109 Virtual Reality Topics & Essay Examples
When writing a virtual reality essay, it is hard to find just one area to focus on. Our experts have outlined 104 titles for you to choose from.

🏆 Best Virtual Reality Topics & Essay Examples
🕶️ good virtual reality research topics, 🤖 interesting virtual reality research paper topics, ❓ research questions about virtual reality.
Humanity has made amazing leaps in technology over the past several years. We have reached frontiers previously thought impossible, like the recreation of virtual environments using computers. These three-dimensional worlds can be accessed and explored by people. This is made possible with VR headsets, such as Oculus Rift or HTC Vive. If you’re eager to find out more, peek at our collection of VR research topics below!
- Virtual Reality Versus Augmented Reality In fact, this amounts to one of the merits of a virtual reality environment. A case example of this type of virtual reality is the Virtual Reality games.
- Virtual Reality Technology The third negative impact of virtual reality is that it causes human beings to start living in the world of fantasy.
- Virtual Reality Tourism Technology In the world of virtual tourism, we can be transported to any country and have the ability to interact and manipulate the elements within the world we are touring in a way that would not […]
- Virtual Reality’s Main Benefits The rapid development and the growing popularity of virtual reality raise a logical interest concerning the advantages and disadvantages that are related to the application of this new technology in various spheres of knowledge and […]
- Virtual Reality Technology for Wide Target Audience Due to the numerous applications in both leisure and industry, as well as massive popularity with audiences of different ages, there is a chance that, in several years, evaluating the target audiences of Virtual Reality […]
- Virtual Reality’s Benefits and Usages in Concurrent Engineering Figure 1: Phases of concurrent engineering Source As shown in the figure above, the initial stage of concurrent engineering is the identification of the components of the design system.
- A Growth Trajectory of the Virtual Reality Drilling Rig Training During the final three months of development, the VR training program will be refined and tested for usability and effectiveness. Collecting feedback from users is essential for the success of the VR drilling rig training […]
- “The Role of Virtual Reality in Criminal Justice Pedagogy” by Smith The journal is titled “The role of virtual reality in criminal justice pedagogy: An examination of mental illness occurring in corrections”.
- Virtual Reality and Cybersecurity As a result, it is the mandate of the framework entities to establish solutions to the inherent barriers to the implementation of the business plan.
- A Stand-Up Comedy Virtual Reality Platform for Qatar Tourism Choosing the right number of avatars, customization of the product, and pricing the product were the three major challenges that were faced in this project. The second challenge that emerged in the development stage was […]
- Entrepreneurial Opportunities in Virtual Reality In terms of the practical context, the research will focus on the organizations and sectors which are the primary beneficiaries of virtual reality and remote work during the pandemic.
- Virtual Reality Space Product Project Challenges During the project, several challenges came up, which included providing leadership to the team, identifying the customer segment for the product, and understanding the “pains” of the customer segment.
- Reflection on Aspects of Virtual Reality Videos For instance, the video Wolves in the Walls has good graphics and gives the independence to look at every section of the set-up separately.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality for Modern Firms The business environment is not an exception, as firms seek to maximize their value through the implementation of high-tech solutions. AR is another major component of contemporary professional training, as it contributes to the better […]
- The Rules of the Virtual Reality Online environment has been providing the platform for casual interactions as well as economic activities for quite a while.
- How Virtual Reality Is Changing the World of Interior Design In order to become competitive in the sphere of luxury interior design, “More” must make its projects look modern and trendy.
- Rusnak’s “The Thirteenth Floor” and The Concept of Virtual Reality In such consideration, this paper conducts a comparative analysis of The Thirteenth Floor and how the concept of virtual reality was developed and is applied in today’s films.
- Top Companies in the Virtual Reality Industry Currently, Google is the leading search engine company, and there are signs that the company might emerge as one of the heavyweights in the virtual reality industry.
- Screen Culture: Immersion and Virtual Reality If paralleling with the world of video games, the protagonist in that projected art work is the most close to the vision that the user could be associated with.
- Virtual Reality: A Powerful New Technology for Filming The creation of VR highlights a new perception of space because, through technology, people can be transmitted to a different environment.
- Internet, Virtual Reality, and World Wide Web Defining the concept of the Internet is a challenging task, mostly because of the changes that it has undergone over the course of its development.
- Virtual Reality Technology and Soccer Training Moreover, the level of interactivity needs to be significant, and the most attention should be devoted to the modeling of situations that are viewed as the most problematic.
- Char Davies’ Osmose as Virtual Reality Environment On the following position, the installment suggests the invitees a chance to trail the discrete interactor’s voyage of imageries from end to end of this counterpart of natural surroundings.
- Virtual Reality in Healthcare Training The objective data will be gathered to inform the exploration of the first question, and it will focus on such performance measures as time, volume, and efficiency of task completion; the number of errors pre- […]
- Scholar VR: Virtual Reality Planning Service Studio To ensure that the small and mid-sized companies in the United Kingdom understand the leverage they can get by using VR technology.
- IOS and Browser Applications and Virtual Reality From the consumer’s point of view, any mobile application is good if it is of interest to the public and covers a large target audience.
- Virtual Reality’ Sports Training System Working Steps The efficiency of the given technology is evidenced by the fact that it is used by various coaches and teams to provide training for their players. For this reason, it is possible to predict the […]
- Virtual Reality Technology in Soccer Training Therefore, it is imperative to invest in this area to protect the safety of our technology and ensure that we have a viable product.
- Virtual Reality Technology in Referee Training Referees need to experience the practical nature of the profession during the training process, and the VR technology will eliminate the underlying challenges to the development of experience in the profession.
- Surgeon Students’ Virtual Reality Learning Programs In order for the students to feel like they are operating on living patients instead of waving instruments in the air, it is necessary to provide the environment that would compensate for the shortcomings of […]
- Virtual Reality and Solitary Confinement Nowadays, the majority of the representatives of the general public all over the world are familiar with the concept of virtual reality, and many of them have already experienced it.
- Samsung Gear Virtual Reality Product Launch The paper at hand is devoted to the analysis of the launch of Samsung Gear VR from different perspectives: the product development model, the business analysis, its technical implementation, etc.
- Virtual Reality in Military Health Care The purpose of the research is to identify the capabilities of VR and its applications in military health care. This study will explore the current uses of VR, its different functionalities, applications in the field […]
- Virtual Reality Ride Experience at Disneyland Florida The basic concept of the proposed ride is to utilize the current advances in VR technology to create a simulated experience for park-goers that is safe, widely usable, and sufficiently immersive that there is a […]
- Imagineering Myths About Virtual Reality Walt Disney Imagineering team, which encompassed a wide range of professionals responsible for various entertainments offered by theme parks, resorts, and other venues, is currently devoting a lot of time and effort to unlock the […]
- Virtual Reality Industry Analysis While it is true that the production and sale of virtual reality headsets could be in the millions in the future as the technology develops and becomes more acceptable, it cannot be stated at the […]
- Virtual Reality in Construction Originally, the use of virtual reality in construction within the past decade has been limited to 3D object design wherein separate 3D representations of the exterior and interior of the buildings are designed utilizing 3D […]
- Virtual Reality in Soccer Training The following work will focus on the analysis of the use of Virtual Reality in the training of soccer players with the evaluation of the practices adopted by particular soccer teams.
- Abstract on Architecture and the Role of Virtual Reality
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Escapism and Virtual Reality
- Strategic Analysis of the Creation of a New Rating System in Virtual Reality Gaming
- Study on Real/Virtual Relationships Through a Mobile Augmented Reality Application
- Benefits and Dangers of Virtual Reality
- Can Virtual Reality Kill?
- Cognitive Psychology & Virtual Reality Systems
- Computer Science and Virtual Reality
- Development of Virtual Reality Technology in the Aspect of Educational Applications
- Difference Between Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
- Role of Virtual Reality in Education
- Humanity Versus Virtual Reality
- Simulation and Virtual Reality in a Sport Management Curriculum Setting
- Smart VR: A Virtual Reality Environment for Mathematics
- Sports Management Curriculum, Virtual Reality, and Traditional Simulation
- SWOT Analysis: The Lego Product and the ‘Virtual Reality’
- The Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality Market Forecast and Opportunities in U.S.
- Tracking Strategy in Increased Reality and Virtual Reality
- Using the Virtual Reality to Develop Educational Games for Middle School Science Classrooms
- What Is Virtual Reality?
- What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Virtual Reality?
- What Do Consumers Prefer for the Attributes of Virtual Reality Head-Mount Displays?
- Virtual Reality and Its Potential to Become the Greatest Technological Advancement
- Lucid Dreams as the First Virtual Reality
- Development of Virtual Reality
- Introduction to Virtual Reality Technology and Society
- Issue “Virtual Reality in Marketing”: Definition, Theory and Practice
- Applying Virtual Reality in Tourism
- Application of Virtual Reality in Military
- Augmented Reality & Virtual Reality Industry Forecast and Analysis to 2013 – 2018
- Breakthrough Virtual Reality Sex Machine
- Components Driving Virtual Reality Today and Beyond
- Data Correlation-Aware Resource Management in Wireless Virtual Reality (VR): An Echo State Transfer Learning Approach
- Gaming to Health Care: Using Virtual Reality in Physical Rehabilitation
- Smart Phones and Virtual Reality in 10 Years
- Evolution of Art in Virtual Reality
- Use of Virtual Reality in Molecular Docking Science Experiments
- Use of Virtual Reality for Concussion Diagnosis
- Virtual Reality as Analgesia: An Alternative Approach for Managing Chronic Pain
- Virtual Reality: The Real Life Implications of Raising a Virtual Child
- When Virtual Reality Meets Realpolitik: Social Media Shaping the Arab Government-Citizen Relationship
- Can Virtual Reality Ever Be Implemented in Routine Clinical Settings?
- What Is More Attractive, Virtual Reality or Augmented Reality?
- What Is Virtual Reality and How It Works?
- What Are the Benefits of Virtual Reality?
- Is Virtual Reality Dangerous?
- How Is Virtual Reality Used in Everyday Life?
