
How to Write a Coursework

Coursework projects do not resemble essays, research papers, or dissertations. They are the combination of all three. Students spend less time writing coursework than on making a term paper, but this type of work requires more time and efforts than an ordinary essay - it is made of several essays. Thanks to our guide, each student can discover how to write coursework. If you are running out of time or lack experience to complete the specific coursework, we recommend using our coursework writing services to hire professional academic writers.
What is Coursework and Why Does It Matter?
Coursework definition: General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) coursework is a typical academic assignment, given in the course of study to evaluate the student’s knowledge, skills, and identify the final grade. Many students face this type of writing in the US colleges. One of the examples is a coursework UTD (The University of Texas at Dallas) - the requirements of this institution are strict, and many students fail to submit their papers and pass the corresponding courses.
Such type of assignment helps to have the ‘detective’ hat on: a student observes, examines, and evaluates the chosen topic using credible, up-to-date, and relevant sources. Working under controlled conditions is important. Participating in every school class will help to prepare good coursework by the end of the term. Take a look at the examples of what students of various profiles may face:
- English Composition - English coursework is an extended essay in most cases. A student has a right to pick the topic. The tutors provide their students with the list of recommended titles to choose from, sources to observe & analyze, and a format (e.g., a comparison between different relevant articles)
- Sciences - coursework for science is a complicated assignment. Such type of work appears in the form of a scientific paper to test what a writer investigates and reports independently.
- Geography - geography coursework is about collecting, reporting, and explaining information to reply to a certain geographical question or offer solutions to the problem. One idea is to explore the usage of a shopping mall or analyze the recent tornado. No matter whether you have to prepare a coursework Columbia or such paper for other educational institutions, keep in mind these differences!
Types of Coursework Explained
English Language coursework is the most common type of this assignment. At advanced GCE level, the student will be expected to write a couple of essays, totaling 3,000 words. Every assignment is 20 marks maximum.

An analytical essay : Evaluate, compare, & contrast 3 different sources of data interconnected by a common theme; written /spoken / multimedia content. Discuss different uses for targeting various audiences. Learn more on our blog.
Original essay with a supportive commentary : A student will have to come up with a single piece of media writing in the observed modes (written, spoken, or multimodal). Add a supporting piece with details about the aspects of English language. English Language & Literature coursework is a bit different. The basic requirements are the same, and the parts are:
An analytical study : Sharing an analysis of the chosen piece and its relation to the related content. It will show how well the writer understands the original piece. Tutors grade such works based on the:
- Use of the proper terminology and the coherence of the written words;
- Understanding & evaluation of the way a structure, form, and language create the written & spoken word;
- Opportunity to observe relationships between various pieces of writing.
Creative writing & commentary : Produce a creative piece that imitates the style of the assessed text. Share comments to backup your understanding. The goal is to show the knowledge, prove the competence, and use appropriate language skills in communicating with the target audience. You will also need a relevant coursework resume (review) in both cases. Keep on reading to learn how to write coursework of A level.
How to Write a Coursework: Guide for Students
Several factors may lead to the coursework being disqualified. It is a serious matter! The risk factors include:
- Plagiarism - it is the worst thing that could happen to any type of academic assignment. Lots of relevant information is available on the world wide web today, and the tutors are strict about the issue of plagiarism. Write everything in your own words! If you decide to insert the quotes from the sources, apply the suggested citation format and develop a list of references. Sign the declaration claiming it is your original project. If you're unsure about how to approach this, seeking professional help by choosing to write my coursework can be a wise decision.
- Word count - do not ignore the specific requirements concerning the length of the coursework. Specify if the footnotes, appendices, & references are included in the word count.
- Topics - go through the list of available themes. If there is an examination planned on the specific topic, try to pick another idea for the coursework.
- Tutor’s assistance - do not ignore the help of your instructor, ask them to provide guidance on what to write. Ask the questions to learn more details, but keep in mind they can go through the 1st draft once and just offer some general recommendations.
Choosing a Topic for Your Project
Dedicate enough time to this extra important question. Select the field of your interest if it is possible to relate it to the course. That is the golden rule of choosing a coursework topic - keep in mind the rest of the hints:
- Analyze the offered list of topics or develop yours
- Pick a topic from the area of your expertise related to the studied subject
- Select the topic you are interested in
- Choose the topic you’ve started to observe in the past
- Check how much relevant, up-to-date information is available on the Internet about each of the topics
- Pick what you can measure, change, & control (they call it a ‘fair test’)
- Use the ideas of previous researchers and students
- Do not choose a topic with a vast scope - you risk struggling to research it correctly
10 Good Coursework Topics
- Non-traditional Forms of Poetry with TC Tolbert
- Documentary Foundations: Usage of Oral Histories with Beth Alvarado
- Traditional Forms of Poetry
- Hermit Crabs: Type of Fiction
- Writing the Autobiographical Poem
- Creative Non-Fiction on the Examples of New Journalists
- Authors without Borders
- Writing the Sticky Stuff
- Socially Engaged Literary Arts
- Common Vocabulary
Research & Data Collection
Research is an integral part of coursework. Have you written research papers before? If yes, you will find it easier to select proper primary & secondary sources and gather the necessary information (evidence to support the main point - thesis). Depending on the required paper format, cite & reference the following sources:
- Books & e-Books
Base the project on a specific hypothesis. The research must start with minimum one hypothesis. The research stage for some topics may consist of visiting websites to collect information. Leave another time for collecting the data as it is the heart of the research. Three methods of data collection are known:
- Direct personal investigation : The one an author does individually (using literature and findings from previous studies);
- Interview/Questionnaire : The researcher should gather the data from the respondents asking questions regarding required data;
- Discussion with community leaders : Community leaders are approached to fetch information for the necessary data.
In case a student works on a scientific experiment, they should pay attention to planning the analysis with the help of rigorous scientific methods (keeping in mind the Health & Safety precautions you take). Review background information and theories. Take notes to express what you expect to occur to compare & contrast it to what happened in real life. In the write-up stage, one has to evaluate and present the findings.

Writing a Coursework Outline
The writing process follows the research. Do not start it without preparing an action plan and scheduling the work - a paper pin for English coursework is based on an extended essay . An outline will look different for the science coursework projects. The goal of creating a plan is to prevent a writer from being disorganized and waffling.

Let us explain coursework outline on the specific example - a project on the global pursuit of lower costs and the role of human rights.
Start with the brief introduction explaining why it might be a topic of interest for many people. Mention those vast corporations like Wal-Mart abuse human rights by choosing and using child labor in the factories.
Provide an overview of the problem . Define human rights and costs. Pick the definitions from the official dictionaries and cite them properly when inserting in the text. Try to explain the terms in your own words.
Develop a body of the coursework , start with the case for & against ethical business practices. Using evidence and examples, list the arguments supporting ethical business practices and another side of the coin. Include a business case for ethical practices after the opening body paragraph.
Move to discussing ethical responsibilities ; explain why business organizations should care about the ethical aspects of their activities. After three sections of the body, one can conclude the paper. It can be a good idea to share a fact or statistics stressing the importance of research problem in the essay conclusion. End up with the reference list that may look this way:
- Klein N (2000) No Logo (Flamingo, London)
- Marcousé I, Gillespie A, Martin B, Surridge M and Wall N (2003) Business Studies 2e (Hodder Arnold, Oxon)
- Royal Dutch Shell (2006) 4th Quarter Financial Report at (site example)

