- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Degrees
- Doctoral Studies
- Theses and Dissertations

How to Pick a Master’s, Ph.D., or Undergraduate Thesis Topic
Last Updated: February 2, 2024 Fact Checked
- Brainstorming Topics
Narrowing Your Focus
- Crafting Your Question
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Danielle Blinka, MA, MPA . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 74,993 times.
Choosing a topic for your thesis , whether it be for a master’s, Ph.D., or undergraduate, can feel like a daunting task, but it can also be exciting. Your thesis is your chance to dive deep into a topic that interests you and contribute something new to your field. To pick the right topic for you, start by brainstorming potential topics without worrying if they're good or not. Then, narrow your topics based on feasibility and your personal strengths. Finally, start researching so you can craft a good thesis question.
Things You Should Know
- Jot down your interests in your topic of study. Then, research your interests and go through your past papers to find unanswered questions in your field.
- Narrow down your interests to potential topics you can add value to. Then, find a professor who has experience in your area of study.
- To formulate your research question, research your topic. Brainstorm a few questions you might ask, then select the one you can best answer.
Brainstorming Possible Topics

- Review all of the classes you've taken and the subjects you've covered.
- Think about why you got into your field of study.
- Consider what you like to read about in your free time, especially things related to your field. This might be books, news articles, or blogs.
- Think of people in your field who you admire or aspire to be like. Then, ask yourself what you like about them.
- Consider if you'll continue your academic studies after graduation, as well as what you'd want to study.

- Consider any lingering questions you had working on past projects as a starting point for your new thesis.
- It’s best to stick to your recent work because it will better reflect your current knowledge and abilities.
- You can use the same topic you used in your prior work, or you can use your old work to point you in the direction of a new topic.
Tip: Your past coursework can also tell you what you didn’t like studying. Consider the assignments that you struggled through and the research topics you hated. Then, avoid topics like them.

- For example, let’s say you’re studying politics. You might read about current presidential candidates and reflect on how their platforms have diverted from the historical platforms for their political party.
- If you’re writing a literature thesis, look at the novels that are being nominated for this year’s literary awards and consider their genre, theme, or style.
- For a thesis on psychology, you might look for news about PTSD research or read articles about pop psychology that people are sharing on social media.
- For an aeronautical engineering thesis, you could read up on what SpaceX is currently working on, or look into NASA’s most recent experiments.
- Check prominent research journals in the field you’re interested in to see what current academic conversations look like.
- Make a list of keywords that show up during your searches so you can look up published theses using sites like ProQuest. That way, you know what topics have already been covered.

- You don’t need a topic that’s completely absent from research, as this would be difficult to examine.
- One way to find a unique angle is to combine 2 topics together. Alternatively, you can build on someone else's work.
- For example, let's say you're studying clinical psychology and want to write about PTSD. You might find that not much research has been done into how people with PTSD cope with workplace conflicts.
- Similarly, let's say you're studying politics and want to look at how political party platforms evolve. You might find that there's a gap in research when it comes to evaluating how voters react to platform changes.

- For instance, you might say, “I’m hoping to be a research professor one day, and I want to focus on modern poetry. Which of these thesis topics do you think would make me most attractive to doctoral programs?”

- Focus on questions that can be researched and don’t have a simple answer. For instance, a question like, “How can we motivate people without offering them extrinsic rewards?” can be researched and doesn’t have a simple answer. Conversely, the question, “When did free verse poems start to become mainstream?” is easy to answer with a simple Internet search.

- You don’t need to plan out your whole life. However, it’s good to have an idea about where you’re going.
- Think about the type of work you want to do, the job title you want to attain, or the types of organizations you want to work with.
- For instance, if you want to be a university professor, you might choose a topic that you plan to continue researching through your doctorate and career as a professor.
- As another example, let's say you want to be a project manager for an engineering firm. You might choose a topic that encompasses both your knowledge of engineering and your interest in motivating other engineers to produce their best work.

- Undergraduate theses may be more broad, while master’s or Ph.D. theses should be more specific.
- Choose the best topics that came to you while you were brainstorming.
- You might enjoy doing this activity with a classmate who’s also working on their thesis. You can bounce ideas off of each other.
- For example, you might write down things like "evolution of political party platforms," "effect of civil war on cultural norms," "themes of literature immediately before and after a social crisis," "effects of robotics on the workforce," "mission to Mars," or "building intrinsic worker motivation."

- For instance, you might love William Shakespeare, but finding a new area of research about his work could prove difficult. Similarly, if you're studying psychology, you'll likely want to avoid writing about older ideas that aren't widely supported anymore, like dream analysis.

- Say something like, “Hi, Dr. Gomez. I know you’re really knowledgeable about morality politics. I’m planning to write my thesis about a topic related to morality politics, so I hoped you might be my thesis supervisor.”
Tip: You don’t need to select your thesis topic before you find a thesis supervisor. Just get a general idea of what area you want to pursue.

- For example, you might say, "I'd like to write my thesis about modern American haiku structure, autobiographical expression in contemporary 21st-century poetry, or poetry in the Internet age."
- Your thesis supervisor will likely want you to choose a topic that they know well and are interested in themselves.
Crafting Your Thesis Question

- This will help you figure out what types of questions to ask about your topic.
- If you can, highlight or mark important passages and summarize sections of text in the margins of the work.
- Talk to your librarian. They can help you find materials that might be of interest to you, and they can pull books or journals related to your topic.
Tip: Save your research materials so that you can use them when writing your thesis. You may not use all of your early research, but some of it will be relevant.

- How did 20th-century warfare alter literary themes?
- How have expanding cultural norms impacted the criteria for literary awards?
- What social changes have impacted diplomatic exchanges among world leaders?
- How does detaching morality from public policy affect the efficacy of legislation?
- How does culture adapt in the aftermath of a civil war?
- How can robotics enhance early childhood education?
- What are the best ways to motivate employees to work harder?
- What treatment protocols can enhance recovery in PTSD patients?

- Think about the process you'd need to use to research the topic, such as a digital search, social experiments, or lab testing. Then, decide if you'd be able to complete these tasks with the time and resources you have.
- List the research materials you have available to you, such as computer databases, library materials, or a laboratory.
- Consider your thesis supervisor’s area of expertise.
- Think about the courses you’ve taken and the skills you’ve developed.
For example... The thesis question "How have expanding cultural norms impacted the criteria for literary awards?" works well because it's researchable and debatable. You can explore cultural norms using social science studies, news or journal articles, and survey results from different decades. Then, study the themes and styles of award-winning literature using articles and books. From there, evaluate the relationship between them, which is up for interpretation.

- Listen to your thesis supervisor’s advice. They’ve likely been doing this for a long time, and they know what it’s like to be in your shoes.
Expert Q&A
- Try to choose your topic as early as you can. This will help you stay on track to finish your thesis on time. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- It’s helpful to do additional research throughout the selection process. If you find texts that might be of use to you later, save them to use in your thesis. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Since you’ll spend at least 1-2 years on your thesis, it’s best to choose a topic that interests you. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.millersville.edu/honorscollege/thesis/choosetopic.php
- ↑ https://www.ceu.edu/article/2019-03-29/how-choose-your-thesis-topic
- ↑ https://hhd.psu.edu/shm/undergraduate/honors-study-hospitality-management/first-steps-choosing-topic-and-thesis-supervisor
- ↑ https://library.maastrichtuniversity.nl/study/thesis-supportall/choose-thesis-topic/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/how-to-write-a-research-question
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
How to Craft Your Ideal Thesis Research Topic
.webp)
Table of contents

Catherine Miller
Writing your undergraduate thesis is probably one of the most interesting parts of studying, especially because you get to choose your area of study. But as both a student and a teacher who’s helped countless students develop their research topics, I know this freedom can be just as intimidating as it is liberating.
Fortunately, there’a a step-by-step process you can follow that will help make the whole process a lot easier. In this article, I’ll show you how to choose a unique, specific thesis topic that’s true to your passions and interests, while making a contribution to your field.
.webp)
Choose a topic that you’re interested in
First things first: double-check with your teachers or supervisor if there are any constraints on your research topic. Once your parameters are clear, it’s time to identify what lights you up — after all, you’re going to be spending a lot of time thinking about it.
Within your field of study, you probably already have some topics that have grabbed your attention more than others. This can be a great place to start. Additionally, consider using the rest of your academic and extra-curricular interests as a source of ideas. At this stage, you only need a broad topic before you narrow it down to a specific question.
If you’re feeling stuck, here are some things to try:
- Look back through old course notes to remind yourself of topics you previously covered. Do any of these inspire you?
- Talk to potential supervisors about your ideas, as they can point you toward areas you might not have considered.
- Think about the things you enjoy in everyday life — whether that’s cycling, cinema, cooking, or fashion — then consider if there are any overlaps with your field of study.
- Imagine you have been asked to give a presentation or record a podcast in the next three days. What topics would you feel confident discussing?
- Watch a selection of existing lectures or explainer videos, or listen to podcasts by experts in your field. Note which topics you feel curious to explore further.
- Discuss your field of study with teachers friends and family, some with existing knowledge and some without. Which aspects do you enjoy talking about?
By doing all this, you might uncover some unusual and exciting avenues for research. For example, when writing my Master’s dissertation, I decided to combine my field of study (English teaching methodology) with one of my passions outside work (creative writing). In my undergraduate course, a friend drew on her lived experience of disability to look into the literary portrayal of disability in the ancient world.
Do your research
Once you’ve chosen your topic of interest, it’s time to dive into research. This is a really important part of this early process because it allows you to:
- See what other people have written about the topic — you don’t want to cover the same old ground as everyone else.
- Gain perspective on the big questions surrounding the topic.
- Go deeper into the parts that interest you to help you decide where to focus.
- Start building your bibliography and a bank of interesting quotations.
A great way to start is to visit your library for an introductory book. For example, the “A Very Short Introduction” series from the Oxford University Press provides overviews of a range of themes. Similar types of overviews may have the title “ A Companion to [Subject]” or “[Subject] A Student Companion”. Ask your librarian or teacher if you’re not sure where to begin.
Your introductory volume can spark ideas for further research, and the bibliography can give you some pointers about where to go next. You can also use keywords to research online via academic sites like JStor or Google Scholar. Check which subscriptions are available via your institution.
At this stage, you may not wish to read every single paper you come across in full — this could take a very long time and not everything will be relevant. Summarizing software like Wordtune could be very useful here.
Just upload a PDF or link to an online article using Wordtune, and it will produce a summary of the whole paper with a list of key points. This helps you to quickly sift through papers to grasp their central ideas and identify which ones to read in full.

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
You can also use Wordtune for semantic search. In this case, the tool focuses its summary around your chosen search term, making it even easier to get what you need from the paper.

As you go, make sure you keep organized notes of what you’ve read, including the author and publication information and the page number of any citations you want to use.
Some people are happy to do this process with pen and paper, but if you prefer a digital method, there are several software options, including Zotero , EndNote , and Mendeley . Your institution may have an existing subscription so check before you sign up.
Narrowing down your thesis research topic
Now you’ve read around the topic, it’s time to narrow down your ideas so you can craft your final question. For example, when it came to my undergraduate thesis, I knew I wanted to write about Ancient Greek religion and I was interested in the topic of goddesses. So, I:
- Did some wide reading around the topic of goddesses
- Learned that the goddess Hera was not as well researched as others and that there were some fascinating aspects I wanted to explore
- Decided (with my supervisor’s support) to focus on her temples in the Argive region of Greece

