This website is intended for healthcare professionals

- { $refs.search.focus(); })" aria-controls="searchpanel" :aria-expanded="open" class="hidden lg:inline-flex justify-end text-gray-800 hover:text-primary py-2 px-4 lg:px-0 items-center text-base font-medium"> Search

Search menu
Barker J, Linsley P, Kane R, 3rd edn. London: Sage; 2016
Ethical guidelines for educational research. 2018; https://tinyurl.com/c84jm5rt
Bowling A Research methods in health, 4th edn. Maidenhead: Open University Press/McGraw-Hill Education; 2014
Gliner JA, Morgan GAMahwah (NJ): Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2000
Critical Skills Appraisal Programme checklists. 2021; https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists
Cresswell J, 4th edn. London: Sage; 2013
Grainger A Principles of temperature monitoring. Nurs Stand. 2013; 27:(50)48-55 https://doi.org/10.7748/ns2013.08.27.50.48.e7242
Jupp VLondon: Sage; 2006
Continuing professional development (CPD). 2021; http://www.hcpc-uk.org/cpd
London: NHS England; 2017 http://www.hee.nhs.uk/our-work/advanced-clinical-practice
Kennedy M, Burnett E Hand hygiene knowledge and attitudes: comparisons between student nurses. Journal of Infection Prevention. 2011; 12:(6)246-250 https://doi.org/10.1177/1757177411411124
Lindsay-Smith G, O'Sullivan G, Eime R, Harvey J, van Ufflen JGZ A mixed methods case study exploring the impact of membership of a multi-activity, multi-centre community group on the social wellbeing of older adults. BMC Geriatrics. 2018; 18 https://bmcgeriatr.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/s12877-018-0913-1.pdf
Morse JM, Pooler C, Vann-Ward T Awaiting diagnosis of breast cancer: strategies of enduring for preserving self. Oncology Nursing Forum. 2014; 41:(4)350-359 https://doi.org/10.1188/14.ONF.350-359
Revalidation. 2019; http://revalidation.nmc.org.uk
Parahoo K Nursing research, principles, processes and issues, 3rd edn. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan; 2014
Polit DF, Beck CT Nursing research, 10th edn. Philadelphia (PA): Wolters Kluwer; 2017
Critiquing a published healthcare research paper
Angela Grainger
Nurse Lecturer/Scholarship Lead, BPP University, and editorial board member
View articles · Email Angela

Research is defined as a ‘systematic inquiry using orderly disciplined methods to answer questions or to solve problems' ( Polit and Beck, 2017 :743). Research requires academic discipline coupled with specific research competencies so that an appropriate study is designed and conducted, leading to the drawing of relevant conclusions relating to the explicit aim/s of the study.
Relevance of research to nursing and health care
For those embarking on a higher degree such as a master's, taught doctorate, or a doctor of philosophy, the relationship between research, knowledge production and knowledge utilisation becomes clear during their research tuition and guidance from their research supervisor. But why should other busy practitioners juggling a work/home life balance find time to be interested in healthcare research? The answer lies in the relationship between the outcomes of research and its relationship to the determination of evidence-based practice (EBP).
The Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC) and the Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) require registered practitioners to keep their knowledge and skills up to date. This requirement incorporates being aware of the current EBP relevant to the registrant's field of practice, and to consider its application in relation to the decisions made in the delivery of patient care.
Advanced clinical practitioners (ACPs) are required to be involved in aspects of research activities ( Health Education England, 2017 ). It is for this reason that practitioners need to know how EBP is influenced by research findings and, moreover, need to be able to read and interpret a research study that relates to a particular evidence base. Reading professional peer-reviewed journals that have an impact factor (the yearly average number of citations of papers published in a previous 2-year period in a given journal is calculated by a scientometric index giving an impact factor) is evidence of continuing professional development (CPD).
