A meta-ethnography of the facilitators and barriers to successful implementation of patient complaints processes in healthcare settings. Health Expect. 2018;21:508–17.
Elmir R, Schmied V. A meta-ethnographic synthesis of fathers′ experiences of complicated births that are potentially traumatic. Midwifery . 2016;32:66–74.
Cullinan S, O’Mahony D, Fleming A, Byrne S. A meta-synthesis of potentially inappropriate prescribing in older patients. Drugs Aging. 2014;31:631–8.
Purc-Stephenson RJ, Thrasher C. Nurses’ experiences with telephone triage and advice: a meta-ethnography. J Adv Nurs. 2010;66:482–94.
Toye F, Seers K, Barker KL. Meta-ethnography to understand healthcare professionals’ experience of treating adults with chronic non-malignant pain. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e018411.
Rubio-Valera M, Pons-Vigués M, Martínez-Andrés M, Moreno-Peral P, Berenguera A, Fernández A. Barriers and facilitators for the implementation of primary prevention and health promotion activities in primary care: a synthesis through meta-ethnography. PLoS One. 2014;9:e89554.
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Lee RP, Hart RI, Watson RM, Rapley T. Qualitative synthesis in practice: some pragmatics of meta-ethnography. Qual Res. 2015;15:334–50.
France EF, Cunningham M, Ring N, Uny I, Duncan EA, Jepson RG, Maxwell M, Roberts RJ, Turley RL, Booth A, Britten N. Improving reporting of meta-ethnography: the eMERGe reporting guidance. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019;19:25.
France EF, Uny I, Ring N, Turley RL, Maxwell M, Duncan EA, Jepson RG, Roberts RJ, Noyes J. A methodological systematic review of meta-ethnography conduct to articulate the complex analytical phases. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019;19:35.
Booth A, Carroll C, Ilott I, Low LL, Cooper K. Desperately seeking dissonance: identifying the disconfirming case in qualitative evidence synthesis. Qual Health Res. 2013;23:126–41.
Thorne S, Jensen L, Kearney MH, Noblit G, Sandelowski M. Qualitative metasynthesis: reflections on methodological orientation and ideological agenda. Qual Health Res. 2004;13:1342–65.
Britten N, Campbell R, Pope C, Donovan J, Morgan M, Pill R. Using meta ethnography to synthesise qualitative research: a worked example. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2002;7:209–15.
Bondas T, Hall EO. Challenges in approaching metasynthesis research. Qual Health Res. 2007;17:113–21.
Finfgeld-Connett D. Metasynthesis findings: potential versus reality. Qual Health Res. 2014;24:1581–91.
Cahill M, Robinson K, Pettigrew J, Galvin R, Stanley M. Qualitative synthesis: a guide to conducting a meta-ethnography. Br J Occup Ther. 2018;81:129–37.
Toye F, Seers K, Allcock N, Briggs M, Carr E, Andrews J, Barker K. ‘Trying to pin down jelly’-exploring intuitive processes in quality assessment for meta-ethnography. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2013;13:46.
Toye F, Seers K, Allcock N, Briggs M, Carr E, Barker K. Meta-ethnography 25 years on: challenges and insights for synthesising a large number of qualitative studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14:80.
Campbell R, Pound P, Morgan M, Daker-White G, Britten N, Pill R, Yardley L, Pope C, Donovan J. Evaluating meta ethnography: systematic analysis and synthesis of qualitative research. Health Technol Assess. 2011;15:1–164.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Wong SS, Wilczynski NL, Haynes RB. Developing optimal search strategies for detecting clinically relevant qualitative. Medinfo. 2004;107:311.
Wilczynski NL, Marks S, Haynes RB. Search strategies for identifying qualitative studies in CINAHL. Qual Health Res. 2007;17:705–10.
McKibbon KA, Wilczynski NL, Haynes RB. Developing optimal search strategies for retrieving qualitative studies in PsycINFO. Eval Health Prof. 2006;29:440–54.
Noyes J, Popay J, Pearson A, Hannes K. 20 qualitative research and Cochrane reviews. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions, vol. 571; 2008.
Dixon-Woods M, Bonas S, Booth A, Jones DR, Miller T, Sutton AJ, Shaw RL, Smith JA, Young B. How can systematic reviews incorporate qualitative research? A critical perspective. Qual Res. 2006;6:27–44.
Benoot C, Hannes K, Bilsen J. The use of purposeful sampling in a qualitative evidence synthesis: a worked example on sexual adjustment to a cancer trajectory. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2016;16:21.
Atkinson LZ, Cipriani A. How to carry out a literature search for a systematic review: a practical guide. BJPsych Adv. 2018;24:74–82.
Dissemination CR. CRD’s guidance for undertaking reviews in health care. Layerthorpe: University of York, Centre for Reviews and Dissemination; 2009.
Hausner E, Waffenschmidt S, Kaiser T, Simon M. Routine development of objectively derived search strategies. Syst Rev. 2012;1:19.
Flemming K, Graham H, Heirs M, Fox D, Sowden A. Smoking in pregnancy: a systematic review of qualitative research of women who commence pregnancy as smokers. J Adv Nurs. 2013;69:1023–36.
Garside R. A comparison of methods for the systematic review of qualitative research: two examples using meta-ethnography and meta-study; 2008. p. 61.
Nye E, Melendez-Torres GJ, Bonell C. Origins, methods and advances in qualitative meta-synthesis. Rev Educ. 2016;4:57–79.
France EF, Ring N, Thomas R, Noyes J, Maxwell M, Jepson R. A methodological systematic review of what’s wrong with meta-ethnography reporting. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14:119.
Majid U, Vanstone M. Appraising qualitative research for evidence syntheses: a compendium of quality appraisal tools. Qual Health Res. 2018;28:2115–31.
Melia KM. Recognizing quality in qualitative research. California: Sage Publications Ltd; 2010.
Programme Critical Appraisal Skills. Qualitative research checklist. Oxford: Critical Appraisal Skills Programme; 2013. https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/ . Accessed 15 Feb 2019.
Kitto SC, Chesters J, Grbich C. Quality in qualitative research. Med J Aust. 2008;188:243–6.
Kuper A, Lingard L, Levinson W. Critically appraising qualitative research. Bmj. 2008;7:337.
Kuper A, Reeves S, Levinson W. An introduction to reading and appraising qualitative research. Bmj. 2008;337:288.
Mays N, Pope C. Assessing quality in qualitative research. Bmj. 2000;320:50–2.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
The Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Appraisal tools for use in JBI Systematic Reviews. Checklist for qualitative research: The Joanna Briggs Institute; 2017. https://joannabriggs.org/sites/default/files/2019-05/JBI_Critical_Appraisal-Checklist_for_Qualitative_Research2017_0.pdf . Accessed 10 Mar 2019.
Dixon-Woods M, Shaw RL, Agarwal S, Smith JA. The problem of appraising qualitative research. BMJ Qual Saf. 2004;13:223–5.
Lewin S, Booth A, Glenton C, Munthe-Kaas H, Rashidian A, Wainwright M, Bohren MA, Tunçalp Ö, Colvin CJ, Garside R, Carlsen B. Applying GRADE-CERQual to qualitative evidence synthesis findings: introduction to the series. Implementation Sci. 2018;13:2.
Singh J. Critical appraisal skills programme. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2013;4:76.
Feast A, Orrell M, Charlesworth G, Poland F, Featherstone K, Melunsky N, Moniz-Cook E. Using meta-ethnography to synthesize relevant studies: capturing the bigger picture in dementia with challenging behavior within families. London: SAGE Publications Ltd; 2018.
Seale C. Quality in qualitative research. Qual Inq. 1999;5:465–78.
Erasmus E. The use of street-level bureaucracy theory in health policy analysis in low-and middle-income countries: a meta-ethnographic synthesis. Health Policy Plan. 2014;29:iii70–8.
Campbell R, Pound P, Pope C, Britten N, Pill R, Morgan M, Donovan J. Evaluating meta-ethnography: a synthesis of qualitative research on lay experiences of diabetes and diabetes care. Soc Sci Med. 2003;56:671–84.
Coventry PA, Small N, Panagioti M, Adeyemi I, Bee P. Living with complexity; marshalling resources: a systematic review and qualitative meta-synthesis of lived experience of mental and physical multimorbidity. BMC Fam Pract. 2015;16:171.
Doyle LH. Synthesis through meta-ethnography: paradoxes, enhancements, and possibilities. Qual Res. 2003;3:321–44.
Strauss A, Corbin J. Basics of qualitative research: grounded theory procedures and techniques. California: Sage Publications Ltd; 1990.
Sleijpen M, Boeije HR, Kleber RJ, Mooren T. Between power and powerlessness: a meta-ethnography of sources of resilience in young refugees. Ethn Health. 2016;21(2):158–80.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:264–9.
Sandelowski M, Voils CI, Barroso J. Defining and designing mixed research synthesis studies. Res Sch. 2006;13(1):29.
Download references
Acknowledgements
This report is independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research, Yorkshire and Humber Applied Research Collaborations. The views expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the National Institute for Health Research or the Department of Health and Social Care.
This research was funded by NIHR CLAHRC Yorkshire and Humber.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Leeds, Leeds, LS2 9JT, UK
Raabia Sattar, Rebecca Lawton & Judith Johnson
Bradford Institute for Health Research, Bradford, BD9 6RJ, UK
National Institute of Health Research for Primary Care Research, Manchester Academic Health Science Centre, University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 9PL, UK
Maria Panagioti
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
RS, RL and JJ originated the idea for this guide to conducting a meta-ethnography. RS, RL and JJ conducted the original meta-ethnography from which annotations and examples are based on within this manuscript. All authors contributed to the development of the method, and read and approved the final manuscript. RS drafted the first version of this manuscript. RS, RL, JJ and MP made significant contributions to the ideas developed and presented in this manuscript.
Authors’ information
RS 1 is a PhD student (MSc, BSc Honours) based in the School of Psychology at the University of Leeds and Bradford Institute for Health Research. RL 2 (PhD, BA) is a Professor in Psychology of healthcare, based at the University of Leeds and Bradford Institute for Health Research. MP 3 (PhD, MSc, BSc Honours) is a senior research fellow based at the Centre for Primary Care, Manchester. JJ 4 (PhD, BSc Honours) is a clinical psychologist based at the University of Leeds and Bradford Institute for Health Research.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Raabia Sattar .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Sattar, R., Lawton, R., Panagioti, M. et al. Meta-ethnography in healthcare research: a guide to using a meta-ethnographic approach for literature synthesis. BMC Health Serv Res 21 , 50 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-06049-w
Download citation
Received : 10 June 2020
Accepted : 26 December 2020
Published : 08 January 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-06049-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Meta-ethnography
- Research methods
- Qualitative synthesis
- Qualitative health research
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- How it works
Published by Nicolas at January 18th, 2024 , Revised On January 23, 2024

What Is Meta Synthesis In Literature Review
Imagine a regular literature review as a jigsaw puzzle, piecing together individual studies to form a picture. Meta-synthesis is like zooming out, taking those same puzzle pieces and creating a stunning mosaic, uncovering deeper patterns and insights that transcend individual studies.
