

Research Basics
- What Is Research?
- Types of Research
- Secondary Research | Literature Review
- Developing Your Topic
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources
- Evaluating Sources
- Responsible Conduct of Research
- Additional Help

A good working definition of research might be:
Research is the deliberate, purposeful, and systematic gathering of data, information, facts, and/or opinions for the advancement of personal, societal, or overall human knowledge.
Based on this definition, we all do research all the time. Most of this research is casual research. Asking friends what they think of different restaurants, looking up reviews of various products online, learning more about celebrities; these are all research.
Formal research includes the type of research most people think of when they hear the term “research”: scientists in white coats working in a fully equipped laboratory. But formal research is a much broader category that just this. Most people will never do laboratory research after graduating from college, but almost everybody will have to do some sort of formal research at some point in their careers.
So What Do We Mean By “Formal Research?”
Casual research is inward facing: it’s done to satisfy our own curiosity or meet our own needs, whether that’s choosing a reliable car or figuring out what to watch on TV. Formal research is outward facing. While it may satisfy our own curiosity, it’s primarily intended to be shared in order to achieve some purpose. That purpose could be anything: finding a cure for cancer, securing funding for a new business, improving some process at your workplace, proving the latest theory in quantum physics, or even just getting a good grade in your Humanities 200 class.
What sets formal research apart from casual research is the documentation of where you gathered your information from. This is done in the form of “citations” and “bibliographies.” Citing sources is covered in the section "Citing Your Sources."
Formal research also follows certain common patterns depending on what the research is trying to show or prove. These are covered in the section “Types of Research.”
- Next: Types of Research >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 11:08 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.iit.edu/research_basics
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Do Research
Last Updated: March 13, 2023 References
This article was co-authored by Matthew Snipp, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . C. Matthew Snipp is the Burnet C. and Mildred Finley Wohlford Professor of Humanities and Sciences in the Department of Sociology at Stanford University. He is also the Director for the Institute for Research in the Social Science’s Secure Data Center. He has been a Research Fellow at the U.S. Bureau of the Census and a Fellow at the Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences. He has published 3 books and over 70 articles and book chapters on demography, economic development, poverty and unemployment. He is also currently serving on the National Institute of Child Health and Development’s Population Science Subcommittee. He holds a Ph.D. in Sociology from the University of Wisconsin—Madison. This article has been viewed 227,156 times.
The idea of doing research may seem daunting, but as long as you keep yourself organized and focus on the question you want to answer, you'll be fine. If you're curious and interested in the topic, you might even find it fun! We here at wikiHow have gathered answers to all your most common questions about how to do research, from finding a good topic to identifying the best sources and writing your final paper.
How do I find a topic to research?

- For example, if you're researching in the political science field, you might be interested in determining what leads people to believe that the 2020 US presidential election was illegitimate.
How do I get started on my research?

- For example, if you're researching the 2020 election, you might find that "absentee ballots" and "voting by mail" come up frequently. Those are issues you could look into further to figure out how they impacted the final election results.
- You don't necessarily have to use the overview articles you look at as resources in your actual paper. Even Wikipedia articles can be a good way to learn more about a topic and you can check the references for more reputable sources that might work for your paper.
What's the best way to keep track of my sources?

- Research papers typically discuss 2 or 3 separate things that work together to answer the research question. You might also want to make a note on the front of which thing that source relates to. That'll make it easier for you to organize your sources later.
- For example, if you're researching the 2020 election, you might have a section of your paper discussing voting by mail. For the sources that directly address that issue, write "voting by mail" in the corner.
What kind of notes should I be taking as I research?

- If you find something that you think would make a good quote, copy it out exactly with quote marks around it, then add the page number where it appears so you can correctly cite it in your paper without having to go back and hunt for it again.
How do I evaluate the quality of a source?

- Does the article discuss or reference another article? (If so, use that article instead.)
- What expertise or authority does the author have?
- When was the material written? (Is it the most up-to-date reference you could use?)
- Why was the article published? (Is it trying to sell you something or persuade you to adopt a certain viewpoint?)
- Are the research methods used consistent and reliable? (Appropriate research methods depend on what was studied.)
What if I'm having a hard time finding good sources?

- For example, if you're writing about the 2020 election, you might find tons of stories online, but very little that is reputable enough for you to use in your paper. Because the election happened so recently, it might be too soon for there to be a lot of solid academic research on it. Instead, you might focus on the 2016 election.
- You can also ask for help. Your instructor might be able to point you toward good sources. Research librarians are also happy to help you.
How do I organize my research for my paper?

- For example, if you're researching the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the 2020 election, you might have sections on social distancing and cleaning at in-person voting locations, the accessibility of mail-in ballots, and early voting.
What's the best way to start writing my paper?

- Include an in-text citation for everything that needs one, even in your initial rough draft. That'll help you make sure that you don't inadvertently misattribute or fail to cite something as you work your way through substantive drafts.
- Write your introduction and conclusion only after you're satisfied that the body of your paper is essentially what you want to turn in. Then, you can polish everything up for the final draft.
How can I make sure I'm not plagiarizing?

- If you have any doubt over whether you should cite something, go ahead and do it. You're better off to err on the side of over-citing than to look like you're taking credit for an idea that isn't yours.
- ↑ https://www.nhcc.edu/student-resources/library/doinglibraryresearch/basic-steps-in-the-research-process
- ↑ Matthew Snipp, PhD. Sociology Professor, Stanford University. Expert Interview. 26 March 2020.
- ↑ https://library.taylor.edu/eng-212/research-paper
- ↑ http://www.butte.edu/departments/cas/tipsheets/research/research_paper.html
- ↑ https://www.potsdam.edu/sites/default/files/documents/support/tutoring/cwc/6-Simple-Steps-for-Writing-a-Research-Paper.pdf
- ↑ https://www.umgc.edu/current-students/learning-resources/writing-center/online-guide-to-writing/tutorial/chapter4/ch4-05.html
Expert Q&A
You might also like.

About This Article

If you need to do research on a particular topic, start by searching the internet for any information you can find on the subject. In particular, look for sites that are sourced by universities, scientists, academic journals, and government agencies. Next, visit your local library and use the electric card catalog to research which books, magazines, and journals will have information on your topic. Take notes as you read, and write down all of the information you’ll need to cite your sources in your final project. To learn how interviewing a first-hand source can help you during your research, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Shenuka Ranawaka
Sep 16, 2016
Did this article help you?

Ismail El Omari
Mar 3, 2022

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services

- Virtual Tour
- Staff Directory
- En Español
You are here
Science, health, and public trust.
September 8, 2021
Explaining How Research Works
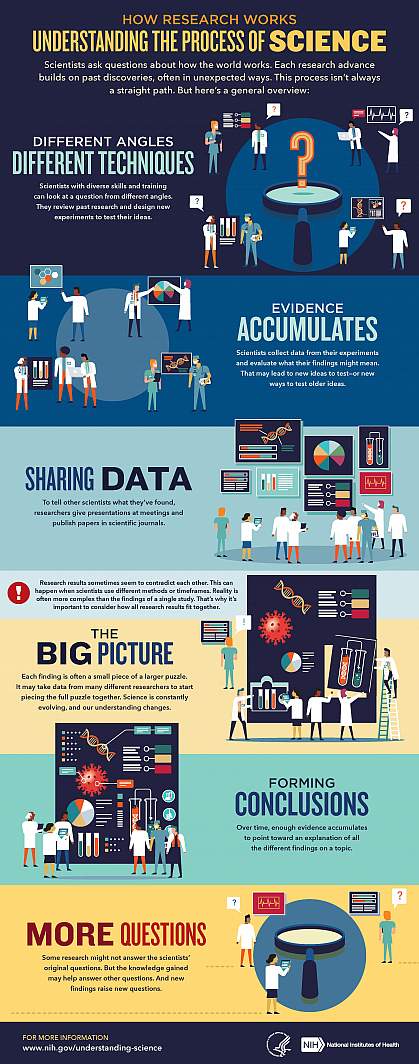
We’ve heard “follow the science” a lot during the pandemic. But it seems science has taken us on a long and winding road filled with twists and turns, even changing directions at times. That’s led some people to feel they can’t trust science. But when what we know changes, it often means science is working.

Explaining the scientific process may be one way that science communicators can help maintain public trust in science. Placing research in the bigger context of its field and where it fits into the scientific process can help people better understand and interpret new findings as they emerge. A single study usually uncovers only a piece of a larger puzzle.
Questions about how the world works are often investigated on many different levels. For example, scientists can look at the different atoms in a molecule, cells in a tissue, or how different tissues or systems affect each other. Researchers often must choose one or a finite number of ways to investigate a question. It can take many different studies using different approaches to start piecing the whole picture together.
Sometimes it might seem like research results contradict each other. But often, studies are just looking at different aspects of the same problem. Researchers can also investigate a question using different techniques or timeframes. That may lead them to arrive at different conclusions from the same data.
Using the data available at the time of their study, scientists develop different explanations, or models. New information may mean that a novel model needs to be developed to account for it. The models that prevail are those that can withstand the test of time and incorporate new information. Science is a constantly evolving and self-correcting process.
Scientists gain more confidence about a model through the scientific process. They replicate each other’s work. They present at conferences. And papers undergo peer review, in which experts in the field review the work before it can be published in scientific journals. This helps ensure that the study is up to current scientific standards and maintains a level of integrity. Peer reviewers may find problems with the experiments or think different experiments are needed to justify the conclusions. They might even offer new ways to interpret the data.
It’s important for science communicators to consider which stage a study is at in the scientific process when deciding whether to cover it. Some studies are posted on preprint servers for other scientists to start weighing in on and haven’t yet been fully vetted. Results that haven't yet been subjected to scientific scrutiny should be reported on with care and context to avoid confusion or frustration from readers.
We’ve developed a one-page guide, "How Research Works: Understanding the Process of Science" to help communicators put the process of science into perspective. We hope it can serve as a useful resource to help explain why science changes—and why it’s important to expect that change. Please take a look and share your thoughts with us by sending an email to [email protected].
Below are some additional resources:
- Discoveries in Basic Science: A Perfectly Imperfect Process
- When Clinical Research Is in the News
- What is Basic Science and Why is it Important?
- What is a Research Organism?
- What Are Clinical Trials and Studies?
- Basic Research – Digital Media Kit
- Decoding Science: How Does Science Know What It Knows? (NAS)
- Can Science Help People Make Decisions ? (NAS)
Connect with Us
- More Social Media from NIH
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of research
(Entry 1 of 2)
Definition of research (Entry 2 of 2)
transitive verb
intransitive verb
- disquisition
- examination
- exploration
- inquisition
- investigation
- delve (into)
- inquire (into)
- investigate
- look (into)
Examples of research in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'research.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Middle French recerche , from recercher to go about seeking, from Old French recerchier , from re- + cerchier, sercher to search — more at search
1577, in the meaning defined at sense 3
1588, in the meaning defined at transitive sense 1
Phrases Containing research
- marketing research
- market research
- operations research
- oppo research
research and development
- research park
- translational research
Dictionary Entries Near research
Cite this entry.
“Research.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/research. Accessed 19 May. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of research.
Kids Definition of research (Entry 2 of 2)
More from Merriam-Webster on research
Nglish: Translation of research for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of research for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about research
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, the words of the week - may 17, birds say the darndest things, a great big list of bread words, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), games & quizzes.

