

Search the United Nations
- What Is Climate Change
- Myth Busters
- Renewable Energy
- Finance & Justice
- Initiatives
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Paris Agreement
- Climate Ambition Summit 2023
- Climate Conferences
- Press Material
- Communications Tips

Causes and Effects of Climate Change
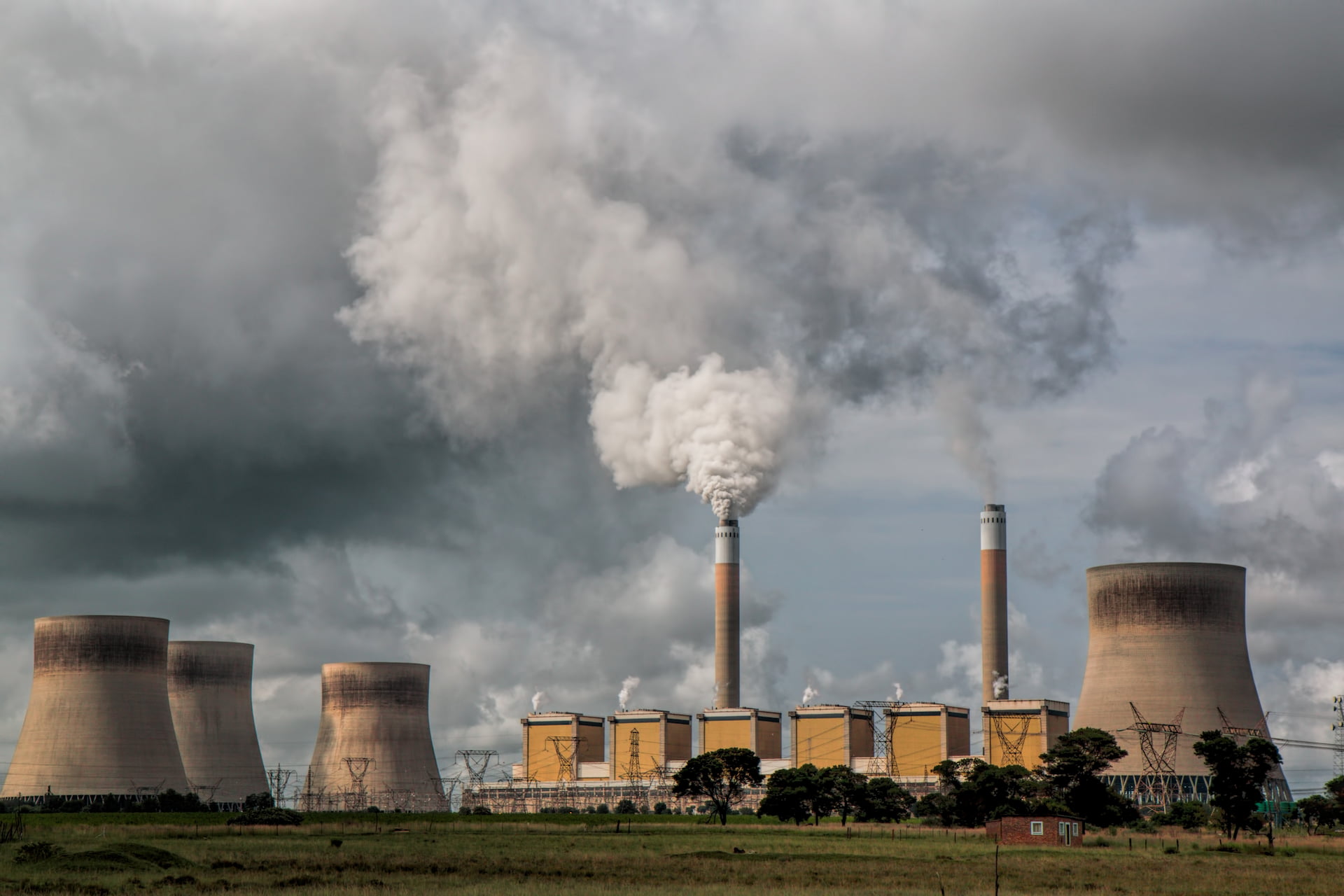
Fossil fuels – coal, oil and gas – are by far the largest contributor to global climate change, accounting for over 75 per cent of global greenhouse gas emissions and nearly 90 per cent of all carbon dioxide emissions. As greenhouse gas emissions blanket the Earth, they trap the sun’s heat. This leads to global warming and climate change. The world is now warming faster than at any point in recorded history. Warmer temperatures over time are changing weather patterns and disrupting the usual balance of nature. This poses many risks to human beings and all other forms of life on Earth.

Sacred plant helps forge a climate-friendly future in Paraguay

El Niño and climate crisis raise drought fears in Madagascar
The El Niño climate pattern, a naturally occurring phenomenon, can significantly disrupt global weather systems, but the human-made climate emergency is exacerbating the destructive effects.
“Verified for Climate” champions: Communicating science and solutions
Gustavo Figueirôa, biologist and communications director at SOS Pantanal, and Habiba Abdulrahman, eco-fashion educator, introduce themselves as champions for “Verified for Climate,” a joint initiative of the United Nations and Purpose to stand up to climate disinformation and put an end to the narratives of denialism, doomism, and delay.
Facts and figures
- What is climate change?
- Causes and effects
- Myth busters
Cutting emissions
- Explaining net zero
- High-level expert group on net zero
- Checklists for credibility of net-zero pledges
- Greenwashing
- What you can do
Clean energy
- Renewable energy – key to a safer future
- What is renewable energy
- Five ways to speed up the energy transition
- Why invest in renewable energy
- Clean energy stories
- A just transition
Adapting to climate change
- Climate adaptation
- Early warnings for all
- Youth voices
Financing climate action
- Finance and justice
- Loss and damage
- $100 billion commitment
- Why finance climate action
- Biodiversity
- Human Security
International cooperation
- What are Nationally Determined Contributions
- Acceleration Agenda
- Climate Ambition Summit
- Climate conferences (COPs)
- Youth Advisory Group
- Action initiatives
- Secretary-General’s speeches
- Press material
- Fact sheets
- Communications tips
Global Warming: Causes and Effects | Essay Example
Struggle with essay about causes and effects of global warming? We’ve got your back covered! In the essay example below, you will learn more about this issue, as well as find out how to write global warming essay introduction and conclusion. Check it now!
Introduction
Global warming causes, effects of global warming, global warming: causes and effects conclusion, works cited.
Global warming is one of the greatest problems facing the world today, because of its frightening effects that are evident in the present world. Global warming is the tremendous increase of the global temperatures, which results due to the trapping of heat in the atmosphere. Signs of global warming are evident all over the world with the increased temperatures, unpredictable climatic conditions, disappearing of some species of birds and animals, and an increase in the sea level.
Although people are not only aware but have also have tasted the impacts of these effects, very few individuals have taken the required action to save the earth from destruction, as most people still embrace practices that are the primary causes of global warming such as the use of fossil fuels, deforestation, and the use of chemical fertilizers.
Therefore, although some natural factors have contribute to global warming, human actions are the primary causes of global warming and unless such practices are controlled, likelihoods of Saving the earth from effects of global warming, for example, drought, flooding, and extinctions of some species of flora and fauna are minimal.
The primary causes of global warming are the most cherished human practices that have existed since time memorial. One of the primary causes of global warming is the increased amount of the carbon dioxide emissions in the environment.
With the ever-increasing use of electricity as one of the primary sources of energy in most sectors of the economy, there has been a continuous release of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Electricity is primarily produced from burning of coal in power plants, and because it is very hard to survive without it, likelihoods of such gases filing the earth are high.
Carbon dioxide is one the gases that trap heat energy in the atmosphere, leading to increased atmospheric temperatures. Another cause of global warming is the ever-increasing emission of greenhouse gases from burning of gasoline. The modern car culture is one of the primary sources of green house gases, as most transportation and manufacturing industry rely on fossil fuels as its primary source of fuels.
Global warming is also a product of some agricultural practices such as planting of rice in paddies. Although agriculture is the backbone of most global economies, some agricultural practices are primary sources of some dangerous greenhouse gases such as methane, as a result of the breaking down of bacteria in areas with limited supply of oxygen (Essick 1).
In addition to increased use of fossil fuels and some agricultural practices that release dangerous gases into the environment, other human practices such as deforestation have also contributed to global warming. Although nowadays most individuals use cooking and other environmentally friendly sources of energy in their homes, the use of forest for fuel is common, because of the numerous trees that are cut daily for charcoal and wood.
Further, the need for land to accommodate the ever-increasing population numbers has forced most societies to encroach into forested or protected land. Deforestation destroys trees that are the primary air purifiers, as they help to remove carbon dioxide from the environment. On the other hand, the use of chemical fertilizers that are rich in nitrogen have also contributed to global warming, as nitrogen compounds have one of the greatest heat-trapping capacity (Markham Para. 1-5).
As a result of the numerous contributions of human actions to global warming, human beings must bear the brunt of their actions, which unless they accept to control, the wellbeing o future generations will be at stake. One evident effects of global warming is the rising level of the sea level, caused by the melting of the ice sheets in Antarctica and Greenland. The effects of such increases are evident, as floods and massive storms have become one of the most prevalent calamities that face most societies year in, year out.
In addition, there has been an increase in other deadly calamities, such as droughts and tropical diseases that are connected to global warming; hence, the need for individuals to cooperate and save the world. Further, as research studies show some species of birds such as the Adélie penguins have drastically reduced in numbers, a case that is likely to become worse if people do not take responsibility for their actions, as most species of flora and fauna will find it very hard to adapt to new ecosystems (Jones 1).
In conclusion, considering the deadly nature of the effects of global warming and because global warming is primarily a product of human activities, there is need for collective responsibility to save Mother Nature. Failure to do this can lead to numerous devastating calamities that will greatly jeopardize the wellbeing of both present and future generations.
Essick, Peter. Causes of global warming . National Geographic society. 2011. Web.
Markham, Derek. Global warming effects and causes . Planet Save. 2009. Web.
Jones, Jeremy. What are the effects of global warming on earth? 2010. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, August 22). Global Warming: Causes and Effects | Essay Example. https://ivypanda.com/essays/global-warming-8/
"Global Warming: Causes and Effects | Essay Example." IvyPanda , 22 Aug. 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/global-warming-8/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'Global Warming: Causes and Effects | Essay Example'. 22 August.
IvyPanda . 2018. "Global Warming: Causes and Effects | Essay Example." August 22, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/global-warming-8/.
1. IvyPanda . "Global Warming: Causes and Effects | Essay Example." August 22, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/global-warming-8/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Global Warming: Causes and Effects | Essay Example." August 22, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/global-warming-8/.
- Environmental Stewardship of Deforestation
- Carbon Dioxide and Greenhouse Effects
- Deforestation Causes and Effects
- Global Warming: Since the Middle of the Twentieth Century and Next
- Global Warming Threats and Solutions
- Global Warming Exploration and Its Facts
- Global Warming Advantages: A New Look at the Phenomenon
- Impact of Global Warming on Arctic Wildlife

The Causes of Climate Change
Human activities are driving the global warming trend observed since the mid-20th century.

- The greenhouse effect is essential to life on Earth, but human-made emissions in the atmosphere are trapping and slowing heat loss to space.
- Five key greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, and water vapor.
- While the Sun has played a role in past climate changes, the evidence shows the current warming cannot be explained by the Sun.
Increasing Greenhouses Gases Are Warming the Planet
Scientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid-20 th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect" 1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space.
Life on Earth depends on energy coming from the Sun. About half the light energy reaching Earth's atmosphere passes through the air and clouds to the surface, where it is absorbed and radiated in the form of infrared heat. About 90% of this heat is then absorbed by greenhouse gases and re-radiated, slowing heat loss to space.
Four Major Gases That Contribute to the Greenhouse Effect
Carbon dioxide.
A vital component of the atmosphere, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is released through natural processes (like volcanic eruptions) and through human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation.
Like many atmospheric gases, methane comes from both natural and human-caused sources. Methane comes from plant-matter breakdown in wetlands and is also released from landfills and rice farming. Livestock animals emit methane from their digestion and manure. Leaks from fossil fuel production and transportation are another major source of methane, and natural gas is 70% to 90% methane.
Nitrous Oxide
A potent greenhouse gas produced by farming practices, nitrous oxide is released during commercial and organic fertilizer production and use. Nitrous oxide also comes from burning fossil fuels and burning vegetation and has increased by 18% in the last 100 years.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
These chemical compounds do not exist in nature – they are entirely of industrial origin. They were used as refrigerants, solvents (a substance that dissolves others), and spray can propellants.
FORCING: Something acting upon Earth's climate that causes a change in how energy flows through it (such as long-lasting, heat-trapping gases - also known as greenhouse gases). These gases slow outgoing heat in the atmosphere and cause the planet to warm.

Another Gas That Contributes to the Greenhouse Effect:
Water vapor.
Water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas, but because the warming ocean increases the amount of it in our atmosphere, it is not a direct cause of climate change. Credit: John Fowler on Unsplash
FEEDBACKS: A process where something is either amplified or reduced as time goes on, such as water vapor increasing as Earth warms leading to even more warming.

Human Activity Is the Cause of Increased Greenhouse Gas Concentrations
Over the last century, burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO 2 ). This increase happens because the coal or oil burning process combines carbon with oxygen in the air to make CO 2 . To a lesser extent, clearing of land for agriculture, industry, and other human activities has increased concentrations of greenhouse gases.
The industrial activities that our modern civilization depends upon have raised atmospheric carbon dioxide levels by nearly 50% since 1750 2 . This increase is due to human activities, because scientists can see a distinctive isotopic fingerprint in the atmosphere.
In its Sixth Assessment Report, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, composed of scientific experts from countries all over the world, concluded that it is unequivocal that the increase of CO 2 , methane, and nitrous oxide in the atmosphere over the industrial era is the result of human activities and that human influence is the principal driver of many changes observed across the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere and biosphere.
"Since systematic scientific assessments began in the 1970s, the influence of human activity on the warming of the climate system has evolved from theory to established fact."

Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
The panel's AR6 Working Group I (WGI) Summary for Policymakers report is online at https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/ .
Evidence Shows That Current Global Warming Cannot Be Explained by Solar Irradiance
Scientists use a metric called Total Solar Irradiance (TSI) to measure the changes in energy the Earth receives from the Sun. TSI incorporates the 11-year solar cycle and solar flares/storms from the Sun's surface.
Studies show that solar variability has played a role in past climate changes. For example, a decrease in solar activity coupled with increased volcanic activity helped trigger the Little Ice Age.
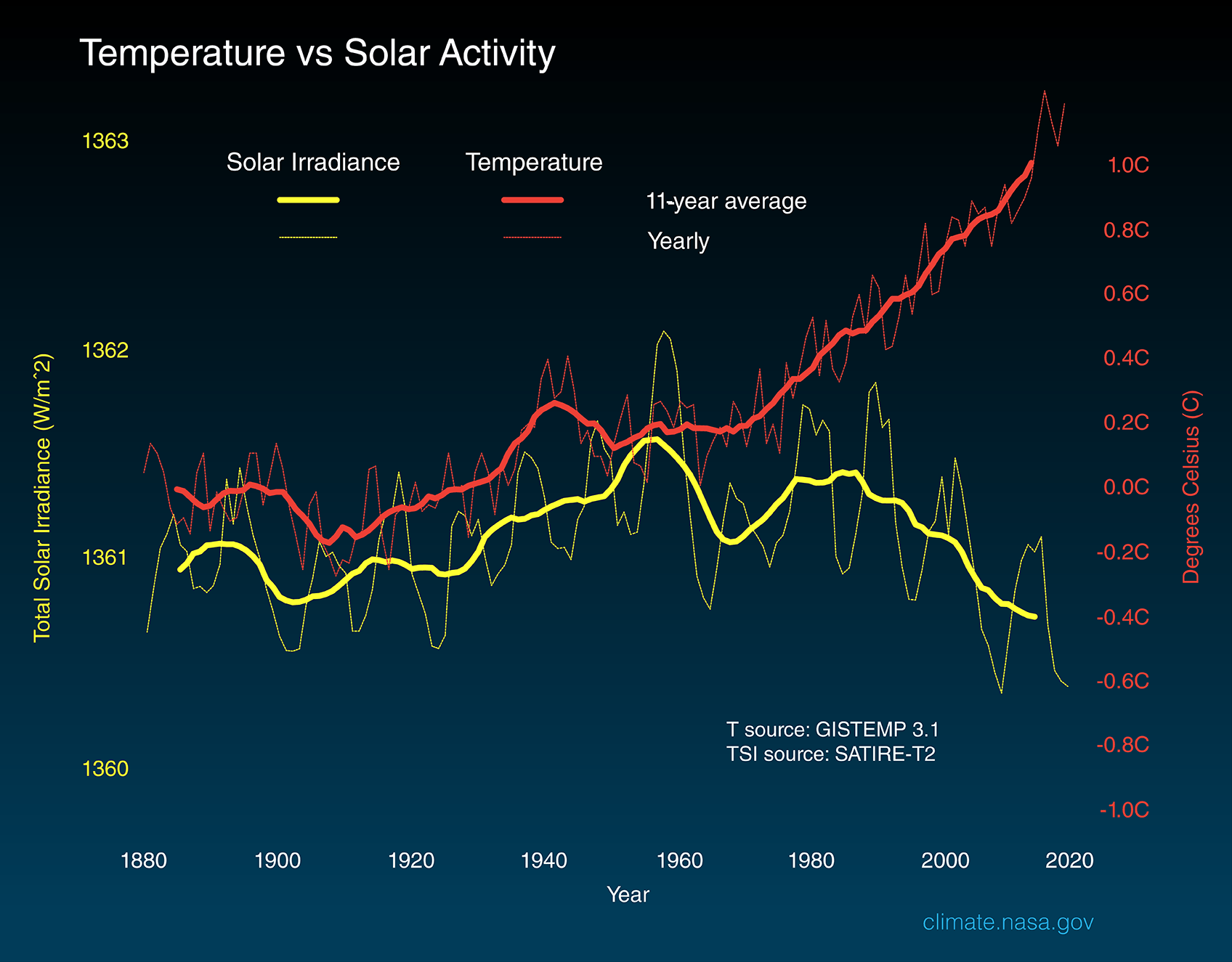
But several lines of evidence show that current global warming cannot be explained by changes in energy from the Sun:
- Since 1750, the average amount of energy from the Sun either remained constant or decreased slightly 3 .
- If a more active Sun caused the warming, scientists would expect warmer temperatures in all layers of the atmosphere. Instead, they have observed a cooling in the upper atmosphere and a warming at the surface and lower parts of the atmosphere. That's because greenhouse gases are slowing heat loss from the lower atmosphere.
- Climate models that include solar irradiance changes can’t reproduce the observed temperature trend over the past century or more without including a rise in greenhouse gases.
1. IPCC 6 th Assessment Report, WG1, Summary for Policy Makers, Sections A, “ The Current State of the Climate ”
IPCC 6 th Assessment Report, WG1, Technical Summary, Sections TS.1.2, TS.2.1 and TS.3.1
2. P. Friedlingstein, et al., 2022: “Global Carbon Budget 2022”, Earth System Science Data ( 11 Nov 2022): 4811–4900. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-14-4811-2022
3. IPCC 6 th Assessment Report, WG1, Chapter 2, Section 2.2.1, “ Solar and Orbital Forcing ” IPCC 6 th Assessment Report, WG1, Chapter 7, Sections 7.3.4.4, 7.3.5.2, Figure 7.6, “ Solar ” M. Lockwood and W.T. Ball, Placing limits on long-term variations in quiet-Sun irradiance and their contribution to total solar irradiance and solar radiative forcing of climate,” Proceedings of the Royal Society A , 476, issue 2228 (24 June 2020): https://doi 10.1098/rspa.2020.0077
Header image credit: Pixabay/stevepb Four Major Gases image credit: Adobe Stock/Ilya Glovatskiy
Discover More Topics From NASA
Explore Earth Science

