How to Compare Two Novels in Comparative Essay
Sam Edwards/Getty Images
- Writing Essays
- Writing Research Papers
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
At some point in your literature studies, probably just about the time you get really good at finding the theme of a novel and coming up with a sound analysis of a single literary piece, you will be required to compare two novels.
Your first task in this assignment will be to develop a good profile of both novels. You can do this by making a few simple lists of traits that might be comparable. For each novel, identify a list of characters and their roles in the story or important characteristics, and any important struggles, time periods, or major symbols (like an element of nature).
You may also attempt to come up with book themes that could be comparable. Sample themes would include:
- Man versus nature (is each main character battling the elements?)
- Individual versus society (does each main character feel like an outsider?)
- Struggle between good and evil (are your characters involved in good v. evil scenarios?)
- Coming of age (do the main characters experience a tough lesson that makes them grow?)
Your assignment will most likely give you direction as to whether you should find specific characters, story characteristics, or overall themes to compare. If it is not that specific, don't worry! You actually have a little more leeway.

Comparing Two Novel Themes
The teacher's goal when assigning this paper is to encourage you to think and analyze. You no longer read for a surface understanding of what happens in a novel; you are reading to understand why things happen and what the deeper meaning behind a character is a setting or an event. In short, you are expected to come up with an interesting comparative analysis.
As an example of comparing novel themes, we will look at The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn and The Red Badge of Courage . Both of these novels contain a "coming of age" theme since both have characters who grow a new awareness through tough lessons. Some comparisons you could make:
- Both characters have to explore the notion of "civilized behavior" in the societies where they exist.
- Each main character has to question the behavior of his male role models and his male peers.
- Each main character leaves his childhood home and encounters challenges.
To craft an essay about these two novels and their similar themes, you would create your own list of similarities like those above, using a list, chart, or a Venn diagram .
Sum up your overall theory about how these themes are comparable to create your thesis statement . Here is an example: "Both characters, Huck Finn and Henry Fleming, embark on a journey of discovery, and each boy finds new understanding when it comes to traditional notions about honor and courage."
You will use your common characteristic list to guide you as you create body paragraphs .
Comparing Main Characters in Novels
If your assignment is to compare the characters of these novels, you would make a list or Venn diagram to make more comparisons:
- Both characters are young men
- Both question society's notion of honor
- Both witness behavior that makes them question their role models
- Both have a nurturing female influence
- Both question their former beliefs
Comparing two novels is not as difficult as it sounds at first. Once you generate a list of traits, you can easily see an outline emerging.
- Venn Diagrams to Plan Essays and More
- Graphic Organizers
- Must-Read Books If You Like 'The Catcher in the Rye'
- Top Conservative Novels
- Write a Compare and Contrast Essay
- Beef Up Critical Thinking and Writing Skills: Comparison Essays
- How to Write a Character Analysis
- Preparing for Final Exams
- How to Find the Theme of a Book or Short Story
- 10 Steps to Writing a Successful Book Report
- 10 Common Themes in Literature
- 5 Novel Setting Maps for Classic American Literature
- The Red Badge of Courage Book Summary
- The Top Coming-of-Age Novels
- How to Write a Great Book Report
- Top Novels for American Literature Classes

Comparing and Contrasting
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you first to determine whether a particular assignment is asking for comparison/contrast and then to generate a list of similarities and differences, decide which similarities and differences to focus on, and organize your paper so that it will be clear and effective. It will also explain how you can (and why you should) develop a thesis that goes beyond “Thing A and Thing B are similar in many ways but different in others.”
Introduction
In your career as a student, you’ll encounter many different kinds of writing assignments, each with its own requirements. One of the most common is the comparison/contrast essay, in which you focus on the ways in which certain things or ideas—usually two of them—are similar to (this is the comparison) and/or different from (this is the contrast) one another. By assigning such essays, your instructors are encouraging you to make connections between texts or ideas, engage in critical thinking, and go beyond mere description or summary to generate interesting analysis: when you reflect on similarities and differences, you gain a deeper understanding of the items you are comparing, their relationship to each other, and what is most important about them.
Recognizing comparison/contrast in assignments
Some assignments use words—like compare, contrast, similarities, and differences—that make it easy for you to see that they are asking you to compare and/or contrast. Here are a few hypothetical examples:
- Compare and contrast Frye’s and Bartky’s accounts of oppression.
- Compare WWI to WWII, identifying similarities in the causes, development, and outcomes of the wars.
- Contrast Wordsworth and Coleridge; what are the major differences in their poetry?
Notice that some topics ask only for comparison, others only for contrast, and others for both.
But it’s not always so easy to tell whether an assignment is asking you to include comparison/contrast. And in some cases, comparison/contrast is only part of the essay—you begin by comparing and/or contrasting two or more things and then use what you’ve learned to construct an argument or evaluation. Consider these examples, noticing the language that is used to ask for the comparison/contrast and whether the comparison/contrast is only one part of a larger assignment:
- Choose a particular idea or theme, such as romantic love, death, or nature, and consider how it is treated in two Romantic poems.
- How do the different authors we have studied so far define and describe oppression?
- Compare Frye’s and Bartky’s accounts of oppression. What does each imply about women’s collusion in their own oppression? Which is more accurate?
- In the texts we’ve studied, soldiers who served in different wars offer differing accounts of their experiences and feelings both during and after the fighting. What commonalities are there in these accounts? What factors do you think are responsible for their differences?
You may want to check out our handout on understanding assignments for additional tips.
Using comparison/contrast for all kinds of writing projects
Sometimes you may want to use comparison/contrast techniques in your own pre-writing work to get ideas that you can later use for an argument, even if comparison/contrast isn’t an official requirement for the paper you’re writing. For example, if you wanted to argue that Frye’s account of oppression is better than both de Beauvoir’s and Bartky’s, comparing and contrasting the main arguments of those three authors might help you construct your evaluation—even though the topic may not have asked for comparison/contrast and the lists of similarities and differences you generate may not appear anywhere in the final draft of your paper.
Discovering similarities and differences
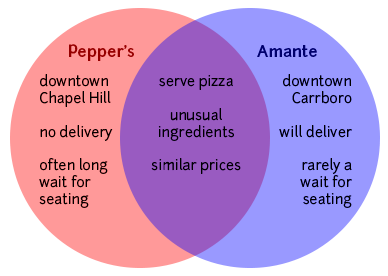
Making a Venn diagram or a chart can help you quickly and efficiently compare and contrast two or more things or ideas. To make a Venn diagram, simply draw some overlapping circles, one circle for each item you’re considering. In the central area where they overlap, list the traits the two items have in common. Assign each one of the areas that doesn’t overlap; in those areas, you can list the traits that make the things different. Here’s a very simple example, using two pizza places:
To make a chart, figure out what criteria you want to focus on in comparing the items. Along the left side of the page, list each of the criteria. Across the top, list the names of the items. You should then have a box per item for each criterion; you can fill the boxes in and then survey what you’ve discovered.
Here’s an example, this time using three pizza places:
As you generate points of comparison, consider the purpose and content of the assignment and the focus of the class. What do you think the professor wants you to learn by doing this comparison/contrast? How does it fit with what you have been studying so far and with the other assignments in the course? Are there any clues about what to focus on in the assignment itself?
Here are some general questions about different types of things you might have to compare. These are by no means complete or definitive lists; they’re just here to give you some ideas—you can generate your own questions for these and other types of comparison. You may want to begin by using the questions reporters traditionally ask: Who? What? Where? When? Why? How? If you’re talking about objects, you might also consider general properties like size, shape, color, sound, weight, taste, texture, smell, number, duration, and location.
Two historical periods or events
- When did they occur—do you know the date(s) and duration? What happened or changed during each? Why are they significant?
- What kinds of work did people do? What kinds of relationships did they have? What did they value?
- What kinds of governments were there? Who were important people involved?
- What caused events in these periods, and what consequences did they have later on?
Two ideas or theories
- What are they about?
- Did they originate at some particular time?
- Who created them? Who uses or defends them?
- What is the central focus, claim, or goal of each? What conclusions do they offer?
- How are they applied to situations/people/things/etc.?
- Which seems more plausible to you, and why? How broad is their scope?
- What kind of evidence is usually offered for them?
Two pieces of writing or art
- What are their titles? What do they describe or depict?
- What is their tone or mood? What is their form?
- Who created them? When were they created? Why do you think they were created as they were? What themes do they address?
- Do you think one is of higher quality or greater merit than the other(s)—and if so, why?
- For writing: what plot, characterization, setting, theme, tone, and type of narration are used?
- Where are they from? How old are they? What is the gender, race, class, etc. of each?
- What, if anything, are they known for? Do they have any relationship to each other?
- What are they like? What did/do they do? What do they believe? Why are they interesting?
- What stands out most about each of them?
Deciding what to focus on
By now you have probably generated a huge list of similarities and differences—congratulations! Next you must decide which of them are interesting, important, and relevant enough to be included in your paper. Ask yourself these questions:
- What’s relevant to the assignment?
- What’s relevant to the course?
- What’s interesting and informative?
- What matters to the argument you are going to make?
- What’s basic or central (and needs to be mentioned even if obvious)?
- Overall, what’s more important—the similarities or the differences?
Suppose that you are writing a paper comparing two novels. For most literature classes, the fact that they both use Caslon type (a kind of typeface, like the fonts you may use in your writing) is not going to be relevant, nor is the fact that one of them has a few illustrations and the other has none; literature classes are more likely to focus on subjects like characterization, plot, setting, the writer’s style and intentions, language, central themes, and so forth. However, if you were writing a paper for a class on typesetting or on how illustrations are used to enhance novels, the typeface and presence or absence of illustrations might be absolutely critical to include in your final paper.
Sometimes a particular point of comparison or contrast might be relevant but not terribly revealing or interesting. For example, if you are writing a paper about Wordsworth’s “Tintern Abbey” and Coleridge’s “Frost at Midnight,” pointing out that they both have nature as a central theme is relevant (comparisons of poetry often talk about themes) but not terribly interesting; your class has probably already had many discussions about the Romantic poets’ fondness for nature. Talking about the different ways nature is depicted or the different aspects of nature that are emphasized might be more interesting and show a more sophisticated understanding of the poems.
Your thesis
The thesis of your comparison/contrast paper is very important: it can help you create a focused argument and give your reader a road map so they don’t get lost in the sea of points you are about to make. As in any paper, you will want to replace vague reports of your general topic (for example, “This paper will compare and contrast two pizza places,” or “Pepper’s and Amante are similar in some ways and different in others,” or “Pepper’s and Amante are similar in many ways, but they have one major difference”) with something more detailed and specific. For example, you might say, “Pepper’s and Amante have similar prices and ingredients, but their atmospheres and willingness to deliver set them apart.”
Be careful, though—although this thesis is fairly specific and does propose a simple argument (that atmosphere and delivery make the two pizza places different), your instructor will often be looking for a bit more analysis. In this case, the obvious question is “So what? Why should anyone care that Pepper’s and Amante are different in this way?” One might also wonder why the writer chose those two particular pizza places to compare—why not Papa John’s, Dominos, or Pizza Hut? Again, thinking about the context the class provides may help you answer such questions and make a stronger argument. Here’s a revision of the thesis mentioned earlier:
Pepper’s and Amante both offer a greater variety of ingredients than other Chapel Hill/Carrboro pizza places (and than any of the national chains), but the funky, lively atmosphere at Pepper’s makes it a better place to give visiting friends and family a taste of local culture.
You may find our handout on constructing thesis statements useful at this stage.
