
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

14.4 Practicing for Successful Speech Delivery
Learning objectives.
- Explain why having a strong conversational quality is important for effective public speaking.
- Explain the importance of eye contact in public speaking.
- Define vocalics and differentiate among the different factors of vocalics.
- Explain effective physical manipulation during a speech.
- Understand how to practice effectively for good speech delivery.
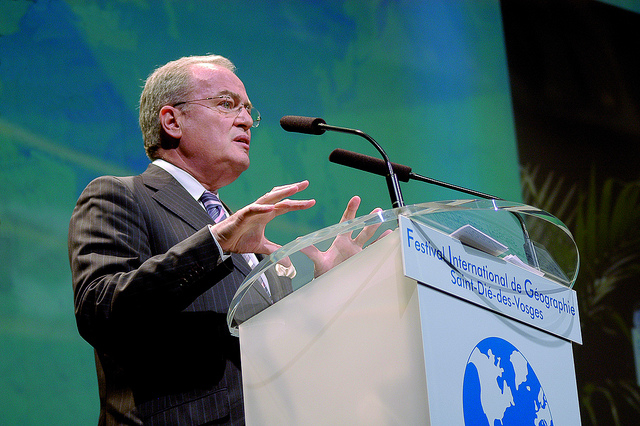

Christian Pierret – Speech – CC BY 2.0.
There is no foolproof recipe for good delivery. Each of us is unique, and we each embody different experiences and interests. This means each person has an approach, or a style, that is effective for her or him. This further means that anxiety can accompany even the most carefully researched and interesting message. Even when we know our messages are strong and well-articulated on paper, it is difficult to know for sure that our presentation will also be good.
We are still obligated to do our best out of respect for the audience and their needs. Fortunately, there are some tools that can be helpful to you even the very first time you present a speech. You will continue developing your skills each time you put them to use and can experiment to find out which combination of delivery elements is most effective for you.
What Is Good Delivery?
The more you care about your topic, the greater your motivation to present it well. Good delivery is a process of presenting a clear, coherent message in an interesting way. Communication scholar Stephen E. Lucas tells us:
Good delivery…conveys the speaker’s ideas clearly, interestingly, and without distracting the audience. Most audiences prefer delivery that combines a certain degree of formality with the best attributes of good conversation—directness, spontaneity, animation, vocal and facial expressiveness, and a lively sense of communication (Lucas, 2009).
Many writers on the nonverbal aspects of delivery have cited the findings of psychologist Albert Mehrabian, asserting that the bulk of an audience’s understanding of your message is based on nonverbal communication. Specifically, Mehrabian is often credited with finding that when audiences decoded a speaker’s meaning, the speaker’s face conveyed 55 percent of the information, the vocalics conveyed 38 percent, and the words conveyed just 7 percent (Mehrabian, 1972). Although numerous scholars, including Mehrabian himself, have stated that his findings are often misinterpreted (Mitchell), scholars and speech instructors do agree that nonverbal communication and speech delivery are extremely important to effective public speaking.
In this section of the chapter, we will explain six elements of good delivery: conversational style, conversational quality, eye contact, vocalics, physical manipulation, and variety. And since delivery is only as good as the practice that goes into it, we conclude with some tips for effective use of your practice time.
Conversational Style
Conversational style is a speaker’s ability to sound expressive and to be perceived by the audience as natural. It’s a style that approaches the way you normally express yourself in a much smaller group than your classroom audience. This means that you want to avoid having your presentation come across as didactic or overly exaggerated. You might not feel natural while you’re using a conversational style, but for the sake of audience preference and receptiveness, you should do your best to appear natural. It might be helpful to remember that the two most important elements of the speech are the message and the audience. You are the conduit with the important role of putting the two together in an effective way. Your audience should be thinking about the message, not the delivery.
Stephen E. Lucas defines conversational quality as the idea that “no matter how many times a speech has been rehearsed, it still sounds spontaneous” [emphasis in original] (Lucas, 2009). No one wants to hear a speech that is so well rehearsed that it sounds fake or robotic. One of the hardest parts of public speaking is rehearsing to the point where it can appear to your audience that the thoughts are magically coming to you while you’re speaking, but in reality you’ve spent a great deal of time thinking through each idea. When you can sound conversational, people pay attention.
Eye Contact
Eye contact is a speaker’s ability to have visual contact with everyone in the audience. Your audience should feel that you’re speaking to them, not simply uttering main and supporting points. If you are new to public speaking, you may find it intimidating to look audience members in the eye, but if you think about speakers you have seen who did not maintain eye contact, you’ll realize why this aspect of speech delivery is important. Without eye contact, the audience begins to feel invisible and unimportant, as if the speaker is just speaking to hear her or his own voice. Eye contact lets your audience feel that your attention is on them, not solely on the cards in front of you.
Sustained eye contact with your audience is one of the most important tools toward effective delivery. O’Hair, Stewart, and Rubenstein note that eye contact is mandatory for speakers to establish a good relationship with an audience (O’Hair, Stewart, & Rubenstein, 2001). Whether a speaker is speaking before a group of five or five hundred, the appearance of eye contact is an important way to bring an audience into your speech.
Eye contact can be a powerful tool. It is not simply a sign of sincerity, a sign of being well prepared and knowledgeable, or a sign of confidence; it also has the power to convey meanings. Arthur Koch tells us that all facial expressions “can communicate a wide range of emotions, including sadness, compassion, concern, anger, annoyance, fear, joy, and happiness” (Koch, 2010).
If you find the gaze of your audience too intimidating, you might feel tempted to resort to “faking” eye contact with them by looking at the wall just above their heads or by sweeping your gaze around the room instead of making actual eye contact with individuals in your audience until it becomes easier to provide real contact. The problem with fake eye contact is that it tends to look mechanical. Another problem with fake attention is that you lose the opportunity to assess the audience’s understanding of your message. Still, fake eye contact is somewhat better than gripping your cards and staring at them and only occasionally glancing quickly and shallowly at the audience.
This is not to say that you may never look at your notecards. On the contrary, one of the skills in extemporaneous speaking is the ability to alternate one’s gaze between the audience and one’s notes. Rehearsing your presentation in front of a few friends should help you develop the ability to maintain eye contact with your audience while referring to your notes. When you are giving a speech that is well prepared and well rehearsed, you will only need to look at your notes occasionally. This is an ability that will develop even further with practice. Your public speaking course is your best chance to get that practice.
Effective Use of Vocalics
Vocalics , also known as paralanguage, is the subfield of nonverbal communication that examines how we use our voices to communicate orally. This means that you speak loudly enough for all audience members (even those in the back of the room) to hear you clearly, and that you enunciate clearly enough to be understood by all audience members (even those who may have a hearing impairment or who may be English-language learners). If you tend to be soft-spoken, you will need to practice using a louder volume level that may feel unnatural to you at first. For all speakers, good vocalic technique is best achieved by facing the audience with your chin up and your eyes away from your notecards and by setting your voice at a moderate speed. Effective use of vocalics also means that you make use of appropriate pitch, pauses, vocal variety, and correct pronunciation.
If you are an English-language learner and feel apprehensive about giving a speech in English, there are two things to remember: first, you can meet with a reference librarian to learn the correct pronunciations of any English words you are unsure of; and second, the fact that you have an accent means you speak more languages than most Americans, which is an accomplishment to be proud of.
If you are one of the many people with a stutter or other speech challenge, you undoubtedly already know that there are numerous techniques for reducing stuttering and improving speech fluency and that there is no one agreed-upon “cure.” The Academy Award–winning movie The King’s Speech did much to increase public awareness of what a person with a stutter goes through when it comes to public speaking. It also prompted some well-known individuals who stutter, such as television news reporter John Stossel, to go public about their stuttering (Stossel, 2011). If you have decided to study public speaking in spite of a speech challenge, we commend you for your efforts and encourage you to work with your speech instructor to make whatever adaptations work best for you.
Volume refers to the loudness or softness of a speaker’s voice. As mentioned, public speakers need to speak loudly enough to be heard by everyone in the audience. In addition, volume is often needed to overcome ambient noise, such as the hum of an air conditioner or the dull roar of traffic passing by. In addition, you can use volume strategically to emphasize the most important points in your speech. Select these points carefully; if you emphasize everything, nothing will seem important. You also want to be sure to adjust your volume to the physical setting of the presentation. If you are in a large auditorium and your audience is several yards away, you will need to speak louder. If you are in a smaller space, with the audience a few feet away, you want to avoid overwhelming your audience with shouting or speaking too loudly.
Rate is the speed at which a person speaks. To keep your speech delivery interesting, your rate should vary. If you are speaking extemporaneously, your rate will naturally fluctuate. If you’re reading, your delivery is less likely to vary. Because rate is an important tool in enhancing the meanings in your speech, you do not want to give a monotone drone or a rapid “machine-gun” style delivery. Your rate should be appropriate for your topic and your points. A rapid, lively rate can communicate such meanings as enthusiasm, urgency, or humor. A slower, moderated rate can convey respect, seriousness, or careful reasoning. By varying rapid and slower rates within a single speech, you can emphasize your main points and keep your audience interested.
Pitch refers to the highness or lowness of a speaker’s voice. Some speakers have deep voices and others have high voices. As with one’s singing voice range, the pitch of one’s speaking voice is determined to a large extent by physiology (specifically, the length of one’s vocal folds, or cords, and the size of one’s vocal tract). We all have a normal speaking pitch where our voice is naturally settled, the pitch where we are most comfortable speaking, and most teachers advise speaking at the pitch that feels natural to you.
While our voices may be generally comfortable at a specific pitch level, we all have the ability to modulate, or move, our pitch up or down. In fact, we do this all the time. When we change the pitch of our voices, we are using inflections . Just as you can use volume strategically, you can also use pitch inflections to make your delivery more interesting and emphatic. If you ordinarily speak with a soprano voice, you may want to drop your voice to a slightly lower range to call attention to a particular point. How we use inflections can even change the entire meaning of what we are saying. For example, try saying the sentence “I love public speaking” with a higher pitch on one of the words—first raise the pitch on “I,” then say it again with the pitch raised on “love,” and so on. “ I love public speaking” conveys a different meaning from “I love public speaking,” doesn’t it?
There are some speakers who don’t change their pitch at all while speaking, which is called monotone . While very few people are completely monotone, some speakers slip into monotone patterns because of nerves. One way to ascertain whether you sound monotone is to record your voice and see how you sound. If you notice that your voice doesn’t fluctuate very much, you will need to be intentional in altering your pitch to ensure that the emphasis of your speech isn’t completely lost on your audience.
Finally, resist the habit of pitching your voice “up” at the ends of sentences. It makes them sound like questions instead of statements. This habit can be disorienting and distracting, interfering with the audience’s ability to focus entirely on the message. The speaker sounds uncertain or sounds as though he or she is seeking the understanding or approval of the listener. It hurts the speaker’s credibility and it needs to be avoided.
The effective use of pitch is one of the keys to an interesting delivery that will hold your audience’s attention.
Pauses are brief breaks in a speaker’s delivery that can show emphasis and enhance the clarity of a message. In terms of timing, the effective use of pauses is one of the most important skills to develop. Some speakers become uncomfortable very quickly with the “dead air” that the pause causes. And if the speaker is uncomfortable, the discomfort can transmit itself to the audience. That doesn’t mean you should avoid using pauses; your ability to use them confidently will increase with practice. Some of the best comedians use the well-timed pause to powerful and hilarious effect. Although your speech will not be a comedy routine, pauses are still useful for emphasis, especially when combined with a lowered pitch and rate to emphasize the important point you do not want your audience to miss.
Vocal Variety
Vocal variety has to do with changes in the vocalics we have just discussed: volume, pitch, rate, and pauses. No one wants to hear the same volume, pitch, rate, or use of pauses over and over again in a speech. Your audience should never be able to detect that you’re about to slow down or your voice is going to get deeper because you’re making an important point. When you think about how you sound in a normal conversation, your use of volume, pitch, rate, and pauses are all done spontaneously. If you try to overrehearse your vocalics, your speech will end up sounding artificial. Vocal variety should flow naturally from your wish to speak with expression. In that way, it will animate your speech and invite your listeners to understand your topic the way you do.
Pronunciation
The last major category related to vocalics is pronunciation , or the conventional patterns of speech used to form a word. Word pronunciation is important for two reasons: first, mispronouncing a word your audience is familiar with will harm your credibility as a speaker; and second, mispronouncing a word they are unfamiliar with can confuse and even misinform them. If there is any possibility at all that you don’t know the correct pronunciation of a word, find out. Many online dictionaries, such as the Wiktionary ( http://wiktionary.org ), provide free sound files illustrating the pronunciation of words.
Many have commented on the mispronunciation of words such as “nuclear” and “cavalry” by highly educated public speakers, including US presidents. There have been classroom examples as well. For instance, a student giving a speech on the Greek philosopher Socrates mispronounced his name at least eight times during her speech. This mispronunciation created a situation of great awkwardness and anxiety for the audience. Everyone felt embarrassed and the teacher, opting not to humiliate the student in front of the class, could not say anything out loud, instead providing a private written comment at the end of class.
One important aspect of pronunciation is articulation , or the ability to clearly pronounce each of a succession of syllables used to make up a word. Some people have difficulty articulating because of physiological problems that can be treated by trained speech therapists, but other people have articulation problems because they come from a cultural milieu where a dialect other than standard American English is the norm. Speech therapists, who generally guide their clients toward standard American English, use the acronym SODA when helping people learn how to more effectively articulate: substitutions , omissions , distortions , and additions .
- Substitutions occur when a speaker replaces one consonant or vowel with another consonant ( water becomes wudda ; ask becomes ax ; mouth becomes mouf ).
- Omissions occur when a speaker drops a consonant or vowel within a word ( Internet becomes Innet ; mesmerized becomes memerized ; probably becomes prolly ).
- Distortions occur when a speaker articulates a word with nasal or slurring sounds ( pencil sounds like mencil ; precipitation sounds like persination ; second sounds like slecond ).
- Additions occur when a speaker adds consonants or vowels to words that are not there ( anyway becomes anyways ; athletic becomes athaletic ; black becomes buhlack ; interpret becomes interpretate ).
Another aspect of pronunciation in public speaking is avoiding the use of verbal surrogates or “filler” words used as placeholders for actual words (like er , um , uh , etc.). You might be able to get away with saying “um” as many as two or three times in your speech before it becomes distracting, but the same cannot be said of “like.” We know of a student who trained herself to avoid saying “like.” As soon as the first speech was assigned, she began wearing a rubber band on her left wrist. Each time she caught herself saying “like,” she snapped herself with the rubber band. It hurt. Very quickly, she found that she could stop inflicting the snap on herself, and she had successfully confronted an unprofessional verbal habit.
Effective Physical Manipulation
In addition to using our voices effectively, a key to effective public speaking is physical manipulation , or the use of the body to emphasize meanings or convey meanings during a speech. While we will not attempt to give an entire discourse on nonverbal communication, we will discuss a few basic aspects of physical manipulation: posture, body movement, facial expressions, and dress. These aspects add up to the overall physical dimension of your speech, which we call self-presentation.
“Stand up tall!” I’m sure we’ve all heard this statement from a parent or a teacher at some point in our lives. The fact is, posture is actually quite important. When you stand up straight, you communicate to your audience, without saying a word, that you hold a position of power and take your position seriously. If however, you are slouching, hunched over, or leaning on something, you could be perceived as ill prepared, anxious, lacking in credibility, or not serious about your responsibilities as a speaker. While speakers often assume more casual posture as a presentation continues (especially if it is a long one, such as a ninety-minute class lecture), it is always wise to start by standing up straight and putting your best foot forward. Remember, you only get one shot at making a first impression, and your body’s orientation is one of the first pieces of information audiences use to make that impression.
Body Movement
Unless you are stuck behind a podium because of the need to use a nonmovable microphone, you should never stand in one place during a speech. However, movement during a speech should also not resemble pacing. One of our authors once saw a speaker who would walk around a small table where her speaking notes were located. She would walk around the table once, toss her chalk twice, and then repeat the process. Instead of listening to what the speaker was saying, everyone became transfixed by her walk-and-chalk-toss pattern. As speakers, we must be mindful of how we go about moving while speaking. One common method for easily integrating some movement into your speech is to take a few steps any time you transition from one idea to the next. By only moving at transition points, not only do you help focus your audience’s attention on the transition from one idea to the next, but you also are able to increase your nonverbal immediacy by getting closer to different segments of your audience.
Body movement also includes gestures. These should be neither overdramatic nor subdued. At one extreme, arm-waving and fist-pounding will distract from your message and reduce your credibility. At the other extreme, refraining from the use of gestures is the waste of an opportunity to suggest emphasis, enthusiasm, or other personal connection with your topic.
There are many ways to use gestures. The most obvious are hand gestures, which should be used in moderation at carefully selected times in the speech. If you overuse gestures, they lose meaning. Many late-night comedy parodies of political leaders include patterned, overused gestures or other delivery habits associated with a particular speaker. However, the well-placed use of simple, natural gestures to indicate emphasis, direction, size is usually effective. Normally, a gesture with one hand is enough. Rather than trying to have a gesture for every sentence, use just a few well-planned gestures. It is often more effective to make a gesture and hold it for a few moments than to begin waving your hands and arms around in a series of gestures.
Finally, just as you should avoid pacing, you will also want to avoid other distracting movements when you are speaking. Many speakers have unconscious mannerisms such as twirling their hair, putting their hands in and out of their pockets, jingling their keys, licking their lips, or clicking a pen while speaking. As with other aspects of speech delivery, practicing in front of others will help you become conscious of such distractions and plan ways to avoid doing them.
Facial Expressions
Faces are amazing things and convey so much information. As speakers, we must be acutely aware of what our face looks like while speaking. While many of us do not look forward to seeing ourselves on videotape, often the only way you can critically evaluate what your face is doing while you are speaking is to watch a recording of your speech. If video is not available, you can practice speaking in front of a mirror.
There are two extremes you want to avoid: no facial expression and overanimated facial expressions. First, you do not want to have a completely blank face while speaking. Some people just do not show much emotion with their faces naturally, but this blankness is often increased when the speaker is nervous. Audiences will react negatively to the message of such a speaker because they will sense that something is amiss. If a speaker is talking about the joys of Disney World and his face doesn’t show any excitement, the audience is going to be turned off to the speaker and his message. On the other extreme end is the speaker whose face looks like that of an exaggerated cartoon character. Instead, your goal is to show a variety of appropriate facial expressions while speaking.
Like vocalics and gestures, facial expression can be used strategically to enhance meaning. A smile or pleasant facial expression is generally appropriate at the beginning of a speech to indicate your wish for a good transaction with your audience. However, you should not smile throughout a speech on drug addiction, poverty, or the oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico. An inappropriate smile creates confusion about your meaning and may make your audience feel uncomfortable. On the other hand, a serious scowl might look hostile or threatening to audience members and become a distraction from the message. If you keep the meaning of your speech foremost in your mind, you will more readily find the balance in facial expression.
Another common problem some new speakers have is showing only one expression. One of our coauthors competed in speech in college. After one of his speeches (about how people die on amusement park rides), one of his judges pulled him aside and informed him that his speech was “creepy.” Apparently, while speaking about death, our coauthor smiled the entire time. The incongruity between the speech on death and dying and the coauthor’s smile just left the judge a little creeped out. If you are excited in a part of your speech, you should show excitement on your face. On the other hand, if you are at a serious part of your speech, your facial expressions should be serious.
While there are no clear-cut guidelines for how you should dress for every speech you’ll give, dress is still a very important part of how others will perceive you (again, it’s all about the first impression). If you want to be taken seriously, you must present yourself seriously. While we do not advocate dressing up in a suit every time you give a speech, there are definitely times when wearing a suit is appropriate.
One general rule you can use for determining dress is the “step-above rule,” which states that you should dress one step above your audience. If your audience is going to be dressed casually in shorts and jeans, then wear nice casual clothing such as a pair of neatly pressed slacks and a collared shirt or blouse. If, however, your audience is going to be wearing “business casual” attire, then you should probably wear a sport coat, a dress, or a suit. The goal of the step-above rule is to establish yourself as someone to be taken seriously. On the other hand, if you dress two steps above your audience, you may put too much distance between yourself and your audience, coming across as overly formal or even arrogant.
Another general rule for dressing is to avoid distractions in your appearance. Overly tight or revealing garments, over-the-top hairstyles or makeup, jangling jewelry, or a display of tattoos and piercings can serve to draw your audience’s attention away from your speech. Remembering that your message is the most important aspect of your speech, keep that message in mind when you choose your clothing and accessories.
Self-Presentation
When you present your speech, you are also presenting yourself. Self-presentation, sometimes also referred to as poise or stage presence, is determined by how you look, how you stand, how you walk to the lectern, and how you use your voice and gestures. Your self-presentation can either enhance your message or detract from it. Worse, a poor self-presentation can turn a good, well-prepared speech into a forgettable waste of time. You want your self-presentation to support your credibility and improve the likelihood that the audience will listen with interest.
Your personal appearance should reflect the careful preparation of your speech. Your personal appearance is the first thing your audience will see, and from it, they will make inferences about the speech you’re about to present.
One of the biggest mistakes novice public speakers make is to use the same gesture over and over again during a speech. While you don’t want your gestures to look fake, you should be careful to include a variety of different nonverbal components while speaking. You should make sure that your face, body, and words are all working in conjunction with each other to support your message.
Practice Effectively
You might get away with presenting a hastily practiced speech, but the speech will not be as good as it could be. In order to develop your best speech delivery, you need to practice—and use your practice time effectively. Practicing does not mean reading over your notes, mentally running through your speech, or even speaking your speech aloud over and over. Instead, you need to practice with the goal of identifying the weaknesses in your delivery, improving upon them, and building good speech delivery habits.
When you practice your speech, place both your feet in full, firm contact with the floor to keep your body from swaying side to side. Some new public speakers find that they don’t know what to do with their hands during the speech. Your practice sessions should help you get comfortable. When you’re not gesturing, you can rest your free hand lightly on a lectern or simply allow it to hang at your side. Since this is not a familiar posture for most people, it might feel awkward, but in your practice sessions, you can begin getting used to it.
Seek Input from Others
Because we can’t see ourselves as others see us, one of the best ways to improve your delivery is to seek constructive criticism from others. This, of course, is an aspect of your public speaking course, as you will receive evaluations from your instructor and possibly from your fellow students. However, by practicing in front of others before it is time to present your speech, you can anticipate and correct problems so that you can receive a better evaluation when you give the speech “for real.”
Ask your practice observers to be honest about the aspects of your delivery that could be better. Sometimes students create study groups just for this purpose. When you create a study group of classroom peers, everyone has an understanding of the entire creative process, and their feedback will thus be more useful to you than the feedback you might get from someone who has never taken the course or given a speech.
If your practice observers seem reluctant to offer useful criticisms, ask questions. How was your eye contact? Could they hear you? Was your voice well modulated? Did you mispronounce any words? How was your posture? Were your gestures effective? Did you have any mannerisms that you should learn to avoid? Because peers are sometimes reluctant to say things that could sound critical, direct questions are often a useful way to help them speak up.
If you learn from these practice sessions that your voice tends to drop at the ends of sentences, make a conscious effort to support your voice as you conclude each main point. If you learn that you have a habit of clicking a pen, make sure you don’t have a pen with you when you speak or that you keep it in your pocket. If your practice observers mention that you tend to hide your hands in the sleeves of your shirt or jacket, next time wear short sleeves or roll your sleeves up before beginning your speech. If you learn through practice that you tend to sway or rock while you speak, you can consciously practice and build the habit of not swaying.
When it is your turn to give feedback to others in your group, assume that they are as interested in doing well as you are. Give feedback in the spirit of helping their speeches be as good as possible.
Use Audio and/or Video to Record Yourself
Technology has made it easier than ever to record yourself and others using the proliferation of electronic devices people are likely to own. Video, of course, allows you the advantage of being able to see yourself as others see you, while audio allows you to concentrate on the audible aspects of your delivery. As we mentioned earlier in the chapter, if neither video nor audio is available, you can always observe yourself by practicing your delivery in front of a mirror.
After you have recorded yourself, it may seem obvious that you should watch and listen to the recording. This can be intimidating, as you may fear that your performance anxiety will be so obvious that everyone will notice it in the recording. But students are often pleasantly surprised when they watch and listen to their recordings, as even students with very high anxiety may find out that they “come across” in a speech much better than they expected.
A recording can also be a very effective diagnostic device. Sometimes students believe they are making strong contact with their audiences, but their cards contain so many notes that they succumb to the temptation of reading. By finding out from the video that you misjudged your eye contact, you can be motivated to rewrite your notecards in a way that doesn’t provide the opportunity to do so much reading.
It is most likely that in viewing your recording, you will benefit from discovering your strengths and finding weak areas you can strengthen.
Good Delivery Is a Habit
Luckily, public speaking is an activity that, when done conscientiously, strengthens with practice. As you become aware of the areas where your delivery has room for improvement, you will begin developing a keen sense of what “works” and what audiences respond to.
It is advisable to practice out loud in front of other people several times, spreading your rehearsals out over several days. To do this kind of practice, of course, you need to have your speech be finalized well ahead of the date when you are going to give it. During these practice sessions, you can time your speech to make sure it lasts the appropriate length of time. A friend of ours was the second student on the program in an event where each student’s presentation was to last thirty to forty-five minutes. After the first student had been speaking for seventy-five minutes, the professor in charge asked, “Can we speed this up?” The student said yes, and proceeded to continue speaking for another seventy-five minutes before finally concluding his portion of the program. Although we might fault the professor for not “pulling the plug,” clearly the student had not timed his speech in advance.
Your practice sessions will also enable you to make adjustments to your notecards to make them more effective in supporting your contact with your audience. This kind of practice is not just a strategy for beginners; it is practiced by many highly placed public figures with extensive experience in public speaking.
Your public speaking course is one of the best opportunities you will have to manage your performance anxiety, build your confidence in speaking extemporaneously, develop your vocal skills, and become adept at self-presentation. The habits you can develop through targeted practice are to build continuously on your strengths and to challenge yourself to find new areas for improving your delivery. By taking advantage of these opportunities, you will gain the ability to present a speech effectively whenever you may be called upon to speak publicly.
Key Takeaways
- Conversational style is a speaker’s ability to sound expressive while being perceived by the audience as natural. Conversational quality is a speaker’s ability to prepare a speech and rehearse a speech but still sound spontaneous when delivering it.
- Eye contact helps capture and maintain an audience’s interest while contributing to the speaker’s credibility.
- Vocalics are the nonverbal components of the verbal message. There are six important vocalic components for a speaker to be aware of: volume (loudness or softness), pitch (highness or lowness), rate (fastness or slowness), pauses (use of breaks to add emphasis), vocal variety (use of a range of vocalic strategies), and pronunciation (using conventional patterns of speech formation).
- Physical manipulation is the use of one’s body to add meaning and emphasis to a speech. As such, excessive or nonexistent physical manipulation can detract from a speaker’s speech.
- Good delivery is a habit that is built through effective practice.
- Find a speech online and examine the speaker’s overall presentation. How good was the speaker’s delivery? Make a list of the aspects of delivery in this chapter and evaluate the speaker according to the list. In what areas might the speaker improve?
- Record a practice session of your speech. Write a self-critique, answering the following questions: What surprised you the most? What is an area of strength upon which you can build? What is one area for improvement?
Koch, A. (2010). Speaking with a purpose (8th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon, p. 233.
Lucas, S. E. (2009). The art of public speaking (9th ed.). Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill, p. 244.
Mehrabian, A. (1972). Nonverbal communication . Chicago, IL: Aldine-Atherton.
Mitchell, O. (n.d.). Mehrabian and nonverbal communication [Web log post]. Retrieved from http://www.speakingaboutpresenting.com/presentation-myths/mehrabian-nonverbal-communication-research
O’Hair, D., Stewart, R., & Rubenstein, H. (2001). A speaker’s guidebook: Text and reference. Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martin’s.
Stossel, J. (2011, March 2). An Academy Award–winning movie, stuttering and me [Web log post]. Retrieved from http://www.humanevents.com/article.php?id=42081
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Speak Like a Pro: The Ultimate Guide to Flawless Speech Delivery Techniques Revealed!
Eloquence Everly

As an affiliate, we may earn a commission from qualifying purchases. We get commissions for purchases made through links on this website from Amazon and other third parties.
Implementing effective speech delivery techniques is essential to captivate and engage your audience. By following these techniques, you can improve your public speaking skills and deliver persuasive and engaging presentations.
Key Takeaways:
- Thoroughly prepare and practice your speech before delivering it.
- Create a distraction-free presentation environment with proper lighting and visibility.
- Pay attention to your personal appearance and maintain good body language during the speech.
- Focus on vocal delivery strategies such as clear enunciation , appropriate loudness and speed , and variations in speed and force .
- Utilize effective body language by maintaining eye contact , using gestures and movement naturally, and avoiding distracting mannerisms.
Preparation for Speech Delivery
Before delivering a speech, thorough preparation is essential. By taking the time to prepare, you can ensure a smooth and confident delivery that captivates your audience . Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Create a Well-Organized Set of Notes: To guide you during your presentation, create a clear and concise set of notes. This will help you stay on track and ensure you cover all your key points. Structure your notes in a logical manner, using headings and bullet points for easy reference.
- Engage in Ample Practice: Practice makes perfect, so dedicate time to rehearse your speech. Familiarize yourself with the content, flow, and timing of your presentation. Practice in front of a mirror, friends, or colleagues to receive feedback and make necessary improvements.
- Prepare the Presentation Environment : The environment in which you deliver your speech can greatly impact its effectiveness. Consider factors such as lighting, visibility, and distractions. Ensure that the room is well-lit and that your audience can see and hear you clearly. Eliminate any distractions or potential interruptions.
- Test and Have a Backup Plan for Audiovisual Equipment : If you will be using audiovisual equipment , such as a microphone or projector, it is crucial to test them beforehand. Check for any technical issues and have a backup plan in case of equipment failure. This will help you avoid any disruptions and allow for a seamless delivery.
By adequately preparing your speech, notes, and the presentation environment , you can set yourself up for success and deliver a confident and impactful presentation to your audience.
Personal Appearance and Body Language
When delivering a speech, your personal appearance and body language significantly impact the impression you make on your audience. Here are some key tips to ensure you project confidence and professionalism:
Dress Appropriately
Choose attire that is suitable for the occasion and reflects your respect for the audience and the topic. Ensure your outfit is clean, well-fitted, and comfortable. Avoid wearing hats or caps that can obstruct your face and hinder your nonverbal communication.
Maintain Good Posture
Stand or sit up straight, with your shoulders back and chin parallel to the ground. This posture exudes confidence and engages your audience . Remember to distribute your weight evenly and avoid excessive shifting or fidgeting.
Eye Contact
Maintaining eye contact is crucial for establishing connection and credibility with your audience. Look directly at individuals while speaking, making an effort to engage different parts of the room. Avoid constantly referring to notes or reading from a script, as this can diminish the impact of your message.
Avoid Distracting Mannerisms
Be mindful of your body language throughout your speech. Minimize excessive hand movements, pacing, or other distracting mannerisms that can detract from your message. Focus on conveying confidence and clarity through calm and composed gestures .
By paying attention to your personal appearance and body language, you can enhance your speech delivery and effectively engage your audience .
Vocal Delivery Strategies
Your vocal delivery plays a crucial role in how your speech is received by the audience. By implementing effective vocal techniques, you can enhance the impact of your message and maintain audience attention. Let’s explore some strategies to improve your vocal delivery :
Enunciation and Clarity
Clear enunciation is vital for effective communication. Ensure that you pronounce your words distinctly and avoid mumbling or garbling. By articulating each word clearly, you enhance the audience’s understanding and engagement with your speech.
Appropriate Loudness and Speed
Adjusting your volume and speed based on the audience, venue, and topic is crucial for effective vocal delivery. Speak loudly enough to be heard, but avoid being overly loud or shouting. Similarly, vary your speed to maintain audience interest and emphasize key points, but avoid speaking too quickly or too slowly.
Variations in Speed, Inflections, and Force
Utilizing variations in speed, inflections, and force adds depth and meaning to your speech. By emphasizing certain words or phrases, you can convey the significance and emotion behind them. Adjusting the pace of your speech can create anticipation or highlight important information. Use this technique strategically to enhance your message and keep your audience engaged.
Minimize Filler Words
Filler words such as “um,” “uh,” and “like” can detract from the impact and clarity of your delivery. Minimize their use to ensure a smooth and impactful presentation. Pausing briefly instead of using filler words can also add emphasis and facilitate better understanding.
“Clear and confident vocal delivery is essential for engaging your audience. Enunciate your words with clarity, speak at an appropriate loudness and speed , utilize variations in speed and force , and minimize the use of filler words. These strategies will help you captivate your audience and effectively convey your message.”
Now that you have learned about effective vocal delivery strategies, let’s move on to exploring the importance of body language in speech delivery.
Effective Use of Body Language
When delivering a speech, your body language can greatly impact how your message is received by the audience. By mastering the art of body language , you can effectively communicate your ideas and captivate your listeners.
Maintaining Eye Contact
One of the most important aspects of body language is maintaining eye contact with your audience. This establishes a connection between you and your listeners, making them feel engaged and involved in your speech. Avoid excessively reading from notes, as this can hinder eye contact and create a barrier between you and your audience. Instead, glance at your notes discreetly when necessary and focus on making eye contact with individuals throughout the room.
Using Gestures and Movement
“Gestures, in my opinion, are the most powerful tool we have in becoming an effective communicator.” – Andrea Foy
Gestures and movement can add depth and emphasis to your speech. Use them naturally to illustrate concepts, reinforce transitions between ideas, and highlight key points. However, it’s important to be mindful of using gestures in a controlled and purposeful manner. Avoid excessive or distracting movements that can draw attention away from your message. Instead, use gestures and movement to enhance your delivery and engage your audience.
Show Enthusiasm and Commitment
When delivering a speech, it’s vital to demonstrate interest and passion in your topic. Show enthusiasm through your body language, such as by smiling, using facial expressions that reflect your emotions, and maintaining an open and confident posture. This not only captures the audience’s attention but also conveys your commitment to the subject matter, making your speech more compelling and memorable.
Avoiding Distracting Mannerisms
While gestures and movement are important, it’s crucial to avoid distracting or aimless mannerisms that can detract from your message. Be aware of any nervous habits, such as fidgeting, excessive hand movements, or aimless shifting of weight. These mannerisms can undermine your credibility and divert the audience’s attention from your speech. Practice self-awareness and aim for body language that is purposeful, controlled, and complementary to your message.
Improving Verbal Delivery
When delivering a speech, your verbal delivery plays a crucial role in engaging your audience. To ensure your message reaches every corner of the room, focus on the following aspects:
- Projection : Speak with enough volume to reach people in the back of the room. This will ensure clear communication and prevent your words from getting lost in the space.
- Comfortable Rate : Speak at a pace that allows your audience to comprehend and absorb your message. Pausing occasionally not only helps you catch your breath but also gives the listeners time to process the information.
- Clear Articulation : Enunciate your words clearly to facilitate understanding. Avoid mumbling or rushing through your sentences, as this can make it difficult for your audience to follow along.
- Vocal Habits : Pay attention to any vocal habits that may distract your listeners. Eliminate vocalized pauses like “um” or “uh” and work on maintaining a steady volume throughout your speech. Avoid speaking more softly at the end of sentences, as it can diminish the impact of your message.
Sample Table: Comparing Verbal Delivery Techniques
By focusing on projection , comfortable rate , clear articulation , and eliminating distracting vocal habits , you can deliver a speech that captivates your audience and ensures effective communication.
Enhancing Nonverbal Delivery
Nonverbal delivery plays a crucial role in enhancing your overall speech delivery and making a lasting impact on your audience. By utilizing effective eye contact, movement , gestures, and an unobtrusive use of notes , you can captivate and engage your listeners. These nonverbal elements add depth and authenticity to your speech, helping to convey your message effectively.
Eye Contact: Making eye contact with individuals in your audience establishes a connection and shows that you are genuinely interested in their presence. Avoid excessive reading from notes, as it can break the eye contact and lessen your impact. Instead, actively engage with your audience, scanning the room and making meaningful eye contact with different individuals throughout your speech.
Movement: Movement on stage or in front of your audience can help you control nervousness and create visual interest. Utilize the space around you, taking purposeful steps and making slight changes in position to capture the attention of your listeners. Movement should be natural and deliberate, enhancing your message rather than distracting from it.
Gestures: Gestures and arm movements can add emphasis and clarify your spoken words. Use them to reinforce key points, illustrate concepts, and enhance the overall impact of your speech. Effective gestures appear natural and are synchronized with the rhythm and flow of your speech, engaging your audience on a visual level and reinforcing the meaning of your words.
Unobtrusive Use of Notes: While it is common to use notes during a speech to stay on track and remember important points, it is essential to use them unobtrusively. Ensure that your notes are legible and well-organized, allowing you to find the information you need without causing distractions. Place your notes discreetly or use a small podium or lectern to hold them, allowing for seamless transitions and maintaining the focus on your delivery.
Avoid any distracting mannerisms or gestures that detract from your communication. Practice incorporating these nonverbal elements into your delivery to create a powerful and engaging speech that leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Managing Nervousness and Overcoming Challenges
Nervousness is a common experience when delivering a speech. However, it’s important to remember that you are not alone in feeling this way. Chances are, many members of your audience are also experiencing nerves. The good news is that most signs of nervousness are invisible to the audience, so you can stay calm and composed even if you’re feeling a bit jittery.
Embrace nervousness as it can actually be a valuable tool in enhancing your speech delivery. It can make you more alert, animated, and enthusiastic about your topic. Instead of trying to suppress it, harness that nervous energy and channel it into your presentation. When you embrace your nerves, you can turn them into a positive force that adds authenticity and passion to your speech.
Handling mistakes is another important aspect of managing nervousness . It’s natural to feel flustered if you make a mistake or lose your place during your speech. However, it’s crucial to remember that these slip-ups happen to everyone at some point. Instead of panicking, take a moment to collect yourself, take a deep breath, and calmly continue from where you left off. Most importantly, don’t dwell on the mistake or draw attention to it. Keep your focus on delivering your message effectively.
By embracing and managing nervousness , you can transform it from a potential obstacle into a catalyst for a powerful and engaging presentation. Embrace the nerves, handle mistakes gracefully, and let your genuine enthusiasm shine through.
Mastering effective speech delivery techniques is essential for becoming a confident and persuasive speaker. By implementing these techniques, such as thorough preparation, proper personal appearance, and effective vocal and nonverbal delivery strategies, you can captivate your audience and deliver impactful presentations.
Preparing well before your speech, organizing your notes, and creating a suitable environment are all crucial steps in ensuring an effective delivery. Your personal appearance and body language contribute greatly to the overall impression you make on your audience. Maintaining eye contact, using gestures and movement, and speaking with clear articulation and appropriate variations in speed and force all enhance your communication.
While it is natural to feel nervous before delivering a speech, embracing this nervousness can actually help enhance your delivery. Remember, you are not alone in experiencing nerves, and most signs of nervousness are invisible to the audience. Embrace the energy that nerves bring and use it to your advantage, channeling it into a more animated and enthusiastic performance.
By following these effective speech delivery techniques, you can confidently communicate your ideas and engage your audience in a persuasive and impactful manner. Remember to always strive for clear and effective communication, and never hesitate to seek further opportunities for growth and improvement in your public speaking skills .
What are some effective speech delivery techniques?
Implementing effective speech delivery techniques involves thorough preparation, proper personal appearance, vocal and nonverbal delivery strategies, and managing nervousness .
How important is speech preparation for effective delivery?
Speech preparation is crucial for effective delivery. Creating well-organized notes, practicing, and preparing the presentation environment and audiovisual equipment are essential steps.
How does personal appearance and body language impact speech delivery?
Personal appearance, such as appropriate dressing and tidy hair, and positive body language help to engage the audience. Standing or sitting up straight, making eye contact, and avoiding distracting mannerisms are key aspects.
What are some vocal delivery strategies for effective speech delivery?
Enunciating clearly, speaking with appropriate loudness and speed, using variations in speed and inflections, and minimizing filler words are important strategies for vocal delivery.
How can body language enhance speech delivery?
Maintaining eye contact, using gestures and movement naturally, and displaying enthusiasm through body language can enhance the impact of your speech.
What are some tips for improving verbal delivery in a speech?
Projecting your voice, speaking at a comfortable rate, articulating words clearly, and eliminating vocal habits are key tips to improve verbal delivery.
How can nonverbal delivery support speech delivery?
Making eye contact with the audience, using movement and gestures, and using notes unobtrusively can make your speech more engaging and effective.
How can one manage nervousness during speech delivery?
Managing nervousness can be achieved by realizing that it’s common, remaining calm and composed, using nervous energy to enhance your delivery, and embracing mistakes as learning opportunities.
What are the key takeaways for effective speech delivery?
By implementing effective speech delivery techniques , one can become a confident and persuasive speaker. Thorough preparation, proper personal appearance, vocal and nonverbal delivery strategies, and managing nervousness are key components.
About the author

Latest Posts

Understanding the 5 R’s of Communication
Effective communication is key for our personal and work lives to grow. Even though digital tools are common, talking face-to-face brings a special touch. Knowing how the human voice works helps make our talks better. It’s also important to spot […]
What are the 6 rules of effective communication?
Being a good communicator is key to both personal and professional success. James Humes, who wrote speeches for presidents, called communication the “language of leadership.” It’s not just about being a good talker, but also about sharing the “what,” “why,” […]

7 Principles of Effective Communication
Good communication depends on several important principles. Although they are not set in stone, they help us talk better. These principles aim at being well-spoken, thorough, clear, interesting, logical, open to feedback, and aiming to achieve something. Key Takeaways: Effective […]

