- 0 Shopping Cart


Case Study – Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro is a city located on Brazil’s south-east coast. It is one of Brazil’s largest settlements with a population of approximately 11.7 million people. The population of Rio de Janeiro has grown for a number of reasons. Natural Increase is one reason for its growth (this is when the birth rate is higher than the death rate ). The population has also grown as the result of urbanisation . The has been caused by rural to urban migration. Millions of people have migrated from Brazil’s rural areas to Rio de Janeiro. 65% of urban growth is a result of migration. This is caused by a variety of push and pull factors.
The rapid growth of Rio de Janeiro’s population has led to a severe shortage of housing. Millions of people have been forced to construct their own homes from scrap materials such as wood, corrugated iron and metals. These areas of temporary accommodation are known as favelas in Brazil. The conditions associated with favelas are very poor. Often families have to share one tap, there is no sewerage provision, disease is common and many people are unemployed.
Favelas are located on the edge of most major Brazilian cities. They are located here for a number of reasons. Firstly, this is the only available land to build on within the city limits. Secondly, industry is located on the edge of the cities. Many people need jobs, therefore, they locate close to factories. Some of these settlements maybe 40 or 50 km from the city centre (on the edge of the city), along main roads and up very steep hillsides.
Rochina Favela, Rio de Janeiro
Rocinha is the largest favela in Brazil. It is located in the southern zone of the city. It is built on a steep hillside overlooking the city, just one kilometre from the beach . It is home to between 60,000 to 150,000 people (though this could be more).
Self-help schemes – Rocinha, Bairro Project
The authorities in Rio de Janeiro have taken a number of steps to reduce problems in favelas. They have set up self-help schemes. This is when the local authority provide local residents with the materials needs to construct permanent accommodation. This includes breeze blocks and cement. The local residents provide labour. The money saved can be spent on providing basic amenities such as electricity and water. Today, almost all the houses in Rocinha are made from concrete and brick. Some buildings are three and four stories tall and almost all houses have basic sanitation, plumbing, and electricity. Compared to simple shanty towns or slums, Rocinha has a better-developed infrastructure and hundreds of businesses such as banks, drug stores, bus lines, cable television, including locally based channel TV ROC, and, at one time, even a McDonalds franchise, though it has since closed. These factors help classify Rocinha as a Favela Bairro , or Favela Neighborhood.
Not all people living in Rio de Janeiro are poor. Many wealthy people live close to the CBD.

Premium Resources
Please support internet geography.
If you've found the resources on this page useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.
Previous Topic Page
Topic home, next topic page, share this:.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
If you've found the resources on this site useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Search Internet Geography
Top posts and pages.
Latest Blog Entries
Pin It on Pinterest
- Click to share
- Print Friendly
Urbanisation Case Study: Rio de Janeiro
The growth of rio de janeiro.
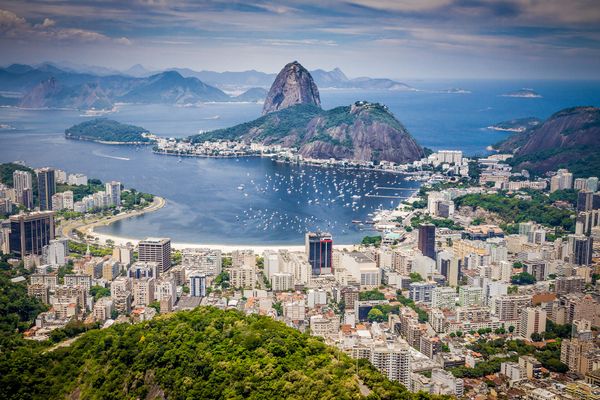
Rio de Janeiro is a major city located in the south-east of Brazil.

Why is Rio de Janeiro important?
- Rio de Janeiro is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Rio de Janeiro hosted the 2016 Olympics and was one of the host cities during the 2014 Football World Cup.
- Rio de Janeiro is a port, industrial centre and centre for banking.