Organizing your paper
There are many different ways to organize a comparison/contrast essay. Here are two:
Subject-by-subject
Begin by saying everything you have to say about the first subject you are discussing, then move on and make all the points you want to make about the second subject (and after that, the third, and so on, if you’re comparing/contrasting more than two things). If the paper is short, you might be able to fit all of your points about each item into a single paragraph, but it’s more likely that you’d have several paragraphs per item. Using our pizza place comparison/contrast as an example, after the introduction, you might have a paragraph about the ingredients available at Pepper’s, a paragraph about its location, and a paragraph about its ambience. Then you’d have three similar paragraphs about Amante, followed by your conclusion.
The danger of this subject-by-subject organization is that your paper will simply be a list of points: a certain number of points (in my example, three) about one subject, then a certain number of points about another. This is usually not what college instructors are looking for in a paper—generally they want you to compare or contrast two or more things very directly, rather than just listing the traits the things have and leaving it up to the reader to reflect on how those traits are similar or different and why those similarities or differences matter. Thus, if you use the subject-by-subject form, you will probably want to have a very strong, analytical thesis and at least one body paragraph that ties all of your different points together.
A subject-by-subject structure can be a logical choice if you are writing what is sometimes called a “lens” comparison, in which you use one subject or item (which isn’t really your main topic) to better understand another item (which is). For example, you might be asked to compare a poem you’ve already covered thoroughly in class with one you are reading on your own. It might make sense to give a brief summary of your main ideas about the first poem (this would be your first subject, the “lens”), and then spend most of your paper discussing how those points are similar to or different from your ideas about the second.
Point-by-point
Rather than addressing things one subject at a time, you may wish to talk about one point of comparison at a time. There are two main ways this might play out, depending on how much you have to say about each of the things you are comparing. If you have just a little, you might, in a single paragraph, discuss how a certain point of comparison/contrast relates to all the items you are discussing. For example, I might describe, in one paragraph, what the prices are like at both Pepper’s and Amante; in the next paragraph, I might compare the ingredients available; in a third, I might contrast the atmospheres of the two restaurants.
If I had a bit more to say about the items I was comparing/contrasting, I might devote a whole paragraph to how each point relates to each item. For example, I might have a whole paragraph about the clientele at Pepper’s, followed by a whole paragraph about the clientele at Amante; then I would move on and do two more paragraphs discussing my next point of comparison/contrast—like the ingredients available at each restaurant.
There are no hard and fast rules about organizing a comparison/contrast paper, of course. Just be sure that your reader can easily tell what’s going on! Be aware, too, of the placement of your different points. If you are writing a comparison/contrast in service of an argument, keep in mind that the last point you make is the one you are leaving your reader with. For example, if I am trying to argue that Amante is better than Pepper’s, I should end with a contrast that leaves Amante sounding good, rather than with a point of comparison that I have to admit makes Pepper’s look better. If you’ve decided that the differences between the items you’re comparing/contrasting are most important, you’ll want to end with the differences—and vice versa, if the similarities seem most important to you.
Our handout on organization can help you write good topic sentences and transitions and make sure that you have a good overall structure in place for your paper.
Cue words and other tips
To help your reader keep track of where you are in the comparison/contrast, you’ll want to be sure that your transitions and topic sentences are especially strong. Your thesis should already have given the reader an idea of the points you’ll be making and the organization you’ll be using, but you can help them out with some extra cues. The following words may be helpful to you in signaling your intentions:
- like, similar to, also, unlike, similarly, in the same way, likewise, again, compared to, in contrast, in like manner, contrasted with, on the contrary, however, although, yet, even though, still, but, nevertheless, conversely, at the same time, regardless, despite, while, on the one hand … on the other hand.
For example, you might have a topic sentence like one of these:
- Compared to Pepper’s, Amante is quiet.
- Like Amante, Pepper’s offers fresh garlic as a topping.
- Despite their different locations (downtown Chapel Hill and downtown Carrboro), Pepper’s and Amante are both fairly easy to get to.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Organizing Academic Research Papers: Multiple Book Review Essay
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
A multiple book essay involves writing a review of two or generally no more than six books that cover the same overall subject area [e.g., analysis of European debt crisis] or that are related to each other in a particular way [e.g., applying grounded theory methods to study student access to education]. The reviews are written in the form of a short scholarly paper [essay] rather than as a descriptive review of the books. The purpose is to compare and contrast the works under review, identifying key themes and critical issues and assessing each writer's contributions to understanding the general topics discussed in each book. Professors assign reviews of multiple books to help students gain experience in evaluating the ways in which different researchers examine and interpret issues related to a specific research problem.
How to Approach Writing Your Review
Developing an Assessment Strategy
As with reviewing a work of collected essays, you must think critically about the research problem under study by multiple authors before you begin writing. The challenge is to develop an argument about each book you are reviewing and then clearly compare, contrast, and ultimately sythesize the themes into an well organized and well supported essay.
Think of a multiple book review essay as a type of compare and contrast paper similar to what you may have written for a general issue-oriented composition class . As you read through each book, write down the following questions and answer them as you read [remember to note the page numbers and from which book you got the information from so you can refer back it later!]. Which questions are most useful will depend upon the type of books you are reviewing and how they are related to each other.
Here are a series of questions to focus your thinking:
- What is the thesis—or main argument—of each book? If the author wanted you to get one idea from the book, what would it be? How does it compare or contrast to the world you know? What has the book accomplished?
- What exactly is the subject or topic of each book? Does the author cover the subject adequately? Does the author cover all aspects of the subject in a balanced fashion? Can you detect any biases? What is the approach to the subject (topical, analytical, chronological, descriptive)?
- How does the author of each book support his or her argument? What evidence does each author use to prove his or her point? Do you find that evidence convincing? Why or why not? Does any of the author's information [or conclusions] conflict with other books you've read, courses you've taken, or just previous assumptions you had about the research problem under study?
- How does the author structure his or her argument? What are the parts that make up the whole? Does the argument make sense to you? Does it persuade you? Why or why not?
- How has each book helped you understand the subject? Would you recommend the book to others? Why or why not?
Beyond the content of the book, you may also consider some information about the author and the circumstances of the text's production:
- Who is the author? Nationality, political persuasion, training, intellectual interests, personal history, and historical context may provide crucial details about how a work takes shape. Does it matter, for example, that the author is affiliated with a particular organization? What difference would it make if the author participated in the events he or she writes about? What other topics has the author written about? Does this work build on prior research or does it seem to represent a new area of research?
- What is the book's genre? Out of what discipline does it emerge? Does it conform to or depart from the conventions of its genre? These questions can provide a historical or other contextual standard upon which to base your evaluations. If you are reviewing the first book ever written on the subject, it will be important for your readers to know this. Keep in mind, though, that declarative statements about being the “first,” the "best," or the "only" book of its kind can be a risky unless you're absolutely certain because your professor [presumably] has a much better understanding of the overall research literature.
Bazerman, Charles. Comparing and Synthesizing Sources . The Informed Writer: Using Sources in the Disciplines. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Comparing and Contrasting . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Comparison and Contrast Essays. Writing Support Centre. University of Western Ontario; Walk, Kerry. How to Write a Compare-and-Contrast Paper. Writing Center. Princeton Writing Program; Rhetorical Strategies: Comparison and Contrast . The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College; Visvis, Vikki and Jerry Plotnick; Writing a Compare/Contrast Essay. The Comparative Essay. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Compare/Contrast Essay . CLRC Writing Center. Santa Barbara City College.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Bibliographic Information
Provide the essential information about each book using the writing style asked for by your professor [e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.]. Depending on how your professor wants you to organize your review, the bibliographic information represents the heading of your review. In general, they would be arranged alphabetically by title and look like this:
Racing the Storm: Racial Implications and Lessons Learned from Hurricane Katrina . Hillary Potter, ed. (Lanham, MD: Lexington Books, 2007. 320 pp) The Sociology of Katrina: Perspectives on a Modern Catastrophe . David L. Brunsma, David Overfelt, and J. Steven Picou, eds. (Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield, 2007. 288 pp.) Through the Eye of Katrina: Social Justice in the United States . Kristin A. Bates and Richelle S. Swan, eds. (Durham, NC: Carolina Academic Press, 2007. 440 pp.) Reviewed by [your name]
II. Thesis Statement
The thesis statement of an essay that compares and contrasts multiple works should contain an idea or claim that unites a discussion of the texts under review . It should include the argument that will be advanced in support of the claims that is being made. To begin, ask yourself: "What is the overarching subject or issue that ties together all of the books?" Why is it important?" In most scholarly works, the author(s) will state the purpose of their book in the preface or in an introductory chapter.
If you cannot find an adequate statement in the author's own words or if you find that the thesis statement is not well-developed, then you will have to compose your own introductory thesis statement that does cover all the material. For a book review essay, this thesis statement will vary in length depending on the number and complxity of books. Regardless of length, it must be succinct, accurate, unbiased, and clear.
If you find it difficult to discern the overall aims and objectives of the book [and, be sure to point this out in your review if you believe it to be a deficiency], you may arrive at an understanding of the purpose by asking yourself a the following questions:
- Why did the author write on this subject rather than on some other subject?
- From what point of view is the work written?
- Was the author trying to give information, to explain something technical, or to convince the reader of a belief’s validity by dramatizing it in action?
- What is the general field or genre, and how does the book fit into it? Review related literature from other books and journal articles to familiarize yourself with the field, if necessary.
- Who is the intended audience?
- What is the author's style? Is it formal or informal? You can evaluate the quality of the writing style by noting some of the following standards: coherence, clarity, originality, forcefulness, correct use of technical words, conciseness, fullness of development, and fluidity.
- Scan the Table of Contents because it can help you understand how the book is organized and will aid in determining the author's main ideas and how they are developed [e.g., chronologically, topically, etc.]
- How did the book affect you? Were any prior assumptions you had on the subject changed, abandoned, or reinforced due to this book? How is the book related to your own course or personal agenda? What personal experiences have you had that relate to the subject?
- How well has the book achieved its goal(s)?
- Would you recommend this book to others? Why or why not?
NOTE : Be sure that your thesis statement includes the rationale behind why your choice of what points to compare and contrast were deliberate and meaningful and not random!
III. Methods of Organization
Organization is critical to writing an essay that compares and contrasts multiple works because you will most likely be discussing a variety of evidence and you must be certain that the logic and narrative flow of your paper can be understood by the reader. Here are some general guidelines to consider:
- If your professor asks you to choose the books to review, identify works that are closely related in some way so they can be easily compared or contrasted.
- Compare according to a single organized idea.
- Choose a method of development [see below] that works well with your organizing idea.
- Use specific and relevant examples to support your analysis.
- Use transitional words or phrases to help the reader understand the similarities and differences in your subject.
- Conclude your paper by restating your thesis, summarizing the main points, and give the reader the final "so what" of the major similarities and/or differences that you discussed. Why are they important?
There are two general methods of organizing your book review essay. If you believe one work extends another, you'll probably use a block method; if you find that two or more works are essentially engaged in a debate, a point-by-point method will help draw attention to the conflict. However, the point-by-point method can come off as a rhetorical ping-pong match. You can avoid this effect by grouping more than one point together, thereby cutting down on the number of times you alternate from one work to another. No matter which method you choose, you do not need to give equal time to similarities and differences. In fact, your paper will be more interesting if you state your main argument(s) as quickly as possible. For example, a book review essay evaluating three research studies that examine different interpretations of conflict resolution among nations in the Middl East might have as few as two or three sentences in the introduction regarding similarities and only a paragraph or two to set up the contrast between the author’s positions. The rest of the essay, whether organized by block method or point-by-point, will be your analysis of the key differences among the books.
