

Concept Papers in Research: Deciphering the blueprint of brilliance
Concept papers hold significant importance as a precursor to a full-fledged research proposal in academia and research. Understanding the nuances and significance of a concept paper is essential for any researcher aiming to lay a strong foundation for their investigation.
Table of Contents
What Is Concept Paper
A concept paper can be defined as a concise document which outlines the fundamental aspects of a grant proposal. It outlines the initial ideas, objectives, and theoretical framework of a proposed research project. It is usually two to three-page long overview of the proposal. However, they differ from both research proposal and original research paper in lacking a detailed plan and methodology for a specific study as in research proposal provides and exclusion of the findings and analysis of a completed research project as in an original research paper. A concept paper primarily focuses on introducing the basic idea, intended research question, and the framework that will guide the research.
Purpose of a Concept Paper
A concept paper serves as an initial document, commonly required by private organizations before a formal proposal submission. It offers a preliminary overview of a project or research’s purpose, method, and implementation. It acts as a roadmap, providing clarity and coherence in research direction. Additionally, it also acts as a tool for receiving informal input. The paper is used for internal decision-making, seeking approval from the board, and securing commitment from partners. It promotes cohesive communication and serves as a professional and respectful tool in collaboration.
These papers aid in focusing on the core objectives, theoretical underpinnings, and potential methodology of the research, enabling researchers to gain initial feedback and refine their ideas before delving into detailed research.
Key Elements of a Concept Paper
Key elements of a concept paper include the title page , background , literature review , problem statement , methodology, timeline, and references. It’s crucial for researchers seeking grants as it helps evaluators assess the relevance and feasibility of the proposed research.
Writing an effective concept paper in academic research involves understanding and incorporating essential elements:

How to Write a Concept Paper?
To ensure an effective concept paper, it’s recommended to select a compelling research topic, pose numerous research questions and incorporate data and numbers to support the project’s rationale. The document must be concise (around five pages) after tailoring the content and following the formatting requirements. Additionally, infographics and scientific illustrations can enhance the document’s impact and engagement with the audience. The steps to write a concept paper are as follows:
1. Write a Crisp Title:
Choose a clear, descriptive title that encapsulates the main idea. The title should express the paper’s content. It should serve as a preview for the reader.
2. Provide a Background Information:
Give a background information about the issue or topic. Define the key terminologies or concepts. Review existing literature to identify the gaps your concept paper aims to fill.
3. Outline Contents in the Introduction:
Introduce the concept paper with a brief overview of the problem or idea you’re addressing. Explain its significance. Identify the specific knowledge gaps your research aims to address and mention any contradictory theories related to your research question.
4. Define a Mission Statement:
The mission statement follows a clear problem statement that defines the problem or concept that need to be addressed. Write a concise mission statement that engages your research purpose and explains why gaining the reader’s approval will benefit your field.
5. Explain the Research Aim and Objectives:
Explain why your research is important and the specific questions you aim to answer through your research. State the specific goals and objectives your concept intends to achieve. Provide a detailed explanation of your concept. What is it, how does it work, and what makes it unique?
6. Detail the Methodology:
Discuss the research methods you plan to use, such as surveys, experiments, case studies, interviews, and observations. Mention any ethical concerns related to your research.
7. Outline Proposed Methods and Potential Impact:
Provide detailed information on how you will conduct your research, including any specialized equipment or collaborations. Discuss the expected results or impacts of implementing the concept. Highlight the potential benefits, whether social, economic, or otherwise.
8. Mention the Feasibility
Discuss the resources necessary for the concept’s execution. Mention the expected duration of the research and specific milestones. Outline a proposed timeline for implementing the concept.
9. Include a Support Section:
Include a section that breaks down the project’s budget, explaining the overall cost and individual expenses to demonstrate how the allocated funds will be used.
10. Provide a Conclusion:
Summarize the key points and restate the importance of the concept. If necessary, include a call to action or next steps.
Although the structure and elements of a concept paper may vary depending on the specific requirements, you can tailor your document based on the guidelines or instructions you’ve been given.
Here are some tips to write a concept paper:

Example of a Concept Paper
Here is an example of a concept paper. Please note, this is a generalized example. Your concept paper should align with the specific requirements, guidelines, and objectives you aim to achieve in your proposal. Tailor it accordingly to the needs and context of the initiative you are proposing.
Download Now!
Importance of a Concept Paper
Concept papers serve various fields, influencing the direction and potential of research in science, social sciences, technology, and more. They contribute to the formulation of groundbreaking studies and novel ideas that can impact societal, economic, and academic spheres.
A concept paper serves several crucial purposes in various fields:

In summary, a well-crafted concept paper is essential in outlining a clear, concise, and structured framework for new ideas or proposals. It helps in assessing the feasibility, viability, and potential impact of the concept before investing significant resources into its implementation.
How well do you understand concept papers? Test your understanding now!
Fill the Details to Check Your Score

Role of AI in Writing Concept Papers
The increasing use of AI, particularly generative models, has facilitated the writing process for concept papers. Responsible use involves leveraging AI to assist in ideation, organization, and language refinement while ensuring that the originality and ethical standards of research are maintained.
AI plays a significant role in aiding the creation and development of concept papers in several ways:
1. Idea Generation and Organization
AI tools can assist in brainstorming initial ideas for concept papers based on key concepts. They can help in organizing information, creating outlines, and structuring the content effectively.
2. Summarizing Research and Data Analysis
AI-powered tools can assist in conducting comprehensive literature reviews, helping writers to gather and synthesize relevant information. AI algorithms can process and analyze vast amounts of data, providing insights and statistics to support the concept presented in the paper.
3. Language and Style Enhancement
AI grammar checker tools can help writers by offering grammar, style, and tone suggestions, ensuring professionalism. It can also facilitate translation, in case a global collaboration.
4. Collaboration and Feedback
AI platforms offer collaborative features that enable multiple authors to work simultaneously on a concept paper, allowing for real-time contributions and edits.
5. Customization and Personalization
AI algorithms can provide personalized recommendations based on the specific requirements or context of the concept paper. They can assist in tailoring the concept paper according to the target audience or specific guidelines.
6. Automation and Efficiency
AI can automate certain tasks, such as citation formatting, bibliography creation, or reference checking, saving time for the writer.
7. Analytics and Prediction
AI models can predict potential outcomes or impacts based on the information provided, helping writers anticipate the possible consequences of the proposed concept.
8. Real-Time Assistance
AI-driven chat-bots can provide real-time support and answers to specific questions related to the concept paper writing process.
AI’s role in writing concept papers significantly streamlines the writing process, enhances the quality of the content, and provides valuable assistance in various stages of development, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the final document.
Concept papers serve as the stepping stone in the research journey, aiding in the crystallization of ideas and the formulation of robust research proposals. It the cornerstone for translating ideas into impactful realities. Their significance spans diverse domains, from academia to business, enabling stakeholders to evaluate, invest, and realize the potential of groundbreaking concepts.
Frequently Asked Questions
A concept paper can be defined as a concise document outlining the fundamental aspects of a grant proposal such as the initial ideas, objectives, and theoretical framework of a proposed research project.
A good concept paper should offer a clear and comprehensive overview of the proposed research. It should demonstrate a strong understanding of the subject matter and outline a structured plan for its execution.
Concept paper is important to develop and clarify ideas, develop and evaluate proposal, inviting collaboration and collecting feedback, presenting proposals for academic and research initiatives and allocating resources.
I got wonderful idea
It helps a lot for my concept paper.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Academic Essay Writing Made Simple: 4 types and tips
The pen is mightier than the sword, they say, and nowhere is this more evident…
![abridged methodology concept paper example What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- AI in Academia
AI vs. AI: How to detect image manipulation and avoid academic misconduct
The scientific community is facing a new frontier of controversy as artificial intelligence (AI) is…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Need for Diversifying Academic Curricula: Embracing missing voices and marginalized perspectives
In classrooms worldwide, a single narrative often dominates, leaving many students feeling lost. These stories,…

- Career Corner
- Trending Now
Recognizing the signs: A guide to overcoming academic burnout
As the sun set over the campus, casting long shadows through the library windows, Alex…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
Designing conceptual articles: four approaches
- Theory/Conceptual
- Open access
- Published: 09 March 2020
- Volume 10 , pages 18–26, ( 2020 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Elina Jaakkola ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4654-7573 1
162k Accesses
500 Citations
43 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
As a powerful means of theory building, conceptual articles are increasingly called for in marketing academia. However, researchers struggle to design and write non-empirical articles because of the lack of commonly accepted templates to guide their development. The aim of this paper is to highlight methodological considerations for conceptual papers: it is argued that such papers must be grounded in a clear research design, and that the choice of theories and their role in the analysis must be explicated and justified. The paper discusses four potential templates for conceptual papers – Theory Synthesis, Theory Adaptation, Typology, and Model – and their respective aims, approach for using theories, and contribution potential. Supported by illustrative examples, these templates codify some of the tacit knowledge that underpins the design of non-empirical papers and will be of use to anyone undertaking, supervising, or reviewing conceptual research.
Similar content being viewed by others

Conceptual review papers: revisiting existing research to develop and refine theory

A Framework for Undertaking Conceptual and Empirical Research
Advancing marketing theory and practice: guidelines for crafting research propositions
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.

