- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy

McGraw Hill My Math Grade 3 Chapter 5 Lesson 6 Answer Key Problem-Solving Investigation: Use Models
All the solutions provided in McGraw Hill Math Grade 3 Answer Key PDF Chapter 5 Lesson 6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Use Models will give you a clear idea of the concepts.
McGraw-Hill My Math Grade 3 Answer Key Chapter 5 Lesson 6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Use Models
Learn the Strategy Mia has 18 items that need to be split evenly among 3 welcome baskets. How many items will Mia put in each basket? 1. Understand What facts do you know? ____ items need to be split evenly among ___ baskets What do you need to find? the number of _____ Answer: 18 items, 3 baskets. We need to find the no of items Mia put in each basket. The number of items is 6.
Explanation: The facts we know are Mia has 18 items No of welcome baskets = 3 To find: How many items will Mia put in each basket? 2. Plan I will make a model to find _____ Answer: The plan is how to find the number of items Mia put in each basket.
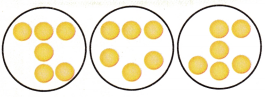
Explanation: I will use counters to model the problem by placing 6 counters at a time in each group. The model shows that 18 ÷ 3 = 6. So, Mia will fill each basket with 6 items.
4. Check Does your answer make sense? Explain. Answer: Yes, the answer is reasonable.
Explanation: We need to divide the no of counters by the number of items. 18 18 ÷ 6 = 3 items. Hence the answer is reasonable.
Practice the Strategy

What do you need to find? ________________ Answer: We need to find out how many pets did she help each day.
2. Plan ________________ Answer: The plan is to find out how many pets she helps each day. We can find that by dividing the given number of pets by the number of days.
3. Solve Answer: Given, No of the pets a veterinarian helped from Monday to Friday is 20. No of days = 4 20 ÷ 4 = 5 Hence the answer is 5 pets. 4. Check
Does your answer make sense? Explain. ________________ ________________ Answer: Yes, the answer makes sense.
Explanation: The plan is to find out how many pets she helps each day. We need to divide the given number of pets by the number of days. Then we will get the answer as we solved. 20 ÷ 4 = 5 pets. Hence the answer is reasonable.
Apply the Strategy
Solve each problem by using a model.

Explanation: Given, Jill has 27 blocks. She divides them equally into bowls. No of the bowls are 3 27 ÷ 3 = 9 There are 12 blocks in each row.
Question 2. The owner of an apartment building needs to fix 16 locks in four of his apartments. Each apartment has the same number of locks that needs to be fixed. How many locks in each apartment need to be fixed? Answer: 16 ÷ 4 = 4 locks
Explanation: No of locks in four of his apartments = 16 No of apartment = 4 16 ÷ 4 = 4 locks There are 4 locks in each apartment that needs to be fixed.
Question 3. A baker used a dozen eggs to make 3 cakes. The recipe called for each cake to have the same number of eggs. How many eggs were used in each cake? (Hint: 1 dozen = 12) Answer: 4 eggs
Explanation: No of eggs = Dozen = 12 No of the cakes he baked = 3 12 ÷ 3 = 4 eggs. Hence there are 4 eggs were used in each cake.
Question 4. There are 13 girls and 11 boys that want to play a game. They need to make 4 teams. How many players will be on each team if each team needs an equal number of players? Answer: 13 + 11 = 24 players 24 ÷ 4 = 6 players
Explanation: Given, No of girls = 13 No of boys = 11 They need to make 4 teams Total no of players = 13 + 11 = 24 24 ÷ 4 = 6 players Therefore there are 6 players on each team.
Review the Strategies
Use any strategy to solve each problem.
- Determine reasonable answers.
- Use an estimate or exact answer.
- Use models.
Question 5. Mathematical PRACTICE 2 Use Number Sense Sarah needs 15 pieces of chalk for a project. Each box contains 3 pieces of chalk. How many boxes of chalk will she need to buy? Answer: 15 × 3 = 45
Explanation: Sarah has 15 pieces of chalk Each box contains 3 pieces of chalk. 15 × 3 = 45 boxes Therefore she needs 45 boxes of chalk to buy.