Table of Contents
This blog will guide you on what is a meta synthesis literature review, its processes and types. Let’s explore deeper.
What Is A Meta Synthesis?
A simple meta-synthesis definition is:
Meta-synthesis represents a sophisticated and systematic approach to distilling knowledge from many primary studies. Unlike traditional literature reviews that summarize individual studies, meta-synthesis involves integrating and synthesizing data from diverse sources. It is a systematic process that goes beyond the surface, extracting meaningful insights by analyzing, comparing, and synthesizing findings from multiple studies.
Importance Of Meta Synthesis Literature Review
The importance of meta synthesis literature review cannot be overstated. As the volume of research papers grows exponentially, the need for methodologies to make sense of this vast sea of information becomes increasingly evident. Meta-synthesis emerges as a beacon in this context, offering a structured and systematic way to navigate the existing literature’s complexities.
- Holistic Perspective: Meta-synthesis enables researchers to move beyond the isolated perspectives of individual studies, fostering a holistic understanding of a particular research question or topic. It provides a panoramic view that transcends the limitations of singular viewpoints.
- Identifying Patterns and Trends: By synthesizing data from multiple studies, meta-synthesis allows for identifying patterns, trends, or recurring themes within the existing literature. This process can unveil hidden insights that may not be apparent when examining studies in isolation.
- Addressing Research Gaps: One of the key contributions of meta-synthesis is its ability to bridge gaps in the existing literature. By systematically integrating findings, researchers can identify areas where knowledge is lacking or conflicting, paving the way for more targeted and informed future research.
- Advancing Knowledge: Through the synthesis of diverse perspectives, meta-synthesis has the potential to generate new knowledge, theories, or conceptual frameworks. It serves as a catalyst for intellectual advancement, pushing the boundaries of understanding within a given field.
Understanding Meta Synthesis Literature Review
Meta-synthesis goes beyond the traditional literature review by employing a systematic and integrative approach to analyze and interpret findings from multiple primary studies. It plays a crucial role in research paper format by offering a more thorough understanding of a specific phenomenon or research question. Meta-synthesis involves synthesizing qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods data to generate new insights, patterns, or theories that may not be apparent when looking at individual studies in isolation.
The primary role of meta synthesis literature review is to bridge gaps between various studies, reconcile conflicting findings, and provide a more holistic perspective on a research topic. It allows researchers to move beyond the surface-level understanding provided by individual studies and identify overarching themes, patterns, or relationships within the existing literature. Meta-synthesis is particularly valuable in fields where research findings are diverse or fragmented, offering a way to distill and integrate knowledge effectively.
Difference Between Traditional Literature Review And Meta Synthesis
The process of meta-synthesis.
The process of meta-synthesis involves a systematic journey through distinct phases, each contributing to the comprehensive understanding and synthesis of existing literature.
Step 1: Identifying Primary Studies
The first step in the meta synthesis literature review process is meticulously identifying relevant primary studies. This involves conducting a comprehensive and systematic literature search, often using databases, academic journals, and other scholarly sources. Researchers employ specific inclusion and exclusion criteria to ensure the selected studies align with the research question or topic of interest.
Key considerations during this phase include the relevance of study designs, publication dates, and the quality of the research. The goal is to cast a wide net, capturing diverse perspectives and insights on the chosen subject.
Step 2: Data Extraction And Synthesis
Once the pool of primary studies is identified, the next phase involves the extraction and synthesis of data. Researchers systematically collect relevant information from each study, including key findings, methodologies, and contextual details. This data extraction process is often guided by a predetermined set of criteria, ensuring consistency and reliability.
The synthesis aspect comes into play as researchers analyze the extracted data, looking for commonalities, differences, and patterns across the studies. This synthesis may involve categorizing information, grouping similar findings, or identifying overarching themes. The goal is to transform individual pieces of data into a cohesive and integrated body of knowledge.
Step 3: Analysis And Interpretation
With the synthesized data in hand, the analysis and interpretation phase begins. Researchers critically examine the collective findings, seeking to understand the literature’s relationships, contradictions, or gaps. This analytical process may involve statistical methods, thematic analysis, or other qualitative and quantitative approaches, depending on the nature of the synthesized data.
Interpretation is a crucial element, requiring researchers to go beyond the surface-level observations and delve into the deeper implications of the synthesized information. This phase aims to draw meaningful conclusions, offer insights into the research question, and contribute to the development of a better understanding of the subject.
Key Components And Steps
- Define Research Question: Clearly articulate the thesis statement or topic that will guide the meta-synthesis process.
- Literature Search: Conduct a systematic and exhaustive search for relevant primary studies using databases, academic journals, and other scholarly sources.
- Screening and Selection: Apply inclusion and exclusion criteria to screen and select studies that align with the research question.
- Data Extraction: Extract pertinent information from selected studies, including key findings, methodologies, and contextual details.
- Data Synthesis: Systematically analyze and synthesize the extracted data, looking for common themes, patterns, or relationships.
- Quality Assessment: Evaluate the quality and rigour of each included study to ensure the validity and reliability of the synthesized findings.
- Analysis and Interpretation: Apply appropriate analytical methods to interpret the synthesized data and draw meaningful conclusions.
- Report Writing: Communicate the results of the meta-synthesis in a clear and organized manner, highlighting key findings and their implications.
The Meta-Analysis we write have:
- Precision and Clarity
- Zero Plagiarism
- High-level Encryption
- Authentic Sources
Types Of Meta-Synthesis
Meta-synthesis is a versatile research methodology that can be tailored to different types of data and research questions. Understanding the various meta synthesis literature review approaches is essential for researchers seeking to employ this method effectively.
Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
Qualitative meta-synthesis focuses on synthesizing findings from qualitative studies. It involves systematically analyzing and integrating data gathered through methods such as interviews, observations, or content analysis. The goal is to uncover common themes, patterns, or conceptual frameworks that emerge across a range of qualitative studies.
The process of qualitative meta synthesis includes:
- Data Extraction: Extracting qualitative data from primary studies.
- Coding and Categorization: Coding and categorizing data to identify recurring themes.
- Synthesis: Integrating and interpreting qualitative findings to derive overarching insights.
- Report Writing: Communicating synthesized qualitative data coherently and comprehensively.
Quantitative Meta-Synthesis
Quantitative meta-synthesis, often called meta-analysis, focuses on synthesizing numerical data from multiple quantitative studies. This approach involves statistical methods to analyze and combine quantitative findings, such as effect sizes or outcome measures. The aim is to provide a quantitative summary that goes beyond the results of individual studies.
The process of quantitative meta synthesis literature review includes:
- Data Extraction: Extracting quantitative data, including statistical results, from primary studies.
- Statistical Analysis: Using statistical methods (e.g., meta-regression, pooling effect sizes) to synthesize numerical data.
- Interpretation: Interpreting the combined quantitative results to draw overarching conclusions.
- Report Writing: Presenting the meta-synthesized quantitative data in a format that facilitates understanding and application.
Mixed-Methods Meta-Synthesis
Mixed-methods meta-synthesis combines qualitative and quantitative approaches to understand a research question comprehensively. This type of meta-synthesis recognizes the value of both types of data and aims to integrate them to offer a more holistic perspective.
Researchers employing mixed-methods meta-synthesis may analyze and synthesize qualitative and quantitative data separately before integrating the findings. Here is the process of mixed-methods meta synthesis.
- Separate Analysis: Independently analyze and synthesize qualitative and quantitative data.
- Integration: Integrating findings from both analyses to derive comprehensive insights.
- Synthesis: Creating a cohesive narrative that captures the synergies between qualitative and quantitative perspectives.
- Report Writing: Presenting integrated findings clearly and coherently, emphasizing the complementary nature of the two types of data.
Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis in meta-synthesis involves systematically comparing and contrasting findings across different studies. This type of meta-synthesis is not restricted to a specific methodological approach but focuses on exploring variations, similarities, or differences in outcomes, methodologies, or contexts across selected studies.
The process of comparative analysis is:
- Identification of Comparisons: Identifying key elements for comparison across primary studies.
- Data Extraction: Extracting relevant data for each identified comparison.
- Analysis: Systematically comparing and contrasting data to identify patterns or trends.
- Synthesis: Synthesizing the comparative findings to draw overarching conclusions.
- Report Writing: Communicating the comparative analysis results in a format that highlights key similarities and differences.
Advantages And Challenges Of Meta-Synthesis
Meta-synthesis, as a powerful research methodology, presents researchers with unique advantages and challenges. A better understanding of both aspects is essential for those considering or conducting meta-synthesis.
Advantages In Research Integration
Comprehensive Insights: Meta-synthesis allows researchers to go beyond the confines of individual studies, providing a comprehensive view of a particular research question or topic. By synthesizing findings from multiple sources like newspapers and journals, it facilitates a more holistic understanding.
- Identification of Patterns: The systematic analysis and integration of data enable the identification of patterns, trends, or recurring themes across various studies. This contributes to the development of overarching concepts or theories that may not be evident when examining studies in isolation.
- Bridging Gaps in Knowledge: Meta-synthesis is effective in addressing gaps in existing literature. By bringing together diverse perspectives, it helps researchers identify areas where knowledge is lacking or where conflicting findings may necessitate further investigation.
- Enhanced Generalizability: The aggregation of findings from different studies can enhance the generalizability of results. This is particularly valuable in fields where individual studies may have limited sample sizes or specific contextual constraints.
- Facilitating Evidence-Based Practice: Meta-synthesis contributes to evidence-based practice by providing a robust foundation for decision-making in various fields, from healthcare to education. Synthesized findings offer a more informed basis for policy development and implementation.
Challenges In Conducting Meta-Synthesis
- Heterogeneity of Studies: One of the primary challenges is dealing with the heterogeneity of studies, including variations in methodologies, participant characteristics, and outcome measures. Integrating diverse data sets requires careful consideration and methodological rigour.
- Quality Assessment: Assessing the quality of primary studies poses a challenge, especially when dealing with diverse research designs. Determining the reliability and validity of studies becomes crucial in ensuring the robustness of the meta-synthesis findings.
- Time-Consuming Process: Conducting meta-synthesis is a time-consuming process, from the exhaustive literature search to the detailed analysis and synthesis of data. Researchers need to allocate sufficient time and resources to execute the methodology effectively.
- Limited Availability of Data: In some cases, data availability may be limited, either due to sparse research on a specific topic or restrictions in accessing certain types of information. This limitation can impact the depth and breadth of the meta-synthesis.