- What Are the Risks of Virtual Reality?
- What Is the Future of Virtual Reality in Education?
- How Do You Think Virtual Reality Devices Will Change Our World?
- What Are Three Disadvantages of Virtual Reality?
- What’s the Point of Virtual Reality?
- How Can Virtual Reality Optimize Education?
- How Did Virtual Reality Affect Our Lives?
- Will Virtual Reality Eventually Replace Our Real Reality?
- What Are Some Cool Virtual Reality Ideas?
- When Will We Have Full-Sensory Virtual Reality?
- What Do I Need to Develop Virtual Reality Games?
- Why Did Virtual Reality Never Take Off so Far?
- What Are Medical Applications of Virtual Reality?
- How Virtual Reality Can Help in Treatment of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder?
- What Are the Biggest Problems Virtual Reality Can Solve?
- What Unsolved Problems Could Virtual Reality Be a Solution For?
- How Would a Fully Immersive Virtual Reality Work?
- When Will Virtual Reality Become Popular?
- What’s the Best Way to Experience Virtual Reality Technology?
- How Will Virtual Reality Change Advertising?
- Which Are the Best Virtual Reality Companies in India?
- What Are the Pros and Cons of Virtual Reality?
- What Are the Coding Languages Required for Virtual Reality?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 109 Virtual Reality Topics & Essay Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/virtual-reality-essay-topics/
"109 Virtual Reality Topics & Essay Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/virtual-reality-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '109 Virtual Reality Topics & Essay Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "109 Virtual Reality Topics & Essay Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/virtual-reality-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "109 Virtual Reality Topics & Essay Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/virtual-reality-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "109 Virtual Reality Topics & Essay Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/virtual-reality-essay-topics/.
- Innovation Titles
- Mobile Technology Paper Topics
- Integrity Questions
- Software Engineering Topics
- Web Technology Essay Topics
- Online Community Essay Topics
- Virtual Team Ideas
- Internet of Things Topics
Virtual Reality - Essay Samples And Topic Ideas For Free
Virtual Reality (VR), a simulated experience that can resemble or be entirely different from the real world, has made significant strides with applications in gaming, education, healthcare, and more. Essays on VR might delve into its technological advancements, its applications, and the societal, ethical, and psychological implications of immersive digital environments. The discussion could also extend to the comparison between VR and augmented reality (AR), exploring how these technologies are reshaping entertainment, communication, and learning experiences. A vast selection of complimentary essay illustrations pertaining to Virtual Reality you can find at PapersOwl Website. You can use our samples for inspiration to write your own essay, research paper, or just to explore a new topic for yourself.
Virtual Reality in the Medical Field
Before I began researching virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR), I knew very little on the subjects of each and even had to look up the definitions. I was aware that Google was working to produce glasses called, Google Cardboard, Sony was also working to produce their own version called, PlayStation VR. I looked at multiple definitions of each of the three realities, virtual, augmented and mixed and have compiled all the information into an easily […]
Virtual Reality (VR) is not a New Technology
Virtual reality can be portrayed as an Immersive Mixed media innovation (Krau, 2016). Today, Virtual reality (VR) is not a new technology (Barnes, 2016). Initial computerized VR started within the late-1960s (VRS, 2016). According to the Oxford English Dictionary, virtual reality alludes to "The computer created simulation of a three-dimensional image or environment that can be associating with in an apparently genuine or physical way by an individual utilizing specific electronic equipment, such as a helmet with a interior screen […]
Future of Video Games
In many centuries, technology has been a big contributor to human history. It has helped humans advance in many different areas of life. It has provided us with the abilities to advance the human race, and gain more knowledge than our previous ancestors. Technology over the years has advanced rapidly. Not that long ago, the very first cell phone was an extraordinary invention that caught the world by storm. It helped talking with people from long distances remotely seem like […]
We will write an essay sample crafted to your needs.
Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual reality has enhance life in all aspects by allowing your senses to feel what your body cannot experience; it allows you to travel, learn, and has a bright future ahead of it. Even though it has experienced obstacles, it is an emerging technology at best. Therefore, what is Virtual reality "Virtual reality is the term used to describe a three-dimensional, computer generated environment which can be explored and interacted with by a person. That person becomes part of this […]
Virtual Reality (VR) Today
Virtual reality (VR) and, to some extent, augmented reality (AR) have been a science fiction dream for many years, possibly going back as far as the 1950s; However, over the past ten to twenty years, these conceptual ideas have made their way into reality and are slowly starting to integrate into society and daily life, also known as "emerging technologies". According to Reede and Bailiff (2016), VR startups have raised more than $1.46 billion in venture capital since 2012, with […]
Specific Fictional Model for Virtual Realit
On November 12, 2018, the Oculus Blog posted, "You haven't seen it until you see it with VR." Even though the public became aware of virtual reality only recently, the concept has been around for decades. It took many years and attempts to reach to the perfection of Virtual Reality Oculus. Technology has evolved, and many inventors have tried to create something that helps viewers feel present at some event or scene. Virtual Reality is a computer invention that tries […]
History of Virtual Reality
Historically, virtual reality in its beginning preceded time through the concept that has been developed and formalized. Every development with VR has contributed to the creation of illusion. Dating back to the nineteenth-century virtual reality is presented in the 360-degree murals intended to fill the entire sight of a person. In top galleries, this modern art has occupied much of the exhibits spaces and is continuing to expand. Virtual reality has branched from pen to paper and paintbrush to canvas […]
A Computer-Based Technology: Virtual Reality
Since human walked into the Information Age, we have seen masses of productive results brought by the Internet and computer, like multimedia and cyberspace, which both are the essential parts of the life of ordinary people. Now it comes to the 18th year of 21st century, with the popularization of smart phone and personal computer, the contents presented on the gleamy screens gradually lose their attraction to people as they did, for at a time where funky things and eyeball-catching […]
The Computer-Generated Simulation Image or Environment – VR
Virtual reality is the computer-generated simulation image or environment that can be interacted with in a seemingly real or physical way by person. It is used for entertainment like video games,simulation, or to see something new. Many companies use virtual reality to sell products like sony,mircrosoft, etc.You can use it to train for a career. It can also be used for designing for example engineers can use it for designing a building or fair ride.It can be used by a […]
Virtual Reality and Identity
Virtual reality as a simulation of a real or imaginary phenomenon allows freedom for the individuals within the environment. The virtual reality has no defined gender roles and defies society's definition of gender and boundaries. This is illustrated in the films the matrix and her the characters exhibit a form of freedom and no clearly defined boundaries. Virtual reality allows the change of identity and total control of the identity of the character. This is displayed by trinity in the […]
Are Virtual Reality Becoming more a Part of our Reality than Before?
Video games have been a part of the world’s culture for the past five or so decades and have affected many people’s lives. Since video games were first released commercially, we have seen the rise of many iconic characters from these games like Mario and Sonic. Although video games seem to be something to play for fun, they are being used today for more than their original intent. Thanks to the gaming community, new technologies like Virtual Reality (VR) have […]
Vr’s Impact to Modern World
About 75 percent of the Forbes World’s Most Valuable Brands have created some form of the virtual reality or augmented reality experience for customers or employees. This must say something if you have companies such as Sony, Facebook(Oculus), and HTC. There’s obviously some potential in virtual reality if people are dedicating part of their companies to this material. The innovation of this technology is certainly amazing but what impact will it have on the future of technology or even businesses, […]
Smart Medicine and Virtual Reality – Use Cases
Virtual reality (VR) – the creation of immersive, computer-generated environments so convincing that they feel like the real thing -- isn’t just for video games and escapism. It is also changing the way that doctors work and greatly improving patients’ lives. Here are five examples of how VR is making medicine smarter. • Curing phobias and PTSD Facing your fears is the best way to overcome a phobia. But for people who are deathly afraid of spiders, needles, flying -- […]
Virtual Reality: Game Transfer Phenomena
Imagine if you were you were floating through space, watching a horror film,s or perhaps playing a video game, and it seemed like you were actually there. With the invention of virtual reality (VR), people are able to explore the illusion of this reality. Virtual reality is computer-generated technology used to create a manufactured environment. There is a range of systems that are used for this purpose such as special headsets and fiber optic gloves. The term virtual reality means […]
What is Virtual Reality? VR Definition and Examples
Virtual Reality (VR) is a powerful technology that has the potential to cause a multitude of social and psychological problems. VR is defined as a “computer-generated display that allows or compels the user to have a feeling of being present in an environment other than the one they are actually in and to interact with that environment (Schroeder, 2). VR creates a three-dimensional situation in which the user is able to fully immerse themself and interact with the environment. Through […]
Virtual Reality in Regards to Health and how it Can be Life-Changing
Exploring Virtual Reality in Health Diego Leon Professor Ron Frazier October 29, 2018, Introduction When most individuals think of technology involving computers, they think it can solely involve two of the five senses we humans have – vision (sight) and hearing (audition). But what if we could interact with more than two sensorial channels? Virtual reality deals with just that. Virtual reality is defined as a “high-end user interface that involves real-time simulation and interaction through […]
Potential Impacts of VR
Introduction Commonly abbreviated as VR, Virtual Reality is an interactive computer-generated experience that takes place within a simulated environment or three-dimensional image (Burdea & Coiffet, 2003). The experience is generated by a blend of interactive software and hardware, and is then presented in a realistic fashion such that the user interacts with and accepts the simulated environment as if it were real. The immersive environment can either be real or artificial, and is typically produced in 3D modeling software before […]
Utilization of PC Innovation: Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality (VR) is the utilization of PC innovation to make a mimicked domain. In contrast to conventional UIs, VR places the client inside an ordeal. Rather than survey a screen before them, clients are submerged and ready to connect with 3D universes. By reenacting whatever number of faculties as could be allowed, for example, vision, hearing, contact, even smell, the PC is changed into a guard to this counterfeit world. As far as possible to close genuine VR encounters […]
Mobile Technology: Virtual Reality
Virtual reality Computer-generated reality or VR reality is the latest user interface opposite to traditional one, indulging person into the 3D environment instead of watching in on any screen, this also makes individuals feel like they are physically in that environment likewise they can touch, see and hear that scene in reality. This work based on tricking the human mind to make them realize what they are feeling that’s real. Virtual Reality can be viewed as a very vivid encounter […]