Why has Rio grown?
- Rio has grown due to natural increase and migration.
- Migrants move to Rio from other places in Brazil, such as the Amazon Basin, as well as from other countries in South America, such as Argentina and Bolivia.
- Portugal was the colonial power that historically controlled Brazil. Because the same language is spoken in both countries, some Portuguese citizens may move to Brazil.

Social opportunities from Rio's growth
- Young people have the chance to go to school and university and medical services can visit people at home to treat 20 different diseases.
- 95% of the population have access to mains water.
- Power supplies have been improved as the city has grown.

Economic opportunities from Rio's growth
- People can get jobs in Rio’s industries such as oil refining, building, shopping and tourism.
- 6% of all employment in Brazil is in Rio.
Challenges of Rio's Growth
As with all urbanisation cases, the rapid growth of a city creates many opportunities, but there will also be growing pains.
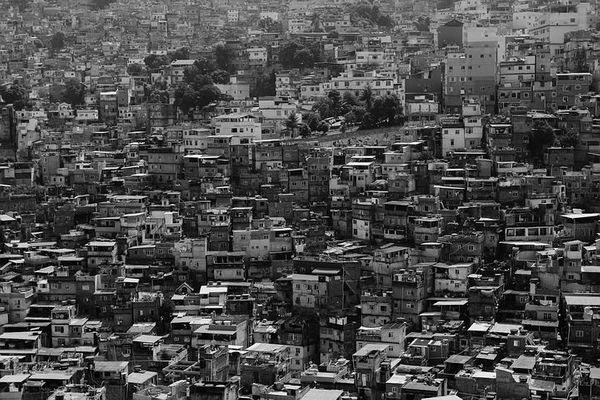

Social challenge - favelas
- Slums in Rio are known as favelas. Rocinha is the largest favela in Rio.

Social challenge - water, sanitation & energy
- 50% of homes in Rio’s favelas have no sewerage.
- 30% of homes in Rio’s favelas have no electricity.
- 12% of homes in Rio’s favelas have no running water.

Social challenge - access to services
- Only 50% of children in Rio stay in school past 14.
- Infant mortality in favelas can be as high as 50 per 1,000 children.
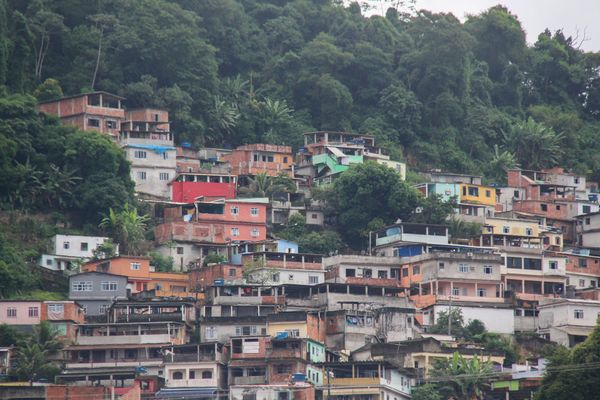

Social challenge - unemployment and crime
- Unemployment rates in favelas are over 20%
- The murder rate can be up to 20 per 1,000 people.
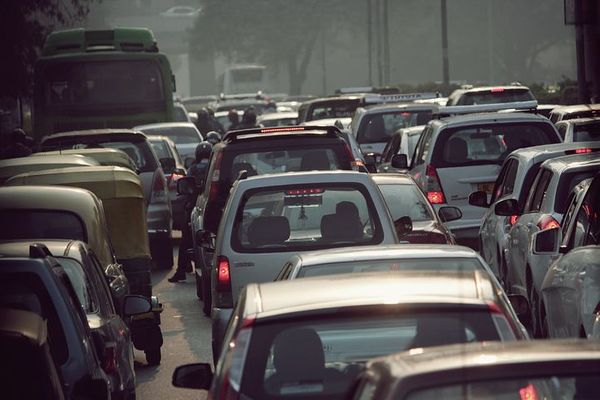