Earth Science in Action

Earth Science Data
Facts About Earth


Russell Millner/Alamy
Defend Our Planet and Most Vulnerable Species
Your donation today will be triple-matched to power NRDC’s next great chapter in protecting our ecosystems and saving imperiled wildlife.
Global Warming 101
Everything you wanted to know about our changing climate but were too afraid to ask.
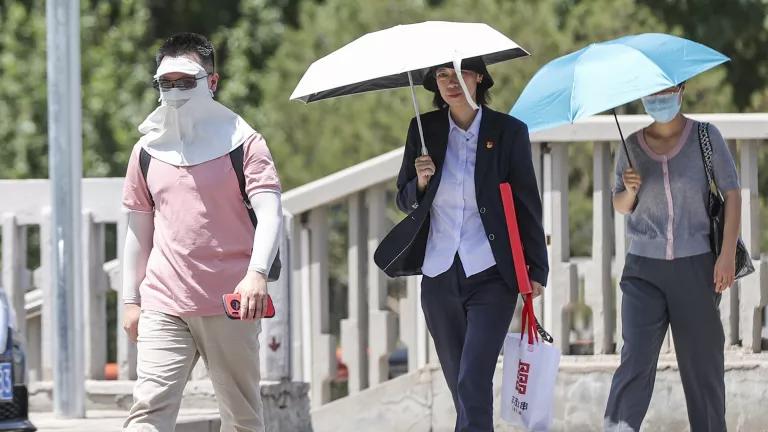

Temperatures in Beijing rose above 104 degrees Fahrenheit on July 6, 2023.
Jia Tianyong/China News Service/VCG via Getty Images

- Share this page block
What is global warming?
What causes global warming, how is global warming linked to extreme weather, what are the other effects of global warming, where does the united states stand in terms of global-warming contributors, is the united states doing anything to prevent global warming, is global warming too big a problem for me to help tackle.
A: Since the Industrial Revolution, the global annual temperature has increased in total by a little more than 1 degree Celsius, or about 2 degrees Fahrenheit. Between 1880—the year that accurate recordkeeping began—and 1980, it rose on average by 0.07 degrees Celsius (0.13 degrees Fahrenheit) every 10 years. Since 1981, however, the rate of increase has more than doubled: For the last 40 years, we’ve seen the global annual temperature rise by 0.18 degrees Celsius, or 0.32 degrees Fahrenheit, per decade.
The result? A planet that has never been hotter . Nine of the 10 warmest years since 1880 have occurred since 2005—and the 5 warmest years on record have all occurred since 2015. Climate change deniers have argued that there has been a “pause” or a “slowdown” in rising global temperatures, but numerous studies, including a 2018 paper published in the journal Environmental Research Letters , have disproved this claim. The impacts of global warming are already harming people around the world.
Now climate scientists have concluded that we must limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius by 2040 if we are to avoid a future in which everyday life around the world is marked by its worst, most devastating effects: the extreme droughts, wildfires, floods, tropical storms, and other disasters that we refer to collectively as climate change . These effects are felt by all people in one way or another but are experienced most acutely by the underprivileged, the economically marginalized, and people of color, for whom climate change is often a key driver of poverty, displacement, hunger, and social unrest.
A: Global warming occurs when carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and other air pollutants collect in the atmosphere and absorb sunlight and solar radiation that have bounced off the earth’s surface. Normally this radiation would escape into space, but these pollutants, which can last for years to centuries in the atmosphere, trap the heat and cause the planet to get hotter. These heat-trapping pollutants—specifically carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapor, and synthetic fluorinated gases—are known as greenhouse gases, and their impact is called the greenhouse effect.
Though natural cycles and fluctuations have caused the earth’s climate to change several times over the last 800,000 years, our current era of global warming is directly attributable to human activity—specifically to our burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, gasoline, and natural gas, which results in the greenhouse effect. In the United States, the largest source of greenhouse gases is transportation (29 percent), followed closely by electricity production (28 percent) and industrial activity (22 percent). Learn about the natural and human causes of climate change .
Curbing dangerous climate change requires very deep cuts in emissions, as well as the use of alternatives to fossil fuels worldwide. The good news is that countries around the globe have formally committed—as part of the 2015 Paris Climate Agreement —to lower their emissions by setting new standards and crafting new policies to meet or even exceed those standards. The not-so-good news is that we’re not working fast enough. To avoid the worst impacts of climate change, scientists tell us that we need to reduce global carbon emissions by as much as 40 percent by 2030. For that to happen, the global community must take immediate, concrete steps: to decarbonize electricity generation by equitably transitioning from fossil fuel–based production to renewable energy sources like wind and solar; to electrify our cars and trucks; and to maximize energy efficiency in our buildings, appliances, and industries.
A: Scientists agree that the earth’s rising temperatures are fueling longer and hotter heat waves , more frequent droughts , heavier rainfall , and more powerful hurricanes .
In 2015, for example, scientists concluded that a lengthy drought in California—the state’s worst water shortage in 1,200 years —had been intensified by 15 to 20 percent by global warming. They also said the odds of similar droughts happening in the future had roughly doubled over the past century. And in 2016, the National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine announced that we can now confidently attribute some extreme weather events, like heat waves, droughts, and heavy precipitation, directly to climate change.
The earth’s ocean temperatures are getting warmer, too—which means that tropical storms can pick up more energy. In other words, global warming has the ability to turn a category 3 storm into a more dangerous category 4 storm. In fact, scientists have found that the frequency of North Atlantic hurricanes has increased since the early 1980s, as has the number of storms that reach categories 4 and 5. The 2020 Atlantic hurricane season included a record-breaking 30 tropical storms, 6 major hurricanes, and 13 hurricanes altogether. With increased intensity come increased damage and death. The United States saw an unprecedented 22 weather and climate disasters that caused at least a billion dollars’ worth of damage in 2020, but, according to NOAA, 2017 was the costliest on record and among the deadliest as well: Taken together, that year's tropical storms (including Hurricanes Harvey, Irma, and Maria) caused nearly $300 billion in damage and led to more than 3,300 fatalities.
The impacts of global warming are being felt everywhere. Extreme heat waves have caused tens of thousands of deaths around the world in recent years. And in an alarming sign of events to come, Antarctica has lost nearly four trillion metric tons of ice since the 1990s. The rate of loss could speed up if we keep burning fossil fuels at our current pace, some experts say, causing sea levels to rise several meters in the next 50 to 150 years and wreaking havoc on coastal communities worldwide.
A: Each year scientists learn more about the consequences of global warming , and each year we also gain new evidence of its devastating impact on people and the planet. As the heat waves, droughts, and floods associated with climate change become more frequent and more intense, communities suffer and death tolls rise. If we’re unable to reduce our emissions, scientists believe that climate change could lead to the deaths of more than 250,000 people around the globe every year and force 100 million people into poverty by 2030.
Global warming is already taking a toll on the United States. And if we aren’t able to get a handle on our emissions, here’s just a smattering of what we can look forward to:
- Disappearing glaciers, early snowmelt, and severe droughts will cause more dramatic water shortages and continue to increase the risk of wildfires in the American West.
- Rising sea levels will lead to even more coastal flooding on the Eastern Seaboard, especially in Florida, and in other areas such as the Gulf of Mexico.
- Forests, farms, and cities will face troublesome new pests , heat waves, heavy downpours, and increased flooding . All of these can damage or destroy agriculture and fisheries.
- Disruption of habitats such as coral reefs and alpine meadows could drive many plant and animal species to extinction.
- Allergies, asthma, and infectious disease outbreaks will become more common due to increased growth of pollen-producing ragweed , higher levels of air pollution , and the spread of conditions favorable to pathogens and mosquitoes.
Though everyone is affected by climate change, not everyone is affected equally. Indigenous people, people of color, and the economically marginalized are typically hit the hardest. Inequities built into our housing , health care , and labor systems make these communities more vulnerable to the worst impacts of climate change—even though these same communities have done the least to contribute to it.
A: In recent years, China has taken the lead in global-warming pollution , producing about 26 percent of all CO2 emissions. The United States comes in second. Despite making up just 4 percent of the world’s population, our nation produces a sobering 13 percent of all global CO2 emissions—nearly as much as the European Union and India (third and fourth place) combined. And America is still number one, by far, in cumulative emissions over the past 150 years. As a top contributor to global warming, the United States has an obligation to help propel the world to a cleaner, safer, and more equitable future. Our responsibility matters to other countries, and it should matter to us, too.
A: We’ve started. But in order to avoid the worsening effects of climate change, we need to do a lot more—together with other countries—to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and transition to clean energy sources.
Under the administration of President Donald Trump (a man who falsely referred to global warming as a “hoax”), the United States withdrew from the Paris Climate Agreement, rolled back or eliminated dozens of clean air protections, and opened up federally managed lands, including culturally sacred national monuments, to fossil fuel development. Although President Biden has pledged to get the country back on track, years of inaction during and before the Trump administration—and our increased understanding of global warming’s serious impacts—mean we must accelerate our efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Despite the lack of cooperation from the Trump administration, local and state governments made great strides during this period through efforts like the American Cities Climate Challenge and ongoing collaborations like the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative . Meanwhile, industry and business leaders have been working with the public sector, creating and adopting new clean-energy technologies and increasing energy efficiency in buildings, appliances, and industrial processes.
Today the American automotive industry is finding new ways to produce cars and trucks that are more fuel efficient and is committing itself to putting more and more zero-emission electric vehicles on the road. Developers, cities, and community advocates are coming together to make sure that new affordable housing is built with efficiency in mind , reducing energy consumption and lowering electric and heating bills for residents. And renewable energy continues to surge as the costs associated with its production and distribution keep falling. In 2020 renewable energy sources such as wind and solar provided more electricity than coal for the very first time in U.S. history.
President Biden has made action on global warming a high priority. On his first day in office, he recommitted the United States to the Paris Climate Agreement, sending the world community a strong signal that we were determined to join other nations in cutting our carbon pollution to support the shared goal of preventing the average global temperature from rising more than 1.5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels. (Scientists say we must stay below a 2-degree increase to avoid catastrophic climate impacts.) And significantly, the president has assembled a climate team of experts and advocates who have been tasked with pursuing action both abroad and at home while furthering the cause of environmental justice and investing in nature-based solutions.
A: No! While we can’t win the fight without large-scale government action at the national level , we also can’t do it without the help of individuals who are willing to use their voices, hold government and industry leaders to account, and make changes in their daily habits.
Wondering how you can be a part of the fight against global warming? Reduce your own carbon footprint by taking a few easy steps: Make conserving energy a part of your daily routine and your decisions as a consumer. When you shop for new appliances like refrigerators, washers, and dryers, look for products with the government’s ENERGY STAR ® label; they meet a higher standard for energy efficiency than the minimum federal requirements. When you buy a car, look for one with the highest gas mileage and lowest emissions. You can also reduce your emissions by taking public transportation or carpooling when possible.
And while new federal and state standards are a step in the right direction, much more needs to be done. Voice your support of climate-friendly and climate change preparedness policies, and tell your representatives that equitably transitioning from dirty fossil fuels to clean power should be a top priority—because it’s vital to building healthy, more secure communities.
You don’t have to go it alone, either. Movements across the country are showing how climate action can build community , be led by those on the front lines of its impacts, and create a future that’s equitable and just for all .
This story was originally published on March 11, 2016 and has been updated with new information and links.
This NRDC.org story is available for online republication by news media outlets or nonprofits under these conditions: The writer(s) must be credited with a byline; you must note prominently that the story was originally published by NRDC.org and link to the original; the story cannot be edited (beyond simple things such as grammar); you can’t resell the story in any form or grant republishing rights to other outlets; you can’t republish our material wholesale or automatically—you need to select stories individually; you can’t republish the photos or graphics on our site without specific permission; you should drop us a note to let us know when you’ve used one of our stories.
Related Stories

Liquefied Natural Gas 101

What’s the Most Energy-Efficient Water Heater?

What Do “Better” Batteries Look Like?
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.
- ENVIRONMENT
What is global warming, explained
The planet is heating up—and fast.
Glaciers are melting , sea levels are rising, cloud forests are dying , and wildlife is scrambling to keep pace. It has become clear that humans have caused most of the past century's warming by releasing heat-trapping gases as we power our modern lives. Called greenhouse gases, their levels are higher now than at any time in the last 800,000 years .
We often call the result global warming, but it is causing a set of changes to the Earth's climate, or long-term weather patterns, that varies from place to place. While many people think of global warming and climate change as synonyms , scientists use “climate change” when describing the complex shifts now affecting our planet’s weather and climate systems—in part because some areas actually get cooler in the short term.
Climate change encompasses not only rising average temperatures but also extreme weather events , shifting wildlife populations and habitats, rising seas , and a range of other impacts. All of those changes are emerging as humans continue to add heat-trapping greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, changing the rhythms of climate that all living things have come to rely on.
What will we do—what can we do—to slow this human-caused warming? How will we cope with the changes we've already set into motion? While we struggle to figure it all out, the fate of the Earth as we know it—coasts, forests, farms, and snow-capped mountains—hangs in the balance.

Understanding the greenhouse effect
The "greenhouse effect" is the warming that happens when certain gases in Earth's atmosphere trap heat . These gases let in light but keep heat from escaping, like the glass walls of a greenhouse, hence the name.
Sunlight shines onto the Earth's surface, where the energy is absorbed and then radiate back into the atmosphere as heat. In the atmosphere, greenhouse gas molecules trap some of the heat, and the rest escapes into space. The more greenhouse gases concentrate in the atmosphere, the more heat gets locked up in the molecules.
For Hungry Minds
Scientists have known about the greenhouse effect since 1824, when Joseph Fourier calculated that the Earth would be much colder if it had no atmosphere. This natural greenhouse effect is what keeps the Earth's climate livable. Without it, the Earth's surface would be an average of about 60 degrees Fahrenheit (33 degrees Celsius) cooler.

