Definition of Concession
Concession is a literary device used in argumentative writing, where one acknowledges a point made by one’s opponent. It allows for different opinions and approaches toward an issue, indicating an understanding of what causes the actual debate or controversy. It demonstrates that the writer is a mature thinker, and has considered the issue from all angles.
Concession writing style also shows that the writer is a logical and fair-minded person, able to realize that every argument has several sides to consider before it is presented. This type of writing can be considered strong as it finds common ground between the writer and his opponent.

Concession Examples
Example #1:.
“Dad, I know taking a trip to another country with my friends may be expensive and unsafe, but I have studied so hard the past year and I think I deserve a vacation. You already know how responsible I have been all my life; I don’t think there will be any problem.”
The above statement is an example of concession writing. It demonstrates the negative aspects of traveling as a young group of boys, but argues against this with the fact that this particular boy has always been a responsible person and is not likely to get into trouble.
Example #2:
“I agree that many students act and lie about being sick, so that they can avoid school for whatever reason. However, most students who do not come to school are actually sick. Being sick, they should be focusing on getting better, not worrying about school and grades just because some students take advantage of the absentee policy.”
This statement also shows the concession form of writing where the writer agrees that some students do lie about being sick, and that the writer is able to understand this issue. At the same time, the writer argues as to why students who are actually sick suffer because of those irresponsible students.
Example #3:
“An individual does have his own right to freedom, but medical evidence proves that second-hand smoke is harmful. Nobody has the right to harm the health of another, and smoking does just that.”
Using concession, the writer has noted that everybody has freedom rights, but argues about the fact that nobody has the right to harm another person’s health, no matter what the case is.
Example #4:
“It is true that issues may sometimes become polarized and debated heatedly. Certainly, there is a need for matters of public concern to be discussed rationally. But that does not mean that such concerns should not be expressed and investigated. After all, improper interference with academic freedom was found to have taken place. And the allegations raised by doctors are ones which deserve further inquiry.”
The above statement demonstrates the concession writing technique, where the writer agrees that debating on issues can turn into a heated argument, but that does not mean the issues should stop being discussed and investigated. Using concession, the writer has considered the different viewpoints of the issue, and then stated his argument.
Example #5: Politics and the English Language (By George Orwell)
“I said earlier that the decadence of our language is probably curable. Those who deny this would argue, if they produced an argument at all, that language merely reflects existing social conditions, and that we cannot influence its development by any direct tinkering with words or constructions. So far as the general tone or spirit of language goes, this may be true, but it is not true in detail.”
This is another example of concession writing showing that the writer is a fair person who has thought about the issue before giving his opinion. The writer agrees with the fact that we cannot do anything to develop the language. However it is not true if we go into details, Orwell says, because writers influence it too.
Function of Concession
Concession writing acknowledges that there are many different views to a story . This type of writing allows for different opinions that can or could be made toward an issue. It also shows that all points, positive as well as negative, have been considered before an argument is put forward. Presenting the other side and then arguing against it with valid points can make it a very strong piece of writing. Acknowledging the other side demonstrates respect for the other opinion. The concession writing technique is also known used as a method of persuasion and reasoning.
Post navigation

What is Concession? Definition, Usage, and Literary Examples
Concession definition.
A concession (kuhn-SEH-shun) in literature is a point yielded to an opposing perspective during an argument. It allows a writer to acknowledge that information presented by an opponent has some amount of validity and should be considered.
Concessions show that a writer doesn’t have tunnel vision when it comes to their subject; instead, they possess a well-rounded, mature perspective that considers other viewpoints. At the same time, a concession doesn’t mean the opponent’s entire argument is correct. It only denotes that one point is legitimate, while the rest of the argument remains faulty or weak.
The word concession comes from the Latin concedere , meaning “to give way.”
Where Concessions Are Used
Concessions are common features of argumentative writing. Essays, academic papers, and other nonfiction writing employ concessions so the reader has a better idea of the dissenting view and the author’s willingness to consider alternative positions. The author will typically grant a concession and immediately qualify it with a but or yet .
Take this excerpt from a 1901 essay by Mark Twain, in which he writes about the government’s decision to fly the American flag during the Philippine-American War:
I was not properly reared, and had the illusion that a flag was a thing which must be sacredly guarded against shameful uses and unclean contacts, lest it suffer pollution; and so when it was sent out to the Philippines to float over a wanton war and a robbing expedition I supposed it was polluted, and in an ignorant moment I said so. But I stand corrected. I concede and acknowledge that it was only the government that sent it on such an errand that was polluted. Let us compromise on that. I am glad to have it that way. For our flag could not well stand pollution, never having been used to it, but it is different with the administration.
Using but in the final sentence lets Twain concede that those who disagree with him are correct that the flag itself is not polluted or even intrinsically pollutable—though the presidential administration at the time is both. Thanks to his concession, Twain can admit to his prior error while making a larger statement about political corruption—and exercise his trademark wit.
Concessions appear in fiction, poetry , and plays as well. They make for compelling storytelling devices that often reveal truths about the character or speaker or the work itself. Tennessee Williams’s The Glass Menagerie opens with Tom making a concession:
Yes, I have tricks in my pocket, I have things up my sleeve. But I am the opposite of a stage magician. He gives you illusion that has the appearance of truth. I give you truth in the pleasant disguise of illusion.
Tom freely admits the will contain illusion while confessing—with the word but —that he is no magician and no dishonesty will occur. The illusion, he says, will only amplify the truth it conceals.
Concessions in Politics and Rhetoric
Concessions are utilized in speeches and debates to inform or persuade listeners of certain facts or ideas. For instance, in his famous Gettysburg Address , Abraham Lincoln said:
The brave men, living and dead, who struggled here, have consecrated it far above our poor power to add or detract. The world will little note, nor long remember, what we say here, but can never forget what they did here.
Lincoln conceded that the world may forget his words, but it will always remember the sacrifices of the soldiers who gave up their lives.
A concession speech is a slightly different type of concession. It is a public speech in which a losing candidate yields to a winning candidate after the results of a vote are determined or, at least, foreseeable given the current vote count. This is from Hillary Clinton’s 2016 concession speech:
I know how disappointed you feel because I feel it too, and so do tens of millions of Americans who invested their hopes and dreams in this effort. This is painful and it will be for a long time, but I want you to remember this. Our campaign was never about one person or even one election, it was about the country we love and about building an America that’s hopeful, inclusive and big-hearted.
Clinton acknowledges that her loss is a personally painful event for many people but that her campaign always had a larger focus on a more united and compassionate America. By doing this, she reminds listeners to continue the hard work of progress and not get bogged down in personal defeat.
These speeches, however, may not include individual concessions at all. The overall speech itself is the concession: the forfeiting of the race and the recognition of the winner.
Concessions vs Rebuttals
Concessions are not rebuttals . Concessions affirm and agree with someone else’s argument, while rebuttals directly challenge someone else’s argument. Put another way, concessions are allowances, while rebuttals are counterarguments. A concession admits that an opposing side has a valid point, and a rebuttal sets out to prove that the opposing side’s point is not valid.
The Function of Concessions
A concession’s primary function is to show common ground between two opposing ideas. In a debate or a written work on a particularly contentious topic, a concession demonstrates a fair approach to the subject—one that isn’t so fanatical that it’s illogical or absurd.
There is also a tactical component involved in concessions. The writer or speaker’s use of concessions paints them as a level-headed, reasonable person who can hear different sides of an issue. This will often make the audience take them more seriously and be more open to what they have to say.
Further Resources on Concessions
The Odegaard Writing & Research Center at the University of Washington delves into concessions and counterarguments in academic writing .
Business Insider has a list of the 10 most memorable concession speeches in United States history .
Dr. Matt Kuefler offers insights into writing concession paragraphs and where you should place them within an essay.
Related Terms
Literary Devices
Literary devices, terms, and elements, concession definition.
A concession is something yielded to an opponent during an argument, such as a point or a fact. Concessions often occur during formal arguments and counterarguments, such as in debates or academic writing. A writer or debater may agree with one aspect of his or her opponent’s ideas and yet disagree with the rest. The writer will allow this one aspect to be true, while proving how the rest is wrong. Conceding certain points can have certain tactical benefits, such as showing how some aspects of the opponent’s arguments are fallacious.
The word concession comes from the Latin word concessionem , which has the same definition of concession, i.e., “allowing or conceding.”
Common Examples of Concession
We can find examples of concessions in debates easily. Usually the person making an argument will state a concession, then follow that with “but” to show how an opponent may be making a misguided argument. Other concessions may start with the phrase “it is true that…” or “certainly.” Here are some concession examples in bold:
- Inequality of wealth is not a new concept. The gap between the super-rich tycoons of today and the poorest employee is not as great as a century ago, given the benefits the government provides. But that does not make it acceptable.
- It is true that issues may sometimes become polarized and debated heatedly. Certainly, there is a need for matters of public concern to be discussed rationally. But that does not mean that such concerns should not be expressed and investigated.
- It is too early to say whether these reforms will prove successful. But the fruits of the policies can perhaps be seen in the fact that the fall in this year’s exam pass rate is negligible compared with last year.
- Piracy and cost-free use of copyright materials deliver short-term gains to users. But if we fail to safeguard the rightful interests of authors, singers and film-makers, all will suffer as they become less resourceful in exploiting their creativity.
We can also find examples of concessions in political debates, such as in Governor John Kasich’s remarks at a 2015 GOP debate:
Our unemployment is half of what it was. Our fracking industry, energy industry may have contributed 20,000 , but if Mr. Trump understood that the real jobs come in the downstream, not in the upstream, but in the downstream. And that’s where we’re going to get our jobs.