Question 6. Brooke volunteers to read with young children 5 nights a month. She spends 2 hours each visit. This month, she volunteered one extra night. How many hours did she read with the children this month? Answer: 12 hours.
Explanation: Number of nights in a month = 5 She spent 2 hours each visit. she volunteered one extra night 5 × 2 = 10 10 + 2 = 12 hours. She read for 12 hours with the children this month.
Question 7. Mathematical PRACTICE 4 Model Math A chef will make pizzas. He has broccoli, peppers, onions, pepperoni, and sausage. How many types of pizzas can be made with one type of vegetable and one type of meat? Name the combinations. Answer: Six different pizzas can be made with one vegetable and one meat.
Explanation: Given, chef has broccoli, peppers, onions, pepperoni, and sausage The combinations are broccoli, pepperoni broccoli, sausage peppers, pepperoni peppers, sausage onions, pepperoni onions, sausage

Explanation: The weight of the brown bear is 700 pounds. The actual weight is 634 pounds. 700 – 634 = 66 pounds. The estimation of the actual weight is 66 pounds.
McGraw Hill My Math Grade 3 Chapter 5 Lesson 6 My Homework Answer Key
Problem Solving
Question 1. Brandon spent $20 on school supplies. He bought five different items that each cost the same amount. How much did each item cost? Use a model to solve. Each item cost _____. Answer: $20 ÷ 5 = $4
Explanation: The cost spent on school supplies = $20 He bought five different items. $20 ÷ 5 = 4 The cost of each item is $4. Each item cost $4.
Question 2. Mathematical PRACTICE 5 Use Math Tools Alice planted 6 tomato plants, 4 bean plants, and 2 pepper plants. Each row had 6 plants. How many rows did Alice plant? Answer: Alice planted 2 rows in total.
Explanation: Given, No of tomato plants = 6 No of bean plants = 4 No of pepper plants = 2 Total plants = 6 + 4 + 2 = 12 There are 6 plants in each row So divide 12 by 6 to get the number of rows used to plant 12 plants. 12 ÷ 6 = 2 Hence the answer is 2 rows.
Question 3. At the circus, there are 18 clowns. The clowns drive around in little cars. If there are 3 clowns in each car, how many cars are there? Answer: 18 ÷ 3 = 6 cars
Explanation: Given, No of clowns = 18 No of the clowns in each car is = 3 18 ÷ 3 = 6 cars There are 6 cars at the circus.
Question 4. Mr. and Mrs. Carson took Sarah, Brent, and Joanie to see a movie. They paid $50 in all. The Carsons spent $15 on snacks. How much did each ticket cost? Answer: $7
Explanation: Given, Mr. and Mrs. Carson took Sarah, Brent, and Joanie to see a movie There are a total of 5 people. They paid $50 in all. The Carsons spent $15 on snacks $50 – 15 = $35 $35 ÷ $5 = $7 Therefore each ticket cost = $7
Question 5. Mrs. Glover had 25 rare coins. She divided them evenly among her 5 grandchildren. How many coins did each grandchild get? Answer: 25 ÷ 5 = 5 coins
Explanation: No of the coins Mrs. Glover has = 25 coins. No of the grandchildren Mrs. Glover has = 5 25 ÷ 5 = 5 coins Therefore each grandchild gets 5 coins.
Question 6. A singer performed 9 songs at a recital. She had 3 weeks to practice. How many songs did she practice each week if she practiced an equal number of songs each week? Answer:

Explanation: No of the songs performed at a recital = 9 No of weeks she had to practice = 3 To find: How many songs did she practice each week if she practiced an equal number of songs each week? 9 ÷ 3 = 3 She practiced 3 songs each week.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Don't have an account? Register
Already have an account? Login

- 4th Grade Math
- Title: My Math
- Author: McGraw Hill
- Edition: Volume 1

Email us and we will contact you short after.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
6th grade (Illustrative Mathematics)
Unit 1: area and surface area, unit 2: introducing ratios, unit 3: unit rates and percentages, unit 4: dividing fractions, unit 5: arithmetic in base ten, unit 6: expressions and equations, unit 7: rational numbers, unit 8: data sets and distribution.

