👀 Turn any prompt into captivating visuals in seconds with our AI-powered design generator ✨ Try Piktochart AI!
- Piktochart Visual
- Video Editor
- AI Design Generator
- Infographic Maker
- Banner Maker
- Brochure Maker
- Diagram Maker
- Flowchart Maker
- Flyer Maker
- Graph Maker
- Invitation Maker
- Pitch Deck Creator
- Poster Maker
- Presentation Maker
- Report Maker
- Resume Maker
- Social Media Graphic Maker
- Timeline Maker
- Venn Diagram Maker
- Screen Recorder
- Social Media Video Maker
- Video Cropper
- Video to Text Converter
- Video Views Calculator
- AI Brochure Maker
- AI Document Generator
- AI Flyer Generator
- AI Infographic
- AI Instagram Post Generator
- AI Newsletter Generator
- AI Report Generator
- AI Timeline Generator
- For Communications
- For Education
- For eLearning
- For Financial Services
- For Healthcare
- For Human Resources
- For Marketing
- For Nonprofits
- Brochure Templates
- Flyer Templates
- Infographic Templates
- Newsletter Templates
- Presentation Templates
- Resume Templates
- Business Infographics
- Business Proposals
- Education Templates
- Health Posters
- HR Templates
- Sales Presentations
- Community Template
- Explore all free templates on Piktochart
- Course: What is Visual Storytelling?
- The Business Storyteller Podcast
- User Stories
- Video Tutorials
- Need help? Check out our Help Center
- Earn money as a Piktochart Affiliate Partner
- Compare prices and features across Free, Pro, and Enterprise plans.
- For professionals and small teams looking for better brand management.
- For organizations seeking enterprise-grade onboarding, support, and SSO.
- Discounted plan for students, teachers, and education staff.
- Great causes deserve great pricing. Registered nonprofits pay less.

Progress Report: How to Write, Structure, and Make Project Progress Visually Attractive

Picture this: Days or weeks into a project, your supervisor asks for a progress report.
Depending on your experience with writing progress reports, you might respond with readiness, anxiety, or confusion. Where do you begin? How do you know you’ve created a satisfactory or even amazing final report? Fear not—the expert team here at Piktochart is here to help.
In this progress reporting guide, we’ll not only give you top tips on how to write a successful report but additionally provide you with progress report templates and checklists to keep you focused on the important stuff. We begin, of course, with the all-important question anyone from a newbie to even a seasoned professional might have: “What is a progress report?”
Table of contents:
What is a progress report, why is a progress report important.
- How to write a progress report
- How to structure a progress report
- Free progress report templates you can edit right away
Progress report checklist
In case you prefer watching over reading, feel free to check out the video summary of this blog post:
A progress report is exactly what it sounds like—a document using simple and straightforward language that explains in detail what has been achieved and what else is needed for project completion. Essentially this document is a status update before the final report, outlining tasks completed by a team member, project manager, or team, along with what else needs to be done.
W hether you need to provide daily progress reports or even quarterly progress reports, this asset outlines the activities you’ve carried out, the tasks you’ve completed, and the milestones you’ve reached vis-à-vis your project plan .
Depending on the scope and complexity of the project, you might need to give a progress report weekly or monthly or for every 25% project milestone.
In terms of audience, a progress report is typically written for a supervisor, colleague, or client. Progress reports can be written from the perspective of one person as well as an entire team or department.
Throughout your career, you’re likely to be creating more reports than you can count (challenge for you: count them and find how many resources you’re using!).
Perhaps you find yourself spending more time crunching data and plugging numbers into graphs than actually working.
Reports don’t have to be as time-consuming as they often are. Progress report templates are time-savers! Get your free Piktochart account so you can follow along as we share more templates below.
We also tapped into the brilliance of Kevan Lee of Buffer in this interactive content experience to help you with your progress report projects.
Dive right in here, and learn some reporting hacks from Kevan .
Sometimes it might feel like writing about your progress in detail is redundant, especially when you’ve been regularly communicating with your supervisor, teammates, and client throughout the course of the project. Like any project manager, you probably think there are more important things to work on.
But this type of professional report is actually quite useful for several reasons.
1. It gets everyone on the same page
Each person who receives a copy of the report will know what has been accomplished and what is remaining. This prevents confusion about what has been or has yet to be done. Additionally, it provides proof and data about the respective project that can be cited and sourced if and when questions arise in the future.
2. Writing progress reports facilitates collaboration
This is especially important when different teams or departments work together. Knowing what another team is prioritizing helps prevent working in silos and also reduces task redundancy. Additionally, progress reporting helps a team identify areas where it can offer help or collaborate with others.
When teams can track progress on where other teams are on the project timeline, project managers get a better idea of the current status. They can reassign resources to make sure everyone is on track to hit the deadline for the current project, which can be tricky if you’re managing remote teams .
If you’d like to learn more about how you can work together with your team on a report, sign up for a free Piktochart account and try our online report maker .
3. It improves transparency and accountability by providing a paper trail
When you submit your report, you’ve placed on record that you’ve accomplished a task or explained why your results were different than expected. Once the document has been accepted, it becomes part of the project’s official documentation.
So, just in case someone accuses you in the future of failing to accomplish a task or not reporting a problem, you can point to the progress report as proof that you did so.
On the flip side, if your project ever gets nominated for an award, you can be sure validators will come seeking documents that explain how the entire thing was accomplished.
4. It improves project evaluation and review
Next time you plan for a project, your team can examine documents, including progress reports, of previous projects to find out what was done right, what went wrong, and what can be improved.
Previous reports can shed light on systemic issues, loopholes, and other causes of delay or failure—both internal and external—that must be avoided or resolved.
5. It provides insights for future planning
When the supervisor knows what tasks have been accomplished, he or she can focus on monitoring progress toward the next stages of the project.
When a report shows that delays have occurred, the supervisor is able to investigate the problems that hindered progress and take steps to prevent them from happening again in the future.
The supervisor will also be able to adjust the project timeline if absolutely needed or instruct teams to double down.
Ultimately, all the valuable insights from the project documentation can increase the chance of success for future projects.
Here is a progress report format example:

How to write progress report s
Have you ever found yourself stuck tapping your pen or staring at a blinking cursor, unable to begin writing?
Writer’s block is not an unusual experience when creating progress reports, especially for those whose jobs typically don’t involve drafting a long document or creating a formal report.
One reason people may find it difficult to write these reports is the thought that they’re not ‘writers.’ Yet, this is simply a negative mindset.
Reports don’t require sophisticated language—in fact, the simpler, the better.
Here are some writing tips on progress reporting:
“Piktochart is my go-to tool when I’m looking for a way to summarize data that is easy for our upper management to review. Piktochart provides me with the tools to display data in a creative, visually appealing way.” – Erica Barto, Selection, Testing & Assessment Specialist at Valero Energy Corporation Create a report, presentation, infographic, or other visuals online with Piktochart. You don’t need any graphic design experience to make professional visual content. Sign up for free .
1. Think of it as a Q&A
Before you start worrying about your reporting frequency and whether you should provide monthly reports or weekly reports, take a step back and focus on the purpose of the report itself.
In essence, the reporting process comes down to Q&A; you’re answering key questions about your progress. Imagine your manager, colleagues, or client asking you their most important questions, and you’re simply providing them with answers on the project status.
For example, let’s say that you’re organizing a weekend fair with food stalls and music and that you’re put in charge of food concessions.
The project plan might require you to have secured letters of intent (LOI) from at least 10 businesses by the end of the first month.
Your progress report would then outline the companies or entrepreneurs who have sent LOIs, including a description of their businesses and plans for their food stalls. If talks are in progress with other businesses that haven’t yet sent LOIs, you can include that and explain when they’re expected to send in their letters.
On the other hand, if you haven’t met your target, you’d have to explain why but also narrate the efforts you have exerted and the expected timeline for achieving the desired results.

2 . Use simple and straightforward language
This doesn’t mean you can’t use technical jargon.
For example, if you’re in the construction business, you don’t have to avoid using terms like “tender” or “variation” or “risk management.”
But otherwise, speak plainly. Use clear and concise language.
One misconception in business writing is that complexity impresses. In truth, it only causes confusion. Fact is, being able to speak plainly about your subject indicates that you understand your subject matter inside out.
Let’s get specific. One thing that makes business documents dreary is the transformation of verbs into nouns—just like I did there.
If we had to rephrase that to keep the verb, we’d write, “transforming verbs into nouns.” It sounds simpler and gets to the point.

3 . Avoid using the passive voice where possible
Sometimes, you can’t avoid using the passive voice in formal documents that prohibit the first-person point-of-view. But when done well, it helps to make your progress reports more relatable.
Going back to the food concession example, a passive sentence would read: “Research on potential food concessionaires was carried out.”
To make that sentence active, give it an actor (which is the team in this case), as in: “The team researched on potential food concessionaires.”
4. Be specific
A study published in the Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience found that when you use concrete words, you tend to engage both the left and right parts of the brain, while the right region tends to remain unstimulated by abstract words.
While the jury is still out on exactly how word meanings are represented in the mind, we can agree that the phrase “a merry sound” doesn’t stir the imagination as much as “tinkling bells”.
“A hot day” doesn’t activate visual imagery as much as “a melting popsicle” does. When a reader’s mind is stimulated by words, it’s less likely to drift off.

Taking the previous example, “researched on potential food concessionaires” doesn’t evoke a visual image. Meanwhile, “built a list of 50 potential food concessionaires” is more concrete, especially when you add details of what food items might be sold.
5. Explain jargon if needed
This depends on who will be reading your progress reports, and if you’re using very specialized jargon that only members of your team would be familiar with.
For example, in a report written by a construction team addressed to the project manager , construction jargon could be used as the recipient obviously understands it.
6. Spell out acronyms when they first occur in the document
Don’t assume that every single person reading the report will understand all the acronyms you use without you spelling them out.
For instance, in construction work, SWMS should first be spelled out as “safe work method statement”. ‘Pre-starts’ should be spelled out as ‘pre-start checks’. So in your report, it would look like this: “safe work method statement (SWMS)”, then all subsequent references are free to just be SWMS.
7. Stick to facts
Avoid providing an opinion, unless it’s part of the project.
For instance, your task might be to analyze data and offer your interpretation and prediction. In that case, you can offer your speculation and point of view, as long as you have evidence to back you up.
8. Use graphics to supplement the text
Avoid writing down a long series of numbers in a sentence. Try using different types of graphs , tables or charts, especially when dealing with a series of numbers.
Here at Piktochart, we have many progress report templates, and the hiring progress report below is a great example.
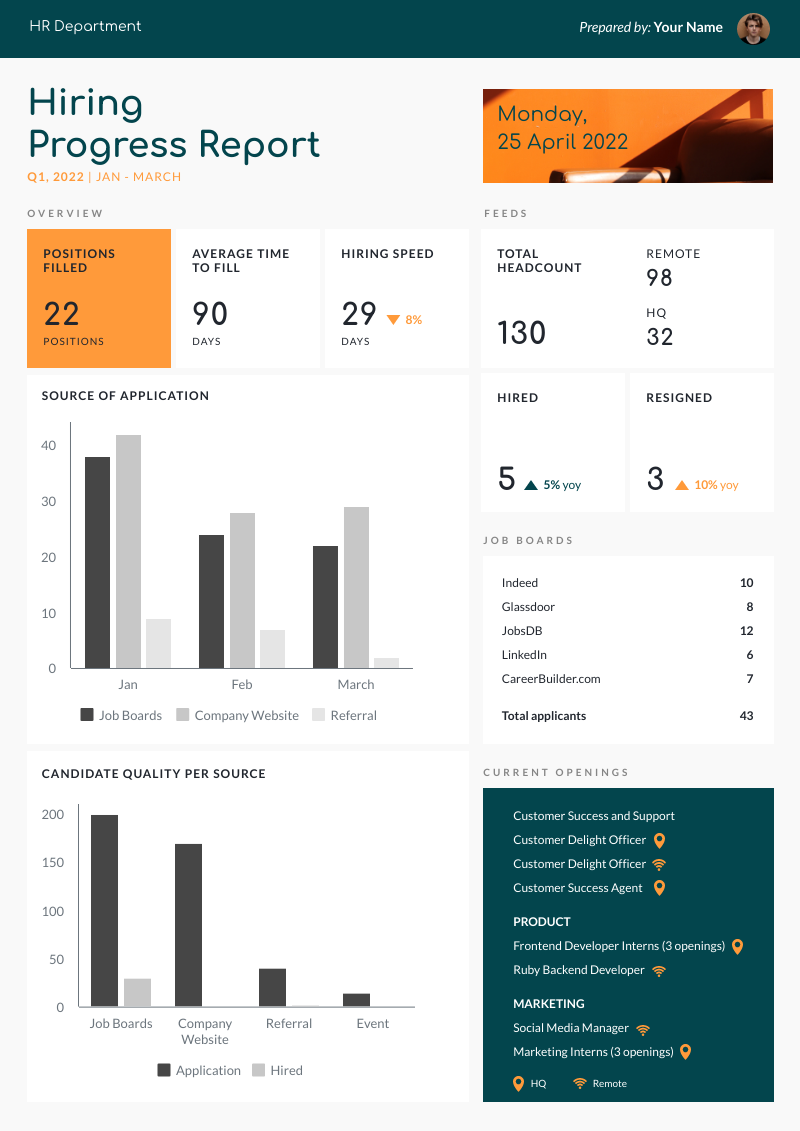
When using graphs or charts, try out several types to determine which ones best present your data. You might use a bar graph , pie chart , line graph , or even scatter plot . When doing so, though, spend time distinguishing different data sets from the others by using labels and colors.
Don’t worry if this sounds daunting—there are plenty of software that can help you visualize data , including the most basic examples, MS Excel and Numbers for Mac.
How to structure progress report s
You may still be wondering about the exact process of how to write a progress report. Armed with all of these practical tips, how do you put the report together?
First, it depends on the type of report, as well as the intended reader. A progress report may be written daily, weekly, or monthly. It may be written for an individual or a team.
As you’ll see in the examples below, the main parts of a progress report are:
1. Introduction
This part provides an overview of the contents of the progress report. It’s best to write this after you’ve completed all the other parts of the report. That way, you’ll be able to provide an accurate summary.
Keep it short and simple. One or two paragraphs will do.
2. Accomplishments
Numbers and details are your friends, especially when writing this section of the progress report. The accomplishments you write should correspond to your goals.

What were your goals for the period covered by the report?
This could be a goal for the day, week, month, or quarter. On the other hand, it could be a team goal, too.
Be concrete when writing goals. For instance:

Avoid providing too much detailed information. The simpler this section is, the easier it is for stakeholders and the project team to see the project priorities.
4. Roadblocks
Explain what situations, if any, prevented you from achieving your goals, or may have hindered the project’s progress.
But don’t stop there. Be proactive and present an action plan and timeline for resolving the roadblocks. Include details, such as funds, materials, and human resources you may need to implement the solution.
Progress reporting templates you can edit right away
To guide you better, here are progress report template examples that are visually attractive and highly readable.
These templates are available if you sign up for a free Piktochart account . Once you log in, use any of the templates below and edit the elements and text to make it your own.
1. Daily progress report s
A daily progress report includes your goals for the day, as well as your accomplishments the previous day. It also explains challenges encountered in performing tasks and achieving goals.
Another section under the daily report is ‘lessons learned’. These need to be directly related to the day’s tasks and challenges, as well as to the previous day’s accomplishments.
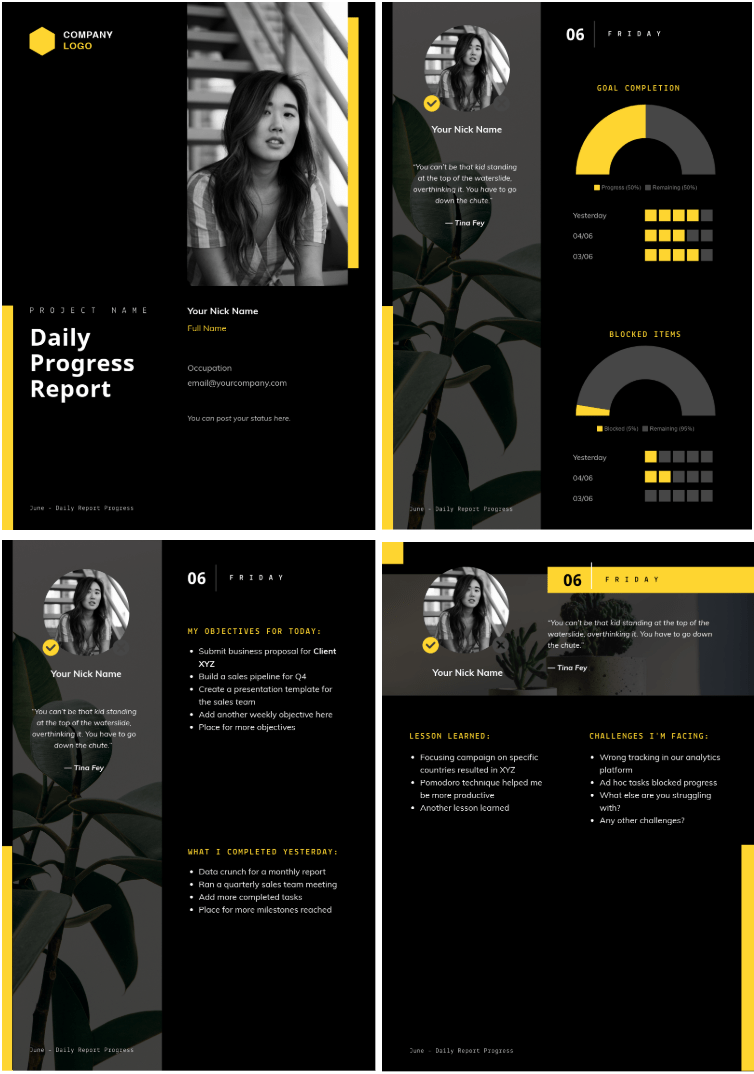
2. Weekly progress report
Weekly progress reports provide a week-by-week breakdown of what has been accomplished and what tasks remain to be completed.
Just like a daily report, a weekly progress report may include challenges and lessons learned. Examples are included in the templates below.
To get a better idea of this, let’s go back to the events example:
- Many potential vendors were attending a week-long industry convention; couldn’t book meetings.
- Potential vendors didn’t read the entire email.

Lessons Learned
- Consider industry events when planning a timeline for contacting clients
- Introductory emails must be short and have readable formatting

3. Monthly progress report ing
A monthly report is necessary for projects with longer durations. The report may provide both monthly and quarterly data on project progress.