Significance of Concession in Literature
Concession examples are somewhat more difficult to find in literature than in other forms of writing, such as academic writing or journalism. This is because authors of literary works don’t usually make arguments that are as explicit as in these other forms of writing. However, some authors will create characters who make concessions to each other in conversation or arguments. Authors also may choose to write concessions to the audience as if guessing what the audience is thinking about a certain situation and writing in response to those assumptions. These are often the more interesting concession examples, as they set up a perceived dialogue between author and reader that, although it is actually one-way, seems to include and challenge the reader.
Examples of Concession in Literature
PORTIA: The quality of mercy is not strain’d, It droppeth as the gentle rain from heaven Upon the place beneath: it is twice blest; It blesseth him that gives and him that takes: ‘Tis mightiest in the mightiest: it becomes The throned monarch better than his crown; His sceptre shows the force of temporal power, The attribute to awe and majesty, Wherein doth sit the dread and fear of kings; But mercy is above this sceptred sway; It is enthroned in the hearts of kings, It is an attribute to God himself; And earthly power doth then show likest God’s When mercy seasons justice.
( The Merchant of Venice by William Shakespeare)
In this famous courtroom scene from William Shakespeare’s The Merchant of Venice , the character of Portia has dressed up as a lawyer and gives a well-known speech about mercy. As part of this monologue, Portia makes the concession that a monarch’s sceptre “shows the force of temporal power,” and that is leads to “dread and fear of kings.” She clearly understands where a king’s power comes from. Yet she believes—and argues—that mercy is an even more impressive thing for a leader to wield. This is because leaders don’t necessarily need to show mercy, and in so doing they show the power of their character. Portia strengthens her argument for mercy by acknowledging that which is usually attributed as the mightiest aspect of a ruler.
She has committed no crime, she has merely broken a rigid and time-honored code of our society, a code so severe that whoever breaks it is hounded from our midst as unfit to live with. She is the victim of cruel poverty and ignorance, but I cannot pity her: she is white.
( To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee)
The above excerpt is another courtroom scene, this time from Harper Lee’s To Kill a Mockingbird . Atticus Finch is arguing the case for his defendant Tom Robinson. He tries to turn the accusation back against Mayella Ewell, the girl who originally accused Tom Robinson of a crime. In this closing speech, Atticus concedes the point that Mayella has not committed a crime in falsely accusing Tom. Atticus also makes the concession that Mayella herself is a victim, though not of the crime on trial; she is a victim of poverty. Yet Atticus affirms that these concessions aren’t enough either to sympathize with what she has done or even what she has undergone. The fact that she is white automatically gives her privileges and thus makes her accusation against an innocent black man all the more inexcusable.
TOM: Yes, I have tricks in my pocket, I have things up my sleeve. But I am the opposite of a stage magician. He gives you illusion that has the appearance of truth. I give you truth in the pleasant disguise of illusion.
( The Glass Menagerie by Tennessee Williams)
Tennessee Williams’s play The Glass Menagerie contains an interesting example of concession right in the very opening lines. The main character and narrator of the play, Tom, addresses the audience directly in his first few lines. He acknowledges that the guise of a play might make everything seem more fictional, and makes the concession that he has “tricks in [his] pocket” and “things up [his] sleeve.” Yet he avers that behind all the tricks, there is much truth in this play. This is an example of a concession directed at the assumptions of the audience that Tom and Tennessee Williams are working against.
Test Your Knowledge of Concession
1. Which of the following statements is the best concession definition? A. A rebuttal against something the author disagrees with. B. An allowance of a common point with an opponent. C. A demonstration of the fallacy in an opponent’s argument. [spoiler title=”Answer to Question #1″] Answer: B is the correct answer.[/spoiler]
2. Why might an author choose to use an example of a concession? A. To address what the readers might be thinking and answer this with the author’s own ideas. B. To convince the reader that the author is the only one with the right point of view. C. To convince the reader that he or she is completely wrong. [spoiler title=”Answer to Question #2″] Answer: A is the correct answer.[/spoiler]
3. Which of the following statements is not an example of concession from a debate between President Barack Obama and Governor Mitt Romney in 2012? A.
OBAMA: And to the [your credit, Romney], you supported us going into Libya and the coalition that we organized. But when it came time to making sure that Gadhafi did not stay in power, that he was captured, Governor, your suggestion was that this was mission creep, that this was mission muddle.
ROMNEY: I congratulate [Obama] on — on taking out Osama bin Laden and going after the leadership in al-Qaeda. But we can’t kill our way out of this mess.
ROMNEY: With the Arab Spring, came a great deal of hope that there would be a change towards more moderation, and opportunity for greater participation on the part of women in public life, and in economic life in the Middle East. But instead, we’ve seen in nation after nation, a number of disturbing events.
[spoiler title=”Answer to Question #3″] Answer: C is the correct answer. Though Romney uses “but,” which could often signal that someone has just made a concession, he is pointing out the failures of policy rather than agreeing with anything that was done.[/spoiler]

Please log in to save materials. Log in
- Concessions
- Counterarguments
- ESL Writing
The Argumentative Essay: The Language of Concession and Counterargument
Explanations and exercises about the use of counterarguments and concessions in argumentative essays.
The Argumentative Essay: The Language of Concession and Counterargument
We have already analyzed the structure of an argumentative essays (also known as a persuasive essay), and have read samples of this kind of essay. In this session we will review the purpose and structure of an argumentative essay, and will focus on practicing the grammar of sentences that present our argument while acknowledging that there is an opposing view point. In other words, we will focus on the grammar of concession and counterargument.
Purpose and structure of an argumentative essay
Take a few minutes to refresh your knowledge about the purpose and structure of argumentative / persuasive essays.
The Purpose of Persuasive Writing
The purpose of persuasion in writing is to convince, motivate, or move readers toward a certain point of view, or opinion. The act of trying to persuade automatically implies more than one opinion on the subject can be argued.
The idea of an argument often conjures up images of two people yelling and screaming in anger. In writing, however, an argument is very different. An argument is a reasoned opinion supported and explained by evidence. To argue in writing is to advance knowledge and ideas in a positive way. Written arguments often fail when they employ ranting rather than reasoning.
Most of us feel inclined to try to win the arguments we engage in. On some level, we all want to be right, and we want others to see the error of their ways. More times than not, however, arguments in which both sides try to win end up producing losers all around. The more productive approach is to persuade your audience to consider your opinion as a valid one, not simply the right one.
The Structure of a Persuasive Essay
The following five features make up the structure of a persuasive essay:
- Introduction and thesis
- Opposing and qualifying ideas
- Strong evidence in support of claim
- Style and tone of language
- A compelling conclusion
Creating an Introduction and a thesis
The persuasive essay begins with an engaging introduction that presents the general topic. The thesis typically appears somewhere in the introduction and states the writer’s point of view.
Avoid forming a thesis based on a negative claim. For example, “The hourly minimum wage is not high enough for the average worker to live on.” This is probably a true statement, but persuasive arguments should make a positive case. That is, the thesis statement should focus on how the hourly minimum wage is low or insufficient.
Acknowledging Opposing Ideas and Limits to Your Argument
Because an argument implies differing points of view on the subject, you must be sure to acknowledge those opposing ideas. Avoiding ideas that conflict with your own gives the reader the impression that you may be uncertain, fearful, or unaware of opposing ideas. Thus it is essential that you not only address counterarguments but also do so respectfully.
Try to address opposing arguments earlier rather than later in your essay. Rhetorically speaking, ordering your positive arguments last allows you to better address ideas that conflict with your own, so you can spend the rest of the essay countering those arguments. This way, you leave your reader thinking about your argument rather than someone else’s. You have the last word.
Acknowledging points of view different from your own also has the effect of fostering more credibility between you and the audience. They know from the outset that you are aware of opposing ideas and that you are not afraid to give them space.
It is also helpful to establish the limits of your argument and what you are trying to accomplish. In effect, you are conceding early on that your argument is not the ultimate authority on a given topic. Such humility can go a long way toward earning credibility and trust with an audience. Audience members will know from the beginning that you are a reasonable writer, and audience members will trust your argument as a result. For example, in the following concessionary statement, the writer advocates for stricter gun control laws, but she admits it will not solve all of our problems with crime:
Although tougher gun control laws are a powerful first step in decreasing violence in our streets, such legislation alone cannot end these problems since guns are not the only problem we face.
Such a concession will be welcome by those who might disagree with this writer’s argument in the first place. To effectively persuade their readers, writers need to be modest in their goals and humble in their approach to get readers to listen to the ideas.
Text above adapted from: Writing for Success – Open Textbook (umn.edu) Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.
Argument, Concession/Acknowledgment and Refutation
We have already seen that as a writer of an argumentative essay, you do not just want to present your arguments for or against a certain issue. You need to convince or persuade your readers that your opinion is the valid one. You convince readers by presenting your points of view, by presenting points of view that oppose yours, and by showing why the points of view different from yours are not as valid as yours. These three elements of an argumentative essay are known as argument (your point of view), concession/acknowledgement/counterargument (admission that there is an opposing point of view to yours) and refutation (showing why the counterargument is not valid). Acknowledging points of view different from yours and refuting them makes your own argument stronger. It shows that you have thought about all the sides of the issue instead of thinking only about your own views.
Identifying argument, counterargument, concession and refutation
We will now look at sentences from paragraphs which are part of an argumentative essay and identify these parts. Read the four sentences in each group and decide if each sentence is the argument, the counterargument, the acknowledgement / concession or the refutation. Circle your choice.
Schools need to replace paper books with e-books.
argument counterargument acknowledgement refutation
Others believe students will get bad eyesight if they read computer screens instead of paper books.
There is some truth to this statement.
However, e-books are much cheaper than paper books.
The best way to learn a foreign language is to visit a foreign country.
Some think watching movies in the foreign language is the best way to learn a language.
Even though people will learn some of the foreign language this way,
it cannot be better than actually living in the country and speaking with the people every day.