- Potential for Publication Bias: There is a risk of publication bias, where studies with positive or statistically significant results are more likely to be published. This bias can skew the synthesis of findings and affect the overall validity of the meta-synthesis.
Examples Of Meta-Synthesis In Literature Review
Meta-synthesis is a part of a thesis or dissertation that has been widely applied across various disciplines, contributing to a deeper understanding of complex research questions. The following examples highlight how meta-synthesis has been employed successfully in literature reviews.
Mental Health Interventions: Meta-synthesis has been utilized to explore the effectiveness of various mental health interventions. Researchers identified common themes by synthesizing findings from qualitative studies on different interventions, facilitating the development of more holistic and patient-centred mental health approaches.
Educational Practices: In education, meta-synthesis has been employed to analyze and integrate research on diverse teaching practices. This has resulted in identifying effective pedagogical strategies and developing evidence-based recommendations for improving educational outcomes.
Impact On Advancing Knowledge
- Understanding Chronic Diseases: Meta-synthesis has played a pivotal role in advancing knowledge about chronic diseases such as diabetes or cardiovascular conditions. By synthesizing qualitative and quantitative studies, researchers have identified key factors influencing disease progression, treatment effectiveness, and patient outcomes.
- Cross-Cultural Perspectives: In cross-cultural studies, meta-synthesis has been instrumental in integrating research from various cultural contexts. This has led to a more nuanced understanding of how cultural factors impact health behaviours, mental health, and overall well-being.
Practical Applications in Various Fields:
- Evidence-Based Healthcare Practices: Meta-synthesis has been widely applied in healthcare to inform evidence-based practices. By synthesizing data from multiple studies, healthcare professionals can make more informed decisions about treatment strategies, interventions, and patient care.
- Public Policy Development: In public policy, meta-synthesis has been utilized to inform decision-making processes. Policymakers can develop more effective and targeted interventions by synthesizing research on social issues, economic factors, and public health outcomes.
Tips For Conducting Effective Meta-Synthesis
Here are some additional tips and tricks to help you conduct an effective meta synthesis.
- Clearly articulate the criteria for including or excluding studies. This ensures that the selected studies align with the research question and contribute to a meaningful synthesis.
- Conduct a thorough and systematic literature search using multiple databases. This helps identify a broad range of relevant studies for potential inclusion.
- Transparently report the decisions made during the meta-synthesis process. Documenting methodological choices, such as the choice of synthesis method or criteria for study inclusion, enhances the replicability and credibility of the research.
- Adhere to established reporting standards for meta-synthesis. This ensures a standardized and comprehensive presentation of methods and findings, aiding in the clear communication of the research.
- Collaborate with researchers from different disciplines to bring diverse perspectives to the meta-synthesis process. Interdisciplinary collaboration can enhance the depth and breadth of the synthesis.
- Subjecting the meta-synthesis process to peer review provides an external evaluation of the methodology and findings. Peer feedback can help identify potential biases, strengthen the research design, and enhance the overall quality of the meta-synthesis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a meta synthesis.
Meta-synthesis is a research method that systematically analyzes and integrates findings from multiple studies, transcending individual perspectives. It aims to distill common themes, patterns, or insights, providing a comprehensive understanding of a specific research question or topic.
What is a meta synthesis study?
A meta-synthesis study is a research approach that systematically reviews, analyzes, and synthesizes findings from multiple individual studies. It aims to generate new insights, patterns, or theories by integrating diverse perspectives on a specific research topic or question.
What is meta synthesis in research?
Meta-synthesis in research is a systematic process of analyzing and integrating findings from multiple studies on a specific topic. It goes beyond summarization, aiming to uncover common themes, patterns, or relationships, providing a holistic understanding that transcends individual study outcomes.
What is meta synthesis qualitative research?
Meta-synthesis in qualitative research involves systematically analyzing and synthesizing findings from multiple qualitative studies. It seeks to uncover overarching themes, patterns, or concepts, providing a comprehensive and interpretive understanding of the phenomenon under investigation.
Are systematic reviews always meta synthesis?
No, systematic reviews are not always meta-synthesis. While both involve a systematic approach to reviewing literature, systematic reviews may summarize findings without integrating them, while meta-synthesis aims explicitly to analyze and synthesize data from multiple studies to generate new insights.
How develop a strategy for meta-synthesis?
Develop a strategy for meta-synthesis by defining a clear research question, establishing rigorous inclusion criteria, conducting a systematic literature search, extracting relevant data, employing appropriate synthesis methods, addressing biases, and transparently reporting the process and findings.
You May Also Like
Looking for a guide on how to write a thesis statement? 1. Understand the assignment 2. Identify topic 3. Research 4. Revise and 5. Finalize
Check out this comprehensive guide to learn how to write a literature review with the help of multiple good literature review examples.
Looking for interesting and manageable research topics in education? Your search ends right here because this blog post provides 50 […]
Ready to place an order?
USEFUL LINKS
Learning resources, company details.
- How It Works
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance
METHODS article
Metasynthesis: an original method to synthesize qualitative literature in psychiatry.

- 1 AP-HP, Cochin Hospital, Maison de Solenn, Paris, France
- 2 Université Paris Descartes, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Paris, France
- 3 CESP, Faculté de médecine, Université Paris-Sud, Faculté de médecine, Université de Versailles Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines (UVSQ), INSERM, Université Paris-Saclay, Villejuif, France
- 4 Service Universitaire de Psychiatrie de l’Adolescent, Centre Hospitalier Argenteuil, Argenteuil, France
- 5 ECSTRA Team, UMR-1153, INSERM, Paris Diderot University, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Paris, France
- 6 Université Paris-Sud, Paris, France
Background: Metasynthesis—the systematic review and integration of findings from qualitative studies—is an emerging technique in medical research that can use many different methods. Nevertheless, the method must be appropriate to the specific scientific field in which it is used. The objective is to describe the steps of a metasynthesis method adapted from Thematic Synthesis and phenomenology to fit the particularities of psychiatric research.
Method: We detail each step of the method used in a metasynthesis published in 2015 on adolescent and young adults suicidal behaviors. We provide clarifications in several methodological points using the latest literature on metasyntheses. The method is described in six steps: define the research question and the inclusion criteria, select the studies, assess their quality, extract and present the formal data, analyze the data, and express the synthesis.
Conclusion: Metasyntheses offer an appropriate balance between an objective framework, a rigorously scientific approach to data analysis and the necessary contribution of the researcher’s subjectivity in the construction of the final work. They propose a third level of comprehension and interpretation that brings original insights, improve the global understanding in psychiatry, and propose immediate therapeutic implications. They should be included in the psychiatric common research toolkit to become better recognized by clinicians and mental health professionals.
The use of qualitative research is proliferating in medical research ( 1 ). Over the past two decades, numerous studies in the field of psychiatry have used a qualitative protocol ( 2 , 3 ), and it has been recognized as a valuable way to “ obtain knowledge that might not be accessible by other methods and to provide extensive data on how people interpret and act upon their illness symptoms ” ( 4 ). What matters most is the respondent’s perspective and the joint construction by the respondent and the researcher of a context-dependent, multiple, and complex reality ( 5 ). In this respect, the qualitative approach is close to that of the psychiatrist: what is important is what the patient feels and experiences and what emerges during the interaction between the patient and the psychiatrist. Indeed, the subjective coconstruction inherent to most of qualitative methods seems especially close to the psychiatric clinical meeting. Both are useful for building up local theory that helps to increase two important aspects of theory: individually relevant theory for clinical work and field-specific general theory for research ( 6 ). Qualitative research offers a thick description (one that encompass all the complexity of the phenomenon, behavior, or context) of a phenomenon and attempts to document the complexity and multiplicity of its experience ( 6 ). Similarly, in their day-to-day clinical work, psychiatrists attribute great importance to complexity and try to place symptoms within the patient’s history, in all of its intricate context—which again plays a crucial role in therapeutic choices.
Some have expressed concern, however, that because qualitative studies are isolated and rarely used to contribute to practical knowledge, they do not play a significant role in the movement toward evidence-based medicine ( 5 ). To alleviate this concern and enable qualitative work to contribute to this movement, an increasing number of teams have worked to develop and apply synthesis methods to these data. Qualitative syntheses refer to a collection of different methods for systematically reviewing and integrating findings from qualitative studies ( 7 ). The aims of such methods are to capture the increasing volume of qualitative research, to facilitate the transfer of knowledge to improve healthcare, and to bring together a broad range of participants and descriptions ( 8 , 9 ). Qualitative syntheses require not only a systematic approach to collecting, analyzing, and interpreting results across multiple studies, but also to develop overarching interpretation emerging from the joint interpretation of the primary studies included in the synthesis ( 10 , 11 ). Therefore, it involves going beyond the findings of any individual study to make the “whole into something more than the parts alone imply” ( 12 ).
Qualitative syntheses are now recognized as valuable tools for examining participants’ meanings, experiences, and perspectives, both deeply (because of the qualitative approach) and broadly (because of the integration of studies from different healthcare contexts and participants). They have been shown to be particularly useful to identify research gaps, to inform the development of primary studies, and to provide evidence for the development, implementation, and evaluation of health interventions ( 13 ). Because of this growing importance, an important work has been done in the last ten years, in order to ensure the quality of qualitative syntheses, such as: describing the methods to ensure reproducibility, develop tools for assessing the quality of the primary articles, and establish reporting guidelines [see, for example, the ENTREQ statement ( 13 ), the GRADE-Cerqual protocol ( 14 ), and the Cochrane or EVIDENT works ( 15 , 16 )].
However, despite some qualitative syntheses have been successfully conducted in the field of mental health ( 2 , 3 , 17 – 20 ), no study considers the methodological specificities inherent to psychiatric epistemological stance ( 7 ). Filling this gap has been one of the aims of our team since 2011. In this methodological article, we aimed to discuss the challenge of implementing metasynthesis to improve the understanding of youths suicide. In this study, we adapted the Thematic Synthesis developed by Thomas and Harden and incorporate a phenomenological approach in order to deal with new rigor with general as well as psychiatric issues ( 21 ). We will present each step of the method (Figure 1 ) and will propose methodological discussions. The detailed description of the findings can be found elsewhere ( 22 ).