The Block Method Present all the information about A, and then present parallel information about B. This pattern tends to work better for shorter book review essays, and those with few sub-topics. The method looks like this:
I. Introduction A. Briefly introduce the significance of the overall subject matter B. Thesis Statement --First supporting point --Second supporting point --Third supporting point II. First book A. Summary of book --Relationship of work to first point --Relationship of work to second point --Relationship of work to third point III. Second book A. Summary of book --Relationship of work to first point --Relationship of work to second point --Relationship of work to third point IV. Third book A. Summary of book --Relationship of work to first point --Relationship of work to second point --Relationship of work to third point V. Conclusion A. Restate thesis B. Summarize how you proved your argument The Point-by-Point Method Present one point about A, and then go to the parallel point about B. Move to the next point, and do the same thing. This pattern tends to work better for long book review essays and those with many sub-topics. The method looks like this:
I. Introduction A. Briefly introduce significance of overall subject matter B. Thesis statement II. Brief explanation of first book III. Brief explanation of second book IV. First comparative point A. Relation of point to first book B. Relation of point to second book V. Second comparative point A. Relation of point to first book B. Relation of point to second book VI. Third comparative point A. Relation of point to first book B. Relation of point to second book VII. Conclusion A. Restate thesis B. Summarize how your proved your argument
IV. Critically Evaluate the Contents
Regardless of whether you choose the block method or the point-by-point method, critical comments should form the bulk of your book review essay . State whether or not you feel the author's treatment of the subject matter is appropriate for the intended audience. Ask yourself:
- Has the purpose of the book been achieved?
- What contribution does the book make to the field?
- Is the treatment of the subject matter objective?
- Are there facts and evidence that have been omitted?
- What kinds of data, if any, are used to support the author's thesis statement?
- Can the same data be interpreted to alternate ends?
- Is the writing style clear and effective?
- Does the book raise important or provocative issues or topics for discussion and further research?
- What has been left out?
Support your evaluation with evidence from each text and, when possible, in relation to other sources. If relevant, make note of each book's format, such as, layout, binding, typography, etc. Are there maps, illustrations? Do they aid in understanding the research problem? This is particular important in books that contain a lot of non-textual elements, such as tables, charts, and illustrations.
NOTE : It is important to carefully distinguish your views from those of the authors, so that you don’t confuse your reader.
V. Examine the Front Matter and Back Matter
Back matter refers to any information included after the final chapter of the book. Front matter refers to anything before the first chapter. Front matter is most often numbered separately from the rest of the text in lower case Roman numerals [i.e. i-xi ]. Critical commentary about front or back matter is generally only necessary if you believe there is something that diminishes the overall quality of the work or there is something that is particularly helpful in understanding the book's contents.
The following back matter may be included in a book and should be considered for evaluation when reviewing the overall quality of the book:
- Table of contents --is it clear? Does it reflect the true contents of the book?
- Author biography --also found as back matter, the biography of author(s) can be useful in determining the authority of the writer and whether the book builds on prior research or represents new research. In scholarly reviews, noting the author's affiliation can be a factor in helping the reader determine the overall validity of work [i.e., are they associated with a research center devoted to studying the research problem under investigation].
- Foreword --in a scholarly books, a foreword may be written by the author or an expert on the subject of the book. The purpose of a foreword is to introduce the reader to the author as well as the book itself, and attempt to establish credibility for both. A foreword does not contribute any additional information about the book's subject matter, but it serves as a means of validating the book's existence. Later editions of a book sometimes have a new foreword prepended [appearing before an older foreword if there was one], which might explain in what respects that edition differs from previous ones.
- Preface --generally describes the genesis, purpose, limitations, and scope of the book and may include acknowledgments of indebtedness to people who have helped the author complerte the study. Is the preface helpful in understanding the study? Does it effectively provide a framework for what's to follow?
- Chronology --also found as back matter, a chronology is generally included to highlight key events related to the subject of the book. Does it contribute to the overall work? Is it detailed or very general?
- List of non-textual elements --if a book contains a lot of charts, photographs, maps, etc., they will often be listed in the front.
- Afterword --this is a short, reflective piece written by the author that takes the form of a concluding section, final commentary, or closing statement. It is worth mentioning in a review if it contributes information about the purpose of the book, gives a call to action, or asks the reader to consider key points made in the book.
- Appendix --is the supplementary material in the appendix or appendices well organized? Do they relate to the contents or appear superfluous? Does it contain any essential information that would have been more appropriately integrated into the text?
- Index --is the index thorough and accurate? Are there elements such as bold text, to help identify specific parts of the book?
- Glossary --are the definitions clearly written? Is the glossary comprehensive or are key terms missing?
- Endotes/Footnotes --check any end notes or footnotes as you read from chapter to chapter. Do they provide important additional information? Do they clarify or extend points made in the body of the text?
- Bibliography/Further Readings --review any bibliography or further readings the author may have included. What kinds of sources [e.g., primary or secondary, recent or old, scholarly or popular, etc.] appear in the bibliography? How does the author make use of them? Make note of important omissions.
NOTE : In reviewing multiple works, compare and contrast the quality of the back and front matter. Be sure to highlight works where the front or back matter is particularly well-organized or effective in supplementing the main content.
VI. Summarize and Comment
Your conclusion should synthesize the key similarities and differences among the books. Avoid stating restating your assessment word for word; your goal is to provide a sense of closure and to leave the reader with a final perspective about the overall subject under review and whether you believe each book has effectively contributed to the overall research literature on the subject. Do not introduce new information or ideas in the conclusion.
Bazerman, Charles. Comparing and Synthesizing Sources . The Informed Writer: Using Sources in the Disciplines. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Comparing and Contrasting . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Comparison and Contrast Essays. Writing Support Centre. University of Western Ontario; Rhetorical Strategies: Comparison and Contrast . The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College; Hooker, Fran and Kate James. Apples to Oranges: Writing a Compare and Contrast Paper. The Writing Center. Webster University; Visvis, Vikki and Jerry Plotnick. The Comparative Essay . The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Compare/Contrast Essay . CLRC Writing Center. Santa Barbara City College.
- << Previous: Writing a Book Review
- Next: Reviewing Collected Essays >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
Your browser is ancient! Upgrade to a different browser or install Google Chrome Frame to experience this site.
Enjoy tips on academic writing and free sample research papers, essays, speeches, book reviews and much more than that. All tips are prepared by the seasoned academic writers, and you can always count on their reliability and practical efficiency. Our well-thought-out sample papers can be used as illustrative examples for your own academic writing. No matter which type of academic assistance you need right now, you can always rely on our professionalism and experience.
Comparison Essay on Two Books
The last two books I chose to read were: “One Hundred Years of Solitude” by Gabriel Garcia Marquez and “Miss Brill” by Katherine Mansfield. These are certainly two different books, but the some main themes are close in a way.
The book “One Hundred Years of Solitude” seemed to me rather unusual, the whole style of the author and the plot itself, and it was rather hard to remember all the names of the heroes.
This book is about 100 years of life of one family – Buendia. They live in an unnamed African country in jungles. It is called even a tale by some of the readers, as this novel is full of supernatural events and unusual characters. I would call it also a kind of a fairy tale, not a novel. Many layers of fantasy are mixed up in the lives of the main heroes of several generations of Buendia family. The story seems to have no plot, it is more like a collection of fantastic stories of each of the members of the family. All of them have their own obsessions, problems and insanity. When you start reading the book you might feel that all the events taking place are absolutely stupid and all the heroes are simply sick, but later on, the novel made me think more deeply about my life and about my relations with other people and even with members of my family. Probably everybody could find something interesting and new in this book.
It is also connected with the unique reality of Latin America – it was between modernity and the stage of pre- industrialization, after a civil war and attacked by imperialism. Thus this was a strategy used by several authors of those times – magic going through ordinary lives, mixing up the reality and fiction.
From the title already the main theme of the novel can be determined – solitude, which applies to every character in a unique way. Here it is not compared with loneliness, more with the obsession by seclusion or even madness. The characters fail to build a communication with each other and pay attention to the problems of others. I am sure all people face loneliness in their lives, it doesn’t matter if they have a lot of friends and happy family, all people feel lack of understanding and lack of support from the surrounding society from time to time, this is the main reason why this book was interesting to me.
Many critics debate whether there is a political message in this novel. Political significance in the story is seen for example when Aureliano learns about two political parties: Conservatives and Liberals and when a war broke out in Macondo. The theme of Latin American political violence is rather important in the whole novel. But it is less connected with human feelings and emotions and was of minor interest for me.
The second book – “Miss Brill” is a story about a woman, about her internal condition, about hurting feeling of loneliness and deep desire to be important, about estrangement. It is a natural desire for every human being to feel a part of the society, to be important and recognized at least for and by the members of his family and friends and colleagues – these all are the important concepts of the narration.
The whole story is an interior monologue of a woman.
It is difficult to find the conflict of the story while reading the first pages, when you are made to feel the spirit of the Sunday day, park with people walking and band playing, when you see everything “through” the mind and feelings of Miss Brill.
At the beginning of the story she seems to live in an illusionary world of “theatre” as she calls it for herself:” They were all on stage. They weren’t only the audience, no only looking on; they were acting.” She doesn’t want to look at herself as some old bench sitter, she prefers to see her as an actress, whose absence in this play everybody would notice. This is a way to escape from gloomy feeling of non-importance to the society and loneliness. Her “little dark room” is a bright contrast to the park, she comes to.
There’s hardly a reader, who could feel indifferent to the emotions of the main heroin. After reading the story one would feel so sorry that she had heard that conversation of the young couple, which spoilt her day and her mood, brightened in a little naive way. Miss Brill seems a kind of a person, who is never able to do any kind of harm to others, who wouldn’t expect to be hurt by others either, who is ready to pay a lot of attention to the problems of other people, as she doesn’t want to live only in her small world of a dark room. But unfortunately, her attempt to leave it and move closer to others brings joy only for some short period of time and then turns into even more painful situation.
It is usually captivating for me to read a book discovering person’s inner world, feelings and emotional experience, that is why this one was also of a great interest to me. This book could probably teach to develop the feelings of sympathy and forbearance towards other people, who might even seem to be strange.