Press ESC to close

Mastering Effective Speech Delivery: From Practice to Performance

Start this journey! Dive into the amazing world of effective speech delivery. Find out the secrets of how to engage an audience. Transform practice into incredible performances!
Connect with the audience from the start. Get their attention with interesting opening lines and stories. This sets the stage for a remarkable speech.
Understand body language and vocal projection. Use facial expressions, gestures, and tone to emphasize your message. Show confidence and be authoritative.
Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech is a shining example of great communication. King inspired millions with his passion and words. It’s proof of the potential of effective speech.
To be a masterful speaker, practice storytelling, connecting with an audience, and using body language. Draw inspiration from great orators. Embrace your inner orator! Make a lasting impact with your words.
Importance of Effective Speech Delivery
Delivering a speech effectively is essential for capturing the audience’s attention and getting your message across. Here are 4 key reasons why:
- Engagement: Deliver your speech in an engaging way and your listeners will stay hooked until the end. This ensures that your message resonates with them.
- Clarity: Delivery makes your speech clearer. This helps people understand your words and the main points of your message.
- Persuasion: Good delivery has a persuasive effect. Use the right tone, gestures, and body language to establish a connection with the audience and sway them towards your viewpoint.
- Rapport-building: Effective delivery builds a rapport between you and the audience. Your confident demeanor builds trust and engagement.
It is also important to remember that delivery requires practice and preparation. Pay attention to vocal variety, pacing, enunciation, body posture, and gestures.
Take Tony Robbins as an example – he once gave an inspiring speech that changed the lives of many. His passion filled every word and the crowd was entranced. By delivering the speech with such passion and conviction, Tony Robbins inspired and empowered the audience, leaving a lasting impact on their lives.
Preparing for Speech Delivery
Maximize potential as a speaker and successfully convey your message with this 6-step guide on prepared speech delivery . Follow these steps:
- Determine the purpose and select the topic .
- Research for relevant information and supportive evidence .
- Create an outline, using headings and subheadings .
- Craft an attention-grabbing intro and clearly state the purpose .
- Follow with a coherent presentation of main points and examples .
- Incorporate visuals like slides or props to enhance understanding .
- Lastly, practice delivery techniques like pacing, modulation, body language, and eye contact . Get feedback from others to refine further.
Don’t forget to refine language for the target audience. Look to Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech for inspiration – a powerful, passionate, and compelling speech that captivated the audience and started a movement.
Practicing Speech Delivery
Learn the art of speech delivery with this 6-step guide !
- Prep : Research & gather info. Organize thoughts and make an outline.
- Warm-up : Do vocal exercises like breathing, tongue twisters & scales.
- Memorize : Get key points down. Practice without notes or prompts.
- Body Language : Check your facial expressions, gestures & posture in a mirror.
- Rehearse : Keep increasing the speed & emphasize important words.
- Feedback : Get constructive criticism from trusted people. Join a club to practice.
Remember, each individual has a unique style. Embrace it & stay open to learning opportunities.
True History: Winston Churchill was a master of speech delivery . His powerful speeches during WWII motivated & inspired the UK. He was meticulous in his prep & used rhetorical devices to great effect. His speech delivery had a major impact on history.
Techniques for Effective Speech Delivery
Speech delivery is key to captivating your audience and getting your message across. To master the skill, here are three techniques to enhance it:
- Body Language: Move and gesture purposefully to engage the audience. Use hand and facial expressions to emphasize points and convey emotions. Stand tall and keep an open posture.
- Vocal Range and Tone: Vary your pitch, volume, and tone. Pause for emphasis and modulate your voice for a dynamic flow.
- Eye Contact: Establish eye contact with your audience to build trust. Look at individuals or small groups. Make your speech personal and persuasive.
Remember, successful speech delivery goes beyond words. To perfect it, rehearse in front of a mirror or record yourself. Practice makes perfect!
Also Read: Find Your Passion: A Path to Self-Discovery and Fulfillment
Overcoming Nervousness
Nerves can trip up even the most eloquent speakers, but with a few effective strategies, you can conquer them. Preparing is key. Invest time in practicing your speech and knowing it backwards and forwards. This will build confidence and reduce nervousness.
Visualize success too. Imagine you’re delivering an awesome speech to a captivated audience. This exercise helps create positive thoughts and boosts your assurance.
Controlled breathing is invaluable for fighting nerves. Slow, deep breaths can soothe the mind and relax the body. Taking care of yourself – like getting enough sleep, eating well and exercising – also helps reduce anxiety.
Let me share an inspiring story. A young executive was set to give a presentation to lots of industry experts. Despite feeling jittery beforehand, she practiced and rehearsed her speech. On the day, she focused on visualizing success and took deep breaths for inner calmness. As she spoke confidently and connected with the audience, her nerves vanished. By using these strategies, she conquered her nerves and gave an outstanding performance.
As this tale shows, conquering nervousness isn’t impossible. With dedication, visualization exercises, controlled breathing and self-care – anyone can beat their anxiety and speak confidently. Remember everyone gets nervous sometimes – how we manage it makes us stand out as confident speakers.
Tips for Captivating the Audience
To captivate your listeners , you need effective speech delivery! Here are some tips to try:
- Be personal: Relate to the audience with anecdotes or experiences.
- Use body language: Use gestures, facial expressions, and posture to make your message more impactful.
- Tell stories: Storytelling adds emotion and helps the audience understand your message better.
- Use visual aids: Slides or props can add visual interest and comprehension to your speech.
- Pause for emphasis: Pauses give time to reflect, create suspense, and highlight important points.
Adapt your speech to meet the needs of your listeners. And don’t forget the power of humor! Incorporate tasteful humor at appropriate moments to keep engagement high.
Did you know? Visuals can increase information retention in the audience by a whopping 400%!
Also Read: Top 100 Commonly Used A to Z Phrasal Verbs for English Fluency
For great speech delivery, it’s important to practice and plan. Engage the audience with body language, vocal variation, and clear pronunciation . Incorporate visuals and tech to boost the impact of the speech. Adapt to the audience’s needs and interests to keep their attention. Remember that practice makes perfect!
To make it unique, include storytelling techniques to engage the audience emotionally. Use rhetorical devices like similes and metaphors . Also, adjust pacing and rhythm for emphasis.
We recall an inspiring incident involving Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. His “I Have a Dream” speech in 1963, inspired millions. His voice and powerful message advocating for racial equality captivated the audience. His ability to connect emotionally, through vivid language and imagery, showcases the power of effective speech delivery. Know More – The Fluent Life
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are some tips for effective speech delivery? A: Some tips for effective speech delivery include practicing beforehand, using body language and gestures, speaking clearly and confidently, and engaging the audience through eye contact.
Q2: How can I improve my speaking voice for better speech delivery? A: To improve your speaking voice, you can try exercises like breathing techniques, vocal warm-ups, and speaking with proper posture. It is also helpful to listen to and mimic good speakers to develop your own style.
Q3: How do I overcome nervousness when delivering a speech?| A: To overcome nervousness when delivering a speech , you can prepare well in advance, practice in front of a mirror or with a supportive audience, focus on your message rather than your fear, and use relaxation techniques such as deep breathing.
Q4: What are some common mistakes to avoid during speech delivery? A: Some common mistakes to avoid during speech delivery include speaking too fast or too slow, using excessive filler words like um or uh, reading directly from notes instead of engaging with the audience, and lacking enthusiasm or energy in delivery.
Q5: How can I keep the audience engaged during my speech? A: To keep the audience engaged during your speech, you can use storytelling, humor, visual aids, rhetorical questions, and interactive elements like asking for volunteers or involving the audience in small activities. It is also important to maintain a confident and enthusiastic delivery.
Q6: What are effective ways to conclude a speech for a strong impact?
A: Effective ways to conclude a speech for a strong impact include summarizing key points, providing a memorable closing statement or call-to-action, using inspirational quotes or stories, and leaving the audience with a thought-provoking question or idea to ponder upon.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Share Article:
You might also like

Public Speaking for Social Impact: A Strong Tool

Public Speaking in Digital Age: Webinars and Online Conferences

Public Speaking Ethics: Principles of Responsible Communication
Other stories, building confidence in public speaking: be successful speaker, effective audience engagement techniques: keep them interested.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9 Delivering a Speech
Introduction
9.1 Managing Public Speaking Anxiety
Sources of speaking anxiety.
Aside from the self-reported data in national surveys that rank the fear of public speaking high for Americans, decades of research conducted by communication scholars shows that communication apprehension is common among college students (Priem & Solomon, 2009). Communication apprehension (CA) is fear or anxiety experienced by a person due to real or perceived communication with another person or persons. CA is a more general term that includes multiple forms of communication, not just public speaking. Seventy percent of college students experience some CA, which means that addressing communication anxiety in a class like the one you are taking now stands to benefit the majority of students (Priem & Solomon, 2009). Think about the jitters you get before a first date, a job interview, or the first day of school. The novelty or uncertainty of some situations is a common trigger for communication anxiety, and public speaking is a situation that is novel and uncertain for many.
Public speaking anxiety is a type of CA that produces physiological, cognitive, and behavioral reactions in people when faced with a real or imagined presentation (Bodie, 2010). Physiological responses to public speaking anxiety include increased heart rate, flushing of the skin or face, and sweaty palms, among other things. These reactions are the result of natural chemical processes in the human body. The fight or flight instinct helped early humans survive threatening situations. When faced with a ferocious saber-toothed tiger, for example, the body released adrenaline, cortisol, and other hormones that increased heart rate and blood pressure to get more energy to the brain, organs, and muscles in order to respond to the threat. We can be thankful for this evolutionary advantage, but our physiology has not caught up with our new ways of life. Our body does not distinguish between the causes of stressful situations, so facing down an audience releases the same hormones as facing down a wild beast.
Cognitive reactions to public speaking anxiety often include intrusive thoughts that can increase anxiety: “People are judging me,” “I’m not going to do well,” and “I’m going to forget what to say.” These thoughts are reactions to the physiological changes in the body but also bring in the social/public aspect of public speaking in which speakers fear being negatively judged or evaluated because of their anxiety. The physiological and cognitive responses to anxiety lead to behavioral changes. All these thoughts may lead someone to stop their speech and return to their seat or leave the classroom. Anticipating these reactions can also lead to avoidance behavior where people intentionally avoid situations where they will have to speak in public.
Addressing Public Speaking Anxiety

While we cannot stop the innate physiological reactions related to anxiety from occurring, we do have some control over how we cognitively process them and the behaviors that result. Research on public speaking anxiety has focused on three key ways to address this common issue: systematic desensitization, cognitive restructuring, and skills training (Bodie,2010).
Although systematic desensitization may sound like something done to you while strapped down in the basement of a scary hospital, it actually refers to the fact that we become less anxious about something when we are exposed to it more often (Bodie, 2010). As was mentioned earlier, the novelty and uncertainty of public speaking is a source for many people’s anxiety. So becoming more familiar with public speaking by speaking more often can logically reduce the novelty and uncertainty of it.
Systematic desensitization can result from imagined or real exposure to anxiety-inducing scenarios. In some cases, an instructor leads a person through a series of relaxation techniques. Once relaxed, the person is asked to imagine a series of scenarios including speech preparation and speech delivery. This is something you could also try to do on your own before giving a speech. Imagine yourself going through the process of preparing and practicing a speech, then delivering the speech, then returning to your seat, which concludes the scenario. Aside from this imagined exposure to speaking situations, taking a communication course like this one is a great way to engage directly in systematic desensitization. Almost all students report that they have less speaking anxiety at the end of a semester than when they started, which is at least partially due to the fact they engaged with speaking more than they would have done if they were not taking the class.
Cognitive Restructuring
Cognitive restructuring entails changing the way we think about something. A first step in restructuring how we deal with public speaking anxiety is to cognitively process through our fears to realize that many of the thoughts associated with public speaking anxiety are irrational (Allen, Hunter & Donohue, 2009). For example, people report a fear of public speaking over a fear of snakes, heights, financial ruin, or even death. It’s irrational to think that the consequences of giving a speech in public are more dire than getting bit by a rattlesnake, falling off a building, or dying. People also fear being embarrassed because they mess up. Well, you cannot literally die from embarrassment, and in reality, audiences are very forgiving and overlook or do not even notice many errors that we, as speakers, may dwell on. Once we realize that the potential negative consequences of giving a speech are not as dire as we think they are, we can move on to other cognitive restructuring strategies.
Communication-orientation modification therapy (COM therapy) is a type of cognitive restructuring that encourages people to think of public speaking as a conversation rather than a performance (Motley, 2009). Many people have a performance-based view of public speaking. This can easily be seen in the language that some students use to discuss public speaking. They say that they “rehearse” their speech, deal with “stage fright,” then “perform” their speech on a “stage.” There is no stage at the front of the classroom; it is a normal floor. To get away from a performance orientation, we can reword the previous statements to say that they “practice” their speech, deal with “public speaking anxiety,” then “deliver” their speech from the front of the room. Viewing public speaking as a conversation also helps with confidence. After all, you obviously have some conversation skills, or you would not have made it to college. We engage in conversations every day. We do not have to write everything we are going to say out on a note card, we do not usually get nervous or anxious in regular conversations, and we are usually successful when we try. Even though we do not engage in public speaking as much, we speak to others in public all the time. Thinking of public speaking as a type of conversation helps you realize that you already have accumulated experiences and skills that you can draw from, so you are not starting from scratch.
Last, positive visualization is another way to engage in cognitive restructuring. Speaking anxiety often leads people to view public speaking negatively. They are more likely to judge a speech they gave negatively, even if it was good. They are also likely to set up negative self-fulfilling prophecies that will hinder their performance in future speeches. To use positive visualization, it is best to engage first in some relaxation exercises such as deep breathing or stretching, and then play through vivid images in your mind of giving a successful speech. Do this a few times before giving the actual speech. Students sometimes question the power of positive visualization, thinking that it sounds corny. Ask an Olympic diver what his or her coach says to do before jumping off the diving board and the answer will probably be “Coach says to image completing a perfect 10 dive.” Likewise a Marine sharpshooter would likely say his commanding officer says to imagine hitting the target before pulling the trigger. In both instances, positive visualization is being used in high-stakes situations. If it is good enough for Olympic athletes and snipers, it is good enough for public speakers.
Skills training is a strategy for managing public speaking anxiety that focuses on learning skills that will improve specific speaking behaviors. These skills may relate to any part of the speech-making process, including topic selection, research and organization, delivery, and self-evaluation. Skills training, like systematic desensitization, makes the public speaking process more familiar for a speaker, which lessens uncertainty. In addition, targeting specific areas and then improving on them builds more confidence, which can in turn lead to more improvement. Feedback is important to initiate and maintain this positive cycle of improvement. You can use the constructive criticism that you get from your instructor and peers in this class to target specific areas of improvement.
Self-evaluation is also an important part of skills training. Make sure to evaluate yourself within the context of your assignment or job and the expectations for the speech. Do not get sidetracked by a small delivery error if the expectations for content far outweigh the expectations for delivery. Combine your self-evaluation with the feedback from your instructor, boss, and/or peers to set specific and measurable goals and then assess whether or not you meet them in subsequent speeches. Once you achieve a goal, mark it off your list and use it as a confidence booster. If you do not achieve a goal, figure out why and adjust your strategies to try to meet it in the future.
Physical Relaxation Exercises
Suggestions for managing speaking anxiety typically address its cognitive and behavioral components, while the physical components are left unattended. While we cannot block these natural and instinctual responses, we can engage in physical relaxation exercises to counteract the general physical signs of anxiety caused by cortisol and adrenaline release, which include increased heart rate, trembling, flushing, high blood pressure, and speech disfluency.
Some breathing and stretching exercises release endorphins, which are your body’s natural antidote to stress hormones. Deep breathing is a proven way to release endorphins. It also provides a general sense of relaxation and can be done discretely, even while waiting to speak. In order to get the benefits of deep breathing, you must breathe into your diaphragm. The diaphragm is the muscle below your lungs that helps you breathe and stand up straight, which makes it a good muscle for a speaker to exercise. To start, breathe in slowly through your nose, filling the bottom parts of your lungs up with air. While doing this, your belly should pooch out. Hold the breath for three to five full seconds and then let it out slowly through your mouth. After doing this only a few times, many students report that they can actually feel a flooding of endorphins, which creates a brief “light-headed” feeling. Once you practice and are comfortable with the technique, you can do this before you start your speech, and no one sitting around you will even notice. You might also want to try this technique during other stressful situations. Deep breathing before dealing with an angry customer or loved one, or before taking a test, can help you relax and focus.
Stretching is another way to release endorphins. Very old exercise traditions like yoga, tai chi, and Pilates teach the idea that stretching is a key component of having a healthy mind and spirit. Exercise in general is a good stress reliever, but many of us do not have the time or willpower to do it. However, we can take time to do some stretching. Obviously, it would be distracting for the surrounding audience if a speaker broke into some planking or Pilates just before his or her speech. Simple and discrete stretches can help get the body’s energy moving around, which can make a speaker feel more balanced and relaxed. Our blood and our energy/ stress have a tendency to pool in our legs, especially when we are sitting.
Vocal Warm-Up Exercises

Vocal warm-up exercises are a good way to warm up your face and mouth muscles, which can help prevent some of the fluency issues that occur when speaking. Newscasters, singers, and other professional speakers use vocal warm-ups. I lead my students in vocal exercises before speeches, which also helps lighten the mood. We all stand in a circle and look at each other while we go through our warm-up list. For the first warm-up, we all make a motorboat sound, which makes everybody laugh. The full list of warm-ups follows and contains specific words and exercises designed to warm up different muscles and different aspects of your voice. After going through just a few, you should be able to feel the blood circulating in your face muscles more. It is a surprisingly good workout!
Top Ten Ways to Reduce Speaking Anxiety
Many factors contribute to speaking anxiety. There are also many ways to address it. The following is a list of the top ten ways to reduce speaking anxiety that I developed with my colleagues, which helps review what we have learned.
- Remember, you are not alone. Public speaking anxiety is common, so do not ignore it—confront it.
- Remember, you cannot literally “die of embarrassment.” Audiences are forgiving and understanding.
- Remember, it always feels worse than it looks.
- Take deep breaths. It releases endorphins, which naturally fight the adrenaline that causes anxiety.
- Look the part. Dress professionally to enhance confidence.
- Channel your nervousness into positive energy and motivation.
- Start your outline and research early. Better information = higher confidence.
- Practice and get feedback from a trusted source. (Do not just practice for your cat.)
- Visualize success through positive thinking.
- Prepare, prepare, prepare! Practice is a speaker’s best friend.
9.2 Delivery Methods and Practice Sessions
There are many decisions to make during the speech-making process. Making informed decisions about delivery can help boost your confidence and manage speaking anxiety. In this section, we will learn about the strengths and weaknesses of various delivery methods. We will also learn how to make the most of your practice sessions.
Delivery Methods
Different speaking occasions call for different delivery methods. While it may be acceptable to speak from memory in some situations, lengthy notes may be required in others. The four most common delivery methods are impromptu, manuscript, memorized, and extemporaneous.
Impromptu Delivery
When using impromptu delivery , a speaker has little to no time to prepare for a speech (LibreTexts, 2021). This means there is little time for research, audience analysis, organizing, and practice. For this reason, impromptu speaking often evokes higher degrees of speaking anxiety than other delivery types. Although impromptu speaking arouses anxiety, it is also a good way to build public speaking skills. Using some of the exercises for managing speaking anxiety discussed earlier in this chapter can help a speaker manage the challenges of impromptu speaking (LibreTexts, 2021). Only skilled public speakers with much experience are usually able to “pull off” an impromptu delivery without looking unprepared. Otherwise, a speaker who is very familiar with the subject matter can sometimes be a competent impromptu speaker, because their expertise can compensate for the lack of research and organizing time.
When Mark Twain famously said, “It usually takes me more than three weeks to prepare a good impromptu speech,” he was jokingly pointing out the difficulties of giving a good impromptu speech, essentially saying that there is no such thing as a good impromptu speech, as good speeches take time to prepare. We do not always have the luxury of preparation, though. So when speaking impromptu, be brief, stick to what you know, and avoid rambling. Quickly organize your thoughts into an introduction, body, and conclusion. Try to determine three key ideas that will serve as the basis of your main points.
When would impromptu speaking be used? Since we have already started thinking of the similarities between public speaking and conversations, we can clearly see that most of our day-to-day interactions involve impromptu speaking. When your roommate asks you what your plans for the weekend are, you do not pull a few note cards out of your back pocket to prompt your response. This type of conversational impromptu speaking is not anxiety inducing because we are talking about our lives, experiences, or something with which we are familiar. This is also usually the case when we are asked to speak publicly with little to no advance warning.
For example, if you are at a meeting for work and you are representing the public relations department, a colleague may ask you to say a few words about a recent news story involving a public relations misstep of a competing company. In this case, you are being asked to speak on the spot because of your expertise. A competent communicator should anticipate instances like this when they might be asked to speak. Of course, being caught completely off guard or being asked to comment on something unfamiliar to you creates more anxiety. In such cases, do not pretend to know something you do not, as that may come back to hurt you later. You can usually mention that you do not have the necessary background information at that time but will follow up later with your comments.
Manuscript Delivery
Speaking from a written or printed document that contains the entirety of a speech is known as manuscript delivery . Manuscript delivery can be the best choice when a speech has complicated information and/or the contents of the speech are going to be quoted or published (LibreTexts, 2021). Despite the fact that most novice speakers are not going to find themselves in that situation, many are drawn to this delivery method because of the security they feel with having everything they are going to say in front of them. Unfortunately, the security of having every word you want to say at your disposal translates to a poorly delivered and unengaging speech (LibreTexts, 2021). Even with every word written out, speakers can still have fluency hiccups and verbal fillers as they lose their place in the manuscript or trip over their words. The alternative, of course, is that a speaker reads the manuscript the whole time, effectively cutting himself or herself off from the audience. One way to make a manuscript delivery more engaging is to use a teleprompter. Almost all politicians who give televised addresses use them.
To make the delivery seem more natural, print the speech out in a larger-than-typical font, triple-space between lines so you can easily find your place, use heavier-than-normal paper so it is easy to pick up and turn the pages as needed, and use a portfolio so you can carry the manuscript securely.
Memorized Delivery
Completely memorizing a speech and delivering it without notes is known as memorized delivery (LibreTexts, 2021). Some students attempt to memorize their speech because they think it will make them feel more confident if they do not have to look at their notes; however, when their anxiety level spikes at the beginning of their speech and their mind goes blank for a minute, many admit they should have chosen a different delivery method. When using any of the other delivery methods, speakers still need to rely on their memory. An impromptu speaker must recall facts or experiences related to their topic, and speakers using a manuscript want to have some of their content memorized so they do not read their entire speech to their audience. The problem with memorized delivery overall is that it puts too much responsibility on our memory, which we all know from experience is fallible (LibreTexts, 2021).
Even with much practice, our memories can fail. If you do opt to use memorized delivery, make sure you have several “entry points” determined, so you can pick up at spots other than the very beginning of a speech if you lose your place and have to start again. Memorized delivery is very useful for speakers who are going to be moving around during a speech when carrying notes would be burdensome. I only recommend memorized delivery in cases where the speech is short (only one to two minutes), the speech is personal (like a brief toast), or the speech will be repeated numerous times (like a tour guide’s story), and even in these cases, it may be perfectly fine to have notes. Many students think that their anxiety and/or delivery challenges will vanish if they just memorize their speech only to find that they are more anxious and have more problems.
Extemporaneous Delivery
Extemporaneous delivery entails memorizing the overall structure and main points of a speech and then speaking from keyword/key-phrase notes (LibreTexts, 2021). This delivery mode brings together many of the strengths of the previous three methods. Since you only internalize and memorize the main structure of a speech, you do not have to worry as much about the content and delivery seeming stale. Extemporaneous delivery brings in some of the spontaneity of impromptu delivery but still allows a speaker to carefully plan the overall structure of a speech and incorporate supporting materials that include key facts, quotations, and paraphrased information (LibreTexts, 2021). You can also more freely adapt your speech to fit various audiences and occasions, since not every word and sentence is predetermined. This can be especially beneficial when you deliver a speech multiple times.
When preparing a speech that you will deliver extemporaneously, you will want to start practicing your speech early and then continue to practice as you revise your content. Investing quality time and effort into the speech-outlining process helps with extemporaneous delivery. As you put together your outline, you are already doing the work of internalizing the key structure of your speech. Read parts of your outline aloud as you draft them to help ensure they are written in a way that makes sense and is easy for you to deliver.
By the time you complete the formal, full-sentence outline, you should have already internalized much of the key information in your speech. Now, you can begin practicing with the full outline. As you become more comfortable with the content of your full outline, start to convert it into your speaking outline. Take out information that you know well and replace it with a keyword or key phrase that prompts your memory. You will probably want to leave key quotes, facts, and other paraphrased information, including your verbal source citation information, on your delivery outline so you make sure to include it in your speech. Once you’ve converted your full outline into your speaking outline, practice it a few more times, making sure to take some time between each practice session so you don’t inadvertently start to memorize the speech word for word. The final product should be a confident delivery of a well-organized and structured speech that is conversational and adaptable to various audiences and occasions.
Practicing Your Speech

Practicing a speech is essential, and practice sessions can be more or less useful depending on how you approach them (Dlugan, 2008). There are three primary phases to the practice process. In the first phase, you practice as you are working through your ideas and drafting your outline. In the second, you practice for someone and get feedback (Dlugan, 2008). In the third, you put the final changes on the speech.
Start practicing your speech early, as you are working through your ideas, by reading sections aloud as you draft them into your working outline. This will help ensure your speech is fluent and sounds good for the audience. Start to envision the audience while you practice and continue to think about them throughout the practicing process. This will help minimize anxiety when you actually have them sitting in front of you. Once you have completed your research and finished a draft of your outline, you will have already practiced your speech several times, as you were putting it together. Now, you can get feedback on the speech as a whole.
You begin to solicit feedback from a trusted source in the second phase of practicing your speech (Dlugan, 2008). This is the most important phase of practicing, and the one that most speakers do not complete. Beginning speakers may be nervous to practice in front of someone. That is normal. However, review the strategies for managing anxiety discussed earlier in this chapter and try to face that anxiety. After all, you will have to face a full audience when you deliver the speech, so getting used to speaking in front of someone can only help you at this point. Choose someone who will give you constructive feedback on your speech. Before you practice for them, explain the assignment or purpose of the speech. When practicing for a classroom speech, you may even want to give the person the assignment guidelines or a feedback sheet that has some key things for them to look for. Ask them for feedback on content and delivery. Almost anyone is good at evaluating delivery, but it is more difficult to evaluate content. In addition, in most cases, the content of your speech will be account for more of your grade. Also, begin to time your speech at this point, so you can determine if it meets any time limits that you have.
In addition to practicing for a trusted source for feedback, you may want to audio or video record your speech (Dlugan, 2008). This can be useful because it provides an objective record that you can then compare with the feedback you got from your friend and to your own evaluation of your speech. The most important part of this phase is incorporating the feedback you receive into your speech. If you practice for someone, get feedback, and then do not do anything with the feedback, then you have wasted your time and theirs. Use the feedback to assess whether or not you met your speaking goals. Was your thesis supported? Was your specific purpose met? Did your speech conform to any time limits that were set? Based on your answers to these questions, you may need to make some changes to your content or delivery, so do not put this part of practicing off to the last minute. Once the content has been revised as needed, draft your speaking outline and move on to the next phase of practice.
During the third and final phase of practice, you are putting the final changes on your speech. You should be familiar with the content based on your early practice sessions. You have also gotten feedback and incorporated that feedback into the speech. Your practice sessions at this point should pre-create, as much as possible, the conditions in which you will be giving your speech. You should have your speaking outline completed so you can practice with it. It is important to be familiar with the content on your note cards or speaking outline so you will not need to rely on it so much during the actual delivery. You may also want to practice in the type of clothing you will be wearing on speech day. This can be useful if you are wearing something you do not typically wear—a suit for example—so you can see how it might affect your posture, gestures, and overall comfort level.
If possible, at least one practice session in the place you will be giving the speech can be very helpful; especially if it is a room you are not familiar with. Make sure you are practicing with any visual aids or technology you will use so you can be familiar with it and it does not affect your speech fluency. (Dlugan, 2008).Continue to time each practice round. If you are too short or too long, you will need to go back and adjust your content some more. Always adjust your content to fit the time limit; do not try to adjust your delivery. Trying to speed talk or stretch things out to make a speech faster or longer is a mistake that will ultimately hurt your delivery, which will hurt your credibility. The overall purpose of this phase of practicing is to minimize surprises that might throw you off on speech day.
Vocal Delivery
Vocal delivery includes components of speech delivery that relate to your voice. These include rate, volume, pitch, articulation, pronunciation, and fluency. Our voice is important to consider when delivering our speech for two main reasons. First, vocal delivery can help us engage and interest the audience. Second, vocal delivery helps ensure we communicate our ideas clearly.
Speaking for Engagement
We have all had the displeasure of listening to an unengaging speaker. Even though the person may care about his or her topic, an unengaging delivery that does not communicate enthusiasm will translate into a lack of interest for most audience members (Davis, 2021). Although a speaker can be visually engaging by incorporating movement and gestures, a flat or monotone vocal delivery can be sedating or even annoying. Incorporating vocal variety in terms of rate, volume, and pitch is key to being a successful speaker.
Rate of speaking refers to how fast or slow you speak (Barnard, 2018). If you speak too fast, your audience will not be able to absorb the information you present. If you speak too slowly, the audience may lose interest. The key is to vary your rate of speaking in a middle range, staying away from either extreme, in order to keep your audience engaged. In general, a higher rate of speaking signals that a speaker is enthusiastic about his or her topic. Speaking slowly may lead the audience to infer that the speaker is uninterested, uninformed, or unprepared to present his or her own topic. These negative assumptions, whether they are true or not, are likely to hurt the credibility of the speaker (Barnard, 2018). The goal is to speak at a rate that will interest the audience and will effectively convey your information. Speaking at a slow rate throughout a speech would likely bore an audience, but that is not a common occurrence.
Volume refers to how loud or soft your voice is. As with speaking rate, you want to avoid the extremes of being too loud or too soft, but still vary your volume within an acceptable middle range (Packard, 2020). When speaking in a typically sized classroom or office setting that seats about twenty-five people, using a volume a few steps above a typical conversational volume is usually sufficient. When speaking in larger rooms, you will need to project your voice. You may want to look for nonverbal cues from people in the back rows or corners, like leaning forward or straining to hear, to see if you need to adjust your volume more. Obviously, in some settings, a microphone will be necessary so the entire audience can hear you. Like rate, audiences use volume to make a variety of judgments about a speaker. Sometimes, softer speakers are judged as meek (Packard, 2020). This may lead to lowered expectations for the speech or less perceived credibility. Loud speakers may be seen as overbearing or annoying, which can lead audience members to disengage from the speaker and message. Be aware of the volume of your voice and, when in doubt, increase your volume a notch, since beginning speakers are more likely to have an issue of speaking too softly rather than too loudly.
Pitch refers to how high or low a speaker’s voice is. As with other vocal qualities, there are natural variations among people’s vocal pitch. Unlike rate and volume, we have less control over pitch. For example, males generally have lower pitched voices than females. Despite these limitations, each person still has the capability to change their pitch across a range large enough to engage an audience. Changing pitch is a good way to communicate enthusiasm and indicate emphasis or closure (Scotti, 2015). In general, our pitch goes up when we are discussing something exciting. Our pitch goes down slightly when we emphasize a serious or important point. Lowering pitch is also an effective way to signal transitions between sections of your speech or the end of your speech, which cues your audience to applaud and avoids an awkward ending.
Of the vocal components of delivery discussed so far, pitch seems to give beginning speakers the most difficulty. It is as if giving a speech temporarily numbs their ability to vary their pitch. Record yourself practicing your speech to help determine if the amount of pitch variety and enthusiasm you think you convey while speaking actually comes through. Speakers often assume that their pitch is more varied and their delivery more enthusiastic than the audience actually perceives it to be (Scotti, 2015). Many students note this on the self-evaluations they write after viewing their recorded speech.
Vocal Variety
Overall, the lesson to take away from this section on vocal delivery is that variety is key. Vocal variety includes changes in your rate, volume, and pitch that can make you look more prepared, seem more credible, and be able to engage your audience better (Moore, 2015). Employing vocal variety is not something that takes natural ability or advanced skills training. It is something that beginning speakers can start working on immediately and everyone can accomplish. The key is to become aware of how you use your voice when you speak, and the best way to do this is to record yourself (Moore, 2015). We all use vocal variety naturally without thinking about it during our regular conversations, and many of us think that this tendency will translate over to our speaking voices. This is definitely not the case for most beginning speakers. Unlike in your regular conversations, it will take some awareness and practice to use vocal variety in speeches. I encourage students to make this a delivery priority early on. Since it is something anyone can do, improving in this area will add to your speaking confidence, which usually translates into better speeches and better grades further on.
Speaking for Clarity
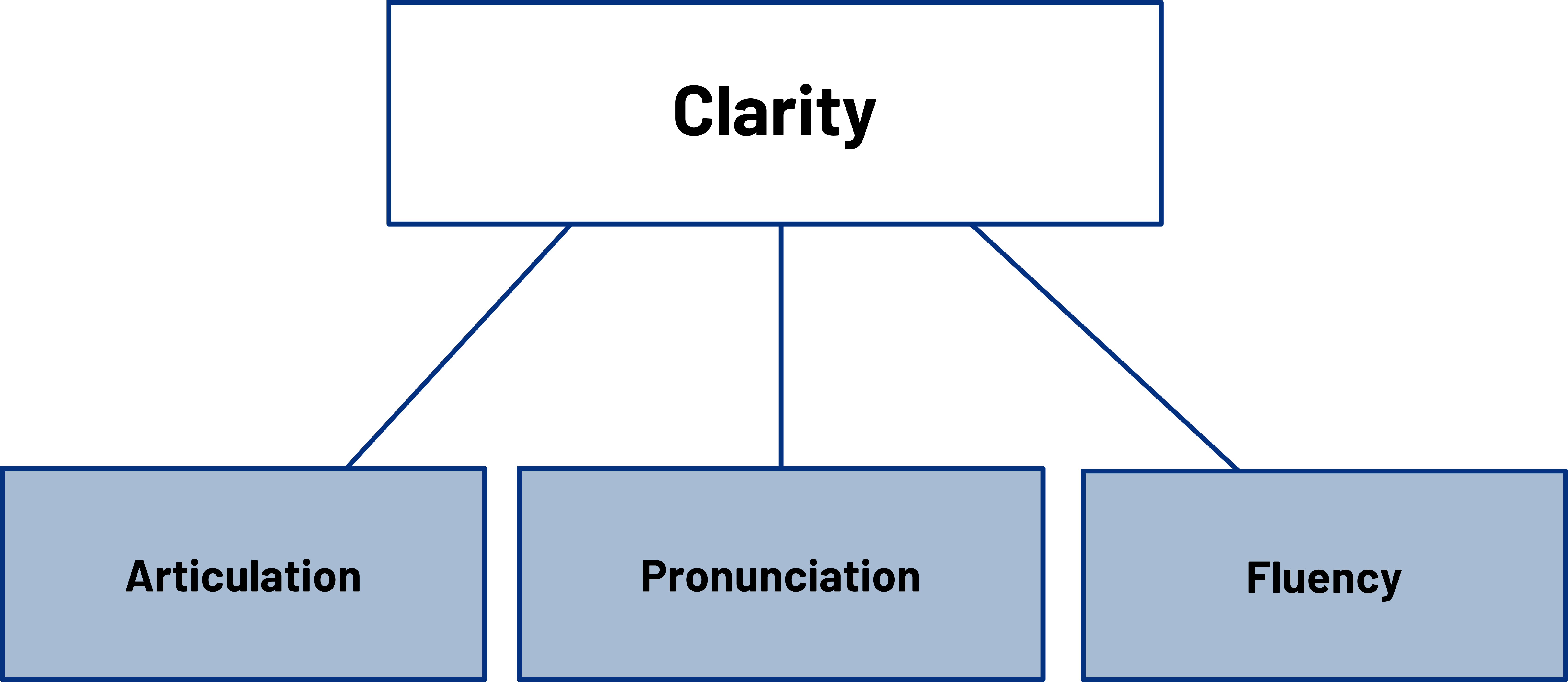
In order to be an effective speaker, your audience should be able to understand your message and digest the information you present (Rampton, 2021). Audience members will make assumptions about our competence and credibility based on how we speak. As with other aspects of speech delivery, many people are not aware that they have habits of speech that interfere with their message clarity. Since most of our conversations are informal and take place with people we know, many people do not make a concerted effort to articulate every word clearly and pronounce every word correctly (Rampton, 2021). Most of the people we talk to either do not notice our errors or do not correct us if they do notice. Since public speaking is generally more formal than our conversations, we should be more concerned with the clarity of our speech.
Articulation
Articulation refers to the clarity of sounds and words we produce. If someone is articulate, they speak words clearly, and speakers should strive to speak clearly. Poor articulation results when speakers do not speak clearly (Ward, 2020). For example, a person may say dinnt instead of didn’t , gonna instead of going to , wanna instead of want to , or hunnerd instead of hundred . Unawareness and laziness are two common challenges to articulation. As with other aspects of our voice, many people are unaware that they regularly have errors in articulation. Recording yourself speak and then becoming a higher self-monitor are effective ways to improve your articulation. Laziness, on the other hand, requires a little more motivation to address. Some people just get in the habit of not articulating their words well. Both mumbling and slurring are examples of poor articulation. In informal settings, this type of speaking may be acceptable, but in formal settings, it will be evaluated negatively. It will hurt a speaker’s credibility. Perhaps the promise of being judged more favorably is enough to motivate a mumbler to speak more clearly.
When combined with a low volume, poor articulation becomes an even greater problem. Doing vocal warm-ups like the ones listed in Section 10.1 “Managing Public Speaking Anxiety” or tongue twisters can help prime your mouth, lips, and tongue to articulate words more clearly. When you notice that you have trouble articulating a particular word, you can either choose a different word to include in your speech or you can repeat it a few times in a row in the days leading up to your speech to get used to saying it.
Pronunciation
Unlike articulation, which focuses on the clarity of words, pronunciation refers to speaking words correctly, including the proper sounds of the letters and the proper emphasis (Shtern, 2017). Mispronouncing words can damage a speaker’s credibility, especially when the correct pronunciation of a word is commonly known. We all commonly run into words that we are unfamiliar with and therefore may not know how to pronounce. Here are three suggestions when faced with this problem. First, look the word up in an online dictionary. Many dictionaries have a speaker icon with their definitions, and when you click on it, you can hear the correct pronunciation of a word. Some words have more than one pronunciation—for example, Caribbean —so choosing either of the accepted pronunciations is fine. Just remember to use consistently that pronunciation to avoid confusing your audience. If a word does not include an audio pronunciation, you can usually find the phonetic spelling of a word, which is the word spelled out the way it sounds.
Second, there will occasionally be words that you cannot locate in a dictionary. These are typically proper nouns or foreign words. In this case, use the “phone-a-friend” strategy. Call up the people you know who have large vocabularies or are generally smart when it comes to words, and ask them if they know how to pronounce it. If they do, and you find them credible, you are probably safe to take their suggestion.
Third, “fake it ‘til you make it” should only be used as a last resort. If you cannot find the word in a dictionary and your smart friends do not know how to pronounce it, it is likely that your audience will also be unfamiliar with the word. In that case, using your knowledge of how things are typically pronounced, decide on a pronunciation that makes sense and confidently use it during your speech. Most people will not question it. In the event that someone does correct you on your pronunciation, thank him or her for correcting you and adjust your pronunciation.
Fluency refers to the flow of your speaking. To speak with fluency means that your speech flows well and that there are not many interruptions to that flow. Two main disfluencies or problems affect the flow of a speech. Fluency hiccups are unintended pauses in a speech that usually result from forgetting what you were saying, being distracted, or losing your place in your speaking notes. Fluency hiccups are not the same as intended pauses, which are useful for adding emphasis or transitioning between parts of a speech. While speakers should try to minimize fluency hiccups, even experienced speakers need to take an unintended pause sometimes to get their bearings or to recover from an unexpected distraction. Fluency hiccups become a problem when they happen regularly enough to detract from the speaker’s message.
Verbal fillers are words that speakers use to fill in a gap between what they were saying and what they are saying next (Hennessy, 2019). Common verbal fillers include um , uh , ah , er , you know , and like . The best way to minimize verbal fillers is to become a higher self-monitor and realize that you use them. Many students are surprised when they watch the video of their first speech and realize they said “um” thirty times in three minutes. Gaining that awareness is the first step in eliminating verbal fillers, and students make noticeable progress with this between their first and second speeches (Hennessy, 2019). If you do lose your train of thought, having a brief fluency hiccup is better than injecting a verbal filler, because the audience may not even notice the pause or may think it was intentional.
9.3 Physical Delivery
Physical delivery.
Many speakers are more nervous about physical delivery than vocal delivery. Putting our bodies on the line in front of an audience often makes us feel more vulnerable than putting our voice out there. Yet most audiences are not as fixated on our physical delivery as we think they are. Knowing this can help relieve some anxiety, but it does not give us a free pass when it comes to physical delivery. We should still practice for physical delivery that enhances our verbal message. Physical delivery of a speech involves nonverbal communication through the face and eyes, gestures, and body movements.
Physical Delivery and the Face
We tend to look at a person’s face when we are listening to them (Hoffler, 2016). Again, this often makes people feel uncomfortable and contributes to their overall speaking anxiety. Many speakers do not like the feeling of having “all eyes” on them, even though having a room full of people avoiding making eye contact with you would be much more awkward. Remember, it is a good thing for audience members to look at you, because it means they are paying attention and interested. Audiences look toward the face of the speaker for cues about the tone and content of the speech.
Facial Expressions

Facial expressions can help bring a speech to life when used by a speaker to communicate emotions and demonstrate enthusiasm for the speech (Hoffler, 2016). As with vocal variety, we tend to use facial expressions naturally and without conscious effort when engaging in day-to-day conversations. Yet many speakers’ expressive faces turn “deadpan” when they stand in front of an audience. Some people naturally have more expressive faces than others do have—think about the actor Jim Carey’s ability to contort his face as an example. However, we can also consciously control and improve on our facial expressions to be speakers that are more effective. As with other components of speech delivery, becoming a higher self-monitor and increasing your awareness of your typical delivery habits can help you understand, control, and improve your delivery. Although you should not only practice your speech in front of a mirror, doing so can help you get an idea of how expressive or unexpressive your face is while delivering your speech.
Facial expressions help set the emotional tone for a speech, and it is important that your facial expressions stay consistent with your message (Hoffler, 2016). In order to set a positive tone before you start speaking, briefly look at the audience and smile. A smile is a simple but powerful facial expression that can communicate friendliness, openness, and confidence. Facial expressions communicate a range of emotions and are associated with various moods or personality traits.
For example, combinations of facial expressions can communicate that a speaker is tired, excited, angry, confused, frustrated, sad, confident, smug, shy, or bored, among other things. Even if you are not bored, for example, a slack face with little animation may lead an audience to think that you are bored with your own speech, which is not likely to motivate them to be interested. So make sure your facial expressions are communicating an emotion, mood, or personality trait that you think your audience will view favorably. Also, make sure your facial expressions match with the content of your speech. When delivering something lighthearted or humorous, a smile, bright eyes, and slightly raised eyebrows will nonverbally enhance your verbal message. When delivering something serious or somber, a furrowed brow, a tighter mouth, and even a slight head nod can enhance that message. If your facial expressions and speech content are not consistent, your audience could become confused by the conflicting messages, which could lead them to question your honesty and credibility.
Eye Contact
Eye contact is an important element of nonverbal communication in all communication settings. Eye contact can also be used to establish credibility and hold your audience’s attention (Barnard, 2017). We often interpret a lack of eye contact to mean that someone is not credible or not competent, and as a public speaker, you do not want your audience thinking either of those things. Eye contact holds attention because an audience member who knows the speaker is making regular eye contact will want to reciprocate that eye contact to show that they are paying attention. This will also help your audience remember the content of your speech better, because acting as if we are paying attention actually leads us to pay attention and better retain information.
Norms for eye contact vary among cultures (Barnard, 2017). Therefore, it may be difficult for speakers from countries that have higher power distances or are more collectivistic to get used to the idea of making direct and sustained eye contact during a speech. In these cases, it is important for the speaker to challenge himself or herself to integrate some of the host culture’s expectations and for the audience to be accommodating and understanding of the cultural differences.
Physical Delivery and the Body
Have you ever gotten dizzy as an audience member because the speaker paced back and forth? Anxiety can lead us to do some strange things with our bodies, like pacing, that we do not normally do, so it is important to consider the important role that your body plays during your speech. We call extra movements caused by anxiety nonverbal adaptors . Most of them manifest as distracting movements or gestures. These nonverbal adaptors, like tapping a foot, wringing hands, playing with a paper clip, twirling hair, jingling change in a pocket, scratching, and many more, can definitely detract from a speaker’s message and credibility. Conversely, a confident posture and purposeful gestures and movement can enhance both.
Posture is the position we assume with our bodies, either intentionally or out of habit. Although people, especially young women, used to be trained in posture, often by having them walk around with books stacked on their heads, you should use a posture that is appropriate for the occasion while still positioning yourself in a way that feels natural. In a formal speaking situation, it is important to have an erect posture that communicates professionalism and credibility (Clayton, 2018). However, a military posture of standing at attention may feel and look unnatural in a typical school or business speech. In informal settings, it may be appropriate to lean on a table or lectern, or even sit among your audience members (Clayton, 2018). Head position is also part of posture. In most speaking situations, it is best to keep your head up, facing your audience. A droopy head does not communicate confidence. Consider the occasion important, as an inappropriate posture can hurt your credibility.
Gestures include arm and hand movements. We all go through a process of internalizing our native culture from childhood. An obvious part of this process is becoming fluent in a language. Perhaps less obvious is the fact that we also become fluent in nonverbal communication, gestures in particular. We all use hand gestures while we speak, but we didn’t ever take a class in matching verbal communication with the appropriate gestures; we just internalized these norms over time based on observation and put them into practice. By this point in your life, you have a whole vocabulary of hand movements and gestures that spontaneously come out while you are speaking. Some of these gestures are emphatic and some are descriptive (Koch, 2007).
Emphatic gestures are the most common hand gestures we use, and they function to emphasize our verbal communication and often relate to the emotions we verbally communicate (Toastmasters International, 2011). Pointing with one finger or all the fingers straight out is an emphatic gesture. We can even bounce that gesture up and down to provide more emphasis. Moving the hand in a circular motion in front of our chest with the fingers spread apart is a common emphatic gesture that shows excitement and often accompanies an increased rate of verbal speaking. We make this gesture more emphatic by using both hands. Descriptive gestures function to illustrate or refer to objects rather than emotions (Toastmasters International, 2011). We use descriptive gestures to indicate the number of something by counting with our fingers or the size, shape, or speed of something. Our hands and arms are often the most reliable and easy-to-use visual aids a speaker can have.
While the best beginning strategy is to gesture naturally, you also want to remain a high self-monitor and take note of your typical patterns of gesturing. If you notice that you naturally gravitate toward one particular gesture, make an effort to vary your gestures more. You also want your gestures to be purposeful, not limp or lifeless.