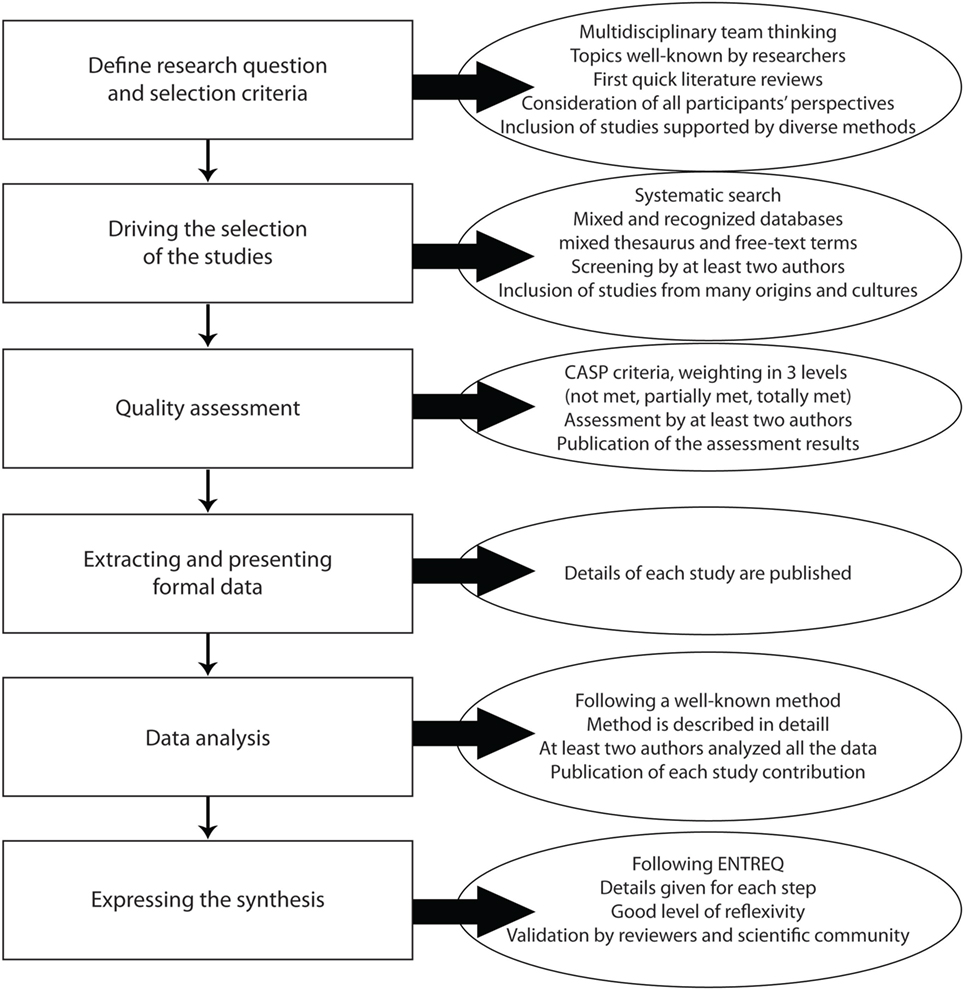
Figure 1 . Distribution in time for articles included in the metasynthesis.
Conducting a Metasynthesis
Before start—constitution of a research group.
The constitution of the research group and the definition of the study method are an important step before engaging in any synthesis work. The researcher must work in collaboration with researchers of diverse backgrounds ( 9 ). A collaborative approach improves quality and rigor and subjects the analytical process to group reflexivity ( 11 ). The research team should include members trained in qualitative synthesis as well as those expert in the topic being studied ( 23 ). As there are many ways to do qualitative syntheses, the research team will have to choose one of them adapted to the research question and to the expertise of the group ( 15 ).
Our team is composed of adolescent and child psychiatrists and psychologists from France and elsewhere (Italy, Chile, and Brazil) and focuses on developing qualitative research ( 24 – 26 ) and metasynthesis in adolescent psychiatry and related fields ( 22 , 27 , 28 ). Our method is adapted from thematic synthesis ( 21 ), which combines and adapts approaches from both metaethnography and grounded theory ( 10 ). Metaethnography, as well as Thematic Synthesis, takes place in six or seven steps from data collection to text coding and finally writing the synthesis. Original authors of metaethnography were trained in grounded theory, a qualitative method developed in the social sciences, laying on conceptual coding combine to construct a new theory. Thematic synthesis allows the researcher to include much more studies in the synthesis and to use tools coming from quantitative reviews, as systematic literature searches. This method perfectly suits to psychiatric research: user-friendliness for both researchers and readers; standardized in its most subjective steps but flexible, to make it adaptable to various patients or situations, such as children, patients with psychological disabilities or psychotic disorders, and to different researchers’ backgrounds (e.g., phenomenology, psychology, or psychoanalysis). We add a phenomenological perspective with a coding close to Smith’s interpretative phenomenological analysis (IPA) ( 29 ). IPA is also a qualitative method of coding a text, laying on phenomenology and hermeneutics. The level of coding is what makes sense to the reader (for example, a letter, a word, a sentence, the absence of a word, or a sentence). Phenomenology allows avoiding never-ending debates about theories of the psyche and focuses on the patient experience which is at the heart of psychiatric care. We understand that published manuscripts provide only thin data sets that are not eligible for a complete phenomenological analysis. Rather we tried to let ourselves guided by the impressions the text generated in us. It was like one article was assimilated as one participant, as it is mainly the voice of the main writer. We applied Smith’s tips on how reading and coding the data.
Define the Research Question and the Selection Criteria
Defining the research question is a crucial substep ( 9 ). This question must be broad enough to be of interest but small enough to be manageable ( 5 , 23 ) and has already been explored by enough studies ( 30 ). Inclusion and exclusion criteria may be fixed on methodological aspects, on participants selected, on thematic focuses or language specificities ( 9 , 31 ).
Youths suicide is a focus that were suitable for qualitative methods. We chose this subject because youth suicide is a major public health issue worldwide as well as a complex disorder that encompasses medical, sociological, anthropological, cultural, psychological, and philosophical issues. It has been widely explored by qualitative research. The lack of effectiveness of current care let us think that new insights could be expected by qualitative exploration. A first selection of articles, as well as an existing literature review on the topic, served to specify some starting information and enable initial decisions, including the definition of the research question, specification of the scope and the inclusion criteria. Then, the questions were constructed through reading and confronting these articles with our first qualitative study in the theme and our clinical knowledge of the theme.
As we wanted to study the therapeutic relationship and barriers to effective care, we decided to include research concerning not only the population being treated (the adolescents and young adults, and their parents), but also the healthcare professionals who care for these patients. A first screening of the literature showed us that optimal scope required a large range of ages, from 15 to 30 years old. The common thread linking all these youths was the importance of their parents in their everyday life. We chose to include only qualitative research, because it remains unclear how to deal with mixed method (combining qualitative and quantitative datasets) ( 23 ). Although databases contain articles in different languages, we chose to include only articles published in English (as most studies are now published in English) and French (as it is our first language) ( 22 , 27 ).
Study Selection
There is a debate on the choice of sampling method, some authors using an exhaustive sampling, some others, an expansive one ( 30 ). We privileged exhaustive systematic searches ( 32 ) since our method allowed large samples and because our target audience was the mental health community, which is accustomed to quantitative systematic reviews ( 9 ). Only journal articles were included, as most scientific data are published in this form ( 33 ). The first selection of articles served to specify the choice of keywords and databases for the electronic search. To ensure both sensitivity and specificity, we decided to use a combined approach of thesaurus terms and free-text terms. This technique maximizes the number of potentially relevant articles retrieved and ensures the highest level of rigor ( 34 ). Keywords were established during research team meetings, and were reported in the article or as supplemental material for more clarity ( 35 ). As each database has its own thesaurus terms, and as keywords encompasses different meanings in each discipline ( 36 ), the keywords were specific for each one.
We used four clusters of keywords: (i) those that concern the topic of interest (such as suicide, obesity, or anorexia nervosa), (ii) those that concern the participants (gender, age, profession, etc.), (iii) those that concern qualitative research (such as qualitative research, interviews, focus groups , or content analysis ), and (iv) those that concern perceptions and understanding, often called “views” ( 33 ) (such as knowledge, perception, self-concept, feeling , or attitude ). The last cluster takes all its importance in the phenomenological perspective of the analysis. An example of the final algorithm used (in the PubMed Web search) is provided in Table 1 .

Table 1 . Algorithm used in the PubMed Web search from Ref. ( 22 ).
Similar work was conducted to select the databases. After consulting reference articles ( 33 , 37 , 38 ), we decided to conduct the search in five electronic databases covering medical, psychological, social, and nursing sciences: MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Social Science Citation Index (SSCI). Not long ago, CINAHL was the most important database for finding qualitative research, but as qualitative research proliferates in medical research, more and more qualitative articles are referenced in MEDLINE ( 33 ) and EMBASE. PsycINFO was a good database for finding qualitative articles with a psychological approach. We decided to add SSCI to broaden and complexity the outlook with a sociological point of view. We followed recommendations published on MEDLINE ( 39 ), CINAHL ( 40 ), EMBASE ( 41 ), and PsycINFO ( 42 ) for choosing search terms. Finally, we decided not to use the methodological databases’ filters for qualitative research, as these have undergone little replication and validation ( 43 ).
We decided to include articles published only in or after 1990. Two points impelled this decision: first, there was very little qualitative research on suicide before the year 2000 and even less before the 1990s (Figure 2 ). Second, we chose to consider as outdated research findings and results published more than 20 years ago were outdated, given the evolution of medical practices ( 44 ). However, this choice must be adapted to the topic of metasynthesis.
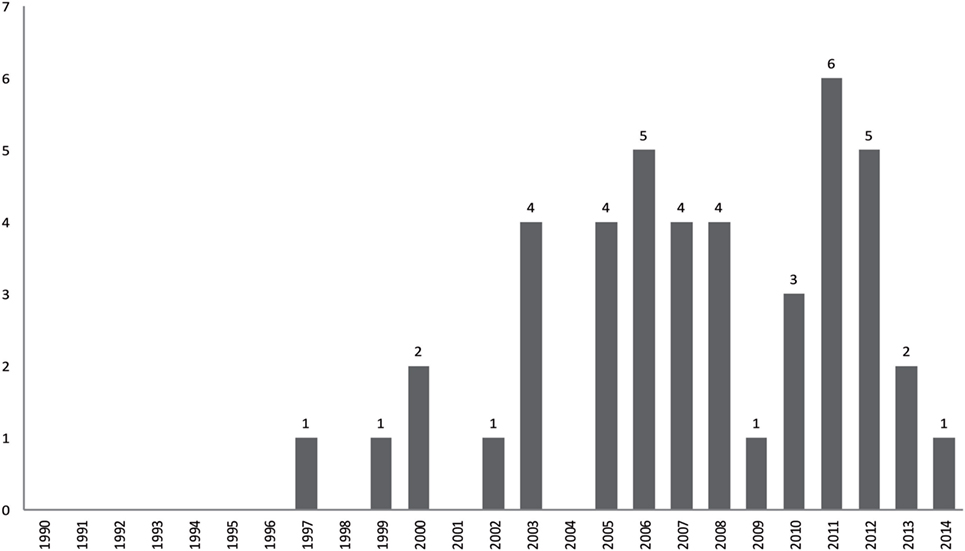
Figure 2 . Flowchart of the metasynthesis steps.