As part of this process, it can be helpful to consider the “5 Ws”: why, what, who, when, and where, as you move from the bigger picture to something more precise.
Why did you choose this research topic?
Come back to the reasons you originally chose your theme. What grabbed you? Why is this topic important to you — or to the wider world? In my example, I knew I wanted to write about goddesses because, as a woman, I was interested in how a society in which female lives were often highly controlled dealt with having powerful female deities. My research highlighted Hera as one of the most powerful goddesses, tying into my key interest.
What are some of the big questions about your topic?
During your research, you’ll probably run into the same themes time and time again. Some of the questions that arise may not have been answered yet or might benefit from a fresh look.
Equally, there may be questions that haven’t yet been asked, especially if you are approaching the topic from a modern perspective or combining research that hasn’t been considered before. This might include taking a post-colonial, feminist, or queer approach to older texts or bringing in research using new scientific methods.
In my example, I knew there were still controversies about why so many temples to the goddess Hera were built in a certain region, and was keen to explore these further.
Who is the research topic relevant to?
Considering the “who” might help you open up new avenues. Is there a particular audience you want to reach? What might they be interested in? Is this a new audience for this field? Are there people out there who might be affected by the outcome of this research — for example, people with a particular medical condition — who might be able to use your conclusions?
Which period will you focus on?
Depending on the nature of your field, you might be able to choose a timeframe, which can help narrow the topic down. For example, you might focus on historical events that took place over a handful of years, look at the impact of a work of literature at a certain point after its publication, or review scientific progress over the last five years.
With my thesis, I decided to focus on the time when the temples were built rather than considering the hundreds of years for which they have existed, which would have taken me far too long.
Where does your topic relate to?
Place can be another means of narrowing down the topic. For example, consider the impact of your topic on a particular neighborhood, city, or country, rather than trying to process a global question.
In my example, I chose to focus my research on one area of Greece, where there were lots of temples to Hera. This meant skipping other important locations, but including these would have made the thesis too wide-ranging.
Create an outline and get feedback
Once you have an idea of what you are going to write about, create an outline or summary and get feedback from your teacher(s). It’s okay if you don’t know exactly how you’re going to answer your thesis question yet, but based on your research you should have a rough plan of the key points you want to cover. So, for me, the outline was as follows:
- Context: who was the goddess Hera?
- Overview of her sanctuaries in the Argive region
- Their initial development
- Political and cultural influences
- The importance of the mythical past
In the final thesis, I took a strong view on why the goddess was so important in this region, but it took more research, writing, and discussion with my supervisor to pin down my argument.
To choose a thesis research topic, find something you’re passionate about, research widely to get the big picture, and then move to a more focused view. Bringing a fresh perspective to a popular theme, finding an underserved audience who could benefit from your research, or answering a controversial question can make your thesis stand out from the crowd.
For tips on how to start writing your thesis, don’t miss our advice on writing a great research abstract and a stellar literature review . And don’t forget that Wordtune can also support you with proofreading, making it even easier to submit a polished thesis.
How do you come up with a research topic for a thesis?
To help you find a thesis topic, speak to your professor, look through your old course notes, think about what you already enjoy in everyday life, talk about your field of study with friends and family, and research podcasts and videos to find a topic that is interesting for you. It’s a good idea to refine your topic so that it’s not too general or broad.
Do you choose your own thesis topic?
Yes, you usually choose your own thesis topic. You can get help from your professor(s), friends, and family to figure out which research topic is interesting to you.
Share This Article:

How to Craft an Engaging Elevator Pitch that Gets Results
.webp)
Eight Steps to Craft an Irresistible LinkedIn Profile
.webp)
7 Common Errors in Writing + How to Fix Them (With Examples)
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
How to Choose a Dissertation Topic – 9 Steps
Choosing a dissertation topic is really difficult.
When I had to choose dissertation topic I agonized for weeks.
And I’ve supervised over 50 students’ dissertations across undergraduate, masters and PhD levels. All of my students agonized over their topics, too.
So you’re not alone in your struggle.
The below tips for choosing a dissertation topic are the ones I wish I was given when I was in the process of looking for a suitable topic.
If only I’d known these points, I would have saved a lot of time and stress for myself. So if these tips only help one person out, I’ll be happy.
These tips really work for just about anybody. They’re particularly useful for undergraduate and Masters level students who are writing dissertations. But, I’m sure most doctoral students will also find these points relevant, too. Especially tips 1 – 3.
Here are my tips on how to choose a dissertation topic – I hope they come in handy, and good luck on your research journey!
Read Also: 25 Sociology Dissertation Ideas
1. It Doesn’t have to be Unique (Yet).
This is the one piece of advice I wish I had gotten when I was choosing my dissertation topic.
Many students feel like they need to find a unique topic that will blow their markers away.
I was this student.
I thought that I had to choose a topic and idea that was going to make a unique contribution to knowledge. I thought I had to discover something, or, at the very least, choose a topic that no one has ever done before.
So here’s what I wish someone had told me:
It doesn’t matter if other people have done the same topic as you.
Don’t even let it phase you for a moment if someone else has chosen your topic. Just choose whatever topic you want.
Well, because your unique contribution doesn’t come at the start. It comes at the end!
You’ll find a way to make a unique contribution after you have completed your literature review . There is always time and space to find a new angle or different way of doing the topic than other people.
So, don’t choose your topic because it’s unique or different.
Then … how should you choose your topic? Points 2 and 3 give you some tips…
2. Make it Relevant to your Career Goals.
The first thing I recommend to all my students is to consider how their topic can help progress their careers.
When giving guidance to my students, I ask them these three questions:
- a) What sort of specialization do you want in your career? If you’re studying teaching, your questions might be: do you want to be a specialized literacy teacher? do you want to be an expert on behavior management? Do you want to be specialized in play-based learning ?
- b) How do you want to differentiate yourself from your competition? Your dissertation topic is going to be the topic you ‘sell’ as your area of expertise in future job interviews. If you want to get a great job, choose a topic that really stands out in the marketplace. Have a think right now for yourself: what areas of your industry are booming? For example, would it be better to specialize in coal or solar panels? Which one would be best to talk about in a job interview in the 21 st Century?
- c) Do you want to be a research pro? Most of my students don’t want to be researchers as a career. They do their dissertations to prove mastery of their topic – that’s all. The research is a means to an end. But, if you think you want to go on to do the next level degree (a PhD one day?) then you’ll want to focus on having a high quality methodology, not just an interesting topic.
So, have a think now: is there a topic that will help you get to where you plan on going? What expert knowledge do you want to be able to ‘sell’ in a future interview?
3. Ensure it’s Interesting to You.
You’re going to be wedded to your chosen for a long time. And by the end of this journey you’re going to hate it.
To make your life easier, choose a topic you’re interested in.
Here’s two ways of approaching this:
Choose a Topic you Think About a Lot.
Choose a dissertation topic that you find yourself talking about, complaining about or raving about to your parents. Choose something that makes you angry, inspired or intrigued.
For the next week or so, I recommend taking notes whenever you find yourself thinking idly about something. Is that something you’ve thought about a lot?
Or, Choose a Topic by Looking over Past Assessment Tasks.
Another way of approaching the search for an interesting topic is to look over past assignments.
What assessment task have you done in the past few years that gripped you? Which one did you enjoy the most when you were studying it?
Zoom in on that topic and see if you can turn it into a dissertation.
Bonus tip: If you found a topic that was based on a previous assessment task, see if you can convince the person who taught that subject to be your dissertation supervisor.
4. Keep it Simple.
Too often, students want to choose a topic that is complex and complicated. They come up with a long, detailed research question (usually with the help of their professor) that, really, is hard to understand!
The best strategy is to come up with a topic that is really, really straightforward. At least, the topic should start as simple and straightforward.
Your topic is going to grow and expand into a monster. It’ll be hard to tame and control. You’ll be following random tangents down rabbit holes that end up being dead-ends. You’ll research aspects of the topic and realize it was a completely pointless exercise.
The way to minimize the crazy growth of your research project is to simplify it right from the start. Make it a really simple idea.
For example, I had a student who wanted to research:
“How big is the gap in mathematics outcomes between children from middle-class and working-class backgrounds by age 16?”
I would think that this topic may be achievable by a top academic with a sizeable research grant, but my student was completing a 10,000 word dissertation for graduating her Bachelor of Arts with Honours.
After several agonizing research meetings, we peeled it back over and again until we ended up with something much simpler and more specific:
“What are teachers’ opinions of the impact of poverty on learning?”
Why is this simpler and more specific?
Well, with the second study, my student has a clear focus group (teachers) and an achievable methodology (interviews). This will be far simpler than somehow conducting tests on 16-year old children, getting a significant amount of children to participate in the study, and then dissecting their mathematics test results by income level.
Instead, we aimed small and simple to ensure the task itself was achievable.
We’re not here to win a Nobel prize. You can do that with your multi-million-dollar post-doctoral research grant. Get your degree first.
5. Ensure it’s Achievable.
This piece of advice builds on the previous advice, to “keep it simple”.
Keeping it simple means making sure you have a clear, small-scale focus.
Esuring the project is achievable means choosing a methodology that won’t break you.
Small Scale Qualitative Studies are Achievable for Anyone
I always suggest to my Undergraduate and Masters level students to aim for a small scale study with no more than 20 research participants.
Now, I know there will be many of you out there who want to do quantitative research studies. And in reality, you can do a quantitative study with a small group of students. These usually involve quantitative action research case studies.
If you’re set on a quantitative study, that’s fine. But find a supervisor with the right experience.
Personally, I usually recommend a qualitative focus group analysis for anyone doing their first dissertation.
The biggest mistake you can make is biting off more than you can chew.
Small scale qualitative studies are the easiest option . They can be achieved within your time frame. And you can certainly still get a very high grade.
So, let’s take the example of the previous research question, which we changed from:
For the first study, you will have to develop skills in quantitative data analysis , find a sizeable cohort of students, get permission from their parents, get special permission to study children you’re your university ethics committee, develop a quality testing mechanism, pilot the test, conduct the test, analyze the data, then interpret it.
For the second study, you will not have to develop complex mathematical skills, bother with getting permission to research children, or deal with the rigor of quantitative analysis.
In other words, you will be able to bypass many hurdles you may face.
That’s the benefit of a small-scale qualitative study. It’s a nice easy first dissertation methodology. You can do it and do it well.
I know my position is controversial, but hey … I’m here to tell you how to avoid problems, not to stand on a soapbox.
Consider Textual Analysis, Semiotic Analysis or Secondary Research
Finding people to interview, survey or participate in your study in any way at all can be intimidating.
I find it interesting and really fulfilling. But I understand if you think it’s too much for you at this point in time.
If you don’t want to have to go out and find research participants for your study, I recommend one of these types of study:
- Textual Analysis : you can look at policy documents or newspaper articles and analyze their ideological positioning , for example;
- Semiotic Analysis : The quintessential semiotic analysis is the analysis of advertising images or movies and the examination of the ways they depict people of different races, social classes or genders;
- Secondary Research: Look over other people’s research and try to identify themes across a range of research studies.
Now, these three different methodologies are far outside of the scope of this discussion, but consult with your dissertation supervisor if you’re overwhelmed by the idea of conducting research with real human beings. One of these three methodologies may help you bypass that process, and make the dissertation feel more achievable for you.
6. Search Online for Inspiration
If you’re still struggling to choose a dissertation topic, go online to get inspiration!
There’s a few ways you can do this. Here’s a few good ones:
a) Google Previous Dissertation Topics
Many universities upload their students’ dissertations onto an online repository. This means there are a ton of open, free to access databases of previous students’ dissertations all over the internet.
Simply google “Dissertation” + “pdf” + a topic you’re interested in. If you’re a masters student, you can do “masters dissertation” + “pdf” + the topic; and if you’re an undegrad, then simply do “undergraduate dissertation” + “pdf” + the topic;. Simple!
Up will pop a ton of dissertations that you can instantly download to check out previous students’ successful dissertation topics.
Another benefit of doing this is that you’ll be able to view and model the structure that previous students have used as well. This can be super beneficial for you early on!
b) Look at Recent Articles Published in Journals focused on your Topic
If you scroll through the recent issues of journals in your topic, you’ll find a range of research topic ideas.
To get access to top journals in your topic, simply google “Scholarly Journal” + your topic. For example, I am a professor in education. So I’d google “Scholarly journal” + “Education”.
The homepages for a ton of journals will pop up in the Google search. Quickly scan through the recent issues of those journals to see if any ideas will pop up that interest you!
c) If you’re Studying Education or Teaching, Check Here
Lastly, a quick plug for another post I’ve written for dissertation students:
- 51+ Dissertation Ideas for Education students .
Go check that out if you want to write a dissertation on the ‘education’ topic.
7. Trust your Dissertation Supervisor
Your dissertation supervisor will have walked many students just like you through the research process before.
Look, I know many dissertation supervisors can be disappointingly aloof and disconnected from your research. And relationships can get very frosty with your supervisors indeed.
Trust your supervisor. They make recommendations for a reason. They know how to navigate the dissertation writing process. If your supervisor makes a recommendation, strong – very strongly – consider it.
Your supervisor also has expertise in one area of research or another. Take advantage of their expertise. Be flexible and let them sway you down certain paths. You need a knowledgeable partner in the research process.
So, trust your supervisor. You need their expertise more than you know.
8. Come up with 3-5 Ideas and Bring them to your Supervisor for Feedback
Your initial dissertation topic ideas will probably need a lot of refinement.
The person who will help you to refine your topic will be your dissertation supervisor. Their main job, unfortunately, is to curb your enthusiasm. It’s to show you what problems you’ll face if you follow certain paths and recommend alterations to ensure your topic is achievable.
So, approach your supervisor with your 3-5 top ideas and watch them do their magic. They should advise you on how to turn your ideas into reality.
Your ideas can be specific or broad – really, it doesn’t matter because you’ll walk out of your supervision meeting with a lot of changed ideas. It doesn’t need to be set in stone.
You could, for example, go up to your supervisor and say something like:
- “I’m interested in Erikson’s theory of development. Do you have any suggestions of how I can use Erikson’s ideas for a dissertation?”
- “I’m really into conservative politics. What ideas do you have for an achievable topic?”
- Any other ideas…
They’ll help you shape and mold your topic into something achievable.
9. Lastly, Stick to your Choice