EL Education Curriculum
You are here.
- ELA 2019 G6:M2:U3:L1
Analyze a Model Problem-Solution Essay
In this lesson, daily learning targets, ongoing assessment.
- Technology and Multimedia
Supporting English Language Learners
Materials from previous lessons, new materials, closing & assessments, you are here:.
- ELA 2019 Grade 6
- ELA 2019 G6:M2
- ELA 2019 G6:M2:U3
Like what you see?
Order printed materials, teacher guides and more.
How to order
Help us improve!
Tell us how the curriculum is working in your classroom and send us corrections or suggestions for improving it.
Leave feedback
Focus Standards: These are the standards the instruction addresses.
- RI.6.2, W.6.2, W.6.4, W.6.5, W.6.9b
Supporting Standards: These are the standards that are incidental—no direct instruction in this lesson, but practice of these standards occurs as a result of addressing the focus standards.
- RI.6.1, RI.6.7
- I can find the gist of a model problem-solution essay. (RI.6.2)
- I can determine the purpose of a model problem-solution essay. (W.6.4)
- I can apply my knowledge of the Painted Essay® to analyze the structure of a model problem-solution essay. (W.6.2)
- Opening A: Entrance Ticket (RI.6.2)
- Work Time A: Annotated, color-coded Model Problem-Solution Essay (W.6.2, W.6.4, W.6.5, W.6.9b)
- Reread the Paint an Essay lesson plan to familiarize yourself with the color-coding and the purpose of each choice of color.
- Gather colored pencils or markers in red, blue, yellow, and green.
- Review the student tasks and example answers to get familiar with what students will be required to do in the lesson (see Materials list).
- Prepare copies of handouts for students, including the entrance ticket (see Materials list).
- Post the learning targets and applicable anchor charts (see Materials list).
Tech and Multimedia
- Work Time A: Display and play the TED Talk: Avery Bang: "Building Bridges and Connecting Communities" in its entirety to provide more context for the model essay.
Supports guided in part by CA ELD Standards 6.I.B.6, 6.I.B.7, 6.I.C.10, 6.I.C.11, 6.I.C.12, 6.II.A.1, 6.II.A.2, 6.II.C.6, and 6.II.C.7.
Important Points in the Lesson Itself
- To support ELLs, this lesson invites students to revisit the Painted Essay® structure, which they were first introduced to in Module 1. Paragraphs and/or sentences of Painted Essays® are color-coded according to the function they serve in an essay. Representing text structure visually is especially supportive for ELLs, as it allows them to more clearly identify relationships across an essay’s ideas without the pressure of interpreting detailed verbal descriptions. In this lesson, students use the familiar Painted Essay® structure to break down and orient themselves to a new essay type: the problem-solution essay.
- ELLs may find it challenging to analyze the Model Problem-Solution Essay: “Bridges to Prosperity” in the allotted time. Remind students that some of the content of this essay should be familiar to them, as they learned about the work of Bridges to Prosperity during the research mini lessons of Unit 2. Clarify that the goal of analyzing the model is not necessarily to understand every word (although a glossary in the ▲ version of the model is available to help close gaps in word understanding), but instead to recognize the purpose of sentences and paragraphs and how they relate to one another. Point out, too, that students will have opportunities throughout Unit 3 to revisit the model essay, piece by piece, for a closer look.