Virtual Reality and Multiple Sclerosis Experiment
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a progressive disease of the central nervous system. According to the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, it is estimated that MS affects more than 2.3 million people worldwide.1 At this time the direct cause of MS is still unknown. However, the immune system attacks and damages the myelin sheath of nerve fibers, a fatty covering that surrounds and protects the nerve fibers. The immune system also attacks oligodendrocytes, which are the myelin-producing cells, as well […]
Virtual Reality Clan Generators: Building Digital Empires in a Virtual World
Ever fancied being the chief of your own virtual clan? Welcome to the world of clan generator games, where you're not just playing a game; you're building an empire, one decision at a time. These aren't your run-of-the-mill video games. They're a blend of strategy, storytelling, and, let's be honest, a bit of power tripping. Whether you're managing resources, diplomatically dealing with neighbors, or leading your digital tribe into battle, these games offer a slice of escapism with a side […]
Development of Virtual and Augmented Reality
Abstract This research paper is about virtual and augmented reality, it goes into detail about the history, the difference between the two, and how they're used in life today. Virtual reality was first experimented with in the 1950's, but Irvan Sutherland is credited for creating the first device dealing with both augmented and virtual reality in 1968. Virtual and augmented reality seem like they're similar, but the difference is that augmented reality is a bridge between the real world and […]
Augmented Reality Virtual Reality and the Music Industry
Although AR/VR technology is still in its infancy, it has already made quite the impact on most (if not all) industries including health care, retail, military/defense, Journalism media, & Architecture. One that especially sticks out to me is the AR/VR effects on Entertainment business, specifically the music industry. Each year hardware developers move us one step closer to a future where AR/VR is used as a common household item. Advances perhaps viewed as miniscule by the general public (i.e. simple […]
Augmented and Virtual Reality in a Business
Since the 1980's the technology to be able to remove oneself from this reality and place them into another simulated reality have been possible. Augmented and Virtual reality have been steadily gaining in popularity for the past 40 years. Looking back to where it was and to where it is today is amazing. According to Ryan Kaiser from Deloitte Consulting, Augmented Reality is a computer-generated image that is on the same field of view as the real world. While Virtual […]
Developing and Testing Photorealistic Avatar with Body Motions and Facial Expressions for Communication in Social Virtual Reality Applications
Developing and Testing Photorealistic Avatar with Body Motions and Facial Expressions for Communication in Social Virtual Reality Applications Abstract Providing effective communication in social virtual reality (VR) applications requires a high level of avatar representation realism and body movement to convey users’ thoughts and behaviours. In this research, we investigate the influence of avatar representation and behaviour on communication in an immersive virtual environment (IVE) by comparing video-based versus model-based avatar representations. Additionally, we introduce a novel VR communication system […]
Subway Surfers: Unraveling the Ultimate Endless Virtual Reality Adventure
Subway Surfers, a mobile gaming phenomenon meticulously crafted by Kiloo and SYBO Games, effortlessly stands out in the realm of endless runner games. This captivating and adrenaline-pumping game has carved an indelible niche for itself, firmly establishing its supremacy in the world of endless runners. In this essay, we will embark on a comprehensive exploration of Subway Surfers, delving into its gameplay dynamics, visual aesthetics, and the compelling reasons why it has become an essential choice for gamers seeking an […]
Technology in Modern Basketball
With basketball getting more and more popular, more people regret basketball as their favorite sport. But basketball has gone through a long period. The system and the level of coach had changed a lot. This made basketball have more different than nowadays. Today I want to introduce some obvious difference between modern basketball and traditional basketball. Firstly, game style had changed a lot, in the past, the players are more expected to shoot mid-range shoot. And different kinds of mid-range […]
BIM-VR Synchronization: Challenges and Solutions
There has been a steady increase in the adoption of BIM in the construction and engineering industry, and also in facility management in the past few decades. The next step is to create a framework that will allow BIM models to be translated into virtual reality models in real time. The current issues in developing virtual reality models are many, and need to be addressed. Some of the issues are that the process takes up a lot of time, and […]
The Simulation Hypothesis: are we Living in a Virtual Reality?
The idea that life as we know it could be a computer simulation might seem like something straight out of science fiction. But this notion has fascinated thinkers from various disciplines, including philosophers, scientists, and technologists. The concept, often called the simulation hypothesis, explores the possibility that our universe is an artificial construct, much like a virtual reality. And it raises some big questions: Are we merely characters in a simulated world run by advanced beings? If we are in […]
Additional Example Essays
- Gender Inequality in Education
- PTSD in Veterans
- Professionalism In Healthcare
- Three Waves of Feminism
- Fahrenheit 451 Technology
- Two main strengths and weaknesses of international law
- Why Movies Are Better Than Books: Advantages of Visual Storytelling
- Benefit of Playing Video Games
Essay about Virtual Reality (VR) Virtual reality is a three-dimensional computer environment that interacts with a person: a person is immersed in this environment using various devices (helmets, glasses, etc.), is part of the virtual world, and controls virtual objects and objects. The idea of immersing a person in the surrounding non-physical environment arose in the Middle Ages in the field of art. Then concave frescoes were created in order to involve a person in what is happening in the image. In the 1830s, the first stereoscopes were created, the principle of which was to place two pictures depicting the same situation from different positions in space in different eyepieces. Thus, one eye saw one picture, the other saw another, and the brain later combined them into a general three-dimensional picture. Nowadays, the same principle of obtaining a three-dimensional image is often used, only smartphones and LCD displays are used instead of pictures. After stereoscopes in the 1920s, the first flight simulators were invented, special devices that allow you to work out all actions when controlling an aircraft. Such simulators were mainly used by the military to train and improve the skills of military personnel. In 1982, the world's first laboratory dedicated to the research and development of virtual reality devices was established in the United States. During the first decade of the 21st century, virtual reality did not gain popularity, but since 2012 VR devices have been actively gaining popularity in the entertainment industry. In 2012, a virtual reality glasses startup Oculus VR was introduced on Kickstarter, which was later bought by Facebook. After the emerging demand for glasses, many IT companies, including Google, Apple, Amazon, Microsoft, Sony and Samsung, HTC, Sony and others, began to develop their own gadgets.
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essays Samples >
- Essay Types >
- Thesis Example
Virtual Reality Theses Samples For Students
14 samples of this type
If you're seeking a possible way to streamline writing a Thesis about Virtual Reality, WowEssays.com paper writing service just might be able to help you out.
For starters, you should browse our large database of free samples that cover most diverse Virtual Reality Thesis topics and showcase the best academic writing practices. Once you feel that you've determined the major principles of content organization and taken away actionable ideas from these expertly written Thesis samples, putting together your own academic work should go much easier.
However, you might still find yourself in a circumstance when even using top-notch Virtual Reality Theses doesn't let you get the job done on time. In that case, you can contact our writers and ask them to craft a unique Virtual Reality paper according to your custom specifications. Buy college research paper or essay now!
Bnfits Of Community Policing Thesis Examples
Make and answer some qs also thesis example, example of other motivation factors that encourage students to shop online: (question 20) thesis.
Don't waste your time searching for a sample.
Get your thesis done by professional writers!
Just from $10/page

Good Thesis On California Fracking Regulation And Agenda Setting
An analysis of the formulation of california senate bill 4, photovoltaic modules effect of tilt angle on soiling thesis.
Photovoltaic (PV) systems are one of the next generation’s renewable energy sources for our world energy demand. PV modules are highly reliable. However, in polluted environments, over time, they will collect grime and dust. There are also limited field data studies about soiling losses on PV modules. The study showed how important it is to investigate the effect of tilt angle on soiling.
Architecture & New Technology in Communication Thesis
The integration of natural user interfaces (nui) for illiterate people theses examples, integration of natural user interfaces for illiterate users, free thesis on fracking regulation and agenda setting, an analysis of the formulation of california senate bill, example of thesis on fracking regulation and agenda setting: an analysis of the formulation of, senate bill 4., example of thesis on the integration of natural user interfaces (nui) for illiterate people, introduction.
This project is undertaken to find out how natural user interfaces can enhance the use of devices for illiterate people. This is given the fact that the rate of illiteracy is an issue of concern in South Africa and the world over. This chapter will focus on previous research which have been carried out and the gap that is lacking in this field. It is important to understand the work that has been carried in order to research on what is still lacking in this field.
What is Natural user interfaces?
Good thesis on the history of wayfinding metaphors and human computer interaction, introduction, example of finance thesis, funds transfer pricing in commercial banks: a simple model: chapter 5, example of does online gaming addiction affect the social lives of people/teenagers thesis, does online gaming addiction affect the social lives of people/teenagers.
Rooji, A.V., et al. (2010). Online Video Game Addiction: Identification of Addicted Adolescent Gamers. Society for the Study of Addiction, Vol. 106, pp. 205-212.
Free Thesis On Fable The Wisdom Of Story And The Dissemination Of Human Experience
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline

- Home
- University of Bedfordshire e-theses
- Masters e-theses
A study on virtual reality and developing the experience in a gaming simulation

Description
Collections.
The following license files are associated with this item:
- Creative Commons
entitlement

Export search results
The export option will allow you to export the current search results of the entered query to a file. Different formats are available for download. To export the items, click on the button corresponding with the preferred download format.
By default, clicking on the export buttons will result in a download of the allowed maximum amount of items.
To select a subset of the search results, click "Selective Export" button and make a selection of the items you want to export. The amount of items that can be exported at once is similarly restricted as the full export.
After making a selection, click one of the export format buttons. The amount of items that will be exported is indicated in the bubble next to export format.
- Publications
- Completed Theses
- Hardware & Infrastructure
- Help our Research
Bachelor and Master Theses
- taken the "Basic Techniques in Computer Graphics" lecture by Prof. Kobbelt if you are a bachelor student
- taken at least one of our “Virtual Reality” lectures or our lab course if you are a master student
- a good working knowledge of C++ or C#
- some experience in the Unreal or Unity game engine
- or an equivalent qualification.