When I did my dissertation, I questioned my topic daily: I’d always be thinking up new, better ideas for my dissertation!
But once you’re locked in, it’s hard to change your mind. You’re going to get ethics permission to conduct your study, not anyone else’s!
So, my advice is simple:
Once you’ve chosen your topic, commit.
If you’re desperate to do another topic, fine, do another degree. If you’re doing your Master’s right now, bank those other ideas for a potential PhD down the track.
But once you’ve made your choice, really … you’ve got to commit, block out all your regrets and dig in.
Don’t worry about your friends who chose a dissertation topic that is better than yours. Stay in your lane, be content with your topic, and create a great product.
Writing a dissertation is an exercise in being practical more than anything. That start from the very first choice: choosing a dissertation topic that’s achievable and good for your career, and will also put you on the path for top marks.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Animism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Magical Thinking Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to come up with a topic for your thesis

Finding a thesis topic
The easiest method to choose a thesis topic, how to choose a thesis topic that will get you a job, ask your supervisor for help, found my thesis topic, now what, further tips on finding a thesis topic, frequently asked questions about coming up with a topic for your thesis, related articles.
Depending on the level of your studies, you will be required to come up with a topic for your thesis by yourself or to choose from a list of broad topics. In either case, you will need to:
- Choose a specific scope
- Narrow it down as much as you can.
- Find a topic by considering specific debates or discussions that interest you.
- Choose a topic based on phenomenon, point of view, and context.
- Consider the relevance of your topic in relation to job market realities.
- Ask your supervisor for help and guidance, as needed.
Tip: Balance your own interests with what can help you grow in your field..
In any case, you can start by asking yourself if you’ve attended any lecture where you were particularly interested in a certain subject and go from there. The following questions might help you shine a light on personal topics of interest:
- What aspect of your studies holds a particular interest for you?
- Was something mentioned in a discussion that you found intriguing?
- Did you read about a theory or idea that spoke to you?
Ideas for a thesis can stem from many sources, so let your mind wander and see if anything tickles your curiosity. A thesis is a chance for you to spend some quality time with a certain aspect of your studies, so you better think of a topic that not only appeals to you but will also help you grow in your field.
Tip: Use phenomenon, point of view, and context to help you choose a balanced thesis topic.
We can all agree that choosing a topic for a thesis or any paper is one, if not the most, difficult steps in writing. However, according to Sahlman's How to Write a Master Thesis Fast , choosing a topic for your thesis is rather easy if you focus on the three following areas:
- Point of view
Focus on a specific phenomenon as the center of your thesis. For example, "queer rights" or "climate change". Next, you choose a point of view. From what perspective do you see the phenomenon? For instance, “American culture” or “legally/ financially”. Finally, you narrow it down to a particular context, such as “from 2000 to 2010” or “small German enterprises in 2017”.
By combining the examples of these three areas, we come up with two potential thesis topics:
The development of queer rights in American culture from 2000 to 2010
Emerging climate change regulations of small German enterprises in 2017
The topic doesn't need to be perfect at first. The idea is to brainstorm with the topics that most interest you in the beginning and slowly come up with with a compelling topic you can brag about at friends’ dinner parties. Here is a list of the top 100 research paper topics for some inspiration.
Tip: Think about how your potential topic can make an intervention into your field of study.
If you will be writing extensively about a specific topic it does not only have to meet the requirements of the academia but it should also expand your professional horizons. According to the article how to pick a masters thesis topic , you should be thinking beyond the completion of your degree.
The author states "use your time as a student to make yourself as attractive to employers as possible." In order to achieve this, make sure that at least one of the three components (phenomenon, point of view and context) is of interest in your desired professional field.
For example, the thesis topics mentioned above would be of great help to people interested in working in the field of human rights and climate change. By choosing a thesis topic related to your professional future, your chances of landing your desired job will be higher, as you could bring fresh and valuable knowledge to your field.
Tip: Ask your supervisor for advice early in the process.
If your topic is still not fully shaped, then take advantage of the greater wisdom of your supervisor and ask for guidance. Arm yourself with enough possible topics and pay your supervisor a visit. Explain what’s your specific point of view and/or context of interest and, luckily, they will steer you in the right direction.
It is certainly not enough to find a topic for your thesis. You also need to make sure that it is a relevant topic and that you will be able to develop it.
- 5 Tips for selecting a thesis topic
- How to come up with a thesis topic
- How to pick a Masters thesis topic
Choosing a topic for your thesis is easy if you focus on the three following areas:
Focus on a specific phenomenon as the center of your thesis. From what perspective do you see the phenomenon? Finally, narrow it down to a particular context . By combining these three areas, you can come up with several possible thesis topics.
Here is a list of the top 100 research paper topics for some inspiration.
The amount of time you need to choose a thesis topic depends on you. If you use the method we explained above, it can take very short time. If you doubt yourself too much, you might end up spending many days choosing a topic.
Here's a YouTube tutorial on How To Choose A Research Topic For A Dissertation Or Thesis (7 Step Method + Examples) by the Grad Coach.
The first person to ask for help if you have trouble finding a thesis topic is your supervisor. Take advantage of their greater wisdom and ask for guidance. Explain them your interests, and, luckily, they will steer you in the right direction.

- How it works

How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
Published by Jamie Walker at August 16th, 2021 , Revised On April 19, 2024
The dissertation is one of the most testing academic assignments for undergraduate, graduate, or doctoral students. When writing a dissertation , you are expected to answer a particular research question and derive findings that can have implications for future research.
Nevertheless, writing can be a daunting task because dissertations are complex academic documents with intricate rules. Particularly, students need to select a good dissertation topic.
However, the prospect of selecting the appropriate topic can be overwhelming because many lack experience writing dissertations . In other cases, students might have limited time for writing as they have to manage their personal and professional needs.
Here we bring to you important guidelines that can facilitate if you are unsure how to choose a dissertation topic that is interesting, relevant, and manageable.
Step 1. Assess the Course Requirements
If you have just started to look for a topic, you might be wondering how I chose a dissertation topic that could leave a lasting impression on my supervisor and help me score a high academic grade.
It is important to note that each course has specific requirements or terms and conditions that guide students to determine the dissertation topic that best suits their needs. The nature and suitability of your chosen dissertation topic are dependent on the academic course being studied.
For example, you might have wanted to know how to choose a thesis topic for a master’s or how to choose a thesis topic for an undergraduate course but overlooked your course requirements.
It is vitally important to look into your course requirements before narrowing down the topics instead of being caught up in confusion.
Your department’s dissertation writing requirements , in some cases, can be very extended and perplexing; specifying the minimum and maximum word count, outline the list of possible topics , and identify the methodological requirements.
On the other hand, the prerequisites might be very limiting and unclear, with only the deadline and word count requirements being specified. No matter the requirements, it is essential to check with the course coordinator if students are unsure about choosing a topic for the dissertation.
ORDER FREE DISSERTATION TOPIC
Step 2. Select an Extensive Field
A prudent practise is to evaluate topics that are interesting for students in their courses. For instance, students can select a familiar topic that guides them during research. It is relatively easy to start research with known topics since you will not have to write from the beginning.
One way to find a topic is to search how to choose a dissertation topic on Google . There is no need to have advanced knowledge about the topic since basic information can guide students to investigate the topic further and narrow it down to something relevant, valuable, and manageable.
At ResearchProspect, we have created hundreds of topics for undergraduate, Masters and Ph.D. students. Please click here to find your topic in our free dissertation topics database, no matter the academic subject. We are the only company in the UK that provides free topics along with an aim and justification to help you get started.
Hire an Expert Writer
Proposal and dissertation orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in academic style
- Plagiarism free
- 100% Confidential
- Never Resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements
Step 3. Search Relevant Academic Literature
This is another important aspect of how to choose a dissertation topic. Students should find reliable and credible books, online dissertation topics databases, and articles to explore possible topics.
Highly rated journals frequently publish articles that introduce readers to new research on any topic. One way of choosing a dissertation topic is to use Google Scholar , which is a good resource for finding relevant journals for any subject.
It includes abstracts of relevant research that can inspire students to select their dissertation topic. Many universities have online libraries that students can access to find information about their specific subjects.
For example, students might want to know how to choose a dissertation topic in English literature . The above methods can assist them in the research process. While reading different books and articles, students should make notes about ideas that can be used to create a list of possible topics.
Also Read: What is Research Problem in Dissertation?
Step 4: Narrow Topic to Niche
Now that you have already completed the preliminary research, the next step would be to evaluate every topic and scrap the ones that are either too broad or too narrow.
The key to choosing a great dissertation topic is to identify a niche that still needs more research or a topic that is still debatable among researchers. You can investigate contemporary issues that have an impact on humans and society.
An example of a niche topic is “Social media strategies for business organizations”.
Another example would be “Identification of barriers that act as obstacles towards the popularity of sustainable architecture”.
Whatever the specific niche, it is crucial that adequate information on the topic is available because of the need to provide a robust theoretical basis for the dissertation. Develop a research problem statement and research questions to further narrow the topic.
Here are some ideas for you to consider;
Identify the time needed to study the academic sources on the topic.
If the list of sources is extensive then it might be necessary to narrow the topic even further.
If you are unable to perform primary research, make sure there is adequate information to complete the objectives of your descriptive dissertation.
Step 5. Evaluate the Best Research Approach when Choosing Topic
Select the research method that is most suitable for your dissertation and meets your degree programme. This is an important stage of choosing a dissertation topic, but there is no need to panic.
The two methods of research employed in academic research are known as primary research and secondary research . It is recommended that students evaluate artefacts or examine various theoretical approaches.
For example, if you have chosen a dissertation topic in education , then you might decide to base your dissertation on primary research because primary research would enable you to address a research problem that is of critical importance to the education industry by filling an obvious gap in knowledge.
On the other hand, if you are testing a hypothesis and you find out that there is sufficient literature already available on the subject, then you could base your dissertation purely on secondary data.
However, dissertations can include one or multiple approaches to research. You should consult with your mentors about the best research method, especially when unsure about how to choose a dissertation topic for a PhD level assignment .
Primary research can be costly and time-consuming, while secondary research is cost-effective and saves time. Selecting the right approach is dependent on the resources and time available to students.
Here are the most notable advantages and disadvantages of primary and secondary research.
Step 6. Demonstrate the Relevance of Topic
Perhaps the most important step is to ensure the topic is relevant to your field of study. Your topic should be academically relevant and aim to fill a gap in existing knowledge or provide new insights into the field.
It should also be socially relevant as the results should promote social change and contribute towards an understanding of society.
Finally, it must be practically relevant by contributing towards problem-solving or improving quality of life. A relevant topic should be interlinked with contemporary subjects, debates, and topics. The research problem can be used to demonstrate the relevance of the topic.
For example, if you are stuck on how to choose a dissertation topic for a master’s course, a master’s dissertation on strategic human resource management could identify the implications of the research for modern firms and their HR practices.
Similarly, if you are doing all this research to choose a doctoral dissertation topic, a doctoral dissertation on a political science topic could assess the implications for policymakers.
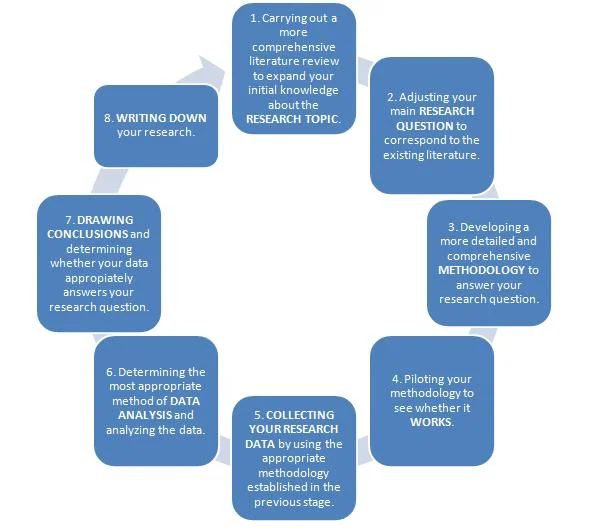
Step 7. Submit the Topic to Committee
Once you have selected a topic, and are ready to proceed, submit the topic with a brief description to the program supervisor or coordinator. Once approved, a dissertation research proposal will be needed as the next step.
If your supervisor doesn’t approve of your chosen topic, there is still no need to panic. You can follow the same steps on how to choose a dissertation topic and send them more suggestions.
Each of the steps described in this article is part of a gradual and systematic process that will assist students in how to choose a dissertation topic. It is important to use planning and preparation because the result of your dissertation project, to some extent, will depend on your chosen topic.
At ResearchProspect, we have created hundreds of free topic suggestions for students. Whether you are an undergraduate, Master’s, or Ph.D. student, you can find an interesting, relevant, suitable, and manageable topic for your research in our free dissertation topics library .
Our dissertation writers can also provide you with free custom topic ideas and a plan/outline on your chosen topic to help you get your topic and plan of research approved by your supervisor.
Order a Proposal
Worried about your dissertation proposal? Not sure where to start?
- Choose any deadline
- Unlimited free amendments
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Completed to match exact requirements
Frequently Asked Questions
Does your dissertation topic matter.
Yes, your dissertation topic matters significantly. It shapes your research, impacts your engagement, and influences your academic and career path. A well-chosen topic aligns with your interests, contributes to your field, and enhances your overall learning experience.
How to choose a dissertation topic?
- Assess the course requirements
- Select an extensive field
- Search relevant academic literature
- Narrow topic to the niche
- Demonstrate the relevance of your topic
- Submit topic to the committee’
Can I change my dissertation topic?
Yes, you can change your dissertation topic, but the process varies by institution and department. Consult with your advisor and review departmental guidelines. Changing topics may require additional time, research, and resources, so weigh the benefits and drawbacks before making a final decision. Always prioritise your academic and research interests.
How to choose a dissertation topic for an undergraduate?
Identify your interests within your field. Explore coursework, readings, and discussions that intrigued you. Conduct preliminary research to gauge existing literature. Discuss potential topics with professors or advisors. Ensure feasibility in terms of data, resources, and time. Opt for a unique angle but remain within the scope of undergraduate expectations.
How many words is a dissertation title?
A dissertation title’s length varies, but it is typically concise. Most titles range between 10 and 15 words. The aim is to be descriptive and clear while capturing the essence of the research. It should give readers an immediate understanding of the topic without being overly lengthy or ambiguous. Always follow institutional guidelines.
Does a dissertation need a title?
Yes, a dissertation needs a title. The title succinctly conveys the essence of the research and provides a first impression to readers. It helps in identifying the work’s main theme and acts as a reference point for scholars, researchers, and anyone engaging with the dissertation. A clear, relevant title is crucial.
Can you do a dissertation on an existing topic?
Yes, dissertations often explore existing topics by offering new insights, methodologies, or perspectives. However, it’s essential to ensure your contribution is original, either by adding new data, analysing existing data differently, or proposing novel interpretations. You can add a new mediator or moderator to ensure originality. Acknowledging existing literature and building upon it is integral to scholarly research.
You May Also Like
Penning your dissertation proposal can be a rather daunting task. Here are comprehensive guidelines on how to write a dissertation proposal.
Here we explore what is research problem in dissertation with research problem examples to help you understand how and when to write a research problem.
How to write a hypothesis for dissertation,? A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested with the help of experimental or theoretical research.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Selecting a Research Topic: Overview
- Refine your topic
- Background information & facts
- Writing help
Here are some resources to refer to when selecting a topic and preparing to write a paper:
- MIT Writing and Communication Center "Providing free professional advice about all types of writing and speaking to all members of the MIT community."
- Search Our Collections Find books about writing. Search by subject for: english language grammar; report writing handbooks; technical writing handbooks
- Blue Book of Grammar and Punctuation Online version of the book that provides examples and tips on grammar, punctuation, capitalization, and other writing rules.
- Select a topic
Choosing an interesting research topic is your first challenge. Here are some tips:
- Choose a topic that you are interested in! The research process is more relevant if you care about your topic.
- If your topic is too broad, you will find too much information and not be able to focus.
- Background reading can help you choose and limit the scope of your topic.
- Review the guidelines on topic selection outlined in your assignment. Ask your professor or TA for suggestions.
- Refer to lecture notes and required texts to refresh your knowledge of the course and assignment.
- Talk about research ideas with a friend. S/he may be able to help focus your topic by discussing issues that didn't occur to you at first.
- WHY did you choose the topic? What interests you about it? Do you have an opinion about the issues involved?
- WHO are the information providers on this topic? Who might publish information about it? Who is affected by the topic? Do you know of organizations or institutions affiliated with the topic?
- WHAT are the major questions for this topic? Is there a debate about the topic? Are there a range of issues and viewpoints to consider?
- WHERE is your topic important: at the local, national or international level? Are there specific places affected by the topic?
- WHEN is/was your topic important? Is it a current event or an historical issue? Do you want to compare your topic by time periods?
Table of contents
- Broaden your topic
- Information Navigator home
- Sources for facts - general
- Sources for facts - specific subjects
Start here for help
Ask Us Ask a question, make an appointment, give feedback, or visit us.
- Next: Refine your topic >>
- Last Updated: Jul 30, 2021 2:50 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mit.edu/select-topic
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
Least Known Ways on How To Choose a Thesis Topic