Sometimes movement of the whole body, instead of just gesturing with hands, is appropriate in a speech. When students are given the freedom to move around, it often ends up becoming floating or pacing, which are both movements that comfort a speaker by expending nervous energy but only serve to distract the audience (Toastmasters International, 2011). Floating refers to speakers who wander aimlessly around, and pacing refers to speakers who walk back and forth in the same path. To prevent floating or pacing, make sure that your movements are purposeful. Many speakers employ the triangle method of body movement where they start in the middle, take a couple steps forward and to the right, then take a couple steps to the left, then return to the center. Obviously, you do not need to do this multiple times in a five- to ten-minute speech, as doing so, just like floating or pacing, tends to make an audience dizzy.
To make your movements appear more natural, time them to coincide with a key point you want to emphasize or a transition between key points. Minimize other movements from the waist down when you are not purposefully moving for emphasis. Speakers sometimes tap or shuffle their feet, rock, or shift their weight back and forth from one leg to the other. Keeping both feet flat on the floor, and still, will help avoid these distracting movements (Toastmasters International, 2011).
Credibility and Physical Delivery
Audience members primarily take in information through visual and auditory channels. Just as the information you present verbally in your speech can add to or subtract from your credibility, nonverbal communication that accompanies your verbal messages affects your credibility.
Professional Dress and Appearance
No matter what professional field you go into, you will need to consider the importance of personal appearance (Caffrey, 2020). Although it may seem petty or shallow to put so much emphasis on dress and appearance, impressions matter, and people make judgments about our personality, competence, and credibility based on how we look. In some cases, you may work somewhere with a clearly laid out policy for personal dress and appearance. In many cases, the suggestion is to follow guidelines for “business casual.”
Despite the increasing popularity of this notion over the past twenty years, people’s understanding of what business casual means is not consistent (Caffrey, 2020). The formal dress codes of the mid-1900s, which required employees to wear suits and dresses, gave way to the trend of business casual dress, which seeks to allow employees to work comfortably while still appearing professional. While most people still dress more formally for job interviews or high-stakes presentations, the day-to-day dress of working professionals varies.
Visual Aids and Delivery
Visual aids play an important role in conveying supporting material to your audience. They also tie to delivery, since using visual aids during a speech usually requires some physical movements. It is important not to let your use of visual aids detract from your credibility (Beqiri, 2018). Many good speeches are derailed by posters that fall over, videos with no sound, and uncooperative PowerPoint presentations.
Figure 9.1: Systematic desensitization can include giving more public speeches, taking communication courses, or imagining public speaking scenarios. William Moreland. 2019. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/GkWP64truqg
Figure 9.2: Vocal warm-up exercises. Andrea Piacquadio. 2020. Pexels license . https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-red-polo-shirt-3779453/
Figure 9.3: Primary phases to the practice process. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 9.4: Three facets of speaking for clarity. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 9.5: Facial expressions set the tone for a speech, and should be consistent with your message. Afif Kusuma. 2021. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/F3dFVKj6q8I
Figure 9.6: To make your movements appear natural, time them to coincide with a key point. Product School. 2019. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/S3hhrqLrgYM
Section 9.1
Allen, M., Hunter, J. E., & Donohue, W. A. (1989). Meta-analysis of self-report data on the effectiveness of public speaking anxiety treatment techniques. Communication Education, 38 (1), 54–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/03634528909378740
Bodie, G. D. (2010). A racing heart, rattling knees, and ruminative thoughts: Defining, explaining, and treating public speaking anxiety. Communication Education, 59 (1), 70–105. https://doi.org/10.1080/03634520903443849
Motley, M. T. (2009). COM therapy. In J. A. Daly, J. C. McCroskey, J. Ayres, T. Hopf, and D. M. Ayers Sonandré (Eds.), Avoiding communication: Shyness, reticence, and communication apprehension (pp. 379-400) (3rd ed.). Hampton Press.
Priem, J. S., & Haunani Solomon, D. (2009). Comforting apprehensive communicators: The effects of reappraisal and distraction on cortisol levels among students in a public speaking class. Communication Quarterly, 57 (3), 259-281.
Section 9.2
Barnard, D. (2018, January 20). Average speaking rate and words per minute . https://virtualspeech.com/blog/average-speaking-rate-words-per-minute
Davis, B. (2021, June 1). Why is audience engagement important? https://www.mvorganizing.org/why-is-audience-engagement-important/
Hennessy, C. (2019, March 27). Verbal filler: How to slow the flow . https://www.throughlinegroup.com/2019/03/27/verbal-filler-how-to-slow-the-flow/
LibreTexts. (2021, February 20). Methods of speech delivery . https://socialsci.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Communication/Public_Speaking/Exploring_Public_Speaking_(Barton_and_Tucker)/11%3A_Delivery/11.02%3A_Methods_of_Speech_Delivery
Moore, K. (2015, January 13). Public speaking tips: Use vocal variety like a pro! https://coachkiomi.com/best-public-speaking-tips-use-vocal-variety/
Packard, D. (2020, July 13). Speaking up: How to increase the volume of your voice . https://packardcommunications.com/speaking-up-how-to-increase-the-volume-of-your-voice/
Rampton, J. (2021, July 27). Learning to speak with clarity . https://www.calendar.com/blog/learning-to-speak-with-clarity/
Scotti, S. (2015, December 1). Vocal delivery: Take command of your voice . https://professionallyspeaking.net/vocal-delivery-take-command-of-your-voice-part-one/
Shtern, A. (2017, April 17). The importance of good pronunciation . https://shaneschools.com/en/the-importance-of-good-pronunciation/
Section 9.3
Barnard, D. (2017, October 24). The importance of eye contact during a presentation . https://virtualspeech.com/blog/importance-of-eye-contact-during-a-presentation
Beqiri, G. (2018, June 21). Using visual aids during a presentation or training session . https://virtualspeech.com/blog/visual-aids-presentation
Caffrey, A. (2020, February 25). The importance of personal appearance . http://www.publicspeakingexpert.co.uk/importanceofpersonalappearance.html
Clayton, D. (2018, October 31). The importance of good posture in public speaking . https://simplyamazingtraining.co.uk/blog/good-posture-public-speaking
Hoffler, A. (2016, June 7). Why facial expressions are important in public speaking . https://www.millswyck.com/2016/06/07/the-importance-of-facial-expression/
Koch, A. (2007). Speaking with a purpose (7th ed.). Pearson, 2007.
Toastmasters International. (2011). Gestures: Your body speaks . https://web.mst.edu/~toast/docs/Gestures.pdf
Fear or anxiety experience by a person due to real or perceived communication with another person or persons. This is a fear or anxiety that involves several types of communication not limited to public speaking.
Type of communication apprehension that produces physiological, cognitive, and behavioral reactions in people when faced with a real or imagined presentation
A type of cognitive restructuring that encourages people to think of public speaking as conversation rather than a performance
When a speaker has little or no time to prepare a speech
Speaking from a well written or printed document that contains the entirety of a speech
Completely memorizing a speech and delivering it without notes
Memorizing the overall structure and main points of a speech and then speaking from keyword/key-phrase notes
Refers to how fast or slow you speak
Refers to how loud or soft you speak
Refers to how high or low a speaker’s voice is
Changes in your rate, volume, and pitch that make you sound more prepared and credible
Refers to the clarity of sounds and words you pronounce
Whether you say the words correctly
Refers to the flow of your speaking
Unintended pauses in a speech that usually result from forgetting what you were saying, being distracted, or losing your place in speaking
The umms, uhhs, and other linguistic pauses of conversation
The feelings expressed on a person’s face
The act of looking directly into one another’s eyes
Extra movements caused by anxiety (i.e., tapping your foot, wringing your hands, playing with a paperclip, twirling hair, or scratching)
The position in which someone holds their body when standing or sitting
A movement of part of the body, especially a hand or the head, to express an idea or meaning
Communication in the Real World Copyright © by Faculty members in the School of Communication Studies, James Madison University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Module 6: Organizing and Outlining Your Speech
Methods of speech delivery, learning objectives.
Identify the four types of speech delivery methods and when to use them.
There are four basic methods of speech delivery: manuscript, memorized, impromptu, and extemporaneous. We’ll look at each method and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each.