Introduction
The major academic journals in the field of marketing acknowledge the need for good conceptual papers that can “bridge existing theories in interesting ways, link work across disciplines, provide multi-level insights, and broaden the scope of our thinking” (Gilson and Goldberg 2015 , p. 128). Indeed, many of the most impactful marketing papers of recent decades are conceptual as this type of research enables theory building unrestricted by the demands of empirical generalization (e.g., Vargo and Lusch 2004 ). Authors crafting conceptual papers can find valuable advice on problematizing (Alvesson and Sandberg 2011 ), theorizing and theory building (Corley and Gioia 2011 ; Cornelissen 2017 ; Shepherd and Suddaby 2017 ), and the types of conceptual contribution that warrant publication (Corley and Gioia 2011 ; MacInnis 2011 ). However, a lack of commonly accepted templates or “recipes” for building the paper means that writing a conceptual piece can be a struggle (Cornelissen 2017 ). As a result, reviewers often face conceptual papers that offer little more than a descriptive literature review or interesting but disjointed ideas.
In empirical papers, the recipe typically is the research design that provides the paper structure and logic, guiding the process of developing new knowledge and offering conventions for reporting the key elements of the research (Flick 2018 , p. 102). The research design explains how the ingredients of the study were selected, acquired, and analyzed to effectively address the research problem, and reviewers can evaluate the robustness of this process by reference to established conventions in the existing literature. As conceptual papers generally do not fit the mold of empirical research, authors and reviewers lack any such recipe book, making the critical issue of analytical rigor more challenging.
This paper addresses issues of methodology and research design for conceptual papers. The discussion is built on previous “how to” guides to conceptual research, and on examples from high quality journals to identify and illustrate different options for conceptual research design. This paper discusses four templates—Theory Synthesis, Theory Adaptation, Typology, and Model—and explicates their aims, their approach to theory use, and their contribution potential. The paper does not focus on theory building itself but supports it, as analytical rigor is a prerequisite for high quality theorizing. Nor is the focus on literature reviews or meta-analyses; while these are important non-empirical forms of research, there are well articulated existing guidelines for such articles (see for example Webster and Watson 2002 ; Palmatier et al. 2018 ).
The ultimate goal of this paper is to direct scholarly attention to the importance of a systematic approach to developing a conceptual paper. Experienced editors and reviewers have noted that researchers sometimes underestimate how difficult it is to write a rigorous conceptual paper and consider this an easy route to publishing—an essay devoid of deeper scholarship (Hirschheim 2008 ). In reality, developing a cogent argument and building a supporting theoretical explanation requires tacit knowledge and skills that doctoral programs seldom teach (Yadav 2010 ; King and Lepak 2011 ). As Fulmer puts it, “in a theoretical paper the author is faced with a mixed blessing: greater freedom and page length within which to develop theory but also more editorial rope with which to hang him/herself” ( 2012 , p. 330).
The paper is organized as follows. The next section outlines key methodological requirements for conceptual studies. Four common types of research design are then identified and discussed with supporting examples. The article ends with conclusions and recommendations for marketing scholars undertaking, supervising, or reviewing conceptual research.
Conceptual papers: some methodological requirements
The term “research design” refers to decisions about how to achieve research goals, linking theories, questions, and goals to appropriate resources and methods (Flick 2018 , p. 102). In short, the research design is a plan for collecting and analyzing evidence that helps to answer the question posed (Ragin 1994 , p. 191). Like any design, the research design should improve usability ; a good research design is the optimal tool for addressing the research problem, and it communicates the logic of the study in a transparent way. In principle, any piece of research should be designed to deliver trustworthy answers to the question posed in a credible and justified manner.
An empirical research design typically involves decisions about the underlying theoretical framing of the study as well as issues of data collection and analysis (e.g. Miller and Salkind 2002 ). Imagine, for example, an empirical paper where the authors did not argue for their sampling criteria or choice of informants, or failed to define the measures used or to show how the results were derived from the data. It can be argued that conceptual papers entail similar considerations (Table 1 ), as the omission of equivalent elements would create similar confusion. In other words, a well-designed conceptual paper must explicitly justify and explicate decisions about key elements of the study. The following sections elaborate more specifically on designing and communicating these “methodological” aspects of conceptual papers.
Explicating and justifying the choice of theories and concepts
Empirical and conceptual papers ultimately share a common goal: to create new knowledge by building on carefully selected sources of information combined according to a set of norms. In the case of conceptual papers, arguments are not derived from data in the traditional sense but involve the assimilation and combination of evidence in the form of previously developed concepts and theories (Hirschheim 2008 ). In that sense, conceptual papers are not without empirical insights but rather build on theories and concepts that are developed and tested through empirical research.
In an empirical study, the researcher determines what data are needed to address the research questions and specifies sampling criteria and research instruments accordingly. In similar fashion, a conceptual paper should explain how and why the theories and concepts on which it is grounded were selected. In simple terms, there are two possible points of departure. The first option is to start from a focal phenomenon that is observable but not adequately addressed in the existing research. The authors may inductively identify differing conceptualizations of that phenomenon, and then argue that the aspect of interest is best addressed in terms of particular concepts or theories. That is, the choice of concepts is based on their fit to the focal phenomenon and their complementary value in conceptualizing it. One key issue here is how the researcher conceptualizes the empirical phenomenon; in selecting particular concepts and theories, the researcher is de facto making an argument about the conceptual ingredients of the empirical phenomenon in question.
A second and perhaps more common approach is to start from a focal theory by arguing that a particular concept, theory, or research domain is internally incoherent or incomplete in some important respect and then introducing other theories to bridge the observed gaps. In this case, the choice of theories or concepts is based on their ability to address the observed shortcoming in the existing literature, i.e. their supplementary value. This simplified account raises a critical underlying question: what is the value that each selected concept, literature stream, or theory brings to the study, and why are they selected in preference to something else?
Explicating the role of different theories and concepts in the analysis
Conceptual papers typically draw on multiple concepts, literature streams, and theories that play differing roles. It is difficult to imagine a (published) empirical paper where the reader could not distinguish empirical data from the literature review. In a conceptual paper, however, it is sometimes difficult to tell which theories provide the “data” and which are framing the analysis. In this regard, Lukka and Vinnari ( 2014 ) drew a useful distinction between domain theory and method theory. A domain theory is “a particular set of knowledge on a substantive topic area situated in a field or domain” (ibid, p. 1309)—that is, an area of study characterized by a particular set of constructs, theories, and assumptions (MacInnis 2011 ). A method theory, on the other hand, is “a meta-level conceptual system for studying the substantive issue(s) of the domain theory at hand” (Lukka and Vinnari 2014 , p. 1309). For example, Brodie et al. ( 2019 ) sought to advance engagement research (domain theory) by drawing new perspectives from service-dominant logic (method theory). The distinction is relative rather than absolute; whether a particular theory is domain or method theory depends on its role in the study in question (Lukka and Vinnari 2014 ). Indeed, a single study can accommodate multiple domain and method theories.
In a conceptual paper, one crucial function of the research design is to explicate the role of each element in the paper; failure to explain this is likely to render the logic of “generating findings” practically invisible to the reader. Defining the roles of different theories also helps to indicate the paper’s positioning, and how its contribution should be evaluated. Typically, the role of the method theory is to provide some new insight into the domain theory—for example, to expand, organize, or offer a new or alternative explanation of concepts and relationships. This means that contribution usually centers on the domain theory, not the method theory (Lukka and Vinnari 2014 ). For example, marketing scholars often use established theories such as resource-based theory, institutional theory, or practice theory as method theories, but any suitable framework (even from other disciplines) can play this role. Footnote 1
Making the chain of evidence visible and easy to grasp
Conceptual papers typically focus on proposing new relationships among constructs; the purpose is thus to develop logical and complete arguments about these associations rather than testing them empirically (Gilson and Goldberg 2015 ). The issue of how to develop logical arguments is hence pivotal. As well as arguing that concepts are linked, authors must provide a theoretical explanation for that link. As that explanation demonstrates the logic of connections between concepts, it is critical for theory building (King and Lepak 2011 ).
In attempting to analyze what constitutes a good argument, Hirschheim ( 2008 ) adopted a framework first advanced by the British philosopher Toulmin ( 1958 ), according to which an argument has three necessary components: claims, grounds, and warrants. Claims refer to the explicit statement or thesis that the reader is being asked to accept as true—the outcome of the research. Grounds are the evidence and reasoning used to support the claim and to persuade the reader. In a conceptual paper, this evidence is drawn from previous studies rather than from primary data. Finally, warrants are the underlying assumptions or presuppositions that link grounds to claims. Warrants are often beliefs implicitly accepted within the given research domain—for example the assumption that organizations strive to satisfy their customers. In a robust piece of research, claims should be substantiated by sufficient grounds, and should be of sufficient significance to make a worthwhile contribution to knowledge (Hirschheim 2008 ).
In practice, the chain of evidence in a conceptual paper is made visible to the reader by explicating the key steps in the argument. How is the studied phenomenon conceptualized? What are the study’s implicit assumptions, stemming from its theoretical underpinnings? Are the premises and axioms used to ground the arguments sufficiently explicit to enable another researcher to arrive at similar analytical conclusions? Conceptual clarity, parsimony, simplicity, and logical coherence are important qualities of any academic study but are arguably all the more critical when developing arguments without empirical data.
A paper’s structure is a strong determinant of how easy it is to follow the chain of argumentation. While there is no single best way to structure a conceptual paper, what successful papers have in common is a careful matching of form and structure to theoretical purpose of the paper (Fulmer 2012 ). The structure should therefore reflect both the aims of the research and the role of the various lenses deployed to achieve those aims—in other words, the structure highlights what the authors seek to explain. A clear structure also contributes to conceptual clarity by making the hierarchy of concepts and their elements intuitively available to the reader, eliminating any noise that might distort the underlying message. As Hirschheim ( 2008 ) noted, a clear structure ensures a place for everything—omitting nothing of importance—and puts everything in its place, avoiding redundancies.
Common types of research design in conceptual papers