Exercise above adapted from: More Practice Recognizing Counterarguments, Acknowledgements, and Refutations. Clyde Hindman. Canvas Commons. Public domain.
More Practice Recognizing Counterarguments, Acknowledgements, and Refutations | Canvas Commons (instructure.com)
Sentence structure: Argument and Concession
Read the following sentences about the issue of cell phone use in college classrooms. Notice the connectors used between the independent and the dependent clauses.
Although cell phones are convenient, they isolate people.
dependent clause independent clause
Cell phones isolate people, even though they are convenient.
independent clause dependent clause
In the sentences above, the argument is “cell phones isolate people”. The counterargument is “cell phones are convenient” and the acknowledgment/concession is expressed by the use of although / even though to make the concession of the opposing argument.
In addition, and most importantly, notice the following:
Which clause contains the writer’s argument? Which clause contains the concession?
The writer’s position is contained in the independent clause and the concession is contained in the dependent clause. This helps the writer to highlight their argument by putting it in the clause that stands on its own and leaving the dependent clause for the concession.
Notice that it doesn’t matter if the independent clause is at the beginning or at the end of the sentence. In both cases, the argument is “cell phones isolate people.”
Notice the difference between these two sentences:
Cell phones are convenient, even though they isolate people.
independent clause dependent clause
Cell phones isolate people, even though they are convenient.
independent clause dependent clause
This pair of sentences shows how the structure of the sentence reflects the point of view of the writer. The argument in the first sentence is that cell phones are convenient. The writer feels this is the important aspect, and thus places it in the independent clause. In the dependent clause, the writer concedes that cell phones isolate people. In contrast, in the second sentence the argument is that cell phones isolate people. The writer feels this is the important aspect and therefore puts this idea in the independent clause. The writer of this sentence concedes that cell phones are convenient, and this concession appears in the dependent clause.
Read the following pairs of sentences and say which sentence in the pair has a positive attitude towards technology in our lives.
A
- Although technology has brought unexpected problems to society, it has become an instrument of progress.
- Technology has brought unexpected problems to society, even though it has become an instrument of progress.
B
- Technology is an instrument of social change, even though there are affordability issues.
- There are affordability issues with technology, even though it is it is an instrument of social change.
Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Maria Antonini de Pino – Evergreen Valley College, San Jose, California, USA
LIST OF SOURCES (in order of appearance)
- Text adapted from: Writing for Success – Open Textbook (umn.edu)
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
- Exercise adapted from: More Practice Recognizing Counterarguments, Acknowledgements, and Refutations. Clyde Hindman. Canvas Commons. Public domain.
Definition of Concession
Concession is a literary device used in argumentative writing, where one acknowledges a point made by one’s opponent. It allows for different opinions and approaches toward an issue, indicating an understanding of what causes the actual debate or controversy. It demonstrates that the writer is a mature thinker, and has considered the issue from all angles.
Concession writing style also shows that the writer is a logical and fair-minded person, able to realize that every argument has several sides to consider before it is presented. This type of writing can be considered strong as it finds common ground between the writer and his opponent.
Concession Examples
Example #1:.
“Dad, I know taking a trip to another country with my friends may be expensive and unsafe, but I have studied so hard the past year and I think I deserve a vacation. You already know how responsible I have been all my life; I don’t think there will be any problem.”
The above statement is an example of concession writing. It demonstrates the negative aspects of traveling as a young group of boys, but argues against this with the fact that this particular boy has always been a responsible person and is not likely to get into trouble.
Example #2:
“I agree that many students act and lie about being sick, so that they can avoid school for whatever reason. However, most students who do not come to school are actually sick. Being sick, they should be focusing on getting better, not worrying about school and grades just because some students take advantage of the absentee policy.”
This statement also shows the concession form of writing where the writer agrees that some students do lie about being sick, and that the writer is able to understand this issue. At the same time, the writer argues as to why students who are actually sick suffer because of those irresponsible students.
Example #3:
“An individual does have his own right to freedom, but medical evidence proves that second-hand smoke is harmful. Nobody has the right to harm the health of another, and smoking does just that.”
Using concession, the writer has noted that everybody has freedom rights, but argues about the fact that nobody has the right to harm another person’s health, no matter what the case is.
Example #4:
“It is true that issues may sometimes become polarized and debated heatedly. Certainly, there is a need for matters of public concern to be discussed rationally. But that does not mean that such concerns should not be expressed and investigated. After all, improper interference with academic freedom was found to have taken place. And the allegations raised by doctors are ones which deserve further inquiry.”
The above statement demonstrates the concession writing technique, where the writer agrees that debating on issues can turn into a heated argument , but that does not mean the issues should stop being discussed and investigated. Using concession, the writer has considered the different viewpoints of the issue, and then stated his argument .
Example #5: Politics and the English Language (By George Orwell)
“I said earlier that the decadence of our language is probably curable. Those who deny this would argue, if they produced an argument at all, that language merely reflects existing social conditions, and that we cannot influence its development by any direct tinkering with words or constructions. So far as the general tone or spirit of language goes, this may be true, but it is not true in detail.”
This is another example of concession writing showing that the writer is a fair person who has thought about the issue before giving his opinion. The writer agrees with the fact that we cannot do anything to develop the language. However it is not true if we go into details, Orwell says, because writers influence it too.
Function of Concession
Concession writing acknowledges that there are many different views to a story. This type of writing allows for different opinions that can or could be made toward an issue. It also shows that all points, positive as well as negative, have been considered before an argument is put forward. Presenting the other side and then arguing against it with valid points can make it a very strong piece of writing. Acknowledging the other side demonstrates respect for the other opinion. The concession writing technique is also known used as a method of persuasion and reasoning.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Paragraphs: Concession
Transitions : although it is true that, certainly, despite, granted that, however, indeed, granted, I admit that, in fact, in spite of, it may appear that, naturally, nevertheless, of course, once in a while, sometimes, still, yet
Example : Mason (2007) and Holmes (2009) vehemently disagree on the fundamental components of primary school education. Despite this strong disagreement, the scholars do agree on the overall importance of formal education for all young children.
Explanation : In these two sentences, the author is highlighting a disagreement between the two scholars. The author begins the second sentence with the transition phrase, "Despite this strong disagreement," however, to make a concession that Mason and Holmes do agree on the importance of formal education for young children.
Transitions Video Playlist
Note that these videos were created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.
- Academic Paragraphs: Introduction to Paragraphs and the MEAL Plan (video transcript)
- Academic Paragraphs: Types of Transitions Part 1: Transitions Between Paragraphs (video transcript)
- Academic Paragraphs: Types of Transitions Part 2: Transitions Within Paragraphs (video transcript)
- Academic Paragraphs: Appropriate Use of Explicit Transitions (video transcript)
- Engaging Writing: Incorporating Transitions (video transcript)
- Engaging Writing: Examples of Incorporating Transitions (video transcript)
- Previous Page: Chronology
- Next Page: Contradict
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.8: Writing Concession and Counterargument
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 123878

- Gabriel Winer & Elizabeth Wadell
- Berkeley City College & Laney College via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative (OERI)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Reading about multiple perspectives
When we read an article or a book, we might imagine we are listening to the voice of the author: one voice (or maybe two or a few voices if there are multiple authors). That one voice is always speaking from a particular point of view, from within a particular culture, and from inside a time period. The author is also not speaking alone, to an empty room. As we read, we can also imagine we are listening to that speaker take their turn in a huge and timeless discussion with thousands of participants, in which the speakers build on and evaluate each others' ideas and argue with each other. Each new study, article, or book adds facts, ideas, and layers of meaning to the discussion. This exchange of ideas, with each new contribution referencing past texts, has been called "the Great Conversation."
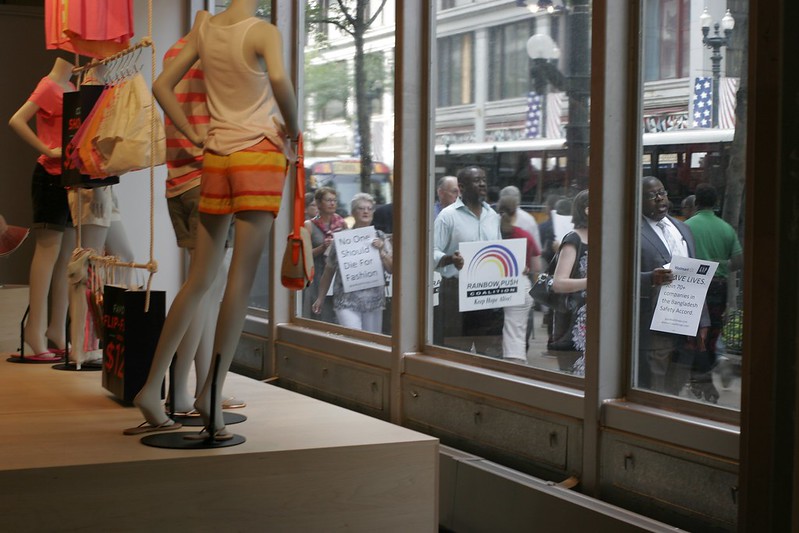
Traditionally, many people talk about this "Great Conversation" as something that happens in the Liberal Arts disciplines of Western (European and American) universities: subjects like philosophy, literature, history, the social sciences, and the arts. Scholars discuss competing explanations for a historical event, or the meaning of a line in a poem, or whether a government policy is fair. But great conversations about truth, meaning, and justice also happen around the world and outside of formal academic discourse. They take place on Twitter and TikTok, in movies, in popular magazines, and in street protests, such as the one in Figure 5.8.1. Many texts you read in college classes are taking their turn in this imaginary discussion: they argue for their position, and explain and respond to other perspectives on the topic.

Let's look at an example:
Noticing multiple perspectives
Notice this!
As you read this article, ask yourself
- What is the writers' thesis?
- What other positions do they explain and then fight back against?
- Where are the places where the writers shift perspectives?