A manuscript page from President George W. Bush’s address to the nation on the day of the 9/11 attacks in 2001.
A manuscript speech is when the speaker writes down every word they will speak during the speech. When they deliver the speech, they have each word planned and in front of them on the page, much like a newscaster who reads from a teleprompter.
The advantage of using a manuscript is that the speaker has access to every word they’ve prepared in advance. There is no guesswork or memorization needed. This method comforts some speakers’ nerves as they don’t have to worry about that moment where they might freeze and forget what they’ve planned to say. They also are able to make exact quotes from their source material.
When the exact wording of an idea is crucial, speakers often read from a manuscript, for instance in communicating public statements from a company.
However, the disadvantage with a manuscript is that the speakers have MANY words in front of them on the page. This prohibits one of the most important aspects of delivery, eye contact. When many words are on the page, the speakers will find themselves looking down at those words more frequently because they will need the help. If they do look up at the audience, they often cannot find their place when the eye returns to the page. Also, when nerves come into play, speakers with manuscripts often default to reading from the page and forget that they are not making eye contact or engaging their audience. Therefore, manuscript is a very difficult delivery method and not ideal. Above all, the speakers should remember to rehearse with the script so that they practice looking up often.
Public Speaking in History
The fall of the Berlin Wall on November 9, 1989, owed in large part to a momentary error made by an East German government spokesperson. At a live press conference, Günter Schabowski tried to explain new rules relaxing East Germany’s severe travel restrictions. A reporter asked, “when do these new rules go into effect?” Visibly flustered, Schabowski said, “As far as I know, it takes effect immediately, without delay.” In fact, the new visa application procedure was supposed to begin the following day, and with a lot of bureaucracy and red tape. Instead, thousands of East Berliners arrived within minutes at the border crossings, demanding to pass through immediately. The rest is history.
The outcome of this particular public-relations blunder was welcomed by the vast majority of East and West German citizens, and hastened the collapse of communism in Eastern and Central Europe. It’s probably good, then, that Schabowski ran this particular press conference extemporaneously, rather than reading from a manuscript.
You can view the transcript for “The mistake that toppled the Berlin Wall” here (opens in new window) .
A memorized speech is also fully prepared in advance and one in which the speaker does not use any notes. In the case of an occasion speech like a quick toast, a brief dedication, or a short eulogy, word-for-word memorization might make sense. Usually, though, it doesn’t involve committing each and every word to memory, Memorizing a speech isn’t like memorizing a poem where you need to remember every word exactly as written. Don’t memorize a manuscript! Work with your outline instead. Practice with the outline until you can recall the content and order of your main points without effort. Then it’s just a matter of practicing until you’re able to elaborate on your key points in a natural and seamless manner. Ideally, a memorized speech will sound like an off-the-cuff statement by someone who is a really eloquent speaker and an exceptionally organized thinker!
The advantage of a memorized speech is that the speaker can fully face their audience and make lots of eye contact. The problem with a memorized speech is that speakers may get nervous and forget the parts they’ve memorized. Without any notes to lean on, the speaker may hesitate and leave lots of dead air in the room while trying to recall what was planned. Sometimes, the speaker can’t remember or find his or her place in the speech and are forced to go get the notes or go back to the PowerPoint in some capacity to try to trigger his or her memory. This can be an embarrassing and uncomfortable moment for the speaker and the audience, and is a moment which could be easily avoided by using a different speaking method.
How to: memorize a speech
There are lots of tips out there about how to memorize speeches. Here’s one that loosely follows an ancient memorization strategy called the method of loci or “memory palace,” which uses visualizations of familiar spatial environments in order to enhance the recall of information.
You can view the transcript for “How to Memorize a Speech” here (opens in new window) .
An impromptu speech is one for which there is little to no preparation. There is often not a warning even that the person may be asked to speak. For example, your speech teacher may ask you to deliver a speech on your worst pet peeve. You may or may not be given a few minutes to organize your thoughts. What should you do? DO NOT PANIC. Even under pressure, you can create a basic speech that follows the formula of an introduction, body, and conclusion. If you have a few minutes, jot down some notes that fit into each part of the speech. (In fact, the phrase “speaking off the cuff,” which means speaking without preparation, probably refers to the idea that one would jot a few notes on one’s shirt cuff before speaking impromptu.) [1] ) An introduction should include an attention getter, introduction of the topic, speaker credibility, and forecasting of main points. The body should have two or three main points. The conclusion should have a summary, call to action, and final thought. If you can organize your thoughts into those three parts, you will sound like a polished speaker. Even if you only hit two of them, it will still help you to think about the speech in those parts. For example, if a speech is being given on a pet peeve of chewed gum being left under desks in classrooms, it might be organized like this.
- Introduction : Speaker chews gum loudly and then puts it under a desk (attention getter, demonstration). Speaker introduces themselves and the topic and why they’re qualified to speak on it (topic introduction and credibility). “I’m Katie Smith and I’ve been a student at this school for three years and witnessed this gum problem the entire time.”
- Body : Speaker states three main points of why we shouldn’t leave gum on desks: it’s rude, it makes custodians have to work harder, it affects the next student who gets nastiness on their seat (forecast of order). Speaker then discusses those three points
- Conclusion : Speaker summarizes those three points (summary, part 1 of conclusion), calls on the audience to pledge to never do this again (call to action), and gives a quote from Michael Jordan about respecting property (final thought).
While an impromptu speech can be challenging, the advantage is that it can also be thrilling as the speaker thinks off the cuff and says what they’re most passionate about in the moment. A speaker should not be afraid to use notes during an impromptu speech if they were given any time to organize their thoughts.
The disadvantage is that there is no time for preparation, so finding research to support claims such as quotes or facts cannot be included. The lack of preparation makes some speakers more nervous and they may struggle to engage the audience due to their nerves.
Extemporaneous
The last method of delivery we’ll look at is extemporaneous. When speaking extemporaneously, speakers prepare some notes in advance that help trigger their memory of what they planned to say. These notes are often placed on notecards. A 4”x6” notecard or 5”x7” size card works well. This size of notecards can be purchased at any office supply store. Speakers should determine what needs to go on each card by reading through their speech notes and giving themselves phrases to say out loud. These notes are not full sentences, but help the speakers, who turn them into a full sentence when spoken aloud. Note that if a quote is being used, listing that quote verbatim is fine.
The advantage of extemporaneous speaking is that the speakers are able to speak in a more conversational tone by letting the cards guide them, but not dictate every word they say. This method allows for the speakers to make more eye contact with the audience. The shorter note forms also prevent speakers from getting lost in their words. Numbering these cards also helps if one gets out of order. Also, these notes are not ones the teacher sees or collects. While you may be required to turn in your speech outline, your extemporaneous notecards are not seen by anyone but you. Therefore, you can also write yourself notes to speak up, slow down, emphasize a point, go to the next slide, etc.
The disadvantage to extemporaneous is the speakers may forget what else was planned to say or find a card to be out of order. This problem can be avoided through rehearsal and double-checking the note order before speaking.
Many speakers consider the extemporaneous method to be the ideal speaking method because it allows them to be prepared, keeps the audience engaged, and makes the speakers more natural in their delivery. In your public speaking class, most of your speeches will probably be delivered extemporaneously.
- As per the Oxford English Dictionary' s entry for "Off the Cuff." See an extensive discussion at Mark Liberman's Language Log here: https://languagelog.ldc.upenn.edu/nll/?p=4130 ↵
- Method of loci definition. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Method_of_loci . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- The mistake that toppled the Berlin Wall. Provided by : Vox. Located at : https://youtu.be/Mn4VDwaV-oo . License : Other . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- How to Memorize a Speech. Authored by : Memorize Academy. Located at : https://youtu.be/rvBw__VNrsc . License : Other . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- Address to the Nation. Provided by : U.S. National Archives. Located at : https://prologue.blogs.archives.gov/2011/09/06/911-an-address-to-the-nation/ . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- Methods of Speech Delivery. Authored by : Misti Wills with Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
12 Delivery: A Recipe for Great Speaking
Megan orcholski, university of wisconsin-milwaukee, learning objectives.
- Understand the importance of delivery and its impact on public speaking.
- Learn what tools create delivery and have a basic understanding of how to use them.
- Be better prepared to deliver a speech!
Imagine you go to a restaurant and order a dish that sounds delicious. When they bring you the food, it is cooked without care, unseasoned, and slopped onto your plate. It doesn’t look or taste very good. You’re hungry, so you eat it. It still has nutritional value, but you don’t enjoy it. You probably won’t remember this meal, and if you do, you will probably only remember how bad it was. When food is cooked, there is a lot of thought that goes into how the person eating the food (the audience) will feel when they eat it. Delivery is similar, as it is the vehicle for how an audience consumes a speech. The audience will get the speech whether it’s perfectly seasoned or thrown together without care. You have the opportunity as a speaker to make your content and performance appetizing to your audience!
Delivery can be thought of as the “icing on the cake,” but let’s break that down. Can you eat cake without icing? Sure. But icing is intended to complement the cake, make it look pretty, and taste better. Similarly, bad delivery can call attention to itself or make the cake worse. As a good friend of mine says, excellent delivery can enhance the content and make it taste sweeter.
Delivery is not always valued as an essential part of presentations by speakers. For example, have you ever had a teacher who was incredibly boring, didn’t look at you, or stumbled through their lectures? You, as the audience, probably wished they had practiced their delivery. To an audience, delivery is important. It can be the difference between an audience tolerating what you are saying and an audience really understanding, enjoying, and remembering your content.
Often, speakers in my class treat delivery like a magical talent that some people are lucky enough to have and others don’t. However, delivery skills can be learned by practice. Imagine speaking to someone who says, “I’m bad at downhill skiing.” You may reply, “Do you ski a lot?” or “Have you taken any lessons?” If someone does not practice and learn basic skills, they cannot expect to do well at a skill like skiing. Speaking is also a skill. It is something which you can practice, train, and improve. Yes, there are certainly some individuals for whom strong delivery seems to come naturally, but anyone can be an effective presenter if they are willing to practice. You do not have to like public speaking to be good at it. So get ready to get great at gifting your messages to audiences!
How to Effectively Use Your Voice
Vocalics also known as paralanguage, refers to the pieces of oral communication which convey meaning beyond the words. Have you heard the proverb, “It’s not what you say, but how you say it?” Vocalics is referring to the “how.” There are five distinct vocalics: volume, pitch, rate, articulation, and pronunciation. The first three (volume, pitch, and rate) are nonverbal components that are present in both oral and verbal communication. Oral, referring to the mouth, can be any sound or noise. Let’s say your blowing air out of your lips, making a loud sigh or humming, you are still using volume, pitch, and rate even though you aren’t saying words. Volume, pitch, and rate work nonverbally or in connection with the words to create meaning. The final two vocalics, articulation and pronunciation, are only present in verbal communication, as they address how words are formed and emphasized.
Vocalics , also known as paralanguage, refers to the pieces of oral communication which convey meaning beyond the words.
Think of vocalics as the basic ingredients of delivery. By learning how to utilize them, you can make unlimited types of delivery dishes. Having an understanding of how vocalics work and the main things they communicate will allow you to have more control over how you are communicating with your audience.
Volume has to do with how loud, or soft, something is. This is probably a pretty familiar concept, but you may not have thought deeply about how volume functions as a communication tool. Volume is associated with power and control. When a person gets louder, it is often because they want to be heard. Imagine a child who is trying to get the attention of busy adults or a customer trying to get the attention of a server at a crowded restaurant. Increasing volume is a way for a speaker to direct focus to themselves. However, the relationship between volume and power is more complicated. Being louder does not necessarily translate to more power. Instead, volume can work in complex ways to create meaning. Sure, getting louder or yelling can communicate importance or control, but so too can a drop in volume. For example, when parents are trying to get children to do something, the indication of it getting serious is often when they go from yelling to talking in a soft, controlled, serious manner. I knew as a child that it was when my parents got very quiet was when I was actually in big trouble!
Try It: Talk to Grandma
For a lot of people, an appropriate volume is a huge problem. Even when they think they are loud enough, it can still be a struggle to hear them well enough to easily understand what they are saying. If you have seen the movie Sister Act , think about the scene where Whoopi Goldberg’s character uses visualization to get the young singer to be loud enough and find her voice. Visualization may work for you too. Start by visualizing an older relative or friend who doesn’t hear very well. Imagine they are coming to see you speak. They will want to be able to hear you. In your head, place them behind the last row of the audience. If you are always making sure they can hear you from behind the last person, your volume should be adequate for the size of the audience and space.
When using volume as a tool of communication, speakers must consider projection. When you are speaking for an audience, you want to be loud enough to be heard. This volume often requires speakers to adjust how they project sound and focus their sound towards a target. [i] If you have had any music or theater training, you probably already understand the basics of focusing and directing your sound. You will want to have strong breath support to properly project. This breath support can be achieved by making sure you are not breathing shallowly with your shoulders, but rather pulling air all the way down to your diaphragm or about two inches below your belly button.
To get louder, people often use the throat and increase how hard the vocal cords are working, but this can strain the voice and also produce a stressed sound. A better way to achieve increased projection is to pull in a lot of air using your diaphragm so that more air can flow over your vocal cords. Your breath support will help you be able to control your volume.
Finally, you will want to focus your projection or have motivation in your volume. We do this all the time, like when we are at a sporting event and cheering your favorite player or when you are at a loud party and want to have a conversation with one person. [ii] You will adjust your volume to match your speaking situation. In these cases, the direction of your projection helps aid your volume in communicating intention and meaning. Use changes in volume meaningfully and deliberately to focus communication, emphasize ideas, or make yourself heard.
Try It: Using your Diaphragm
Breath support is crucial for projecting your voice without straining your vocal cords. To make sure you are breathing deeply enough, place your hand below your belly button. When you fill yourself with air, your hand should rise. To start, try laying down. This technique can help you to breathe deeply and relax. You can also see your hand move! If you find that your shoulders or chest are moving, you are probably not breathing deeply enough. To help, visualize that you are pulling from your toes. Your toes are not part of the breathing process, but thinking about drawing from your whole body can help deepen your breath.
Pitch deals with where your voice is resonating on the musical scale. If you start humming, a musician would be able to match the tone of your hum on their musical instrument. All of us have a pitch we naturally tend to. Our pitch is based on both the make-up of our body, specifically the length of one’s vocal folds and size of the vocal tract, and our socialization. Pitch is determined by how much your vocal folds are vibrating. Vibrating fast at a high cycle produces a higher pitch, whereas fewer vibrations create a lower pitch. [i] While our biology determines our abilities and range, a person may also vary or control their pitch based on cultural and social roles. Pitch is often used to communicate gender, as the physiological makeup is connected to sex. Female voices are, on average, about an octave higher than male voices. This claim is a generalization and can vary based on the individual. But this idea was demonstrated on a daily basis before everyone had a cell phone and the main phone used was a house phone. If a person unfamiliar with the house called, they had to rely solely on a person’s pitch to determine gender and age. Many of us, who grew up with a house phone, have a story of being mistaken for someone else in the household or being labeled with a gender we don’t identify with. Though our bodies may limit our pitch, we do have the ability to utilize pitch variation to give meaning to our words.
As with the other vocalics, pitch gets more interesting when it changes. Intonation refers to how your pitch rises and falls, creating vocal variety. When pitch rises, the voice communicates uncertainty or indecisiveness. This can be seen when we ask questions. However, some people tend to go up at the end of their sentences even when it is not a question. [ii] For example, imagine saying the phrase “I like your shirt” to a friend. Try it right now with your tone going up at the end. Now say it with your tone staying the same or coming down. Your intonation drastically changes the meaning.
Intonation refers to how your pitch rises and falls, creating vocal variety.
As a speaker, you want to be careful you are not communicating hesitancy or uncertainty when you intend to communicate confidence. Similarly, the dropping of pitch communicates certainty or finality. An example of this is in the Wizard of Oz when the Winkie guards are marching outside of the Wicked Witch’s castle. You can hear them sing, “O-Ee-Yah! Eoh-Ah!” [iii] Not only can you hear them change their intonation throughout the song, but their pitch lowers at the end of the phrase, creating finality to what may otherwise be meaningless sounds.
Try It: Play Around
Speakers do not tend to use as much vocal variety as they are capable of because they are not aware of how much variation they could have. One way to explore pitch is to specifically practice trying different tonal changes when you are speaking. First, to warm up, make noise all the way up and down the tonal scale. Start by making a high pitch and then falling to as low as you can comfortably go. Then go back up. (If you have a piano, you can plunk out notes or do scales). Once you’ve established your range, then pick a line or two in your speech, use the Pledge of Allegiance, or anything else you know very well. Try to speak those sentences in at least ten different ways. Each time, change your tone to play with how you could say the line or phrase. Pay attention to how your tone will impact the audience’s understanding of what you are saying. Focusing on your impact can be especially important on the last line of an argument or the end of the speech. Working to bring your pitch up in the middle of the sentence and dropping it at the end for finality can help you finish strong.
At its most basic, rate deals with speed, specifically how quickly or how slowly the words are spoken. This speed not only deals with the sounds within a word, but also the spaces between words. The speed at which words are spoken is connected to perceptions of emotional control. A fast rate is associated with uncontrolled or extreme emotion, whereas a slow rate is associated with controlled emotion. Think of an excited child trying to tell you a story. Their quick pace may sound frantic or frenzied. Now contrast that with how President Obama spoke during his public speeches. He typically has a very deliberate pace that communicated his command of the situation. You will want to pay attention to your rate in general, but you are also able to vary your rate to communicate meaning. For example, when you have something that is very important, slowing down the rate can help the point come across as important to the audience.
Speaking too quickly is a common problem, but you can train yourself to speak slower. Unfortunately, trying to “be slower!” doesn’t usually help. One tip is to think of putting little tiny spacers between your words. This way, it is easier to be understood, even at a fast pace. It’s like a friendship bracelet–if you put all of the beautiful, glamorous beads together, it looks gaudy. So, you separate them by clear or white spacer beads, making the beauty easier to look at and more fluid. By giving your words tiny spaces around them, your articulation will be stronger, and your words will be easier to understand. Some students also benefit from simply writing “pause” or “breath” on their note cards. These words can remind you to slow your rate, even if you are nervous during your speech.
Pacing can be an effective way of creating meaning and allowing your audience to absorb those meanings. A well-placed pause or giving more time to an explanation can help your audience understand and retain the information you are telling them. Your speaking rate is especially important because your audience is trying to mentally digest what you are saying. They cannot control the speed with which they receive the information, but you can help your audience have time to absorb and process information by being conscious of your rate.
Speakers often throw out information without much thought to the speed or pacing. Think about spoon-feeding a baby. Baby’s don’t have much control over how fast they receive their food. If you feed them too fast, they will cough and choke, and baby food will potentially come out their nose! When you feed a baby, you adjust your speech based on how long it takes the baby to taste, swallow, and enjoy the food. You want to do the same thing with your audience. Pay attention to how they are reacting and how they are absorbing the information. Observation is especially important during transitions of points or topics. Have you ever fed a baby a bite of peas and then a bite of bananas? It’s hilarious. The baby makes weird funny faces because their expectations were violated—they were expecting peas and got bananas instead. When you switch food, you often take a pause, maybe give the baby a sip of water. You want them to know you are moving to a different food. Similarly, a speaker should utilize their delivery to lead the audience from one point to the next. By paying attention to your pacing, your audience will be able to retain and remember more of your information.
Try It: Object Toss
One way to help you with your pacing is to picture your words as tangible objects going toward your audience. To practice this, get a bowl of cotton balls, pennies, scarves, or other lightweight objects. While you are practicing your speech, toss the objects toward a pretend audience (a blanket works great for this). However, you have to toss and speak at the same pace! This action shows a speaker very quickly how fast they are going. Now, one potential risk of this exercise is that you may start to find a rhythm with your tossing that may lull you into an unnatural speaking rhythm. You want your rate to sound natural and conversational, so once you get the pace under control, stop physically tossing and work to speak at that comfortable pace.
Articulation and Pronunciation
Articulation deals with how the words come out of your mouth, specifically how the words are shaped. Pronunciation is articulation combined with cultural influences to create ways of saying words that are identifiable to specific regions or groups of people. While two separate concepts, they often work in tandem when we are dealing with language. As a speaker, you want to make sure the audience can understand you. Paying attention to how you form your words can help you avoid mumbling or slurring your words together.
Pronunciation is grounded in culture and expectations can vary depending on your audience and specific speaking context. A dialect, which refers to how a person or group specifically forms their words and arranges their grammar, may impact how you are communicating with your audience. You may want to be aware if the audience has a similar or different dialect than you. For example, if you grew up in the Midwest, you may refer to Pepsi as “pop” with the o sounding more like an a. Whereas, those in the south would refer to it as a “coke” with a long o sound. And then there is the rest of the nation who say “soda.” People often forget they have a dialect and will sometimes view other dialects as inferior. But everyone has a dialect that delineates from ethnic heritage as well as regional locations. Being aware of dialect is important in public speaking because parts of your dialect may not be familiar to a group who uses a different one. You may end up using a term common to you, but unfamiliar to your audience. You may also pronounce a word in a way that the audience wouldn’t understand. By being aware of these issues, you can address them in your presentation if necessary.
Try It: All it Takes is a Pencil
If you are struggling with articulation or worried you are mumbling, a pencil can help your mouth realize how it’s forming words. Put the pencil in your mouth horizontally, and bite down on it. Say your speech with the pencil in your mouth until your words can be completely understood. Once you are understandable, pull the pencil out of your mouth WHILE YOU ARE TALKING. You should be able to feel the difference. This exercise can help train the muscles how to properly enunciate.
Vocal Variety
While there are different vocalics, they function together to create meaning and vocal variety . Be aware of how volume, pitch, rate, articulation, and pronunciation are working together in your speech to communicate to the audience. What does it do to a sentence when you get quieter, slow down, and drop your pitch all at the same time? How about getting louder, speeding up, and raising your pitch all while over articulating? These tools are excellent for helping to craft meaning beyond your words. Being aware of how they interact with each other can increase your ability to utilize them for making meaning when you are speaking.
Types of Vocalics
Volume has to do with how loud, or soft, something is.
Pitch deals with where your voice is resonating on the musical scale.
Rate deals with speed, specifically how quickly or how slowly the words are spoken.
Articulation deals with how the words come out of your mouth, specifically how the words are shaped.
Pronunciation is grounded in culture and expectations can vary depending on your audience and specific speaking context.
Vocal variety is when there are different vocalics being used, and they function together to create meaning.
How to Effectively Use your Body
To develop strong delivery skills, speakers need to realize the extent of the body’s power. Your body is an incredibly complex tool that is continuously making meaning. To start to understand this, do some people watching. What can you determine about a person based on the way they stand or how they move? Do you know how they are feeling based on their facial expressions? Beginning speakers are often quick to take their body for granted and not consciously employ choices of movement or expression. To better understand the tools of physical delivery, we will discuss kinesics and the multiple parts of nonverbal communication. Then, we will discuss proxemics or your body in relation to other objects, before ending with a discussion of appearance.
Similar to the vocalics, your body movements add to the words you are saying. Kinesics refers to how the body is interpreted as nonverbal communication and how physical movements are able to communicate on their own. Think about how often you move your body and what those movements signal to those around you. From popping your hip and crossing your arms to communicate impatience to a late friend, waving at a neighbor as you pass by, or even initiating a hug to a loved one, the movement of our bodies transmits meaning to those observing us. The significance of kinesics is heightened in a public speaking context because of the specific nature and focus of the presentation.
Kinesics refers to how the body is interpreted as nonverbal communication and how physical movements are able to communicate on their own.
Most of us have a basic understanding of posture , even if just from being told to “stand up straight” as a kid. However, posture is more than just standing up straight. It deals with the arrangement of your bones and muscles so that each area is allowed to do its job to its best ability. Good posture allows your body to support and control its structure without unnecessary tension in your frame or strain in the muscles. [i]
To think about your posture as a speaker, it’s helpful to think of the ranges in which your body could arrange itself. The first range is contraction to expansion. How broad are you letting your shoulders expand? How much space are you allowing your arms to take up? The amount of space you take up communicates to the audience. The next range is withdrawal and approach. Are you leaning forward or sinking back as you speak? When you move in your speech, is it toward or away from the audience? While this happens while walking, withdrawal and approach can also be communicated while standing. Think of how a lean forward communicates advancement whereas leaning back tends to communicate moving away.
Finally, general body orientation, or where all of your parts are in relationship to each other, is important. A neutral body posture is when both feet are flat on the floor, weight is balanced, arms hang gently, and muscles are relaxed. A neutral body posture is not the way most people tend to stand. Many people pop their hip or cross their legs. These stances do not provide a strong foundation to pull breath and initiate movement. As with all of the other components of delivery, there is not an ultimate right or wrong way to stand. Rather, thinking about your stance in relation to your message and audience is the most important consideration.
Try It: Roll it Up and Pull the String
Walk around a mall for a bit and you will be amazed by the popped hips, crossed legs, leaning, and general disregard for a balanced and strong posture. However, when you’re giving a speech, you want your body to look powerful and confident. Instead of forcing your body into an unnatural position, help your body find perfect posture on its own. Stand up straight and find balance with your weight equally distributed between both legs. Picture your spine as building blocks and, starting at your head, roll your spine down block by block until you are comfortably doubled over (do not stretch beyond your capabilities). Here, breathe deeply a few times. As you breathe, feel your back rise and fall with the inhale and exhale. Then slowly, block by block, roll back up until your head is gently floating on tip of your neck. Picture a string connected to your spine that comes out of the top of your head. By gently “pulling” that string at the end, your body should naturally lift into the correct posture. You don’t want to be tense. It may help to think “Bones up, Muscles down.”
While all of the pieces of our body are important for communicating, our arms and hands are arguably the most moveable and versatile. They can help enhance the emotional impact of your verbal message. Gestures are when our arms and hands use their different types of movements to create emphasis, meaning, and symbols. Two of the most well-known categories are emblems and illustrators. Understanding emblems and illustrators can help you know more about how your gestures are communicating. An emblem happens when the body creates something which can be interpreted as a verbal word or phrase. For example, holding your index finger and your middle finger into a “V” with the other fingers closed can be interpreted as the peace sign or the number 2. To be an emblem, Steven R. Brydon and Michael D. Scott argue a gesture must do three things: [i]
- It must have specific meaning for the audience members.
- It must be used intentionally by the speaker to purposely generate meaning.
- It must be easily translated into a few words.
Emblems are very specific to the context. For example, signaling to a train or truck driver by making a fist with a bent elbow and pumping it up and down means “honk your horn.” But that same gesture after scoring a goal in a soccer game can mean “YES!”
Emblems are also very connected to culture. Because of this, you will want to be aware of what meaning you are communicating with your emblem. For example, most of us know that connecting your thumb and index finger into a circle with your other fingers flared up means okay in the United States. However, if you did the same gesture in Japan it means “money” and in France, it means “zero” or “worthless.”
Illustrators are similar to emblems, but instead of being directly translated, they aid the verbal messages and are more generalized meanings. For example, you can describe how big or small an object is, but it is even more effective to also show with your hands. The visualization is aided because of how your motions connect to what you are saying. To demonstrate the importance of illustrators, attempt to give directions or describe something specific without using your hands. It’s very difficult to do!
Types of Gestures
An emblem happens when the body creates something which can be interpreted as a verbal word or phrase.
Illustrators are similar to emblems, but instead of being directly translated, they aid the verbal messages and are more generalized meanings.
Facial Expressions
Faces are fantastic places for expression and communication. Facial expressions are when a speaker uses their face to communicate. The face is often completely forgotten as a communicative space. Speakers should be very aware of their face to both increase their communication and prevent sending unintentional messages to the audience. When thinking about facial expressions, it’s important to avoid a blank or unexpressive face. You also don’t want to rely on one facial expression the whole time. Like your vocal tone, your face helps convey meaning. You want it to match your topic and change with the specific information in your speech. Smiling, for example, is incredibly underused. Many speakers get nervous about speaking and forget the elemental power of a smile. Obviously, there are times and topics for which a smile would not be the appropriate facial expression. But just as we do in conversations with our friends, do not be afraid to use your face to help communicate.
Eye Contact
Eye contact is important for establishing a connection and communicating with the audience. Eye contact is when the speaker meaningfully connects to the audience with their eyes. The first step to utilizing eye contact is to know your information well enough to be able to speak while making eye contact. This step may seem like common sense, but it can be incredibly difficult to do. Most beginning speakers rely very heavily on their notes or manuscript. I have often told students that I’m jealous of the podium or notecard because it gets all their attention! It may seem scary to look up at the audience, but sustained eye contact has the power to make you feel both physically and emotionally closer to each other. [i] In Western culture, eye contact works to establish a connection, communicate confidence, and affirm credibility.
Once you’re able to look up at the audience, it is important to practice looking directly in the eyes of the audience members. You cannot fake eye contact! If you can see your audience, they will know whether you are actually looking at them or if you are looking over the top of their heads. [ii] Direct eye contact is especially important if it is a smaller audience. If it is a larger audience or if you are on a lighted stage and can’t see the individuals in the audience, you will still want to direct your energy at specific spots to make it feel personal. There is no set time for how long to hold eye contact, as it is another variable which changes with the situation and circumstances. However, most speakers think they are holding their eye contact for longer than they are. Audiences gain a tremendous amount of energy and connection through eye contact, so making sure you are holding your eye contact for a significant amount of time is important.
Try It: Holding Eye Contact
One of my favorite mentors from college does this activity in class to show how really effective eye contact should make you feel. He will look at someone and say “Hi! You are my favorite. You are the only person I care about in this room. All these other people don’t mean anything to me. I have to look over there for a minute, but I’ll be right back…don’t forget you’re my favorite!” Then he looks to the next person and says, “Hi! You’re my favorite. You’re the only person I care about in this room…” After three or four people you understand how eye contact can make you feel like you are important and being spoken to at the individual level.[1] To practice eye contact, rehearse in front of objects with eyes. Obviously, a practice audience is the best. But if you don’t have one, you can use stuffed animals, pictures, posters, or anything that has eyes you can connect with. Set a few up around the room and practice playing connect the dots with your eyes while you speak. This will help you practice moving your attention from person to person instead of glancing at the wall, the clock, the floor on your way from one individual to another.
Make your Movement Matter
To make choices about your movement, you first need to be conscious of your body while speaking. I once watched a student twirl the lanyard from the keys in his pocket for most of his speech. When he saw the video, he was shocked because he had no memory of what his hands were doing during the speech. The brain is complicated and tricky. You need to train your brain to recognize and control what your body is doing while you speak. This training is comparable to a basketball player doing layups over and over or a baseball player practicing their swing. You want to know the movements so well that your muscle memory takes over while you are speaking. Many people will either not move at all or move for no particular reason.
Remember, movement helps aid in the communication process. In the same way, you are carefully selecting your words, you also want to choose your movements. If you don’t have a justified reason to move, you do not need to move. Save your energy for when the movement aids your message. One visualization that helps me is picturing my body as full of energy. That energy has to be used for certain things, such as making a sound to say the words, thinking about what comes next, and moving my head to have good eye contact. Sometimes the body does things that waste energy. Many people have ineffective habits, such as crossing legs, leaning on the podium, or pacing. Personally, I sway. If left to my own devices, I would sway the entire time I teach a course. Which would be incredibly distracting and unnecessary, not to mention tiring. So, I employ body consciousness to focus that energy into my words instead of wasting it swaying. This consciousness can take a lot of practice and mental energy. However, by employing body control and making conscious movements, you can increase your audience connection and enhance your topic.
Parts of Kinesics
Posture is the arrangement of your bones and muscles so that each area of the body is allowed to do its job to its best ability.
Gestures are when our arms and hands use their different types of movements to create emphasis, meaning, and symbols.
Facial expressions are when a speaker uses their face to communicate.
Eye contact is when the speaker meaningfully connects to the audience with their eyes.
Proxemics deals with space and location, specifically with how close humans are to each other. There is certainly a physical aspect to how bodies move together in spaces. There is also a cultural connection to proxemics. Think about how you are around certain people. You probably have a specific comfortable distance you usually stand away from people, and that distance most likely varies based on who the other person is. You may also have that one friend who has no personal space and will talk very close to you.
Proxemics deals with space and location, specifically with how close humans are to each other.
Proxemics is important in public speaking. If a podium or table is in the room, you will need to make a choice whether to stand behind, in front, or move the object out of the way. You do not want to be too far away from our audience, as a connection with the audience is important. However, you also don’t want to be too close, potentially making your audience uncomfortable or cutting off eye contact to parts of your audience. If you choose to move during your speech, pay attention when you are moving away and when you are moving toward them. Increasing or decreasing your distance during specific parts of your speech can enhance your message.
How you look matters, but I often find my students oversimplify this idea. There isn’t one way to look or appear. My students frequently ask if they have to “dress up” for their speeches. I point out that appearance doesn’t appear anywhere in my grading rubric, but appearance impacts a speaker’s ethos. It is more important that you are thinking critically about your speaking appearance than relying on one way to always look.
When you have to speak in public, consider the details of the situation. Is there anything specific you should wear to the occasion? How will your clothing communicate? Will it interact with your meaning? In an advanced public speaking course I taught, an experienced public speaker who showed up to every speech day in a full suit and pantyhose. This student was a self-proclaimed nerd and a huge Trekkie, so for a humorous speech assignment, she chose the topic of Star Trek. In the feedback session, a classmate said, “it’s too bad you don’t have a Star Trek uniform. That would have really added to your speech.” The student’s face fell—of course she owned a uniform! But, it had never occurred to her to wear it because she was so used to dressing up for speeches. For her final speech, she wore her Star Trek uniform and noted how it was the first public speech she’d ever given in anything other than a suit, citing that as part of her growth. As long as you are critically thinking about your appearance during a speech, you will be able to make conscious choices about what to wear.
Types of Preparation and Delivery
There are four styles of delivery that tend to be most useful for public speaking: manuscript, memory, impromptu, and extemporaneous.
Speaking from a Manuscript
In my experience, speaking from a manuscript is the type of delivery people tend to want to try. I have had students say it makes them feel more safe and comfortable to have every word planned out. That is an advantage of speaking from a manuscript. Manuscript speaking should be used in cases where getting the exact words correct are very important. In cases of intense or emotional speaking, a manuscript can also be the best delivery method. I had the opportunity to give my father’s eulogy when I was 21. This was an instance when I choose to use a manuscript in order to have a very well-constructed speech in an emotional time. There may be formal contexts where a manuscript would be preferred or follows the norms of the occasion. Former President Obama is an excellent example of someone who employs manuscript speaking in emotional times like after the Sandy Hook Elementary School shooting. A manuscript allowed the president to be comforting even in the face of tragedy.
If you plan to speak from a manuscript, you need to be aware of the challenges this type of speaking creates. Effectively speaking from a manuscript is harder than most people anticipate. Remember, the words are only part of the issue. As we have seen in this chapter, there are so many other components that go into delivery. Reading from a manuscript often causes speakers to talk very fast and not look up enough to connect with the audience. Because of this, manuscript speaking often leads to an uninteresting or disconnected performance. But, this does not mean manuscript delivery can’t be done well. Delivery from a manuscript can be effective with a significant amount of time and practice.
Speaking from Memory
There are some instances that may benefit from a memorized speech . For example, you may find yourself in a situation where memorization is required, such a speaking contest. You may find times you don’t want to use notes, such as at a wedding giving a toast. Memorization can be very beneficial, especially if the speech is short or the material is very familiar to you. First, memorization is the method that allows for the most audience connection. Since you don’t notes or a script to look at, you can engage your body, face, and eyes with the audience the entire time. Practicing your material thoroughly can put the speaker at ease.
But, like manuscript speaking, people greatly underestimate how much work it takes to speak from memory effectively. Different people have varying abilities when it comes to memorizing, but it almost always takes longer to memorize than people anticipate. You can’t just memorize the words, but rather you must know the material deeply in order to confidently speak from memory. Additionally, while the payoff can be great, so is the risk. Even with a lot of practice, speaking from memory may increase nerves and there is always a chance of a forgetting the material. Even if a speaker is well rehearsed, blanking in the moment is possible. You will want to practice blanking and know how to handle it if it happens. Finally, you will need to work hard to speak in the moment. While this method does allow you the most freedom with your voice and body in the moment, it is common to sound over-rehearsed or on autopilot. Make sure you are staying in the moment by really talking to your audience instead of at them.
Try It: Tips for Memorizing
- The more you can do to help your brain remember, the easier it will be to learn your speech. One way to help is to color-code your script by point. If your intro is one color, your first point is a different color and so on, it will help your brain remember the pieces of your speech. Another way to help is to stand in the places you plan to give each point. If you plan to move, placing your color-coded part in that place to help you associate the words with the space can be very effective. This process mimics how Greek orators memorized long stories and passages. They would walk, associating the ideas with where they were.
- Combine content memorization with word for word memorization. Use your outline to memorize the flow of ideas, the main points and where they go. Then, if you mess up or forget the individual words in a spot, you will be able to default to talking about the main ideas or jumping to the next part you remember.
- Practice in multiple contexts. Moving contexts will help your brain recall in many different circumstances. If you only ever practice in the car, your body will not be used to standing to deliver. Practicing in multiple spaces and for actual people can help increase the trustworthiness of the memory recall.
Impromptu Speaking
Impromptu speaking happens when a person has little or no time to prepare for the speaking situation. You may be thinking that this mode of delivery sounds terrifying, but you actually already practice impromptu speaking quite often. Anytime someone asks you for a short introduction about yourself, you speak to a group about yourself for a few minutes; or, when someone asks what you thought of the movie you just saw and you give a detailed answer, you are employing impromptu speaking. This method is not one that should be chosen for a speech you have time to or are required to prepare. Instead, think of this more as a skill or a recognition of circumstance to improve your speaking in these moments.
One key to impromptu speaking is to practice active listening. If you are in a meeting or a class where you know you may be called on to share your thoughts, intensely listening to what is happening and mentally engaging in the ideas will help you formulate your answer if someone asks you to talk. Anticipating impromptu opportunities can always be helpful in mentally preparing. I have been to several funerals and memorials where they open up the floor for people to share memories or say a few words. In these cases, I start thinking about what I want to say in advance by going over the order of my brief message in my head. In some cases, you may even want to jot down a few quick notes to help you stay focused.
Extemporaneous Speaking
The definition of extemporaneous speaking is to speak from limited notes. Extemporaneous speaking often gets confused with impromptu or off-the-cuff speaking, with people assuming you don’t have to prepare much before the speech. But, extemporaneous speaking is actually an engaged process that forces you to do a lot of research, organizing, and writing before you actively practice your delivery. There are several advantages of extemporaneous speaking. First, you are prepared but flexible in the moment. This level of preparation can prevent you from sounding robotic and encourage you to react to your specific audience in the speaking moment. Second, this type of speaking allows you opportunities to connect with the audience while not having to rely on your memory recall to know every word. Finally, you can adapt to your audience and the situation. If the audience laughs or reacts really well to something, you can mention it or add a reaction. If you are running out of time, you can make adjustments quickly to make sure you get out the most important information with the remaining speaking time.
The main disadvantage of extemporaneous speaking is that most people are not familiar with this process and it takes some getting used to. Beginning speakers, even if they are attempting extemporaneous speaking, will often make outlines with too many details and not practice enough which usually turns into reading a script. The process for practicing a strong extemporaneous speech can feel very different than other types of speaking methods. Instead of spending the majority of the time crafting each word, you need to practice talking. This practice can feel non-intuitive to writers or people who want their speech to sound perfect. Instead of writing every word, you want to craft a strong outline to use while you speak. Then, you want to stand up and practice it. I will say that again so you really believe me—stand up and try it!! Do not wait until you think you have everything perfect. You will run out of time, as it will never be perfect. And, practicing will help you make your outline stronger. Strengthening your outline with help you speak better in the moment. Go back and forth until you think you have a strong grasp on the concepts and can speak from your notes in the strong way you practiced.
This type of delivery is often the most effective and the one you will probably utilize the most beyond speaking classes. I highly encourage you to learn this skill and to practice it. You want to have a grasp of all of the styles of delivery. If you are in a class, that is a great place to practice extemporaneous speaking and get better at it. That way you understand and can use the multiple methods of delivering speeches. Extemporaneous speaking is often the most employed style in prepared speeches. It is what you will likely use in your job or at events you’ve been asked to speak. Learning how to do it well will be incredibly useful.
Remember, the most important thing is to choose the method that fits you and the situation best. You may also want to consider your strengthens and weaknesses as a speaker. The more you are critically thinking about the speech and it’s circumstances, the better qualified you are to make choices about how to best get your message to the audience.
Delivery and Audience Connection
You are not a tv.
Many speakers suffer from what I have termed “the TV effect.” Have you ever noticed your TV doesn’t care about you? If you are watching it and you have to leave to get a snack, the TV just keeps on playing. It doesn’t wait, and it doesn’t pause. Or, you laugh out loud at something in a show. The TV doesn’t pause for your laughter or even recognize you have laughed. At times, speakers act this way. They are nervous and just want to get the speech done. So, they get up and go! However, the brilliance of performance is how we can adjust in the moment and react to what is happening in our current situation. Your speaking is enhanced by the audiences’ reactions, the space you are speaking in, and how you are performing in the moment. Keep working to utilize the tools in this chapter to enhance your delivery during live performances.
You are not a train
The fear of doing something “wrong” often prevents speakers from achieving an audience connection. They are afraid they will mess up. I’ve even seen speakers ask to “start over” as if I am in control of them. Speakers often act like they are a train on train tracks. When it’s time to go, they go! They are chugging along, not looking up, not pausing, not paying attention to the audience, because they are afraid they will mess up and fall off the tracks. If a train is disturbed in its route, it doesn’t have a lot of options. It can go forward, backward, or just fall over. You are not on train tracks. Rather, you are in a field on a fairly trampled path. You have crafted the way to go but may veer off for one reason or another. If that happens, pick some berries, and find a way back to the path. Your audience may think that’s part of the journey or might be pleasantly surprised by the detour.
You are a tour guide!
Remember, your speech is a new destination where your audience has never been, and you are their tour guide. If you throw them onto the bus, hit the gas at 100 miles an hour, and never point out the sights, they are not going to enjoy the tour. You have the power to make it enjoyable for them. Help them onto the bus. Make sure they are comfortable. Connect with them. Go at a decent pace for them, so they don’t feel like you’re going to “crash.” Remember, that pace might be different than you want to go as the driver. Have you ever ridden with someone who is driving just a little too fast? They know they are in control because they are driving. But, the passenger does not necessarily feel comfortable. Adjust your pace with the audience in mind. Point out the important parts of your speech using emphasis. Make sure they can hear you. By being a good tour guide, your audience will definitely enjoy the trip!
Being yourself
When learning how to speak, speakers often fall into a few delivery traps when they are trying to deliver the speech “correctly.” They rely on reading or ignore their audience. Even when they conquer some of these basic delivery strategies, they still revert back and sound like a generic speaker. They fall into vocal patterns and don’t choose the pacing for their material or audience. They sound fine on the surface, but they don’t sound like themselves. In an attempt to do the speech “right,” speakers end up not actually being effective because they are not making conscious choices with themselves and the audience in mind.
Even if you are nervous, keep working to channel the verbal and physical qualities that are unique to you. Audiences want personality. Do not be afraid to let yours come through. You do not need to sound scripted or robotic to be an effective speaker. In fact, most people prefer someone who they can tell is a person beyond the confines of the speaking moment. One thing that can help you relax into being your engaging self is to think of yourself as an audience member. What do you enjoy? How do you want to be talked to? If you don’t enjoy monotone speaking (and few do), then work to have vocal variety. If you don’t want to work to hear and understand the words, work to be loud enough. If you prefer someone who is smiling, connected and engaging you, then work to be that person! You have the power to be entertaining! It takes practice, but you are capable of engaging the audience as yourself.
Audience participation
It is tempting to think of a speech as a speaker standing in front of an audience dumping information on them. But, as we have learned in this chapter, delivering a speech is an interactive performance that involves both the speaker and the audience. The level of audience participation may vary based on the speech and situation. For example, there may be times you ask questions to the audience that you actually want them to answer. Make sure you are patient and give them enough time to answer, as they may be used to answering a speaker’s questions.
Regulators , or gestures that control the flow of interaction can be used here. This may involve head nodding or moving your arms in a way to encourage your audience to participate. You may even find yourself in situations where there is a question and answer session as part of your speaking opportunity. The more you know about your topic, the more at ease you will be during this period. It is common to fear that an audience member might ask a question and you don’t know the answer. If this happens, there is no need to fake your way through an answer. Just explain how you don’t have that specific information and potentially discuss where they could find it.
Regulators are gestures that control the flow of interaction.
Actively listening to the question posed will help you formulate an answer. Don’t be afraid to be short and sweet. Often by that time, the audience has sat through your whole speech. While there are certainly times and occasions for drawn-out answers and discussions, be aware of how long you take to answer. They may be looking for a short supplement to what you already covered.
You have the power!
In the end, remember you are in charge of your vocal and physical choices as a speaker. It doesn’t always feel that way, but with practice and exercises, you will gain more awareness of what your voice and body are doing during a speech. Then, you will be able to make conscious choices to control them in order to make your speech more impactful. By working on delivery alongside the construction of your speech, you ensure your audience with be engaged and listening to you. Your practicing will help get your audience interested in your topic, retain what you are saying, and think deeply about your concepts.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2017 by Josh Miller; Marnie Lawler-Mcdonough; Megan Orcholski; Kristin Woodward; Lisa Roth; and Emily Mueller is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 5: Presenting Your Speech Module
Techniques for Effective Delivery
Use of your body.
As you stand before an audience, be confident and be yourself. Remember, you planned for this speech, you prepared well, and you practiced so that you know the material you will present. You are probably the expert in the room on this subject. If not, why are you the one making the presentation?
You need to consider not only what you say, but also how your body will support you and your words. When your actions are wedded to your words, the impact of your speech will be strengthened. If your platform behavior includes mannerisms unrelated to your spoken message, those actions will call attention to themselves and away from your speech.
Here are five areas on which to focus as you plan, practice, and present:
- Gripping or leaning on the lectern
- Finger tapping
- Lip biting or licking
- Toying with a pen or jewelry
- Adjusting hair or clothing
- Chewing gum
- Head wagging
These all have two things in common: They are physical manifestations of simple nervousness and they are performed unconsciously. When you make a verbal mistake, you can easily correct it, because you can hear your own words. However, you cannot see yourself, so most distracting mannerisms go uncorrected. You cannot eliminate distractions unless you know they exist.
The first step in self-improvement is to learn what you want to change. In speech preparation, nothing is as revealing as a video of your self. The first step in eliminating any superfluous behavior is to obtain an accurate picture of your body’s image while speaking. This should include:
- Body movement
- Facial expressions
- Eye contact
- 2. Build Self-Confidence by Being Yourself: The most important rule for making your body communicate effectively is to be yourself. The emphasis should be on the sharing of ideas, not on the performance. Strive to be as genuine and natural as you are when you speak to family members and friends.Many people say, “I’m okay in a small group, but when I get in front of a larger group I freeze. ” The only difference between speaking to a small informal group and to a sizable audience is the number of listeners. To compensate for this, you need only to amplify your natural behavior. Be authentically yourself, but amplify your movements and expressions just enough so that the audience can see them.
- 4. Build Self-confidence through Preparation: Nothing influences a speaker’s mental attitude more than the knowledge that s/he is thoroughly prepared. This knowledge leads to self- confidence, which is a vital ingredient of effective public speaking.How many of us have ever experienced a situation in which we had not prepared well for a presentation? How did we come across? On the other hand, think of those presentations that did go well. These are the ones for which we were properly prepared.
Facial Expressions
Leave that deadpan expression to poker players. A speaker realizes that appropriate facial expressions are an important part of effective communication. In fact, facial expressions are often the key determinant of the meaning behind the message. People watch a speaker’s face during a presentation. When you speak, your face -more clearly than any other part of your body -communicates to others your attitudes, feelings, and emotions.
Remove expressions that do not belong on your face. Inappropriate expressions include distracting mannerisms or unconscious expressions not rooted in your feelings, attitudes, and emotions. In much the same way that some speakers perform random, distracting gestures and body movements, nervous speakers often release excess energy and tension by unconsciously moving their facial muscles (e.g., licking lips, tightening the jaw).
One type of unconscious facial movement which is less apt to be read clearly by an audience is involuntary frowning. This type of frowning occurs when a speaker attempts to deliver a memorized speech. There are no rules governing the use of specific expressions. If you relax your inhibitions and allow yourself to respond naturally to your thoughts, attitudes, and emotions, your facial expressions will be appropriate and will project sincerity, conviction, and credibility.
Eye Contact
Eye contact is the cement that binds together speakers and their audiences. When you speak, your eyes involve your listeners in your presentation. Jan Costagnaro says, “When you maintain eye contact, you present an air of confidence in yourself and what you are communicating. People who are listening to what you are saying will take you more seriously, and will take what you say as important. If you lose eye contact or focus on everything else but the person(s) you are speaking to, you may not be taken seriously and the truth in your points may be lost. ” There is no surer way to break a communication bond between you and the audience than by failing to look at your listeners. No matter how large your audience may be, each listener wants to feel that you are speaking directly to him/her.
The adage, “The eyes are the mirror of the soul, ” underlines the need for you to convince people with your eyes, as well as your words. Only by looking at your listeners as individuals can you convince them that you are sincere and are interested in them and that you care whether they accept your message. When you speak, your eyes also function as a control device you can use to ensure the audience’s attentiveness and concentration.
Eye contact can also help to overcome nervousness by making your audience a known quantity. Effective eye contact is an important feedback device that makes the speaking situation a two-way communication process. By looking at your audience, you can determine how they are reacting.
When you develop the ability to gauge the audience’s reactions and adjust your presentation accordingly, you will be a much more effective speaker. The following supporting tips will help you be more confident and improve your ability to make eye contact:
Know your material. Know the material so well that you do not have to devote your mental energy to the task of remembering the sequence of ideas and words.
Prepare well and rehearse enough so that you do not have to depend too heavily on notes. Many speakers, no matter how well prepared, need at least a few notes to deliver their message. If you can speak effectively without notes, by all means do so. But if you choose to use notes, they should be only a delivery outline, using key words. Notes are not a substitute for preparation and practice.
Establish a personal bond with listeners. Begin by selecting one person and talking to him/ her personally. Maintain eye contact with that person long enough to establish a visual bond (about five to ten seconds). This is usually the equivalent of a sentence or a thought. Then shift your gaze to another person. In a small group, this is relatively easy to do. But, if you are addressing hundreds or thousands of people, it is impossible. What you can do is pick out one or two individuals in each section of the room and establish personal bonds. Then, each listener will get the impression you are talking directly to him/her.
Monitor visual feedback. While you are talking, your listeners are responding with their own nonverbal messages. Use your eyes to actively seek out this valuable feedback. If individuals aren’t looking at you, they may not be listening either. Make sure they can hear you. Then work to actively engage them.
Your Appearance Matters
Multiple studies have has shown that appearance influences everything from employment to social status. Whether we like to admit it or not, ours is a culture obsessed with appearance. Attractive people are more likely to get the job, get the promotion, and get the girl (or guy). Bonnie Berry’s 2008 research on physical appearance also shows that communicator attractiveness influences how an audience perceives the credibility of the speaker. Overall, more attractive speakers were thought to be more credible (51).
So what does that mean for you as you prepare for a speech? Bottom line: Make an effort. If your listeners will have on suits and dresses, wear your best suit or dress -the outfit that brings you the most compliments. Make sure that every item of clothing is clean and well tailored. Certainly a speaker who appears unkempt gives the impression to the audience that s/he doesn’t really care, and that’s not the first impression that you want to send to your listeners.
Fundamentals of Public Speaking Copyright © by Lumen Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Aesthetics and Delivery
Learning Objectives
- Define verbal delivery
- Understand the benefits of effective vocal delivery
- Explore techniques for evoking senses through language
- Utilize specific techniques to enhance vocal delivery
Humans are communicators. We rely on processes of communication to make sense of our world and we rely on others’ communicating with us to create shared meaning. Through symbols, we use and adapt language with one another and our communities.
The same is true for speeches, but what symbols you select and how you portray them—what we’ll call verbal delivery — are central to your audience and how they experience or comprehend what you say.
For example, consider your favorite podcaster or podcast series. We love crime podcasts! Despite being reliant on vocal delivery only, the presenters’ voices paint an aesthetic picture as they walk us through stories around crime, murder, and betrayal. So, how do they do it? What keeps millions of people listening to podcasts and returning to their favorite verbal-only speakers? Is it how they say it? Is it the language they choose? All of these are important parts of effective vocal delivery.
Below, we begin discussing vocal delivery—language choices, projection, vocal enunciation, and more.
Language and Aesthetics
It was 5 p.m. As she looked out the smudged window over the Kansas pasture, the wind quickly died down and the rolling clouds turned a slight gray-green. Without warning, a siren blared through the quiet plains as she pulled her hands up to cover her ears. Gasping for breath, she turned toward the basement and flew down the stairs as the swirling clouds charged quickly toward the farm house.
What’s happening in this story? What are you picturing? A treacherous tornado? A devastating storm rumbling onto a small Kansas farm? If so, the language in the story was successful.
Like this example demonstrates, the language that you use can assist audiences in creating a mental picture or image – creating a visualization is a powerful tool as a speaker.
Aesthetics is, certainly, based on how you deliver or embody your speech. But aesthetics also incorporates language choices and storytelling – techniques that craft a meaningful picture and encompass how you deliver the information or idea to your audience. In this section, we will extend our conversation from Chapter 5 about language to explore vivid language, implementing rhetorical techniques, and storytelling as an aesthetic tool to create resonance with your audience.
Vivid Language
Vivid language evokes the senses and is language that arouses the sensations of smelling, tasting, seeing, hearing, and feeling. Think of the word “ripe.” What is “ripe?” Do ripe fruits feel a certain way? Smell a certain way? Taste a certain way? Ripe is a sensory word. Most words just appeal to one sense, like vision. Think of color. How can you make the word “blue” more sensory? How can you make the word “loud” more sensory? How would you describe the current state of your bedroom or dorm room to leave a sensory impression? How would you describe your favorite meal to leave a sensory impression?
In the opening Kansas storm example above, the author may want the audience to sense danger or a certain intensity around the approaching tornado. To create that audience experience, you must craft language that emphasizes these elements.
When using vivid language, you’re trying to bring those sensations to life in a way that can create a vivid experience for your audience. “How can I best represent this idea?” you might ask or “how can I best create a scenario where the audience feels like they’re a part of the scene?”
Viivd language can take time to craft. As you work through your speech, determine where you’d like the audience to experience a particular sensation, and focus on integrating vivid language.
Remember that pathos is a persuasive appeal that is at your disposal, and using vivid language can assist in creating an emotional experience and sensation for the audience.
Rhetorical Techniques
There are several traditional techniques that have been used to engage audiences and make ideas more attention-getting and memorable. These are called rhetorical techniques. Although “rhetorical” is associated with persuasive speech, these techniques are also effective with other types of speeches. We suggest using alliteration, parallelism, and rhetorical tropes.
Alliteration is the repetition of initial consonant sounds in a sentence or passage. In his “I Have a Dream Speech,” Dr. Martin Luther King said, “I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.” Do you notice how the consonant of “C” resounds throughout?
Parallelism is the repetition of sentence structures. It can be useful for stating your main ideas. Which one of these sounds better?
“Give me liberty or I’d rather die.”
“Give me liberty or give me death.”
The second one uses parallelism. Quoting again from JFK’s inaugural address: “Let every nation know, whether it wishes us well or ill, that we shall pay any price, bear any burden, meet any hardship, support any friend, oppose any foe to assure the survival and the success of liberty.” The repetition of the three-word phrases in this sentence (including the word “any” in each) is an example of parallelism.
Tropes are a turning of the text where the literal meaning is changed or altered to provide new insight (Brummett, 2019). This is often referred to as figurative language, or using comparisons with objects, animals, activities, roles, or historical or literary figures. A literal statement would say, “The truck is fast.” Figurative says, “The truck is as fast as…“ or “The truck runs like…”
You are likely most familiar with the metaphor – one type of trope. Metaphors are direct comparisons, such as “When he gets behind the wheel of that truck, he is Kyle Busch at Daytona.” Here are some more examples of metaphors:
Love is a battlefield.
Upon hearing the charges, the accused clammed up and refused to speak without a lawyer.
Every year a new crop of activists is born.
Similes are closely related to metaphors, and use “like” or “as” when crafting a comparison. “The truck runs like,” is the beginning of a simile.
Tropes are useful because they assist the audience in seeing an idea in a new way or a new light. This can be particularly helpful if you’re struggling to create a vivid experience but have been unsuccessful at evoking the senses. A metaphor can assist by comparing your argument with an idea that the audience is familiar with. If you’re trying to evoke a particular felt sense, make sure the compared idea can conjure up that particular feeling.
Whatever trope you use, the goal is to craft an interesting comparison or turn the text in a unique way that leads to great comprehension for the audience.
Storytelling
Stories and storytelling, in the form of anecdotes and narrative illustrations, are a powerful tool as a public speaker. For better or worse, audiences are likely to remember anecdotes and narratives long after a speech’s statistics are forgotten. Human beings love stories and will often will walk away from a speech moved by or remembering a powerful story or example.
So, what makes a good story?
As an art form, storytelling may include:
- Attention to sequence, or the order of the story;
- Embedding a dramatic quality (or using pathos);
- The use of imagery (or figurative language).
While there is no “one-model-fits-all” view of storytelling, we often know a good story when we hear one, and they are a helpful way to expand your argument and place it in a context.
If you have personal experience with an argument or advocacy that you select, it may be helpful to provide a short story for the audience that provides insight into what you know. Remember that anecdotes are a form of evidence, and we can feel more connected with an idea if the story is related to something a speaker has been through. For example, if you selected police brutality as a speech advocacy, embedding a story about police violence may support your thesis statement and allow your audience to visualize what that might be like. It may draw them in to see a perspective that they hadn’t considered.
Similarly, consider the placement of your story. While your speech may rely on a longer narrative form as an organizational pattern, it’s more likely that you’ll integrate a short story within your speech. We most commonly recommend stories as:
- The attention getter
- Evidence within a main point
- A way to wrap up the speech and leave the audience with something meaningful to consider.
Stories, rhetorical techniques, and vivid language are important mechanisms to evoke language with aesthetics. In addition to what you say, verbal delivery also includes how you say it, including: vocal projection, verbal enunciation and punctuation, and vocal rate.
You may have experienced a situation where an audience notified a speaker that they couldn’t be heard. “Louder!” Here, the audience is letting the speaker know to increase their volume , or the relative softness or loudness of one’s voice. In this example, the speaker needed to more fully project their vocals to fit the speaking-event space by increasing their volume. In a more formal setting, however, an audience may be skeptical to give such candid feedback, so it is your job to prepare.
Projection is a strategy to vocally fill the space ; thus, the space dictates which vocal elements need to be adapted because every person in the room should comfortably experience your vocal range. If you speak too softly (too little volume or not projecting), your audience will struggle to hear and understand and may give up trying to listen. If you speak with too much volume, your audience may feel that you are yelling at them, or at least feel uncomfortable with you shouting. The volume you use should fit the size of the audience and the room.
Vocal Enunciation and Punctuation
Vocal enunciation is often reduced to pronouncing words correctly, but enunciation also describes the expression of words and language.
Have you ever spoken to a friend who replied, “Stop that! You’re mumbling.” If so, they’re signaling to you that they aren’t able to understand your message. You may have pronounced the words correctly but had indistinct enunciation of the words, leading to reduced comprehension.
One technique to increase enunciation occurs during speech rehearsal, and it’s known as the “dash” strategy: e-nun-ci-ate e- ve – ry syll – a – bal in your pre- sen -ta- tion .
The dashes signify distinct vocal enunciation to create emphasis and expression. However, don’t go overboard! The dash strategy is an exaggerated exercise, but it can lead to a choppy vocal delivery.
Instead, use the dash strategy to find areas where difficult and longer words need more punctuated emphasis and, through rehearsal, organically integrate those areas of emphasis into your presentational persona.
Verbal punctuation is the process of imagining the words as they’re written to insert purposeful, punctuated pauses to conclude key thoughts. Your speech is not a run-on sentence. Verbal punctuation allows decisiveness and avoids audiences wondering, “is this still the same sentence?”
Verbal punctuation is a strategy to minimize vocalized fillers , including common fillers of “like, and, so, uh.” Rather than use a filler to fill a vocal void in the speech, punctuate the end of the sentence through a decisive pause (like a period in writing!).
We know what you’re thinking: “there’s no way that reducing fillers is this easy.” You’re partially right. We all use vocalized fillers, particularly in informal conversation, but the more you rehearse purposeful punctuation and decisive endings to your well-crafted thoughts and arguments, the fewer filler words you will use.
It is also helpful to ask for input and feedback from friends, colleagues, or teachers. “What are my filler words?” We have listed common fillers, but you may unconsciously rely on different words. One author, for example, was never aware that they used “kind of” until a colleague pointed the filler out. Once you’re aware of your filler words, work to carefully, consciously, and meticulously try to catch yourself when you say it. “Consciously” is key here, because you need to bring an awareness about your fillers to the forefront of your brain.
Pace and Rate
How quickly or slowly you say the words of your speech is the rate . A slower rate may communicate to the audience that you do not fully know the speech. “Where is this going?” they may wonder. It might also be slightly boring if the audience is processing information faster than it’s being presented.
By contrast, speaking too fast can be overly taxing on an audience’s ability to keep up with and digest what you are saying. It sometimes helps to imagine that your speech is a jog that you and your friends (the audience) are taking together. You (as the speaker) are setting the pace based on how quickly you speak. If you start sprinting, it may be too difficult for your audience to keep up and they may give up halfway through. Most people who speak very quickly know they speak quickly, and if that applies to you, just be sure to practice slowing down and writing yourself delivery cues in your notes to maintain a more comfortable rate.
You will want to maintain a good, deliberate rate at the beginning of your speech because your audience will be getting used to your voice. We have all called a business where the person answering the phone mumbles the name of the business in a rushed way. We aren’t sure if we called the right number. Since the introduction is designed to get the audience’s attention and interest in your speech, you will want to focus on clear vocal rate here.
You might also consider varying the rate depending on the type of information being communicated. While you’ll want to be careful going too slow consistently, slowing your rate for a difficult piece of supporting material may be helpful. Similarly, quickening your rate in certainly segments can communicate an urgency.
And although awkward, watching yourself give a speech via recording (or web cam) is a great way to gauge your natural rate and pace.
Vocal Pauses
The common misconception for public speaking students is that pausing during your speech is bad, but pausing (similar to and closely aligned with punctuation) can increase both the tone and comprehension of your argument. This is especially true if you are making a particularly important point or wanting a statement to have powerful impact: you will want to give the audience a moment to digest what you have said. You may also be providing new or technical information to an audience that needs additional time to absorb what you’re saying.
For example, consider the following statement: “Because of issues like pollution and overpopulation, in 50 years the earth’s natural resources will be so depleted that it will become difficult for most people to obtain enough food to survive.” Following a statement like this, you want to give your audience a brief moment to fully consider what you are saying. Remember that your speech is often ephemeral : meaning the audience only experiences the speech once and in real time (unlike reading where an audience can go back).
Use audience nonverbal cues and feedback (and provide them as an audience member) to determine if additional pauses may be necessary for audience comprehension. Audiences are generally reactive and will use facial expressions and body language to communicate if they are listening, if they are confused, angry, or supportive.
Of course, there is such a thing as pausing too much, both in terms of frequency and length. Someone who pauses too often may appear unprepared. Someone who pauses too long (more than a few seconds) runs the risk of the audience feeling uncomfortable or, even worse, becoming distracted or letting their attention wander.
Pauses should be controlled to maintain attention of the audience and to create additional areas of emphasis.
In this chapter, we introduced verbal delivery as a core component of your speech aesthetics. Verbal delivery includes language – including vivid language, tropes, and storytelling. In addition, projection, rate, punctuation, enunciation, and pausing all work to deliver an effective presentation. The “rehearsal” chapter will assist as you consider the verbal dynamics of your speech and begin to strategize best practices for deliver as you prepare to present.
In Chapter 9, we’ll continue discussing aesthetics by integrating nonverbal delivery.
Speak Out, Call In: Public Speaking as Advocacy Copyright © 2019 by Meggie Mapes is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Quick links
Controlling speech anxiety, vocal variety, body language, practicing and preparation, general delivery tips.
As we know, words communicate meaning. But the way we say words also communicates meaning . This is why effective speakers devote time to improving their delivery.
So what exactly is delivery? Delivery is the speaker’s physical (vocal and bodily) actions during a speech. The main purpose of delivery is to enhance, not distract from, the message. In order to help you avoid distracting from your message, we’ve created a document about what not to do while delivering a speech.
We consider several aspects of delivery: controlling speech anxiety , vocal variety , body language , and practice .
It’s important to thoughtfully consider both the organization and oral style of the speech before discussing the principles of delivery. It doesn’t matter how great your delivery is if the speech is disorganized and hard to understand.
If you’re confident about organization and oral style , it’s time to work on delivery!
To control your speech anxiety the first step is simple: practice. The better you know your speech, the more comfortable you’ll feel. Comfort generally helps reduce anxiety.
In addition, it would be incredibly helpful to practice in the same room you’ll be giving the speech or to practice in front of other people. Both of these situations will simulate the speaking experience, and make the actual speaking experience feel less foreign, and less anxiety provoking.
You’ll be most anxious in the first minute of the speech. After the first minute (or so) anxiety levels tend to stabilize and decrease. Since the first minute can be the most challenging, it may be wise to memorize your opening.
For additional methods to deal with speech anxiety, this article will prove useful. If you’re in a rush, here are a few quick tips summarized:
- Visualize your success.
- Find a friendly face.
- Take a few calming breaths.
Even the best orators still get nervous when speaking; it’s normal, so don’t worry about it.
Please contact the Center for Counseling and Wellness if your anxiety is daily and inhibiting.
Vocal variety is essential to a captivating delivery. In oral rhetoric classes, you’ll learn about effective vocal variety. You may have an excellently written speech, but if delivered without vocal variety, it will be boring and dry. However, not every speech assignment at Calvin is for an oral rhetoric class. So what is vocal variety and how does one use it?
Vocal variety includes elements such as pitch, tone, volume, and rate .
How do I speak with vocal variety?
To learn about pitch, tone, volume, and rate variation, watch this video by Florida International University's Comm Art Studio from 1:10 to 6:09.
Additional tips related to vocal variety:
- Practice in everyday conversation to make vocal changes second nature.
- If you’re using a notecard, use slash marks or asterisks to mark cardinal places to vary pitch or slow down.
- Pause or slow down to emphasize important words or concepts.
- Speed up to solicit excitement or energy.
- Use a lower pitch to create an authoritative tone.
Many extraordinary speakers rely heavily on vocal variation. Listen to Meghan Markle, now the Duchess of Sussex, in her 2015 address to the United Nations. Markle frequently changes pitch and rate--pitch to make the speech interesting and rate to emphasize different points. (At 5:20-6:05 she slows down to emphasize her message; this is an effective rate change.)
Sometimes our voices sound scratchy when we speak. This may be vocal fry.
What is vocal fry and how to avoid it?
Vocal fry is the lowest voice register of the human voice. It sounds muffled and unclear. Speaking professionals recommend you avoid it during public speaking. If you think vocal fry may be a problem for you, watch this short video .
If you need help or someone to listen, come to the Rhetoric Center!
Many speakers use notecards for guidance through speech delivery. Notecards aren’t the same as the outline . Normally, the outline is turned in to the teacher and consists of complete sentences. The notecards would be the reverse: they are guideposts for the speaker, normally written as single words, phrases, or bullet points that are easy to glance read during a speech.
Note cards can also be used for notes about the delivery. Many speakers use slash marks to signal places where a pause would help. If you sound monotone or struggle with vocal variety, note places where vocal variation would be appropriate.
For a deeper look on how to use notecards, check out this resource from Oral Communication Center, Hamilton College.
Some people recommend using only one or two notecards. Typically, we at the Rhetoric Center don’t recommend that it’s better to have more cards to make sure you don’t get lost.
While you’re using notecards, it’s tempting to forget to make eye contact with the audience; remember, eye contact will communicate confidence.
For an example, look at this notecard for a speech about the Orlando shooting.
For further direction, check out Hamilton College or visit the Rhetoric Center.
Body language communicates meaning just like your words and how you say them. Consider what your body language says about you and your message while you’re speaking. For instance, your body language can affect your tone, your audience’s attention, and your audience perception of you.
Body language and movement affects the tone of your speech or presentation. For instance, how much moving should take place during a eulogy? Probably none. In a eulogy you want to be more composed. However, in a more energetic environment, such as an informative speech, it would be more acceptable to use movement. For example, Michelle Obama, in her campaign speech for Hillary Clinton , uses energetic body language to excite voters about voting for her preferred candidate.
Body language can either gain or lose the attention of your audience over the course of a speech. If used conservatively and properly, it can make your speech more interesting and engaging. If used excessively and carelessly, it can distract your audience from your message.
Confidence or insecurity
Body language communicates confidence or insecurity. If your back is turned to the audience, you’re pacing back and forth, or your hands are in your pockets, you’ll probably come off as insecure. On the other hand, walking with confidence and using hand gestures meaningfully will communicate confidence.
Now that you’re aware of how body language can affect your speeches, let’s consider how to use our body language while speaking.
What do I move and how?
Need some options for body movement? Watch from (6:52-9:55) for fundamental body movement concepts during a speech. Pay attention, but also put it to practice!
A few suggestions on body movement:
- Face the audience and don’t turn your back to them.
- Be in the center of room and don’t walk to near to the edges.
- Don’t put your hands in your pockets or on your hips; this creates emotional barriers.
Practicing is critical to the performance and success of the speech. When practicing, it’s normal to touch up and fix slight wording issues, but at this point in the writing process the speech should be pretty much finished. If you still have more to write, we recommend the speech writing and organization pages.
How do you practice for a speech?
Keep practicing and don’t always start at the beginning; change where you start practicing.
If you always start with the beginning, then you’ll know the beginning best, and the rest will get progressively harder. You should know every part of the speech equally well if you keep changing your starting location. However, memorizing the first few lines isn’t a bad idea because the first few lines will be the hardest to recite when confronted by speech anxiety.
This resource from University of Hawai'i Maui Community College Speech Department will prove helpful when practicing speeches. Read the “Do’s” and “Don'ts” carefully.
It’s also beneficial to imitate the environment of the speech. This can be done by practicing in front of people and in the real space you’ll be giving the speech in. It’ll be easier to deliver if it’s not your first time seeing the space.
Watch two examples related to preparation: one bad and one good .
- Avoid filler words. Filler words, such as “umm” and “like,” take away from your credibility as a speaker, affecting how the audience receives your message.
- Maintain eye contact; it demonstrates confidence!
- If you slip up, don’t apologize. Apologizing makes you appear insecure and affects your credibility as a speaker.
- Pauses help. They can make a speech somber and serious. President Obama used pauses for effective emotional measures in his speech following the shooting at Sandy Hook elementary school , particularly in his introduction.
- Slow down; you deliver the speech faster than your practiced it. Even if your practice trials were perfectly timed, it’s common for speakers to speed up the actual delivery.
For additional tips, check out this resource on general guidelines for speech delivery (The Writing Resources Center, Swem Library, College of William & Mary).
If you have any questions or would like a Rhetoric Center consultant to listen to your speech, schedule an appointment.
In this presentation, business tycoon Elon Musk appears extremely nervous and unprepared. This probably results from the fact that Musk doesn't practice his speeches . To see how fragmented and clustered the speech is watch the first 1:30. In addition to being fragmented and clustered, Musk uses filler words, such as “um” and “eh,” like air. This makes him appear insecure. Ironically, this is an important speech updating the world on a possible mission to Mars, delivered by an important man who needs no introduction, yet the beginning of the speech sounds amateur because of his lack of preparation. Further practice would’ve made him seem more natural and effective, and therefore would’ve reduced his anxiety.
Practice helps, even for Elon Musk.
On the other hand, practice puts the most nervous speakers at peace during their presentations.
Winston Churchill, on June 18 1940, delivered one of the most enduring speeches in English history: “Their Finest Hour.” This World War II speech was given via broadcast to the British people and just after France had accepted the German armistice.
It was only a month into Churchill’s ministership, and he was terrified of public speaking because of his speech impediment. However, according to Carmine Gallo from Forbes , Churchill’s practice helped him overcome his anxiety. If you listen to 26:55-30:02 of Churchill’s speech, you can clearly identify his rhythm and diction; this would be impossible to achieve without considerable preparation and knowledge of his own speech.
This note card was used for a speech commemorating the victims of the Pulse shooting in Orlando, Florida.
For starters, the notecard is legible and uses slash marks as possible places to pause when reading. These pauses, a form of vocal variety, place emphasis on each name being read, which would trigger an emotional response. However, more information could probably be fit on the bottom of the card. Perhaps something to prompt the next sentence.
It’s important that the notecard doesn’t use full sentences; rather, use trigger words and phrases. Compare the notecard to the outline version of the first sentence: “Today, I wanted to individually remember those lost on June 12, 2016.” The word “individually” is nowhere near as important as “remember.” So “individually” gets put on the card and not “remember.”
Furthermore, things that must be exact need to be written on the cards. This includes dates, names, and quotes. You don’t want to say (or pronounce) any of these incorrectly as it could reduce your credibility.
Michael Bay, the famous film director, didn’t prepare sufficiently for this speech. This embarrassing mess resulted from a miscommunication between Bay and the teleprompt person. However, this could’ve been prevented with preparation. For starters, Bay should have had a backup, hard copy version of the speech. This may not have been ideal, but it would’ve prevented the disaster.
Make sure you have a backup plan .
Bay’s problems didn’t end with his miscommunication; he also didn’t know when to begin the speech. He started before his introducer asked him the first question. If prepared, he would’ve known how to start. In addition, the final question about his movies was a simple throw away by the interviewer in attempt to save Bay. Bay said he couldn’t read the teleprompter, apologized, and left. He didn’t need the teleprompter to answer this question about his movies (that he has spend hundreds or thousands of hours working on). This demonstrates unpreparedness; If he knew the speech, rather than just relying on the teleprompter, he would’ve been able to answer the last question.
On the other hand, careful preparation can make for a great speech. For Monica Lewinsky's Ted Talk on “The Price of Shame” she had no teleprompter, so she used paper notes, which can be seen on the small podium in front of her. Even though she used paper notes, her speech was well practiced. This is evident in her consistent eye-contact, lack of mistakes, and how she carried the room with evidently prepared diction and vocal variety.
- Faculty & Staff
- Admitted Students
- Administration
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Vision 2030
- Sustainability
- Media Center
- Campus & Location
- Consumer Information
- Safer Spaces
- Majors & Programs
- Graduate Programs
- Online Programs »
- First-Year Opportunities
- Academic Calendar
- Course Offerings
- The Calvin Core
- Calvin Academy for Lifelong Learning
- Off-Campus Programs
- Student Services
- Centers & Institutes
- Global Campus
- Hekman Library »
- Request Information
- Facts & Standards
- Cost & Aid »
- Internationals
- Military & Veterans »
- Residence Life
- Faith & Worship
- Student Involvement & Activities
- Life in Grand Rapids
- Careers & Outcomes
- Multicultural & International Students
- Wellness & Safety
- Service Learning
- Arts Collective
- Box Office »
- Get Involved
- CalvinKnights.com
- Outdoor Recreation
- Intramurals
- Group Fitness
- Sports Camps