CPD fulfils part of the HCPC's and the NMC's required professional revalidation process ( HCPC, 2021 ; NMC, 2019 ). For CPD in relation to revalidation, practitioners can give the publication details of a research paper, along with a critique of that paper, highlighting the relevance of the paper's findings to the registrant's field of practice.
Defining evidence-based practice
According to Barker et al (2016:4.1) EBP is the integration of research evidence and knowledge to current clinical practice and is to be used at a local level to ensure that patients receive the best quality care available. Because patients are at the receiving end of EBP it is important that the research evidence is credible. This is why a research study has to be designed and undertaken rigorously in accordance with academic and scientific discipline.
The elements of EBP
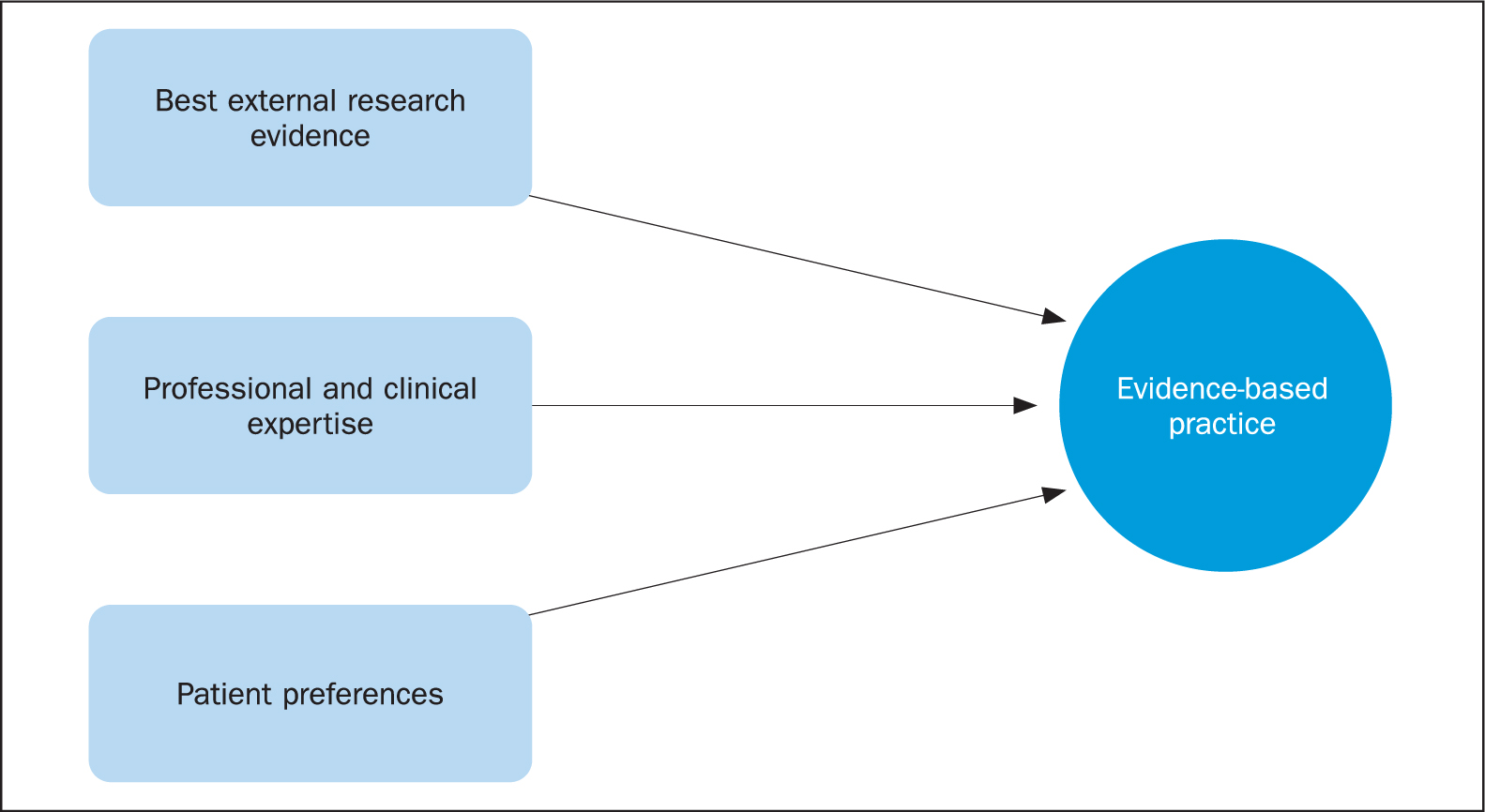
EBP comprises three elements ( Figure 1 ). The key element is research evidence, followed by the expert knowledge and professional opinion of the practitioner, which is important especially when there is no research evidence—for example, the most appropriate way to assist a patient out of bed, or perform a bed bath. Last, but in no way of least importance, is the patient's preference for a particular procedure. An example of this is the continued use of thermal screening dots for measuring a child's temperature on the forehead, or in the armpit because children find these options more acceptable than other temperature measuring devices, which, it is argued, might give a more accurate reading ( Grainger, 2013 ).
Understanding key research principles
To interpret a published research study requires an understanding of key research principles. Research authors use specific research terms in their publications to describe and to explain what they have done and why. So without an awareness of the research principles underpinning the study, how can readers know if what they are reading is credible?
Validity and reliability have long been the two pillars on which the quality of a research study has been judged ( Gliner and Morgan, 2000 ). Validity refers to how accurately a method measures what it is intended to measure. If a research study has a high validity, it means that it produces results that correspond to real properties, characteristics, and variations in the part of the physical or social world that is being studied ( Jupp, 2006 ).
Reliability is the extent to which a measuring instrument, for example, a survey using closed questions, gives the same consistent results when that survey is repeated. The measurement is considered reliable if the same result can be consistently achieved by using the same methods under the same circumstances ( Parahoo, 2014 ).
The research topic is known as the phenomenon in a singular sense, or phenomena if what is to be researched is plural. It is a key principle of research that it is the nature of the phenomenon, in association with the study's explicit research aim/s, that determines the research design. The research design refers to the overall structure or plan of the research ( Bowling, 2014 :166).
Methodology means the philosophy underpinning how the research will be conducted. It is essential for the study's research design that an appropriate methodology for the conduct and execution of the study is selected, otherwise the research will not meet the requirements of being valid and reliable. The research methods will include the design for data sampling, how recruitment into the study will be undertaken, the method/s used for the actual data collection, and the subsequent data analysis from which conclusions will be drawn (see Figure 2 ).

Quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods studies
A quantitative methodology is where the phenomenon lends itself to an investigation of data that can be numerically analysed using an appropriate statistical test/s. Quantitative research rests on the philosophical view that science has to be neutral and value-free, which is why precise measurement instruments are required ( Box 1 ). Quantitative research is influenced by the physical sciences such as mathematics, physics, and chemistry. The purpose of quantitative studies is to identify whether there are any causal relationships between variables present in the phenomenon. In short, a variable is an attribute that can vary and take on different values, such as the body temperature or the heart rate ( Polit and Beck, 2017 :748).
Quantitative studies can sometimes have a hypothesis. A hypothesis is a prediction of the study's outcome, and the aim of the study is to show either that the hypothesis is demonstrated as proven, or that it is not proven. Often a hypothesis is about a predicted relationship between variables. There are two types of variables, independent and dependent. An independent variable causes a change in the specific phenomenon being studied, while a dependent variable is the change in that phenomenon. The first example in Box 1 might help to clarify the difference.
An example of a hypothesis would be that older people who have a history of falls have a reduction in the incidence of falls due to exercise therapy. The causal relationship is between the independent variable— the exercise therapy—and the dependent variable—a falls reduction.
A qualitative methodology aims to explore a phenomenon with the aim of understanding the experience of the phenomenon from the perspective of those affected by it. Qualitative research is influenced by the social and not the physical sciences. Concepts and themes arise from the researcher/s interpretation of the data gained from observations and interviews. The collected data are non-numerical and this is the distinction from a quantitative study. The data collected are coded in accordance with the type of method being used in the research study, for example, discourse analysis; phenomenology; grounded theory. The researcher identifies themes from the data descriptions, and from the data analysis a theoretical understanding is seen to emerge.
A qualitative methodology rests on the philosophical view that science cannot be neutral and value-free because the researcher and the participants are part of the world that the research study aims to explore.
Unlike quantitative studies, the results of which can often be generalised due to the preciseness of the measuring instruments, qualitative studies are not usually generalisable. However, knowledge comparisons can be made between studies that have some similarity of focus. For example, the uncovering of causative or aggravating factors leading to the experiences of pain management for oncology patients, and for patients who have rheumatoid arthritis, or another long-term health problem for which pain is a characteristic feature. The validity of a qualitative study relates to the accurate representation of the data collected and analysed, and which shows that data has been saturated, meaning no new data or analysed findings are forthcoming. This is demonstrated in a clear data audit trail, and the study's findings are therefore seen as credible (see the second example in Box 1 ).
Box 1.Research study examples
- An example of a quantitative research study Kennedy and Burnett (2011) conducted a survey to determine whether there were any discernible differences in knowledge and attitudes between second- and third-year pre-registration nursing students toward hand-hygiene practices. The collected data and its subsequent analysis is presented in numerical tables and graphs, but these are supported by text explaining the research findings and how these were ascertained. For full details, see 10.1177/1757177411411124
- 2. An example of a qualitative research study Morse et al (2014) undertook an exploratory study to see what coping strategies were used by women awaiting a possible diagnosis of breast cancer. Direct quotes from the study participants appeared in the writing up of the research because it is a requirement of qualitative research that there be a transparent data audit trail. The research showed two things, both essential requirements of qualitative research. First, how the collected data were saturated to ensure that no data had been left inadequately explored, or that the data coding had been prematurely closed and, second, having captured the breadth and depth of the data findings, the researchers showed how the direct quotes were thematically coded to reveal the women's coping strategies. For full details, see 10.1188/14.ONF.350-359
- 3. An example of a mixed-methods study Lindsay-Smith et al (2018) investigated and explored the impact on elderly people's social wellbeing when they were members of a community that provided multi-activities. The study combined a quantitative survey that recorded participants' sociodemographic characteristics and measured participation in activities with a focus group study to gauge participants' perceptions of the benefits of taking part in the activities. For full details, see https://bmcgeriatr.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/s12877-018-0913-1.pdf
Sometimes a study cannot meet its stated research aims by using solely a quantitative or a qualitative methodology, so a mixed-methods approach combining both quantitative and qualitative methods for the collection and analysis of data are used. Cresswell (2013) explains that, depending on the aim and purpose of the study, it is possible to collect either the quantitative data first and analyse these, followed by the qualitative data and their analysis. This is an explanatory/exploratory sequence. Or the qualitative data may be collected first and analysed, followed by the quantitative; an exploratory/explanatory process. Whichever approach is used, the cumulative data analyses have to be synthesised to give a clear picture of the overall findings ( Box 1 ).
The issue of bias
Bias is a negative feature of research because it relates to either an error in the conceptualisation of the study due to the researcher/s adopting a skewed or idiosyncratic perspective, or to errors in the data analysis. Bias will affect the validity and reliability of a study, so it is important that any bias is eliminated in quantitative studies, or minimised and accounted for in qualitative studies.
Scientific and ethical approval
It should be noted that, before any research study proceeds, the research proposal for that study must have been reviewed and agreed to by a scientific and ethics committee. The purpose of a scientific and ethics committee is to see that those recruited into a study are not harmed or damaged, and that the study will contribute to the advancement of knowledge. The committee pays particular attention to whether any bias might have been introduced to a study. The researchers will have detailed the reason why the study is required, the explicit aim/s and purpose of the study, the methodology of the study, and its subsequent design, including the chosen research methods for the collection of the data (sampling and study recruitment), and what method/s will be used for data analysis.
A literature review is undertaken and the established (published) international literature on the research topic is summarised to highlight what is already known on the topic and/or to show any topic gaps that have not yet been researched. The British Educational Research Association (BERA) (2018) also gives guidance for research proposals that are deemed to be educational evaluation studies, including ‘close-practice’ research studies. Any ethical issues such as how people will be recruited into the study, the gaining of informed voluntary consent, any conflict of interest between the researcher/s and the proposed research topic, and whether the research is being funded or financially supported by a particular source will also have been considered.
Critiquing a published research paper
It is important to remember that a published paper is not the research report. It is a sample of the research report. The research author/s are presenting their research findings as a succinct summary. Only a passing mention might be made that ethical approval and voluntary informed consent were obtained. However, readers can be assured that all publications in leading journals with a good reputation are subject to an external peer review process. Any concerns about a paper's content will have been ironed out prior to publication.
It will be apparent that there are several particular research designs. The Critical Skills Appraisal Programme (CASP) provides online information to help the interpretation of each type of study, and does this by providing questions to help the reader consider and critique the paper ( CASP, 2021 ).
General points for critiquing a paper include the following:
- The paper should be readable and have explicit statements on the purpose of the research, its chosen methodology and design
- Read the paper thoroughly to get a feel for what the paper is saying
- Consider what the researcher/s says about any ethical issues and how these have been handled
- Look at how the data were collected and analysed. Are the explanations for these aspects clear? In a quantitative study, are any graphs or charts easy to understand and is there supporting text to aid the interpretation of the data? In a qualitative study, are direct quotes from the research participants included, and do the researcher/s show how data collected from interviews and observations were coded into data categories and themes?
- In a mixed-method study, how are the quantitative and qualitative analyses synthesised?
- Do the conclusions seem to fit the handling of the data's analysis?
- An important test of validity is whether the study's title relates well to the content of the paper and, conversely, whether the content reflect a corresponding match to the study's title.
Finally, remember that the research study could have been conducted using a different methodological design provided the research aims would still have been met, but a critique of the paper relates to what has been published and not what otherwise might have been done.