Sources: “One Hundred Years of Solitude” by Gabriel Garcia Marquez “Miss Brill” by Katherine Mansfield
- Free Samples
- Writing Tips
April 11, 2013
15 min read
The Reading Brain in the Digital Age: The Science of Paper versus Screens
E-readers and tablets are becoming more popular as such technologies improve, but research suggests that reading on paper still boasts unique advantages
By Ferris Jabr

Getty Images

On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
In a viral YouTube video from October 2011 a one-year-old girl sweeps her fingers across an iPad's touchscreen, shuffling groups of icons. In the following scenes she appears to pinch, swipe and prod the pages of paper magazines as though they too were screens. When nothing happens, she pushes against her leg, confirming that her finger works just fine—or so a title card would have us believe. The girl's father, Jean-Louis Constanza , presents "A Magazine Is an iPad That Does Not Work" as naturalistic observation—a Jane Goodall among the chimps moment—that reveals a generational transition. "Technology codes our minds," he writes in the video's description. "Magazines are now useless and impossible to understand, for digital natives"—that is, for people who have been interacting with digital technologies from a very early age. Perhaps his daughter really did expect the paper magazines to respond the same way an iPad would. Or maybe she had no expectations at all—maybe she just wanted to touch the magazines. Babies touch everything . Young children who have never seen a tablet like the iPad or an e-reader like the Kindle will still reach out and run their fingers across the pages of a paper book; they will jab at an illustration they like; heck, they will even taste the corner of a book. Today's so-called digital natives still interact with a mix of paper magazines and books, as well as tablets, smartphones and e-readers; using one kind of technology does not preclude them from understanding another. Nevertheless, the video brings into focus an important question: How exactly does the technology we use to read change the way we read? How reading on screens differs from reading on paper is relevant not just to the youngest among us , but to just about everyone who reads—to anyone who routinely switches between working long hours in front of a computer at the office and leisurely reading paper magazines and books at home; to people who have embraced e-readers for their convenience and portability, but admit that for some reason they still prefer reading on paper; and to those who have already vowed to forgo tree pulp entirely. As digital texts and technologies become more prevalent, we gain new and more mobile ways of reading—but are we still reading as attentively and thoroughly? How do our brains respond differently to onscreen text than to words on paper? Should we be worried about dividing our attention between pixels and ink or is the validity of such concerns paper-thin? Since at least the 1980s researchers in many different fields—including psychology, computer engineering, and library and information science—have investigated such questions in more than one hundred published studies. The matter is by no means settled. Before 1992 most studies concluded that people read slower, less accurately and less comprehensively on screens than on paper. Studies published since the early 1990s , however, have produced more inconsistent results: a slight majority has confirmed earlier conclusions, but almost as many have found few significant differences in reading speed or comprehension between paper and screens. And recent surveys suggest that although most people still prefer paper—especially when reading intensively—attitudes are changing as tablets and e-reading technology improve and reading digital books for facts and fun becomes more common. In the U.S., e-books currently make up between 15 and 20 percent of all trade book sales. Even so, evidence from laboratory experiments , polls and consumer reports indicates that modern screens and e-readers fail to adequately recreate certain tactile experiences of reading on paper that many people miss and, more importantly, prevent people from navigating long texts in an intuitive and satisfying way. In turn, such navigational difficulties may subtly inhibit reading comprehension. Compared with paper, screens may also drain more of our mental resources while we are reading and make it a little harder to remember what we read when we are done. A parallel line of research focuses on people's attitudes toward different kinds of media. Whether they realize it or not, many people approach computers and tablets with a state of mind less conducive to learning than the one they bring to paper.
"There is physicality in reading," says developmental psychologist and cognitive scientist Maryanne Wolf of Tufts University, "maybe even more than we want to think about as we lurch into digital reading—as we move forward perhaps with too little reflection. I would like to preserve the absolute best of older forms, but know when to use the new." Navigating textual landscapes Understanding how reading on paper is different from reading on screens requires some explanation of how the brain interprets written language. We often think of reading as a cerebral activity concerned with the abstract—with thoughts and ideas, tone and themes, metaphors and motifs. As far as our brains are concerned, however, text is a tangible part of the physical world we inhabit. In fact, the brain essentially regards letters as physical objects because it does not really have another way of understanding them. As Wolf explains in her book Proust and the Squid , we are not born with brain circuits dedicated to reading. After all, we did not invent writing until relatively recently in our evolutionary history, around the fourth millennium B.C. So the human brain improvises a brand-new circuit for reading by weaving together various regions of neural tissue devoted to other abilities, such as spoken language, motor coordination and vision. Some of these repurposed brain regions are specialized for object recognition —they are networks of neurons that help us instantly distinguish an apple from an orange, for example, yet classify both as fruit. Just as we learn that certain features—roundness, a twiggy stem, smooth skin—characterize an apple, we learn to recognize each letter by its particular arrangement of lines, curves and hollow spaces. Some of the earliest forms of writing, such as Sumerian cuneiform , began as characters shaped like the objects they represented —a person's head, an ear of barley, a fish. Some researchers see traces of these origins in modern alphabets: C as crescent moon, S as snake. Especially intricate characters—such as Chinese hanzi and Japanese kanji —activate motor regions in the brain involved in forming those characters on paper: The brain literally goes through the motions of writing when reading, even if the hands are empty. Researchers recently discovered that the same thing happens in a milder way when some people read cursive. Beyond treating individual letters as physical objects, the human brain may also perceive a text in its entirety as a kind of physical landscape. When we read, we construct a mental representation of the text in which meaning is anchored to structure. The exact nature of such representations remains unclear, but they are likely similar to the mental maps we create of terrain—such as mountains and trails—and of man-made physical spaces, such as apartments and offices. Both anecdotally and in published studies , people report that when trying to locate a particular piece of written information they often remember where in the text it appeared. We might recall that we passed the red farmhouse near the start of the trail before we started climbing uphill through the forest; in a similar way, we remember that we read about Mr. Darcy rebuffing Elizabeth Bennett on the bottom of the left-hand page in one of the earlier chapters. In most cases, paper books have more obvious topography than onscreen text. An open paperback presents a reader with two clearly defined domains—the left and right pages—and a total of eight corners with which to orient oneself. A reader can focus on a single page of a paper book without losing sight of the whole text: one can see where the book begins and ends and where one page is in relation to those borders. One can even feel the thickness of the pages read in one hand and pages to be read in the other. Turning the pages of a paper book is like leaving one footprint after another on the trail—there's a rhythm to it and a visible record of how far one has traveled. All these features not only make text in a paper book easily navigable, they also make it easier to form a coherent mental map of the text. In contrast, most screens, e-readers, smartphones and tablets interfere with intuitive navigation of a text and inhibit people from mapping the journey in their minds. A reader of digital text might scroll through a seamless stream of words, tap forward one page at a time or use the search function to immediately locate a particular phrase—but it is difficult to see any one passage in the context of the entire text. As an analogy, imagine if Google Maps allowed people to navigate street by individual street, as well as to teleport to any specific address, but prevented them from zooming out to see a neighborhood, state or country. Although e-readers like the Kindle and tablets like the iPad re-create pagination—sometimes complete with page numbers, headers and illustrations—the screen only displays a single virtual page: it is there and then it is gone. Instead of hiking the trail yourself, the trees, rocks and moss move past you in flashes with no trace of what came before and no way to see what lies ahead. "The implicit feel of where you are in a physical book turns out to be more important than we realized," says Abigail Sellen of Microsoft Research Cambridge in England and co-author of The Myth of the Paperless Office . "Only when you get an e-book do you start to miss it. I don't think e-book manufacturers have thought enough about how you might visualize where you are in a book." At least a few studies suggest that by limiting the way people navigate texts, screens impair comprehension. In a study published in January 2013 Anne Mangen of the University of Stavanger in Norway and her colleagues asked 72 10th-grade students of similar reading ability to study one narrative and one expository text, each about 1,500 words in length. Half the students read the texts on paper and half read them in pdf files on computers with 15-inch liquid-crystal display (LCD) monitors. Afterward, students completed reading-comprehension tests consisting of multiple-choice and short-answer questions, during which they had access to the texts. Students who read the texts on computers performed a little worse than students who read on paper. Based on observations during the study, Mangen thinks that students reading pdf files had a more difficult time finding particular information when referencing the texts. Volunteers on computers could only scroll or click through the pdfs one section at a time, whereas students reading on paper could hold the text in its entirety in their hands and quickly switch between different pages. Because of their easy navigability, paper books and documents may be better suited to absorption in a text. "The ease with which you can find out the beginning, end and everything inbetween and the constant connection to your path, your progress in the text, might be some way of making it less taxing cognitively, so you have more free capacity for comprehension," Mangen says. Supporting this research, surveys indicate that screens and e-readers interfere with two other important aspects of navigating texts: serendipity and a sense of control. People report that they enjoy flipping to a previous section of a paper book when a sentence surfaces a memory of something they read earlier, for example, or quickly scanning ahead on a whim. People also like to have as much control over a text as possible—to highlight with chemical ink, easily write notes to themselves in the margins as well as deform the paper however they choose. Because of these preferences—and because getting away from multipurpose screens improves concentration—people consistently say that when they really want to dive into a text, they read it on paper. In a 2011 survey of graduate students at National Taiwan University, the majority reported browsing a few paragraphs online before printing out the whole text for more in-depth reading. A 2008 survey of millennials (people born between 1980 and the early 2000s) at Salve Regina University in Rhode Island concluded that, "when it comes to reading a book, even they prefer good, old-fashioned print". And in a 2003 study conducted at the National Autonomous University of Mexico, nearly 80 percent of 687 surveyed students preferred to read text on paper as opposed to on a screen in order to "understand it with clarity". Surveys and consumer reports also suggest that the sensory experiences typically associated with reading—especially tactile experiences—matter to people more than one might assume. Text on a computer, an e-reader and—somewhat ironically—on any touch-screen device is far more intangible than text on paper. Whereas a paper book is made from pages of printed letters fixed in a particular arrangement, the text that appears on a screen is not part of the device's hardware—it is an ephemeral image. When reading a paper book, one can feel the paper and ink and smooth or fold a page with one's fingers; the pages make a distinctive sound when turned; and underlining or highlighting a sentence with ink permanently alters the paper's chemistry. So far, digital texts have not satisfyingly replicated this kind of tactility (although some companies are innovating, at least with keyboards ). Paper books also have an immediately discernible size, shape and weight. We might refer to a hardcover edition of War and Peace as a hefty tome or a paperback Heart of Darkness as a slim volume. In contrast, although a digital text has a length—which is sometimes represented with a scroll or progress bar—it has no obvious shape or thickness. An e-reader always weighs the same, regardless of whether you are reading Proust's magnum opus or one of Hemingway's short stories. Some researchers have found that these discrepancies create enough " haptic dissonance " to dissuade some people from using e-readers. People expect books to look, feel and even smell a certain way; when they do not, reading sometimes becomes less enjoyable or even unpleasant. For others, the convenience of a slim portable e-reader outweighs any attachment they might have to the feel of paper books. Exhaustive reading Although many old and recent studies conclude that people understand what they read on paper more thoroughly than what they read on screens, the differences are often small. Some experiments, however, suggest that researchers should look not just at immediate reading comprehension, but also at long-term memory. In a 2003 study Kate Garland of the University of Leicester and her colleagues asked 50 British college students to read study material from an introductory economics course either on a computer monitor or in a spiral-bound booklet. After 20 minutes of reading Garland and her colleagues quizzed the students with multiple-choice questions. Students scored equally well regardless of the medium, but differed in how they remembered the information. Psychologists distinguish between remembering something—which is to recall a piece of information along with contextual details, such as where, when and how one learned it—and knowing something, which is feeling that something is true without remembering how one learned the information. Generally, remembering is a weaker form of memory that is likely to fade unless it is converted into more stable, long-term memory that is "known" from then on. When taking the quiz, volunteers who had read study material on a monitor relied much more on remembering than on knowing, whereas students who read on paper depended equally on remembering and knowing. Garland and her colleagues think that students who read on paper learned the study material more thoroughly more quickly; they did not have to spend a lot of time searching their minds for information from the text, trying to trigger the right memory—they often just knew the answers. Other researchers have suggested that people comprehend less when they read on a screen because screen-based reading is more physically and mentally taxing than reading on paper. E-ink is easy on the eyes because it reflects ambient light just like a paper book, but computer screens, smartphones and tablets like the iPad shine