The 8 Key Elements of Highly Effective Speech
…and why your words barely matter.
Posted July 10, 2012 | Reviewed by Ekua Hagan
I’d like you to take a moment to experience the following sentence, taken from a recent article exploring the nature of human consciousness: “Neuroplastic mechanisms relevant to the growing number of empirical studies of the capacity of directed attention and mental effort systematically alter brain function.”
Exciting? Hardly! In fact, most of the words you read barely register in your brain, and most of the words you speak barely register in the listener’s brain. In fact, research shows that words are the least important part of communication when you have face-to-face conversations with others. So before you utter another word to another person, memorize this list of the 8 key elements of highly effective speech:
- Gentle eye contact
- Kind facial expression
- Warm tone of voice
- Expressive hand and body gestures
- Relaxed disposition
- Slow speech rate
- The words themselves
Effective communication is based on trust, and if we don’t trust the speaker, we’re not going to listen to their words. Trust begins with eye contact because we need to see the person’s face to evaluate if they are being deceitful or not. In fact, when we are being watched, cooperation increases. [1] When we are not being watched, people tend to act more selfishly, with greater dishonesty. [2]
Gentle eye contact increases trustworthiness and encourages future cooperation, [3] and a happy gaze will increase emotional trust. [4] However, if we see the slightest bit of anger or fear on the speaker’s face, our trust will rapidly decrease. [5] But you can’t fake trustworthiness because the muscles around your mouth and eyes that reflect contentment and sincerity are involuntary. Solution: if you think about someone you love, or an event that brought you deep joy and satisfaction, a "Mona Lisa" smile will appear on your face and the muscles around your eyes will soften.
The tone of your voice is equally important when it comes to understanding what a person is really trying to say. If the facial expression expresses one emotion , but if the tone conveys a different one, neural dissonance takes place in the brain, causing the person confusion. [6] The result: trust erodes, suspicion increases, and cooperation decreases.
Researchers at the University of Amsterdam found that expressions of anger, contempt, disgust, fear, sadness, and surprise were better communicated through vocal tone than facial expression, whereas the face was more accurate for communicating expressions of joy, pride, and embarrassment . [7] And in business, a warm supportive voice is the sign of transformational leadership , generating more satisfaction, commitment, and cooperation between other members of the team. [8]
You can easily train your voice to convey more trust to others, and all you have to do is slow down and drop your pitch. This was tested at the University of Houston: when doctors reduced their speaking rate and pitch, especially when delivering bad news, the listener perceived them “as more caring and sympathetic.” [9] Harvard's Ted Kaptchuk also discovered that using a warm voice would double the healing power of a therapeutic treatment. [10]
If you want to express joy, your voice needs to become increasingly melodic, whereas sadness is spoken with a flat and monotonic voice. When we are angry, excited, or frightened, we raise the pitch and intensity of our voice, and there’s a lot of variability in both the speed and the tone. However, if the emotion is incongruent with the words you are using, it will create confusion for the listener. [11]
Gestures, and especially hand movements, are also important because they help orchestrate the language comprehension centers of your brain. [12] In fact, your brain needs to integrate both the sounds and body movements of the person who is speaking in order to accurately perceive what is meant. [13] From an evolutionary perspective, speech emerged from hand gestures and they both originate the same language area of the brain. [14] If our words and gestures are incongruent, it will create confusion in the listener’s brain. [15] Our suggestion: practice speaking in front of a mirror, consciously using your hands to “describe” the words you are speaking.

Your degree of relaxation is also reflected in your body language , facial expressions, and tone of voice, and any form of stress will convey a message of distrust . Why? Your stress tells the observer’s brain that there may be something wrong, and that stimulates defensive posturing in the listener. Research shows that even a one-minute relaxation exercise will increase activity in those parts of the brain that control language, communication, social awareness, mood-regulation, and decision-making . [16] Thus, a relaxed conversation allows for increased intimacy and empathy. Stress, however, causes us to talk too much because it hinders our ability to speak with clarity.
When you speak, slow down! Slow speech rates will increase the ability for the listener to comprehend what you are saying, and this is true for both young and older adults. [17] Slower speaking will also deepen that person’s respect for you, [18] Speaking slowly is not as natural as it may seem, and as children we automatically speak fast. But you can teach yourself, and your children to slow down by consciously cutting your speech rate in half. A slow voice has a calming effect on a person who is feeling anxious , whereas a loud fast voice will stimulate excitement, anger, or fear. [19]
Try this experiment: pair up with a partner and speak so slowly that … you … leave … 5 … seconds … of … silence … between … each … word. You’ll become aware of your negative inner speech that tells you that you should babble on endlessly and as fast as possible. It’s a trap, because the listener’s brain can only recall about 10 seconds of content! That’s why, when we train people in Compassionate Communication, we ask participants to speak only one sentence at a time, slowly, and then listen deeply as the other person speaks for ten seconds or less. This exercise will increase your overall consciousness about the importance of the first 7 elements of highly effective communication. Then, and only then, will you truly grasp the deeper meaning that is imparted by each word spoken by others.
But what about written communication, where you only have access to the words? When it comes to mutual comprehension, the written word pales in comparison to speech. To compensate, your brain imposes arbitrary meanings onto the words. You, the reader, give the words emotional impact that often differs from what the writer intended, which is why so many email correspondences get misinterpreted. And unless the writer fills in the blanks with specific emotional words and descriptive speech – storytelling – the reader will experience your writing as being flat, boring , dry, and probably more negative than you intended.
The solution: help the reader “paint a picture” in their mind with your words. Use concrete nouns and action verbs because they are easier for the reader’s brain to visualize. Words like “sunset” or “eat” are easy to see in the mind's eye, but words like “freedom” or “identify” force the brain to sort through too many conceptual frameworks. Instead, our lazy brain will skip over as many words as possible, especially the abstract ones. When this happens the deeper levels of meaning and feeling will be lost.
For more information on how to improve your speaking and listening skills, along with additional exercises to practice, see Words Can Change Your Brain: 12 Conversation Strategies for Building Trust, Reducing Conflict, and Increasing Intimacy (Newberg & Waldman, 2012, Hudson Street Press).
[1] Cues of being watched enhance cooperation in a real-world setting. Bateson M, Nettle D, Roberts G. Biol Lett. 2006 Sep 22;2(3):412-4.
[2] Effects of anonymity on antisocial behavior committed by individuals. Nogami T, Takai J. Psychol Rep. 2008 Feb;102(1):119-30.
[3] Eyes are on us, but nobody cares: are eye cues relevant for strong reciprocity? Fehr E, Schneider F. Proc Biol Sci. 2010 May 7;277(1686):1315-23.
[4] Evaluating faces on trustworthiness: an extension of systems for recognition of emotions signaling approach/avoidance behaviors. Todorov A. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008 Mar;1124:208-24.
[5] Common neural mechanisms for the evaluation of facial trustworthiness and emotional expressions as revealed by behavioral adaptation. Engell AD, Todorov A, Haxby JV. Perception. 2010;39(7):931-41.
[6] Use of affective prosody by young and older adults. Dupuis K, Pichora-Fuller MK. Psychol Aging. 2010 Mar;25(1):16-29.
[7] "Worth a thousand words": absolute and relative decoding of nonlinguistic affect vocalizations. Hawk ST, van Kleef GA, Fischer AH, van der Schalk J. Emotion. 2009 Jun;9(3):293-305.
[8] Leadership = Communication? The Relations of Leaders' Communication Styles with Leadership Styles, Knowledge Sharing and Leadership Outcomes. de Vries RE, Bakker-Pieper A, Oostenveld W. J Bus Psychol. 2010 Sep;25(3):367-380.
[9] Voice analysis during bad news discussion in oncology: reduced pitch, decreased speaking rate, and nonverbal communication of empathy. McHenry M, Parker PA, Baile WF, Lenzi R. Support Care Cancer. 2011 May 15.
[10] Components of placebo effect: randomised controlled trial in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Kaptchuk TJ, Kelley JM, Conboy LA, Davis RB, Kerr CE, Jacobson EE, Kirsch I, Schyner RN, Nam BH, Nguyen LT, Park M, Rivers AL, McManus C, Kokkotou E, Drossman DA, Goldman P, Lembo AJ. BMJ. 2008 May 3;336(7651):999-1003.
[11] Use of affective prosody by young and older adults. Dupuis K, Pichora-Fuller MK. Psychol Aging. 2010 Mar;25(1):16-29.
[12] Gestures orchestrate brain networks for language understanding. Skipper JI, Goldin-Meadow S, Nusbaum HC, Small SL. Curr Biol. 2009 Apr 28;19(8):661-7.
[13] When language meets action: the neural integration of gesture and speech. Willems RM, Ozyürek A, Hagoort P. Cereb Cortex. 2007 Oct;17(10):2322-33.
[14] When the hands speak. Gentilucci M, Dalla Volta R, Gianelli C. J Physiol Paris. 2008 Jan-May;102(1-3):21-30. Epub 2008 Mar 18.
[15] How symbolic gestures and words interact with each other. Barbieri F, Buonocore A,Volta RD, Gentilucci M. Brain Lang. 2009 Jul;110(1):1-11.
[16i] Short-term meditation training improves attention and self-regulation. Tang YY, Ma Y, Wang J, Fan Y, Feng S, Lu Q, Yu Q, Sui D, Rothbart MK, Fan M, Posner MI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Oct 23;104(43):17152-6.
[17] Comprehension of speeded discourse by younger and older listeners. Gordon MS, Daneman M, Schneider BA. Exp Aging Res. 2009 Jul-Sep;35(3):277-96.
[18] Celerity and cajolery: rapid speech may promote or inhibit persuasion through its impact on message elaboration. Smith SM, Shaffer, DR. Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 1991 Dec;17(6):663-669.
[19] Voices of fear and anxiety and sadness and depression: the effects of speech rate and loudness on fear and anxiety and sadness and depression. Siegman AW, Boyle S. J Abnorm Psychol. 1993 Aug;102(3):430-7. The angry voice: its effects on the experience of anger and cardiovascular reactivity. Siegman AW, Anderson RA, Berger T. Psychosom Med. 1990 Nov-Dec;52(6):631-43.

Andrew Newberg, M.D ., and Mark Robert Waldman are the authors of Words Can Change Your Brain .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 6: Delivery
This chapter is adapted from Stand up, Speak out: The Practice and Ethics of Public Speaking , CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 .
How do I effectively deliver my speech?
Wahoo! You have finally written your speech. You have carefully chosen just the right language, you’ve considered all listening styles, and you are confident that you have created a meaningful speech that will capture your audience’s attention. Now, it’s time to learn how to effectively deliver your speech.
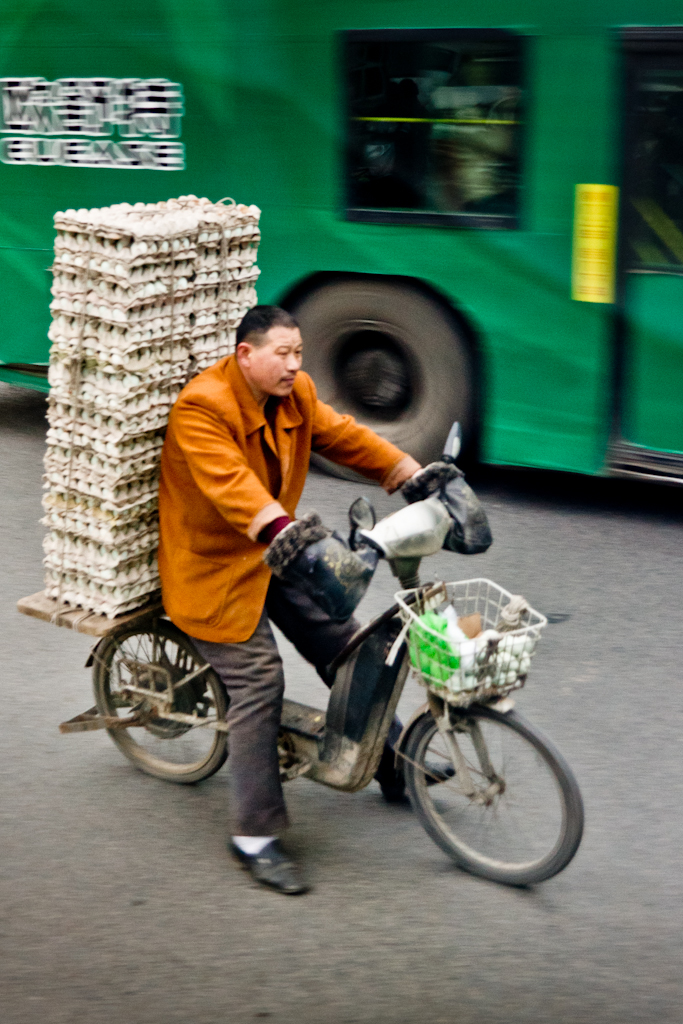

How we deliver a speech is just as important, if not more so, than the message we want to convey. If you have worked hard on preparing the verbal part of your speech, you may feel that delivery is just an “extra” that requires much time or effort. After all, your speech is carefully planned, researched, and polished. It is committed safely to paper and hard drive. It’s a carefully constructed, logically crafted, ethical message. The words alone should engage your audience’s attention and interest—right?
After all the work you put into building such a message, you might wish that you could simply read it to the audience. However, reading a speech occurs in only a few circumstances—when the message is highly technical, complex, and extremely important, such as a new medical discovery; when international protocols and etiquette are crucially important and the world is listening; or when the speaker is representing a high-ranking person, such as a president or a king, who is unable to be present. For this public speaking class, you will not be encouraged to read your speech. Instead, you will be asked to give an extemporaneous presentation. We will examine what that means.
Delivering the nonverbal part of your speech as well as your message is a presentation of yourself. Through eye contact, vocal expression, body posture, gestures, and facial display, you enhance your message and invite your audience to give their serious attention to it—and to you. Your credibility, your sincerity, and your topic knowledge become apparent through your nonverbal behaviors.
The interplay between your speech’s verbal and nonverbal components can either bring the message vividly to life or confuse or bore the audience. Therefore, it is best that you neither overdramatize your delivery behaviors nor downplay them. This is a balance achieved through rehearsal, trial and error, and experience.
In this chapter, we are going to examine effective speech-delivery strategies. First, to help you enhance your delivery, we will explore speech delivery’s four basic methods. Second, we will discuss how to prepare your delivery for different environments. Third, we will talk about how to effectively use notecards to enhance your delivery. Finally, we will examine good delivery characteristics and give some effective practicing strategies for the day when you will deliver your speech.

The easiest approach to speech delivery is not always the best. Substantial work goes into carefully preparing an interesting and ethical message, so it is understandable that students may have the impulse to avoid messing it up by simply reading it word for word. But students who do this miss out on one of the major reasons for studying public speaking: to learn ways to connect with one’s audience and to increase one’s confidence in doing so. You already know how to read, and you already know how to talk. But public speaking is neither reading nor talking.
Public speaking is more formal than talking. During a speech, you present yourself professionally. This doesn’t mean you must wear a suit or dress up, unless your instructor asks you to, but it does mean making yourself presentable by being well-groomed and wearing clean, appropriate clothes. It also means being prepared to use language correctly and appropriately for the audience and the topic, to make eye contact with your audience, and to look like you know your topic very well.
While public speaking is more formal than talking, it is less formal than reading. Speaking allows for meaningful pauses, eye contact, small changes in word order, and vocal emphasis. Reading is more or less exactly replicating words on paper without using any nonverbal interpretation. Speaking—as you will realize if you think about excellent speakers who you have seen and heard—provides a more animated message.
The next sections introduce four delivery methods that can help you balance between too much and too little formality when publicly speaking.
Impromptu Speaking
Impromptu speaking means to present a short message without advance preparation. Impromptu speeches often occur when someone is asked to say a few words or give a toast on a special occasion. You have probably done impromptu speaking many times in informal, conversational settings. Self-introductions in group settings are examples of impromptu speaking: “Hi, my name is Steve, and I’m a volunteer with the Homes for the Brave Program.” Another example of impromptu speaking occurs when you answer a question such as, “What did you think of the documentary?”
The advantage of this kind of speaking is that it’s spontaneous and responsive in an animated group context. The disadvantage is that the speaker is given little or no time to contemplate his or her message’s central theme. As a result, the message may be disorganized and difficult for listeners to follow.
Here is a step-by-step guide that may be useful if you are called upon to give an impromptu public speech.
- Take a moment to collect your thoughts and plan your main point.
- Thank the person for inviting you to speak.
- Deliver your message, making your main point as briefly as you can while still covering it adequately and at a pace that your listeners can follow.
- Thank the person again for the opportunity to speak.
- Stop talking.
As you can see, impromptu speeches are generally most successful when they are brief and focus on a single point.
Extemporaneous Speaking
Extemporaneous speaking means to present a carefully planned and rehearsed speech, spoken in a conversational manner, and using brief notes. By using notes rather than a full manuscript, the extemporaneous speaker can establish and maintain eye contact with the audience and assess how well they are understanding the speech as it progresses. The opportunity to assess is also an opportunity to restate more clearly any idea or concept that the audience seems to have trouble grasping.
For instance, suppose you are speaking about workplace safety and you use the term “sleep deprivation.” If you notice your audience’s eyes glazing over, this might not be a result of their own sleep deprivation, but rather that they are uncertain about what you mean. If this happens, you can add a short explanation; for example, “Sleep deprivation is sleep loss serious enough to threaten one’s cognition, hand-to-eye coordination, judgment, and emotional health.” You might also, or instead, provide a concrete example to illustrate the idea. Then you can resume your message, having clarified an important concept.
Speaking extemporaneously has some advantages. It promotes the likelihood that you, the speaker, will be perceived as knowledgeable and credible. In addition, your audience is likely to pay better attention to the message because it is both verbally and nonverbally engaging. The disadvantage of extemporaneous speaking is that it requires a great deal of preparation for both the verbal and the nonverbal components of the speech. Adequate preparation cannot be achieved the day before you’re scheduled to speak.
Because extemporaneous speaking is the style used in most public speaking situations, most of the information in this chapter is targeted to this kind of speaking.
Manuscript Speaking
Manuscript speaking means to read a written message word-for-word. During a manuscript speech, the speaker maintains his or her attention on the printed page, except when using visual aids.
The advantage to reading from a manuscript is that you are reading the exact original words. As we mentioned at the beginning of this chapter, in some circumstances, this can be extremely important. For example, reading a statement about your organization’s legal responsibilities to customers may require that the original words be exact. In reading one word at a time, in order, the only errors would typically be mispronouncing a word or stumbling over complex sentence structure.
However, there are costs involved in manuscript speaking. First, it’s typically an uninteresting way to present. Unless the speaker has rehearsed the reading as a complete performance, animated with vocal expression and gestures—as poets do in a poetry slam and actors do in a reader’s theater—the presentation tends to be dull. Keeping one’s eyes glued to the script precludes eye contact with the audience. For this kind of straight manuscript speech to hold an audience’s attention, the audience must be already interested in the message before the delivery begins.
It is worth noting that professional speakers, actors, news reporters, and politicians often read from an autocue device, such as a TelePrompTer, especially when appearing on television where eye contact with the camera is crucial. With practice, a speaker can achieve a conversational tone and give the impression of speaking extemporaneously while using an autocue device. However, success in this medium depends on two factors: first, the speaker is already an accomplished public speaker who has learned to use a conversational tone while delivering a prepared script, and second, the speech is written in a style that sounds conversational.
Memorized Speaking
Memorized speaking means to recite a written message that the speaker has committed to memory. Actors, of course, recite from memory whenever they perform from a script in a stage play, television program, or movie scene. When it comes to speeches, memorization can be useful when the message needs to be exact and the speaker doesn’t want to be confined by notes.
The advantage of memorizing a speech is that it enables the speaker to maintain eye contact with the audience throughout the speech. Being note-free means that you can move freely around the stage and use your hands to make gestures. If your speech requires visual aids, this freedom is even more of an advantage. However, there are some real and potential costs. First, unless you also plan and memorize every vocal cue—the subtle but meaningful variations in speech delivery, which include using pitch, tone, volume, and pace—and you gesture and use facial expression, your presentation will be flat and uninteresting and even the most fascinating topic will suffer. You might end up speaking in a monotone or a sing-song repetitive delivery pattern. You might also present your speech in a rapid machine-gun style that fails to emphasize the most important points. Second, if you lose your place and start trying to ad lib, the contrast in your delivery style will alert your audience that something is wrong. More frighteningly, if you go completely blank during the presentation, it will be extremely difficult to find your place and keep going.
How do different speaking contexts affect my delivery?
You may be asked to speak in different contexts or venues. Do you use the same delivery gestures and vocal variation in each context?

The Reverend Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. gave his famous “I Have a Dream” speech on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial at a gigantic civil rights rally on an August afternoon in 1963. His lectern was bristling with microphones placed there for news coverage and for recording the historic event. His audience, estimated to number a quarter of a million people, extended as far as the eye could see. He was the last speaker of the day, delivering his speech after more than a dozen civil rights leaders and world-famous performers such as Joan Baez, Mahalia Jackson, and Charlton Heston had occupied the stage (Ross, 2007). King gave us his speech in the assertive ringing tones of inspired vision. Nothing less would have worked that day.
Most of us will never speak to so many people at once. Even a television appearance will probably command a much smaller audience than the crowd that heard King’s speech. Even though you don’t expect an audience of such size or setting or symbolic importance, you should still be prepared to adapt to the setting in which you will speak.
Our public speaking audiences, circumstances, and physical contexts will vary. At some point in your life, you may run for public office or rise to a leadership role in a business or volunteer organization. Or, you may be responsible for informing coworkers about a new policy, regulation, or opportunity. You may be asked to deliver remarks in the context of a worship service, wedding, or funeral. You may be asked to introduce a keynote speaker or simply to make an important announcement in some context. Sometimes, you will speak in a familiar environment, at other times, you may speak at an unfamiliar location with very little time to get used to speaking with a microphone. These are contexts and situations we address in the following subsections.
Using Lecterns
A lectern is a small raised surface, usually with a slanted top, where a speaker can place notes during a speech. While a lectern adds formality to the speaking situation, it allows speakers the freedom to do two things: to come out from behind the lectern to establish more immediate contact with the audience and to use both hands to gesture.
However, for new speakers who feel anxious, it is all too tempting to grip the lectern’s edges with both hands for security. You might even wish you could hide behind it. Be aware of these temptations so you can manage them effectively and present yourself to your audience in a manner they will perceive as confident. One way to achieve this is to use the lectern only as a place to rest your notes. Try stepping to the side or front of the lectern when speaking with free hands, only occasionally standing at the lectern to consult your notes. This will enhance your eye contact as well as free up your hands for gesturing.
Speaking in a Small or Large Physical Space
If you are accustomed to being in a classroom of a certain size, you will need to make adjustments when speaking in a smaller or larger space than what you are used to.
A large auditorium can be intimidating, especially for speakers who feel shy and exposed when facing an audience. However, the maxim that “Proper preparation prevents poor performance” is just as true here as anywhere. If you have prepared and practiced well, you can approach a large-venue speaking engagement with confidence. In terms of practical adjustments, be aware that your voice is likely to echo, so you will want to speak more slowly than usual and pause to mark the ends of phrases and sentences. Similarly, your facial expressions and gestures should be larger so that they are visible from farther away. If you are using visual aids, they need to be large enough to be visible from the back of the auditorium.
Limited space is not as disconcerting for most speakers as an enormous space, but it has the advantage of minimizing the tendency to pace back and forth while you speak. We have all seen dramatic soliloquies in movies and plays where an actor moves around the stage, but this is generally not good speech strategy. A small space also requires that you carefully manage your notecards and visual aids, as your audience will be able to see up close what you are doing with your hands. Do your best to minimize fumbling, including setting up in advance or arriving early to decide how to organize your materials in the physical space.
Speaking Outdoors
Outdoor settings can be charming, but they are prone to distractions. If you’re giving a speech in a setting that is picturesquely beautiful, it may be difficult to maintain the audience’s attention. If you know this ahead of time, you might plan your speech to focus more on mood than information and perhaps to make reference to the lovely view.
More typically, outdoor speech venues can pose weather challenges, sun glare, and uninvited guests, such as ants and pigeons. If the venue is located near a busy highway, it might be difficult to make yourself heard over the ambient noise. You might lack the usual accommodations, such as a lectern or table. Whatever the situation, you will need to use your best efforts to project your voice clearly without sounding like you’re yelling.
Using a Microphone
Most people today are familiar with microphones that are built into video recorders and other electronic devices, but they may be new at using a microphone to deliver a speech. One overall principle to remember is that a microphone only amplifies, it does not clarify. If you are not enunciating clearly, the microphone will merely enable your audience to hear amplified mumbling.
Microphones come in numerous styles and sizes. Generally, the easiest microphone to use is the clip-on style worn on the front of your shirt. If you look closely at many television personalities and news anchors, you will notice these tiny microphones clipped to their clothing. They require very little adapting. You simply have to avoid looking down—at your notes, for instance—because your voice will be amplified when you do so.
Lectern and handheld microphones require more adapting. If they’re too close to your mouth, they can screech. If they’re too far away, they might not pick up your voice. Some microphones are directional, meaning that they are only effective when you speak directly into them. If there is any opportunity to do so, ask for tips about how to use a particular microphone and practice with it for a few minutes. Ask someone to listen from a middle row in the audience and to signal whether you can be heard well. The best plan, of course, is to have access to the microphone for practice ahead of the speaking date.
Often a microphone is provided when it isn’t necessary. If the room is small or the audience is close to you, do not feel obligated to use the microphone. Sometimes an amplified voice can feel less natural and less compelling than a direct voice. However, if you forgo the microphone, make sure to speak loudly enough for all audience members to hear you—not just those in front.
Audience Size
A small audience provides an opportunity for a more intimate, minimally formal tone. If your audience has only eight to twelve people, you can generate greater audience contact. You do not have to revamp your speech just because the audience is small. When the presentation is over, there will most likely be opportunities to answer questions and to contact your listeners individually.
Your classroom audience may be as many as twenty to thirty students. The format for this size audience is still formal but conversational. Depending on how your instructor structures the class, you may or may not be asked to leave time after your speech for questions and answers.
Some audiences are much larger. If you have an audience that fills an auditorium, or if you have an auditorium with only a few people in it, you still have a clearly formal task. Despite the audience size, you should be guided as much as possible by your preparation.
How do I use notes effectively when I speak?
It’s much work to prepare a good speech, and you want to present it effectively so that your audience will benefit as much as possible. We’ve already said that extemporaneous speaking provides the best opportunity for speaker-audience contact and that speaking extemporaneously means you do not have your full manuscript or outline with you. Instead, you will use notecards, which should have notes, not the full text of your speech. This can also be done with an autocue device, such as the TelePrompTer, which does not provide a full word-for-word script.
We have developed a system for creating highly effective notecards. Our system has been used effectively both in public speaking courses and in freshman composition courses. Surprisingly, the system uses only five cards. For many people, this does not sound like nearly enough cards. However, we make the case that you can do a good job with five cards, and we have seen many students do just that.
The Purpose of Speaker Notes
First, using notes adds to a speaker’s credibility. If you depend on a full manuscript to get through your delivery, your listeners might believe you don’t know your speech’s content. Second, the temptation to read the entire speech directly from a manuscript is nearly overwhelming, even if you’re only carrying it as a safety net. Third, well-prepared cards are more gracefully handled than sheets of paper, and they don’t rattle if your hands tremble from nervousness. Finally, cards look better than paper. Five carefully prepared cards, together with practice, will help you more than you might think.
Key Tips for Using Notes
Plan on using just five cards, written on one side only. Get 4 × 6 cards. Use one card for the introduction, one card for each of your three main points, and one card for the conclusion.
Include Only Keywords
Your cards should include keywords and phrases, not full sentences. Arrange the words and phrases in order so that you can stay organized and avoid forgetting important points.
One exception to the keyword guideline is including an extended or highly technical quotation from an authoritative source. If it is critically important to present an exact quotation, you may add one additional card that will contain the quotation and its citation. If you plan to use such a quotation, make sure it has central importance in your speech.
Hold Your Notes Naturally
Using notes is a normal part of presenting. You do not need to conceal them from the audience; in fact, trying to hide and use your notes at the same time tends to be very awkward and distracting. Some instructors recommend that you avoid gesturing while holding your notes in your hand because nervous shaking is more noticeable. If this is the case for you, practice gesturing with your free hand, or put your cards down if you need to use both hands. Other instructors recommend treating notecards as a natural extension of your hand, as they believe it is distracting to put your notes down and pick them up again. Whichever rule you follow, remember that the reason to use notecards is to contribute to your overall appearance, confidence, and credibility.
Tips for Holding your Notecards:
- Try not to hold your notecards with both hands in front of your belly. This closes you off to the audience.
- Use only one hand.
- Relax your hand to your side when not gesturing.
- Raise your hand to your side when getting ready to read your notecard so it doesn’t block the front of your body.
- Raise your hand high enough to read the notecard without dropping your head.
Prepare Notecards to Trigger Recall
The trick to selecting the words to write on your cards is to identify the keywords that will trigger a recall sequence. For instance, if the word “Fukushima” brings to mind the nuclear power plant meltdown that followed the earthquake and tsunami that hit Japan in 2011, then that one word on your notecard should propel you through a sizable sequence of points and details. Once you have delivered that material, perhaps you’ll glance at your card again to remind yourself of the keyword or phrase that comes next.
You must discover what works for you and then select those words that tend to jog your recall. Having identified what works, make a preliminary set of five cards, and write on one side only. Number the cards, and practice with them. Revise and refine them the way you would an outline. If you must, rewrite an entire card to make it work better, and test it the next time you practice.
Always practice with your notecards—and with any visual aids you plan to use. Practicing is also the best way to discover what might go wrong with your notes and what steps to take to make things go smoothly.
Write in Large Letters
Write in large enough letters to read your cards by glancing, not peering at them. A few keywords and phrases, written in large, bold print with plenty of white space between them, helps. If the lighting in your speech location is likely to have glare, be sure to write your notes in ink, as pencil can be hard to read in poor lighting.
Using Notecards Effectively
If you use as much care in developing your five notecards as you do your speech, they should serve you well. If you lose your place or go blank during the speech, you will only need a few seconds to find where you were and get going again. For instance, if you know that you presented the introduction and the first main point, which centers on the Emancipation Proclamation, you can readily go to your second card and remind yourself that your next main point is about the Thirteenth Amendment to the US Constitution.
In addition, using your notecards allows you to depart from the exact prepared wording in your manuscript. To recover from losing your place, you can transpose a word or phrase to make your recovery graceful. It allows you to avoid feeling pressured to say every single word in your manuscript.
Under no circumstances should you ever attempt to put your entire speech on cards in little tiny writing. You will end up reading words to your audience instead of telling them your meaning, and your speech’s visual aspect will be spoiled by you squinting to read your cards.
How do I practice to deliver a successful speech?
Now that you have your notecards prepared, you are ready to practice your speech.

