
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Variations in Fetal Position and Presentation |
During pregnancy, the fetus can be positioned in many different ways inside the mother's uterus. The fetus may be head up or down or facing the mother's back or front. At first, the fetus can move around easily or shift position as the mother moves. Toward the end of the pregnancy the fetus is larger, has less room to move, and stays in one position. How the fetus is positioned has an important effect on delivery and, for certain positions, a cesarean delivery is necessary. There are medical terms that describe precisely how the fetus is positioned, and identifying the fetal position helps doctors to anticipate potential difficulties during labor and delivery.
Presentation refers to the part of the fetus’s body that leads the way out through the birth canal (called the presenting part). Usually, the head leads the way, but sometimes the buttocks (breech presentation), shoulder, or face leads the way.
Position refers to whether the fetus is facing backward (occiput anterior) or forward (occiput posterior). The occiput is a bone at the back of the baby's head. Therefore, facing backward is called occiput anterior (facing the mother’s back and facing down when the mother lies on her back). Facing forward is called occiput posterior (facing toward the mother's pubic bone and facing up when the mother lies on her back).
Lie refers to the angle of the fetus in relation to the mother and the uterus. Up-and-down (with the baby's spine parallel to mother's spine, called longitudinal) is normal, but sometimes the lie is sideways (transverse) or at an angle (oblique).
For these aspects of fetal positioning, the combination that is the most common, safest, and easiest for the mother to deliver is the following:
Head first (called vertex or cephalic presentation)
Facing backward (occiput anterior position)
Spine parallel to mother's spine (longitudinal lie)
Neck bent forward with chin tucked
Arms folded across the chest
If the fetus is in a different position, lie, or presentation, labor may be more difficult, and a normal vaginal delivery may not be possible.
Variations in fetal presentation, position, or lie may occur when
The fetus is too large for the mother's pelvis (fetopelvic disproportion).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains growths such as fibroids .
The fetus has a birth defect .
There is more than one fetus (multiple gestation).

Position and Presentation of the Fetus
Variations in fetal position and presentation.
Some variations in position and presentation that make delivery difficult occur frequently.
Occiput posterior position
In occiput posterior position (sometimes called sunny-side up), the fetus is head first (vertex presentation) but is facing forward (toward the mother's pubic bone—that is, facing up when the mother lies on her back). This is a very common position that is not abnormal, but it makes delivery more difficult than when the fetus is in the occiput anterior position (facing toward the mother's spine—that is facing down when the mother lies on her back).
When a fetus faces up, the neck is often straightened rather than bent,which requires more room for the head to pass through the birth canal. Delivery assisted by a vacuum device or forceps or cesarean delivery may be necessary.
Breech presentation
In breech presentation, the baby's buttocks or sometimes the feet are positioned to deliver first (before the head).
When delivered vaginally, babies that present buttocks first are more at risk of injury or even death than those that present head first.
The reason for the risks to babies in breech presentation is that the baby's hips and buttocks are not as wide as the head. Therefore, when the hips and buttocks pass through the cervix first, the passageway may not be wide enough for the head to pass through. In addition, when the head follows the buttocks, the neck may be bent slightly backwards. The neck being bent backward increases the width required for delivery as compared to when the head is angled forward with the chin tucked, which is the position that is easiest for delivery. Thus, the baby’s body may be delivered and then the head may get caught and not be able to pass through the birth canal. When the baby’s head is caught, this puts pressure on the umbilical cord in the birth canal, so that very little oxygen can reach the baby. Brain damage due to lack of oxygen is more common among breech babies than among those presenting head first.
In a first delivery, these problems may occur more frequently because a woman’s tissues have not been stretched by previous deliveries. Because of risk of injury or even death to the baby, cesarean delivery is preferred when the fetus is in breech presentation, unless the doctor is very experienced with and skilled at delivering breech babies or there is not an adequate facility or equipment to safely perform a cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation is more likely to occur in the following circumstances:
Labor starts too soon (preterm labor).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains abnormal growths such as fibroids .
Other presentations
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.
In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.
Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor. If they do not, a cesarean delivery is usually recommended.
In transverse lie, the fetus lies horizontally across the birth canal and presents shoulder first. A cesarean delivery is done, unless the fetus is the second in a set of twins. In such a case, the fetus may be turned to be delivered through the vagina.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Appointments at Mayo Clinic
- Pregnancy week by week
- Fetal presentation before birth
The way a baby is positioned in the uterus just before birth can have a big effect on labor and delivery. This positioning is called fetal presentation.
Babies twist, stretch and tumble quite a bit during pregnancy. Before labor starts, however, they usually come to rest in a way that allows them to be delivered through the birth canal headfirst. This position is called cephalic presentation. But there are other ways a baby may settle just before labor begins.
Following are some of the possible ways a baby may be positioned at the end of pregnancy.
Head down, face down
When a baby is head down, face down, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput anterior position. This the most common position for a baby to be born in. With the face down and turned slightly to the side, the smallest part of the baby's head leads the way through the birth canal. It is the easiest way for a baby to be born.
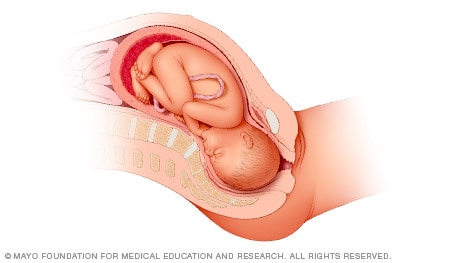
Head down, face up
When a baby is head down, face up, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput posterior position. In this position, it might be harder for a baby's head to go under the pubic bone during delivery. That can make labor take longer.
Most babies who begin labor in this position eventually turn to be face down. If that doesn't happen, and the second stage of labor is taking a long time, a member of the health care team may reach through the vagina to help the baby turn. This is called manual rotation.
In some cases, a baby can be born in the head-down, face-up position. Use of forceps or a vacuum device to help with delivery is more common when a baby is in this position than in the head-down, face-down position. In some cases, a C-section delivery may be needed.
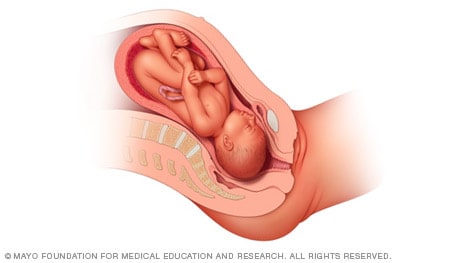
Frank breech
When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a frank breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Most babies in a frank breech position are born by planned C-section.

Complete and incomplete breech
A complete breech presentation, as shown below, is when the baby has both knees bent and both legs pulled close to the body. In an incomplete breech, one or both of the legs are not pulled close to the body, and one or both of the feet or knees are below the baby's buttocks. If a baby is in either of these positions, you might feel kicking in the lower part of your belly.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a complete or incomplete breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies in a complete or incomplete breech position are born by planned C-section.

When a baby is sideways — lying horizontal across the uterus, rather than vertical — it's called a transverse lie. In this position, the baby's back might be:
- Down, with the back facing the birth canal.
- Sideways, with one shoulder pointing toward the birth canal.
- Up, with the hands and feet facing the birth canal.
Although many babies are sideways early in pregnancy, few stay this way when labor begins.
If your baby is in a transverse lie during week 37 of your pregnancy, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of your health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a transverse lie, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies who are in a transverse lie are born by C-section.
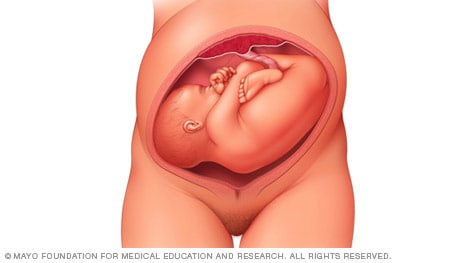
If you're pregnant with twins and only the twin that's lower in the uterus is head down, as shown below, your health care provider may first deliver that baby vaginally.
Then, in some cases, your health care team may suggest delivering the second twin in the breech position. Or they may try to move the second twin into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
Your health care team may suggest delivery by C-section for the second twin if:
- An attempt to deliver the baby in the breech position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to have the baby delivered vaginally in the breech position.
- An attempt to move the baby into a head-down position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to move the baby to a head-down position.
In some cases, your health care team may advise that you have both twins delivered by C-section. That might happen if the lower twin is not head down, the second twin has low or high birth weight as compared to the first twin, or if preterm labor starts.
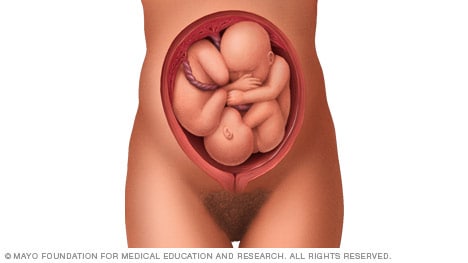
- Landon MB, et al., eds. Normal labor and delivery. In: Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Holcroft Argani C, et al. Occiput posterior position. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Frequently asked questions: If your baby is breech. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/if-your-baby-is-breech. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Hofmeyr GJ. Overview of breech presentation. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Strauss RA, et al. Transverse fetal lie. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Chasen ST, et al. Twin pregnancy: Labor and delivery. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Cohen R, et al. Is vaginal delivery of a breech second twin safe? A comparison between delivery of vertex and non-vertex second twins. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine. 2021; doi:10.1080/14767058.2021.2005569.
- Marnach ML (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. May 31, 2023.
Products and Services
- A Book: Obstetricks
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy
- 3rd trimester pregnancy
- Fetal development: The 3rd trimester
- Overdue pregnancy
- Pregnancy due date calculator
- Prenatal care: 3rd trimester
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
- Healthy Lifestyle
Your gift holds great power – donate today!
Make your tax-deductible gift and be a part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine.