Selecting a Research Topic: Overview
- Refine your topic
- Background information & facts
- Writing help
Here are some resources to refer to when selecting a topic and preparing to write a paper:
- MIT Writing and Communication Center "Providing free professional advice about all types of writing and speaking to all members of the MIT community."
- Search Our Collections Find books about writing. Search by subject for: english language grammar; report writing handbooks; technical writing handbooks
- Blue Book of Grammar and Punctuation Online version of the book that provides examples and tips on grammar, punctuation, capitalization, and other writing rules.
- Select a topic
Choosing an interesting research topic is your first challenge. Here are some tips:
- Choose a topic that you are interested in! The research process is more relevant if you care about your topic.
- If your topic is too broad, you will find too much information and not be able to focus.
- Background reading can help you choose and limit the scope of your topic.
- Review the guidelines on topic selection outlined in your assignment. Ask your professor or TA for suggestions.
- Refer to lecture notes and required texts to refresh your knowledge of the course and assignment.
- Talk about research ideas with a friend. S/he may be able to help focus your topic by discussing issues that didn't occur to you at first.
- WHY did you choose the topic? What interests you about it? Do you have an opinion about the issues involved?
- WHO are the information providers on this topic? Who might publish information about it? Who is affected by the topic? Do you know of organizations or institutions affiliated with the topic?
- WHAT are the major questions for this topic? Is there a debate about the topic? Are there a range of issues and viewpoints to consider?
- WHERE is your topic important: at the local, national or international level? Are there specific places affected by the topic?
- WHEN is/was your topic important? Is it a current event or an historical issue? Do you want to compare your topic by time periods?
Table of contents
- Broaden your topic
- Information Navigator home
- Sources for facts - general
- Sources for facts - specific subjects
Start here for help
Ask Us Ask a question, make an appointment, give feedback, or visit us.
- Next: Refine your topic >>
- Last Updated: Jul 30, 2021 2:50 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mit.edu/select-topic
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of research in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- He has dedicated his life to scientific research.
- He emphasized that all the people taking part in the research were volunteers .
- The state of Michigan has endowed three institutes to do research for industry .
- I'd like to see the research that these recommendations are founded on.
- It took months of painstaking research to write the book .
- absorptive capacity
- dream something up
- modularization
- nanotechnology
- non-imitative
- operational research
- think outside the box idiom
- think something up
- uninventive
- study What do you plan on studying at university?
- major US She majored in philosophy at Harvard.
- cram She's cramming for her history exam.
- revise UK I'm revising for tomorrow's test.
- review US We're going to review for the test tomorrow night.
- research Scientists are researching possible new treatments for cancer.
- The amount of time and money being spent on researching this disease is pitiful .
- We are researching the reproduction of elephants .
- She researched a wide variety of jobs before deciding on law .
- He researches heart disease .
- The internet has reduced the amount of time it takes to research these subjects .
- adjudication
- interpretable
- interpretive
- interpretively
- investigate
- reinvestigate
- reinvestigation
- risk assessment
- run over/through something
- run through something
You can also find related words, phrases, and synonyms in the topics:
Related word
Research | american dictionary, research | business english, examples of research, collocations with research.
These are words often used in combination with research .
Click on a collocation to see more examples of it.
Translations of research
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
a computer program designed to have a conversation with a human being, usually over the internet

Searching out and tracking down: talking about finding or discovering things

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun Verb
- Business Noun Verb
- Collocations
- Translations
- All translations
To add research to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add research to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
What Is Research and Why We Do It
- First Online: 23 June 2020
Cite this chapter

- Carlo Ghezzi 2
2991 Accesses
2 Altmetric
The notions of science and scientific research are discussed and the motivations for doing research are analyzed. Research can span a broad range of approaches, from purely theoretical to practice-oriented; different approaches often coexist and fertilize each other. Research ignites human progress and societal change. In turn, society drives and supports research. The specific role of research in Informatics is discussed. Informatics is driving the current transition towards the new digital society in which we will live in the future.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
In [ 34 ], P.E. Medawar discusses what he calls the “snobismus” of pure versus applied science. In his words, this is one of the most damaging forms of snobbism, which draws a class distinction between pure and applied science.
Originality, rigor, and significance have been defined and used as the key criteria to evaluate research outputs by the UK Research Excellence Framework (REF) [ 46 ]. A research evaluation exercise has been performed periodically since 1986 on UK higher education institutions and their research outputs have been rated according to their originality, rigor, and significance.
The importance of realizing that “we don’t know” was apparently first stated by Socrates, according to Plato’s account of his thought. This is condensed in the famous paradox “I know that I don’t know.”
This view applies mainly to natural and physical sciences.
Roy Amara was President of the Institute for Future, a USA-based think tank, from 1971 until 1990.
The Turing Award is generally recognized as the Nobel prize of Informatics.
See http://uis.unesco.org/apps/visualisations/research-and-development-spending/ .
Israel is a very good example. Investments in research resulted in a proliferation of new, cutting-edge enterprises. The term start-up nation has been coined by Dan Senor and Saul Singer in their successful book [ 51 ] to characterize this phenomenon.
https://ec.europa.eu/programmes/horizon2020/en/h2020-section/societal-challenges .
https://ec.europa.eu/programmes/horizon2020/en/h2020-section/cross-cutting-activities-focus-areas .
This figure has been adapted from a presentation by A. Fuggetta, which describes the mission of Cefriel, an Italian institution with a similar role of Fraunhofer, on a smaller scale.
The ERC takes an ecumenical approach and calls the research sector “Computer Science and Informatics.”
I discuss here the effect of “big data” on research, although most sectors of society—industry, finance, health, …—are also deeply affected.
Carayannis, E., Campbell, D.: Mode 3 knowledge production in quadruple helix innovation systems. In: E. Carayannis, D. Campbell (eds.) Mode 3 Knowledge Production in Quadruple Helix Innovation Systems: 21st-Century Democracy, Innovation, and Entrepreneurship for Development. SpringerBriefs in Business, New York, NY (2012)
Google Scholar
Etzkowitz, H., Leydesdorff, L.: The triple helix – university-industry-government relations: A laboratory for knowledge based economic development. EASST Review 14 (1), 14–19 (1995)
Harari, Y.: Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind. Random House (2014). URL https://books.google.it/books?id=1EiJAwAAQBAJ
Harari, Y.: Homo Deus: A Brief History of Tomorrow. Random House (2016). URL https://books.google.it/books?id=dWYyCwAAQBAJ
Hopcroft, J.E., Motwani, R., Ullman, J.D.: Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages, and Computation (3rd Edition). Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc., USA (2006)
MATH Google Scholar
Medawar, P.: Advice To A Young Scientist. Alfred P. Sloan Foundation series. Basic Books (2008)
OECD: Frascati Manual. OECD Publishing (2015). https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264239012-en . URL https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/content/publication/9789264239012-en
REF2019/2: Panel criteria and working methods (2019). URL https://www.ref.ac.uk/media/1084/ref-2019_02-panel-criteria-and-working-methods.pdf
Senor, D., Singer, S.: Start-Up Nation: The Story of Israel’s Economic Miracle. McClelland & Stewart, Toronto, Canada (2011)
Stokes, D.E.: Pasteur’s Quadrant: Basic Science and Technological Innovation. Brookings Institution Press, Washington, D.C. (1997)
Thurston, R.H.: The growth of the steam engine. Popular Science Monthly 12 (1877)
Vardi, M.Y.: The long game of research. Commun. ACM 62 (9), 7–7 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3352489 . URL http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/3352489
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria, Politecnico di Milano, Milano, Italy
Carlo Ghezzi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Carlo Ghezzi .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Ghezzi, C. (2020). What Is Research and Why We Do It. In: Being a Researcher. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-45157-8_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-45157-8_1
Published : 23 June 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-45156-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-45157-8
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Research On or In – Which Is Correct?
If you are conducting research, do you say that you are conducting research “on” a subject or “in” a subject? Prepositions often confuse people, so we’ll be answering that question here today.
Both “research on” and “research in” are correct in the right contexts. You can conduct research “in” a field of study, but you conduct research “on” a particular subject. This means both “on” and “in” are grammatically correct as long as you use them appropriately.

Don’t you just love the vague aspects of English? The truth is, “research” can be followed up by many prepositions. They can all be correct, as long as you use them in the right context. As far as “on” or “in” are concerned, the correct preposition depends on the scope of the research.
Let’s look at some examples:
- Diane conducts research in astronomy.
- Diane conducts research on black holes.
The distinction here is the difference between a field of study and a subject that is being studied. You can conduct research “in” a field of study, but you cannot conduct research “in” a subject. For example, consider this sentence:
- Diane conducts research in black holes.
Obviously, that doesn’t sound right at all. That would imply that Diane physically conducts research within black holes. That’s why she can conduct research “on” black holes”, not “in them”. However, when it comes to field of study, you can say “on” or “in”.
That’s because some things are a field of study, but also a standalone subject. For example, “astronomy” is a field of science that includes many things, such as planetary orbits, stars, and black holes. But you can also study the subject of astronomy as a whole, instead of something that falls under its umbrella.
The main point is to remember the following: you can conduct research “in” a field of study, but not “in” a subject. You can conduct research “on” a subject, or a field of study if it is a subject itself.
Research On
You can conduct research “on” a subject. This is appropriate because “on” specifies that you are “doing” research directly to the subject in question. This is why “research on” is the most common way of saying this. Most anything can be a subject, so it’s often appropriate to say “research on” a subject.
- Conducting research on heart failure has been very interesting for me.
- I don’t know why anyone would want to perform research on illnesses.
- Conducting research on various aspects of chemistry is my life’s work.
- Hey, how’s your research on the connection between smoking and lung cancer going?
In all of these examples, research is being done directly to a particular subject. That’s why you would say “research on” in these scenarios.
Research In
You can conduct research “in” a field of knowledge, but not “in” a subject. This can be a little confusing because fields of knowledge are also subjects. Not all subjects are fields of study, but all fields of study are subjects. Knowing the difference mostly comes down to how it sounds to say.
Consider these examples:
- Tana is conducting research in the field of sociology.
- For my project, I will be conducting research in the area of chemistry.
- Conducting research in mathematics sounds very tedious.
- I don’t have any interest regarding research in astrology.
In these examples, the thing being researched is a field of study. Thus, you can say that you are doing research “in” those fields.
Research About
You can do “research about” things. This phrase is more about what your research is seeking to accomplish, rather than what field or subject you are conducting research on. Consider the following examples:
- My research about the behavior of animals in captivity is going well.
- Conducting research about the link between humans and pets will be exciting.
- Research about how people behave without applied moral standards would be difficult.
- I want you to do research about how black holes really work.
In these sentences, “research about” is used to describe what specifically someone is researching. That said, most people would accept using it to say that you are researching “on” or “in” a field of study or a subject as well.
Research Into
“Research into” can be used mostly synonymously with all of the other options. You can conduct research “into” a field of study or “into” a subject. That means it can be used in all the same situations as those phrases. For example:
- Vlad is conducting research into the effects of drawing blood.
- Many scientists are conducting research into how dolphins communicate.
- I am conducting research into human nature.
- Research into the potential power of a Yellowstone volcano eruption is frightening.
You can conduct research in, on, into, or about a field of study. However you can only conduct research on, about, or into a subject. Basically, the only thing you need to remember is that you shouldn’t say “research in” a subject.