The results of database searches were entered into a bibliographic software program (Zotero©) for automatic removal of duplicates. Then, two authors independently screened all titles and abstracts and selected the studies according to our inclusion criteria (defined earlier). If the abstract was not sufficient, we read the full text. Disagreements were resolved during working group meetings. Full texts of potentially relevant articles were then examined, and a second selection was performed. At this phase, we also checked each article’s reference list looking for new articles we might have overlooked. The final selection represented from 2 to 3% of the total initially obtained. This rate is consistent with the findings of other metasyntheses ( 23 ). For clarity, the selection process was also presented in a flowchart (Figure 3 ). We referred to STARLITE principles to report our literature search ( 45 ) (Table 2 ).
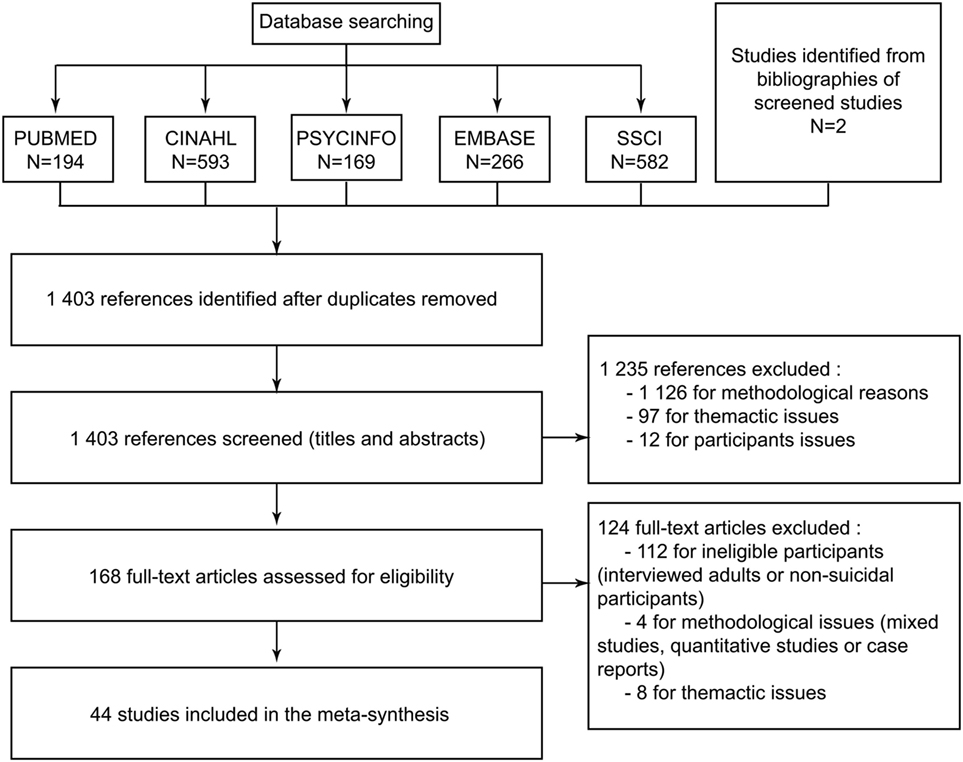
Figure 3 . Flowchart for selecting studies from Ref. ( 22 ).

Table 2 . STARLITE principles applied to the literature search report of Ref. ( 22 ).
Quality Assessment of Included Studies
There is no consensus about whether quality criteria should be applied to qualitative research, or, for those who think they should be, about which criteria to use and how to apply them. Nevertheless a growing number of researchers are choosing to appraise studies for metasyntheses ( 46 ) and some authors state that a good metasynthesis can no longer avoid this methodological step ( 7 ). The reasons and methods for quality assessment fit into three general approaches: assessment of study conduct, appraisal of study reporting, and an implicit judgment of the content and utility of the findings for theory development ( 13 ). There is certainly not one best appraisal tool, but rather a wide choice of good ones ( 8 ).
We chose the Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP) ( 47 ), which is the most frequently used instrument ( 46 ), addresses all the principles and assumptions underpinning qualitative research ( 13 ). It is one of the instruments recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration ( 48 ) and has been used in several important thematic analyses of medical topics. As proposed by Boeije et al., we weighted our assessment by applying a three-point scale to each criterion (0 = criterion not met; 1/P = criterion partially met; 2/T = criterion totally met) ( 49 ) (Table 3 ).

Table 3 . Evaluation of the quality of the studies according to the Critical Appraisal Skill Programme (CASP) from Ref. ( 22 ).
We have not excluded any study on quality criteria. We think that the goal of the quality assessment is not to help selecting the more rigorous article. Either, this step is important to improve the overall rigor of the metasynthesis: by easily evaluating the quality of each article, the readers will have the possibility to make their own evaluation of the quality of the results of the metasynthesis ( 9 ). To enhance the rigor of the synthesis, we published the full results of this assessment ( 50 ).
Extracting and Presenting the Formal Data
To understand the context of each study, readers need the formal data about each study: the number and type of participants in each study, its location, and the method of data collection and of analysis. These data must be extracted and presented in a way that enables readers to form their own opinions about the studies included. We presented these data systematically, in a table with the following headings:
– Identification of the study.
– Summary of the study’s aim.
– Country where the study took place.
– Details about the participants: age, gender, type, and number.
– Method of data collection (e.g., semistructured interviews or focus groups).
– Analysis method (grounded theory, phenomenology, thematic, etc.).
Data Analysis
This step is probably the most subjective: its performance is highly influenced by the authors’ backgrounds ( 13 ). There are many ways to analyze, as many as there are authors. All researchers build on their personal knowledge and background for the analysis, sometimes described as bricolage , following Claude Levi-Strauss: “ the bricoleur combines techniques, methods, and materials to work on any number of projects and creations. Whereas a typical construction process might be limited by the history or original use of individual pieces, the bricoleur works outside of such limitations, reorganizing pieces to construct new meaning. In other words, unlike linear, step-by-step processes, the bricoleur steps back and works without exhaustive preliminary specifications ” ( 51 , 52 ). The synthesis will inevitably be only one possible interpretation of the data ( 9 ), as it depends on the authors’ judgment and insights ( 21 ). The qualitative synthesis does not result simply from a coding process, but rather from the researchers’ configuration of segments of coded data “ assembled into a novel whole ” ( 53 ).
In this process, the multidisciplinary team is essential to assess rigor and develop richer and more complex understandings. Triangulation of the analyses is enhanced when researchers with diverse background consider the same data set ( 11 ). “ Collaborative working not only improve quality and rigour, but subjects the analytical process to group reflexivity ” ( 54 ).
The first step of this process involved carefully reading and rereading each study ( 21 ). It is an active reading, with the intention of appraising, familiarizing, identifying, extracting, recording, organizing, comparing, relating, mapping, stimulating and verifying. In other words, it is reading with “ the intention of collating a synthesizable set of accounts ” ( 11 ).
The second step was coding: at least two different researchers coded each part of the data (whole manuscripts), performing a line-by-line coding, close to the phenomenological analysis described by Smith et al. ( 29 ).
In the third step, the codes were grouped and categorized into a hierarchical tree structure. This step is very close to the translation work described by Noblit and Hare ( 12 ). It involves comparing themes across articles to match themes from one article with those from another while ensuring that each key theme captured similar themes from different articles. We obtained a list of descriptive themes very close to the data.
In our example, we highlighted the sentence “You’re going to school, you’re getting an education, but you’re depressed” and coded it depressed . The code is then combined with others in a theme named “The experience of distress.”
Finally, in the last and most subjective step of the analysis, we generated analytical themes, which depended largely on the “judgment and insights of the reviewers” ( 21 ). This step is very similar the development of third-order interpretations—“ the synthesis of both first and second order constructs into a new model or theory about a phenomenon ” ( 23 )—and requires going beyond the content of original studies to achieve a higher level of interpretation and going beyond the descriptive synthesis to propose a more conceptual line-of-argument ( 21 , 23 ). This work has two types of underlying aims. The first type may be theoretical, by enabling a higher level of comprehension of a phenomenon; in medical science, this may be to better describe and understand a pathology. The second type may be to answer clinical questions about pathology and care directly.
In our example, we clearly fulfilled the second aim. The results leaded us to discuss new insights about suicidal youths’ care. The experience of incomprehension shared by all the protagonists of the care interferes with the capacity for empathy of both family members and professionals. We could use the concepts of intersubjectivity to witness the violence driven by the suicidal act.
Writing the Synthesis
Throughout the analysis process, the authors build themes that take place in the story they are telling about the participant’s experience ( 21 ). Then, the expression of the synthesis is our story of the studied phenomenon.
The results of the metasynthesis consist of the themes that we developed in the analysis. They are built by first and second order constructs. We did not define actual third-order themes; rather, third-order constructs helped us to build the synthesis into a story. We organized the themes into superordinate themes, which are interpretations of the themes and can be considered third-order interpretations.
For example, in one of the developed theme called the experience of distress we described that the young people experienced depressive symptoms. The participants described feelings of sadness, sorrow, mental pain, despair, detachment, anger, and irritability . The authors interpreted that as despair . We organized all these closed related feeling into the individual experience of distress . We decide not to speak about depression , first because some healthcare professionals repeated that they may diagnose depression “ but certainly not on a routine basis ” ( 22 ), then because we adopted a phenomenological approach and we felt that distress encompasses a broader and more complex experience.
Metasynthesis results prepare the framework for the discussion, the most interpretative part of the review, where hypothesis and proposals are presented. We offer our understanding of the participants’ experience. Both our presentation and our discourse are influenced by our aim: to answer clinical questions by suggesting specific actions or considerations for care; the discussion and the answers are intended to be useful for the readers of our article, as well as for us ( 23 ).
Our conclusion is that “ the violence of the message of a suicidal act and the fears associated with death lead to incomprehension and interfere with the capacity for empathy of both family members and professionals. The issue in treatment is to be able to witness this violence so that the patient feels understood and heard, and thus to limit recurrences ” ( 22 ). This issue is clear and simple and it leads to an immediate application to clinical practice which is described in the implication for practice chapter.
Finally, we discuss the limitation of the findings. The principal limitations were methodological (with our method, the access to participants’ data is partial), and in the sampling (we didn’t take in consideration the influence of gender on the experience of suicidal behavior). That exercise enhances the credibility of the publication, enabling readers to measure the importance and generalizability of the findings.
The written synthesis has to fulfill the standard for reporting synthesis of qualitative research. We chose to refer to Tong and al. ENTREQ statement ( 13 ) attached to the publication.