Additional Elements
Supporting materials and pictures are a must! The sciences & geography projects require tables, charts, graphs, and other types of images to illustrate the complicated topic. Not only should you add the pictures - it is essential to interpret and reference each of them. A separate part of the coursework where the student list and explains every visual element is Appendix , and it is an optional part. The presence of appendix increases the chances to earn an A+.
How to Write an Introduction for Coursework?
Most of the students underestimate the role of introduction & conclusion when it comes to writing an essay. An eye-catchy introduction is a key to success. The primary purposes of a coursework introduction are:
- To grab the reader’s attention
- To introduce the topic
- To explain the research importance
- To come up with a compelling thesis statement
The opening paragraph shows the depth of the writer’s acquaintance with the topic. Look at the expert tips below. They will help to learn how to write a coursework introduction to make the tutor want to read your entire paper.
What Is an Introduction?
The introduction of GCSE coursework is the opening paragraph that aims to interpret the central questions and purposes of the entire paper. It should have several elements to be effective. Those are:
- A hook sentence
- Background information
- Problem significance
- Solid thesis statement
Advice from our Experienced Writer
How to write an introduction to coursework? The quality of this part predetermines paper’s success. Look at some common mistakes writers do while working on the coursework introduction - try to prevent them!
Ignoring the prompt. Many students tend to neglect the tutor’s instructions. It is critical to read the prompt several times, highlight the main points, research question, rules, and grading rubric details.
Missing a plan. The prompt does not always say to develop a coursework outline. Without a plan for every separate section, it is impossible to write a flawless piece step-by-step. No matter whether you have to write a term paper, research paper, dissertation, or C3 coursework, get ready with the detailed plan. Once you understand how to write an introduction, it will be easier to develop the rest of the paper.
For those who need a helping hand in ensuring their work meets all the standards and deadlines, don't hesitate to buy coursework from trusted professionals.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
.webp)
We have to use cookies to be sure that our website functions properly. Click here for more information about our Cookie Policy and then tap Allow to continue your work
Top Special Offer! Check discount here
Get 13% off your first order - use TopStart13 discount code now!
- Admission Essay Writing
- Essay Writers for Hire
- Essays for Sale
- Pay for Research Paper
- Research Paper Writing
- Write My Dissertation
- Write Papers for Money
- Essay Editing
- Research Paper Editing
- Buy Assignments
- How it works
- Conclusion Generator
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Testimonials
- Tips and Hacks
How to Write a Coursework ✔ Tips by Academic Experts
Writing coursework is a unique task, but it’s also extremely common. Students must work on this assignment every year, but they inevitably face problems because coursework simultaneously functions as an essay, dissertation, and research paper. It borrows elements from different academic tasks and helps determine your final grade, so it’s important to do everything correctly. Because of academic pressure, it might take months to get everything together, and you’ll have to apply much effort to succeed. But don’t worry; our thoughtful guide will show you how to deal with it. You can buy coursework online if your time is already short, but if you’re ready for intense work, study the tips we developed!
Coursework Definition and Its Types
What is a coursework? It’s an academic task involving written and practical elements that seek to demonstrate a student’s knowledge of the subject. In every case, it comprises extensive research, and the coursework grade will play a decisive role in your final performance assessment. The point of this assignment lies in encouraging students’ critical thinking and boosting their research skills.
After fulfilling every part of the task, students gain invaluable experience that is bound to facilitate their future studies. Depending on their subject, they might face coursework of different types. Writing, practical study, and experiment are the three most common options. We’ll discuss them in more depth below so that you know what you should expect.
Explaining Three Main Types of Coursework
Writing a coursework means creating something between an essay and a dissertation. It’s the simplest and the most common coursework type that can take a variety of shapes across different disciplines. For instance, if someone is studying Literature, their professor might give them a list of questions that they’ll need to answer in a written format, explaining what made them think this way and justifying their position with arguments. They might also give you a specific topic that you’ll need to explore. Learning how to write an introduction and performing a literature review would be essential here: you’ll rely on other sources and your personal interpretations to create a complete picture of your subject. Your faculty will expect to see logical links between ideas, a documented research base consisting of credible sources, as well as your thoughtful observations.
What is academic coursework practical study? This is a more complex type of work. Imagine that we study History. Our topic entails establishing how the portrayal of women evolved in China. We’ll have to do theoretical research consulting other relevant sources, but the focus will be on practical elements. Choosing forms of art depicting women through the ages and finding and selecting excerpts from ancient literature about them would form the basis of our knowledge and insights.
So, when working on your coursework, do practical research that comes from you and your unique effort. This is similar to the experiment type: the only difference is that with the latter, you’ll have to focus on a practical part in particular. Choosing your area of research is vital: you need a hypothesis, a focus group you could use as a sample, and a special research design. You could interview people, send questionnaires to them, observe them, etc. In both tasks, your professor will value your original insights and the thoroughness of your research.
Facts that Might Earn You an Automatic Falling Grade
Another crucial element students must know is the examples of coursework violations. Everyone wants to avoid it for obvious reasons, but not everyone succeeds. Plagiarism is the first and worst issue. It may ruin everything you’ve worked for. Some faculties use softer approaches: they have a threshold of about 10% plagiarism. Their coursework will be deemed original if their students don’t deviate from this norm. But other professors might fail you even for one uncited claim. That is why you must use plagiarism detectors before submitting your work anywhere. Also, pay attention to claims people don’t know about and which you use in your coursework. For example, if you claim that women wore only dresses in China in 1200, you’ll need to point out a source from which you got this info. Ask your parents or friends if they know this information: if the answer is no, make a citation.
Word count within your coursework essay is also important. If your professor told everyone to write 2000 words, yet you wrote 1500, they might fail you either entirely or partly. Take your time. Writing more isn’t a good idea as well. Sure, it might win you more points for effort, but some professors won’t be happy with having extra work, and your grade will suffer. Select a good topic that corresponds to your subject and academic level. To be safe, get approval from your supervisor in advance because there is nothing worse than wasting months on work that will bring you nothing but failure. If you worry too much or the assignment is too important, and you think you lack time or knowledge, know that TopEssayWriting is aware of all these nuances and is willing to take care of it. Get the best essay writers for hire , and they’ll craft and perfect your coursework by the day you need it. Unlike students, they have extensive experience, and they’ll guarantee solid original research, appropriate word count and topic, as well as perfect formatting.
A Plan of Writing Coursework for Students
You know coursework definition already; you have heard about its types and nuances they entail. But how to write this kind of project? We’re going to list all relevant steps and describe them. First of all, take a look at the image below. It features a summary of each step. You can save and use it whenever you need it; share it with friends who might struggle with their coursework, too.

- Choosing a topic: look for inspiring ideas online, consider your sphere of interest, or consult your professor to pick the best topic.
- Research and collecting data: use Google Scholar or any other academic database to locate relevant academic articles, books, or websites. They must be credible.
- Organization: Analyze and categorize your findings.
- Developing outline: create an outline listing the major topics you plan on working within each of your paragraphs.
- Making the first draft: write an initial version of your paper by relying on your draft and briefly explore all ideas from it.
- Editing coursework: edit your coursework and flesh out your points until everything looks perfect.
But now, let’s review each stage of writing coursework thoroughly.
Step 1: Knowing What Topic to Choose
Selecting a strong topic is one of the guarantees of success. If you like it, if it’s relevant and has a lot of materials dedicated to it, you’ll enjoy doing research, and your professor will likely enjoy reading it. Some tips for making a good final choice: consult your supervisor if you have a trust-based relationship and know they’ll welcome it. If not, try online lists. There are plenty of them — in fact, we’ll offer you three potential topics right here! Just ensure your topic is broad enough to warrant lengthy research and avoid trite ideas. No one wants to hear about capital punishment, abortions, or marijuana because these topics are incredibly overused. Check these examples out.
1) Effect of Crowd Behavior on Victim Blaming
This example of coursework topic is interesting because most people can relate to it, plus it offers a wide territory for research. Everyone was a victim once in some minor or major way. Did you feel like you were blamed for something that happened to you? Or perhaps you felt inclined to blame someone when learning about what they experienced? The area of crowd behavior is also fascinating. Twenty people can be decent and law-abiding, but they can do horrifying things when put together. Why is that? Explore both topics, combine them using logical links, and enjoy many articles that could guide you.
2) Should There Be Any Regulations Concerning Fictional Content?
This coursework example is intriguing because it concerns a relevant topic. There is an increasing number of people who think that watching TV shows about murders or unequal relationships might automatically make viewers murderers and abusers. Take one or both sides of the issue; research them, their history, and examples of bans on fiction in the past; you could also choose any perspective from which to view it, be it legal, ethical, philosophical, or even religious.
3) What Strategies Can Help a Small Country Win a War against a Large Country
The value of this topic is its relevance. The war in Ukraine demonstrates how a large empire cannot defeat a small country. Ukraine is far from winning, so explore the current situation and past examples involving similar circumstances. It could be interesting and educational both.
Step 2: Starting Your Research
Doing research is a crucial step in coursework writing. Once students pick a topic, they must find sources that will help them explore their subject and make strong points. We suggest using both primary and secondary sources. The former include raw materials like interviews, memos, or reports; the latter are typical research articles with second-hand information. You can easily find a big collection of diverse sources on Google Scholar or in your college library. Just ensure that your chosen source is credible. If it’s a blog by an enthusiast, stay away from it. Wiki is a big no since any person can edit it. Check if the article has DOI, use websites with .edu or .gov, and rely on books published by academic houses. Remember that the fresher a source is, the more its relevance increases. Some professors insist students shouldn’t use articles older than 3 or 5 years.
Step 3: Organization
Take notes as you research or make a table with sources you’ll use, might use, or won’t use. It’ll help keep your research process organized. This organization is crucial as it allows you to categorize your findings, making it easier to reference them later. By sorting the information into different themes or arguments, you can identify areas where you have enough data and areas where further research might be needed. This step also helps in avoiding redundancy and ensuring that all your sources are relevant and contribute meaningfully to your argument. An organized approach to your research not only streamlines the writing process but also ensures a well-rounded and thorough exploration of your topic.
Step 4: Working on an Outline
What is coursework outline? It’s a short summary of key points that will be present in your essay. First, deal with technical elements: make a timeline of when you’ll be doing what. If you have four months to complete your coursework, dedicate month 1 to research, month 2 to outlines and drafts, month 3 to writing, and month 4 to final polishing. Having a schedule always helps stay on track. You’ll also need to structure your outline properly. Here is a potential overview of its structure:
- Introduction: include your thesis and sketch your topic’s background here.
- Literature Review: Summarize the current state of research on your topic.
- Methodology: describe how you collected data and what samples you used.
- Main Body: List the main ideas or arguments—present data, quotes, or examples to support your points.
- Analysis & Discussion: Interpret and analyze the results of your research.
- Conclusion: make recommendations for future research
- References: List all sources cited in your coursework in the appropriate format.
- Appendices: Include any additional material like charts, graphs, or raw data.