Reading and critiquing a research article
Nurses use research to answer questions about their practice, solve problems, improve the quality of patient care, generate new research questions, and shape health policy. Nurses who confront questions about practice and policy need strong, high-quality, evidence-based research. Research articles in peer-reviewed journals typically undergo a rigorous review process to ensure scholarly standards are met. Nonetheless, standards vary among reviewers and journals. This article presents a framework nurses can use to read and critique a research article.
When deciding to read an article, determine if it’s about a question you have an interest in or if it can be of use in your practice. You may want to have a research article available to read and critique as you consider the following questions.
Does the title accurately describe the article?
A good title will pique your interest but typically you will not know until you are done reading the article if the title is an accurate description. An informative title conveys the article’s key concepts, methods, and variables.
Is the abstract representative of the article?
The abstract provides a brief overview of the purpose of the study, research questions, methods, results, and conclusions. This helps you decide if it’s an article you want to read. Some people use the abstract to discuss a study and never read further. This is unwise because the abstract is just a preview of the article and may be misleading.
Does the introduction make the purpose of the article clear?
A good introduction provides the basis for the article. It includes a statement of the problem, a rationale for the study, and the research questions. When a hypothesis is being tested, it should be clearly stated and include the expected results.
Is a theoretical framework described?
When a theoretical framework is used, it should inform the study and provide a rationale. The concepts of the theoretical framework should relate to the topic and serve as a basis for interpreting the results. Some research doesn’t use a theoretical framework, such as health services research, which examines issues such as access to care, healthcare costs, and healthcare delivery. Clinical research such as comparing the effectiveness of two drugs won’t include a theoretical framework.
Is the literature review relevant to the study and comprehensive? Does it include recent research?
The literature review provides a context for the study. It establishes what is, and is not known about the research problem. Publication dates are important but there are caveats. Most literature reviews include articles published within the last 3 to 5 years. It can take more than a year for an article to be reviewed, revised, accepted, and published, causing some references to seem outdated.
Literature reviews may include older studies to demonstrate important changes in knowledge over time. In an area of study where little or no research has been conducted, there may be only a few relevant articles that are a decade or more old. In an emerging area of study there may be no published research, in which case related research should be referenced. If you are familiar with the area of research, review the references to determine if well-known and highly regarded studies are included.
Does the methods section explain how a research question was addressed?
The methods section provides enough information to allow the study to be replicated. Components of this section indicate if the design is appropriate to answer the research question(s).
- Did the researcher select the correct sample to answer the research questions and was the size sufficient to obtain valid results?
- If a data collection instrument was used, how was it created and validated?
- If any materials were used, such as written guides or equipment, were they described?
- How were data collected?
- Was reliability and validity accounted for?
- Were the procedures listed in a step-by-step manner?
Independent and dependent variables should be described and terms defined. For example, if patient falls in the hospital are considered the dependent variable, or outcome, what are the independent variables, or factors, being investigated that may influence the rate at which patient falls occur? In this example, independent variables might include nurse staffing, registered nurse composition (such as education and certification), and hospital Magnet ® status.
Is the analytical approach consistent with the study questions and research design?
The analytical approach relates to the study questions and research design. A quantitative study may use descriptive statistics to summarize the data and other tests, such as chi squares, t-tests, or regression analysis, to compare or evaluate the data. A qualitative study may use such approaches as coding, content analysis, or grounded theory analysis. A reader who is unfamiliar with the analytical approach may choose to rely on the expertise of the journal’s peer reviewers who assessed whether the analytical approach was correct.
Are the results presented clearly in the text and in tables and figures?
Results should be clearly summarized in the text, tables, and figures. Tables and figures are only a partial representation of the results and critical information may be only in the text. In a quantitative study, the significance of the statistical tests is important. The presentation of qualitative results should avoid interpretation, which is reserved for the discussion.
Are the limitations presented and their implications discussed?
It is essential that the limitations of the study be presented. These are the factors that explain why the results may need to be carefully interpreted, may only be generalized to certain situations, or may provide less robust results than anticipated. Examples of limitations include a low response rate to a survey, not being able to establish causality when a cross-sectional study design was used, and having key stakeholders refuse to be interviewed.
Does the discussion explain the results in relation to the theoretical framework, research questions, and significance of the study?
The discussion serves as an opportunity to explain the results in respect to the research questions and the theoretical framework. Authors use the discussion to interpret the results and explain the meaning and significance of the study. It’s also important to distinguish the study from others that preceded it and provide recommendations for future research.
Depending on the research, it may be equally important for the investigators to present the clinical and/or practical significance of the results. Relevant policy recommendations are also important. Evaluate if the recommendations are supported by the data or seem to be more of an opinion. A succinct conclusion typically completes the article.
Once you’re done reading the article, how do you decide if the research is something you want to use?
Determine the scientific merit of the study by evaluating the level and quality of the evidence. There are many scales to use, several of which can be found in the Research Toolkit on the American Nurses Association’s website http://www.nursingworld.org/research-toolkit.aspx . Consider what you learned and decide if the study is relevant to your practice or answered your question as well as whether you can implement the findings.
A new skill
A systematic approach to reading and critiquing a research article serves as a foundation for translating evidence into practice and policy. Every nurse can acquire this skill.
Louise Kaplan is director of the nursing program at Saint Martin’s University in Lacey, Washington. At the end of this article is a checklist for evaluating an article.
Selected references
Hudson-Barr D. How to read a research article. J Spec Pediatr Nurs . 2004;9(2):70-2.
King’s College D. Leonard Corgan Library. Reading a research article. http://www.lib.jmu.edu/ilworkshop08/materials/studyguide3.pdf . Accessed September 5, 2012.
Oliver D, Mahon SM. Reading a research article part I: Types of variables. Clin J Oncol Nurs . 2005;9(1):110-12.
Oliver D, Mahon SM. Reading a research article part II: Parametric and nonparametric statistics. Clin J Oncol Nurs . 2005;9(2):238-240.
Oliver D, Mahon SM. Reading a research article part III: The data collection instrument. Clin J Oncol Nurs . 2006;10(3):423-26.
Rumrill P, Fitzgerald S, Ware, M. Guidelines for evaluating research articles. Work . 2000;14(3):257-63.
15 Comments .
very helpful resource to critique any research article
I like it helped me a lot in my critical appraisal. thank you very much.
This article will help me with my understanding of how to read and critique a research article. This article was helpful in breaking down this information very basic to get a clear, concise understanding. Now I can take this information and go to the next level in my discussions
Great information and I will use this article for future reference.
This checklist and explanation for a literature review and/or reading and critiquing a research article was very helpful. As I only have 2 more classes to get my degree, I wish I knew this info 2 semesters ago! I will also pass this along to coworkers that will be going back to school in the near future.
Great article, I enjoyed the information. Thank You for this resource. Carolyn Martinez
Fantastic guide to the interpretation of clinical trials. Found this so helpful!
Great information and article. Thank you for the information.
well explained. its sometimes hard for P.G students to understand the concept but these guidelines are helpful to learn for novice.
This is great,am looking for guilgline on how to do research critique and this is just the solution.Thnks weldone
Unsure how to appropriately critique an article, thank you for your infomation
I am currently taking a Health Service Research course and was not sure how to sturcture my assignment. Thanks for posting this article!
very informative…very helpful to students doing research work.
Great timing; have just been asked to review and article and you provide the guide! Will share with colleagues.
I will be passing this article on to a friend who is taking a nursing research class. This article is a great reference for nursing students.
Comments are closed.