There is no foolproof recipe for delivering a good speech. Each of us is unique and embody different experiences and interests. This means that each person has a delivery style or approach that is most effective for her or him. This further means that anxiety can accompany even the most carefully researched and interesting message. Even when we know our messages are strong and well-articulated on paper, it is difficult to know for sure that our delivery will also be good.
We are obligated to do our best out of respect for our audience and their needs. Fortunately, there are some tools that can help you improve even the very first time you present a speech. You will continue developing your skills each time you put them to use. Have fun, and experiment to find out which delivery elements are most effective for you.
What Is Good Delivery?
The more you care about your topic, the more motivated you are to present it well. Good delivery means to present a clear, coherent message in an interesting way. Communication scholar Stephen E. Lucas tells us the following:
Good delivery…conveys the speaker’s ideas clearly, interestingly, and without distracting the audience. Most audiences prefer delivery that combines a certain degree of formality with the best attributes of good conversation—directness, spontaneity, animation, vocal and facial expressiveness, and a lively sense of communication (Lucas, 2009).
Many people who write about delivery cite the findings of psychologist Albert Mehrabian, who asserts that the bulk of what an audience understands about your message is based on nonverbal communication. Specifically, Mehrabian is often credited with finding that when audiences decoded a speaker’s meaning, the speaker’s face conveyed 55 percent of the information, the vocalics conveyed 38 percent, and the words conveyed just 7 percent (Mehrabian, 1972). Although numerous scholars, including Mehrabian himself, have stated that his findings are often misinterpreted (Mitchell), scholars and speech instructors do agree that nonverbal communication and speech delivery are extremely important to effective public speaking.
In this section, we will explain six good delivery elements: conversational style, conversational quality, eye contact, vocalics, physical manipulation, and variety. And since delivery is only as good as the practice that goes into it, we conclude with some effective practicing tips.
Conversational Style
Conversational style is a speaker’s ability to sound expressive and spontaneous, which allows the audience to perceive the speaker as natural. It’s a style that approaches the way you normally express yourself in a much smaller group than your classroom audience. This means that you want to avoid having your presentation come across as didactic or overly exaggerated. You might not feel natural while you’re using a conversational style, but for your audience’s sake, do your best to appear natural. It might be helpful to remember that the two most important speech elements are the message and the audience. You are the conduit, and it is your role to effectively put the two together. Your audience should be thinking about the message, not the delivery.
Stephen E. Lucas defines conversational quality as the idea that “no matter how many times a speech has been rehearsed, it still sounds spontaneous” (Lucas, 2009). No one wants to hear a speech that is so well rehearsed that it sounds fake or robotic. One of the hardest parts of public speaking is rehearsing to the point where it can appear to your audience that the thoughts are magically coming to you while you’re speaking, but in reality, you’ve spent much time thinking through each idea. When you can sound conversational, people pay attention.
Eye Contact
Eye contact is a speaker’s ability to have visual contact with everyone in the audience. Your audience should feel that you’re speaking to them, not simply uttering main and supporting points. If you are new to public speaking, you may find it intimidating to look audience members in the eye, but if you recall speakers who did not maintain eye contact, you’ll realize why this speech-delivery element is so important. Without eye contact, the audience begins to feel invisible and unimportant, as if the speaker is just speaking to hear her or his own voice. Eye contact lets your audience feel that your attention is on them, not solely on the cards in front of you.
Sustaining eye contact with your audience is one of the most important effective delivery tools. O’Hair, Stewart, and Rubenstein note that eye contact is mandatory for speakers to establish a good relationship with an audience (O’Hair, Stewart, & Rubenstein, 2001). Whether a speaker is speaking before a group of five or five hundred, eye contact is an important way to bring an audience into your speech.
While eye contact is a powerful tool, it is not simply a sign of sincerity, of being well-prepared and knowledgeable, or a sign of confidence; it also has the power to convey meanings. Arthur Koch tells us that all facial expressions “can communicate a wide range of emotions, including sadness, compassion, concern, anger, annoyance, fear, joy, and happiness” (Koch, 2010).
If you find your audience’s gaze too intimidating, you might feel tempted to resort to faking eye contact with them by looking at the wall just above their heads or by sweeping your gaze around the room until it becomes easier for you to provide real eye contact. But, the problem with fake eye contact is that it tends to look mechanical. Another problem with fake eye contact is that you lose the opportunity to assess how well your audience understands your message. Still, fake eye contact is somewhat better than gripping your cards, staring at them, and only occasionally glancing quickly and shallowly at the audience.
This is not to say that you may never look at your notecards. On the contrary, one of the skills in extemporaneous speaking is the ability to alternate one’s gaze between the audience and one’s notes. Rehearsing your presentation in front of a few friends should help you develop the ability to maintain eye contact with your audience while referring to your notes. When you are giving a speech that is well-prepared and well-rehearsed, you will only need to look at your notes occasionally. You’ll develop this ability even further with practice. Your public speaking course is your best chance to get that practice.
Effective Use of Vocalics
Vocalics, also known as paralanguage, is the subfield of nonverbal communication that examines how we use our voices to communicate orally. This means that you speak loudly enough for all audience members to hear you clearly—even those in the back of the room, and that you enunciate clearly enough to be understood by all audience members—even those who may have a hearing impairment or who may be English-language learners. If you tend to be soft-spoken, practice using a louder volume level that may feel unnatural to you at first. For all speakers, good vocalic technique is best achieved by facing the audience with your chin up, looking away from your notecards, and setting your voice at a moderate speed. Using vocalics effectively also means that you use appropriate pitch, pauses, vocal variety, and correct pronunciation.
If you are an English-language learner and feel apprehensive about giving a speech in English, there are two things to remember: first, you can meet with a reference librarian to learn the correct pronunciations of any English words you are unsure of; and second, the fact that you have an accent means you speak more languages than most Americans, which is an accomplishment to be proud of.
If you are one of the many people with a stutter or other speech challenge, you undoubtedly already know that there are numerous techniques for reducing stuttering and improving speech fluency and that there is no one agreed-upon “cure.” The Academy Award–winning movie The King’s Speech did much to increase public awareness of what a person with a stutter goes through when it comes to public speaking. It also prompted some well-known individuals who stutter, such as television news reporter John Stossel, to go public about their stuttering (Stossel, 2011). If you have decided to study public speaking in spite of a speech challenge, we commend you for your efforts and encourage you to work with your speech instructor to make whatever adaptations work best for you.
Volume refers to how loud or soft a speaker’s voice is. As mentioned, public speakers need to speak loudly enough to be heard by everyone in the audience. In addition, volume is often needed to overcome ambient noise, such as the air conditioner hum or the dull traffic roar passing by. In addition, you can use volume strategically to emphasize your speech’s most important points. Select these points carefully; if you emphasize everything, nothing will seem important. You also want to be sure to adjust your volume to the presentation’s physical setting. If you are in a large auditorium and your audience is several yards away, speak louder. If you are in a smaller space, with the audience a few feet away, avoid overwhelming your audience with shouting or speaking too loudly.
Rate is the speed at which a person speaks. To keep your speech delivery interesting, your rate should vary. If you are speaking extemporaneously, your rate will naturally fluctuate. If you’re reading, your delivery is less likely to vary. Because rate is an important tool in enhancing your speech’s meaning, you do not want to give a monotone drone or a rapid machine-gun-style delivery. Your rate should be appropriate for your topic and your points. A rapid, lively rate communicates enthusiasm, urgency, or humor. A slower, moderated rate conveys respect, seriousness, or careful reasoning. By varying rapid and slower rates within a single speech, you emphasize your main points and keep your audience interested.
Pitch refers to how high or low a speaker’s voice is. Some speakers have deep voices and others have high voices. As with your singing-voice range, your speaking-voice pitch is determined mostly by physiology, specifically your vocal folds or cords’ length and your vocal tract size. We all have a normal speaking pitch where our voice is naturally settled—it is the pitch where we are most comfortable speaking and the pitch that feels most natural to you.
While our voices may be generally comfortable at a specific pitch level, we all modulate or move our pitch up or down. In fact, we do this all the time. When we change our voice’s pitch, we are using inflections. Just as you can use volume strategically, you can also use pitch inflections to make your delivery more interesting and emphatic. If you ordinarily speak with a soprano voice, you may want to drop your voice to a slightly lower range to call attention to a particular point. How we use inflections can even change the entire meaning of what we are saying. For example, try saying the sentence “I love public speaking” with a higher pitch on one of the words—first raise the pitch on “I,” then say it again with the pitch raised on “love,” and so on. “ I love public speaking” conveys a different meaning from “I love public speaking,” doesn’t it?
There are some speakers who don’t change their pitch at all while speaking, which is called monotone. While very few people are completely monotone, some speakers slip into monotone patterns because they are nervous. One way to ascertain whether you sound monotone is to record your voice and listen to how you sound. If you notice that your voice doesn’t fluctuate very much, you will need to intentionally alter your pitch to ensure that your speech’s emphasis isn’t completely lost on your audience.
Finally, resist the habit of pitching your voice up at the ends of sentences. It makes them sound like questions instead of statements. This habit can be disorienting and distracting, interfering with the audience’s ability to focus entirely on the message. The speaker sounds uncertain or sounds as though he or she is seeking the listener’s understanding or approval. It hurts the speaker’s credibility, so avoid doing it.
Effectively using pitch is one of the keys to delivering an interesting speech that will hold your audience’s attention.
Pauses are brief breaks in a speaker’s delivery that can show emphasis and enhance a message’s clarity. In terms of timing, using pauses effectively is one of the most important skills to develop. Some speakers become uncomfortable very quickly with the dead air that the pause causes. And if the speaker is uncomfortable, the discomfort can transmit itself to the audience. That doesn’t mean you should avoid using pauses; your ability to use them confidently will increase with practice. Some of the best comedians use the well-timed pause to powerful and hilarious effect. Although your speech will not be a comedy routine, pauses are still useful for emphasis, especially when combined with a lowered pitch and rate to emphasize the important point you do not want your audience to miss.
Vocal Variety
Vocal variety has to do with changes in the vocalics we have just discussed: volume, pitch, rate, and pauses. No one wants to hear the same volume, pitch, rate, or pauses used over and over again in a speech. Your audience should never be able to detect that you’re about to slow down or that your voice is going to get deeper because you’re making an important point. When you think about how you sound in a normal conversation, you use volume, pitch, rate, and pauses spontaneously. If you try to over rehearse your vocalics, your speech will end up sounding artificial. Vocal variety should flow naturally from your wish to speak with expression. In that way, it will animate your speech and invite your listeners to understand your topic the way you do.
Pronunciation
The last major category related to vocalics is pronunciation, or the conventional patterns of speech used to form a word. Word pronunciation is important for two reasons: first, mispronouncing a word your audience is familiar with will harm your credibility as a speaker; and second, mispronouncing a word they are unfamiliar with can confuse and even misinform them. If there is any possibility at all that you don’t know the correct pronunciation of a word, find out. Many online dictionaries, such as the Wiktionary , provide free sound files that illustrate how to pronounce words.
Many people have commented on how some highly educated public speakers, including US presidents, have mispronounced words such as nuclear and cavalry. There are classroom examples as well. For instance, a student giving a speech on the Greek philosopher Socrates mispronounced his name at least eight times during her speech. This mispronunciation created a very awkward and anxious situation for the audience. Everyone felt embarrassed, and the teacher, opting not to humiliate the student in front of the class, did not say anything out loud, but instead, provided a private written comment at the end of class.
One important aspect of pronunciation is articulation, or the ability to clearly pronounce each succession of syllables used to make up a word. Some people have difficulty articulating because of physiological problems that can be treated by trained speech therapists, but other people have articulation problems because they come from a cultural milieu where a dialect other than standard American English is the norm. Speech therapists, who generally guide their clients toward standard American English, use the acronym SODA when helping people learn how to more effectively articulate, which means substitutions, omissions, distortions, and additions.
- Substitutions occur when a speaker replaces one consonant or vowel with another consonant, for example, water becomes wudda ; ask becomes ax ; mouth becomes mouf .
- Omissions occur when a speaker drops a consonant or vowel within a word: Internet becomes Innet ; mesmerized becomes memerized ; probably becomes prolly .
- Distortions occur when a speaker articulates a word with nasal or slurring sounds, for instance, pencil sounds like mencil ; precipitation sounds like persination ; second sounds like slecond .
- Additions occur when a speaker adds consonants or vowels to words that are not there, for example, anyway becomes anyways ; athletic becomes athaletic ; black becomes buhlack ; interpret becomes interpretate .
Another aspect of public speaking pronunciation is to avoid using verbal surrogates. These are filler words used as placeholders for actual words, such as like er, um, uh , etc. You might be able to get away with saying um as many as two or three times in your speech before it becomes distracting, but the same cannot be said of like. We know of a student who trained herself to avoid saying like. As soon as the first speech was assigned, she began wearing a rubber band on her left wrist. Each time she caught herself saying like, she snapped herself with the rubber band. It hurt. Very quickly, she found that she could stop inflicting the snap on herself, and she had successfully confronted an unprofessional verbal habit.
Effective Self-Presentation
In addition to using our voices effectively, another key to great public speaking is using our bodies effectively. This means to use the body to emphasize or convey meanings during a speech. While we will not attempt to give an entire discourse on nonverbal communication, we will discuss a few basic aspects of physical manipulation: posture, body movement, facial expressions, and dress. These aspects add up to the overall physical dimension of your speech, which we call self-presentation.
“Stand up tall!” I’m sure we’ve all heard this statement from a parent or a teacher at some point in our lives. The fact is, posture is actually quite important. When you stand up straight, you communicate to your audience, without saying a word, that you hold a position of power and you take your position seriously. If, however, you are slouching, hunched over, or leaning on something, you could be perceived as ill prepared, anxious, lacking credibility, or not serious about your speaking responsibilities. While speakers often assume a more casual posture as the presentation continues, especially if it is a long one—such as a ninety-minute class lecture—it is always wise to start by standing up straight and putting your best foot forward. Remember, you only get one shot at making a first impression, and your body’s orientation is one of the first pieces of information audiences use to make that impression.
Body Movement
Unless you are stuck behind a podium because you are using a non-movable microphone, never stand in one place during a speech. However, moving during a speech should also not resemble pacing. For example, there was once a speaker who would walk around a small table where her speaking notes were located. She would walk around the table once, toss her chalk twice, and then repeat the process. Instead of listening to what the speaker was saying, everyone became transfixed by her walk-and-chalk-toss pattern. As speakers, we must be mindful of how we go about moving while speaking. One common method for easily integrating movement into your speech is to walk a few steps when you transition from one idea to the next. By only moving at transition points, you help focus your audience’s attention on the transition from one idea to the next, and you increase your nonverbal immediacy by getting closer to different segments of your audience.
Body movement also includes gestures. These should be neither overdramatic nor subdued. At one extreme, arm-waving and fist-pounding will distract from your message and reduce your credibility. At the other extreme, not gesturing at all is wasting an opportunity to suggest emphasis, enthusiasm, or another personal connection with your topic.
There are many ways to use gestures. The most obvious are hand gestures. Use gestures moderately at carefully selected times during your speech. If you overuse gestures, they lose meaning. Many late-night comedy parodies of political leaders include patterned, overused gestures or other delivery habits associated with a particular speaker. However, well-placed, simple, natural gestures that indicate emphasis, direction, or the size of something is usually effective. Normally, a gesture with one hand is enough. Rather than trying to use a gesture for every sentence, use only a few well-planned gestures. It is often more effective to make a gesture and hold it for a few moments than to begin waving your hands and arms around in a series of gestures.
Finally, just as you should avoid pacing, avoid other distracting movements when you are speaking. Many speakers have unconscious mannerisms such as twirling their hair, putting their hands in and out of their pockets, jingling their keys, licking their lips, or clicking a pen while speaking. As with other speech-delivery aspects, practicing in front of others will help you to be conscious of such distractions and help you to plan ways to avoid doing them.
Facial Expressions
Faces are amazing, and they convey much information. As speakers, we must be acutely aware of what our face looks like while speaking. While many of us do not look forward to seeing ourselves on video, often the only way to critically evaluate what your face is doing while you are speaking is to watch a recording of your speech. If video is not available, practice speaking in front of a mirror.
There are two extremes you want to avoid: no facial expression and over animated facial expressions. First, do not show a completely blank face while speaking. Some people just do not show much emotion with their faces naturally, but this blankness is often increased when the speaker is nervous. Audiences will react negatively to such a speaker’s message because they will sense that something is amiss. If a speaker is talking about the joys of Disney World, and his face doesn’t show any excitement, the audience is going to be turned off to the speaker and his message. The other extreme is the speaker whose face looks like that of an exaggerated cartoon character. Instead, your goal is to show a variety of appropriate facial expressions while speaking.
Like vocalics and gestures, use facial expression strategically to enhance meaning. A smile or pleasant facial expression is generally appropriate at the beginning of a speech to indicate your wish for a good transaction with your audience. However, you should not smile throughout a speech on drug addiction, poverty, or the Gulf of Mexico’s oil spill. An inappropriate smile creates confusion about your meaning and may make your audience feel uncomfortable. On the other hand, a serious scowl might look hostile or threatening to an audience and distract from the message. If you keep your speech’s meaning foremost in your mind, you will more readily find a facial-expression balance.
Another common problem some new speakers have is showing only one expression. For example, during a college speech competition, one speaker discussed how people die on amusement park rides. One of the judges pulled the speaker aside and informed him that his speech was creepy. Apparently, while speaking about death, the speaker smiled the entire time. The incongruity between the speech on death and dying and the speaker smiling left the judge a little creeped out. If you are excited in a part of your speech, show excitement on your face. On the other hand, if you are at a serious part of your speech, show a serious facial expression.
While there are no clear-cut guidelines for how to dress, it is still a very important part of how others will perceive you—again, it’s all about the first impression. If you want to be taken seriously, you must present yourself seriously. While we do not advocate dressing up in a suit every time you give a speech, there are definitely times when wearing a suit is appropriate.
One general rule to determine dress is the “step-above rule,” which states that you should dress one step above your audience. If your audience is going to be dressed casually in shorts and jeans, then wear nice casual clothing, such as a pair of neatly pressed slacks and a collared shirt or blouse. If, however, your audience is going to be wearing business casual attire, then wear a sport coat, a dress, or a suit. The goal of the step-above rule is to establish yourself as someone to be taken seriously. On the other hand, if you dress two steps above your audience, you may put too much distance between yourself and your audience and come across as overly formal or even arrogant.
Another general dressing rule is to avoid wearing something distracting. Overly tight or revealing garments, over-the-top hairstyles or makeup, jangling jewelry draw your audience’s attention away from your speech (unless your speech is about these items). Remember that your message is your speech’s most important aspect—keep that message in mind when you choose your clothing and accessories.
Remember…You are your visual aid.
Self-Presentation
When you present your speech, you are also presenting yourself. Self-presentation, sometimes also referred to as poise or stage presence, is determined by how you look, how you stand, how you walk to the lectern, and how you use your voice and gestures. Your self-presentation can either enhance your message or detract from it. Worse, a poor self-presentation can turn a good, well-prepared speech into a forgettable waste of time. You want your self-presentation to support your credibility and improve the likelihood that the audience will listen with interest.
Your personal appearance should reflect your carefully prepared speech. Your personal appearance is the first thing your audience will see, and from it, they will make inferences about the speech you’re about to present.
A big mistake that novice public speakers make is to use the same gesture over and over during a speech. While you don’t want your gestures to look fake, be careful to include various different nonverbal components while speaking. Make sure that your face, body, and words are all working in conjunction with each other to support your message.
Practice Effectively
You might get away with presenting a hastily practiced speech, but the speech will not be as good as it could be. To develop your best speech delivery, practice—and use your practice time effectively. Practicing does not mean reading over your notes, mentally running through your speech, or even speaking your speech aloud over and over. Instead, practice with the goal of identifying the weaknesses in your delivery, improving upon them, and building good speech-delivery habits.
When you practice your speech, place both your feet in full, firm contact with the floor to keep your body from swaying side to side. Some novice public speakers find that they don’t know what to do with their hands while speaking. Your practice sessions will help you get comfortable. When you’re not gesturing, rest your free hand lightly on a lectern, or simply allow it to hang at your side. Since this is not a familiar posture for most people, it might feel awkward; but during practice, you’ll begin to get used to it.
Seek Input from Others
Because we can’t see ourselves as others see us, one great way to improve your delivery is to seek constructive criticism from others. This, of course, is an aspect of your public speaking course, as you will receive evaluations from your instructor and possibly from fellow students. However, by practicing in front of others before speech time, you will learn to anticipate and correct problems so that you can receive a better evaluation when you give your speech for real.
Ask your practice observers to be honest about what you can improve upon. Sometimes, students create study groups just for this purpose. When you create a peer study group, everyone understands the entire creative process, and their feedback will thus be more useful to you than the feedback you might get from someone who has never taken the course or given a speech.
If your practice observers seem reluctant to offer useful criticisms, ask them questions; for example, how was your eye contact? Could they hear you? Was your voice well-modulated? Did you mispronounce any words? How was your posture? Were your gestures effective? Did you have any mannerisms that you should learn to avoid? Because peers are sometimes reluctant to say things that could sound critical, direct questions are often a useful way to help them speak up.
If you learn from these practice sessions that your voice tends to drop at the ends of sentences, make a conscious effort to support your voice as you conclude each main point. If you learn that you have a habit of clicking a pen, make sure you don’t have a pen with you when you speak or that you keep it in your pocket. If your practice observers mention that you tend to hide your hands in your shirt or jacket sleeves, next time, wear short sleeves, or roll your sleeves up before beginning your speech. If you learn through practice that you tend to sway or rock while you speak, consciously practice and build the habit of not swaying.
When it is your turn to give feedback to others in your group, assume that they are as interested in doing as well as you are. Give feedback in the spirit of helping them deliver the most engaging speech as possible.
Use Audio and/or Video to Record Yourself
Technology and the myriad electronic devices people are likely to own, has made it easier than ever to record yourself and others. Video, of course, allows you the advantage of being able to see yourself as others see you, while audio allows you to concentrate on your delivery’s audible aspects. As we mentioned earlier in the chapter, if neither video nor audio is available, you can always observe yourself by practicing your delivery in front of a mirror.
After you have recorded yourself, it may seem obvious that you will watch and listen to the recording. This can be intimidating, as you may fear that your performance anxiety will be so obvious that everyone will notice it in the recording. But students are often pleasantly surprised when they watch and listen to their recordings, as even students with very high anxiety find out that they come across in a speech much better than they expected.
A recording can also be a very effective diagnostic device. Sometimes, students believe they are making strong contact with their audiences, but their cards contain so many notes that they succumb to reading them. If you see in the video that you misjudged your eye contact, motivate yourself to rewrite your notecards in a way that doesn’t provide the opportunity to do so much reading.
It is most likely that in viewing your recording, you’ll discover your strengths and see weaknesses you can strengthen.
Good Delivery Is a Habit
Luckily, public speaking is an activity that, when done conscientiously, strengthens with practice. As you become aware of areas to improve, you will begin to develop a keen sense of what works and what audiences respond to.
Practice out loud in front of other people several times, spreading your rehearsals out over several days. To practice, of course, your speech needs to be finalized well ahead of your delivery date. During these practice sessions, time yourself to make sure your speech is the appropriate time length. For an example, during a classroom presentation in which each speech was to last thirty to forty-five minutes, the first student spoke for seventy-five minutes before the professor asked, “Can we speed this up?” The student said, “Yes,” and proceeded to continue speaking for another seventy-five minutes before finally concluding his speech. Although we might fault the professor for not stopping him sooner, clearly the student had not timed his speech in advance.
Your practice sessions will also enable you to make adjustments to your notecards to make them more effective in supporting your contact with your audience. This kind of practice is not just a strategy for beginners; it is practiced by many highly placed public figures with extensive experience in public speaking.
Your public speaking course is one of the best opportunities you will have to manage your performance anxiety, to build your extemporaneous speaking confidence, to develop your vocal skills, and to become adept at self-presentation. Through targeted practice, you’ll develop habits that build continuously on your strengths and that challenge you to find new areas for improving your delivery. By taking advantage of these opportunities, you will gain the ability to present a speech effectively whenever you may be called upon to speak publicly.
University of Minnesota. (2011). Stand up, Speak out: The Practice and Ethics of Public Speaking . University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing. https://open.lib.umn.edu/publicspeaking/ .
Media References
Gray, D. (2006, May 16). Blank index card! [Image]. Flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/davegray/147874576/
Maryland GovPics. (2014, April 23). House of Ruth Luncheon [Image]. Flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/mdgovpics/13998836494/
Mou, M. (2012, September 22). Empty [Image]. Flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/39017338@N08/8010877703/
Pierret, C. (2009, October 1). Speech [Image]. Flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/christianpierret/5260307759/
Swigart, S. (2011, March 14). Egg delivery [Image]. Flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/smswigart/5611768370
Public Speaking Copyright © 2022 by Sarah Billington and Shirene McKay is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

14.4 Practicing for Successful Speech Delivery
Learning objectives.
- Explain why having a strong conversational quality is important for effective public speaking.
- Explain the importance of eye contact in public speaking.
- Define vocalics and differentiate among the different factors of vocalics.
- Explain effective physical manipulation during a speech.
- Understand how to practice effectively for good speech delivery.
There is no foolproof recipe for good delivery. Each of us is unique, and we each embody different experiences and interests. This means each person has an approach, or a style, that is effective for her or him. This further means that anxiety can accompany even the most carefully researched and interesting message. Even when we know our messages are strong and well-articulated on paper, it is difficult to know for sure that our presentation will also be good.
We are still obligated to do our best out of respect for the audience and their needs. Fortunately, there are some tools that can be helpful to you even the very first time you present a speech. You will continue developing your skills each time you put them to use and can experiment to find out which combination of delivery elements is most effective for you.
What Is Good Delivery?
The more you care about your topic, the greater your motivation to present it well. Good delivery is a process of presenting a clear, coherent message in an interesting way. Communication scholar Stephen E. Lucas tells us:
Good delivery…conveys the speaker’s ideas clearly, interestingly, and without distracting the audience. Most audiences prefer delivery that combines a certain degree of formality with the best attributes of good conversation—directness, spontaneity, animation, vocal and facial expressiveness, and a lively sense of communication. Lucas, S. E. (2009). The art of public speaking (9th ed.). Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill, p. 244.
Many writers on the nonverbal aspects of delivery have cited the findings of psychologist Albert Mehrabian, asserting that the bulk of an audience’s understanding of your message is based on nonverbal communication. Specifically, Mehrabian is often credited with finding that when audiences decoded a speaker’s meaning, the speaker’s face conveyed 55 percent of the information, the vocalics conveyed 38 percent, and the words conveyed just 7 percent. Mehrabian, A. (1972). Nonverbal communication . Chicago, IL: Aldine-Atherton. Although numerous scholars, including Mehrabian himself, have stated that his findings are often misinterpreted, Mitchell, O. (n.d.). Mehrabian and nonverbal communication [Web log post]. Retrieved from http://www.speakingaboutpresenting.com/presentation-myths/mehrabian-nonverbal-communication-research scholars and speech instructors do agree that nonverbal communication and speech delivery are extremely important to effective public speaking.
In this section of the chapter, we will explain six elements of good delivery: conversational style, conversational quality, eye contact, vocalics, physical manipulation, and variety. And since delivery is only as good as the practice that goes into it, we conclude with some tips for effective use of your practice time.
Conversational Style
Conversational style A speaker’s ability to sound expressive and be perceived by the audience as natural. is a speaker’s ability to sound expressive and to be perceived by the audience as natural. It’s a style that approaches the way you normally express yourself in a much smaller group than your classroom audience. This means that you want to avoid having your presentation come across as didactic or overly exaggerated. You might not feel natural while you’re using a conversational style, but for the sake of audience preference and receptiveness, you should do your best to appear natural. It might be helpful to remember that the two most important elements of the speech are the message and the audience. You are the conduit with the important role of putting the two together in an effective way. Your audience should be thinking about the message, not the delivery.
Stephen E. Lucas defines conversational quality A speaker’s ability to prepare a speech and rehearse a speech but still sound spontaneous when delivering the speech. as the idea that “no matter how many times a speech has been rehearsed, it still sounds spontaneous” [emphasis in original]. Lucas, S. E. (2009). The art of public speaking (9th ed.). Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill, p. 247. No one wants to hear a speech that is so well rehearsed that it sounds fake or robotic. One of the hardest parts of public speaking is rehearsing to the point where it can appear to your audience that the thoughts are magically coming to you while you’re speaking, but in reality you’ve spent a great deal of time thinking through each idea. When you can sound conversational, people pay attention.
Eye Contact
Eye contact A speaker’s ability to have visual contact with everyone in his or her audience. is a speaker’s ability to have visual contact with everyone in the audience. Your audience should feel that you’re speaking to them, not simply uttering main and supporting points. If you are new to public speaking, you may find it intimidating to look audience members in the eye, but if you think about speakers you have seen who did not maintain eye contact, you’ll realize why this aspect of speech delivery is important. Without eye contact, the audience begins to feel invisible and unimportant, as if the speaker is just speaking to hear her or his own voice. Eye contact lets your audience feel that your attention is on them, not solely on the cards in front of you.
Sustained eye contact with your audience is one of the most important tools toward effective delivery. O’Hair, Stewart, and Rubenstein note that eye contact is mandatory for speakers to establish a good relationship with an audience. O’Hair, D., Stewart, R., & Rubenstein, H. (2001). A speaker’s guidebook: Text and reference. Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martin’s. Whether a speaker is speaking before a group of five or five hundred, the appearance of eye contact is an important way to bring an audience into your speech.
Eye contact can be a powerful tool. It is not simply a sign of sincerity, a sign of being well prepared and knowledgeable, or a sign of confidence; it also has the power to convey meanings. Arthur Koch tells us that all facial expressions “can communicate a wide range of emotions, including sadness, compassion, concern, anger, annoyance, fear, joy, and happiness.” Koch, A. (2010). Speaking with a purpose (8th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon, p. 233.
If you find the gaze of your audience too intimidating, you might feel tempted to resort to “faking” eye contact with them by looking at the wall just above their heads or by sweeping your gaze around the room instead of making actual eye contact with individuals in your audience until it becomes easier to provide real contact. The problem with fake eye contact is that it tends to look mechanical. Another problem with fake attention is that you lose the opportunity to assess the audience’s understanding of your message. Still, fake eye contact is somewhat better than gripping your cards and staring at them and only occasionally glancing quickly and shallowly at the audience.
This is not to say that you may never look at your notecards. On the contrary, one of the skills in extemporaneous speaking is the ability to alternate one’s gaze between the audience and one’s notes. Rehearsing your presentation in front of a few friends should help you develop the ability to maintain eye contact with your audience while referring to your notes. When you are giving a speech that is well prepared and well rehearsed, you will only need to look at your notes occasionally. This is an ability that will develop even further with practice. Your public speaking course is your best chance to get that practice.
Effective Use of Vocalics
Vocalics Subfield of nonverbal communication that examines how we use our voices to communicate orally; also known as paralanguage. , also known as paralanguage, is the subfield of nonverbal communication that examines how we use our voices to communicate orally. This means that you speak loudly enough for all audience members (even those in the back of the room) to hear you clearly, and that you enunciate clearly enough to be understood by all audience members (even those who may have a hearing impairment or who may be English-language learners). If you tend to be soft-spoken, you will need to practice using a louder volume level that may feel unnatural to you at first. For all speakers, good vocalic technique is best achieved by facing the audience with your chin up and your eyes away from your notecards and by setting your voice at a moderate speed. Effective use of vocalics also means that you make use of appropriate pitch, pauses, vocal variety, and correct pronunciation.
If you are an English-language learner and feel apprehensive about giving a speech in English, there are two things to remember: first, you can meet with a reference librarian to learn the correct pronunciations of any English words you are unsure of; and second, the fact that you have an accent means you speak more languages than most Americans, which is an accomplishment to be proud of.
If you are one of the many people with a stutter or other speech challenge, you undoubtedly already know that there are numerous techniques for reducing stuttering and improving speech fluency and that there is no one agreed-upon “cure.” The Academy Award–winning movie The King’s Speech did much to increase public awareness of what a person with a stutter goes through when it comes to public speaking. It also prompted some well-known individuals who stutter, such as television news reporter John Stossel, to go public about their stuttering. Stossel, J. (2011, March 2). An Academy Award–winning movie, stuttering and me [Web log post]. Retrieved from http://www.humanevents.com/article.php?id=42081 If you have decided to study public speaking in spite of a speech challenge, we commend you for your efforts and encourage you to work with your speech instructor to make whatever adaptations work best for you.
Volume The loudness or softness of a speaker’s voice. refers to the loudness or softness of a speaker’s voice. As mentioned, public speakers need to speak loudly enough to be heard by everyone in the audience. In addition, volume is often needed to overcome ambient noise, such as the hum of an air conditioner or the dull roar of traffic passing by. In addition, you can use volume strategically to emphasize the most important points in your speech. Select these points carefully; if you emphasize everything, nothing will seem important. You also want to be sure to adjust your volume to the physical setting of the presentation. If you are in a large auditorium and your audience is several yards away, you will need to speak louder. If you are in a smaller space, with the audience a few feet away, you want to avoid overwhelming your audience with shouting or speaking too loudly.
Rate The fastness or slowness of a person’s speech delivery. is the speed at which a person speaks. To keep your speech delivery interesting, your rate should vary. If you are speaking extemporaneously, your rate will naturally fluctuate. If you’re reading, your delivery is less likely to vary. Because rate is an important tool in enhancing the meanings in your speech, you do not want to give a monotone drone or a rapid “machine-gun” style delivery. Your rate should be appropriate for your topic and your points. A rapid, lively rate can communicate such meanings as enthusiasm, urgency, or humor. A slower, moderated rate can convey respect, seriousness, or careful reasoning. By varying rapid and slower rates within a single speech, you can emphasize your main points and keep your audience interested.
Pitch The highness or lowness of a speaker’s voice. refers to the highness or lowness of a speaker’s voice. Some speakers have deep voices and others have high voices. As with one’s singing voice range, the pitch of one’s speaking voice is determined to a large extent by physiology (specifically, the length of one’s vocal folds, or cords, and the size of one’s vocal tract). We all have a normal speaking pitch where our voice is naturally settled, the pitch where we are most comfortable speaking, and most teachers advise speaking at the pitch that feels natural to you.
While our voices may be generally comfortable at a specific pitch level, we all have the ability to modulate, or move, our pitch up or down. In fact, we do this all the time. When we change the pitch of our voices, we are using inflections Changes in the pitch of a speaker’s voice. . Just as you can use volume strategically, you can also use pitch inflections to make your delivery more interesting and emphatic. If you ordinarily speak with a soprano voice, you may want to drop your voice to a slightly lower range to call attention to a particular point. How we use inflections can even change the entire meaning of what we are saying. For example, try saying the sentence “I love public speaking” with a higher pitch on one of the words—first raise the pitch on “I,” then say it again with the pitch raised on “love,” and so on. “ I love public speaking” conveys a different meaning from “I love public speaking,” doesn’t it?
There are some speakers who don’t change their pitch at all while speaking, which is called monotone The vocal quality of staying at a constant pitch level without inflections. . While very few people are completely monotone, some speakers slip into monotone patterns because of nerves. One way to ascertain whether you sound monotone is to record your voice and see how you sound. If you notice that your voice doesn’t fluctuate very much, you will need to be intentional in altering your pitch to ensure that the emphasis of your speech isn’t completely lost on your audience.
Finally, resist the habit of pitching your voice “up” at the ends of sentences. It makes them sound like questions instead of statements. This habit can be disorienting and distracting, interfering with the audience’s ability to focus entirely on the message. The speaker sounds uncertain or sounds as though he or she is seeking the understanding or approval of the listener. It hurts the speaker’s credibility and it needs to be avoided.
The effective use of pitch is one of the keys to an interesting delivery that will hold your audience’s attention.
Pauses Brief breaks in a speaker’s deliver designed to show emphasis. are brief breaks in a speaker’s delivery that can show emphasis and enhance the clarity of a message. In terms of timing, the effective use of pauses is one of the most important skills to develop. Some speakers become uncomfortable very quickly with the “dead air” that the pause causes. And if the speaker is uncomfortable, the discomfort can transmit itself to the audience. That doesn’t mean you should avoid using pauses; your ability to use them confidently will increase with practice. Some of the best comedians use the well-timed pause to powerful and hilarious effect. Although your speech will not be a comedy routine, pauses are still useful for emphasis, especially when combined with a lowered pitch and rate to emphasize the important point you do not want your audience to miss.
Vocal Variety
Vocal variety Changes in volume, pitch, rate, and pauses. has to do with changes in the vocalics we have just discussed: volume, pitch, rate, and pauses. No one wants to hear the same volume, pitch, rate, or use of pauses over and over again in a speech. Your audience should never be able to detect that you’re about to slow down or your voice is going to get deeper because you’re making an important point. When you think about how you sound in a normal conversation, your use of volume, pitch, rate, and pauses are all done spontaneously. If you try to overrehearse your vocalics, your speech will end up sounding artificial. Vocal variety should flow naturally from your wish to speak with expression. In that way, it will animate your speech and invite your listeners to understand your topic the way you do.
Pronunciation
The last major category related to vocalics is pronunciation The conventional patterns of speech used to form a word. , or the conventional patterns of speech used to form a word. Word pronunciation is important for two reasons: first, mispronouncing a word your audience is familiar with will harm your credibility as a speaker; and second, mispronouncing a word they are unfamiliar with can confuse and even misinform them. If there is any possibility at all that you don’t know the correct pronunciation of a word, find out. Many online dictionaries, such as the Wiktionary ( http://wiktionary.org ), provide free sound files illustrating the pronunciation of words.
Many have commented on the mispronunciation of words such as “nuclear” and “cavalry” by highly educated public speakers, including US presidents. There have been classroom examples as well. For instance, a student giving a speech on the Greek philosopher Socrates mispronounced his name at least eight times during her speech. This mispronunciation created a situation of great awkwardness and anxiety for the audience. Everyone felt embarrassed and the teacher, opting not to humiliate the student in front of the class, could not say anything out loud, instead providing a private written comment at the end of class.
One important aspect of pronunciation is articulation The ability to clearly pronounce each of a succession syllables used to make up a word. , or the ability to clearly pronounce each of a succession of syllables used to make up a word. Some people have difficulty articulating because of physiological problems that can be treated by trained speech therapists, but other people have articulation problems because they come from a cultural milieu where a dialect other than standard American English is the norm. Speech therapists, who generally guide their clients toward standard American English, use the acronym SODA when helping people learn how to more effectively articulate: substitutions Common articulation problem in which a speaker replaces one consonant or vowel with another consonant. , omissions Common articulation problem in which a speaker drops a consonant or vowel within a word. , distortions Common articulation problem in which a speaker articulates a word in a different or unusual manner usually caused by nasal sounds or slurring of words. , and additions Common articulation problem in which a speaker adds consonants or vowels to words. .
- Substitutions occur when a speaker replaces one consonant or vowel with another consonant ( water becomes wudda ; ask becomes ax ; mouth becomes mouf ).
- Omissions occur when a speaker drops a consonant or vowel within a word ( Internet becomes Innet ; mesmerized becomes memerized ; probably becomes prolly ).
- Distortions occur when a speaker articulates a word with nasal or slurring sounds ( pencil sounds like mencil ; precipitation sounds like persination ; second sounds like slecond ).
- Additions occur when a speaker adds consonants or vowels to words that are not there ( anyway becomes anyways ; athletic becomes athaletic ; black becomes buhlack ; interpret becomes interpretate ).
Another aspect of pronunciation in public speaking is avoiding the use of verbal surrogates “Filler” words used as placeholders for actual words (like, er , um , uh , etc.). or “filler” words used as placeholders for actual words (like er , um , uh , etc.). You might be able to get away with saying “um” as many as two or three times in your speech before it becomes distracting, but the same cannot be said of “like.” We know of a student who trained herself to avoid saying “like.” As soon as the first speech was assigned, she began wearing a rubber band on her left wrist. Each time she caught herself saying “like,” she snapped herself with the rubber band. It hurt. Very quickly, she found that she could stop inflicting the snap on herself, and she had successfully confronted an unprofessional verbal habit.
Effective Physical Manipulation
In addition to using our voices effectively, a key to effective public speaking is physical manipulation The use of the body to emphasize meanings or convey meanings during a speech. , or the use of the body to emphasize meanings or convey meanings during a speech. While we will not attempt to give an entire discourse on nonverbal communication, we will discuss a few basic aspects of physical manipulation: posture, body movement, facial expressions, and dress. These aspects add up to the overall physical dimension of your speech, which we call self-presentation.
“Stand up tall!” I’m sure we’ve all heard this statement from a parent or a teacher at some point in our lives. The fact is, posture is actually quite important. When you stand up straight, you communicate to your audience, without saying a word, that you hold a position of power and take your position seriously. If however, you are slouching, hunched over, or leaning on something, you could be perceived as ill prepared, anxious, lacking in credibility, or not serious about your responsibilities as a speaker. While speakers often assume more casual posture as a presentation continues (especially if it is a long one, such as a ninety-minute class lecture), it is always wise to start by standing up straight and putting your best foot forward. Remember, you only get one shot at making a first impression, and your body’s orientation is one of the first pieces of information audiences use to make that impression.
Body Movement
Unless you are stuck behind a podium because of the need to use a nonmovable microphone, you should never stand in one place during a speech. However, movement during a speech should also not resemble pacing. One of our authors once saw a speaker who would walk around a small table where her speaking notes were located. She would walk around the table once, toss her chalk twice, and then repeat the process. Instead of listening to what the speaker was saying, everyone became transfixed by her walk-and-chalk-toss pattern. As speakers, we must be mindful of how we go about moving while speaking. One common method for easily integrating some movement into your speech is to take a few steps any time you transition from one idea to the next. By only moving at transition points, not only do you help focus your audience’s attention on the transition from one idea to the next, but you also are able to increase your nonverbal immediacy by getting closer to different segments of your audience.
Body movement also includes gestures. These should be neither overdramatic nor subdued. At one extreme, arm-waving and fist-pounding will distract from your message and reduce your credibility. At the other extreme, refraining from the use of gestures is the waste of an opportunity to suggest emphasis, enthusiasm, or other personal connection with your topic.
There are many ways to use gestures. The most obvious are hand gestures, which should be used in moderation at carefully selected times in the speech. If you overuse gestures, they lose meaning. Many late-night comedy parodies of political leaders include patterned, overused gestures or other delivery habits associated with a particular speaker. However, the well-placed use of simple, natural gestures to indicate emphasis, direction, size is usually effective. Normally, a gesture with one hand is enough. Rather than trying to have a gesture for every sentence, use just a few well-planned gestures. It is often more effective to make a gesture and hold it for a few moments than to begin waving your hands and arms around in a series of gestures.
Finally, just as you should avoid pacing, you will also want to avoid other distracting movements when you are speaking. Many speakers have unconscious mannerisms such as twirling their hair, putting their hands in and out of their pockets, jingling their keys, licking their lips, or clicking a pen while speaking. As with other aspects of speech delivery, practicing in front of others will help you become conscious of such distractions and plan ways to avoid doing them.
Facial Expressions
Faces are amazing things and convey so much information. As speakers, we must be acutely aware of what our face looks like while speaking. While many of us do not look forward to seeing ourselves on videotape, often the only way you can critically evaluate what your face is doing while you are speaking is to watch a recording of your speech. If video is not available, you can practice speaking in front of a mirror.
There are two extremes you want to avoid: no facial expression and overanimated facial expressions. First, you do not want to have a completely blank face while speaking. Some people just do not show much emotion with their faces naturally, but this blankness is often increased when the speaker is nervous. Audiences will react negatively to the message of such a speaker because they will sense that something is amiss. If a speaker is talking about the joys of Disney World and his face doesn’t show any excitement, the audience is going to be turned off to the speaker and his message. On the other extreme end is the speaker whose face looks like that of an exaggerated cartoon character. Instead, your goal is to show a variety of appropriate facial expressions while speaking.
Like vocalics and gestures, facial expression can be used strategically to enhance meaning. A smile or pleasant facial expression is generally appropriate at the beginning of a speech to indicate your wish for a good transaction with your audience. However, you should not smile throughout a speech on drug addiction, poverty, or the oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico. An inappropriate smile creates confusion about your meaning and may make your audience feel uncomfortable. On the other hand, a serious scowl might look hostile or threatening to audience members and become a distraction from the message. If you keep the meaning of your speech foremost in your mind, you will more readily find the balance in facial expression.
Another common problem some new speakers have is showing only one expression. One of our coauthors competed in speech in college. After one of his speeches (about how people die on amusement park rides), one of his judges pulled him aside and informed him that his speech was “creepy.” Apparently, while speaking about death, our coauthor smiled the entire time. The incongruity between the speech on death and dying and the coauthor’s smile just left the judge a little creeped out. If you are excited in a part of your speech, you should show excitement on your face. On the other hand, if you are at a serious part of your speech, your facial expressions should be serious.
While there are no clear-cut guidelines for how you should dress for every speech you’ll give, dress is still a very important part of how others will perceive you (again, it’s all about the first impression). If you want to be taken seriously, you must present yourself seriously. While we do not advocate dressing up in a suit every time you give a speech, there are definitely times when wearing a suit is appropriate.
One general rule you can use for determining dress is the “step-above rule,” which states that you should dress one step above your audience. If your audience is going to be dressed casually in shorts and jeans, then wear nice casual clothing such as a pair of neatly pressed slacks and a collared shirt or blouse. If, however, your audience is going to be wearing “business casual” attire, then you should probably wear a sport coat, a dress, or a suit. The goal of the step-above rule is to establish yourself as someone to be taken seriously. On the other hand, if you dress two steps above your audience, you may put too much distance between yourself and your audience, coming across as overly formal or even arrogant.
Another general rule for dressing is to avoid distractions in your appearance. Overly tight or revealing garments, over-the-top hairstyles or makeup, jangling jewelry, or a display of tattoos and piercings can serve to draw your audience’s attention away from your speech. Remembering that your message is the most important aspect of your speech, keep that message in mind when you choose your clothing and accessories.
Self-Presentation
When you present your speech, you are also presenting yourself. Self-presentation, sometimes also referred to as poise or stage presence, is determined by how you look, how you stand, how you walk to the lectern, and how you use your voice and gestures. Your self-presentation can either enhance your message or detract from it. Worse, a poor self-presentation can turn a good, well-prepared speech into a forgettable waste of time. You want your self-presentation to support your credibility and improve the likelihood that the audience will listen with interest.
Your personal appearance should reflect the careful preparation of your speech. Your personal appearance is the first thing your audience will see, and from it, they will make inferences about the speech you’re about to present.
One of the biggest mistakes novice public speakers make is to use the same gesture over and over again during a speech. While you don’t want your gestures to look fake, you should be careful to include a variety of different nonverbal components while speaking. You should make sure that your face, body, and words are all working in conjunction with each other to support your message.
Practice Effectively
You might get away with presenting a hastily practiced speech, but the speech will not be as good as it could be. In order to develop your best speech delivery, you need to practice—and use your practice time effectively. Practicing does not mean reading over your notes, mentally running through your speech, or even speaking your speech aloud over and over. Instead, you need to practice with the goal of identifying the weaknesses in your delivery, improving upon them, and building good speech delivery habits.
When you practice your speech, place both your feet in full, firm contact with the floor to keep your body from swaying side to side. Some new public speakers find that they don’t know what to do with their hands during the speech. Your practice sessions should help you get comfortable. When you’re not gesturing, you can rest your free hand lightly on a lectern or simply allow it to hang at your side. Since this is not a familiar posture for most people, it might feel awkward, but in your practice sessions, you can begin getting used to it.
Seek Input from Others
Because we can’t see ourselves as others see us, one of the best ways to improve your delivery is to seek constructive criticism from others. This, of course, is an aspect of your public speaking course, as you will receive evaluations from your instructor and possibly from your fellow students. However, by practicing in front of others before it is time to present your speech, you can anticipate and correct problems so that you can receive a better evaluation when you give the speech “for real.”
Ask your practice observers to be honest about the aspects of your delivery that could be better. Sometimes students create study groups just for this purpose. When you create a study group of classroom peers, everyone has an understanding of the entire creative process, and their feedback will thus be more useful to you than the feedback you might get from someone who has never taken the course or given a speech.
If your practice observers seem reluctant to offer useful criticisms, ask questions. How was your eye contact? Could they hear you? Was your voice well modulated? Did you mispronounce any words? How was your posture? Were your gestures effective? Did you have any mannerisms that you should learn to avoid? Because peers are sometimes reluctant to say things that could sound critical, direct questions are often a useful way to help them speak up.
If you learn from these practice sessions that your voice tends to drop at the ends of sentences, make a conscious effort to support your voice as you conclude each main point. If you learn that you have a habit of clicking a pen, make sure you don’t have a pen with you when you speak or that you keep it in your pocket. If your practice observers mention that you tend to hide your hands in the sleeves of your shirt or jacket, next time wear short sleeves or roll your sleeves up before beginning your speech. If you learn through practice that you tend to sway or rock while you speak, you can consciously practice and build the habit of not swaying.
When it is your turn to give feedback to others in your group, assume that they are as interested in doing well as you are. Give feedback in the spirit of helping their speeches be as good as possible.
Use Audio and/or Video to Record Yourself
Technology has made it easier than ever to record yourself and others using the proliferation of electronic devices people are likely to own. Video, of course, allows you the advantage of being able to see yourself as others see you, while audio allows you to concentrate on the audible aspects of your delivery. As we mentioned earlier in the chapter, if neither video nor audio is available, you can always observe yourself by practicing your delivery in front of a mirror.
After you have recorded yourself, it may seem obvious that you should watch and listen to the recording. This can be intimidating, as you may fear that your performance anxiety will be so obvious that everyone will notice it in the recording. But students are often pleasantly surprised when they watch and listen to their recordings, as even students with very high anxiety may find out that they “come across” in a speech much better than they expected.
A recording can also be a very effective diagnostic device. Sometimes students believe they are making strong contact with their audiences, but their cards contain so many notes that they succumb to the temptation of reading. By finding out from the video that you misjudged your eye contact, you can be motivated to rewrite your notecards in a way that doesn’t provide the opportunity to do so much reading.
It is most likely that in viewing your recording, you will benefit from discovering your strengths and finding weak areas you can strengthen.
Good Delivery Is a Habit
Luckily, public speaking is an activity that, when done conscientiously, strengthens with practice. As you become aware of the areas where your delivery has room for improvement, you will begin developing a keen sense of what “works” and what audiences respond to.
It is advisable to practice out loud in front of other people several times, spreading your rehearsals out over several days. To do this kind of practice, of course, you need to have your speech be finalized well ahead of the date when you are going to give it. During these practice sessions, you can time your speech to make sure it lasts the appropriate length of time. A friend of ours was the second student on the program in an event where each student’s presentation was to last thirty to forty-five minutes. After the first student had been speaking for seventy-five minutes, the professor in charge asked, “Can we speed this up?” The student said yes, and proceeded to continue speaking for another seventy-five minutes before finally concluding his portion of the program. Although we might fault the professor for not “pulling the plug,” clearly the student had not timed his speech in advance.
Your practice sessions will also enable you to make adjustments to your notecards to make them more effective in supporting your contact with your audience. This kind of practice is not just a strategy for beginners; it is practiced by many highly placed public figures with extensive experience in public speaking.
Your public speaking course is one of the best opportunities you will have to manage your performance anxiety, build your confidence in speaking extemporaneously, develop your vocal skills, and become adept at self-presentation. The habits you can develop through targeted practice are to build continuously on your strengths and to challenge yourself to find new areas for improving your delivery. By taking advantage of these opportunities, you will gain the ability to present a speech effectively whenever you may be called upon to speak publicly.
Key Takeaways
- Conversational style is a speaker’s ability to sound expressive while being perceived by the audience as natural. Conversational quality is a speaker’s ability to prepare a speech and rehearse a speech but still sound spontaneous when delivering it.
- Eye contact helps capture and maintain an audience’s interest while contributing to the speaker’s credibility.
- Vocalics are the nonverbal components of the verbal message. There are six important vocalic components for a speaker to be aware of: volume (loudness or softness), pitch (highness or lowness), rate (fastness or slowness), pauses (use of breaks to add emphasis), vocal variety (use of a range of vocalic strategies), and pronunciation (using conventional patterns of speech formation).
- Physical manipulation is the use of one’s body to add meaning and emphasis to a speech. As such, excessive or nonexistent physical manipulation can detract from a speaker’s speech.
- Good delivery is a habit that is built through effective practice.
- Find a speech online and examine the speaker’s overall presentation. How good was the speaker’s delivery? Make a list of the aspects of delivery in this chapter and evaluate the speaker according to the list. In what areas might the speaker improve?
- Record a practice session of your speech. Write a self-critique, answering the following questions: What surprised you the most? What is an area of strength upon which you can build? What is one area for improvement?
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
Speech Delivery

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.
In this article:
Types of Speech Delivery
Aspects of physical delivery.
There are four primary types of speech delivery: Manuscript, Memorized, Impromptu, and Extemporaneous.