Our method is based on Thomas and Harden Thematic Synthesis ( 21 ). After a broad-scale review of literature on the topic of metasynthesis, we have decided to clarify the definition of some aspects of the method and modify or expand others, because we wanted both a medical and a psychological approach. For example, we opted to use a systematic search method and a weighted version of the CASP to assess quality.
Most metasynthesis authors argue that these reviews achieve a third-order level of interpretation, that is, that they are more than the sum of their results. If, as we think, qualitative research can achieve a moderate level of generalization with clinical implications, metasyntheses may transform these findings into more highly abstracted and generalizable theoretical frameworks. We “ push their findings toward the nomothetic end of the idiographic-nomothetic continuum ” ( 44 ). Qualitative specialists certainly do not shy away from stressing the importance of context in their studies, or from arguing that the context of one study may not be applicable to others. It is true that, in a way, metasyntheses decontextualize concepts to attain greater generalizability ( 44 ). But we can relate this act to the response of clinicians reading a qualitative article: they will try to apply the concepts to their own situations ( 21 ). Authors of metasyntheses are proposing their own interpretation of the concept and its generalizability. The scientific value of metasynthesis lies in its role as a summary of several studies and as the interpretation of varying context, as well as in its ability to weight each result and to propose greater generalizability.
Qualitative research is an invaluable method for gaining new insights into mental disorders ( 6 ). Its development in recent years requires that we improve methods for synthesizing their results. We think this way of doing metasynthesis is appropriate to psychiatric research in its intermediate position that stresses both progress in the general comprehension of disorders and direct clinical implications. It offers an appropriate balance between three components: an objective framework, which includes the selection, inclusion, and appraisal of studies; a rigorously scientific approach to data analysis; and the necessary contribution of the researcher’s subjectivity in the construction of the final work. The balance for a qualitative metasynthesis is, we think, very similar to the clinical approach to each patient. It necessitates a robust scientific background, a rigorous step-by-step—symptom by symptom—progression, and finally a part of art that depends on each clinician: the subjective part of therapy.
Finally, we think that metasyntheses enable insights that no other method can provide. Qualitative research sheds new light on scientific questions by emphasizing the participants’ subjective understanding and experience ( 6 ). Metasynthesis proposes a third level of comprehension and interpretation that brings original insights. In our study ( 22 ), we emphasized an original point in the relationship that was no found in any result from each primary study: the difficulty of professionals and parents to understand and cope with suicide as an obstacle to the care of the suicidal adolescent. Therefore, our study’s analysis went deeper and proposed original results.
Author Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments and final approval: JL, AR-L, MO, and MM. Conducted the literature review: JL and MO. Performed the experiments: JL, MO, and AR-L. Wrote the article: JL (all the article), AR-L (analysis), MO (introduction and analysis), and MM (discussion).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Jo Ann Cahn for revising our English.
1. Shuval K, Harker K, Roudsari B, Groce NE, Mills B, Siddiqi Z, et al. Is qualitative research second class science? A quantitative longitudinal examination of qualitative research in medical journals. PLoS One (2011) 6:e16937. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016937
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
2. Malpass A, Shaw A, Sharp D, Walter F, Feder G, Ridd M, et al. “Medication career” or “Moral career”? The two sides of managing antidepressants: a meta-ethnography of patients’ experience of antidepressants. Soc Sci Med (2009) 68:154–68. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2008.09.068
3. Cairns VA, Reid GS, Murray C. Family members’ experience of seeking help for first-episode psychosis on behalf of a loved one: a meta-synthesis of qualitative research. Early Interv Psychiatry (2015) 9(3):185–99. doi:10.1111/eip.12157
4. Espíndola CR, Blay SL. Anorexia nervosa’s meaning to patients: a qualitative synthesis. Psychopathology (2009) 42:69–80. doi:10.1159/000203339
5. Evans D, Pearson A. Systematic reviews of qualitative research. Clin Eff Nurs (2001) 5:111–9. doi:10.1054/cein.2001.0219
6. Whitley R, Crawford MJ. Qualitative research in psychiatry. Can J Psychiatry Rev Can Psychiatr (2005) 50:108–14. doi:10.1177/070674370505000206
7. Ring N. A Guide to Synthesising Qualitative Research for Researchers Undertaking Health Technology Assessments and Systematic Reviews . Edinburgh: NHS Quality Improvement Scotland (2011).
Google Scholar
8. Hannes K, Booth A, Harris J, Noyes J. Celebrating methodological challenges and changes: reflecting on the emergence and importance of the role of qualitative evidence in Cochrane reviews. Syst Rev (2013) 2:84. doi:10.1186/2046-4053-2-84
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
9. Toye F, Seers K, Allcock N, Briggs M, Carr E, Barker K. Meta-ethnography 25 years on: challenges and insights for synthesising a large number of qualitative studies. BMC Med Res Methodol (2014) 14:80. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-14-80
10. Barnett-Page E, Thomas J. Methods for the synthesis of qualitative research: a critical review. BMC Med Res Methodol (2009) 9:59. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-9-59
11. Lee RP, Hart RI, Watson RM, Rapley T. Qualitative synthesis in practice: some pragmatics of meta-ethnography. Qual Res (2014) 15:334–50. doi:10.1177/1468794114524221
12. Noblit GW, Hare RD. Meta-Ethnography: Synthesizing Qualitative Studies . Newbury Park: SAGE (1988).
13. Tong A, Flemming K, McInnes E, Oliver S, Craig J. Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research: ENTREQ. BMC Med Res Methodol (2012) 12:181. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-12-181
14. Lewin S, Glenton C, Munthe-Kaas H, Carlsen B, Colvin CJ, Gülmezoglu M, et al. Using qualitative evidence in decision making for health and social interventions: an approach to assess confidence in findings from qualitative evidence syntheses (GRADE-CERQual). PLoS Med (2015) 12:e1001895. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001895
15. Noyes J, Booth A, Hannes K, Harden A, Harris J, Lewin S, et al. Supplemental Guidance for Inclusion of Qualitative Research in Cochrane Systematic Reviews of Interventions (2016). Available from: http://methods.cochrane.org/qi/supplemental-handbook-guidance
16. Booth A. EVIDENT Guidance for Reviewing the Evidence: A Compendium of Methodological Literature and Websites (2016). Available from: https://www.academia.edu/21598179/EVIDENT_Guidance_for_Reviewing_the_Evidence_a_compendium_of_methodological_literature_and_websites
17. Khan N, Bower P, Rogers A. Guided self-help in primary care mental health: meta-synthesis of qualitative studies of patient experience. Br J Psychiatry (2007) 191:206–11. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.106.032011
18. Knowles SE, Toms G, Sanders C, Bee P, Lovell K, Rennick-Egglestone S, et al. Qualitative meta-synthesis of user experience of computerised therapy for depression and anxiety. PLoS One (2014) 9:e84323. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0084323
19. Daker-White G, Rogers A. What is the potential for social networks and support to enhance future telehealth interventions for people with a diagnosis of schizophrenia: a critical interpretive synthesis. BMC Psychiatry (2013) 13:279. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-13-279
20. Price O, Baker J, Bee P, Lovell K. Learning and performance outcomes of mental health staff training in de-escalation techniques for the management of violence and aggression. Br J Psychiatry (2015) 206:447–55. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.114.144576
21. Thomas J, Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol (2008) 8:45. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-8-45
22. Lachal J, Orri M, Sibeoni J, Moro MR, Revah-Levy A. Metasynthesis of youth suicidal behaviours: perspectives of youth, parents, and health care professionals. PLoS One (2015) 10:e0127359. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0127359
23. Atkins S, Lewin S, Smith H, Engel M, Fretheim A, Volmink J. Conducting a meta-ethnography of qualitative literature: lessons learnt. BMC Med Res Methodol (2008) 8:21. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-8-21
24. Lachal J, Speranza M, Schmitt A, Spodenkiewicz M, Falissard B, Moro MR, et al. Depression in adolescence: from qualitative research to measurement. Adolesc Psychiatry (2012) 2:296–308. doi:10.2174/2210676611202040296
25. Lachal J, Speranza M, Taïeb O, Falissard B, Lefèvre H, Moro MR, et al. Qualitative research using photo-elicitation to explore the role of food in family relationships among obese adolescents. Appetite (2012) 58:1099–105. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2012.02.045
26. Orri M, Paduanello M, Lachal J, Falissard B, Sibeoni J, Revah-Levy A. Qualitative approach to attempted suicide by adolescents and young adults: the (neglected) role of revenge. PLoS One (2014) 9:e96716. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0096716
27. Lachal J, Orri M, Speranza M, Falissard B, Lefevre H, Moro M-R, et al. Qualitative studies among obese children and adolescents: a systematic review of the literature. Obes Rev (2013) 14:351–68. doi:10.1111/obr.12010
28. Orri M, Farges O, Clavien P-A, Barkun J, Revah-Lévy A. Being a surgeon – the myth and the reality: a meta-synthesis of surgeons' perspectives about factors affecting their practice and well-being. Ann Surg (2014) 260:721–9. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000000962
29. Smith JA. Interpretative phenomenological analysis. Qualitative Psychology: A Practical Guide to Research Methods . Trowbridge: SAGE (2008).
30. Finfgeld-Connett D, Johnson ED. Literature search strategies for conducting knowledge-building and theory-generating qualitative systematic reviews. J Adv Nurs (2013) 69:194–204. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2012.06037.x
31. Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions . Cochrane: John Wiley & Sons (2011).