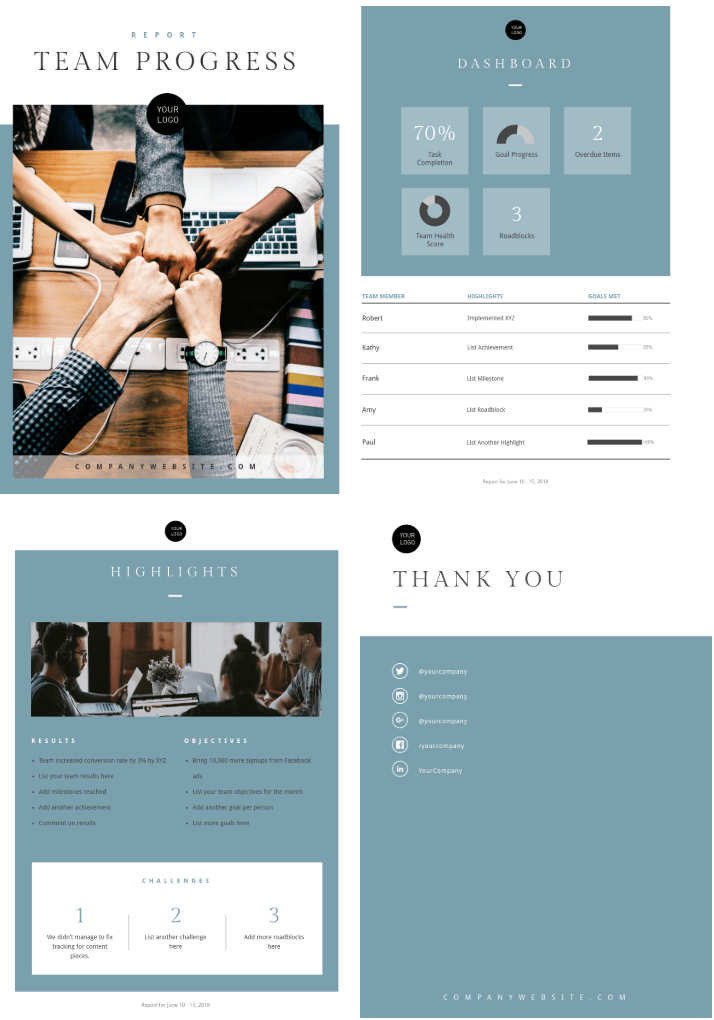
4. Team progress report s
Team progress reports provide information on both team and individual milestones and progress status. Now this one is more complicated, simply because it involves several people who may have worked on different tasks.
It’s not enough to just let one person make the report. Of course, one person can do the typing, but everyone must provide input and feedback.
One way to keep a record of different team members’ input is to keep track of edits they have made.
To do this, simply enable tracking of changes on a Word document, or on Pages for Mac users. When working on a collaborative tool like Google Docs , click the pencil icon on the top-right part of the window, and choose “Edits become suggestions” on the drop-down menu. Here’s what that looks like:
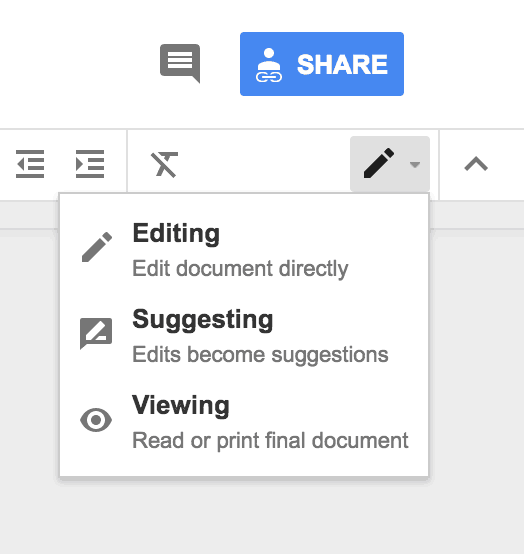
On the other hand, team members can insert comments or questions. Again, you can do this easily on a Word document, as well as on software that let you comment on shared documents, like Google Docs and Piktochart .
Here’s what it looks like in Piktochart (learn more about this feature in our guide to annotated comments for teams ):
Here’s one example of Piktochart’s many team project report templates .
One last thing… You’ve finally finished typing up your report—breathe a sigh of relief, but don’t hit ‘send’ just yet.
Go over it at least once (better to do it more than once, especially if it’s a team report). Re-read the article, edit the content as needed, then ask a teammate to proofread with a fresh pair of eyes.
Other Posts

25 Green Color Palette Combinations (With Hexes and Name Codes)

How to Make Any Image Background Transparent

8 Best AI Banner Generators in 2024

Research Progress Report

Progress reports . You heard of them, you may even think they are useful or useless. You may also think that as a student, you don’t have to write them. However, this is not always the case. A research progress report is nothing short as one of the necessary reports you need to make. When it comes to writing reports, a lot of students may feel the need to complain due to the fact that writing reports can be boring or simply a waste of time. What they don’t know is that giving a report is useful for their professors, especially when it is used as a way to know the progress of their performance, school projects, or research activities. So take a good look at these examples to help you out with your research progress report.
10+ Research Progress Report Examples
1. research progress report template.

- Google Docs
2. Summer Stipend Research Progress Report
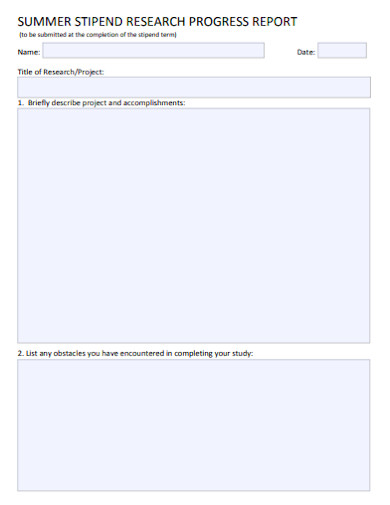
Size: 31 KB
3. Biomedical Research Progress Report

Size: 150 KB
4. Research Performance Progress Report
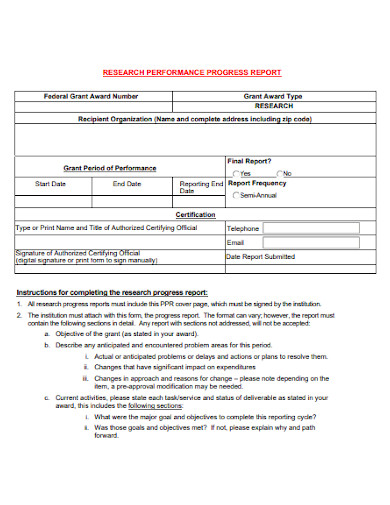
Size: 76 KB
5. Weekly Research Progress Report
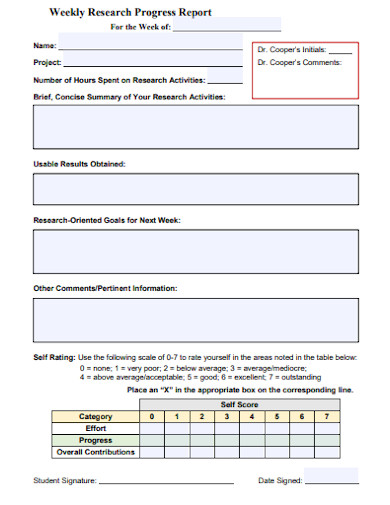
Size: 103 KB
6. Printable Research Progress Report

Size: 681 KB
7. Research Fellow Progress Report
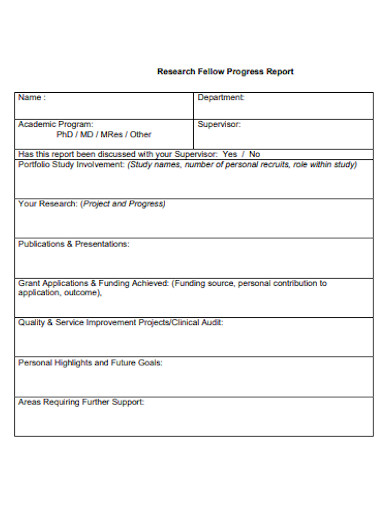
8. Human Research Progress Report

Size: 117 KB
9. Editable Research Progress Report

Size: 113 KB
10. Candidate Research Progress Report

Size: 290 KB
11. Annual Research Progress Report
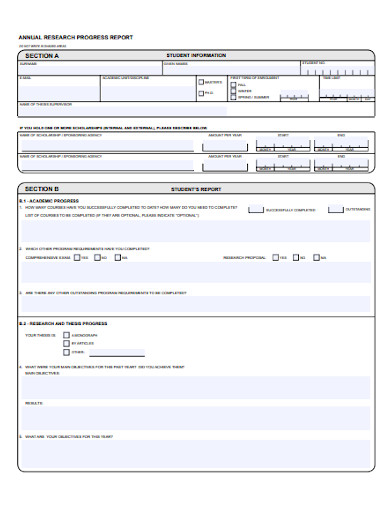
What Is a Research Progress Report?
The progress of your research . Whether that progress will be a lot or not as much. The report consists of the detailed progress you give to your superior or for students’ cases to their professors on how their research assignment or research project is going. In addition to that, a research progress report not only consists of the exact progress, but it also consists of what you have been doing, how the research is going, and of course the information you are going to be giving or the evidence whether positive or negative. Everything is written there. A research progress report is a document that clearly states what it is supposed to state.
How to Write a Research Progress Report?
To write a research progress report , there are a lot of ways to do so. Regardless of how you plan it out, draft it out and finalize it, there are still some things you have to think about when you want to proceed. Here are some tips that will get you started with your research progress report.
1. Write the Title of Your Report
The title of your report should at least be about what your research is about. It does not have to be something too fancy that the whole point of the report is lost or too obvious that would make the report redundant.
2. State the Achievements That Have Been Done
Any achievement that has been done or recorded should be written down, no matter how minuscule or large these achievements are. Progress is progress and it should also be recorded.
3. State the Name of the Researchers
The researchers names should also at least be a part of the report, especially if it is a group research. It is always best to add the names of the people involved in helping you with the progress of your report or the progress of your research. Give them some credit.
4. Give the Expected Publication for the Research
There are some who may be asking for the expected publication of your research . If this were the case, at least give the expected date of the research; however, as for the report, when you are done writing it, you should immediately check if you have everything written for it to be presentable.
5. Add the Statistics and Evidence to Support Your Report
The statistics and evidence to support your report should also be present. The reason for having to add evidence for a progress report is to show your professors or your superiors enough to compare the previous progress reports to the current report, regardless if there is any progress or the lack of it.
What is a research progress report?
A research progress report is a document that summarizes the progress of a research made by students. In order for their professors to know the exact ongoing of their research, the students are tasked to write about what is going on with their report and how far are they to achieving it.
Are there other ways to write a research progress report?
There are other ways, but the most common is writing it in an essay form. Of course, you can also fill out a form that states a research progress report form. But it is usual to present it in paragraph form in order for your professors to see the details of the statistics given.
Is a research progress report short or long?
A general research progress report is expected to be a page long. However, this would depend on how much progress you have made throughout your research and how much reports you have done in order to compare from your previous ones.
We are taught to write progress reports while we are still in school, so when we are out there in the real world, we are able to understand the reason and the purpose of writing these kinds of reports. A research progress report is simply just another kind of progress report that we are taught to write. It helps your teachers know where your progress is at the moment and how long are they going to expect your research project to be completed.
Report Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate a report on the impact of technology in the classroom on student learning outcomes
Prepare a report analyzing the trends in student participation in sports and arts programs over the last five years at your school.
- Free Project Management Software
- Agile Project Management Software
- Project Management Software for Nonprofits
- Organization Apps to Boost Productivity
- Resource Management Software
- Monday Review
- ClickUp Review
- Monday Pricing
- ClickUp Pricing
- Wrike Pricing
- Asana Pricing
- Smartsheet Pricing
- Teamwork Pricing
- Airtable Pricing
- Scoro Pricing
- Asana vs Monday
- ClickUp vs Monday
- Wrike vs Asana
- Trello vs Asana
- ClickUp vs Asana
- What is Agile Project Management?
- Key Benefits of Agile Methodology
- Most Important Agile Metrics
- Agile Manifesto: Values and Principles
- Agile Project Management Certifications
Progress Report: What is it & How to Write it? (+Examples)
Picture this: You're a project manager juggling multiple tasks, deadlines, and team members. Keeping the balance between different tasks is hard but very important.
Enter the progress report, your secret weapon in conquering chaos and ensuring smooth sailing.
But what exactly is a progress report, and how do you craft one effectively? In this blog post, I'll demystify progress reports and guide you through the process of writing one.
From daily progress reports to weekly progress reports, using practical progress report templates and a tried-and-true format.
What is a Progress Report?
A progress report is a vital tool in project management , designed to keep different types of stakeholders informed about the ongoing status of a project.
It's a concise document highlighting current achievements, challenges, and goals, allowing the project manager to track progress and make necessary adjustments.
Project progress reports are one of the most important types of project management reports . They help maintain transparency, communication, and accountability within a team, ensuring everyone is on the same page. They also provide valuable insights for decision-makers, helping them gauge the project's overall health and success.
Here's what you can expect to find in a typical progress report:
- Project Overview: A brief summary of the project's objectives and scope.
- Current Status: A snapshot of where the project stands regarding completed tasks, milestones reached, and overall progress.
- Challenges and Issues: Any technical difficulties, resource constraints, or personnel issues.
- Next Steps: The immediate tasks and goals on the horizon and how the team plans to tackle them.
- Progress Report Format: The layout of the report can vary depending on the organization's preferences or industry standards.
Writing a progress report can seem daunting, but it doesn't have to be. You'll create a valuable document that keeps everyone informed and aligned by breaking it down into manageable sections and using clear, concise language.
Embrace the progress report writing skill and watch your team's productivity and communication soar.
Why are Progress Reports Important?

Progress reports play a vital role in project management, serving as a communication tool to keep stakeholders updated. Let's delve into why progress reports are crucial for the success of any project or business.
Transparency and Accountability
Progress reports eliminate ambiguity and promote transparency. By regularly sharing project updates with stakeholders, the project team is held accountable for their work. This accountability ensures everyone is on track to meet the project milestones and objectives.
Identify Potential Issues Early
Progress reports help identify potential problems before they escalate. Team members can spot bottlenecks, delays, and other issues by examining project data and analyzing the progress report.
Early detection enables the team to take prompt action and prevent these issues from derailing the project.
Effective Decision-Making
Armed with accurate and timely information from progress reports, project managers and stakeholders can make informed decisions.
When a project progresses smoothly, management can allocate resources more efficiently or plan for future phases. On the other hand, if a project encounters challenges, swift decisions can be made to reallocate resources or change course.
Maintaining Momentum
A progress report's important aspect is maintaining momentum. When team members see their progress documented and shared, it fosters a sense of accomplishment and motivation.
This positive reinforcement encourages teams to keep pushing forward and maintain their productivity.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
Progress reports facilitate better communication and collaboration among team members. By sharing updates and insights, the entire team stays informed, reducing the chances of miscommunication or misunderstandings.
Moreover, progress reports provide a platform for team members to ask questions, provide feedback, and offer support.
Performance Tracking
Business progress reports, such as quarterly, monthly, or annual progress reports, help track performance over time.
By comparing past reports, management can gauge the business's overall health and identify trends or patterns. This historical data can inform future strategies and drive continuous improvement.
How to Write a Progress Report
Step 1: define the purpose.
The first step in writing a progress report is understanding its purpose. Progress reports inform stakeholders about the project's status, including what has been accomplished, any challenges encountered, and future planning. This allows project managers to keep everyone in the loop and make informed decisions.
The purpose of this monthly progress report is to update the management team on the project's status. It presents an overview of completed tasks, in-progress tasks, upcoming tasks, and any challenges faced during the reporting period. This report will also provide insight into key performance metrics and future planning .
Step 2: Know Your Audience
Determine who will read the progress report. Is it for higher-ups, clients, or team members? Tailor the language, tone, and level of detail accordingly.
Step 3: Set the Timeframe
Decide the reporting period – weekly, monthly, or quarterly. Choose a timeframe that best suits your project's pace and stakeholder expectations.
Step 4: Collect Information
Gather data on tasks completed, team members involved, and any obstacles faced. Consult previous progress reports, project documentation , and team members for accurate information.
Step 5: Organize Content
Break down the report into logical sections. Here’s what we suggest:
- Summary: A brief overview of the report's contents.
- Completed Tasks: List tasks accomplished during the reporting period.
- In-Progress Tasks: Describe ongoing tasks and their current status.
- Upcoming Tasks: Outline tasks scheduled for the next reporting period.
- Challenges: Discuss any obstacles encountered and how they were addressed.
- Key Metrics: Highlight key project performance indicators and progress towards goals.
- Future Planning: Discuss plans for the next reporting period and any adjustments needed.
Step 6: Write the Summary
Craft a concise summary that provides a snapshot of the report. Mention key achievements, challenges, and plans for the future. Keep it brief but informative.
This progress report covers our team's accomplishments during Q1, with a particular focus on the completion of the website redesign and the initiation of our social media marketing campaign. We've encountered some challenges in coordinating with external vendors, but we've implemented solutions to overcome those obstacles .
Step 7: Detail Completed Tasks
List all tasks completed during the reporting period. Include the following information:
- Task description
- Team members involved
- Start and end dates
- Any relevant metrics (e.g., hours spent, budget used)
- Task 1 – Implement a user login system.
- Team members: Jeff and Sarah.
- Start date: January 1st.
- End date: January 15th.
- Metrics: 98% successful login rate.
Step 8: Discuss In-Progress Tasks
Outline ongoing tasks, their current status, and expected completion dates. Explain any delays and their impact on the project timeline .
- Task 2 – Develop a mobile app.
- Current status: 70% completed.
- Expected completion date: February 15th.
Step 9: Describe Upcoming Tasks
Identify tasks scheduled for the next reporting period. Provide details such as:
- Assigned team members
- Estimated start and end dates
- Dependencies on other tasks
- Task 3 – Launch marketing campaign.
- Assigned team members: Anas and Mark.
- Estimated start date: February 16th.
- Estimated end date: March 1st.
- Dependencies: Completion of mobile app development.
Step 10: Address Challenges
Discuss any challenges encountered during the reporting period. Describe how they were resolved or any plans to address them in the future.
- Challenge 1 – Unforeseen technical issues causing delays.
- Resolution: Increased resources and adjusted project timeline to accommodate the additional time required.
Step 11: Present Key Metrics
Highlight key project management performance indicators and progress toward project goals. Use visuals like charts or graphs to make the data more digestible.
- Metric 1 – User registration rate.
- Current status: 500 new users per week.
- Target goal: 1,000 new users per week.
Step 12: Plan for the Future
Discuss plans for the next reporting period, including any adjustments required. This may involve reallocating resources, revising timelines, or redefining objectives.
In the next reporting period, our focus will shift to improving user retention and engagement. We plan to implement new features based on user feedback and optimize the onboarding process.
Step 13: Proofread and Revise
Review the report for clarity, accuracy, and readability. Ensure all information is presented in a clear, concise manner.
Step 14: Submit the Report
Submit the progress report to the relevant stakeholders, ensuring they have ample time to review and provide feedback.
Example Progress Report Template
Use this template as a starting point for your progress report:
By following these steps and guidelines, you'll be well-equipped to write an effective progress report that keeps stakeholders informed and drives project success. Clear communication is key to maintaining momentum and ensuring everyone is on the same page.
Examples of Progress Reports
1. business progress report.

A business progress report helps track company growth, accomplishments, and areas for improvement. It includes:
- Revenue and sales figures.
- Market trends and competition.
- Operational efficiency.
- Employee performance.
- Goals and milestones achieved.
2. Quarterly Progress Reports

These reports offer a snapshot of a project or business every three months. They cover:
- Major achievements.
- Challenges faced and solutions.
- Key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Updated project timeline.
- Budget status.
3. Monthly Progress Reports
Monthly progress reports provide more frequent updates on projects or departments. They highlight:
- Accomplishments and setbacks.
- Progress towards monthly goals.
- Resource utilization.
- Issues and risks.
- Action items for the upcoming month.
4. Project Status

Project status reports focus on a specific project's progress. They showcase:
- Project documentation updates.
- Completed tasks and upcoming deliverables.
- Risks and issues encountered.
- Team members' performance.
- Changes to project scope or timeline.
5. Personal Progress
Personal progress reports help individuals track their growth and development. They include:
- Personal goals and objectives.
- Achievements and lessons learned.
- Skill development and training.
- Performance feedback.
- Areas for improvement and action plans.
Best Practices for Writing Progress Reports

Know Your Target Audience
When you create a progress report, start by identifying your target audience . Project stakeholders, team members, and future decision-makers should all benefit from your report.
Write in such a way that it is easy for them to understand. Avoid technical jargon and explain industry-specific language so everyone stays on the same page.
Reporting Frequency and Dates
Establish a reporting frequency for your progress reports. Whether weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly, maintain consistency. Include report dates and the expected completion date of the current project to provide a clear timeline.
Stick to the Project's Scope
Focus on the project's scope and stay within the project's purpose. Don't digress or include unrelated details. A concise report ensures that readers remain engaged and informed.
Review Previous Reports
Refer to the previous report to identify any changes or developments. Highlight the work completed, project deliverables , and any updates to the project plan. Doing so will maintain continuity and keep stakeholders informed about the department's progress.
Prioritize and Organize
Arrange project priorities logically, focusing on the most critical aspects first. Organize the information in a clear, easy-to-follow format. Use headings, subheadings, and bullet points for better readability.
Be Transparent About Problems
Don't shy away from discussing problems or challenges. Addressing issues helps stakeholders understand the project's status and any hurdles that may affect successful completion. Offer potential solutions or workarounds to demonstrate proactive thinking.
Back Up Progress with Relevant Data
Use relevant data to support your progress. Figures, charts, and percentages can provide a quick overview of the project's status. Make sure your data is accurate, up-to-date, and presented in an easy-to-understand format.
Highlight Team Member Contributions
Acknowledge team members who have made significant contributions to the project. This recognition boosts morale and encourages continued excellence.
Include Future Projections
Discuss what's next for the project, such as upcoming tasks or milestones. This helps stakeholders understand the trajectory of the project and anticipate the work ahead.
Keep it Simple and Actionable
Present complex ideas in a simple, easy-to-understand language. Break down complicated concepts into manageable chunks. Offer actionable insights and practical takeaways, so stakeholders can quickly grasp the project details.
Establish a Database
Create a database to store all progress reports. This repository helps stakeholders access past reports and provides valuable insights for future projects. It also ensures that information is preserved and easily accessible when needed.
Proofread and Edit
Before sharing your progress report, proofread and edit for clarity, consistency, and accuracy. This step ensures that your report is polished, professional, and easy to understand.
Progress Reporting FAQs
A progress report is most valuable when you're working on a long-term project. It's a way to keep stakeholders updated on progress and share important insights.
The primary purpose of a progress report is to provide a clear and concise overview of a project's status. This includes: – Communicating progress toward goals – Identifying potential issues and solutions – Demonstrating accountability and commitment to the project – Providing a step-by-step guide of completed tasks and upcoming work – Offering visual aids, like charts and graphs, to illustrate data A well-crafted progress report keeps stakeholders informed and fosters collaboration. It's also valuable for maintaining momentum and motivation throughout the project.
Writing Progress Reports Does Not Need to Be Hard
So, you've reached the end of this blog post. You're now equipped with the knowledge and tools to make progress report writing a breeze. Remember, it doesn't have to be a daunting task.
Keep it simple, stick to the facts, and let your progress shine. Talk about what you achieved, any challenges you faced, and how you overcame them. Use a clear, concise, structured format to ensure your message is easily understood.
To simplify the process, check out our guide on project reporting tools .
Ask yourself:
- What are the key takeaways from this period?
- How can I best communicate the status of the project?
- Are there any challenges that need addressing?
Considering these questions will make your progress report informative, actionable, and engaging. And don't forget, practice makes perfect. The more progress reports you write, the easier and more efficient the process will become.
Explore Further
- Essential Components of Project Management
- Best Project Management Software 2023
- The Inspiring History of Project Management. How Did It Begin?
- 9 Essential Roles In Project Management
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Official Writing
- Report Writing
How to Write a Progress Report
Last Updated: May 11, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Ksenia Derouin . Ksenia Derouin is a Business Strategy Specialist, OBM, and Artist based in Grand Rapids, Michigan. With over ten years of professional experience, Ksenia works with wellness and social impact sector solopreneurs and organizations to support their business strategy, operations, marketing, and program development. Her mission is to support business owners in building thriving businesses and creating impact so that they can achieve a sense of purpose, career fulfillment, and financial independence. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 439,333 times.
Progress reports are an important part of project management, whether it's your dissertation or a project at work. You'll need to use these to keep your supervisors, your colleagues, or your clients updated about the project you're working on. You'll be focusing on what you've accomplished and what still needs to be done.
Beginning the Process

- Progress report for a research program or project is going to be slightly different than for a project at work. In this case you are more likely to need to cite information and are less likely to need to consider things like cost (although not always).
- A work report for a client is going to read somewhat differently than for a superior at work. You'll need to consider why you're writing this report for them.