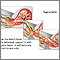
Cephalic presentation
October 14, 2016
A cephalic presentation or head presentation or head-first presentation is a situation at childbirth where the fetus is in a longitudinal lie and the head enters the pelvis first; the most common form of cephalic presentation is the vertex presentation where the occiput is the leading part (the part that first enters the birth canal). All other presentations are abnormal (malpresentations) which are either more difficult to deliver or not deliverable by natural means.
The movement of the fetus to cephalic presentation is called head engagement. It occurs in the third trimester. In head engagement, the fetal head descends into the pelvic cavity so that only a small part (or none) of it can be felt abdominally. The perineum and cervix are further flattened and the head may be felt vaginally. Head engagement is known colloquially as the baby drop, and in natural medicine as the lightening because of the release of pressure on the upper abdomen and renewed ease in breathing. However, it severely reduces bladder capacity, increases pressure on the pelvic floor and the rectum, and the mother may experience the perpetual sensation that the fetus will “fall out” at any moment.
The vertex is the area of the vault bounded anteriorly by the anterior fontanelle and the coronal suture, posteriorly by the posterior fontanelle and the lambdoid suture and laterally by 2 lines passing through the parietal eminences.
In the vertex presentation the occiput typically is anterior and thus in an optimal position to negotiate the pelvic curve by extending the head. In an occiput posterior position, labor becomes prolonged and more operative interventions are deemed necessary. The prevalence of the persistent occiput posterior is given as 4.7 %
The vertex presentations are further classified according to the position of the occiput, it being right, left, or transverse, and anterior or posterior:
Left Occipito-Anterior (LOA), Left Occipito-Posterior (LOP), Left Occipito-Transverse (LOT); Right Occipito-Anterior (ROA), Right Occipito-Posterior (ROP), Right Occipito-Transverse (ROT);
By Mikael Häggström – Own work, Public Domain
Cephalic presentation. (2016, September 17). In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia . Retrieved 05:18, September 17, 2016, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Cephalic_presentation&oldid=739815165
Insert/edit link
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Supplements
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
What Is Cephalic Position?
The ideal fetal position for labor and delivery
- Why It's Best
Risks of Other Positions
- Determining Position
- Turning a Fetus
The cephalic position is when a fetus is head down when it is ready to enter the birth canal. This is one of a few variations of how a fetus can rest in the womb and is considered the ideal one for labor and delivery.
About 96% of babies are born in the cephalic position. Most settle into it between the 32nd and 36th weeks of pregnancy . Your healthcare provider will monitor the fetus's position during the last weeks of gestation to ensure this has happened by week 36.
If the fetus is not in the cephalic position at that point, the provider may try to turn it. If this doesn't work, some—but not all—practitioners will attempt to deliver vaginally, while others will recommend a Cesarean (C-section).
Getty Images
Why Is the Cephalic Position Best?
During labor, contractions dilate the cervix so the fetus has adequate room to come through the birth canal. The cephalic position is the easiest and safest way for the baby to pass through the birth canal.
If the fetus is in a noncephalic position, delivery becomes more challenging. Different fetal positions have a range of difficulties and varying risks.
A small percentage of babies present in noncephalic positions. This can pose risks both to the fetus and the mother, and make labor and delivery more challenging. It can also influence the way in which someone can deliver.
A fetus may actually find itself in any of these positions throughout pregnancy, as the move about the uterus. But as they grow, there will be less room to tumble around and they will settle into a final position.
It is at this point that noncephalic positions can pose significant risks.
Cephalic Posterior
A fetus may also present in an occiput or cephalic posterior position. This means they are positioned head down, but they are facing the abdomen instead of the back.
This position is also nicknamed "sunny-side up."
Presenting this way increases the chance of a painful and prolonged delivery.
There are three different types of breech fetal positioning:
- Frank breech: The legs are up with the feet near the head.
- Footling breech: One or both legs is lowered over the cervix.
- Complete breech: The fetus is bottom-first with knees bent.
A vaginal delivery is most times a safe way to deliver. But with breech positions, a vaginal delivery can be complicated.
When a baby is born in the breech position, the largest part—its head—is delivered last. This can result in them getting stuck in the birth canal (entrapped). This can cause injury or death.
The umbilical cord may also be damaged or slide down into the mouth of the womb, which can reduce or cut off the baby's oxygen supply.
Some providers are still comfortable performing a vaginal birth as long as the fetus is doing well. But breech is always a riskier delivery position compared with the cephalic position, and most cases require a C-section.
Likelihood of a Breech Baby
You are more likely to have a breech baby if you:
- Go into early labor before you're full term
- Have an abnormally shaped uterus, fibroids , or too much amniotic fluid
- Are pregnant with multiples
- Have placenta previa (when the placenta covers the cervix)
Transverse Lie
In transverse lie position, the fetus is presenting sideways across the uterus rather than vertically. They may be:
- Down, with the back facing the birth canal
- With one shoulder pointing toward the birth canal
- Up, with the hands and feet facing the birth canal
If a transverse lie is not corrected before labor, a C-section will be required. This is typically the case.
Determining Fetal Position
Your healthcare provider can determine if your baby is in cephalic presentation by performing a physical exam and ultrasound.
In the final weeks of pregnancy, your healthcare provider will feel your lower abdomen with their hands to assess the positioning of the baby. This includes where the head, back, and buttocks lie
If your healthcare provider senses that the fetus is in a breech position, they can use ultrasound to confirm their suspicion.
Turning a Fetus So They Are in Cephalic Position
External cephalic version (ECV) is a common, noninvasive procedure to turn a breech baby into cephalic position while it's still in the uterus.
This is only considered if a healthcare provider monitors presentation progress in the last trimester and notices that a fetus is maintaining a noncephalic position as your delivery date approaches.
External Cephalic Version (ECV)
ECV involves the healthcare provider applying pressure to your stomach to turn the fetus from the outside. They will attempt to rotate the head forward or backward and lift the buttocks in an upward position. Sometimes, they use ultrasound to help guide the process.
The best time to perform ECV is about 37 weeks of pregnancy. Afterward, the fetal heart rate will be monitored to make sure it’s within normal levels. You should be able to go home after having ECV done.
ECV has a 50% to 60% success rate. However, even if it does work, there is still a chance the fetus will return to the breech position before birth.
Natural Methods For Turning a Fetus
There are also natural methods that can help turn a fetus into cephalic position. There is no medical research that confirms their efficacy, however.
- Changing your position: Sometimes a fetus will move when you get into certain positions. Two specific movements that your provider may recommend include: Getting on your hands and knees and gently rocking back and forth. Another you could try is pushing your hips up in the air while laying on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor (bridge pose).