32. France EF, Ring N, Thomas R, Noyes J, Maxwell M, Jepson R. A methodological systematic review of what’s wrong with meta-ethnography reporting. BMC Med Res Methodol (2014) 14:119. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-14-119
33. Stansfield C, Brunton G, Rees R. Search wide, dig deep: literature searching for qualitative research. An analysis of the publication formats and information sources used for four systematic reviews in public health. Res Synth Methods (2014) 5(2):142–51. doi:10.1002/jrsm.1100
34. Shaw RL, Booth A, Sutton AJ, Miller T, Smith JA, Young B, et al. Finding qualitative research: an evaluation of search strategies. BMC Med Res Methodol (2004) 4:5. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-4-5
35. Dixon-Woods M, Booth A, Sutton AJ. Synthesizing qualitative research: a review of published reports. Qual Res (2007) 7:375–422. doi:10.1177/1468794107078517
36. Bassett R, McGibbon E. A critical participatory and collaborative method for scoping the literature. Qual Quant (2013) 47:3249–59. doi:10.1007/s11135-012-9715-2
37. Booth A. Chapter 3: searching for studies. In: Noyes J, Booth A, Hannes K, Harden A, Harris J, Lewin S, Lockwood C, editors. Supplementary Guidance for Inclusion of Qualitative Research in Cochrane Systematic Reviews of Interventions . Cochrane Collaboration Qualitative Methods Group (2011). Available from: http://cqrmg.cochrane.org/supplemental-handbook-guidance
38. Tong A, Palmer S, Craig JC, Strippoli GFM. A guide to reading and using systematic reviews of qualitative research. Nephrol Dial Transplant (2016) 31(6):897–903. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfu354
39. Wong SS-L, Wilczynski NL, Haynes RB; Hedges Team. Developing optimal search strategies for detecting clinically relevant qualitative studies in MEDLINE. Stud Health Technol Inform (2004) 107:311–6. doi:10.3233/978-1-60750-949-3-311
40. Wilczynski NL, Marks S, Haynes RB. Search strategies for identifying qualitative studies in CINAHL. Qual Health Res (2007) 17:705–10. doi:10.1177/1049732306294515
41. Walters LA, Wilczynski NL, Haynes RB; Hedges Team. Developing optimal search strategies for retrieving clinically relevant qualitative studies in EMBASE. Qual Health Res (2006) 16:162–8. doi:10.1177/1049732305284027
42. McKibbon KA, Wilczynski NL, Haynes RB. Developing optimal search strategies for retrieving qualitative studies in PsycINFO. Eval Health Prof (2006) 29:440–54. doi:10.1177/0163278706293400
43. Flemming K, Briggs M. Electronic searching to locate qualitative research: evaluation of three strategies. J Adv Nurs (2007) 57:95–100. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2006.04083.x
44. Finfgeld-Connett D. Generalizability and transferability of meta-synthesis research findings. J Adv Nurs (2010) 66:246–54. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2009.05250.x
45. Booth A. “Brimful of STARLITE”: toward standards for reporting literature searches. J Med Libr Assoc (2006) 94:421–e205.
46. Hannes K, Macaitis K. A move to more systematic and transparent approaches in qualitative evidence synthesis: update on a review of published papers. Qual Res (2012) 12:402–42. doi:10.1177/1468794111432992
47. CASP. Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) Qualitative Research Checklist (2013). Available from: http://docs.wixstatic.com/ugd/dded87_25658615020e427da194a325e7773d42.pdf
48. Noyes J, Popay J, Pearson A, Hannes K, Booth A. Chapter 20: qualitative research and Cochrane reviews. In: Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions . Cochrane: John Wiley & Sons (2015), 571–592.
49. Boeije HR, van Wesel F, Alisic E. Making a difference: towards a method for weighing the evidence in a qualitative synthesis: weighing evidence in qualitative synthesis. J Eval Clin Pract (2011) 17:657–63. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2753.2011.01674.x
50. Walsh D, Downe S. Meta-synthesis method for qualitative research: a literature review. J Adv Nurs (2005) 50:204–11. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2005.03380.x
51. Kinn LG, Holgersen H, Ekeland T-J, Davidson L. Metasynthesis and bricolage: an artistic exercise of creating a collage of meaning. Qual Health Res (2013) 23:1285–92. doi:10.1177/1049732313502127
52. Lévi-Strauss C. The Savage Mind . Chicago: University of Chicago Press (1966).
53. Sandelowski M, Leeman J. Writing usable qualitative health research findings. Qual Health Res (2012) 22:1404–13. doi:10.1177/1049732312450368
54. Barry CA, Britten N, Barber N, Bradley C, Stevenson F. Using reflexivity to optimize teamwork in qualitative research. Qual Health Res (1999) 9:26–44. doi:10.1177/104973299129121677
Keywords: qualitative research, metasynthesis, metaethnography, qualitative evidence synthesis, psychiatry, suicide
Citation: Lachal J, Revah-Levy A, Orri M and Moro MR (2017) Metasynthesis: An Original Method to Synthesize Qualitative Literature in Psychiatry. Front. Psychiatry 8:269. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00269
Received: 05 September 2017; Accepted: 17 November 2017; Published: 01 December 2017
Reviewed by:
Copyright: © 2017 Lachal, Revah-Levy, Orri and Moro. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jonathan Lachal, jonathan.lachal@gmail.com
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.

Which review is that? A guide to review types.
- Which review is that?
- Review Comparison Chart
- Decision Tool
- Critical Review
- Integrative Review
- Narrative Review
- State of the Art Review
- Narrative Summary
- Systematic Review
- Meta-analysis
- Comparative Effectiveness Review
- Diagnostic Systematic Review
- Network Meta-analysis
- Prognostic Review
- Psychometric Review
- Review of Economic Evaluations
- Systematic Review of Epidemiology Studies
- Living Systematic Reviews
- Umbrella Review
- Review of Reviews
- Rapid Review
- Rapid Evidence Assessment
- Rapid Realist Review
- Qualitative Evidence Synthesis
- Qualitative Interpretive Meta-synthesis
Qualitative Meta-synthesis
- Qualitative Research Synthesis
- Framework Synthesis - Best-fit Framework Synthesis
- Meta-aggregation
- Meta-ethnography
- Meta-interpretation
- Meta-narrative Review
- Meta-summary
- Thematic Synthesis
- Mixed Methods Synthesis
- Narrative Synthesis
- Bayesian Meta-analysis
- EPPI-Centre Review
- Critical Interpretive Synthesis
- Realist Synthesis - Realist Review
- Scoping Review
- Mapping Review
- Systematised Review
- Concept Synthesis
- Expert Opinion - Policy Review
- Technology Assessment Review
- Methodological Review
- Systematic Search and Review
" Qualitative meta-synthesis is an intentional and coherent approach to analyzing data across qualitative studies. It is a process that enables researchers to identify a specific research question and then search for, select, appraise, summarize, and combine qualitative evidence to address the research question" (Erwin et al, 2011).
Further Reading/Resources
Erwin, E. J., Brotherson, M. J., & Summers, J. A. (2011). Understanding qualitative metasynthesis: Issues and opportunities in early childhood intervention research. Journal of Early Intervention , 33 (3), 186-200 . Full Text Finlayson, K. W., & Dixon, A. (2008). Qualitative meta-synthesis: a guide for the novice. Nurse researcher , 15 (2). Full Text Finfgeld-Connett, D. (2018). A guide to qualitative meta-synthesis . New York, NY, USA:: Routledge. Catalogue Link
Douglas, S. N., Jensen, E. J., & West, P. (2022). Barriers and Benefits Experienced by Caregivers Seeking Medical Care for Their Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: a Qualitative Meta-synthesis. Review Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders , 1-13. Full Text
References Erwin, E. J., Brotherson, M. J., & Summers, J. A. (2011). Understanding qualitative metasynthesis: Issues and opportunities in early childhood intervention research. Journal of Early Intervention , 33 (3), 186-200 . Full Text
- << Previous: Qualitative Interpretive Meta-synthesis
- Next: Qualitative Research Synthesis >>
- Last Updated: Apr 30, 2024 9:02 AM
- URL: https://unimelb.libguides.com/whichreview

Systematic Reviews & Other Review Types
- What is a Systematic Review?
- What is a Scoping Review?
- What is a literature review?
- What is a Rapid Review?
- What is a Mixed Methods Review?
- What is a Network Meta-Analysis?
- What is an Overview of Reviews?
What is a Meta-Syntheses?
- What is an Integrative Review?
- What is a Diagnostic Test Accuracy Review?
- What is a Living Systematic Review?
A meta-synthesis brings together qualitative data to form a new interpretation of the research field. It helps to generate new theories or an explanatory theory of why the intervention works or not. It creates a hypothesis for future testing or comparison with trial outcomes.
Meta-syntheses are best designed t o re-interpret meaning across many qualitative studies.
(S. Atkins et al (2008)
Meta-Syntheses Resources:
- What makes a good systematic review and metaanalysis?
- Protocol-developing meta-ethnography reporting guidelines (eMERGe)
- Conducting a meta-ethnography
- Cochrane Qualitative & Implementation Methods Group
- Emerge Project
How a Meta-Syntheses differs from a Systematic Review
Timeframe: 12 months or less.
Question: " A clearly formulated question helps to set boundaries for the scope and depth of a meta-ethnography" (Atkins S.)
Sources and searches: Not as exhaustive as a systematic review, unless the question requires exhaustive searching. Can search within a particular setting. Search specifically for qualitative studies if possible (be careful with search filters). Search may rely more heavily on inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Selection: Different screening process--includes repeated reading of articles to connect and record concepts or themes.
Appraisal: Focus is on the translation of studies and then systematically compared or 'translated' within and across studies while retaining the structure of the relationships between central concepts/themes and includes a 'thematic analysis'.
Synthesis: Qualitative Differs from a Meta-Analysis (Quantitative) "The goal is not aggregative in the sense of 'adding studies together' as with a meta-analysis. On the contrary, it is interpretative in broadening understanding of a particular phenomenon." (Source: Grant et al (2009))
There are 3 types of synthesis that may be used. A second level of synthesis is possible.
- Reciprocal Translation: Concepts in one study can incorporate those of another.
- Refutational Translation: Concepts in different studies contradict one another.
- Line of Argument Synthesis: Studies identify different aspects of the topic that can be drawn together in a new interpretation.
(France EF, Ring N et al 1988)
Limitations of a Meta-Syntheses
- Only appropriate for high-quality qualitative studies
- Can only accommodate a limited number of primary studies
- Choice of a meta-ethnography may not be confirmed until pool of evidence known
- Requires significant methodological skill and experience with qualitative methods
- May take time to engage with the evidence and develop theory
- Requires further interpretation by policy makers and practitioners
Source: M. Petticrew et al (2013) and Li T. et al (2001)
Other names for a Meta-Syntheses
Meta-synthesis, Meta-ethnography, Qualitative Evidence Synthesis, Qualitative Meta-Synthesis, Meta narrative review (related)
Temple Attribution
Adapted with permission from Temple University Libraries. https://guides.temple.edu/systematicreviews
- Last Updated: Mar 13, 2024 4:27 PM
- URL: https://touromed.libguides.com/review_types

Evidence Synthesis and Systematic Reviews
- Common Review Types
Diagnostic Test Accuracy Review
Integrative reviews, living systematic reviews, mapping reviews.
Meta-ethnography (also known as meta-synthesis)
- Mixed Methods Reviews
Network Meta Analysis
Overview of reviews (umbrella review), review of complex interventions.
- Resources for Reviews by Discipline and Type
- Tools for Evidence Synthesis
- Grey Literature
Definition : "Systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy provide a summary of test performance based on all available evidence, evaluate the quality of published studies, and account for variation in findings between studies." JBI Reviewers Handbook
When to use : When assessing the evidence from diagnostic test accuracy studies
Limitations : The unfamiliarity of methods and accuracy metrics makes it difficult to convey results to a wide audience. Results can be misinterpreted.