- How are your readers connected to the project? How will the outcome of the project affect them? (The connection and how they're affected is going to be different for your superior than for the client, for example.)
- Consider what decision your readers are going to need to make after reading the progress report (what support, money, time are they investing, for example.
- Consider the information your reader is going to need to know to oversee and participate in the project effectively. What technical aspects of the project will they need to know. Are they comfortable with technical jargon?

- A progress report could be a brief oral report at weekly or monthly staff meetings.
- It could be periodic emails to colleagues.
- It could be formal or informal memos to supervisors.
- It can also be formal reports for clients or government agencies.

- When it comes to information for a client or government agency, or thesis review board, you err on the side of formality.
- No matter the formality or informality of your tone you want it to be clear, focused, and honest.
Writing Your Report

- You might choose to do a bulleted list. It's a very clear way to present the material and it's easy to skim and still get the needed information. However, it can be a slightly less formal way of writing a progress report so it might be better to use it for memos to supervisors and emails to colleagues.
- You may also consider adding in graphs or tables. This might be especially good if you're writing a progress report for a project in which you're trying to get funding, or show why you deserve the funding you've been given.

- Adding subheadings to your can make this even clearer, because it lets your readers or audience know what to expect in each subsection. If there is material that they are particularly interested in they'll be able to jump right to that part.

- The heading should include the date, when the report was submitted, the name and the position of the recipient, the writer’s name and position, and the subject of the report.

- Make sure to include: the purpose of the report, introduce the project, remind that this is an update on the progress of the project.

- Specify tasks that have been accomplished since the last report and what tasks are ongoing.
- Discuss problems that you’ve encountered, issues that need to be addressed, and potential solutions for those problems and issues.
- Address changes that have happened and why they needed to be made.
- You can also include things like personnel changes, difficulty in obtaining material, what cost overruns you may have encountered, any delays or problems with technology or security.
- It also helps to provide a timeline of the project with any relevant due dates.

- You really do want to make sure say whether the deadline for the project has changed or not.
- Avoid sugarcoating any problems for your audience, but don’t alarm them unnecessarily or promise anything you can’t deliver.

Avoiding Common Difficulties

- For example: if your project is about reigniting a local, nonprofit arts organization, it might be tempting to go off into a discussion of the deplorable state of arts funding, but it won't really help detail how your project is coming along.

- Depending on who you're writing the report for you might be cut down to a specific page limit. A good rule of thumb is to keep it as short as possible, while making sure that you fit in the appropriate information.

Community Q&A
- Try to judge your supervisor's style. She may have a preference for the types of reports she likes to see. Some may want to see more lists or bulleted information; others will like to know as little as possible to get by. Still others may prefer as much information as possible, no matter how many pages it takes. Thanks Helpful 36 Not Helpful 10
- Be specific throughout the progress summary, but try not to be overly wordy. Thanks Helpful 18 Not Helpful 6

- In order not to be caught unprepared when it's time for a progress report, it's a good idea to record information as you go along so it's easy to put all the information together. Thanks Helpful 8 Not Helpful 6
You Might Also Like

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about improving your business, check out our in-depth interview with Ksenia Derouin .
- ↑ https://pressbooks.bccampus.ca/technicalwriting/chapter/progressreports/
- ↑ https://pressbooks.pub/coccoer/chapter/progress-reports/
- ↑ https://ohiostate.pressbooks.pub/feptechcomm/chapter/2-audience/
- ↑ https://pressbooks.bccampus.ca/technicalwriting/chapter/figurestables/
- ↑ https://www.e-education.psu.edu/styleforstudents/c6_p10.html
About This Article

To write a progress report, start by deciding how you want to present your info, like with a bulleted list or a graph. You can also add subsections to your report, which can help keep things clear and easy to follow. Then, write your heading across the top of the paper and include relevant details like the date and subject of the report. Below that, add an introduction using italics to give a brief overview of the report. Next, include details in the body, like specific tasks you worked on, and conclude it by addressing what’s next for your project. To learn why considering your audience can help you write a progress report, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Mwape Kalombo
Dec 7, 2018
Did this article help you?

Jul 25, 2017
Mary Holloway
Jul 4, 2021
Samira Khosrawi
Mar 8, 2017
Ranjeet Deshmukh
Jul 31, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Write a Professional Progress Report
How to Write a Professional Progress Report
Written by: Daleska Pedriquez Jun 28, 2022

The first time I had to do a professional progress report, I panicked. I didn’t know where to begin my report or what to include. So I did some research and asked my co-workers for advice.
I’m glad I did because they shared some useful tips on how to create a progress report . They also pointed me toward a ton of progress report templates to use as a starting point.
Now, I’ve filled out countless progress reports and learned some valuable lessons along the way. So, gather around everyone! I’ll show you the magic of using progress reports for your business, including how to incorporate data visualization.
Let’s get started!
Click to jump ahead:
What is a progress report?
Why are work progress reports important, what are the benefits of the project progress reports, how to write a progress report, 3 tips to write great reports, faqs about writing a professional progress report.
Let’s start with the basics. A progress report includes a detailed description of the current status of a project, as well as forecasts for the future. You can use this type of report to share insights on project status and performance. You may also project results and timelines based on the milestones your team has achieved and the challenges you’ve faced so far.
These reports often contain a summary of communications between a team member and a project manager. This helps stakeholders get a snapshot of how a project is progressing.
Keep in mind: a progress report may be for your team alone, your company as a whole or your board of executives. Depending on the audience, you may want to include more or less granular information.
This may seem obvious, but reporting on progress is key for keeping your team on track. Consistent project updates will ensure everyone is working on the right tasks, at the right time. These reports also provide an opportunity for reflection…
What’s going well? What isn’t? Do the project objectives still make sense? Do they need adjusting? By taking the time to reflect before a project is finished, you’ll be able to catch any problems, adjust and increase your chances of success.
Project progress reports offer several benefits to both project managers and stakeholders involved in a project. Here’s a closer look at the benefits of creating a professional progress report:
Improves team collaboration
As I mentioned, progress reports are all about keeping teams on the same page. Generally, everyone on your team would receive a copy of the report. That way, everyone can see what’s done and what remains to be done.
This is also a good way to keep your team motivated during long projects. By reporting on everything that’s been accomplished, they can see just how far they’ve come.
In the initial phases of a project, your progress report may be as simple as a timeline. This type of report works well during the planning stages, too. For example, check out this weekly reporting template:

You can customize this template however you need. Style the text, swap out the colors, add in your logo and voilà… you have a professionally branded report.
Guides decision-making throughout a project
Again, if you wait until the end of a project to reflect, you may miss opportunities to course-correct along the way. No project plan is perfect. There will always be unforeseen circumstances. A task that requires more time. A team member that drops out of the race…
A progress report can help you deal with these hiccups. By proactively checking in on a project, you can make decisions about the best use of resources. Or even, whether you need to switch lanes entirely!
Creates a detailed audit trail for all projects
While a progress report isn’t an audit, it does provide a record of all the work undertaken during a project. In other words, it’s useful if you or your company need to create an audit trail using project execution records.
Of course, progress reports are also useful if you’re answering to execs, giving updates to your fellow execs or simply referring back to the next time around.

Take this quarterly project status report as an example. Using this template, you can share a high-level overview of a project with a simple progress bar featuring a clear percentage, or swap in any chart to depict progress. With Venngage’s editor, you just have to double-click on the chart and input the appropriate value.
Promotes transparency and accountability
Transparency and accountability are buzzwords in business, but with good reason. Without transparency, there’s no accountability. And without accountability, well, your project is going to be a slog.
Progress reports are a great way to maintain transparency and accountability throughout a project. Not only can you see exactly who’s done (and doing) what, but you can also highlight the allocation of funding and resources, as well as results.

Now that we’ve talked about the perks of using a progress report to visualize your company’s projects , let’s dig into the good stuff. Here’s how to write a detailed progress report:
1. Determine your report’s objectives
Of course, your report will have different objectives depending on the format. If you’re putting together a weekly report, those objectives may be tasks accomplished. You may also include notes about roadblocks or problems solved.
A monthly or quarterly report will likely look at larger milestones instead and give a broader overview of the progress made on a project. This type of regular project evaluation may also compare progress to previous months.

Pro tip: while designing in Venngage, you can create a new color scheme, or use one of the many automated color palettes available. If you’re on a business plan, you’ll also have access to My Brand Kit , which allows you to upload logos, choose fonts and set color palettes. Then, you can easily apply your visual branding to every design.
2. Collect all your data
Once you’ve established your objectives, you can gather the necessary data to report on them.
For example, with a weekly report, you may need to check in with your team members to get a status update on their tasks. With a monthly report, you may be able to pull results, in addition to a broader status update.
Whatever claims you include in your report, just make sure you can back them up with data. If you’re saying a project is 90% complete, that percentage should be calculated based on real numbers, not estimates.

In general, you’ll share a broader progress update on the first page of your report. Then, the following pages will show the supporting data.
3. Perform a detailed data analysis
Now for the fun part. (Yup, I’m a data nerd.)
Analyzing your data is the logical next step. I like to start by organizing my data into buckets. For example, I might have a bucket for tasks accomplished, outstanding tasks, blockers, budget and key learnings to date.
Often, I’ll include a bucket for outstanding questions. And I analyze all of the above to identify patterns and make informed predictions.
Once you have all this information, make a note of which pieces of data can be visualized. Graphs, charts and other visuals help simplify complex data and reduce the amount of text you’ll need in your report. (More on visualizing your data in just a sec!)

Pro tip: when creating a report in Venngage on a Business Plan , you can collaborate in real-time with your team members and invite them to work on a design. You can also leave comments and get feedback, right on the platform. Alternatively, you can share your design online, via email or download a high-resolution PNG, PDF or interactive PDF.
4. Outline and edit your report
Ah, the outline. I create an outline for everything I write, whether it’s a blog, business plan, or yes, a progress report. In my experience, it’s the best way to avoid writer’s block. With a detailed outline, you’ll never get stuck staring at a blank screen again.
At this point, you know your objectives. You’ve collected and analyzed all your data. All that’s left is to turn it into a story .
I like to start with objectives and work my way backward. In my outline, I’ll cover objectives on the first page. Each one gets its own heading with supporting data underneath. I’ll also include a high-level description of my project on the first page.
I like to organize the following sections by objective, too. This creates a natural hierarchy while keeping goals and objectives top of mind.

5. Nail down the length of your report
Keep in mind that you don’t want your report to be the length of a bible! No one has the time or attention span for that. Here’s a quick rule of thumb: a progress report should be around two to three pages.
This should give you enough space to state your objectives, present supporting data, showcase progress and make any predictions. If your outline is more than three pages, have another look and see what you can trim. As all good writers know, sometimes you have to kill your darlings .
6. Design your report using visuals
A picture is worth a thousand words — there’s a reason we’ve all heard this saying a thousand times!
Engaging visuals are the perfect way to turn dry data into meaningful, digestible statements. But you don’t have to create these visuals from scratch or hire a designer for that matter. By starting with one of Venngage’s templates , you can simply customize the visuals to suit your needs.

For example, this project management status report template includes several images, charts and icons. You can swap out the images with your own or browse over three million high-quality, royalty-free photos to find something suitable.
You can also change the icons to reflect your data. With Venngage, you get access to over 40,000 icons with thousands of diverse options to reflect a range of skin tones and cultural backgrounds. Plus, you can change the charts to best represent your data .
By using visuals in your design, you’ll break up walls of text and make your report both aesthetically pleasing and easy to understand. In the end, this will help you improve communication and impress any stakeholders involved.
With Venngage’s report maker , the design process is quick and easy. And best of all, you can do it all yourself — exactly the way you envisioned.
Related : 5 Best Report Creators for Businesses in 2022
7. Get feedback from your team
Before sharing your final report, consider getting feedback from your team.
They may have additional insights to share on a project’s progress. They can also help spot faulty data and prevent any embarrassing retractions down the line. This is also just good for morale. The more involved your team feels in a project, the more invested they’ll be.
8. Finalize your report
Last step: proofreading.
Make sure to double-check everything, from spelling and grammar to project details and data visualizations. This step ties in with my point above. Getting a second pair of eyes to proofread your report is always a good idea.
When you’ve been staring at something for weeks, it can be hard to catch mistakes. Your team members can look at your report with fresh eyes and share fresh insights.

In the data-heavy example above, a misplaced comma or rogue denominator could make all the difference. So don’t skip that final once over! At the end of the day, the goal is to create a report that’s as accurate as possible.
I’ve talked a lot about how to use visuals to create an engaging, full-featured progress report. But what about words, you ask?
Keep these three quick tips in mind to breeze through the writing part, too:
1. Stay focused
And I mean hyper-focused.
Remember the first step in this guide: determine your report’s objectives. By staying focused on your objectives, you’ll avoid unnecessary tangents. Plus, you’ll have a lot less editing to do when it comes time to kill your darlings!
If a point doesn’t tie back to your objectives, skip it. This will give your entire report a sense of direction. It will also help your team members digest and retain the information.
2. Discuss your objectives in a balanced manner
If you have multiple objectives, make sure you give each one its due.
It’s true, one objective may be more important than the other. For example, you might dedicate more real estate to outlining project tasks than predicting future progress. Just make sure to weigh positive and negative data fairly.
You don’t want a rose-colored report, so to speak. This will set unrealistic expectations and be more harmful than helpful down the line. Instead, use all the available data to share a balanced perspective in your progress report.
3. Use a consistent reporting style
Reports are no place for flowery language.
To make your report as effective as possible, use straightforward, simple language. Make sure to define any acronyms or technical terms at the beginning of your report. And remember the three Cs while you’re writing: be clear, concise and compelling.

What are the three types of progress reports?
There are three types of reports based on the time span they cover:
- Weekly: These reports typically cover a team member’s individual progress and how it affects the entire project.
- Monthly: These progress reports typically provide a broader overview of a project, including team member progress, methods and projections. Monthly reports are usually data-dependent and require more visuals than weekly reports.
- Quarterly: These detailed reports cover a three-month period. Quarterly reports include a lot more data and will require more visuals to make them digestible and engaging as a result.
What are the qualities of a good progress report?
The qualities of a good progress report are:
- Comprehensiveness: Provide a total overview of a project using clear objectives, simple language and a balanced ratio of text and images in your layout.
- Data-backed: Make sure your report includes accurate data that you’ve double-checked for any discrepancies.
- Rich in visuals: Leverage engaging visuals to break up the text in your report and turn your data into a compelling, easily digestible story.
Write a detailed professional progress report and achieve your goals
I know from personal experience that writing a progress report can be daunting at first.
But with these tips and templates, I’m confident you can do it. So go ahead, give it a try. Create a beautiful, raise-winning report with Venngage for free. Just remember to clearly define your objectives first… and don’t skimp on visuals!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
- Project Evaluation
- Project Management Methodologies
- Project Management Metrics
- Project Portfolio Management
- Proof of Concept Templates
- Punch List Templates
- Requirement Gathering Process
- Requirements Traceability Matrix
- Resource Scheduling
- Roles and Responsibilities Template
- Stakeholder Identification
- Stakeholder Mapping
- Team Alignment Map
- Team Charter
- Templates for Managers
- What is Project Baseline
- Work Log Templates
- Workback Schedule
- Workload Management
- Work Breakdown Structures
- Agile Team Structure
- Avoding Scope Creep
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts
- Precision VS Accuracy
- Scrum-Spike
- User Story Guide
- Creating Project Charters
- Guide to Team Communication
- How to Prioritize Tasks
- Mastering RAID Logs
- Overcoming Analysis Paralysis
- Understanding RACI Model
- Eisenhower Matrix Guide
- Guide to Multi Project Management
- Procure-to-Pay Best Practices
- Procurement Management Plan Template to Boost Project Success
- Project Execution and Change Management
- Project Plan and Schedule Templates
- Resource Planning Templates for Smooth Project Execution
- Risk Management and Quality Management Plan Templates
- Risk Management in Software Engineering
- Stage Gate Process
- Stakeholder Management Planning
- Understanding the S-Curve
- Visualizing Your To-Do List
- 30-60-90 Day Plan
- Work Plan Template
- Weekly Planner Template
- Task Analysis Examples
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts for Planning
- Inventory Management Tecniques
- Inventory Templates
- Six Sigma DMAIC Method
- Visual Process Improvement
- Value Stream Mapping
- Creating a Workflow
- Fibonacci Scale Template
- Supply Chain Diagram
- Kaizen Method
- Procurement Process Flow Chart
- Guide to State Diagrams
- UML Activity Diagrams
- Class Diagrams & their Relationships
- Visualize flowcharts for software
- Wire-Frame Benefits
- Applications of UML
- Selecting UML Diagrams
- Create Sequence Diagrams Online
- Activity Diagram Tool
- Archimate Tool
- Class Diagram Tool
- Graphic Organizers
- Social Work Assessment Tools
- Using KWL Charts to Boost Learning
- Editable Timeline Templates
- Kinship Diagram Guide
- Power of Visual Documentation
- Graphic Organizers for Teachers & Students
- Visual Documentation Techniques
- Visual Tool for Visual Documentation
- Conducting a Thematic Analysis
- Visualizing a Dichotomous Key
- 5 W's Chart
- Circular Flow Diagram Maker
- Cladogram Maker
- Comic Strip Maker
- Course Design Template
- AI Buyer Persona
- AI Data Visualization
- AI Diagrams
- AI Project Management
- AI SWOT Analysis
- Best AI Templates
- Brainstorming AI
- Pros & Cons of AI
- AI for Business Strategy
- Using AI for Business Plan
- AI for HR Teams
- BPMN Symbols
- BPMN vs UML
- Business Process Analysis
- Business Process Modeling
- Capacity Planning Guide
- Case Management Process
- How to Avoid Bottlenecks in Processes
- Innovation Management Process
- Project vs Process
- Solve Customer Problems
- Spaghetti Diagram
- Startup Templates
- Streamline Purchase Order Process
- What is BPMN
- Approval Process
- Employee Exit Process
- Iterative Process
- Process Documentation
- Process Improvement Ideas
- Risk Assessment Process
- Tiger Teams
- Work Instruction Templates
- Workflow Vs. Process
- Process Mapping
- Business Process Reengineering
- Meddic Sales Process
- SIPOC Diagram
- What is Business Process Management
- Process Mapping Software
- Business Analysis Tool
- Business Capability Map
- Decision Making Tools and Techniques
- Operating Model Canvas
- Mobile App Planning
- Product Development Guide
- Product Roadmap
- Timeline Diagrams
- Visualize User Flow
- Sequence Diagrams
- Flowchart Maker
- Online Class Diagram Tool
- Organizational Chart Maker
- Mind Map Maker
- Retro Software
- Agile Project Charter
- Critical Path Software
- Brainstorming Guide
- Brainstorming Tools
- Visual Tools for Brainstorming
- Brainstorming Content Ideas
- Brainstorming in Business
- Brainstorming Questions
- Brainstorming Rules
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Brainstorming Workshop
- Design Thinking and Brainstorming
- Divergent vs Convergent Thinking
- Group Brainstorming Strategies
- Group Creativity
- How to Make Virtual Brainstorming Fun and Effective
- Ideation Techniques
- Improving Brainstorming
- Marketing Brainstorming
- Rapid Brainstorming
- Reverse Brainstorming Challenges
- Reverse vs. Traditional Brainstorming
- What Comes After Brainstorming
- Flowchart Guide
- Spider Diagram Guide
- 5 Whys Template
- Assumption Grid Template
- Brainstorming Templates
- Brainwriting Template
- Innovation Techniques
- 50 Business Diagrams
- Business Model Canvas
- Change Control Process
- Change Management Process
- Macro Environmental Analysis
- NOISE Analysis
- Profit & Loss Templates
- Scenario Planning
- What are Tree Diagrams
- Winning Brand Strategy
- Work Management Systems
- Balanced Scorecard
- Developing Action Plans
- Guide to setting OKRS
- How to Write a Memo
- Improve Productivity & Efficiency
- Mastering Task Analysis
- Mastering Task Batching
- Monthly Budget Templates
- Program Planning
- Top Down Vs. Bottom Up
- Weekly Schedule Templates
- Kaizen Principles
- Opportunity Mapping
- Strategic-Goals
- Strategy Mapping
- T Chart Guide
- Business Continuity Plan
- Developing Your MVP
- Incident Management
- Needs Assessment Process
- Product Development From Ideation to Launch
- Value-Proposition-Canvas
- Visualizing Competitive Landscape
- Communication Plan
- Graphic Organizer Creator
- Fault Tree Software
- Bowman's Strategy Clock Template
- Decision Matrix Template
- Communities of Practice
- Goal Setting for 2024
- Meeting Templates
- Meetings Participation
- Microsoft Teams Brainstorming
- Retrospective Guide
- Skip Level Meetings
- Visual Documentation Guide
- Weekly Meetings
- Affinity Diagrams
- Business Plan Presentation
- Post-Mortem Meetings
- Team Building Activities
- WBS Templates
- Online Whiteboard Tool
- Communications Plan Template
- Idea Board Online
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Genograms in Social Work Practice
- Conceptual Framework
- How to Conduct a Genogram Interview
- How to Make a Genogram
- Genogram Questions
- Genograms in Client Counseling
- Understanding Ecomaps
- Visual Research Data Analysis Methods
- House of Quality Template
- Customer Problem Statement Template
- Competitive Analysis Template
- Creating Operations Manual
- Knowledge Base
- Folder Structure Diagram
- Online Checklist Maker
- Lean Canvas Template
- Instructional Design Examples
- Genogram Maker
- Work From Home Guide
- Strategic Planning
- Employee Engagement Action Plan
- Huddle Board
- One-on-One Meeting Template
- Story Map Graphic Organizers
- Introduction to Your Workspace
- Managing Workspaces and Folders
- Adding Text
- Collaborative Content Management
- Creating and Editing Tables
- Adding Notes
- Introduction to Diagramming
- Using Shapes
- Using Freehand Tool
- Adding Images to the Canvas
- Accessing the Contextual Toolbar
- Using Connectors
- Working with Tables
- Working with Templates
- Working with Frames
- Using Notes
- Access Controls
- Exporting a Workspace
- Real-Time Collaboration
- Notifications
- Meet Creately VIZ
- Unleashing the Power of Collaborative Brainstorming
- Uncovering the potential of Retros for all teams
- Collaborative Apps in Microsoft Teams
- Hiring a Great Fit for Your Team
- Project Management Made Easy
- Cross-Corporate Information Radiators
- Creately 4.0 - Product Walkthrough
- What's New
How to Write a Solid Progress Report for Project Success