If you are interested in writing your thesis with us, you should inform yourself about our recent research topics first. Watch our research and theses (examples of theses in progress or finished) sections as well as a (non-complete) list of currently open theses below.
In case you are interested in one of these fields or topics, please send an appropriate request directly to [email protected] via E-Mail.
- Thematic interests (and hint to open thesis if applicable)
- Possibly more concrete suggestions for topics
- Motivation: Why do you want to write your thesis with us?
- Any previous experience and knowledge (programming skills, relevant software skills, finished projects, relevant attended courses, internships or the like)
- Desired earliest and latest start date
- Overview of grades
Advanced Interaction with Spatial UI
Interactions with menus in virtual reality are common when using immersive applications. However, due to various effects such as the lever effect, Heisenberg effect, etc., which are common in standard interaction techniques, menus can be cumbersome to use. This thesis aims to develop and evaluate an advanced interaction technique that aims to overcome the shortcomings of standard interactions. Prior experience with Unreal Engine’s C++ code or a strong willingness to learn independently and C++ proficiency is a must. A basic understanding of study design is advantageous. Contact: Marcel Krüger, M.Sc.
- Open access
- Published: 01 May 2024
The effectiveness of virtual reality training on knowledge, skills and attitudes of health care professionals and students in assessing and treating mental health disorders: a systematic review
- Cathrine W. Steen 1 , 2 ,
- Kerstin Söderström 1 , 2 ,
- Bjørn Stensrud 3 ,
- Inger Beate Nylund 2 &
- Johan Siqveland 4 , 5
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 480 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
416 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Virtual reality (VR) training can enhance health professionals’ learning. However, there are ambiguous findings on the effectiveness of VR as an educational tool in mental health. We therefore reviewed the existing literature on the effectiveness of VR training on health professionals’ knowledge, skills, and attitudes in assessing and treating patients with mental health disorders.
We searched MEDLINE, PsycINFO (via Ovid), the Cochrane Library, ERIC, CINAHL (on EBSCOhost), Web of Science Core Collection, and the Scopus database for studies published from January 1985 to July 2023. We included all studies evaluating the effect of VR training interventions on attitudes, knowledge, and skills pertinent to the assessment and treatment of mental health disorders and published in English or Scandinavian languages. The quality of the evidence in randomized controlled trials was assessed with the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool 2.0. For non-randomized studies, we assessed the quality of the studies with the ROBINS-I tool.
Of 4170 unique records identified, eight studies were eligible. The four randomized controlled trials were assessed as having some concern or a high risk of overall bias. The four non-randomized studies were assessed as having a moderate to serious overall risk of bias. Of the eight included studies, four used a virtual standardized patient design to simulate training situations, two studies used interactive patient scenario training designs, while two studies used a virtual patient game design. The results suggest that VR training interventions can promote knowledge and skills acquisition.
Conclusions
The findings indicate that VR interventions can effectively train health care personnel to acquire knowledge and skills in the assessment and treatment of mental health disorders. However, study heterogeneity, prevalence of small sample sizes, and many studies with a high or serious risk of bias suggest an uncertain evidence base. Future research on the effectiveness of VR training should include assessment of immersive VR training designs and a focus on more robust studies with larger sample sizes.
Trial registration
This review was pre-registered in the Open Science Framework register with the ID-number Z8EDK.
Peer Review reports
A robustly trained health care workforce is pivotal to forging a resilient health care system [ 1 ], and there is an urgent need to develop innovative methods and emerging technologies for health care workforce education [ 2 ]. Virtual reality technology designs for clinical training have emerged as a promising avenue for increasing the competence of health care professionals, reflecting their potential to provide effective training [ 3 ].
Virtual reality (VR) is a dynamic and diverse field, and can be described as a computer-generated environment that simulates sensory experiences, where user interactions play a role in shaping the course of events within that environment [ 4 ]. When optimally designed, VR gives users the feeling that they are physically within this simulated space, unlocking its potential as a dynamic and immersive learning tool [ 5 ]. The cornerstone of the allure of VR is its capacity for creating artificial settings via sensory deceptions, encapsulated by the term ‘immersion’. Immersion conveys the sensation of being deeply engrossed or enveloped in an alternate world, akin to absorption in a video game. Some VR systems will be more immersive than others, based on the technology used to influence the senses. However, the degree of immersion does not necessarily determine the user’s level of engagement with the application [ 6 ].
A common approach to categorizing VR systems is based on the design of the technology used, allowing them to be classified into: 1) non-immersive desktop systems, where users experience virtual environments through a computer screen, 2) immersive CAVE systems with large projected images and motion trackers to adjust the image to the user, and 3) fully immersive head-mounted display systems that involve users wearing a headset that fully covers their eyes and ears, thus entirely immersing them in the virtual environment [ 7 ]. Advances in VR technology have enabled a wide range of VR experiences. The possibility for health care professionals to repeatedly practice clinical skills with virtual patients in a risk-free environment offers an invaluable learning platform for health care education.
The impact of VR training on health care professionals’ learning has predominantly been researched in terms of the enhancement of technical surgical abilities. This includes refining procedural planning, familiarizing oneself with medical instruments, and practicing psychomotor skills such as dexterity, accuracy, and speed [ 8 , 9 ]. In contrast, the exploration of VR training in fostering non-technical or ‘soft’ skills, such as communication and teamwork, appears to be less prevalent [ 10 ]. A recent systematic review evaluates the outcomes of VR training in non-technical skills across various medical specialties [ 11 ], focusing on vital cognitive abilities (e.g., situation awareness, decision-making) and interprofessional social competencies (e.g., teamwork, conflict resolution, leadership). These skills are pivotal in promoting collaboration among colleagues and ensuring a safe health care environment. At the same time, they are not sufficiently comprehensive for encounters with patients with mental health disorders.
For health care professionals providing care to patients with mental health disorders, acquiring specific skills, knowledge, and empathic attitudes is of utmost importance. Many individuals experiencing mental health challenges may find it difficult to communicate their thoughts and feelings, and it is therefore essential for health care providers to cultivate an environment where patients feel safe and encouraged to share feelings and thoughts. Beyond fostering trust, health care professionals must also possess in-depth knowledge about the nature and treatment of various mental health disorders. Moreover, they must actively practice and internalize the skills necessary to translate their knowledge into clinical practice. While the conventional approach to training mental health clinical skills has been through simulation or role-playing with peers under expert supervision and practicing with real patients, the emergence of VR applications presents a compelling alternative. This technology promises a potentially transformative way to train mental health professionals. Our review identifies specific outcomes in knowledge, skills, and attitudes, covering areas from theoretical understanding to practical application and patient interaction. By focusing on these measurable concepts, which are in line with current healthcare education guidelines [ 12 ], we aim to contribute to the knowledge base and provide a detailed analysis of the complexities in mental health care training. This approach is designed to highlight the VR training’s practical relevance alongside its contribution to academic discourse.
A recent systematic review evaluated the effects of virtual patient (VP) interventions on knowledge, skills, and attitudes in undergraduate psychiatry education [ 13 ]. This review’s scope is limited to assessing VP interventions and does not cover other types of VR training interventions. Furthermore, it adopts a classification of VP different from our review, rendering their findings and conclusions not directly comparable to ours.
To the best of our knowledge, no systematic review has assessed and summarized the effectiveness of VR training interventions for health professionals in the assessment and treatment of mental health disorders. This systematic review addresses the gap by exploring the effectiveness of virtual reality in the training of knowledge, skills, and attitudes health professionals need to master in the assessment and treatment of mental health disorders.
This systematic review follows the guidelines of Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis [ 14 ]. The protocol of the systematic review was registered in the Open Science Framework register with the registration ID Z8EDK.
We included randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, and pretest–posttest studies, which met the following criteria: a) a population of health care professionals or health care professional students, b) assessed the effectiveness of a VR application in assessing and treating mental health disorders, and c) reported changes in knowledge, skills, or attitudes. We excluded studies evaluating VR interventions not designed for training in assessing and treating mental health disorders (e.g., training of surgical skills), studies evaluating VR training from the first-person perspective, studies that used VR interventions for non-educational purposes and studies where VR interventions trained patients with mental health problems (e.g., social skills training). We also excluded studies not published in English or Scandinavian languages.
Search strategy
The literature search reporting was guided by relevant items in PRISMA-S [ 15 ]. In collaboration with a senior academic librarian (IBN), we developed the search strategy for the systematic review. Inspired by the ‘pearl harvesting’ information retrieval approach [ 16 ], we anticipated a broad spectrum of terms related to our interdisciplinary query. Recognizing that various terminologies could encapsulate our central ideas, we harvested an array of terms for each of the four elements ‘health care professionals and health care students’, ‘VR’, ‘training’, and ‘mental health’. The pearl harvesting framework [ 16 ] consists of four steps which we followed with some minor adaptions. Step 1: We searched for and sampled a set of relevant research articles, a book chapter, and literature reviews. Step 2: The librarian scrutinized titles, abstracts, and author keywords, as well as subject headings used in databases, and collected relevant terms. Step 3: The librarian refined the lists of terms. Step 4: The review group, in collaboration with a VR consultant from KildeGruppen AS (a Norwegian media company), validated the refined lists of terms to ensure they included all relevant VR search terms. This process for the element VR resulted in the inclusion of search terms such as ‘3D simulated environment’, ‘second life simulation’, ‘virtual patient’, and ‘virtual world’. We were given a peer review of the search strategy by an academic librarian at Inland Norway University of Applied Sciences.