Developing a topic for any given subject is no easy task for anyone. Whether you are in high school, undergraduate or postgraduate level, this is no mean feat. That is why you need to learn how to come up with a thesis topic painstakingly. The key to unlocking all this lies in the next few lines. Journey with me as we master the art of choosing a thesis topic together.
What Are Thesis Project Ideas?
You will quickly know how to pick a thesis topic if you understand what it means. A thesis topic gives you the unique opportunity to showcase your mastery of the field of study you have invested in for years. It also presents you with a chance to contribute to the body of knowledge on a specific subject within your studying area.
Now that you understand a thesis topic knowing how to find a thesis topic becomes an exciting rather than a dreadful moment. Let me show you the fun part of it all.
How To Find Good Thesis Topics: Underlying Challenges
The little attention that all of us give to such an essential part of the writing process is what kills it. Instead of investing hundreds of hours and tremendous effort, many students have underrated this crucial research writing aspect. Below are some of the stumbling blocks to picking a thesis subject:
Most scholars do not understand how cumbersome the whole process is Lack of an effective system of counseling on how to choose a dissertation topic Time constraint for Masters and Ph.D. students
Most students will end up in their final years of study, having no idea how to pick a thesis topic and proceed with their research work.
But this ought not to be the case. With the expert tricks and tips below, you will know how to choose a thesis topic for masters or Ph.D. with ease. Scroll down for more.
How To Pick a Topic For Your Thesis Painstakingly
While these tips may not be the magic formula or secret ‘topic portion’ to selecting thesis ideas, they are essential for starters. They provide you with a good foundation on which to formulate your topic ideas.
Here we go!
Having a researchable topic: First of all, consider all the resources at hand – time, money, and sources. Then, you can choose a thesis topic that you can do justice to effortlessly. The topic should interest you first: I find it odd to do something that I don’t like. Therefore, your thesis topic should ignite the motivation and enthusiasm in you to work it out. What are your strengths? Consider what you are good at, powerful suits that can be applied to a research project. Look at every available resource or things in your life that can propel you to choosing a dissertation topic. Originality, context, and execution: It would be blunt for a reader to bump into a topic that he/she has encountered somewhere else. The thesis topic you choose should be original and one that fits within the context of your audience. Formulate a question: Many thought-provoking questions can act as a stepping stone to your quality thesis topic. Look for gaps in the already published works: None of us knows everything, but we at least know something. Therefore, you can read the published results with an open mind, identify the missing links, and then write on them. Have a specific perspective: From what unique point of view do you wish to present your phenomenon? Embrace creativity: All of us are creative in our unique ways. Making use of your imagination can be a gold mine to finding a top-notch thesis topic. Brainstorm with classmates: This is one of the most common yet misused ways of finding thesis topics. To get the best out of this, brainstorm ideas to expand your knowledge base. Consult your faculty: It will help identify the structure, in-house style, or possible thesis topics for your particular research field.
What excuse do you have now for not coming up with a thrilling thesis topic thick and fast? Here are some professionally handpicked thesis topics examples to get you started:
The Best Thesis Topic Ideas in 2023
- The place of democracy in the US following the violence at its Capitol
- How the coronavirus has changed interpersonal relationships
- The rise of feminists in the 21st century
- The impact of social media in mobilizing and creating awareness
- Why you should always put on your mask
- Is China taking over the world economy?
Interesting Thesis Topic Ideas
- Emerging business ethics in the digital space
- Effectiveness of the death sentence for capital offenses
- Impact of Mandatory Minimum sentencing
- Drunk driving during festivities
- Why doping is still a threat in athletics
- Legalization of marijuana
Controversial Thesis Topics
- Abortion and human rights
- The role of religion
- 5G and coronavirus
- Origin of coronavirus
- Is assisted suicide legal?
- Gun control policies
Easy Thesis Topics
- Legal drinking age
- Masks and coronavirus prevention
- The role of mentors
- Is TV causing obesity?
- Internet and moral decay
- Is homework beneficial?
Master Thesis Ideas
- College admission policies
- Online writing sites
- Is it legal to pay for thesis?
- Sex education in schools
- Alternative energy sources
- Geoengineering
If you still haven’t found what you were looking for, our pro thesis writers are here for you. We offer cheap, quality online writing help to all students. Try us today.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
1000+ FREE Research Topics & Title Ideas
If you’re at the start of your research journey and are trying to figure out which research topic you want to focus on, you’ve come to the right place. Select your area of interest below to view a comprehensive collection of potential research ideas.

Research Topic FAQs
What (exactly) is a research topic.
A research topic is the subject of a research project or study – for example, a dissertation or thesis. A research topic typically takes the form of a problem to be solved, or a question to be answered.
A good research topic should be specific enough to allow for focused research and analysis. For example, if you are interested in studying the effects of climate change on agriculture, your research topic could focus on how rising temperatures have impacted crop yields in certain regions over time.
To learn more about the basics of developing a research topic, consider our free research topic ideation webinar.
What constitutes a good research topic?
A strong research topic comprises three important qualities : originality, value and feasibility.
- Originality – a good topic explores an original area or takes a novel angle on an existing area of study.
- Value – a strong research topic provides value and makes a contribution, either academically or practically.
- Feasibility – a good research topic needs to be practical and manageable, given the resource constraints you face.
To learn more about what makes for a high-quality research topic, check out this post .
What's the difference between a research topic and research problem?
A research topic and a research problem are two distinct concepts that are often confused. A research topic is a broader label that indicates the focus of the study , while a research problem is an issue or gap in knowledge within the broader field that needs to be addressed.
To illustrate this distinction, consider a student who has chosen “teenage pregnancy in the United Kingdom” as their research topic. This research topic could encompass any number of issues related to teenage pregnancy such as causes, prevention strategies, health outcomes for mothers and babies, etc.
Within this broad category (the research topic) lies potential areas of inquiry that can be explored further – these become the research problems . For example:
- What factors contribute to higher rates of teenage pregnancy in certain communities?
- How do different types of parenting styles affect teen pregnancy rates?
- What interventions have been successful in reducing teenage pregnancies?
Simply put, a key difference between a research topic and a research problem is scope ; the research topic provides an umbrella under which multiple questions can be asked, while the research problem focuses on one specific question or set of questions within that larger context.
How can I find potential research topics for my project?
There are many steps involved in the process of finding and choosing a high-quality research topic for a dissertation or thesis. We cover these steps in detail in this video (also accessible below).
How can I find quality sources for my research topic?
Finding quality sources is an essential step in the topic ideation process. To do this, you should start by researching scholarly journals, books, and other academic publications related to your topic. These sources can provide reliable information on a wide range of topics. Additionally, they may contain data or statistics that can help support your argument or conclusions.
Identifying Relevant Sources
When searching for relevant sources, it’s important to look beyond just published material; try using online databases such as Google Scholar or JSTOR to find articles from reputable journals that have been peer-reviewed by experts in the field.
You can also use search engines like Google or Bing to locate websites with useful information about your topic. However, be sure to evaluate any website before citing it as a source—look for evidence of authorship (such as an “About Us” page) and make sure the content is up-to-date and accurate before relying on it.
Evaluating Sources
Once you’ve identified potential sources for your research project, take some time to evaluate them thoroughly before deciding which ones will best serve your purpose. Consider factors such as author credibility (are they an expert in their field?), publication date (is the source current?), objectivity (does the author present both sides of an issue?) and relevance (how closely does this source relate to my specific topic?).
By researching the current literature on your topic, you can identify potential sources that will help to provide quality information. Once you’ve identified these sources, it’s time to look for a gap in the research and determine what new knowledge could be gained from further study.
How can I find a good research gap?
Finding a strong gap in the literature is an essential step when looking for potential research topics. We explain what research gaps are and how to find them in this post.
How should I evaluate potential research topics/ideas?
When evaluating potential research topics, it is important to consider the factors that make for a strong topic (we discussed these earlier). Specifically:
- Originality
- Feasibility
So, when you have a list of potential topics or ideas, assess each of them in terms of these three criteria. A good topic should take a unique angle, provide value (either to academia or practitioners), and be practical enough for you to pull off, given your limited resources.
Finally, you should also assess whether this project could lead to potential career opportunities such as internships or job offers down the line. Make sure that you are researching something that is relevant enough so that it can benefit your professional development in some way. Additionally, consider how each research topic aligns with your career goals and interests; researching something that you are passionate about can help keep motivation high throughout the process.
How can I assess the feasibility of a research topic?
When evaluating the feasibility and practicality of a research topic, it is important to consider several factors.
First, you should assess whether or not the research topic is within your area of competence. Of course, when you start out, you are not expected to be the world’s leading expert, but do should at least have some foundational knowledge.
Time commitment
When considering a research topic, you should think about how much time will be required for completion. Depending on your field of study, some topics may require more time than others due to their complexity or scope.
Additionally, if you plan on collaborating with other researchers or institutions in order to complete your project, additional considerations must be taken into account such as coordinating schedules and ensuring that all parties involved have adequate resources available.
Resources needed
It’s also critically important to consider what type of resources are necessary in order to conduct the research successfully. This includes physical materials such as lab equipment and chemicals but can also include intangible items like access to certain databases or software programs which may be necessary depending on the nature of your work. Additionally, if there are costs associated with obtaining these materials then this must also be factored into your evaluation process.
Potential risks
It’s important to consider the inherent potential risks for each potential research topic. These can include ethical risks (challenges getting ethical approval), data risks (not being able to access the data you’ll need), technical risks relating to the equipment you’ll use and funding risks (not securing the necessary financial back to undertake the research).
If you’re looking for more information about how to find, evaluate and select research topics for your dissertation or thesis, check out our free webinar here . Alternatively, if you’d like 1:1 help with the topic ideation process, consider our private coaching services .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Choosing a Research Topic
Search Grad Grow
This article from the Chronicle of Higher Education discusses and offers advice on how to choose a dissertation topic that is compelling, manageable, and worthwhile. Although it is written for scientists, this article provides valuable insights that are applicable to other fields. Also available via the Tomorrow's Professor Archive.
View Website
Grad Grow Competencies