- Playing stimulating sounds: Fetuses gravitate to sound. You may be successful at luring a fetus out of breech position by playing music or a recording of your voice near your lower abdomen.
- Chiropractic care: A chiropractor can try the Webster technique. This is a specific chiropractic analysis and adjustment which enables chiropractors to establish balance in the pregnant person's pelvis and reduce undue stress to the uterus and supporting ligaments.
- Acupuncture: This is a considerably safe way someone can try to turn a fetus. Some practitioners incorporate moxibustion—the burning of dried mugwort on certain areas of the body—because they believe it will enhance the chances of success.
A Word From Verywell
While most babies are born in cephalic position at delivery, this is not always the case. And while some fetuses can be turned, others may be more stubborn.
This may affect your labor and delivery wishes. Try to remember that having a healthy baby, and staying well yourself, are your ultimate priorities. That may mean diverting from your best laid plans.
Speaking to your healthcare provider about turning options and the safest route of delivery may help you adjust to this twist and feel better about how you will move ahead.
Glezerman M. Planned vaginal breech delivery: current status and the need to reconsider . Expert Rev Obstet Gynecol. 2012;7(2):159-166. doi:10.1586/eog.12.2
Cleveland Clinic. Fetal positions for birth .
MedlinePlus. Breech birth .
UT Southwestern Medical Center. Can you turn a breech baby around?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. If your baby is breech .
Roecker CB. Breech repositioning unresponsive to Webster technique: coexistence of oligohydramnios . Journal of Chiropractic Medicine . 2013;12(2):74-78. doi:10.1016/j.jcm.2013.06.003
By Cherie Berkley, MS Berkley is a journalist with a certification in global health from Johns Hopkins University and a master's degree in journalism.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Health Topics
- Drugs & Supplements
- Medical Tests
- Medical Encyclopedia
- About MedlinePlus
- Customer Support
Your baby in the birth canal
During labor and delivery, your baby must pass through your pelvic bones to reach the vaginal opening. The goal is to find the easiest way out. Certain body positions give the baby a smaller shape, which makes it easier for your baby to get through this tight passage.
The best position for the baby to pass through the pelvis is with the head down and the body facing toward the mother's back. This position is called occiput anterior.
Information
Certain terms are used to describe your baby's position and movement through the birth canal.
FETAL STATION
Fetal station refers to where the presenting part is in your pelvis.
- The presenting part. The presenting part is the part of the baby that leads the way through the birth canal. Most often, it is the baby's head, but it can be a shoulder, the buttocks, or the feet.
- Ischial spines. These are bone points on the mother's pelvis. Normally the ischial spines are the narrowest part of the pelvis.
- 0 station. This is when the baby's head is even with the ischial spines. The baby is said to be "engaged" when the largest part of the head has entered the pelvis.
- If the presenting part lies above the ischial spines, the station is reported as a negative number from -1 to -5.
In first-time moms, the baby's head may engage by 36 weeks into the pregnancy. However, engagement may happen later in the pregnancy, or even during labor.
This refers to how the baby's spine lines up with the mother's spine. Your baby's spine is between their head and tailbone.
Your baby will most often settle into a position in the pelvis before labor begins.
- If your baby's spine runs in the same direction (parallel) as your spine, the baby is said to be in a longitudinal lie. Nearly all babies are in a longitudinal lie.
- If the baby is sideways (at a 90-degree angle to your spine), the baby is said to be in a transverse lie.
FETAL ATTITUDE
The fetal attitude describes the position of the parts of your baby's body.
The normal fetal attitude is commonly called the fetal position.
- The head is tucked down to the chest.
- The arms and legs are drawn in towards the center of the chest.
Abnormal fetal attitudes include a head that is tilted back, so the brow or the face presents first. Other body parts may be positioned behind the back. When this happens, the presenting part will be larger as it passes through the pelvis. This makes delivery more difficult.
DELIVERY PRESENTATION
Delivery presentation describes the way the baby is positioned to come down the birth canal for delivery.
The best position for your baby inside your uterus at the time of delivery is head down. This is called cephalic presentation.
- This position makes it easier and safer for your baby to pass through the birth canal. Cephalic presentation occurs in about 97% of deliveries.
- There are different types of cephalic presentation, which depend on the position of the baby's limbs and head (fetal attitude).
If your baby is in any position other than head down, your doctor may recommend a cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation is when the baby's bottom is down. Breech presentation occurs about 3% of the time. There are a few types of breech:
- A complete breech is when the buttocks present first and both the hips and knees are flexed.
- A frank breech is when the hips are flexed so the legs are straight and completely drawn up toward the chest.
- Other breech positions occur when either the feet or knees present first.
The shoulder, arm, or trunk may present first if the fetus is in a transverse lie. This type of presentation occurs less than 1% of the time. Transverse lie is more common when you deliver before your due date, or have twins or triplets.
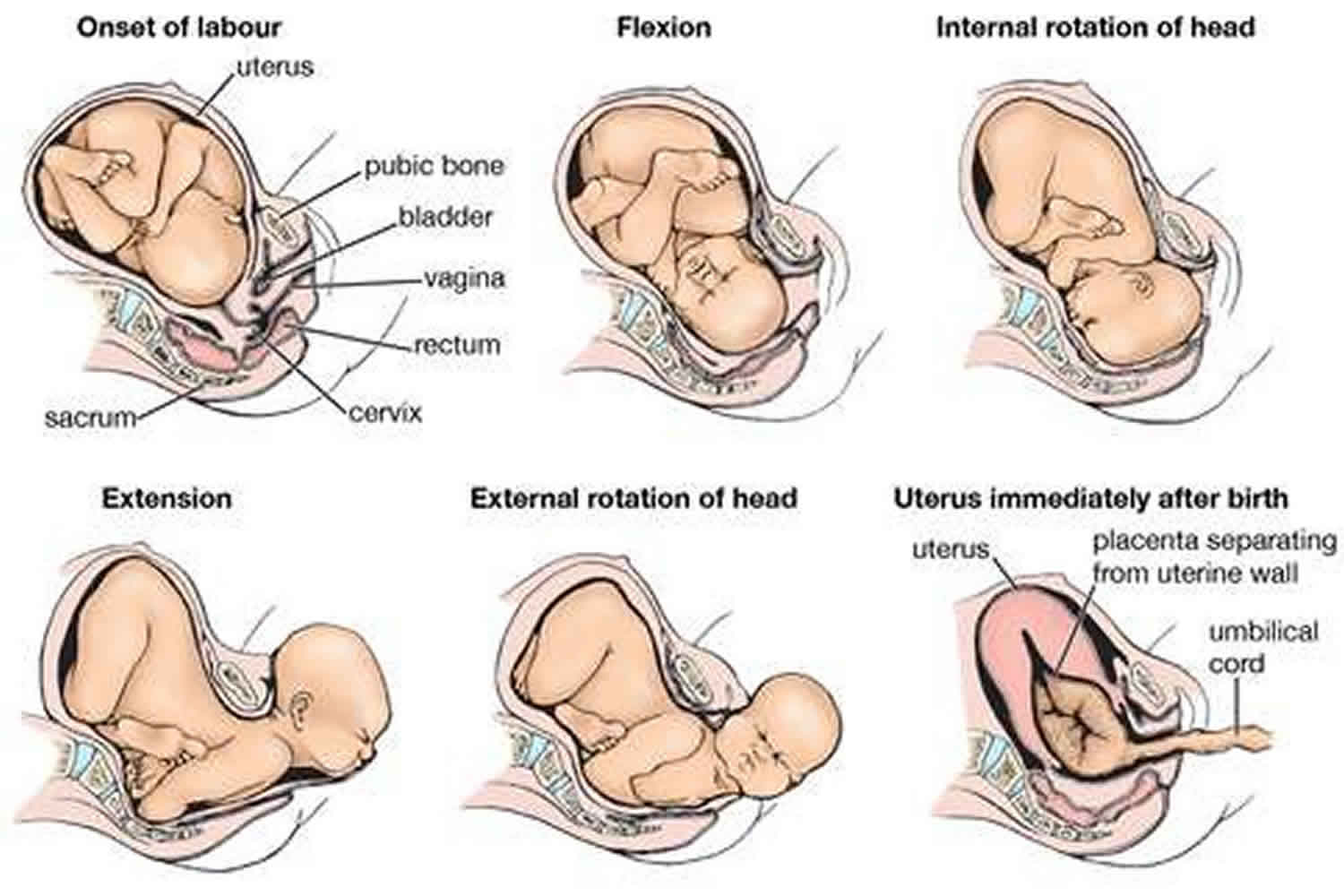
CARDINAL MOVEMENTS OF LABOR
As your baby passes through the birth canal, the baby's head will change positions. These changes are needed for your baby to fit and move through your pelvis. These movements of your baby's head are called cardinal movements of labor.
- This is when the widest part of your baby's head has entered the pelvis.
- Engagement tells your health care provider that your pelvis is large enough to allow the baby's head to move down (descend).
- This is when your baby's head moves down (descends) further through your pelvis.
- Most often, descent occurs during labor, either as the cervix dilates or after you begin pushing.
- During descent, the baby's head is flexed down so that the chin touches the chest.
- With the chin tucked, it is easier for the baby's head to pass through the pelvis.
Internal Rotation
- As your baby's head descends further, the head will most often rotate so the back of the head is just below your pubic bone. This helps the head fit the shape of your pelvis.
- Usually, the baby will be face down toward your spine.
- Sometimes, the baby will rotate so it faces up toward the pubic bone.
- As your baby's head rotates, extends, or flexes during labor, the body will stay in position with one shoulder down toward your spine and one shoulder up toward your belly.
- As your baby reaches the opening of the vagina, usually the back of the head is in contact with your pubic bone.
- At this point, the birth canal curves upward, and the baby's head must extend back. It rotates under and around the pubic bone.
External Rotation
- As the baby's head is delivered, it will rotate a quarter turn to be in line with the body.
- After the head is delivered, the top shoulder is delivered under the pubic bone.
- After the shoulder, the rest of the body is usually delivered without a problem.
Alternative Names
Shoulder presentation; Malpresentations; Breech birth; Cephalic presentation; Fetal lie; Fetal attitude; Fetal descent; Fetal station; Cardinal movements; Labor-birth canal; Delivery-birth canal
Barth WH. Malpresentations and malposition. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 17.
Kilpatrick SJ, Garrison E, Fairbrother E. Normal labor and delivery. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 11.
Review Date 11/10/2022
Updated by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Related MedlinePlus Health Topics
- Childbirth Problems