- Which connecting words signal the change?
Reading from an online magazine: ‘ Plastic-free ’ fashion is not as clean or green as it seems
We have all become more aware of the environmental impact of our clothing choices. The fashion industry has seen a rise in “green”, “eco” and “sustainable” clothing. This includes an increase in the use of natural fibres, such as wool, hemp, and cotton, as synthetic fabrics, like polyester, acrylic and nylon, have been vilified by some.
However, the push to go “natural” obscures a more complex picture.
Natural fibres in fashion garments are products of multiple transformation processes, most of which are reliant on intensive manufacturing as well as advanced chemical manipulation. While they are presumed to biodegrade, the extent to which they do has been contested by a handful of studies. Natural fibres can be preserved over centuries and even millennia in certain environments. Where fibres are found to degrade they may release chemicals, for example from dyes, into the environment.
When they have been found in environmental samples, natural textile fibres are often present in comparable concentrations than their plastic alternatives. Yet, very little is known of their environmental impact. Therefore, until they do biodegrade, natural fibres will present the same physical threat as plastic fibres. And, unlike plastic fibres, the interactions between natural fibres and common chemical pollutants and pathogens are not fully understood.
Fashion’s environmental footprint
It is within this scientific context that fashion’s marketing of alternative fibre use is problematic. However well-intentioned, moves to find alternatives to plastic fibres pose real risks of exacerbating the unknown environmental impacts of non-plastic particles.
To assert that all these problems can be resolved by buying “natural” simplifies the environmental crisis we face. To promote different fibre use without fully understanding its environmental ramifications suggests a disingenuous engagement with environmental action. It incites “superficial green” purchasing that exploits a culture of plastic anxiety. Their message is clear: buy differently, buy “better”, but don’t stop buying.
Yet the “better” and “alternative” fashion products are not without complex social and environmental injustices. Cotton, for example, is widely grown in countries with little legislation protecting the environment and human health.
The drying up of the Aral Sea in central Asia, formally the fourth largest lake in the world, is associated with the irrigation of cotton fields that dry up the rivers that feed it. This has decimated biodiversity and devastated the region’s fishing industry. The processing of natural fibres into garments is also a major source of chemical pollution, where factory wastewaters are discharged into freshwater systems, often with little or no treatment.
Organic cotton and Woolmark wool are perhaps the most well-known natural fabrics being used. Their certified fibres represent a welcomed material change, introducing to the marketplace new fibres that have codified, improved production standards. However, they still contribute fibrous particles into the environment over their lifetime.
More generally, fashion’s systemic low pay, deadly working conditions, and extreme environmental degradation demonstrate that too often our affordable fashion purchases come at a higher price to somebody and somewhere.
Slow down fast fashion
It is clear then that a radical change to our purchasing habits is required to address fashion’s environmental crisis. A crisis that is not defined by plastic pollution alone.
We must reassess and change our attitudes towards our clothing and reform the whole lifecycle of our garments. This means making differently, buying less and buying second hand. It also means owning for longer, repurposing, remaking and mending.
Fashion’s role in the plastic pollution problem has contributed to emotive headlines, in which purchasing plastic-fibred clothing has become highly moralised. In buying plastic-fibred garments, consumers are framed complicit in poisoning the oceans and food supply. These limited discourses shift accountability onto the consumer to “buy natural”. However, they do little to equally challenge the environmental and social ills of these natural fibres and the retailers’ responsibilities to them.
Thomas Stanton , PhD researcher in the Geography and Department of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, University of Nottingham and Kieran Phelan , PhD Researcher in economic geography, University of Nottingham
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article .
When you write a paper, you are contributing to this "Great Conversation," and you also have to make these same moves. In an argumentative paper, you argue for your own perspective and support your main idea with evidence from other writers who agree with you. However, another important part of your job is to explain other points of view on the topic and respond to them with counterargument and/or concession.
Writing about multiple perspectives
Which perspectives should i include.
Sometimes, if you are writing about a controversial topic with clear opposite sides, it will be easy to identify different perspectives. It's like a debate. Here's an example:
- Thesis: The government should strengthen regulations on water pollution from factories.
- Opposite perspective: Opponents of this plan argue that regulations are not an effective way to reduce pollution.
But "multiple perspectives" doesn't always mean "opposite perspectives." The big questions we think deeply about often lead to more complicated discussions. If you have a more nuanced thesis, it might be harder to think of what the other perspectives are. Here's an example:
- Thesis: Although labor conditions in sweatshops are clearly human rights violations that demand international action, boycotts are actually not the most effective strategy to improve the situation.
- Exploring another perspective: It's true that labor conditions are terrible; workers, sometimes children, work long hours in dangerous factories for low pay.
- Exploring another perspective: Admittedly, many human rights advocates have called for boycotts.
- Exploring another perspective: Granted, boycotts have sometimes been an effective tool for reducing worker exploitation in other industries.
As you research and draft your paper, ask yourself—and your sources—these questions:
- Who? Are they credible sources?
- Why? Is there anything valid about their position? Is it based on values that you (and probably your reader) reject?
- What evidence do they use? Is it solid? Does it actually support their position?
- Is their position logical? Did they use any logical fallacies?
- Is there any factual evidence that seems to contradict my idea?
- What is a problem or concern with my idea? What are some drawbacks?
- What are the limits to my idea?
- What is an exception to my idea?
- What are some possible bad consequences that could result from my idea or plan?
- Why will my idea or plan be hard to do?
- If my idea or plan is so great, why isn't everyone already doing it?
How do multiple perspectives make an argument stronger?
Wait—why would you want to talk about the positions of people who think you're wrong? Wouldn't that weaken your argument?
Actually, no. Carefully explaining the other sides of the topic builds both ethos and logos. Imagine your reader reading your paper, taking in your reasons for why your thesis is true, and saying to themselves, "But what about this problem?" or "I heard that was a bad idea because..." You are communicating to your reader: "See? In case you don't believe me, I already thought about the other sides. Here's what my opponents say, and here's why I'm still right!"
Where do multiple perspectives go in a paper?
In journalistic articles like "‘ Plastic-free ’ Fashion is Not as Clean or Green as it Seems," writers often jump back and forth between perspectives throughout the text. A customary U.S. college argumentative essay typically includes one or more separate body paragraphs dedicated to explaining and responding to perspectives besides your own. Depending on the logic of your ideas, the order of your body paragraphs might follow one of these patterns:
- other perspectives come first, before your regular body paragraphs, to take on readers' possible doubts and objections and get them out of the way before explaining more about your reasons.
- other perspectives come last, after you have made your main case and before your conclusion.
- other perspectives go before or after the particular regular body paragraph they relate to.
Your introduction should also touch on the existence of these other perspectives, and your thesis statement may also directly address them, but you do not need to list every specific perspective in the introduction.
What goes in this special kind of body paragraph?
You start these paragraphs by stating another perspective. Then you explain that idea with specific detail (and often text evidence). Then you respond to that idea in a way that strengthens your overall argument. You may respond to the other positions with one of these two strategies, or a combination of both:
- counterargument : the other position is wrong (this is also called refutation)
- concession : the other position is a little bit true, but overall I'm still right
The key to keeping it all clear is to use connecting words to show which side you are focusing on and when you are changing sides.
Table 5.8.1 provides ideas and possible language to write a paragraph naming, explaining, and responding to other perspectives:
The models in Figure 5.8.2 are expressing two perspectives with their T-shirt slogans.
Concession/counterargument in action
Let's look at an example of a concession/counterargument paragraph in a student essay:
Here is a concession/counterargument paragraph from the student essay. The overall thesis of the whole essay is this:
Although some defend the fast fashion industry’s aesthetic and economic contributions, it has devastating impacts on labor rights and the environment, and needs serious regulations by all nations to stop the damage.
Read the paragraph and look for the following elements:
- What other position do they explain and then fight back against?
- Where are the places where the writer shifts perspectives?
Which parts are counterarguments, and which are concessions?
Despite the clear injustices of garment production, some argue that the fashion industry provides work to people with few better choices in developing countries. According to reporter Stephanie Vatz, companies began outsourcing clothing manufacturing jobs in the 1970s, and by 2013, only two percent of clothing was made in the U.S. The same lack of labor protections that allows terrible working conditions in developing countries also guarantees low labor costs that motivate U.S. companies to relocate their factory sources. Benjamin Powell, the director of the Free Market Institute, justifies sweatshop labor, insisting that this model is "part of the process that raises living standards and leads to better working conditions and development over time (qtd. in Ozdamar-Ertekin 3). This argument is compelling from a distance, but even if it may be true to some degree when we look at the history of economic development, it disregards the humanity of the garment workers. These people continue to work long hours in brutal conditions, generating huge profits for the factory and retail owners. Saying that their lives could be even worse without this exploitation is actually just an excuse for greed.
For suggested answers, see 5.12: Analyzing Arguments Answer Key
Licenses and attributions
Authored by Gabriel Winer, Berkeley City College. License: CC BY NC.
Student essay paragraph from "Deadly Fashion" authored by Maroua Abdelghani and Ruri Tamimoto. License: CC BY NC
CC Licensed Content: Previously Published
"‘ Plastic-free ’ Fashion is Not as Clean or Green as it Seems" is republished from The Conversation , licensed under CC-BY-ND .

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

4.6 Concessions and Counter Arguments: Practice
Learning objectives.
- Identify concessions and counterarguments
- Practice writing concessions and counterargument
Concession Statement Practice
Read the following paragraphs, in order to determine when the author makes concessions to his own argument.
Which sentences offer clear concessions to the author’s own argument? There is one clear concession offered in each paragraph .
Select the highlighted part of a sentence to try and identify the correct concession.
Let’s try another. Select the highlighted part of a sentence to try and identify the correct concession.
In both cases, the authors offer the concession – what an opponent of his argument would state – and then the authors counter that concession with their own point, a first step towards counter-arguing.