Choose a Great Thesis Topic in 4 Easy Steps!

No matter how much you enjoy the research process, choosing a great thesis topic is always a challenge.
What is a thesis topic anyway?
A thesis topic is just what it sounds like—it is the subject you aim to write your thesis about.
A thesis is a long, in-depth research paper that focuses on one specific subject. A thesis topic is just what it sounds like—it is the subject you aim to write your thesis about.
Theses are usually shorter for undergraduate students and book-length for Ph.D. students. However, one thing is always true. Regardless of whether you are an undergraduate or a graduate student, finding the right thesis topic isn’t easy!
Since you are reading this article, you are clearly wondering how you can choose a great thesis topic. We’ll walk you through some simple steps, give you insider tips to find the right thesis topic, and help you begin your research journey with confidence.
What makes a thesis topic great?
Your thesis topic will need to be clear and address a clearly defined research question. At the same time, the answer should contribute to a broader understanding of the research field.
The search for a good thesis statement begins with a good research question. Your thesis is the answer to that question. As the thesis is a relatively long research paper, a good research question should be sufficiently broad. In general, this will mean avoiding “yes/no” questions or reframing such questions.
For instance, instead of asking
“Does race influence standardized testing in high schools in the UK?”
Reframe your question as
“How does race influence standardized testing in high schools in the UK?”
This will allow you to explore different aspects, analyze interactions among variables, and write a longer, more substantive paper.
While your thesis topic should be broad enough, it should never be vague. Your thesis topic will need to be clear and address a clearly defined research question. At the same time, the answer should contribute to a broader understanding of the research field.
If you create a thesis based on research questions like “ How many kinds of fungi are there in the world? ” or “ What is love? ,” you are going to end up writing a long, frustrating paper. A good thesis topic will answer a much more specific question, like:
“ What kinds of fungi grow in the vicinity of drainage pipes? ” or
“ How do people in Myanmar express love during courtship rituals? ”
In other words, a great thesis topic is your answer to a:
- Somewhat broad
- Very precise and
- Somewhat open-ended question.
While yes/no questions can be acceptable on rare occasions, you should avoid them or rephrase them, especially in science fields.
Finally, a great thesis topic fills a niche in a research field where research on the topic already exists, but there is still more to be discovered or new aspects to be explored. Alternatively, thesis topics could offer a fresh take on an old topic or rebuttals to a well-known theory. You don’t need to necessarily perform groundbreaking research; however, a great thesis topic will always offer a unique element that could make your thesis stand out.
Step 1: Choosing a thesis topic - Getting started
Although thesis topics should ideally be chosen based on the relevance of the topic and its academic merit, requirements related to your assignment/program should also be taken into consideration before finalizing the topic. While this seems quite basic, it is in fact key to choosing your thesis topic. The requirements of your program or class will determine the scope of what you can research.
Every program differs in its requirements, which is why it is so important to check these details beforehand. Some programs might have a specific list of acceptable topics and a narrow range of allowable methodologies. Other programs might just have a minimum word count and a final deadline. This is why knowing the requirements is so important before you move on to the next step of brainstorming.
Step 2: Brainstorming thesis topic ideas
One of the first places to look for a thesis topic is your own past work, such as papers you have written or assignments you have completed.
Once you know the limitations and requirements for your thesis, it is time to begin brainstorming specific ideas. This is often the hardest part of choosing a thesis topic! Especially if your program or school doesn’t narrow down your topic choices, you may find yourself gazing out the window with a hazy mind. So where should you begin brainstorming?
One of the first places to look for a thesis topic is your own past work, such as papers you have written or assignments you have completed. What courses have you particularly enjoyed that are related to your major field of study? What topics have you written about already?
You must make a list of papers you have written as part of your program and rank them on a scale of most to least interesting. You can do this even if you are in a program that is not very writing intensive. Cross the boring half off your list and focus on the more interesting topics. Do any topics catch your eye? If you aren’t feeling excited about anything you’ve already researched, talk to your classmates or colleagues . What areas in your field are you interested in or passionate about? Do your friends, classmates, or peers have any ideas? You can also skim some articles from popular journals in your field to see the current trending research topics. The more you read, the better the chances of you stumbling on an interesting thesis topic.
Once you have come up with some potential thesis topics, it’s a good idea to rank them in order, so you at least have a list of your top three topics. You then need to do some preliminary research and consultations before you finally settle on one topic, and it’s always important to have backups in case your favorite choice isn’t viable.
Step 3: Preliminary research - Reviewing the literature
Any thesis based on a shorter paper will be longer and more involved than the original version.
Now that you have shortlisted your potential thesis topics, it is time to conduct some preliminary research on each topic by finding out what other research studies have been conducted so far. If you had chosen your potential thesis topics from papers you previously wrote, you might be familiar with the literature already. However, that doesn’t mean you can skip the literature review. Any thesis based on a shorter paper will be longer and more involved than the original version. The thesis is expected to cover new angles, which means you need to do some preliminary research .
Where can you find articles for your preliminary research?
Google Scholar is a great resource, and so is the academic library available at your institution. If you are a student, you may have access to a journal database like JSTOR through your university. Even if you don’t, more and more articles are freely available via open-access journals these days, so a quick Google Scholar search will help you find relevant information. If you find a particularly good article, check out the sources the author(s) have referenced for relevant articles to read.
It’s very possible that you will find yourself completely wanting to change your thesis topic once you start the literature review. That’s ok! If you come across something interesting or inspiring, you should read more about it to see if it would be a good thesis topic. However, you should set yourself some limits. If you take the freedom to simply read what interests you, it is possible you will never be able to decide on a thesis topic. Always remember to limit the time allowed to read about a potential new research interest.
Step 4: Finalizing your choice
Even the most interesting topics can become tortuous after spending enough time reading and writing about them.
Once you feel confident that you have narrowed down your potential thesis topics to a handful of options, it’s time to decide. This choice should not be made lightly—your thesis can take over your life . Even the most interesting topics can become tortuous after spending enough time reading and writing about them. With that in mind, you need to make sure your topic meets the following requirements:
- Is your proposed research feasible?
- Can you access all of the necessary research materials? Will you be able to obtain all of the necessary resources for conducting a research study? Will you be able to travel if it was required?
- Do you find the thesis topic interesting? Do you expect the interest to be sustained over the duration of the study?
- Is your topic meaningful and relevant in your field?
- Has anyone already published a paper on your thesis topic from the perspective research question?
- Do you have a suitable advisor willing to oversee the project?
You will need to extensively consult with your advisor, who will hopefully be able to give you the extra bit of guidance necessary to finalize your choice. If your advisor will be chosen depending on your thesis topic, see if you can consult with your potential advisors. Otherwise, talk to a trusted faculty member or mentor to get feedback on your proposed thesis topic. Your thesis topic will need to be approved by your advisor before it is finalized.
Selecting a thesis topic can be daunting, but once you have made your decision, you are ready for the real work to begin. No matter what topic you choose, you are about to embark on a great endeavor. Check out our site for more tips on how to write a good thesis, where to find the best thesis editing services, and more about thesis editing and proofreading services.
Editor’s pick
Get free updates.
Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights from the research and publishing industry!
Review Checklist
Below is a checklist for you to follow as you go through the process of choosing a thesis topic.
Check the requirements for selecting a thesis topic:
Make a note of the word count requirements and the final deadline before you begin
Check for any preliminary deadlines before the final deadline. For example, if there is a proposal deadline, or individual chapter deadlines.
Discuss with your professor to see if they have any specific requirements or limitations for your research.
Inquire about any requirements for your methodology; if a literature review is acceptable; or if you are required to do fieldwork.
Check to see if there is a minimum acceptable study size in case you are expected to do your own fieldwork.
Look out for any other requirements related to your fieldwork like specific required sources or any possible restrictions.
Review your past work and current trending research for potential topics
Talk to friends and professors about interests
Review relevant journals and publications for inspiration
Rank potential topics in the order of how interesting you find them
Review the literature on potential topics
Discuss the feasibility of your proposed topic with your advisor
Select your thesis topic
How do I begin my search for thesis topic ideas? +
- Start with your previous writing work.
- Shortlist topics you have an interest in or are passionate about
- Talk to your supervisors, peers and colleagues for suggestions
- Read popular journals for hot research topics
- Rank your top three thesis topic ideas in order of preference
- Finally, consult your advisor before seeking approval
How do I know if my thesis topic is promising and unique? +
- Begin with identifying a strong research question
- Always avoid yes/no type questions when finalizing a research question
- Make sure your thesis topic addresses all aspects of your clearly defined research question
- The topic should be broad never vague and precise
- It should contribute to a better understanding of the research field

- Thesis SupportAll
- Academic writing
- Getting started tips
How to choose a thesis topic
- Fear of failure
- Perfectionism
- Procrastination
- Relationship with your supervisor
- Stress Management
- Time Management
- Writer’s block
- Thesis bookshelf
Criteria to help you decide
Choose a topic you like.
This may be the most important criteria. It is often not an easy decision and requires time you have to invest in order to decide on your topic. Your (quality of) life will be much better if the hours spend on your project are spent enjoyably. What’s more, the quality of your research, writing, and arguments will be much better if you feel a genuine passion for your work. Choose a topic you find both fascinating and significant.
Seek feedback
Discuss your ideas with peers and others, make your ideas explicit and seek feedback. Know that the thesis is a major project, but it isn’t your life’s research. Adequate feedback should help you narrow down your topic to realistic proportions.
Consider your future career
Select a topic that will be helpful in your career path. If your goal is an academic career, pick a topic that you can easily modify into journal articles and maybe lends itself well to future research. If you are going into industry, choose a topic that will make you more marketable.
Select a manageable topic
Use the expertise you have gained in you study and avoid exploring a completely new idea. Do your research and find a topic that fits into existing bodies of literature, but that builds upon theory and expands it. In doing so make sure this topic has not been done before. Finally; think carefully before you choose a controversial topic, think carefully about whether it might restrict your employment, tenure, or publishing opportunities.
Theoretical background
A simplified but very usable technique based on this theory consists of listing the advantages and disadvantages of each option. The list will result in a T-model in which you indicate all the positive points of an alternative on the left side and all the negative points on the right side. Subsequently, you value each aspect by grading it with a number. Eventually, you count the numbers together for the two lists and you will see directly whether the advantages outweigh the disadvantages.
Questions to ask yourself
- What are my major interests?
- What major personal experience relative to my discipline do I have?
- What courses were most exciting?
- What theories and concepts are interesting?
- What do I want to avoid?
- What data do I need?
- What research methods do I like?
- What are my career goals? (Articulate and answer your individual questions too.)
Otto Taborsky model
The following model by Otto Taborsky displays stages you should go through while choosing your thesis topic.
- Realise you have to choose
- Accept the uncertainty of the decision you will have to make
- Freely explore
- Make a decision
- Execution of your decision
Contact & Support
Ask your librarian - contact a library specialist.
- CEU PU - Deutsch
- Közép-európai Egyetem
How to Choose Your Thesis Topic