Cephalic Presentation Definition

Cephalic presentation is the most common type of fetal presentation, in which the baby is in a head-down position in the uterus. In this position, the baby’s head is the first part of the body to come out of the mother’s vagina. Cephalic presentation is also sometimes called vertex presentation, although the latter is only one of the different categories of the former. This fetus turning to this position happens during the last three months of pregnancy.
The process by which the fetus moves from a breech to a cephalic position is known as head engagement. This occurs when the baby’s head is able to move down into the pelvis. The chin and forehead will press against the sacrum, and the occiput will press against the back of the mother’s pubic bone.
Other Types of Cephalic Presentations
The cephalic presentation can be further classified, according to the degree of flexion of the fetal head. A presentation is considered vertex if the fetal head is well-flexed. An incomplete flexion is called a sinciput presentation, a partially deflexed head is called a brow presentation, and a completely extended head is called a face presentation.
This image shows how often the term ‘Cephalic presentation” is used in relation to other, similar birth terms:

Other Types of Fetal Presentations
There are other types of presentations , including breech presentation, shoulder presentation, and transverse presentation . Breech presentation occurs when the baby’s buttocks or feet are the first to come out of the vagina. Shoulder presentation occurs when the baby’s arm or shoulder is the first to come out of the vagina. Transverse presentation occurs when the baby is lying across the uterus, instead of head-down.
These presentations other types of presentations, but they are much less common than cephalic presentation. In fact, breech presentation occurs in only about 3 percent of births, and shoulder presentation occurs in only 1 percent of births. transverse presentation occurs in even fewer pregnancies, about 0.5 percent. Giving birth with these presentations come along with certain risks.
Do you know a man who wants to learn more about birth? Send him our way ! Also, men and women are welcome to join our free public community of Dads helping Dads be better at birth.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
What Are Leopold's Maneuvers?
Ariel Skelley / Getty Images
- What Are Leopold's Maneuvers?
- How Are Leopold's Maneuvers Performed?
Why Are They Performed?
Fetal weight estimate, risks and contraindications.
Leopold's maneuvers are a non-invasive way to estimate your baby's position and size in utero. The four maneuvers are the fundal grip, the umbilical grip, Pawlik's grip, and the pelvic grip. These maneuvers are performed in late pregnancy by trained healthcare providers who palpate (examine by touch) the pregnant person's abdomen to determine the baby's size and placement in the uterus.
"This process allows medical professionals to not only make a birth weight estimate but also address any underlying problems that may occur down the road," explains Mackenzie Schutz , RN. Knowing if the baby is head down is important at the end of pregnancy in order to plan for a safe delivery.
These maneuvers get their name from the influential 19th-century German obstetrician and gynecologist Christian Gerhard Leopold, who discussed and propagated their use among other physicians. They may also be called Leopold maneuvers. Learn more about Leopold's maneuvers, including why, when, and how they are performed during pregnancy.
How Are Leopold's Maneuvers Performed?
There are four distinct maneuvers, each with a different technique.
- Fundal grip : A healthcare provider palpates the upper abdomen with both hands to feel for the fetus's head, trunk, and bottom in order to get an idea of its size and position.
- Pawlik's grip : A provider uses their fingers and thumb to feel what part of the fetus is in the lower abdomen, just above the birth canal, to see if they're in the right position. This maneuver assesses fetal weight and amniotic fluid volume.
- Pelvic grip : A provider moves their fingers towards the pelvis, then slides their hands over the side of the uterus to determine where the fetus's brow is located.
- Umbilical grip : A provider applies deep pressure with the palm of one hand while using the other hand to feel the uterus. This allows them to identify the location of the fetus's back and small parts.
Leopold's maneuvers should only be performed by qualified medical professionals who have received training on how to perform them safely. You shouldn't attempt to do them yourself.
"Leopold maneuvers a wonderful way to determine quickly how the fetus is lying in a person's uterus," explains Kecia Gaither , OB/GYN, doctor of maternal-fetal medicine, and director of perinatal services at NYC Health and Hospitals/Lincoln. "And, in experienced hands, they can give an estimate of fetal weight."
They're also low-cost, non-invasive, and don't require the use of expensive equipment such as an ultrasound . Plus they tell your provider how ready your baby is for birth so they can better prepare for your labor.
Ideal Position
At the beginning of your pregnancy, your fetus will move around your womb freely, but towards the end, they should get into a position that's optimal for vaginal delivery. Before birth, your baby should be head-down, facing your back, with their chin tucked to their chest so that their head is ready to enter the pelvis. This is called the cephalic presentation and it is the ideal position for childbirth.
Most babies will settle into this position between the 32nd and 36th week of pregnancy. This position makes labor less complicated. Around 96% of babies will be born in the cephalic position.
Cephalic Posterior Position
This position is also known as an occiput position or it's sometimes nicknamed "sunny-side-up." It means that your baby is positioned head down, but they're facing out instead of towards your spine. This position could increase your chances of a painful and prolonged delivery.
Breech Position
A breech position means that your baby's bottom is facing downwards. There are three different breech positions:
- Frank breech: The baby's legs are up, with feet near the head
- Footling breech: One or both legs are lowered in the cervix
- Complete breech: The baby's bottom is first and its knees are bent
Any of these positions can make for a riskier delivery, so you are at risk of a C-section delivery if the baby doesn't change position before labor.
Transverse Lie
Your baby might also be in a transverse lie position at the end of the third trimester, which means they are lying sideways across your uterus instead of vertically. If they don't change position, it could make for dangerous labor, so a C-section will be required.
Leopold's maneuvers can also be used to estimate how big your baby is. Fetal weight estimates help your healthcare provider plan for birth, too. In general, a baby who is estimated to be 10 pounds or more might require a C-section birth because your baby could get caught in the birth canal.
There are no known risks for using Leopold's maneuvers, as long as they are being performed by qualified medical professionals. However, they are as accurate at determining the position or estimated weight of your baby before the 36th week of your pregnancy. So, your medical provider will not likely use them before your 36-week checkup.
For your own comfort, your provider will likely ask you to pee before they do the procedure, because a full bladder can make it difficult to really determine your baby's position with accuracy.
Your provider might also not use these maneuvers if you were in an accident. "If blunt force trauma has occurred during pregnancy, it may be best to use an ultrasound to avoid any further bruising that could be worsened by palpating," explains Shutz.
Leopold's maneuvers are typically very accurate, but it is possible that your healthcare provider will still perform an ultrasound prior to your delivery to confirm your baby's position, particularly if they are concerned that your baby has moved or is in a transverse or breech position.
Leopold's maneuvers are difficult to perform on people who are obese because it is difficult to feel the baby's position.
They are also more complicated to perform on patients who have polyhydramnios , which is when you have too much amniotic fluid surrounding your baby, as well as people with fibroids.