In marked contrast to empirical research, there is no widely shared understanding of basic types of research design in respect to conceptual papers, with the exception of literature reviews and meta-analyses. To address this issue, the present study considers four such types: Theory Synthesis, Theory Adaptation, Typology , and Model (see Table 2 ). These types serve to clarify differences of methodological approach—that is, how the argument is structured and developed—rather than the types of conceptual contributions that are the main consideration of MacInnis ( 2011 ). The four types discussed here derive from an analysis of goal setting, structuring, and logic of argumentation in multiple articles published in high quality journals. It should be said that the list is not exhaustive, and other researchers would no doubt have formulated differing perspectives. Nevertheless, the presented scheme can inspire researchers to explore and explicate one’s approach to conceptual research, and perhaps to formulate an alternative approach. It should also be noted that the goals of a conceptual article can be as varied as in any other form of academic research. Table 2 identifies some possible or likely goals for each suggested type; these are not mutually exclusive and are often combined.
Theory synthesis
A theory synthesis paper seeks to achieve conceptual integration across multiple theories or literature streams. Such papers offer a new or enhanced view of a concept or phenomenon by linking previously unconnected or incompatible pieces in a novel way. Papers of this type contribute by summarizing and integrating extant knowledge of a concept or phenomenon. According to MacInnis ( 2011 ), summarizing helps researchers see the forest for the trees by encapsulating, digesting, and reducing what is known to a manageable whole. Integration enables researchers to see a concept or phenomenon in a new way by transforming previous findings and theory into a novel higher-order perspective that links phenomena previously considered distinct (MacInnis 2011 ). For example, a synthesis paper might chart a new or unstructured phenomenon that has previously been addressed in piecemeal fashion across diverse domains or disciplines. Such papers may also explore the conceptual underpinnings of an emerging theory or explain conflicting research findings by providing a more parsimonious explanation that pulls disparate elements into a more coherent whole.
This kind of systematization is especially helpful when research on a given topic is fragmented across different literatures, helping to identify and underscore commonalities that build coherence (Cropanzano 2009 ). For example, in their review of conceptualizations of customer experience across multiple literature fields, Becker and Jaakkola’s ( 2020 ) analysis of the compatibility of various elements and assumptions provided a new integrative view that could be generalized across settings and contexts. In more mature fields, synthesis can help to identify gaps in the extant research, which is often the goal of systematic literature reviews. However, gap spotting is seldom a sufficient source of contribution as the main aim of a conceptual paper should be to enhance existing theoretical understanding on the studied phenomenon or concept. The synthesis paper represents a form of theorizing that emphasizes narrative reasoning that seeks to unveil “big picture” patterns and connections rather than specific causal mechanisms (Delbridge and Fiss 2013 ).
Although there is sometimes a fine line between theory synthesis and literature review, there remains a clear distinction between the two. While a well-crafted literature review takes stock of the field and can provide valuable insights into its development, scope, or future prospects, it remains within the existing conceptual or theoretical boundaries, describing extant knowledge rather than looking beyond it. In the case of a conceptual paper, the literature review is a necessary tool but not the ultimate objective. Moreover, in a theory synthesis paper, the role of the literature review is to unravel the components of a concept or phenomenon and it must sometimes reduce or exclude incommensurable elements. A lack of elegance occurs when authors attempt to hammer together separate research ideas in a series of “minireviews” instead of attending to a single conceptual theme (Cropanzano 2009 ). For example, a literature review that seeks to integrate multiple research perspectives may instead merely summarize in separate chapters what each has to say about the concept. Typically, different research perspectives employ differing terms and structure, or categorize conceptual elements in distinct ways. Integration and synthesis requires that the researcher explicates and unravels the conceptual underpinnings and building blocks that different perspectives use to conceptualize a phenomenon, and the looks for common ground on which to build a new and enhanced conceptualization.
A theory synthesis paper may seek to increase understanding of a relatively narrow concept or empirical phenomenon. For example, Lemon and Verhoef ( 2016 ) summarized the conceptual background and extant conceptualizations of customer journeys to produce a new integrative view. They framed the journey phenomenon in terms of the consumer purchasing process and organized the extant research within this big picture. Similarly, arguing that the knowledge base of relationship marketing and business networks perspectives was unduly fragmented, Möller ( 2013 ) deployed a metatheoretical lens to construct an articulated theory map that accommodated various domain theories, leading to the development of two novel middle-range theories.
Ultimately, a theory synthesis paper can integrate an extensive set of theories and phenomena under a novel theoretical umbrella. One good example is Vargo and Lusch’s ( 2004 ) seminal article, which pulled together key ingredients from diverse fields such as market orientation, relationship marketing, network management, and value management into a novel integrative narrative to formulate the more parsimonious framework of service-dominant logic. In so doing, they drew on resource based theory, structuration theory, and institutional theory as method theories to organize and synthesize concepts and themes from middle-range literature fields (e.g., Vargo and Lusch 2004 , 2016 ). While extant research provided the basis for a novel framework, existing concepts were decomposed into such fine-grained ingredients that the resulting integration was a new theoretical view in its own right rather than a summary of existing concepts.
Theory adaptation
Papers that focus on theory adaptation seek to amend an existing theory by using other theories. While empirical research may gradually extend some element of theory within a given context, theory-based adaptation attempts a more immediate shift of perspective. Theory adaptation papers develop contribution by revising extant knowledge—that is, by introducing alternative frames of reference to propose a novel perspective on an extant conceptualization (MacInnis 2011 ). The point of departure for such papers, then, is the problematization of a particular theory or concept. For example, the authors might argue that certain empirical developments or insights from other streams of literature render an existing conceptualization insufficient or conflicted, and that some reconfiguration or shift of perspective or scope is needed to better align the concept or theory to its purpose or to reconcile certain inconsistencies. Typically, the researcher draws from another theory that is equipped to guide this shift. The contribution of this type of a paper is often positioned to the domain where the focal concept is situated.
The starting point for the theory adaptation paper is the theory or concept of interest (domain theory). Other theories are used as tools, or method theories (Lukka and Vinnari 2014 ) to provide an alternative frame of reference to adjust or expand its conceptual scope. One “method” of adaptation is to switch the level of analysis; for example, Alexander et al. ( 2018 ) provided new insights into the influence of institutions on customer engagement by shifting from a micro level analysis of customer relationships—the prevailing view in the field—to meso and macro level views, adapting Chandler and Vargo’s ( 2011 ) process of oscillating foci. Another option is to use an established theory to explore new aspects of the domain theory (Yadav 2010 ). As one example of this type of design, Brodie et al. ( 2019 ) argued for the practical and theoretical importance of expanding the scope of engagement research in two ways: from a focus on consumers to a broad range of actors, and from dyadic firm-customer relationships to networks. As well as justifying why a particular extension or change of focus is needed, a theory adaptation paper must also show that the selected method theory is the best available option. For example, Brodie et al. ( 2019 ) explained that they employed service-dominant logic to broaden the conceptual scope of engagement research because it offered a lens for understanding actor-to-actor interactions in networks. Similarly, Hillebrand et al. ( 2015 ) used multiplicity theory to revise existing perspectives on stakeholder marketing by viewing stakeholder networks as continuous rather than discrete. They argued that this provides a more accurate understanding of markets characterized by complex value exchange and dispersed control.
A typology paper classifies conceptual variants as distinct types. The aim is to develop a categorization that “explains the fuzzy nature of many subjects by logically and causally combining different constructs into a coherent and explanatory set of types” (Cornelissen 2017 ). A typology paper provides a more precise and nuanced understanding of a phenomenon or concept, pinpointing and justifying key dimensions that distinguish the variants.
Typology papers contribute through differentiation— distinguishing, dimensionalizing, or categorizing extant knowledge of the phenomenon, construct, or theory in question (MacInnis 2011 ). Typologies reduce complexity (Fiss 2011 ). They demonstrate how variants of an entity differ, and hence organize complex networks of concepts and relationships, and may help by recognizing their differing antecedents, manifestations, or effects (MacInnis 2011 ). Typologies also offer a multidimensional view of the target phenomenon by categorizing theoretical features or dimensions as distinct profiles that offer coordinates for empirical research (Cornelissen 2017 ). For example, the classic typologies elaborated by Mills and Margulies ( 1980 ) and Lovelock ( 1983 ) assigned services to categories reflecting different aspects of the relationship between customers and the service organization, facilitating prediction of organizational behavior and marketing action. These theory-based typologies have informed numerous empirical applications.
The starting point for a typology paper is typically recognition of an important but fragmented research domain characterized by differing manifestations of a concept or inconsistent findings regarding drivers or outcomes. The researcher accumulates knowledge of the focal topic and then organizes it to capture the variability of particular characteristics of the concept or phenomenon. For example, after exploring different approaches to service innovation, Helkkula et al. ( 2018 ) proposed a typology of four archetypes. They suggested that variance within the extant research could be explained by differences of theoretical perspective and argued that each type had distinct implications for value creation.
The dimensions of a typology can also be differentiated by applying another theory (i.e. methods theory) that provides a logical explanation of why differences exist and why they are relevant. For example, to examine the boundaries of resource integration, Dong and Sivakumar ( 2017 ) developed a typology of customer participation, using dimensions drawn from resource-based theory, to address the fundamental resource deployment questions of whether there is a choice in terms of who performs a task and what task is performed (Kozlenkova et al. 2014 ).
Snow and Ketchen Jr. ( 2014 ) argued that well-developed typologies are more than just classification systems; rather, a typology articulates relationships among constructs and facilitates testable predictions (cf. Doty and Glick 1994 ). In this way, a typology can propose multiple causal relationships in a given setting (Fiss 2011 ). While a typology paper enhances understanding of a phenomenon by delineating its key variants, it can be seen to differ from a synthesis or adaptation paper by virtue of its explanatory character. This is the typology’s raison d’etre; types always explain something, and the dimensions that distinguish types account for the different drivers, outcomes, or contingencies of particular variants of the phenomenon. By accommodating asymmetric causal relations, typologies facilitate the development of configurational arguments beyond simple correlations (Fiss 2011 ).
The model paper seeks to build a theoretical framework that predicts relationships between concepts. A conceptual model describes an entity and identifies issues that should be considered in its study: it can describe an event, an object, or a process, and explain how it works by disclosing antecedents, outcomes, and contingencies related to the focal construct (Meredith 1993 ; MacInnis 2011 ). This typically involves a form of theorizing that seeks to create a nomological network around the focal concept, employing a formal analytical approach to examine and detail the causal linkages and mechanisms at play (Delbridge and Fiss 2013 ). A model paper identifies previously unexplored connections between constructs, introduces new constructs, or explains why elements of a process lead to a particular outcome (Cornelissen 2017 ; Fulmer 2012 ).