Finding your thesis topic is not an easy task. We are supposed to find something interesting, innovative and relevant within our disciplinary fields. The anxiety increases every day as the deadline for submitting our thesis topic and possible supervisor is closer. This is perhaps harder than writing the thesis itself. Here are a few tips that can help you find something that is interesting, feasible and perhaps original.
1. Identify something you are interested in or passionate about
You decided to study in this program for a reason, so remind yourself constantly what topics you find appealing inside this field. From the beginning, keep track of those discussions or issues that ring a bell for you. While reading or during the lessons, try to identify those moments in which you are puzzled or interested. Write them down in a notebook, or in your cellphone. Try to articulate your thoughts on the subject, writing them or recording your voice. If you find that there is a topic that you keep referring to, you might have found something already. This is a huge step, perhaps the main one.
2. Discuss your interests with people
The greatest ideas are not inventions of geniuses that work in isolation. Knowledge depends greatly on collaboration and dialogue. So, don't feel bad if you cannot come up with something on your own―no one does. Instead, try to discuss your interests with people, even if there are still very general ones. Talk to your classmates and your teachers. Try to ask people if they know something about this subject and if they can give you references. This will help you narrow down your interest and identify possible questions or gaps.
3. Talk to the faculty
While talking to your classmates is very important, I strongly advise you to talk to a few of your teachers very early, even if you don't have anything in mind yet. They can give you great guidance and help you identify who to work with, what to read, and what the interesting gaps in the field are. If you don't know which professors you can approach, you can check their research fields on the department's website and find who works with topics related to your general interests. You can also ask second-year students if they know which professors might be able to help you. Contact them by email, explaining generally what you are curious about and asking for an appointment during their office hours. Discuss your broad interests with them. You can start the discussion by asking for bibliographic references, a particular question, or about their knowledge on this particular topic. Tell them that you are trying to narrow down your thesis topic, they probably will give you suggestions and ideas. Even if the teacher is not the right fit for your subject, she or he can tell you who in the department might be. Usually, professors are really willing to help, so don't be afraid to talk to them.
3. Use your class assignments to develop your interests
Try to use the class assignments as much as possible to develop aspects of those topics that ring a bell for you. This will help you to explore and to start narrowing down what exactly you are really interested in. It will give you the chance to examine the bibliography related to the subject and to articulate some thoughts about it. In my case, one small assignment during my first semester ended up being my MA thesis and the topic of my research project for my PhD application. So, don't underestimate the small assignments! A small fascination can develop into a great passion.

Top Stories


5 Tips for Choosing Your EdD Dissertation Topic
Faculty Insights Industry Advice Education
Associate teaching professor Corliss Thompson shares her top tips for choosing your EdD dissertation topic.
You’ve learned more about why you should earn your Doctor of Education (EdD), and now you’re ready to apply. As part of the Northeastern application process, however, you’re required to submit a problem of practice that you want to pursue throughout the course of your doctoral program.
But how do you arrive at that problem of practice and narrow your area of interest down into a specific dissertation topic? Here are some tips to keep in mind.
Download Our Free Guide to Earning Your EdD
Learn how an EdD can give you the skills to enact organizational change in any industry.
DOWNLOAD NOW
Tips for Choosing a Dissertation Topic
1. pick a topic you’re passionate about..
A lot of work goes into your dissertation—from the literature review, where you’re conducting a critical analysis of what’s been published on your topic, to interviewing stakeholders and actually writing the dissertation itself. Each of those steps take time, so you want to choose a topic that will keep you engaged and hold your interest.
When trying to decide your area of focus, consider the challenges you’re motivated to address and the difference you want to make both during and at the end of your EdD program. The goal is that you will continuously build off your dissertation research and leverage the work in a way that positively impacts your organization and/or community.
2. Ensure your topic is manageable.
You want to select a topic you can complete during the duration of your EdD program that is also aligned with your budget. If you need to travel or perform longitudinal research, your idea might not be achievable. Find what available, attainable data you can, and use that to narrow down your research into a dissertation that’s more manageable.
3. Embrace the unknown.
Although you’re passionate about your topic and it’s manageable, there will still be lingering questions about your subject. Be prepared to explore what you don’t know and deepen what you already do know. Strong research typically results in more questions.
Be ready to ask questions of yourself, others, and the literature, and get comfortable with not knowing the answer. As you’re thinking about your dissertation, keep track of inquiries that emerge around different ideas. Those may help you hone in on a topic.
4. Leverage your peers.
One benefit of enrolling in an EdD program is the diversity of backgrounds and opinions you’ll find within your cohort. At Northeastern, EdD instruction is primarily online, which enables students to connect and collaborate with professionals from around the world.
Vasiliki Goudanas Mavroudhis, a recent graduate of Northeastern’s EdD program, emphasized this benefit in her piece on what it’s like to be in an online doctoral program , saying:
The ability to not only have a cohort-based network, but one that crossed cohorts and continents, allowed me to have a far richer and deeper experience. I learned from students with different perspectives who came from different industries across a number of countries.
When fleshing out your dissertation, use that global network to your advantage. Ask your peers for constructive feedback. It’s likely they’ll have suggestions on how you can approach your topic from different cultural perspectives.
5. Know it’s OK to change your topic.
It’s natural for your dissertation topic to evolve the more research you complete and experts you interview. Actually, it’s expected.
Switching topics halfway through the program might seem like more work, but you will have already gone through the research process once and laid the foundation for your dissertation. As you approach your topic from different perspectives, it’s understandable if your own viewpoint changes a bit.
If you’re in need of inspiration, here are some examples of doctoral research Northeastern students have recently conducted:
- “The Drop Out Decisions of Latino College Students”
- “Changing the Experiences of African Refugee Youth”
- “Supporting Students Through Mindful Mentoring”
- “The Transitioning Student Veteran: Finding Your Civilian Career Through Academic Success”
- “Bridging the Gap Between Training and Educating in Adult Learning”
- “Watch out for Shards from the Glass Ceiling: A Study of Women Higher Educational Administrators’ Leadership Development Experiences”

Subscribe below to receive future content from the Graduate Programs Blog.
About corliss thompson, phd, related articles.

What is Learning Analytics & How Can it Be Used?

Reasons To Enroll in a Doctor of Education Program

Why I Chose to Pursue Learning Analytics
Did you know.
The median annual salary for professional degree holders is $97,000. (BLS, 2020)
Doctor of Education
The degree that connects advanced research to real-world problem solving.
Most Popular:
Tips for taking online classes: 8 strategies for success, public health careers: what can you do with an mph, 7 international business careers that are in high demand, edd vs. phd in education: what’s the difference, 7 must-have skills for data analysts, in-demand biotechnology careers shaping our future, the benefits of online learning: 8 advantages of online degrees, how to write a statement of purpose for graduate school, the best of our graduate blog—right to your inbox.
Stay up to date on our latest posts and university events. Plus receive relevant career tips and grad school advice.
By providing us with your email, you agree to the terms of our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
Keep Reading:

5 Homeland Security Careers for the Future

The Top 3 Job Requirements For a Homeland Security Career

What Are Security Studies?