A Word From Verywell
Leopold's maneuvers are usually performed after 36 weeks by your healthcare provider to determine your baby's position and estimate their birth weight. This will help you and your provider be better prepared for your labor and determine if it might be safer to perform a c-section. The maneuvers should not hurt and they are very accurate, though your provider might still perform an ultrasound to confirm any findings.
Superville SS, Siccardi MA. Leopold maneuvers. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. If your baby is breech .
Kachlík D, Kästner I, Baca V. Christian Gerhard Leopold: Fascinating history of a productive obstetrician gynecologist . Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2012;67(1):1-5. doi:10.1097/OGX.0b013e31823662d7
Tell N, Omuso I, Hunter K, Khandelwal M. Accuracy of Leopold's maneuver compared to ultrasound in estimating fetal birth weight . Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133(1):23S-24S. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000559397.09291.a3
Glezerman M. Planned vaginal breech delivery: current status and the need to reconsider . Expert Rev Obstet Gynecol . 2012;7(2):159-166. doi:10.1586/eog.12.2
Cleveland Clinic. Fetal positions for birth .
Wei Y, Yang H. [Variation of prevalence of macrosomia and cesarean section and its influencing factors] . Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2015;50(3):170-6. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567x.2015.03.002
Superville SS, Siccardi MA. Leopold maneuvers . In: StatPearls . StatPearls Publishing.
By Simone Scully Simone is the health editorial director for performance marketing at Verywell. She has over a decade of experience as a professional journalist covering pregnancy, parenting, health, medicine, science, and lifestyle topics.
- Getting Pregnant
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
- Birth Clubs
- See all in Community
- Ovulation Calculator
- How To Get Pregnant
- How To Get Pregnant Fast
- Ovulation Discharge
- Implantation Bleeding
- Ovulation Symptoms
- Pregnancy Symptoms
- Am I Pregnant?
- Pregnancy Tests
- See all in Getting Pregnant
- Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Pregnant Sex
- Weight Gain Tracker
- Signs of Labor
- Morning Sickness
- COVID Vaccine and Pregnancy
- Fetal Weight Chart
- Fetal Development
- Pregnancy Discharge
- Find Out Baby Gender
- Chinese Gender Predictor
- See all in Pregnancy
- Baby Name Generator
- Top Baby Names 2023
- Top Baby Names 2024
- How to Pick a Baby Name
- Most Popular Baby Names
- Baby Names by Letter
- Gender Neutral Names
- Unique Boy Names
- Unique Girl Names
- Top baby names by year
- See all in Baby Names
- Baby Development
- Baby Feeding Guide
- Newborn Sleep
- When Babies Roll Over
- First-Year Baby Costs Calculator
- Postpartum Health
- Baby Poop Chart
- See all in Baby
- Average Weight & Height
- Autism Signs
- Child Growth Chart
- Night Terrors
- Moving from Crib to Bed
- Toddler Feeding Guide
- Potty Training
- Bathing and Grooming
- See all in Toddler
- Height Predictor
- Potty Training: Boys
- Potty training: Girls
- How Much Sleep? (Ages 3+)
- Ready for Preschool?
- Thumb-Sucking
- Gross Motor Skills
- Napping (Ages 2 to 3)
- See all in Child
- Photos: Rashes & Skin Conditions
- Symptom Checker
- Vaccine Scheduler
- Reducing a Fever
- Acetaminophen Dosage Chart
- Constipation in Babies
- Ear Infection Symptoms
- Head Lice 101
- See all in Health
- Second Pregnancy
- Daycare Costs
- Family Finance
- Stay-At-Home Parents
- Breastfeeding Positions
- See all in Family
- Baby Sleep Training
- Preparing For Baby
- My Custom Checklist
- My Registries
- Take the Quiz
- Best Baby Products
- Best Breast Pump
- Best Convertible Car Seat
- Best Infant Car Seat
- Best Baby Bottle
- Best Baby Monitor
- Best Stroller
- Best Diapers
- Best Baby Carrier
- Best Diaper Bag
- Best Highchair
- See all in Baby Products
- Why Pregnant Belly Feels Tight
- Early Signs of Twins
- Teas During Pregnancy
- Baby Head Circumference Chart
- How Many Months Pregnant Am I
- What is a Rainbow Baby
- Braxton Hicks Contractions
- HCG Levels By Week
- When to Take a Pregnancy Test
- Am I Pregnant
- Why is Poop Green
- Can Pregnant Women Eat Shrimp
- Insemination
- UTI During Pregnancy
- Vitamin D Drops
- Best Baby Forumla
- Postpartum Depression
- Low Progesterone During Pregnancy
- Baby Shower
- Baby Shower Games
Breech, posterior, transverse lie: What position is my baby in?

Fetal presentation, or how your baby is situated in your womb at birth, is determined by the body part that's positioned to come out first, and it can affect the way you deliver. At the time of delivery, 97 percent of babies are head-down (cephalic presentation). But there are several other possibilities, including feet or bottom first (breech) as well as sideways (transverse lie) and diagonal (oblique lie).
Fetal presentation and position
During the last trimester of your pregnancy, your provider will check your baby's presentation by feeling your belly to locate the head, bottom, and back. If it's unclear, your provider may do an ultrasound or an internal exam to feel what part of the baby is in your pelvis.
Fetal position refers to whether the baby is facing your spine (anterior position) or facing your belly (posterior position). Fetal position can change often: Your baby may be face up at the beginning of labor and face down at delivery.
Here are the many possibilities for fetal presentation and position in the womb.
Medical illustrations by Jonathan Dimes
Head down, facing down (anterior position)
A baby who is head down and facing your spine is in the anterior position. This is the most common fetal presentation and the easiest position for a vaginal delivery.
This position is also known as "occiput anterior" because the back of your baby's skull (occipital bone) is in the front (anterior) of your pelvis.
Head down, facing up (posterior position)
In the posterior position , your baby is head down and facing your belly. You may also hear it called "sunny-side up" because babies who stay in this position are born facing up. But many babies who are facing up during labor rotate to the easier face down (anterior) position before birth.
Posterior position is formally known as "occiput posterior" because the back of your baby's skull (occipital bone) is in the back (posterior) of your pelvis.
Frank breech
In the frank breech presentation, both the baby's legs are extended so that the feet are up near the face. This is the most common type of breech presentation. Breech babies are difficult to deliver vaginally, so most arrive by c-section .
Some providers will attempt to turn your baby manually to the head down position by applying pressure to your belly. This is called an external cephalic version , and it has a 58 percent success rate for turning breech babies. For more information, see our article on breech birth .
Complete breech
A complete breech is when your baby is bottom down with hips and knees bent in a tuck or cross-legged position. If your baby is in a complete breech, you may feel kicking in your lower abdomen.
Incomplete breech
In an incomplete breech, one of the baby's knees is bent so that the foot is tucked next to the bottom with the other leg extended, positioning that foot closer to the face.
Single footling breech
In the single footling breech presentation, one of the baby's feet is pointed toward your cervix.
Double footling breech
In the double footling breech presentation, both of the baby's feet are pointed toward your cervix.
Transverse lie
In a transverse lie, the baby is lying horizontally in your uterus and may be facing up toward your head or down toward your feet. Babies settle this way less than 1 percent of the time, but it happens more commonly if you're carrying multiples or deliver before your due date.
If your baby stays in a transverse lie until the end of your pregnancy, it can be dangerous for delivery. Your provider will likely schedule a c-section or attempt an external cephalic version , which is highly successful for turning babies in this position.
Oblique lie
In rare cases, your baby may lie diagonally in your uterus, with his rump facing the side of your body at an angle.
Like the transverse lie, this position is more common earlier in pregnancy, and it's likely your provider will intervene if your baby is still in the oblique lie at the end of your third trimester.
Was this article helpful?
What to know if your baby is breech

What's a sunny-side up baby?

What happens to your baby right after birth

How your twins’ fetal positions affect labor and delivery

BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies .
Ahmad A et al. 2014. Association of fetal position at onset of labor and mode of delivery: A prospective cohort study. Ultrasound in obstetrics & gynecology 43(2):176-182. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23929533 Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Gray CJ and Shanahan MM. 2019. Breech presentation. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448063/ Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Hankins GD. 1990. Transverse lie. American Journal of Perinatology 7(1):66-70. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2131781 Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Medline Plus. 2020. Your baby in the birth canal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002060.htm Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]