Environmental challenges from Rio's growth
- There is no waste disposal service in the favelas, so rubbish piles up.
- Air pollution caused by fumes from cars and factories causes around 5,000 deaths a year.
- High numbers of cars on the roads leads to severe traffic congestion.
1 The Challenge of Natural Hazards
1.1 Natural Hazards
1.1.1 Types of Natural Hazards
1.1.2 Hazard Risk
1.1.3 Consequences of Natural Hazards
1.1.4 End of Topic Test - Natural Hazards
1.1.5 Exam-Style Questions - Natural Hazards
1.2 Tectonic Hazards
1.2.1 Tectonic Plates
1.2.2 Tectonic Plates & Convection Currents
1.2.3 Plate Margins
1.2.4 Volcanoes
1.2.5 Effects of Volcanoes
1.2.6 Responses to Volcanic Eruptions
1.2.7 Earthquakes
1.2.8 Earthquakes 2
1.2.9 Responses to Earthquakes
1.2.10 Case Studies: The L'Aquila & Kashmir Earthquakes
1.2.11 Earthquake Case Study: Chile 2010
1.2.12 Earthquake Case Study: Nepal 2015
1.2.13 Living with Tectonic Hazards 1
1.2.14 Living with Tectonic Hazards 2
1.2.15 End of Topic Test - Tectonic Hazards
1.2.16 Exam-Style Questions - Tectonic Hazards
1.2.17 Tectonic Hazards - Statistical Skills
1.3 Weather Hazards
1.3.1 Global Atmospheric Circulation
1.3.2 Surface Winds
1.3.3 UK Weather Hazards
1.3.4 Tropical Storms
1.3.5 Features of Tropical Storms
1.3.6 Impact of Tropical Storms 1
1.3.7 Impact of Tropical Storms 2
1.3.8 Tropical Storms Case Study: Katrina
1.3.9 Tropical Storms Case Study: Haiyan
1.3.10 UK Weather Hazards Case Study: Somerset 2014
1.3.11 End of Topic Test - Weather Hazards
1.3.12 Exam-Style Questions - Weather Hazards
1.3.13 Weather Hazards - Statistical Skills
1.4 Climate Change
1.4.1 Evidence for Climate Change
1.4.2 Causes of Climate Change
1.4.3 Effects of Climate Change
1.4.4 Managing Climate Change
1.4.5 End of Topic Test - Climate Change
1.4.6 Exam-Style Questions - Climate Change
1.4.7 Climate Change - Statistical Skills
2 The Living World
2.1 Ecosystems
2.1.1 Ecosystems
2.1.2 Ecosystem Cascades & Global Ecosystems
2.1.3 Ecosystem Case Study: Freshwater Ponds
2.2 Tropical Rainforests
2.2.1 Tropical Rainforests - Intro & Interdependence
2.2.2 Adaptations
2.2.3 Biodiversity of Tropical Rainforests
2.2.4 Deforestation
2.2.5 Case Study: Deforestation in the Amazon Rainforest
2.2.6 Sustainable Management of Rainforests
2.2.7 Case Study: Malaysian Rainforest
2.2.8 End of Topic Test - Tropical Rainforests
2.2.9 Exam-Style Questions - Tropical Rainforests
2.2.10 Deforestation - Statistical Skills
2.3 Hot Deserts
2.3.1 Overview of Hot Deserts
2.3.2 Biodiversity & Adaptation to Hot Deserts
2.3.3 Case Study: Sahara Desert
2.3.4 Desertification
2.3.5 Case Study: Thar Desert
2.3.6 End of Topic Test - Hot Deserts
2.3.7 Exam-Style Questions - Hot Deserts
2.4 Tundra & Polar Environments
2.4.1 Overview of Cold Environments
2.4.2 Adaptations in Cold Environments
2.4.3 Biodiversity in Cold Environments
2.4.4 Case Study: Alaska
2.4.5 Sustainable Management
2.4.6 Case Study: Svalbard
2.4.7 End of Topic Test - Tundra & Polar Environments
2.4.8 Exam-Style Questions - Cold Environments
3 Physical Landscapes in the UK
3.1 The UK Physical Landscape
3.1.1 The UK Physical Landscape
3.2 Coastal Landscapes in the UK
3.2.1 Types of Wave
3.2.2 Weathering & Mass Movement
3.2.3 Processes of Erosion & Wave-Cut Platforms
3.2.4 Headlands, Bays, Caves, Arches & Stacks
3.2.5 Transportation
3.2.6 Deposition
3.2.7 Spits, Bars & Sand Dunes
3.2.8 Case Study: Landforms on the Dorset Coast
3.2.9 Types of Coastal Management 1
3.2.10 Types of Coastal Management 2
3.2.11 Coastal Management Case Study - Holderness
3.2.12 Coastal Management Case Study: Swanage
3.2.13 Coastal Management Case Study - Lyme Regis