Martin holds a Master’s degree in Finance and International Business. He has six years of experience in professional communication with clients, executives, and colleagues. Furthermore, he has teaching experience from Aarhus University. Martin has been featured as an expert in communication and teaching on Forbes and Shopify. Read more about Martin here .
- “Work On The Field” or “Work In The Field”?
- Bachelor Of or Bachelor In – Which Is Correct?
- What Does “Ethical Implications” Mean?
- Are TV Shows Italicized? (APA, AP, MLA, and Chicago)

Register to get your text revised right away for FREE ⚡
Today more than 1001 people got their English checked.

By continuing to use this website, you agree to our Terms of Service .
Get a FREE revision 🎁
Register a new account, welcome back, confirm your email.
Please click the link that we've sent to this address to post your question to our experts. Ok, I'll check my email
not your email? Change it now
Set a new email
Here you can set your new address email. Remember to use a valid email address. We will send you an email to confirm your account.
Facebook Login Discontinued
Unfortunately, the Facebook login method has been discontinued.
To access your TextRanch account, please click the "Reset Password" button below and input your Facebook Email. Our team will send you an email with further instructions.
If you don't remember your email, please fill out this form .
Your text is being reviewed by one of our Experts. We will notify you when your revision is ready.
Or wait in this page
Leave this page open, and your corrected text will appear as soon as it's ready!

You need to add a payment method to get our special promo ⚡
Enter your email below to get instant access to the first Chapter of our Ebook
Downloaded more than 1320 times today.
Add payment method
NOTE: Credits are valid for one year.
We're so happy that you liked your revision! Your feedback helps us improve our service. Want more FREE revisions ? 🎁
Step 1 out of 2!
Like us on Facebook by clicking the like button below:
Almost there!
Last step (2/2)
Share TextRanch on Facebook by clicking on the button below.
Congrats! You've just earned 3 credits!
Closing your account will prevent you from accessing your past revisions, and you will no longer be eligible for a FREE daily revision.
There is no cost to keep your TextRanch account, and we store all of your past revisions in a secure and private manner.
Help us understand
If we didn't meet your expectations, we'd really like to know more. Please tell us why you are closing your account:
The best way to perfect your writing.
Discover why 1,026,573 users count on TextRanch to get their English corrected!
1. Input your text below. 2. Get it corrected in a few minutes by our editors. 3. Improve your English!
One of our experts will correct your English.

📝 ️Notes for your editor
Let our editor help you, include background information, explanations of unusual words and special terms, or instructions about specific improvements you want.
"research about" vs "research on"
Last Updated: March 22, 2024
research about
This phrase is correct and commonly used in English.
- The documentary offers new research about the life of dolphins.
- The article presents research about the impact of technology on society.
- The report includes research about the future of artificial intelligence.
- The study provides important research about climate change.
- The seminar focused on research about mental health issues.
Alternatives:
- study about
- investigation about
- analysis about
- examination about
- exploration about
research on
- She is doing research on the impact of social media on teenagers.
- The professor's research on renewable energy sources is groundbreaking.
- Their research on the history of the city provided valuable insights.
- The team's research on consumer behavior led to important discoveries.
- The study focused on research on the benefits of exercise.
- investigation on
- analysis on
- examination on
- exploration on
Related Comparisons
Thanks to TextRanch, I was able to score above 950 on TOEIC, and I got a good grade on ACTFL OPIC as well. + Read the full interview
I love TextRanch because of the reliable feedback. The editors' comments are helpful and the customer service is amazing. + Read the full interview
TextRanch has helped me to improve my written skills as well as to communicate more naturally, like a local English speaker. + Read the full interview
TextRanch is amazingly responsive and really cares about the client. It's the best online service that I have ever used! + Read the full interview
I started to use TextRanch when I began to learn English. It has been an awesome way to improve my English skills. + Read the full interview
I love that TextRanch editors are real people who revise the text and provide feedback – it makes it so personal. + Read the full interview
I sometimes wonder if my English expressions make sense clearly and TextRanch helps me a lot in such cases. + Read the full interview
TextRanch has been really helpful in improving the flow and repairing the structure of my sentences. + Read the full interview
“Faster than AI"
“This was very helpful and I personally think this site is the best."
“It was extremely thorough and very helpful!"
“7 years without any disappointment. Always 100% satisfied. You guys are the best in the world at what you do. Thank you so much :)"
“In a world of text messages and online communication, this is great to have as a live tool. Thank you."
“Without textranch I would be stuck!"
“Accuracy and fast response. Personal comments from editor. Thank you."
“I wasn't aware of this service, it's fascinating and more reliable than standard IA tools available on the internet"
“The fact that you can get reliable fast feedback on your texts."
“you guys are better than grammarly i'm being honest here"
“OMG! This is really good than any other text correction tools I've used so far. Highly recommend this."
“Very fast and accurate. thank you."
“I love this app because it's help to writing skills all of students ♥️"
“This was exactly the mistake I was looking for, the wording dind´t sound right at first. Better than grammarly!"
“The immediate help that I received was reassuring and very satisfactory. Thanks."
“this helps A LOT for my studies."
“Woow!! I would never have expected such precision! Thank you soooo much!!"
“Real Time Editor and not AI. Many Thanks."
“The very first thing excites me about Textranch is how much your editors care."
“The fact that texts are checked by human editors rather than by AI, etc. I appreciate this!"
“Feel welcome, immediate response, high quality feedback"
“This is the best app that I have ever seen"
“Quick response and got what I intend to say. Grammar correction is excellent because the meaning is retained."
“Excellent, I truly loved this textRanch for quick revision. This textRanch for quick revision is a 10/10 for me."
⚡️Ask our Editor now.
Fresh content for your texts, so you can be more professional.
estimated time: 30 minutes , directly in your inbox

Want to improve your English business writing?
More than 150,000 people like you receive our weekly newsletter to master their English skills!
Why choose TextRanch?
Lowest prices Up to 50% lower than other online editing sites.
Fastest Times Our team of editors is working for you 24/7.
Qualified Editors Native English experts for UK or US English.
Top Customer Service We are here to help. Satisfaction guaranteed!
College Info Geek
How to Do Research in 7 Simple Steps
C.I.G. is supported in part by its readers. If you buy through our links, we may earn an affiliate commission. Read more here.

It’s 2 am, and you’re on your fifth cup of coffee (or was it your sixth?). You’re crouched at a table in some dark corner of the library surrounded by fifteen open books. Equally as many tabs are open on your laptop, and you still haven’t written a word of the paper that’s due in 7 hours.
Many things can explain how you got to this point, including procrastination , poor organization , and a messy schedule .
Very often, however, the problem is a lack of research skills .
And it’s not your fault. High school does a poor job of teaching you how to do research, and most college classes do little better. It feels like you’re expected to figure it out through trial and error.
I think we can do better than that, however. In this guide, I’m going to show you the 7-step process for researching everything from a 10-page term paper to a final presentation. Not only will you learn how to do better research; you’ll also learn how to research more efficiently.
What Is Research?
Before we go any further, what is research?
At its core, research is an attempt to answer a question. This could be anything from “How can we reduce infant mortality rates?” to “Why does salt make food taste good?”
To answer your question, you consult books, academic papers, newspaper articles, historical records, or anything else that could be helpful. The broad term for these things is “sources.”
And, usually, once you’ve done the research, you present or summarize it in some way. In many cases, this means writing an essay or another type of scholarly paper, but it could also mean giving a presentation or even creating a YouTube video.
Even if you have no interest in academia, research is an extremely useful skill to learn. When you know how to do research, it’s much easier to improve your life and work more effectively . Instead of having to ask someone every time you have a question, research will help you solve problems yourself (and help others in turn).
Note: Research can also mean conducting surveys, performing experiments, or going on archaeological digs. While these activities are crucial for advancing human knowledge, I won’t be discussing them here. This article focuses on the research you can do with only a library and an internet connection.
The 7 Steps of the Research Process
Research can feel overwhelming, but it’s more manageable when you break it down into steps. In my experience, the research process has seven main steps:
- Find a topic
- Refine your topic
- Find key sources
- Take notes on your sources
- Create your paper or presentation
- Do additional research as necessary
- Cite your sources
Let’s look at each of these steps in more detail.
1. Find a Topic
If you don’t have a topic, your research will be undirected and inefficient. You’ll spend hours reading dozens of sources, all because you didn’t take a few minutes to develop a topic.
How do you come up with a topic? My number one suggestion is to create a mind map.
A mind map is a visual way to generate ideas. Here’s how it works:
- Get a piece of paper and a pen. Make sure the paper isn’t too small — you want lots of room for your ideas.
- Draw an oval in the center of the paper.
- Inside that oval, write a super vague topic. Start with whatever your professor has assigned you.
- Draw lines from the oval towards the edges of the paper.
- Draw smaller ovals connected to each of these lines.
- Inside the smaller ovals, write more specific ideas/topics related to the central one.
- Repeat until you’ve found 3-5 topic ideas.
When I write it out step by step, it sounds kind of strange. But trust me, it works . Anytime I’m stuck on a writing assignment, this method is my go-to. It’s basically magic.
To see what mind mapping looks like in practice, check out this clip:
Want to create a digital mind map like the one Thomas uses in the video? Check out Coggle .
2. Refine Your Topic
Okay, so now you have a list of 3-5 topics. They’re all still pretty general, and you need to narrow them down to one topic that you can research in depth.
To do this, spend 15 minutes doing some general research on each topic. Specifically, take each topic and plug it into your library’s catalog and database search tools.
The details of this process will vary from library to library. This is where consulting a librarian can be super helpful. They can show you how to use the tools I mentioned, as well as point you to some you probably don’t know about.
Furthermore, I suggest you ask your professor for recommendations. In some cases, they may even have created a resource page specifically for your assignment.
Once you’ve found out where to search, type in your topic. I like to use a mixture of the library catalog, a general academic database like EBSCO Host , and a search on Google Scholar .
What exactly are you trying to find? Basically, you’re trying to find a topic with a sufficient quantity and variety of sources.
Ideally, you want something with both journal articles and books, as this demonstrates that lots of scholars are seriously engaging with the topic.
Of course, in some cases (if the topic is very cutting edge, for example), you may be only able to find journal articles. That’s fine, so long as there are enough perspectives available.
Using this technique, you’ll be able to quickly eliminate some topics. Be ruthless. If you’re not finding anything after 15 minutes, move on. And don’t get attached to a topic.
Tip: If you find two topics with equal numbers of sources available, ask your professor to help you break the tie. They can give you insight into which topic is super common (and thus difficult to write about originally), as well as which they find more interesting.
Now that you have your topic, it’s time to narrow down your sources.
3. Find Key Sources
If you’ve picked a good topic, then you probably have lots of sources to work with. This is both a blessing and a curse. A variety of sources shows that there’s something worth saying about your topic, and it also gives you plenty of material to cite.
But this abundance can quickly turn into a nightmare in which you spend hours reading dense, mind-numbing material without getting any closer to actually producing a paper.
How do you keep this from happening? Choose 3–5 key sources and focus on them intently. Sure, you may end up needing more sources, especially if this is a long paper or if the professor requires it. But if you start out trying to read 15 sources, you’re likely to get overwhelmed and frustrated.
Focusing on a few key sources is powerful because it:
- Lets you engage deeply with each source.
- Gives you a variety of perspectives.
- Points you to further resources.
- Keeps you focused.
4. Read and Take Notes
But what do you do with these sources, exactly? You need to read them the right way . Follow these steps to effectively read academic books and articles:
Go through the article and look at the section headings. If any words or terms jump out at you, make note of them. Also, glance at the beginning sentences of each section and paragraph to get an overall idea of the author’s argument.
The goal here isn’t to comprehend deeply, but to prime your mind for effective reading .
Write down any questions you have after skimming the article, as well as any general questions you hope the article can answer. Always keep your topic in mind.
Read Actively
Now, start reading. But don’t just passively go through the information like you’re scrolling through Tumblr. Read with a pen or pencil in hand , underlining any unfamiliar terms or interesting ideas.
Make notes in the margins about other sources or concepts that come to mind. If you’re reading a library book, you can make notes on a separate piece of paper.
Once you’ve finished reading, take a short break. Have a cup of tea or coffee. Go for a walk around the library. Stretch. Just get your mind away from the research for a moment without resorting to distracting, low-density fun .
Now come back to the article and look at the things you underlined or noted. Gather these notes and transfer them to a program like Evernote .
If you need to look up a term, do that, and then add that definition to your notes. Also, make note of any sources the author cites that look helpful.
But what if I’m reading a book? Won’t this take forever? No, because you’re not going to read the entire book.
For most research you’ll do in college, reading a whole academic book is overkill . Just skim the table of contents and the book itself to find chapters or sections that look relevant.
Then, read each of those in the same way you would read an article. Also, be sure to glance at the book’s bibliography, which is a goldmine for finding additional sources.
Note: The above method is a variation on the classic SQ3R method , adapted slightly since we’re not interested in taking notes from textbooks .
5. Create Your Paper or Presentation
“You can’t turn in raw research.”
Research is crucial to crafting a great paper or presentation, but it’s also a great way to procrastinate. I had classmates in college who would spend 8 hours researching a 5-page paper. That’s way too much!
At some point, you need to stop researching and start writing (or whatever method you’re using to present your research).
How do you decide when to stop researching? There’s no strict rule, but in general I wouldn’t spend more than 30 minutes per page of the final paper.
So if the final paper is supposed to be 10 pages, don’t spend more than 5 hours researching it.
6. Do Additional Research (As Necessary)
Once you’ve started writing the draft of your paper, you’ll probably find a few gaps. Maybe you realize that one scholar’s argument isn’t relevant to your paper, or that you need more information for a particular section. In this case, you are free to return to researching as necessary.
But again, beware the trap of procrastination masquerading as productivity! Only do as much additional research as you need to answer your question. Don’t get pulled into rabbit holes or dragged off on tangents. Get in there, do your research, and get back to writing .
To keep yourself focused, I suggest keeping a separate document or piece of paper nearby to note points that need additional research.
Every time you encounter such a point, make note of it in the document and then keep writing. Only stop when you can’t get any further without additional research.
It’s much better to get a full draft done first. Otherwise, you risk suffering a cognitive switching penalty , making it harder to regain your focus.
7. Cite Your Sources
Whether you’re creating an oral presentation, essay, or video, you’ll need to cite your sources. Plagiarism is a serious offense, so don’t take any chances.
How to cite your sources depends on the subject and the professor’s expectations. Chicago, MLA, and APA are the most common citation formats to use in college, but there are thousands more.
Luckily, you don’t need to painstakingly type each of your citations by hand or slog through a style manual. Instead, you can use a tool like Zotero to track and generate your citations. To make things even easier, install the Zotero Connector browser extension. It can automatically pull citation information from entries in an online library catalog.
Once you’ve collected all of your sources, Zotero can generate a properly formatted works cited page or bibliography at just the click of a button.
For help setting up and using Zotero, read this guide . If you need further assistance, ask a librarian.
Go Research With Confidence
I hope you now understand how to do research with more confidence. If you follow the procedures I’ve covered in this article, you’ll waste less time, perform more effective research, and ultimately have the material for a winning essay.
Curious about how to use your research to write a great research paper? Check out this guide .
Image Credits: picking book from shelf
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research