Should I Go To Grad School: 4 Questions to Consider

- How to Choose a PhD Research Topic
- Finding a PhD
Introduction
Whilst there are plenty of resources available to help prospective PhD students find doctoral programmes, deciding on a research topic is a process students often find more difficult.
Some advertised PhD programmes have predefined titles, so the exact topic is decided already. Generally, these programmes exist mainly in STEM, though other fields also have them. Funded projects are more likely to have defined titles, and structured aims and objectives.
Self funded projects, and those in fields such as arts and humanities, are less likely to have defined titles. The flexibility of topic selection means more scope exists for applicants to propose research ideas and suit the topic of research to their interests.
A middle ground also exists where Universities advertise funded PhD programmes in subjects without a defined scope, for example: “PhD Studentship in Biomechanics”. The applicant can then liaise with the project supervisor to choose a particular title such as “A study of fatigue and impact resistance of biodegradable knee implants”.
If a predefined programme is not right for you, then you need to propose your own research topic. There are several factors to consider when choosing a good research topic, which will be outlined in this article.
How to Choose a Research Topic
Our first piece of advice is to PhD candidates is to stop thinking about ‘finding’ a research topic, as it is unlikely that you will. Instead, think about developing a research topic (from research and conversations with advisors).
Consider several ideas and critically appraise them:
- You must be able to explain to others why your chosen topic is worth studying.
- You must be genuinely interested in the subject area.
- You must be competent and equipped to answer the research question.
- You must set achievable and measurable aims and objectives.
- You need to be able to achieve your objectives within a given timeframe.
- Your research question must be original and contribute to the field of study.
We have outlined the key considerations you should use when developing possible topics. We explore these below:
Focus on your interests and career aspirations
It is important to choose a topic of research that you are genuinely interested in. The decision you make will shape the rest of your career. Remember, a full-time programme lasts 3-4 years, and there will be unforeseen challenges during this time. If you are not passionate about the study, you will struggle to find motivation during these difficult periods.
You should also look to your academic and professional background. If there are any modules you undertook as part of your Undergraduate/Master degree that you particularly enjoyed or excelled in? These could form part of your PhD research topic. Similarly, if you have professional work experience, this could lead to you asking questions which can only be answered through research.
When deciding on a PhD research topic you should always consider your long-term career aspirations. For example, as a physicist, if you wish to become an astrophysicist, a research project studying black holes would be more relevant to you than a research project studying nuclear fission.
Read dissertations and published journals
Reading dissertations and published journals is a great way to identify potential PhD topics. When reviewing existing research ask yourself:
- What has been done and what do existing results show?
- What did previous projects involve (e.g. lab-work or fieldwork)?
- How often are papers published in the field?
- Are your research ideas original?
- Is there value in your research question?
- Could I expand on or put my own spin on this research?
Reading dissertations will also give you an insight into the practical aspects of doctoral study, such as what methodology the author used, how much data analysis was required and how was information presented.
You can also think of this process as a miniature literature review . You are searching for gaps in knowledge and developing a PhD project to address them. Focus on recent publications (e.g. in the last five years). In particular, the literature review of recent publications will give an excellent summary of the state of existing knowledge, and what research questions remain unanswered.
If you have the opportunity to attend an academic conference, go for it! This is often an excellent way to find out current theories in the industry and the research direction. This knowledge could reveal a possible research idea or topic for further study.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Discuss research topic ideas with a PhD supervisor
Discuss your research topic ideas with a supervisor. This could be your current undergraduate/masters supervisor, or potential supervisors of advertised PhD programmes at different institutions. Come to these meetings prepared with initial PhD topic ideas, and your findings from reading published journals. PhD supervisors will be more receptive to your ideas if you can demonstrate you have thought about them and are committed to your research.
You should discuss your research interests, what you have found through reading publications, and what you are proposing to research. Supervisors who have expertise in your chosen field will have insight into the gaps in knowledge that exist, what is being done to address them, and if there is any overlap between your proposed research ideas and ongoing research projects.
Talking to an expert in the field can shape your research topic to something more tangible, which has clear aims and objectives. It can also find potential shortfalls of your PhD ideas.
It is important to remember, however, that although it is good to develop your research topic based on feedback, you should not let the supervisor decide a topic for you. An interesting topic for a supervisor may not be interesting to you, and a supervisor is more likely to advise on a topic title which lends itself to a career in academia.
Another tip is to talk to a PhD student or researcher who is involved in a similar research project. Alternatively, you can usually find a relevant research group within your University to talk to. They can explain in more detail their experiences and suggest what your PhD programme could involve with respect to daily routines and challenges.
Look at advertised PhD Programmes
Use our Search tool , or look on University PhD listing pages to identify advertised PhD programmes for ideas.
- What kind of PhD research topics are available?
- Are these similar to your ideas?
- Are you interested in any of these topics?
- What do these programmes entail?
The popularity of similar PhD programmes to your proposed topic is a good indicator that universities see value in the research area. The final bullet point is perhaps the most valuable takeaway from looking at advertised listings. Review what similar programmes involve, and whether this is something you would like to do. If so, a similar research topic would allow you to do this.
Writing a Research Proposal
As part of the PhD application process , you may be asked to summarise your proposed research topic in a research proposal. This is a document which summarises your intended research and will include the title of your proposed project, an Abstract, Background and Rationale, Research Aims and Objectives, Research Methodology, Timetable, and a Bibliography. If you are required to submit this document then read our guidance on how to write a research proposal for your PhD application.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
Published on 11 November 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George.
Choosing your dissertation topic is the first step in making sure your research goes as smoothly as possible. When choosing a topic, it’s important to consider:
- Your institution and department’s requirements
- Your areas of knowledge and interest
- The scientific, social, or practical relevance
- The availability of data and resources
- The timeframe of your dissertation
You can follow these steps to begin narrowing down your ideas.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Step 1: check the requirements, step 2: choose a broad field of research, step 3: look for books and articles, step 4: find a niche, step 5: consider the type of research, step 6: determine the relevance, step 7: make sure it’s plausible, step 8: get your topic approved, frequently asked questions.
The very first step is to check your program’s requirements. This determines the scope of what it is possible for you to research.
- Is there a minimum and maximum word count?
- When is the deadline?
- Should the research have an academic or a professional orientation?
- Are there any methodological conditions? Do you have to conduct fieldwork, or use specific types of sources?
Some programs have stricter requirements than others. You might be given nothing more than a word count and a deadline, or you might have a restricted list of topics and approaches to choose from. If in doubt about what is expected of you, always ask your supervisor or department coordinator.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Start by thinking about your areas of interest within the subject you’re studying. Examples of broad ideas include:
- Twentieth-century literature
- Economic history
- Health policy
To get a more specific sense of the current state of research on your potential topic, skim through a few recent issues of the top journals in your field. Be sure to check out their most-cited articles in particular. For inspiration, you can also search Google Scholar , subject-specific databases , and your university library’s resources.
As you read, note down any specific ideas that interest you and make a shortlist of possible topics. If you’ve written other papers, such as a 3rd-year paper or a conference paper, consider how those topics can be broadened into a dissertation.
After doing some initial reading, it’s time to start narrowing down options for your potential topic. This can be a gradual process, and should get more and more specific as you go. For example, from the ideas above, you might narrow it down like this:
- Twentieth-century literature Twentieth-century Irish literature Post-war Irish poetry
- Economic history European economic history German labor union history
- Health policy Reproductive health policy Reproductive rights in South America
All of these topics are still broad enough that you’ll find a huge amount of books and articles about them. Try to find a specific niche where you can make your mark, such as: something not many people have researched yet, a question that’s still being debated, or a very current practical issue.
At this stage, make sure you have a few backup ideas – there’s still time to change your focus. If your topic doesn’t make it through the next few steps, you can try a different one. Later, you will narrow your focus down even more in your problem statement and research questions .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
There are many different types of research , so at this stage, it’s a good idea to start thinking about what kind of approach you’ll take to your topic. Will you mainly focus on:
- Collecting original data (e.g., experimental or field research)?
- Analysing existing data (e.g., national statistics, public records, or archives)?
- Interpreting cultural objects (e.g., novels, films, or paintings)?
- Comparing scholarly approaches (e.g., theories, methods, or interpretations)?
Many dissertations will combine more than one of these. Sometimes the type of research is obvious: if your topic is post-war Irish poetry, you will probably mainly be interpreting poems. But in other cases, there are several possible approaches. If your topic is reproductive rights in South America, you could analyse public policy documents and media coverage, or you could gather original data through interviews and surveys .
You don’t have to finalise your research design and methods yet, but the type of research will influence which aspects of the topic it’s possible to address, so it’s wise to consider this as you narrow down your ideas.
It’s important that your topic is interesting to you, but you’ll also have to make sure it’s academically, sociallym or practically relevant to your field.
- Academic relevance means that the research can fill a gap in knowledge or contribute to a scholarly debate in your field.
- Social relevance means that the research can advance our understanding of society and inform social change.
- Practical relevance means that the research can be applied to solve concrete problems or improve real-life processes.
The easiest way to make sure your research is relevant is to choose a topic that is clearly connected to current issues or debates, either in society at large or in your academic discipline. The relevance must be clearly stated when you define your research problem .
Before you make a final decision on your topic, consider again the length of your dissertation, the timeframe in which you have to complete it, and the practicalities of conducting the research.
Will you have enough time to read all the most important academic literature on this topic? If there’s too much information to tackle, consider narrowing your focus even more.
Will you be able to find enough sources or gather enough data to fulfil the requirements of the dissertation? If you think you might struggle to find information, consider broadening or shifting your focus.
Do you have to go to a specific location to gather data on the topic? Make sure that you have enough funding and practical access.
Last but not least, will the topic hold your interest for the length of the research process? To stay motivated, it’s important to choose something you’re enthusiastic about!
Most programmes will require you to submit a brief description of your topic, called a research prospectus or proposal .
Remember, if you discover that your topic is not as strong as you thought it was, it’s usually acceptable to change your mind and switch focus early in the dissertation process. Just make sure you have enough time to start on a new topic, and always check with your supervisor or department.
Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
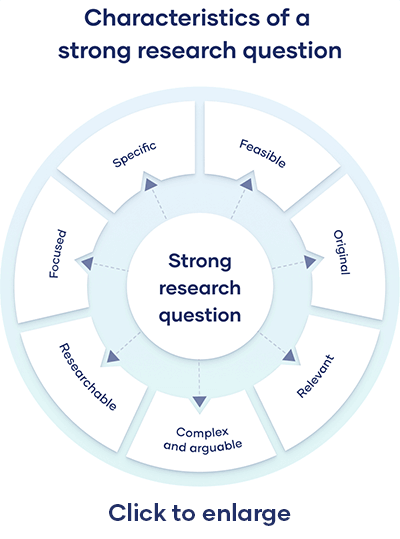
You can assess information and arguments critically by asking certain questions about the source. You can use the CRAAP test , focusing on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
Ask questions such as:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert?
- Why did the author publish it? What is their motivation?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence?
A dissertation prospectus or proposal describes what or who you plan to research for your dissertation. It delves into why, when, where, and how you will do your research, as well as helps you choose a type of research to pursue. You should also determine whether you plan to pursue qualitative or quantitative methods and what your research design will look like.
It should outline all of the decisions you have taken about your project, from your dissertation topic to your hypotheses and research objectives , ready to be approved by your supervisor or committee.
Note that some departments require a defense component, where you present your prospectus to your committee orally.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2022, November 11). How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/choosing-a-topic/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a dissertation | 5 essential questions to get started, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples.

How To Write A Research Paper With AI
To write a research paper, ensure you understand the assignment, choose an engaging topic, conduct thorough research, develop a clear thesis statement, and create a structured outline. Write while integrating research findings, then revise for clarity and coherence. Finally, edit for accuracy and adhere to formatting guidelines to present a polished and professional paper. You can use an A.I. writing assistant to optimize and streamline entire writing.

Fredrick Eghosa
May 21, 2024

Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
How to write a research paper using ai, start by brainstorming ideas., narrow down your focus., consider the relevance of these ideas to your field:, review existing literature for inspiration., record key details you discover, organize these facts by themes or categories:, finalize your research paper.

- A research paper is a detailed and organized document presenting a study's findings or investigation on a particular topic.
- To write a research paper effectively, begin by understanding the assignment requirements. Choose a suitable topic, conduct thorough research, and formulate a clear thesis statement. Develop an organized outline to structure your writing process and draft your research paper accordingly.
- You can use CoWriter as your A.I. writing assistant to enhance your research paper. It can assist in improving clarity, coherence, and overall quality. Our A.I. tool is beneficial for editing and refining your writing to ensure a polished and effective research paper.
- Understanding the Assignment
- The expected length of the paper
- Word count or page limit
- formatting guidelines (such as font size, margins, and citation style)
- Choosing a Topic
- Begin by brainstorming potential topics that interest you or relate to the assignment's subject area and your field of study.
- Consider recent developments, controversies, or unanswered questions within the field that intrigue you.
- Review your list of ideas and narrow it down to a specific research question or thesis statement.
- Avoid overly broad topics; aim for a focused and manageable research scope.
- Evaluate the relevance of each potential topic to the course or subject area.
- Choose a significant topic within the academic community or real-world context.
- Conduct preliminary research to identify existing literature on your potential topics.
- Determine if enough scholarly materials are available to support your research and provide context for your study. By doing so, you can avoid starting to write and then realizing that more evidence or facts are needed to support your research.

- Conducting Research
- Take Note of Interesting Facts
- Write down the most relevant details of each exciting fact, including the source (author, publication, website), date, and context.
- Organize your notes by topic, source, or relevance to easily retrieve interesting facts later.
- Note the significance of the fact and why it stood out to you concerning your research topic. Don't just put it down vaguely. Include brief comments or thoughts alongside the highlighted information to provide context or explain its relevance.
- Categorize exciting facts based on common themes, topics, or research questions.
- Create separate sections or folders within your note-taking system to facilitate easy retrieval and organization.
- Developing a Thesis Statement

- Creating an Outline
- Familiarize yourself with the standard components of a research paper outline, which typically include:
- Introduction
- Body paragraphs (with subtopics or main points)
- Select a suitable outline format based on your preference or your assignment's requirements.
- Determine the main sections of your research paper that will form the basis of your outline. Each section should correspond to a significant aspect of your paper, such as:
- Literature review
- Methodology
- Arrange the main points logically, ensuring a coherent progression of ideas and precise transitions between sections.
- Incorporate subheadings and subtopics. Organize subtopics hierarchically to reflect the relationship between different ideas and concepts.
- Outline the supporting evidence, examples, or data that someone will use to substantiate each main point or argument. Ensure that each piece of evidence directly supports the corresponding argument and contributes to the overall coherence of the paper.

- Get to Writing
- Ensure that your research documents, notes, and sources are readily accessible while you write. Keep them open or easily accessible on your computer or workspace.
- Use your outline to structure your writing and organize critical points and sections. Continuously refer to your outline to ensure it focuses on your research paper's main objectives and flow.
- Incorporate relevant research findings, evidence, quotes, and data into your writing to support your arguments and assertions. Always cite your sources accurately using the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago) as you integrate information from your research.
- Compare different perspectives and interpretations in your research as you write to provide a comprehensive analysis and discussion of the topic.

- Revise and Edit Your Research Paper Using AI
- To identify and correct grammatical errors, punctuation issues, and spelling mistakes. CoWriter provides real-time feedback and suggestions to enhance the readability and professionalism of your writing.
- Identify verbose or unclear sentences to improve clarity and conciseness in your writing. Our A.I. tool suggests revisions to simplify complex language and enhance overall comprehension.
- Ensure consistency in terminology, formatting, and style throughout your research paper. CoWriter can detect inconsistencies in language usage and offer suggestions for maintaining uniformity.
- To enhance the structure and coherence of your sentences, CoWriter can act as your writing assistant, analyzing sentence patterns and suggesting restructuring or combining sentences to improve flow and readability.
Join other 3200+ writers now!
Ready to take the next big step for your writing?
Lead engineering teams at Figma, Pitch, and Protocol Labs.
Related posts

May 20, 2024
10 Literary Analysis Essay Examples
To write a literary analysis essay always understand the assignment thoroughly and identify the key elements e.g. plot, characters, and themes. Select a central theme to focus on and put together evidence to support your analysis.

Mar 18, 2024
How to Edit an Essay Written by AI to Perfection
To edit an AI-written essay perfectly, carefully read the text to ensure it makes sense and conveys your ideas. Please review the entire piece to grasp its tone, purpose, and quality, as AI-generated content often lacks logical progression and may have gaps, awkward transitions, or readability issues.

Mar 11, 2024
5 Best AI Writer for Research Papers
The best AI writers for research papers are CoWriter, SciSpace Literature Review, Wordtune, Trinka, and Paperpal. These AI writers offer different functionalities, from grammar and citation checking to plagiarism detection and content generation.

Mar 16, 2024
10 Best AI Co-Writers
The best AI co-writers are CoWriter, HIX.AI, Copy.ai, Wordtune, Scalenut, Rytr, HyperWrite, Texta, TextCortex, and Writesonic. They can help generate ideas, overcome writer's block, and improve the flow of your writing.

The 5 Best AI Writer for Students
The best AI writers for students are CoWriter, Jasper, AI-Writer, Rytr, and Article Forge. Choosing the best AI writer for students depends on their needs. Some prioritize grammar and clarity assistance, while others focus on paraphrasing and summarizing.