Resources :
- Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy
- Diagnostic test accuracy systematic reviews
Definition : "A review method that summarizes past empirical or theoretical literature to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular phenomenon or healthcare problem (Broome 1993). Integrative reviews, thus, have the potential to build nursing science, informing research, practice, and policy initiatives. Well-done integrative reviews present the state of the science, contribute to theory development, and have direct applicability to practice and policy."
When to use : To review experimental and non-experimental research simultaneously, to define concepts, to review theories, to review evidence/point out gaps in the literature, to analyze methodological issues. Good for nursing issues.
Limitations : The combination and complexity of incorporating diverse methodologies can contribute to lack of rigor, inaccuracy, and bias, methods of analysis, synthesis, and conclusion-drawing remain poorly formulated, issues related to combining empirical and theoretical reports.
Resources :
- Conducting integrative reviews: a guide for novice nursing researchers.
- Strategies for completing a successful integrative review
Definition : A systematic review which is continually updated, incorporating relevant new evidence as it becomes available by continual, active monitoring of the evidence. They immediately include any new important evidence identified and are supported by up-to-date communication about the status of the review.
When to use : When there is a high priority (or emerging) question for policy and practice, important uncertainty in the existing evidence, emerging evidence that is likely to impact on what is currently known.
Limitations : Time consuming with continuous work flows, frequent searching and screening, team members must have a long term commitment to the project, frequent statistical analysis-can lead to inflated false-positive rate, may require technological tools to support screening, data extraction and critical analysis or risk of bias assessment, no clear agreement on methods to manage data synthesis
- Guidance for the production and publication of Cochrane living systematic reviews: Cochrane Reviews in living mode
- Living Systematic Reviews: An Emerging Opportunity to Narrow the Evidence-Practice Gap
Definition : Mapping reviews are focused on a visual synthesis of the data and are question based rather than topic based like the scoping review.
When to use : When there is an abundance and a diversity of research, as a first step to a systematic review, or to identify gaps in a topic area.
Limitations : The broad nature and rapid search may mean that some articles will be missed. They may require additional expertise or training for creating the visual output. "Foundational work is needed to better standardize the methods and products of an evidence map..." (Miake et. al. 2016)
- Systematic Mapping Studies in Software Engineering
- What is an evidence map? A systematic review of published evidence maps and their definitions, methods, and products.
Definition : A meta-ethnography brings together qualitative data to form a new interpretation of the research field. It helps to build new theories and is not to be confused with a meta-analysis which tests a hypothesis using quantitative data. It primarily generates theory such as program theory, implementation theory, or an explanatory theory of why the intervention works or not; hypothesis for future testing or comparison with trial outcomes.
When to use : Meta-ethnography are best designed to re-interpret meaning across many qualitative studies which could be across subject areas.
Limitations : Only appropriate for high-quality qualitative studies, can only accommodate a limited number of primary studies, choice of a meta-ethnography may not be confirmed until pool of evidence known, requires significant methodological skill and experience with qualitative methods, may take time to engage with the evidence and develop theory.
- Conducting a meta-ethnography of qualitative literature: lessons learnt.
- Meta-ethnography in healthcare research: a guide to using a meta-ethnographic approach for literature synthesis
Definition : Synthesizes qualitative and quantitative evidence to provide a more inclusive answer to informs clinical policy or organizational decisions.
When to use : For multidisciplinary topics or topics with a body of literature that includes quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods studies, to determine not only the effects of interventions but also their appropriateness, to identify research gaps, to provide an explanation for possible heterogeneity between trials, to answer multiple questions in one systematic review.
Limitations : They require significant methodological skill, they are resource intensive because they may take time to engage with the evidence and develop theory. They are not inherently reproducible or transparent because of the highly iterative nature of the interpretative process
- Toolkit for mixed studies reviews
- Five common pitfalls in mixed methods systematic reviews: lessons learned
Definition : "Network meta-analysis compares multiple interventions simultaneously by analyzing studies making different comparisons in the same analysis." Source: M. Petticrew et al. (2013)
When to use : For conditions with multiple interventions, where there are many combinations of direct or indirect interactions, to make treatment estimates for an entire treatment network instead of scanning each individual pair-wise comparison, to give the "full picture" to clinicians, potential to more explicitly "rank" treatments using summary outputs
Limitations : Requires specialist statistical expertise and software, assumes that all interventions included in the "network" are equally applicable to all populations and contexts of the studies included.
- How to Conduct a Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
- Undertaking network meta-analyses
- Synthesizing evidence on complex interventions: how meta-analytical, qualitative, and mixed-method approaches can contribute.
Definition : A systematic review of systematic reviews. Examines two or more systematic reviews or evidence syntheses. "The intent of this kind of review is to include systematic reviews or meta-analyses as the main study type and thus examine only the highest level of evidence." Blackwood D (2016)
When to use : When synthesizing and combining relevant data from existing systematic reviews or meta-analyses to make better decisions, to provide clinical decision makers with the evidence they need when there are many systematic reviews.
Limitations : Limited evidence sources. It is impossible to do an umbrella review without a core of systematic reviews on the topic.
- Overviews of Reviews
- Umbrella Reviews
- Summarizing systematic reviews: methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach.
Definition : reviews of interventions that have multiple components and complicated/multiple causal pathways, feedback loops, synergies, and/or mediators and moderators of effect. They may also have additional complexity through population, implementation and/or context.
When to use : When the intervention has multiple components and any component may have an interventional effect, including the specific component of the intervention, between the intervention and study participants, with the intervention context, or a combination of these aspects.
Limitations : Difficulty knowing whether an intervention is simple or complex, may be more time consuming than a non-complex review as inputs from stakeholders and the use of theory may be necessary, may require substantial adaptation of conventional review methods.
- Intervention complexity
- Practical Tools and Guidance for Systematic Review of Complex Interventions.
- << Previous: Common Review Types
- Next: Resources for Reviews by Discipline and Type >>
- Last Updated: May 16, 2024 11:28 AM
- URL: https://guides.temple.edu/systematicreviews
Temple University
University libraries.
See all library locations
- Library Directory
- Locations and Directions
- Frequently Called Numbers

Need help? Email us at [email protected]

COMMENTS
Metasynthesis—the systematic review and integration of findings from qualitative studies—is an emerging technique in medical research that can use many different methods. Nevertheless, the method must be appropriate to the specific scientific field in which it is used. The objective is to describe the steps of a metasynthesis method adapted ...
The goal of research synthesis is to understand results reported in individual studies in the context of other studies. These descriptions of past research identify gaps in the literature, integrate research findings, and develop scientific knowledge (Cooper 2009, 2016).With emphasis being placed on how a study was conducted, reported outcomes, and best practice suggestions, meta-analysis and ...
when conducting a qualitative meta-synthesis: (1) theory building; (2) theory explication; and (3) theory development. It is illuminating, and a holistic view of the phenomena results from the synthesis of qualitative findings from numerous studies. The meta-synthesis approach has been determined to be an appropriate
A meta-synthesis of qualitative health research is a structured approach to analyzing primary data across the findings sections of published peer-reviewed papers reporting qualitative research. The analysis of this evidence involves qualitative and sometime quantitative methods with the aim of improving health outcomes, research, services, or ...
An increasing number of meta-synthesis papers are appearing in the nursing and midwifery literature. Methods. Literature on the technique of meta-synthesis and examples of meta-synthesis papers were searched and reviewed. A meta-synthesis exercise was undertaken, and this informed reflection and critique of the method. Findings.
Several different approaches to qualitative meta-synthesis have emerged, with most connected to the meta-ethnographic procedures originally outlined in 1988. This paper: (1) discusses the key philosophical and methodological issues in the literature on qualitative meta-synthesis, (2) highlights key methods that are used in qualitative meta ...
Abstract. A meta-synthesis of qualitative health research is a structured approach to analyzing primary data across the findings sections of published peer-reviewed papers reporting qualitative research. A meta-synthesis of qualitative research provides evidence for health care and service decision-making to inform improvements in both policy ...
Background: Metasynthesis—the systematic review and integration of findings from qualitative studies—is an emerging technique in medical research that can use many different methods. Nevertheless, the method must be appropriate to the specific scientific field in which it is used. The objective is to describe the steps of a metasynthesis method adapted from Thematic Synthesis and ...
How to perform a systematic literature review: A guide for healthcare researchers, practitioners and students by Edward Purssell and Niall McCrae. ISBN: 9783030496722 ... Cochrane: 21.10 Selecting a qualitative evidence synthesis and data extraction method Types of meta-synthesis: thematic, framework, and meta-ethnography. Meta-synthesis ...
We used a meta-synthesis approach to systematically review, summarize, and understand elements in previously published literature (Walsh and Downe, 2005;Saldaña, 2016;Levitt, 2018).
Because meta-synthesis requires studies to be similar in terms of method and approach (Walsh & Downe, 2005), studies that use the keyword qualitative but are essentially literature reviews ...
Illustrate the role of meta-analysis in the synthesis of prior studies and resolve the variabilities. ... (RevMan) is a web-based software that manages the entire literature review process and meta-analysis. The meta-analyst uploads all studies to RevMan library, where they can be managed and exanimated for inclusion. ... For example, a meta ...
Doing a meta-ethnographic synthesis: a step-by-step guide with illustrated examples Phase 1: getting started. The initial stage requires the authors to identify an area of interest [].The reviewers need to consider if a synthesis of the topic is required and whether a qualitative synthesis and the meta-ethnographic approach fits with the research question [].
Journal of Advanced Nursing 50(2), 204-211 Meta-synthesis method for qualitative research: a literature review Aim. This paper discusses the purpose and stages of meta-synthesis and the epis ...
A simple meta-synthesis definition is: Meta-synthesis represents a sophisticated and systematic approach to distilling knowledge from many primary studies. Unlike traditional literature reviews that summarize individual studies, meta-synthesis involves integrating and synthesizing data from diverse sources.
Background: Metasynthesis—the systematic review and integration of findings from qualitative studies—is an emerging technique in medical research that can use many different methods. Nevertheless, the method must be appropriate to the specific scientific field in which it is used. The objective is to describe the steps of a metasynthesis ...
"Qualitative meta-synthesis is an intentional and coherent approach to analyzing data across qualitative studies. It is a process that enables researchers to identify a specific research question and then search for, select, appraise, summarize, and combine qualitative evidence to address the research question" (Erwin et al, 2011).
Timeframe: 12 months or less. Question: "A clearly formulated question helps to set boundaries for the scope and depth of a meta-ethnography" (Atkins S.)Sources and searches: Not as exhaustive as a systematic review, unless the question requires exhaustive searching. Can search within a particular setting. Search specifically for qualitative studies if possible (be careful with search filters).
Definition: "A review method that summarizes past empirical or theoretical literature to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular phenomenon or healthcare problem (Broome 1993).Integrative reviews, thus, have the potential to build nursing science, informing research, practice, and policy initiatives. Well-done integrative reviews present the state of the science, contribute ...