In June and July 2021, we performed comprehensive searches for publications dating from January 1985 to the present. This period for the inclusion of studies was chosen since VR systems designed for training in health care first emerged in the early 1990s. The searches were carried out in seven databases: MEDLINE and PsycInfo (on Ovid), ERIC and CINAHL (on EBSCOhost), the Cochrane Library, Web of Science Core Collection, and Scopus. Detailed search strategies from each database are available for public access at DataverseNO [ 17 ]. On July 2, 2021, a search in CINAHL yielded 993 hits. However, when attempting to transfer these records to EndNote using the ‘Folder View’—a feature designed for organizing and managing selected records before export—only 982 records were successfully transferred. This discrepancy indicates that 11 records could not be transferred through Folder View, for reasons not specified. The process was repeated twice, consistently yielding the same discrepancy. The missing 11 records pose a risk of failing to capture relevant studies in the initial search. In July 2023, to make sure that we included the latest publications, we updated our initial searches, focusing on entries since January 1, 2021. This ensured that we did not miss any new references recently added to these databases. Due to a lack of access to the Cochrane Library in July 2023, we used EBMR (Evidence Based Medicine Reviews) on the Ovid platform instead, including the databases Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and Cochrane Clinical Answers. All references were exported to Endnote and duplicates were removed. The number of records from each database can be observed in the PRISMA diagram [ 14 ], Fig. 1 .
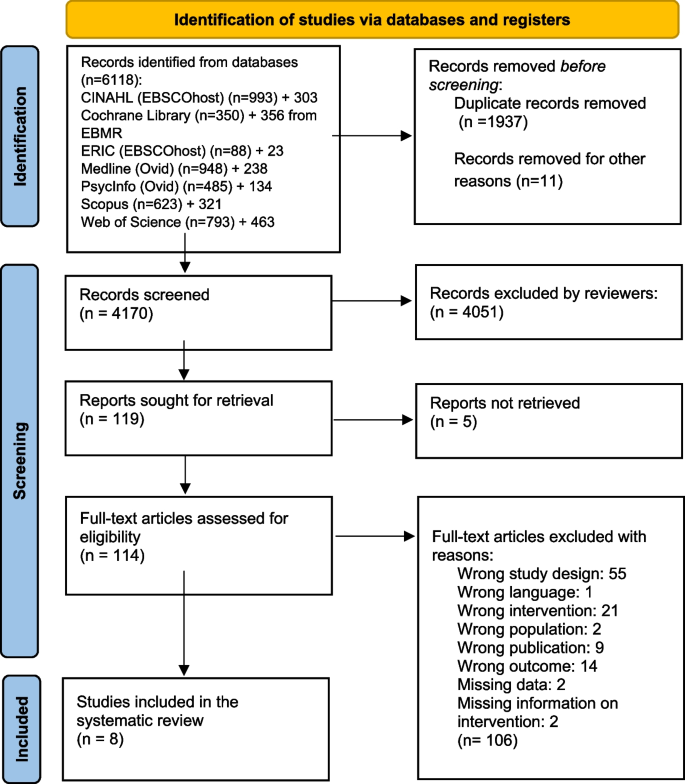
PRISMA flow chart of the records and study selection process
Study selection and data collection
Two reviewers (JS, CWS) independently assessed the titles and abstracts of studies retrieved from the literature search based on the eligibility criteria. We employed the Rayyan website for the screening process [ 18 ]. The same reviewers (JS, CWS) assessed the full-text articles selected after the initial screening. Articles meeting the eligibility criteria were incorporated into the review. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion.
Data extracted from the studies by the first author (CWS) and cross-checked by another reviewer (JS) included: authors of the study, publication year, country, study design, participant details (education, setting), interventions (VR system, class label), comparison types, outcomes, and main findings. This data is summarized in Table 1 and Additional file 1 . In the process of reviewing the VR interventions utilized within the included studies, we sought expertise from advisers associated with VRINN, a Norwegian immersive learning cluster, and SIMInnlandet, a center dedicated to simulation in mental health care at Innlandet Hospital Trust. This collaboration ensured a thorough examination and accurate categorization of the VR technologies applied. Furthermore, the classification of the learning designs employed in the VP interventions was conducted under the guidance of an experienced VP scholar at Paracelcus Medical University in Salzburg.
Data analysis
We initially intended to perform a meta-analysis with knowledge, skills, and attitudes as primary outcomes, planning separate analyses for each. However, due to significant heterogeneity observed among the included studies, it was not feasible to carry out a meta-analysis. Consequently, we opted for a narrative synthesis based on these pre-determined outcomes of knowledge, skills, and attitudes. This approach allowed for an analysis of the relationships both within and between the studies. The effect sizes were calculated using a web-based effect size calculator [ 27 ]. We have interpreted effect sizes based on commonly used descriptions for Cohen’s d: small = 0.2, moderate = 0.5, and large = 0.8, and for Cramer’s V: small = 0.10, medium = 0.30, and large = 0.50.
Risk of bias assessment
JS and CWS independently evaluated the risk of bias for all studies using two distinct assessment tools. We used the Cochrane risk of bias tool RoB 2 [ 28 ] to assess the risk of bias in the RCTs. With the RoB 2 tool, the bias was assessed as high, some concerns or low for five domains: randomization process, deviations from the intended interventions, missing outcome data, measurement of the outcome, and selection of the reported result [ 28 ].
We used the Risk Of Bias In Non-randomized Studies of Interventions (ROBINS-I) tool [ 29 ] to assess the risk of bias in the cohort and single-group studies. By using ROBINS-I for the non-randomized trials, the risk of bias was assessed using the categories low, moderate, serious, critical or no information for seven domains: confounding, selection of participants, classification of interventions, deviations from intended interventions, missing data, measurement of outcomes, and selection of the reported result [ 29 ].
We included eight studies in the review (Fig. 1 ). An overview of the included studies is presented in detail in Table 1 .
Four studies were RCTs [ 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 ], two were single group pretest–posttest studies [ 23 , 26 ], one was a controlled before and after study [ 25 ], and one was a cohort study [ 24 ]. The studies included health professionals from diverse educational backgrounds, including some from mental health and medical services, as well as students in medicine, social work, and nursing. All studies, published from 2009 to 2021, utilized non-immersive VR desktop system interventions featuring various forms of VP designs. Based on an updated classification of VP interventions by Kononowicz et al. [ 30 ] developed from a model proposed by Talbot et al. [ 31 ], we have described the characteristics of the interventions in Table 1 . Four of the studies utilized a virtual standardized patient (VSP) intervention [ 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 ], a conversational agent that simulates clinical presentations for training purposes. Two studies employed an interactive patient scenario (IPS) design [ 25 , 26 ], an approach that primarily uses text-based multimedia, enhanced with images and case histories through text or voice narratives, to simulate clinical scenarios. Lastly, two studies used a virtual patient game (VP game) intervention [ 19 , 24 ]. These interventions feature training scenarios using 3D avatars, specifically designed to improve clinical reasoning and team training skills. It should be noted that the interventions classified as VSPs in this review, being a few years old, do not encompass artificial intelligence (AI) as we interpret it today. However, since the interventions include some kind of algorithm that provides answers to questions, we consider them as conversational agents, and therefore as VSPs. As the eight included studies varied significantly in terms of design, interventions, and outcome measures, we could not incorporate them into a meta-analysis.
The overall risk of bias for the four RCTs was high [ 19 , 20 , 22 ] or of some concern [ 21 ] (Fig. 2 ). They were all assessed as low or of some concern in the domains of randomization. Three studies were assessed with a high risk of bias in one [ 19 , 20 ] or two domains [ 22 ]; one study had a high risk of bias in the domain of selection of the reported result [ 19 ], one in the domain of measurement of outcome [ 20 ], and one in the domains of deviation from the intended interventions and missing outcome data [ 22 ]. One study was not assessed as having a high risk of bias in any domain [ 21 ].
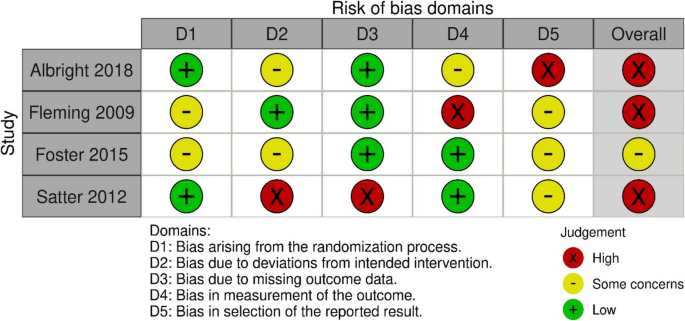
Risk of bias summary: review authors assessments of each risk of bias item in the included RCT studies
For the four non-randomized studies, the overall risk of bias was judged to be moderate [ 26 ] or serious [ 23 , 24 , 25 ] (Fig. 3 ). One study had a serious risk of bias in two domains: confounding and measurement of outcomes [ 23 ]. Two studies had a serious risk of bias in one domain, namely confounding [ 24 , 25 ], while one study was judged not to have a serious risk of bias in any domain [ 26 ].
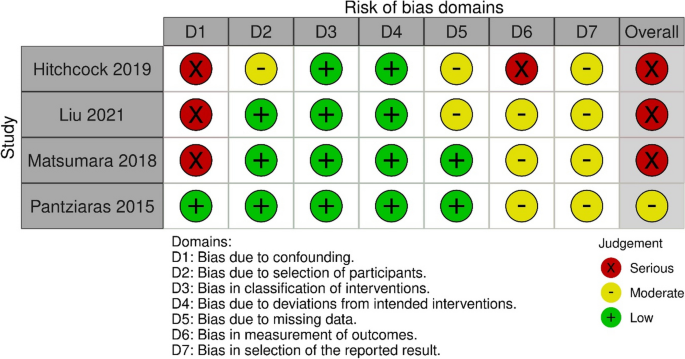
Risk of bias summary: review authors assessments of each risk of bias item in the included non-randomized studies
Three studies investigated the impact of virtual reality training on mental health knowledge [ 24 , 25 , 26 ]. One study with 32 resident psychiatrists in a single group pretest–posttest design assessed the effect of a VR training intervention on knowledge of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptomatology, clinical management, and communication skills [ 26 ]. The intervention consisted of an IPS. The assessment of the outcome was conducted using a knowledge test with 11 multiple-choice questions and was administered before and after the intervention. This study reported a significant improvement on the knowledge test after the VR training intervention.