Adding just a few lines would be sufficient here. This outline will come in handy more often than you think: it will remind you whenever you forget what you want to do.
Take nuances of your formatting style into consideration, too. APA, for example, requires a title page and an abstract. This is how to reference a claim: “King Valluar died in 1444, leaving a record number of 214 children behind (Foster, 2022).” Add a page number when using a direct quote like this: (Foster, 2022, p. 13).
Our suggestion: stay strictly on topic. Understand its final point, break it into major points, and make every section in an outline concise and clear.
Don’t forget about additional elements — preparing them at this stage could boost your productivity later. Some topics require visual illustrations or the presence of tables. Include them. Cite them, make sure they are readable and have good quality; if you’re making them yourself, double-check them repeatedly.
Step 5: Creating the Draft
Start your academic coursework by consulting your outline. Introduction is particularly important as it’s the first section your readers see. Make it engaging by starting with a hook, an intriguing claim guaranteed to secure people’s interest. It could be a controversial claim, a powerful statement, statistics, etc.
Introduce the topic background and explain what you’re trying to achieve by writing this coursework. After this, it’ll be simpler to move toward the next sections. Don’t feel compelled to develop every point to perfection: brushing against the most important aspects would be enough for now. Keep your structure clean; don’t make paragraphs longer than 200 words. Cite sources in each paragraph at least once, preferably more often.
Step 6: Starting Editing Rounds
Read your draft. Identify its weak spots and correct them. It is time to do it if you didn’t develop your points properly. Keep expanding paragraphs until you reach the required word count, and everything feels complete. Cut the pieces you consider less relevant if the word count is too long.
With this done, check your coursework again for grammar, formatting, and style. Eliminate typos, catch instances of informal language usage (contractions, phrasal verbs, slang, etc.), and compare your formatting to a template. Remember that you could edit paper online with professionals. Our editing service is affordable and accurate, and our experts could give you content and/or proofreading assistance, combing through your text and removing every problem in it.
Exclusive Tips Based on Our Writers’ Personal Experience
As you probably figured out by now, our writers have seen numerous coursework examples in their work. Their years-long experience speaks for itself. We surveyed them, and they identified the three most widespread mistakes students made in their coursework and gave three pieces of advice.
- Failure to follow instructions. It seems like such an obvious thing, but no, multiple students keep treating their instructions inattentively. If professors asked them to explore 5 points, many explored 3 or 4; if they asked to write 3000 words, some wrote much less or much more than that. Finally, some students don’t understand their prompt, research the wrong topic, or not performing the kind of study they were asked to do.
- Lack of coherence. Only some people are good writers. Students often need to be more balanced between ideas erratically, skipping over connections or not elaborating on their point.
- Technical issues. Grammar or formatting mistakes, typos, or informal words are parasites that often slip into students’ texts without them noticing it.
- Re-read your prompt several times. Even if you’re confident you understood everything correctly, better be safe than sorry. Re-read instructions slowly, lingering on each element.
- Ask for help if needed. It doesn’t matter what’s wrong: if you cannot finish your coursework but you want plagiarism free papers of the highest quality, consult experts. They’ll help you.
- Don’t worry about seemingly losing time. Some students think that writing outlines or drafts is redundant. Yes, they might take time, but you’ll save it because you’ll spend far less time on actual writing. Create a solid preparatory base for yourself.
Create Well-Crafted Coursework and Secure Your Success
You know how to define coursework, what types exist, how to protect yourself from a bad grade, and which steps to follow to write a great project. Apply this knowledge in your studies! Start working on your coursework step by step, creating section after section and polishing each until even the strictest professor feels impressed. If something is amiss, contact TopEssayWriting ASAP and formulate your request. We are here every day and each night, serving students and connecting them with the best writers. Order personalized coursework examples, ask us to write a chapter or the entire work, demand editing or grading. Our services are always open to you. Get even more knowledge and succeed in your writing!
Related Blog Posts
Coursework writing poses an endless number of problems to students. It's time-consuming and exhausting. Rely on this guide and gain a deep understanding of this task!
There are many inspiring persuasive essay topics out there, and we tried to gather many of them in one place. Choose the best one for your paper.
- Terms and Conditions
- Money Back Guarantee
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
Customer support
- Buy Argumentative Essay
- Buy Coursework
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Reaction Paper
- Buy Research Paper
- Buy College Essays
- Buy Narrative Essay
- Buy Thesis Paper
- Expository Essay Writing
- Law Essay Writing
- Dissertation Writing
- APA Paper Writing
- MBA Essay Writing
- Nursing Paper Writing
- Graduate Essay
- Plagiarism Free Essays
- Research Paper for Sale
- Write My Assignment
- Write My Research Paper
- Write My Thesis
- Write My College Essay
- Coursework Writing Service
- History Essay Writing Service
- Business Essay Writing Service
- Psychology Essay Writing Service
- Book Review Writing Service
- Literature Review Writing Service
- Finance Essay Writing Service
- Persuasive Essay Writing Service
- Economics Essay Writing Service
- Descriptive Essay Writing Service
- Analytical Essay Writing Service


ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay Sauce
Welcome to Essay Sauce – the free student essay website for college and university students. Whether you’re writing an essay, preparing your dissertation or putting together coursework, you’ll find thousands of free essay, dissertation and coursework examples for you to use as inspiration for your own work, together with a wide range of useful guides. You can find essays sorted by some popular essay topics here .
Student essay categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays
Popular essay topics:
- 1984 essays
- A Midsummer Night's Dream
- A Raisin in the Sun
- Abortion essays
- Airbnb essays
- Amazon essays
- American Dream essays
- Animal Farm essays
- Animal testing essays
- Anne Frank essays
- Antony and Cleopatra essays
- Apple essays
- Argumentative essay examples
- Artificial intelligence essays
- Beowulf essays
- Boeing essays
- Brave New World essays
- Brexit essays
- Canterbury Tales
- Carol Ann Duffy essays
- Charles Dickens essays
- Charlotte Bronte essays
- Child Development essays
- Civil War essays
- Climate change essays
- Cloud Computing essays
- Coca cola essays
- Cold War essays
- Colin Kaepernick essays
- Corporate social responsibility
- Costco essays
- Death of a Salesman
- Death penalty essays
- Deforestation essays
- Diabetes essays
- Disney essays
- Don Quixote
- Drugs essays
- Edgar Allen Poe essays
- Essays on Coronavirus
- Essays on LGBTQ+ rights
- Essays on mental health
- Essays on racism
- Essays on Target Corp
- Euthanasia essays
- Facebook essays
- Fahrenheit 451 essays
- Fake news essays
- Fashion essays
- Fast fashion essays
- Feminism essays
- Frankenstein essays
- Gene editing essays
- General Motors essays
- Genocide essays
- George Orwell essays
- Globalisation essays
- Google essays
- Great Depression essays
- Gun control essays
- Hamlet essays
- Heart of Darkness essays
- Holocaust essays
- Huckleberry Finn Essays
- Human resource management essays
- Immigration essays
- Internet of Things (IoT) essays
- Jane Austen essays
- Jekyll and Hyde essays
- Johnson & Johnson essays
- Julius Caesar essays
- King Lear essays
- Langston Hughes essays
- Lord of the Flies essays
- Macbeth essays
- Margaret Atwood essays
- Martin Luther King Essays
- Marxism essays
- McDonald's essays
- Microsoft essays
- Much Ado About Nothing essays
- Nestlé essays
- Netflix essays
- Niccolo Machiavelli essays
- Nike essays
- Nuclear energy
- Nursing reflective essay examples
- Of Mice and Men
- Online learning essays
- Oscar Wilde essays
- Othello essays
- PepsiCo essays
- PESTEL analysis examples
- Police brutality essays
- Porter's Five Forces Analysis Examples
- Pride and Prejudice
- Primark essays
- Procter & Gamble essays
- Reflective essay examples
- Research Proposal Examples
- Romeo and Juliet essays
- Shakespeare essays
- Shakespeare's Poetry
- Shakespeare's Richard III
- Slavery essays
- Social media essays
- Starbucks essays
- Statutory interpretation essays
- Suffragette essays
- SWOT analysis examples
- Terrorism essays
- Tesla essays
- The Catcher in the Rye
- The Crucible (Arthur Miller)
- The Fall of the House of Usher
- The Fault in Our Stars essays
- The Great Gatsby essays
- The Merchant of Venice essays
- The Odyssey by Homer
- The Scarlet Letter
- The Tempest essays
- Things Fall Apart
- To Kill a Mockingbird essays
- Twelfth Night essays
- Uber essays
- Utilitarianism essays
- Vaccination essays
- Video games essays
- Walmart essays
- World War I essays
- World War II
- Wuthering Heights
We have a range of resources on this website including essay examples on a very wide range of topics. Our main categories are above. We have an additional free essays section , a coursework section, lesson plans and a range of guides . We are constantly working to add new essays and to tidy-up those that already appear on this site.
As not all of our essays are stored in our database, you can use Google to search this site for any topic. Format your query like this:
Please be kind – we work on this site in our own time, without pay, to help you!
How to Write a Coursework
What is coursework.
Let’s begin with a coursework definition. A coursework paper is an academic paper written during or after a course. The aim of this paper is to show your writing abilities and how well have you understood the course program. A coursework paper is an independent study that involves active reading and thinking. This paper allows you to communicate your ideas within a certain discipline and track your progress in a particular field of knowledge.
How to Do a Coursework Paper: What’s So Special
A coursework paper is usually assigned to students with the aim to test their knowledge in a particular theme or course. Typically coursework papers are written in the form of extended essays at the end of the year. Depending on your course, you will be completing normal coursework as homework which will be controlled by your teacher.
This paper may take the form of an extended essay, a record of field works, a report, a case study, a book review, a presentation of received information, and more. For example, during math classes your coursework may take the form of answers to a list of questions.
The coursework assignment is usually accompanied by a list of requirements that the student needs to consider while coursework writing. Activities involved in coursework writing may differ from one course to another. The topic for coursework may be assigned by the teacher or of your choice.
If you need to write a coursework paper for the first time, or you just want to improve your writing skills – this guide is for you. In the following paragraphs we will tell you how to write a coursework paper step by step, as well as give helpful tips and an example paper.
How to Write a Coursework Paper Step by Step
1. Come up with the topic. It is necessary to pick a good topic for the coursework paper, as it should be interesting enough to motivate you to make the research and write a great paper. Don’t pick a topic too wide, as you won’t be able to write about everything in the limited word count. You can look through already completed coursework on your course to see what good topics look like. On this there is no need to come up with the full title – you need to find the right direction. If you were assigned a particular topic, then you should check attentively what you are asked to do.
Note: Arrange a meeting with your supervisor for advice. Make a list of interesting topics and ask him or her what topic is better to choose. The teacher will point out what topic is from the right perspective and good to discuss, and what topic is better to put away. If you are lucky enough, you may be advised on a list of books and other sources that contain necessary information related to the topic.
Also, consider the fact that in the future you can mention your coursework in your resume. Think about your future career ahead of time and how to write relevant coursework, resume that contains such projects will be highly appreciated.
2. Conduct a preliminary reading. Conduct research to find out more information about the topic and narrow it down. Choose only reliable and relevant sources of information. Mention the most useful information that you can use as a source for citation and basis for your research.
Try to store all information, links, and documents in one place. Such a habit will be helpful when writing more voluminous works like theses and dissertations. Ask your tutor to help you choose the right topic for your project if you experience troubles with choosing the right one.
Take notes along the research. You can create a document on your desktop and save the most powerful quotes (with links to the source) or just make a bullet list of ideas and main points that came into your mind while reading sources. Always mention the resource for proper referencing.
3. Create a plan. When you have an informational basis, it will be time to create a plan that will help you organize your ideas and time. Don’t strive for perfection, as you can change the plan during writing coursework – it may become clear that some chapters are odd or you need to add a chapter to make everything clear about the topic. You can use any creative techniques and brainstorm to come up with the list of points.
The typical structure of a coursework paper looks like this:
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Body paragraph
- References list
Select your own paragraphs according to the information available, and ask your tutor for coursework help if necessary. Remember, proper planning is a good way to be sure that your thoughts move in the right way, so that your coursework will have unity and coherence.
4. Conduct research. Choose the most appropriate type of research and choose the needed tools. If you need to conduct a field study or an experiment, keep in mind that you will need to plan them ahead and consider the peculiarities of conducting the particular type of research (resources, people, admissions, etc.). Take notes while conducting the research and analyze the results.
5. Start writing body paragraph(s). Following the paper plan, start creating body paragraphs. Make sure that you highlight one particular idea for one paragraph. It is important to consider requirements and principles of academic conventions while preparing your paper.
Write this paragraph with the idea that your reader is intelligent, but doesn’t know much about your topic. Don’t state well-known information or repeat something that you have already described. Each paragraph should give an answer to a certain question, so make sure that you have created transitions between paragraphs and how it all refers to the main topic.
Use diagrams, tables, and charts to illustrate the received data. Make a short interpretation of the data below the illustration. Use only the data that is directly connected to the paragraph. Add headings and descriptions if necessary. Support materials that don’t relate directly to the paragraph can be attached in the appendix.
6. End your paper with a relevant coursework resume. In the conclusion, it is necessary to sum up the work done and draw conclusions. Repeat the main points in brief form and express your opinion on the current state of the problem. If the assignment asks you to answer a certain question, state the final answer in the conclusion.
How to write the conclusion of coursework? Do the same as with the introduction.
What should be in the conclusion?
- Introductory text about the goal and objectives of the work
- A brief description of the object and subject of research
- Conclusions, for each chapter, starting with the first, sequentially stated
- Conclusion on the compliance of the work performed with its plan, goals, and objectives
- Confirmed evidence of the relevance and significance of the work performed
- Identified tasks and directions for the development of the subject matter of coursework.
7. When all parts mentioned above will be written, it will be time to write the introduction. Why have we left this part for last? It is quite simple. The best time to write an introduction is when you have the full text of your paper and you can say that you know everything about your work. This will help you make your introduction engaging and full of needed information. Don’t forget to write a thesis statement that will cover the main goal of your paper.
The introduction should contain the following:
- Justification of the relevance of the chosen topic
- Review of the degree of knowledge of the problem
- Goals and objectives of coursework
- Subject and object of research
- Description of the structure of coursework
- Characteristics of the literature used
- Description of the research methods used.
8. Edit and proofread the text. As you will finish the last sentence of your paper, put the text aside for some time. Reread your text several times with fresh eyes. Make a grammar and spelling check. Ask a friend or relative who is skillful in academic writing to proofread your text. Also, make sure that your text is readable and logically structured. Each paragraph should smoothly flow into the next. Answer the following questions to be sure that your text doesn’t need corrections:
- Have you identified the key issue in the thesis statement?
- Have you selected relevant primary and secondary sources?
- Have you clearly structured the text?
- Is the information presented in a logical manner?
- Have you demonstrated the relationships between paragraphs?
- Does your writing adhere to the requirements?
- Have you properly referenced sources in an appropriate manner?
- Have you analyzed sources properly? Have you used summarization?
- Does your research fully answer the main question?
- Are data and illustrations at the right place?
9. Prepare for the oral presentation (if required). Some coursework assignments ask students to make a presentation of their research and give an oral presentation. Ask your teacher how much time you will be given for the presentation. Your presentation should have the same structure as your paper. Include only the most interesting and important points in your paper.
Coursework Example Analyzed
We think that theory is good, but practice is better. We accompany this guide with an example you can use as a model essay and learn how a finished coursework paper should look. In the following sample the author discussed the ways of preventing age discrimination in the workplace. Look how the author approaches the topic and organizes ideas into a well-structured text. Please, note that this sample is not a full work – it is only an excerpt of a coursework paper. Check our blog for more coursework examples ! You can use such coursework examples during the writing process to avoid any mistakes in your paper.
Click the images to see their full size.
Tips on How to Write a Coursework Paper
We have gathered a list of tips that you should consider while writing to produce a well-crafted text.
- If you encounter a problem with your coursework, don’t hesitate to ask your teacher for help.
- Make your introduction shine. Professors usually read the introduction with high attention, so don’t spoil the first impression from your work with weak words in the introduction.
- Start working on your coursework as soon as possible. Make a timetable to be sure that you will complete your work on time. This will help you to keep calm, because you won’t be writing in a rush.
- Divide the work into several parts. It is too hard to complete a paper just in one sitting.
- Ask for help if you don’t understand some points in your assignment. Ask the teacher who has assigned this coursework to assist you in your work.
- Always mention sources that you have used in your paper and properly cite this source according to the required formatting style.
- Pay attention to the research part of your paper. Your writing shouldn’t just be a summary of the sources. Gather as much information about the topic as you can.
- Save all versions of your coursework. It will be especially useful if you decide to cut a big part of the text, and then used it once again in another context.
- Strive to finish the final draft of your paper ahead of the deadline. This will allow you to leave more time for corrections and ask your supervisor to give feedback on your paper.
How to Write a Coursework without Mistakes
Here we have gathered a list of mistakes students frequently make while writing coursework papers. It is important to know what points you need to consider to create a good paper. Read them all to be able to avoid them and improve your paper.
- Don’t exceed the word limit. Don’t think that more words will give you a better mark. One of the aims of academic writing is to present information in a correct and concise way.
- Avoid personal opinions in the body paragraph. Leave your thoughts to the conclusion.
- Don’t list references that you haven’t used in your paper just to increase the number.
- If you have found a completed coursework paper on similar topic, don’t copy it! You may be accused of plagiarism.
- Don’t skip formatting and editing the paper. Pay attention to this point, as organizing your text in the wrong way can lower your grade.
- Don’t include in your coursework information that doesn’t relate to your topic.
- Don’t fail to read instructions and demands attentively. Read the instructions provided by your professor and analyze them. Make sure that you have understood everything.
- Don’t concentrate on grammar and spelling while writing. This may distract you from important ideas and mistakes you will correct when you finish the text.
- Don’t forget to leave enough time for the research.
In this article we have gathered an extensive list of advice about how to do coursework papers. We hope that you will find our guide and tips on writing a coursework paper helpful. If you are still experiencing some troubles with your paper, for example, if you are uncertain what type of research you need to do, ask your teacher for advice.
How to Choose Coursework Topics
- Ask your supervising teacher for help. Don’t be afraid to ask your teacher or coursework writer for help. You are still studying and no one will judge you for this. If you already have some English coursework ideas , your instructor will help you to express them in the right words. Also, he or she can tell you if you have enough information for this or that topic or if you should refuse from writing about this theme. Also, your instructor can help you to find reliable sources thatare crucial for writing coursework.
- Define your area of interests. It would be easier to write on the topic that makes you feel enthusiastic. If you can’t find one, choose the least boring for you. Anyway, we sure you’ll find some interesting information no matter what topic you choose.
- Think over prospects. If you decide what college or university you would like to enter, find the information about the projects in this or that institution affiliation. Also, you should think about your future profession. Sometimes, when you don’t have working experience, your coursework can be taken into account. So, think of your future occupation now and take steps toward your goal.
In this article we have gathered an extensive list of advice about how to do coursework papers. We hope that you will find our guide and tips on writing a coursework paper helpful. If you are still experiencing some troubles with your writing, for example, with a research paper, you can always ask us for help. Just leave a request, “ write my research paper ” on our site.
Give your grades a boost
Original papers by high quality experts
Free preview and unlimited revisions
Flexible prices
- Retirement Farewell Speech Example
- Farewell Speech Example
- Business Owner Farewell Speech Sample
- Receiving a Twenty Year Service Award
- Princeton Graduation Speech
- Never Giving up on a Dream
- Medical Student Graduation Speech
Semi-formal
- Tribute Presentation Sample
- Greenpeace Organization
- Treatments of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Marketing Manager Speech Sample
- Demographic Policy and Abortion in China
- Causes of Teenage Drug Addiction
- Positive Effects of Classical Music
- Developing of Professional Skills of the Employees
- College Psychologist Speech
- How to Plan an International Trip Essay
- Demonstrating a Marketing Plan for New Product Line
- Destructive Effects of GMO on Children
- Child Adoption Speech
- Become a Volunteer
- Why Videos Go Viral
- Party Planning for Children’s Birthday Parties
- Modern Relationship Problems Presentation Sample
- The Advantages of Jogging
- Let’s Become Vegetarians
- Killing Routines
Academic Essay Examples and Samples
Being the most important writing task for college and university students, it is important to look through samples of essays to get a clear picture of how to write one on your own.
How to Write an Academic Essay: The Full Guide
Writing an academic essay, whether for a school assignment or a scholarly publication, requires a unique set of skills. Unlike casual writing or opinion pieces, an academic paper requires the author to present a clear and well-reasoned argument on a particular topic. If you’re struggling with your work a little bit, a free literature review generator can be a useful resource. The purpose of the essay could be to inform, persuade, or describe, but regardless of the type of academic essay, the process of essay writing largely remains the same. This guide to essay writing will walk you through the process of crafting an excellent essay, from the initial brainstorming phase to the final proofreading stage.
Types of Academic Essays
There are several types of academic essays, each with its own purpose and structure. The narrative essay tells a story in a structured manner, often presented in chronological order. The descriptive essay aims to paint a vivid picture for the reader, describing an experience or an object in great detail.
An expository essay or informative essay, is designed to educate the reader about a particular topic. It’s a facts-based essay that requires thorough research and a clear, concise presentation of the information.
Lastly, a persuasive essay or argumentative essay, aims to convince the reader of a certain viewpoint. It’s essential to present clear arguments and evidence to support your stance in this type of essay.
Knowing the specific characteristics and objectives of these essay types can help you in determining the best approach for your academic writing.
Proper Format for Your Academic Writing
The structure of an academic essay is typically divided into three main sections: the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
The introduction , or opening paragraph, presents the topic of your essay and provides a glimpse of your thesis statement or central idea. This section should grab the reader’s attention and provide some context for your main argument.
The body paragraphs , or main sections of your essay, provide the bulk of your argument. Each paragraph should contain a single point or idea that supports your thesis statement. It’s important to present your points in a logical order and provide clear evidence for each of your arguments.
The conclusion of your essay, provides a wrap-up of your main argument and final thoughts on the topic. This section should not introduce any new ideas but rather summarize your key points and reaffirm your thesis statement.
Properly structuring your essay and ensuring that each section fulfills its purpose is crucial for creating a compelling and well-organized academic paper.
How to Create an Outline for Academic Essay: A Step-By-Step Approach
Creating an outline for your essay can make the writing process much smoother. It helps you organize your thoughts, keep your essay focused on your thesis statement, and ensure that each of your body paragraphs serves a distinct purpose in your argument.
Start by brainstorming ideas related to your topic and organizing them into a logical order. Once you have a general idea of what you want to cover, you can develop your thesis statement, the central idea that will guide your essay.
Next, create a list of main points or arguments that support your thesis. Each of these will become a body paragraph in your essay. For each point, consider the evidence or examples you can use to support it.
Once you have your outline, you’re ready to start writing. Begin with a draft and don’t worry about making it perfect. Focus on getting your ideas down first, then revise and edit until you have a polished academic essay.
In conclusion, writing an academic essay involves careful planning, a clear understanding of the essay type, and meticulous attention to structure and format. By following these guidelines, you can craft an academic paper that effectively communicates your ideas and meets the standards of scholarly writing. Whether you’re new to academic writing or looking to refine your skills, this guide provides a comprehensive overview to help you succeed in your academic writing endeavors.
Research and Planning for an Academic Essay
Before you begin writing an academic essay, it’s essential to do your homework. This involves understanding the essay prompt, researching the topic, and planning your essay. Research is a crucial part of academic writing. Unlike narrative or descriptive essays, where personal experience or observation can be the primary source of information, an expository or persuasive essay relies heavily on facts and evidence. Therefore, it’s vital to gather reliable and relevant sources that can provide a solid foundation for your argument. Planning, on the other hand, helps in organizing your thoughts and ideas coherently. A well-crafted outline serves as a roadmap for your essay, ensuring that you stay on topic and effectively address the thesis statement.
Crafting a Strong Thesis Statement
The thesis statement is a crucial component of an academic essay. This single sentence serves as the cornerstone of your argument, succinctly presenting the main point or central idea of your essay. A strong thesis statement is clear, concise, and specific. It makes a claim that requires support through evidence and provides a roadmap for your essay’s direction. For a persuasive essay, it’s essential to take a stance, while an expository essay would require a thesis statement that articulates the focus of your investigation.
Writing Engaging Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs form the meat of your academic essay. These main sections contain the supporting arguments or ideas that validate your thesis statement. Each paragraph should start with a topic sentence that presents one aspect of your argument, followed by evidence or examples to support it. It’s also crucial to provide analysis or explanation showing how the evidence supports your point. Remember, these paragraphs need to be cohesive, maintaining a logical flow of ideas from one to the next.
Mastering the Art of Introduction and Conclusion
The introduction and conclusion of your essay act as the ‘bookends’ to your argument. The opening paragraph, or introduction, sets the tone for your essay. It provides the context, introduces the topic, and presents the thesis statement. It’s crucial to make the introduction engaging to grab the reader’s interest.
The conclusion, on the other hand, brings closure to your essay. It’s your chance to revisit the main points, reinforce the thesis statement, and provide final thoughts or implications of your argument. Be careful not to introduce new ideas in the conclusion; it should merely wrap up the essay by synthesizing the information presented.
Proofreading and Editing Your Essay
After drafting your essay, the final steps are proofreading and editing. This process involves checking for grammatical errors, ensuring your arguments make sense, and verifying that you’ve adequately addressed your thesis statement. It’s a good idea to take a break before you start proofreading so you can approach your work with fresh eyes. If possible, ask a peer or mentor to review your essay, as they might catch mistakes that you’ve overlooked.
Writing an academic essay can be a challenging yet rewarding process. It requires critical thinking, thorough research, and meticulous attention to detail. By following these guidelines and tips, you’re well on your way to crafting an excellent academic essay that effectively communicates your ideas and arguments.
Putting It All Together: The Journey of Academic Essay Writing
In conclusion, academic essay writing is a systematic process that requires a blend of creativity, critical thinking, and a firm grasp of essay structure. Whether you’re crafting a narrative, expository, persuasive, or descriptive essay, understanding the unique demands of each type is crucial. Each essay type serves a distinct purpose, be it presenting a compelling story, delivering well-researched information, or asserting an argument convincingly.
From choosing a topic and crafting a robust thesis statement to structuring engaging body paragraphs and bringing your thoughts to a powerful close, each step contributes to the overall coherence and impact of your academic paper. Beyond writing, the importance of meticulous proofreading and editing cannot be overstated, as they ensure your scholarly writing meets the high standards expected of it.
With practice and dedication, you can improve your academic writing skills and deliver excellent essays consistently. Remember, writing is as much a journey as it is a destination. So, embrace the process, learn from your experiences, and strive to make each essay better than the last.
Birth Rate Issue in South Korea. Essay Sample and References
Overview: South Korea is currently facing a significant challenge with its declining birth rate. The country’s birth rate has been on a downward trend for…
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation. Essay Sample and References
Overview: Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation represent two distinct types of motivation that drive human behavior and decision-making. Intrinsic motivation refers to engaging in an activity…
Influence of religion on Literature – Essay Sample and References
Overview: Religion has exerted a profound influence on literature throughout history, shaping themes, narratives, and literary techniques. This interplay between religion and literature reflects the…
Suzuki Shinichi Theory in singing in early childhood education – Essay Sample and References
Overview: The Suzuki Shinichi Theory in singing for early childhood education revolves around the educational philosophy and methods developed by Dr. Suzuki, primarily known for…
Hirschi’s Social Bond Theory
The following sample is meant to be a source of inspiration for students in their academic pursuits. In the realm of criminology, theories that explain…
Another Brick In The Wall Meaning
The following review example can serve as a guide for students trying to find inspiration when writing an assignment on “Another Brick In The Wall:…
Rationalism vs Empiricism
The following review example can serve as a guide for students trying to find inspiration when writing an assignment on “Difference between rationalism and empiricism”.…