Memorized , like it sounds, involves committing your entire speech to memory. Once again, this sounds great. But, practically speaking, who has time to memorize even a short speech? And like a manuscript speech, you can’t adapt to feedback from the audience.
An Impromptu speech is one that you are asked to deliver with little or no preparation. Chances are, that if you’re on this site, impromptu speeches aren’t what you are expected to deliver.
Finally, the Extemporaneous speech is a speech delivered with some prepared structure, such as notes or an outline, but is otherwise delivered off-the-cuff. In most cases, this is going to be your best choice. The notes allow you to structure your speech, without handcuffing you in the event that your audience needs you to adapt. Also, you will sound more natural and conversational, and this will help hold audience attention.
There are six aspects of physical delivery that will be covered in this section: voice use, facial expressions, eye contact, gesturing, and movement.
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
Effective voice use involves several elements. Naturally, one of the most important aspects is volume. As a speaker, you must be loud enough to be heard by everyone in the room, but not so loud that you sound unnatural or bossy. Monitor the nonverbal feedback of audience members in the back of the room, if they are leaning forward or concentrating abnormally hard, you may need to speak up. It is also necessary to vary the pitch, rate, and tone of your voice to avoid sounding monotonous. We’ve all experienced the agony of listening to a monotonous-voiced speaker. This doesn’t mean that you need to be extremely flamboyant or obnoxious. Overall, you should just strive for a casual, conversational voice.
Your audience gathers a lot of information from your facial expressions . If your facial expressions and your spoken words conflict, the audience is likely to believe your face. So make sure that your facial expressions mesh with the feelings and ideas being expressed. Basically, a good rule of thumb for facial expressions (as well as gestures) is to do what comes naturally. There is no need to be overly theatrical with your facial expressions in a speech. And remember, if it’s at all appropriate, you can’t go wrong with a smile.
The simple rule on eye contact is this: The more, the better. A good strategy for eye contact is to make brief (a beat or two) eye contact with members of the audience in one section of the audience and then move to another section. Ideally, you should be making eye contact with someone whenever words are being spoken in your speech. Beware of this trap: People naturally tend to focus their eye contact on the person that is giving them the best nonverbal feedback (smiling, nodding, etc.). If you find yourself focusing too much on this person, work on moving to others.
One of the most common questions that people have about public speaking is: What do I do with my hands? The quick and easy answer is: Whatever comes naturally (unless clutching the podium is what comes naturally). The key to good gesturing is variety, which most of us have in our everyday gestures.
The final aspect of physical delivery is movement . If you are positioned behind a podium, your movements are obviously going to be restricted. But if you are not using a podium, feel free to walk to different parts of the stage as you deliver your speech. This keeps different parts of the audience involved and adds variety. Don’t just wander in place, though. If your feet move, go somewhere.
Visual Aids
Speech Anxiety
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class

Shortform Books
The World's Best Book Summaries
Speech Delivery: The Art of Public Speaking
This article is an excerpt from the Shortform book guide to "Talk Like TED" by Carmine Gallo. Shortform has the world's best summaries and analyses of books you should be reading.
Like this article? Sign up for a free trial here .
What makes a good speech delivery? What can you do to deliver your speech in the most impactful and persuasive way possible?
Speech delivery is how you say the words you’ve prepared. It involves many factors, such as how loudly you speak, the pitch of your speech, and how often you pause between points.
Here is how to improve your speech delivery, according to Carmine Gallo.
What Is Speech Delivery?
As the name suggests, speech delivery is how you deliver your speech: your tone, your pace, your body language, your demeanor. However, Gallo focuses on the one element of speech delivery that he believes is crucial to success: the speed of your speech. Speak too quickly, and people will struggle to understand what you’re saying. Speak too slowly, and your audience will swiftly become bored.
So, what speed is “just right”? After analyzing many TED talks, Gallo has concluded that the optimal rate of speech when giving a talk is around 190 words per minute. He argues that this is a conversational speed—for instance, the speed of speech you’d adopt if you were talking to a friend about your favorite TV show. Therefore, it’s a rate of speech that seems both natural and authentic.
An Exception to the Rule
There are some exceptions to this 190-words-per-minute rule. For instance, it’s acceptable to vary the speed of your speech to reflect the tone or content of what you’re saying. For example, when photographer Lisa Kristine gave a TED talk on modern slavery in 2012, she slowed down her rate of speech when she made the important point that despite slavery being illegal worldwide, it still exists almost everywhere. Making this point slowly added emphasis and gravitas to Kristine’s words.
Meanwhile, when Dr. Jill Bolte Taylor gave a 2013 TEDxYouth talk on how the brain changes throughout puberty, the rate of her speech delivery increase to 220 words per minute. She decided to speak this quickly to emphasize the swift nature of the brain’s transformation at this time of life.
Confident Body Language
Rehearse holding your body in a way that suggests you’re sure of yourself and your opinions. If you fail to appear confident in your convictions, your audience will trust you and your opinions less. After all, why would they believe or agree with what you’re saying if you don’t seem certain of it yourself?
There are a number of things you can do to exude confidence through body language:
- Stand up straight—don’t slouch.
- Hold your head up high, rather than looking downwards.
- Make frequent eye contact with the audience.
- Resist the urge to fidget—for instance, play with your hair or scratch your nose.
If you’re not sure which of these confident actions you’re taking already and which you aren’t, video yourself making a speech. Then, watch the video and identify where your problem areas lie.
Fake It ‘Till You Make It
If you’re already feeling confident about your speech delivery, confident body language will likely come naturally. However, if you’re feeling nervous or insecure, you may doubt your ability to hold your body in a way that’s contradictory to your emotions.
If you’re in the latter situation, don’t be afraid to “fake it ‘till you make it.” In other words, keep practicing confident body language no matter how insecure you actually feel. Studies have shown that doing so can actually make you feel more confident. Standing in a confident position increases your levels of testosterone —a hormone which, amongst other functions, increases your confidence—while simultaneously reducing levels of the stress hormone cortisol.
Researchers claim the so-called “power pose” is particularly effective at boosting confidence levels. This involves stretching your arms as wide as possible for two minutes.
Don’t Be Boring
As well as ensuring that your body language is confident, you also need to make sure that it’s not too boring. A common mistake that speakers make is staying still and rooted to the same spot for the entirety of their presentation. Such rigidity will make you seem dull and unenthusiastic about your topic. Instead, continually walk around your presentation space or stage, moving from one end to the other. Your constant movement will keep your audience engaged and make you seem more dynamic.
Hand Gestures
As you speak, don’t simply hide your hands in your pockets. Instead, use gestures to add emphasis to what you’re saying. For example, if you’re talking about how much a problem has grown in size, create a small circle with your hands and expand it. If you want to emphasize that you’ve personally experienced this problem, point at yourself.
Using hand gestures has a number of benefits:
- It prevents you from using your hands to fidget, thus helping you to exude confidence.
- Movement of any kind—including hand movement—makes you more interesting to watch, and therefore grips your audience’s attention.
- Studies have shown that making hand gestures will increase the audience’s confidence in you and what you’re saying.
Four Tips for Using Hand Gestures
Tip #1: Don’t use gestures too often. They’ll lose their impact and may become overly distracting. Only use gestures to punctuate crucial points of your presentation—for example, your main argument, or the conclusion of a story you’re telling.
Tip #2: Only use gestures that feel comfortable and natural to you. In particular, don’t try to mimic another person’s gesturing style—for example, that of a politician or famous speaker—if it’s out of your comfort zone. The gestures will seem forced and you’ll seem inauthentic.
Tip 3: Don’t overthink which gestures to use. Settle on those that feel the most natural and appropriate to the situation.
Tip #4: Keep your gestures within the “power sphere.” This is the area of the body from the eyes down to the navel. Placing your hands any lower than the navel suggests a lack of confidence and energy.
The ‘Eager Nonverbal’ Strategy
If you’re struggling to come up with appropriate hand gestures to use in your speech or presentation, consider applying the ‘eager nonverbal’ strategy. This is a three-pronged strategy that involves:
- Using hand movements that are expansive and animated: for example, opening your arms wide with your palms open.
- Using hand movements that project outward, towards the audience: for example, pointing in their direction.
- Leaning your body forward, again towards the audience.
Research has shown that using the eager nonverbal strategy can persuade others to act in the way you desire. For example, in one study, shoppers were more likely to buy candy from salespeople who implemented this strategy than from those who didn’t. In the case of a presentation, using the eager nonverbal strategy may help you to persuade your audience to adopt your idea or agree with your point of view.
Remember: As noted in the tips above, you should only implement someone else’s gesturing strategy—including the eager nonverbal strategy—if it feels natural and comfortable for you.
———End of Preview———
Like what you just read read the rest of the world's best book summary and analysis of carmine gallo's "talk like ted" at shortform ..
Here's what you'll find in our full Talk Like TED summary :
- The 9 key principles to good public speaking
- How to apply the public speaking strategies of popular TED talks
- How storytelling enhances your appeal to audiences
- ← Get Rid of Fear and Stop Playing It Safe
- James Clear: What Does It Take to Form a Habit? →

Darya Sinusoid
Darya’s love for reading started with fantasy novels (The LOTR trilogy is still her all-time-favorite). Growing up, however, she found herself transitioning to non-fiction, psychological, and self-help books. She has a degree in Psychology and a deep passion for the subject. She likes reading research-informed books that distill the workings of the human brain/mind/consciousness and thinking of ways to apply the insights to her own life. Some of her favorites include Thinking, Fast and Slow, How We Decide, and The Wisdom of the Enneagram.
You May Also Like

5 Accountability Exercises: Solve Issues & Preserve Relationships

How to End a Conversation Without Burning Bridges

Netflix Feedback Culture: The 4-Steps to Success

How to Break Up With Someone Without Hurting Them: 4 Tips

How to Work With a Red Personality Type

Tips for Memorizing a Speech Without Sounding Scripted
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

14.3: Speech Delivery- Body Language and Voice
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 106495

- Lisa Coleman, Thomas King, & William Turner
- Southwest Tennessee Community College
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Explain the role of facial expressions and eye contact in speech delivery.
- Explain the role of posture, gestures, and movement in speech delivery.
- Explain the connection between personal appearance and credibility in speech delivery.
- Explain the connection between visual aids and speech delivery.
- Identify elements of vocal delivery that make a speech more engaging.
- Identify elements of vocal delivery that make a speech clearer.
- Discuss the relationship between vocal delivery and speaker credibility.
The interplay between the verbal and nonverbal components of your speech can either bring the message vividly to life or confuse or bore the audience. Therefore, it is best that you neither overdramatize your speech delivery behaviors nor downplay them. This is a balance achieved through rehearsal, trial and error, and experience. One way to think of this is in terms of the Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Goldilocks Paradigm: you don’t want to overdo the delivery because you might distract your audience by looking hyper or overly animated. Conversely, someone whose delivery is too understated (meaning they don’t move their hands or feet at all) looks unnatural and uncomfortable, which can also distract. Just like Goldilocks, you want a delivery that is “just right.” This middle ground between too much and too little is a much more natural approach to public speaking delivery. This natural approach will be covered in more detail in the following sections where we discuss specific aspects of your delivery and what you need to think about while actually giving your speech.
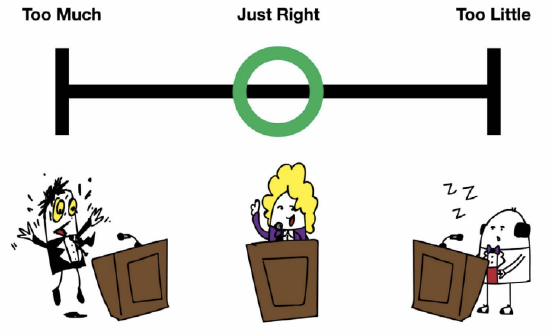
Nonverbal Delivery
Many speakers are more nervous about physical delivery than vocal delivery. Putting our bodies on the line in front of an audience often makes us feel more vulnerable than putting our voice out there. Yet most audiences are not as fixated on our physical delivery as we think they are. Knowing this can help relieve some anxiety, but it doesn’t give us a free pass when it comes to physical delivery. We should still practice for physical delivery that enhances our verbal message. Audience members primarily take in information through their eyes and ears. Beyond the actual words of your speech, the nonverbal communication that accompanies your verbal messages affects your credibility.
Gestures are any arm and hand movements used during your speech . We all use hand gestures while we speak, but we didn’t even take a class in matching verbal communication with the appropriate gestures; we have just internalized these norms over time based on observation and put them into practice. By this point in your life, you have a whole vocabulary of hand movements and gestures that spontaneously come out while you’re speaking. Some of these gestures are emphatic and some are descriptive (Koch, 2007).
Emphatic gestures are the most common hand gestures we use, and they function to emphasize our verbal communication and often relate to the emotions we verbally communicate . Pointing with one finger or all the fingers straight out is an emphatic gesture. We can even bounce that gesture up and down to provide more emphasis. Moving the hand in a circular motion in front of our chest with the fingers spread apart is a common emphatic gesture that shows excitement and often accompanies an increased rate of verbal speaking. We make this gesture more emphatic by using both hands. Descriptive gestures function to illustrate or refer to objects rather than emotions. We use descriptive gestures to indicate the number of something by counting with our fingers or the size, shape, or speed of something . Our hands and arms are often the most reliable and easy-to-use visual aids a speaker can have. While it can be beneficial to plan a key gesture or two in advance, it is generally best to gesture spontaneously in a speech, just as you would during a regular conversation.
It may sound funny, but due to speech anxiety, we have seen more than one student unknowingly incorporate “jazz hands” (shaking your hands at your sides with fingers opened wide) at various points in their speech. While certainly an extreme example, this and behaviors like it can easily become distracting. At the other end of the scale, people who don’t know what to do with their hands or use the “too little” sometimes hold their arms stiffly at their sides, behind their backs, or in their pockets, all of which can also look unnatural and distracting.
However, with all that said, if you have nothing else to do with your hands, such as meaningful gestures, the default position for them is to be resting gently on the sides of the lectern (see Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)). You don’t want to grip the lectern tightly, but resting them on the edges keeps them in a position to move your notes on if you need to or use them to gesture. As stated above, you want to practice this way beforehand so you are used to speaking this way when you come to class.

Sometimes the movement of the whole body, instead of just gesturing with hands, is appropriate in a speech. Just like your hands, a lot of nervous energy is going to try to work its way out of your body through your feet. On the “too much” end, this is most common when people start “dancing” behind the lectern Another variation is twisting feet around each other or the lower leg. On the other end are those who put their feet together, lock their knees, and never move from that position. Both of these options look unnatural, and therefore will prove to be distracting to your audience. Locking your knees can also lead to loss of oxygen in your brain, not a good state to be in because it can cause you to faint.
The default position for your feet, then, is to have them shoulder-width apart with your knees slightly bent (see Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)). Again, you want to look and feel natural, so it is fine to adjust your weight or move out from behind the lectern, but constant motion (or perpetual stillness) will not lead to a good overall delivery.
These two sections on gestures and feet mention “energy.” Public speakers need to look energetic—not hyperactive, but engaged and upbeat about communicating their message. Slumping, low and unvarying pitch and rate, and lack of gestures telegraph “I don’t care” to an audience.
There is a very simple rule when it comes to what you should bring with you to the lectern when you give your speech: Only bring to the lectern what you absolutely need to give the speech . Anything else you have with you will only serve as a distraction for both you and the audience. For the purposes of this class, the only objects you should need to give your speech are whatever materials you are speaking from, and possibly a visual aid if you are using one. Beyond that, don’t bring pens, laptops, phones, lucky charms, or notebooks with you to the lectern. These extra items can ultimately become a distraction themselves when they fall off the lectern or get in your way. Some students like to bring their electronic tablet, laptop computer, or cell phone with them, but there are some obvious disadvantages to these items, especially if you don’t turn the ringer on your cell phone off. Cell phones are not usually large enough to serve as presentation notes; we’ve seen students squint and hold the phone up to their faces.
Not only do you need to be aware of what you bring with you, but you should also be aware of what you have on your person as well. Sometimes, in the course of dressing for a speech, we can overlook simple issues that can cause problems while speaking. Some of these can include:
- Jewelry that ‘jingles’ when you move, such as heavy bracelets;
- Uncomfortable shoes or shoes that you are not used to (don’t make speech day the first time you try wearing high heels);
- Anything with fringe, zippers, or things hanging off it. They might become irresistible to play with while speaking;
- For those with longer hair, remember that you will be looking down at your notes and then looking back up. Don’t be forced to “fix” your hair or tuck it behind your ear every time you look up. Use a barrette, hairband, or some other method to keep your hair totally out of your face so that the audience can see your eyes and you won’t have to adjust your hair constantly. It can be very distracting to an audience to watch a speaker pull hair from his face after every sentence.
The Lectern and Posture
Extra movements caused by anxiety are called nonverbal adaptors , and most of them manifest as distracting movements or gestures. These nonverbal adaptors, like tapping a foot, wringing hands, playing with a paper clip, twirling hair, jingling change in a pocket, scratching, and many more, can definitely detract from a speaker’s message and credibility. Conversely, a confident posture and purposeful gestures and movement can enhance both.
A lectern is a tool for you to use that should ultimately make your speech easier to give, and you need to use it that way. On the “too much” end, some people want to trick their audience into thinking they are not nervous by leaning on the podium in a relaxed manner, sometimes going so far as to actually begin tipping the podium forward. Your lectern is NOT part of your skeletal system, to prop you up, so don’t do this. On the “too little” end are those who are afraid to touch it, worried that they will use it incorrectly or somehow knock it over (you won’t!).
As always, you want the “Goldilocks” middle ground. Just rest your notes and hands on it, but don’t lean on the lectern or “hug” it. Practicing with a lectern (or something similar to a lectern) will eliminate most of your fears about using it.
Posture is the position we assume with our bodies, either intentionally or out of habit . The lectern use is related to posture. Most of us let gravity pull us down. One of the muscle memory tricks of public speaking is to roll your shoulders back. Along with making your shoulder muscles feel better, doing so with feet apart and knees bent, rolling your shoulders back will lead to a more credible physical presence—you’ll look taller and more energetic. You’ll also feel better, and you’ll have a larger lung capacity for breathing to support your tone and volume. In a formal speaking situation, it’s important to have an erect posture that communicates professionalism and credibility. However, a military posture of standing at attention may feel and look unnatural in a typical school or business speech. In informal settings, it may be appropriate to lean on a table or lectern, or even sit among your audience members.

Facial Expressions
Remember, it’s a good thing for audience members to look at you because it means they’re paying attention and interested. Audiences look for f acial expressions of the speaker, or cues about the tone and content of the speech seen on the face . Facial expressions can help bring a speech to life when used by a speaker to communicate emotions and demonstrate enthusiasm for the speech. We tend to use facial expressions naturally and without conscious effort when engaging in day-to-day conversations. Yet many speakers’ expressive faces turn “deadpan” when they stand in front of an audience. Some people naturally have more expressive faces than others—think about the actor Jim Carey’s ability to contort his face as an example. But we can also consciously control and improve on our facial expressions to be more effective speakers. As with other components of speech delivery, becoming a higher self-monitor and increasing your awareness of your typical delivery habits can help you understand, control, and improve your delivery. Although you shouldn’t only practice your speech in front of a mirror, doing so can help you get an idea of how expressive or unexpressive your face is while delivering your speech.

Facial expressions help set the emotional tone for a speech, and it is important that your facial expressions stay consistent with your message. In order to set a positive tone before you start speaking, briefly look at the audience and smile. A smile is a simple but powerful facial expression that can communicate friendliness, openness, and confidence. Facial expressions communicate a range of emotions and are also associated with various moods or personality traits. For example, combinations of facial expressions can communicate that a speaker is tired, excited, angry, confused, frustrated, sad, confident, smug, shy, or bored, among other things. Even if you aren’t bored, for example, a slack face with little animation may lead an audience to think that you are bored with your own speech, which isn’t likely to motivate them to be interested. So make sure your facial expressions are communicating an emotion, mood, or personality trait that you think your audience will view favorably. Also, make sure your facial expressions match the content of your speech. When delivering something lighthearted or humorous, a smile, bright eyes, and slightly raised eyebrows will nonverbally enhance your verbal message. When delivering something serious or somber, a furrowed brow, a tighter mouth, and even a slight head nod can enhance that message. If your facial expressions and speech content are not consistent, your audience could become confused by the conflicting messages, which could lead them to question your honesty and credibility.
“Getting Competent”: Improving Facial Expressions
My very first semester teaching, I was required by my supervisor to record myself teaching and evaluate what I saw. I was surprised by how serious I looked while teaching. My stern, expressionless face was due to my anxiety about being a beginning teacher and my determination to make sure I covered the content for the day. I didn’t realize that it was also making me miss opportunities to communicate how happy I was to be teaching and how passionate I was about the content. I just assumed those things would come through in my delivery. I was wrong. The best way to get an idea of the facial expressions you use while speaking is to record your speech using a computer’s webcam, much like you would look at and talk to the computer when using Skype or another video-chat program. The first time you try this, minimize the video window once you’ve started recording so you don’t get distracted by watching yourself. Once you’ve recorded the video, watch the playback and take notes on your facial expressions. Answer the following questions:
- Did anything surprise you? Were you as expressive as you thought you were?
- What facial expressions did you use throughout the speech?
- Where did your facial expressions match with the content of your speech? Where did your facial expressions not match with the content of your speech?
- Where could you include more facial expressions to enhance your content and/or delivery?
You can also have a friend watch the video and give you feedback on your facial expressions to see if your assessment matches with theirs. Once you’ve assessed your video, re-record your speech and try to improve your facial expressions and delivery. Revisit the previous questions to see if you improved.
Eye Contact
We tend to look at a person’s face when we are listening to them. Again, this often makes people feel uncomfortable and contributes to their overall speaking anxiety. Many speakers don’t like the feeling of having “all eyes” on them, even though having a room full of people avoiding making eye contact with you would be much more awkward.
As we’ve said consistently throughout this book, your audience is the single biggest factor that influences every aspect of your speech. And since eye contact is how you establish and maintain a rapport with your audience during your speech, it is an extremely important element of your delivery. Your professor may or may not indicate a standard for how much eye contact you need during the speech, such as 50%, but he or she will absolutely want to see you making an effort to engage your audience by looking directly at them. Eye contact has the power to make people feel welcome/unwelcome, comfortable/uncomfortable, listened to / ignored, and so on. As a speaker, eye contact can also be used to establish credibility and hold your audience’s attention. We often interpret a lack of eye contact to mean that someone is not credible or not competent, and as a public speaker, you don’t want your audience thinking either of those things.
What is important to note here is that you want to establish genuine eye contact with your audience and not “fake” eye contact. There have been a lot of techniques generated for “faking” eye contact, and none of them look natural. For example, these are not good ideas:
- Three points on the back wall – You may have heard that instead of making eye contact, you can just pick three points on the back wall and look at those. What ends up happening, though, is you look like you are staring off into space and your audience will spend the majority of your speech trying to figure out what you are looking at. To avoid this, look around the entire room, including the front, back, left, and right sides of the space.
- The swimming method – This happens when someone is reading his or her speech and looks up quickly and briefly to try to make it seem like they are making eye contact, not unlike a swimmer who pops his head out of the water for a breath before going back under. Eye contact is more than just physically moving your head; it is about looking at your audience and establishing a connection. In general, your eye contact should last at least five seconds at a time and should be with individuals throughout the room.
- The stare down – Since you will, to some degree, be graded on your eye contact, some students think (either consciously or not), that the best way to ensure they get credit for establishing eye contact is to always and exclusively look directly at their professor. While we certainly appreciate the attention, we want to see that you are establishing eye contact with your entire audience, not just one person. Also, this behavior is uncomfortable for the instructor.
Eye contact holds attention because an audience member who knows the speaker is making regular eye contact will want to reciprocate that eye contact to show that they are paying attention. This will also help your audience remember the content of your speech better because acting like we’re paying attention actually leads us to pay attention and better retain information.
Norms for eye contact vary among cultures. Therefore it may be difficult for speakers from countries that have higher power distances or are more collectivistic to get used to the idea of making direct and sustained eye contact during a speech. In these cases, it is important for the speaker to challenge himself or herself to integrate some of the host culture’s expectations and for the audience to be accommodating and understanding of the cultural differences.
Tips for Having Effective Eye Contact
- Once in front of the audience, establish eye contact before you speak.
- Make slow and deliberate eye contact, sweeping through the whole audience from left to right.
- Despite what high school speech teachers or others might have told you, do not look over the audience’s heads, at the back wall, or the clock. Unless you are in a huge auditorium, it will just look to the audience like you are looking over their heads.
- Do not just make eye contact with one or a few people that you know or that look friendly. Also, do not just make eye contact with your instructor or boss. Even if it’s comforting for you as the speaker, it is usually awkward for the audience member.
- Try to memorize your opening and closing lines so you can make full eye contact with the audience. This will strengthen the opening and closing of your speech and help you make a connection with the audience.
Personal Appearance
Looking like a credible and prepared public speaker will make you feel more like one and will make your audience more likely to perceive you as such. This applies to all speaking contexts: academic, professional, and personal. Although the standards for appropriate personal appearance vary between contexts, meeting them is key. You may have experienced a time when your vocal and physical delivery suffered because you were not “dressed the part.” "Dressing the part" makes you feel more confident, which will come through in your delivery. Ideally, you should also be comfortable in the clothes you’re wearing. If the clothes are dressy, professional, and nice but ill-fitting, then the effect isn’t the same. Avoid clothes that are too tight or too loose. "Looking the part" is just as important as "dressing the part," so make sure you are cleaned and groomed in a way that’s appropriate for the occasion. The following “Getting Real” box goes into more detail about professional dress in a variety of contexts.
“Getting Real”: Professional Dress and Appearance
No matter what professional field you go into, you will need to consider the importance of personal appearance. Although it may seem petty or shallow to put so much emphasis on dress and appearance, impressions matter, and people make judgments about our personality, competence, and credibility based on how we look. In some cases, you may work somewhere with a clearly laid out policy for personal dress and appearance. In many cases, the suggestion is to follow guidelines for “business casual.” Despite the increasing popularity of this notion over the past twenty years, people’s understanding of what business casual means is not consistent (Cullen, 2008). The formal dress codes of the mid-1900s, which required employees to wear suits and dresses, gave way to the trend of business casual dress, which seeks to allow employees to work comfortably while still appearing professional (Heathfield, S. M., 2012). While most people still dress more formally for job interviews or high-stakes presentations, the day-to-day dress of working professionals varies. Here are some tips for maintaining “business casual” dress and appearance:
- Things to generally avoid. Jeans, hats, flip-flops, exposed underwear, exposed stomachs, athletic wear, heavy cologne/perfume, and chewing gum.
- General dress guidelines for men. Dress pants or khaki pants, button-up shirt or collared polo/golf shirt tucked in with belt, and dress shoes; jacket and/or tie are optional.
- General dress guidelines for women. Dress pants or skirt, blouse or dress shirt, dress, and closed-toe dress shoes; jacket is optional.
- Finishing touches. Make sure shoes are neat and polished, not scuffed or dirty; clothes should be pressed, not wrinkled; make sure fingernails are clean and trimmed/groomed; and remove any lint, dog hair, and so on from clothing.
Obviously, these are general guidelines and there may be exceptions. It’s always a good idea to see if your place of business has a dress code, or at least guidelines. If you are uncertain whether or not something is appropriate, most people recommend to air on the side of caution and choose something else. While consultants and professionals usually recommend sticking to dark colors such as black, navy, and charcoal and/or light colors such as white, khaki, and tan, it is OK to add something that expresses your identity and makes you stand out, like a splash of color or a nice accessory like a watch, eyeglasses, or a briefcase. In fact, in the current competitive job market, employers want to see that you are serious about the position, can fit in with the culture of the organization, and are confident in who you are (Verner, 2008).
- What do you think is the best practice to follow when dressing for a job interview?
- In what professional presentations would you want to dress formally? Business casual? Casual?
- Aside from the examples listed previously, what are some other things to generally avoid, in terms of dress and appearance, when trying to present yourself as a credible and competent communicator/speaker?
- In what ways do you think you can conform to business-casual expectations while still preserving your individuality?
Verbal Delivery
Vocal delivery includes components of speech delivery that relate to your voice. Incorporating vocal variety in terms of volume, pitch, rate, and pauses is key to being a successful speaker. Our voice is important to consider when delivering our speech for two main reasons. First, vocal delivery can help us engage and interest the audience. Second, vocal delivery helps ensure that our ideas are communicated clearly. We have all had the displeasure of listening to an unengaging speaker. Even though the person may care about his or her topic, an unengaging delivery that doesn’t communicate enthusiasm will translate into a lack of interest for most audience members. Although a speaker can be visually engaging by incorporating movement and gestures, a flat or monotone vocal delivery can be sedating or even annoying.
Volume refers to the relative softness or loudness of your voice . Like most of the other issues we’ve discussed in this section, the proper volume for a given speaking engagement usually falls on the scale in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): The Goldilocks Paradigm of Delivery. If you speak too softly (“too little” volume), your audience will struggle to hear and understand you and may give up trying to listen. If you speak with “too much” volume, your audience may feel that you are yelling at them, or at least feel uncomfortable with you shouting. The volume you use should fit the size of the audience and the room.
When speaking in a typically sized classroom or office setting that seats about twenty-five people, using a volume a few steps above a typical conversational volume is usually sufficient. When speaking in larger rooms, you will need to project your voice. You may want to look for nonverbal cues from people in the back rows or corners, like leaning forward or straining to hear, to see if you need to adjust your volume more. Obviously, in some settings, a microphone will be necessary to be heard by the entire audience. Softer speakers are sometimes judged as meek, which may lead to lowered expectations for the speech or less perceived credibility. Louder speakers may be seen as overbearing or annoying, which can lead audience members to disengage from the speaker and message. Be aware of the volume of your voice and, when in doubt, increase your volume a notch, since beginning speakers are more likely to have an issue of speaking too softly rather than too loudly.

Public speaking relies on the voice for interest, credibility, audibility, and clarity. The British Prime Minister of the 19th century was quoted saying, “There is no greater index of character so sure as the voice.” While that seems exaggerated today, a public speaker at any level cannot ignore the energy, loudness, and clarity in their voice. There are four steps to voice production: breathing (produced by the lungs, which are largely responsible for the vocal characteristic of volume); phonation (the production of the sound in the vocal folds, which close and vibrate to produce sound for speaking as the air is exhaled over them; phonation creates pitch); resonation (a type of amplification of the sound in the larynx, oral cavity, and nasal cavity, which creates the characteristic of quality); and articulation, which produces the sounds of language others can understand and is responsible for rate and for being understood.
The visual in Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\) shows a cutaway of these parts of the anatomy. Your instructor may give you more directions on maximizing the power of your voice to achieve more variety and power. In section 11.6 we include a vocal exercise for doing so. We have all listened to a low-energy, monotone, monorate speaker and know how hard it is, so you should pay attention to your recording, perhaps by closing your eyes and just listening, to see if your voice is flat and lifeless.