3.2.14 End of Topic Test - Coastal Landscapes in the UK
3.2.15 Exam-Style Questions - Coasts
3.3 River Landscapes in the UK
3.3.1 The River Valley
3.3.2 River Valley Case Study - River Tees
3.3.3 Erosion
3.3.4 Transportation & Deposition
3.3.5 Waterfalls, Gorges & Interlocking Spurs
3.3.6 Meanders & Oxbow Lakes
3.3.7 Floodplains & Levees
3.3.8 Estuaries
3.3.9 Case Study: The River Clyde
3.3.10 River Management
3.3.11 Hard & Soft Flood Defences
3.3.12 River Management Case Study - Boscastle
3.3.13 River Management Case Study - Banbury
3.3.14 End of Topic Test - River Landscapes in the UK
3.3.15 Exam-Style Questions - Rivers
3.4 Glacial Landscapes in the UK
3.4.1 Erosion
3.4.2 Landforms Caused by Erosion
3.4.3 Landforms Caused by Transportation & Deposition
3.4.4 Snowdonia
3.4.5 Land Use in Glaciated Areas
3.4.6 Tourism in Glacial Landscapes
3.4.7 Case Study - Lake District
3.4.8 End of Topic Test - Glacial Landscapes in the UK
3.4.9 Exam-Style Questions - Glacial Landscapes
4 Urban Issues & Challenges
4.1 Urban Issues & Challenges
4.1.1 Urbanisation
4.1.2 Urbanisation Case Study: Lagos
4.1.3 Urbanisation Case Study: Rio de Janeiro
4.1.4 UK Cities
4.1.5 Case Study: Urban Regen Projects - Manchester
4.1.6 Case Study: Urban Change in Liverpool
4.1.7 Case Study: Urban Change in Bristol
4.1.8 Sustainable Urban Life
4.1.9 End of Topic Test - Urban Issues & Challenges
4.1.10 Exam-Style Questions - Urban Issues & Challenges
4.1.11 Urban Issues -Statistical Skills
5 The Changing Economic World
5.1 The Changing Economic World
5.1.1 Measuring Development
5.1.2 Classifying Countries Based on Wealth
5.1.3 The Demographic Transition Model
5.1.4 Physical & Historical Causes of Uneven Development
5.1.5 Economic Causes of Uneven Development
5.1.6 How Can We Reduce the Global Development Gap?
5.1.7 Case Study: Tourism in Kenya
5.1.8 Case Study: Tourism in Jamaica
5.1.9 Case Study: Economic Development in India
5.1.10 Case Study: Aid & Development in India
5.1.11 Case Study: Economic Development in Nigeria
5.1.12 Case Study: Aid & Development in Nigeria
5.1.13 Economic Development in the UK
5.1.14 Economic Development UK: Industry & Rural
5.1.15 Economic Development UK: Transport & North-South
5.1.16 Economic Development UK: Regional & Global
5.1.17 End of Topic Test - The Changing Economic World
5.1.18 Exam-Style Questions - The Changing Economic World
5.1.19 Changing Economic World - Statistical Skills
6 The Challenge of Resource Management
6.1 Resource Management
6.1.1 Global Distribution of Resources
6.1.2 Food in the UK
6.1.3 Water in the UK 1
6.1.4 Water in the UK 2
6.1.5 Energy in the UK
6.1.6 Resource Management - Statistical Skills
6.2.1 Areas of Food Surplus & Food Deficit
6.2.2 Food Supply & Food Insecurity
6.2.3 Increasing Food Supply
6.2.4 Case Study: Thanet Earth
6.2.5 Creating a Sustainable Food Supply
6.2.6 Case Study: Agroforestry in Mali
6.2.7 End of Topic Test - Food
6.2.8 Exam-Style Questions - Food
6.2.9 Food - Statistical Skills
6.3.1 The Global Demand for Water
6.3.2 What Affects the Availability of Water?
6.3.3 Increasing Water Supplies
6.3.4 Case Study: Water Transfer in China
6.3.5 Sustainable Water Supply
6.3.6 Case Study: Kenya's Sand Dams
6.3.7 Case Study: Lesotho Highland Water Project
6.3.8 Case Study: Wakel River Basin Project
6.3.9 Exam-Style Questions - Water
6.3.10 Water - Statistical Skills
6.4.1 Global Demand for Energy
6.4.2 Factors Affecting Energy Supply
6.4.3 Increasing Energy Supply: Renewables
6.4.4 Increasing Energy Supply: Non-Renewables
6.4.5 Carbon Footprints & Energy Conservation
6.4.6 Case Study: Rice Husks in Bihar
6.4.7 Exam-Style Questions - Energy
6.4.8 Energy - Statistical Skills
Jump to other topics