What is Research: Definition, Methods, Types & Examples

The search for knowledge is closely linked to the object of study; that is, to the reconstruction of the facts that will provide an explanation to an observed event and that at first sight can be considered as a problem. It is very human to seek answers and satisfy our curiosity. Let’s talk about research.
Content Index
What is Research?
What are the characteristics of research.
- Comparative analysis chart
Qualitative methods
Quantitative methods, 8 tips for conducting accurate research.
Research is the careful consideration of study regarding a particular concern or research problem using scientific methods. According to the American sociologist Earl Robert Babbie, “research is a systematic inquiry to describe, explain, predict, and control the observed phenomenon. It involves inductive and deductive methods.”
Inductive methods analyze an observed event, while deductive methods verify the observed event. Inductive approaches are associated with qualitative research , and deductive methods are more commonly associated with quantitative analysis .
Research is conducted with a purpose to:
- Identify potential and new customers
- Understand existing customers
- Set pragmatic goals
- Develop productive market strategies
- Address business challenges
- Put together a business expansion plan
- Identify new business opportunities
- Good research follows a systematic approach to capture accurate data. Researchers need to practice ethics and a code of conduct while making observations or drawing conclusions.
- The analysis is based on logical reasoning and involves both inductive and deductive methods.
- Real-time data and knowledge is derived from actual observations in natural settings.
- There is an in-depth analysis of all data collected so that there are no anomalies associated with it.
- It creates a path for generating new questions. Existing data helps create more research opportunities.
- It is analytical and uses all the available data so that there is no ambiguity in inference.
- Accuracy is one of the most critical aspects of research. The information must be accurate and correct. For example, laboratories provide a controlled environment to collect data. Accuracy is measured in the instruments used, the calibrations of instruments or tools, and the experiment’s final result.
What is the purpose of research?
There are three main purposes:
- Exploratory: As the name suggests, researchers conduct exploratory studies to explore a group of questions. The answers and analytics may not offer a conclusion to the perceived problem. It is undertaken to handle new problem areas that haven’t been explored before. This exploratory data analysis process lays the foundation for more conclusive data collection and analysis.
LEARN ABOUT: Descriptive Analysis
- Descriptive: It focuses on expanding knowledge on current issues through a process of data collection. Descriptive research describe the behavior of a sample population. Only one variable is required to conduct the study. The three primary purposes of descriptive studies are describing, explaining, and validating the findings. For example, a study conducted to know if top-level management leaders in the 21st century possess the moral right to receive a considerable sum of money from the company profit.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
- Explanatory: Causal research or explanatory research is conducted to understand the impact of specific changes in existing standard procedures. Running experiments is the most popular form. For example, a study that is conducted to understand the effect of rebranding on customer loyalty.
Here is a comparative analysis chart for a better understanding:
It begins by asking the right questions and choosing an appropriate method to investigate the problem. After collecting answers to your questions, you can analyze the findings or observations to draw reasonable conclusions.
When it comes to customers and market studies, the more thorough your questions, the better the analysis. You get essential insights into brand perception and product needs by thoroughly collecting customer data through surveys and questionnaires . You can use this data to make smart decisions about your marketing strategies to position your business effectively.
To make sense of your study and get insights faster, it helps to use a research repository as a single source of truth in your organization and manage your research data in one centralized data repository .
Types of research methods and Examples

Research methods are broadly classified as Qualitative and Quantitative .
Both methods have distinctive properties and data collection methods .
Qualitative research is a method that collects data using conversational methods, usually open-ended questions . The responses collected are essentially non-numerical. This method helps a researcher understand what participants think and why they think in a particular way.
Types of qualitative methods include:
- One-to-one Interview
- Focus Groups
- Ethnographic studies
- Text Analysis
Quantitative methods deal with numbers and measurable forms . It uses a systematic way of investigating events or data. It answers questions to justify relationships with measurable variables to either explain, predict, or control a phenomenon.
Types of quantitative methods include:
- Survey research
- Descriptive research
- Correlational research
LEARN MORE: Descriptive Research vs Correlational Research
Remember, it is only valuable and useful when it is valid, accurate, and reliable. Incorrect results can lead to customer churn and a decrease in sales.
It is essential to ensure that your data is:
- Valid – founded, logical, rigorous, and impartial.
- Accurate – free of errors and including required details.
- Reliable – other people who investigate in the same way can produce similar results.
- Timely – current and collected within an appropriate time frame.
- Complete – includes all the data you need to support your business decisions.
Gather insights

- Identify the main trends and issues, opportunities, and problems you observe. Write a sentence describing each one.
- Keep track of the frequency with which each of the main findings appears.
- Make a list of your findings from the most common to the least common.
- Evaluate a list of the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats identified in a SWOT analysis .
- Prepare conclusions and recommendations about your study.
- Act on your strategies
- Look for gaps in the information, and consider doing additional inquiry if necessary
- Plan to review the results and consider efficient methods to analyze and interpret results.
Review your goals before making any conclusions about your study. Remember how the process you have completed and the data you have gathered help answer your questions. Ask yourself if what your analysis revealed facilitates the identification of your conclusions and recommendations.
LEARN MORE ABOUT OUR SOFTWARE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS
Data Information vs Insight: Essential differences
May 14, 2024

Pricing Analytics Software: Optimize Your Pricing Strategy
May 13, 2024

Relationship Marketing: What It Is, Examples & Top 7 Benefits
May 8, 2024

The Best Email Survey Tool to Boost Your Feedback Game
May 7, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
How to Do Research: A Step-By-Step Guide: Step 1: Develop a Topic
- Get Started
- 1a. Select a Topic
- 1b. Develop Research Questions
- 1c. Identify Keywords
- 1d. Find Background Information
- 1e. Refine a Topic
- 2a. Search Strategies
- 2d. Articles
- 2e. Videos & Images
- 2f. Databases
- 2g. Websites
- 2h. Grey Literature
- 2i. Open Access Materials
- 3a. Evaluate Sources
- 3b. Primary vs. Secondary
- 3c. Types of Periodicals
- 4a. Take Notes
- 4b. Outline the Paper
- 4c. Incorporate Source Material
- 5a. Avoid Plagiarism
- 5b. Zotero & MyBib
- 5c. MLA Formatting
- 5d. MLA Citation Examples
- 5e. APA Formatting
- 5f. APA Citation Examples
- 5g. Annotated Bibliographies
Developing a Topic
Developing a good research question can sometimes be the most difficult part of the research process. If you are struggling, follow the links below.
- Select a topic
- Develop research questions
- Identify keywords
- Find background information
- Refine your topic
Choosing a Topic - Video Overview
Video has been posted with permission from Pfau Library, California State University-San Bernardino.
- << Previous: Get Started
- Next: 1a. Select a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Feb 21, 2024 11:01 AM
- URL: https://libguides.elmira.edu/research
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

‘The scientist is not in the business of following instructions.’