Progress reports are like project status updates that help everyone involved understand how things are going. Writing a solid progress report is crucial for keeping your project on track and ensuring its success. In this guide, we’ll break down the process of creating a great progress report, making it easy for you to communicate your project’s progress effectively. We have also included progress report templates for you to get started right away.
Progress Report Template
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

What is a Progress Report
A progress report is a document that provides an overview of the status, advancements, and achievements of a project or task. It typically outlines what has been accomplished, what is currently in progress, and any challenges or obstacles encountered. Progress reports are commonly used in various settings, such as work, education, or personal projects, to keep stakeholders informed about the project’s developments and to ensure everyone is on the same page regarding the current state of affairs.
Progress Report Templates to Keep Track of Project Progress
Daily Progress Report Template
Project Status Report Template
Project Status Summary
Project Dashboard Template
Project Status Summary Template
Why You Need to Use a Progress Report
A progress report promotes a culture of collaboration, accountability, and continuous improvement in project management. Here are several reasons why a progress report is important.
Clear communication: Keeps everyone on the same page by sharing what’s happening in a project.
Tracking achievements: Highlights what has been successfully completed, boosting team morale.
Problem-solving: Identifies and addresses challenges, helping to find solutions and stay on track.
Decision-making: Provides real-time information for informed decision-making during the project.
Accountability: Holds team members responsible for their tasks and deadlines.
Learning and improvement: Creates a record of progress, facilitating learning for future projects.
Efficiency: Keeps the team working efficiently by preventing confusion and misunderstandings.
Collaboration: Encourages collaboration and coordination among team members.
Key Components of a Progress Report
The following components of a progress report collectively provide a comprehensive view of the project’s progress, challenges, and future plans, enabling effective communication and decision-making.
- Introduction : Brief overview of the project, including its purpose and objectives.
- Work completed : Summary of tasks or milestones achieved since the last report.
- Work in progress : Description of current activities, tasks underway, and their status.
- Challenges and issues : Identification and discussion of any problems, roadblocks, or challenges faced.
- Achievements : Recognition and celebration of significant accomplishments and milestones.
- Upcoming tasks : Outline of the next steps, tasks, or milestones planned for the future.
- Timeline and schedule : Review or adjustment of the project timeline or schedule, if necessary.
- Budget overview : Overview of the project’s financial status, including spendings and any budget changes.
- Recommendations : Suggestions for improvements or changes to improve project efficiency.
- Conclusion : A brief summary and conclusion, often including an overall project status assessment.
Challenges of Creating and Using a Progress Report
While project reports are handy for keeping track of project progress, they can pose some challenges.
Time-consuming: Writing a progress report can take time away from actual project work.
Communication issues: Making sure that everyone understands the report may be challenging.
Data accuracy: Getting accurate information for the report can sometimes be difficult.
Overlooking details: Important details may be unintentionally left out.
Balancing detail and brevity: Finding the right level of detail without making the report too lengthy can be tricky.
Tracking complex projects: Managing and reporting progress for complex projects may pose a challenge.
Ensuring regular updates: Getting everyone to consistently update progress can be a hurdle, especially in dynamic work environments.
Best Practices for Creating an Effective Progress Report
Creating an effective progress report involves following some best practices:
- Keep your report clear and straightforward, avoiding jargon or overly complex language.
- Highlight the most important information, emphasizing achievements and addressing challenges.
- Use a consistent format and structure for easy comprehension.
- Submit reports on time to make sure that the information is relevant and up-to-date.
- Provide enough detail to convey the message, but avoid unnecessary information that may overwhelm.
- Use charts or diagrams to visually represent data and trends for better understanding.
- Include potential solutions when discussing challenges, promoting a proactive approach.
Create Your Next Progress Report with Creately
Simplify the process of creating progress reports and streamline project management, communication, and improve overall project success with Creately ’s visual collaboration platform.
Task tracking and assignment
Use the built-in project management tools to create, assign, and track tasks right on the canvas. Assign responsibilities, set due dates, and monitor progress with Agile Kanban boards, Gantt charts, timelines and more. Create task cards containing detailed information, descriptions, due dates, and assigned responsibilities.
Notes and attachments
Record additional details and attach documents, files, and screenshots related to your tasks and projects with per item integrated notes panel and custom data fields. Or easily embed files and attachments right on the workspace to centralize project information. Work together on project documentation with teammates with full multiplayer text and visual collaboration.
Real-time collaboration
Get any number of participants on the same workspace and track their additions to the progress report in real-time. Collaborate with others in the project seamlessly with true multi-user collaboration features including synced previews and comments and discussion threads. Use Creately’s Microsoft Teams integration to brainstorm, plan, run projects during meetings.
Pre-made templates
Get a head start with ready-to-use progress report templates and other project documentation templates available right inside the app. Explore 1000s more templates and examples for various scenarios in the community.
Comprehensive shape libraries
Create any visual aid from flowcharts to timelines with comprehensive shape libraries for over 70 types of diagrams including icons. Illustrate or make annotations easily with freehand drawing and format text without leaving the keyboard with markdown shortcuts.
Progress reports are indispensable in project management. They foster communication, accountability, and a culture of continuous improvement. Make use of the progress report templates we have provided to track your progress and stay organized.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.

Progress Report: What is it & How to Write it? (Steps & Format)
Want to create a progress report to highlight the project’s achievements? No worries, we have got you covered! Read on…
A quick question – on a scale of 1 to 10, how important is it to regularly keep track and provide project updates to your supervisors, colleagues, or clients? The answer is 12! Simply, because nobody likes being left in the dark!
For any project in a company, people around it need to be well-informed about the project status, the research being done by the project team, their decisions, and the scope for improvement. These updates are an integral part of project management and ensure that every team member is operating efficiently with their goals being met on time.
One way to showcase the status of your project and keep track of it is to write a powerful progress report!
In fact, the American Society for Training and Development shows that having a specific place to check your progress increases the probability of meeting a goal by 95%.
Progress reports are a great place for project managers to inform and engage their supervisors, clients, or associates, about the progress they have made on a project over a certain period.
If executed well, progress reports provide a quick overview of how things are humming along, offering valuable insights to increase productivity, provide the necessary guidance, and quickly solve emerging difficulties.
However, writing a progress report can be a little daunting, especially, when you have a diverse team and various sub-projects to manage. Well, don’t fret! We’re going to fix that. In this blog post, we’ll teach you everything about progress reports, why they are important, and how you can write one that will make everyone say ‘wow’!
What is the Progress Report? (Definition)
A progress report is a document that explains in detail how much progress you have made towards the completion of your ongoing project.
A progress report is a management tool used in all types of organizations, that outlines the tasks completed, activities carried out, and target achieved vis-à-vis your project plan.
In a progress report, you explain any or all of the following:
- The amount of work complete?
- What part of the work is currently in progress?
- The problems or unexpected things that have occurred?
- What work is pending?
- How the project is going in general?
Read more: How To Write An Impressive Project Proposal?

Why are Progress Reports Important?
No project manager wakes up thinking “ I wish I could make reports for my supervisor and team all day” ! We get it. Writing progress reports are not very fun.
However, you know that writing progress reports are part of the deal. Progressive reporting demands talking with your team or client to understand the goals and showcase the information that closely relates to the said goals.
Whether the report is about updating the investors, marketing performance, or resource management. These reports let everyone see what’s going well and what isn’t.
It also assists managers to see the overall success or failure of projects. Furthermore, progress reports help to:
1. Make Information Transparent
The glue that holds together any relationship is visibility and transparency. A well-defined progress report directly presents how your work affects the project’s bottom line and showcases the rights and wrongs!
By adding transparency to your project plan, you can build an unmatched level of credibility and trust with your team and clients.
2. Encourage Constant Interaction
Creating and discussing progress reports results in constant communication and keeps everyone in the loop. Being in constant contact with others on a weekly or monthly basis ensures a clear understanding of roles and responsibilities.
3. Improve Project Evaluation and Review
Previous progress reports will help you in clarifying loopholes, and systemic issues, and examine documents to find out what went wrong, what can be done right, and which area needs improvement.
4. Provides Insight for Future Planning
When a progress report shows all the delays that have occurred, the supervisor or a project manager can monitor and investigate the issue that hindered progress and take additional steps to prevent them from happening in the future.
Read more: How to Write Project Reports that ‘Wow’ Your Clients?
How to Write a Progress Report with 4 Simple Steps?
Progress reports are essential documents for tracking project plans and initiatives, but if the readers and writers are not in sync, these reports can be a hit-or-miss exercise for everyone involved.
Therefore, here are some steps to help you deliver the right information to the right people at the right time.
Step 1. Explain the purpose of your report
There are many reasons for someone to write a progress report. Obviously, for many of them, it’s to brief the progress and status of the project.
Readers might also want to know detailed information about the project’s purpose, its duration, and other important insights.
Step 2. Define your audience
Once you have sorted out the purpose of writing the progress report, consider the type of audience you will be targeting and the details that your readers are going to acknowledge in the report.
These can be, what decisions your readers are going to need to make after reading the progress report, the information they are going to need to know to oversee and participate in the project effectively, etc.
Step 3. Create a “work completed” section
In this section, you should describe everything that has already been done and the best way to do this is to mention the completed tasks chronologically.
You can specify dates, tasks you and your team were working on, information on key findings, etc.
Step 4. Summarize your progress report
In the summary section, provide the essential details about the to-do and completed work. Also, add a short description of the problems your team encountered, recommendations from your supervisor for their resolution, and whether any assistance on the project is required.
Read more: Business Report: What is it & How to Write it? (Steps & Format)
Creating a Progress Report that Stands Out with Bit.ai !
If you are planning to show a progress report that looks exactly like any other bland report, chances are your readers are just going to skim it along the way or won’t read it at all.
Well, to lure your reader’s attention and proudly display the work you have done on the project, you have to make the progress report irresistibly compelling!
How about awesome visuals, accompanied by quality content that could grab the reader’s interest and encourage them to read the whole thing? No doubt, everybody likes reading something easy to grasp and visually stunning!
Luckily, we have got the perfect tool for you that will provide a reading experience like never before and bring your grey-scale progress reports to come alive! A solution like Bit.ai
Bit is a new-age cloud-based document collaboration tool that helps teams create, share, manage, and track interactive workplace documents.
Bit helps you make sure your reports are more than just plain bland text and images. Thus, apart from allowing multiple users to collaborate on reports, Bit also allows users to share any sort of rich media like campaign video, tables, charts, One Drive files, Excel Spreadsheets, GIFs, Tweets, Pinterest boards, etc. Anything on the internet with a link can be shared and Bit will automatically turn it into visual content.
Bit has a very minimal design aesthetic which makes every design element pop, awesome readability, and rich features that will prevent collaborators from messing up any documents and help them rethink the way they work!
Besides writing progress reports, you can easily create other beautiful documents like the statement of work , project documentation, operational plan , roadmap, project charter , etc. in a common workplace for other team members to collaborate, document, share their knowledge, brainstorm ideas, store digital assets, and innovate together.
The best part is that this knowledge is safely secured in your workspaces and can be shared (or kept private) with anyone in your organization or the public!
All-in-all Bit is like Google Docs on steroids! So, no more settling for those boring text editors when you have an excessively robust solution to walk you through!
Still, not sure how Bit can help you create that perfect progress report to woo your readers? Let’s see some more of Bit’s awesome capabilities!
Key Benefits of Creating Your Progress Reports on Bit.ai
Simple, clean UI: Bit has a very minimal design aesthetic to it, allowing a newbie to quickly get on board with the platform. Even though the platform is feature-rich, it does a great job as to not overwhelm a new user and provides a systematic approach to work.
Organization of information: Information is often scattered in cloud storage apps, emails, Slack channels, and more. Bit brings all your information in one place by allowing you to organize information in workspaces and folders. Bring all your documents, media files, and other important company data in one place.
Brand consistency: Focus on the content and let Bit help you with the design and formatting. Bit documents are completely responsive and look great on all devices. With amazing templates and themes, Bit docs provide you with the type of brand and design consistency that is unheard of in the documentation industry
Smart search: Bit has very robust search functionality that allows anyone to search and find their documents swiftly. You can search workspaces, folders, document titles, and the content inside of documents with Bit’s rich-text search.
Media integrations: Companies use an average of 34 SaaS apps! No wonder why most of our time is spent hopping from one app to the next, looking for information. This is why Bit.ai integrates with over 100+ popular applications (YouTube, Typeform, LucidChart, Loom, Google Drive, etc) to help teams weave information in their documents beyond just text and images.
Multiple ways of sharing : Bit documents can be shared in three different states :
- Live state : A live state meaning that all changes that you make to the document will update in real-time. If you are sharing your documents with clients, partners, or customers they will always get your most up-to-date changes.
- Embeds : You can embed Bit documents on any website or blog. Bit docs are fully responsive and render perfectly on your website.
- Tracking : You can track your documents and gather real-time insights to understand how users interact with your content. See how much time users spend viewing documents, scroll ratio, user information, and more.
Our team at bit.ai has created a few more templates to make your business processes more efficient. Make sure to check them out before you go, y our team might need them!
- Training Manual Template
- Brainstorming Template
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Employee Handbook Template
- Transition Plan Template
- Customer Service Training Manual Template
- Employee Contract Template
- Performance Improvement Plan Template
A well-defined progress report is like the pulse of a project! It determines your relationship with your readers, highlights all the updates- big or small, and keeps everyone on the same page. Remember, depending on the complexity and scope of the project, you might need to share your progress report on a weekly or monthly basis for better efficiency!
Once you follow all the steps that are mentioned above, your reports are surely going to feel like a breeze of fresh air to your readers, making you look credible and professional. So what are you waiting for?
Do you write such reports in your organization, if yes, which tool do you use? Let us know in the comments below or tweet us @bit_ai
Further reads:
- Technical Report: What is it & How to Write it? (Steps & Structure Included)
- 11 Amazing Goal Tracking Apps and Tools! (Free & Paid)
- 7 Types of Reports Your Business Certainly Needs!
- Performance Report: What is it & How to Create it? (Steps Included)
- Formal Reports: What are they & How to Create them!
- KPI Report: What it is & How to Create a Perfect One?
- How to Write a Project Charter Document?

Document Creation: 12 Dos and Don'ts to Keep in Mind!
10 Best Apps for Writing a Book!
Related posts
Scientific paper: what is it & how to write it (steps and format), 3 project proposal examples you must check out, elevator pitch: what is it & how to write one, letter of resignation: definition, examples and format, 13 programming blogs and websites to improve your coding skills, 11 proposal software you must try out.