Where to go next

- Supplements
- Vitamins and Minerals
- Weight Loss & Lifestyle
- Food Additives
Cephalic presentation
A cephalic presentation or head presentation or head-first presentation is a situation at childbirth where the fetus is in a longitudinal lie and the head enters the pelvis first; the most common form of cephalic presentation is the vertex presentation where the occiput is the leading part (the part that first enters the birth canal). All other presentations are abnormal (malpresentations) which are either more difficult to deliver or not deliverable by natural means. Non-cephalic presentations are the breech presentation (3.5%) and the shoulder presentation (0.5%). In vertex presentations the head of the fetus most commonly faces to the right and slightly to the rear. This position is said to be the most usual one because the fetus is thus best accommodated to the shape of the uterus. In face presentation it may be necessary to turn the fetus before delivery if the chin is directed backward.
Bedside ultrasound can be employed to confirm the presentation and position of the fetal presenting part. Particular mention should be noted in the case of breech presentation due to its increased risks regarding fetal morbidity and mortality compared with the cephalic presenting fetus. In breech presentation the buttocks or the legs are the first to pass through the pelvis. The feet may be alongside the buttocks, or the legs may be extended against the face. Because the head is the last part of the fetus to be delivered in breech birth, there is some danger that the fetus will be asphyxiated; there is also danger that the umbilical cord will be compressed during birth of the head. About 25% of fetuses will be in breech presentation at 28 weeks, and this decreases to about 3% to 4% of term pregnancies 1 . Most of these patients will be delivered by cesarean delivery. Transverse presentation, which occurs only once in several hundred labors, requires turning of the fetus before vaginal delivery or else delivery by cesarean section.
The movement of the fetus to cephalic presentation is called head engagement. It occurs in the third trimester. In head engagement, the fetal head descends into the pelvic cavity so that only a small part (or none) of it can be felt abdominally. The perineum and cervix are further flattened and the head may be felt vaginally. Head engagement is known colloquially as the baby drop, and in natural medicine as the lightening because of the release of pressure on the upper abdomen and renewed ease in breathing. However, it severely reduces bladder capacity, increases pressure on the pelvic floor and the rectum, and the mother may experience the perpetual sensation that the fetus will “fall out” at any moment.
In the vertex presentation the head is flexed and the occiput leads the way. This is the most common configuration and seen at term in 95% of singletons. If the head is extended, the face becomes the leading part. Face presentations account for less than 1% of presentations at term. In the sinicipital presentation the large fontanelle is the presenting part; with further labor the head will either flex or extend more so that in the end this presentation leads to a vertex or face presentation. In the brow presentation the head is slightly extended, but less than in the face presentation. The chin presentation is a variant of the face presentation with maximum extension of the head.
Many factors determine the optimal way to deliver a baby. A vertex presentation is the ideal situation for a vaginal birth, however, occiput posterior positions tend to proceed more slowly, often requiring an intervention in the form of forceps, vacuum extraction, or Cesarean section 2 . In a large study, a majority of brow presentations were delivered by Cesarean section, however, because of ‘postmaturity’, factors other than labor dynamics may have played a role 3 . Most face presentations can be delivered vaginally as long as the chin is anterior; there is no increase in fetal or maternal mortality 4 . Mento-posterior positions cannot be delivered vaginally in most cases (unless rotated) and are candidates for Cesarean section in contemporary management 4 .
Vertex presentation
The vertex is the area of the vault bounded anteriorly by the anterior fontanelle and the coronal suture, posteriorly by the posterior fontanelle and the lambdoid suture and laterally by 2 lines passing through the parietal eminences.
In the vertex presentation the occiput typically is anterior and thus in an optimal position to negotiate the pelvic curve by extending the head. In an occiput posterior position, labor becomes prolonged and more operative interventions are deemed necessary. The prevalence of the persistent occiput posterior is given as 4.7%.
The vertex presentations are further classified according to the position of the occiput, it being right, left, or transverse, and anterior or posterior:
- Left Occipito-Anterior (LOA), Left Occipito-Posterior (LOP), Left Occipito-Transverse (LOT);
- Right Occipito-Anterior (ROA), Right Occipito-Posterior (ROP), Right Occipito-Transverse (ROT);
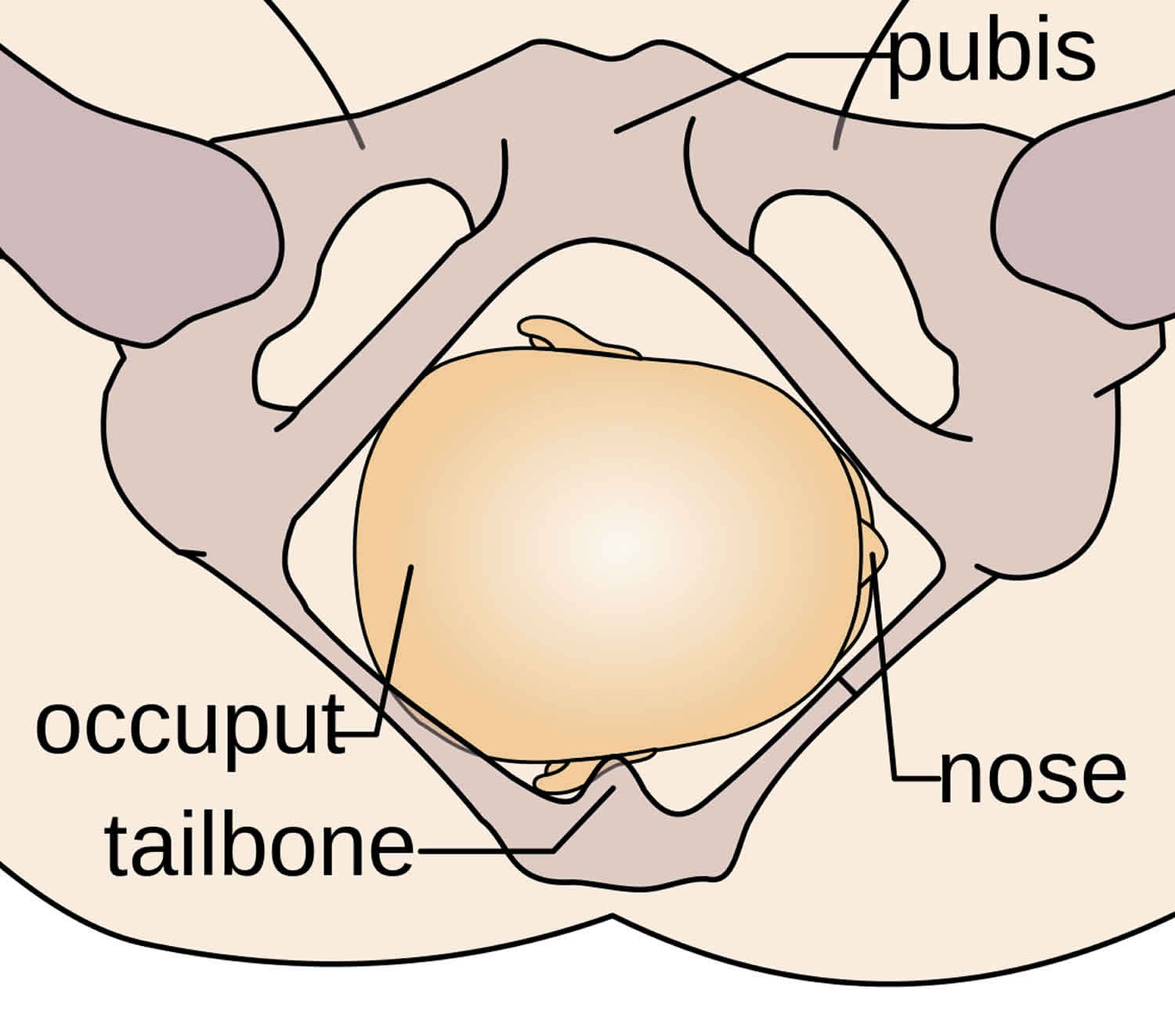
The Occipito-Anterior position is ideal for birth – it means that the baby is lined up so as to fit through the pelvis as easily as possible. The baby is head down, facing the spine, with its back anterior. In this position, the baby’s chin is tucked onto its chest, so that the smallest part of its head will be applied to the cervix first. The position is usually “Left Occiput Anterior”, or LOA. Occasionally, the baby may be “Right Occiput Anterior”, or ROA.
Figure 1. Vertex presentation
Face presentation
Factors that predispose to face presentation are prematurity, macrosomia, anencephaly and other malformations, cephalopelvic disproportion, and polyhydramnios 5 . In an uncomplicated face presentation duration of labor is not altered. Perinatal losses with face presentation occur with traumatic version and extraction and midforceps procedures. Duff 6 indicates that the prevalence of face presentations is about 1/500–600, while Benedetti et al. 7 found it to be 1/1,250 term deliveries.
Face presentations are classified according to the position of the chin (mentum):
- Left Mento-Anterior (LMA), Left Mento-Posterior (LMP), Left Mento-Transverse (LMT);
- Right Mento-Anterior (RMA), Right Mento-Posterior (RMP), Right Mento-Transverse (RMT);
Brow presentation
While some consider the brow presentation as an intermediate stage towards the face presentation, others disagree. Thus Bhal et al. indicated that both conditions are about equally common (1/994 face and 1/755 brow positions), and that prematurity was more common with face while postmaturity was more common with brow positions 3 .
Oskie presentation
The Oskie presentation is similar to the Occipito-Anterior position, where the baby is head down, facing the spine, with back on the ventral side of the uterus; however, in this position, while the torso is aligned with the mother’s longitudinal axis, the legs of the fetus are extended straight along the frontal axis of the mother, as if the baby is creating a right angle with its body. For the Oskie position to occur the baby’s head must be far down the pelvis in order to allow room for leg extension, typically the arms are bent, tucked against the baby’s body. There are no known complications for labor and delivery. This presentation is rare and is not well researched.
- Shanahan MM, Gray CJ. External Cephalic Version. [Updated 2019 Jun 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2019 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482475
- [Effects of persistent occiput posterior presentation on mode of delivery]. Z Geburtshilfe Perinatol. 1994 Aug;198(4):117-9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7975796
- A population study of face and brow presentation. J Obstet Gynaecol. 1998 May;18(3):231-5. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15512065
- [Face presentation: retrospective study of 32 cases at term]. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2006 May;34(5):393-6. Epub 2006 Apr 21. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16630740
- Face and brow presentation: independent risk factors. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2008 Jun;21(6):357-60. doi: 10.1080/14767050802037647. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18570114
- Diagnosis and management of face presentation. Obstet Gynecol. 1981 Jan;57(1):105-12. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7005774
- Face presentation at term. Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Feb;55(2):199-202. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7352081
Cervical effacement
Cervical mucus plug.
The author Health Jade Team
You might also like.