The second study examined the effect of a VR training intervention on knowledge of dementia [ 25 ], employing a controlled before and after design. Seventy-nine medical students in clinical training were divided into two groups, following a traditional learning program. The experimental group received an IPS intervention. The outcome was evaluated with a knowledge test administered before and after the intervention with significantly higher posttest scores in the experimental group than in the control group, with a moderate effects size observed between the groups.
A third study evaluated the effect of a VR training intervention on 299 undergraduate nursing students’ diagnostic recognition of depression and schizophrenia (classified as knowledge) [ 24 ]. In a prospective cohort design, the VR intervention was the only difference in the mental health related educational content provided to the two cohorts, and consisted of a VP game design, developed to simulate training situations with virtual patient case scenarios, including depression and schizophrenia. The outcome was assessed by determining the accuracy of diagnoses made after reviewing case vignettes of depression and schizophrenia. The study found no statistically significant effect of VR training on diagnostic accuracy between the simulation and the non-simulation cohort.
Summary: All three studies assessing the effect of a VR intervention on knowledge were non-randomized studies with different study designs using different outcome measures. Two studies used an IPS design, while one study used a VP game design. Two of the studies found a significant effect of VR training on knowledge. Of these, one study had a moderate overall risk of bias [ 26 ], while the other was assessed as having a serious overall risk of bias [ 25 ]. The third study, which did not find any effect of the virtual reality intervention on knowledge, was assessed to have a serious risk of bias [ 24 ].
Three RCTs assessed the effectiveness of VR training on skills [ 20 , 21 , 22 ]. One of them evaluated the effect of VR training on clinical skills in alcohol screening and intervention [ 20 ]. In this study, 102 health care professionals were randomly allocated to either a group receiving no training or a group receiving a VSP intervention. To evaluate the outcome, three standardized patients rated each participant using a checklist based on clinical criteria. The VSP intervention group demonstrated significantly improved posttest skills in alcohol screening and brief intervention compared to the control group, with moderate and small effect sizes, respectively.
Another RCT, including 67 medical college students, evaluated the effect of VR training on clinical skills by comparing the frequency of questions asked about suicide in a VSP intervention group and a video module group [ 21 ]. The assessment of the outcome was a psychiatric interview with a standardized patient. The primary outcome was the frequency with which the students asked the standardized patient five questions about suicide risk. Minimal to small effect sizes were noted in favor of the VSP intervention, though they did not achieve statistical significance for any outcomes.
One posttest only RCT evaluated the effect of three training programs on skills in detecting and diagnosing major depressive disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) [ 22 ]. The study included 30 family physicians, and featured interventions that consisted of two different VSPs designed to simulate training situations, and one text-based program. A diagnostic form filled in by the participants after the intervention was used to assess the outcome. The results revealed a significant effect on diagnostic accuracy for major depressive disorder for both groups receiving VR training, compared to the text-based program, with large effect sizes observed. For PTSD, the intervention using a fixed avatar significantly improved diagnostic accuracy with a large effect size, whereas the intervention with a choice avatar demonstrated a moderate to large effect size compared to the text-based program.
Summary: Three RCTs assessed the effectiveness of VR training on clinical skills [ 20 , 21 , 22 ], all of which used a VSP design. To evaluate the effect of training, two of the studies utilized standardized patients with checklists. The third study measured the effect on skills using a diagnostic form completed by the participants. Two of the studies found a significant effect on skills [ 20 , 22 ], both were assessed to have a high risk of bias. The third study, which did not find any effect of VR training on skills, had some concern for risk of bias [ 21 ].
Knowledge and skills
One RCT study with 227 health care professionals assessed knowledge and skills as a combined outcome compared to a waitlist control group, using a self-report survey before and after the VR training [ 19 ]. The training intervention was a VP game designed to practice knowledge and skills related to mental health and substance abuse disorders. To assess effect of the training, participants completed a self-report scale measuring perceived knowledge and skills. Changes between presimulation and postsimulation scores were reported only for the within treatment group ( n = 117), where the composite postsimulation score was significantly higher than the presimulation score, with a large effect size observed. The study was judged to have a high risk of bias in the domain of selection of the reported result.
One single group pretest–posttest study with 100 social work and nursing students assessed the effect of VSP training on attitudes towards individuals with substance abuse disorders [ 23 ]. To assess the effect of the training, participants completed an online pretest and posttest survey including questions from a substance abuse attitudes survey. This study found no significant effect of VR training on attitudes and was assessed as having a serious risk of bias.
Perceived competence
The same single group pretest–posttest study also assessed the effect of a VSP training intervention on perceived competence in screening, brief intervention, and referral to treatment in encounters with patients with substance abuse disorders [ 23 ]. A commonly accepted definition of competence is that it comprises integrated components of knowledge, skills, and attitudes that enable the successful execution of a professional task [ 32 ]. To assess the effect of the training, participants completed an online pretest and posttest survey including questions on perceived competence. The study findings demonstrated a significant increase in perceived competence following the VSP intervention. The risk of bias in this study was judged as serious.
This systematic review aimed to investigate the effectiveness of VR training on knowledge, skills, and attitudes that health professionals need to master in the assessment and treatment of mental health disorders. A narrative synthesis of eight included studies identified VR training interventions that varied in design and educational content. Although mixed results emerged, most studies reported improvements in knowledge and skills after VR training.
We found that all interventions utilized some type of VP design, predominantly VSP interventions. Although our review includes a limited number of studies, it is noteworthy that the distribution of interventions contrasts with a literature review on the use of ‘virtual patient’ in health care education from 2015 [ 30 ], which identified IPS as the most frequent intervention. This variation may stem from our review’s focus on the mental health field, suggesting a different intervention need and distribution than that observed in general medical education. A fundamental aspect of mental health education involves training skills needed for interpersonal communication, clinical interviews, and symptom assessment, which makes VSPs particularly appropriate. While VP games may be suitable for clinical reasoning in medical fields, offering the opportunity to perform technical medical procedures in a virtual environment, these designs may present some limitations for skills training in mental health education. Notably, avatars in a VP game do not comprehend natural language and are incapable of engaging in conversations. Therefore, the continued advancement of conversational agents like VSPs is particularly compelling and considered by scholars to hold the greatest potential for clinical skills training in mental health education [ 3 ]. VSPs, equipped with AI dialogue capabilities, are particularly valuable for repetitive practice in key skills such as interviewing and counseling [ 31 ], which are crucial in the assessment and treatment of mental health disorders. VSPs could also be a valuable tool for the implementation of training methods in mental health education, such as deliberate practice, a method that has gained attention in psychotherapy training in recent years [ 33 ] for its effectiveness in refining specific performance areas through consistent repetition [ 34 ]. Within this evolving landscape, AI system-based large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT stand out as a promising innovation. Developed from extensive datasets that include billions of words from a variety of sources, these models possess the ability to generate and understand text in a manner akin to human interaction [ 35 ]. The integration of LLMs into educational contexts shows promise, yet careful consideration and thorough evaluation of their limitations are essential [ 36 ]. One concern regarding LLMs is the possibility of generating inaccurate information, which represents a challenge in healthcare education where precision is crucial [ 37 ]. Furthermore, the use of generative AI raises ethical questions, notably because of potential biases in the training datasets, including content from books and the internet that may not have been verified, thereby risking the perpetuation of these biases [ 38 ]. Developing strategies to mitigate these challenges is imperative, ensuring LLMs are utilized safely in healthcare education.
All interventions in our review were based on non-immersive desktop VR systems, which is somewhat surprising considering the growing body of literature highlighting the impact of immersive VR technology in education, as exemplified by reviews such as that of Radianti et al. [ 39 ]. Furthermore, given the recent accessibility of affordable, high-quality head-mounted displays, this observation is noteworthy. Research has indicated that immersive learning based on head-mounted displays generally yields better learning outcomes than non-immersive approaches [ 40 ], making it an interesting research area in mental health care training and education. Studies using immersive interventions were excluded in the present review because of methodological concerns, paralleling findings described in a systematic review on immersive VR in education [ 41 ], suggesting the potential early stage of research within this field. Moreover, the integration of immersive VR technology into mental health care education may encounter challenges associated with complex ethical and regulatory frameworks, including data privacy concerns exemplified by the Oculus VR headset-Facebook integration, which could restrict the implementation of this technology in healthcare setting. Prioritizing specific training methodologies for enhancing skills may also affect the utilization of immersive VR in mental health education. For example, integrating interactive VSPs into a fully immersive VR environment remains a costly endeavor, potentially limiting the widespread adoption of immersive VR in mental health care. Meanwhile, the use of 360-degree videos in immersive VR environments for training purposes [ 42 ] can be realized with a significantly lower budget. Immersive VR offers promising opportunities for innovative training, but realizing its full potential in mental health care education requires broader research validation and the resolution of existing obstacles.
This review bears some resemblance to the systematic review by Jensen et al. on virtual patients in undergraduate psychiatry education [ 13 ] from 2024, which found that virtual patients improved learning outcomes compared to traditional methods. However, these authors’ expansion of the commonly used definition of virtual patient makes their results difficult to compare with the findings in the present review. A recognized challenge in understanding VR application in health care training arises from the literature on VR training for health care personnel, where ‘virtual patient’ is a term broadly used to describe a diverse range of VR interventions, which vary significantly in technology and educational design [ 3 , 30 ]. For instance, reviews might group different interventions using various VR systems and designs under a single label (virtual patient), or primary studies may use misleading or inadequately defined classifications for the virtual patient interventions evaluated. Clarifying the similarities and differences among these interventions is vital to inform development and enhance communication and understanding in educational contexts [ 43 ].
Strengths and limitations
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic review to evaluate the effectiveness of VR training on knowledge, skills, and attitudes in health care professionals and students in assessing and treating mental health disorders. This review therefore provides valuable insights into the use of VR technology in training and education for mental health care. Another strength of this review is the comprehensive search strategy developed by a senior academic librarian at Inland Norway University of Applied Sciences (HINN) and the authors in collaboration with an adviser from KildeGruppen AS (a Norwegian media company). The search strategy was peer-reviewed by an academic librarian at HINN. Advisers from VRINN (an immersive learning cluster in Norway) and SIMInnlandet (a center for simulation in mental health care at Innlandet Hospital Trust) provided assistance in reviewing the VR systems of the studies, while the classification of the learning designs was conducted under the guidance of a VP scholar. This systematic review relies on an established and recognized classification of VR interventions for training health care personnel and may enhance understanding of the effectiveness of VR interventions designed for the training of mental health care personnel.