The model paper contributes to extant knowledge by delineating an entity: its goal is “to detail, chart, describe, or depict an entity and its relationship to other entities” (MacInnis 2011 ). In a conceptual article, creative scope is unfettered by data-related limitations, allowing the researcher to explore and model emerging phenomena where few empirical data are available (Yadav 2010 ). The model paper typically contributes by providing a roadmap for understanding the entity in question by delineating the focal concept, how it changes, the processes by which it operates, or the moderating conditions that may affect it (MacInnis 2011 ).
A model paper typically begins from a focal phenomenon or construct that warrants further explanation. For example, Huang and Rust ( 2018 ) sought to explain the process and mechanism by which artificial intelligence (AI) will replace humans in service jobs. They employed literature that tackles key variables associated with the target phenomenon: service research illuminates the focal phenomenon, technology-enabled services, and research across multiple disciplines discusses the likely impact of AI on human labor. By synthesizing this literature pool, they identified four types of intelligence and then built a theory that could predict the impact of AI on human service labor. This involved a particular kind of formal reasoning, supported by research from multiple disciplines and real-world applications (Huang and Rust 2018 ). In other words, the authors use method theories and deductive reasoning to explain relationships between key variables, facilitated by theories in use (MacInnis 2011 ).
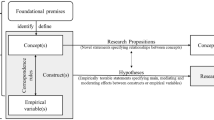
Model papers typically summarize arguments in the form of a figure that depicts the salient constructs and their relationships, or as a set of formal propositions that are logical statements derived from the conceptual framework (Meredith 1993 ). For example, Payne et al. ( 2017 ) used resource-based theory to develop a conceptual model of the antecedents and outcomes of customer value propositions. While figures and propositions of this kind help the reader by condensing the paper’s main message, Delbridge and Fiss ( 2013 ) noted that they are also a double-edged sword. At their best, propositions distill the essence of an argument into a parsimonious and precise form, but by virtue of this very ability, they also put a spotlight on the weaknesses in the argument chain. According to Cornelissen ( 2017 ), the researcher should therefore be clear about the “causal agent” in any proposed relationship between constructs when developing propositions—in other words, the trigger or force that drives a particular outcome or effect. Careful consideration and justification of the choice of theories and the manner in which they are integrated to produce the arguments is hence pivotal in sharpening and clarifying the argumentation to convince reviewers and readers.
Conclusions
This paper highlights the role of methodological considerations in conceptual papers by discussing alternative types of research design, in the hope of encouraging researchers to critically assess and develop conceptual papers accordingly. Authors of conceptual papers should readily answer the following questions: What is the logic of creating new knowledge? Why are particular information sources selected, and how are they analyzed? What role does each theory play? For reviewers, assessing conceptual papers can be difficult not least because the generally accepted and readily available guidelines for evaluating empirical research seldom apply directly to non-empirical work. By asking these questions, reviewers and supervisors can evaluate whether the research design of a paper or thesis is carefully crafted and clearly communicated to the reader.
The paper identifies four types of conceptual papers—Theory Synthesis, Theory Adaptation, Typology, and Model—and discusses their aims, methods of theory use, and potential contributions. Although this list is not exhaustive, these types offer basic templates for designing conceptual research and determining its intended contribution (cf. MacInnis 2011 ). Careful consideration of these alternative types can facilitate more conscious selection of approach and structure for a conceptual paper. Researchers can also consider opportunities for combining types. In many cases, mixing two types can be an attractive option. For example, after distinguishing types of service innovation in terms of their conceptual underpinnings, Helkkula et al. ( 2018 ) synthesized a novel conceptualization of service innovation that exploited the strengths of each type and mitigated their limitations. Typologies can also provide the basis for models, and synthesis can lead to theory adaptation.
This paper highlights the many alternative routes along which conceptual papers can advance extant knowledge. We should consider conceptual papers not just as a means to take stock, but to break new ground. Empirical research takes time to accumulate, and the scope for generalization is relatively narrow. In contrast, conceptual papers can strive to advance understanding of a concept or phenomenon in big leaps rather than incremental steps. To be taken seriously, any such leap must be grounded in thorough consideration and justification of an appropriate research design.
A discussion of how different theoretical lenses can be integrated is beyond the scope of this paper, but see for example Okhuysen and Bonardi ( 2011 ) and Gioia and Pitre ( 1990 ).
Alexander, M. J., Jaakkola, E., & Hollebeek, L. D. (2018). Zooming out: Actor engagement beyond the dyadic. Journal of Service Management, 29 (3), 333–351.
Article Google Scholar
Alvesson, M., & Sandberg, J. (2011). Generating research questions through problematization. Academy of Management Review, 36 (2), 247–271.
Google Scholar
Becker, L., & Jaakkola, E. (2020). Customer experience: Fundamental premises and implications for research. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science . https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-019-00718-x .
Brodie, R. J., Fehrer, J. A., Jaakkola, E., & Conduit, J. (2019). Actor engagement in networks: Defining the conceptual domain. Journal of Service Research, 22 (2), 173–188.
Chandler, J. D., & Vargo, S. L. (2011). Contextualization and value-in-context: How context frames exchange. Marketing Theory, 11 (1), 35–49.
Corley, K. G., & Gioia, D. A. (2011). Building theory about theory building: What constitutes a theoretical contribution? Academy of Management Review, 36 (1), 12–32.
Cornelissen, J. (2017). Editor’s comments: Developing propositions, a process model, or a typology? Addressing the challenges of writing theory without a boilerplate. Academy of Management Review, 42 (1), 1–9.
Cropanzano, R. (2009). Writing nonempirical articles for Journal of Management: General thoughts and suggestions. Journal of Management, 35 (6), 1304–1311.
De Brentani, U., & Reid, S. E. (2012). The fuzzy front-end of discontinuous innovation: Insights for research and management. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 29 (1), 70–87.
Delbridge, R., & Fiss, P. C. (2013). Editors’ comments: Styles of theorizing and the social organization of knowledge. Academy of Management Review, 38 (3), 325–331.
Dong, B., & Sivakumar, K. (2017). Customer participation in services: Domain, scope, and boundaries. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (6), 944–965.
Doty, D. H., & Glick, W. H. (1994). Typologies as a unique form of theory building: Toward improved understanding and modeling. Academy of Management Review, 19 (2), 230–251.
Eckhardt, G. M., Houston, M. B., Jiang, B., Lamberton, C., Rindfleisch, A., & Zervas, G. (2019). Marketing in the sharing economy. Journal of Marketing, 83 (5), 5–27.
Edvardsson, B., Kristensson, P., Magnusson, P., & Sundström, E. (2012). Customer integration within service development—A review of methods and an analysis of insitu and exsitu contributions. Technovation, 32 (7–8), 419–429.
Fiss, P. C. (2011). Building better causal theories: A fuzzy set approach to typologies in organizational research. Academy of Management Journal, 54 , 393–420.
Flick, U. (2018). An introduction to qualitative research . London: Sage Publications.
Fulmer, I. S. (2012). Editor's comments: The craft of writing theory articles—Variety and similarity in AMR. Academy of Management Review, 37 , 327–331.
Gilson, L. L., & Goldberg, C. B. (2015). Editors’ comment: So, what is a conceptual paper? Group & Organization Management, 40 (2), 127–130.
Gioia, D., & Pitre, E. (1990). Multiparadigm perspectives on theory building. Academy of Management Review, 15 (4), 584–602.
Hartmann, N. N., Wieland, H., & Vargo, S. L. (2018). Converging on a new theoretical foundation for selling. Journal of Marketing, 82 (2), 1–18.
Helkkula, A., Kowalkowski, C., & Tronvoll, B. (2018). Archetypes of service innovation: Implications for value cocreation. Journal of Service Research, 21 (3), 284–301.
Hillebrand, B., Driessen, P. H., & Koll, O. (2015). Stakeholder marketing: Theoretical foundations and required capabilities. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43 (4), 411–428.
Hirschheim, R. (2008). Some guidelines for the critical reviewing of conceptual papers. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 9 (8), 432–441.
Huang, M. H., & Rust, R. T. (2018). Artificial intelligence in service. Journal of Service Research, 21 (2), 155–172.
King, A. W., & Lepak, D. (2011). Editors’ comments: Myth busting—What we hear and what we’ve learned about AMR. Academy of Management Review, 36 (2), 207–214.
Kozlenkova, I. V., Samaha, S. A., & Palmatier, R. W. (2014). Resource-based theory in marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 42 (1), 1–21.
Lemon, K. N., & Verhoef, P. C. (2016). Understanding customer experience throughout the customer journey. Journal of Marketing, 80 , 69–96.
Lovelock, C. H. (1983). Classifying services to gain strategic marketing insights. Journal of Marketing, 47 (3), 9–20.
Lukka, K., & Vinnari, E. (2014). Domain theory and method theory in management accounting research. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, 27 (8), 1308–1338.
MacInnis, D. J. (2011). A framework for conceptual contributions in marketing. Journal of Marketing, 75 (4), 136–154.
MacInnis, D. J., & De Mello, G. E. (2005). The concept of hope and its relevance to product evaluation and choice. Journal of Marketing, 69 (1), 1–14.
Meredith, J. (1993). Theory building through conceptual methods. International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 13 (5), 3–11.
Miller, D. C., & Salkind, N. J. (2002). Elements of research design. In Handbook of research design & social measurement, ed. by Miller D.C. & Salkind, J.J. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Mills, P. K., & Margulies, N. (1980). Toward a core typology of service organizations. Academy of Management Review, 5 (2), 255–266.
Möller, K. (2013). Theory map of business marketing: Relationships and networks perspectives. Industrial Marketing Management, 42 (3), 324–335.
Okhuysen, G., & Bonardi, J. (2011). The challenges of building theory by combining lenses. Academy of Management Review, 36 (1), 6–11.
Palmatier, R. W., Houston, M. B., & Hulland, J. (2018). Review articles: Purpose, process, and structure. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 46 (1), 1–5.
Payne, A., Frow, P., & Eggert, A. (2017). The customer value proposition: Evolution, development, and application in marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (4), 467–489.
Ragin, C. C. (1994). Constructing social research . Thousand Oaks: Pine Forge Press.
Shepherd, D. A., & Suddaby, R. (2017). Theory building: A review and integration. Journal of Management, 43 (1), 59–86.
Snow, C. C., & Ketchen Jr., D. J. (2014). Typology-driven theorizing: A response to Delbridge and Fiss. Academy of Management Review, 39 (2), 231–233.
Toulmin, S. (1958). The uses of argument . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Vargo, S. L., & Lusch, R. F. (2004). Evolving to a new dominant logic for marketing. Journal of Marketing, 68 , 1–17.
Vargo, S. L., & Lusch, R. F. (2016). Institutions and axioms: An extension and update of service-dominant logic. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 44 (1), 5–23.
Webster, J., & Watson, R. T. (2002). Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. MIS Quarterly , xiii–xxiii.
White, K., Habib, R., & Hardisty, D. J. (2019). How to SHIFT consumer behaviors to be more sustainable: A literature review and guiding framework. Journal of Marketing, 83 (3), 22–49.
Yadav, M. S. (2010). The decline of conceptual articles and implications for knowledge development. Journal of Marketing, 74 (1), 1–19.
Download references
Open access funding provided by University of Turku (UTU) including Turku University Central Hospital.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Turku School of Economics, University of Turku, FIN-20014, Turku, Finland
Elina Jaakkola
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Elina Jaakkola .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Jaakkola, E. Designing conceptual articles: four approaches. AMS Rev 10 , 18–26 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13162-020-00161-0
Download citation
Received : 12 November 2019
Accepted : 04 February 2020
Published : 09 March 2020
Issue Date : June 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13162-020-00161-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Conceptual research
- Theoretical article
- Methodology
- Research design
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