- Work to Become Effective Learners anchor chart (one for display; from Module 1, Unit 1, Lesson 1, Work Time A)
- Work to Become Ethical People anchor chart (one for display; from Module 1, Unit 1, Lesson 1, Work Time A)
- Work to Contribute to a Better World anchor chart (one for display; from Module 1, Unit 3, Lesson 8, Closing and Assessment A)
- Paint an Essay lesson plan (for teacher reference) (from Module 1, Unit 2, Lesson 6, Work Time A)
- Criteria for Effective Informative Writing anchor chart (one for display; from Module 1, Unit 2, Lesson 8, Work Time B)
- The Boy Who Harnessed the Wind (text; one per student; from Module 2, Unit 1, Lesson 1, Work Time A)
- The Painted Essay® template (one per student; from Module 1, Unit 2, Lesson 6, Work Time A)
- Independent reading journal (one per student; begun in Module 1, Unit 1, Lesson 6, Work Time B)
- Entrance Ticket: Unit 3, Lesson 1 (answers for teacher reference)
- Model Problem-Solution Essay: "Bridges to Prosperity" (example for teacher reference)
- Entrance Ticket: Unit 3, Lesson 1 (one per student)
- Model Problem-Solution Essay: “Bridges to Prosperity” (one per student and one for display)
- Model Problem-Solution Essay: “Bridges to Prosperity” ▲
- Colored pencils (red, yellow, blue, green; one of each per student)
- Informative Writing Checklist (one per student and one for display)
Each unit in the 6-8 Language Arts Curriculum has two standards-based assessments built in, one mid-unit assessment and one end of unit assessment. The module concludes with a performance task at the end of Unit 3 to synthesize students' understanding of what they accomplished through supported, standards-based writing.
Copyright © 2013-2024 by EL Education, New York, NY.
Get updates about our new K-5 curriculum as new materials and tools debut.
Help us improve our curriculum..
Tell us what’s going well, share your concerns and feedback.
Terms of use . To learn more about EL Education, visit eleducation.org
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
McGraw Hill My Math Grade 3 Chapter 5 Lesson 6 My Homework Answer Key. Problem Solving. Question 1. Brandon spent $20 on school supplies. He bought five different items that each cost the same amount. How much did each item cost? Use a model to solve. Each item cost _____. Answer: $20 ÷ 5 = $4. Explanation: The cost spent on school supplies = $20
The model shows that 28 ÷ 7 = 4. So, Lucy can make 4 puzzles. Check Use multiplication to check. 4 × 7 = 28 So, the answer is correct. Lesson 6 Problem Solving: Use Models $4 Program: GMH CCM Component: SE PDF Pass Vendor: Quad Graphics Grade: 3 Lesson 6 My Homework 281 eHelp Operations and Algebraic Thinking 3.OA.4, 3.OA.7
Lesson 6: Problem Solving Investigation: Solve a Simpler Problem 1. Divide 4-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers: word problems 5 Chapter 5. Add and Subtract Decimals ... Lesson 6: Hands On: Use Models to Subtract Unlike Fractions 1. Subtract fractions with unlike denominators using models
6. means to rename a number using place value. 7. The answer to an addition sentence is called the . 8. Estimate the exact answer before solving the problem to see if your answer is . Vocabulary Check Draw place-value blocks to show the sum. 2. 632 + 354 = 3. 216 + 775 = Problem Solving 4. 4 Model Math Luisa has 183 pennies. Her dad
5. 1. 1. 1. 1. This document includes the IXL® skill alignments to McGraw-Hill's My Math curriculum. IXL provides skill alignments as a service to teachers, students, and parents. The skill alignments are provided by IXL and are not affiliated with, sponsored by, reviewed, approved or endorsed by McGraw-Hill or any other third party. IXL® and ...
MTTC Lower Elementary Education (PK-3) Math Subtest [Subarea Two Objective #5-B] Teacher 8 terms. drjason_ampel
Lesson 6 Problem Solving: Use the Four-Step Plan Homework Helper A six-digit number has a 2 in the thousands place, a 5 in the tens place, a 3 in the hundred thousands place, and zeros in each of the remaining places. What is the number? Use the four-step plan to solve this problem. Understand I know that there is a number with six digits.
We provide step by step help with Math homework assignments from 5th grade McGraw Hill textbooks to improve their grades and get an inddepth understanding of the lesson. ... Lesson 6: Problem Solving: Solve a Simpler Problem Free Sample Complete Paid ... Lesson 6: Hands On: Use Models to Subtract Unlike Fractions Free Sample Complete Paid ...