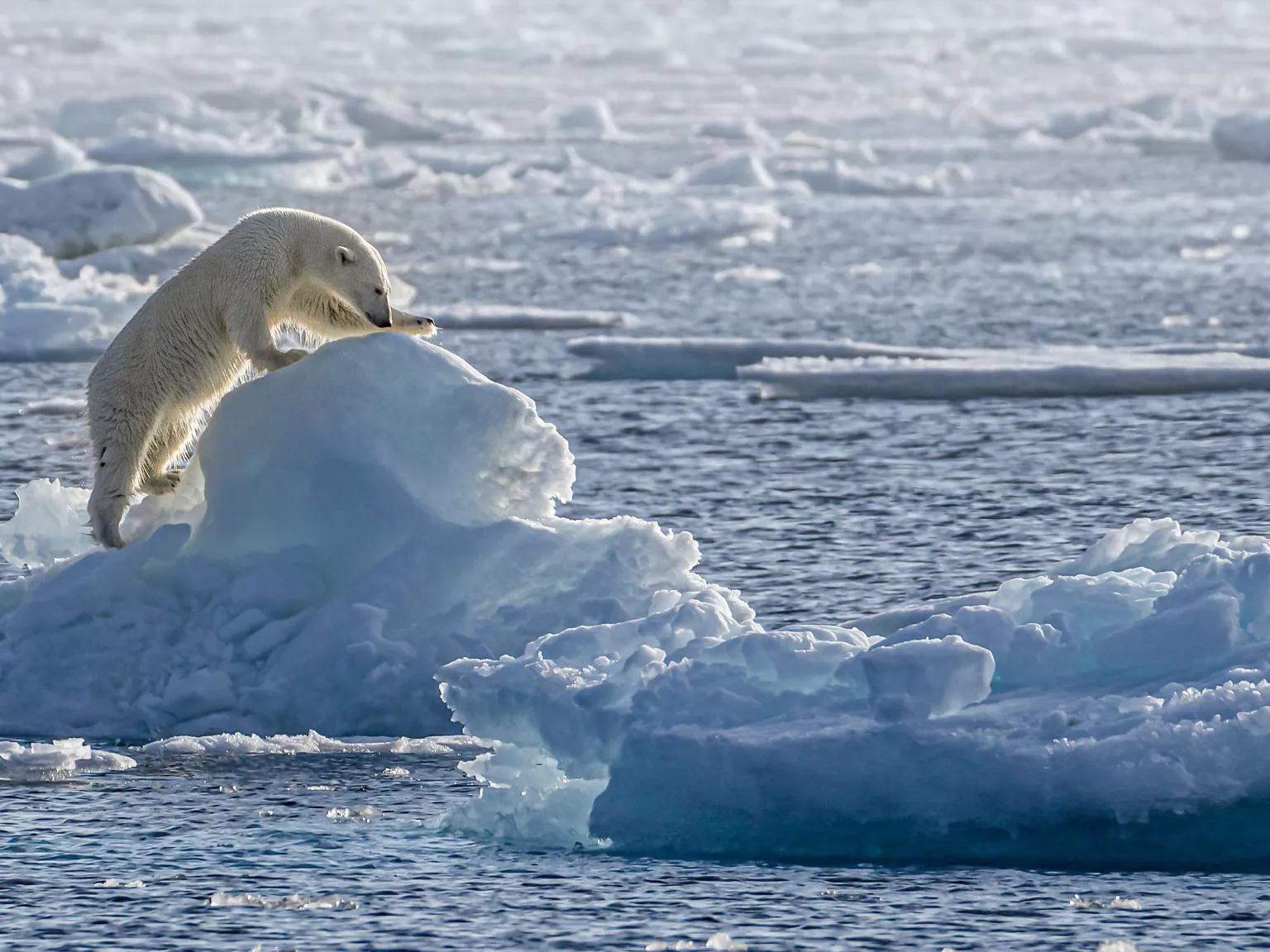
A polar bear stands sentinel on Rudolf Island in Russia’s Franz Josef Land archipelago, where the perennial ice is melting.
In 1895, the Swedish chemist Svante Arrhenius discovered that humans could enhance the greenhouse effect by making carbon dioxide , a greenhouse gas. He kicked off 100 years of climate research that has given us a sophisticated understanding of global warming.
Levels of greenhouse gases have gone up and down over the Earth's history, but they had been fairly constant for the past few thousand years. Global average temperatures had also stayed fairly constant over that time— until the past 150 years . Through the burning of fossil fuels and other activities that have emitted large amounts of greenhouse gases, particularly over the past few decades, humans are now enhancing the greenhouse effect and warming Earth significantly, and in ways that promise many effects , scientists warn.
Aren't temperature changes natural?
Human activity isn't the only factor that affects Earth's climate. Volcanic eruptions and variations in solar radiation from sunspots, solar wind, and the Earth's position relative to the sun also play a role. So do large-scale weather patterns such as El Niño .
You May Also Like

How global warming is disrupting life on Earth

These breathtaking natural wonders no longer exist

The Gulf of Maine is warming fast. What does that mean for lobsters—and everything else?
But climate models that scientists use to monitor Earth’s temperatures take those factors into account. Changes in solar radiation levels as well as minute particles suspended in the atmosphere from volcanic eruptions , for example, have contributed only about two percent to the recent warming effect. The balance comes from greenhouse gases and other human-caused factors, such as land use change .
The short timescale of this recent warming is singular as well. Volcanic eruptions , for example, emit particles that temporarily cool the Earth's surface. But their effect lasts just a few years. Events like El Niño also work on fairly short and predictable cycles. On the other hand, the types of global temperature fluctuations that have contributed to ice ages occur on a cycle of hundreds of thousands of years.
For thousands of years now, emissions of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere have been balanced out by greenhouse gases that are naturally absorbed. As a result, greenhouse gas concentrations and temperatures have been fairly stable, which has allowed human civilization to flourish within a consistent climate.

Greenland is covered with a vast amount of ice—but the ice is melting four times faster than thought, suggesting that Greenland may be approaching a dangerous tipping point, with implications for global sea-level rise.
Now, humans have increased the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere by more than a third since the Industrial Revolution. Changes that have historically taken thousands of years are now happening over the course of decades .
Why does this matter?
The rapid rise in greenhouse gases is a problem because it’s changing the climate faster than some living things can adapt to. Also, a new and more unpredictable climate poses unique challenges to all life.
Historically, Earth's climate has regularly shifted between temperatures like those we see today and temperatures cold enough to cover much of North America and Europe with ice. The difference between average global temperatures today and during those ice ages is only about 9 degrees Fahrenheit (5 degrees Celsius), and the swings have tended to happen slowly, over hundreds of thousands of years.
But with concentrations of greenhouse gases rising, Earth's remaining ice sheets such as Greenland and Antarctica are starting to melt too . That extra water could raise sea levels significantly, and quickly. By 2050, sea levels are predicted to rise between one and 2.3 feet as glaciers melt.
As the mercury rises, the climate can change in unexpected ways. In addition to sea levels rising, weather can become more extreme . This means more intense major storms, more rain followed by longer and drier droughts—a challenge for growing crops—changes in the ranges in which plants and animals can live, and loss of water supplies that have historically come from glaciers.
Related Topics
- ENVIRONMENT AND CONSERVATION
- CLIMATE CHANGE

What is the ozone layer, and why does it matter?

Why deforestation matters—and what we can do to stop it

There's a frozen labyrinth atop Mount Rainier. What secrets does it hold?

Chile’s glaciers are dying. You can actually hear it.

These caves mean death for Himalayan glaciers
- Environment
- Perpetual Planet
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Essay on Effects of Global Warming for Students and Children
500+ words essay on effects of global warming.
Global warming refers to climate change that causes an increase in the average of Earth’s temperature. Natural events and human influences are believed to be top contributions towards the increase in average temperatures. Global warming is a rise in the surface and atmospheric temperature of the earth that has changed various life forms on the earth. The issues that ascertain global warming are divided into two broad categories – “natural” and “human influences” of global warming.

Natural Causes of Global Warming
The climate has been continuously changing for centuries. One natural cause of global warming is greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases are carbon monoxide and sulphur dioxide . It traps the solar rays and prevents them from escaping the surface of the earth.
This causes an increase in the temperature of the earth. Volcanic eruptions are another reason for global warming. A single volcanic eruption can release a great amount of carbon dioxide and ash to the atmosphere. Increased carbon dioxide leads to a rise in the temperature of the earth.
Also, methane gas is another contributor to global warming. Methane is also a greenhouse gas. Methane is twenty times more effective in trapping heat in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide. Usually, methane gas is released from many areas like animal waste, landfill, natural gas, and others.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Human Influences on Global Warming
Human influence has been a very serious issue now as it is contributing more than natural causes of global warming. Since human evolution, the earth has been changing for many years until now and it is still changing because of our modern lifestyle. Human activities include industrial production, burning fossil fuel, mining of minerals, cattle rearing and deforestation.
Industries, transportation such as cars, buses, trucks burn fuel to power machines, which eventually releases carbon dioxide and monoxide from the exhaust, leading to an increase in a temperature rise of Earth’s atmosphere.
Another contributor is mining. During the process of mining, the methane gas trapped below the earth escapes. Rearing cattle also causes the release of methane from manure. Another cause is the most common but most dangerous – deforestation.
Deforestation is a human influence because human have been cutting down trees to produce paper, wood, build houses and more. Trees can absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and their absence can lead to the concentration of such gases.
The Effect of Global Warming
The impact that global warming is causing on earth is extremely serious. There are many hazardous effects that will happen in the future if global warming continues. It includes melting of polar ice caps, leading to an increase in sea level drowning coastlines and slowly submerging continents.
Recent studies by National Snow and Ice Datacenter “if the ice melted today the seas would rise about 230 feet”. Another effect is climate change leading to the extinction of various species. More hurricanes, cyclonic storms, heat waves, drought, and extreme rainfalls will occur causing disaster to humankind.
The solution to Stop Global Warming
We humans need to work together towards the prevention of global warming. To reduce global warming we can contribute by reducing the production and concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. We need to curb usage of gasoline, electricity and other activities including mining and industrialization that cause global warming.
Another way to reduce global warming is through recycling. Recycling can help reduce open burning of garbage by reusing plastic bags, bottles, papers or glass. We need to stop open burning dry leaves or burning garbage. It contributes to releasing carbon dioxide and toxins. Besides, we should reduce deforestation and start planting more trees. Trees will help improve the temperature on earth and prevent drastic climatic change.
From today’s scenario, we can derive that our earth is “sick” and we humans need to “heal” it. Global Warming has already caused many problems for human and we need to prevent disasters of the future. Our generation needs to take care of the earth with immediate effect to safeguard future generations or they will suffer the consequences of global warming.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Global Warming: Definition, Causes, Effects, and Risks
97% of scientists agree that global warming is largely man-made.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/RebeccaCoffey-2326e2f024b74d70b880218f4a4417ff.jpg)
- Webster University and California State University, Long Beach
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ScreenShot2021-04-07at1.57.45PM-bcef177316c94cdf998457c694cce6d5.png)
- University of Tennessee
- Planet Earth
- Climate Crisis
- Recycling & Waste
- Natural Disasters
- Transportation
The Cause of Global Warming
- Greenhouse Gases
- Global Warming Is Largely Man-Made
How Greenhouse Gases Warm the Globe
Deforestation, the effects of global warming, the risks of global warming.
Since 1880, when record keeping began, Earth's temperatures levels have been rising steadily. The pace of global warming then increased in the middle of the twentieth century, and it did again by the end of the century. As a result, Earth is now experiencing its warmest climate in modern history. So said scientists collaborating on the 2017 report of the United States Global Change Research Program.
The sun is the primary source of heat throughout the solar system. Solar radiation and average global temperatures usually rise and fall together. Over at least the past 40 years, however, that hasn’t been the case.
The Physical-Meteorological Observatory of the World Radiation Center Davos in Switzerland is one of the institutes tracking solar radiation. As reported in the peer-reviewed journal Solar Variability and Planetary Climates, their instruments determined that solar energy levels go up and down constantly, but on average they dropped slightly during the period between 1978 and 2007, even while average global temperatures soared. NASA has also published a graph charting an extension through 2020 of solar radiation and global temperature data.
If the sun is not causing the rise in global temperatures, what is?
Greenhouse Gases Cause Global Warming
Bruce B. Clarke / Getty Images
As explained by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), global warming is mostly caused by the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and a small group of synthetic chemicals called hydrofluorocarbons. The gases trap close to Earth’s surface the heat resulting from solar radiation and stop it from leaving Earth’s atmosphere for space.
Global Warming From Greenhouse Gases Is Largely Man-Made
A small percentage of global warming is caused when geological events like volcanoes add carbon dioxide to Earth’s atmosphere. The amount isn’t insignificant. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) has estimated that volcanoes contribute about 260 million tons of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere each year.
However, most scientists agree that global warming is largely caused by human activity. In 2016, as reported by the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Research Letters, “anthropogenic” was the verdict of 90%-100% of publishing climate scientists.
This echoed earlier findings published in 2013 by the same journal; a team of nine climate scientists examined 11,944 peer-reviewed, published papers. Of those papers that included an opinion about the cause of global warming, 97.1% described it as caused by humans.
According to the EPA, most greenhouse gases are put into the atmosphere when fossil fuels are burned as part of industrial or agricultural processes, though some (the hydrofluorocarbons) are spewed into the air by and from refrigeration, air conditioning, building insulation, and fire extinguishing products.
While methane is 28 times more effective than carbon dioxide in trapping heat in Earth’s atmosphere, the EPA has called carbon dioxide the single greenhouse gas most responsible for global warming. This is largely because it is the most abundant and it persists in the atmosphere for 300-1,000 years.
Trapping solar radiation close to Earth, the greenhouse gases warm oceans, waterways, and Earth’s surface in much the same way that insulated glass panels warm the plants growing inside a human-made greenhouse—hence the popular term “greenhouse effect” in climate change lingo.
While human-driven processes create global warming by putting greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, humans also deprive Earth of its natural ability to clear greenhouse gases and regulate temperatures.
Photosynthesis is a metabolic process through which plants convert light into glucose, which they use as energy. As part of the process, plants respirate, “inhaling” atmospheric carbon dioxide and exhaling oxygen. By pulling carbon dioxide out of the air, plants serve a vital anti-global warming function.
As described by a 2020 report of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), forests cover 31% of land area worldwide. The FAO estimated that some 420 million hectares (over 1 billion acres) of forest have been intentionally destroyed since 1990, with agricultural expansion conducted by large, for-profit companies being the main driver of that destruction.
With deforestation, Earth is losing one of its primary methods of keeping temperatures from climbing precipitously.
Key Takeaways: Causes of Global Warming
- Global warming is mostly caused by the “greenhouse gases” carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and a small group of synthetic chemicals called hydrofluorocarbons.
- For the most part, greenhouse gases are put into the atmosphere as a result of agricultural and industrial processes.
- While industrial and agricultural activities create global warming, deforestation deprives Earth of its natural ability to clear greenhouse gases and regulate temperatures.
Global warming destroys habitats and imperils life in terrestrial waterways and on Earth’s surface. In a way, though, oceans are the primary victims of rising temperatures.
Covering about 70% of Earth’s surface, oceans might be expected to suffer about 70% of the injury. Instead, the effect on them is surprisingly outsized. In October 2021, the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) reported that more than 90% of the excess heat trapped in and near Earth since the 1970s has been absorbed by oceans.
Changes in ocean systems typically take long periods of time to complete. Unfortunately, as the EPA has warned, those changes may take just as long to rectify.
Threatening Ocean Life
In a 10-year survey concluded in 2010, more than 2,700 scientists from 80 countries contributed to 540 ocean expeditions that counted and cataloged marine species. The survey identified 156,291 species in United States waters alone. According to NOAA, that number may be as much as 91% too low.
Regardless of whether they are known or unknown, most marine life occupies a particular space in the food web upon which humans rely. By drastically stressing ocean habitat, rising temperatures profoundly imperil a broad swath of ocean life.
Creating Droughts, Floods, and Unstable Weather
Oceans create weather on sea and land. Currents power breezes, storms, trade winds, and weather fronts. Evaporation of seawater creates clouds and, ultimately rain.
NOAA has reported that, if the world continues to warm, the speed of global winds are projected to increase. Increased wind speed will cause a greater disturbance of ocean water, which then will increase the potential of hurricane development and rainfall.
Profound oceanic changes could contribute to a feedback loop of hot and cold weather, some of it extreme and much of it catastrophic and unpredictable. Increased evaporation over ocean water could create catastrophic floods and shift precipitation patterns enough to also create new desert areas.
Contributing to Sea Level Rise and Arctic Amplification
NOAA has predicted that, as a warming world melts sea ice in polar areas, sea levels all over the world will continue to rise. Unfortunately, as outlined in an article in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Communications, a destructive feedback loop called “ arctic amplification ” may also continue. (This is currently happening particularly strongly in areas near the North Pole.)
Normally, white sea ice is so highly reflective that about 80% of the sunlight reaching it gets immediately reflected towards the sun. This keeps oceans cold.
Unfortunately, maintaining low ocean temperatures is a bigger job than ice alone can handle. In recent summers, unusually warm air near the North Pole has been melting sea ice, exposing bare patches of dark ocean.
Dark ocean readily absorbs sunlight. When this happens, ocean temperatures rise, and adjacent areas of sea ice start to melt from underneath. This generates a feedback loop: newly vanished ice allows more sunlight to be absorbed and more ocean to warm and more ice to melt from underneath and more sunlight to be absorbed from above. And so on.
For more than four decades, temperatures in the Arctic have risen at two to three times the pace of the rest of the world. As the differential between temperatures at the poles and those in mid-latitudes gets smaller, jet streams may weaken, and weather fronts may stall.
As reported in a review article published by NASA, many scientists have already traced arctic amplification to higher temperatures and extreme weather events throughout Earth’s mid-latitudes.
Protecting the Planet but Hurting Coral and Shellfish
As threatened as they are by global warming, oceans serve an enormous protective function against it: according to NASA, they are a carbon “sink,” storing carbon dioxide for millions of years and keeping it out of the atmosphere altogether.
There’s an unfortunate side effect, however, to oceans’ remarkable ability to sequester carbon. Carbon causes the pH balance of ocean water to drop, rendering the water more acidic. As explained by NOAA, in the years since the Industrial Revolution, the acidity of the oceans has increased by 30%. Under these conditions the exoskeletons and shells that marine animals such as coral and shellfish create become thinner, making the animals easier for predators to eat.
Global warming presents risks to almost every system on Earth. Its effects on the environment can already be seen and are expected to worsen in coming decades. A few of the more salient are:
- Sea Levels Are Rising. NASA has predicted that sea levels could rise as much as 8 feet by 2100. If they do, many coastal areas will be permanently submerged, and cities and vast areas of agricultural lands will be lost. This could cause a massive migration crisis while also devastating food supplies worldwide.
- Extreme Weather Events. In 2020 and 2021, global warming fueled lethal hurricanes that caused both coastal and inland floods. The nonprofit First Street Foundation Research Lab, a collection of 180 collaborating research labs and commercial partners, has warned that, within 30 years, about 25% of critical infrastructure locations like police stations, airports, and hospitals will be lost to ruinous floods.
- Droughts. NASA has predicted that unstable weather will continue to cause the sorts of droughts that have recently plagued Russia and central Asia , southeast Asia , Africa, Australia , and the western United States .
- Wildfires. The number and intensity of wildfires may increase. Droughts help spark wildfires. Unfortunately, combustion adds to a drought area's atmospheric carbon dioxide loads.
- Extinction. Land and sea species will continue to go extinct. A 2015 study published in the peer-reviewed journal Science Advances showed that vertebrate species are disappearing up to 100 times faster than the rate at which they went extinct 200 years ago.
Key Takeaways: The Effect of Global Warming on Oceans
- More than 90% of the excess heat trapped by greenhouse gases since the 1970s has been absorbed by oceans.
- By drastically stressing ocean habitat, rising temperatures profoundly imperil a broad swath of ocean life—and the entire global food web.
- Oceans create weather on sea and on land. Changes in ocean temperature disrupt weather patterns and threaten the world’s food supply.
" World of Change: Global Temperatures ." National Aeronautics and Space Administration .
Wuebbles, D.J., et al. " Executive Summary ." Climate Science Special Report: Fourth National Climate Assessment , vol. 1, 2017, pp. 12-34., doi:10.7930/J0DJ5CTG
" Is the Sun Causing Global Warming? " National Aeronautics and Space Administration .
Frohlich, C. " Solar Irradiance Variability since 1978 ." Solar Variability and Planetary Climates , vol. 23, 2006, pp. 53-65., doi:10.1007/978-0-387-48341-2_5
" The Causes of Climate Change ." National Aeronautics and Space Administration .
" Overview of Greenhouse Gases ." Environmental Protection Agency .
" Volcanoes Can Affect Climate ." United States Geological Survey .
Cook, John, et al. " Consensus on Consensus: A Synthesis of Consensus Estimates on Human-Caused Global Warming ." Environmental Research Letters , vol. 11, no. 4, 2016, pp. 048002., doi:10.1088/1748-9326/11/4/048002
Cook, John, et al. " Quantifying the Consensus on Anthropogenic Global Warming in the Scientific Literature ." Environmental Research Letters , vol. 8, no. 2, 2013, pp. 024024., doi:10.1088/1748-9326/8/2/024024
" Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks ." Environmental Protection Agency .
" Reducing Hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) Use and Emissions in the Federal Sector Through SNAP ." Environmental Protection Agency .
" CarbonTracker - CH4 ." National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration .
Buis, Alan. " The Atmosphere: Getting a Handle on Carbon Dioxide ." National Aeronautics and Space Administration , 2019.
Baslam, Marouane, et al. " Photosynthesis in a Changing Global Climate: Scaling Up and Scaling Down in Crops ." Frontiers in Plant Science , vol. 11, 2020, pp. 882., doi:10.3389/fpls.2020.00882
" The State of the World's Forests ." Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations , 2020.
" How Much Water Is in the Ocean? " National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration .
Dahlman, Luann and Rebecca Lindsey. " Climate Change: Ocean Heat Content ." National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , 2021.
" Climate Change Indicators: Oceans ." Environmental Protection Agency .
" What Is the Consensus of Marine Life ." National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration .
" How Many Species Live in the Ocean? " National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration .
Whited, Brittany. " Three Ways Climate Change Is Harming Marine Species ." Environmental Protection Agency , 2016.
" How Does the Ocean Affect Climate and Weather on Land? " National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration .
Knutson, Tom. " Global Warming and Hurricanes ." NOAA's Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory , 2021.
" Climate Change Indicators: Weather and Climate ." Environmental Protection Agency .
Lindsey, Rebecca. " Understanding the Arctic Polar Vortex ." National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , 2021.
Lindsey, Rebecca " Climate Change: Global Sea Level ." National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , 2021.
Dai, Aiguo, et al. " Arctic Amplification Is Caused by Sea-Ice Loss Under Increasing CO2 ." Nature Communications , vol. 10, 2019, pp. 121., doi:10.1038/s41467-018-07954-9
Lindsey, Rebecca and Michon Scott. " Climate Change: Arctic Sea Ice Summer Minimum ." National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , 2021.
" 2020 Tied for Warmest Year on Record, NASA Analysis Shows ." National Aeronautics and Space Administration , 2021.
Cohen, J., et al. " Arctic Change and Possible Influence on Mid-Latitude Climate and Weather: A U.S. Cliver White Paper ." U.S. Cliver , 2018., doi:10.5065/D6TH8KGW
" Climate Variability ." National Aeronautics and Space Administration .
" A Primer on pH ." National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration .
" Effects of Ocean and Coastal Acidification on Marine Life ." Environmental Protection Agency .
" The Effects of Climate Change ." National Aeronautics and Space Administration .
Porter, Jeremy, et. al. " Community Flood Risk and Infrastructure: Examining National Flood Impacts Using a High Precision Risk Assessment Tool ." First Street Foundation , 2021.
" The Impact of Wildfires on Climate and Air Quality ." National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration .
Ceballos, Gerardo, et al. " Accelerated Modern Human-Induced Species Losses: Entering the Sixth Mass Extinction ." Science Advances , vol. 1, no. 5, 2015., doi:10.1126/sciadv.1400253
- What's the Difference Between Global Warming and Climate Change?
- What Are Greenhouse Gases and the Greenhouse Effect?
- What Are Carbon Sinks? How Do They Impact Climate Change?
- What Is Arctic Amplification? Definition, Causes, and Environmental Implications
- What Is Geoengineering, and How Does It Impact Climate Change?
- How to Discuss Climate Change With Your Uncle
- How Do Glaciers, Ice Sheets, Sea Ice, and Icebergs Differ?
- What Is Climate Sensitivity? Definition and Examples
- How Do Volcanoes Contribute to Climate Change?
- Earth Is Trapping 'Unprecedented' Amount of Heat, Says NASA
- The Health Effects of Global Warming
- Climate Crisis Got Worse in 2020, UN Report Says
- How Much Air Pollution Comes From Cars?
- Three Types of Global Warming Solutions and Their Economic Benefits
- What Is Fracking? Definition, History, and Environmental Impact
- What Caused the Permian Extinction?