How to write a concept paper effectively
Planning to Write
Sunaina Singh

What is a concept paper?
Simply put, a concept paper is a preliminary document that sets out to explain what a proposed study is about, why it is being undertaken, and how it will be carried out. It scrutinizes a concept or idea and provides an overview of the project a researcher wants to embark on.
A researcher might need to write a concept paper to obtain permission to undertake the research project or to seek financial support for it. This means that a well-framed and compelling concept paper has high chances of convincing the target reader that the proposed research project is worth carrying out. In other words, an impressive concept paper might help a researcher secure the approvals or grants they are looking for.

Why write a concept paper?
Concept papers are typically prepared by entrepreneurs working on a business proposal or product, or by students and researchers in academia. Such documents are aimed at securing feedback on a research idea and seeking potential investors or funders. In fact, such a document might even help determine whether a project idea is feasible in the first place.
In academia, a concept paper might be needed before an undergraduate, master’s, or doctoral candidate commences work on a research project with a supervisor. Even advanced career researchers or principal investigators might need to draft a concept paper when submitting a project proposal to a funding body to obtain the necessary grants.
Listed below are some reasons why concept papers are important.
1. To explore and expand an idea: Researchers can use concept papers to transform an incipient research idea into a focused, high-quality study proposal. The paper is also a means to obtain feedback that can be used to strengthen a detailed proposal at a later stage.
2. To draw the interest of funding agencies : Through an effective concept paper, an investigator can justify why their project is worthy of funding. If the project is within the mission of the funding body and has potential to advance the field, the investigator has a high chance of success in obtaining the required grants.
3. To identify potential flaws or gaps beforehand: Putting in time and effort in writing a concept paper will help develop a focused description of the project and will allow the researcher to examine the problem from all angles. At early stages, experts or funders might spot potential gaps and weaknesses in the proposed project. Accordingly, the researcher can identify solutions and improve the proposal (e.g., in terms of the goals or methodology).
4. To serve as the foundation of the full proposal: A concept paper is preliminary, as it precedes a full proposal. Funding agencies often ask for concept papers before the full proposal submission. This helps assess whether the identified experimental methods are appropriate and can be performed within the specific timeframe drawn up for the project.
5. To help a researcher stick to project timelines: A concept paper defines a timeline, which helps the investigator to keep the project on track, manage time effectively, and reach the targeted milestones successfully.
How should a concept paper be structured?
A concept paper could be within 5 pages for proposals for master’s or PhD projects. Concept papers written as part of funding applications might even be up to 20 pages long. The format and flow of the paper would depend on the type of project and expected outcome.
Funding bodies requesting concept papers might provide a template or format, which should be adhered to. However, if templates or formats are not specified, a concept paper may be structured according to the chief elements described below.
1. An impactful title: The title should be sufficiently informative and leave a lasting impression. It should reflect the purpose and significance of the study. The title should not be too long (ideally within 15 words). The title could even be in the form of a question.
2. A clear mission statement: In a few sentences, the study objective(s) or research question should be stated. Given that the main objective of a concept paper is to convince the reader that the proposed project is worth executing, it must convey the novelty and research rationale in a convincing manner.
3. A brief yet effective overview: A concept paper should present a survey of the problem, supported by a preliminary literature review of the research topic. However, the review need not be too detailed. The paper should provide a summary of what is already known about the topic and an explanation of what knowledge gaps the research is expected to fill. Any contradictory theories may also be indicated.
4. An outline of the proposed methods: The methods that the researcher plans to use to answer the research question should be described. This section would cover ethical issues (if applicable), experimental materials and methods, the type of data to be collected, and the methods by which the data will be collected and analyzed. The estimated time to achieve different research goals should also be indicated.
5. A statement of the expected implications : A concept paper would be incomplete without a concise section on short-term and long-term impacts of the research, potential applications, impact on society and policies, and any other future visions. Know how to write a statement of the problem in a step-by-step way.
What are the key points to remember when drafting a concept paper?
1. Keep the reader in mind: If the concept paper targets experts in the field or potential collaborators/partners, it should be tailored accordingly, e.g., it can contain technical language. If the audience comprises potential sponsors/funders, the concept paper should be streamlined, keeping in mind their priorities and requirements. Such a version should contain minimal jargon and be easily digestible by non-specialists.
Bonus takeaway exclusively for community members
2. Note that a concept paper is not a journal article: Concept papers differ from journal articles in that the primary aim of a concept paper is to convince a sponsor of the feasibility and significance of a project. In that sense, it is akin to a sales pitch! It should highlight the project’s purpose and impact. To strengthen one’s case, previously awarded grants or published papers may also be indicated.
3. Make a good impression: While a concept paper should be cogent and compelling, it goes without saying that the document should be well-written and well-formatted, as well as free of grammatical, spelling, or punctuation errors. Clarity, consistency, and conciseness are key. In the absence of a formatting template, basic formatting should be in place, e.g., uniform font, adequate line spacing, and appropriate margins. Under Editage’s Scientific Editing Service , a researcher can have a concept paper assessed by a subject matter expert for an in-depth critique on the content and further checked and corrected by editors for language and readability.
Are you brimming with ideas for a research project? Now that you know the main elements that might give your proposal an edge over others, maybe you are ready to set a project in motion by starting with a concept paper.
Related reading:
- 5 Practical tips for writing your first scientific paper [Download publication schedule planner]
- The basics of writing a statement of the problem for your research proposal
- What reviewers look for in a grant proposal
Create a free account and access this bonus resource