This review has some limitations. As we aimed to measure the effect of the VR intervention alone and not the effect of a blended training design, the selection of included studies was limited. Studies not covered in this review might have offered different insights. Given the understanding that blended learning designs, where technology is combined with other forms of learning, have significant positive effects on learning outcomes [ 44 ], we were unable to evaluate interventions that may be more effective in clinical settings. Further, by limiting the outcomes to knowledge, skills, and attitudes, we might have missed insights into other outcomes that are pivotal to competence acquisition.
Limitations in many of the included studies necessitate cautious interpretation of the review’s findings. Small sample sizes and weak designs in several studies, coupled with the use of non-validated outcome measures in some studies, diminish the robustness of the findings. Furthermore, the risk of bias assessment in this review indicates a predominantly high or serious risk of bias across most of the studies, regardless of their design. In addition, the heterogeneity of the studies in terms of study design, interventions, and outcome measures prevented us from conducting a meta-analysis.
Further research
Future research on the effectiveness of VR training for specific learning outcomes in assessing and treating mental health disorders should encompass more rigorous experimental studies with larger sample sizes. These studies should include verifiable descriptions of the VR interventions and employ validated tools to measure outcomes. Moreover, considering that much professional learning involves interactive and reflective practice, research on VR training would probably be enhanced by developing more in-depth study designs that evaluate not only the immediate learning outcomes of VR training but also the broader learning processes associated with it. Future research should also concentrate on utilizing immersive VR training applications, while additionally exploring the integration of large language models to augment interactive learning in mental health care. Finally, this review underscores the necessity in health education research involving VR to communicate research findings using agreed terms and classifications, with the aim of providing a clearer and more comprehensive understanding of the research.
This systematic review investigated the effect of VR training interventions on knowledge, skills, and attitudes in the assessment and treatment of mental health disorders. The results suggest that VR training interventions can promote knowledge and skills acquisition. Further studies are needed to evaluate VR training interventions as a learning tool for mental health care providers. This review emphasizes the necessity to improve future study designs. Additionally, intervention studies of immersive VR applications are lacking in current research and should be a future area of focus.
Availability of data and materials
Detailed search strategies from each database is available in the DataverseNO repository, https://doi.org/10.18710/TI1E0O .
Abbreviations
Virtual Reality
Cave Automatic Virtual Environment
Randomized Controlled Trial
Non-Randomized study
Virtual Standardized Patient
Interactive Patient Scenario
Virtual Patient
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
Standardized Patient
Artificial intelligence
Inland Norway University of Applied Sciences
Doctor of Philosophy
Frenk J, Chen L, Bhutta ZA, Cohen J, Crisp N, Evans T, et al. Health professionals for a new century: transforming education to strengthen health systems in an interdependent world. Lancet. 2010;376(9756):1923–58.
Article Google Scholar
World Health Organization. eLearning for undergraduate health professional education: a systematic review informing a radical transformation of health workforce development. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015.
Google Scholar
Talbot T, Rizzo AS. Virtual human standardized patients for clinical training. In: Rizzo AS, Bouchard S, editors. Virtual reality for psychological and neurocognitive interventions. New York: Springer; 2019. p. 387–405.
Chapter Google Scholar
Merriam-Webster dictionary. Springfield: Merriam-Webster Incorporated; c2024. Virtual reality. Available from: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/virtual%20reality . [cited 2024 Mar 24].
Winn W. A conceptual basis for educational applications of virtual reality. Technical Publication R-93–9. Seattle: Human Interface Technology Laboratory, University of Washington; 1993.
Bouchard S, Rizzo AS. Applications of virtual reality in clinical psychology and clinical cognitive neuroscience–an introduction. In: Rizzo AS, Bouchard S, editors. Virtual reality for psychological and neurocognitive interventions. New York: Springer; 2019. p. 1–13.
Waller D, Hodgson E. Sensory contributions to spatial knowledge of real and virtual environments. In: Steinicke F, Visell Y, Campos J, Lécuyer A, editors. Human walking in virtual environments: perception, technology, and applications. New York: Springer New York; 2013. p. 3–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8432-6_1 .
Choudhury N, Gélinas-Phaneuf N, Delorme S, Del Maestro R. Fundamentals of neurosurgery: virtual reality tasks for training and evaluation of technical skills. World Neurosurg. 2013;80(5):e9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2012.08.022 .
Gallagher AG, Ritter EM, Champion H, Higgins G, Fried MP, Moses G, et al. Virtual reality simulation for the operating room: proficiency-based training as a paradigm shift in surgical skills training. Ann Surg. 2005;241(2):364–72. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sla.0000151982.85062.80 .
Kyaw BM, Saxena N, Posadzki P, Vseteckova J, Nikolaou CK, George PP, et al. Virtual reality for health professions education: systematic review and meta-analysis by the Digital Health Education Collaboration. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(1):e12959. https://doi.org/10.2196/12959 .
Bracq M-S, Michinov E, Jannin P. Virtual reality simulation in nontechnical skills training for healthcare professionals: a systematic review. Simul Healthc. 2019;14(3):188–94. https://doi.org/10.1097/sih.0000000000000347 .
World Health Organization. Transforming and scaling up health professionals’ education and training: World Health Organization guidelines 2013. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/transforming-and-scaling-up-health-professionals%E2%80%99-education-and-training . Accessed 15 Jan 2024.
Jensen RAA, Musaeus P, Pedersen K. Virtual patients in undergraduate psychiatry education: a systematic review and synthesis. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2024;29(1):329–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-023-10247-6 .
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2021;10(1):89. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-021-01626-4 .
Rethlefsen ML, Kirtley S, Waffenschmidt S, Ayala AP, Moher D, Page MJ, et al. PRISMA-S: an extension to the PRISMA statement for reporting literature searches in systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2021;10(1):39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-020-01542-z .
Sandieson RW, Kirkpatrick LC, Sandieson RM, Zimmerman W. Harnessing the power of education research databases with the pearl-harvesting methodological framework for information retrieval. J Spec Educ. 2010;44(3):161–75. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022466909349144 .
Steen CW, Söderström K, Stensrud B, Nylund IB, Siqveland J. Replication data for: the effectiveness of virtual reality training on knowledge, skills and attitudes of health care professionals and students in assessing and treating mental health disorders: a systematic review. In: Inland Norway University of Applied S, editor. V1 ed: DataverseNO; 2024. https://doi.org/10.18710/TI1E0O .
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A. Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5(1):210. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4 .
Albright G, Bryan C, Adam C, McMillan J, Shockley K. Using virtual patient simulations to prepare primary health care professionals to conduct substance use and mental health screening and brief intervention. J Am Psych Nurses Assoc. 2018;24(3):247–59. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078390317719321 .
Fleming M, Olsen D, Stathes H, Boteler L, Grossberg P, Pfeifer J, et al. Virtual reality skills training for health care professionals in alcohol screening and brief intervention. J Am Board Fam Med. 2009;22(4):387–98. https://doi.org/10.3122/jabfm.2009.04.080208 .
Foster A, Chaudhary N, Murphy J, Lok B, Waller J, Buckley PF. The use of simulation to teach suicide risk assessment to health profession trainees—rationale, methodology, and a proof of concept demonstration with a virtual patient. Acad Psych. 2015;39:620–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40596-014-0185-9 .
Satter R. Diagnosing mental health disorders in primary care: evaluation of a new training tool [dissertation]. Tempe (AZ): Arizona State University; 2012.
Hitchcock LI, King DM, Johnson K, Cohen H, McPherson TL. Learning outcomes for adolescent SBIRT simulation training in social work and nursing education. J Soc Work Pract Addict. 2019;19(1/2):47–56. https://doi.org/10.1080/1533256X.2019.1591781 .
Liu W. Virtual simulation in undergraduate nursing education: effects on students’ correct recognition of and causative beliefs about mental disorders. Comput Inform Nurs. 2021;39(11):616–26. https://doi.org/10.1097/CIN.0000000000000745 .
Matsumura Y, Shinno H, Mori T, Nakamura Y. Simulating clinical psychiatry for medical students: a comprehensive clinic simulator with virtual patients and an electronic medical record system. Acad Psych. 2018;42(5):613–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40596-017-0860-8 .
Pantziaras I, Fors U, Ekblad S. Training with virtual patients in transcultural psychiatry: Do the learners actually learn? J Med Internet Res. 2015;17(2):e46. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.3497 .
Wilson DB. Practical meta-analysis effect size calculator [Online calculator]. n.d. https://campbellcollaboration.org/research-resources/effect-size-calculator.html . Accessed 08 March 2024.
Sterne JA, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Br Med J. 2019;366:l4898.
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. Br Med J. 2016;355:i4919. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i4919 .
Kononowicz AA, Zary N, Edelbring S, Corral J, Hege I. Virtual patients - what are we talking about? A framework to classify the meanings of the term in healthcare education. BMC Med Educ. 2015;15(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-015-0296-3 .
Talbot TB, Sagae K, John B, Rizzo AA. Sorting out the virtual patient: how to exploit artificial intelligence, game technology and sound educational practices to create engaging role-playing simulations. Int J Gaming Comput-Mediat Simul. 2012;4(3):1–19.
Baartman LKJ, de Bruijn E. Integrating knowledge, skills and attitudes: conceptualising learning processes towards vocational competence. Educ Res Rev. 2011;6(2):125–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2011.03.001 .
Mahon D. A scoping review of deliberate practice in the acquisition of therapeutic skills and practices. Couns Psychother Res. 2023;23(4):965–81. https://doi.org/10.1002/capr.12601 .
Ericsson KA, Lehmann AC. Expert and exceptional performance: evidence of maximal adaptation to task constraints. Annu Rev Psychol. 1996;47(1):273–305.