Unlock your full potential with GoStudent tutoring
Affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of your home
Tutors are matched to your specific learning needs
30+ school subjects covered
Urbanisation Case Study: Lagos

- 2023 Predicted Papers
- A-Level Biology
- A-Level Chemistry
- A-Level Maths
- A-Level Psychology
- GCSE Science
- GCSE Further Maths (Level 2, Level 3, FSMQ)
- GCSE History
- GCSE Citizenship
- GCSE Geography
- Group Code Registration Form
- Biology Reading List
- Chemistry Reading List
- The Ultimate guide to the EPQ
- UCAS and University
- How to help your child succeed in exams
- How to succeed in homeschooling
- Teacher Shop
- Group Registration
- Group Registration FAQs
- Your Profile
GCSE Geography – Case Study – Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Environmental isues.
Quiz summary.
0 of 15 Questions completed

Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Quiz complete. Results are being recorded.
0 of 15 Questions answered correctly
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), ( 0 )
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0 , ( 0 ) 0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0 )
- Not categorized 0%
1 . Question
How many deaths is it estimated are caused by air pollution in Rio each year?
2 . Question
On which coastline is Rio?
- Mediterraen.
3 . Question
Which city is the most congested in the whole of South America?
- Rio de Janeiro.
- Buenos Aires.
4 . Question
In Rio, by what percentage has car ownership grown over the last decade?
5 . Question
To reduce congestion on coastal raods what have the authorities in Rio done to improve traffic flow?
- Made them one-way.
- Shut them at peak times.
- Made them pedestrian only
- Limit number of cars.
6 . Question
Rio’s Guanabara Bay, is highly polluted. By how much has commercial fishing declined in the last 20 years?
7 . Question
How many polluted rivers flow into Guanabara Bay?
8 . Question
Approximately how many tonnes of raw serage pours into Guanabara Bay each day?
9 . Question
Approximately how many tonnes of industrial waste pours into Guanabara Bay each day?
10 . Question
Which of the following is NOT one of the reasons that Guanabara Bay is polluted?
- Ships empty fuel into sea.
- Oil spills from refinery.
- Raw sewage from the favelas.
11 . Question
What is the term that describes the pollution haze that hangs over the city of Rio?
12 . Question
What disease is likely in the favelas due to waste being dumped into the open sewers?
- Chicken pox.
13 . Question
To combat the refuse problem a power plant has been set up utilising the gas from rotting rubbish. What is the gas called?
14 . Question
A new power plant plant has been set up to use the gas from rotting rubbish from the flavelas. How many tonnes of rubbish does it use each day?
15 . Question
What is the term used to describe the gradual increase in the concentration of phosphorus, nitrogen, and other plant nutrients in Guanabara Bay?
- Eutrophication.
- Electrification.
- Gentrification.
- Sophistication.
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Privacy Overview
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Registration confirmation will be emailed to you.
Have an account?