light directly into people's faces. Depending on the model of the device, glare, pixilation and flickers can also tire the eyes. LCDs are certainly gentler on eyes than their predecessor, cathode-ray tubes (CRT), but prolonged reading on glossy self-illuminated screens can cause eyestrain, headaches and blurred vision. Such symptoms are so common among people who read on screens—affecting around 70 percent of people who work long hours in front of computers—that the American Optometric Association officially recognizes computer vision syndrome . Erik Wästlund of Karlstad University in Sweden has conducted some particularly rigorous research on whether paper or screens demand more physical and cognitive resources. In one of his experiments 72 volunteers completed the Higher Education Entrance Examination READ test—a 30-minute, Swedish-language reading-comprehension exam consisting of multiple-choice questions about five texts averaging 1,000 words each. People who took the test on a computer scored lower and reported higher levels of stress and tiredness than people who completed it on paper. In another set of experiments 82 volunteers completed the READ test on computers, either as a paginated document or as a continuous piece of text. Afterward researchers assessed the students' attention and working memory, which is a collection of mental talents that allow people to temporarily store and manipulate information in their minds. Volunteers had to quickly close a series of pop-up windows, for example, sort virtual cards or remember digits that flashed on a screen. Like many cognitive abilities, working memory is a finite resource that diminishes with exertion. Although people in both groups performed equally well on the READ test, those who had to scroll through the continuous text did not do as well on the attention and working-memory tests. Wästlund thinks that scrolling—which requires a reader to consciously focus on both the text and how they are moving it—drains more mental resources than turning or clicking a page, which are simpler and more automatic gestures. A 2004 study conducted at the University of Central Florida reached similar conclusions. Attitude adjustments An emerging collection of studies emphasizes that in addition to screens possibly taxing people's attention more than paper, people do not always bring as much mental effort to screens in the first place. Subconsciously, many people may think of reading on a computer or tablet as a less serious affair than reading on paper. Based on a detailed 2005 survey of 113 people in northern California, Ziming Liu of San Jose State University concluded that people reading on screens take a lot of shortcuts—they spend more time browsing, scanning and hunting for keywords compared with people reading on paper, and are more likely to read a document once, and only once. When reading on screens, people seem less inclined to engage in what psychologists call metacognitive learning regulation—strategies such as setting specific goals, rereading difficult sections and checking how much one has understood along the way. In a 2011 experiment at the Technion–Israel Institute of Technology, college students took multiple-choice exams about expository texts either on computers or on paper. Researchers limited half the volunteers to a meager seven minutes of study time; the other half could review the text for as long as they liked. When under pressure to read quickly, students using computers and paper performed equally well. When managing their own study time, however, volunteers using paper scored about 10 percentage points higher. Presumably, students using paper approached the exam with a more studious frame of mind than their screen-reading peers, and more effectively directed their attention and working memory. Perhaps, then, any discrepancies in reading comprehension between paper and screens will shrink as people's attitudes continue to change. The star of "A Magazine Is an iPad That Does Not Work" is three-and-a-half years old today and no longer interacts with paper magazines as though they were touchscreens, her father says. Perhaps she and her peers will grow up without the subtle bias against screens that seems to lurk in the minds of older generations. In current research for Microsoft, Sellen has learned that many people do not feel much ownership of e-books because of their impermanence and intangibility: "They think of using an e-book, not owning an e-book," she says. Participants in her studies say that when they really like an electronic book, they go out and get the paper version. This reminds Sellen of people's early opinions of digital music, which she has also studied. Despite initial resistance, people love curating, organizing and sharing digital music today. Attitudes toward e-books may transition in a similar way, especially if e-readers and tablets allow more sharing and social interaction than they currently do. Books on the Kindle can only be loaned once , for example. To date, many engineers, designers and user-interface experts have worked hard to make reading on an e-reader or tablet as close to reading on paper as possible. E-ink resembles chemical ink and the simple layout of the Kindle's screen looks like a page in a paperback. Likewise, Apple's iBooks attempts to simulate the overall aesthetic of paper books, including somewhat realistic page-turning. Jaejeung Kim of KAIST Institute of Information Technology Convergence in South Korea and his colleagues have designed an innovative and unreleased interface that makes iBooks seem primitive. When using their interface, one can see the many individual pages one has read on the left side of the tablet and all the unread pages on the right side, as if holding a paperback in one's hands. A reader can also flip bundles of pages at a time with a flick of a finger. But why, one could ask, are we working so hard to make reading with new technologies like tablets and e-readers so similar to the experience of reading on the very ancient technology that is paper? Why not keep paper and evolve screen-based reading into something else entirely? Screens obviously offer readers experiences that paper cannot. Scrolling may not be the ideal way to navigate a text as long and dense as Moby Dick , but the New York Times , Washington Post , ESPN and other media outlets have created beautiful, highly visual articles that depend entirely on scrolling and could not appear in print in the same way. Some Web comics and infographics turn scrolling into a strength rather than a weakness. Similarly, Robin Sloan has pioneered the tap essay for mobile devices. The immensely popular interactive Scale of the Universe tool could not have been made on paper in any practical way. New e-publishing companies like Atavist offer tablet readers long-form journalism with embedded interactive graphics, maps, timelines, animations and sound tracks. And some writers are pairing up with computer programmers to produce ever more sophisticated interactive fiction and nonfiction in which one's choices determine what one reads, hears and sees next. When it comes to intensively reading long pieces of plain text, paper and ink may still have the advantage. But text is not the only way to read.
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essays Samples >
- Essay Types >
- Research Paper Example
Novel Research Papers Samples For Students
282 samples of this type
If you're looking for a viable method to simplify writing a Research Paper about Novel, WowEssays.com paper writing service just might be able to help you out.
For starters, you should browse our vast collection of free samples that cover most diverse Novel Research Paper topics and showcase the best academic writing practices. Once you feel that you've determined the basic principles of content structuring and taken away actionable insights from these expertly written Research Paper samples, putting together your own academic work should go much easier.
However, you might still find yourself in a situation when even using top-notch Novel Research Papers doesn't allow you get the job done on time. In that case, you can contact our writers and ask them to craft a unique Novel paper according to your custom specifications. Buy college research paper or essay now!
Charles Dickens Great Expectations Research Paper Samples
The element of nostalgia in the novel, good example of research paper on the depiction of violence in fight club, free name research paper example, ‘instructor’s name’.
Don't waste your time searching for a sample.
Get your research paper done by professional writers!
Just from $10/page
Free A Good Man Is Hard To Find Research Paper Sample
Research paper on catcher and the rye, insecurity and safeguarding ideal: the catcher in the rye, good research paper about bodega dreams, free research paper about the outsiders, good example of research paper on the theme of power in the harry potter series, nationalism, religion and gender in the good lord birdand the farming research papers example, hazel grace lancaster (character analysis) research paper.
[Subject/Course] [Submission Date]
The Difference Between Novel, Novella And Short Story Research Paper Example
Free the kite runner by khaled hosseini research paper example, example of hesses siddhartha and its impact on culture and society research paper, hermann hesse, good primary evidence: the crowd made speculations that roger chillingworth was lost research paper example.
Thesis Statement 1: Society has a way of punishing people they envy by emphasizing the latter’s weakness and making a ridicule out of that individual only to boost their personal worth. - Claim: When the beautiful and poised Hester Prynne arrived at Boston, she came alone awaiting for the arrival of her husband Roger Chillingworth, however, to everyone’s knowledge. This made the women of Boston threatened by her.
Good Example Of Research Paper On Salman Rushdie
The expedition of humpry clinker research paper samples, introduction, what is the relationship between love and duty in sula, and which one is ultimately research paper example, english: what is the relationship between love and duty in sula, and which one is ultimately privileged, the use of literary devices in literature research papers example, classic english literature: research paper, free frankenstein by mary shelley: its influence on science and popular culture research paper sample, free heart of darkness research paper sample, good example of beneath the lion's gaze research paper, madame bovary research paper sample, free how is guanyin (avalokiteshvara) reflected in the journey to the west research paper example, good example of orwells 1984: implications on the real world we live in today research paper, good research paper on wuthering heights, good example of exploring the issue of innocence in daisy miller research paper, good wuthering heights research paper example, analytical research essay research paper examples, free how does the toni morrison in the bluest eyes develop the character of pecola research paper example, how does the toni morrison, in “the bluest eyes,” develop the character of pecola so as to expose and attack “racial self-loathing” in the black community, sample research paper on across a hundred mountains, revealing the masque of immigration, good the brief wondrous life of oscar wao research paper example, sample research paper on the old man and the sea, good research paper on symbolism in the scarlet letter, good research paper on a christmas carol.
What is the meaning of life for Scrooge at the beginning of the novel, what is the meaning of life for the Bob Cratchit family, what makes them happy; What seems to be Marley's message about freedom, what ways was Scrooge free, was there a progression, what message does this novel have about personal freedom of choice; what is Scrooges' moral character
Introduction:
Literary analysis: beloved research papers examples, example of charlie and the chocolate factory research paper, the great gatsby research paper, example of research paper on suicide and choice in chopins the awakening, the handmaids tale research paper example, research paper on harlem renaissance writer- langston hughes, interview with susan minot research paper, a symbolic representation research paper examples, research paper on persepolis: the story of a childhood. marjane satrapi. 2004, absurdism in the stranger by albert camus research paper examples, adventures of huckleberry finn research paper example, life and works of norman mailer research paper sample, free research paper on feminism in mary shelleys frankenstein, the invisible man by ralph ellison research paper examples, example of research paper on of mice and men, free research paper on magical realism in latin american literature, walking towards the heart of darkness research paper example, free research paper on interdisciplinary research on the novel frankenstein, research paper on how "to kill a mockingbird" portrays race and how we as a society treat those different, research paper on the impact of society in mary shelley's frankenstein, english literature, research paper on this paper is a combination compare/contrast essay and , comparing, symbolism in a farewell to arms research paper, general purpose: to analyze.
Specific purpose: To analyze for my audience the use of symbolism in Ernest Hemingway’s novel A Farewell to Arms Central idea: The novel contains many instances of symbolism; the symbolism primarily corresponds to Hemingway’s feelings about war and the people who are in wars. I. Introduction
A. Hemingway uses symbolism throughout the novel
1. He condemns warfare. 2. He admires people who serve during wartime.
B Thesis and preview of main points
Free research paper on mama day, similarities between emily brontës life and wuthering heights research paper example, huck finns voyage of moral self-discovery research paper sample, the compassionate morality of a perfect sap-head, the things they carried- tim o'brien research paper example.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago—a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian—another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in Note 13.8 “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” .
Table 13.1 Section Headings
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
Glossary of research terms.
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
This glossary is intended to assist you in understanding commonly used terms and concepts when reading, interpreting, and evaluating scholarly research. Also included are common words and phrases defined within the context of how they apply to research in the social and behavioral sciences.
- Acculturation -- refers to the process of adapting to another culture, particularly in reference to blending in with the majority population [e.g., an immigrant adopting American customs]. However, acculturation also implies that both cultures add something to one another, but still remain distinct groups unto themselves.
- Accuracy -- a term used in survey research to refer to the match between the target population and the sample.
- Affective Measures -- procedures or devices used to obtain quantified descriptions of an individual's feelings, emotional states, or dispositions.
- Aggregate -- a total created from smaller units. For instance, the population of a county is an aggregate of the populations of the cities, rural areas, etc. that comprise the county. As a verb, it refers to total data from smaller units into a large unit.
- Anonymity -- a research condition in which no one, including the researcher, knows the identities of research participants.
- Baseline -- a control measurement carried out before an experimental treatment.
- Behaviorism -- school of psychological thought concerned with the observable, tangible, objective facts of behavior, rather than with subjective phenomena such as thoughts, emotions, or impulses. Contemporary behaviorism also emphasizes the study of mental states such as feelings and fantasies to the extent that they can be directly observed and measured.
- Beliefs -- ideas, doctrines, tenets, etc. that are accepted as true on grounds which are not immediately susceptible to rigorous proof.
- Benchmarking -- systematically measuring and comparing the operations and outcomes of organizations, systems, processes, etc., against agreed upon "best-in-class" frames of reference.
- Bias -- a loss of balance and accuracy in the use of research methods. It can appear in research via the sampling frame, random sampling, or non-response. It can also occur at other stages in research, such as while interviewing, in the design of questions, or in the way data are analyzed and presented. Bias means that the research findings will not be representative of, or generalizable to, a wider population.