Roumeliotis KI, Tselikas ND. ChatGPT and Open-AI models: a preliminary review. Future Internet. 2023;15(6):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15060192 .
Kasneci E, Sessler K, Küchemann S, Bannert M, Dementieva D, Fischer F, et al. ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learn Individ Differ. 2023;103:102274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2023.102274 .
Thirunavukarasu AJ, Ting DSJ, Elangovan K, Gutierrez L, Tan TF, Ting DSW. Large language models in medicine. Nat Med. 2023;29(8):1930–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-023-02448-8 .
Touvron H, Lavril T, Gautier I, Martinet X, Marie-Anne L, Lacroix T, et al. LLaMA: open and efficient foundation language models. arXivorg. 2023;2302.13971. https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2302.13971 .
Radianti J, Majchrzak TA, Fromm J, Wohlgenannt I. A systematic review of immersive virtual reality applications for higher education: design elements, lessons learned, and research agenda. Comput Educ. 2020;147:103778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103778 .
Wu B, Yu X, Gu X. Effectiveness of immersive virtual reality using head-mounted displays on learning performance: a meta-analysis. Br J Educ Technol. 2020;51(6):1991–2005. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.13023 .
Di Natale AF, Repetto C, Riva G, Villani D. Immersive virtual reality in K-12 and higher education: a 10-year systematic review of empirical research. Br J Educ Technol. 2020;51(6):2006–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.13030 .
Haugan S, Kværnø E, Sandaker J, Hustad JL, Thordarson GO. Playful learning with VR-SIMI model: the use of 360-video as a learning tool for nursing students in a psychiatric simulation setting. In: Akselbo I, Aune I, editors. How can we use simulation to improve competencies in nursing? Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2023. p. 103–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-10399-5_9 .
Huwendiek S, De leng BA, Zary N, Fischer MR, Ruiz JG, Ellaway R. Towards a typology of virtual patients. Med Teach. 2009;31(8):743–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/01421590903124708 .
Ødegaard NB, Myrhaug HT, Dahl-Michelsen T, Røe Y. Digital learning designs in physiotherapy education: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-020-02483-w .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mole Meyer, adviser at SIMInnlandet, Innlandet Hospital Trust, and Keith Mellingen, manager at VRINN, for their assistance with the categorization and classification of VR interventions, and Associate Professor Inga Hege at the Paracelcus Medical University in Salzburg for valuable contributions to the final classification of the interventions. The authors would also like to thank Håvard Røste from the media company KildeGruppen AS, for assistance with the search strategy; Academic Librarian Elin Opheim at the Inland Norway University of Applied Sciences for valuable peer review of the search strategy; and the Library at the Inland Norway University of Applied Sciences for their support. Additionally, we acknowledge the assistance provided by OpenAI’s ChatGPT for support with translations and language refinement.
Open access funding provided by Inland Norway University Of Applied Sciences The study forms a part of a collaborative PhD project funded by South-Eastern Norway Regional Health Authority through Innlandet Hospital Trust and the Inland University of Applied Sciences.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Mental Health Department, Innlandet Hospital Trust, P.B 104, Brumunddal, 2381, Norway
Cathrine W. Steen & Kerstin Söderström
Inland Norway University of Applied Sciences, P.B. 400, Elverum, 2418, Norway
Cathrine W. Steen, Kerstin Söderström & Inger Beate Nylund
Norwegian National Advisory Unit On Concurrent Substance Abuse and Mental Health Disorders, Innlandet Hospital Trust, P.B 104, Brumunddal, 2381, Norway
Bjørn Stensrud
Akershus University Hospital, P.B 1000, Lørenskog, 1478, Norway
Johan Siqveland
National Centre for Suicide Research and Prevention, Oslo, 0372, Norway
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
CWS, KS, BS, and JS collaboratively designed the study. CWS and JS collected and analysed the data and were primarily responsible for writing the manuscript text. All authors contributed to the development of the search strategy. IBN conducted the literature searches and authored the chapter on the search strategy in the manuscript. All authors reviewed, gave feedback, and granted their final approval of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Cathrine W. Steen .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable .
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: table 2..
Effects of VR training in the included studies: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and non-randomized studies (NRSs).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Steen, C.W., Söderström, K., Stensrud, B. et al. The effectiveness of virtual reality training on knowledge, skills and attitudes of health care professionals and students in assessing and treating mental health disorders: a systematic review. BMC Med Educ 24 , 480 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05423-0
Download citation
Received : 19 January 2024
Accepted : 12 April 2024
Published : 01 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05423-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Health care professionals
- Health care students
- Virtual reality
- Mental health
- Clinical skills
- Systematic review
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

COMMENTS
109 Virtual Reality Topics & Essay Examples. Updated: Mar 2nd, 2024. 8 min. When writing a virtual reality essay, it is hard to find just one area to focus on. Our experts have outlined 104 titles for you to choose from. We will write.
28 essay samples found. Virtual Reality (VR), a simulated experience that can resemble or be entirely different from the real world, has made significant strides with applications in gaming, education, healthcare, and more. Essays on VR might delve into its technological advancements, its applications, and the societal, ethical, and ...
Virtual reality and educational games are two gaming areas that undergo active development at the moment, and there is a possibility that the use of VR in edutainment may be beneficial for education quality. In this thesis, we studied an impact that virtual reality might have on the effectiveness of some types of a game-based education.
Virtual reality (VR) refers to a computer-generated, three-dimensional virtual environment that users can interact with, typically accessed via a computer that is capable of projecting 3D information via a display, which can be isolated screens or a wearable display, e.g., a head-mounted display (HMD), along with user identification sensors .
Make And Answer Some Qs Also Thesis Example. - Thesis: Human's intelligence in visual reality world: Tron and the Matrix. - The thesis goes further to provide information on how Tron was designed, works, and its associated dangers. It portrays the matrix as a controller of both the virtual as well as the real world.
• Human-centeredcomputing→ Userstudies; Virtual reality; Collaborative interaction. KEYWORDS virtual reality, co-located, social, low-cost, head-mounted display, body representation ACM Reference Format: Katy Madier. 2019. Enabling Low-cost Co-located Virtual Reality Experiences. In Master Thesis: University of Michigan, 2019, Ann Arbor, MI.
The effects of nature in virtual reality on psychological wellbeing Chan, Sarah Hian May 2021 Chan, S. H. M. (2021). ... Authorship Attribution Statement This thesis contains material from 2 papers published in the following ... Few people would challenge the notion that nature is good for us.
This thesis is the final academic project in the master's program in Innovation through Business, Engineering, and Design, with a specialization in business ... Metaverse is a virtual reality idea where people create avatars that exist in a three-dimensional virtual world. While the use of virtual realities
To this aim, in this dissertation, I explore the intersections between learning and immersive virtual technology, in an attempt to uncover ways to design more effective virtual tools for learning ...
Developments in Virtual Reality (VR) technology are currently arousing great scientific interest because in just a few years, VR has found its niche not only in the specialised public, but also in ...
Abstract. Engineering is the shrewd application of science to the exploitation and transformation. of natural resources for the benefit of humanity. Humankind has always resorted to engineering. in order to overcome limitations, overpower challenges and improve life in the planet. In recent.
Virtual reality is an emerging technology that has existed for some time, allowing both the hardware and software to become refined. ... mapping out current uses and identifying potential areas for application. Furthermore, the thesis explores how virtual reality could be applied to enhance leadership development in organizations and what ...
Abstract. Virtual reality (VR) is a powerful and interactive technology that changes our life unlike any other. Virtual reality, which can also be termed as immersive multimedia, is the art of ...
2. COVID-19 Pandemic, Stress, and Mental Health Disturbances. Stress refers to positive and negative cognitive, emotional, behavioral, and biological responses to a perceived threat [18,19,20].Stress is also a common life sphere for the indicators for the measurement of quality of life (QoL) [].It gauges well-being [].A study suggested that one way of managing stress is by taking time out to ...
Abstract. Virtual Reality (VR) is an experience where a person is provided with the freedom of viewing and moving in a virtual world [1]. The experience is not constrained to a limited control. Here, it was triggered interactively according to the user's physical movement [1] [2]. So the user feels as if they are seeing the real world; also ...
This thesis is two-fold: First, state-of-the-art concepts for natural gazing behavior during conversations and, e.g., while thinking or ideling, should be enhanced by an environment-aware gazing. Therefore, e.g., recent research on gaze prediction for humans immersed in a virtual environment or shall be applied.
This thesis study is designed to document the process and analyze the results of a study conducted to determine the relationship between realism in rendering and the user's spatial memory of the space which was experienced when in virtual reality. This study is being developed in order to
Thesis Statement The primary objective of this research is to develop and investigate a user interface that supports learning to be implemented in the virtual reality application Anatomy Builder VR, an ongoing project from the Department of Visualization. Through the conception of this interface,
1.1. Statement of the Problem 1.2. Structure of the Thesis 1. BACKGROUND AND RELATED WORK 2.1. Learning Theories 2.1.1 Constructivism and Constructionism 2.1.2 Socio-cultural Theories 2.1.3 Cooperative Learning 2.1.4 Motivation 2.1.5 Narrative 2.2. Virtual Reality in Education 2.2.1 Networked Text-based Virtual Worlds 2.2.2 VR in the schools
2019, while most of the theses were completed as master's thesis. While theses on virtual reality are mostly completed at Bahçeşehir University, they intensify on the Department of Computer Education and Instructional Technology in terms of department type. In the theses, especially virtual reality game
Bachelor and Master Theses. We regularly offer proposals for bachelor and master thesis projects in all areas across our research activities and related subjects, which cover most topics in Virtual Reality and (Immersive) Visualization. The thesis topics are usually specified in cooperation with one of our research assistants or PostDocs and/or ...
Virtual reality (VR) training can enhance health professionals' learning. However, there are ambiguous findings on the effectiveness of VR as an educational tool in mental health. We therefore reviewed the existing literature on the effectiveness of VR training on health professionals' knowledge, skills, and attitudes in assessing and treating patients with mental health disorders.