Glimpse of next-generation internet

Epic science inside a cubic millimeter of brain

Venki Ramakrishnan.
Niles Singer/Harvard Staff Photographer
Science is making anti-aging progress. But do we want to live forever?
Nobel laureate details new book, which surveys research, touches on larger philosophical questions
Anne J. Manning
Harvard Staff Writer
Mayflies live for only a day. Galapagos tortoises can reach up to age 170. The Greenland shark holds the world record at over 400 years of life.
Venki Ramakrishnan, Nobel laureate and author of the newly released “ Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for Immortality ,” opened his packed Harvard Science Book Talk last week by noting the vast variabilities of lifespans across the natural world. Death is certain, so far as we know. But there’s no physical or chemical law that says it must happen at a fixed time, which raises other, more philosophical issues.
The “why” behind these enormous swings, and the quest to harness longevity for humans, have driven fevered attempts (and billions of dollars in research spending) to slow or stop aging. Ramakrishnan’s book is a dispassionate journey through current scientific understanding of aging and death, which basically comes down to an accumulation of chemical damage to molecules and cells.
“The question is whether we can tackle aging processes, while still keeping us who we are as humans,” said Ramakrishnan during his conversation with Antonio Regalado, a writer for the MIT Technology Review. “And whether we can do that in a safe and effective way.”
Even if immortality — or just living for a very, very long time — were theoretically possible through science, should we pursue it? Ramakrishnan likened the question to other moral ponderings.
“There’s no physical or chemical law that says we can’t colonize other galaxies, or outer space, or even Mars,” he said. “I would put it in that same category. And it would require huge breakthroughs, which we haven’t made yet.”
In fact, we’re a lot closer to big breakthroughs when it comes to chasing immortality. Ramakrishnan noted the field is moving so fast that a book like his can capture but a snippet. He then took the audience on a brief tour of some of the major directions of aging research. And much of it, he said, started in unexpected places.
Take rapamycin, a drug first isolated in the 1960s from a bacterium on Easter Island found to have antifungal, immunosuppressant, and anticancer properties. Rapamycin targets the TOR pathway, a large molecular signaling cascade within cells that regulates many functions fundamental to life. Rapamycin has garnered renewed attention for its potential to reverse the aging process by targeting cellular signaling associated with physiological changes and diseases in older adults.
Other directions include mimicking the anti-aging effects of caloric restriction shown in mice, as well as one particularly exciting area called cellular reprogramming. That means taking fully developed cells and essentially turning back the clock on their development.
The most famous foundational experiment in this area was by Kyoto University scientist and Nobel laureate Shinya Yamanaka, who showed that just four transcription factors could revert an adult cell all the way back to a pluripotent stem cell, creating what are now known as induced pluripotent stem cells.
Ramakrishnan , a scientist at England’s MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, won the 2009 Nobel Prize in chemistry for uncovering the structure of the ribosome. He said he felt qualified to write the book because he has “no skin in the game” of aging research. As a molecular biologist who has studied fundamental processes of how cells make proteins, he had connections in the field but wasn’t too close to any of it.
While researching the book, he took pains to avoid interviewing scientists with commercial ventures tied to aging.
The potential for conflicts of interest abound.
The world has seen an explosion in aging research in recent decades, with billions of dollars spent by government agencies and private companies . And the consumer market for products is forecast to hit $93 billion by 2027 .
As a result, false or exaggerated claims by companies promising longer life are currently on the rise, Ramakrishnan noted. He shared one example: Supplements designed to lengthen a person’s telomeres, or genetic segments that shrink with age, are available on Amazon.
“Of course, these are not FDA approved. There are no clinical trials, and it’s not clear what their basis is,” he said.
But still there appears to be some demand.
Get the best of the Gazette delivered to your inbox
By subscribing to this newsletter you’re agreeing to our privacy policy
Share this article
You might like.
George Whitesides became a giant of chemistry by keeping it simple

Physicists demo first metro-area quantum computer network in Boston

Researchers publish largest-ever dataset of neural connections
Finding right mix on campus speech policies
Legal, political scholars discuss balancing personal safety, constitutional rights, academic freedom amid roiling protests, cultural shifts
Good genes are nice, but joy is better
Harvard study, almost 80 years old, has proved that embracing community helps us live longer, and be happier
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research: What Companies Don’t Know About How Workers Use AI
- Jeremie Brecheisen

Three Gallup studies shed light on when and why AI is being used at work — and how employees and customers really feel about it.
Leaders who are exploring how AI might fit into their business operations must not only navigate a vast and ever-changing landscape of tools, but they must also facilitate a significant cultural shift within their organizations. But research shows that leaders do not fully understand their employees’ use of, and readiness for, AI. In addition, a significant number of Americans do not trust business’ use of AI. This article offers three recommendations for leaders to find the right balance of control and trust around AI, including measuring how their employees currently use AI, cultivating trust by empowering managers, and adopting a purpose-led AI strategy that is driven by the company’s purpose instead of a rules-heavy strategy that is driven by fear.
If you’re a leader who wants to shift your workforce toward using AI, you need to do more than manage the implementation of new technologies. You need to initiate a profound cultural shift. At the heart of this cultural shift is trust. Whether the use case for AI is brief and experimental or sweeping and significant, a level of trust must exist between leaders and employees for the initiative to have any hope of success.
- Jeremie Brecheisen is a partner and managing director of The Gallup CHRO Roundtable.
Partner Center
Cornell Chronicle
- Architecture & Design
- Arts & Humanities
- Business, Economics & Entrepreneurship
- Computing & Information Sciences
- Energy, Environment & Sustainability
- Food & Agriculture
- Global Reach
- Health, Nutrition & Medicine
- Law, Government & Public Policy
- Life Sciences & Veterinary Medicine
- Physical Sciences & Engineering
- Social & Behavioral Sciences
- Coronavirus
- News & Events
- Public Engagement
- New York City
- Photos of the Week
- Big Red Sports
- Freedom of Expression
- Student Life
- University Statements
Around Cornell
- All Stories
- In the News
- Expert Quotes
- Cornellians

News directly from Cornell's colleges and centers
Research: Technology is changing how companies do business
By sarah mangus-sharpe.
A new study from the Cornell SC Johnson College of Business advances understanding of the U.S. production chain evolution amidst technological progress in information technology (IT), shedding light on the complex connections between business IT investments and organizational design. Advances in IT have sparked significant changes in how companies design their production processes. In the paper " Production Chain Organization in the Digital Age: Information Technology Use and Vertical Integration in U.S. Manufacturing ," which published April 30 in Management Science, Chris Forman , the Peter and Stephanie Nolan Professor in the Dyson School of Applied Economics and Management , and his co-author delved into what these changes mean for businesses and consumers.
Forman and Kristina McElheran, assistant professor of strategic management at University of Toronto, analyzed U.S. Census Bureau data of over 5,600 manufacturing plants to see how the production chains of businesses were affected by the internet revolution. Their use of census data allowed them to look inside the relationships among production units within and between companies and how transaction flows changed after companies invested in internet-enabled technology that facilitated coordination between them. The production units of many of the companies in their study concurrently sold to internal and external customers, a mix they refer to as plural selling. They found that the reduction in communication costs enabled by the internet shifted the mix toward more sales outside of the firm, or less vertical integration.
The research highlights the importance of staying ahead of the curve in technology. Companies that embrace digital technologies now are likely to be the ones that thrive in the future. And while there are still many unanswered questions about how these changes will play out, one thing is clear: The relationship between technology and business is only going to become more and more intertwined in the future.
Read the full story on the Cornell SC Johnson College of Business news site, BusinessFeed.
Media Contact
Media relations office.
Get Cornell news delivered right to your inbox.
You might also like