About Bit.ai
Bit.ai is the essential next-gen workplace and document collaboration platform. that helps teams share knowledge by connecting any type of digital content. With this intuitive, cloud-based solution, anyone can work visually and collaborate in real-time while creating internal notes, team projects, knowledge bases, client-facing content, and more.
The smartest online Google Docs and Word alternative, Bit.ai is used in over 100 countries by professionals everywhere, from IT teams creating internal documentation and knowledge bases, to sales and marketing teams sharing client materials and client portals.
👉👉Click Here to Check out Bit.ai.
Recent Posts
Ai for social media marketing: tools & tactics to boost engagement, a guide to building a client portal for your online course, knowledge management vs document management, 11 must-try ai tools for market research in 2024, 15 employee management software for 2024: a quick guide, document management workflow: what is it & how to create it.
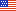
- About Grants
Research Performance Progress Report (RPPR)
The RPPR is used by recipients to submit progress reports to NIH on their grant awards. This page provides an overview of the annual RPPR, the final RPPR and the interim RPPR and provides resources to help you understand how to submit a progress report.
Types of RPPRs
Progress reports document recipient accomplishments and compliance with terms of award. There are three types of RPPRs, all of which use the NIH RPPR Instruction Guide .
Annual RPPR – Use to describe a grant’s scientific progress, identify significant changes, report on personnel, and describe plans for the subsequent budget period or year.
Final RPPR – Use as part of the grant closeout process to submit project outcomes in addition to the information submitted on the annual RPPR, except budget and plans for the upcoming year.
Interim RPPR – Use when submitting a renewal (Type 2) application. If the Type 2 is not funded, the Interim RPPR will serve as the Final RPPR for the project. If the Type 2 is funded, the Interim RPPR will serve as the annual RPPR for the final year of the previous competitive segment. The data elements collected on the Interim RPPR are the same as for the Final RPPR, including project outcomes.
Submitting the RPPR
Only the project director/principal investigator (PD/PI) or their PD/PI delegate can initiate RPPRs. For multi-PD/PI grants only the Contact PI or the Contact PD/PI’s delegate can initiate the RPPR.
Signing Officials typically submit the annual RPPR, but may delegate preparation (Delegate Progress Report) to any PD/PI within the organization on behalf of the Contact PD/PI. Additionally, a Principal Investigator (PI) can delegate “Progress Report” to any eRA Commons user in their organization with the Assistant (ASST) role. This delegation provides the ASST with the ability to prepare Annual, Interim and Final RPPRs on behalf of the PI. However, only a Signing Official (SO) or PI (if delegated Submit by the SO) are allowed to submit the Annual, Interim, and Final RPPRs.
Follow the instructions in the RPPR User Guide to submit the RPPR, Interim RPPR or Final RPPR. The User Guide includes instructions for how to submit your RPPRs in the eRA Commons, how to complete the web-based forms, and what information is required. Instructions for completing the scientific portion of the report (see the elements below) may be found in Chapters 6 and 7.
The following resources may help with RPPR initiation and submission:
Annual RPPR Due Dates:
- Streamlined Non-Competing Award Process (SNAP) RPPRs are due approximately 45 days before the next budget period start date.
- Non-SNAP RPPRs are due approximately 60 days before the next budget period start date.
- Multi-year funded (MYF) RPPRs are due annually on or before the anniversary of the budget/project period start date of the award.
- The exact start date for a specific award may be found in grants status in eRA Commons.
Interim and Final RPPR Dues Dates:
- 120 days from period of performance end date for the competitive segment
The RPPR requests various types of information, including:
Accomplishments
What were the major goals and objectives of the project?
What was accomplished under these goals?
What opportunities for training and professional development did the project provide?
How were the results disseminated to communities of interest?
What do you plan to do during the next reporting period to accomplish the goals and objectives?
publications, conference papers, and presentations
website(s) or other Internet site(s)
technologies or techniques
inventions, patent applications, and/or licenses
other products, such as data or databases, physical collections, audio or video products, software, models, educational aids or curricula, instruments or equipment, research material, interventions (e.g., clinical or educational), or new business creation.
Participants and Other Collaborating Organizations
Changes/Problems (not required for Final or Interim RPPR)
Changes in approach and reasons for change
Actual or anticipated problems or delays and actions or plans to resolve them
Changes that have a significant impact on expenditures
Significant changes in use or care of human subjects, vertebrate animals, biohazards, and/or select agents
Budgetary Information (not required for Final or Interim RPPR)
Project Outcomes (only required on Final and Interim RPPR)
- Concise summary of the outcomes or findings of the award, written for the general public in clear and comprehensible language, without including any proprietary, confidential information or trade secrets
This page last updated on: November 2, 2022
- Bookmark & Share
- E-mail Updates
- Help Downloading Files
- Privacy Notice
- Accessibility
- National Institutes of Health (NIH), 9000 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, Maryland 20892
- NIH... Turning Discovery Into Health
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Writing Progress Reports
Stacey Corbitt
Chapter Overview
It may seem like technical writing – indeed, many kinds of professional business writing – must be huge undertakings involving much effort and endless detail. With all the emphasis on being complete, accurate, and collaborative, do you wonder whether you can develop enough skill during college to compete as a writer in a technical or other business position? You may be hoping there’s an engineering or other professional position out there where you can stay under the radar and do your job without having to write anything important.
There is good news on this matter, and then there is great news.
First, the good news: virtually all entry-level professional positions present opportunities to practice writing in a variety of situations and for multiple types of readers. Writing in technical fields, as you may now realize, can require significant time commitment and collaboration, as well as various other “soft skills.” As a result, employees working to gain experience in the field may be tapped frequently to complete writing tasks.
Do you wonder exactly how the preceding paragraph is good news? Consider the great news: the day-to-day business of technical writing is largely short, direct reporting for specific purposes and audiences. While short reports aren’t necessarily easy to write, they do offer opportunities to practice crafting clear and concise documents. The progress report is one of several standard forms of short reports. This chapter aims to help students understand how to plan and write progress reports that meet the needs of their assignments as well as the standards of professionalism required by their fields of study and work.
What is the audience and purpose of a progress report?
Progress reports are typically requested and reviewed by one or more stakeholders in a project. Stakeholders is a general term for people who have a business interest in the subject project and may need progress reports because of fiscal, legal, financial, or other responsibility for the work in question. While progress reports may be required by the person or group at the next level of responsibility above your own, the readership and reach of your periodic progress reports can be greater than you know, sometimes applying to the top tier of an organization.
Put simply, stakeholders use progress reports to communicate about work on projects, including levels of completion and delays alike. These reports provide a number of opportunities for communication, including but not limited to
- reporting early research findings
- notifying stakeholders about problems
- discussing potential changes in planned work, schedule, and other project factors
- evaluating work completed
As with all technical writing opportunities, careful characterization of the audience and the context in which the report will be used is crucial to successfully achieving the purpose of a progress report. In addition to these standard considerations, other specific questions a writer should ask in preparation for writing a progress report include the following:
- Has the requestor specified a form you must use? If so, do you have the most up-to-date form and specifications to follow?
- What is the date of expected delivery for this report? What is the expected frequency of reporting? For example, do you need to report once weekly, or more or less frequently?
- Is supporting documentation necessary? If so, how should you include it?
- Is there an oral presentation component required with this report?
- Have you set aside enough time to complete this report and obtain a peer review?
In a word, the key to writing efficient, clear progress reports is preparation . Always take the time needed to ask these practical questions about the rhetorical situation in which you will be writing a progress report for any project.
What is the necessary content for a progress report?
Depending upon the information you collect through the questioning activity outlined in the previous section, the specific content your project progress report will need can vary. In general, though, you might think about the content required in a progress report in a specific way: that is, part of the content comes from the past; part of it discusses the work you are doing today; and the third part of the content represents the project’s future.
Activity: begin drafting a progress report
Begin with an individual or group project in which you are currently involved, whether for your writing course or another class. Proceed by making notes in response to the following directions.
- Next, a brief discussion of the work you are doing today or this week will address the present tense portion of your discussion.
- Third, from the same point of view in the present moment, look ahead of you at all the project-related work you want to address between now and the next reporting milestone. Write a quick description of what plans you have for the project’s future, using the future tense to describe what you and your team will begin, what you will complete, and so on.
- Finally, build a draft timeline that displays the entire list of tasks for your project, whether completed, ongoing, or to begin at a point in the future. You may consider developing a Gantt chart , like the one presented in Figure 11.7, shown below and adapted from Exploring Business, published by University of Minnesota (2016) .
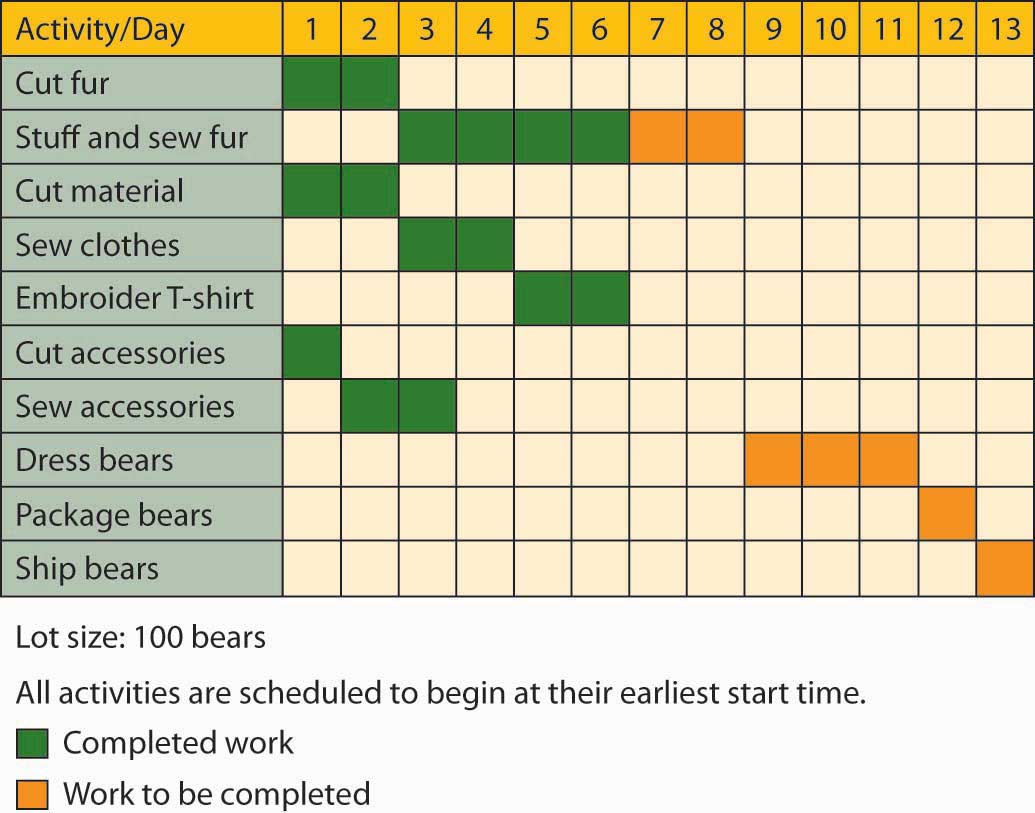
Use the notes you have prepared in this activity to complete the Homework at the end of this chapter.
What are the important stylistic considerations for a progress report?
If you put yourself in the position of the typical audience for a progress report, you can identify the characteristics that are most important for that reader’s use of the document. As you know, writing that is clear, concise, complete, and correct is vital to the success of any technical document in reaching its audience and accomplishing its purpose. With regard to progress reports, particularly those written in business, one additional quality critical to success is brevity . The progress report is an ideal demonstration of writing that should include only significant details and nothing extraneous. To the extent a progress report for your work can be accomplished in one single-spaced page, do not make it longer.
Use active construction
Because they constitute a direct communication from the writer to one or more identified readers, progress reports are frequently presented in one of the common business correspondence formats: namely, an email, memo, or letter report. Correspondence is a genre of writing that lends itself to the use of personal pronouns like I , we , and you in particular. Being able to use a first-person voice with personal pronouns gives writers an advantage toward writing progress reports: personal pronouns make it easier to use active constructions.
Using the active voice, or active construction , essentially means that you construct sentences and passages in which the following characteristics are evident:
- The subject performs the action of the verb rather than receiving the action of the verb.
- The use of forms of “to be,” also known as state of being verbs, is minimized.
- The emphasis of an active sentence is on the subject and verb, rather than on an object.
Consider the following examples:
Notice that the nouns first written in each sentence – my sister, the carpool, and my glasses – are all receiving the action of the verbs in the sentences.
Notice also that each of those verb phrases includes a form of to be : was bitten, is being organized, and have…been seen .
Finally, notice that the same word follows the verb phrase in each sentence – by – creating a prepositional phrase that indicates the noun or pronoun performing the action in each sentence.
Now examine the same three statements below, written in the active voice:
Notice the change in arrangement of words in each statement. You can identify the subject that appears at the beginning of each sentence; followed by the verb or verb phrase that indicates the action being performed by the subject; and finally the direct object of the sentence that receives the action of the verb. The numbers in parentheses in both sets of examples indicate the total number of words in each sentence.
What are your thoughts about converting sentence construction from passive to active for purposes of being clear in a progress report? Discuss the question with a partner in class and make some notes about your observations. Do you think the active construction has advantages over passive construction? Does active construction have disadvantages?
Near the beginning of this section, you read “… personal pronouns make it easier to use active constructions.” Do you think that statement is true? Discuss why or why not.
Stick to the facts
Your goal is to write an excellent progress report by making your work clear and complete while keeping the document brief. In the previous section, you practiced revising sentences from passive to active construction, a tactic that increases clarity while usually decreasing overall sentence length. Another useful practice in writing short reports – particularly those for the workplace – is to resist sharing your opinions, suggestions, and other unrequested content. Concentrate on reporting the facts and responding to exactly what the reader has requested.
What organizational structure should be used for a progress report?
Recall that one of your earliest tasks in preparing to write a progress report is to discover what information you must report and whether a specific form is required. In the event these details are not part of the assignment you receive, you may need to determine the clearest and most efficient way to organize the body of your report. Consider the following possibilities.
As is the case with structural considerations for any technical report, the most important point in choosing an organizational pattern is to make that pattern clear to the reader. Keep in mind that the structures delineated in the previous table are intended to guide the development of the body of your report in the event you do not receive specific guidance from the project manager or your instructor. Similarly, you may have to decide whether the report should be submitted as a letter, a memo, an email, a presentation, or another format that may be preferred by your reader.
In her 2019 book Technical Writing Essentials: Introduction to Professional Communications in the Technical Fields , author Suzan Last provides the following suggested outline of elements to include in a progress report generally (pp. 178-179):
Progress Reports: a Structural Overview
1. Introduction
Review the details of your project’s purpose, scope, and activities. The introduction may also contain the following:
- date the project began; date the project is scheduled to be completed
- people or organization working on the project
- people or organization for whom the project is being done
- overview of the contents of the progress report.
2. Project status
This section (which could have sub-sections) should give the reader a clear idea of the current status of your project. It should review the work completed, work in progress, and work remaining to be done on the project, organized into sub-sections by time, task, or topic. These sections might include
- Direct reference to milestones or deliverables established in previous documents related to the project
- Timeline for when remaining work will be completed
- Any problems encountered or issues that have arisen that might affect completion, direction, requirements, or scope.
3. Conclusion
The final section provides an overall assessment of the current state of the project and its expected completion, usually reassuring the reader that all is going well and on schedule. It can also alert recipients to unexpected changes in direction or scope, or problems in the project that may require intervention.
4. References section if required.
Chapter conclusion
Progress reports are an ideal example of workplace technical writing for science and engineering students to study. Progress reports represent short, clear documents with a specific purpose. These reports use typical business correspondence formats to communicate detailed technical information to a known audience. A successful progress report’s other characteristics include
- sentences constructed in the active voice
- factual information without opinions, speculation, or extraneous content
- an appropriate pattern of organization
Use the notes and project schedule you prepared in the Activity earlier in this chapter to write a progress report for your current research project. Address all of the following considerations, but do not use this list to organize your report:
- Confirm with your instructor the required report format – email, letter, memorandum, or presentation
- Determine the appropriate organizational pattern – chronological, priority, or topic – for the body of the report
- summarize and evaluate research findings to date
- present the project schedule
- problems, changes, delays, and questions
Last, S. (2019, January 1). Technical writing essentials . BCcampus OpenEd: University of Victoria. License: CC-BY-4.0 . https://pressbooks.bccampus.ca/technicalwriting
University of Minnesota. (2016, April 8). Exploring business . University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 . https://open.lib.umn.edu/exploringbusiness/
Mindful Technical Writing Copyright © 2020 by Stacey Corbitt is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
How to write an effective progress report

As someone who has written hundreds of progress reports, I know that writing a good progress report can keep people in the loop about how your project or product is moving. Additionally, it helps build trust by actively letting everyone know how things are going, what may have changed, and where you may need support. It can be a very helpful tool.

Getting started with writing progress updates can be a little tricky. There are some key steps you’ll want to navigate to ensure that your progress reports are effective, helpful, and meeting the needs of your team and stakeholders.
In this article, we’ll talk about what a progress report is, why they’re important, the elements of a progress report, and more.
What is a progress report?
A progress report is a document, usually in the form of a weekly email, that lets key stakeholders and team members who are involved in your project stay up-to-date on how things are going.
These updates can include the progress from this week, whether or not the project is on track, and if any additional leadership support is necessary to keep the project going smoothly and eliminate blockers or challenges.
Why are progress reports important?
Progress reports are important because they help build trust in the project team by keeping stakeholders in the loop with clear communication. A good progress report ensures that stakeholders don’t sit and wonder how a project is going.
Another benefit? They can help you spot issues and elevate them before problems stack up and take your project off course. You can also use a progress report to escalate blockers, or potential blockers, to the stakeholders who may be able to assist you in clearing them. Need approval before you move forward with a key part of the project? You can outline that in your update and let everyone know to expect this before it happens.
Progress reports also help keep a pulse on the pace of the project. If you know that you have important dates coming up, knowing that you have a regular time you’ll need to check in on the progress of the project can help you know if you’re on schedule.
If things start to get off track, you’ll be able to course-correct easier. And, since a progress report keeps your stakeholders in the loop, there are no big surprises to anyone if something doesn’t go according to plan.
What’s included in a progress report?
The first important thing is to really understand what your stakeholders want to see in an update. Are there particular parts of the project they might be concerned about and want more detailed insights into how that part of the project is going? If so, you may want to come up with a list and build your outline from there.
A comprehensive progress report typically includes:
- A summary of activities completed by the team
- What progress was made, and how the team is tracking toward their goals
- What challenges there were, if any
- Action items and any next steps
Activity summary
In the activity summary, you can be as detailed as is helpful to communicate to stakeholders. Ask if your stakeholders want either an in-depth or high-level summary of the work that was completed by the team.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
For example, some stakeholders want to be able to see each individual item the team completed. Some stakeholders think that a high-level summary of features is enough information. You can customize the level of detail in your activity summary for your stakeholders and team.
Progress update
Your activity summary and progress updates might sound similar, but activities are usually more task-oriented while progress is usually either an outcome or progress toward a specific outcome.
For example, let’s say that your progress update outlines that your engineering team spent time writing code for a new feature this week. Your progress report may include details about customer feedback about the new feature that your UX designer gathered.
Challenges and obstacles
While it may not be easy to talk about challenges or difficulties during a project, your stakeholders will want to know what challenges came up, how they were handled, if they’ve changed the timeline of the project, and if the team needs any help.
A great way to talk through the challenges section of your progress report is to follow a simple format:
- A brief description of the challenge encountered. This should be no longer than 2–3 sentences.
- A brief outline of how the challenge was addressed
- A clear statement of whether or not the challenge is still being resolved
- A clear ask for help, if help or support is needed
For example, here’s how this might sound in an actual progress report:
Dealing with API challenges with VendorX
This week, we had an outage in production due to a breaking API change that was made by VendorX. The customer impact was that our app was unavailable for 30 minutes. Customers saw an error message. To resolve the issue, we reached out to VendorX tech support and let them know the issue was impacting our app. They were able to resolve it, and our customers no longer have this issue.

Next steps and action items
At the end of the progress report, you’ll want to give a brief description of what the team plans to do next on the project to keep momentum. This can include the upcoming tasks or activities the team intends to tackle and how this keeps the project moving forward.
More great articles from LogRocket:
- How to implement issue management to improve your product
- 8 ways to reduce cycle time and build a better product
- What is a PERT chart and how to make one
- Discover how to use behavioral analytics to create a great product experience
- Explore six tried and true product management frameworks you should know
- Advisory boards aren’t just for executives. Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
If you are dealing with a challenge, this section may also include the challenge’s impact on progress and how you may need to plan accordingly.
If you’re thinking that sounds like a lot to keep up with, there’s a great way to make it easier — use a template.
Using a template to make progress reports that are quick and easy to read
Progress report templates are easy to create and iterate over time as the needs of the project change. Templates can make writing your progress report faster and easier. Another key benefit of using a template? It’s easier to ask for help from your teammates to help fill in the key details because you can ask them to fill out key sections.
Templates also help your stakeholders know what to expect each week. By sending the same format each week, it can make it easy to know where the relevant information they need will be located in the progress report.
Here is a very simple template on Google Docs that you can use as a weekly progress report. Go to File > Make a copy to download it and, as we’ll go over next, you can customize it how you like to fit the needs of your project:
Tips for customizing a template
Progress reports aren’t one-size-fits-all. In fact, they should be customized to fit the needs of your project! Here are some tips to help customize a generic template:
- Make sections clear — Clearly outline the sections of your progress report, and let everyone know what you’ll be addressing in each section. Remember the key sections: activities, progress made, challenges or blockers encountered, and actions and next steps. You may want to include other sections, but you’ll want to include at least those four
- Include other sections as needed for your project — Depending on the type of project, you may also include area-specific updates. If you are building a new software product, you may also include an update on KPIs or customer feedback. If you work on an engineering team, you may need to update on code quality or test coverage metrics. Remember, this is for you and for your stakeholders to communicate, so customizing it to everyone’s needs is important
- Add some fun — Maybe you highlight new learnings, a fun fact, or a customer research anecdote as a part of your update
- Use emojis — Another way to make sections stand out is to add emojis. On a Mac, you can use Control + Command + Space to pull up the emoji keyboard. On a Windows machine, you can use the Windows Key + Period . Add emojis to your sections to add a little fun, and make each section’s purpose stand out visually. Adding an emoji can help visually call out sections. You can also use emojis for whether or not something is on track by using colors and color coding.
- Make updating and reading metrics easy by using tables — If you’re reporting on a lot of metrics , make those easy to update by utilizing tables when and where you can. On the left side, include the name of the metric. On the right, include the number. Voila, an easy-to-read and easy-to-update metrics table
Once you’ve got the template, where do you store it? Ideally, put the template where you can quickly and easily access it and send it. Do you use a document repository like Sharepoint or Confluence? You can create a page that you can duplicate and edit. If you use something like Notion, you can save the page as a template that you can quickly and easily apply to any page within Notion.
Another thing to consider is how you plan to send the update each week. One option is to link to a document repository that has all of the updates linked and just schedule an automated email to send to key stakeholders with a link to the homepage. Another option? Copy and paste the text from your update into an email and link to older updates that live elsewhere.
When to update your template
If you feel trapped using a template, know that you can customize them and change them over time. As the project changed and evolved, so did our progress updates. It’s okay to change them! In fact, sometimes it’s necessary. So how do you know when it’s time to change your template?
- You regularly get questions from stakeholders about aspects of your project that are not answered in the current template
- The project has taken on a completely new direction but you haven’t updated your progress report to capture these new aspects of the project
- You’ve added another team or aspect to the project but their work is not reflected in the template
All of these are signs that it’s time to update the template to include more or different information. This can be a great time to pause and ask your stakeholders what new information would be helpful for them to read about in the progress report.
Incorporating progress report comments
Your stakeholders may have follow-up questions or comments about your progress report. This is great news because it means that your stakeholders are involved and staying up to date! Of course, they may have positive feedback or negative feedback. How do you handle either situation?
Handling negative feedback about your progress report from stakeholders
You’ve sent out the progress report, and you’re excited to hear all of the positive comments on how much progress the team is making. Then the comments start rolling in, and they are disappointingly not positive. How do you address negative comments from stakeholders?
There is negative feedback about the formatting
Sometimes, stakeholders may have negative feedback about how the progress report looks instead of commenting on the contents of the report itself. This can be a good thing — they have an interest in the process!
Take their feedback into consideration and potentially make updates to the template to make incorporating their feedback easier from week to week. If there’s a way to make the report easier to read, make those adjustments. If data is missing that would help make decisions — and if the data is available — consider adding it to subsequent progress reports.
There is negative feedback about the progress being made
Sometimes, stakeholders will have questions or comments related to how quickly the project is moving or the challenges the team is encountering. Here are some steps on how to handle this when it comes up.
- First, try to understand where the stakeholder is coming from. Are they curious about why a challenge arose? Are they concerned about the progress so far? Are they nervous about missing a critical deadline? You may need to reach out to that stakeholder to understand their concerns or feedback better so that you know how you can help
- Once you understand where the concern is coming from, now you can work to address the stakeholder’s feedback or criticism. If they address a challenge that has come up, it may be a good time to escalate the support you need in clearing the blocker. If they’re addressing that it seems like the project is off-track, reiterate what you or the team are doing to ensure that the project stays on track
- Sometimes, negative feedback occurs because someone is missing context or does not have all the information. In this case, it can be helpful to ensure that the stakeholder understands
Handling positive feedback about your progress report
When you get positive feedback about the progress you’re making, this is a great time to share that feedback with the entire team and celebrate. There are ways to incorporate this kind of feedback into your team’s rhythms.
One way is to surface positive feedback at a daily standup or weekly team meeting, letting them know that the leadership team or external stakeholders are happy with the progress are cheering you on. If appropriate, inviting a stakeholder to a team meeting and letting them know they’re excited about the progress can be a fun addition.
Conclusion and key takeaways
Progress reports can help keep your stakeholders in the loop, build trust, and keep them up to date about what’s happening within your project. Remember that good progress reports adapt and change as you get feedback from your stakeholders and as the project needs change. Templating your progress reports can help you save time and allow others to contribute as you assign segments to other members of the team.
Remember that you can also keep it fun by adding your touch to it. If negative feedback arises, incorporate what you can. And when positive feedback comes up, remember to pass it on.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #collaboration and communication