Concession and Counterargument Practice
Look at the following statements. In the first example, you are given the objection. The goal is to be able to structure the objection into a concession, and once you’ve done that, your next step is to reasonably counter it. You’ve been given an example to start. Your goal, in terms of structure, is to follow this pattern:
- [Some might argue/It seems logical to argue that] add your possible Objection and Rationale for that Objection.
- [However], add your Assertion offered as a counter-point.
The first example is done for you.
Possible Objection : Video games cause children to shoot people
Your Assertion: Violent media existed before video games
Concession and Counter-Argument: Some might argue that video games cause children to shoot people. After all, youth violence appears to be on the rise in today’s world . However , violent media existed before video games, and in order to blame video games, we would have to ignore the historical outrage at things like movies, comic books, rock and roll, and Dungeons and Dragons.
In this second scenario, you are given your assertion. This is slightly more difficult, but the goal here is to come up with a reasonable concession, and then to use the objection to structure a concession, and the assertion to structure a reasonable counter. You’ve been given an example to start:
Your Assertion: Requiring students to dress professionally restricts personal freedom.
Possible Objection : A mandatory dress code would encourage post-secondary students to take their education more seriously.
Concession and Counter-Argument: Although it seems logical to argue that a mandatory dress code would encourage post-secondary students to take their education more seriously , requiring students to dress professionally restricts their personal freedom. Furthermore, post-secondary institutions like Fanshawe College are not professional workplaces, and many students learn more effectively when they dress comfortably.
Putting the Pieces Together Copyright © 2020 by Andrew Stracuzzi and André Cormier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Conceding and Refuting in English
- Pronunciation & Conversation
- Writing Skills
- Reading Comprehension
- Business English
- Resources for Teachers
- TESOL Diploma, Trinity College London
- M.A., Music Performance, Cologne University of Music
- B.A., Vocal Performance, Eastman School of Music
Conceding and refuting are important language functions in English. Here are a few short definitions:
Concede : Admit that another person is right about something.
Refute : Prove that someone else is wrong about something.
Often, speakers of English will concede a point, only to refute a larger issue:
- It's true that working can be tedious. However, without a job, you won't be able to pay the bills.
- While you might say that the weather has been really bad this winter, it's important to remember that we needed lots of snow in the mountains.
- I agree with you that we need to improve our sales figures. On the other hand, I don't feel we should change our overall strategy at this time.
It's common to concede and refute at work when discussing strategy or brainstorming. Conceding and refuting are also very common in all types of debates including political and social issues.
When trying to make your point, it's a good idea to first frame the argument. Next, concede a point if applicable. Finally, refute a larger issue.
Framing the Issue
Begin by introducing a general belief that you would like to refute. You can use general statements, or speak about specific people that you would like to refute. Here are some formulas to help you frame the issue:
Person or institution to be refuted + feel / think / believe / insist / that + opinion to be refuted
- Some people feel that there is not enough charity in the world.
- Peter insists that we haven’t invested enough in research and development.
- The board of directors believes that students should take more standardized tests.
Making the Concession:
Use the concession to show that you have understood the gist of your opponent’s argument. Using this form, you will show that while a specific point is true, the overall understanding is incorrect. You can begin with an independent clause using subordinators that show opposition:
While it’s true / sensible / evident / likely that + specific benefit of argument,
While it’s evident that our competition has outspent us on, ... While it’s sensible to measure students’ aptitudes, ...
Although / Even though / Though it's true that + opinion,
Although it's true that our strategy hasn't worked to date, ... Even though it’s true that the country is currently struggling economically, ...
An alternate form is to first concede by stating that you agree or can see the advantage of something in a single sentence. Use concession verbs such as:
I concede that / I agree that / I admit that
Refuting the Point
Now it’s time to make your point. If you've used a subordinator (while, although, etc.), use your best argument to finish the sentence:
it’s also true / sensible / evident that + refutation it’s more important / essential / vital that + refutation the bigger issue / point is that + refutation we must remember / take into consideration / conclude that + refutation
… it’s also evident that financial resources will always be limited. … the bigger point is that we do not have the resources to spend. … we must remember that standardized testing such as the TOEFL leads to rote learning.
If you've made a concession in a single sentence, use a linking word or phrase such as however, nevertheless, on the contrary, or above all to state your refutation:
However, we currently do not have that capability. Nevertheless, we've succeeded in attracting more customers to our stores. Above all, the people's will needs to be respected.
Making Your Point
Once you’ve refuted a point, continue to provide evidence to further back up your point of view.
It is clear / essential / of utmost importance that + (opinion) I feel / believe / think that + (opinion)
- I believe that charity can lead to dependence.
- I think that we need to focus more on our successful products rather than develop new, untested merchandise.
- It is clear that students are not expanding their minds through rote learning for tests.
Complete Refutations
Let’s take a look a few concessions and refutations in their completed form:
Students feel that homework is an unnecessary strain on their limited time. While it's true that some teachers assign too much homework, we must remember the wisdom in the saying "practice makes perfect." It is essential that information we learn is repeated to fully become useful knowledge.
Some people insist that profit is the only viable motivation for a corporation. I concede that a company must profit to stay in business. However, the larger issue is that employee satisfaction leads to improved interactions with clients. It is clear that employees who feel they are compensated fairly will consistently give their best.
More English Functions
Conceding and refuting are known as language functions. In other words, language which is used to achieve a specific purpose. You can learn more about a wide variety of language functions and how to use them in everyday English.
- Modifying Words and Phrases to Express Opinions
- Subordinate Clauses: Concessive, Time, Place and Reason Clauses
- Teaching Conversational Skills Tips and Strategies
- Comparing and Contrasting in English
- Violence in the Media Needs To Be Regulated
- Compromise Role Play Lesson
- Phrases for Performing Well in Business Meetings
- Text Organization
- Persuasive Writing: For and Against
- Men and Women: Equal at Last?
- Paragraph Writing
- Adverb Placement in English
- Reuniting, Catching Up, and Updating in English
- Sentence Connectors: Showing Opposition in Written English
- Learn to Order Events for Narrative Writing Assignments
- Expressing Enthusiasm or Joy

Concession paragraphs for “do I agree / disagree essays”
Home » IELTS academic task 2 » Concession paragraphs for "do I agree / disagree essays"
What does concession mean?
Concession is when you have your that you believe in and support, however, you can see there is some validity to the other side as well.
You concede that the other side of the argument is also valid.
It shows that you have looked at the issue from all of its sides and you can come up with a reasoned mature response.
This is important if you are aiming for Band 7, 8 or 9, because it shows you can think and write complex ideas in English.
What is a concession paragraph?
Basically, a concession paragraph is where you’ll talk about the side you don’t really support before going on to the side that you do support.
Essentially you write about both sides of the issue.
Examples of concession paragraphs in task 2 questions
Take this typical task 2 question:
A person’s worth nowadays seems to be judged according to social status and material possessions. Old fashioned values such as honor, kindness, and trust no longer seem important. To what extent do you agree or disagree with this opinion?
Step 1: Identify the keywords We are judged on social status and material possession ... honor , kindness , and trust no longer seem important .
The second statement is extreme.
We can all pretty much agree that social status and material possessions are important and we are judged by them often whether we like it or not, but if you look at the second statement, it does seem a little extreme and a little absolute that these values are no longer seem important .
How do you write your position?
First, make your position clear from your introduction.
You can use "While" to start the essay, it shows contrast and forces you to include both sides of the argument immediately.
While we clearly live in a materialistic society that puts great worth on money and status, principles like integrity and honesty remain a core part of who we are.
What am I really saying here? I’m agreeing that we are judged according to social status and material possessions, but we really place a lot of value on honor, kindness, and trust.
I’m disagreeing with that idea that they are no longer important, we’re still people with integrity.
It’s a partial agreement, a concession.
Where do we place our concession paragraph?
It comes right after your introduction and then the second body paragraph would be the side that you support more.
This is not only a writing convention but also used in formal debates.
We first we talk about the side that we disagree with and then we talk about the side that we do agree with.
This gives our side of the argument more weight, it acts like an anchor, and it remains fresher in the mind of the reader (the examiner).
Audio tutorial
You can download or listen to the audio version here:
| Direct Download Here | Stitcher | iTunes | Spotify | Soundcloud | Transcript |
Tutorials and Tips to Prepare for Task 2
- How to Get Ideas for Task 2
- Band 9 Sample Essay
- Extremely Useful Sentences for Task 2
- Five Powerful Sentence Structures to use in your IELTS Writing test
- How to use comparisons in Task 2
- How to write an IELTS Essay Conclusion
- IELTS Cohesion and Coherence
- 3 ways to paraphrase for your Task 2 introduction
- Marking Criteria for IELTS Writing
- Topics Sentences for Your Essays
- 7 Ways to Improve your Sentences in Your IELTS Essays
- Grammar for IELTS Writing
- Academic Collocations for Task 2
- Free Essay Band Score Evaluation
- Sign up to claim your free IELTS materials
- Jump to Band 7 or it’s Free
- IELTS Writing Evaluation
- IELTS Band Score Calculator
- Book Your Online IELTS Test
- Sample Topic Answers
- Useful Sentences
- Sample Task 2 Questions 2022
- Introduction to Paraphrasing
- Model Band 9 Essay
- Five Band 9 Words
- Model Band 7 Essay
- Differences Band 9 vs Band 7 Essay
- Band 6.5 Essay
- Academic Collocations
- Topic Sentences
- Discuss Both Views
- Tutorial: To What Extent Essays
- Paraphrasing Introductions
- Essay Structures
- Essay Plans
- Describe a Pie Chart
- Using Percentages
- Map Vocabulary
- Describe Flow Charts
- Describe a Bar Chart
- How to get Band 9
- AT 1 Sample Questions 2022
- Describe a Graphic
- GT Task 1 Questions 2022
- IELTS Vocabulary
- Google Play / Podcasts
- Apple Podcast
- Android App
- Task 2 Sample Questions
- AT 1 Questions
Company addresses: HK Office: BW ENGLISH SERVICES HK Ltd, Unit 2512, 25/F, Langham Place Office Tower, 8 Argyle Street, Mongkok, Hong Kong UK Office: BW ENGLISH SERVICES, 120 High Road, East Finchley, N29ED, London, England, United Kingdom +44 20 3951 8271 ($1/min).

- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
A Guide to Rebuttals in Argumentative Essays

4-minute read
- 27th May 2023
Rebuttals are an essential part of a strong argument. But what are they, exactly, and how can you use them effectively? Read on to find out.
What Is a Rebuttal?
When writing an argumentative essay , there’s always an opposing point of view. You can’t present an argument without the possibility of someone disagreeing.
Sure, you could just focus on your argument and ignore the other perspective, but that weakens your essay. Coming up with possible alternative points of view, or counterarguments, and being prepared to address them, gives you an edge. A rebuttal is your response to these opposing viewpoints.
How Do Rebuttals Work?
With a rebuttal, you can take the fighting power away from any opposition to your idea before they have a chance to attack. For a rebuttal to work, it needs to follow the same formula as the other key points in your essay: it should be researched, developed, and presented with evidence.
Rebuttals in Action
Suppose you’re writing an essay arguing that strawberries are the best fruit. A potential counterargument could be that strawberries don’t work as well in baked goods as other berries do, as they can get soggy and lose some of their flavor. Your rebuttal would state this point and then explain why it’s not valid:
Read on for a few simple steps to formulating an effective rebuttal.
Step 1. Come up with a Counterargument
A strong rebuttal is only possible when there’s a strong counterargument. You may be convinced of your idea but try to place yourself on the other side. Rather than addressing weak opposing views that are easy to fend off, try to come up with the strongest claims that could be made.
In your essay, explain the counterargument and agree with it. That’s right, agree with it – to an extent. State why there’s some truth to it and validate the concerns it presents.
Step 2. Point Out Its Flaws
Now that you’ve presented a counterargument, poke holes in it . To do so, analyze the argument carefully and notice if there are any biases or caveats that weaken it. Looking at the claim that strawberries don’t work well in baked goods, a weakness could be that this argument only applies when strawberries are baked in a pie.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Step 3. Present New Points
Once you reveal the counterargument’s weakness, present a new perspective, and provide supporting evidence to show that your argument is still the correct one. This means providing new points that the opposer may not have considered when presenting their claim.
Offering new ideas that weaken a counterargument makes you come off as authoritative and informed, which will make your readers more likely to agree with you.
Summary: Rebuttals
Rebuttals are essential when presenting an argument. Even if a counterargument is stronger than your point, you can construct an effective rebuttal that stands a chance against it.
We hope this guide helps you to structure and format your argumentative essay . And once you’ve finished writing, send a copy to our expert editors. We’ll ensure perfect grammar, spelling, punctuation, referencing, and more. Try it out for free today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a rebuttal in an essay.
A rebuttal is a response to a counterargument. It presents the potential counterclaim, discusses why it could be valid, and then explains why the original argument is still correct.
How do you form an effective rebuttal?
To use rebuttals effectively, come up with a strong counterclaim and respectfully point out its weaknesses. Then present new ideas that fill those gaps and strengthen your point.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Argumentative Essays

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
What is an argumentative essay?
The argumentative essay is a genre of writing that requires the student to investigate a topic; collect, generate, and evaluate evidence; and establish a position on the topic in a concise manner.
Please note : Some confusion may occur between the argumentative essay and the expository essay. These two genres are similar, but the argumentative essay differs from the expository essay in the amount of pre-writing (invention) and research involved. The argumentative essay is commonly assigned as a capstone or final project in first year writing or advanced composition courses and involves lengthy, detailed research. Expository essays involve less research and are shorter in length. Expository essays are often used for in-class writing exercises or tests, such as the GED or GRE.
Argumentative essay assignments generally call for extensive research of literature or previously published material. Argumentative assignments may also require empirical research where the student collects data through interviews, surveys, observations, or experiments. Detailed research allows the student to learn about the topic and to understand different points of view regarding the topic so that she/he may choose a position and support it with the evidence collected during research. Regardless of the amount or type of research involved, argumentative essays must establish a clear thesis and follow sound reasoning.
The structure of the argumentative essay is held together by the following.
- A clear, concise, and defined thesis statement that occurs in the first paragraph of the essay.
In the first paragraph of an argument essay, students should set the context by reviewing the topic in a general way. Next the author should explain why the topic is important ( exigence ) or why readers should care about the issue. Lastly, students should present the thesis statement. It is essential that this thesis statement be appropriately narrowed to follow the guidelines set forth in the assignment. If the student does not master this portion of the essay, it will be quite difficult to compose an effective or persuasive essay.
- Clear and logical transitions between the introduction, body, and conclusion.
Transitions are the mortar that holds the foundation of the essay together. Without logical progression of thought, the reader is unable to follow the essay’s argument, and the structure will collapse. Transitions should wrap up the idea from the previous section and introduce the idea that is to follow in the next section.
- Body paragraphs that include evidential support.
Each paragraph should be limited to the discussion of one general idea. This will allow for clarity and direction throughout the essay. In addition, such conciseness creates an ease of readability for one’s audience. It is important to note that each paragraph in the body of the essay must have some logical connection to the thesis statement in the opening paragraph. Some paragraphs will directly support the thesis statement with evidence collected during research. It is also important to explain how and why the evidence supports the thesis ( warrant ).
However, argumentative essays should also consider and explain differing points of view regarding the topic. Depending on the length of the assignment, students should dedicate one or two paragraphs of an argumentative essay to discussing conflicting opinions on the topic. Rather than explaining how these differing opinions are wrong outright, students should note how opinions that do not align with their thesis might not be well informed or how they might be out of date.
- Evidential support (whether factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal).
The argumentative essay requires well-researched, accurate, detailed, and current information to support the thesis statement and consider other points of view. Some factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal evidence should support the thesis. However, students must consider multiple points of view when collecting evidence. As noted in the paragraph above, a successful and well-rounded argumentative essay will also discuss opinions not aligning with the thesis. It is unethical to exclude evidence that may not support the thesis. It is not the student’s job to point out how other positions are wrong outright, but rather to explain how other positions may not be well informed or up to date on the topic.
- A conclusion that does not simply restate the thesis, but readdresses it in light of the evidence provided.
It is at this point of the essay that students may begin to struggle. This is the portion of the essay that will leave the most immediate impression on the mind of the reader. Therefore, it must be effective and logical. Do not introduce any new information into the conclusion; rather, synthesize the information presented in the body of the essay. Restate why the topic is important, review the main points, and review your thesis. You may also want to include a short discussion of more research that should be completed in light of your work.
A complete argument
Perhaps it is helpful to think of an essay in terms of a conversation or debate with a classmate. If I were to discuss the cause of World War II and its current effect on those who lived through the tumultuous time, there would be a beginning, middle, and end to the conversation. In fact, if I were to end the argument in the middle of my second point, questions would arise concerning the current effects on those who lived through the conflict. Therefore, the argumentative essay must be complete, and logically so, leaving no doubt as to its intent or argument.
The five-paragraph essay
A common method for writing an argumentative essay is the five-paragraph approach. This is, however, by no means the only formula for writing such essays. If it sounds straightforward, that is because it is; in fact, the method consists of (a) an introductory paragraph (b) three evidentiary body paragraphs that may include discussion of opposing views and (c) a conclusion.
Longer argumentative essays
Complex issues and detailed research call for complex and detailed essays. Argumentative essays discussing a number of research sources or empirical research will most certainly be longer than five paragraphs. Authors may have to discuss the context surrounding the topic, sources of information and their credibility, as well as a number of different opinions on the issue before concluding the essay. Many of these factors will be determined by the assignment.
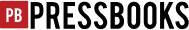
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
21 Argument, Counterargument, & Refutation
In academic writing, we often use an Argument essay structure. Argument essays have these familiar components, just like other types of essays:
- Introduction
- Body Paragraphs
But Argument essays also contain these particular elements:
- Debatable thesis statement in the Introduction
- Argument – paragraphs which show support for the author’s thesis (for example: reasons, evidence, data, statistics)
- Counterargument – at least one paragraph which explains the opposite point of view
- Concession – a sentence or two acknowledging that there could be some truth to the Counterargument
- Refutation (also called Rebuttal) – sentences which explain why the Counterargument is not as strong as the original Argument
Consult Introductions & Titles for more on writing debatable thesis statements and Paragraphs ~ Developing Support for more about developing your Argument.
Imagine that you are writing about vaping. After reading several articles and talking with friends about vaping, you decide that you are strongly opposed to it.
Which working thesis statement would be better?
- Vaping should be illegal because it can lead to serious health problems.
Many students do not like vaping.
Because the first option provides a debatable position, it is a better starting point for an Argument essay.
Next, you would need to draft several paragraphs to explain your position. These paragraphs could include facts that you learned in your research, such as statistics about vapers’ health problems, the cost of vaping, its effects on youth, its harmful effects on people nearby, and so on, as an appeal to logos . If you have a personal story about the effects of vaping, you might include that as well, either in a Body Paragraph or in your Introduction, as an appeal to pathos .
A strong Argument essay would not be complete with only your reasons in support of your position. You should also include a Counterargument, which will show your readers that you have carefully researched and considered both sides of your topic. This shows that you are taking a measured, scholarly approach to the topic – not an overly-emotional approach, or an approach which considers only one side. This helps to establish your ethos as the author. It shows your readers that you are thinking clearly and deeply about the topic, and your Concession (“this may be true”) acknowledges that you understand other opinions are possible.