NurseLine Newsletter
- First Name *
- Last Name *
- Hidden Referrer
*By submitting your e-mail, you are opting in to receiving information from Healthcom Media and Affiliates. The details, including your email address/mobile number, may be used to keep you informed about future products and services.
Test Your Knowledge
Recent posts.

Effective clinical learning for nursing students

Nursing professional development at night

Engaging nurses in scholarly work

Mentorship matters

2023 nursing trends and salary survey results

NCLEX vs Next Generation

Patient care assistant training


Re-imagining nursing’s social contract with the public

Is there a nurse in the House? Or the Senate?

Prevent compassion fatigue through self-compassion

Implementing trauma-informed care

Addressing transgender myths

Motivate Gen Z nursing students

Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome

Pulmonary hypertension: Consider the “zebra”
Making sense of research: A guide for critiquing a paper
Affiliation.
- 1 School of Nursing, Griffith University, Meadowbrook, Queensland.
- PMID: 16114192
- DOI: 10.5172/conu.14.1.38
Learning how to critique research articles is one of the fundamental skills of scholarship in any discipline. The range, quantity and quality of publications available today via print, electronic and Internet databases means it has become essential to equip students and practitioners with the prerequisites to judge the integrity and usefulness of published research. Finding, understanding and critiquing quality articles can be a difficult process. This article sets out some helpful indicators to assist the novice to make sense of research.
Writing, reading, and critiquing reviews
Écrire, lire et revue critique, douglas archibald.
1 University of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada;
Maria Athina Martimianakis
2 University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Why reviews matter
What do all authors of the CMEJ have in common? For that matter what do all health professions education scholars have in common? We all engage with literature. When you have an idea or question the first thing you do is find out what has been published on the topic of interest. Literature reviews are foundational to any study. They describe what is known about given topic and lead us to identify a knowledge gap to study. All reviews require authors to be able accurately summarize, synthesize, interpret and even critique the research literature. 1 , 2 In fact, for this editorial we have had to review the literature on reviews . Knowledge and evidence are expanding in our field of health professions education at an ever increasing rate and so to help keep pace, well written reviews are essential. Though reviews may be difficult to write, they will always be read. In this editorial we survey the various forms review articles can take. As well we want to provide authors and reviewers at CMEJ with some guidance and resources to be able write and/or review a review article.
What are the types of reviews conducted in Health Professions Education?
Health professions education attracts scholars from across disciplines and professions. For this reason, there are numerous ways to conduct reviews and it is important to familiarize oneself with these different forms to be able to effectively situate your work and write a compelling rationale for choosing your review methodology. 1 , 2 To do this, authors must contend with an ever-increasing lexicon of review type articles. In 2009 Grant and colleagues conducted a typology of reviews to aid readers makes sense of the different review types, listing fourteen different ways of conducting reviews, not all of which are mutually exclusive. 3 Interestingly, in their typology they did not include narrative reviews which are often used by authors in health professions education. In Table 1 , we offer a short description of three common types of review articles submitted to CMEJ.
Three common types of review articles submitted to CMEJ
More recently, authors such as Greenhalgh 4 have drawn attention to the perceived hierarchy of systematic reviews over scoping and narrative reviews. Like Greenhalgh, 4 we argue that systematic reviews are not to be seen as the gold standard of all reviews. Instead, it is important to align the method of review to what the authors hope to achieve, and pursue the review rigorously, according to the tenets of the chosen review type. Sometimes it is helpful to read part of the literature on your topic before deciding on a methodology for organizing and assessing its usefulness. Importantly, whether you are conducting a review or reading reviews, appreciating the differences between different types of reviews can also help you weigh the author’s interpretation of their findings.
In the next section we summarize some general tips for conducting successful reviews.
How to write and review a review article
In 2016 David Cook wrote an editorial for Medical Education on tips for a great review article. 13 These tips are excellent suggestions for all types of articles you are considering to submit to the CMEJ. First, start with a clear question: focused or more general depending on the type of review you are conducting. Systematic reviews tend to address very focused questions often summarizing the evidence of your topic. Other types of reviews tend to have broader questions and are more exploratory in nature.
Following your question, choose an approach and plan your methods to match your question…just like you would for a research study. Fortunately, there are guidelines for many types of reviews. As Cook points out the most important consideration is to be sure that the methods you follow lead to a defensible answer to your review question. To help you prepare for a defensible answer there are many guides available. For systematic reviews consult PRISMA guidelines ; 13 for scoping reviews PRISMA-ScR ; 14 and SANRA 15 for narrative reviews. It is also important to explain to readers why you have chosen to conduct a review. You may be introducing a new way for addressing an old problem, drawing links across literatures, filling in gaps in our knowledge about a phenomenon or educational practice. Cook refers to this as setting the stage. Linking back to the literature is important. In systematic reviews for example, you must be clear in explaining how your review builds on existing literature and previous reviews. This is your opportunity to be critical. What are the gaps and limitations of previous reviews? So, how will your systematic review resolve the shortcomings of previous work? In other types of reviews, such as narrative reviews, its less about filling a specific knowledge gap, and more about generating new research topic areas, exposing blind spots in our thinking, or making creative new links across issues. Whatever, type of review paper you are working on, the next steps are ones that can be applied to any scholarly writing. Be clear and offer insight. What is your main message? A review is more than just listing studies or referencing literature on your topic. Lead your readers to a convincing message. Provide commentary and interpretation for the studies in your review that will help you to inform your conclusions. For systematic reviews, Cook’s final tip is most likely the most important– report completely. You need to explain all your methods and report enough detail that readers can verify the main findings of each study you review. The most common reasons CMEJ reviewers recommend to decline a review article is because authors do not follow these last tips. In these instances authors do not provide the readers with enough detail to substantiate their interpretations or the message is not clear. Our recommendation for writing a great review is to ensure you have followed the previous tips and to have colleagues read over your paper to ensure you have provided a clear, detailed description and interpretation.
Finally, we leave you with some resources to guide your review writing. 3 , 7 , 8 , 10 , 11 , 16 , 17 We look forward to seeing your future work. One thing is certain, a better appreciation of what different reviews provide to the field will contribute to more purposeful exploration of the literature and better manuscript writing in general.
In this issue we present many interesting and worthwhile papers, two of which are, in fact, reviews.
Major Contributions
A chance for reform: the environmental impact of travel for general surgery residency interviews by Fung et al. 18 estimated the CO 2 emissions associated with traveling for residency position interviews. Due to the high emissions levels (mean 1.82 tonnes per applicant), they called for the consideration of alternative options such as videoconference interviews.
Understanding community family medicine preceptors’ involvement in educational scholarship: perceptions, influencing factors and promising areas for action by Ward and team 19 identified barriers, enablers, and opportunities to grow educational scholarship at community-based teaching sites. They discovered a growing interest in educational scholarship among community-based family medicine preceptors and hope the identification of successful processes will be beneficial for other community-based Family Medicine preceptors.
Exploring the global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on medical education: an international cross-sectional study of medical learners by Allison Brown and team 20 studied the impact of COVID-19 on medical learners around the world. There were different concerns depending on the levels of training, such as residents’ concerns with career timeline compared to trainees’ concerns with the quality of learning. Overall, the learners negatively perceived the disruption at all levels and geographic regions.
The impact of local health professions education grants: is it worth the investment? by Susan Humphrey-Murto and co-authors 21 considered factors that lead to the publication of studies supported by local medical education grants. They identified several factors associated with publication success, including previous oral or poster presentations. They hope their results will be valuable for Canadian centres with local grant programs.