Food sensitivity

Cancrum oris
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
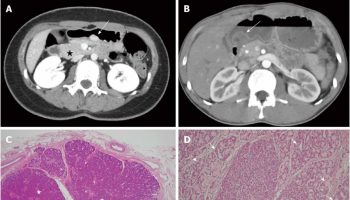
Ectopic pancreas
Hyperamylasemia

- Mammary Glands
- Fallopian Tubes
- Supporting Ligaments
- Reproductive System
- Gametogenesis
- Placental Development
- Maternal Adaptations
- Menstrual Cycle
- Antenatal Care
- Small for Gestational Age
- Large for Gestational Age
- RBC Isoimmunisation
- Prematurity
- Prolonged Pregnancy
- Multiple Pregnancy
- Miscarriage
- Recurrent Miscarriage
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
- Breech Presentation
- Abnormal lie, Malpresentation and Malposition
- Oligohydramnios
- Polyhydramnios
- Placenta Praevia
- Placental Abruption
- Pre-Eclampsia
- Gestational Diabetes
- Headaches in Pregnancy
- Haematological
- Obstetric Cholestasis
- Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy
- Epilepsy in Pregnancy
- Induction of Labour
- Operative Vaginal Delivery
- Prelabour Rupture of Membranes
- Caesarean Section
- Shoulder Dystocia
- Cord Prolapse
- Uterine Rupture
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism
- Primary PPH
- Secondary PPH
- Psychiatric Disease
- Postpartum Contraception
- Breastfeeding Problems
- Primary Dysmenorrhoea
- Amenorrhoea and Oligomenorrhoea
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
- Endometriosis
- Endometrial Cancer
- Adenomyosis
- Cervical Polyps
- Cervical Ectropion
- Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia + Cervical Screening
- Cervical Cancer
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Ovarian Cysts & Tumours
- Urinary Incontinence
- Genitourinary Prolapses
- Bartholin's Cyst
- Lichen Sclerosus
- Vulval Carcinoma
- Introduction to Infertility
- Female Factor Infertility
- Male Factor Infertility
- Female Genital Mutilation
- Barrier Contraception
- Combined Hormonal
- Progesterone Only Hormonal
- Intrauterine System & Device
- Emergency Contraception
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Genital Warts
- Genital Herpes
- Trichomonas Vaginalis
- Bacterial Vaginosis
- Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
- Obstetric History
- Gynaecological History
- Sexual History
- Obstetric Examination
- Speculum Examination
- Bimanual Examination
- Amniocentesis
- Chorionic Villus Sampling
- Hysterectomy
- Endometrial Ablation
- Tension-Free Vaginal Tape
- Contraceptive Implant
- Fitting an IUS or IUD
Abnormal Fetal lie, Malpresentation and Malposition
Original Author(s): Anna Mcclune Last updated: 1st December 2018 Revisions: 12
- 1 Definitions
- 2 Risk Factors
- 3.2 Presentation
- 3.3 Position
- 4 Investigations
- 5.1 Abnormal Fetal Lie
- 5.2 Malpresentation
- 5.3 Malposition
The lie, presentation and position of a fetus are important during labour and delivery.
In this article, we will look at the risk factors, examination and management of abnormal fetal lie, malpresentation and malposition.
Definitions
- Longitudinal, transverse or oblique
- Cephalic vertex presentation is the most common and is considered the safest
- Other presentations include breech, shoulder, face and brow
- Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (the fetal occiput facing anteriorly) – this is ideal for birth
- Other positions include occipito-posterior and occipito-transverse.
Note: Breech presentation is the most common malpresentation, and is covered in detail here .
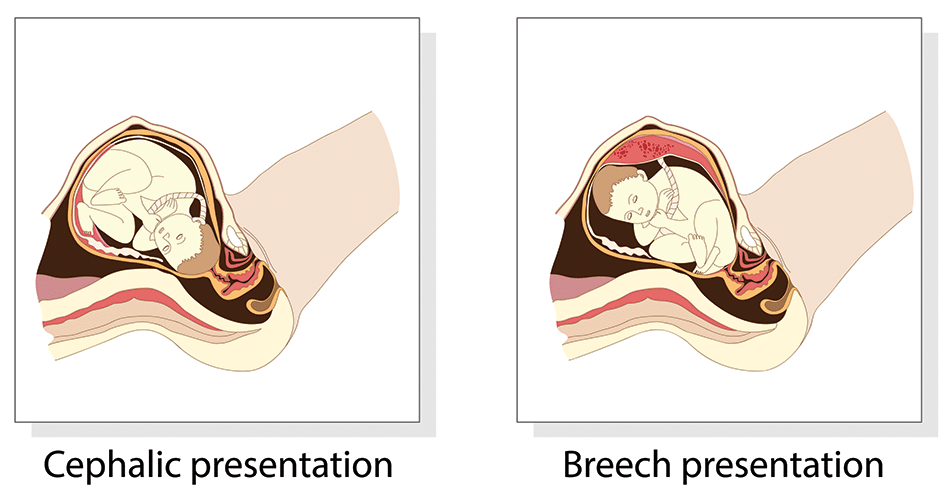
Fig 1 – The two most common fetal presentations: cephalic and breech.
Risk Factors
The risk factors for abnormal fetal lie, malpresentation and malposition include:
- Multiple pregnancy
- Uterine abnormalities (e.g fibroids, partial septate uterus)
- Fetal abnormalities
- Placenta praevia
- Primiparity
Identifying Fetal Lie, Presentation and Position
The fetal lie and presentation can usually be identified via abdominal examination. The fetal position is ascertained by vaginal examination.
For more information on the obstetric examination, see here .
- Face the patient’s head
- Place your hands on either side of the uterus and gently apply pressure; one side will feel fuller and firmer – this is the back, and fetal limbs may feel ‘knobbly’ on the opposite side
Presentation
- Palpate the lower uterus (above the symphysis pubis) with the fingers of both hands; the head feels hard and round (cephalic) and the bottom feels soft and triangular (breech)
- You may be able to gently push the fetal head from side to side
The fetal lie and presentation may not be possible to identify if the mother has a high BMI, if she has not emptied her bladder, if the fetus is small or if there is polyhydramnios .
During labour, vaginal examination is used to assess the position of the fetal head (in a cephalic vertex presentation). The landmarks of the fetal head, including the anterior and posterior fontanelles, indicate the position.
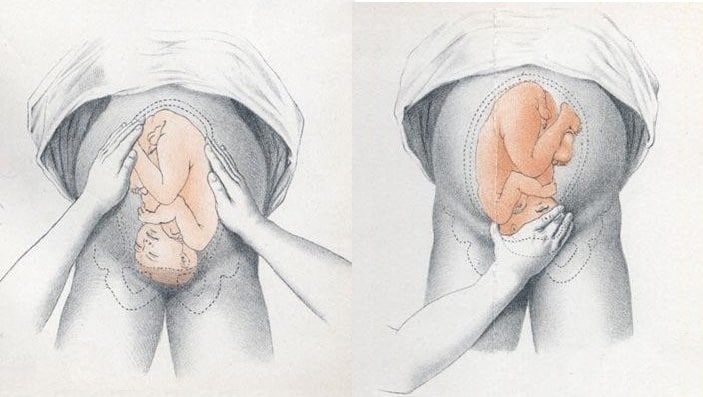
Fig 2 – Assessing fetal lie and presentation.
Investigations
Any suspected abnormal fetal lie or malpresentation should be confirmed by an ultrasound scan . This could also demonstrate predisposing uterine or fetal abnormalities.
Abnormal Fetal Lie
If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted – ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation.
ECV is the manipulation of the fetus to a cephalic presentation through the maternal abdomen.
It has an approximate success rate of 50% in primiparous women and 60% in multiparous women. Only 8% of breech presentations will spontaneously revert to cephalic in primiparous women over 36 weeks gestation.
Complications of ECV are rare but include fetal distress , premature rupture of membranes, antepartum haemorrhage (APH) and placental abruption. The risk of an emergency caesarean section (C-section) within 24 hours is around 1 in 200.
ECV is contraindicated in women with a recent APH, ruptured membranes, uterine abnormalities or a previous C-section .
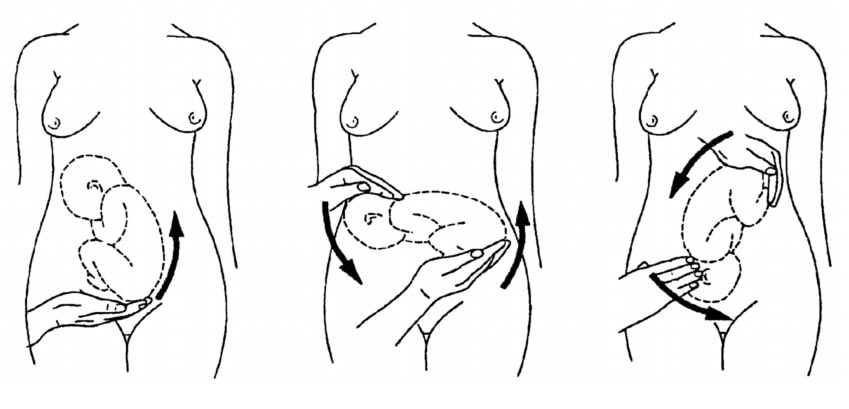
Fig 3 – External cephalic version.
Malpresentation
The management of malpresentation is dependent on the presentation.
- Breech – attempt ECV before labour, vaginal breech delivery or C-section
- Brow – a C-section is necessary
- If the chin is anterior (mento-anterior) a normal labour is possible; however, it is likely to be prolonged and there is an increased risk of a C-section being required
- If the chin is posterior (mento-posterior) then a C-section is necessary
- Shoulder – a C-section is necessary
Malposition
90% of malpositions spontaneously rotate to occipito-anterior as labour progresses. If the fetal head does not rotate, rotation and operative vaginal delivery can be attempted. Alternatively a C-section can be performed.
- Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (the fetal occiput facing anteriorly) - this is ideal for birth
If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted - ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation.
- Breech - attempt ECV before labour, vaginal breech delivery or C-section
Found an error? Is our article missing some key information? Make the changes yourself here!
Once you've finished editing, click 'Submit for Review', and your changes will be reviewed by our team before publishing on the site.
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. To find out more, read our privacy policy .
Privacy Overview
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of cephalic
Examples of cephalic in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'cephalic.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Middle French céphalique , from Latin cephalicus , from Greek kephalikos , from kephalē head; akin to Old High German gebal skull, Old Norse gafl gable, Tocharian A śpāl head
1571, in the meaning defined at sense 1
Phrases Containing cephalic
cephalic index
Dictionary Entries Near cephalic
Cite this entry.
“Cephalic.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/cephalic. Accessed 17 May. 2024.
Medical Definition
Medical definition of cephalic.
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, birds say the darndest things, a great big list of bread words, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 8 uncommon words related to love, games & quizzes.