Climate Change: Evidence and Causes: Update 2020 (2020)
Chapter: conclusion, c onclusion.
This document explains that there are well-understood physical mechanisms by which changes in the amounts of greenhouse gases cause climate changes. It discusses the evidence that the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and are still increasing rapidly, that climate change is occurring, and that most of the recent change is almost certainly due to emissions of greenhouse gases caused by human activities. Further climate change is inevitable; if emissions of greenhouse gases continue unabated, future changes will substantially exceed those that have occurred so far. There remains a range of estimates of the magnitude and regional expression of future change, but increases in the extremes of climate that can adversely affect natural ecosystems and human activities and infrastructure are expected.
Citizens and governments can choose among several options (or a mixture of those options) in response to this information: they can change their pattern of energy production and usage in order to limit emissions of greenhouse gases and hence the magnitude of climate changes; they can wait for changes to occur and accept the losses, damage, and suffering that arise; they can adapt to actual and expected changes as much as possible; or they can seek as yet unproven “geoengineering” solutions to counteract some of the climate changes that would otherwise occur. Each of these options has risks, attractions and costs, and what is actually done may be a mixture of these different options. Different nations and communities will vary in their vulnerability and their capacity to adapt. There is an important debate to be had about choices among these options, to decide what is best for each group or nation, and most importantly for the global population as a whole. The options have to be discussed at a global scale because in many cases those communities that are most vulnerable control few of the emissions, either past or future. Our description of the science of climate change, with both its facts and its uncertainties, is offered as a basis to inform that policy debate.
A CKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The following individuals served as the primary writing team for the 2014 and 2020 editions of this document:
- Eric Wolff FRS, (UK lead), University of Cambridge
- Inez Fung (NAS, US lead), University of California, Berkeley
- Brian Hoskins FRS, Grantham Institute for Climate Change
- John F.B. Mitchell FRS, UK Met Office
- Tim Palmer FRS, University of Oxford
- Benjamin Santer (NAS), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
- John Shepherd FRS, University of Southampton
- Keith Shine FRS, University of Reading.
- Susan Solomon (NAS), Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Kevin Trenberth, National Center for Atmospheric Research
- John Walsh, University of Alaska, Fairbanks
- Don Wuebbles, University of Illinois
Staff support for the 2020 revision was provided by Richard Walker, Amanda Purcell, Nancy Huddleston, and Michael Hudson. We offer special thanks to Rebecca Lindsey and NOAA Climate.gov for providing data and figure updates.
The following individuals served as reviewers of the 2014 document in accordance with procedures approved by the Royal Society and the National Academy of Sciences:
- Richard Alley (NAS), Department of Geosciences, Pennsylvania State University
- Alec Broers FRS, Former President of the Royal Academy of Engineering
- Harry Elderfield FRS, Department of Earth Sciences, University of Cambridge
- Joanna Haigh FRS, Professor of Atmospheric Physics, Imperial College London
- Isaac Held (NAS), NOAA Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory
- John Kutzbach (NAS), Center for Climatic Research, University of Wisconsin
- Jerry Meehl, Senior Scientist, National Center for Atmospheric Research
- John Pendry FRS, Imperial College London
- John Pyle FRS, Department of Chemistry, University of Cambridge
- Gavin Schmidt, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
- Emily Shuckburgh, British Antarctic Survey
- Gabrielle Walker, Journalist
- Andrew Watson FRS, University of East Anglia
The Support for the 2014 Edition was provided by NAS Endowment Funds. We offer sincere thanks to the Ralph J. and Carol M. Cicerone Endowment for NAS Missions for supporting the production of this 2020 Edition.
F OR FURTHER READING
For more detailed discussion of the topics addressed in this document (including references to the underlying original research), see:
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), 2019: Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate [ https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc ]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM), 2019: Negative Emissions Technologies and Reliable Sequestration: A Research Agenda [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/25259 ]
- Royal Society, 2018: Greenhouse gas removal [ https://raeng.org.uk/greenhousegasremoval ]
- U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP), 2018: Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume II: Impacts, Risks, and Adaptation in the United States [ https://nca2018.globalchange.gov ]
- IPCC, 2018: Global Warming of 1.5°C [ https://www.ipcc.ch/sr15 ]
- USGCRP, 2017: Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume I: Climate Science Special Reports [ https://science2017.globalchange.gov ]
- NASEM, 2016: Attribution of Extreme Weather Events in the Context of Climate Change [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/21852 ]
- IPCC, 2013: Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) Working Group 1. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis [ https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1 ]
- NRC, 2013: Abrupt Impacts of Climate Change: Anticipating Surprises [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/18373 ]
- NRC, 2011: Climate Stabilization Targets: Emissions, Concentrations, and Impacts Over Decades to Millennia [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/12877 ]
- Royal Society 2010: Climate Change: A Summary of the Science [ https://royalsociety.org/topics-policy/publications/2010/climate-change-summary-science ]
- NRC, 2010: America’s Climate Choices: Advancing the Science of Climate Change [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/12782 ]
Much of the original data underlying the scientific findings discussed here are available at:
- https://data.ucar.edu/
- https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu
- https://iridl.ldeo.columbia.edu
- https://ess-dive.lbl.gov/
- https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/
- https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/
- http://scrippsco2.ucsd.edu
- http://hahana.soest.hawaii.edu/hot/

Climate change is one of the defining issues of our time. It is now more certain than ever, based on many lines of evidence, that humans are changing Earth's climate. The Royal Society and the US National Academy of Sciences, with their similar missions to promote the use of science to benefit society and to inform critical policy debates, produced the original Climate Change: Evidence and Causes in 2014. It was written and reviewed by a UK-US team of leading climate scientists. This new edition, prepared by the same author team, has been updated with the most recent climate data and scientific analyses, all of which reinforce our understanding of human-caused climate change.
Scientific information is a vital component for society to make informed decisions about how to reduce the magnitude of climate change and how to adapt to its impacts. This booklet serves as a key reference document for decision makers, policy makers, educators, and others seeking authoritative answers about the current state of climate-change science.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
Switch between the Original Pages , where you can read the report as it appeared in print, and Text Pages for the web version, where you can highlight and search the text.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.
ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Global warming.
The causes, effects, and complexities of global warming are important to understand so that we can fight for the health of our planet.
Earth Science, Climatology
Tennessee Power Plant
Ash spews from a coal-fueled power plant in New Johnsonville, Tennessee, United States.
Photograph by Emory Kristof/ National Geographic

Global warming is the long-term warming of the planet’s overall temperature. Though this warming trend has been going on for a long time, its pace has significantly increased in the last hundred years due to the burning of fossil fuels . As the human population has increased, so has the volume of fossil fuels burned. Fossil fuels include coal, oil, and natural gas, and burning them causes what is known as the “greenhouse effect” in Earth’s atmosphere.
The greenhouse effect is when the sun’s rays penetrate the atmosphere, but when that heat is reflected off the surface cannot escape back into space. Gases produced by the burning of fossil fuels prevent the heat from leaving the atmosphere. These greenhouse gasses are carbon dioxide , chlorofluorocarbons, water vapor , methane , and nitrous oxide . The excess heat in the atmosphere has caused the average global temperature to rise overtime, otherwise known as global warming.
Global warming has presented another issue called climate change. Sometimes these phrases are used interchangeably, however, they are different. Climate change refers to changes in weather patterns and growing seasons around the world. It also refers to sea level rise caused by the expansion of warmer seas and melting ice sheets and glaciers . Global warming causes climate change, which poses a serious threat to life on Earth in the forms of widespread flooding and extreme weather. Scientists continue to study global warming and its impact on Earth.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
February 21, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Essay on Global Warming
- Updated on
- Apr 27, 2024

Being able to write an essay is an integral part of mastering any language. Essays form an integral part of many academic and scholastic exams like the SAT , and UPSC amongst many others. It is a crucial evaluative part of English proficiency tests as well like IELTS , TOEFL , etc. Major essays are meant to emphasize public issues of concern that can have significant consequences on the world. To understand the concept of Global Warming and its causes and effects, we must first examine the many factors that influence the planet’s temperature and what this implies for the world’s future. Here’s an unbiased look at the essay on Global Warming and other essential related topics.