Get Instant Access

for this article
Published on: Jul 15, 2021
- Research Planning
- Research Funding
You're looking to give wings to your academic career and publication journey. We like that!
Why don't we give you complete access! Create a free account and get unlimited access to all resources & a vibrant researcher community.
One click sign-in with your social accounts

Sign up via email
1536 visitors saw this today and 1210 signed up.
Subscribe to Conducting Research
Confirm that you would also like to sign up for free personalized email coaching for this stage.
Related Reading

A young researcher's guide to a systematic review

The basics of converting your PhD thesis into journal articles

A young researcher's guide to writing a clinical case report
How to write a concept paper effectively 7 min read
Conquering plagiarism in nursing research and authorship 10 min read
"Brazilian researchers need not despair" 8 min read
50 Motivational quotes and tips, 1 for each week of 2019 37 min read
How to collaborate effectively and ensure your research gets the attention it deserves 16 min read
Trending Searches
- Statement of the problem
- Background of study
- Scope of the study
- Types of qualitative research
- Rationale of the study
- Concept paper
- Literature review
- Introduction in research
- Under "Editor Evaluation"
- Ethics in research
Recent Searches
- Review paper
- Responding to reviewer comments
- Predatory publishers
- Scope and delimitations
- Open access
- Plagiarism in research
- Journal selection tips
- Editor assigned
- Types of articles
- "Reject and Resubmit" status
- Decision in process
- Conflict of interest
How To Write a Concept Paper for Academic Research: An Ultimate Guide

A concept paper is one of the first steps in helping you fully realize your research project. Because of this, some schools opt to teach students how to write concept papers as early as high school. In college, professors sometimes require their students to submit concept papers before suggesting their research projects to serve as the foundations for their theses.
If you’re reading this right now, you’ve probably been assigned by your teacher or professor to write a concept paper. To help you get started, we’ve prepared a comprehensive guide on how to write a proper concept paper.
Related: How to Write Significance of the Study (with Examples)
Table of Contents
What is the concept paper, 1. academic research concept papers, 2. advertising concept papers, 3. research grant concept papers, concept paper vs. research proposal, tips for finding your research topic, 2. think of research questions that you want to answer in your project, 3. formulate your research hypothesis, 4. plan out how you will achieve, analyze, and present your data, 2. introduction, 3. purpose of the study, 4. preliminary literature review, 5. objectives of the study, 6. research questions and hypotheses, 7. proposed methodology, 8. proposed research timeline, 9. references, sample concept paper for research proposal (pdf), tips for writing your concept paper.
Generally, a concept paper is a summary of everything related to your proposed project or topic. A concept paper indicates what the project is all about, why it’s important, and how and when you plan to conduct your project.
Different Types of the Concept Paper and Their Uses

This type of concept paper is the most common type and the one most people are familiar with. Concept papers for academic research are used by students to provide an outline for their prospective research topics.
These concept papers are used to help students flesh out all the information and ideas related to their topic so that they may arrive at a more specific research hypothesis.
Since this is the most common type of concept paper, it will be the main focus of this article.
Advertising concept papers are usually written by the creative and concept teams in advertising and marketing agencies.
Through a concept paper, the foundation or theme for an advertising campaign or strategy is formed. The concept paper can also serve as a bulletin board for ideas that the creative and concept teams can add to or develop.
This type of concept paper usually discusses who the target audience of the campaign is, what approach of the campaign will be, how the campaign will be implemented, and the projected benefits and impact of the campaign to the company’s sales, consumer base, and other aspects of the company.
This type of concept paper is most common in the academe and business world. Alongside proving why your research project should be conducted, a research grant concept paper must also appeal to the company or funding agency on why they should be granted funds.
The paper should indicate a proposed timeline and budget for the entire project. It should also be able to persuade the company or funding agency on the benefits of your research project– whether it be an increase in sales or productivity or for the benefit of the general public.
It’s important to discuss the differences between the two because a lot of people often use these terms interchangeably.
A concept paper is one of the first steps in conducting a research project. It is during this process that ideas and relevant information to the research topic are gathered to produce the research hypothesis. Thus, a concept paper should always precede the research proposal.
A research proposal is a more in-depth outline of a more fleshed-out research project. This is the final step before a researcher can conduct their research project. Although both have similar elements and structures, a research proposal is more specific when it comes to how the entire research project will be conducted.
Getting Started on Your Concept Paper
1. find a research topic you are interested in.
When choosing a research topic, make sure that it is something you are passionate about or want to learn more about. If you are writing one for school, make sure it is still relevant to the subject of your class. Choosing a topic you aren’t invested in may cause you to lose interest in your project later on, which may lower the quality of the research you’ll produce.
A research project may last for months and even years, so it’s important that you will never lose interest in your topic.
- Look for inspiration everywhere. Take a walk outside, read books, or go on your computer. Look around you and try to brainstorm ideas about everything you see. Try to remember any questions you might have asked yourself before like why something is the way it is or why can’t this be done instead of that .
- Think big. If you’re having trouble thinking up a specific topic to base your research project on, choosing a broad topic and then working your way down should help.
- Is it achievable? A lot of students make the mistake of choosing a topic that is hard to achieve in terms of materials, data, and/or funding available. Before you decide on a research topic, make sure you consider these aspects. Doing so will save you time, money, and effort later on.
- Be as specific as can be. Another common mistake that students make is that they sometimes choose a research topic that is too broad. This results in extra effort and wasted time while conducting their research project. For example: Instead of “The Effects of Bananas on Hungry Monkeys” , you could specify it to “The Effects of Cavendish Bananas on Potassium-deficiency in Hungry Philippine Long-tailed Macaques in Palawan, Philippines”.
Now that you have a general idea of the topic of your research project, you now need to formulate research questions based on your project. These questions will serve as the basis for what your project aims to answer. Like your research topic, make sure these are specific and answerable.
Following the earlier example, possible research questions could be:
- Do Cavendish bananas produce more visible effects on K-deficiency than other bananas?
- How susceptible are Philippine long-tailed macaques to K-deficiency?
- What are the effects of K-deficiency in Philippine long-tailed macaques?
After formulating the research questions, you should also provide your hypothesis for each question. A research hypothesis is a tentative answer to the research problem. You must provide educated answers to the questions based on your existing knowledge of the topic before you conduct your research project.
After conducting research and collecting all of the data into the final research paper, you will then have to approve or disprove these hypotheses based on the outcome of the project.
Prepare a plan on how to acquire the data you will need for your research project. Take note of the different types of analysis you will need to perform on your data to get the desired results. Determine the nature of the relationship between different variables in your research.
Also, make sure that you are able to present your data in a clear and readable manner for those who will read your concept paper. You can achieve this by using tables, charts, graphs, and other visual aids.
Related: How to Make Conceptual Framework (with Examples and Templates)
Generalized Structure of a Concept Paper
Since concept papers are just summaries of your research project, they are usually short and no longer than 5 pages. However, for big research projects, concept papers can reach up to more than 20 pages.
Your teacher or professor may give you a certain format for your concept papers. Generally, most concept papers are double-spaced and are less than 500 words in length.
Even though there are different types of concept papers, we’ve provided you with a generalized structure that contains elements that can be found in any type of concept paper.

The title for your paper must be able to effectively summarize what your research is all about. Use simple words so that people who read the title of your research will know what it’s all about even without reading the entire paper.
The introduction should give the reader a brief background of the research topic and state the main objective that your project aims to achieve. This section should also include a short overview of the benefits of the research project to persuade the reader to acknowledge the need for the project.
The Purpose of the Study should be written in a way that convinces the reader of the need to address the existing problem or gap in knowledge that the research project aims to resolve. In this section, you have to go into more detail about the benefits and value of your project for the target audience/s.
This section features related studies and papers that will support your research topic. Use this section to analyze the results and methodologies of previous studies and address any gaps in knowledge or questions that your research project aims to answer. You may also use the data to assert the importance of conducting your research.
When choosing which papers and studies you should include in the Preliminary Literature Review, make sure to choose relevant and reliable sources. Reliable sources include academic journals, credible news outlets, government websites, and others. Also, take note of the authors for the papers as you will need to cite them in the References section.
Simply state the main objectives that your research is trying to achieve. The objectives should be able to indicate the direction of the study for both the reader and the researcher. As with other elements in the paper, the objectives should be specific and clearly defined.
Gather the research questions and equivalent research hypotheses you formulated in the earlier step and list them down in this section.
In this section, you should be able to guide the reader through the process of how you will conduct the research project. Make sure to state the purpose for each step of the process, as well as the type of data to be collected and the target population.
Depending on the nature of your research project, the length of the entire process can vary significantly. What’s important is that you are able to provide a reasonable and achievable timeline for your project.
Make sure the time you will allot for each component of your research won’t be too excessive or too insufficient so that the quality of your research won’t suffer.
Ensure that you will give credit to all the authors of the sources you used in your paper. Depending on your area of study or the instructions of your professor, you may need to use a certain style of citation.
There are three main citation styles: the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), and the Chicago style.
The APA style is mostly used for papers related to education, psychology, and the sciences. The APA citation style usually follows this format:

The MLA citation style is the format used by papers and manuscripts in disciplines related to the arts and humanities. The MLA citation style follows this format:

The Chicago citation style is usually used for papers related to business, history, and the fine arts. It follows this citation format:

This is a concept paper sample provided by Dr. Bernard Lango from the Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology (modified for use in this article). Simply click the link above the download the PDF file.
- Use simple, concise language. Minimize the use of flowery language and always try to use simple and easy-to-understand language. Too many technical or difficult words in your paper may alienate your readers and make your paper hard to read.
- Choose your sources wisely. When scouring the Internet for sources to use, you should always be wary and double-check the authenticity of your source. Doing this will increase the authenticity of your research project’s claims and ensure better data gathered during the process.
- Follow the specified format, if any. Make sure to follow any specified format when writing your concept paper. This is very important, especially if you’re writing your concept paper for class. Failure to follow the format will usually result in point deductions and delays because of multiple revisions needed.
- Proofread often. Make it a point to reread different sections of your concept paper after you write them. Another way you can do this is by taking a break for a few days and then coming back to proofread your writing. You may notice certain areas you’d like to revise or mistakes you’d like to fix. Make proofreading a habit to increase the quality of your paper.
Written by Ruth Raganit
in Career and Education , Juander How
Ruth Raganit
Ruth Raganit obtained her Bachelor of Science degree in Geology from the University of the Philippines – Diliman. Her love affair with Earth sciences began when she saw a pretty rock and wondered how it came to be. She also likes playing video games, doing digital art, and reading manga.
Browse all articles written by Ruth Raganit
Copyright Notice
All materials contained on this site are protected by the Republic of the Philippines copyright law and may not be reproduced, distributed, transmitted, displayed, published, or broadcast without the prior written permission of filipiknow.net or in the case of third party materials, the owner of that content. You may not alter or remove any trademark, copyright, or other notice from copies of the content. Be warned that we have already reported and helped terminate several websites and YouTube channels for blatantly stealing our content. If you wish to use filipiknow.net content for commercial purposes, such as for content syndication, etc., please contact us at legal(at)filipiknow(dot)net
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

What are the Main Elements of a Research Concept Paper

Title page-provides a tentative title for the dissertation. The title of the Concept Paper should be a stand-alone statement that can fully describe the project by summarizing the main idea of the manuscript. The title should concisely identify the variables being investigated and the relationship among those variables (American Psychological Association [APA], 2010). Words should serve a useful purpose; avoid words that do not add substance or words that are misleading. The title of the Concept Paper may become the title of the dissertation. Statement of the Problem — provides the purpose for the research. This section of the Concept Paper introduces the problem under investigation, addresses why the researcher wants to investigate this problem, and how the research findings may help. Supporting documentation, including statistical data if available, should be used to emphasize the need for this research. This section is one of the most important sections of the Concept Paper; its serves to gain the reader's attention and support. You care about the research, but the reader may need some convincing. The first few sentences of the Concept Paper should intrigue the reader to spike his or her interest and encourage further reading. As you begin to write the problem statement of your Concept Paper, consider your research. First consider why you feel the problem is important. Consider how your study relates to previous work in the field, how you will link your hypotheses and objectives to theory, and how the hypotheses relate to the research design. Finally, consider the theoretical and practical implications involved in your research project (APA, 2010). A well-developed, concise, and clear problem statement will lay the foundation for a strong Concept Paper and the dissertation that follows. Preliminary Literature Review — provides identification of major literature that supports and validates the topic; focuses on areas that offer support for new research, and offers the student an opportunity to analyze and synthesize past research in the context of their present problem. For the Concept Paper, the student should connect their research project to a theoretical model reported in the literature. The most successful research projects have been based on the research of predecessors, and this section of the Concept Paper provides enough of a description of previous research to plant seeds in the mind of the reader suggesting more information is needed. A strong Concept Paper is based on a wide-range literature review that is condensed into a summary of key points. Goal Statement-provides a broad or abstract intention, including the research goals and objectives. This part of the Concept Paper tells the reader " who, what and when " regarding the research goal. Research Questions-provides a preliminary view of the questions the student will investigate. Questions are based on theory, past research, experience, and need. These questions will direct the research methodology; their inclusion in the Concept Paper links the research problem with the methodology. For some, composing the research questions may be the most difficult part of the research project, or possibly the most difficult aspect of writing the Concept Paper. The questions will direct everything that will be done; therefore, it is important that they are accurate and focused to the main research problem. These research questions will specifically direct the research and the type of analyses conducted, as such their compatibility is essential. An Abridged Methodology-provides the student's best idea on how to conduct the research and analyze the data. The goals and objects identified in previous sections of the Concept Paper should relate to the research methods described in this section. For the Concept Paper, the methodology is simplified or summarized, serving as a general outline of the methods that will be employed. Timeline-provides a range of time for completion of the project, highlighting key elements for each stage of the project. This element is unique to the Concept Paper and provides the student structure for managing sections of the project within a realistic time frame. References-provides references to the material cited in the literature review and elsewhere in the Concept Paper.
Related Papers
Journal of Engineering, Design and Technology
Pantaleo Rwelamila
le voice presley
Mîna Florina
Stella Atter
Reward Goodluck
Moomal Hussain
Wan Mohd Farid Wan Yusof
RELATED PAPERS
Yamilcca Barahona
European Societies
Claire Wallace
Jurnal Kesehatan
Ari Kusmiwiyati
Colloid & Polymer Science
Anna Maria Papini
La Segona República. Mallorca, 1931-1936
Gabriel Barceló Bauzà
Revista Avances en …
David Velazquez Miranda
International Journal of Computer Applications
R.k Bhardwaj
Antimicrobial Resistance and Infection Control
Ilker Uckay
Academia Biology
Mario Coca Morante
SOCIETY. INTEGRATION. EDUCATION. Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference
Alla Plaude
Journal of Power Sources
Philippe Stevens
Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C
Bashir Adam
International Journal of Medical and Surgical Sciences
Gabriel Fonseca
Professor Ari Vilela
Visionario Digital
Frontiers in Education
Slava Lopez Rodriguez
RADS Journal of Biological Research & Applied Sciences
Muhammad mubassir Khan
Biotechnology Progress
juan villafana
njjfr hggtgrf
https://www.ohchr.org/es/calls-for-input/2023/call-input-right-access-and-take-part-scientific-progress
Lucía Carolina Colombato
International Journal of Economic and Enviromental Geology
International Journal of Economic and Enviromental Geology , Sakina Riaz
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.172(2); 2005 Jan 18

Research letter
How should abridged scientific articles be presented in journals a survey of readers and authors, associated data.
SEVERAL SCIENTIFIC AND GENERAL MEDICAL JOURNALS publish full-length articles on their Web sites and abridged versions in their print journals. We surveyed a stratified random sample of BMJ readers and authors to elicit their preferred format for the abridged print version. Each participant received a research paper abridged in 3 different formats: conventional abridged version, journalistic version and enhanced-abstract version. Overall, 45% (95% confidence interval [CI] 42%–48%) of the respondents said they liked the conventional version most, 31% (95% CI 28%–34%) preferred the journalistic version and 25% (95% CI 22%–27%) preferred the enhanced-abstract version. Twenty-eight percent (95% CI 25%–32%) indicated that use of the journalistic format for abridged articles would very likely stop them from submitting papers to BMJ , and 13% (95% CI 11%–16%) said the use of the enhanced-abstract version would stop them from submitting to BMJ . Publishers of general medical journals who publish shortened articles should consider that authors and readers prefer a more conventional style of abridged papers.
To allow critical appraisal of a scientific paper, a certain amount of space is needed to describe the methods and results. Editorial space is scarce, however, and editors struggle to meet the expectations of both authors and readers. Moreover, it seems that many readers read only parts of scientific papers. Now that electronic publishing is available, several scientific and general medical journals have adopted strategies to publish detailed articles on their Web sites, often in advance of the print journal publication, with a more concise presentation appearing in the print journal.
Since 2000 most papers in BMJ have been published in their full-length form on the journal's Web site and in an abridged form in the print journal. 1 Currently the abridgement is simply a condensed version of the full-length paper (about 30%–50% shorter). The conventional structure of scientific papers is maintained, and the original wording is hardly altered.
There are many alternative forms of presenting abridged scientific information. “Serious” magazines such as The Economist use a journalistic approach, presenting the salient information at the beginning and more technical details later in the text. Medical journals such as Evidence-Based Medicine use enhanced abstracts, in which details of the results are presented (including a table or figure), and the main text — if there is any — provides context and interpretation.
We performed a survey to find which format of short version — the conventional approach, a journalistic version or a version with an enhanced abstract — of scientific articles is preferred by readers and authors. We randomly sampled 2 papers each of 6 study designs (randomized controlled trial, systematic review, meta-analysis, cohort study, case–control study and qualitative study) published in conventional abridged form 2 , 3 in BMJ between January 2000 and June 2002. The conventional format is a condensed version of the full-length paper and contains 1300–1500 words; the structure of the paper (Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion) is retained. 3 For each paper we prepared 2 additional abridged formats: a journalistic version 4 and an enhanced-abstract version (see the online appendix at www.cmaj.ca/cgi/content/full/172/2/203/DC1 for a sample of 3 abridgements of 1 paper). The journalistic version was based on a style typically used by “serious” newspapers, with the following subheadings: “Why we carried out this study,” “The background,” “What were the main findings?,” “How did we perform the study?” and “Why are these results important?” This format had no abstract, the paper starting instead with the main findings and conclusions in the first paragraph, followed by less salient details. The enhanced-abstract version provided detailed results in the abstract (including a table or figure), and the main body of the text was explanatory, focusing on the context and discussion.
We drew a stratified random sample from 1728 UK and non-UK readers and 360 corresponding authors of a research paper published in BMJ between January 2000 and June 2002. Each participant received all 3 abridged versions of 1 of 12 research papers. The study design of the paper and the order of versions were allocated randomly to each participant.
We asked the respondents to rank the 3 versions in order of preference and to indicate how strongly they felt about their preference. We also asked participants whether use of either of the journalistic or enhanced-abstract formats instead of the conventional format would prevent them from submitting papers to BMJ in the future. We offered a book voucher as an incentive and sent 2 reminders to nonrespondents. 4
Of the sample of 2088 respondents, 55 were excluded (43 had incorrect mailing addresses, and 12, being both readers and authors, were selected more than once because of overlap in the databases). Of the 2033 eligible participants, 1002 (49%) responded. The response rate was higher for authors (220/321 [68%]) than readers (782/1712 [46%]). Item nonresponse was minimal.
A total of 45% (95% confidence interval [CI] 42%–48%) of the respondents (446/997) (42% of readers and 56% of authors) said that they liked the conventional abridged version most ( Fig. 1 ). The next most preferred format was the journalistic version (31% [95% CI 28%–34%] [306/997]), followed by the enhanced-abstract version (25% [95% CI 22%–27%] [245/997]). When we stratified for location (UK v. non-UK) and audience (reader v. author), the conventional abridged version remained the preferred version, except among UK readers, who gave the 3 versions similar rankings ( Fig. 1 ).