Gallery Heading
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Broad Public Support for Legal Abortion Persists 2 Years After Dobbs
By more than 2 to 1, americans say medication abortion should be legal, table of contents.
- Other abortion attitudes
- Overall attitudes about abortion
- Americans’ views on medication abortion in their states
- How statements about abortion resonate with Americans
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology
Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand Americans’ views on the legality of abortion, as well as their perceptions of abortion access. For this analysis, we surveyed 8,709 adults from April 8 to 14, 2024. Everyone who took part in this survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for the report and its methodology .
Nearly two years after the Supreme Court overturned the 1973 Roe v. Wade decision guaranteeing a national right to abortion, a majority of Americans continue to express support for abortion access.
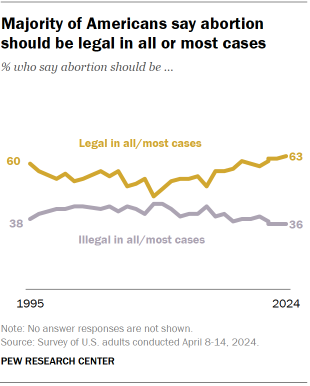
About six-in-ten (63%) say abortion should be legal in all or most cases. This share has grown 4 percentage points since 2021 – the year prior to the 2022 decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization that overturned Roe.
The new Pew Research Center survey, conducted April 8-14, 2024, among 8,709 adults, surfaces ongoing – and often partisan – divides over abortion attitudes:
- Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents (85%) overwhelmingly say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, with near unanimous support among liberal Democrats.
- By comparison, Republicans and Republican leaners (41%) are far less likely to say abortion should be legal in all or most cases. However, two-thirds of moderate and liberal Republicans still say it should be.
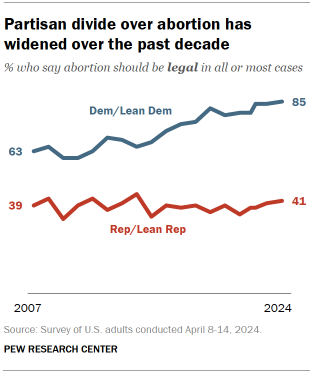
Since before Roe was overturned, both parties have seen a modest uptick in the share who say abortion should be legal.
As in the past, relatively few Americans (25%) say abortion should be legal in all cases, while even fewer (8%) say it should be illegal in all cases. About two-thirds of Americans do not take an absolutist view: 38% say it should be legal in most cases, and 28% say it should be illegal in most cases.
Related: Americans overwhelmingly say access to IVF is a good thing
Women’s abortion decisions
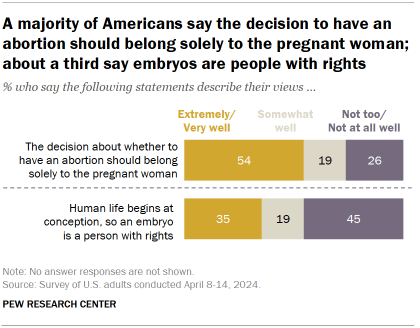
A narrow majority of Americans (54%) say the statement “the decision about whether to have an abortion should belong solely to the pregnant woman” describes their views extremely or very well. Another 19% say it describes their views somewhat well, and 26% say it does not describe their views well.
Views on an embryo’s rights
About a third of Americans (35%) say the statement “human life begins at conception, so an embryo is a person with rights” describes their views extremely or very well, while 45% say it does not describe their views well.
But many Americans are cross-pressured in their views: 32% of Americans say both statements about women’s decisions and embryos’ rights describe their views at least somewhat well.
Abortion access
About six-in-ten Americans in both parties say getting an abortion in the area where they live would be at least somewhat easy, compared with four-in-ten or fewer who say it would be difficult.
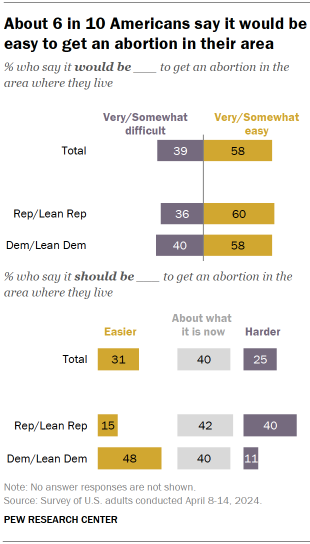
However, U.S. adults are divided over whether getting an abortion should be easier or harder:
- 31% say it should be easier for someone to get an abortion in their area, while 25% say it should be harder. Four-in-ten say the ease of access should be about what it is now.
- 48% of Democrats say that obtaining an abortion should be easier than it is now, while just 15% of Republicans say this. Instead, 40% of Republicans say it should be harder (just 11% of Democrats say this).
As was the case last year, views about abortion access vary widely between those who live in states where abortion is legal and those who live in states where it is not allowed.
For instance, 20% of adults in states where abortion is legal say it would be difficult to get an abortion where they live, but this share rises to 71% among adults in states where abortion is prohibited.
Medication abortion
Americans say medication abortion should be legal rather than illegal by a margin of more than two-to-one (54% vs. 20%). A quarter say they are not sure.
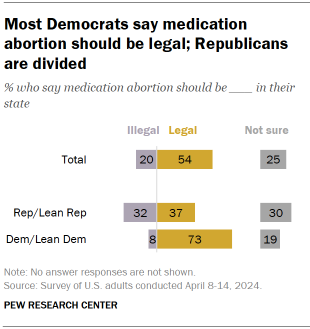
Like opinions on the legality of abortion overall, partisans differ greatly in their views of medication abortion:
- Republicans are closely split but are slightly more likely to say it should be legal (37%) than illegal (32%). Another 30% aren’t sure.
- Democrats (73%) overwhelmingly say medication abortion should be legal. Just 8% say it should be illegal, while 19% are not sure.
Across most other demographic groups, Americans are generally more supportive than not of medication abortion.
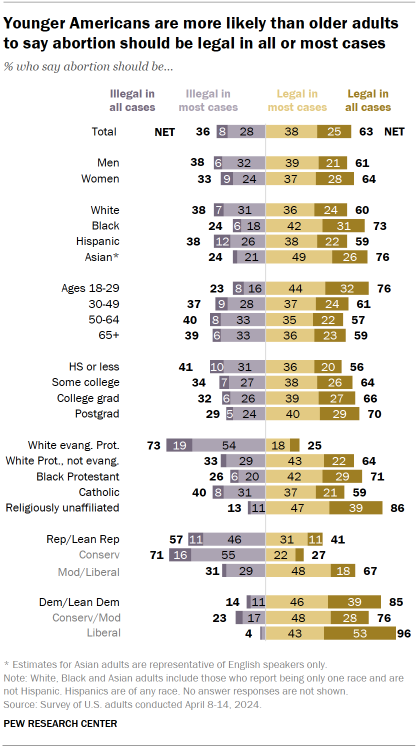
Across demographic groups, support for abortion access has changed little since this time last year.
Today, roughly six-in-ten (63%) say abortion should be legal in all (25%) or most (38%) cases. And 36% say it should be illegal in all (8%) or most (28%) cases.
While differences are only modest by gender, other groups vary more widely in their views.
Race and ethnicity
Support for legal abortion is higher among Black (73%) and Asian (76%) adults compared with White (60%) and Hispanic (59%) adults.
Compared with older Americans, adults under 30 are particularly likely to say abortion should be legal: 76% say this, versus about six-in-ten among other age groups.
Those with higher levels of formal education express greater support for legal abortion than those with lower levels of educational attainment.
About two-thirds of Americans with a bachelor’s degree or more education (68%) say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, compared with six-in-ten among those without a degree.
White evangelical Protestants are about three times as likely to say abortion should be illegal (73%) as they are to say it should be legal (25%).
By contrast, majorities of White nonevangelical Protestants (64%), Black Protestants (71%) and Catholics (59%) say abortion should be legal. And religiously unaffiliated Americans are especially likely to say abortion should be legal (86% say this).
Partisanship and ideology
Democrats (85%) are about twice as likely as Republicans (41%) to say abortion should be legal in all or most cases.
But while more conservative Republicans say abortion should be illegal (76%) than legal (27%), the reverse is true for moderate and liberal Republicans (67% say legal, 31% say illegal).
By comparison, a clear majority of conservative and moderate Democrats (76%) say abortion should be legal, with liberal Democrats (96%) overwhelmingly saying this.
Views of abortion access by state
About six-in-ten Americans (58%) say it would be easy for someone to get an abortion in the area where they live, while 39% say it would be difficult.
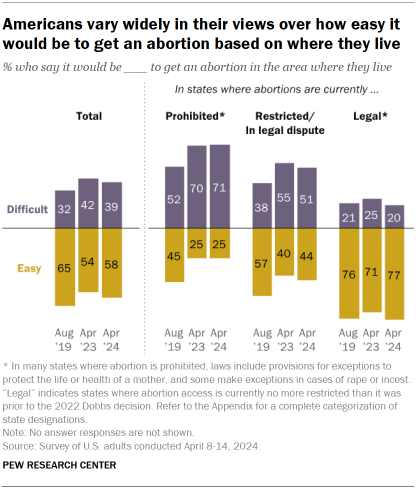
This marks a slight shift since last year, when 54% said obtaining an abortion would be easy. But Americans are still less likely than before the Dobbs decision to say obtaining an abortion would be easy.
Still, Americans’ views vary widely depending on whether they live in a state that has banned or restricted abortion.
In states that prohibit abortion, Americans are about three times as likely to say it would be difficult to obtain an abortion where they live as they are to say it would be easy (71% vs. 25%). The share saying it would be difficult has risen 19 points since 2019.
In states where abortion is restricted or subject to legal challenges, 51% say it would be difficult to get an abortion where they live. This is similar to the share who said so last year (55%), but higher than the share who said this before the Dobbs decision (38%).
By comparison, just 20% of adults in states where abortion is legal say it would be difficult to get one. This is little changed over the past five years.
Americans’ attitudes about whether it should be easier or harder to get an abortion in the area where they live also varies by geography.
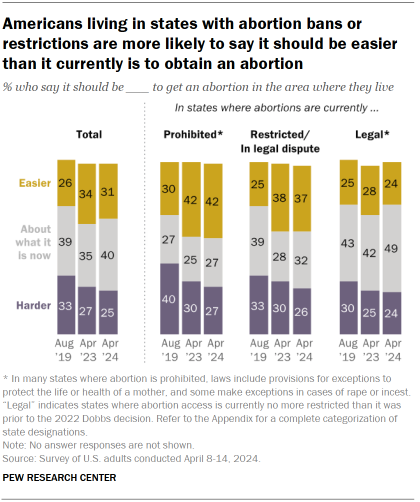
Overall, a decreasing share of Americans say it should be harder to obtain an abortion: 33% said this in 2019, compared with 25% today.
This is particularly true of those in states where abortion is now prohibited or restricted.
In both types of states, the shares of Americans saying it should be easier to obtain an abortion have risen 12 points since before Roe was overturned, as the shares saying it should be harder have gradually declined.
By comparison, changes in views among those living in states where abortion is legal have been more modest.
While Americans overall are more supportive than not of medication abortion (54% say it should be legal, 20% say illegal), there are modest differences in support across groups:
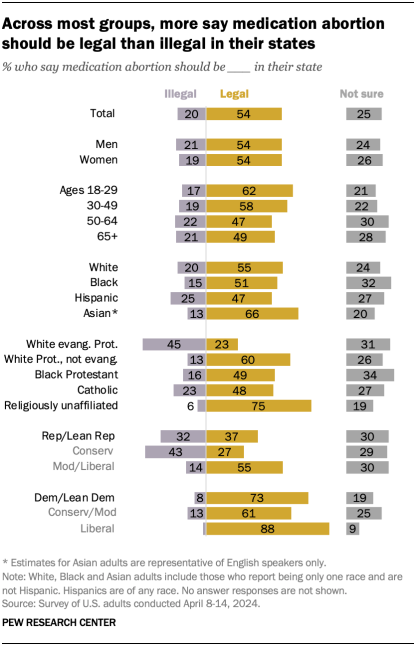
- Younger Americans are somewhat more likely to say medication abortion should be legal than older Americans. While 59% of adults ages 18 to 49 say it should be legal, 48% of those 50 and older say the same.
- Asian adults (66%) are particularly likely to say medication abortion should be legal compared with White (55%), Black (51%) and Hispanic (47%) adults.
- White evangelical Protestants oppose medication abortion by about two-to-one (45% vs. 23%), with White nonevangelicals, Black Protestants, Catholics and religiously unaffiliated adults all being more likely than not to say medication abortion should be legal.
- Republicans are closely divided over medication abortion: 37% say it should be legal while 32% say it should be illegal. But similar to views on abortion access overall, conservative Republicans are more opposed (43% illegal, 27% legal), while moderate and liberals are more supportive (55% legal, 14% illegal).
Just over half of Americans (54%) say “the decision about whether to have an abortion should belong solely to the pregnant woman” describes their views extremely or very well, compared with 19% who say somewhat well and 26% who say not too or not at all well.
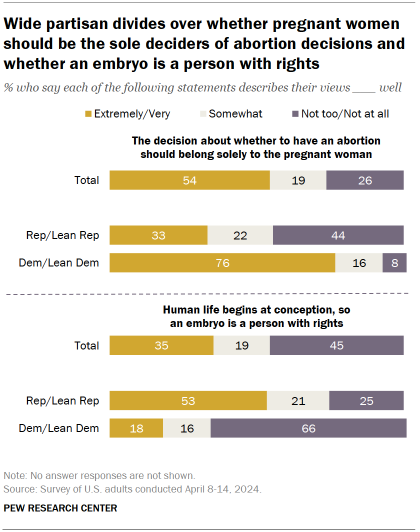
Democrats (76%) overwhelmingly say this statement describes their views extremely or very well, with just 8% saying it does not describe their views well.
Republicans are more divided: 44% say it does not describe their views well while 33% say it describes them extremely or very well. Another 22% say it describes them somewhat well.
Fewer Americans (35%) say the statement “human life begins at conception, so an embryo is a person with rights” describes their views extremely or very well. Another 19% say it describes their views somewhat well while 45% say it describes them not too or not at all well.
(The survey asks separately whether “a fetus is a person with rights.” The results are roughly similar: 37% say that statement describes their views extremely or very well.)
Republicans are about three times as likely as Democrats to say “an embryo is a person with rights” describes their views extremely or very well (53% vs. 18%). In turn, Democrats (66%) are far more likely than Republicans (25%) to say it describes their views not too or not at all well.
Some Americans are cross-pressured about abortion
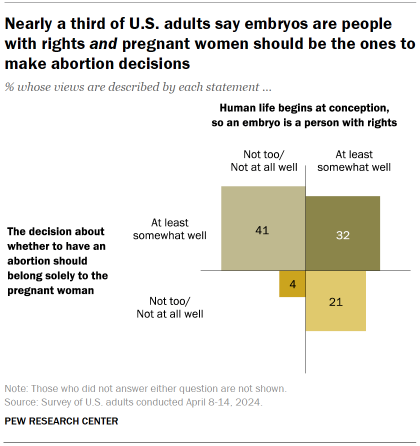
When results on the two statements are combined, 41% of Americans say the statement about a pregnant woman’s right to choose describes their views at least somewhat well , but not the statement about an embryo being a person with rights. About two-in-ten (21%) say the reverse.
But for nearly a third of U.S. adults (32%), both statements describe their views at least somewhat well.
Just 4% of Americans say neither statement describes their views well.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Partisanship & Issues
Support for legal abortion is widespread in many places, especially in Europe
Public opinion on abortion, americans overwhelmingly say access to ivf is a good thing, what the data says about abortion in the u.s., nearly a year after roe’s demise, americans’ views of abortion access increasingly vary by where they live, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
- Rules/Help/FAQ Help/FAQ
- Members Current visitors
- Interface Language
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
- Spanish-English / Español-Inglés
- Spanish-English Grammar / Gramática Español-Inglés
Research in or research on
- Thread starter Fenix689
- Start date Feb 8, 2010
- Feb 8, 2010
Hi there, I would be very glad if someone could tell me what is the right preposition used with "research": A)(to do) research in... B)(to do) research on... c)(To do) research about... (is this posible) thanks beforehand.
Senior Member
A or B are possible. One does research in a particular field of study. He does research in cardiology. One does research on a particular subject. He does research on heart disease.
- Nov 7, 2018
"Research into" gets over 36 million hits on Google. "They are carrying out/ conducting /doing some fascinating research into/on the language of dolphins ." RESEARCH | meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary
More From Forbes
How important is research for bs/md programs.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Direct medical programs, often referred to as BS/MD programs, are some of the most competitive programs in the country. With programs at Baylor University, Brown University and Case Western Reserve University accepting less than 3% of all its applicants, these programs are often more competitive than the Ivy League. They are looking for exceptional students who are completely committed to becoming physicians. That means the students have spent the better part of their high school career pursuing STEM-focused activities, including physician shadowing, volunteering in healthcare settings and leadership positions in clubs.
Many BS/MD hopefuls pursue research as a way to build their resume.
Numerous BS/MD programs like Rensselaer Polytechnic University, like to see students with extensive research experience. Its program, aptly named the Physician-Scientist Program, wants to see students who will not only participate in research during their tenure in the program but also lead and create their own research projects. The University of South Carolina’s Accelerated Undergraduate to M.D. program has an extensive research and thesis component that is required throughout the student’s academic career. The University of Rochester offers funding for summer research for its BS/MD students. Similarly, the University of Illinois at Chicago looks for students who can demonstrate their “research aptitude.”
What Type Of Research Do BS/MD Programs Accept?
High school students have access to a wide array of research opportunities. School-related options could include science fair projects or AP Seminar and AP Research. Students might also choose to pursue camps or programs over the summer, which allows them to dedicate more time to research. Other students find independent research projects with a local professor. Alternatively, others opt to write a literature review paper to get published.
When BS/MD admission officers review applications, they don’t pit one type of experience against another. They know not every student will be able to find a local professor who allows them to research with them or can afford to do a paid summer program that spans numerous weeks or months. Consequently, they typically will consider holistically the depth of a student’s research experience, irrespective of the type of research the student completes.
Virtual Or In-Person Programs?
Both virtual and in-person experiences can add value to a BS/MD application. However, it depends on the program’s learning objectives and deliverables. Some students don’t have the flexibility to travel to an in-person camp and spend multiple weeks or months there. The University of Pittsburgh’s Guaranteed Admission Program says that “while in-person experiences are encouraged, virtual or remote experiences will be considered when evaluating the applicant.” For those students who have other obligations, a virtual camp might be the perfect fit and still offer a valuable experience.
‘Ghost Of Tsushima’ Is Already Flooded With Negative Reviews On Steam
Wwe smackdown results, winners and grades with stratton vs. belair, biden trump debates what to know as trump pushes for 2 more faceoffs, does the research topic matter.
The research experience doesn’t necessarily have to align with the student’s research interests, but it can often be helpful if it does. However, BS/MD admission officers know that high school students are still exploring their interests, which will likely evolve over the years. An opportunity that doesn’t align with the student’s interest will still be valuable because it allows the student to gain valuable skills that they can leverage to other research experiences in the future.
Summer programs might give students a chance to explore dual interests. Some students interested in medicine might also want to explore computer science or Artificial Intelligence, so finding an opportunity that allows them to blend those interests might be ideal. For example, Rising Researchers , a sister company of Moon Prep, is hosting two five-week summer camps that allow students to practice AI and Machine Learning to study human diseases. Other camps, like Penn Summer Academies, allow students to apply coding skills to other areas of study.
How Long Should The Research Experience Be?
The typical length of a research experience, especially one in the summer, can vary from as short as one week to up to eight weeks. A longer research experience can give students a more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter and, importantly, the opportunity to build meaningful relationships with their mentor and fellow students. However, the duration is not the sole determinant of a meaningful experience. Students should also look to see what the tangible outcomes of the program, such as a research paper, skills gained, letter of recommendation and more.
For students who find an independent research experience, the relationship might span several months or even years. Those experiences might result in more fruitful research results and a strong relationship between the student and the mentor.
Are Publications Required?
An experience resulting in a research publication is an added bonus, but it isn’t a requirement. If a student writes a research paper, even if not published, can still demonstrate the student’s scientific writing ability and add value to their college application.
Every BS/MD program is different, and the admission officers' value of research might vary from program to program. Ultimately, BS/MD programs are looking for students who are passionate about medicine and have had extensive experiences to affirm that passion. The College of New Jersey stated in an interview with Moon Prep that they are looking for passionate students, be it a deep involvement in Boy Scouts, Taekwondo or music. Therefore, students should never feel obligated to research if it does not align with their interests. Being genuine in their activities and demonstrating their passions is how to build a resume that stands out to BS/MD admission officers.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
Princeton University
Meet spot the ‘bot: course explores learning to live with robots.
By Aaron Nathans
May 16, 2024