Short Essay on Global Warming and Climate Change?
Since the industrial and scientific revolutions, Earth’s resources have been gradually depleted. Furthermore, the start of the world’s population’s exponential expansion is particularly hard on the environment. Simply put, as the population’s need for consumption grows, so does the use of natural resources , as well as the waste generated by that consumption.
Climate change has been one of the most significant long-term consequences of this. Climate change is more than just the rise or fall of global temperatures; it also affects rain cycles, wind patterns, cyclone frequencies, sea levels, and other factors. It has an impact on all major life groupings on the planet.
Also Read: World Population Day
What is Global Warming?
Global warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth’s average surface temperature over the past century, primarily due to the greenhouse gases released by people burning fossil fuels . The greenhouse gases consist of methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and chlorofluorocarbons. The weather prediction has been becoming more complex with every passing year, with seasons more indistinguishable, and the general temperatures hotter.
The number of hurricanes, cyclones, droughts, floods, etc., has risen steadily since the onset of the 21st century. The supervillain behind all these changes is Global Warming. The name is quite self-explanatory; it means the rise in the temperature of the Earth.
Also Read: What is a Natural Disaster?
What are the Causes of Global Warming?
According to recent studies, many scientists believe the following are the primary four causes of global warming:
- Deforestation
- Greenhouse emissions
- Carbon emissions per capita
Extreme global warming is causing natural disasters , which can be seen all around us. One of the causes of global warming is the extreme release of greenhouse gases that become trapped on the earth’s surface, causing the temperature to rise. Similarly, volcanoes contribute to global warming by spewing excessive CO2 into the atmosphere.
The increase in population is one of the major causes of Global Warming. This increase in population also leads to increased air pollution . Automobiles emit a lot of CO2, which remains in the atmosphere. This increase in population is also causing deforestation, which contributes to global warming.
The earth’s surface emits energy into the atmosphere in the form of heat, keeping the balance with the incoming energy. Global warming depletes the ozone layer, bringing about the end of the world. There is a clear indication that increased global warming will result in the extinction of all life on Earth’s surface.
Also Read: Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation, and Wildlife Resources
Solutions for Global Warming
Of course, industries and multinational conglomerates emit more carbon than the average citizen. Nonetheless, activism and community effort are the only viable ways to slow the worsening effects of global warming. Furthermore, at the state or government level, world leaders must develop concrete plans and step-by-step programmes to ensure that no further harm is done to the environment in general.
Although we are almost too late to slow the rate of global warming, finding the right solution is critical. Everyone, from individuals to governments, must work together to find a solution to Global Warming. Some of the factors to consider are pollution control, population growth, and the use of natural resources.
One very important contribution you can make is to reduce your use of plastic. Plastic is the primary cause of global warming, and recycling it takes years. Another factor to consider is deforestation, which will aid in the control of global warming. More tree planting should be encouraged to green the environment. Certain rules should also govern industrialization. Building industries in green zones that affect plants and species should be prohibited.
Also Read: Essay on Pollution
Effects of Global Warming
Global warming is a real problem that many people want to disprove to gain political advantage. However, as global citizens, we must ensure that only the truth is presented in the media.
This decade has seen a significant impact from global warming. The two most common phenomena observed are glacier retreat and arctic shrinkage. Glaciers are rapidly melting. These are clear manifestations of climate change.
Another significant effect of global warming is the rise in sea level. Flooding is occurring in low-lying areas as a result of sea-level rise. Many countries have experienced extreme weather conditions. Every year, we have unusually heavy rain, extreme heat and cold, wildfires, and other natural disasters.
Similarly, as global warming continues, marine life is being severely impacted. This is causing the extinction of marine species as well as other problems. Furthermore, changes are expected in coral reefs, which will face extinction in the coming years. These effects will intensify in the coming years, effectively halting species expansion. Furthermore, humans will eventually feel the negative effects of Global Warming.
Also Read: Concept of Sustainable Development
Sample Essays on Global Warming
Here are some sample essays on Global Warming:
Essay on Global Warming Paragraph in 100 – 150 words
Global Warming is caused by the increase of carbon dioxide levels in the earth’s atmosphere and is a result of human activities that have been causing harm to our environment for the past few centuries now. Global Warming is something that can’t be ignored and steps have to be taken to tackle the situation globally. The average temperature is constantly rising by 1.5 degrees Celsius over the last few years.
The best method to prevent future damage to the earth, cutting down more forests should be banned and Afforestation should be encouraged. Start by planting trees near your homes and offices, participate in events, and teach the importance of planting trees. It is impossible to undo the damage but it is possible to stop further harm.
Also Read: Social Forestry
Essay on Global Warming in 250 Words
Over a long period, it is observed that the temperature of the earth is increasing. This affected wildlife, animals, humans, and every living organism on earth. Glaciers have been melting, and many countries have started water shortages, flooding, and erosion and all this is because of global warming.
No one can be blamed for global warming except for humans. Human activities such as gases released from power plants, transportation, and deforestation have increased gases such as carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants in the earth’s atmosphere. The main question is how can we control the current situation and build a better world for future generations. It starts with little steps by every individual.
Start using cloth bags made from sustainable materials for all shopping purposes, instead of using high-watt lights use energy-efficient bulbs, switch off the electricity, don’t waste water, abolish deforestation and encourage planting more trees. Shift the use of energy from petroleum or other fossil fuels to wind and solar energy. Instead of throwing out the old clothes donate them to someone so that it is recycled.
Donate old books, don’t waste paper. Above all, spread awareness about global warming. Every little thing a person does towards saving the earth will contribute in big or small amounts. We must learn that 1% effort is better than no effort. Pledge to take care of Mother Nature and speak up about global warming.
Also Read: Types of Water Pollution
Essay on Global Warming in 500 Words
Global warming isn’t a prediction, it is happening! A person denying it or unaware of it is in the most simple terms complicit. Do we have another planet to live on? Unfortunately, we have been bestowed with this one planet only that can sustain life yet over the years we have turned a blind eye to the plight it is in. Global warming is not an abstract concept but a global phenomenon occurring ever so slowly even at this moment. Global Warming is a phenomenon that is occurring every minute resulting in a gradual increase in the Earth’s overall climate. Brought about by greenhouse gases that trap the solar radiation in the atmosphere, global warming can change the entire map of the earth, displacing areas, flooding many countries, and destroying multiple lifeforms. Extreme weather is a direct consequence of global warming but it is not an exhaustive consequence. There are virtually limitless effects of global warming which are all harmful to life on earth. The sea level is increasing by 0.12 inches per year worldwide. This is happening because of the melting of polar ice caps because of global warming. This has increased the frequency of floods in many lowland areas and has caused damage to coral reefs. The Arctic is one of the worst-hit areas affected by global warming. Air quality has been adversely affected and the acidity of the seawater has also increased causing severe damage to marine life forms. Severe natural disasters are brought about by global warming which has had dire effects on life and property. As long as mankind produces greenhouse gases, global warming will continue to accelerate. The consequences are felt at a much smaller scale which will increase to become drastic shortly. The power to save the day lies in the hands of humans, the need is to seize the day. Energy consumption should be reduced on an individual basis. Fuel-efficient cars and other electronics should be encouraged to reduce the wastage of energy sources. This will also improve air quality and reduce the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Global warming is an evil that can only be defeated when fought together. It is better late than never. If we all take steps today, we will have a much brighter future tomorrow. Global warming is the bane of our existence and various policies have come up worldwide to fight it but that is not enough. The actual difference is made when we work at an individual level to fight it. Understanding its import now is crucial before it becomes an irrevocable mistake. Exterminating global warming is of utmost importance and each one of us is as responsible for it as the next.
Also Read: Essay on Library: 100, 200 and 250 Words
Essay on Global Warming UPSC
Always hear about global warming everywhere, but do we know what it is? The evil of the worst form, global warming is a phenomenon that can affect life more fatally. Global warming refers to the increase in the earth’s temperature as a result of various human activities. The planet is gradually getting hotter and threatening the existence of lifeforms on it. Despite being relentlessly studied and researched, global warming for the majority of the population remains an abstract concept of science. It is this concept that over the years has culminated in making global warming a stark reality and not a concept covered in books. Global warming is not caused by one sole reason that can be curbed. Multifarious factors cause global warming most of which are a part of an individual’s daily existence. Burning of fuels for cooking, in vehicles, and for other conventional uses, a large amount of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, and methane amongst many others is produced which accelerates global warming. Rampant deforestation also results in global warming as lesser green cover results in an increased presence of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere which is a greenhouse gas. Finding a solution to global warming is of immediate importance. Global warming is a phenomenon that has to be fought unitedly. Planting more trees can be the first step that can be taken toward warding off the severe consequences of global warming. Increasing the green cover will result in regulating the carbon cycle. There should be a shift from using nonrenewable energy to renewable energy such as wind or solar energy which causes less pollution and thereby hinder the acceleration of global warming. Reducing energy needs at an individual level and not wasting energy in any form is the most important step to be taken against global warming. The warning bells are tolling to awaken us from the deep slumber of complacency we have slipped into. Humans can fight against nature and it is high time we acknowledged that. With all our scientific progress and technological inventions, fighting off the negative effects of global warming is implausible. We have to remember that we do not inherit the earth from our ancestors but borrow it from our future generations and the responsibility lies on our shoulders to bequeath them a healthy planet for life to exist.
Also Read: Essay on Disaster Management
Climate Change and Global Warming Essay
Global Warming and Climate Change are two sides of the same coin. Both are interrelated with each other and are two issues of major concern worldwide. Greenhouse gases released such as carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants in the earth’s atmosphere cause Global Warming which leads to climate change. Black holes have started to form in the ozone layer that protects the earth from harmful ultraviolet rays.
Human activities have created climate change and global warming. Industrial waste and fumes are the major contributors to global warming.
Another factor affecting is the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation and also one of the reasons for climate change. Global warming has resulted in shrinking mountain glaciers in Antarctica, Greenland, and the Arctic and causing climate change. Switching from the use of fossil fuels to energy sources like wind and solar.
When buying any electronic appliance buy the best quality with energy savings stars. Don’t waste water and encourage rainwater harvesting in your community.
Also Read: Essay on Air Pollution
Tips to Write an Essay
Writing an effective essay needs skills that few people possess and even fewer know how to implement. While writing an essay can be an assiduous task that can be unnerving at times, some key pointers can be inculcated to draft a successful essay. These involve focusing on the structure of the essay, planning it out well, and emphasizing crucial details.
Mentioned below are some pointers that can help you write better structure and more thoughtful essays that will get across to your readers:
- Prepare an outline for the essay to ensure continuity and relevance and no break in the structure of the essay
- Decide on a thesis statement that will form the basis of your essay. It will be the point of your essay and help readers understand your contention
- Follow the structure of an introduction, a detailed body followed by a conclusion so that the readers can comprehend the essay in a particular manner without any dissonance.
- Make your beginning catchy and include solutions in your conclusion to make the essay insightful and lucrative to read
- Reread before putting it out and add your flair to the essay to make it more personal and thereby unique and intriguing for readers
Also Read: I Love My India Essay: 100 and 500+ Words in English for School Students
Ans. Both natural and man-made factors contribute to global warming. The natural one also contains methane gas, volcanic eruptions, and greenhouse gases. Deforestation, mining, livestock raising, burning fossil fuels, and other man-made causes are next.
Ans. The government and the general public can work together to stop global warming. Trees must be planted more often, and deforestation must be prohibited. Auto usage needs to be curbed, and recycling needs to be promoted.
Ans. Switching to renewable energy sources , adopting sustainable farming, transportation, and energy methods, and conserving water and other natural resources.
Relevant Blogs
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Digvijay Singh
Having 2+ years of experience in educational content writing, withholding a Bachelor's in Physical Education and Sports Science and a strong interest in writing educational content for students enrolled in domestic and foreign study abroad programmes. I believe in offering a distinct viewpoint to the table, to help students deal with the complexities of both domestic and foreign educational systems. Through engaging storytelling and insightful analysis, I aim to inspire my readers to embark on their educational journeys, whether abroad or at home, and to make the most of every learning opportunity that comes their way.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
This was really a good essay on global warming… There has been used many unic words..and I really liked it!!!Seriously I had been looking for a essay about Global warming just like this…
Thank you for the comment!
I want to learn how to write essay writing so I joined this page.This page is very useful for everyone.
Hi, we are glad that we could help you to write essays. We have a beginner’s guide to write essays ( https://leverageedu.com/blog/essay-writing/ ) and we think this might help you.
It is not good , to have global warming in our earth .So we all have to afforestation program on all the world.
thank you so much
Very educative , helpful and it is really going to strength my English knowledge to structure my essay in future
Thank you for the comment, please follow our newsletter to get more insights on studying abroad and exams!
Global warming is the increase in 𝓽𝓱𝓮 ᴀᴠᴇʀᴀɢᴇ ᴛᴇᴍᴘᴇʀᴀᴛᴜʀᴇs ᴏғ ᴇᴀʀᴛʜ🌎 ᴀᴛᴍᴏsᴘʜᴇʀᴇ

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Arab States
Asia and the pacific, europe & central asia, latin america & the caribbean.
You’re using an outdated browser. Old browsers are unstable, unsafe and do not support the features of of this website. Please upgrade to continue.
Your browser does not support JavaScript. This site relies on JavaScript to structure its navigation and load images across all pages. Please enable JavaScript to continue.
What is climate change mitigation and why is it urgent?
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Facebook
- Share on twitter
- Share via email

- Climate change mitigation involves actions to reduce or prevent greenhouse gas emissions from human activities.
- Mitigation efforts include transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, adopting regenerative agricultural practices and protecting and restoring forests and critical ecosystems.
- Effective mitigation requires a whole-of-society approach and structural transformations to reduce emissions and limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
- International cooperation, for example through the Paris Agreement, is crucial in guiding and achieving global and national mitigation goals.
- Mitigation efforts face challenges such as the world's deep-rooted dependency on fossil fuels, the increased demand for new mineral resources and the difficulties in revamping our food systems.
- These challenges also offer opportunities to improve resilience and contribute to sustainable development.
What is climate change mitigation?
Climate change mitigation refers to any action taken by governments, businesses or people to reduce or prevent greenhouse gases, or to enhance carbon sinks that remove them from the atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun in our planet’s atmosphere, keeping it warm.
Since the industrial era began, human activities have led to the release of dangerous levels of greenhouse gases, causing global warming and climate change. However, despite unequivocal research about the impact of our activities on the planet’s climate and growing awareness of the severe danger climate change poses to our societies, greenhouse gas emissions keep rising. If we can slow down the rise in greenhouse gases, we can slow down the pace of climate change and avoid its worst consequences.
Reducing greenhouse gases can be achieved by:
- Shifting away from fossil fuels : Fossil fuels are the biggest source of greenhouse gases, so transitioning to modern renewable energy sources like solar, wind and geothermal power, and advancing sustainable modes of transportation, is crucial.
- Improving energy efficiency : Using less energy overall – in buildings, industries, public and private spaces, energy generation and transmission, and transportation – helps reduce emissions. This can be achieved by using thermal comfort standards, better insulation and energy efficient appliances, and by improving building design, energy transmission systems and vehicles.
- Changing agricultural practices : Certain farming methods release high amounts of methane and nitrous oxide, which are potent greenhouse gases. Regenerative agricultural practices – including enhancing soil health, reducing livestock-related emissions, direct seeding techniques and using cover crops – support mitigation, improve resilience and decrease the cost burden on farmers.
- The sustainable management and conservation of forests : Forests act as carbon sinks , absorbing carbon dioxide and reducing the overall concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Measures to reduce deforestation and forest degradation are key for climate mitigation and generate multiple additional benefits such as biodiversity conservation and improved water cycles.
- Restoring and conserving critical ecosystems : In addition to forests, ecosystems such as wetlands, peatlands, and grasslands, as well as coastal biomes such as mangrove forests, also contribute significantly to carbon sequestration, while supporting biodiversity and enhancing climate resilience.
- Creating a supportive environment : Investments, policies and regulations that encourage emission reductions, such as incentives, carbon pricing and limits on emissions from key sectors are crucial to driving climate change mitigation.

Photo: Stephane Bellerose/UNDP Mauritius

Photo: La Incre and Lizeth Jurado/PROAmazonia
What is the 1.5°C goal and why do we need to stick to it?
In 2015, 196 Parties to the UN Climate Convention in Paris adopted the Paris Agreement , a landmark international treaty, aimed at curbing global warming and addressing the effects of climate change. Its core ambition is to cap the rise in global average temperatures to well below 2°C above levels observed prior to the industrial era, while pursuing efforts to limit the increase to 1.5°C.
The 1.5°C goal is extremely important, especially for vulnerable communities already experiencing severe climate change impacts. Limiting warming below 1.5°C will translate into less extreme weather events and sea level rise, less stress on food production and water access, less biodiversity and ecosystem loss, and a lower chance of irreversible climate consequences.
To limit global warming to the critical threshold of 1.5°C, it is imperative for the world to undertake significant mitigation action. This requires a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 45 percent before 2030 and achieving net-zero emissions by mid-century.
What are the policy instruments that countries can use to drive mitigation?
Everyone has a role to play in climate change mitigation, from individuals adopting sustainable habits and advocating for change to governments implementing regulations, providing incentives and facilitating investments. The private sector, particularly those businesses and companies responsible for causing high emissions, should take a leading role in innovating, funding and driving climate change mitigation solutions.
International collaboration and technology transfer is also crucial given the global nature and size of the challenge. As the main platform for international cooperation on climate action, the Paris Agreement has set forth a series of responsibilities and policy tools for its signatories. One of the primary instruments for achieving the goals of the treaty is Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) . These are the national climate pledges that each Party is required to develop and update every five years. NDCs articulate how each country will contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhance climate resilience. While NDCs include short- to medium-term targets, long-term low emission development strategies (LT-LEDS) are policy tools under the Paris Agreement through which countries must show how they plan to achieve carbon neutrality by mid-century. These strategies define a long-term vision that gives coherence and direction to shorter-term national climate targets.

Photo: Mucyo Serge/UNDP Rwanda

Photo: William Seal/UNDP Sudan
At the same time, the call for climate change mitigation has evolved into a call for reparative action, where high-income countries are urged to rectify past and ongoing contributions to the climate crisis. This approach reflects the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) which advocates for climate justice, recognizing the unequal historical responsibility for the climate crisis, emphasizing that wealthier countries, having profited from high-emission activities, bear a greater obligation to lead in mitigating these impacts. This includes not only reducing their own emissions, but also supporting vulnerable countries in their transition to low-emission development pathways.
Another critical aspect is ensuring a just transition for workers and communities that depend on the fossil fuel industry and its many connected industries. This process must prioritize social equity and create alternative employment opportunities as part of the shift towards renewable energy and more sustainable practices.
For emerging economies, innovation and advancements in technology have now demonstrated that robust economic growth can be achieved with clean, sustainable energy sources. By integrating renewable energy technologies such as solar, wind and geothermal power into their growth strategies, these economies can reduce their emissions, enhance energy security and create new economic opportunities and jobs. This shift not only contributes to global mitigation efforts but also sets a precedent for sustainable development.
What are some of the challenges slowing down climate change mitigation efforts?
Mitigating climate change is fraught with complexities, including the global economy's deep-rooted dependency on fossil fuels and the accompanying challenge of eliminating fossil fuel subsidies. This reliance – and the vested interests that have a stake in maintaining it – presents a significant barrier to transitioning to sustainable energy sources.
The shift towards decarbonization and renewable energy is driving increased demand for critical minerals such as copper, lithium, nickel, cobalt, and rare earth metals. Since new mining projects can take up to 15 years to yield output, mineral supply chains could become a bottleneck for decarbonization efforts. In addition, these minerals are predominantly found in a few, mostly low-income countries, which could heighten supply chain vulnerabilities and geopolitical tensions.
Furthermore, due to the significant demand for these minerals and the urgency of the energy transition, the scaled-up investment in the sector has the potential to exacerbate environmental degradation, economic and governance risks, and social inequalities, affecting the rights of Indigenous Peoples, local communities, and workers. Addressing these concerns necessitates implementing social and environmental safeguards, embracing circular economy principles, and establishing and enforcing responsible policies and regulations .
Agriculture is currently the largest driver of deforestation worldwide. A transformation in our food systems to reverse the impact that agriculture has on forests and biodiversity is undoubtedly a complex challenge. But it is also an important opportunity. The latest IPCC report highlights that adaptation and mitigation options related to land, water and food offer the greatest potential in responding to the climate crisis. Shifting to regenerative agricultural practices will not only ensure a healthy, fair and stable food supply for the world’s population, but also help to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Photo: UNDP India

Photo: Nino Zedginidze/UNDP Georgia
What are some examples of climate change mitigation?
In Mauritius , UNDP, with funding from the Green Climate Fund, has supported the government to install battery energy storage capacity that has enabled 50 MW of intermittent renewable energy to be connected to the grid, helping to avoid 81,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide annually.
In Indonesia , UNDP has been working with the government for over a decade to support sustainable palm oil production. In 2019, the country adopted a National Action Plan on Sustainable Palm Oil, which was collaboratively developed by government, industry and civil society representatives. The plan increased the adoption of practices to minimize the adverse social and environmental effects of palm oil production and to protect forests. Since 2015, 37 million tonnes of direct greenhouse gas emissions have been avoided and 824,000 hectares of land with high conservation value have been protected.
In Moldova and Paraguay , UNDP has helped set up Green City Labs that are helping build more sustainable cities. This is achieved by implementing urban land use and mobility planning, prioritizing energy efficiency in residential buildings, introducing low-carbon public transport, implementing resource-efficient waste management, and switching to renewable energy sources.
UNDP has supported the governments of Brazil, Costa Rica, Ecuador and Indonesia to implement results-based payments through the REDD+ (Reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation in developing countries) framework. These include payments for environmental services and community forest management programmes that channel international climate finance resources to local actors on the ground, specifically forest communities and Indigenous Peoples.
UNDP is also supporting small island developing states like the Comoros to invest in renewable energy and sustainable infrastructure. Through the Africa Minigrids Program , solar minigrids will be installed in two priority communities, Grand Comore and Moheli, providing energy access through distributed renewable energy solutions to those hardest to reach.
And in South Africa , a UNDP initative to boost energy efficiency awareness among the general population and improve labelling standards has taken over commercial shopping malls.