AQA GCSE Geography - Rio Case Study
10th - 12th grade.
27 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
Rural-urban migration has created squatter settlements in Rio called
Shanty Towns
villa miseria
What % of people in Rocinha have sanitation?
Families often share one tap, and 12% have no access to running water but what % of houses have water piped directly to their houses
Unemployment levels are high (20%) and wages are below __________ per month in the favelas
Life expectancy is lower in the favelas
What is the name of the Largest Favela in Brazil?
Santa Marta
What is urban sprawl?
The sprawl of people from rural areas to urban areas.
The main city centre in an urban area.
The spreading of rural areas into surrounding rural areas to accommodate the need for extra land space due to a rise in ecological footpint.
The spreading of urban areas into surrounding rural areas to accommodate an expanding population.
The movement of people from one country to another is called...
Rural to urban migration
International movement
Annual migration
What is urbanisation?
Urbanisation is the migration of people from rural areas to cities that results in the expansion of urban areas.
Urbanisation is the migration of people from poor countries to rich countries.
Urbanisation is the migration of people from urban to rural areas that results in the reduction of urban areas.
Push factor
things that make people want to leave an area such as high crime, lack of education & health services
things that attract people to move to an area such as greater employment opportunities
Pull factor
Slum housing, unreliable power systems, congested roads and poor public transport, inefficient ports and inadequate schools.
rapid urbanisation challenges
rapid urbanisation benefits
- 13. Multiple Choice Edit 30 seconds 1 pt What is population density? A measure of people per metre The rate of death minus the rate of births A measure of people per square kilometre A measure of how many people live in one house
- 14. Multiple Choice Edit 30 seconds 1 pt To be a Megacity, the population has to be above 8 million 11 million 15 million 10 million
Which continent has the most megacities?
North America
What is a favela?
A Brazilian food made with rice
A slum or shantytown
An area of a city where rich people live
A Brazilian storm with high winds
How do Favelas get electricity?
Giant batteries
In most cases it is illegally tapped from the public grid
Hydro electricity
Which statement about Rio's favelas is false?
There are up to 1,000 favelas in Rio
Favelas are often built on steep hillsides where landslides are common
The number of people living in favelas has declined in recent years
Rocinha is the largest favela in Rio
Favelas are illegal settlements where people have built homes on land they do not own.
Are Favela's at risk from fires and why?
Yes as they are cramped and close together and often built from flammable materials
No as they have an excellent fire service.
Yes because there are few roads for the excellent fire service to get their fire engines to fires.
No because it has regular monsoons.
Which statement about Rio is false?
Rio has a major port exporting coffee, sugar and iron ore.
Banking, finance and insurance is an important part of Rio's economy.
Rio is one of the most visited cities in the northern hemisphere.
Rio hosted the 2014 World Cup and 2016 Olympics.
Which of the following cities was already a megacity in 1950?
There are ---- megacities in the world as of 2019
less than 15
more than 25
Overcrowding is a major problem in Rio's favelas. On average, the population density is about
12,000 people per square kilometre
8,000 people per square kilometre
37,000 people per square kilometre
51,000 people per square kilometre
A continent with no Megacities
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search
AQA GCSE Geography Rio de Janeiro Knowledge Organiser
Subject: Geography
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Assessment and revision
Last updated
26 November 2018
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest
Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
I edited it to work for Edexcel IGCSE spec. Thanks so much.
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Live revision! Join us for our free exam revision livestreams Watch now →