- Case Study -- the collection and presentation of detailed information about a particular participant or small group, frequently including data derived from the subjects themselves.
- Causal Hypothesis -- a statement hypothesizing that the independent variable affects the dependent variable in some way.
- Causal Relationship -- the relationship established that shows that an independent variable, and nothing else, causes a change in a dependent variable. It also establishes how much of a change is shown in the dependent variable.
- Causality -- the relation between cause and effect.
- Central Tendency -- any way of describing or characterizing typical, average, or common values in some distribution.
- Chi-square Analysis -- a common non-parametric statistical test which compares an expected proportion or ratio to an actual proportion or ratio.
- Claim -- a statement, similar to a hypothesis, which is made in response to the research question and that is affirmed with evidence based on research.
- Classification -- ordering of related phenomena into categories, groups, or systems according to characteristics or attributes.
- Cluster Analysis -- a method of statistical analysis where data that share a common trait are grouped together. The data is collected in a way that allows the data collector to group data according to certain characteristics.
- Cohort Analysis -- group by group analytic treatment of individuals having a statistical factor in common to each group. Group members share a particular characteristic [e.g., born in a given year] or a common experience [e.g., entering a college at a given time].
- Confidentiality -- a research condition in which no one except the researcher(s) knows the identities of the participants in a study. It refers to the treatment of information that a participant has disclosed to the researcher in a relationship of trust and with the expectation that it will not be revealed to others in ways that violate the original consent agreement, unless permission is granted by the participant.
- Confirmability Objectivity -- the findings of the study could be confirmed by another person conducting the same study.
- Construct -- refers to any of the following: something that exists theoretically but is not directly observable; a concept developed [constructed] for describing relations among phenomena or for other research purposes; or, a theoretical definition in which concepts are defined in terms of other concepts. For example, intelligence cannot be directly observed or measured; it is a construct.
- Construct Validity -- seeks an agreement between a theoretical concept and a specific measuring device, such as observation.
- Constructivism -- the idea that reality is socially constructed. It is the view that reality cannot be understood outside of the way humans interact and that the idea that knowledge is constructed, not discovered. Constructivists believe that learning is more active and self-directed than either behaviorism or cognitive theory would postulate.
- Content Analysis -- the systematic, objective, and quantitative description of the manifest or latent content of print or nonprint communications.
- Context Sensitivity -- awareness by a qualitative researcher of factors such as values and beliefs that influence cultural behaviors.
- Control Group -- the group in an experimental design that receives either no treatment or a different treatment from the experimental group. This group can thus be compared to the experimental group.
- Controlled Experiment -- an experimental design with two or more randomly selected groups [an experimental group and control group] in which the researcher controls or introduces the independent variable and measures the dependent variable at least two times [pre- and post-test measurements].
- Correlation -- a common statistical analysis, usually abbreviated as r, that measures the degree of relationship between pairs of interval variables in a sample. The range of correlation is from -1.00 to zero to +1.00. Also, a non-cause and effect relationship between two variables.
- Covariate -- a product of the correlation of two related variables times their standard deviations. Used in true experiments to measure the difference of treatment between them.
- Credibility -- a researcher's ability to demonstrate that the object of a study is accurately identified and described based on the way in which the study was conducted.
- Critical Theory -- an evaluative approach to social science research, associated with Germany's neo-Marxist “Frankfurt School,” that aims to criticize as well as analyze society, opposing the political orthodoxy of modern communism. Its goal is to promote human emancipatory forces and to expose ideas and systems that impede them.
- Data -- factual information [as measurements or statistics] used as a basis for reasoning, discussion, or calculation.
- Data Mining -- the process of analyzing data from different perspectives and summarizing it into useful information, often to discover patterns and/or systematic relationships among variables.
- Data Quality -- this is the degree to which the collected data [results of measurement or observation] meet the standards of quality to be considered valid [trustworthy] and reliable [dependable].
- Deductive -- a form of reasoning in which conclusions are formulated about particulars from general or universal premises.
- Dependability -- being able to account for changes in the design of the study and the changing conditions surrounding what was studied.
- Dependent Variable -- a variable that varies due, at least in part, to the impact of the independent variable. In other words, its value “depends” on the value of the independent variable. For example, in the variables “gender” and “academic major,” academic major is the dependent variable, meaning that your major cannot determine whether you are male or female, but your gender might indirectly lead you to favor one major over another.
- Deviation -- the distance between the mean and a particular data point in a given distribution.
- Discourse Community -- a community of scholars and researchers in a given field who respond to and communicate to each other through published articles in the community's journals and presentations at conventions. All members of the discourse community adhere to certain conventions for the presentation of their theories and research.
- Discrete Variable -- a variable that is measured solely in whole units, such as, gender and number of siblings.
- Distribution -- the range of values of a particular variable.
- Effect Size -- the amount of change in a dependent variable that can be attributed to manipulations of the independent variable. A large effect size exists when the value of the dependent variable is strongly influenced by the independent variable. It is the mean difference on a variable between experimental and control groups divided by the standard deviation on that variable of the pooled groups or of the control group alone.
- Emancipatory Research -- research is conducted on and with people from marginalized groups or communities. It is led by a researcher or research team who is either an indigenous or external insider; is interpreted within intellectual frameworks of that group; and, is conducted largely for the purpose of empowering members of that community and improving services for them. It also engages members of the community as co-constructors or validators of knowledge.
- Empirical Research -- the process of developing systematized knowledge gained from observations that are formulated to support insights and generalizations about the phenomena being researched.
- Epistemology -- concerns knowledge construction; asks what constitutes knowledge and how knowledge is validated.
- Ethnography -- method to study groups and/or cultures over a period of time. The goal of this type of research is to comprehend the particular group/culture through immersion into the culture or group. Research is completed through various methods but, since the researcher is immersed within the group for an extended period of time, more detailed information is usually collected during the research.
- Expectancy Effect -- any unconscious or conscious cues that convey to the participant in a study how the researcher wants them to respond. Expecting someone to behave in a particular way has been shown to promote the expected behavior. Expectancy effects can be minimized by using standardized interactions with subjects, automated data-gathering methods, and double blind protocols.
- External Validity -- the extent to which the results of a study are generalizable or transferable.
- Factor Analysis -- a statistical test that explores relationships among data. The test explores which variables in a data set are most related to each other. In a carefully constructed survey, for example, factor analysis can yield information on patterns of responses, not simply data on a single response. Larger tendencies may then be interpreted, indicating behavior trends rather than simply responses to specific questions.
- Field Studies -- academic or other investigative studies undertaken in a natural setting, rather than in laboratories, classrooms, or other structured environments.
- Focus Groups -- small, roundtable discussion groups charged with examining specific topics or problems, including possible options or solutions. Focus groups usually consist of 4-12 participants, guided by moderators to keep the discussion flowing and to collect and report the results.
- Framework -- the structure and support that may be used as both the launching point and the on-going guidelines for investigating a research problem.
- Generalizability -- the extent to which research findings and conclusions conducted on a specific study to groups or situations can be applied to the population at large.
- Grey Literature -- research produced by organizations outside of commercial and academic publishing that publish materials, such as, working papers, research reports, and briefing papers.
- Grounded Theory -- practice of developing other theories that emerge from observing a group. Theories are grounded in the group's observable experiences, but researchers add their own insight into why those experiences exist.
- Group Behavior -- behaviors of a group as a whole, as well as the behavior of an individual as influenced by his or her membership in a group.
- Hypothesis -- a tentative explanation based on theory to predict a causal relationship between variables.
- Independent Variable -- the conditions of an experiment that are systematically manipulated by the researcher. A variable that is not impacted by the dependent variable, and that itself impacts the dependent variable. In the earlier example of "gender" and "academic major," (see Dependent Variable) gender is the independent variable.
- Individualism -- a theory or policy having primary regard for the liberty, rights, or independent actions of individuals.
- Inductive -- a form of reasoning in which a generalized conclusion is formulated from particular instances.
- Inductive Analysis -- a form of analysis based on inductive reasoning; a researcher using inductive analysis starts with answers, but formulates questions throughout the research process.
- Insiderness -- a concept in qualitative research that refers to the degree to which a researcher has access to and an understanding of persons, places, or things within a group or community based on being a member of that group or community.
- Internal Consistency -- the extent to which all questions or items assess the same characteristic, skill, or quality.
- Internal Validity -- the rigor with which the study was conducted [e.g., the study's design, the care taken to conduct measurements, and decisions concerning what was and was not measured]. It is also the extent to which the designers of a study have taken into account alternative explanations for any causal relationships they explore. In studies that do not explore causal relationships, only the first of these definitions should be considered when assessing internal validity.
- Life History -- a record of an event/events in a respondent's life told [written down, but increasingly audio or video recorded] by the respondent from his/her own perspective in his/her own words. A life history is different from a "research story" in that it covers a longer time span, perhaps a complete life, or a significant period in a life.
- Margin of Error -- the permittable or acceptable deviation from the target or a specific value. The allowance for slight error or miscalculation or changing circumstances in a study.
- Measurement -- process of obtaining a numerical description of the extent to which persons, organizations, or things possess specified characteristics.
- Meta-Analysis -- an analysis combining the results of several studies that address a set of related hypotheses.
- Methodology -- a theory or analysis of how research does and should proceed.
- Methods -- systematic approaches to the conduct of an operation or process. It includes steps of procedure, application of techniques, systems of reasoning or analysis, and the modes of inquiry employed by a discipline.
- Mixed-Methods -- a research approach that uses two or more methods from both the quantitative and qualitative research categories. It is also referred to as blended methods, combined methods, or methodological triangulation.
- Modeling -- the creation of a physical or computer analogy to understand a particular phenomenon. Modeling helps in estimating the relative magnitude of various factors involved in a phenomenon. A successful model can be shown to account for unexpected behavior that has been observed, to predict certain behaviors, which can then be tested experimentally, and to demonstrate that a given theory cannot account for certain phenomenon.
- Models -- representations of objects, principles, processes, or ideas often used for imitation or emulation.
- Naturalistic Observation -- observation of behaviors and events in natural settings without experimental manipulation or other forms of interference.
- Norm -- the norm in statistics is the average or usual performance. For example, students usually complete their high school graduation requirements when they are 18 years old. Even though some students graduate when they are younger or older, the norm is that any given student will graduate when he or she is 18 years old.
- Null Hypothesis -- the proposition, to be tested statistically, that the experimental intervention has "no effect," meaning that the treatment and control groups will not differ as a result of the intervention. Investigators usually hope that the data will demonstrate some effect from the intervention, thus allowing the investigator to reject the null hypothesis.
- Ontology -- a discipline of philosophy that explores the science of what is, the kinds and structures of objects, properties, events, processes, and relations in every area of reality.
- Panel Study -- a longitudinal study in which a group of individuals is interviewed at intervals over a period of time.
- Participant -- individuals whose physiological and/or behavioral characteristics and responses are the object of study in a research project.
- Peer-Review -- the process in which the author of a book, article, or other type of publication submits his or her work to experts in the field for critical evaluation, usually prior to publication. This is standard procedure in publishing scholarly research.
- Phenomenology -- a qualitative research approach concerned with understanding certain group behaviors from that group's point of view.
- Philosophy -- critical examination of the grounds for fundamental beliefs and analysis of the basic concepts, doctrines, or practices that express such beliefs.
- Phonology -- the study of the ways in which speech sounds form systems and patterns in language.
- Policy -- governing principles that serve as guidelines or rules for decision making and action in a given area.
- Policy Analysis -- systematic study of the nature, rationale, cost, impact, effectiveness, implications, etc., of existing or alternative policies, using the theories and methodologies of relevant social science disciplines.