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
The evolving role of AI product managers
An AI product manager plays a crucial role in translating complex project requirements into products that align with user needs.
Leader Spotlight: Engaging customers authentically, with Dianna Lyngholm
Dianna Lyngholm, Director of Creative Services + CX at FUN.com, talks about strategies for creating an authentic relationship with customers.

The digital marketing funnel: Stages and strategies
The digital marketing funnel is a visual representation of the customer’s journey as it moves through online channels.

Leader Spotlight: Building products in an increasingly competitive market, with Ashlee Richards
Ashlee Richards talks about how the legalization of sports betting has added new players to the market and changed the competitive landscape.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Progress Report

- 6-minute read
- 28th September 2021
A progress report is a business document that provides updates on a project’s progress toward meeting a goal. Typically, you’ll provide a progress report for a supervisor/manager, team member, or business client to summarize a project’s status and what still needs to be completed or improved.
But how do you write an effective progress report for your business’s projects ? In our guide below, we set out the typical structure of a progress report.
1. Header Information
A progress report should start with a header that includes key details about the report and the project. Typically, this will include the:
- Reporting period and/or the date of submission.
- Name(s) and position(s) of the report’s recipient(s).
- Name(s) and position(s) of the report’s author(s).
- Subject or title of the report/project.
This will help the recipient to understand the contents of the report at a glance.
2. Introduction
The introductory paragraph of a progress report should outline the purpose and timeframe of the project, plus any other important details or insights.
You can also include an overview of what the rest of your progress report will cover.
3. Work Completed
The next section of your report should be titled “Work Completed.” Here, you can provide a chronological list of the project tasks that you have already completed and their corresponding dates. You can also include key findings from those tasks.
4. Problems Encountered
The next section should outline any problems encountered in the project so far. You should then explain either how those problems were solved or how they will be solved, and whether any extra help will be required to do so. You will also need to mention if those problems prompted any changes to the project.
5. Future Plans
To highlight the goals for the remainder of the project, the next section of your report should outline any future project tasks with their corresponding dates or deadlines, anticipated problems, and/or ideas for the project as you move forward.
End your progress report with a brief summary of key completed tasks, ongoing tasks, and major issues encountered. You don’t need to go into too much detail here, though. Stick to the essential details.
5 Tips on How to Write a Progress Report
We also have some helpful tips you can use when writing a progress report:
- Adapt the structure – While the structure outlined above will work for most projects, you can adapt it to suit your requirements. For instance, for a complex project with multiple goals, you may need to break it down into sections, detailing the progress, problems, and plans for each objective.
- Choose an appropriate frequency – For ongoing progress reports, think about whether to schedule daily, weekly, or monthly updates.
- Write clearly – Make sure to write clearly and concisely . Keep your sentences simple, straightforward, and easy to understand.
- Know your audience – If you’re writing a report for someone outside of your organization or team, explain any industry-specific language you use.
- Keep it professional – Make sure to use a formal tone , avoiding colloquial terms and phrases, slang, contractions, and other informal language.
Finally, to be sure your report looks and sounds professional, have it proofread. You can try our proofreading services by uploading a trial document for free today!
Example Progress Report
To see what a progress report might look like, check out our example report below:
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Date: September 24, 2021 To: J. Seymour, Head of Planning From: A. Boleyn, Planning Assistant Subject: Migration to new planning software
Since November 2016, Exemplar Inc. has used the PlanULike package to manage the company’s everyday operations. However, when we expanded to new territories in July 2021, the limitations of the software became evident, especially with regard to currency conversions when budgeting for projects in Europe. As a result, in August 2021, the decision was made to migrate to new planning software. This report covers the progress in this project made up until September 24, 2021.
Work Completed
- August 30 – Research completed into available planning software packages. The PlanZone software is selected based on its flexible budgeting capabilities.
- September 6 – A timeline is developed for installation and implementation of the new software package, with an initial deadline of September 30.
- September 10 – Head of Human Resources, Jack Thacker, begins developing in-house instructional materials for the new software.
- September 18 – Software is acquired and installed. Provisional version of internal training program is developed and tested with key staff members.
- September 21 – IT department identifies software compatibility problems with older hardware in operations department. New equipment purchased.
- September 24 – New computer hardware installed. After testing, training program is extended to heads of department in planning and operations.
Problems Encountered
The key problem encountered thus far has been a compatibility issue between the new software and some of the company’s existing hardware. Head of IT, Simon Robinson, reports that this was due to PlanZone including graphical features that Exemplar Inc. does not use and had not been factored into the initial planning.
Due to speedy delivery and installation of new hardware, this has not significantly affected the timeframe for the migration. But the unexpected expense does mean that the project is now significantly over budget.
In addition, the testing of the in-house training program took longer than anticipated to complete. Key staff are now familiar with the new software, but the deadline for company-wide training has been extended to November 15, 2021.
Future Plans
The improved training program will continue until November 15, 2021, when all relevant staff are expected to be familiar with the new software, after which all operational planning will use PlanZone, and the PlanULike systems will be deprecated by November 30, 2021. Due to exceeding the budget allocated for this project, a meeting will be scheduled for heads of department to discuss how the extra expenses may impact budgeting for other projects.
The company has acquired and installed new planning software (PlanZone), which is projected to enhance project planning and ease operations in new territories. However, unexpected hardware and training issues have slowed progress. Deadlines for the migration have thus been extended. Meanwhile, implications of the extra expenses will be factored into budgeting for upcoming projects.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Writing a progress/status report
By michael ernst, january, 2010.
Writing a weekly report about your research progress can make your research more successful, less frustrating, and more visible to others, among other benefits.
One good format is to write your report in four parts:
- Quote the previous week's plan. This helps you determine whether you accomplished your goals.
- State this week's progress. This can include information such as: what you have accomplished, what you learned, what difficulties you overcame, what difficulties are still blocking you, your new ideas for research directions or projects, and the like.
- Give the next week's plan. A good format is a bulleted list, so we can see what you accomplished or did not. Try to make each goal measurable: there should be no ambiguity as to whether you were able to finish it. It's good to include longer-term goals as well.
- Give an agenda for the meeting. Some people like to send this as a separate message, which is fine.
The report need not be onerous. It can be a few paragraphs or a page, so it shouldn't take you long to write. Minimize details that are not relevant to your audience, such as classwork and the like, in order to keep the report focused; you will spend less time writing it, and make it more likely to be read.
Writing the progress report has many benefits.
Writing the report will make you more productive, because it will force you to think about your work in a manner concretely enough to write down. Any time that you spend organizing your thoughts will more than pay itself back in better understanding and improved productivity. When a project is complete, it is all too easy to forget some of your contributions. You can look back over your progress reports to remember what was difficult, and to think about how to work more productively in the future. You may be able to re-use some of the text when writing up your results.
Writing the report will make your meetings more productive. When you have a weekly research meeting, the report should be sent 24 hours in advance, to help everyone prepare. (Two hours is not an acceptable alternative: it does not let everyone — both you and others — mull over the ideas.) Don't delay your report because you want to wait until you have better results to report. Instead, send the report on schedule, and if you get more results in the next 24 hours, you can discuss those at the meeting.
Writing the report will give you feedback from a new point of view. The report enables others outside your research project to know what you are doing. Those people may respond with ideas or suggestions, which can help get you unstuck or give you additional avenues to explore. It also keeps you on their radar screen and reminds them of your work, which a good thing if you don't meet with them frequently. (For PhD students, a periodic report to the members of your thesis committee can pay big dividends.)
Writing the report helps explain (to yourself especially, but also to others) how you spent your time — even if there isn't as much progress as you would have preferred, you can see that you did work hard, and how to be more efficient or effective in the future.
If your meetings are more frequent than weekly, then the progress report should also be more frequent. If your meetings are less frequent, it's a good idea to still send a progress report each week.
Important tip: Throughout the day, maintain a log of what you have done. This can be a simple text file. You can update it when you start and end a task, or at regular intervals throughout the day. It takes only a moment to maintain the log, and it makes writing the report easy. By contrast, without a log you might forget what you have done during the week, and writing the report could take a long time.
Back to Advice compiled by Michael Ernst .
Learn / Guides / Performance reporting guide
Back to guides
Progress reporting 101: how to review your projects in 5 steps
Projects tend to take on a life of their own—twisting and turning with each new development, milestone, and lesson.
But as you collaborate with more stakeholders and journey further into the heart of a project, the details can become overwhelming, and you may begin to lose sight of where you’ve been and where you need to go. This is where progress reports have a vital role to play.
Last updated
Reading time.

This guide teaches you what a progress report is, and when and how to create one, so you can update stakeholders, solve problems, plan your next steps, and learn from past projects .
Add insights to your progress reporting
Use Hotjar to understand how customers interact with your website and product to add detail and direction to your progress report.
What is progress reporting?
Progress reporting is an ongoing study into the development of a project, usually for the team members involved. It focuses on events and tactical details, like progress drivers and anticipated roadblocks, to assess what your project has achieved and where you’ll take it next.
For example, imagine a design manager creating a progress report for a homepage redesign project. They’ll use the progress report document to share insights from the product management team and summarize recent discussions to give everyone the same context moving forward.
A status report is another performance reporting type that the design manager could use, but it isn’t interchangeable with a progress report. While a progress report is an ongoing study of the project for the team, a status report is a snapshot of current progress for stakeholders. For example, while the homepage redesign progress report contains hands-on details for the design team, a status report for this project would tell the C-suite that the team completed its first two milestones ahead of schedule.
Progress reporting is vital for project management because it consolidates information and identifies the next steps. The benefits of progress reporting include:
When to create a progress report
If progress reporting is an ongoing look at your project, when and how often should you create a progress document? There are two options.
Create a progress report at regular intervals
Regular progress reporting—like weekly for shorter projects or monthly for more significant initiatives—helps when you have many stakeholders or the project moves quickly. For example, cross-functional collaboration benefits from a regular recap and check-in since not every person will be in every meeting or work session.
Create a progress report after milestones
Alternatively, projects with smaller teams benefit from progress reporting after milestones rather than on a consistent cadence. For example, a one-person social media team would check in with their marketing manager as they complete phases of a new campaign or feature launch.
How to create a progress report in 5 simple steps
While progress reporting benefits a wide range of roles and projects, the basic structure is always the same. Here’s a 5-step progress report template to follow.
Step 1: clarify goals and timeline
First, you need to briefly explain the project to give context to the rest of the report. Clarifying project goals and timelines brings priorities to the surface to make it easier for stakeholders reading the report to catch up.
Details to include:
Project summary: a brief overview of the project
Product objective: your immediate product goals and the long-term initiative they support. Think of these as objectives and key results (OKRs).
Milestones: the main tasks you've already completed or still need to complete for a high-level understanding of the project scope
Timeline: the progress you've made in the project’s reporting period
To illustrate the first step in progress reporting, let’s use the homepage redesign example from earlier. The design manager leading the project says their team is updating the website’s homepage to reflect rebranding and increase engagement. Then, the manager lists the major milestones, including wireframing, prototyping, and testing over a 3-month period, which they’re halfway through.
Step 2: consider stakeholders
Reading a progress report that has nothing to do with you is confusing at best and boring at worst—so be sure to tailor your document to its audience.
Determining who’s going to see and use the report influences what details you need to include. For example, a C-suite leader cares more about customer activation progress than a debate over whether the homepage banner should be cerulean or cyan.
Project owner: who’s in charge of the project
Team: who’s on the team, and their role in the project
Report prepared for: who will read the report and if they had a particular motivation, question, or concern
Definitions: stakeholders might not know certain cross-functional terms. For example, your graphic designers probably haven’t reviewed a Google Analytics glossary in a while.
In our example homepage redesign project, the design team needs effective cross-functional collaboration . Throughout the project, they’ll work with the product team to test design effectiveness and with the marketing team to create copy and imagery for their target audience. Since the design manager knows this, the progress report needs to have insights across groups and summarize discussions different functions may miss.
All together now! 👯
Effective collaboration and communication can make or break a project, whether you work with one other person or five other functions. Asynchronous communication in a shared document for project updates or new ideas is a must. Here at Hotjar, we’ve also established rules for what gets a meeting.
Every meeting requires an owner (usually the organizer) whose duties include the following:
Establishing a clear objective and agenda: what’s the purpose of the call, who’s attending, and why?
Listing relevant data and required reading so all participants can prepare
Documenting the meeting’s output and actions to share with the team on an agreed-upon channel (e.g. email, Trello, Discourse).
Learn more about our strategies and tools for better collaboration .
Step 3: share recent updates
Progress reporting is an ongoing process, so you need to reference developments about questions or concerns stakeholders brought up in the previous report. If this is your first progress report, compare progress to any assumptions you had.
Problem resolutions: any prior issues you resolved and how you did it
Answers to questions: queries from previous progress reports that need to be addressed
New insights: an overview of new data, metrics, priorities, or lessons that impact the project
Testing results: results and learnings from A/B tests or customer interviews
For example, the design manager would include a screenshot of their data dashboard to provide a summary of how the first prototype of the homepage redesign performs. The progress report would also have notes from a cross-functional meeting that answered a previous question about the customer journey .
Hotjar’s Dashboard presents key sessions and user behavior data in charts and graphs so you don’t have to switch between multiple analytics sources
Step 4: identify drivers and blockers
Your progress report is the place to consolidate all your important Slack messages, meeting outcomes, and personal notes as you work through the project.
Documenting what’s helping and hindering the project gets everyone on the same page, helps you prioritize the next steps, and creates a record you can learn from and reference in the future.
Product experience (PX) insights: data that reveals how customers interact with your product or website to understand the project’s impact
Delays: anything that slows the project down
Questions: team questions or unknowns
Progress drivers: details that positively impact the project (so you know what to do more of next time!)
Upcoming events and milestones: what you’ll work on next
Let’s go back to our homepage redesign project. In this step, the design manager reminds the team they’ll be out on vacation next week and that there’s an upcoming meeting of designers, product managers, and marketing folks to watch customer recordings together . The meeting’s goal is to get new perspectives on the response to the new page design, and the team needs to document the results to include in the next progress report.
Bring your progress reports to life with product experience insights
PX insights help you break out of your team silo and get an outside perspective from the people you’re trying to help—your customers.
Hotjar (hi, that’s us! 👋) is a product experience insights platform that adds data-informed decision-making to your progress report. Hotjar gives you:
Heatmaps (free forever) to uncover where website visitors pay the most attention
Recordings to see exactly how customers interact with your product
Surveys to learn what customers love and hate about your product
Feedback to get real-time thoughts on your design
Interviews to hear how customers describe their goals and preferences
Funnels to learn where and why customers drop off
Plus, adding context to your progress report with PX insights increases stakeholder buy-in with tangible results, gets new team members up to speed, and creates a knowledge base of your efforts to reference in the future .
Hotjar's tools give you a new perspective on your customers’ experiences
Step 5: list the next steps
Your progress report becomes actionable when you summarize what you’ve learned and create an action plan.
As you create subsequent progress reports for a project, you can assess whether the tasks you'd initially set out to do were indeed the ones that took up your time. This information lets you rework future planning or rein in a project that’s straying off course.
Tasks: deliverables needed, timeframes, and who’s responsible for what
Follow-ups: meetings to schedule or stakeholders to loop in
For example, with the progress report, the design team recognizes the need to follow up with the marketing team for the homepage’s new copy. They also need to review comments the website development team left on the first version of their homepage wireframe.
If you’re only ever focused on implementation, you’ll waste time and budget on tactics without knowing if they actually delivered growth or not. You should be constantly evaluating performance data, both qualitative and quantitative, to inform your efforts. Then, by packaging this data up in monthly, quarterly, or annual performance insights, you can use the reports to increase your organizational impact.
Use customer insights to support your progress reports
Progress reporting supports projects by clarifying what has happened and what will happen. But you need the right insights to understand project progress and decide what to do next.
As much as confident teammates and company veterans may think they know what’s best, you need to learn from customers to create for customers . When you prioritize customer empathy and curiosity, you create an accurate and impactful progress report.
Rather than relying on assumptions or guesses, teams need to use customer and PX insights—information that helps you test and correct as you work through a project. This customer-driven data helps you focus on what matters and get results, preventing you from going too far down a path to nowhere.
Progress reporting FAQs
Progress reporting is an ongoing study into the development of a project, usually for the team members involved. It focuses on events and tactical details like progress drivers and anticipated roadblocks. The goal of a progress report is to assess where the project has been and where you’ll take it next.
For example, imagine a design manager creates a progress report for a home page redesign project. They update the design team on insights from the product management team and summarize recent discussions to give everyone the same context moving forward.
What are the benefits of a progress report?
A progress report lets you:
Consolidate the main takeaways from recent collaboration , which means everyone is on the same page
Review project and product planning regularly to make continuous adjustments that keep you close to your customers and goals
Work through issues and questions with your teammates and stakeholders
When should you use a progress report?
There are two scenarios you can use a progress report:
At regular intervals , like weekly or daily progress reports for short projects or a monthly progress report for larger initiatives. Use this method if you have a lot of stakeholders or the project moves quickly. For example, a cross-functional collaboration benefits from a regular recap and check-in.
After milestones , like when the team is stuck or after you complete a significant task. Use this method if the project has fewer stakeholders, like a one-person team checking in with their boss as they complete phases of the project or as part of a product roadmap .
How do you create a progress report?
Clarify goals and timeline : what is the project and when will you work on it?
Consider the stakeholders : who’s involved?
Share recent updates : what have you done so far?
Identify drivers and blockers : what’s helping and hindering the project?
List next steps : what will you do next?
Trend report
Previous chapter
Status report
Next chapter
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Table of Contents