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Geography news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Geography Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
Topic Videos
Topic Video for AQA GCSE Geography: Water Transfer Case Study - Lesotho Highlands Water Project (Water Resources 5)
Last updated 25 May 2024
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
This topic video looks at the Lesotho Highlands Water Project that transfers water from Lesotho to South Africa, including details of the project, along with the benefits and drawbacks for both countries.
It is part of the AQA GCSE Geography course - Paper 2: Unit C - The Challenge of Resource Management.
You might also like
Topic video for aqa gcse geography: immediate and long-term responses to tectonic hazards (tectonic hazards 9), topic video for aqa gcse geography: immediate and long-term responses to weather hazards (weather hazards 9), topic video for aqa gcse geography: human causes of climate change (climate change 4), topic video for aqa gcse geography: scale of deforestation (tropical rainforests 3), topic video for aqa gcse geography: challenges in svalbard (cold environments 4), topic video for aqa gcse geography: landforms of erosion - caves, arches, stacks and stumps (coastal landscapes 5), topic video for aqa gcse geography: foot miles and carbon footprints (uk resource overview 2), topic video for aqa gcse geography: increasing food supply (food resources 4), our subjects.
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Rio de Janeiro is found in Brazil and is the second largest city in Brazil; it was the capital city of Brazil until 1960. Brazil can be found in South America. Rio de Janeiro is a city with global influence, and is well known around the world for a variety of reasons: Source: Pens & Patrons. Rio's carnivals are world famous, attracting around ...
Learn about and revise the challenges that some British cities face, including regeneration and urban sustainability, with GCSE Bitesize Geography (OCR).
Case Study Rio de Janeiro - Rio de Janeiro is a city located on Brazil's south-east coast. ... AQA Geography. The Challenge of Natural Hazards; Physical Landscapes in the UK; The Living World; The Changing Economic World. ... AQA GCSE Geography Pre-release Resources 2024 24 March 2024 - 10:27 pm. GCSE Geography Mind Maps 14 March 2024 - 2:02 pm.
Environmental challenges from Rio's growth. There is no waste disposal service in the favelas, so rubbish piles up. Air pollution caused by fumes from cars and factories causes around 5,000 deaths a year. High numbers of cars on the roads leads to severe traffic congestion. Rio de Janeiro is a major city located in the south-east of Brazil.
Terms in this set (43) Location of Rio. Rio is on Brazil's Atlantic coast, 23 degrees south and 43 degrees west. Importance of Rio. - It is a major financial, industrial, regional, national and international centre for companies and industries. - It hosted the 2014 World Cup and 2016 Olympic Games. Causes of Rio's growth. - It was settled by ...
#gcsegeography #aqageography #sundaymorningcoffee DOWNLOAD LAST MINUTE MOCKS HERE:https://www.mrbowater.com/storeMock exam papers - NO WRITING!Timestamps:01:...
A summary of the GCSE Rio de Janeiro Case Study, this is for AQA Geography and is from the section of urban Issues and Challenges.ContentsHistoryEconomyelect...
The average semi detached house price in Anfield is£101,000 and in Woolton it is £230,000. Anfield and Toxteth are among the most deprived areas in England. achieve lower exam results. The proportion of students achieving 5 A*-C GCSEs in Woolton is 75% and in Anfield is only 54%. Economic - Housing Inequalities.
A Higher Geography guide to understanding urban change in a developing world city. ... GCSE; Scotland. Early Level; 1st Level; 2nd Level; 3rd Level; ... Developing country case study: Rio de Janeiro;
Key figures for the Rio case study Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. hello quizlet. Home. Expert Solutions. Create. Subjects. Exams. IELTS® TOEFL® TOEIC® View all. Arts and Humanities ... AQA GCSE Geography - Rio Case Study. Flashcards; Learn; Test; Match; Q-Chat; 23S.