Exploring the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on medical learner wellness: a needs assessment for the development of learner wellness interventions by Stephana Cherak and team 22 studied learner-wellness in various training environments disrupted by the pandemic. They reported a negative impact on learner wellness at all stages of training. Their results can benefit the development of future wellness interventions.
Program directors’ reflections on national policy change in medical education: insights on decision-making, accreditation, and the CanMEDS framework by Dore, Bogie, et al. 23 invited program directors to reflect on the introduction of the CanMEDS framework into Canadian postgraduate medical education programs. Their survey revealed that while program directors (PDs) recognized the necessity of the accreditation process, they did not feel they had a voice when the change occurred. The authors concluded that collaborations with PDs would lead to more successful outcomes.
Experiential learning, collaboration and reflection: key ingredients in longitudinal faculty development by Laura Farrell and team 24 stressed several elements for effective longitudinal faculty development (LFD) initiatives. They found that participants benefited from a supportive and collaborative environment while trying to learn a new skill or concept.
Brief Reports
The effect of COVID-19 on medical students’ education and wellbeing: a cross-sectional survey by Stephanie Thibaudeau and team 25 assessed the impact of COVID-19 on medical students. They reported an overall perceived negative impact, including increased depressive symptoms, increased anxiety, and reduced quality of education.
In Do PGY-1 residents in Emergency Medicine have enough experiences in resuscitations and other clinical procedures to meet the requirements of a Competence by Design curriculum? Meshkat and co-authors 26 recorded the number of adult medical resuscitations and clinical procedures completed by PGY1 Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians in Emergency Medicine residents to compare them to the Competence by Design requirements. Their study underscored the importance of monitoring collection against pre-set targets. They concluded that residency program curricula should be regularly reviewed to allow for adequate clinical experiences.
Rehearsal simulation for antenatal consults by Anita Cheng and team 27 studied whether rehearsal simulation for antenatal consults helped residents prepare for difficult conversations with parents expecting complications with their baby before birth. They found that while rehearsal simulation improved residents’ confidence and communication techniques, it did not prepare them for unexpected parent responses.
Review Papers and Meta-Analyses
Peer support programs in the fields of medicine and nursing: a systematic search and narrative review by Haykal and co-authors 28 described and evaluated peer support programs in the medical field published in the literature. They found numerous diverse programs and concluded that including a variety of delivery methods to meet the needs of all participants is a key aspect for future peer-support initiatives.
Towards competency-based medical education in addictions psychiatry: a systematic review by Bahji et al. 6 identified addiction interventions to build competency for psychiatry residents and fellows. They found that current psychiatry entrustable professional activities need to be better identified and evaluated to ensure sustained competence in addictions.
Six ways to get a grip on leveraging the expertise of Instructional Design and Technology professionals by Chen and Kleinheksel 29 provided ways to improve technology implementation by clarifying the role that Instructional Design and Technology professionals can play in technology initiatives and technology-enhanced learning. They concluded that a strong collaboration is to the benefit of both the learners and their future patients.
In his article, Seven ways to get a grip on running a successful promotions process, 30 Simon Field provided guidelines for maximizing opportunities for successful promotion experiences. His seven tips included creating a rubric for both self-assessment of likeliness of success and adjudication by the committee.
Six ways to get a grip on your first health education leadership role by Stasiuk and Scott 31 provided tips for considering a health education leadership position. They advised readers to be intentional and methodical in accepting or rejecting positions.
Re-examining the value proposition for Competency-Based Medical Education by Dagnone and team 32 described the excitement and controversy surrounding the implementation of competency-based medical education (CBME) by Canadian postgraduate training programs. They proposed observing which elements of CBME had a positive impact on various outcomes.
You Should Try This
In their work, Interprofessional culinary education workshops at the University of Saskatchewan, Lieffers et al. 33 described the implementation of interprofessional culinary education workshops that were designed to provide health professions students with an experiential and cooperative learning experience while learning about important topics in nutrition. They reported an enthusiastic response and cooperation among students from different health professional programs.
In their article, Physiotherapist-led musculoskeletal education: an innovative approach to teach medical students musculoskeletal assessment techniques, Boulila and team 34 described the implementation of physiotherapist-led workshops, whether the workshops increased medical students’ musculoskeletal knowledge, and if they increased confidence in assessment techniques.
Instagram as a virtual art display for medical students by Karly Pippitt and team 35 used social media as a platform for showcasing artwork done by first-year medical students. They described this shift to online learning due to COVID-19. Using Instagram was cost-saving and widely accessible. They intend to continue with both online and in-person displays in the future.
Adapting clinical skills volunteer patient recruitment and retention during COVID-19 by Nazerali-Maitland et al. 36 proposed a SLIM-COVID framework as a solution to the problem of dwindling volunteer patients due to COVID-19. Their framework is intended to provide actionable solutions to recruit and engage volunteers in a challenging environment.
In Quick Response codes for virtual learner evaluation of teaching and attendance monitoring, Roxana Mo and co-authors 37 used Quick Response (QR) codes to monitor attendance and obtain evaluations for virtual teaching sessions. They found QR codes valuable for quick and simple feedback that could be used for many educational applications.
In Creation and implementation of the Ottawa Handbook of Emergency Medicine Kaitlin Endres and team 38 described the creation of a handbook they made as an academic resource for medical students as they shift to clerkship. It includes relevant content encountered in Emergency Medicine. While they intended it for medical students, they also see its value for nurses, paramedics, and other medical professionals.
Commentary and Opinions
The alarming situation of medical student mental health by D’Eon and team 39 appealed to medical education leaders to respond to the high numbers of mental health concerns among medical students. They urged leaders to address the underlying problems, such as the excessive demands of the curriculum.
In the shadows: medical student clinical observerships and career exploration in the face of COVID-19 by Law and co-authors 40 offered potential solutions to replace in-person shadowing that has been disrupted due to the COVID-19 pandemic. They hope the alternatives such as virtual shadowing will close the gap in learning caused by the pandemic.
Letters to the Editor
Canadian Federation of Medical Students' response to “ The alarming situation of medical student mental health” King et al. 41 on behalf of the Canadian Federation of Medical Students (CFMS) responded to the commentary by D’Eon and team 39 on medical students' mental health. King called upon the medical education community to join the CFMS in its commitment to improving medical student wellbeing.
Re: “Development of a medical education podcast in obstetrics and gynecology” 42 was written by Kirubarajan in response to the article by Development of a medical education podcast in obstetrics and gynecology by Black and team. 43 Kirubarajan applauded the development of the podcast to meet a need in medical education, and suggested potential future topics such as interventions to prevent learner burnout.
Response to “First year medical student experiences with a clinical skills seminar emphasizing sexual and gender minority population complexity” by Kumar and Hassan 44 acknowledged the previously published article by Biro et al. 45 that explored limitations in medical training for the LGBTQ2S community. However, Kumar and Hassen advocated for further progress and reform for medical training to address the health requirements for sexual and gender minorities.
In her letter, Journey to the unknown: road closed!, 46 Rosemary Pawliuk responded to the article, Journey into the unknown: considering the international medical graduate perspective on the road to Canadian residency during the COVID-19 pandemic, by Gutman et al. 47 Pawliuk agreed that international medical students (IMGs) do not have adequate formal representation when it comes to residency training decisions. Therefore, Pawliuk challenged health organizations to make changes to give a voice in decision-making to the organizations representing IMGs.
In Connections, 48 Sara Guzman created a digital painting to portray her approach to learning. Her image of a hand touching a neuron showed her desire to physically see and touch an active neuron in order to further understand the brain and its connections.
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 22, Issue 1
- How to appraise qualitative research
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Calvin Moorley 1 ,
- Xabi Cathala 2