Research Report
Definition:
Research Report is a written document that presents the results of a research project or study, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions, in a clear and objective manner.
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the findings of the research to the intended audience, which could be other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public.
Components of Research Report
Components of Research Report are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the research report and provides a brief overview of the research question or problem being investigated. It should include a clear statement of the purpose of the study and its significance or relevance to the field of research. It may also provide background information or a literature review to help contextualize the research.
Literature Review
The literature review provides a critical analysis and synthesis of the existing research and scholarship relevant to the research question or problem. It should identify the gaps, inconsistencies, and contradictions in the literature and show how the current study addresses these issues. The literature review also establishes the theoretical framework or conceptual model that guides the research.
Methodology
The methodology section describes the research design, methods, and procedures used to collect and analyze data. It should include information on the sample or participants, data collection instruments, data collection procedures, and data analysis techniques. The methodology should be clear and detailed enough to allow other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the study in a clear and objective manner. It should provide a detailed description of the data and statistics used to answer the research question or test the hypothesis. Tables, graphs, and figures may be included to help visualize the data and illustrate the key findings.
The discussion section interprets the results of the study and explains their significance or relevance to the research question or problem. It should also compare the current findings with those of previous studies and identify the implications for future research or practice. The discussion should be based on the results presented in the previous section and should avoid speculation or unfounded conclusions.
The conclusion summarizes the key findings of the study and restates the main argument or thesis presented in the introduction. It should also provide a brief overview of the contributions of the study to the field of research and the implications for practice or policy.
The references section lists all the sources cited in the research report, following a specific citation style, such as APA or MLA.
The appendices section includes any additional material, such as data tables, figures, or instruments used in the study, that could not be included in the main text due to space limitations.
Types of Research Report
Types of Research Report are as follows:
Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master’s or Doctoral degree, although it can also be written by researchers or scholars in other fields.
Research Paper
Research paper is a type of research report. A research paper is a document that presents the results of a research study or investigation. Research papers can be written in a variety of fields, including science, social science, humanities, and business. They typically follow a standard format that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion sections.
Technical Report
A technical report is a detailed report that provides information about a specific technical or scientific problem or project. Technical reports are often used in engineering, science, and other technical fields to document research and development work.
Progress Report
A progress report provides an update on the progress of a research project or program over a specific period of time. Progress reports are typically used to communicate the status of a project to stakeholders, funders, or project managers.
Feasibility Report
A feasibility report assesses the feasibility of a proposed project or plan, providing an analysis of the potential risks, benefits, and costs associated with the project. Feasibility reports are often used in business, engineering, and other fields to determine the viability of a project before it is undertaken.
Field Report
A field report documents observations and findings from fieldwork, which is research conducted in the natural environment or setting. Field reports are often used in anthropology, ecology, and other social and natural sciences.
Experimental Report
An experimental report documents the results of a scientific experiment, including the hypothesis, methods, results, and conclusions. Experimental reports are often used in biology, chemistry, and other sciences to communicate the results of laboratory experiments.
Case Study Report
A case study report provides an in-depth analysis of a specific case or situation, often used in psychology, social work, and other fields to document and understand complex cases or phenomena.
Literature Review Report
A literature review report synthesizes and summarizes existing research on a specific topic, providing an overview of the current state of knowledge on the subject. Literature review reports are often used in social sciences, education, and other fields to identify gaps in the literature and guide future research.
Research Report Example
Following is a Research Report Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance among High School Students
This study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students. The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The findings indicate that there is a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students. The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers, as they highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities.
Introduction:
Social media has become an integral part of the lives of high school students. With the widespread use of social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat, students can connect with friends, share photos and videos, and engage in discussions on a range of topics. While social media offers many benefits, concerns have been raised about its impact on academic performance. Many studies have found a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance among high school students (Kirschner & Karpinski, 2010; Paul, Baker, & Cochran, 2012).
Given the growing importance of social media in the lives of high school students, it is important to investigate its impact on academic performance. This study aims to address this gap by examining the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students.
Methodology:
The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The questionnaire was developed based on previous studies and was designed to measure the frequency and duration of social media use, as well as academic performance.
The participants were selected using a convenience sampling technique, and the survey questionnaire was distributed in the classroom during regular school hours. The data collected were analyzed using descriptive statistics and correlation analysis.
The findings indicate that the majority of high school students use social media platforms on a daily basis, with Facebook being the most popular platform. The results also show a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students.
Discussion:
The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. The negative correlation between social media use and academic performance suggests that strategies should be put in place to help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. For example, educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this study provides evidence of the negative impact of social media on academic performance among high school students. The findings highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. Further research is needed to explore the specific mechanisms by which social media use affects academic performance and to develop effective strategies for addressing this issue.
Limitations:
One limitation of this study is the use of convenience sampling, which limits the generalizability of the findings to other populations. Future studies should use random sampling techniques to increase the representativeness of the sample. Another limitation is the use of self-reported measures, which may be subject to social desirability bias. Future studies could use objective measures of social media use and academic performance, such as tracking software and school records.
Implications:
The findings of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. Educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. For example, teachers could use social media platforms to share relevant educational resources and facilitate online discussions. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. They could also engage in open communication with their children to understand their social media use and its impact on their academic performance. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students. For example, schools could implement social media policies that restrict access during class time and encourage responsible use.
References:
- Kirschner, P. A., & Karpinski, A. C. (2010). Facebook® and academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1237-1245.
- Paul, J. A., Baker, H. M., & Cochran, J. D. (2012). Effect of online social networking on student academic performance. Journal of the Research Center for Educational Technology, 8(1), 1-19.
- Pantic, I. (2014). Online social networking and mental health. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 17(10), 652-657.
- Rosen, L. D., Carrier, L. M., & Cheever, N. A. (2013). Facebook and texting made me do it: Media-induced task-switching while studying. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(3), 948-958.
Note*: Above mention, Example is just a sample for the students’ guide. Do not directly copy and paste as your College or University assignment. Kindly do some research and Write your own.
Applications of Research Report
Research reports have many applications, including:
- Communicating research findings: The primary application of a research report is to communicate the results of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public. The report serves as a way to share new knowledge, insights, and discoveries with others in the field.
- Informing policy and practice : Research reports can inform policy and practice by providing evidence-based recommendations for decision-makers. For example, a research report on the effectiveness of a new drug could inform regulatory agencies in their decision-making process.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research in a particular area. Other researchers may use the findings and methodology of a report to develop new research questions or to build on existing research.
- Evaluating programs and interventions : Research reports can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and interventions in achieving their intended outcomes. For example, a research report on a new educational program could provide evidence of its impact on student performance.
- Demonstrating impact : Research reports can be used to demonstrate the impact of research funding or to evaluate the success of research projects. By presenting the findings and outcomes of a study, research reports can show the value of research to funders and stakeholders.
- Enhancing professional development : Research reports can be used to enhance professional development by providing a source of information and learning for researchers and practitioners in a particular field. For example, a research report on a new teaching methodology could provide insights and ideas for educators to incorporate into their own practice.
How to write Research Report
Here are some steps you can follow to write a research report:
- Identify the research question: The first step in writing a research report is to identify your research question. This will help you focus your research and organize your findings.
- Conduct research : Once you have identified your research question, you will need to conduct research to gather relevant data and information. This can involve conducting experiments, reviewing literature, or analyzing data.
- Organize your findings: Once you have gathered all of your data, you will need to organize your findings in a way that is clear and understandable. This can involve creating tables, graphs, or charts to illustrate your results.
- Write the report: Once you have organized your findings, you can begin writing the report. Start with an introduction that provides background information and explains the purpose of your research. Next, provide a detailed description of your research methods and findings. Finally, summarize your results and draw conclusions based on your findings.
- Proofread and edit: After you have written your report, be sure to proofread and edit it carefully. Check for grammar and spelling errors, and make sure that your report is well-organized and easy to read.
- Include a reference list: Be sure to include a list of references that you used in your research. This will give credit to your sources and allow readers to further explore the topic if they choose.
- Format your report: Finally, format your report according to the guidelines provided by your instructor or organization. This may include formatting requirements for headings, margins, fonts, and spacing.
Purpose of Research Report
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the results of a research study to a specific audience, such as peers in the same field, stakeholders, or the general public. The report provides a detailed description of the research methods, findings, and conclusions.
Some common purposes of a research report include:
- Sharing knowledge: A research report allows researchers to share their findings and knowledge with others in their field. This helps to advance the field and improve the understanding of a particular topic.
- Identifying trends: A research report can identify trends and patterns in data, which can help guide future research and inform decision-making.
- Addressing problems: A research report can provide insights into problems or issues and suggest solutions or recommendations for addressing them.
- Evaluating programs or interventions : A research report can evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions, which can inform decision-making about whether to continue, modify, or discontinue them.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies.
When to Write Research Report
A research report should be written after completing the research study. This includes collecting data, analyzing the results, and drawing conclusions based on the findings. Once the research is complete, the report should be written in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
In academic settings, research reports are often required as part of coursework or as part of a thesis or dissertation. In this case, the report should be written according to the guidelines provided by the instructor or institution.
In other settings, such as in industry or government, research reports may be required to inform decision-making or to comply with regulatory requirements. In these cases, the report should be written as soon as possible after the research is completed in order to inform decision-making in a timely manner.
Overall, the timing of when to write a research report depends on the purpose of the research, the expectations of the audience, and any regulatory requirements that need to be met. However, it is important to complete the report in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
Characteristics of Research Report
There are several characteristics of a research report that distinguish it from other types of writing. These characteristics include:
- Objective: A research report should be written in an objective and unbiased manner. It should present the facts and findings of the research study without any personal opinions or biases.
- Systematic: A research report should be written in a systematic manner. It should follow a clear and logical structure, and the information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand and follow.
- Detailed: A research report should be detailed and comprehensive. It should provide a thorough description of the research methods, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research report should be accurate and based on sound research methods. The findings and conclusions should be supported by data and evidence.
- Organized: A research report should be well-organized. It should include headings and subheadings to help the reader navigate the report and understand the main points.
- Clear and concise: A research report should be written in clear and concise language. The information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand, and unnecessary jargon should be avoided.
- Citations and references: A research report should include citations and references to support the findings and conclusions. This helps to give credit to other researchers and to provide readers with the opportunity to further explore the topic.
Advantages of Research Report
Research reports have several advantages, including:
- Communicating research findings: Research reports allow researchers to communicate their findings to a wider audience, including other researchers, stakeholders, and the general public. This helps to disseminate knowledge and advance the understanding of a particular topic.
- Providing evidence for decision-making : Research reports can provide evidence to inform decision-making, such as in the case of policy-making, program planning, or product development. The findings and conclusions can help guide decisions and improve outcomes.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research on a particular topic. Other researchers can build on the findings and conclusions of the report, which can lead to further discoveries and advancements in the field.
- Demonstrating expertise: Research reports can demonstrate the expertise of the researchers and their ability to conduct rigorous and high-quality research. This can be important for securing funding, promotions, and other professional opportunities.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies. Producing a high-quality research report can help ensure compliance with these requirements.
Limitations of Research Report
Despite their advantages, research reports also have some limitations, including:
- Time-consuming: Conducting research and writing a report can be a time-consuming process, particularly for large-scale studies. This can limit the frequency and speed of producing research reports.
- Expensive: Conducting research and producing a report can be expensive, particularly for studies that require specialized equipment, personnel, or data. This can limit the scope and feasibility of some research studies.
- Limited generalizability: Research studies often focus on a specific population or context, which can limit the generalizability of the findings to other populations or contexts.
- Potential bias : Researchers may have biases or conflicts of interest that can influence the findings and conclusions of the research study. Additionally, participants may also have biases or may not be representative of the larger population, which can limit the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Accessibility: Research reports may be written in technical or academic language, which can limit their accessibility to a wider audience. Additionally, some research may be behind paywalls or require specialized access, which can limit the ability of others to read and use the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
7. COMMON DOCUMENT TYPES
You write a progress report to inform a supervisor, associate, or client about progress you have made on a project over a specific period of time. Periodic progress reports are common on projects that go on for several months (or more). Whoever is paying for this project wants to know whether tasks are being completed on schedule and on budget. If the project is not on schedule or on budget, they want to know why and what additional costs and time will be needed.
Progress reports answer the following questions for the reader:
- How much of the work is complete?
- What part of the work is currently in progress?
- What work remains to be done?
- When and how will the remaining work be completed?
- What changes, problems or unexpected issues, if any, have arisen?
- How is the project going in general?
Purpose of a Progress Report
The main function of a progress report is persuasive: to reassure clients and supervisors that you are making progress, that the project is going smoothly, and that it will be completed by the expected date — or to give reasons why any of those might not be the case. They also offer the opportunity to do the following:
- Provide a brief look at preliminary findings or in-progress work on the project
- Give your clients or supervisors a chance to evaluate your work on the project and to suggest or request changes
- Give you a chance to discuss problems in the project and thus to forewarn the recipients
- Force you to establish a work schedule, so that you will complete the project on time.
Format of a Progress Report
Depending on the size of the progress report, the length and importance of the project, and the recipient, a progress report can take forms ranging from a short informal conversation to a detailed, multi-paged report. Most commonly, progress reports are delivered in following forms:
- Memo : a short, semi-formal report to someone within your organization (can range in length from 1-4 pages)
- Letter : a short, semi-formal report sent to someone outside your organization
- Formal report: a long, formal report sent to someone within or outside of your organization
- Presentation : an oral presentation given directly to the target audience.
Organizational Patterns for Progress Reports
The recipient of a progress report wants to see what you’ve accomplished on the project, what you are working on now, what you plan to work on next, and how the project is going in general. The information is usually arranged with a focus either on time or on task, or a combination of the two:
- Focus on time: shows time period (previous, current, and future) and tasks completed or scheduled to be completed in each period
- Focus on specific tasks: shows order of tasks (defined milestones) and progress made in each time period
- Focus on larger goals : focus on the overall effect of what has been accomplished.
Information can also be arranged by report topic. You should refer to established milestones or deliverables outlined in your original proposal or job specifications. Whichever organizational strategy you choose, your report will likely contain the elements described below.
1. Introduction
Review the details of your project’s purpose, scope, and activities. The introduction may also contain the following:
- date the project began; date the project is scheduled to be completed
- people or organization working on the project
- people or organization for whom the project is being done
- overview of the contents of the progress report.
2. Project status
This section (which could have sub-sections) should give the reader a clear idea of the current status of your project. It should review the work completed, work in progress, and work remaining to be done on the project, organized into sub-sections by time, task, or topic. These sections might include
- Direct reference to milestones or deliverables established in previous documents related to the project
- Timeline for when remaining work will be completed
- Any problems encountered or issues that have arisen that might affect completion, direction, requirements, or scope.
3. Conclusion
The final section provides an overall assessment of the current state of the project and its expected completion, usually reassuring the reader that all is going well and on schedule. It can also alert recipients to unexpected changes in direction or scope, or problems in the project that may require intervention.
4. References section if required.
Technical Writing Essentials Copyright © by Suzan Last and UNH College of Professional Studies Online is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- FRONT MATTER
- TABLE OF CONTENTS
Progress Reports
Progress reports are common and critical documents in science and engineering, typically when you are part of a research team reporting to a funding agency about your progress on work you are doing for that agency. The basic point of a progress report is to summarize the status, progress, and likely future for a particular project. In a progress report you are often expected to commit to an exact schedule for the project completion, discuss the status of the materials being used and account for the money spent, and summarize concretely both the current findings and the predicted results. The professionalism of the progress report is often vital to the future of the project.
In classes and projects involving writing, progress reports are used as a way for you to summarize your progress to your teacher or advisor, who will typically give feedback on whether he or she is satisfied with your progress. These reports could feel like a mere formality or a waste of time to you, but they are an excellent opportunity to articulate some of the key sentences of your final report and even pose questions in writing to your audience. The rules for writing progress reports are a lot more flexible in a classroom or lab than they are on the job, with a lot less at stake, so you should take full advantage of the opportunity for practice.
For more ideas on writing progress reports, I recommend that you visit:
"Progress Reports" article from the Department of Engineering at Penn State
"Guidelines for Writing Reports" from networklearning.org
Style for Progress Reports
The following stylistic advice can be applied to most progress reports you write:
- Include a working title and the words "Progress Report" at the top of the page.
- Use section headings in the report to simplify both the writing and reading process.
- Open the report with a "Scope and Purpose" section, where you give a condensed version of your future report’s introduction and objective.
- Always include a section entitled, for example, "Progress," which summarizes the work’s pace and progress and explains any snafus, dilemmas, or setbacks.
- Always include a section entitled, for example, "Remaining Work," which honestly assesses the work that must still be completed. Think right on the page in this section, posing questions, speculating meaningfully, exploring your options.
- Always include a section that projects the expected results. Commit to a schedule for obtaining those results if possible.
- If necessary, include a section in which you directly solicit advice from your teacher or advisor. Be forthright and professional about the nature of the advice you need.
- Keep your paragraphs short and focused—just a few paragraphs per section, typically.
- Your tone can often be straightforward and familiar—therefore, as a rule, you can use "I" and "you" freely—but do not lapse into informality.
- Avoid being overly optimistic, pessimistic, apologetic, cocky, or self-deprecating.

Why Are Progress Reports Important in Research?
Did your supervisor ask you to write a progress report? A significant part of your supervisor’s job is to be a project manager and be accountable to funders. Remember, your research project is just one cog in the wheel of science in your lab. Therefore, your supervisor will need reports on the progress of each project. Their job is to evaluate your progress and adjust your action plan if things go wrong. These reports are not simply a report of your results.
Set SMART Goals
First, set “SMART” goals for your project (SMART = Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic and Time-targeted goals). I like SMART goals because they are more than a list of things to achieve. They are part of an action plan. Your progress reports will help you check whether your goals are on track.
Progress Report Intervals
Your supervisor will tell you how often they need progress reports. The time interval depends on the nature of your work. I like to monitor my projects regularly , on a daily, weekly and monthly basis.
- Daily: this is an informal walk around the lab where I have a quick chat with my team members on what they are doing. I also set myself a daily “to do” list.
- Weekly: my team meets once a week for coffee and an informal journal club. After discussing a paper, we give a quick verbal report on our progress during the past week and any challenges that have arisen. If we find that someone is struggling or their work needs further discussion, we schedule a meeting.
- Monthly: once a month we write a formal progress report of our work and meet on a one-to-one basis to discuss it.
Purpose of Progress Reports
Your report should include your results obtained so far, experiments you are working on, plans for future work and any problems you might have with your work. It is a report on your overall plan. This plan needs constant assessment to ensure you reach your goals and to help you make informed decisions and justify any changes.
Progress reports also keep stakeholders informed. Anyone involved with your project wants to know:
- That you are working on the project and making progress.
- What findings you have made so far.
- That you are evaluating your work as you
- If you foresee any challenges.
- Any problems you encounter are being addressed.
- That you can manage your plan and schedule.
- That your project will be completed on time.
How to Write a Progress Report
Ask your supervisor if they have a template that they want you to use. Supervisors that manage many projects find it easier to keep track of all the information if it is presented in a consistent format. Write your report in concise, simple language. Progress report styles vary. However, most reports require the following sections :
- Project information . State the project name, any project ID codes, the names of all the researchers involved, report date and anticipated completion date.
- Introduction : This is a summary of your Write a short overview of the purpose of the project and its main objectives. You could add a summary of the results obtained so far, future goals, how much of the project has been completed, whether it will be completed on time, and whether you are within the budget.
- Progress: This section gives details of your objectives and how much you have completed so far. List your milestones, give details of your results, and include any tables and figures here. Some stakeholders like a completion rate which can be given as a percentage.
- Risks and Issues: Discuss any challenges that have arisen or that you Describe how you plan to solve them. If you need to make changes to your project, give reasons in this section.
- Round off with a reassuring paragraph that your research is on schedule. Give a summary of goals you will be working on next and when you expect to complete them.
Progress reports are an essential part of the research. They help to manage projects and secure funding. Many stakeholders need to know that you have completed certain stages of your project before releasing further funds.
Have you written any progress reports? Let us know how you manage your projects in the comments section below.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- AI in Academia
AI vs AI: How to detect image manipulation and avoid academic misconduct
The scientific community is facing a new frontier of controversy as artificial intelligence (AI) is…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Need for Diversifying Academic Curricula: Embracing missing voices and marginalized perspectives
In classrooms worldwide, a single narrative often dominates, leaving many students feeling lost. These stories,…

- Career Corner
- Trending Now
Recognizing the signs: A guide to overcoming academic burnout
As the sun set over the campus, casting long shadows through the library windows, Alex…

Reassessing the Lab Environment to Create an Equitable and Inclusive Space
The pursuit of scientific discovery has long been fueled by diverse minds and perspectives. Yet…

- Reporting Research
How to Improve Lab Report Writing: Best practices to follow with and without AI-assistance
Imagine you’re a scientist who just made a ground-breaking discovery! You want to share your…
13 Behavioral Questions & Tips to Answer Them Like a Pro!
7 Steps of Writing an Excellent Academic Book Chapter
When Your Thesis Advisor Asks You to Quit

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
51+ SAMPLE Research Progress Report in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages

Research Progress Report | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages
51+ sample research progress report, what is a research progress report, different types of research progress report, basic elements of a research progress report, how to write a research progress report, what are some examples of research progress reports, why is a research progress report important, what are the significant steps in writing a research progress report, how to write a phd progress report.