Classical vs Operant Conditioning
The following review example can serve as a guide for students trying to find inspiration when writing an assignment on “Classical and operant conditioning”. Classical…
Was Fidel Castro a Good or a Bad Leader?
The following review example can serve as a guide for students trying to find inspiration when writing an assignment on the question “Was Fidel Castro…
Themes in The Crucible
The following review example can serve as a guide for students trying to find inspiration when writing an assignment on the themes in “The Crucible”…
Lord of the Flies Themes
The following review example can serve as a guide for students trying to find inspiration when writing an assignment on the themes of “Lord of…
Malcolm X vs Martin Luther King
The following sample is meant to be a source of inspiration for students in their academic pursuits. The American civil rights movement, a pivotal era…
Fate vs Free Will in Macbeth
Shakespeare’s “Macbeth,” written in the early 17th century, stands as a timeless masterpiece that delves into the profound and often debated theme of fate in…
Why Is Of Mice And Men Banned
John Steinbeck’s “Of Mice and Men” is not just a book; it’s a journey into the heart of American literature, a journey that has captivated…
Who Dies In Romeo And Juliet
The following sample is meant to be a source of inspiration for students in their academic pursuits. In the world of literature, the death of…
Was Julius Caesar a Good Leader?
The following review example can serve as a guide for students trying to find inspiration when writing an assignment on the question “Was Julius Caesar…
Why is Iago Jealous of Othello?
The following review example can serve as a guide for students trying to find inspiration when writing an assignment on “Othello”. In “Othello,” William Shakespeare…
Themes in To Kill a Mockingbird
The following review example can serve as a guide for students trying to find inspiration when writing an assignment on the themes in “To Kill…
Is Listening to Music a Hobby?
The following argumentative essay example can serve as a guide for students trying to find inspiration when writing an assignment on hobbies and music in…
Of Mice and Men Theme
The following review example can serve as a guide for students trying to find inspiration when writing a discussion piece on the Of Mice and…
Remember Me
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
IB English HLE Explained
Free introductory guide to IB English Higher Level Essay (HLE) by IB44 and IB45 graduates Lareina Shen and Saesha Grover.
In this guide, LitLearn students (and 2022 IB grads!) Lareina Shen and Saesha Grover share their wisdom on how to conquer the IB English Higher Level Essay (HLE).
Lareina achieved an IB44, and Saesha achieved an IB45 as well as the coveted IB7 in IB English Literature HL, so you are in safe hands.
Meet your instructor Jackson Huang, Founder of LitLearn. His mission is to make IB English as pain-free as possible with fun, practical lessons. Jackson scored an IB45 and was accepted to Harvard, Amherst, Williams Colleges, and full scholarships to University of Melbourne & Queensland.