- Population -- the target group under investigation. The population is the entire set under consideration. Samples are drawn from populations.
- Position Papers -- statements of official or organizational viewpoints, often recommending a particular course of action or response to a situation.
- Positivism -- a doctrine in the philosophy of science, positivism argues that science can only deal with observable entities known directly to experience. The positivist aims to construct general laws, or theories, which express relationships between phenomena. Observation and experiment is used to show whether the phenomena fit the theory.
- Predictive Measurement -- use of tests, inventories, or other measures to determine or estimate future events, conditions, outcomes, or trends.
- Principal Investigator -- the scientist or scholar with primary responsibility for the design and conduct of a research project.
- Probability -- the chance that a phenomenon will occur randomly. As a statistical measure, it is shown as p [the "p" factor].
- Questionnaire -- structured sets of questions on specified subjects that are used to gather information, attitudes, or opinions.
- Random Sampling -- a process used in research to draw a sample of a population strictly by chance, yielding no discernible pattern beyond chance. Random sampling can be accomplished by first numbering the population, then selecting the sample according to a table of random numbers or using a random-number computer generator. The sample is said to be random because there is no regular or discernible pattern or order. Random sample selection is used under the assumption that sufficiently large samples assigned randomly will exhibit a distribution comparable to that of the population from which the sample is drawn. The random assignment of participants increases the probability that differences observed between participant groups are the result of the experimental intervention.
- Reliability -- the degree to which a measure yields consistent results. If the measuring instrument [e.g., survey] is reliable, then administering it to similar groups would yield similar results. Reliability is a prerequisite for validity. An unreliable indicator cannot produce trustworthy results.
- Representative Sample -- sample in which the participants closely match the characteristics of the population, and thus, all segments of the population are represented in the sample. A representative sample allows results to be generalized from the sample to the population.
- Rigor -- degree to which research methods are scrupulously and meticulously carried out in order to recognize important influences occurring in an experimental study.
- Sample -- the population researched in a particular study. Usually, attempts are made to select a "sample population" that is considered representative of groups of people to whom results will be generalized or transferred. In studies that use inferential statistics to analyze results or which are designed to be generalizable, sample size is critical, generally the larger the number in the sample, the higher the likelihood of a representative distribution of the population.
- Sampling Error -- the degree to which the results from the sample deviate from those that would be obtained from the entire population, because of random error in the selection of respondent and the corresponding reduction in reliability.
- Saturation -- a situation in which data analysis begins to reveal repetition and redundancy and when new data tend to confirm existing findings rather than expand upon them.
- Semantics -- the relationship between symbols and meaning in a linguistic system. Also, the cuing system that connects what is written in the text to what is stored in the reader's prior knowledge.
- Social Theories -- theories about the structure, organization, and functioning of human societies.
- Sociolinguistics -- the study of language in society and, more specifically, the study of language varieties, their functions, and their speakers.
- Standard Deviation -- a measure of variation that indicates the typical distance between the scores of a distribution and the mean; it is determined by taking the square root of the average of the squared deviations in a given distribution. It can be used to indicate the proportion of data within certain ranges of scale values when the distribution conforms closely to the normal curve.
- Statistical Analysis -- application of statistical processes and theory to the compilation, presentation, discussion, and interpretation of numerical data.
- Statistical Bias -- characteristics of an experimental or sampling design, or the mathematical treatment of data, that systematically affects the results of a study so as to produce incorrect, unjustified, or inappropriate inferences or conclusions.
- Statistical Significance -- the probability that the difference between the outcomes of the control and experimental group are great enough that it is unlikely due solely to chance. The probability that the null hypothesis can be rejected at a predetermined significance level [0.05 or 0.01].
- Statistical Tests -- researchers use statistical tests to make quantitative decisions about whether a study's data indicate a significant effect from the intervention and allow the researcher to reject the null hypothesis. That is, statistical tests show whether the differences between the outcomes of the control and experimental groups are great enough to be statistically significant. If differences are found to be statistically significant, it means that the probability [likelihood] that these differences occurred solely due to chance is relatively low. Most researchers agree that a significance value of .05 or less [i.e., there is a 95% probability that the differences are real] sufficiently determines significance.
- Subcultures -- ethnic, regional, economic, or social groups exhibiting characteristic patterns of behavior sufficient to distinguish them from the larger society to which they belong.
- Testing -- the act of gathering and processing information about individuals' ability, skill, understanding, or knowledge under controlled conditions.
- Theory -- a general explanation about a specific behavior or set of events that is based on known principles and serves to organize related events in a meaningful way. A theory is not as specific as a hypothesis.
- Treatment -- the stimulus given to a dependent variable.
- Trend Samples -- method of sampling different groups of people at different points in time from the same population.
- Triangulation -- a multi-method or pluralistic approach, using different methods in order to focus on the research topic from different viewpoints and to produce a multi-faceted set of data. Also used to check the validity of findings from any one method.
- Unit of Analysis -- the basic observable entity or phenomenon being analyzed by a study and for which data are collected in the form of variables.
- Validity -- the degree to which a study accurately reflects or assesses the specific concept that the researcher is attempting to measure. A method can be reliable, consistently measuring the same thing, but not valid.
- Variable -- any characteristic or trait that can vary from one person to another [race, gender, academic major] or for one person over time [age, political beliefs].
- Weighted Scores -- scores in which the components are modified by different multipliers to reflect their relative importance.
- White Paper -- an authoritative report that often states the position or philosophy about a social, political, or other subject, or a general explanation of an architecture, framework, or product technology written by a group of researchers. A white paper seeks to contain unbiased information and analysis regarding a business or policy problem that the researchers may be facing.
Elliot, Mark, Fairweather, Ian, Olsen, Wendy Kay, and Pampaka, Maria. A Dictionary of Social Research Methods. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 2016; Free Social Science Dictionary. Socialsciencedictionary.com [2008]. Glossary. Institutional Review Board. Colorado College; Glossary of Key Terms. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Glossary A-Z. Education.com; Glossary of Research Terms. Research Mindedness Virtual Learning Resource. Centre for Human Servive Technology. University of Southampton; Miller, Robert L. and Brewer, John D. The A-Z of Social Research: A Dictionary of Key Social Science Research Concepts London: SAGE, 2003; Jupp, Victor. The SAGE Dictionary of Social and Cultural Research Methods . London: Sage, 2006.
- << Previous: Independent and Dependent Variables
- Next: 1. Choosing a Research Problem >>
- Last Updated: May 22, 2024 12:03 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Get Started Here:
- Homeowners & Homebuyers

- Leadership & Organization
- Reports & Plans
- Do Business with Us
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Equal Employment Opportunity / No FEAR Act
- FOIA & Privacy
- Information Quality
- Budget, Finances, and Performance
- Workforce Ombuds
- FHFA Policies
- Fannie Mae & Freddie Mac
- Federal Home Loan Bank System
- Examiner Resources
- Legal Documents & Suspensions
- Rulemaking & Federal Register
- Advisory Bulletins
- Dodd-Frank Act Stress Tests
- LIBOR Transition
- History of Fannie Mae & Freddie Mac Conservatorships
- Senior Preferred Stock Purchase Agreements
2024 Scorecard
- FHFA Stats Blog
- Meet the Experts
- Mortgage Translations Home
- Search or Browse Documents
- COVID-19 Resources
- Borrower Education Materials
- Interpretive Services
- Language Translation Disclosure
Working Paper 24-05: Tracking Our Footprint: CO2 Emissions from US Single-Family Homes
Becka Brolinson, Jessica Shui, and November Wilson
Abstract:
We estimate residential energy use and CO2 emissions for single-family homes using administrative data from approximately 45 million property appraisals, or 1.8 billion property-month observations. First, we find that from 2013 to 2021, CO2 emissions decreased by 11.5 percent in aggregate in our sample. Emissions from electricity use decreased by 20.8 percent, while emissions from natural gas use for home heating increased by 11 percent over the same time. Second, we estimate that the majority of the decline in CO2 emissions from properties in our sample can be attributed to the greening of US energy generation, rather than changes over time to property-level characteristics. Third, we show that aggregate emissions estimates from the property-level data closely align with aggregate emissions estimates using publicly available state-level data in 2020, providing validation of our approach using property-level data and demonstrating that for aggregate estimates, state-level data is sufficient.
Want to Subscribe?

© 2024 Federal Housing Finance Agency
The Macroeconomic Impact of Climate Change: Global vs. Local Temperature
This paper estimates that the macroeconomic damages from climate change are six times larger than previously thought. We exploit natural variability in global temperature and rely on time-series variation. A 1°C increase in global temperature leads to a 12% decline in world GDP. Global temperature shocks correlate much more strongly with extreme climatic events than the country-level temperature shocks commonly used in the panel literature, explaining why our estimate is substantially larger. We use our reduced-form evidence to estimate structural damage functions in a standard neoclassical growth model. Our results imply a Social Cost of Carbon of $1,056 per ton of carbon dioxide. A business-as-usual warming scenario leads to a present value welfare loss of 31%. Both are multiple orders of magnitude above previous estimates and imply that unilateral decarbonization policy is cost-effective for large countries such as the United States.
Adrien Bilal gratefully acknowledges support from the Chae Family Economics Research Fund at Harvard University. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data
Mentioned in the News
More from nber.
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .

Advertisement
Supported by
She Survived a Train Accident. Her Train Wreck of a Dad Is Next.
In Garth Risk Hallberg’s new novel, a teenage rebel and her father reconnect amid a sea of their own troubles.
- Share full article

By Dwight Garner
- Barnes and Noble
- Books-A-Million
When you purchase an independently reviewed book through our site, we earn an affiliate commission.
THE SECOND COMING , by Garth Risk Hallberg
Garth Risk Hallberg’s ambitious but uneven and exhausting new novel, “The Second Coming,” takes its title from an unreleased live album by Prince. One of the book’s central characters, a 13-year-old girl named Jolie Aspern, is on a Manhattan subway platform listening to a bootleg version when her phone slips from her hand and clatters onto the tracks below.
She climbs down after it. A train heaves into view. Oh no! Jolie is rescued, but she is hurt and shaken up. Was she suicidal or just foolish? The next day she is the subject of a New York Post headline: “APP-ETITE FOR DESTRUCTION.”
This early scene is one of many needle drops in Hallberg’s multigenerational and music-drenched novel, which is set primarily in 2011 but frequently flashes forward a decade, and backward even further. By the end, the novel has become a mixtape of sorts, with sections named after songs.
“The Second Coming” never becomes a great rock or music novel. Hallberg doesn’t make you feel what his characters are getting out of these songs. But this is certainly a novel that, to annex a thought from Annie Proulx in “The Shipping News,” makes you realize that one of the bummers of existence is that “there is no background music.”
This is Hallberg’s second novel, if you don’t count “A Field Guide to the North American Family,” a 2007 novella. His first, “ City on Fire ,” a sprawling New York City story set in part during the blackout of July 13, 1977, made an impact when it was published in 2015. It made best-seller lists. Frank Rich gave it a yea-saying review on the cover of The Times Book Review, though he also had a lot of caveats.
Speaking of The New York Post, it ran a “City on Fire” review, too. Its headline was: “Overhyped novel ‘City on Fire’ is a steaming pile of literary dung.” My opinion of the novel is closer to Rich’s, but The Post’s dissent registers with me. Hallberg is an intelligent writer, but he’s a wild and frequently sloppy one. His narratives don’t click into gear; his curveball only sometimes makes it over the plate.
Jolie, the girl who jumped on the subway tracks, is one of the most precocious eighth graders in recent literary history. She wears black and quotes Philip Larkin on how your parents mess you up. She name-checks Itzhak Perlman. She goes alone to a zendo to work on re-centering. Before long she will dye her hair pink, give herself a mental patient’s haircut, get a lot of piercings and stop talking altogether. She’ll drop acid.