Best Free AI Paper Writer
The best free AI paper writers are CoWriter, Rytr, Simplified, CopyAI, Writesonic, Grammarly, and Paperpal. These tools can help you brainstorm or start and polish your paper.

Mar 24, 2024
10 Steps to Writing an Informative Essay with an Outline
To write an informative essay with an outline, pick a topic, research it, and create an outline. Write an introduction with a hook and thesis, followed by body paragraphs with evidence. Conclude by summarizing the main points and restating the thesis. Finally, edit, cite sources, and submit.

Mar 25, 2024
Jenni AI Review and Best Alternatives
Jenni.AI is an AI writer designed to assist with academic research and writing. It offers a great selection of features for academic purposes, including a built-in research engine. The best alternatives for Jenni AI you can try are CoWriter, Jasper AI, Copy AI, Frase.io, and Writesonic.

The Good AI Review and Best Alternatives
Good AI is a handy platform that uses smart technology to assist with writing tasks. Its AI essay writer lets users quickly create 1,500-word, well-structured, and informative essays.

Mar 27, 2024
How to Write a Biography Essay and Biography Essay Examples
To write a biography essay, choose an exciting subject, research extensively, and develop a thesis statement. Then, structure your essay chronologically or thematically, starting with a captivating introduction, exploring the subject's life in the body paragraphs, and concluding with its contemporary significance.

Apr 12, 2024
How is a narrative essay organized?
A narrative essay tells a story chronologically, beginning with an introduction, moving into a body where events build to a climax, and finishing with a resolution or final reflection.

How to Write a Biography Essay With Examples

The Best Free AI APA Citation Generator
The best free AI APA citation generators are CoWriter, Grammarly, SciSpace APA Citation Generator, Scribbr AI Citation Generators, Quillbot AI Citation Generators, Junia.ai, and Simplified. These generators use intelligent algorithms to automatically create citations for different sources, saving time and ensuring formatting and APA citation style accuracy.

30 AI Prompts to Humanize Your Essay
AI prompts to humanize your essay are invaluable tools for students who want to humanize their AI-generated essays. With prompts for different writing styles and objectives, you can add personality, storytelling, humor, and clarity to their content.

The 7 Best AI Bibliography Generator
The best AI bibliography generators are CoWriter, Zotero, EndNote, Cite This For Me, Citation Machine, CiteMaker, and KnightCite. These tools streamline the citation process by supporting various citation styles, source types, and formatting options, ensuring accuracy and adherence to academic standards.

Apr 16, 2024
The Best Free Outline Generator for Essays
The best free outline generators for essay writing are CoWriter, Ahrefs Free AI Outline Generator, ClickUp, Jenni AI Essay Outline Generator, GitMind, Rytr, and Simplified. They streamline the process by generating structured outlines based on prompts and parameters.

The Best Free AI MLA Citation Generator
The best free AI MLA citation generators are CoWriter, Opendemia, Scribbr MLA Citation Generator, MyBib, Citefast, Cite This For Me's MLA Citation Generator, and QuillBot M.L.A. Citation Generator. They stay updated on the latest MLA guidelines and can handle various source types like books, articles, and websites.

Apr 21, 2024
How To Write A Research Proposal With AI
To write a research paper using A.I., define your research topic and formulate straightforward, specific research questions, use A.I. to streamline the literature reviews, refine methodologies, and create a structured proposal outline, draft your proposal using the outline you created.

Can AI Write An Annotated Bibliography
A.I. can write an annotated bibliography by curating and organizing relevant sources. It can generate concise summaries that outline each source's content, relevance, and significance to your research. A.I. writing assistant streamlines the process of compiling an annotated bibliography, saving time and effort while ensuring the inclusion of informative annotations for each source.

How To Write A Historical Essay Introduction
To write a historical essay introduction, begin with an engaging hook, like a thought-provoking quote or a question. Follow this with background details about your topic and conclude with a clear thesis statement. Utilize CoWriter to assist in composing your introduction.
.jpg%3Ftable%3Dblock%26id%3D011c22f2-6b48-44a5-a3ab-00a65e117aee%26cache%3Dv2&optimizer=image&quality=80&width=280)
How To Write a 4-Paragraph Essay
To write a 4-paragraph essay effectively, start by thoroughly researching your topic. This step is crucial for gathering supporting information. Next, create a structured outline that divides your essay into four clear paragraphs. Draft your thesis statement to convey the topic of your essay. With the outline in place, draft your essay following the outlined structure. Finally, take time to edit and proofread your essay.

How To Write A Curatorial Statement With AI
To write a curatorial statement with AI, begin by conducting thorough research into the historical context of your exhibition and the backgrounds of the artworks, including their styles and mediums. Develop a clear and concise outline to structure your statement effectively. Write the content of your statement and edit it for clarity and correctness. Use CoWriter to streamline and enhance the entire writing and editing process.

How To Write A Discussion Essay
To write a discussion essay, start with a clear introduction introducing the topic and presenting your main argument. Next, develop the body paragraphs, each addressing a specific aspect or viewpoint related to the topic, supported by evidence and facts. Then address counterarguments to strengthen your argument. Conclude your discussion essay by summarizing key points and restating your main argument, leaving readers with a compelling closing thought.

Difference Between Paraphrasing And Summarizing
Paraphrasing involves restating the content of a passage in your own words, while Summarizing involves concisely stating the main points of a work or passage. Paraphrasing usually Retains more detail from the original text, while summarizing focuses on capturing the main points of the original text. Paraphrasing can be similar to or longer than the original text, while summaries are usually Significantly shorter.

10 Evaluation Essay examples
An evaluation essay can take different styles; there are argumentative evaluation essays, analytical evaluation essays, Descriptive evaluation essays, and comparative evaluation essays. To write an evaluation essay, start by choosing a suitable topic, setting evaluation criteria, gathering evidence to back your evaluation, creating an outline to guide your evaluation essay, writing your evaluation, and editing to ensure the final draft is error-free.

10 Expository Essay Examples
There are different types of expository essays, such as descriptive essays, process essays, comparison and contrast essays, cause-and-effect essays, and problem-and-solution essays. To write an expository essay, you must start by thoroughly understanding the purpose of the essay, conducting research, writing your thesis, creating an outline for your essay, drafting your essay, and editing it.

How To Write Essays With CoWriter
To write an essay using CoWriter, sign up on CoWriter to access its writing tools. Choose a suitable for your essay and conduct research using CoWriter to gather relevant sources. Develop a thesis statement and create an outline using CoWriter. Write the essay with the help of our AI writing assistant and cite relevant sources. Lastly, edit and proofread the final draft.

COMMENTS
To recap, the "Big 5" assessment criteria include: Topic originality and novelty. Value and significance. Access to data and equipment. Time requirements. Ethical compliance. Be sure to grab a copy of our free research topic evaluator sheet here to fast-track your topic selection process.
1. Write down your main interests related to your field of study. Since you'll likely spend 2 years or more working on your thesis, it's best to pick something that interests you. Plus, this topic could shape the path you take in the future by directing where you go for your further studies or what type of job you get.
To choose a thesis research topic, find something you're passionate about, research widely to get the big picture, and then move to a more focused view. Bringing a fresh perspective to a popular theme, finding an underserved audience who could benefit from your research, or answering a controversial question can make your thesis stand out ...
Step 1: Check the requirements. Step 2: Choose a broad field of research. Step 3: Look for books and articles. Step 4: Find a niche. Step 5: Consider the type of research. Step 6: Determine the relevance. Step 7: Make sure it's plausible. Step 8: Get your topic approved. Other interesting articles.
8. Come up with 3-5 Ideas and Bring them to your Supervisor for Feedback. Your initial dissertation topic ideas will probably need a lot of refinement. The person who will help you to refine your topic will be your dissertation supervisor. Their main job, unfortunately, is to curb your enthusiasm.
Step 5: Narrow down, then evaluate. By this stage, you should have a healthy list of research topics. Step away from the ideation and thinking for a few days, clear your mind. The key is to get some distance from your ideas, so that you can sit down with your list and review it with a more objective view.
Thesis topic quick guide. Find a topic by considering specific debates or discussions that interest you. Choose a topic based on phenomenon, point of view, and context. Consider the relevance of your topic in relation to job market realities. Ask your supervisor for help and guidance, as needed.
Step 5. Evaluate the Best Research Approach when Choosing Topic. Select the research method that is most suitable for your dissertation and meets your degree programme. This is an important stage of choosing a dissertation topic, but there is no need to panic.
Instead, try implementing a more systematic approach to selecting your dissertation topic: Get a handle on the basics. Review previous dissertations. Identify your areas of interest. Conduct a literature review. Narrow down your topic options. Submit a proposal and receive approval of your dissertation topic.
Choosing a dissertation topic can be both challenging and rewarding. While there are many factors in the process of your research you cannot change - time, resources, and institutional requirements - you can impact your dissertation topic by taking time to understand how you really want to spend the weeks and months, and possibly years ...
Select a topic. Choosing an interesting research topic is your first challenge. Here are some tips: Choose a topic that you are interested in! The research process is more relevant if you care about your topic. Narrow your topic to something manageable. If your topic is too broad, you will find too much information and not be able to focus.
Having a researchable topic: First of all, consider all the resources at hand - time, money, and sources. Then, you can choose a thesis topic that you can do justice to effortlessly. The topic should interest you first: I find it odd to do something that I don't like. Therefore, your thesis topic should ignite the motivation and enthusiasm ...
1. Take advantage of the resources available. Use the resources offered by your university to help with your decision making. This might include your research center or applicable seminars. 2. Tap into your peers. Meet with each of your cohorts and ask them to weigh in on your topic and plans for research. 3.
Find the perfect research topic for your dissertation or thesis. Get the FREE list of 1000+ research ideas plus our proposal template! About Us; Services. 1-On-1 Coaching. ... There are many steps involved in the process of finding and choosing a high-quality research topic for a dissertation or thesis. We cover these steps in detail in this ...
Choosing a Research Topic. Search Grad Grow. This article from the Chronicle of Higher Education discusses and offers advice on how to choose a dissertation topic that is compelling, manageable, and worthwhile. Although it is written for scientists, this article provides valuable insights that are applicable to other fields.
Step 1: Choosing a thesis topic - Getting started. Although thesis topics should ideally be chosen based on the relevance of the topic and its academic merit, requirements related to your assignment/program should also be taken into consideration before finalizing the topic.
The following model by Otto Taborsky displays stages you should go through while choosing your thesis topic. Realise you have to choose. Accept the uncertainty of the decision you will have to make. Freely explore. Compare. Make a decision. Execution of your decision. Choosing a topic is most likely one of the most important choices you will ...
The anxiety increases every day as the deadline for submitting our thesis topic and possible supervisor is closer. This is perhaps harder than writing the thesis itself. Here are a few tips that can help you find something that is interesting, feasible and perhaps original. 1. Identify something you are interested in or passionate about.
A good thesis topic is a general idea that is in need of development, verification or refutation. Your thesis topic should be of interest to you, your advisor, and the research community. If it is not, it may be difficult to stay motivated or to "sell" the idea. When searching for a topic, remember that your thesis should attempt to solve a ...
Tips for Choosing a Dissertation Topic. 1. Pick a topic you're passionate about. A lot of work goes into your dissertation—from the literature review, where you're conducting a critical analysis of what's been published on your topic, to interviewing stakeholders and actually writing the dissertation itself.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
Consider several ideas and critically appraise them: You must be able to explain to others why your chosen topic is worth studying. You must be genuinely interested in the subject area. You must be competent and equipped to answer the research question. You must set achievable and measurable aims and objectives.
Table of contents. Step 1: Check the requirements. Step 2: Choose a broad field of research. Step 3: Look for books and articles. Step 4: Find a niche. Step 5: Consider the type of research. Step 6: Determine the relevance. Step 7: Make sure it's plausible. Step 8: Get your topic approved.
Choosing a dissertation topic can be as daunting as the research process itself. Your dissertation is a significant piece of work, and the pressure to select the perfect topic can be overwhelming.
In this video, learn how to choose a research topic using AI tools. Choosing a research topic is one of the most challenging things about conducting research...
Choosing a dissertation topic is one of the most challenging yet crucial steps for university students pursuing a degree in law. A well-chosen topic not only reflects a student's interest and passion but also sets the stage for their research journey. If you're struggling to find the right topic, this blog will provide a comprehensive guide ...
To write a research paper, ensure you understand the assignment, choose an engaging topic, conduct thorough research, develop a clear thesis statement, and create a structured outline. Write while integrating research findings, then revise for clarity and coherence. Finally, edit for accuracy and adhere to formatting guidelines to present a polished and professional paper. You can use an A.I ...