SPOT, a Boston Dynamics robot, performs tasks in response to QR codes. Vivian Chen ’25 holds the code, while Vasumathi Venkat ’25, Aaron Serianni ’25 and Prof. Alexander Glaser observe. Photo by Aaron Nathans
The kids packed into Cotsen Children’s Library for their chance to meet SPOT, who descended a small staircase, sat on its hind legs, and then walked around on command.
SPOT — now a viral social media star — isn’t a real dog; it’s a Boston Dynamics robot. And the event, part of an interdisciplinary Princeton Engineering and Anthropology course, was an effort to get the kids comfortable with a technology that can come off as intimidating. The Princeton students who were serving as SPOT’s operators encouraged the kids to pet the robot when it was off.
“Some asked ‘what does the robot eat?’ Well, it doesn’t, you just stick it on your charger, like the docking station. I explained to them it’s a lot like your phone, or your video game controller,” said one of the students, Vasumathi Venkat, a junior majoring in electrical and computer engineering.
The class, “Robots in Human Ecology: A Hands-on Course for Anthropologists, Engineers, and Policymakers,” allows students to collaborate with the robot in a variety of lively ways. They discuss potential roles, meanings, and ethics of robots in society, as well as gaining hands-on experience manipulating the robot for generating ethically-sound and community-engaged applications on campus. The class, made possible by the 250th Anniversary Fund for Innovation in Undergraduate Education, is led by Alexander Glaser, associate professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering and international affairs, as well as Ryo Morimoto , assistant professor of anthropology and the Richard Stockton Bicentennial Preceptor.

The students neither invented nor built the robot, and while an increasing number of labs at Princeton are working to develop cutting-edge robotic devices, the purpose of this class was different: to help people better relate to a world that includes robots.
And what better way to make a robot relatable than to dance with it? One group of students created a project that made a splash on social media. They created a TikTok account for the robot, “SPOTlight,” which shows SPOT in various musical videos. In one video that received 4.5 million views, student Gigi Schadrack ‘25 line dances with the robot in a lab, complete with both jumping up on cue. In one that received 1.4 million views, she ballet dances with the robot.
In another popular video, the robot has fallen over on its side, and needs help getting back up on a mat.
Schadrack said the TikTok videos are part of an effort to demystify robotics, gather data, entertain, and engage audiences in discussions about interactions between humans and robots.
… Dancer: @G Disclaimer: this account is run by Princeton University students exploring use cases with Spot, a @Boston Dynamics robot. #robot #dance #robotics #tech #ballet #technology #princeton #princetonuniversity #viral #fyp ♬ Black Swan – Swan Lake – Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
Schadrack said she did not expect millions of views, but in following viral trends on TikTok, as well as best practices regarding the platform’s algorithm, she did expect healthy engagement with the posts.
“A gift of going viral meant eliciting a wide range of comments and replies,” Sami said. “As a group, we grappled with how our playful, performative content exists in dialogue with higher-stakes impacts of technology. Navigating our audience reaction taught us to consciously situate our work amidst the many uses of robots, as well as to listen openly to the discordant, plural voices on the internet.”
The majority of TikTok’s users are from Generation Z, which is the group that will most need to familiarize itself with human-robot interactions, Schadrack said.
Aaron Serianni ’25, a math major, said the class gave him a good sense of how industrial robots work, and what their limitations are, as well as their advantages. As sleek as SPOT may be, “it’s quite a limited use case,” he said. “I can imagine what it would take to broaden the uses of robots in everyday life.”
Vivian Chen ’25, an electrical and computer engineering major, said she loves robots, but this class allowed her to look at the technology in a broader context. “This is a great interdisciplinary course where we can learn with anthropologists, policymakers, and people in different fields,” she said. The course helped show how they feel about robots, she said, allowing her to work with her classmates on a group project “to see how we can influence the community and their perceptions about robotics.”

Related News

How do you make a robot smarter?

Data drives quicker, safer decisions for race cars and robots

Caterbot? Robotapillar? It crawls with ease through loops and bends

New initiatives bring Princeton to the fore of AI innovation

Science has an AI problem. This group says they can fix it.

Mengdi Wang makes a play at decoding disease

Alexander Glaser
Related department.

Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
- Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Reproductive rights in America
Despite state bans, abortions nationwide are up, driven by telehealth.

Elissa Nadworny

Abortion rights activists at the Supreme Court in Washington, D.C. on March 26, the day the case about the abortion drug mifepristone was heard. The number of abortions in the U.S. increased, a study says, surprising researchers. Drew Angerer/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
Abortion rights activists at the Supreme Court in Washington, D.C. on March 26, the day the case about the abortion drug mifepristone was heard. The number of abortions in the U.S. increased, a study says, surprising researchers.
In the 18 months following the Supreme Court's decision that ended federal protection for abortion, the number of abortions in the U.S. has continued to grow, according to The Society of Family Planning's WeCount project .
"We are seeing a slow and small steady increase in the number of abortions per month and this was completely surprising to us," says Ushma Upadhyay , a professor and public health scientist at the University of California, San Francisco who co-leads the research. According to the report, in 2023 there were, on average, 86,000 abortions per month compared to 2022, where there were about 82,000 abortions per month. "Not huge," says Upadhyay, "but we were expecting a decline."