What is UNDP’s role in supporting climate change mitigation?
UNDP aims to assist countries with their climate change mitigation efforts, guiding them towards sustainable, low-carbon and climate-resilient development. This support is in line with achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those related to affordable and clean energy (SDG7), sustainable cities and communities (SDG11), and climate action (SDG13). Specifically, UNDP’s offer of support includes developing and improving legislation and policy, standards and regulations, capacity building, knowledge dissemination, and financial mobilization for countries to pilot and scale-up mitigation solutions such as renewable energy projects, energy efficiency initiatives and sustainable land-use practices.
With financial support from the Global Environment Facility and the Green Climate Fund, UNDP has an active portfolio of 94 climate change mitigation projects in 69 countries. These initiatives are not only aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, but also at contributing to sustainable and resilient development pathways.
Explore More Stories
Pacific shores, solar solutions: harnessing renewable energy in the pacific islands.

Photo: Yuichi Ishida/UNDP Timor-Leste
West Africa has great potential for solar energy. It’s time to release it.
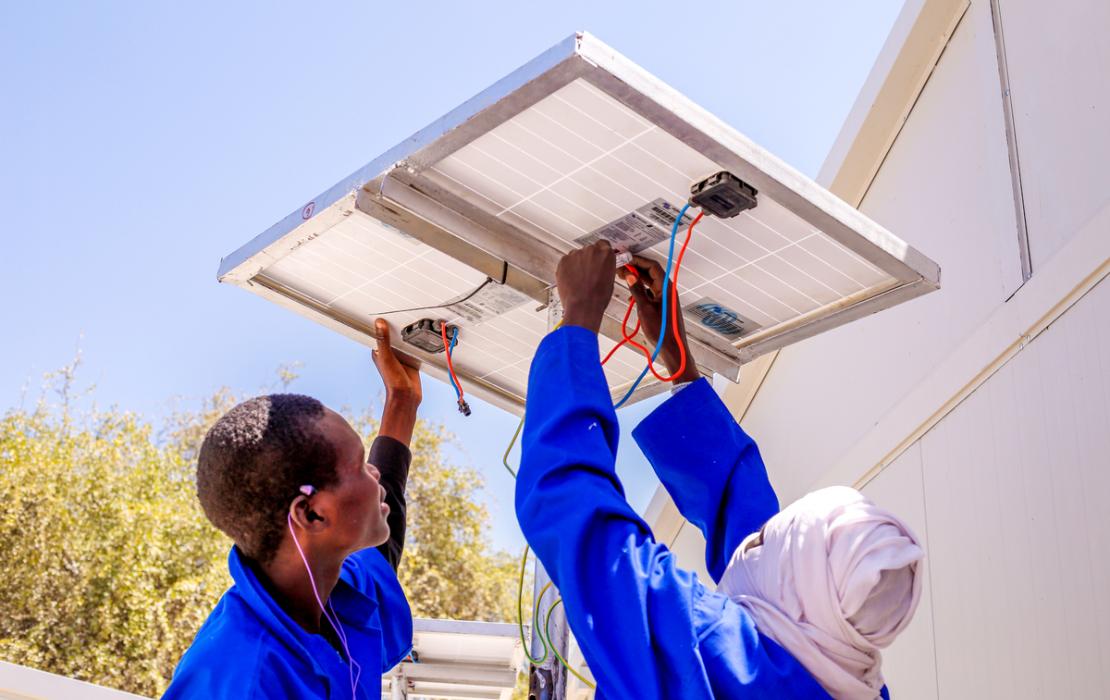

Photo: UNDP Niger
Electric vehicles are driving a greener future in Viet Nam

Ho Tuan Anh delivers goods with his new e-motorbike. Photo by: Phan Huong Giang/UNDP Viet Nam
Why the Western Balkans are choosing decarbonization

Photo: UNDP Bosnia and Herzegovina
Six lessons on how to achieve future-smart energy efficient buildings
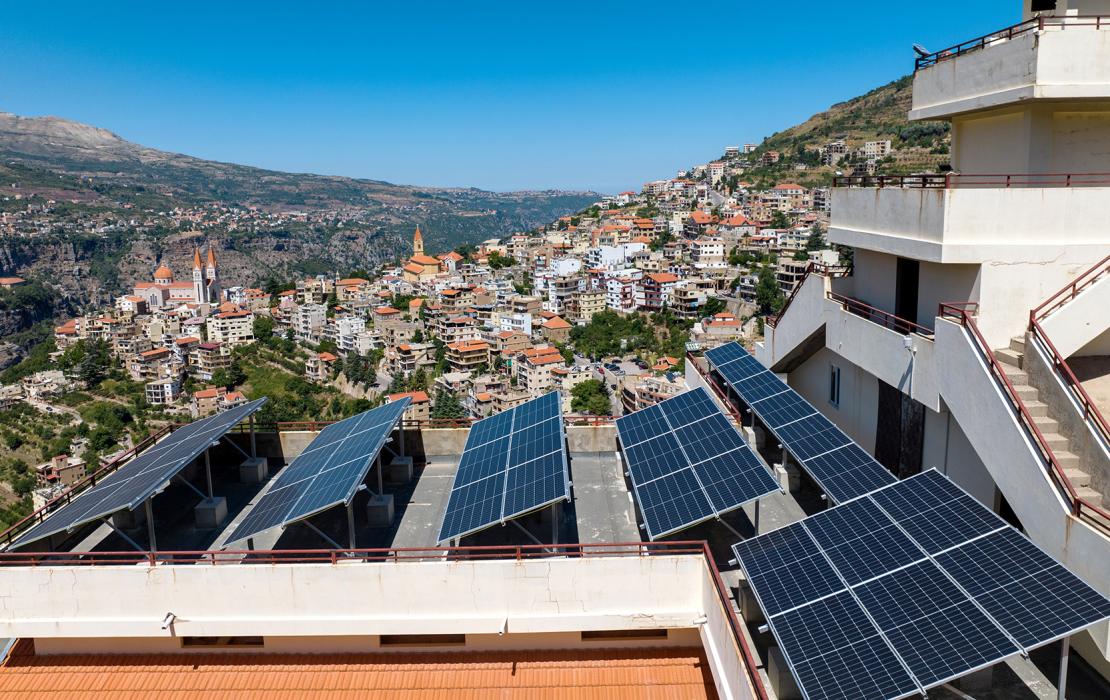

Solar photovoltaic systems on roofs in Lebanon. Photo: Fouad Choufany / UNDP Lebanon
Six ways to achieve sustainable energy for all
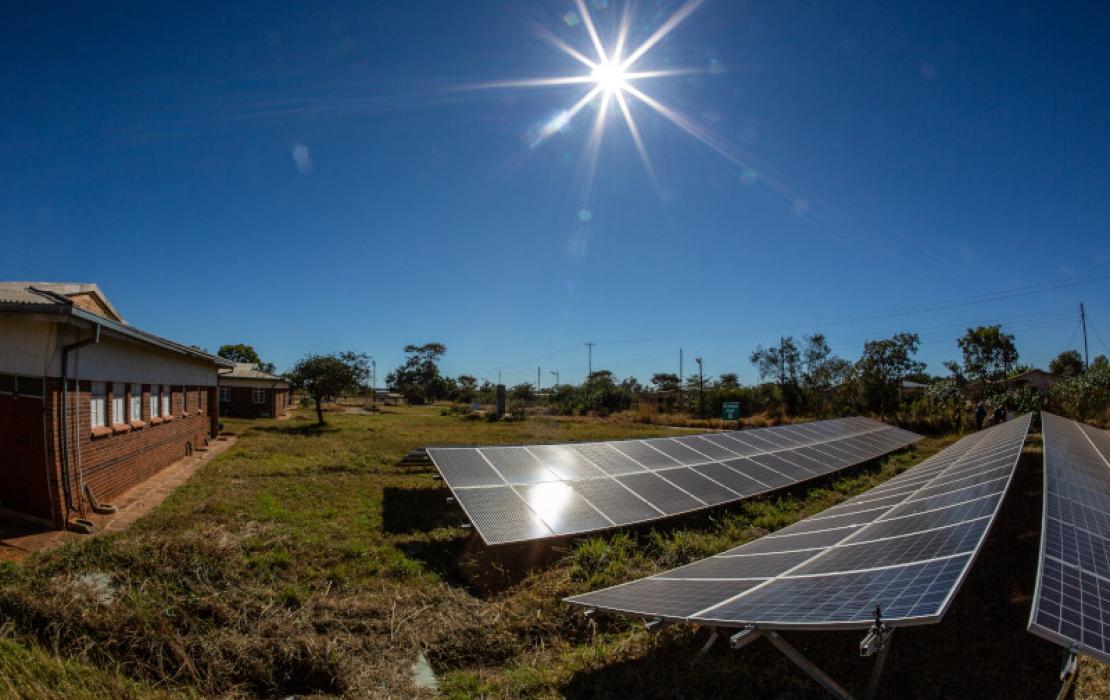

Photo: UNDP Zimbabwe

Global Warming Definition, Causes, Effects, Impacts, Solutions
Global Warming is a long-term increase in average global temperature. Read about Global Warming Definition, Causes, Effects, Impact on Climate Change & Solutions for the UPSC exam.

Table of Contents
What is Global Warming?
Global Warming is a long-term increase in average global temperature. It is considered a natural phenomenon, but anthropogenic activities on earth, particularly post Industrial Revolution , have led to an increase in the rate of this temperature increase. Various Reports published by the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) have time and again highlighted that since 1850 human activities have led to an increase of about 1 degree Celsius in average global temperature. Most of this warming has taken place in the second half of the 20th century. The fact that 5 of the hottest recorded year have occurred since 2015 can help us better understand the calamitous impact of anthropogenic activities.
Global Warming Causes
Green House Gases also known as GHGs in the atmosphere trap the solar radiations that are reflected by the earth’s surface. Under normal circumstances, most of these radiations escape into outer space. However, the release of GHGs by anthropogenic activities has increased their concentration in the atmosphere. Thus, the earth is getting hotter and hotter.
Some of the common GHGs include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons, and water vapour, among others. The global warming potential of each GHG is different. For example, methane has a 25-time warming potential than carbon dioxide. Similarly, nitrous oxide has more than 250 times the warming potential than carbon dioxide. The top anthropogenic activities that are responsible for the release of GHGs are shown below.
Global Warming and Green House Effect
Both phenomena are related to each other. Green House Gases also known as GHGs in the atmosphere trap the solar radiations that are reflected by the earth’s surface. Under normal circumstances, most of these radiations escape into outer space. However, the release of GHGs by anthropogenic activities has increased their concentration in the atmosphere. This is the primary cause of Global Warming .
Global Warming Effects
Increase in the average temperature of the earth.
According to IPCC reports, human-induced global warming is responsible for nearly 1 degree Celsius temperature rise vis a vis pre-industrial level. Data from NASA suggest that 2016 has been the hottest year on record.
Frequency of Extreme Weather Events is Increasing
Across the globe, extreme weather events have increased in occurrence. For example, forest fires in California have become an annual event. Also, it is increasing in frequency each year. Most recently, we have recorded the phenomena of heat waves in Antarctica. The intensity of cyclones in the Bay of Bengal region has increased. Similarly, the frequency of occurrence of El Niño and La Niña has reduced from once in 8–10 years to once in 3–4 years now. More frequent episodes of floods and drought are being recorded every year across the world.
Melting of Ice
According to IPCC, there is 10% less permafrost in North Hemisphere at present compared to the 1900s. Remote sensing data suggest Arctic ice is melting fast. Experts suggest that not only will the sea level rise with the melting of glaciers, but there is also a danger of new bacteria and viruses being released into the environment which has so far been trapped in ice sheets. This may lead to outbreaks of disease and pandemics which are beyond the control of human medical sciences.
Sea Level Rise and Acidification of Ocean
A report published by WMO, suggests that the rate of sea level rise has doubled for the period between 2013 and 2021 compared to the rate for the period between 1993 and 2002. Earth scientists are suggesting that if this phenomenon continues, many human-inhabited coastal areas will be submerged into the sea in the coming decades. Also, with the concentration of carbon dioxide rising in the atmosphere, oceans are absorbing more of it. This is leading to ocean acidification. The impact of this phenomenon can be disastrous for ocean biodiversity, particularly the coral reefs.
Adverse Impact on Terrestrial Ecosystems of the Earth
It has been recorded that many flora and fauna species are heading northwards in Northern Hemisphere. Significant changes have been observed in the migratory movements of birds across the world. Early arrival to their summer feeding and breeding grounds is quite evident. Expert biologists suggest that rising temperatures in the tropical and subtropical regions may lead to an outbreak of new diseases, which in turn may render many floral and faunal species extinct.
Social and Economic Impact
A rising number of extreme weather events will have an adverse impact on agriculture and fisheries. Rising global temperatures will have a negative impact on the productivity of human beings, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions of the earth. The impact on life and livelihoods of indigenous people across the world will be even more pronounced.
Global Warming Solutions
Global cooperation for reduction of emissions.
It is time that the target of containing the global average temperature rise within 1.5 degrees Celsius of pre-industrial levels is taken seriously. Also, global efforts should be based on a spirit of Common But Differentiated Responsibility. This will ensure that historical injustices done to the global south are duly acknowledged, and they have an equal chance to transform themselves into developed countries. Countries must act proactively to achieve Net Zero Emission status at the earliest.
Transition to Cleaner and Greener Forms of Energy
Thermal power plants based on coal should be made more efficient and inefficient ones should be phased off. Also, mass adoption of renewable forms of energy like solar should be promoted. Similarly, avenues for using hydrogen as energy fuel should be looked into. We must also explore the possibility of Nuclear fusion for energy generation, in addition to making nuclear fission-based energy generation safer.
Changes in Agricultural Practices and Land Use
Agriculture based on the use of nitrogenous fertilizers must be replaced with organic farming techniques. Also, methane gas released from agricultural and cattle waste must be trapped as biogas for domestic usage. Massive afforestation drives must be organized. Urban governments must make it a point to include green spaces in urban planning.
Improving Transportation System
The advent of E-vehicles is a welcome change, but we need to make the batteries used in these vehicles more efficient. Urban planners must make public transportation systems inherent as a benchmark of good urban planning. Also, urban planning should be such that it promotes more walking and cycling habits among the residents.
Behavioural Changes
All the above discussions will have no meaning if we as individuals are not sensitive enough. We need to make reducing, reusing and recycling a mantra of our living. It should be our civic duty to save water, and wildlife and raise awareness among others.
Solar Geoengineering
Solar geoengineering, a proposed climate intervention method, aims to counteract global warming by reflecting a portion of the sun’s rays back into space. One prominent approach involves injecting substances like sulphur dioxide into the upper atmosphere to create reflective aerosols. These particles can scatter sunlight, reducing the Earth’s temperature. However, solar geoengineering is a topic of debate, with concerns about its side effects, such as disrupted weather patterns and potential geopolitical risks. Research in this field is ongoing, but it remains a theoretical concept with limited practical implementation.
Can Solar Geoengineering Halt Global Warming?
Solar geoengineering, specifically solar radiation management (SRM), is under scrutiny as a potential method to mitigate global warming. SRM involves reflecting sunlight away from Earth, often by injecting substances like sulphur dioxide into the upper atmosphere to create reflective aerosols. However, its effectiveness remains a subject of debate, with concerns about potential side effects and ethical implications. While research in this field is ongoing, solar geoengineering is currently in a theoretical stage, with limited practical implementation.
Global Warming Conclusion
It is rightly said that “Charity begins at home.” Climate action will be more efficient if we go by this spirit. To begin with, each individual can make sure that what is happening in their house and immediate surroundings is in harmony with the environment. If this can happen, all the policies we are making at the local, national, regional and global levels will give far better results.
Global Warming UPSC
Each year, we read about rising global temperatures. Also, catching the headlines is the news related to disasters caused by events like cyclones, forest fires, floods and drought. All these phenomena can be attributed to one single cause which is global warming.
Global Warming is a long-term increase in average global temperature. It is considered a natural phenomenon, but anthropogenic activities on earth, particularly post-Industrial Revolution, have led to an increase in the rate of this temperature increase.
Sharing is caring!
Why is global warming a problem?
Global Warming at present rate can lead to disastrous impacts like rising sea level, out break of new diseases, extreme weather events among others.
What are 3 causes of global warming?
Human induced green house gas emission due to activities like agriculture, industrial emissions, transportation are the top 3 causes of global warming.
What are 5 effects of global warming?
Rising sea level, out break of new diseases, extreme weather events, changes in biodiversity and melting of glaciers are top 5 effects of global warming.
Why global warming is important?
Global warming at its natural rate is important to keep up the temperature of earth within the range that makes it habitable. This makes global warming important.
Can we control global warming?
Number of mitigation measures like shifting to cleaning forms of energy and transportation can be taken to control global warming.
Who help with global warming?
Global Warming is a collective challenge for entire humanity. Citizens, civil societies, governments and businesses must act in unison to address it.
I, Sakshi Gupta, am a content writer to empower students aiming for UPSC, PSC, and other competitive exams. My objective is to provide clear, concise, and informative content that caters to your exam preparation needs. I strive to make my content not only informative but also engaging, keeping you motivated throughout your journey!