She’s already a pint-size rock ’n’ roll survivor. As The Onion once joked about Kurt Cobain and Courtney Love’s daughter, she seems to have been born ready to enter prehab.
She is her father’s daughter. Ethan Aspern is a washed-up actor who has been arrested on drug charges, gone through 12-step programs and burned every bridge he’s crossed. He walks around uttering things like “I’m only going to let you down.” He is not lying. He is scruffy, outstandingly handsome and has a heart of gold that’s visible from a satellite. When Ethan learns about Jolie’s accident, he comes back into her life after many years away and hopes to make amends, if he is not arrested first for abducting her.
Ethan has a tangled back story, with complicated parents of his own. His mother is a serious artist. And the novel summarizes his father’s story this way: “Naval Academy, Yale Divinity, a summer sailing for William F. Buckley of all people. And then right back to Annapolis for a chaplain gig.” Little of this material is picked up in the novel. This information is an indication of Hallberg’s flickering interest in big, interlocking American themes. Scenes play across Sept. 11 and Occupy Wall Street, and take us into Covid.
Hallberg is often at his best when he’s not reaching for big effects, when he gives himself room to breathe. Here’s Ethan defending his hometown, Ocean City, N.J.:
Like, did the Hamptons have stand-mounted binoculars that offered up only darkness unless you paid a quarter? Or the game with the giant mallets and the flying rubber frogs? Did the Hamptons have that? How about not one but two amusement parks called the Jolly Roger, each with a Tilt-a-Whirl so ultra-sketch you had to sign a waiver?
This novel’s scope and ambition are reminiscent of Jonathan Franzen’s novels. But Hallberg’s writing is more in the mold of Richard Ford. Like Ford, he’s enamored of New Jersey settings and lets crucial scenes play out over holidays, for supplemental resonance. He’s given to epigrammatic summing-up statements every other page or so. Ford’s are better; they’re crisper bites of the apple.
We follow Jolie and Ethan around. The narrative baton is passed among unreliable narrators. A lot of the sentences and dialogue are of the sort that might sound good in a Steve Earle song (“But what if I were to try calling on your better angels?”) but not so much in cold print, especially when they pile up.
Ethan is a familiar figure. He’s a beautiful loser, an amiable screw-up of the genus Jim Harrison once classified as the “nifty guy at loose ends.” We know this creature from Thomas McGuane’s novels, and from Barry Hannah’s, and from Harrison’s, among other writers. Hallberg’s amiable screw-up, unlike those in his predecessors’ fiction, is never much fun to be around.
Ethan is almost entirely sexless as well, which gives the novel a deracinated feeling. Like Ryan Gosling in “Barbie,” he seems to have only a smooth plastic panel down there.
Katie Roiphe has written about how a now not-so-young generation of male writers have jettisoned their carnal appetites for empathetic cuddling. The critic Elaine Blair, too, has thought through the new skittishness about sex in fiction written by men, the “fearful suspicion that if a man gets what he wants, sexually speaking, he is probably exploiting someone.”
Younger women hurl themselves in front of Ethan, who is still in his early 30s for much of the novel. When he does sleep with one, even after getting to know her, the vibe is one of disgust and sharp regret. It’s as if he has run over a small animal with a lawn mower.
He blames his weakness on his surroundings: “Apparently he’d been in California long enough to weaken a little on the numinous, the vibrational, and he couldn’t help but think that the sex was somehow related to his feeling of having upset the power balance between them.” Jolie’s first stab at sexual contact is porn-like, horrible, pitilessly bleak.
This novel, like Ethan’s life, lurches sideways. There are many, many characters — siblings, parents, parole officers, lovers, spouses, drug dealers, old friends. There is little sense of momentum; the pages never turn themselves. It is so intensely written that it gave me a headache, as if I had been grinding my teeth. I was glad when it was over.
THE SECOND COMING | By Garth Risk Hallberg | Knopf | 586 pp. | $32
Dwight Garner has been a book critic for The Times since 2008, and before that was an editor at the Book Review for a decade. More about Dwight Garner
Explore More in Books
Want to know about the best books to read and the latest news start here..
An assault led to Chanel Miller’s best seller, “Know My Name,” but she had wanted to write children’s books since the second grade. She’s done that now with “Magnolia Wu Unfolds It All.”
When Reese Witherspoon is making selections for her book club , she wants books by women, with women at the center of the action who save themselves.
The Nobel Prize-winning author Alice Munro, who died on May 14 , specialized in exacting short stories that were novelistic in scope , spanning decades with intimacy and precision.
“The Light Eaters,” a new book by Zoë Schlanger, looks at how plants sense the world and the agency they have in their own lives.
Each week, top authors and critics join the Book Review’s podcast to talk about the latest news in the literary world. Listen here .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
At this point, you want your outline to include that you want X quote here, and you will support it by saying Y and Z. I like to use two pieces of evidence for each paragraph. When analyzing and comparing two books in an essay, this makes it easy because each piece of evidence can come from each novel. Or you can switch off paragraphs, going ...
Comparing Main Characters in Novels. If your assignment is to compare the characters of these novels, you would make a list or Venn diagram to make more comparisons: Both characters are young men. Both question society's notion of honor. Both witness behavior that makes them question their role models. Both have a nurturing female influence.
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
Comparative analysis asks writers to make an argument about the relationship between two or more texts. Beyond that, there's a lot of variation, but three overarching kinds of comparative analysis stand out: Subordinate (A → B) or (B → A): Using a theoretical text (as a "lens") to explain a case study or work of art (e.g., how Anthony Jack ...
The questions of my paper revolve around the attractive nature of war. Ernest Hemingway' For Whom the Bell Tolls is an important novel from the perspective of my research, mostly because it presents a varied and self-critical attitude. At first it seems like a traditional, heroic war story with a self-sacrificing hero.
Suppose that you are writing a paper comparing two novels. For most literature classes, the fact that they both use Caslon type (a kind of typeface, like the fonts you may use in your writing) is not going to be relevant, nor is the fact that one of them has a few illustrations and the other has none; literature classes are more likely to focus ...
It involves taking two or more subjects and analyzing the differences and similarities between them. You might find yourself comparing all kinds of things in an academic essay: historical figures, literary works, policies, research methods, etc. Doing so is an important part of constructing arguments.
A multiple book essay involves writing a review of two or generally no more than six books that cover the same overall subject area [e.g., analysis of European debt crisis] or that are related to each other in a particular way [e.g., applying grounded theory methods to study student access to education].
Compare-contrast essays require students to analyze texts and draw conclusions based on similarities and differences between elements within the texts. This type of analysis is challenging, because it requires multiple levels of thinking. However, by comparing literary works, students will uncover universal themes in ...
Level Up Your Team. See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Great stories tend to be rooted in some degree of real world events and conditions, and capturing these real world elements requires research. Learn the most effective way to conduct book research for your next novel or short story.
June 22-24, 2011. Abstract. The aim of this paper is to achieve a literary appreciation to the Noli and t he Fili, i n. view of their literary context. Rizal's two novels have been pri marily ...
This study investigated readers' experiences of critical thinking and reading, comparing fiction and nonfiction. As previous research has shown links between fiction reading and increased social and cognitive capacities, and such capacities are argued to be necessary for critical thinking, this study sought to explore a potentially unique relationship between reading fiction and critical ...
Leavy uses two short stories, The Scrub Club (pp. 95-145) and Visual Music (pp. 147-193), as well as excerpts from a novella, The Wrong Shoe (pp. 195-210), and two novels, Waiting Room (pp. 211-231) and Low-Fat Love (pp. 233-256), to illustrate features of fiction-based research, which she describes in the first section of the book.
the study was to find possible differences in using punctuation marks betw een English novel ' A Tale of Two Cities ' and ISSN 1799-2591 Theory and Practice in Language Studies, Vol. 5, No. 11 ...
It aligns with previous research, namely that novels provide many positive things regarding the English language. Authentic texts help students in terms of words, phrases, and expressions that are ...
The last two books I chose to read were: "One Hundred Years of Solitude" by Gabriel Garcia Marquez and "Miss Brill" by Katherine Mansfield. These are certainly two different books, but the some main themes are close in a way. The book "One Hundred Years of Solitude" seemed to me rather unusual, the whole style of the author and the plot itself, and it was rather hard to remember ...
second part is a literary research paper analyzing one of Murakami's core tropes, how it has ... those late, lonely hours, with my pen rushing across the manuscript paper, I finished my first two novels, Hear the Wind Sing and Pinball, 1973. I personally1 call those two books my "kitchen table novels."
The title of this book is The Process of Research Writing, and in the nutshell, that is what the book is about. A lot of times, instructors and students tend to separate "thinking," "researching," and "writing" into different categories that aren't necessarily very well connected. First you think, then you research, and then you write.
Comparison Between Two Novels - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document provides a comparison of the short stories "A Jury of Her Peers" by Susan Glaspell and "Hands" by Sherwood Anderson. It summarizes the plots, characters, settings, and key themes of both stories. The main themes explored are gender roles, loneliness ...
appear in book format. Schwarz (2006) defined GNs as "a longer and more artful version of the comic book bound as a 'real' book" (p. 58). GNs have also been described as "an original book-length story, either fiction or nonfiction, published in comic book style" (Gorman, 2003, p.xii). Regardless of the slight variations in
Paper books also have an immediately discernible size, shape and weight. We might refer to a hardcover edition of War and Peace as a hefty tome or a paperback Heart of Darkness as a slim volume ...
Sula is a novel by Nobel Prize winning author Toni Morrison. Morrison wrote the novel in 1973. The novel, set in Ohio, features two girls named Nel and Sula who live contrasting lives. Whereas Nel comes from a stable family that believes in social institutions, Sula comes from a dysfunctional family (Morrison).
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
This paper explores ideas for future research on application or user fees in programs administered by the Employment and Training Administration (in the U.S. Department of Labor). The paper briefly reviews federal law and regulations, related research studies, and key factors that can be used to guide possible research. The paper focuses on research related to use of fees with employers who ...
Pages. 81. Sadako and the Thousand Paper Cranes [1] is a children's historical novel written by Canadian-American author Eleanor Coerr and published in 1977. It is based on the story of Sadako Sasaki . The book has been translated into many languages and published in many places, to be used for peace education programs in primary schools .
Grey Literature-- research produced by organizations outside of commercial and academic publishing that publish materials, such as, working papers, research reports, and briefing papers. Grounded Theory-- practice of developing other theories that emerge from observing a group. Theories are grounded in the group's observable experiences, but ...
The Israel Lobby and U.S. Foreign Policy is a book by John Mearsheimer, Professor of Political Science at the University of Chicago, and Stephen Walt, Professor of International Relations at Harvard Kennedy School at Harvard University, published in late August 2007.It was a New York Times Best Seller.. The book describes the lobby as a "loose coalition of individuals and organizations who ...
Fairness We value varied perspectives and thoughts and treat others with impartiality. Accountability We are responsible for carrying out our work with transparency and professional excellence. Integrity We are committed to the highest ethical and professional standards to inspire trust and confidence in our work. Respect We treat others with dignity, share information and resources, and ...
Working Paper 32450. DOI 10.3386/w32450. Issue Date May 2024. This paper estimates that the macroeconomic damages from climate change are six times larger than previously thought. We exploit natural variability in global temperature and rely on time-series variation. A 1°C increase in global temperature leads to a 12% decline in world GDP.
This is Hallberg's second novel, if you don't count "A Field Guide to the North American Family," a 2007 novella. His first, "City on Fire," a sprawling New York City story set in part ...