Here are some ways to introduce a Counterargument:
- Some people believe that vaping is not as harmful as smoking cigarettes.
- Critics argue that vaping is safer than conventional cigarettes.
- On the other hand, one study has shown that vaping can help people quit smoking cigarettes.
Your paragraph would then go on to explain more about this position; you would give evidence here from your research about the point of view that opposes your own opinion.
Here are some ways to begin a Concession and Refutation:
- While this may be true for some adults, the risks of vaping for adolescents outweigh its benefits.
- Although these critics may have been correct before, new evidence shows that vaping is, in some cases, even more harmful than smoking.
- This may have been accurate for adults wishing to quit smoking; however, there are other methods available to help people stop using cigarettes.
Your paragraph would then continue your Refutation by explaining more reasons why the Counterargument is weak. This also serves to explain why your original Argument is strong. This is a good opportunity to prove to your readers that your original Argument is the most worthy, and to persuade them to agree with you.
Activity ~ Practice with Counterarguments, Concessions, and Refutations
A. Examine the following thesis statements with a partner. Is each one debatable?
B. Write your own Counterargument, Concession, and Refutation for each thesis statement.
Thesis Statements:
- Online classes are a better option than face-to-face classes for college students who have full-time jobs.
- Students who engage in cyberbullying should be expelled from school.
- Unvaccinated children pose risks to those around them.
- Governments should be allowed to regulate internet access within their countries.
Is this chapter:
…too easy, or you would like more detail? Read “ Further Your Understanding: Refutation and Rebuttal ” from Lumen’s Writing Skills Lab.
Note: links open in new tabs.
reasoning, logic
emotion, feeling, beliefs
moral character, credibility, trust, authority
goes against; believes the opposite of something
ENGLISH 087: Academic Advanced Writing Copyright © 2020 by Nancy Hutchison is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Advertisement
Supported by
Hillary Clinton Has Some Tough Words for Democrats, and for Women
In an interview for a forthcoming book, Mrs. Clinton also suggested that if Donald Trump won in November “we may never have another actual election.”
- Share full article

By Lisa Lerer and Elizabeth Dias
Lisa Lerer covers politics and Elizabeth Dias covers religion. They are the authors of “The Fall of Roe: The Rise of a New America,” a forthcoming book from which this interview is adapted.
Hillary Clinton criticized her fellow Democrats over what she described as a decades-in-the-making failure to protect abortion rights, saying in her first extended interview about the fall of Roe v. Wade that her party underestimated the growing strength of anti-abortion forces until many Democrats were improbably “taken by surprise” by the landmark Dobbs decision in 2022.
In wide-ranging and unusually frank comments, Mrs. Clinton said Democrats had spent decades in a state of denial that a right enshrined in American life for generations could fall — that faith in the courts and legal precedent had made politicians, voters and officials unable to see clearly how the anti-abortion movement was chipping away at abortion rights, restricting access to the procedure and transforming the Supreme Court, until it was too late.
“We didn’t take it seriously, and we didn’t understand the threat,” Mrs. Clinton said. “Most Democrats, most Americans, did not realize we are in an existential struggle for the future of this country.”
She said: “We could have done more to fight.”
Mrs. Clinton’s comments came in an interview conducted in late February for a forthcoming book, “The Fall of Roe: The Rise of a New America.”
The interview represented Mrs. Clinton’s most detailed comments on abortion rights since the Supreme Court decision that led to the procedure becoming criminalized or restricted in 21 states . She said not only that her party was complacent but also that if she had been in the Senate at the time she would have worked harder to block confirmation of Trump-appointed justices.
And in a blunt reflection about the role sexism played in her 2016 presidential campaign, she said women were the voters who abandoned her in the final days because she was not “perfect.” Overhanging the interview was the understanding that had she won the White House, Roe most likely would have remained a bedrock feature of American life. She assigned blame for the fall of Roe broadly but pointedly, and notably spared herself from the critique.
Some Democrats will most likely agree with Mrs. Clinton’s assessment. But as the party turns its focus to wielding abortion as an electoral weapon, there has been little public reckoning among Democrats over their role in failing to protect abortion rights.
Even when they held control of Congress, Democrats were unwilling to pass legislation codifying abortion rights into federal law. While frequently mentioned in passing to rally their base during election season, the issue rarely rose to the top of their legislative or policy agenda. Many Democrats, including President Biden, often refused even to utter the word.
Until Roe fell, many in the party believed the federal right to an abortion was all but inviolable, unlikely to be reversed even by a conservative Supreme Court. The sense of denial extended to the highest ranks of the party — but not, Mrs. Clinton argued, to her.
“One thing I give the right credit for is they never give up,” she said. “They are relentless. You know, they take a loss, they get back up, they regroup, they raise more money.” She added: “It’s tremendously impressive the way that they operate. And we have nothing like it on our side.”
Mrs. Clinton did not express regret for any inaction herself. Rather, she said her efforts to raise alarms during her 2016 campaign went unheeded and were dismissed as “alarmist” by voters, politicians and members of her own party. In that race, she had talked about the threats to abortion rights on the campaign trail and most memorably in the third presidential debate, vowing to protect Roe when Mr. Trump promised to appoint judges who would overturn it.
But even then, internal campaign polling and focus groups showed that the issue did not resonate strongly with key groups of voters, because they did not believe Roe was truly at risk.
Now, as the country prepares to face its third referendum on Mr. Trump, she offered a stark warning about the 2024 election. A second Trump administration would go far beyond abortion rights to target women’s health care, gay rights, civil rights — and even the core tenets of American democracy itself, she said.
“This election is existential. I mean, if we don’t make the right decision in this election in our country, we may never have another actual election. I will put that out there because I believe it,” she said. “And if we no longer have another actual election, we will be governed by a small minority of right-wing forces that are well organized and well funded and are getting exactly what they want in terms of turning the clock back on women.”
Mrs. Clinton described those forces and her former opponent as part of a “global phenomena” restricting women’s rights, pointing to a push by Xi Jinping, the Chinese leader, pressing women to focus on raising children ; the violent policing of women who violate Iran’s conservative dress code ; and what she described as the misogyny of President Vladimir V. Putin of Russia.
“Authoritarians, whether they be political or religious based, always go after women. It’s just written in the history. And that’s what will happen in this country,” Mrs. Clinton said.
Mrs. Clinton viewed her remarks as another attempt to ring an alarm before the 2024 election.
“More people have got to wake up, because this is the beginning,” she said. “They really want us to just shut up and go home. That’s their goal. And nobody should be in any way deluded. That’s what they will force upon us if they are given the chance .”
But she also seemed to expect that many would dismiss her concerns once again. “Oh, my God, there she goes again,” she said, describing what she anticipated would be the reaction to her interview. “I mean, she’s just so, you know, so out there .”
But she added: “I know history will prove me right. And I don’t take any comfort in that because that’s not the kind of country or world I want for my grandchildren.”
Embodying the Roe era
Nearly eight years after her final campaign, Mrs. Clinton remains one of the most prominent women in American politics, and the only woman in the country’s history to capture the presidential nomination of a major party.
Her life encapsulates what could be seen as the Roe era in American life. She embodies the professional and personal changes that swept the lives of American women over the past half-century. Roe was decided in 1973, the same year Mrs. Clinton graduated from law school. Its fall was accelerated in 2016 by her loss to Donald J. Trump, which set in motion a transformation of the Supreme Court.
Had Mrs. Clinton won the White House in 2016, history would have turned out very differently. She would most likely have appointed two or even three justices to the Supreme Court, securing an abortion-rights legal majority that probably would have not only upheld Roe but also delivered rulings that expanded access to the procedure.
Instead, Mrs. Clinton said Democrats neglected abortion rights from the ballot box to Congress to the Supreme Court.
Along with her prediction for the future, Mrs. Clinton offered a detailed assessment of the past. For her, the meaning of the ruling in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization was clear — and devastating.
“It says that we are not equal citizens,” she said, referring to women. “It says that we don’t have autonomy, agency and privacy to make the most personal of decisions. It says that we should be rethinking our lives and our roles in the world.”
She blasted Justice Samuel A. Alito Jr., who wrote the Supreme Court’s majority opinion in the case, saying his decision was “terrible,” “poorly reasoned” and “historically inaccurate.”
Mrs. Clinton accused four justices — John G. Roberts Jr., Neil M. Gorsuch, Brett M. Kavanaugh and Amy Coney Barrett — of being “teed up to do the bidding” of conservative political and religious organizations and leaders — though she believed many Democrats had not realized that during those justices’ confirmation hearings.
“It is really hard to believe that people are going to lie to you under oath, that even so-called conservative justices would upend precedents to arrive at ridiculous decisions on gun rights and campaign finance and abortion,” she said. “It’s really hard to accept that .”
Yet, she also had tough words for her former colleagues. In the Senate, she said, Democratic lawmakers did not push hard enough to block the confirmation of the justices who would go on to overturn federal abortion rights. When asked in confirmation hearings if they believed Roe was settled law, the nominees noted that Roe was precedent and largely avoided stating their opinion on the decision.
Those justices “all lied in their confirmation hearings,” she said, referring to Justices Gorsuch, Kavanaugh and Coney Barrett, all of whom were appointed by Mr. Trump. “They just flat-out lied. And Democrats did nothing in the Senate.”
She added: “If I’d still been in the Senate, and on the Judiciary Committee, I think, you know, I hope I would have tried to do more about what were just outright prevarications.”
It is unclear how Democrats could have stopped those justices from reaching the bench given that they did not control the Senate during their confirmation hearings. When Mr. Trump took office, Republicans also had unified control of 24 state legislatures, making it all but impossible for Democrats to stop conservatives from pushing through increasingly restrictive laws.