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- UPSC Online Coaching
- UPSC Exam 2024
- UPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Mains Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPSC Age Limit 2024
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- UPSC Syllabus in Hindi
- UPSC Full Form

Recent Posts
- UPPSC Exam 2024
- UPPSC Calendar
- UPPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPPSC Application Form 2024
- UPPSC Eligibility Criteria 2024
- UPPSC Admit card 2024
- UPPSC Salary And Posts
- UPPSC Cut Off
- UPPSC Previous Year Paper
BPSC Exam 2024
- BPSC 70th Notification
- BPSC 69th Exam Analysis
- BPSC Admit Card
- BPSC Syllabus
- BPSC Exam Pattern
- BPSC Cut Off
- BPSC Question Papers
IB ACIO Exam
- IB ACIO Salary
- IB ACIO Syllabus
CSIR SO ASO Exam
- CSIR SO ASO Exam 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Result 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date
- CSIR SO ASO Question Paper
- CSIR SO ASO Answer key 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Syllabus 2024
Study Material Categories
- Daily The Hindu Analysis
- Daily Practice Quiz for Prelims
- Daily Answer Writing
- Daily Current Affairs
- Indian Polity
- Environment and Ecology
- Art and Culture
- General Knowledge
- Biographies
IMPORTANT EXAMS

- Terms & Conditions
- Return & Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Environmental Changes Are Fueling Human, Animal and Plant Diseases, Study Finds
Biodiversity loss, global warming, pollution and the spread of invasive species are making infectious diseases more dangerous to organisms around the world.

By Emily Anthes
Several large-scale, human-driven changes to the planet — including climate change, the loss of biodiversity and the spread of invasive species — are making infectious diseases more dangerous to people, animals and plants, according to a new study.
Scientists have documented these effects before in more targeted studies that have focused on specific diseases and ecosystems. For instance, they have found that a warming climate may be helping malaria expand in Africa and that a decline in wildlife diversity may be boosting Lyme disease cases in North America.
But the new research, a meta-analysis of nearly 1,000 previous studies, suggests that these patterns are relatively consistent around the globe and across the tree of life.
“It’s a big step forward in the science,” said Colin Carlson, a biologist at Georgetown University, who was not an author of the new analysis. “This paper is one of the strongest pieces of evidence that I think has been published that shows how important it is health systems start getting ready to exist in a world with climate change, with biodiversity loss.”
In what is likely to come as a more surprising finding, the researchers also found that urbanization decreased the risk of infectious disease.
The new analysis, which was published in Nature on Wednesday, focused on five “global change drivers” that are altering ecosystems across the planet: biodiversity change, climate change, chemical pollution, the introduction of nonnative species and habitat loss or change.
The researchers compiled data from scientific papers that examined how at least one of these factors affected various infectious-disease outcomes, such as severity or prevalence. The final data set included nearly 3,000 observations on disease risks for humans, animals and plants on every continent except for Antarctica.
The researchers found that, across the board, four of the five trends they studied — biodiversity change, the introduction of new species, climate change and chemical pollution — tended to increase disease risk.
“It means that we’re likely picking up general biological patterns,” said Jason Rohr, an infectious disease ecologist at the University of Notre Dame and senior author of the study. “It suggests that there are similar sorts of mechanisms and processes that are likely occurring in plants, animals and humans.”
The loss of biodiversity played an especially large role in driving up disease risk, the researchers found. Many scientists have posited that biodiversity can protect against disease through a phenomenon known as the dilution effect.
The theory holds that parasites and pathogens, which rely on having abundant hosts in order to survive, will evolve to favor species that are common, rather than those that are rare, Dr. Rohr said. And as biodiversity declines, rare species tend to disappear first. “That means that the species that remain are the competent ones, the ones that are really good at transmitting disease,” he said.
Lyme disease is one oft-cited example. White-footed mice, which are the primary reservoir for the disease, have become more dominant on the landscape, as other rarer mammals have disappeared, Dr. Rohr said. That shift may partly explain why Lyme disease rates have risen in the United States. (The extent to which the dilution effect contributes to Lyme disease risk has been the subject of debate, and other factors, including climate change, are likely to be at play as well.)
Other environmental changes could amplify disease risks in a wide variety of ways. For instance, introduced species can bring new pathogens with them, and chemical pollution can stress organisms’ immune systems. Climate change can alter animal movements and habitats, bringing new species into contact and allowing them to swap pathogens .
Notably, the fifth global environmental change that the researchers studied — habitat loss or change — appeared to reduce disease risk. At first glance, the findings might appear to be at odds with previous studies, which have shown that deforestation can increase the risk of diseases ranging from malaria to Ebola. But the overall trend toward reduced risk was driven by one specific type of habitat change: increasing urbanization.
The reason may be that urban areas often have better sanitation and public health infrastructure than rural ones — or simply because there are fewer plants and animals to serve as disease hosts in urban areas. The lack of plant and animal life is “not a good thing,” Dr. Carlson said. “And it also doesn’t mean that the animals that are in the cities are healthier.”
And the new study does not negate the idea that forest loss can fuel disease; instead, deforestation increases risk in some circumstances and reduces it in others, Dr. Rohr said.
Indeed, although this kind of meta-analysis is valuable for revealing broad patterns, it can obscure some of the nuances and exceptions that are important for managing specific diseases and ecosystems, Dr. Carlson noted.
Moreover, most of the studies included in the analysis examined just a single global change drive. But, in the real world, organisms are contending with many of these stressors simultaneously. “The next step is to better understand the connections among them,” Dr. Rohr said.
Emily Anthes is a science reporter, writing primarily about animal health and science. She also covered the coronavirus pandemic. More about Emily Anthes
Explore the Animal Kingdom
A selection of quirky, intriguing and surprising discoveries about animal life..
Scientists say they have found an “alphabet” in the songs of sperm whales , raising the possibility that the animals are communicating in a complex language.
Indigenous rangers in Australia’s Western Desert got a rare close-up with the northern marsupial mole , which is tiny, light-colored and blind, and almost never comes to the surface.
For the first time, scientists observed a primate in the wild treating a wound with a plant that has medicinal properties.
A new study resets the timing for the emergence of bioluminescence back to millions of years earlier than previously thought.
Scientists are making computer models to better understand how cicadas emerge collectively after more than a decade underground .

TrendyDigests
Global Warming Myth Debunked: No Pause Since 1998, Earth Continues to Heat Up
Posted: May 14, 2024 | Last updated: May 14, 2024

The notion that global warming ceased after the climatic peak of 1998 has circulated for years among climate change deniers.

However, this myth has been thoroughly debunked by the scientific community, and the reality is that the planet continues to warm at an alarming rate.

In 1998, the world experienced an exceptional rise in temperatures due to an intense El Niño event. This naturally occurring climate pattern led to the spread of misinformation that global warming had halted.

However, the misrepresentation of data, focusing on short-term trends, fails to acknowledge the ongoing long-term warming trend.

The evidence is irrefutable; the years following 1998 have been markedly warmer.

For instance, "the top ten warmest years have all been since 2010," with eight of those years occurring between 2015 and 2023. The myth of a warming pause has been further eroded by recent years’ record-breaking temperatures.

One must differentiate between weather, which is short-term and climate, the long-term accumulation of atmospheric data. The continuous elevation in global temperatures is indicative of climate change, not temporary weather patterns.
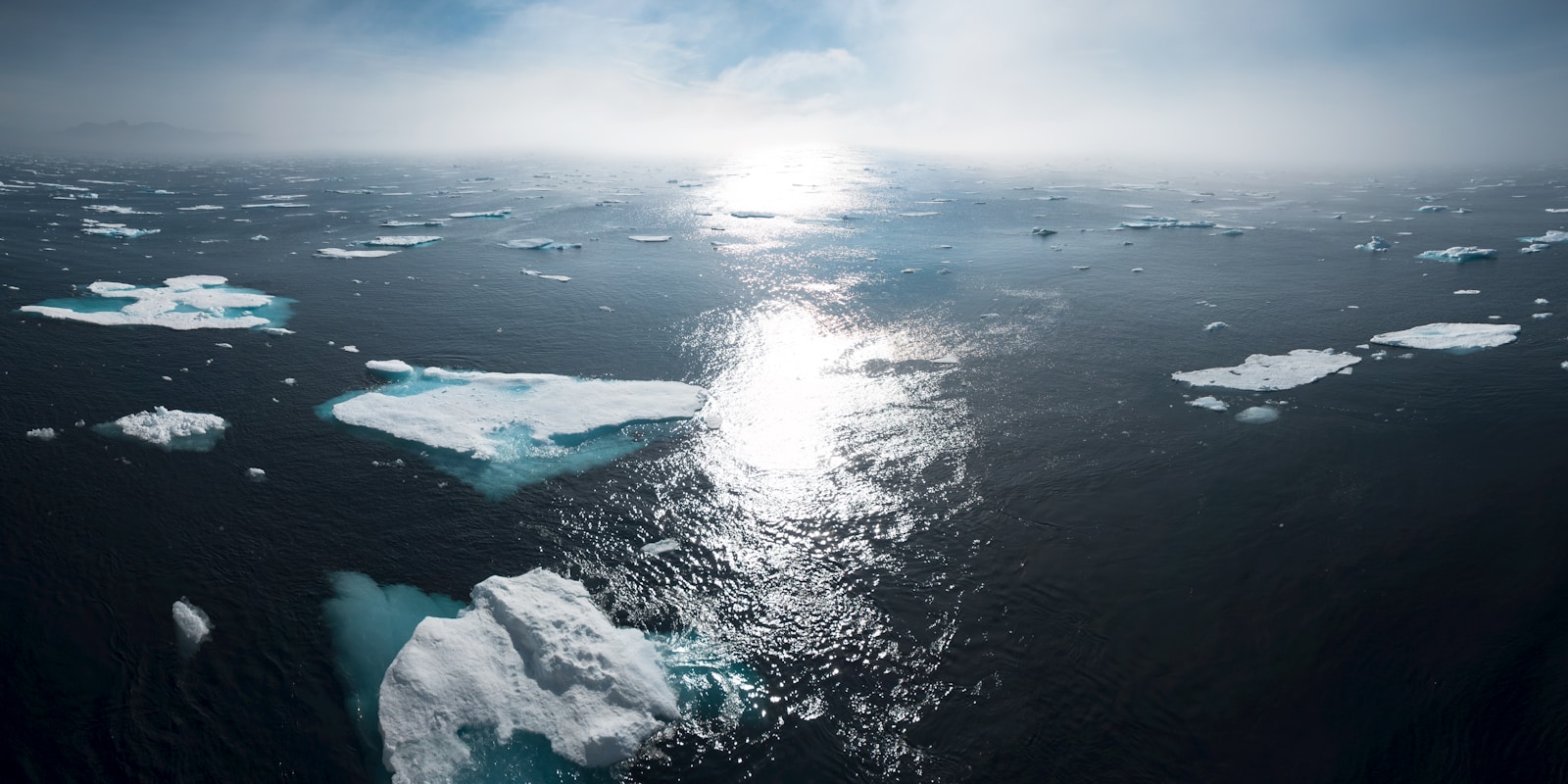

The 1998 spike was an anomaly superimposed on a persistent warming trend caused by human activities. This is further supported by the fact that more than 90% of global warming heat is absorbed by the oceans, which have shown a steady increase in temperature since well before 1998.

The Earth’s climate system has not been driven solely by CO2 levels; year-to-year variability often results from natural events like El Niño and La Niña.

These phenomena cause short-term impacts on global temperatures but do not alter the long-term warming trend. "Attributing these short-term peaks or lulls to a halt in global warming is nothing more than cherry-picking data," a practice that ignores comprehensive trends.

Global land and ocean temperature records and satellite data all confirm that the climate continues to warm. The oceans, which absorb most of the heat trapped by greenhouse gases, have reached record temperatures, reinforcing the reality of ongoing global warming.

Furthermore, climate models have accurately simulated observed temperatures, dispelling notions that recent warmer or cooler years deviate from the expected range of variability. The Earth's warming since the industrial revolution is a consequence of increased greenhouse gases and cannot be explained solely by natural variability.

Contrary to the misleading claims that temperatures have flatlined, the last eight years have been unusually warm, exceeding 1.2C above pre-industrial levels. This stands as a testament to the continued effect of human emissions on the planet's climate.
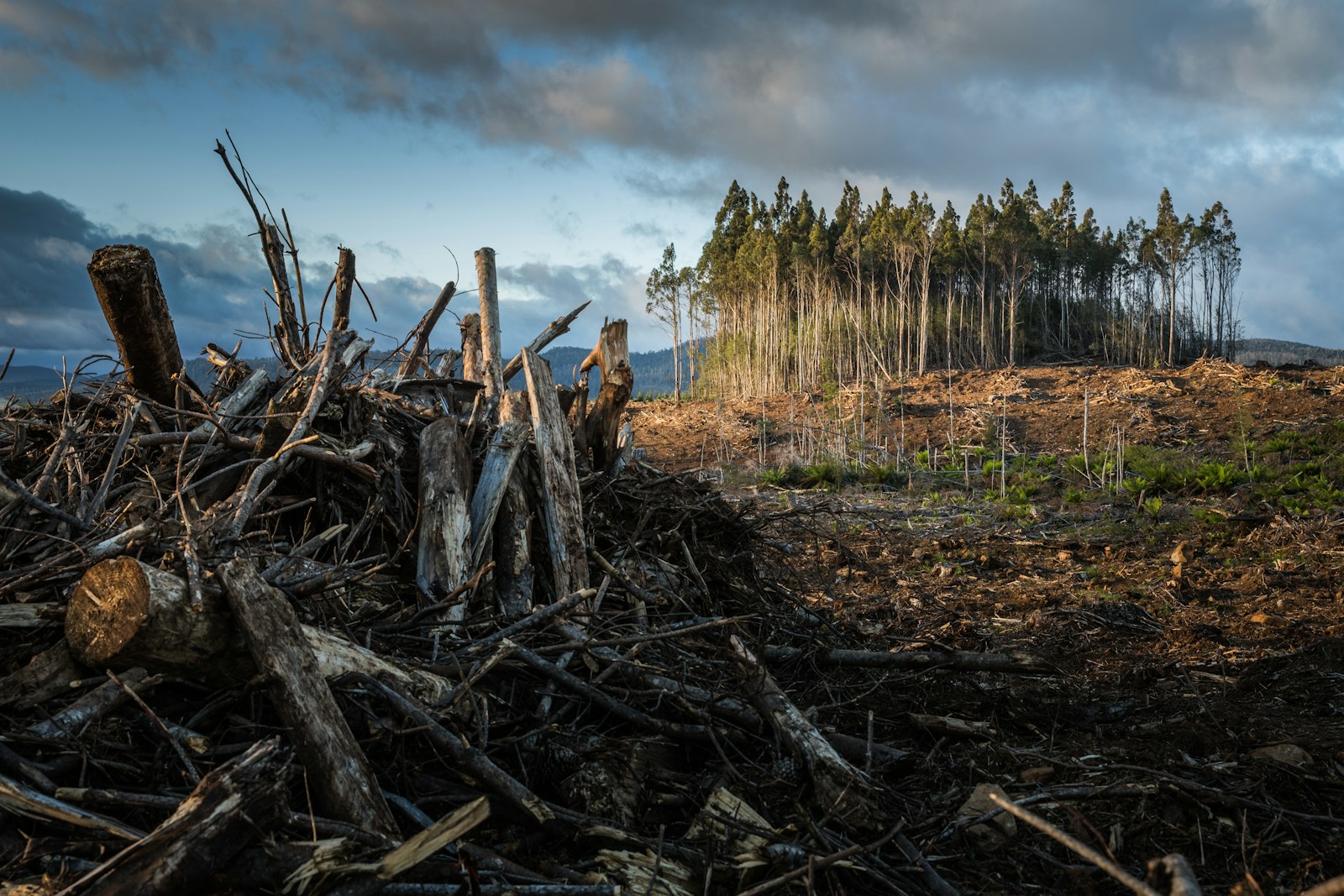

In conclusion, global warming has not paused since 1998. Instead, Earth's climate system is experiencing a persistent rise in temperatures, a situation exacerbated by human-induced factors.