Pitch is the relative highness or lowness of your voice , and like everything, you can have too much or too little (with regard to the variation of it). Too much pitch variation occurs when people “sing” their speeches, and their voices oscillate between very high pitched and very low pitched. While uncommon, this is sometimes attributed to nerves. More common is too little variation in pitch , which is known as being monotone .
Delivering a speech in a monotone manner is usually caused by reading too much; generally, the speaker’s focus is on saying the words correctly (because they have not practiced). They forget to speak normally to show their interest in the topic, as we would in everyday conversation. Changing our pitch is a good way to communicate enthusiasm and indicate emphasis or closure. In general, our pitch goes up when we are discussing something exciting. Our pitch goes down slightly when we emphasize a serious or important point. Lowering the pitch is also an effective way to signal transitions between sections of your speech or the end of your speech, which cues your audience to applaud and avoids an awkward ending.
For most people, changing pitch isn’t a major issue, but if you think it might be for you, ask the people in your practice audience what they think. You can also record yourself practicing your speech to help determine if the amount of pitch variety and enthusiasm you think you convey while speaking actually comes through. Generally, if we are interested in and passionate about communicating our thoughts, we are not likely to be monotone. We are rarely monotone when talking to friends and family about matters of importance to us, so pick topics you care about.
The rate of speaking refers to how fast or slow you speak . Too little rate (i.e. speaking too slowly) will make it sound like you may not fully know your speech or what you are talking about, and will ultimately cost you some credibility with your audience. It may also result in the audience being bored and lose focus on what you are saying. Speaking slowly may lead the audience to infer that the speaker is uninterested, uninformed, or unprepared to present his or her own topic. These negative assumptions, whether they are true or not, are likely to hurt the credibility of the speaker. Rate is one reason you should try to record yourself, even if just audio on your phone, beforehand and be mindful of time when you practice. Your voice’s rate will affect the time it takes to give the speech.
By contrast, too much rate (i.e. speaking too fast) can be overly taxing on an audience’s ability to keep up with and digest what you are saying. It sometimes helps to imagine that your speech is a jog or run that you and your friends (the audience) are taking together. You (as the speaker) are setting the pace based on how quickly you speak. If you start sprinting, it may be too difficult for your audience to keep up and they may give up halfway through. Some people naturally speak faster than others, which is fine, but we can all alter our rate of speaking with practice. If you find that you are a naturally fast speaker, make sure that you do not “speed talk” through your speech when practicing it. As always, recording and timing your speech during practice helps. You can also include reminders to “slow down” on your speaking outline.
You especially will want to maintain a good, deliberate rate at the beginning of your speech because your audience will be getting used to your voice. We have all called a business where the person answering the phone mumbles the name of the business in a rushed way. We aren’t sure if we called the right number. Since the introduction is designed to get the audience’s attention and interest in your speech, you will want to focus on clear delivery there. Regulating rate is another reason why video-recording yourself can be so helpful because we often do not realize how fast we speak.
The common misconception for public speaking students is that pausing during your speech is bad, but that isn’t necessarily true. You pause in normal conversations, so you shouldn’t be afraid of pausing while speaking. This is especially true if you are making a particularly important point or want for a statement to have a more powerful impact: you will want to give the audience a moment to digest what you have said.
For example, consider the following statement: “Because of issues like pollution and overpopulation, in 50 years the earth’s natural resources will be so depleted that it will become difficult for most people to obtain enough food to survive.” Following a statement like this, you want to give your audience just a brief moment to fully consider what you are saying. Hopefully, they will think something along the lines of What if I’m still alive then? or What will my children do ? and become more interested in hearing what you have to say
Of course, there is such a thing as pausing too much, both in terms of frequency and length. Someone who pauses too often (after each sentence) may come off seeming like they don’t know their speech very well. Someone who pauses too long (more than a few seconds), runs the risk of the audience feeling uncomfortable or, even worse becoming distracted or letting their attention wander. We are capable of processing words more quickly than anyone can speak clearly, which is one of the reasons listening is difficult. Pauses should be controlled to maintain the attention of the audience.
Vocalized pauses
At various points during your speech, you may find yourself in need of a brief moment to collect your thoughts or prepare for the next section of your speech. At those moments, you will be pausing, but we don’t always like to let people know that we’re pausing. So what many of us do in an attempt to “trick” the audience is fill in those pauses with sounds so that it appears that we haven’t actually paused. These are known as vocalized pauses , or sometimes “fillers.” Another term for them is “nonfluencies.”
Everyone uses vocalized pauses to some degree, but not everyone’s vocalized pauses are problematic. This obviously becomes an issue when the vocalized pauses become distracting due to their overuse. We have little doubt that you can remember a time when you were speaking to someone who said the word “like” after every three words and you became focused on it. One of your authors remembers attending a wedding and (inadvertently) began counting the number of times the best man said “like” during his toast (22 was the final count). The most common vocalized pause is “uh,” but then there are others. Can you think of any?
The bad news here is that there is no quick fix for getting rid of your vocalized pauses. They are so ingrained into all of our speech patterns that getting rid of them is a challenge. However, there is a two-step process you can employ to begin eliminating them. First, you need to identify what your particular vocalized pause is. Do you say “um,” “well,” or “now” before each sentence? Do you finish each thought with, “you know?” Do you use “like” before every adjective (as in “he was like so unhappy”)?
After figuring out what your vocalized pause is, the second step is to carefully and meticulously try to catch yourself when you say it. If you hear yourself saying “uh,” remind yourself, I need to try to not say that. Catching yourself and being aware of how often you use vocalized pauses will help you begin the process of reducing your dependence on them and hopefully get rid of them completely. If you do lose your train of thought, having a brief silent pause is better than injecting a vocalized pause, because the audience may not even notice the pause or may think it was intentional.
Common Causes of Vocalized Pauses
- Lack of preparation. Effective practice sessions are the best way to prevent these.
- Not writing for speaking. If you write your speech the way you’ve been taught to write papers, you will have these vocalized pauses. You must translate the written words into something easier for you to present orally. To do this, read your speech aloud and edit as you write to make sure your speech is easy for you to speak.
- A poorly prepared speaking outline. Whether it is on paper or note cards, sloppy writing, unorganized bullet points, or incomplete/insufficient information on a speaking outline leads to these.
- Distractions. Audience members and the external environment are unpredictable. Hopefully, audience members will be polite and will silence their phones, avoid talking while the speaker is presenting, and avoid moving excessively. There could also be external noise that comes through a door or window. A speaker can also be distracted by internal noise such as thinking about other things.
Vocal Variety
Overall, the lesson to take away from this section on vocal delivery is that variety is key. Vocal variety includes changes in your rate, volume, and pitch that can make you look more prepared, seem more credible, and be able to engage your audience better. Employing vocal variety is not something that takes natural ability or advanced skills training. It is something that beginning speakers can start working on immediately and everyone can accomplish. The key is to become aware of how you use your voice when you speak, and the best way to do this is to record yourself. We all use vocal variety naturally without thinking about it during our regular conversations, and many of us think that this tendency will translate over to our speaking voices. This is definitely not the case for most beginning speakers. Unlike in your regular conversations, it will take some awareness and practice to use vocal variety in speeches. Since it’s something anyone can do, improving in this area will add to your speaking confidence, which usually translates into better speeches and better grades further on.
Articulation
Articulation refers to the clarity of sounds and words we produce . If someone is articulate, they speak words clearly, and speakers should strive to speak clearly. Poor articulation results when speakers do not speak clearly. For example, a person may say dinnt instead of didn’t , gonna instead of going to , wanna instead of want to , or hunnerd instead of hundred . Unawareness and laziness are two common challenges to articulation. As with other aspects of our voice, many people are unaware that they regularly have errors in articulation. Recording yourself speak and then becoming a higher self-monitor are effective ways to improve your articulation. Laziness, on the other hand, requires a little more motivation to address. Some people just get in the habit of not articulating their words well. Both mumbling and slurring are examples of poor articulation. In more informal settings, this type of speaking may be acceptable, but in a formal setting, it will be negatively received, which will hurt a speaker’s credibility. Perhaps the promise of being judged more favorably, which may help a person become more successful, is enough to motivate a mumbler to speak more clearly.
When combined with a low volume, poor articulation becomes an even greater problem. When you notice that you have trouble articulating a particular word, you can either choose a different word to include in your speech or you can repeat it a few times in a row in the days leading up to your speech to get used to saying it.
Pronunciation
Unlike articulation, which focuses on the clarity of words, pronunciation refers to speaking words correctly, including the proper sounds of the letters and the proper emphasis . Mispronouncing words can damage a speaker’s credibility, especially when the correct pronunciation of a word is commonly known. I have actually heard someone, presenting on the topic of pronunciation, mispronounce the word pronunciation , saying “pro-NOUN-ciation” instead of “pro-NUN-ciation.” In such a case, it would not be unwarranted for the audience to question the speaker’s expertise on the subject.
We all commonly run into words that we are unfamiliar with and therefore may not know how to pronounce. Here are three suggestions when faced with this problem. The first is to look the word up in an online dictionary. Many dictionaries have a speaker icon with their definitions, and when you click on it, you can hear the correct pronunciation of a word. Some words have more than one pronunciation—for example, Caribbean —so choosing either of the accepted pronunciations is fine. Just remember to consistently use that pronunciation to avoid confusing your audience. If a word doesn’t include audio pronunciation, you can usually find the phonetic spelling of a word, which is the word spelled out the way it sounds. There will occasionally be words that you can’t locate in a dictionary. These are typically proper nouns or foreign words. In this case, you can “phone-a-friend.” Call up the people you know who have large vocabularies or are generally smart when it comes to words, and ask them if they know how to pronounce them. If they do, and you find them credible, you’re probably safe to take their suggestion. The third option is to “fake it ‘til you make it” and should only be used as a last resort. If you can’t find the word in a dictionary and your smart friends don’t know how to pronounce it, it’s likely that your audience will also be unfamiliar with the word. In that case, using your knowledge of how things are typically pronounced, decide on a pronunciation that makes sense and confidently use it during your speech. Most people will not question it. In the event that someone does correct you on your pronunciation, thank him or her for correcting you and adjust your pronunciation.
The ten items listed above represent the major delivery issues you will want to be aware of when giving a speech, but it is by no means an exhaustive list. There is, however, one final piece of delivery advice we would like to offer. We know that no matter how hard you practice and how diligent you are in preparing for your speech, you are most likely going to mess up some aspect of your speech when you give it in class, at least a little. That’s normal. Everyone does it. The key is to not make a big deal about it or let the audience know you messed up. Odds are that they will never even realize your mistake if you don’t tell them there was a mistake. Saying something like “I can’t believe I messed that up” or “Can I start over?” just telegraphs to the audience your mistake. In fact, you have most likely never heard a perfect speech delivered in your life. It is likely that you just didn’t realize that the speaker missed a line or briefly forgot what they wanted to say.
As has been the driving maxim of this chapter, this means that you need to
Practice your speech beforehand, at home or elsewhere, the way you will give it in class .
Since you know you are likely going to make some sort of mistake in class, use your practice time at home to work on how you will deal with those mistakes. If you say a word incorrectly or start reading the wrong sentence, don’t go back and begin that section anew. That’s not what you would do in class, so just correct yourself and move on. If you practice dealing with your mistakes at home, you will be better prepared for the inevitable errors that will find their way into your speech in class.
A final thought on practice. We have all heard, “Practice makes perfect.” That is not always true. Practice makes permanent; the actions become habitual. If you practice incorrectly, your performance will be incorrect. Be sure your practice is correct.
Key Takeaways
- Facial expressions help communicate emotions and enthusiasm while speaking. Make sure that facial expressions are consistent with the content being presented. Record yourself practicing your speech in order to evaluate your use of facial expressions.
- Eye contact helps establish credibility and keep your audience’s attention while you’re speaking.
- Posture should be comfortable and appropriate for the speaking occasion.
- Emphatic and descriptive gestures enhance the verbal content of our speech. Gestures should appear spontaneous but be purposeful.
- Movements from the waist down should be purposefully used to emphasize a point or as a transition during a speech.
- Audience members will make assumptions about your competence and credibility based on dress and personal appearance. Make sure your outer presentation of self is appropriate for the occasion and for the impression you are trying to project.
- Visual aids can add to your speech but can also interfere with your delivery and negatively affect your credibility if not used effectively.
- Speakers should use vocal variety, which is changes in rate, volume, and pitch, to make a speech more engaging.
- Speakers should use proper articulation and pronunciation to make their message clear.
- Interruptions to the fluency of a speech, including fluency hiccups and verbal fillers, detract from the speaker’s message and can lessen a speaker’s credibility.
- Identify three goals related to delivery that you would like to accomplish in this course. What strategies/tips can you use to help achieve these goals?
- What nonverbal adaptors have you noticed that others use while speaking? Are you aware of any nonverbal adaptors that you have used? If so, what are they?
- Getting integrated: Identify some steps that speakers can take to ensure that their dress and physical appearance enhance their credibility. How might expectations for the dress and physical appearance vary from context to context (academic, professional, personal, and civic)?
- Record yourself practicing your speech. How does your speech sound in terms of vocal variety? Cite specific examples.
- Listen to your recorded speech again. How would you evaluate your articulation and pronunciation? Cite specific examples.
- Over the course of a day, take note of verbal fillers that you tend to use. List them here so you can be a higher self-monitor and begin to notice and lessen your use of them.
Cullen, L. T., “What (Not) to Wear to Work,” Time , June 9, 2008, 49.
Heathfield, S. M., “Dress for Success: A Business Casual Dress Code,” About.com , accessed February 7, 2012, http://humanresources.about.com/od/workrelationships/a/dress_code.htm .
Koch, A., Speaking with a Purpose , 7th ed. (Boston, MA: Pearson, 2007), 105.
Verner, A., “Interview? Ditch the Navy Suit,” The Globe and Mail , December 15, 2008, L1.

- Choosing Good Topics
- Controversial
- Demonstration
- Extemporaneous
- Informative
- School/College
- Special Occasion
- Public Speaking Help
- Writing a Speech
- Free Sample Speeches
- Share Your Speech
- Speech Delivery Tips

Effective speech delivery is an important part of public speaking. No matter how inspiring, informative or persuasive the speech you have written, poor delivery will leave your audience feeling flat, and your presentation will be less than memorable.
There are some (lucky!) people that seem to be born to speak in public. The rest of us, however, may need a little coaching and prodding to deliver our speeches more eloquently.
Whilst it might take some work to feel like a polished pro, using the following practical speech delivery tips will certainly help to get you on your way to being a more effective, dynamic speaker.
Body Language
The way you present yourself, physically , begins speaking for you before you say your first word.
When you get up to speak before an audience, make sure that your body language does not betray you. Practice good posture, but avoid being stiff.
Even at a formal business event, you do not want to appear wooden in your physical appearance. Avoid fidgeting and keep your head high.
Little signs of nervousness can damage your presentation, so try to keep these kinds of nervous tics at bay. If you're struggling, try holding a tiny object such as a paper-clip. Some people find that unobtrusively playing with such an item helps them appear otherwise calm and relaxed!
Once you feel that you are projecting a calm, relaxed and confident aura, then it's time to think about how to deliver your words as effectively as possible.
You have to project your voice . Some people get nervous and mumble while giving public speeches.
Improving your speech delivery is all about getting your message across, so make sure that everyone can hear you. If you have a microphone available, by all means use it. If not, simply concentrate on the person at the back of the room and imagine that you are speaking to them directly. This will ensure you pitch your voice at just the right level.
Try to avoid speaking in a monotone fashion. In an effort to be clear and concise, people often become monotone... and that equals bored listeners!
While you don't want to go overboard and have too much emotion in your voice, you should be animated enough to let your listeners know that you are a human speaker and not an animatronic robot.
Nothing causes listeners to drift off faster than a monotone speaker, so avoid this habit at all costs.
Don't be a ditherer!
A final tip for delivering your speech is to avoid the nervous little words, like "um", "ah", and "mmm" . Many people don't realize it, but they use these little space fillers constantly in their every day speaking.
Don't let them creep into YOUR public speaking. Nothing indicates a speaker who is nervous or unprepared faster than these habitual, little sounds.
Record yourself giving your speech before the actual event. If you notice them popping up in your speech, take measures to cut them out when you give your speech in front of an audience.

Public speaking can cause a lot of anxiety for people who are not used to doing it. Even the seasoned pros and naturals get nervous sometimes.
Keep these tips in mind and practice the art of good speech delivery prior to your speaking engagement, to give a talk that will wow your audience.
Free email delivery
MASTER INFORMATIVE SPEAKING WITH OUR FREE CHECKLIST!
We are offering you a FREE SpeakFlight Informative Speaking Preparation Checklist. This valuable resource is packed with step-by-step guidance to help you create compelling, memorable, and effective informative speeches.
Share this page
You might like these.

Practice Public Speaking at Home
How to practice public speaking at home

Public Speaking Exercises You Can Do at Home
Public speaking exercises you can do at home. Discover some simple exercises to help you prepare for your next public speaking presentation.

Public Speaking Made Easy
Public speaking made easy! Giving a speech doesn't have to be as scary as it sounds. With some tried and true tips you can become a better public speaker!
Related speech delivery tips and guides
- Guide to Speech Writing
- The Importance of Public Speaking
- Public Speaking for Kids
- Public Speaking Jokes
Writing Tips...
- Effective Speech Writing - How to Keep Your Audience Hooked!
- How to Come Up with Topic Ideas
- Speech Titles
- Speech Introductions
Speech Delivery Tips...
- Build Your Confidence
- Effective Public Speaking
- How to Hypnotize Your Audience
- Public Speaking Exercises
- Tips for Using a Microphone
- Using Visual Aids
- Best Speech Topics

Easily search your speech type
Just check out the sitemap for best-speech-topics.com , which lists all the pages on the site, or use the search box below:
Return to the Top of the Page
Get to Know Us
- Privacy Policy
Attention Grabbers
- Positive Quotes for Kids
- Quotes for Graduation Speeches
- Poems & Quotes on Death
- Quotes on Retirement
Most Popular Pages
- Free Samples
- Good Speech Topics
- Hypnotize Your Audience
- Welcome Speech
Select a Speech Topic
- Argumentative
- Commemorative
- Inspirational
- Interesting
- Other Topics
Let Us Help You
- How To Write a Speech
- Demonstration Outline
- Informative Outline
- Introductions
- Using a Microphone
- Speech Help
- Speeches Made Easy
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
- Speech delivery
Vocal aspects of speech delivery
9 features of effective speech delivery, plus how to maximize your vocal potential .
By: Susan Dugdale
There's an old saying, one I'm sure you will have heard over and over again: It's not what you say, but HOW you say it.
It means the way you deliver what you have to say, significantly influences how the people listening will respond.
Will they be interested? Will they want to hear more? Will they lean forward in their chairs? Will they smile?
Or will they politely switch off? Turn away? And, less politely, fiddle with their phones?
Those responses, the positive and the negative, interested or disinterested, are in part determined by the affect of the vocal aspects of your speech on your audience.

What's on this page
- how we speak matters - how the quality of our voice's impact on our lives
- the nine vocal aspects of speech delivery
- how to make your voice work for you
- how to get an overview of your voice quality
- how to work with each of the nine vocal aspects of speech delivery: tips, exercises and links to further resources
- references
How we speak matters
It's not ALL about content; the words we say. We could be sharing something of real interest and benefit to our listeners. However if we deliver it in a way that fails to engage them, it is more likely to be ignored and quickly forgotten.
Scholarly research confirms this. ( * Check the foot of the page for references.)
The outcome of a job interview, a business proposal, a sales presentation, or an important oral communication of any sort is influenced by voice quality. As is how effective we are as leaders, teachers, call center workers, pastors, and reporters.
In any sphere dependent on voice we judge each other, consciously or unconsciously, based on the quality of speech we hear.
We decide this person doesn't really know what they're talking about because every second word they use is a filler: an um, an ahh, or a 'like'. That one is intelligent because their voice sounds authoritative: confident and strong and this woman will never inspire respect because her voice is too high and too breathy.
How we speak matters. In some instances, it matters a great deal.
Nine vocal aspects of speech delivery
The overall quality of speech delivery comes from a blend of nine distinct vocal aspects.
These are:
- pronunciation
- articulation
- pausing/silence
Your voice is a powerful personal advocate
The broad characteristics of our voices are dictated by biological inheritance, for instance whether they are typical male (lower register) or female (higher register) voices. That aside, barring impairment, many habitual unhelpful speech mannerisms can be modified.
We do not need to be a victims of our own voices. A voice can be trained and vocal habits changed.
Often a person will be strong in some areas, and weaker in others.
For example, you may have excellent volume but speak too quickly.
Or perhaps you have very little tonal variation which, unfortunately, makes you boring to listen to! However your pronunciation and articulation are good.
Your voice is potentially your most powerful personal advocate. It speaks for you, embodying and carrying your message.
Return to top
Making your voice work well for you
To realize its power, to maximize its vocal potential, what's needed is:
- an awareness of how we habitually speak and how that might be impacting on our lives,
- the willingness to change,
- and, the determination to persevere, to keep practicing.
Developing good, flexible vocal delivery does not mean denying your roots, for instance, removing any traces of accent or any other cultural, or class, identifiers. It is about recognizing, honoring and working with your voice to fully empower yourself to achieve what you want to.
Start from where you are
The place to start is to find out as much you can about your current vocal habits.
If you've don't belong to a public speaking group, like Toastmasters International , where feedback on how you speak is an essential part of the program, this can be a bit tricky.
Ideally what you want is an objective overview highlighting the areas needing attention.
If any of your presentations have been recorded, play them back. Look, listen and list the areas you are weakest in. That's where you start.
If you don't have recordings, perhaps you have a mentor, a trusted work colleague, or friend who has seen and heard you present. Ask them for feedback. Be specific about you want from them. Generalized comments are not useful. What you need is information like:
- It would be good to consider the tone of your words. What fits one setting doesn't necessarily fit another. Talking about "bros" at our last formal business meeting didn't go down well, even if you were joking.
- Do try going slower, especially when you're covering new material. I noticed some people struggling to keep up.
- The volume of your voice is good. Everybody can hear you quite comfortably.
(If you want it, here's more on asking for and giving speech evaluations . The page includes a link to a printable speech evaluation form.)
Make your own recordings
If you don't have recordings of presentations and you don't feel you can ask someone for feedback, the last option is make recordings of yourself across a range of different types of material. *
- Read aloud or retell 1 - 2 minutes of well known child's story eg. The Three Little Pigs.
- Read aloud for 1 -2 minutes from an informative article on a subject you know little about.
- Make an impromptu speech 1 - 2 minutes long on a subject on your choice. (Click this link and you'll find dozens of impromptu speech topics to choose from.)
Play back your recordings, and listen as objectively as you can. What do you notice?
Too fast? Not enough pausing between one idea and the next next? Stumbling over certain words? A monotone delivery? Lots of filler words?
Choose the most glaring as your starting point.
* There is a difference between reading aloud and speaking aloud because they call on different skills. What you hear when you play back your recordings will give you an indication of what you habitually do, rather than being definitive. But that's good enough to work with!
Working with pronunciation
"You like "po-tay-to" and I like "po-tah-to" You like "to-may-to" and I like "to-mah-to"; Po-tay-to, po-tah-to, to-may-to, to-mah-to! Let's call the whole thing off!"
The famous lyrics from the 1937 song Let's Call the Whole Thing Off by George and Ira Gershwin highlights differences in American and English pronunciation, as well as class distinction. (A British accent is so much more refined, my dear. ☺)
The song, a jazz classic, has been covered by many great singers over the years. Here is the original version by Fred Astaire and Ginger Rogers, from the 1937 show "Shall We Dance". (To watch a YouTube clip of their song and dance routine, click the image.)

The song also highlights the age old debate about the 'right' way to pronounce words. * That said, some ways really are better than others.
Pronounce names correctly
It's always good practice to take care to pronounce any name, (a person's, a country's, etc.), as best you can, to ask for a demonstration if you don't how to begin tackling it, and to apologize for mangling it if you're completely unaccustomed to producing its sounds correctly. That shows courtesy and respect.
Look those strangers up!
You don't have to muddle around guessing how words you don't know, or that you've never heard spoken, might sound.
One the easiest ways of finding out is to look them up in an online dictionary. You'll find audio clips along with all the other information generally found in a hard-copy dictionary.
Here's an example for the word 'advocate' from the Cambridge English Dictionary . Directly under the main heading there are two audio clips: one demonstrating a UK pronunciation and the other is US.
Accent and pronunciation
Everyone has an accent, whether they think so or not!
The type of accent we have depends on our first language or mother tongue. It's from that we develop our primary linguistic habits: how we use our mouths (lips, teeth, lips etc.) to shape the sounds of words, and the rhythmic, tonal and pitch patterns we habitually use.
An accent becomes more noticeable to others when:
- we move away from the people we grew up with - eg. go to live in a different part of the country, or another country. For example, although English is the primary language in UK and USA, there are multiple regional differences in each of them. The English spoken in Newcastle, England is vastly different to that spoken in the southern US states. (To hear the difference click: How To Do A Southern Accent FAST and then click: Learn A Geordie Accent | Newcastle Accent Tutorial .)
- we speak another language. Unless we are extremely good at absorbing and replicating the unique sounds of differing languages, what we tend to do is to superimpose the second (third, fourth...) language we learn over our first. So if we grow up speaking Hindi or Chinese Mandarin, our English naturally echoes that patterning.
When accent becomes a problem
Accent only becomes a problem if the people you're speaking to can not readily understand you. If you are regularly asked to either slow down or repeat what you've said then it's time to do something about it.
Unfortunately if you make people work too hard to grasp what you're telling them you may find yourself being avoided because communicating with you is tiring. That has all sorts of potentially difficult knock-on effects!
Three ways to lessen the impact of an accent
1. identify the sounds that challenge you.
Identify the specific sounds and letter combinations you have difficulty with. The most common are 'th,' 'v' and 'w,' and 'l' and 'r'.
Find out how they should be sounded. What shape is the mouth? What work does the tongue do to produce the sound? Practice, a lot, and use a mirror to look while you are doing it to check that you are replicating it is as best you can.
It will feel most strange, however persevere.
Here's a link to Mrs Tongue Does Her Housework - a set of tongue exercises for articulation. They'll help.

2. Slow down
If you have an accent you know listeners find hard to understand, help them by slowing the rate of your speech down. When you speak more slowly you'll quite naturally be more careful with your pronunciation.
3. Read aloud
Read out loud, and do it regularly every day. It could be a child's story, a newspaper article... anything at all.
Follow the patterning of the punctuation as a guide for when to change your intonation and to pause. And try to sound the ends of the words cleanly.
Every few days record at least a minute of yourself, and keep the samples. Over time you'll hear the progress you're making.
For more on using punctuation to help you deliver speech well, please see effective tips for using pauses in speeches . You'll find step by step guidelines for practice with audio examples.
A language lives, therefore it changes!
* English word usage and pronunciation shifts and changes with its speakers and the times. It's a living dynamic language. What was 'right' fifty years ago may now be a quaint remnant from a bygone era. To a large extent 'right' pronunciation depends on who is speaking, who is listening and where they are. Context is everything. For more: Phonological Change in the English Language - by Jonnie Robinson, Lead Curator for Spoken English, British Library, UK.
Working with articulation
To articulate well, is to speak distinctly or clearly. It is to say 'want to' instead of 'wanna', 'don't you' instead of 'doncha' and 'going to' instead of 'gunna'.
You can articulate beautifully while pronouncing a word incorrectly, and vice versa.
(Often the mispronunciation comes from having a read a word and never hearing it used in conversation. Those silent letters can cause so much confusion! Debris is not pronounced 'de-bris' but 'de-bree'. And similarly debut is not 'de-but' but 'day-boo'.)
Mumbling, indistinct articulation, and slurring, running words together instead of leaving spaces between them, makes it hard for people to understand what you're saying.
Although it might be regarded as normal in an informal setting, in a formal one, for instance giving a presentation to colleagues, it can lessen your credibility. It's interpreted as a lack of authority, confidence and competence, as if you don't know what you're talking about.
If you know you mumble, and slur your words together, try tongue twisters . These are fun and effective.
Working with pitch
Pitch refers to how high or low a voice is.
The voice range, the pitch at the top if we speak as high as we can comfortably , and the bottom if we speak as low as we can, is governed by physiology: the size of the larynx plus the length and thickness of our vocal cords.
Men have a lower pitch range, and women higher, mostly due to difference in body sizes.
Studies have shown voice pitch directly influences our choice of leaders. We attribute wisdom, authority, experience, competency and confidence to people with lower voices.
Despite the range being fixed we can still vary the pitch to better fit what we are speaking about, and who we are speaking to.
For example: if the subject is important and a point needs to be made, lower the pitch.
If you want to signal the end of a sentence, or the wrap up of a subject, lower the pitch.
If you want to signal excitement and enthusiasm, lift the pitch.
Experiment with pitch
Try these this exercise. It quite clearly illustrates the potential and power of pitch.
Record yourself as you say each of the sentences below at the top, middle and bottom of your pitch range.
Play them back. Notice what happens to the intensity and the way you perceive the emotional content of the sentences. There will be a distinct variation between each.
- Her Grandmother died yesterday.
- I want a new car.
- This dinner is delicious.
- People should love their neighbors as themselves.
Keep playing. Read an article aloud, a children's story, a recipe book..., anything. The idea is to develop flexibility - to be able to choose appropriately, knowing what the impact of the pitch of your voice is likely to have on your audience.
Voice pitch and leadership
Studies have shown voice pitch directly influences our choice of leaders. We attribute wisdom, authority, experience, competency and confidence to people with lower voices.
For more please see:
- How Voice Pitch Influences Our Choice of Leaders by Casey Klofstad, Stephen Nowicki & Rindy Anderson, American Scientist, 2016, Vol.104. No.5
- Sounds like a winner: voice pitch influences perception of leadership capacity in both men and women by Susan Peters, Casey Klofstad, & Rindy Anderson, Proceedings of the Royal Society, 2012, Volume 279, Issue 1738
Working with tone

How many times have you heard someone say: "Do not speak to me in that tone of voice!"?
What they're responding to is not the words they heard but HOW they were delivered. It's their perception or understanding of the speaker's intent or feeling. They're listening beyond the words.
As an example I made three recordings of "Do not talk to me in that tone of voice."
You'll hear differences in speaking rate (the speed the words are said), pitch, stresses (which words, or syllables of a word, have been given more emphasis), pausing (the silences between the words), volume and the amount of breath used. The combination of all these elements creates tone.
Although the words are the same, the recordings carry differing messages.
- Do not talk to me in that tone of voice
- Do not talk to me in that tone of voice
The first says I'm becoming extremely irritated by the way you are speaking to me. I do not like it, and I'm warning you that if you persist there may be consequences!
The second says I find you really attractive and amusing, despite your cheekiness! The tone contradicts the meaning of the words.
The third says I'm agitated and distressed about how you talking to me. It makes me feel very anxious. Stop being so mean!
Becoming conscious of tone
Taking control of tone means aligning your true speech intent, or purpose, with your content, and your audience. For credibility you need all three working together harmoniously.
"I am really happy to be here.", delivered as if you are utterly bored and can't wait to get out the door is not going to build confidence in anything else you say! Likewise a serious message can be completely undermined through a flippant, breathy, 'like', 'um', 'ah' filled delivery.
Take time to think through what you want to achieve. How can you best do that? How do you need to shape your content, and its delivery, for your audience?
The answers will vary. Different audiences will respond differently. What went down well today with one group may not with another tomorrow.
Know your default tone
It also helps to know what our own default tonal qualities are. By default I mean 'home' tone: the one we use without thinking about it.
We all have tonal biases. Part of becoming aware of tone is to know what you may be doing quite unintentionally.
Some of us come across as fairly restrained. To some people that may seem disinterested, hesitant or defensive. However, others could interpret it is as careful, considered, and thoughtful!
Some of us come across as very expressive. That may read as impulsive, egotistical, and loud by some people. Or on the flip side: enthusiastic, confident and competent, to others.
Practice exercises for tone
To play with tone take a simple sentence, like 'Do not talk to me in that tone of voice', say it as many different ways as you can and record yourself.
Say it as if you are happy, bored, angry, anxious, sad, afraid, important, serious... Listen for the differences.
Now do the same thing with a paragraph or two from a presentation you've given. Or from an informative article.
Again, listen. Hard.
Working with volume

Volume means how loud or soft a voice is.
Ideally you want a balance, everybody to hear you comfortably. That means a voice that is neither too soft so that everybody is struggling to hear you, nor too loud so that everybody plugs their fingers into their ears.
Understanding and controlling the volume of your voice is essential. Without it you run the risk of completely compromising your presentation. It maybe fabulous but if it's either bellowed, or not heard, it will be wasted. And of those two possibilities, not heard, a voice that is too soft, is more common.
Ways to ensure you are heard
Minimize any noise distractions you can.
Be aware of creating audible competition for your own voice.
- Don't wear clinking, clanking, tinkling jewelry. Or clothing that rustles when you move.
- If you're a compulsive fiddler: a pen clicker, a bunch of keys rattler..., remove the temptation.
If there are external noises you don't have direct control over, see if closing doors and windows will help.
If people are talking, applauding or laughing, wait for silence before speaking.
Reorganize the room and the people
If possible, match the audience size with the room, ahead of your presentation.
Don't be afraid to reorganize either the room's furniture or the people before you begin. If you find you have a huge room and a small spread out audience, ask them to move closer together, and to the front. It may take a few minutes but it will save you from the stress of trying to make sure everybody can hear you easily, and that will be appreciated.
Voice projection or a microphone for volume?
In larger spaces, to reach the people sitting furthest away from you, if you're not using a microphone you'll need to project your voice.
Voice projection is not the same as shouting. If you do that you'll strain yourself.
Learning to project your voice is an excellent skill to have. It will enable to speak in large spaces easily. You'll find specific exercises to help develop it here: vocal variety| exercises for volume .
If you're planning to use a microphone make sure you can get some practice in the space before you're front of your audience. They can squeak and squawk in the most alarming ways if you don't use them as you're supposed to. Not much fun, if your learning curve is public.☺
And lastly, volume check with the audience. Ask them before you get too far into your presentation. Don't wait for the tell-tale signs of an audience struggling to hear you: leaning forward, turning their heads to the side so your voice reaches their ears more easily, whispering to ask each other what you're saying...
Using volume to enhance your message
Aside from enabling people to hear you, learning to skillfully moderate volume to enhance your message is particularly effective.
For example, a softer, lower voice fits a sad or tragic story more appropriately than one that is boisterously loud.
An important point can be emphasized by a switch in volume: up or down. Excitement is built by gradually increasing the volume.
The key is practice: listening to yourself and others to identify what is effective, and experimenting. One volume will not fit an entire presentation from beginning to end.
If you are habitually too quiet, too soft, it will be assumed you're shy, and perhaps unsure of either your material or yourself. If you are constantly loud, people will wonder why it is you need to dominate. Loud may be interpreted as arrogant and insensitive. We need a range.
Working with speech rate
Rate of speech is the speed you speak at.
Some people speak fast naturally. Others are slower. Speech rate only becomes an issue if the speed we habitually use is a barrier to communicating effectively.
For example if you're giving someone a series of directions and speak very quickly, it's likely they'll ask you to repeat them several times. You quite literally went too quickly for them to take them all in, and remember them in the right sequence.
And at the other end of the scale, if you speak too slowly, you'll find listeners becoming impatient because they are waiting too long for information. If don't hurry up, you'll lose their interest.
An ideal speech rate depends on multiple variables: the material you're sharing, its complexity, whether it's new to the audience or not, the audience themselves, their attitude toward what you're bringing, perhaps their age, gender, cultural bias... In a word, context.
To be effective, speech rate needs to flexible. How fast, how slow depends on context.
- Speech rat e : Do you speak too fast, too slow or just right? Two ways to test yourself.
- How to develop a flexible speaking rate : 6 exercises
- How many words per minute in a speech : a useful quick reference guide for the number of words needed for 1 - 10 minute speeches if you speak at a slow, average or fast pace.
Working with fluency
The American Speech Language Hearing Association (ASHA) defines fluency as referring to continuity, smoothness, rate, and effort in speech production.
The typical disfluencies every speaker uses from time to time are called fillers; repeated meaningless words (sounds) or phrases like um, err, yeah, eh, basically, actually, really, you know, as I was saying, in a manner of speaking, for what it's worth... Their principal purpose is to give the speaker time to think of what to say next.
Unfortunately, if used extensively, the respite they provide comes at a cost. The presence of excess fillers reduces the effectiveness of the message being delivered and the speaker's credibility.
Sentence test to show the impact of fillers
Try saying the sentence below aloud and really listen to yourself as you speak. Do you believe what you're saying?
(The bold words are the heart of the communication. The rest are fillers you can do without.)
"Yeah, well, um, I'd just like to say, um, like, you know, I think this is , um, a great opportunity and um, yeah, you know, like I can't wait to get started. "
Diagnosing fillers
How do you know if you've got a bad case of fillers?
It's not the sort of thing many people will tell you about. Generally it's considered rude to comment directly on another person's habitual speech patterns. (Nevertheless that doesn't stop us from making judgments about a person based purely on their speech!)
Here are two ways to find out whether you 'um and ahhh' excessively for yourself.
1. Record yourself
Use a voice recorder to capture unrehearsed speech segments. The easiest way to do this is to ask yourself questions like:
- What do you like about your present job?
- Where would you like to be in five years time?
- What's your favorite thing to do on a Sunday afternoon?
Listen to your answers and take note of the fillers.
2. Ask a friend or trusted colleague to count them for you.
Tell them you're on a mission to reduce the number of fillers you use in your everyday or unrehearsed speech and you'd like them to note every instance they hear one over a specified time. Five or ten minutes should be enough.
This will give you a list of your habitual phrases or disfluencies, and the frequency of their use.
Your score might look like this:
- "I dunno" - 3
- "Well, actually" - 4
If you decide the frequency of fillers weakened your message, distracted your listeners and undermined your credibility, it's time to work on them.
Strategies and exercises to increase fluency
Prepare more thoroughly
When we've thought ahead and rehearsed a presentation * we are less likely to use lots of fillers. That's because we know what we are going to say. We are not reaching for words, and having to give ourselves time (by using fillers) to find them. They are already there.
And neither are we anxious - another cause of an outbreak of fillers. Fear chases the ability to think clearly away and given the opportunity, fillers will always rush to fill in the blanks.
*I have two pages on effectively preparing for a speech or presentation: how to rehearse which is supplemented by how to practice public speaking .
Racing means we get to the end of what we'd thought out to say faster. And often before we've had time to think ahead and consider what we are going to say next.
When that happens there's a break in the flow of information while we scrabble for the right words. Inevitably the gap is bridged by fillers.
The remedy is to slow the pace even if it means cutting back on content to fit a time allowance. It lessens the pressure you put yourself under.
Your audience will thank you for it, twice over. Once for giving them time to really take in what you're sharing and secondly for not muddling your message.
Fall in love with silence
Embrace the pause! Train yourself to stop talking, to breathe, to think, and then speak. It's doable, although changing your filler habit may take concerted practice. (You'll find specific exercises to help here: Quick and easy effective tips for using pauses in speeches .)
Banishing fillers with impromptu speaking practice
To speed your progress give yourself regular practice. Here's a collection of impromptu public speaking topics to get you started.
Record yourself. Five minutes a day for a week will make a huge difference. Keep those recordings. To monitor your progress, after a couple of days replay the first few recordings you made and compare them to the most recent.
For more: Definitions and examples of filler words by Richard Nordquist, thoughtco.com
Working with pauses
Ifeverybodyspokewithoutanypausesatalllifewouldbeutterlychaoticalmostunbearable!
That translated is: If everybody spoke without any pauses at all life would be utterly chaotic. Almost unbearable!
It's the spaces between the words, and the punctuation, that allows us to read and understand written language.
A similar thing happens in spoken language. It's called pausing. Planned pauses, deliberate silences, make what we say so much more powerful.
As Mark Twain said: "The right word might be effective but nothing has ever been as effective as a rightly time pause."

Practicing pausing
Fully embracing the pause takes practice.
A strange time distortion often occurs when talking in public. When we're the focus of attention it goes very slowly. Saying nothing for a second or two, or more, can feel like an age, and the temptation is to rush to fill the gap. We need to train ourselves to relish the moment, to enjoy it.
For more on the benefits of pausing, an easily learned method to teach yourself to pause, plus practice exercises with audio examples see: Quick and easy effective tips for using pauses in speeches .
Working with breath
The quality of our voice, how it sounds, is dependent on how we breathe.
We need to control our air flow in order to speak with a rich full voice. And aside from allowing us to find and use our best voice, good breathing also helps us channel public speaking nerves effectively.
If you want to improve your voice begin with breathing. Everything else: tone, pitch, speaking rate, articulation, pronunciation, pausing, volume, and fluency is affected by how you breathe.
For an introduction to two easily learned diaphragmatic breathing techniques see: breathing exercises to build competence and confidence .
References for those who want more
- Psychology Today: It's not what you say - It's how you say it .
- Forbes: Five Strategies To Help You Sound Like The Leader You Want To Be
- Researchgate.net: The effect of voice quality on hiring decisions
- Journal of Organizational Behavior: To speak up effectively or often? The effects of voice quality and voice frequency on peers' and managers' evaluations .
- Science Daily: "What does your voice say about you? Links between personality and vocal characteristics."
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Explain why having a strong conversational quality is important for effective public speaking. Explain the importance of eye contact in public speaking. Define vocalics and differentiate among the different factors of vocalics. Explain effective physical manipulation during a speech. Understand how to practice effectively for good speech delivery.
Mastering effective speech delivery techniques is essential for becoming a confident and persuasive speaker. By implementing these techniques, such as thorough preparation, proper personal appearance, and effective vocal and nonverbal delivery strategies, you can captivate your audience and deliver impactful presentations.
The two basic principles underlying effective speech delivery are simple. that the speaker uses the most appropriate delivery style or method for the speech content, its purpose and its audience. that audience engagement is highest when a speaker has thoroughly prepared and practiced. A speech is successful when the speaker fulfills both of them.
Maximize potential as a speaker and successfully convey your message with this 6-step guide on prepared speech delivery. Follow these steps: Determine the purpose and select the topic. Research for relevant information and supportive evidence. Create an outline, using headings and subheadings.
In short, a well-researched and well-prepared speech is not much without effective delivery. This chapter covers important information about managing public speaking anxiety, choosing the appropriate delivery method, practicing your speech, and employing effective vocal and physical delivery to enhance speaker credibility.
Learning Objectives. Identify the four types of speech delivery methods and when to use them. There are four basic methods of speech delivery: manuscript, memorized, impromptu, and extemporaneous. We'll look at each method and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each.
We focus on the "public" at the expense of the "speaking.". To become effective at public speaking, you must do just the opposite: focus on the speaking and let go of the "public.". Think of it as a conversation between you and the audience. If you can carry on a relaxed conversation with one or two people, you can give a great speech.
These are called the delivery modes, or simply, ways of delivering speeches. The three modes are impromptu delivery, manuscript delivery, and extemporaneous delivery. Each of these involves a different relationship between a speech text, on the one hand, and the spoken word, on the other. These are described in detail below.
Because of this, manuscript speaking often leads to an uninteresting or disconnected performance. But, this does not mean manuscript delivery can't be done well. Delivery from a manuscript can be effective with a significant amount of time and practice. Speaking from Memory. There are some instances that may benefit from a memorized speech ...
Effective eye contact is an important feedback device that makes the speaking situation a two-way communication process. By looking at your audience, you can determine how they are reacting. When you develop the ability to gauge the audience's reactions and adjust your presentation accordingly, you will be a much more effective speaker.
Conclusion. In this chapter, we introduced verbal delivery as a core component of your speech aesthetics. Verbal delivery includes language - including vivid language, tropes, and storytelling. In addition, projection, rate, punctuation, enunciation, and pausing all work to deliver an effective presentation.
of the speech process, however, even the most impressive delivery has little meaning. On the other hand, combined with a well-prepared and practiced presentation, delivery can be ... Key Issues in Effective Speech Delivery 337 As a speaker, your goal is not to eliminate feelings of apprehension, but to use them
As we know, words communicate meaning. But the way we say words also communicates meaning. This is why effective speakers devote time to improving their delivery. So what exactly is delivery? Delivery is the speaker's physical (vocal and bodily) actions during a speech. The main purpose of delivery is to enhance, not distract from, the message.
So before you utter another word to another person, memorize this list of the 8 key elements of highly effective speech: Gentle eye contact. Kind facial expression. Warm tone of voice. Expressive ...
This is a balance achieved through rehearsal, trial and error, and experience. In this chapter, we are going to examine effective speech-delivery strategies. First, to help you enhance your delivery, we will explore speech delivery's four basic methods. Second, we will discuss how to prepare your delivery for different environments.
Explain why having a strong conversational quality is important for effective public speaking. Explain the importance of eye contact in public speaking. Define vocalics and differentiate among the different factors of vocalics. Explain effective physical manipulation during a speech. Understand how to practice effectively for good speech delivery.
Types of Speech Delivery. There are four primary types of speech delivery: Manuscript, Memorized, Impromptu, and Extemporaneous. Manuscript speaking, like it sounds, involves reading your speech word-for-word from it's written form. The advantage to delivering a speech this way is that you can perfectly plan and control the wording of your ...
What Is Speech Delivery? As the name suggests, speech delivery is how you deliver your speech: your tone, your pace, your body language, your demeanor. However, Gallo focuses on the one element of speech delivery that he believes is crucial to success: the speed of your speech. Speak too quickly, and people will struggle to understand what you ...
Vocal delivery includes components of speech delivery that relate to your voice. Incorporating vocal variety in terms of volume, pitch, rate, and pauses is key to being a successful speaker. Our voice is important to consider when delivering our speech for two main reasons. First, vocal delivery can help us engage and interest the audience.
Effective speech delivery is an important part of public speaking. No matter how inspiring, informative or persuasive the speech you have written, poor delivery will leave your audience feeling flat, and your presentation will be less than memorable. There are some (lucky!) people that seem to be born to speak in public.
9 features of effective speech delivery, plus how to maximize your vocal potential ... Developing good, flexible vocal delivery does not mean denying your roots, for instance, removing any traces of accent or any other cultural, or class, identifiers. It is about recognizing, honoring and working with your voice to fully empower yourself to ...
Introduction 9 lectures • 21min. Writing an effective speech involves several key steps to ensure your message is. 01:02. Stories and Examples: Humanize your speech by including personal stories. 01:48. Define Your Purpose: Determine the primary goal of your speech. 03:03. Craft a Compelling Introduction: Start with a strong opening. 03:45.