What is IB English HLE?
The HL Essay (HLE) is a 1200-1500 word essay about a text studied in the IB English course. For Lang Lit, the work you choose to analyze can be literary or non-literary, but for IB English Literature the text must be literary.
The HLE will make up 25% of your final IB English HL grade , and it is graded externally. You must choose your own line of inquiry (i.e. a question that you will answer in your HLE–more on this later).
How do I choose my text for HLE?
Do NOT choose the “easiest” text. Life is always better when you do things you're interested in, and that advice applies to the HLE, too. Choose the literary / non-literary work that interests you the most, so that you can (semi?)-enjoy the HLE planning and writing process.
You could start by thinking of a theme that you find particularly interesting and determining which text studied in class demonstrates this theme well.
How do I choose my line of inquiry for HLE?
The line of inquiry is the core question that you will answer in your essay. A quick example might be:
"To what extent is masculinity undermined by the characterisation of Little Thomas?"
Now, it's your job to forge your destiny and come up with your own line of inquiry. But it's not a complete free-for all! There are rules. The main rule is that your line of inquiry must fall under one of the 7 main concepts of IB English (see below for a quick summary).
This summary is vague, so let's go in-depth on a couple of these concepts to really show you what you should be doing in the HLE.
Identity is what makes you, YOU. Here are some questions the concern your own personal identity:
- What is your favourite colour? And why is it your favourite?
- What makes you different from others? Why do you think these qualities came to be?
- How would someone describe you in three words?
Now apply this same logic to characters within your text.
- How would you describe this character in three words?
- How do their actions within a text influence your view of their identity?
- How has the author crafted this character to make you view the character in a certain way?
Let's take a look at a concrete example of how we might choose evidence and quotes for a HLE on cultural identity. This example is based on a Vietnamese work in translation “Ru” by author Kim Thúy. For context, “Ru” is an autobiographical fictional account which explores Kim Thúy's move from Vietnam to Canada as an immigrant and her consequent struggles. The structure of her novel is largely lyrical and poetic.
Let's look at a section from her novel that may help us come up with an essay idea based on the concept of Identity. When she returns to Vietnam, she attends a restaurant, however this becomes a major awakening for her in terms of how she views her own personal identity. Kim narrates within her novel:
The first time I carried a briefcase, the first time I went to a restaurant school for young adults in Hanoi, wearing heels and a straight skirt, the waiter for my table didn't understand why I was speaking Vietnamese with him. Page 77, Rú
This is a perfect quote for the Identity concept. Can you see why? Let's think through it together…
Why would the waiter be confused if Kim, a “briefcase”-carrying individual in “heels” and a “straight skirt”, was speaking Vietnamese with him?
What does being “Vietnamese” look like to the waiter? Why does Kim not conform to his expectation? Was it perhaps due to what she was wearing?
Now, if we look at the section which follows this in the novel, we are able to see the impact this had on the character of Kim's sense of identity.
the young waiter reminded me that I couldn't have everything, that I no longer had the right to declare I was Vietnamese because I no longer had their fragility, their uncertainty, their fears. And he was right to remind me. Page 77, Rú
Here, we can clearly see that this character is now questioning her Vietnamese cultural identity. This is just one example that demonstrates the concept of Identity.
Culture seems to be this confusing thing. Does it have to do with religion? Race? Beliefs? What does it mean? Does the monster from Frankenstein fit into a certain culture?
The easiest way to put it is this: Culture is the way someone lives. It is their “way of life.” Think of it as an umbrella term. “Culture” can include so many different things; the list just goes on, for example religion, values, customs, beliefs, cuisine, etc.
Now think, how would I form an essay from this concept?
- When you read a text in class, you will notice that authors let you form an opinion on the culture of certain characters or groups within a text, but how is this done?
- How does the author represent the culture of a certain community?
- What types of patterns in daily routines are discussed?
It seems odd writing an essay about “creativity” because… like… how can anyone definitively say what ‘counts' as being creative–or not? When I say the word creativity , I think of new inventions, or maybe those weird and wacky art installations living inside those ‘modern art' museums. But hey, what's creative to me might not be creative to you!

When formulating a HLE on the concept of creativity we have two main pointers for you. Look for:
- Interesting + Unique techniques or literary devices used within a text by the author. You can learn more in the Learn Analysis section of LitLearn.
- Recurring stylistic choices by the author
Now, for this concept, let's look at how we might select supportive evidence and quotations for a HLE on creativity within the narrative style of author Mary Shelley in “Frankenstein”. The narrative style uses epistolary narration . This is a narrative technique in which a story is told through letters. This was something that I found both interesting and recurring within Frankenstein, which I believe worked to create a personal touch within the novel.
Additionally, Mary Shelley allows different characters to narrate Frankenstein during different volumes. Let's investigate this! I have written out different character profiles of the narrators below:

These 3 characters, each relate a part of the novel Frankenstein. This is an example of a creative authorial choice that allows us, as readers to explore different points of view within the text. This is just one example of a creative aspect of a text which you can analyze for your HLE.
Representation
Representation is all about how something is portrayed, conveyed, shown, described, illustrated, depicted . There are many different things that can be ‘represented' within a text, and it doesn't have to be tangible.
For instance, you can look at how a belief, idea or attitude is depicted within a text through different characters or devices.
Again, let's explore a concrete example to make things clear: this time the graphic novel “Persepolis”. We'll consider an HLE on how a text represents the impact of political turmoil on society .
Chapter 10 of “Persepolis” highlights societal changes occurring due to the Iranian Revolution. The panels below list the authorial choices relevant to the negative representation of political change in a society. When looking at the techniques highlighted in the slides below, think about how you feel when you look at the panels below. Can you sense a more positive or negative feeling?