The myth of a warming hiatus is a stark reminder to critically assess the data and beware of selective statistics that ignore the broader context of climate science.
Relevant articles: - What has global warming done since 1998? , Skeptical Science - Global Warming Stopped in 1998 , OSS Foundation - Annual 1998 Global Climate Report , National Centers for Environmental Information (.gov) - Factcheck: No, global warming has not ‘paused’ over the past eight years , Carbon Brief
More for You
Donald Trump Suffers Huge Vote Against Him In Maryland, Nebraska
Suspect who randomly attacked actor Steve Buscemi in broad daylight identified by NYPD: report
Doctor shares what happens to our bodies moments before we die
15 Jobs That Pay Insanely Well
The backbone of America’s economy was just dealt a serious blow
Radish Greens Are Totally Edible. Here's How To Prepare Them
King County Raises Minimum Wage to Highest Level In the Country
E. Jean Carroll, who won $83 million from Donald Trump, says he will lose the 2024 election
The 5 most common deathbed regrets, according to a palliative care nurse
‘A dangerous precedent’: Hawaii property owner left stunned after $500K home was mistakenly built on her Paradise Park lot. Now she’s being sued
Retired But Want To Work? Try These 8 Jobs for Seniors That Pay Weekly
The 16 worst-paying college majors, five years after graduation
This Is Our Most Popular Soup Recipe of All Time
This type of supplement may increase heart disease risk, new study finds
Trump trial ends with 'f-bombs': Cohen pressed in tirades against 'mob boss Trump'
Cheryl Strayed on Her New Sober-ish Life
Cancelled show becomes one of Netflix’s biggest hits
This is the salary it takes to be considered rich in every state
14 Mistakes Almost Everyone Makes With Scallops
Dad who sacrificed his savings to pay for son's college calls student loan forgiveness a 'bitter pill'
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
The huge solar storm is keeping power grid and satellite operators on edge

Geoff Brumfiel
Willem Marx

NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of solar flares early Saturday afternoon. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration says there have been measurable effects and impacts from the geomagnetic storm. Solar Dynamics Observatory hide caption
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of solar flares early Saturday afternoon. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration says there have been measurable effects and impacts from the geomagnetic storm.
Planet Earth is getting rocked by the biggest solar storm in decades – and the potential effects have those people in charge of power grids, communications systems and satellites on edge.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration says there have been measurable effects and impacts from the geomagnetic storm that has been visible as aurora across vast swathes of the Northern Hemisphere. So far though, NOAA has seen no reports of major damage.

The Picture Show
Photos: see the northern lights from rare, solar storm.
There has been some degradation and loss to communication systems that rely on high-frequency radio waves, NOAA told NPR, as well as some preliminary indications of irregularities in power systems.
"Simply put, the power grid operators have been busy since yesterday working to keep proper, regulated current flowing without disruption," said Shawn Dahl, service coordinator for the Boulder, Co.-based Space Weather Prediction Center at NOAA.
NOAA Issues First Severe Geomagnetic Storm Watch Since 2005

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
- Amazon Music
- Amazon Alexa
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
"Satellite operators are also busy monitoring spacecraft health due to the S1-S2 storm taking place along with the severe-extreme geomagnetic storm that continues even now," Dahl added, saying some GPS systems have struggled to lock locations and offered incorrect positions.
NOAA's GOES-16 satellite captured a flare erupting occurred around 2 p.m. EDT on May 9, 2024.
As NOAA had warned late Friday, the Earth has been experiencing a G5, or "Extreme," geomagnetic storm . It's the first G5 storm to hit the planet since 2003, when a similar event temporarily knocked out power in part of Sweden and damaged electrical transformers in South Africa.
The NOAA center predicted that this current storm could induce auroras visible as far south as Northern California and Alabama.
Extreme (G5) geomagnetic conditions have been observed! pic.twitter.com/qLsC8GbWus — NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center (@NWSSWPC) May 10, 2024
Around the world on social media, posters put up photos of bright auroras visible in Russia , Scandinavia , the United Kingdom and continental Europe . Some reported seeing the aurora as far south as Mallorca, Spain .
The source of the solar storm is a cluster of sunspots on the sun's surface that is 17 times the diameter of the Earth. The spots are filled with tangled magnetic fields that can act as slingshots, throwing huge quantities of charged particles towards our planet. These events, known as coronal mass ejections, become more common during the peak of the Sun's 11-year solar cycle.
A powerful solar storm is bringing northern lights to unusual places
Usually, they miss the Earth, but this time, NOAA says several have headed directly toward our planet, and the agency predicted that several waves of flares will continue to slam into the Earth over the next few days.
While the storm has proven to be large, predicting the effects from such incidents can be difficult, Dahl said.
Shocking problems
The most disruptive solar storm ever recorded came in 1859. Known as the "Carrington Event," it generated shimmering auroras that were visible as far south as Mexico and Hawaii. It also fried telegraph systems throughout Europe and North America.

Stronger activity on the sun could bring more displays of the northern lights in 2024
While this geomagnetic storm will not be as strong, the world has grown more reliant on electronics and electrical systems. Depending on the orientation of the storm's magnetic field, it could induce unexpected electrical currents in long-distance power lines — those currents could cause safety systems to flip, triggering temporary power outages in some areas.
my cat just experienced the aurora borealis, one of the world's most radiant natural phenomena... and she doesn't care pic.twitter.com/Ee74FpWHFm — PJ (@kickthepj) May 10, 2024
The storm is also likely to disrupt the ionosphere, a section of Earth's atmosphere filled with charged particles. Some long-distance radio transmissions use the ionosphere to "bounce" signals around the globe, and those signals will likely be disrupted. The particles may also refract and otherwise scramble signals from the global positioning system, according to Rob Steenburgh, a space scientist with NOAA. Those effects can linger for a few days after the storm.
Like Dahl, Steenburgh said it's unclear just how bad the disruptions will be. While we are more dependent than ever on GPS, there are also more satellites in orbit. Moreover, the anomalies from the storm are constantly shifting through the ionosphere like ripples in a pool. "Outages, with any luck, should not be prolonged," Steenburgh said.

What Causes The Northern Lights? Scientists Finally Know For Sure
The radiation from the storm could have other undesirable effects. At high altitudes, it could damage satellites, while at low altitudes, it's likely to increase atmospheric drag, causing some satellites to sink toward the Earth.
The changes to orbits wreak havoc, warns Tuija Pulkkinen, chair of the department of climate and space sciences at the University of Michigan. Since the last solar maximum, companies such as SpaceX have launched thousands of satellites into low Earth orbit. Those satellites will now see their orbits unexpectedly changed.
"There's a lot of companies that haven't seen these kind of space weather effects before," she says.
The International Space Station lies within Earth's magnetosphere, so its astronauts should be mostly protected, Steenburgh says.
In a statement, NASA said that astronauts would not take additional measures to protect themselves. "NASA completed a thorough analysis of recent space weather activity and determined it posed no risk to the crew aboard the International Space Station and no additional precautionary measures are needed," the agency said late Friday.

People visit St Mary's lighthouse in Whitley Bay to see the aurora borealis on Friday in Whitley Bay, England. Ian Forsyth/Getty Images hide caption
People visit St Mary's lighthouse in Whitley Bay to see the aurora borealis on Friday in Whitley Bay, England.
While this storm will undoubtedly keep satellite operators and utilities busy over the next few days, individuals don't really need to do much to get ready.
"As far as what the general public should be doing, hopefully they're not having to do anything," Dahl said. "Weather permitting, they may be visible again tonight." He advised that the largest problem could be a brief blackout, so keeping some flashlights and a radio handy might prove helpful.
I took these photos near Ranfurly in Central Otago, New Zealand. Anyone can use them please spread far and wide. :-) https://t.co/NUWpLiqY2S — Dr Andrew Dickson reform/ACC (@AndrewDickson13) May 10, 2024
And don't forget to go outside and look up, adds Steenburgh. This event's aurora is visible much further south than usual.
A faint aurora can be detected by a modern cell phone camera, he adds, so even if you can't see it with your eyes, try taking a photo of the sky.
The aurora "is really the gift from space weather," he says.
- space weather
- solar flares
- solar storm
The Rise and Impact of Nazi Ideology on Global History
This essay about the rise and impact of Nazi ideology examines how Adolf Hitler’s regime, from 1933 to 1945, utilized extreme beliefs of racial purity and national superiority to seize and maintain control in Germany. It discusses the origins of these ideas in the post-World War I era, highlighting how economic and social unrest were exploited to foster xenophobia and nationalism. The essay further explores the devastating consequences of these ideologies, including the Holocaust and World War II. It also looks at the Nazi influence on German culture and economy, and the international aftermath, such as the establishment of the United Nations and the Nuremberg Trials. The essay concludes by reflecting on the historical lessons of Nazi Germany, emphasizing the importance of upholding human dignity and opposing extremism to prevent similar atrocities.
How it works
Adolf Hitler oversaw the Nazi system from 1933 to 1945, and it is widely regarded as one of the cruelest and most destructive forces in contemporary history. Its effects, which were mostly caused by radical ideas of national superiority and racial purity, have reverberated through decades in both painful memories and profound lessons.
The origins of Nazi ideology can be discovered in the turbulent years following World War I, when Germany was overcome by social unrest, national humiliation, and economic hardship. Widespread unrest was sparked by the Treaty of Versailles, which forced Germany to pay heavy reparations.
Hitler’s ascent to power and the growth of his National Socialist German Workers’ Party (NSDAP) were made possible by this unsettling time. Hitler manipulated public opinion to grab power by promising to restore Germany to its former greatness and placing the blame for the country’s misery on minorities like Jews, Romani people, and others.
Central to Nazi belief was the notion of an “Aryan master race,” a racially defined group of Northern European descent, supposedly superior in biology and destined to rule. This pseudoscientific racial theory was propagated through aggressive propaganda and education, aiming to indoctrinate the German populace into fervent nationalism and xenophobia. The Nazis’ emphasis on racial purity led to the heinous Holocaust, where six million Jews, along with millions of others deemed undesirable, were systematically exterminated in concentration camps.
Economically, the Nazi regime undertook massive rearmament programs and state-controlled initiatives to eradicate unemployment. These policies, although temporarily stabilizing the economy and reducing unemployment, were inherently linked to militaristic expansionism. The remilitarization of the Rhineland, the annexation of Austria, and the invasion of Poland were all steps that precipitated World War II, a conflict that would eventually claim more lives and cause more destruction than any other war in human history.
Culturally, the Nazis sought to reshape German society. The arts and media were censored and aligned with Nazi ideologies, suppressing all forms of dissent and promoting the glorification of the regime. Music, literature, and films were co-opted to serve the state’s propaganda needs, often portraying the Nazis as Germany’s saviors and champions of a better future.
The international ramifications of Nazi Germany were profound. The aggressive expansionist policy and the ideology of racial superiority led to the reshaping of international borders and the realignment of global powers. The repercussions of Nazi actions prompted the establishment of the United Nations, designed to prevent such atrocities from ever recurring. The Nuremberg Trials, where key Nazi officials were prosecuted, set precedents in international law, particularly concerning war crimes and crimes against humanity.
In the aftermath of the Nazi regime’s fall, Germany was left in ruins, divided into East and West during the Cold War, and burdened with the moral and physical reconstruction of a society misled by tyrannical rule. The process of denazification was initiated by the Allied powers to purge German and Austrian society, culture, press, economy, judiciary, and politics of any remnants of the National Socialist ideology.
Today, the study of Nazi Germany serves as a grim reminder of the dangers posed by extremist ideologies and unchecked power. It highlights the importance of vigilance and responsibility in democratic societies to prevent the recurrence of such dark chapters in human history. Moreover, it teaches the value of cultural diversity and human rights, underscoring the catastrophic consequences when these principles are abandoned.
In reflecting on the era of Nazi Germany, we not only contemplate the depths of human cruelty but also recognize the resilient spirit of those who survived and the lessons they imparted. Such reflections are crucial for fostering a world that upholds human dignity and opposes tyranny in all its forms.
Cite this page
The Rise and Impact of Nazi Ideology on Global History. (2024, May 12). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-rise-and-impact-of-nazi-ideology-on-global-history/
"The Rise and Impact of Nazi Ideology on Global History." PapersOwl.com , 12 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-rise-and-impact-of-nazi-ideology-on-global-history/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Rise and Impact of Nazi Ideology on Global History . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-rise-and-impact-of-nazi-ideology-on-global-history/ [Accessed: 15 May. 2024]
"The Rise and Impact of Nazi Ideology on Global History." PapersOwl.com, May 12, 2024. Accessed May 15, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-rise-and-impact-of-nazi-ideology-on-global-history/
"The Rise and Impact of Nazi Ideology on Global History," PapersOwl.com , 12-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-rise-and-impact-of-nazi-ideology-on-global-history/. [Accessed: 15-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Rise and Impact of Nazi Ideology on Global History . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-rise-and-impact-of-nazi-ideology-on-global-history/ [Accessed: 15-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Modern global warming is the result of an increase in magnitude of the so-called greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxides, and other greenhouse gases. In 2014 the IPCC first reported that concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and ...
Q.1 List the causes of Global Warming. A.1 There are various causes of global warming both natural and manmade. The natural one includes a greenhouse gas, volcanic eruption, methane gas and more. Next up, manmade causes are deforestation, mining, cattle rearing, fossil fuel burning and more.
The most important cause of global warming is greenhouse gases, which trap hot air in the Earth's atmosphere instead of allowing that heat to escape into space. Greenhouse gasses build up in the earth's atmosphere, effectively insulating the planet just as a greenhouse used to grow fruits and vegetables traps heat.
The El Niño climate pattern, a naturally occurring phenomenon, can significantly disrupt global weather systems, but the human-made climate emergency is exacerbating the destructive effects.
Carbon dioxide is one the gases that trap heat energy in the atmosphere, leading to increased atmospheric temperatures. Another cause of global warming is the ever-increasing emission of greenhouse gases from burning of gasoline. The modern car culture is one of the primary sources of green house gases, as most transportation and manufacturing ...
Takeaways Increasing Greenhouses Gases Are Warming the Planet Scientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid-20th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect"1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space. Life on Earth depends on energy coming from the Sun. About half the light […]
A: Global warming occurs when carbon dioxide (CO 2) and other air pollutants collect in the atmosphere and absorb sunlight and solar radiation that have bounced off the earth's surface. Normally ...
What are the effects of global warming? One of the most concerning impacts of global warming is the effect warmer temperatures will have on Earth's polar regions and mountain glaciers. The Arctic ...
Causes and Effects of Climate Change Learn the human impact and consequences of climate change for the environment, and our lives. REFERENCE Causes of global warming, explained
We often call the result global warming, but it is causing a set of changes to the Earth's climate, or long-term weather patterns, that varies from place to place. While many people think of ...
500+ Words Essay on Effects of Global Warming. Global warming refers to climate change that causes an increase in the average of Earth's temperature. Natural events and human influences are believed to be top contributions towards the increase in average temperatures. Global warming is a rise in the surface and atmospheric temperature of the ...
Global warming has far-reaching consequences, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, biodiversity loss, and negative impacts on human health. This essay will delve into the causes, effects, and solutions to global warming, highlighting the importance of taking action to mitigate its impacts.
Of those papers that included an opinion about the cause of global warming, 97.1% described it as caused by humans. Anton Petrus / Getty Images How Greenhouse Gases Warm the Globe
Average global temperatures have increased by 2.2 degrees Fahrenheit, or 1.2 degrees Celsius, since 1880, with the greatest changes happening in the late 20th century. Land areas have warmed more ...
C ONCLUSION. This document explains that there are well-understood physical mechanisms by which changes in the amounts of greenhouse gases cause climate changes. It discusses the evidence that the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and are still increasing rapidly, that climate change is occurring, and that most of ...
Global warming is the long-term warming of the planet's overall temperature. Though this warming trend has been going on for a long time, its pace has significantly increased in the last hundred years due to the burning of fossil fuels.As the human population has increased, so has the volume of . fossil fuels burned.. Fossil fuels include coal, oil, and natural gas, and burning them causes ...
These effects will intensify in the coming years, effectively halting species expansion. Furthermore, humans will eventually feel the negative effects of Global Warming. Also Read: Concept of Sustainable Development. Sample Essays on Global Warming. Here are some sample essays on Global Warming: Essay on Global Warming Paragraph in 100 - 150 ...
A rise in global temperatures can lead to additional changes in the environment, such as rising sea levels. Since an increase in the temperature causes the glaciers and icebergs to melt at a rapid pace, it causes the sea levels to rise. On the Weather: Global Warming causes intense heat waves by significantly increasing the temperature which ...
Another cause of global warming is greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases are carbon monoxide and sulphur dioxide it trap the solar heats rays and prevent it from escaping from the surface of the earth. This has cause the temperature of the earth increase. Volcanic eruptions are another issue that causes global warming.
Global Warming Causes And Effects Analysis Environmental Sciences Essay 'Global warming' is one facet of the broader term 'climate change'. It is the increase in the average temperature of the Earth's surface air and oceans from the mid-20th ...
Global Warming Essay 6 (2500 words) "Global warming refers to the increase in the temperatures of the global surface causing various effects on the climate of the world," (Spencer, 2003). Changes in climate will include change in the patterns of rainfall, rise in the sea level among other climate changes.
What is the 1.5°C goal and why do we need to stick to it? In 2015, 196 Parties to the UN Climate Convention in Paris adopted the Paris Agreement, a landmark international treaty, aimed at curbing global warming and addressing the effects of climate change.Its core ambition is to cap the rise in global average temperatures to well below 2°C above levels observed prior to the industrial era ...
This is the primary cause of Global Warming. Global Warming Effects Increase in the Average Temperature of the Earth. According to IPCC reports, human-induced global warming is responsible for nearly 1 degree Celsius temperature rise vis a vis pre-industrial level. Data from NASA suggest that 2016 has been the hottest year on record.
Biodiversity loss, global warming, pollution and the spread of invasive species are making infectious diseases more dangerous to organisms around the world. By Emily Anthes Several large-scale ...
In conclusion, global warming has not paused since 1998. Instead, Earth's climate system is experiencing a persistent rise in temperatures, a situation exacerbated by human-induced factors.
The particles may also refract and otherwise scramble signals from the global positioning system, according to Rob Steenburgh, a space scientist with NOAA. Those effects can linger for a few days ...
Essay Example: Adolf Hitler oversaw the Nazi system from 1933 to 1945, and it is widely regarded as one of the cruelest and most destructive forces in contemporary history. Its effects, which were mostly caused by radical ideas of national superiority and racial purity, have reverberated through
'Sponge City' has been widely accepted as a green transformation direction of China's urbanization. Such a mid-to long-term construction strategy will bring about prominent economic stimulation effects and complicated environmental impacts, whereas the research is far from sufficiency. This study developed a methodology based on the Hybrid Life Cycle Assessment to quantify the impact of the ...