Shots - Health News
What's at stake in the supreme court mifepristone case.
The slight increase comes despite the fact that 14 states had total abortion bans in place during the time of the research. According to the report, there were about 145,000 fewer abortions in person in those states since the Dobbs decision, which triggered many of the restrictive state laws.
"We know that there are people living in states with bans who are not getting their needed abortions," says Upadhyay. "The concern we have is that that might be overlooked by these increases."
Florida, California and Illinois saw the largest surges in abortions, which is especially interesting given Florida's recent 6-week ban that started on May 1.

Abortion rights opponents demonstrate in New York City, on March 23. Some states' abortion bans are known as "heartbeat bills," because they make abortion illegal after cardiac activity starts, usually around six weeks of pregnancy. Kena Betancur/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
Abortion rights opponents demonstrate in New York City, on March 23. Some states' abortion bans are known as "heartbeat bills," because they make abortion illegal after cardiac activity starts, usually around six weeks of pregnancy.
The latest report also captures for the first time the impact of providers offering telehealth abortions from states with protections for doctors and clinics known as shield laws – statutes that say they can't be prosecuted or held liable for providing abortion care to people from other states.
Between July and December 2023, more than 40,000 people in states with abortion bans and telehealth restrictions received medication abortion through providers in states protected by shield laws. Abortion pills can be prescribed via telehealth appointments and sent through the mail; the pills can safely end pregnancies in the first trimester.
The report includes abortions happening within the U.S. health care system, and does not include self-managed abortions, when people take pills at home without the oversight of a clinician. For that reason, researchers believe these numbers are still an undercount of abortions happening in the U.S.
Tessa Longbons Cox is a senior research associate at Charlotte Lozier Institute, a research organization that opposes abortion. She says the WeCount report, "highlights a concerning trend" that policies around mail-order abortion pills are boosting abortion rates. "By recklessly removing in-person medical visits and safeguards, abortion advocates have put women's health and safety last," Longbons Cox says in a statement.
Accounting for the increases
A major factor in the uptick in abortions nationwide is the rise of telehealth, made possible in part by regulations first loosened during the coronavirus pandemic.
According to the report, telehealth abortions now make up 19% of all abortions in the U.S. In comparison, the first WeCount report which spanned April 2022 through August 2022 showed telehealth abortions accounted for just 4% of all abortions. Research has shown that telehealth abortions are as safe and effective as in-clinic care.
"It's affordable, it's convenient, and it feels more private," says Jillian Barovick, a midwife in Brooklyn and one of the co-founders of Juniper Midwifery , which offers medication abortion via telehealth to patients in six states where abortion is legal. The organization saw its first patient in August 2022 and now treats about 300 patients a month.

A Supreme Court abortion pill case with potential consequences for every other drug
"Having an in-clinic abortion, even a medication abortion, you could potentially be in the clinic for hours, whereas with us you get to sort of bypass all of that," she says. Instead, patients can connect with a clinician using text messages or a secure messaging platform. In addition to charging $100 dollars for the consultation and medication – which is well below the average cost of an abortion – Barovick points to the cost savings of not having to take off work or arrange child care to spend multiple hours in a clinic.
She says her patients receive their medication within 1 to 4 business days, "often faster than you can get an appointment in a clinic."
A study published in JAMA Internal Medicine on Monday followed about 500 women who had medication abortions with the pills distributed via mail order pharmacy after an in-person visit with a doctor. More than 90% of the patients were satisfied with the experience; there were three serious adverse events that required hospitalization.
In addition to expansions in telehealth, there have been new clinics in states like Kansas, Illinois and New Mexico, and there's been an increase in funding for abortion care – fueled by private donors and abortion funds.
The impact of shield laws
During the period from October to December 2023, nearly 8,000 people per month in states with bans or severe restrictions accessed medication abortions from clinicians providing telehealth in the 5 states that had shield laws at the time. That's nearly half of all monthly telehealth abortions.
"It's telemedicine overall that is meeting the need of people who either want to or need to remain in their banned or restricted state for their care," says Angel Foster, who founded The MAP, a group practice operating a telehealth model under Massachusetts' shield laws. "If you want to have your abortion care in your state and you live in Texas or Mississippi or Missouri, right now, the shield law provision is by far the most dominant way that you'd be able to get that care."
Foster's group offers medication abortions for about 500 patients a month. About 90% of their patients are in banned or restrictive states; about a third are from Texas, their most common state of origin, followed by Florida.
"Patients are scared that we are a scam," she says, "they can't believe that we're legit."
Since the WeCount data was collected, additional states including Maine and California have passed shield laws protecting providers who offer care nationwide. The new shield laws circumvent traditional telemedicine laws, which often require out-of-state health providers to be licensed in the states where patients are located. States with abortion bans or restrictions and/or telehealth bans hold the provider at fault, not the patient.

The NPR Politics Podcast
One small pill — one big court case.
Existing lawsuits brought by abortion opponents, including the case awaiting a Supreme Court decision, have the potential to disrupt this telehealth surge by restricting the use of the drug mifepristone nationwide. If the Supreme Court upholds an appeals court ruling, providers would be essentially barred from mailing the drug and an in-person doctor visit would be required.
There is also an effort underway in Louisiana to classify abortion pills as a controlled substance.
- abortion bans
- Abortion rights

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A user asks which preposition to use in the phrase "do research on or about a topic". Other users reply with their opinions and examples, suggesting that "on" is more common and natural.
Examples: "My research into the university's recent news highlights its extensive community outreach". Research "on" wrongly hits the ear here because it can sound like you're stupidly attempting to say you put together this news yourself, when the sentence makes it clear you did not. "My research on the reception of the ...
do research on. This phrase is correct and commonly used in English. This phrase is used to indicate the topic or subject of the research being conducted. It is followed by the specific area of study or investigation. Examples: I need to do research on the effects of climate change. She is doing research on new technologies in education.
Research is the deliberate, purposeful, and systematic gathering of data, information, facts, and/or opinions for the advancement of personal, societal, or overall human knowledge. Based on this definition, we all do research all the time. Most of this research is casual research. Asking friends what they think of different restaurants, looking ...
Start writing the middle, or body, of your paper. Get your ideas down, then see if you need to do any research. Since your introduction and conclusion summarize your paper, it's best to write those last. [8] Include an in-text citation for everything that needs one, even in your initial rough draft.
Step 4: Create a research design. The research design is a practical framework for answering your research questions. It involves making decisions about the type of data you need, the methods you'll use to collect and analyze it, and the location and timescale of your research. There are often many possible paths you can take to answering ...
Abstractspiepr Abs1. Every day people do research as they gather information to learn about something of interest. In the scientific world, however, research means something different than simply gathering information. Scientific research is characterized by its careful planning and observing, by its relentless efforts to understand and explain ...
Placing research in the bigger context of its field and where it fits into the scientific process can help people better understand and interpret new findings as they emerge. A single study usually uncovers only a piece of a larger puzzle. Questions about how the world works are often investigated on many different levels.
Research is defined as a meticulous and systematic inquiry process designed to explore and unravel specific subjects or issues with precision. This methodical approach encompasses the thorough collection, rigorous analysis, and insightful interpretation of information, aiming to delve deep into the nuances of a chosen field of study.
The meaning of RESEARCH is studious inquiry or examination; especially : investigation or experimentation aimed at the discovery and interpretation of facts, revision of accepted theories or laws in the light of new facts, or practical application of such new or revised theories or laws. How to use research in a sentence.
The research process is more relevant if you care about your topic. Narrow your topic to something manageable. If your topic is too broad, you will find too much information and not be able to focus. Background reading can help you choose and limit the scope of your topic. Review the guidelines on topic selection outlined in your assignment.
RESEARCH definition: 1. a detailed study of a subject, especially in order to discover (new) information or reach a…. Learn more.
For research help, use one of the following options: Ask the GTL General Information & Research Help Phone: (607) 735-1862 Research Help Email: [email protected]. For help registering a device, password reset and more: EC IT Resources and Services
Research can span a broad range of approaches, from purely theoretical to practice-oriented; different approaches often coexist and fertilize each other. Research ignites human progress and societal change. In turn, society drives and supports research. The specific role of research in Informatics is discussed.
Research About. You can do "research about" things. This phrase is more about what your research is seeking to accomplish, rather than what field or subject you are conducting research on. Consider the following examples: My research about the behavior of animals in captivity is going well.
to do research about biology; to do research throughout biology; These are just some common prepositions (they all have different meanings), a list of the top 50 can be viewed here. With the edit. I'm speaking about researching something of a little value, not a social subject or a scientific matter or anything, more like a research (insert ...
Both 'research on' and 'research about' are commonly used phrases in English, but they are used in slightly different contexts. 'Research on' is typically used when referring to the specific topic or subject of the research, while 'research about' is more general and can refer to the overall investigation or study. Last Updated: March 22, 2024.
Do additional research as necessary. Cite your sources. Let's look at each of these steps in more detail. 1. Find a Topic. If you don't have a topic, your research will be undirected and inefficient. You'll spend hours reading dozens of sources, all because you didn't take a few minutes to develop a topic.
Research is the careful consideration of study regarding a particular concern or research problem using scientific methods. According to the American sociologist Earl Robert Babbie, "research is a systematic inquiry to describe, explain, predict, and control the observed phenomenon. It involves inductive and deductive methods.".
Developing a good research question can sometimes be the most difficult part of the research process. If you are struggling, follow the links below. Select a topic; Develop research questions; Identify keywords; Find background information; Refine your topic
Apr 6, 2007. #12. elroy said: "To research a subject" (not ON a subject) suggests something relatively in-depth. "To do research on a subject" suggests little or partial research. "To conduct" or "carry out" research on a subject would be a more elevated way to express the same idea. As was said, definitely not "make."
Ramakrishnan, a scientist at England's MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, won the 2009 Nobel Prize in chemistry for uncovering the structure of the ribosome. He said he felt qualified to write the book because he has "no skin in the game" of aging research. As a molecular biologist who has studied fundamental processes of how cells make ...
But research shows that leaders do not fully understand their employees' use of, and readiness for, AI. In addition, a significant number of Americans do not trust business' use of AI.
The research highlights the importance of staying ahead of the curve in technology. Companies that embrace digital technologies now are likely to be the ones that thrive in the future. And while there are still many unanswered questions about how these changes will play out, one thing is clear: The relationship between technology and business ...
The new Pew Research Center survey, conducted April 8-14, 2024, among 8,709 adults, surfaces ongoing - and often partisan - divides over abortion attitudes: Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents (85%) overwhelmingly say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, with near unanimous support among liberal Democrats.
English - United States. Feb 8, 2010. #2. A or B are possible. One does research in a particular field of study. He does research in cardiology. One does research on a particular subject. He does research on heart disease.
Many BS/MD hopefuls pursue research as a way to build their resume. Numerous BS/MD programs like Rensselaer Polytechnic University, like to see students with extensive research experience. Its ...
A class this spring "Robots in Human Ecology: A Hands-on Course for Anthropologists, Engineers, and Policymakers," allowed students to collaborate with a robot in a variety of lively ways. They discussed potential roles, meanings, and ethics of robots in society, and gained hands-on experience manipulating the robot for generating ethically-sound and community-engaged applications on campus.
Telehealth accounts for 19% of all abortions, new research finds. And while the number of abortions did plummet in ban states, overall abortions across the country are up.