Cool, but what do we do to turn all this into an actual HL essay? Here is a sample response. The introduction might begin like this:
In the captivating graphic novel “Persepolis,” the author Marjane Satrapi explores the social and political impacts of the Iranian revolution. In particular, Satrapi conveys a disapproving viewpoint on political turmoil within the text. Throughout the graphic novel, Satrapi carefully represents how social isolation, hypocrisy and confusion is experienced by a young girl living in Tehran, as a result of political turmoil. Example HLE Introduction
Then, in a body paragraph, on one of the key ideas mentioned above, we could analyze the different literary techniques. For example, Panel 1 is a great representation of the experience of confusion in the midst of political turmoil:
Marji is the younger girl pictured in the panels above. While her parents appear quite concerned by the news on the TV, she appears to not be in full comprehension of the cause for their distress. This is demonstrated by the visual imagery and dialogue, in panel 7, for instance, if you observe the facial expressions by each of the characters. Example of analysis in body paragraph
This is just a short example from one particular text. To help you unpack any text, try look for the following when analyzing chapter to chapter:
- What is the main idea of the chapter?
- Why did the author write it? What purpose does it serve?
- What do you believe is the overarching importance of the passage?
Brainstorming Tips
If you're having trouble picking your text and line of inquiry, then use this simple 20-minute process to brainstorm potential questions for your HLE:
- For each text / non-literary work, go through each concept in the table below.
- Write down a question for each of the two prompts for each category.
- Repeat for all of your texts.
- Pick the question-text combination that has the greatest potential for strong analysis.
How do I ensure my HLE question has a good scope?
Choosing a question with good scope is extremely important, and it's one of the biggest challenges in the HLE. Here's why:
- If your scope is too broad , you may have too much to write about in order to answer the question, and therefore you won't be able to write deep analysis (which is super important–more on this later…)
- If your scope is too narrow , you may not have enough to write about and end up overanalyzing unnecessary and obscure details. Also something to avoid!
So, to help you get the balance just right , here are three examples of HLE questions, specifically for the concept of Identity which we mentioned in the table above (by the way, the example is a made-up novel for illustration purposes).
- Too broad: “How does Irene Majov in her novel Deadly Men effectively make her narrator a powerful mouthpiece?”
- Too narrow: “How does Irene Majov in her novel Deadly Men effectively make her narrator a powerful mouthpiece for the concerns of Asian-Americans toward discrimination in the workforce in the 21st century?”
- Just right: “How does Irene Majov in her novel Deadly Men effectively make her narrator a powerful mouthpiece for the concerns of Asian-Americans in the 21st century?”
How to get a 7 on IB English HLE
There are many things that contribute to a 7 in your HLE and your IB English grade overall. But if we had to boil it down to one secret, one essential fact… then it'd have to be this: Get really good at analysis .
Analysis is the key to a 7 in IB English. It doesn't matter if it's Paper 1, Paper 2, HLE, IO… You must learn how to analyze quotes at a deep level, and structure your analysis in a way that flows and delights your teachers and examiners.
Start with the basics
Start with the basic foundations of analysis for free inside LitLearn's Learn Analysis course.
Our free and Pro resources have helped IB English students skyrocket their grade in weeks, days and even overnight... Learn Analysis for IB English , the simplest guide to a 7 in IB English.
Basic Analysis
No sign up or credit card required.
Free signup required.
Pro members only
Level up to Advanced Analysis
Since you're in HL, you'll also be needing Advanced Analysis skills if you want to impress your examiner. We've got all of that covered inside our Pro lessons.
Advanced Analysis
Finding Quotes
Also, you'll need to find good quotes for your text. Some good sources where you can find relevant quotes include Goodreads , SparkNotes , LitCharts , and Cliffnotes . Of course, you could just find quotes yourself directly–this will ensure your quotes are unique.
Understanding the IB English HLE rubric
An essential step to getting a high mark on the HL Essay is understanding the rubric! It is SO important that you know what IB English examiners are looking for when grading your essay, as this helps you to shape the content of your essay to match (or even exceed) their expectations.
The IB English HL Essay is graded out of 20 marks . There are 4 criteria, each worth 5 marks.
Use the checklist below to make sure you're not making simple mistakes! Note that this is not the official marking criteria, and I strongly recommend that you reading the official rubric provided by your teacher.
Criterion A: Knowledge, understanding, and interpretation
- Accurate summary of text in introduction
- Focused and informative thesis statement
- Effective and relevant quotes
- Relevant and effective summary and ending statement in conclusion
Criterion B: Analysis and evaluation
- Relevant analysis of a variety of stylistic features
- Relevant analysis of tone and/or atmosphere
- Relevant analysis of broader authorial choices i.e. characterization, point of view, syntax, irony, etc.
Criterion C: Focus, organization, and development
- Introduction, body paragraphs, conclusion
- Organized body paragraphs – topic sentence, evidence, concluding statement/link to question
- Appropriate progression of ideas and arguments in which evidence (i.e. quotes) are effectively implemented
Criterion D: Language
- Use expansions (e.g. “do not”) instead of contractions (e.g. “don't”)
- Use of a variety of connecting phrases e.g. “furthermore”, “nonetheless”, “however”, etc.
- Complete sentence structures and subject-verb agreement
- Correct usage of punctuation
- Appropriate register – no slang
- Historic present tense : the use of present tense when recounting past events. For example, we want to write “In The Hunger Games , Peeta and Katniss work together to win as a district” instead of using the word “worked”.
- Avoid flowery/dictionary language just to sound smart; it is distracting and difficult to read. As long as you concisely communicate your message using appropriate language, you will score a high mark under this criterion.
Here's everything we discussed:
- IB English HLE is tough work! Start early.
- Brainstorm using the table of concepts to come up with a strong HLE question. Don't give up on this!
- Analysis is the key to a 7 in IB English HLE (and in fact all IB English assessment). Check out LitLearn's course Learn Analysis for IB English for immediate help on the exact steps to improve in IB English analysis.
Good luck, and may the odds be ever in your favor 💪
Questionbank
Paper 1 Practice Exams
Past Paper 1 Solutions
Paper 2 Guide
From Struggling to Succeeding in IB English
How IB English students like you have improved their grades with LitLearn Pro... Read the reviews.
IB4 to IB6 in 12 days " LitLearn helped me understand exactly what I was doing wrong and how to improve upon those mistakes. " Read the full review
IB6 to IB7 in 1 week " I ended with a 7 in English Literature HL and I am so happy about that. Thank you Jackson. " Read the full review

IB5 to Perfect 20/20 in 1 week " I managed to be the only person in my IB cohort of 120 students to get a perfect score of 20/20 " Read the full review

IB4 to IB6 in 2 weeks " The lessons are really effective in grabbing my attention and making English more fun to learn. "

IB4 to IB6 in 1 day " With just day 1 of the course, I improved immediately and overnight when I did a practice essay and improved by 4 marks from my previous grades " Read the full review
IB5 to IB7 " I got 5s since my first year of DP and now my final grade is 7! I can't thank you enough 🙂 LitLearn is truly a lifesaver. "
Every resource to ace IB English
Voted #1 IB English Resource 2022 by IB Students & Teachers at ibresources.org
Learn Analysis
Master the essential skill of IB English with a step-by-step course.
Questionbank
Practice analysis with 60+ short questions and IB7 answers.
Exam prep guide, practice papers, past paper solutions.
Exam prep, planning and writing guide. Exemplar essay.
Individual Oral
Preparation guide, examples and full exemplar script.
Higher Level Essay
Crash course on HLE basics.
Economics Formative Coursework Essay
The main issue that needs to be addressed under the case is the concern of market failure. The growth in cities has pressured urban transportation systems characterized by congestion and delays. The problem has further caused an escalation in health challenges propagated by the adverse effects of the unsustainable transport system. The primary argument is on the poor allocation of merit goods and the inefficient allocation of resources resulting in negative externalities, which require appropriate solutions.
Failure by Urban Transport Systems to Deliver Efficient Market
Market failure occurs once the market needs to provide an adequate quantity of a product to meet the demand in the market or what is provided is inferior quality. There are four main market failure types: public goods, monopoly, externality, and information asymmetry. Market failure is denoted by a high level of inefficiency or poor allocation of resources as a result of the shortcomings of the market (Gillespie, 2019). As a result, the market becomes chaotic since individual decisions cannot result in the good of the public resulting in negative externalities.