For years, she said, Democrats failed to “invest in the kind of parallel institutions” to the conservative legal establishment. Efforts to start the American Constitution Society, she said, never quite grew as large as the better established Federalist Society, a network of conservative lawyers, officials and justices that includes members of the Supreme Court.
“I just think that most of us who support the rights of women and privacy and the right to make these difficult decisions yourself, you know, we just couldn’t believe what was happening. And as a result, they slowly, surely and very effectively got what they wanted,” she said. “Our side was complacent and kind of taking it for granted and thinking it would never go away.”
‘As a woman, I’m supposed to be perfect’
Mrs. Clinton was born in 1947, when abortion was criminalized and contraception was banned or restricted in more than two dozen states. In Arkansas, where she practiced law while her husband served as governor, she watched the rise of the religious right and the anti-abortion movement.
From the time she arrived in Washington as first lady, Mrs. Clinton fought openly for abortion rights. She famously declared that “human rights are women’s rights, and women’s rights are human rights” in a 1995 speech at the World Conference on Women in Beijing. When she became a senator, Mrs. Clinton voted against the partial-birth abortion ban, unlike more than a dozen of her fellow Democrats. As Barack Obama’s secretary of state, she made a mission of expanding women’s reproductive health across the globe.
In 2016, Planned Parenthood endorsed her candidacy, the first time the organization waded into a presidential primary. In her campaign, Mrs. Clinton promised to appoint judges who would preserve Roe, opposed efforts in Congress to pass a 20-week abortion ban and pushed for the repeal of the Hyde Amendment, which banned the federal funding of abortions.
Even her language was updated. For years, when it came to abortion, she championed her belief in a phrase popularized by her husband during his 1992 presidential campaign: “safe, legal and rare.”
In a private, previously unreported meeting recounted in the book, campaign aides told Mrs. Clinton to drop the phrase during her 2016 run. Her staff explained that increasingly progressive abortion-rights activists thought calling for the procedure to be “rare” would offer a political concession to the anti-abortion movement. And with so many new restrictions being passed in conservative-controlled states, abortion was increasingly difficult to obtain, particularly for poorer women, making “rare” the wrong focus for their message. Abortion should be “safe, legal, accessible and affordable,” they told her.
“Well, that doesn’t make any sense,” she said in response at the time. “That’s stupid.”
In the interview, Mrs. Clinton said she quickly came to embrace the shift in language. What she and other Democrats had tried to do in 1992 with “safe, legal and rare” was “send a signal that we understand Roe v. Wade has a certain theory of the case about trimesters,” she explained. But by 2016, the world had changed.
“Too many women, particularly too many young women did not understand the effort that went into creating the underlying theory of Roe v. Wade. And the young women on my campaign made a very compelling argument that making it safe and legal was really the goal,” she said. “I kind of just pocketed the framework of Roe.”
Still, Mrs. Clinton felt like many of her warnings over the issue were ignored by much of the country.
When she delivered a speech in Wisconsin in March 2016, arguing that Supreme Court justices selected by Mr. Trump could “demolish pillars of the progressive movement,” Mrs. Clinton said that “people kind of rolled their eyes at me.”
Mrs. Clinton said she saw her defeat in that election as inextricable from her gender. As she has in the past, she blamed the former F.B.I. director James Comey’s last-minute reopening of the investigation of her private email server for her immediate defeat. Mr. Comey had raised questions about her judgment and called her “extremely careless” but recommended no criminal charges. Other political strategists have faulted her message, strategy and various missteps by her campaign for her loss in 2016.
“But once he did that to me, the people, the voters who left me, were women,” she said. “They left me because they just couldn’t take a risk on me, because as a woman, I’m supposed to be perfect. They were willing to take a risk on Trump — who had a long list of, let’s call them flaws, to illustrate his imperfection — because he was a man, and they could envision a man as president and commander in chief.”
Mrs. Clinton said she was shocked by how little the reports of Mr. Trump’s sexual misconduct and assault seemed to affect the race. They did not disqualify him from the presidency, at least not among most Republicans and conservative Christians. But his promises to appoint justices that would reverse Roe helped him win, she said.
“Politically, he threw his lot in with the right on abortion and was richly rewarded,” she said.
Lisa Lerer is a national political reporter for The Times, based in New York. She has covered American politics for nearly two decades. More about Lisa Lerer
Elizabeth Dias is The Times’s national religion correspondent, covering faith, politics and values. More about Elizabeth Dias

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Concession writing style also shows that the writer is a logical and fair-minded person, able to realize that every argument has several sides to consider before it is presented. This type of writing can be considered strong as it finds common ground between the writer and his opponent. Concession Examples
Updated on February 12, 2020. Concession is an argumentative strategy by which a speaker or writer acknowledges (or appears to acknowledge) the validity of an opponent's point. Verb: concede. Also known as concessio . The rhetorical power of concession, says Edward P.J. Corbett, resides in an ethical appeal: "The audience gets the impression ...
Concession Definition. A concession (kuhn-SEH-shun) in literature is a point yielded to an opposing perspective during an argument. It allows a writer to acknowledge that information presented by an opponent has some amount of validity and should be considered. Concessions show that a writer doesn't have tunnel vision when it comes to their ...
A concession is something yielded to an opponent during an argument, such as a point or a fact. Concessions often occur during formal arguments and counterarguments, such as in debates or academic writing. A writer or debater may agree with one aspect of his or her opponent's ideas and yet disagree with the rest.
4.5 Identifying Concessions and Counter Arguments. Learning Objectives. Identify the parts of a reasonable concession. Evaluate paragraphs for concessions. Apply concession format to a series of sentences. Let's take some time to learn how to concede logical points and then to counter them appropriately. These skills are INCREDIBLY IMPORTANT.
The Argumentative Essay: The Language of Concession and Counterargument. We have already analyzed the structure of an argumentative essays (also known as a persuasive essay), and have read samples of this kind of essay. In this session we will review the purpose and structure of an argumentative essay, and will focus on practicing the grammar ...
Making concessions also demonstrates your ability as a writer by showing that you have researched and considered you argument from multiple perspectives in order to come to an informed decision. Naturally, what you don't want to do is present a counterargument and not address it. It might be tempting to do this in your conclusion; you may ...
Definition of Concession. Concession is a literary device used in argumentative writing, where one acknowledges a point made by one's opponent. It allows for different opinions and approaches toward an issue, indicating an understanding of what causes the actual debate or controversy. It demonstrates that the writer is a mature thinker, and ...
A concession is a literary device that occurs in argumentative writing in which one acknowledges another's point. E.g. In the midst of the heated debate, the politician made a concession, acknowledging the valid points raised by the opposition and demonstrating a willingness to find common ground for the greater good.
trying to persuade our reader to reject. Many subordinators allow them to show concession. These concessive subordinators are particularly effective in both comparison and contrast and argument essays. They allow the writer to concede that an opponent's point has value while also de-emphasizing the opponent's point to the reader.
In academic essays, the thesis statement is the heart of your argument: It tells readers exactly what your paper will discuss and what position you'll take on the topic. Some thesis statements include concessions, which are statements that acknowledge a different, valid perspective on the topic or that admit ...
Explanation: In these two sentences, the author is highlighting a disagreement between the two scholars. The author begins the second sentence with the transition phrase, "Despite this strong disagreement," however, to make a concession that Mason and Holmes do agree on the importance of formal education for young children.
Here is a concession/counterargument paragraph from the student essay. The overall thesis of the whole essay is this: Although some defend the fast fashion industry's aesthetic and economic contributions, it has devastating impacts on labor rights and the environment, and needs serious regulations by all nations to stop the damage.
Concession and Counterargument Practice. Look at the following statements. In the first example, you are given the objection. The goal is to be able to structure the objection into a concession, and once you've done that, your next step is to reasonably counter it. You've been given an example to start.
The SAT essay assignment—to explain how an author "builds an argument to persuade" his or her audience—asks you to locate and analyze the building blocks of an argumentative essay. Just what makes an argument persuasive, though, can seem unclear, especially if students have a limited concept of what it means to make a "strong ...
You might want to start with some rough draft outlining of your reasoning and consider what argumentative strategies will work best for you. Recall that an argument is an assertion plus reasoning. Three basic strategies for constructing your line of reasoning are (1) reasons, (2) concessions, and (3) refutations.
1. Introduction. The concessive relation is defined by Aarts (1988: 40) as follows: 'The concessive relation expresses a semantic discrepancy between the matrix and subordinate clauses: what is said in one clause is surprising and unexpected in the light of what is said in the other clause.'. Aarts' definition highlights the semantic ...
Here are a few short definitions: Concede: Admit that another person is right about something. Refute: Prove that someone else is wrong about something. Often, speakers of English will concede a point, only to refute a larger issue: It's true that working can be tedious. However, without a job, you won't be able to pay the bills.
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
What does concession mean? Concession is when you have your that you believe in and support, however, you can see there is some validity to the other side as well. You concede that the other side of the argument is also valid. It shows that you have looked at the issue from all of its sides and you can come up with a reasoned mature response.
Step 1. Come up with a Counterargument. A strong rebuttal is only possible when there's a strong counterargument. You may be convinced of your idea but try to place yourself on the other side. Rather than addressing weak opposing views that are easy to fend off, try to come up with the strongest claims that could be made.
The argumentative essay is commonly assigned as a capstone or final project in first year writing or advanced composition courses and involves lengthy, detailed research. Expository essays involve less research and are shorter in length. Expository essays are often used for in-class writing exercises or tests, such as the GED or GRE.
Debatable thesis statement in the Introduction. Argument - paragraphs which show support for the author's thesis (for example: reasons, evidence, data, statistics) Counterargument - at least one paragraph which explains the opposite point of view. Concession - a sentence or two acknowledging that there could be some truth to the ...
In the interview, Mrs. Clinton said she quickly came to embrace the shift in language. What she and other Democrats had tried to do in 1992 with "safe, legal and rare" was "send a signal ...