Research Progress Report Template

Research Performance Progress Report

Research Internship Progress Report

Research Progress and Advisory Committee Meeting Report
Graduate Student Research Progress Tracking Report

Annual Research Progress Report
Graduate Student Research Progress Report

Human Subjects Research Progress Report

Research Progress Report Proposal
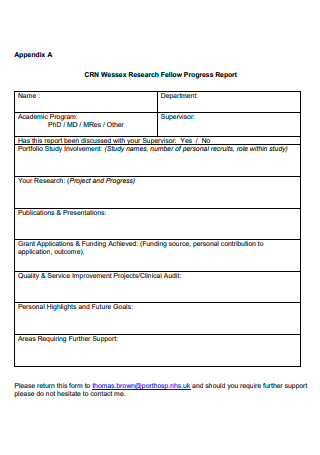
Research Progress Report Example

Printable Research Progress Report
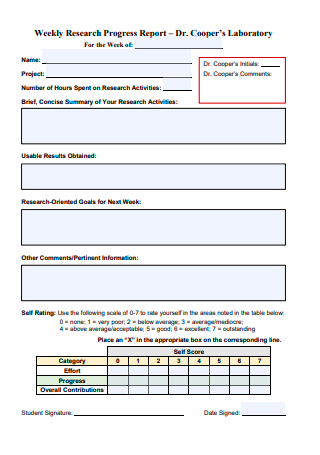
Weekly Research Progress Report

Sample Research Progress Report

Research Center Progress Report Format

Graduate Research Grant Progress Report

Quarterly Research Progress Report
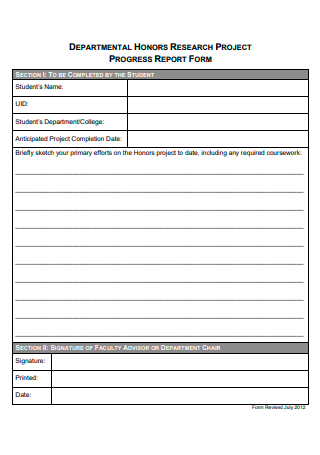
Research Project Progress Report Form

Research Training Progress Report

Competitive Research Grant One Year Progress Report

Basic Research Progress Report

Formal Research Progress Report

Research Support Program Progress Report

Research Progress Report in PDF

Agricultural Research Student Progress Report

Science Research Project Progress Report

Ph.D Research Progress Report

Sponsored Research Progress Report

Research Awards Performance Progress Report
Program Research Progress Report

Human Research Progress Report

Faculty Research Proposal Progress Report

Research Ethic Board Annual Progress Report

Funded Research Progress Report

Research Grant Progress Report

Dissertation Research Progress Report
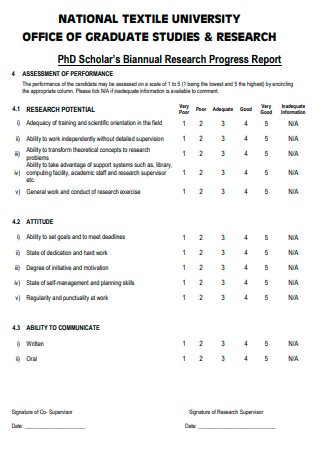
Scholars Bi-Annual Research Progress Report

Research Progress Report Summary

Research In Progress Report

Research Foundation Annual Progress Report

Simple Research Progress Report

Post Graduate Student Research Work Progress Report Form

Standard Research Progress Report

Research Administration Progress Report

Research Progress Report Evaluation Form

Quarterly Research Performance Progress Report

Student Water Research Grant Progress Report Form

Research and Development Progress Report
Research Project Review and Progress Report
Research Student Progress Report
Student Research Project Work Progress Report

Research Student Annual Review Progress Report

Cancer Research Progress Report Summary
1. research performance progress report, 2. research internship progress report , 3. research administration progress report, 4. research center progress report format, step 1: create a cover page, step 2: make the executive summary, step 3: define the participants of the research program, step 4: describe the research project accomplishments, step 5: proofread, revise, and prepare the final research progress report, share this post on your network, file formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 12+ sample construction daily report in ms word | pdf.
Introducing our comprehensive sample Construction Daily Report the cornerstone of effective project management in the construction industry. With this easy-to-use report, you'll gain valuable insights into daily activities report,…
25+ SAMPLE Food Safety Reports in PDF | MS Word

Proper food handling ensures that the food we intake is clean and safe. If not, then we expose ourselves to illnesses and food poisoning. Which is why a thorough…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
The state of diversity in US private equity
It’s been almost two years since the killing of George Floyd provided the spark for a racial reckoning in the United States, which inspired many public and private institutions globally to renew their focus on diversity, equity, and inclusion (DE&I). Within the last year, numerous private equity (PE) firms have accelerated efforts to ensure tangible strides in the diversity of their workforce. In this article, we step back to examine recent North American statistics, assess the industry’s progress to date, and contemplate PE’s DE&I priorities for the next year.
Based on recent data, North American PE has made strides on the diversity of talent within their firms:
- US PE firms have increased their percentage of ethnically diverse talent and women employees, surpassing corporate America at their junior levels.
- Promotion rates for women are increasing at all levels at and above principal/director, with women today comprising roughly the same percentage of the total workforce in midlevel positions (roughly 30 to 35 percent) in PE as in corporate America.
- 2020 saw a significant bump in the percentage of women promoted into the C-suite of PE firms, surpassing the rate of men (6 percent of eligible women were promoted compared with 1 percent of eligible men).
However, there is more work to be done on DE&I for PE:
- PE is behind corporate America in ethnic diversity in the C-suite, and the ethnic diversity PE maintains earlier in the talent pipeline primarily comprises Asian employees, with low representation from Black and Hispanic and Latinx populations.
- Gender parity for promotions is lacking at all steps in the pipeline up to the managing director (MD) role, and the number of women in the uppermost roles, particularly in the C-suite, continues to be minute. For PE to continue its DE&I progress, it’s crucial for the industry to focus on gender parity for promotions to vice president (VP), principal/director, MD, and C-suite roles.
- Furthermore, firmwide diversity statistics tend to mask the disparity on deal teams, as greater gender and ethnic diversity typically exist in noninvesting and support functions of PE firms.
The data that follow (see sidebar, “Our methodology”) identify key aspects of the PE talent pipeline where recent progress has been made and where the industry falls behind corporate America. We conclude with insights from an industry icon, Sandra Horbach, head of US buyout and growth for Carlyle, as well as steps PE leaders could take in the next year to accelerate DE&I efforts .
Ethnic diversity: Some progress, with important caveats
The US PE firms we analyzed have been more ethnically diverse at entry-level through principal/director roles than corporate America for the past few years. PE also roughly matches the corporate world in the percentage of people of color (POC) who are MDs or MD equivalents.
Our methodology
Data included in this article come from the 2021 Women in the Workplace report , which is based on research from 423 companies across the United States and Canada, building on similar research conducted annually by McKinsey and LeanIn.Org since 2015, as well as research from McKinsey in 2012. In addition, more than 65,000 employees from 88 companies were surveyed on their workplace experiences. PE data come from analysis of roughly 30,000 employees in North American PE firms, encompassing 18 large and medium-size US-based PE firms, and are part of a larger data set that also looked at 34 banking and consumer finance companies, as well as 49 asset management firms and institutional investors.
Some meaningful caveats temper these statistics. Although PE matches all US companies in POC holding MD or equivalent roles, parity is not overly impressive: in both sectors, only about 16 percent of men and roughly a fifth of women in such roles are POC. Moreover, PE is still far behind US corporations in ethnic diversity at the C-suite level: only approximately 11 percent of C-suite executives are ethnically diverse (compared with closer to 20 percent of corporate America’s executives) (Exhibit 1).
PE has led corporate America for some time on the ethnic diversity of entry-level ranks—and recently pulled ahead on gender diversity in junior roles
While PE has often been viewed as behind on ethnic and gender diversity, in fact, our Women in the Workplace reports reveal that PE firms have been more ethnically diverse at junior levels than corporate America for the past few years. That is primarily due to the disproportionate hiring of Asians, who constitute more than 60 percent of POC in PE today and are close to double (at 24 percent) the workforce in junior roles than in the corporate sphere (where Asians represent about 13 to 14 percent of the workforce).
Despite the headwinds of the COVID-19 pandemic, PE saw growth in the percentage of White women entering the industry. More women entered the arena at both the entry/associate and senior-associate levels in PE compared with the corporate sphere (Exhibit 2). This recent increase in PE’s gender diversity is notable not only because the percentage of women in junior-level roles in PE now exceeds women in junior-level roles in corporate America but also because this female majority provides hope for gender parity over time in PE’s more senior ranks.
PE still is behind corporate America on gender diversity at the top
The PE firms we examined are still behind corporate America on diversity at the senior levels, with only 20 percent women MDs in PE compared with 27 percent women senior vice presidents or C-suite leaders who report directly to the CEO in corporate America. That discrepancy is even larger as you look across the C-suite (15 percent in PE compared with 24 percent in corporate America) (Exhibit 3).
PE firms that aspire to improve gender diversity at the top may want to examine external hiring, retention, and promotion processes through to the MD level.
Many women investors believe their gender is an obstacle to promotion in their PE careers
A poll of women investors at the October 2021 McKinsey’s Women in Private Equity Global Forum 1 One hundred and forty-three women across North American and European private equity and principal investing firms joined the October 26, 2021, McKinsey Women in Private Equity Forum, representing 46 firms. Sixty-five women answered the North American female investor poll, representing all levels of the deal team and comprising 24 PE firms and pensions in North America. found that 54 percent reported believing “my career trajectory is limited or evaluation for promotion is somewhat slowed due to my gender.” The poll also revealed that 38 percent of respondents reported believing “my promotion is not affected by my gender,” and 8 percent felt their gender was an advantage.
Indeed, these statistics on sentiment reflect the reality for women across PE firms as a whole (in investing and noninvesting roles) at junior levels in PE today. Over the past two years, men in PE were promoted at higher rates than women in almost all roles, with only the percentage of women promoted into the C-suite surpassing the rate of men. While the total number of overall promotions in PE declined in 2020 (compared with pre-COVID-19 levels in 2019), the delta in gender promotion parity grew for junior ranks (that is, VP and senior-associate promotions).
However, statistics on the promotion of women into PE’s senior ranks do suggest some positive signs of change: at each level above VP, the delta between eligible men and women being promoted narrowed in 2020, with significant jumps in promotion percentages for women (Exhibit 4).
While total numbers remain small, US PE has made significant strides toward promotion parity on gender for the most senior positions in 2020
While the gap in promotion rates by gender shrunk for the top half of the PE funnel, given the innate disparity in the base numbers to date, there are still very few women in top leadership positions in PE. Hypothetically, if we were to consider a US PE firm with 100 VPs and 75 principal/directors—in 2020, three women and six men would have been promoted to principal/director, and one woman and five men would have been promoted to MD. Whereas in 2019, using the hypothetical firm, only two women and 11 men would have been promoted to principal/director, and zero women and seven men to MD (Exhibit 5).
Therefore, despite strides in hiring at entry-level roles, to improve gender representation throughout the pipeline, PE must focus on debiasing promotion processes and providing equitable coaching and sponsorship of women to achieve promotion parity between the genders and to ultimately improve the representation of women at mid and senior levels in US PE firms.
To improve gender representation throughout the pipeline, PE must focus on debiasing promotion processes and providing equitable coaching and sponsorship of women.
The next wave in PE DE&I improvements will focus on defining the bar
Despite the progress in promotion rates at the senior level in the past year, the absolute number of new women senior executives is still drastically lower than men (today, only one in five MDs in investing and noninvesting roles is a woman). To continue to progress in retaining and promoting diverse talent, PE firms must focus on defining the bar for each role within the investing hierarchy. The next wave of DE&I progress for PE will occur by firms articulating expected outcomes or performance milestones and core capabilities for each role. By doing this, PE will also take a key step toward debiasing the feedback and promotion processes, thereby creating a more equitable and inclusive playing field, where diverse talent can excel with fewer headwinds.
At McKinsey’s Women in Private Equity Forum in October 2021, Sandra Horbach, renowned leader in the PE space, and MD and cohead of US buyout and growth at Carlyle, shared tips with women professionals in investing roles on succeeding in PE 2 Ms. Horbach was the keynote speaker at the forum. :
Here’s my advice. I would say, “Keep at it.” If you feel like your career is going to be limited, go and find other firms. There are so many firms out there now. The most important thing is to be brave. Be your own advocate, and don’t cower away from the challenging assignments. In fact, volunteer [for them].
(The full interview is available here .) Ms. Horbach’s advice rings true: despite the progress on DE&I over the past two years, realizing a new, more equitable culture that permeates PE will take time. Women (and other underrepresented groups) continue to need to take it upon themselves and “keep at it” as they push to advance in their careers in PE.
However, we are seeing leading PE firms push to redefine recruiting, hiring, and promotion processes for investing roles, further examining potential biases at play in their definition of a successful hire or MD at their firms today. They are recognizing a need for transparency on the desired skills, capabilities, and, above all, the outcomes that a leader in their firm achieves. By pinpointing the skills and expected professional outcomes for each level, firms minimize the primacy of the style with which success is achieved and zero in on actual achievements. People of diverse gender and ethnic backgrounds may have different approaches to challenges that are no less effective than the styles more familiar to today’s PE MDs. Defining the results that matter for each role is crucial to broadening the lens, without lowering the bar, for candidates to receive equitable sponsorship, mentorship, debiased feedback, and ultimately fair promotion.
Defining the results that matter for each role is crucial to broadening the lens, without lowering the bar.
Within the last year, numerous firms have accelerated efforts to ensure tangible advancement in diversity metrics. While the industry has helped itself by introducing classes of entry-level employees with more ethnic and gender diversity than prior years, the gap in promotion parity at the first rung has simultaneously grown and exists in some form thereafter through each level to MD. This gap limits the diverse mix of talent that can flow up to upper-management ranks. To change that, a culture shift needs to take place within firms’ hiring, retention, and promotion practices. Horbach’s comments recognize the need to make this shift: “You can have the best policies in the world, but you also need a culture that supports diverse employees,” she said.
The business case for diversity is clear across industries, but particularly in PE. Increasingly, institutional investors are demanding that GPs provide and improve upon diversity metrics for their firms and portfolios in order to raise new capital. But the need to improve upon the diversity of talent in PE goes beyond fundraising. As Horbach shared, “The most successful deal teams continually develop their network and relationships.… I always say if you meet a management team for the first time at a management meeting, you have already lost the deal.” Diverse deal teams bring a broader set of relationships, perspectives, and experiences that can be crucial to relating to management teams and, ultimately, to closing deals. In an increasingly competitive industry, diversity is an edge that counts.

The authors wish to thank Claudy Jules for thought leadership on PE DE&I topics and Krista Frysinger and Lara Sibinelli for contributions to this article.
This article was edited by Katy McLaughlin, a senior editor in the Southern California office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

How private equity can catalyze diversity, equity, and inclusion in the workplace

Women in the Workplace 2022

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Think of it as a Q&A. Before you start worrying about your reporting frequency and whether you should provide monthly reports or weekly reports, take a step back and focus on the purpose of the report itself. In essence, the reporting process comes down to Q&A; you're answering key questions about your progress.
Here are some tips that will get you started with your research progress report. 1. Write the Title of Your Report. The title of your report should at least be about what your research is about. It does not have to be something too fancy that the whole point of the report is lost or too obvious that would make the report redundant. 2.
A progress report is a vital tool in project management, designed to keep different types of stakeholders informed about the ongoing status of a project. It's a concise document highlighting current achievements, challenges, and goals, allowing the project manager to track progress and make necessary adjustments.
NIH IMPAC II Database: Comprehensive NIH-Wide grant information, including applications, payments, specific aims, progress reports, publications, etc. RPPR: Progress report module. Review Module: Reviewers and review staff interact to submit scores. xTRAIN: Trainee appointment module for T32 and R25.
Make sure to include: the purpose of the report, introduce the project, remind that this is an update on the progress of the project. 5. Do the body of the proposal. The body of proposal, whether it's broken into sections and subsections, is basically just a more detailed version of the introduction.
Now that we've talked about the perks of using a progress report to visualize your company's projects, let's dig into the good stuff. Here's how to write a detailed progress report: 1. Determine your report's objectives. Of course, your report will have different objectives depending on the format.
Best Practices for Creating an Effective Progress Report. Creating an effective progress report involves following some best practices: Keep your report clear and straightforward, avoiding jargon or overly complex language. Highlight the most important information, emphasizing achievements and addressing challenges.
Step 1. Explain the purpose of your report. There are many reasons for someone to write a progress report. Obviously, for many of them, it's to brief the progress and status of the project. Readers might also want to know detailed information about the project's purpose, its duration, and other important insights. Step 2.
There are three types of RPPRs, all of which use the NIH RPPR Instruction Guide. Annual RPPR - Use to describe a grant's scientific progress, identify significant changes, report on personnel, and describe plans for the subsequent budget period or year. Final RPPR - Use as part of the grant closeout process to submit project outcomes in ...
Determine the appropriate organizational pattern - chronological, priority, or topic - for the body of the report. Include an Introduction, body, conclusion, and references (if appropriate). In the body section, address the following items: summarize and evaluate research findings to date. present the project schedule.
Here are some tips to help customize a generic template: Make sections clear — Clearly outline the sections of your progress report, and let everyone know what you'll be addressing in each section. Remember the key sections: activities, progress made, challenges or blockers encountered, and actions and next steps.
Choose an appropriate frequency - For ongoing progress reports, think about whether to schedule daily, weekly, or monthly updates. Write clearly - Make sure to write clearly and concisely. Keep your sentences simple, straightforward, and easy to understand. Know your audience - If you're writing a report for someone outside of your ...
Writing a progress/status report by Michael Ernst January, 2010. Writing a weekly report about your research progress can make your research more successful, less frustrating, and more visible to others, among other benefits. One good format is to write your report in four parts: Quote the previous week's plan. This helps you determine whether ...
Step 1: clarify goals and timeline. First, you need to briefly explain the project to give context to the rest of the report. Clarifying project goals and timelines brings priorities to the surface to make it easier for stakeholders reading the report to catch up. Details to include:
Progress Report. A progress report provides an update on the progress of a research project or program over a specific period of time. Progress reports are typically used to communicate the status of a project to stakeholders, funders, or project managers. ... Overall, the timing of when to write a research report depends on the purpose of the ...
Sample Progress Report. The following short progress report, written by a student in geology, provides an excellent example of how concrete and affirmative a progress report can be. Note the specificity even in the title, and how sections such as "Remaining Questions" and "Expected Results" demonstrate that the writer, even though he is two ...
1. Abstract. Present the background of your research project, list its main goals, describe the methods to be used and the expected results as well as their impact for the field and beyond. 2. Progress to Date. Present the research work you have undertaken since your last progress report, describe the results obtained (including publications ...
You write a progress report to inform a supervisor, associate, or client about progress you have made on a project over a specific period of time. Periodic progress reports are common on projects that go on for several months (or more). Whoever is paying for this project wants to know whether tasks are being completed on schedule and on budget.
Style for Progress Reports. The following stylistic advice can be applied to most progress reports you write: Include a working title and the words "Progress Report" at the top of the page. Use section headings in the report to simplify both the writing and reading process. Open the report with a "Scope and Purpose" section, where you give a ...
Monthly: once a month we write a formal progress report of our work and meet on a one-to-one basis to discuss it. Purpose of Progress Reports. Your report should include your results obtained so far, experiments you are working on, plans for future work and any problems you might have with your work. It is a report on your overall plan.
Step 3: Define the Participants of the Research Program. If you are creating an annual progress report, list the organizations currently participating in the research project, state the type of organizations for each business/industry, university, non-profit, etc., and describe the type and level of each involvement.
Use the section headings (outlined above) to assist with your rough plan. Write a thesis statement that clarifies the overall purpose of your report. Jot down anything you already know about the topic in the relevant sections. 3 Do the Research. Steps 1 and 2 will guide your research for this report.
Abstract. This guide for writers of research reports consists of practical suggestions for writing a report that is clear, concise, readable, and understandable. It includes suggestions for terminology and notation and for writing each section of the report—introduction, method, results, and discussion. Much of the guide consists of ...
products of your research (e.g., talks, papers, poster, software, etc.). Was there a change in direction of research and/or advisor, and how was it motivated? Keep in mind that your input also serves the advisor(s), readers, and your mentor to . assess your progress, so please formulate clearly and concisely. P. rovide some . minimal . context ...
Data included in this article come from the 2021 Women in the Workplace report, which is based on research from 423 companies across the United States and Canada, building on similar research conducted annually by McKinsey and LeanIn.Org since 2015, as well as research from McKinsey in 2012.In addition, more than 65,000 employees from 88 companies were surveyed on their workplace experiences.