Chapter 6 305 3 jump ropes Problem Solving • Model Division COMMON CORE STANDARD—3.OA.A.3 Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division. 5. WRITE Math Write a word problem about equal groups and act it out to solve. Lesson 6.1 Practice and Homework
oom use. Lesson 6 Problem-Solving Practice Slope and Similar Triangles 1. The slope of a roof line is also called the pitch. Find the pitch of the roof shown. y O x B A 2. A carpenter is building a set of steps for a bunk bed. The plan for the steps is shown below. Using points A and B, find the slope of the line up the steps. Then
We provide step by step help with Math homework assignments from 4th grade McGraw Hill textbooks to improve their grades and get an inddepth understanding of the lesson. ... Lesson 4: Problem Solving: Make a Model Free Sample Complete Paid Version. Lesson 5: Divide with Remainders ... Lesson 8: Problem Solving: Use Logical Reasoning Free Sample ...
Practice and Homework Lesson 6.8 COMMON CORE STANDARDS—1.NBT.B.2a, 1.NBT.B.3 Understand place value. Chapter 6 three hundred seventy-seven 377 Problem Solving • Show Numbers in Different Ways Use to show the number two different ways. Draw both ways. 1. 62 2. 38 3. Math Draw to show 55 three different ways.
Unit 6: Expressions and equations. 0/3000 Mastery points. Lesson 1: Tape diagrams and equations Lesson 2: Truth and equations Lesson 3: Staying in balance Lesson 4: Practice solving equations and representing situations with equations Lesson 5: A new way to interpret a over b Extra practice: Equations Lesson 6: Write expressions where letters ...
Use repeated subtraction to divide. 63 ÷ 9 = Algebra Use the inverse operation to find each unknown. 5. 16 ÷ 8 = ÷ × 8 = 16 = 6. 9 = 4 4 × 9 = = 7. 64 ÷ 8 = × 8 = 64 = Problem Solving 2 Use Algebra For Exercises 8 and 9, write a division sentence with a symbol for the unknown. Then solve. 8. Michael, the chef, has 18 pineapple slices to ...
14. (-9x + 2) + (-8x - 2) 17. GEOMETRY A rectangle has side lengths of (3x + 6) inches and (2x - 4) inches. Write an expression to represent the perimeter of the rectangle. Then find the value of x if the perimeter is 94 inches. 18. CRUISE SHIPS The table shows the number of cruise ships in a harbor on various days.
A. Analyze a Model - W.6.4 (25 minutes) Distribute and display the Model Problem-Solution Essay: "Bridges to Prosperity" or the Model Problem-Solution Essay: "Bridges to Prosperity." . Invite students to follow along, reading silently in their heads as you read the model aloud. Using a total participation technique, invite responses ...
Write a mixed number for each model. 3. 4. Algebra Write an equation that represents each mixed number as a sum of whole numbers and unit fractions. 5. 4 1 _ 4 6. 1 5 _ 6 Problem Solving 7. 2 Use Number Sense There are 2 whole bagels and three-fourths of a third bagel. Write a mixed number that represents the amount of bagels. 8.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations.
1. Fill in the table by selecting the correct answers for each. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1. Fill in the table by selecting the correct answers for each., 2. 4sin (2π/3x), 3. 3sin (2π/3πx) and more.
Write the division sentence shown by the model. 1. Lesson 3 My Homework 345 ... Write the division sentence shown by the model. 2. Problem Solving Use models to find each quotient. Draw the equal groups. 3. There are 70 cards. Each person gets 5 cards. How many people are there? 70 ÷ 5 = There are people. 4. 2 Reason There are 83 apples.
Lesson 2 Hands On: Use Models to Multiply Practice 1. Shade the models to find 3 × 0.7. ×3 0.7 = Homework Helper Find 0.2 × 3 using decimal models. The two rows of each model that are shaded represent 0.2. 3 0.2 So, 0.2 × 3 = 0.6. Need help? connectED.mcgraw-hill.com The shaded parts are combined onto one model. 0.2 0.2 Six tenths of the ...
Lesson 8 My Homework 617 eHelp Number and Operations — Fractions 3.NF.1, 3.NF.2, 3.NF.2 a, 3.NF.2b, ... 6 Problem Solving 5. 3 Justify Conclusions Harvey practiced the piano for _5 8 of an hour. Annika practiced the piano for _5 6 of an hour. Use the models to determine who practiced the piano for a longer period of time. 6.