Figure 1 above visualizes the problem of market failure involving the public transport system. The diagram indicates that point A is the equilibrium point where the supply equals market demand; at this point, MPB = MPC. However, when the supply goes down, the supply curve shifts to the left such that equilibrium shifts from point A to B. Therefore, a shortfall in supply causes a negative externality since demand cannot go down despite a fall in supply.
The negative externality that affects the transport system gives rise to several challenges leading to the increased preference for private transport, as the public system is ineffective. The trend further introduces health challenges, and the increased emission of greenhouse gases leads to climate change. There is a need for a sustainable transport system to be established to provide a safe system without compromising people’s health and the destruction of the environment.
Policy Option to Ensure Efficient and Sustainable Urban Transport Systems in the Future: Subsidy
Investment in the transport system is capital-intensive and would require the government to develop incentives to attract private involvement to remedy the situation. One critical approach the government can consider is providing incentives, which will bring down the cost of acquiring the equipment needed to attract the public to prefer the public transport system. The government facilitates a subsidy as an advantage to a person, a business entity, or an institution to entice them to participate in providing goods or services for the public good. The government can provide the subsidy directly by giving monetary payments or reducing prices (Gillespie, 2019). An indirect subsidy is provided through various means, including a favorable tax regime, labor benefits, and enhanced welfare programs. The intention is to relieve the investor of the burdens they face in providing goods and services that benefit the general public. They help support market behavior that will result in positive externalities.
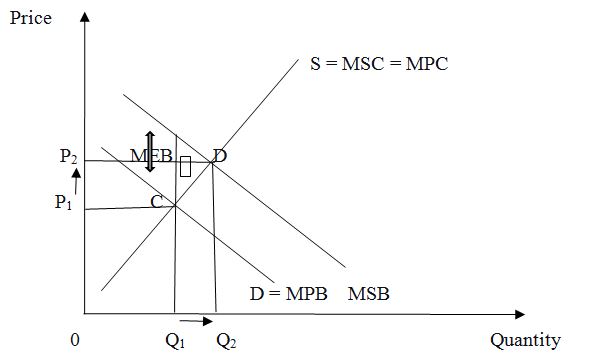
Figure 2 above shows the reverse of the first diagram due to the introduction of subsidies. The subsidies introduced by the government will support investment that will improve the quality of public transport. The increased supply of public transport services will cause the supply curve to shift from left to right resulting in positive externalities. Therefore, the equilibrium point will shift from C to D.
An example is when the government offers subsidies to private investors in a public rail transport system in a city. The system’s efficiency will attract more users from the public, hence reducing the number of private cars on roads, reducing congestion on the roads, accidents, and pollution due to gas emissions.
Introducing subsidies may attract new entrants, which will increase competition leading to better services following the participation of more players. It will further boost the provision of merit goods that generate positive externalities. On the contrary, subsidies may force the government to divert resources from preference areas to support a few businesses. Gillespie (2019) states that the population may suffer due to a lack of other essential services. Subsidies can distort the market as they involve a monetary gain rather than enhanced efficiency. The government may face challenges in removing the subsidies once people become accustomed to their benefits.
Considering the positive externalities of the solution, the policy should be adopted.
Policy Option to Ensure Efficient and Sustainable Urban Transport Systems in the Future: Odd-Even Rule
The government can consider implementing traffic restrictions based on even-and odd-numbered license plate systems. The system works by setting conditions or specific routes to be used by cars depending on whether they have an odd- or even-numbered number plate. The decision can involve indicating the days when odd-numbered and even-numbered vehicles can use the roads.
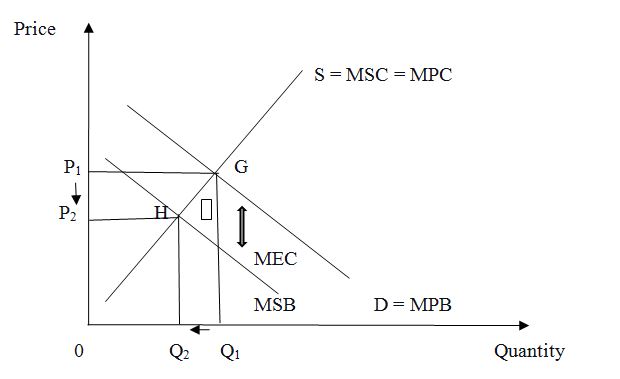
Restricting the number of private cars on the roads through the odd-even rule will reduce the number of cars on the public transport system. As a result, there will be a shift in the demand curve from right to left such that the equilibrium shifts from point G to H. Therefore, more people will have to use the public transport system, which means fewer cars on the roads.
The odd-even rule has been applied successfully in India to manage pollution in New Delhi, particularly during Diwali celebrations when the smog increases. However, the government made exceptions for using electric cars and two-wheelers.
The approach helps reduce gas emissions since the number of cars on the road is restricted, thus reducing pollution. In addition, fewer cars on the public transport system reduce congestion and accidents, ensuring the population enjoys a higher quality of life (Gillespie, 2019). However, the policy may inconvenience many people since they would feel that their freedoms are being interfered with by the state. The government can be exposed to activist acts from human rights bodies, including legal action.
The odd-even rule is suitable in modern and organized cities where the public transport system is efficient. We may need a better transport system to be effectively deployed in cities with a poor transport system as it will significantly inconvenience the citizens.
Policy Option to Ensure Efficient and Sustainable Urban Transport Systems in the Future: Subsidize the Use of Clean Energy Sources
The government can create a friendly operating environment by subsidizing sustainable means of transport that involve the use of clean sources of energy, such as electricity.
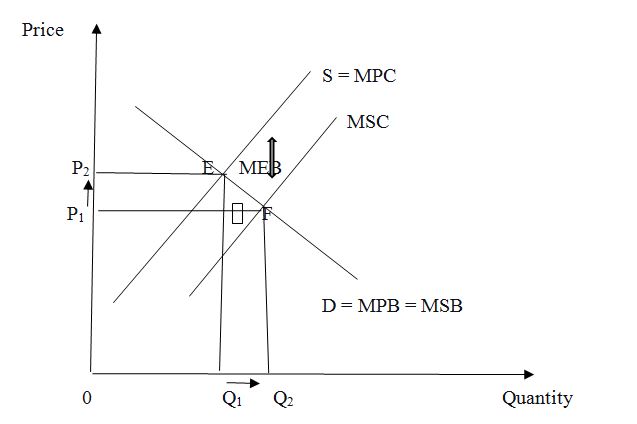
Government subsidies targeting to promote the use of clean energy will boost preference for sustainable means of transport, especially the use of electric cars. The solution will introduce positive externalities since there will be less pollution, reducing the effects of climate change (Gillespie, 2019). As indicated in figure 3 above, an increase in the demand for electric cars will cause the demand curve to shift from left to right; hence the equilibrium will move from E to F.
The United States is among the top countries that produce a vast amount of carbon gas emissions to the environment. The government can subsidize the large-scale use of electric cars, such as from companies like tesla.
The increased use of electric cars will reduce the amount of carbon gas emissions to the environment and ultimately reduce pollution and the effects of climate change. However, the technology is capital-intensive since the production of cars is at an early stage of development, and the necessary infrastructure, including charging points, must be developed.
In the short term, the solution can be avoided as the government supports basic programs that will facilitate implementation in the long run.
In conclusion, the government can consider supporting businesses by providing subsidies to promote the use of renewable energy. Supporting the private sector will create jobs by attracting colossal investment and supporting cities’ better development. Additionally, the government can engage in more than one policy action. For instance, while providing subsidies in one city, the administration can implement travel restrictions in another part of the city where the approach would not cause significant inconveniences and would be more acceptable to the population.
Reference List
Gillespie A.R. (2019) Foundations in Economics. 5 th Ed. Oxford University Press
- AgorDawn: Marketing Obstacles and Recommendations
- Student Performance: Examination & Other Forms of Assessment
- Tobacco Use Prevention Programs in Atlanta
- The Issue of Economic Justice
- The Effects of Stimulus Checks on the Economy
- The Concept of Economic Justice
- Missouri Compromise: Economic Equality Among American States
- The Gentrification Issue in Harlem, New York City
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, December 4). Economics Formative Coursework. https://ivypanda.com/essays/economics-formative-coursework/
"Economics Formative Coursework." IvyPanda , 4 Dec. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/economics-formative-coursework/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Economics Formative Coursework'. 4 December.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Economics Formative Coursework." December 4, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/economics-formative-coursework/.
1. IvyPanda . "Economics Formative Coursework." December 4, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/economics-formative-coursework/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Economics Formative Coursework." December 4, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/economics-formative-coursework/.
Home / Essay Samples / Education / Learning / Coursework
Coursework Essay Examples
Human-environment relationship: insights from green criminology.
Environment is a vital part of our life even when we face economic crisis, war and other type of social problems. Environment matters as it provides us air, food, shelter and other needs. Although environment is an inseparable part of our life, we often ignore...
Post Exam Self Reflection in Biology
Biology is GE class that I’ve tried to stay away from the beginning of college. My weakness is not good at English and having bad memory. therefore, to memorize the biological vocabulary or terms and its definition is really a big challenge for me. I...
Trying to find an excellent essay sample but no results?
Don’t waste your time and get a professional writer to help!
You may also like
- Indian Education
- Sex Education
- College Education
- Vocational Education
- Academic Achievements
- No Child Left
- Critical Thinking Essays
- Illiteracy Essays
- Online Classes Essays
- Coaching Essays
- Education System Essays
- American Education System Essays
- Brainology Essays
- Common Core Standards Essays
- Issues in Education Essays
- Learning Styles Essays
samplius.com uses cookies to offer you the best service possible.By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .--> -->