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.2(3699); 1931 Nov 28
THE MECHANISM OF CEPHALIC PRESENTATIONS
Full text is available as a scanned copy of the original print version. Get a printable copy (PDF file) of the complete article (471K), or click on a page image below to browse page by page.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Occiput or cephalic anterior: This is the best fetal position for childbirth. It means the fetus is head down, facing the birth parent's spine (facing backward). Its chin is tucked towards its chest. The fetus will also be slightly off-center, with the back of its head facing the right or left. This is called left occiput anterior or right ...
Head first (called vertex or cephalic presentation) Facing backward (occiput anterior position) Spine parallel to mother's spine (longitudinal lie) Neck bent forward with chin tucked. Arms folded across the chest . If the fetus is in a different position, lie, or presentation, labor may be more difficult, and a normal vaginal delivery may not ...
Frank breech. When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head.
A cephalic presentation or head presentation or head-first presentation is a situation at childbirth where the fetus is in a longitudinal lie and the head enters the pelvis first; the most common form of cephalic presentation is the vertex presentation, where the occiput is the leading part (the part that first enters the birth canal). All other presentations are abnormal (malpresentations ...
Head Down, Facing Down (Cephalic Presentation) This is the most common position for babies in-utero. In the cephalic presentation, the baby is head down, chin tucked to chest, facing their mother's back. This position typically allows for the smoothest delivery, as baby's head can easily move down the birth canal and under the pubic bone ...
cephalic presentation: [ prez″en-ta´shun ] that part of the fetus lying over the pelvic inlet; the presenting body part of the fetus. See also position and lie . breech presentation presentation of the fetal buttocks, knees, or feet in labor; the feet may be alongside the buttocks (complete breech presentation); the legs may be extended ...
The term presentation describes the leading part of the fetus or the anatomical structure closest to the maternal pelvic inlet during labor. The presentation can roughly be divided into the following classifications: cephalic, breech, shoulder, and compound. Cephalic presentation is the most common and can be further subclassified as vertex, sinciput, brow, face, and chin. The most common ...
A cephalic presentation or head presentation or head-first presentation is a situation at childbirth where the fetus is in a longitudinal lie and the head enters the pelvis first; the most common form of cephalic presentation is the vertex presentation where the occiput is the leading part (the part that first enters the birth canal). All other presentations are abnormal (malpresentations ...
The cephalic position is when a fetus is head down when it is ready to enter the birth canal. This is one of a few variations of how a fetus can rest in the womb and is considered the ideal one for labor and delivery. About 96% of babies are born in the cephalic position. Most settle into it between the 32nd and 36th weeks of pregnancy.
Vertex Presentation. A vertex presentation is the ideal position for a fetus to be in for a vaginal delivery. It means the fetus is head down, headfirst and facing your spine with its chin tucked to its chest. Vertex presentation describes a fetus being head-first or head down in the birth canal.
The cephalic presentation can be further categorized based on the degree of flexion of the fetal head: ... A simple ruler for rapid and direct measurements in centimeters. With this technique, the intersecting diameters of the inlet, midpelvis, and outlet are added to give three respective values. The normal ranges for these values are 22 to 24 ...
Types. Cephalic presentation: head (most common); Breech presentation: buttocks or feet. Frank breech: flexed hips and extended knees (buttocks presenting); Complete breech: thighs and legs flexed (cannonball position); Single footling breech: hip of one leg is flexed and the knee of the other is extended (one foot presenting); Double footling breech: both thighs and legs are extended (feet ...
Cephalic presentation occurs in about 97% of deliveries. There are different types of cephalic presentation, which depend on the position of the baby's limbs and head (fetal attitude). If your baby is in any position other than head down, your doctor may recommend a cesarean delivery. Breech presentation is when the baby's bottom is down ...
Cephalic presentation is the most common type of fetal presentation, in which the baby is in a head-down position in the uterus. In this position, the baby's head is the first part of the body to come out of the mother's vagina. Cephalic presentation is also sometimes called vertex presentation, although the latter is only one of the ...
This is called the cephalic presentation and it is the ideal position for childbirth. Most babies will settle into this position between the 32nd and 36th week of pregnancy. This position makes labor less complicated. Around 96% of babies will be born in the cephalic position.
Fetal presentation, or how your baby is situated in your womb at birth, is determined by the body part that's positioned to come out first, and it can affect the way you deliver. ... This is called an external cephalic version, and it has a 58 percent success rate for turning breech babies. For more information, ...
Face presentation. When the child's head becomes bent back (extended) so that it enters and passes through the pelvis face first, the condition is known as a face, or cephalic, presentation. The chin is then the leading pole and follows the same course that is followed by the back of the head in occipital presentations.
Fetal presentation is a reference to the part of the fetus that is overlying the maternal pelvic inlet. The most common relationship between fetus and mother is the longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation. A breech fetus also is a longitudinal lie, with the fetal buttocks as the presenting part.
The movement of the fetus to cephalic presentation is called head engagement. It occurs in the third trimester. In head engagement, the fetal head descends into the pelvic cavity so that only a small part (or none) of it can be felt abdominally. The perineum and cervix are further flattened and the head may be felt vaginally.
Abnormal Fetal Lie. If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted - ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation. ECV is the manipulation of the fetus to a cephalic presentation through the maternal abdomen. It has an approximate success rate of 50% in primiparous women and 60% in multiparous women.
The meaning of CEPHALIC is of or relating to the head. How to use cephalic in a sentence.
THE MECHANISM OF CEPHALIC PRESENTATIONS - PMC. Journal List. Br Med J. v.2 (3699); 1931 Nov 28. PMC2315500. As a library, NLM provides access to scientific literature. Inclusion in an NLM database does not imply endorsement of, or agreement with, the contents by NLM or the National Institutes of Health.