- 1 Nursing Research and Diversity in Care, School of Health and Social Care , London South Bank University , London , UK
- 2 Institute of Vocational Learning , School of Health and Social Care, London South Bank University , London , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Calvin Moorley, Nursing Research and Diversity in Care, School of Health and Social Care, London South Bank University, London SE1 0AA, UK; Moorleyc{at}lsbu.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2018-103044
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
In order to make a decision about implementing evidence into practice, nurses need to be able to critically appraise research. Nurses also have a professional responsibility to maintain up-to-date practice. 1 This paper provides a guide on how to critically appraise a qualitative research paper.
What is qualitative research?
- View inline
Useful terms
Some of the qualitative approaches used in nursing research include grounded theory, phenomenology, ethnography, case study (can lend itself to mixed methods) and narrative analysis. The data collection methods used in qualitative research include in depth interviews, focus groups, observations and stories in the form of diaries or other documents. 3
Authenticity
Title, keywords, authors and abstract.
In a previous paper, we discussed how the title, keywords, authors’ positions and affiliations and abstract can influence the authenticity and readability of quantitative research papers, 4 the same applies to qualitative research. However, other areas such as the purpose of the study and the research question, theoretical and conceptual frameworks, sampling and methodology also need consideration when appraising a qualitative paper.
Purpose and question
The topic under investigation in the study should be guided by a clear research question or a statement of the problem or purpose. An example of a statement can be seen in table 2 . Unlike most quantitative studies, qualitative research does not seek to test a hypothesis. The research statement should be specific to the problem and should be reflected in the design. This will inform the reader of what will be studied and justify the purpose of the study. 5
Example of research question and problem statement
An appropriate literature review should have been conducted and summarised in the paper. It should be linked to the subject, using peer-reviewed primary research which is up to date. We suggest papers with a age limit of 5–8 years excluding original work. The literature review should give the reader a balanced view on what has been written on the subject. It is worth noting that for some qualitative approaches some literature reviews are conducted after the data collection to minimise bias, for example, in grounded theory studies. In phenomenological studies, the review sometimes occurs after the data analysis. If this is the case, the author(s) should make this clear.
Theoretical and conceptual frameworks
Most authors use the terms theoretical and conceptual frameworks interchangeably. Usually, a theoretical framework is used when research is underpinned by one theory that aims to help predict, explain and understand the topic investigated. A theoretical framework is the blueprint that can hold or scaffold a study’s theory. Conceptual frameworks are based on concepts from various theories and findings which help to guide the research. 6 It is the researcher’s understanding of how different variables are connected in the study, for example, the literature review and research question. Theoretical and conceptual frameworks connect the researcher to existing knowledge and these are used in a study to help to explain and understand what is being investigated. A framework is the design or map for a study. When you are appraising a qualitative paper, you should be able to see how the framework helped with (1) providing a rationale and (2) the development of research questions or statements. 7 You should be able to identify how the framework, research question, purpose and literature review all complement each other.
There remains an ongoing debate in relation to what an appropriate sample size should be for a qualitative study. We hold the view that qualitative research does not seek to power and a sample size can be as small as one (eg, a single case study) or any number above one (a grounded theory study) providing that it is appropriate and answers the research problem. Shorten and Moorley 8 explain that three main types of sampling exist in qualitative research: (1) convenience (2) judgement or (3) theoretical. In the paper , the sample size should be stated and a rationale for how it was decided should be clear.
Methodology
Qualitative research encompasses a variety of methods and designs. Based on the chosen method or design, the findings may be reported in a variety of different formats. Table 3 provides the main qualitative approaches used in nursing with a short description.
Different qualitative approaches
The authors should make it clear why they are using a qualitative methodology and the chosen theoretical approach or framework. The paper should provide details of participant inclusion and exclusion criteria as well as recruitment sites where the sample was drawn from, for example, urban, rural, hospital inpatient or community. Methods of data collection should be identified and be appropriate for the research statement/question.
Data collection
Overall there should be a clear trail of data collection. The paper should explain when and how the study was advertised, participants were recruited and consented. it should also state when and where the data collection took place. Data collection methods include interviews, this can be structured or unstructured and in depth one to one or group. 9 Group interviews are often referred to as focus group interviews these are often voice recorded and transcribed verbatim. It should be clear if these were conducted face to face, telephone or any other type of media used. Table 3 includes some data collection methods. Other collection methods not included in table 3 examples are observation, diaries, video recording, photographs, documents or objects (artefacts). The schedule of questions for interview or the protocol for non-interview data collection should be provided, available or discussed in the paper. Some authors may use the term ‘recruitment ended once data saturation was reached’. This simply mean that the researchers were not gaining any new information at subsequent interviews, so they stopped data collection.
The data collection section should include details of the ethical approval gained to carry out the study. For example, the strategies used to gain participants’ consent to take part in the study. The authors should make clear if any ethical issues arose and how these were resolved or managed.
The approach to data analysis (see ref 10 ) needs to be clearly articulated, for example, was there more than one person responsible for analysing the data? How were any discrepancies in findings resolved? An audit trail of how the data were analysed including its management should be documented. If member checking was used this should also be reported. This level of transparency contributes to the trustworthiness and credibility of qualitative research. Some researchers provide a diagram of how they approached data analysis to demonstrate the rigour applied ( figure 1 ).
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Example of data analysis diagram.
Validity and rigour
The study’s validity is reliant on the statement of the question/problem, theoretical/conceptual framework, design, method, sample and data analysis. When critiquing qualitative research, these elements will help you to determine the study’s reliability. Noble and Smith 11 explain that validity is the integrity of data methods applied and that findings should accurately reflect the data. Rigour should acknowledge the researcher’s role and involvement as well as any biases. Essentially it should focus on truth value, consistency and neutrality and applicability. 11 The authors should discuss if they used triangulation (see table 2 ) to develop the best possible understanding of the phenomena.
Themes and interpretations and implications for practice
In qualitative research no hypothesis is tested, therefore, there is no specific result. Instead, qualitative findings are often reported in themes based on the data analysed. The findings should be clearly linked to, and reflect, the data. This contributes to the soundness of the research. 11 The researchers should make it clear how they arrived at the interpretations of the findings. The theoretical or conceptual framework used should be discussed aiding the rigour of the study. The implications of the findings need to be made clear and where appropriate their applicability or transferability should be identified. 12
Discussions, recommendations and conclusions
The discussion should relate to the research findings as the authors seek to make connections with the literature reviewed earlier in the paper to contextualise their work. A strong discussion will connect the research aims and objectives to the findings and will be supported with literature if possible. A paper that seeks to influence nursing practice will have a recommendations section for clinical practice and research. A good conclusion will focus on the findings and discussion of the phenomena investigated.
Qualitative research has much to offer nursing and healthcare, in terms of understanding patients’ experience of illness, treatment and recovery, it can also help to understand better areas of healthcare practice. However, it must be done with rigour and this paper provides some guidance for appraising such research. To help you critique a qualitative research paper some guidance is provided in table 4 .
Some guidance for critiquing qualitative research
- ↵ Nursing and Midwifery Council . The code: Standard of conduct, performance and ethics for nurses and midwives . 2015 https://www.nmc.org.uk/globalassets/sitedocuments/nmc-publications/nmc-code.pdf ( accessed 21 Aug 18 ).
- Barrett D ,
- Cathala X ,
- Shorten A ,
Patient consent for publication Not required.
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:

COMMENTS
Critique research articles mean careful and critical appraisal of strength and limitations of a piece of research, rather than hunting for and exposing mistake (Polt and Beck 2008). A critical review is an evaluation of an academic article or essay. It makes judgment, positive or negative, about the text using various criteria.
in nursing that care has its foundations in sound research and it is essential that all nurses have the ability to critically appraise research to identify what is best practice. This article is a step-by step-approach to critiquing quantitative research to help nurses demystify the process and decode the terminology. Key words: Quantitative ...
Critiquing a published healthcare research paper. 25 March 2021. Advanced Clinical Practice. Angela Grainger. 02 March 2021. Volume 30 · Issue 6. ISSN (print): 0966-0461. ISSN (online): 2052-2819. References.
Senior Policy Fellow, Department of Nursing Practice and Policy [email protected] Framework for How to Read and Critique a Research Study 1. Critiquing the research article a. Title - Does it accurately describe the article? b. Abstract - Is it representative of the article? c. Introduction - Does it make the purpose of the article ...
Critiquing Nursing Research. Defined. Critical evaluation/appraisal of research. studies through using specific criteria in. which the evaluator makes precise and. objective judgments about the ...
Introduction. Developing and maintaining proficiency in critiquing research have become a core skill in today's evidence-based nursing. In addition, understanding, synthesising and critiquing research are fundamental parts of all nursing curricula at both pre- and post-registration levels (NMC, 2011).This paper presents a guide, which has potential utility in both practice and when undertaking ...
The first step is to critique and appraise the research evidence. Through critiquing and appraising the research evidence, dialog with colleagues, and changing practice based on evidence, NPs can improve patient outcomes ( Dale, 2005) and successfully translate research into evidence-based practice in today's ever-changing health care ...
Reading and critiquing a research article. October 11, 2012. Nurses use research to answer questions about their practice, solve problems, improve the quality of patient care, generate new research questions, and shape health policy. Nurses who confront questions about practice and policy need strong, high-quality, evidence-based research.
Title, keywords and the authors. The title of a paper should be clear and give a good idea of the subject area. The title should not normally exceed 15 words 2 and should attract the attention of the reader. 3 The next step is to review the key words. These should provide information on both the ideas or concepts discussed in the paper and the ...
Abstract. When caring for patients, it is essential that nurses are using the current best practice. To determine what this is, nurses must be able to read research critically. But for many qualified and student nurses, the terminology used in research can be difficult to understand, thus making critical reading even more daunting.
Critiquing a published healthcare research paper. Critiquing a published healthcare research paper Br J Nurs. 2021 Mar 25;30(6):354-358. doi: 10.12968/bjon .2021.30 ... 1 Senior Nurse Lecturer-Research and Publications Lead, School of Nursing, BPP University, London. PMID: 33769869 DOI: 10.12968/bjon.2021.30.6.354 No abstract available ...
Abstract. Learning how to critique research articles is one of the fundamental skills of scholarship in any discipline. The range, quantity and quality of publications available today via print, electronic and Internet databases means it has become essential to equip students and practitioners with the prerequisites to judge the integrity and ...
Critique: Andrew P. Reimer. 10. Evaluation of a Meditation Intervention to Reduce the Effects of Stressors Associated With Compassion Fatigue Among Nurses. Critique: Jacqueline Rhoads and Joyce J. Fitzpatrick. 11. Patient Safety Culture and Nurse-Reported Adverse Events in Outpatient Hemodialysis Units.
The following paper is a critique of the research article, "The Use of Personal Digital Assistants at the Point of Care in an Undergraduate Nursing Program" (Goldsworthy, Lawrence, and Goodman, 2006). The purpose of this critique is to evaluate the content within each section of the article. The critique is guided by Nieswiadomy's ...
With a consistent, robust critiquing template, this content can easily be applied to countless additional research studies.Key Features:Comprises the only text to offer research critiques in nursingProvides actual examples of critiques of published research papers by experienced nurse researchers and educatorsShowcases a diverse range of ...
This is an example of how a critique for a peer-reviewed quantitative article should be done. It is quite very detailed as each section answers the questions. ... Nursing Research Critique #1 Sample Paper. Course: Medical Surgical Nursing (3343) 18 Documents. Students shared 18 documents in this course.
Critiquing a published healthcare research paper. Angela Grainger; Angela Grainger. Senior Nurse Lecturer-Research and Publications Lead, School of Nursing, BPP University, London. ... Nursing research, principles, processes and issues. 3rd edn. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan; 2014 Google Scholar; Polit DF, Beck CT.
Smith, A.A. (2010) Critique of a qualitative interview study of nursing pain management in hospitalized patients receiving cancer treatments. Res. Evid. Eval. 1:11-14 Critique of the Methodology Sampling The study clearly stated that they use a sample of convenience, which although a weak sampling method, was plainly and honestly stated. The
Critical appraisal is the assessment of research studies' worth to clinical practice. Critical appraisal—the heart of evidence-based practice—involves four phases: rapid critical appraisal, evaluation, synthesis, and recommendation. This article reviews each phase and provides examples, tips, and caveats to help evidence appraisers ...
Review Papers and Meta-Analyses. Peer support programs in the fields of medicine and nursing: a systematic search and narrative review by Haykal and co-authors 28 described and evaluated peer support programs in the medical field published in the literature. They found numerous diverse programs and concluded that including a variety of delivery ...
Critiquing nursing research. Categories: Nursing Research. Download. Essay, Pages 11 (2740 words) Views. 3072. Through the Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) code of professional conduct (NMC, 2004) nurses supply high standards of care to patients and clients. One code nurses adhere to is clause 6 which pronounces nurses must maintain ...
Use these guidelines to critique your selected research article to be included in your research proposal. You do not need to address all the questions indicated in this guideline, and only include the questions that apply. 2. Prepare your report as a paper with appropriate headings and use APA format 5thedition.
In order to make a decision about implementing evidence into practice, nurses need to be able to critically appraise research. Nurses also have a professional responsibility to maintain up-to-date practice.1 This paper provides a guide on how to critically appraise a qualitative research paper. Qualitative research concentrates on understanding phenomena and may focus on meanings, perceptions ...