Rio de Janeiro Revision - AQA GCSE Geography. Subject: Geography. Age range: 14-16. Resource type: Assessment and revision. File previews. pptx, 997.97 KB. An overview of the Rio case study in urban issues and challenges. This provides an overview for the topic and allows students to consolidate their knowldege by completing activities.
environment - Case studies/examples Section A - Urban issues and challenges 1. Rio De Janeiro - Urban growth Describe, explain and assess a case study of a major city in an LIC or NEE to illustrate: Describe the location and explain the importance of the city, regionally, nationally and internationally
A CASE STUDY COLLECTION GCSE GEOGRAPHY AQA . 1 Contents Paper 1: Living in the Physical Environment The Challenges of Natural Hazards 1. Haiti Earthquake (2011) ... 10. Rio de Janeiro (Urban change in a major NEE city) Page 11 11. Sheffield (Urban changes in a major UK city) Page 12 12. ...
A case study of a major city in an LIC or NEE. Location Rio de Janeiro is situated on razil's Atlantic coast. The cultural capital of razil, staged the 2014 football World Cup and the 2016 Olympics. Causes of growth Rio has grown rapidly over the last 50 years to become a major industrial, administrative, commercial and tourist centre.
aphg - migration vocab. 40 terms. Andrealovestacos. Preview. Test 3. 37 terms. Myrnnah1950. Preview. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Location of Rio, Importance of Rio, Causes of Rio's growth and more.
Environmental isues. AQA GCSE Geography GCSE Geography - Case Study - Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Environmental isues. How many deaths is it estimated are caused by air pollution in Rio each year? 1. 2. 3. 5 million. 4.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like In 5 points, Where is Rio located?, What fraction of the population live in favelas?, Why is Rio important regionally? and more. ... GCSE AQA geography paper 1 case studies. 40 terms. chloerandle. Preview. Abbotts hall farm case study. 11 terms. C0xy2509. Preview. Geog - Urban ...
27%. 34%. United Nations Population Division License: CC BY-4.0. Since the 1950s, LICs have seen rapid growth in urbanisation, particularly in South America, Asia and Africa. Between the 1950s and 2000, urban population living in NEEs have doubled and LICs by 2021, developed countries saw growth slow by less than half.
Subject: Geography. Age range: 14-16. Resource type: Worksheet/Activity. File previews. pub, 1.19 MB. An A3 case study note taking sheet. Using the Rio case study notes in the Oxford Book for the AQA GCSE Geography Spec. Outline can be used for other case studies, just change the questions. Creative Commons "Sharealike".
AQA GCSE Geography - Rio Case Study quiz for 10th grade students. Find other quizzes for Geography and more on Quizizz for free!
Summary AQA Geography - Rio de Janeiro (Brazil) Case Study. Module. Geography. Institution. GCSE. Everything you need to know about the Rio Case Study for AQA GCSE Geography Paper 2. It goes through specific details which will give you information that allows you to achieve high marks in the 6 and 9 mark questions.
Age range: 14-16. Resource type: Assessment and revision. File previews. pptx, 180.95 KB. A revision sheet to recap elements of the city of Rio de Janeiro. For the new (2016) AQA GCSE geography. This is the city the Oxford textbook uses as a case study of a city in a NEE. Ideally printed A3. Creative Commons "Sharealike".
This topic video looks at large-scale agriculture in the Indus River Basin, which is the largest continuous irrigation system in the world, along with the pros and cons of producing food in this way. It is part of the AQA GCSE Geography course - Paper 2: Unit C - The Challenge of Resource Management.
I'm thinking tropical storms case study nine marker because there wasn't much of tropical storms last year. 2 Report. Reply. Reply 43. 1 week ago. user01430. 11. Not the uk weather hazard. 0 Report. Reply. ... GCSE Geography Study Group 2023-2024; AQA A-level Physics Paper 3 (7408/3) - 17th June 2024 [Exam Chat] AQA GCSE Geography Paper 2 (8035 ...
This topic video looks at the Lesotho Highlands Water Project that transfers water from Lesotho to South Africa, including details of the project, along with the benefits and drawbacks for both countries. It is part of the AQA GCSE Geography course - Paper 2: Unit C - The Challenge of Resource Management.