Fig. 1: Type of short version of scientific article most preferred by BMJ authors and readers, stratified for audience (authors v. readers) and geographic location (UK v. non-UK). Error bars represent the 95% confidence interval.
Most respondents (87% [95% CI 85%–89%] [863/994]) liked their first choice “a lot.” Thirteen percent (95% CI 11%–15%) (127/994) liked their first choice only “a little,” and none said they “don't like it at all.” Four respondents (0.4%) did not have an opinion.
A total of 268 respondents said they were unlikely to submit a paper to BMJ in the future. Of the remaining 734 respondents, 28% (95% CI 25%–32%) indicated that use of the journalistic format for abridgement would very likely stop them from submitting papers to BMJ , and 13% (95% CI 11%–16%) said that use of the enhanced-abstract format as abridgement would.
Our findings that a conventional abridged version was preferred by BMJ authors and readers and that many respondents indicated that use of journalistic and enhanced-abstract formats would prevent them from submitting future papers to the journal are important signals for editors. They indicate that contributors' opinions should be considered when planning major changes for the presentational style of scientific papers.
The main limitation of our study is the low response rate for readers (46%), despite strategies to optimize response rates. 4 However, we believe that the information we received from readers is still useful, since we have no reason to believe that any particular selection mechanism is active other than lack of interest in the presentation of research papers.
Publishers of scientific and general medical journals who use or are considering using abridgements of scientific articles should bear in mind that a conventional format of abridged papers may be the choice most likely to satisfy both readers and authors.
Supplementary Material
This article has been peer reviewed.
Contributors: All authors contributed substantially to study conception and design and to data interpretation. Fabian Waechter and Sara Schroter collected the data. Marcus Müllner performed the data analysis and wrote the first draft. All authors gave final approval of the submitted version to be published.
Competing interests: Marcus Müllner works as an associate editor with BMJ and was involved in the conception, birth and further development of the electronic-long, paper-short model. At the time the research was conducted, Fabian Waechter was employed by the BMJ to conduct this and other research projects related to medical publishing. Sara Schroter is employed by the BMJ to conduct research into editorial processes such as peer review.
Correspondence to: Dr. Marcus Müllner, Univ. Klinik für Notfallmedizin, Allgemeines Krankenhaus Wien, Währinger Gürtel 18-20 / 6D, A-1090, Austria; fax +41 1 40400 2512; [email protected]
- No category
Module - Concept Paper

Related documents

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Concept Paper, although highly abridged, is comprised of many of the same items found in a dissertation. ... An Abridged Methodology — provides the student's best idea on how to conduct the research and analyze the data. The goals identified in previous sections of the Concept Paper should relate to the research methods described in ...
Additionally, infographics and scientific illustrations can enhance the document's impact and engagement with the audience. The steps to write a concept paper are as follows: 1. Write a Crisp Title: Choose a clear, descriptive title that encapsulates the main idea. The title should express the paper's content.
The concept paper, sometimes called a prospectus, preliminary proposal, or pre-proposal, is a useful tool for several purposes. It helps clarify and organize ideas in a written form and provides the basis for a funding search. From the concept paper, an individual is able to develop any number of grant applications for the same idea.
follow these steps: 1. Concept paper title. Every pa per must have a title and concept paper is not left out as one needs to have a title that. summarizes what the paper is about. The title should ...
to interest potential funders. to develop potential solutions or investigations into project ideas. to determine whether a project idea is fundable. to serve as the foundation of a full proposal. Funders that request concept papers often provide a template or format. If templates or formats are not provided, the following can serve as a useful ...
An Abridged Methodology — provides the student's best idea on how to conduct the research and analyze the data. The goals and objects identified in previous sections of the Concept Paper should relate to the research methods described in this section. ... For the Concept Paper, the methodology is simplified or summarized, serving as a ...
The paper discusses four potential templates for conceptual papers - Theory Synthesis, Theory Adaptation, Typology, and Model - and their respective aims, approach for using theories, and contribution potential. Supported by illustrative examples, these templates codify some of the tacit knowledge that underpins the design of non-empirical ...
Funders that request concept papers often provide a template or format. If templates or formats are not provided, the following can serve as a useful concept paper structure. THE FIVE ELEMENTS OF A CONCEPT PAPER 1. The first section, the Introduction, identifies how and where the applicant's mission and the funder's mission intersect or align.
To explore and expand an idea: Researchers can use concept papers to transform an incipient research idea into a focused, high-quality study proposal. The paper is also a means to obtain feedback that can be used to strengthen a detailed proposal at a later stage. 2. To draw the interest of funding agencies: Through an effective concept paper ...
Concept Paper vs. Research Proposal. Getting Started on Your Concept Paper. 1. Find a research topic you are interested in. Tips for finding your research topic. 2. Think of research questions that you want to answer in your project. 3. Formulate your research hypothesis.
concept paper is a means to develop your ideas into a research study using a flexible framework. Concept papers are useful for sharing research ideas with other ... For example, use the heading ... have the option to write an abridged methods section or a fully detailed method section. Timeline -- provides a range of time for completion of the ...
In this very short video, I discussed How to Write the Methodology of a #ConceptPaper or a #Research Proposal for an Experimental Study. Link to the Guide on...
An Abridged Methodology -- provides the student's best idea on how to conduct the research and analyze the data. The goals and objects identified in previous sections of the Concept Paper should relate to the research methods described in this section. ... For the Concept Paper, the methodology is simplified or summarized, serving as a ...
We drew a stratified random sample from 1728 UK and non-UK readers and 360 corresponding authors of a research paper published in BMJ between January 2000 and June 2002. Each participant received all 3 abridged versions of 1 of 12 research papers. The study design of the paper and the order of versions were allocated randomly to each participant.
A concept paper provides an. overview of the project, and helps funding agencies eliminate proposals that are likely to be. disapproved. Hence, it helps save time and effort for both the proponents and the funding. agencies. A concept paper has several uses: First, it serves as a foundation of the full proposal.
Abstract. By way of an exemplary elucidation, we sketch a proposal on how the development and refinement of concepts can serve as a cross-disciplinary methodology in the study of affect and ...
Example of a methodology in a research paper The following example of a methodology in a research paper provides insight into the structure and content to consider when writing your own: This research article discusses the psychological and emotional impact of a mental health support program for employees. The program provided prolonged and tailored help to job seekers via a job support agency ...
10. Physical Setting and Location. 11. Public Policy. Th e Center for Association Leadership partnered with a specialist in behavioral research who guided the development of both a process and a set of tools that included multiple data inputs, in multiple for-mats. We structured the process and the instruments together.
ABRIDGED METHODOLOGY & TIMELINE.docx - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This study examines the effectiveness of urine as a fertilizer for pechay growth. Researchers will observe pechay plants fertilized with pure urine, water mixed with urine, and no urine (the control) over one month at a farm in Cagayan de Oro City ...
It involves analyzing the concept by examining examples and specifying its characteristics to arrive at a working definition that can be consistently used throughout the paper. ... Abridged Methodology: ... Guidelines in Writing a Concept Paper. Cost and methodology should be reasonable. The budget, methodology, and timeline should be clearly ...
abridged methodology. ... true. for concept paper, it is the simplified version of the methods, serving only as general outline if methods. research design. research participants. population, sample techniques and size starte the time during which participants will be involved. research instrument. mention what, how instrument will be used.
The set of examples in this Abridged Guide follows the 'Harvard' author-date style and are based on the following publication: Style manual for authors, editors and printers 2002, 6th edn, rev. Snooks & Co., John Wiley & Sons Australia, Milton, Qld. Should the item you need to reference not be covered in this Abridged Guide, please refer to ...